Verizon MI424WR User Manual

Wireless
Broadband
Router
User’s
Manual
MI424WR
Rev. E

i
Table of Contents
1 Introduction 1
Package Contents 1
Minimum System Requirements 2
Features 2
Getting to Know the Router 4
2 Connecting the Router 9
Setting Up the Router 9
Computer Network Configuration 11
Configuring the Router 13
Home Page 15
3 Configuring My Network Settings 17
Accessing My Network 17
Using My Network 18
4 Creating a Wireless Network 25
Overview 25
Wireless Status 26
Basic Security Settings 28
Advanced Security Settings 30
Configuring a Wireless Windows XP Client 38
Connecting a Wireless Windows XP Client 40
5 Using Network Connections 45
Network (Home/Office) 46
Ethernet Connection 51
Coax Connection 54
Broadband Ethernet Connection 57
Coax Broadband Connection 62
WAN PPPoE/WAN PPPoE 2 68
6 Configuring the Router’s Security 75
General 77
Access Control 79
Port Forwarding 82
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) Host 83
Port Triggering 84
Remote Administration 86
Static NAT 88
Advanced Filtering 89
Security Log 92

ii
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
ii
7 Using Parental Controls 99
Activating Parental Controls 99
Rule Summary 102
8 Using Advanced Settings 103
Firmware Upgrade 105
Configuration File 108
System Settings 109
Date and Time 114
Scheduler Rules 115
Routing 117
IP Address Distribution 119
Diagnostics 123
Restoring Default Settings 124
Reboot the Router 124
MAC Cloning 125
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Table 125
Users 126
QoS 127
Local Administration 127
Remote Administration 128
Dynamic DNS 128
DNS Server 130
Network Objects 132
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) 134
Protocols 135
SIP ALG 136
MGCP ALG 136
9 Monitoring the Router 137
Router Status 137
Advanced Status 138
10 Troubleshooting 141
A Quality of Service 145
Traffic Priority 145
Traffic Shaping 149

iii
Table of Contents
B Specifications 161
General 161
Wireless Operating Range 162
LED Indicators 162
Environmental 162

iv
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
© 2008 Verizon
Verizon and the Verizon logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Verizon.
© 2008 Actiontec Electronics, Inc.
Actiontec and the Actiontec logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Actiontec Electronics, Inc.
All other names are properties of their respective owners.
Product photos may differ from actual product. Specifications are subject to change without notice.

1
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Wireless Broadband Router. The Wireless
Broadband Router supports Multimedia over Coax Alliance (MoCA), a network-
ing standard that allows digital entertainment and information to be transmitted
and distributed to multiple devices over coaxial cables. The Router also supports
Ethernet and Wi-Fi networking, making it the most versatile router available. If
you want to take your home or office networking to the next level, the Wireless
Broadband Router is sure to be one of the keys to your success.
Package Contents
s Wireless Broadband Router
s Black Power adapter
s Yellow cable (Ethernet, 6 ft.)
s White cable (Ethernet, 10 ft.)
s Quick Start Guide
s Installation Guide
s User Manual CD
s Wireless Networking Guide
1

2
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
s Wall-mount template
s Vertical stand
Minimum System Requirements
s Computer with Ethernet capability
s Microsoft Windows 98SE, Me, 2000, XP, or Vista; Mac OS 9 or greater;
Linux/BSD, Unix
s Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher; Netscape Navigator 7.0 or higher
s TCP/IP network protocol installed on each computer
Features
s Supports multiple networking standards, including:
WAN - Ethernet and MoCA interfaces
LAN - 802.11g, 802.11b, Ethernet, and MoCA
s Integrated wired networking with 4-port 10/100 Mbps Ethernet switch
and MoCA
s Integrated wireless networking with 802.11g access point featuring:
802.11g enabled to support speeds up to 54 Mbps wirelessly
802.11b backward compatible, communicating with 802.11b wireless
products at speeds up to 11 Mbps
s Enterprise-level security, including :
Fully customizable firewall with Stateful Packet Inspection
Content filtering with URL-keyword based filtering, parental control,
customizable filtering policies per computer, and E-mail notification
Denial of service protection against IP spoofing attacks, intrusion and
scanning attacks, IP fragment overlap, ping of death, and fragmentation
attacks
Event logging
3
Chapter 1 Introduction
Intrusion detection
MAC address filtering
NAT
DMZ hosting
Access control
Advanced wireless protection featuring WPA, WEP 64/128 bit encryption,
802.1x authentication, and MAC address filtering
ICSA certified
! Other Features
DHCP server option
DHCP server/PPPoE server auto-detection
DNS server
LAN IP and WAN IP address selection
MAC address cloning
Port forwarding
PPPoE support
QoS support (end to end layer 2/3) featuring Diffserv, 802.1p/q prioriti-
zation, configurable upstream/downstream traffic shaping, random early
detection and pass-through of WAN-side DSCPs, PHBs, and queuing to
LAN-side devices
Remote management and secured remote management using HTTPS
Reverse NAT
Static NAT
Static routing
Time zone support
VLAN multicast support
VPN IPSec (VPN passthrough only)

4
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
Getting to Know the Router
This section contains a quick description of the Router’s lights (LEDs), ports, etc.
The Router features several indicator lights on its front panel, and a series of ports
and switches on its rear panel.
Front Panel
The front panel of the Router features a series of indicator lights: Power, WAN
Ethernet, WAN Coax, Internet, LAN Ethernet (4), LAN Coax, USB, and Wireless.
Power Light
The Power light displays the Router’s current status. If the Power light glows
steadily green, the Router is receiving power and fully operational. When the
Power light flashes rapidly, the Router is initializing. If the Power light is not illuminated or glows red when the Power cord is plugged in and the Power switch is
turned on, the Router has suffered a critical error and technical support should
be contacted.
WAN Ethernet Light
The WAN Ethernet light illuminates when the Router is connected to the
Internet via Ethernet. If flashing, data traffic is passing across the port.
WAN Coax Light
The WAN Coax light glows steadily or flashes when the Router is connected to
the Internet via coaxial cable.
Internet Light
When the Internet light glows steadily green, the Router is connected to the ISP
(Internet Service Provider). If it glows amber, there is a physical connection to
the ONT (Optical Network Terminator), but authentication has not taken place
(i.e., no IP address is present).

5
Chapter 1 Introduction
LAN Ethernet Lights (1, 2, 3, 4)
The LAN Ethernet lights illuminate when the Router is connected to a local
network via one or more of its Ethernet ports. If flashing, data traffic is passing
across the port(s).
LAN Coax Light
The LAN Coax light glows steadily or flashes when the Router is connected to a
local network via its Coax port.
USB Light
The USB light illuminates when the Router is connected to a device via a
USB cable.
Wireless Light
The Wireless light illuminates when the Router’s wireless access point is turned
on. If flashing, data traffic is passing across the wireless connection.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup
WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) provides an easier way to set up a wireless network.
Instead of entering passwords or multiple keys on each wireless client (laptop,
printer, external hard drive, etc.), the Router can create a wireless network that
only requires pressing buttons (one on the Router, and one on the client [either
built-in, or on a compatible wireless card]) to allow wireless clients to join the
Router’s wireless network. Although the WPS button is included on the router,
the WPS functionality is not enabled until a future firmware release. The button
is included so that WPS can be activated with a future firmware release without
having to change the Router. The GUI does not include the WPS option.

6
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Router features eight ports (Coax, Power, LAN Ethernet [4],
WAN Ethernet, and USB), a Power switch, aReset button, and a wireless antenna.
Coax Port
The Coax port connects the Router to the ISP or other devices using a
coaxial cable.
Power Port
The Power port connects the Router to an electrical wall outlet via the
Power cord.
Power Switch
The Power switch powers the Router on and off.
Reset Button
To restore the Router’s factory default settings, press and hold the Reset button
for approximately ten seconds. The reset process will start about ten seconds
after releasing the button. When the Router resets, all the lights on the front
panel turn off, and then some of the lights start flashing. The Router has completed its reset process when the Power light glows steadily green.
"
Caution: Do not unplug the Power cord from the Router dur-
ing the reset process. Doing so may result in the loss of the
Router’s configuration information. If this occurs, reset the
Router again.

7
Chapter 1 Introduction
LAN Ethernet Ports (4)
The LAN Ethernet ports connect devices to the Router via Ethernet cables to cre-
ate a local area network (LAN). The LAN Ethernet ports are 10/100 Mbps auto-
sensing ports, and either a straight-through or crossover Ethernet cable can be
used when connecting devices to the ports.
WAN Ethernet Port
The WAN Ethernet port connects the Router to the ISP using an Ethernet cable.
USB Port
The USB port provides up to 5 VDC for attached devices (to charge a cell phone,
for example). In the future, with a firmware release upgrade, the USB host functionality will be available for devices such as external storage and cameras.
Wireless Antenna
The Router’s wireless antenna is used to transmit a wireless signal to other wireless devices on the wireless network.

8
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
This page left intentionally blank.

9
Connecting the
Router
Connecting a computer or local network to the Wireless Broadband Router is a
simple procedure, varying slightly depending on the computer’s operating system but designed to seamlessly integrate the Router with the computer or local
network. Moreover, configuration to access the GUI is not required when taking
advantage of Universal Plug-and-Play support in Windows XP.
The Windows default network settings dictate that in most cases, the setup procedure described in the “Computer Network Configuration” will be unnecessary. For
example, the default DHCP setting in Windows 2000 is “client,” requiring no further
modification.
However, we advise following the setup procedure described below to verify all communication parameters are valid and the physical cable connections are correct.
Setting Up the Router
There are three parts to setting up the Router: Connecting the Cables, Configuring
the Router, and Connecting Other Computers/Set Top Boxes.
Connecting the Cables
!
Note: If a different router was being used, disconnect it. Remove
all router components, including power supplies and cables,
since they will not work with the Wireless Broadband Router.
1. Get the Router and black Power cord from the box.
2. Plug the black Power cord in the black port on the back of the Router and
then into a power outlet.
3. Turn the Router on.
4. Make sure the Power light on the front of the Router glows steadily green.
5. Plug the yellow Ethernet cable from the box into one of the four yellow
Ethernet ports on the back of the Router.
2

10
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
6. Make sure the computer is powered on, then plug the other end of the yellow
Ethernet cable into an Ethernet port on the computer.
7. Make sure at least one of the Ethernet LAN lights on the front of the Router
glows steadily green. This may take a few moments.
8. The phone company previously installed a high-speed wall jack somewhere in
the house. Locate it and note its type (Ethernet or coaxial). If Ethernet, follow
steps 8a and 8b. If coaxial, follow steps 9a and 9b. Then, continue to step 10.
a) If connecting via Ethernet, get the white Ethernet cable from the box and
plug one end in the white port on the back of the Router.
b) Plug the other end of the white Ethernet cable into the high-speed
Ethernet jack.
9. a) If connecting via coaxial cable, get a coaxial cable and connect one end to
the red Coax port on the back of the Router.
b) Connect the other end of the coaxial cable to a coax jack.
10. Make sure the Ethernet WAN light (if connecting via Ethernet) or Coax WAN
light (if connecting via coaxial cable) on the front of the Router glows steadily
green. If connecting via coaxial cable, this may take a few minutes.
!
Note: If the Ethernet WAN light or Coax WAN light does not
illuminate, make sure the cable (Ethernet or coaxial) is connected properly at both ends.

11
Chapter 2 Connecting the Router
Computer Network Configuration
Each network interface on the computer should either be configured with a statically defined IP address and DNS address, or instructed to automatically obtain an
IP address using the Network DHCP server. The Router is set up, by default, with an
active DHCP server, and we recommend leaving this setting as is.
Configuring Dynamic IP Addressing
To set up a computer to use dynamic IP addressing:
Windows XP
1. Select Network Connections in the Control Panel.
2. Right-click Ethernet Local Area Connection, then click Properties.
3. In the “General” tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then click
Properties.
4. The “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window appears.
5. Click the “Obtain an IP address automatically” radio button.
6. Click the “Obtain DNS server address automatically” radio button.
7. Click OK in the “(TCP/IP) Properties” screen, then click OK in the “Local
Area Connection Properties” screen to save the settings.
Windows 2000
1. Select Network and Dialing Connections in the Control Panel.
2. Right-click on the Ethernet connection’s icon, then click Properties.
3. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) component, then click Properties.
4. The “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties” window appears.
5. Click the “Obtain an IP address automatically” radio button.
6. Click the “Obtain DNS server address automatically” radio button.

12
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
Windows 98/Me
1. Select Network in the Control Panel.
2. Select the TCP/IP settings for the network card, then click Properties.
3. Click the “Obtain an IP address automatically” radio button in the “IP
Address” tab.
4. Click Disable DNS in the DNS configuration tab.
5. Click OK in the “TCP/IP Properties” screen.
6. Click OK in the “Network” screen to reboot and save the settings.
Windows NT
1. Click Network in the Control Panel. The “Network” window appears.
2. In the “Protocol” tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) then click
Properties.
3. In the “IP Address” tab, click the “Obtain an IP address automatically” radio
button.
4. In the “DNS” tab, verify no DNS server is defined in the “DNS Service Search
Order” text box and no suffix is defined in the “Domain Suffix Search
Order” text box.
Macintosh OS X
1. Click on the Apple icon in the top left corner of the desktop.
2. From the menu that appears, select System Preferences.
3. The “System Preferences” window appears. Click Network.
4. From the “Network” window, make sure “Ethernet” in the list on the left is
highlighted and displays “Connected.”
5. Click Assist me.
6. From the tab that appears, click Diagnostics.
7. Follow the instructions in the “Network Diagnostics” assistant.
13
Chapter 2 Connecting the Router
Linux
1. Login into the system as a super-user, by entering “su” at the prompt.
2. Type “ifconfig” to display the network devices and allocated IPs.
3. Type “pump -i <dev>,” where <dev> is the network device name.
4. Type “ifconfig” again to view the newly allocated IP address.
5. Make sure no firewall is active on device <dev>.
Configuring the Router
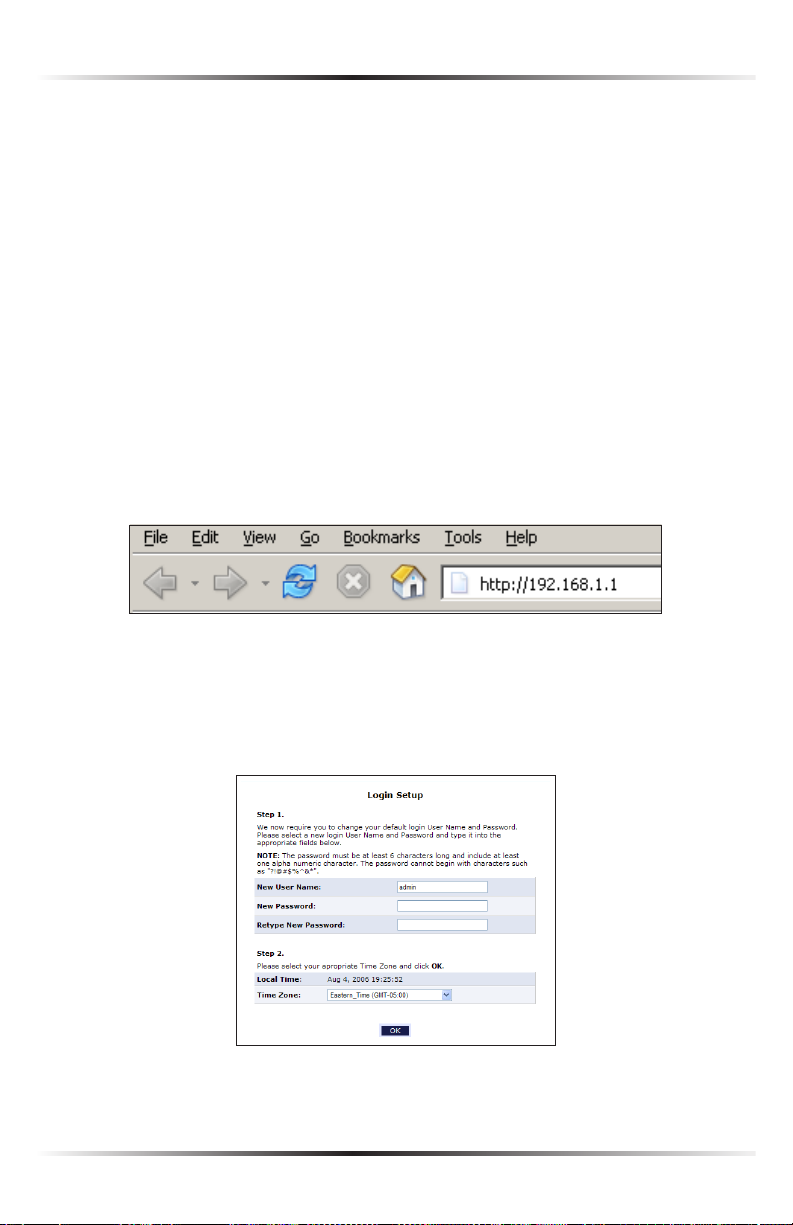
1. Open a web browser on the computer connected to the Router. In the
“Address” text box, type:
http://192.168.1.1
then press Enter on the keyboard.
2. The “Login Setup” screen appears. Select a new user name and password and
enter them in the appropriate text boxes (the password must be entered twice,
for validation purposes). Write the new user name and password down on a
piece of paper and keep it in a safe place, since they will be needed to access
the Router’s GUI (Graphical User Interface) in the future.

14
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
3. In the bottom part of the screen, select the correct time zone from the “Time
Zone” drop-down list, then click OK at the bottom of the screen.
The Router is now configured.
Connecting Other Computers/Set Top Boxes
The Router can connect to other computers or set top boxes in three ways: via
Ethernet, via wireless connection, or via coaxial cable.
Ethernet
1. Get an Ethernet cable and plug one end into one of the open yellow
Ethernet ports on the back of the Router.
2. Plug the other end of the Ethernet cable into an Ethernet port on the computer.
3. Make sure the corresponding Ethernet LAN light on the front of the Router
glows steadily green.
4. Repeat these steps for each computer to be connected to the Router
via Ethernet.
Wireless
1. Make sure each computer to be connected wirelessly has built-in wireless or
an attached wireless adapter.
2. Make sure the computer uses the same ESSID and WEP key as the Router by
launching the computer’s wireless application
3. Enter the ESSID and WEP key found on the sticker on the bottom of the
Router in the computer’s wireless settings and click Save. Make sure to con-
figure the computer to use 64/40-bit WEP encryption.
4. Make sure the changes were implemented by surfing the Internet from
the computer.
5. Repeat these steps for every other computer to be connected to the
Router wirelessly.
15
Chapter 2 Connecting the Router
Coaxial
1. Make sure all set top boxes are turned off.
2. Disconnect any adapter currently connected to the coaxial jack in the room
where the Router is.
3. Connect one end of the coaxial cable to the coaxial wall jack, and the other
end to the red Coax port on the back of the Router.
4. Power up the set top box.
5. Make sure the Coax LAN light on the front of the Router glows steadily
green. This may take a few minutes. When it does, the set top box is connected to the Router.
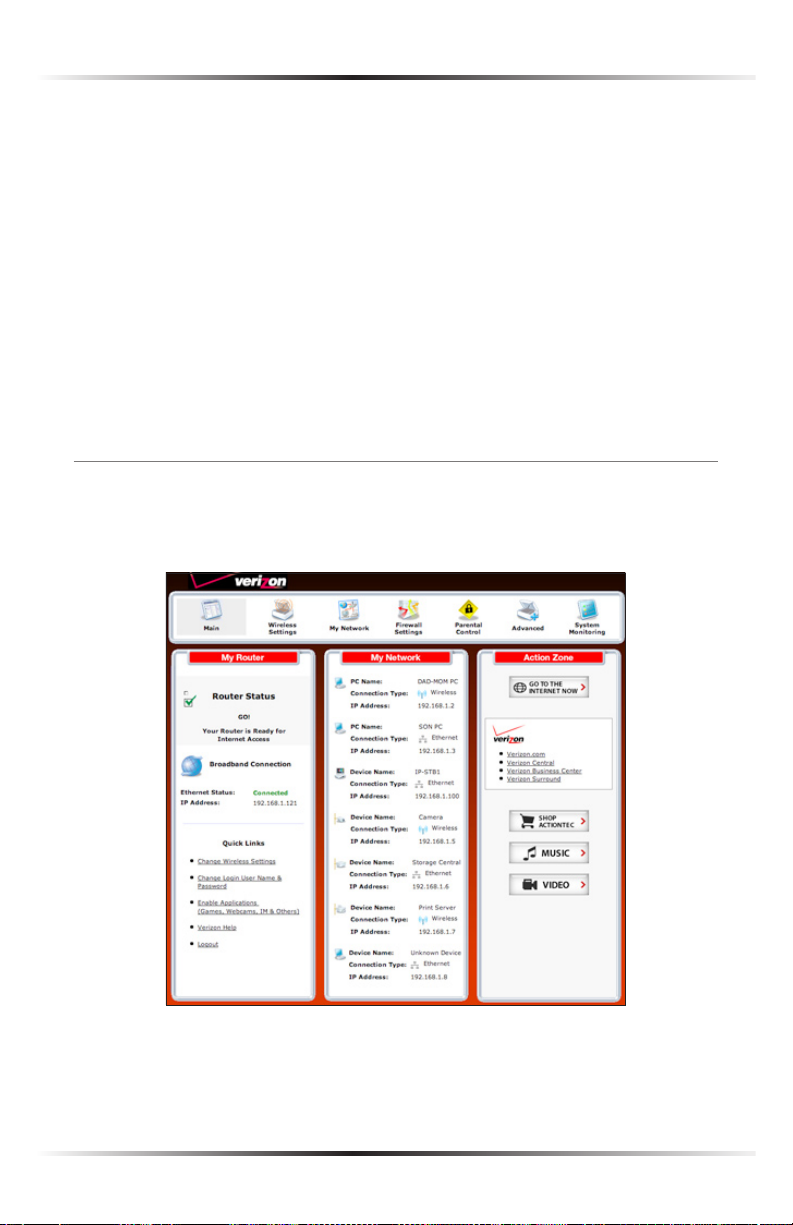
Main Screen
After logging into the Router’s GUI (see “Configuring the Router” at the beginning
of this chapter), the “Main” screen appears.
The Main screen has a menu occupying the top of the screen. Below that, the
screen is divided into three columns: “My Router,” “My Network,” and
“Action Zone.”

16
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
Menu
The Main screen’s menu contains links to all of the configuration options of the
Router: Wireless Setup (explained in chapter 4 of this manual), My Network
(chapter 5), Firewall (chapter 6), Parental Controls (chapter 7), Advanced (chap-
ter 8), and System Monitoring (chapter 9).
My Router
This section displays the status of the Router’s network and Internet connection.
A green light signifies the Router is connected; a yellow light means the Router is
attempting to connect; and a red light signifies the Router’s connection is down.
Broadband Connection
The “Broadband Connection” section of the My Router column displays the state
of the Router’s broadband connection (“Connected” or “Disconnected”) for the
two connection options (“Coax Status” and “Ethernet Status”), and the WAN IP
address of the broadband connection.
Quick Links
The “Quick Links” section of the My Router column contains a list of frequently
accessed settings, including “Change Wireless Settings,” “Change Login User
Name & Password,” “Enable Gaming,” and “Logout.”
My Network
The “My Network” column of the Main screen displays the connection type, name,
and IP address of all devices connected to the Router’s network. The icon associated
with the device will be displayed normally (signifying an active device) or shaded
(signifying the device has not been active for at least 60 seconds). The user can also
configure the basic settings of each device by clicking on its icon. These settings are
described in more detail in chapter 3, “Configuring My Network Settings.”
Action Zone
This column contains links to various Verizon Web sites, and other informational
links. Clicking on the icon above “Go to Internet Now” connects the user to the
home page configured on the user’s web browser.
17
Configuring My
Network Settings
Once the Wireless Broadband Router is physically connected and the MegaControl
Panel’s Main screen is displayed in a web browser, a list of the devices connected
to the Router’s network appears in the “My Network” column of the screen. From
here, some basic network settings can be configured.
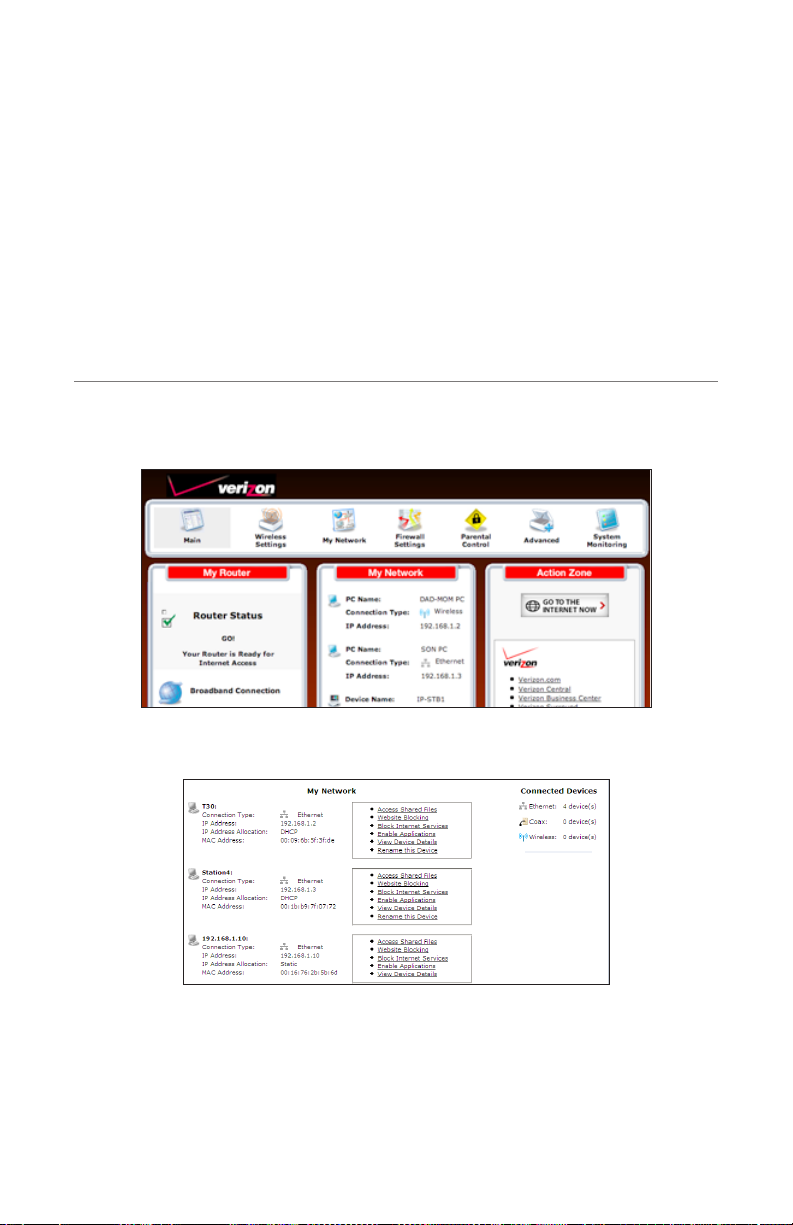
Accessing My Network
To access My Network, click on “My Network” in the Main screen.
The “My Network” screen appears:
On the far right side of the screen, in the “Connected Devices” section, is list of the
devices currently connected to the network, listed by connection type and number. The rest of the screen contains the “My Network” section, which displays each
device connected to the network, and a series of basic configuration settings.
3

18
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
Using My Network
Various settings can be accessed for a particular device, as follows.
Access Device
For devices that can be accessed (such as Internet cameras and networked hard
drives), locate it in the My Network column, then click Access Devices to use the
device over the network.
Access Shared Files
To access the shared files on a particular device, locate the device in the My
Network column, then click Access Shared Files. A list of shared files appears on
the screen.
Website Blocking
Clicking “Website Blocking” generates the “Parental Control” screen. For more
information about using parental controls, see chapter 7, “Using Parental
Controls.”
Block Internet Services
Internet services blocking is used to prevent a device on the network from accessing particular services on the Internet, such as receiving email or downloading
from FTP sites. To set up Internet services blocking on a networked device, locate
the device in the My Network column, then click Block Internet Services. The
“Access Control” screen appears.
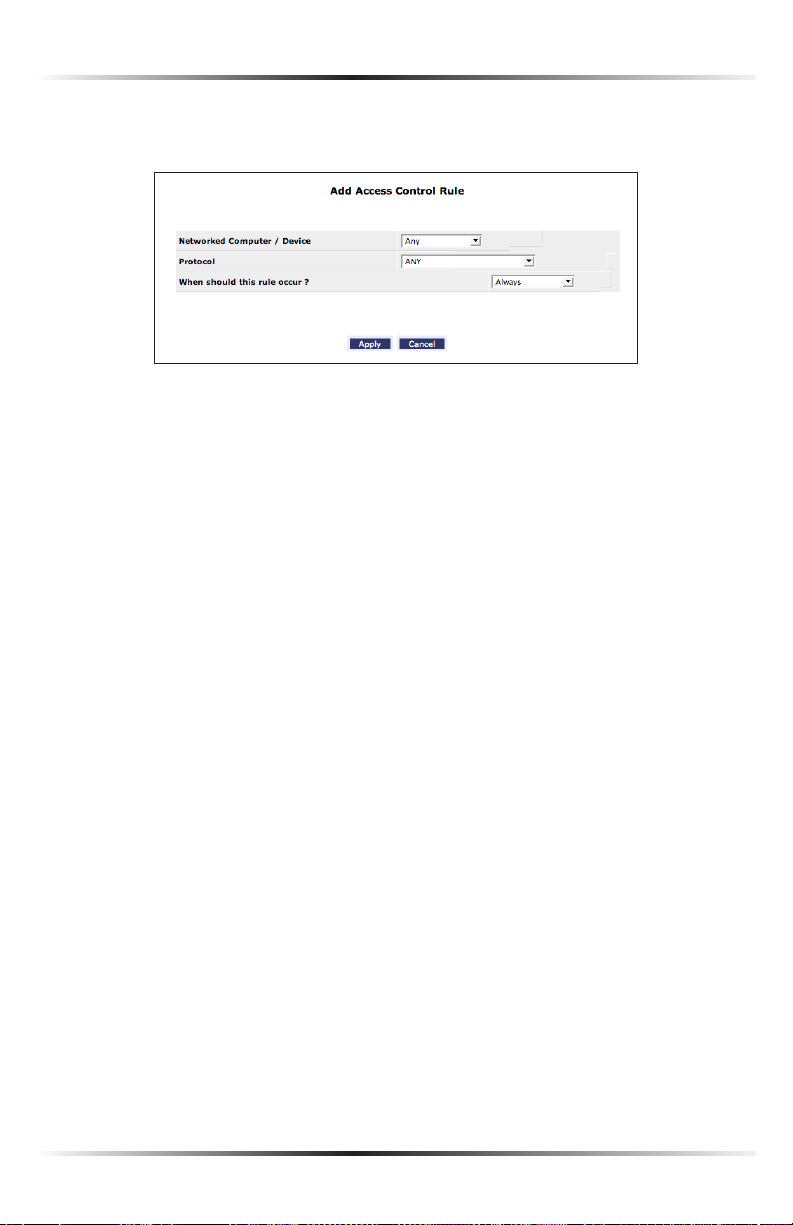
19
Chapter 3 Configuring My Network Settings
1. Click Add in the “Networked computer/Device” column. The “Add Access
Control Rule” screen appears.
2. If this access control rule applies to all networked devices, select “Any” from
the “Networked Computer/Device” list box. If this rule applies to certain
devices only, select “User Defined” and click Add. Then, in the “Edit Network
Object” screen, add a network object (for more details about adding network
objects, see the “Advanced Settings” chapter of this manual).
3. Select the Internet protocol to be blocked from the “Protocol” drop-down list.
4. If this rule will be active all the time, select “Always” from the “When should this
rule occur?” drop-down list. If the rule will only be active at certain times, select
“Specify Schedule” and click Add. Then, add a schedule rule (for more details
about schedule rules, see the “Advanced Settings” chapter of this manual).
!
Note: Make sure the Router’s date and time settings for your time
zone are set correctly for schedule rules to function properly.
5. Click Apply to save the changes. The Access Control screen will display a sum-
mary of the access control rule.
!
Note: To block a service that is not included in the list, select
“User Defined” from the Protocol drop-down menu. The “Edit
Service” screen appears. Define the service, then click Apply. The
service will then be automatically added to the top section of the
“Add Access Control Rule” screen, and will be selectable.

20
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
The user may disable an access control and the service made available without
having to remove the service from the Access Control table. This may be useful to
make the service available only temporarily, with the expectation that the restriction will be reinstated later.
s 4OTEMPORARILYDISABLEANACCESSCONTROLCLEARTHECHECKBOXNEXTTOTHE
network computer/device.
s 4OREINSTATETHERESTRICTIONATALATERTIMESELECTTHECHECKBOXNEXTTOTHE
network computer/device.
s 4OREMOVEANACCESSRESTRICTIONFROMTHE!CCESS#ONTROLTABLECLICKRemove
for the service. The service will be removed from the Access Control table.
!
Note: When Web Filtering is enabled, HTTP services cannot be
blocked by access control.
Enable Application
Activating “Enable Application” (also known as port forwarding) allows the network to be exposed to the Internet in certain limited and controlled ways, enabling
some applications to work from the local network (game, voice, and chat applications, for example), as well as allowing Internet access to servers in the local network. To set this up on a networked device, locate the device in the My Network
column, then click Enable Applications. The “Port Forwarding” screen appears.
1. Click Add. The “Add Port Forwarding Rule” screen appears.
2. Enter the local IP address or the host name of the computer providing the ser-
vice in the “Networked Computer/Device” text box. Note that only one local
network computer can be assigned to provide a specific service or application.

21
Chapter 3 Configuring My Network Settings
3. Select the Internet protocol to be provided from the “Protocol” drop-down
list. Depending on the protocol selected, additional options appear in
the screen.
4. To select a port to forward communications to (this is optional), select
“Specify” from the “Forward to Port” drop-down list, then, in the text box
that appears, enter the port number. If no port is identified, select “Same as
Incoming Port.”
5. If this port will be active all the time, select “Always” from the “When should this
rule occur?” drop-down list. If the rule will only be active at certain times, select
“Specify Schedule” and click Add. Then, add a schedule rule (for more details
about schedule rules, see the “Advanced Settings” chapter of this manual).
6. Click Apply to save the changes.
!
Note: Some applications, such as FTP, TFTP, PPTP, and H323,
require the support of special specific Application Level Gateway
(ALG) modules to work inside the local network. Data packets
associated with these applications contain information that allows
them to be routed correctly. An ALG is needed to handle these
packets and ensure they reach their intended destinations. The
Router is equipped with a robust list of ALG modules, enabling
maximum functionality in the local network.
The ALG is automatically assigned based on the destination port.
View Device Details
To view information about a networked device, or to test a device’s connection,
locate the device in the My Network column, then click View Device Details. The
“Host Information” screen appears.
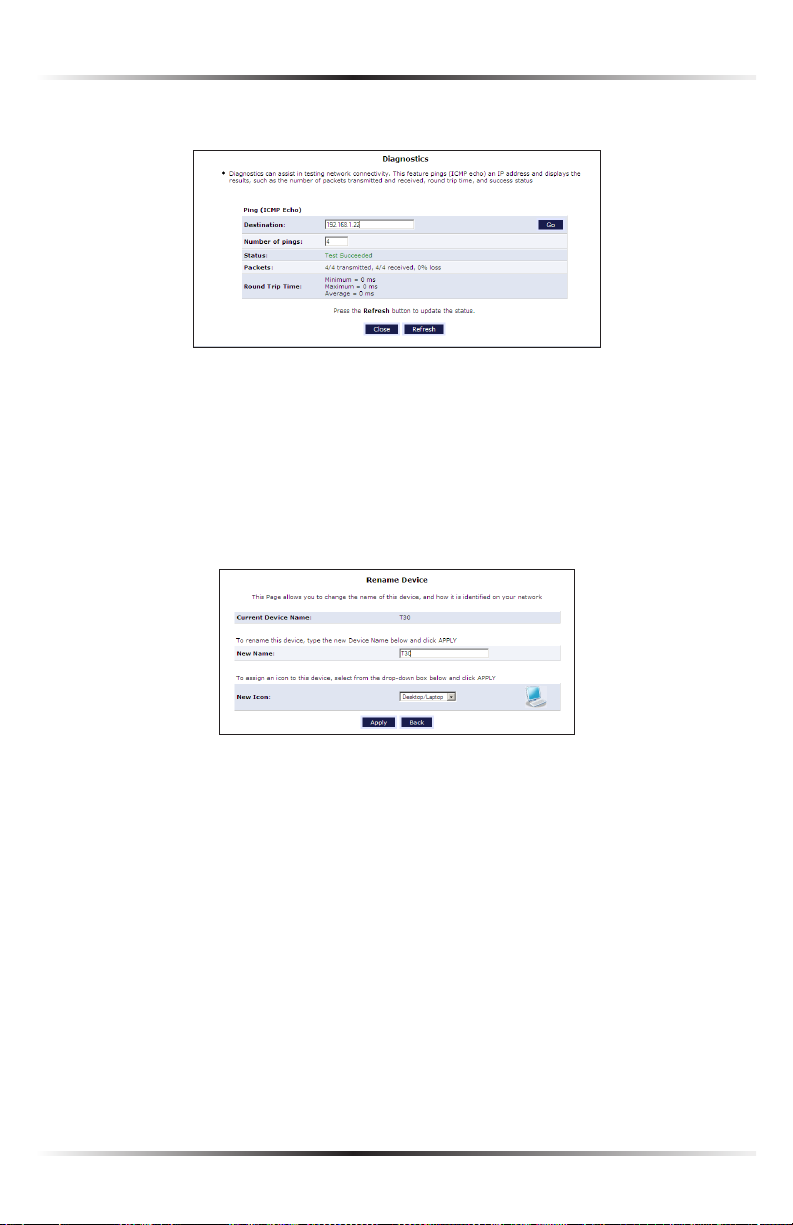
22
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
1. Click Test Connectivity. The “Diagnostics” screen appears.
2. The Router automatically runs a ping test, and the results are displayed in the
Diagnostics screen.
Rename This Device
To rename a networked device, locate the device in the My Network column, then
click Rename This Device. The “Rename Device” screen appears.
Enter the new name of the device in the “New Name” text box and, if needed,
select a new icon for the device from the “New Icon” drop-down list.

23
Creating a Wireless
Network
This chapter explains how to create a wireless network using the Wireless
Broadband Router, including accessing and configuring wireless security options.
Overview
The Wireless Broadband Router provides the user with wireless connectivity over
the 802.11b and g standards (the most common wireless standards). 802.11b has
a maximum data rate of 11 Mbps, while 802.11g has a maximum data rate of 54
Mbps. Both operate in the 2.4 GHz range.
The Router’s wireless feature is turned on, with wireless security activated, by default.
The level of security is 64/40-bit WEP, with a unique WEP key already entered. This
information is displayed on a sticker located on the bottom of the Router.
The Router integrates multiple layers of security. These include the IEEE 802.1x
port-based authentication protocol, RADIUS client, EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS,
EAP-PEAP, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and
firewall and VPN applications.
Connecting a Wireless Client
To connect a wireless client to the Router:
!
Note: The following procedure assumes the Router’s default wire-
less settings are intact. If they have been changed, use the new ESSID
and wireless security settings. For more details, see the “Connecting
a Wireless Windows XP Client” section of this chapter.
1. In the wireless client’s configuration interface, enter the Router’s ESSID
(found on a sticker on the bottom of the Router’s case) in the appropriate
text box or field (this varies depending on the wireless client’s manufacturer).
2. Enter the Router’s WEP key (also found on the sticker on the bottom of the
Router’s case) in the wireless client’s configuration interface.
3. Save the changes and exit the wireless client’s configuration interface. The cli-
ent should now detect and join the Router’s wireless network. If not, check the
wireless client’s documentation, or contact its manufacturer.
4
24
Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
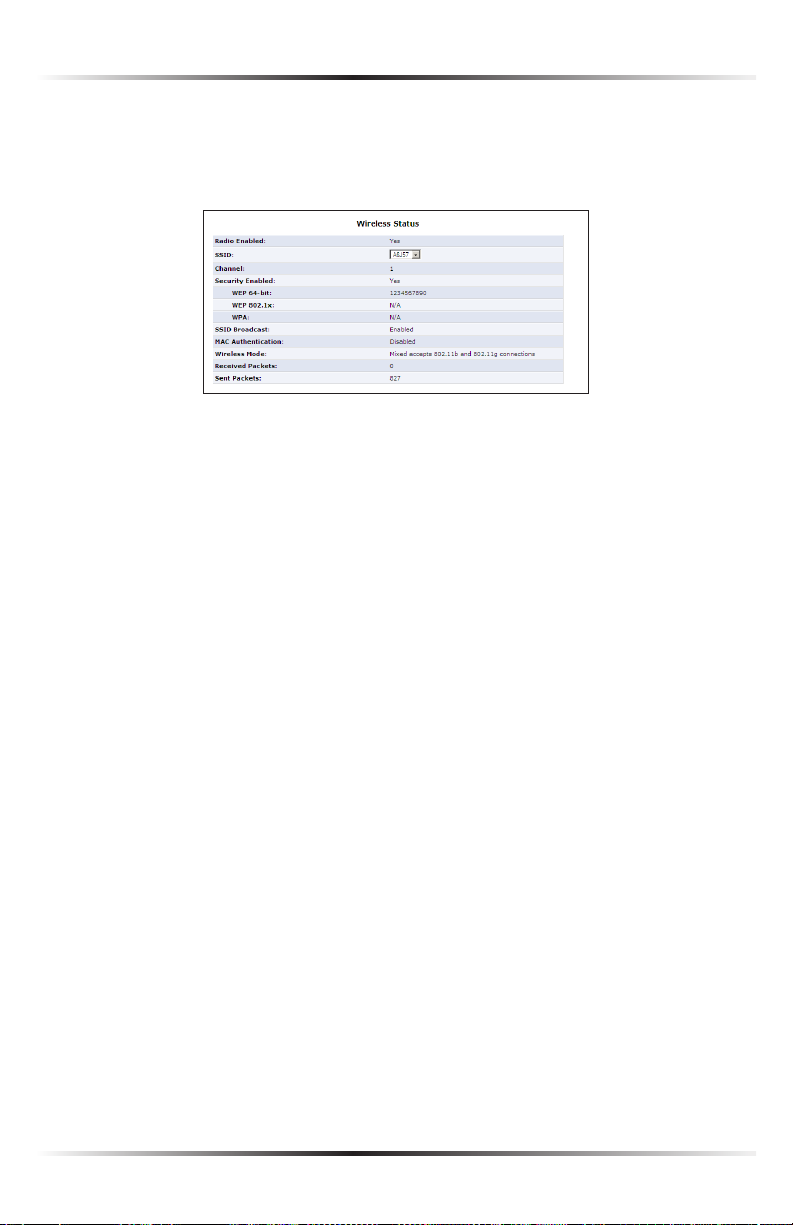
Wireless Status
Clicking on the “Wireless Settings” icon from the Main screen’s menu generates the
“Wireless Status” screen, which displays the current status of the wireless connection.
Radio Enabled
Displays whether the Router’s wireless radio is active.
SSID
The SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the network name shared among all devices
on a particular wireless network. The SSID must be identical for all devices on the
wireless network. It is case-sensitive and cannot exceed 32 characters. Make sure
the SSID is the same for all devices to be connected to the wireless network. The
Router comes from the factory with an SSID already entered and displayed here.
The default SSID can also be found on a sticker on the bottom of the Router.
Channel
Displays the channel to which the wireless connection is currently set. All devices
on the wireless network must be on the same channel to function correctly.
Security Enabled
Displays what kind of security is active on the wireless connection, and the security
encryption key.

25
Chapter 4 Creating a Wireless Network
SSID Broadcast
Displays whether the Router is broadcasting its SSID. If activated, the SSID of the
Router’s wireless network is broadcast wirelessly.
MAC Authentication
Displays whether the Router is using MAC (Media Access Control) address authen-
tication to allow wireless devices to join the network.
Wireless Mode
Displays the types of wireless device that can join the network. Options include
802.11b, 802.11g, or Mixed (allows both 802.11b- and 802.11g-equipped wireless
devices to join the network).
Packets Sent/Received
Displays the number of packets sent and received since the Router’s wireless capability was activated.
 Loading...
Loading...