Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 1
Section 1. Using the CLI..................................................................................................... 10
1.1 CLI Command Modes............................................................................................................. 10
1.1.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................... 10
1.1.2 User EXEC Mode ..................................................................................................................... 11
1.1.3 Privileged EXEC Mode ............................................................................................................. 11
1.1.4 Global Configuration Mode....................................................................................................... 12
1.1.5 Interface Configuration and Specific Configuration Modes ...................................................... 12
1.2 Starting the CLI....................................................................................................................... 13
1.3 Editing Features ..................................................................................................................... 14
1.3.1 Entering Commands................................................................................................................. 14
Section 2. AAA Commands................................................................................................ 17
aaa authentication login........................................................................................................17
aaa authentication enable..................................................................................................... 19
login authentication............................................................................................................... 21
enable authentication............................................................................................................ 22
ip http authentication............................................................................................................. 23
ip https authentication........................................................................................................... 24
show authentication methods ............................................................................................... 25
password............................................................................................................................... 26
enable password................................................................................................................... 27
username.............................................................................................................................. 28
Section 3. Address Table Commands................................................................................ 29
bridge address ...................................................................................................................... 29
bridge multicast filtering ........................................................................................................ 30
bridge multicast address....................................................................................................... 31
bridge multicast forbidden address....................................................................................... 32
bridge multicast forward-all................................................................................................... 33
bridge multicast forbidden forward-all................................................................................... 34
bridge aging-time .................................................................................................................. 35
clear bridge ........................................................................................................................... 36
port security .......................................................................................................................... 37
port security routed secure-address ..................................................................................... 38
show bridge address-table.................................................................................................... 39
show bridge address-table static .......................................................................................... 40
show bridge address-table count.......................................................................................... 41
show bridge multicast address-table..................................................................................... 42
show bridge multicast filtering............................................................................................... 44
Page 3

show ports security ............................................................................................................... 45
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 2
Section 4. Clock.................................................................................................................. 47
clock set ................................................................................................................................ 47
clock source .......................................................................................................................... 48
clock timezone ...................................................................................................................... 49
clock summer-time................................................................................................................ 50
sntp authentication-key .........................................................................................................52
sntp authenticate................................................................................................................... 53
sntp trusted-key .................................................................................................................... 54
sntp client poll timer .............................................................................................................. 55
sntp broadcast client enable ................................................................................................. 56
sntp anycast client enable..................................................................................................... 57
sntp client enable (Interface)................................................................................................. 58
sntp unicast client enable......................................................................................................59
sntp unicast client poll........................................................................................................... 60
sntp server ............................................................................................................................ 61
show clock ............................................................................................................................ 62
show sntp configuration ........................................................................................................ 63
show sntp status ................................................................................................................... 64
Section 5. Configuration and Image Files........................................................................... 65
copy ...................................................................................................................................... 65
delete .................................................................................................................................... 68
delete startup-config ............................................................................................................. 69
show running-config.............................................................................................................. 70
show startup-config............................................................................................................... 71
Section 6. Ethernet Configuration Commands ................................................................... 72
interface ethernet .................................................................................................................. 72
interface range ethernet........................................................................................................73
shutdown............................................................................................................................... 74
description............................................................................................................................. 75
speed .................................................................................................................................... 76
duplex ................................................................................................................................... 77
negotiation ............................................................................................................................ 78
flowcontrol............................................................................................................................. 79
mdix ...................................................................................................................................... 80
back-pressure ....................................................................................................................... 81
clear counters ....................................................................................................................... 82
set interface active ................................................................................................................ 83
show interfaces advertise ..................................................................................................... 84
Page 4

show interfaces configuration ............................................................................................... 86
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 3
show interfaces status ..........................................................................................................87
show interfaces description................................................................................................... 89
show interfaces counters ...................................................................................................... 90
port storm-control include-multicast...................................................................................... 93
port storm-control broadcast enable ..................................................................................... 94
port storm-control broadcast rate.......................................................................................... 95
show ports storm-control....................................................................................................... 96
Section 7. GVRP Commands............................................................................................. 97
gvrp enable (Global) ............................................................................................................. 97
gvrp enable (Interface).......................................................................................................... 98
garp timer.............................................................................................................................. 99
gvrp vlan-creation-forbid ..................................................................................................... 100
gvrp registration-forbid........................................................................................................101
clear gvrp statistics ............................................................................................................. 102
show gvrp configuration...................................................................................................... 103
show gvrp statistics............................................................................................................. 104
show gvrp error-statistics .................................................................................................... 105
Section 8. IGMP Snooping Commands............................................................................ 106
ip igmp snooping (Global)................................................................................................... 106
ip igmp snooping (Interface) ............................................................................................... 107
ip igmp snooping host-time-out........................................................................................... 108
ip igmp snooping mrouter-time-out ..................................................................................... 109
ip igmp snooping leave-time-out......................................................................................... 110
show ip igmp snooping mrouter.......................................................................................... 111
show ip igmp snooping interface......................................................................................... 112
show ip igmp snooping groups ........................................................................................... 113
Section 9. IP Addressing Commands............................................................................... 114
ip address ........................................................................................................................... 114
ip address dhcp................................................................................................................... 115
ip default-gateway............................................................................................................... 116
show ip interface................................................................................................................. 117
arp....................................................................................................................................... 118
arp timeout.......................................................................................................................... 119
clear arp-cache ................................................................................................................... 120
show arp ............................................................................................................................. 121
ip domain-name ..................................................................................................................122
ip name-server.................................................................................................................... 123
ip host ................................................................................................................................. 124
Page 5

clear host ............................................................................................................................ 125
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 4
clear host dhcp.................................................................................................................... 126
show hosts .......................................................................................................................... 127
Section 10. LACP Commands............................................................................................ 128
lacp system-priority ............................................................................................................. 128
lacp port-priority .................................................................................................................. 129
lacp timeout......................................................................................................................... 130
show lacp ethernet..............................................................................................................131
show lacp port-channel ....................................................................................................... 133
Section 11. Line Commands .............................................................................................. 134
line ...................................................................................................................................... 134
speed .................................................................................................................................. 135
exec-timeout ....................................................................................................................... 136
history ................................................................................................................................. 137
history size .......................................................................................................................... 138
terminal history.................................................................................................................... 139
terminal history size ............................................................................................................ 140
show line ............................................................................................................................. 141
Section 12. Management ACL............................................................................................ 142
management access-list ..................................................................................................... 142
permit (Management).......................................................................................................... 144
deny (Management)............................................................................................................ 145
management access-class ................................................................................................. 146
show management access-list............................................................................................ 147
show management access-class ........................................................................................ 148
Section 13. PHY Diagnostics Commands .......................................................................... 149
test copper-port tdr.............................................................................................................. 149
show copper-ports tdr ......................................................................................................... 150
show copper-ports cable-length.......................................................................................... 151
show fiber-ports optical-transceiver .................................................................................... 152
Section 14. Port Channel Commands ................................................................................ 153
interface port-channel ......................................................................................................... 153
interface range port-channel ............................................................................................... 154
channel-group ..................................................................................................................... 155
show interfaces port-channel .............................................................................................. 156
Page 6

Section 15. Port Monitor Commands.................................................................................. 157
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 5
port monitor......................................................................................................................... 157
port monitor vlan-tagging .................................................................................................... 158
show ports monitor..............................................................................................................159
Section 16. QoS Commands.............................................................................................. 160
qos ...................................................................................................................................... 160
show qos............................................................................................................................. 161
priority-queue out num-of-queues....................................................................................... 162
show qos interface..............................................................................................................163
traffic-shape ........................................................................................................................ 165
wrr-queue cos-map............................................................................................................. 166
qos map dscp-queue .......................................................................................................... 167
qos trust (Global) ................................................................................................................ 168
qos trust (Interface)............................................................................................................. 169
qos cos................................................................................................................................ 170
show qos map..................................................................................................................... 171
Section 17. Radius Commands.......................................................................................... 172
radius-server host ............................................................................................................... 17
radius-server key ................................................................................................................ 17
radius-server retransmit...................................................................................................... 175
radius-server source-ip ....................................................................................................... 17
radius-server timeout .......................................................................................................... 17
radius-server deadtime ....................................................................................................... 17
show radius-servers............................................................................................................ 1
79
Section 18. RMON Commands .......................................................................................... 18
show rmon statistics............................................................................................................18
rmon collection history ........................................................................................................ 18
show rmon collection history............................................................................................... 18
show rmon history...............................................................................................................18
rmon alarm.......................................................................................................................... 187
show rmon alarm ................................................................................................................ 1
89
rmon event.......................................................................................................................... 19
show rmon events............................................................................................................... 19
show rmon log..................................................................................................................... 19
rmon table-size ................................................................................................................... 19
2
4
6
7
8
0
0
2
3
4
1
2
3
5
Page 7

Section 19. SNMP Commands........................................................................................... 196
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 6
snmp-server community...................................................................................................... 19
6
snmp-server view................................................................................................................198
snmp-server group..............................................................................................................
snmp-server user ................................................................................................................20
snmp-server engineID local ................................................................................................ 20
snmp-server enable traps ................................................................................................... 20
snmp-server filter ................................................................................................................ 20
snmp-server host ................................................................................................................20
199
0
2
4
5
6
snmp-server v3-host ........................................................................................................... 207
snmp-server trap authentication ......................................................................................... 20
snmp-server contact ........................................................................................................... 2
snmp-server location........................................................................................................... 21
snmp-server set .................................................................................................................. 21
show snmp.......................................................................................................................... 21
show snmp engineid ........................................................................................................... 21
8
09
0
1
2
4
show snmp views................................................................................................................ 215
show snmp groups.............................................................................................................. 216
show snmp filters ................................................................................................................ 21
show snmp users ................................................................................................................ 2
Section 20. Spanning-Tree Commands ............................................................................. 22
spanning-tree ...................................................................................................................... 22
spanning-tree mode ............................................................................................................ 22
spanning-tree forward-time ................................................................................................. 22
spanning-tree hello-time ..................................................................................................... 22
spanning-tree max-age ....................................................................................................... 22
8
19
0
0
1
2
3
4
spanning-tree priority ..........................................................................................................225
spanning-tree disable.......................................................................................................... 226
spanning-tree cost ..............................................................................................................22
spanning-tree port-priority................................................................................................... 22
spanning-tree portfast ......................................................................................................... 2
spanning-tree link-type........................................................................................................ 23
spanning-tree pathcost method .......................................................................................... 23
spanning-tree bpdu ............................................................................................................. 23
7
8
29
0
1
2
clear spanning-tree detected-protocols............................................................................... 233
spanning-tree guard root..................................................................................................... 23
spanning-tree mst priority ................................................................................................... 23
spanning-tree mst max-hops .............................................................................................. 23
spanning-tree mst port-priority ............................................................................................ 23
spanning-tree mst cost........................................................................................................ 23
spanning-tree mst configuration.......................................................................................... 2
4
5
6
7
8
39
instance (mst) ..................................................................................................................... 240
Page 8

name (mst).......................................................................................................................... 241
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 7
revision (mst) ...................................................................................................................... 24
show (mst) .......................................................................................................................... 24
exit (mst) ............................................................................................................................. 24
abort (mst)........................................................................................................................... 24
show spanning-tree............................................................................................................. 24
2
3
4
5
6
Section 21. Syslog Commands .......................................................................................... 24
logging on ........................................................................................................................... 24
logging ................................................................................................................................ 2
logging console................................................................................................................... 25
8
8
49
0
logging buffered .................................................................................................................. 251
logging buffered size...........................................................................................................252
clear logging........................................................................................................................ 25
logging file........................................................................................................................... 25
clear logging file.................................................................................................................. 25
aaa logging ......................................................................................................................... 25
file-system logging .............................................................................................................. 25
management logging .......................................................................................................... 25
3
4
5
6
7
8
show logging....................................................................................................................... 259
show logging file ................................................................................................................. 26
show syslog-servers ........................................................................................................... 26
Section 22. System Management....................................................................................... 26
1
3
4
ping ..................................................................................................................................... 264
traceroute............................................................................................................................ 26
reload.................................................................................................................................. 26
hostname ............................................................................................................................ 2
show users.......................................................................................................................... 27
show system ....................................................................................................................... 27
show version....................................................................................................................... 27
6
8
69
0
1
2
show system id ................................................................................................................... 273
system language web..........................................................................................................274
Section 23. User Interface.................................................................................................. 275
enable ................................................................................................................................. 27
disable................................................................................................................................. 276
login .................................................................................................................................... 27
configure ............................................................................................................................. 27
exit (Configuration).............................................................................................................. 27
exit ...................................................................................................................................... 2
5
7
8
9
80
Page 9

end.......................................................................................................................................281
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 8
help......................................................................................................................................28
terminal data-dump ............................................................................................................. 28
show history ........................................................................................................................ 28
2
3
4
show privilege ..................................................................................................................... 285
Section 24. VLAN Commands............................................................................................ 286
vlan database...................................................................................................................... 28
vlan ..................................................................................................................................... 28
interface vlan....................................................................................................................... 288
interface range vlan ............................................................................................................28
name ................................................................................................................................... 2
90
switchport mode.................................................................................................................. 29
switchport access vlan ........................................................................................................ 29
switchport trunk allowed vlan .............................................................................................. 29
switchport trunk native vlan................................................................................................. 29
switchport general allowed vlan .......................................................................................... 295
switchport general pvid ....................................................................................................... 29
switchport general ingress-filtering disable ......................................................................... 29
switchport general acceptable-frame-type tagged-only ...................................................... 29
switchport forbidden vlan .................................................................................................... 29
switchport protected............................................................................................................
300
ip internal-usage-vlan..........................................................................................................30
show vlan ............................................................................................................................ 302
show vlan internal usage .................................................................................................... 303
show interfaces switchport.................................................................................................. 30
Section 25. Web Server...................................................................................................... 30
ip http server ....................................................................................................................... 307
6
7
9
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
1
4
7
ip http exec-timeout..............................................................................................................308
ip https server ..................................................................................................................... 309
ip http port ........................................................................................................................... 3
ip https port ......................................................................................................................... 3
show ip http......................................................................................................................... 31
Section 26. 802.1x Commands .......................................................................................... 31
aaa authentication dot1x..................................................................................................... 31
dot1x system-auth-control................................................................................................... 31
dot1x port-control ................................................................................................................ 31
dot1x re-authentication ....................................................................................................... 31
10
11
2
3
3
4
5
6
Page 10

dot1x timeout re-authperiod................................................................................................ 317
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 9
dot1x re-authenticate .......................................................................................................... 3
dot1x timeout quiet-period .................................................................................................. 3
dot1x timeout tx-period ....................................................................................................... 3
dot1x max-req..................................................................................................................... 3
18
19
20
21
dot1x timeout supp-timeout................................................................................................. 32
dot1x timeout server-timeout .............................................................................................. 323
show dot1x.......................................................................................................................... 324
show dot1x users................................................................................................................3
show dot1x statistics...........................................................................................................3
ADVANCED FEATURES.................................................................................................... 3
dot1x auth-not-req............................................................................................................... 3
27
29
31
31
dot1x multiple-hosts............................................................................................................33
dot1x single-host-violation .................................................................................................. 33
dot1x guest-vlan.................................................................................................................. 334
dot1x guest-vlan enable...................................................................................................... 33
show dot1x advanced ......................................................................................................... 3
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................. 3
36
38
2
2
3
5
Page 11
Section 1. Using the CLI
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 10
This chapter describes how to start using the CLI and describes implemented command editing features to assist
in using the CLI.
1.1 CLI Command Modes
1.1.1 Introduction
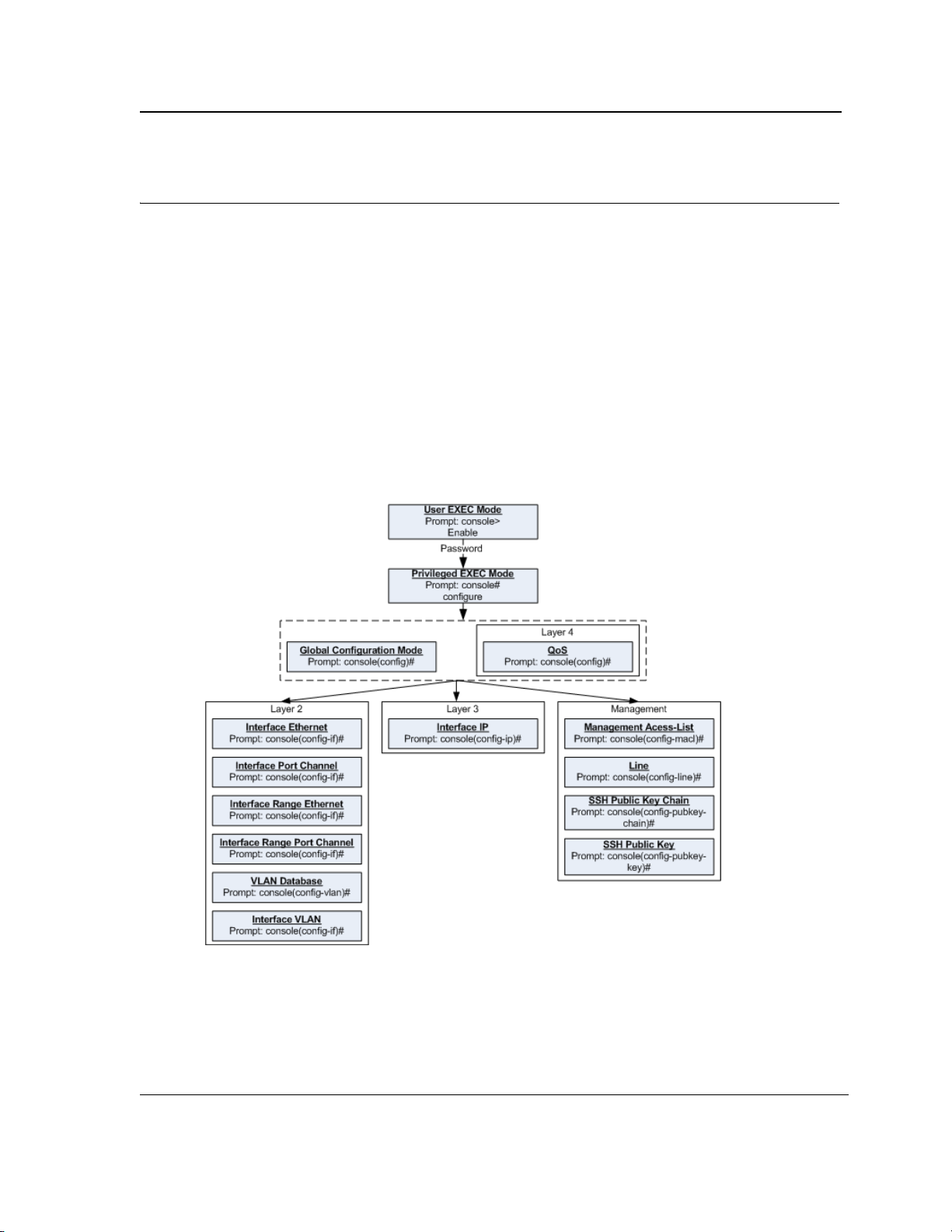
To assist in configuring the device, the Command Line Interface (CLI) is divided into different command modes.
Each command mode has its own set of specific commands. Entering a question mark "?" at the system prompt
(console prompt) displays a list of commands available for that particular command mode.
From each mode, a specific command is used to navigate from one command mode to another. The standard
order to access the modes is as follows: User EXEC mode, Privileged EXEC mode, Global Configuration mode,
and Interface Configuration mode. The following figure illustrates the command mode access path.
When starting a session, the initial mode is the User EXEC mode. Only a limited subset of commands is available
in User EXEC mode. This level is reserved for tasks that do not change the configuration. To enter the next level,
the Privileged EXEC mode, a password is required.
The Privileged EXEC mode gives access to commands that are restricted on User EXEC mode and provides
access to the device Configuration mode.
Page 12

The Global Configuration mode manages the device configuration on a global level.
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 11
The Interface Configuration mode configures specific interfaces in the device.
1.1.2 User EXEC Mode
After logging into the device, the user is automatically in User EXEC command mode unless the user is defined as
a privileged user. In general, the User EXEC commands allow the user to perform basic tests, and list system
information.
The user-level prompt consists of the device host name followed by the angle bracket (>).
Console>
The default host name is Console unless it has been changed using the hostname command in the Global Configuration mode.
1.1.3 Privileged EXEC Mode
Privileged access is password protected to prevent unauthorized use because many of the privileged commands
set operating system parameters. The password is not displayed on the screen and is case sensitive.
Privileged users enter directly into the Privileged EXEC mode. To enter the Privileged EXEC mode from the User
EXEC mode, perform the following steps:
1. At the prompt enter the enable command and press <Enter>. A password prompt is displayed.
2. Enter the password and press <Enter>. The password is displayed as *. The Privileged EXEC mode prompt
is displayed. The Privileged EXEC mode prompt consists of the device host name followed by #.
Console#
To return from the Privileged EXEC mode to the User EXEC mode, use the disable command. The following
example illustrates how to access the Privileged EXEC mode and return to the User EXEC mode:
Console>
Enter Password: ******
Console#
Console#
Console>
The exit command is used to return from any mode to the previous mode except when returning to the User
EXEC mode from the Privileged EXEC mode. For example, the exit command is used to return from the Interface
Configuration mode to the Global Configuration mode.
enable
disable
Page 13
1.1.4 Global Configuration Mode
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 12
Global Configuration mode commands apply to features that affect the system as a whole, rather than just a specific interface. The configure Privileged EXEC mode command is used to enter the Global Configuration mode.
To enter the Global Configuration mode perform the following steps:
1. At the Privileged EXEC mode prompt enter the configure command and press <Enter>. The Global Configu-
ration mode prompt is displayed. The Global Configuration mode prompt consists of the device host name
followed by (config) and #.
Console(config)#
To return from the Global Configuration mode to the Privileged EXEC mode, the user can use one of the following
commands:
• exit
• end
• <Ctrl+Z>
The following example illustrates how to access the Global Configuration mode and return to the Privileged EXEC
mode:
Console#
Console#
Console(config)#
Console#
configure
exit
1.1.5 Interface Configuration and Specific Configuration Modes
Interface Configuration mode commands modify specific interface operations. The following are the Interface Configuration modes:
• Line Interface — Contains commands to configure the management connections. These include commands
such as line timeout settings, etc. The line Global Configuration mode command is used to enter the Line
Configuration command mode.
• VLAN Database — Contains commands to create a VLAN as a whole. The vlan database Global Configura-
tion mode command is used to enter the VLAN Database Interface Configuration mode.
• Management Access List — Contains commands to define management access-lists. The management
access-list Global Configuration mode command is used to enter the Management Access List Configuration
mode.
• Ethernet — Contains commands to manage port configuration. The interface ethernet Global Configuration
mode command is used to enter the Interface Configuration mode to configure an Ethernet type interface.
• Port Channel — Contains commands to configure port-channels, for example, assigning ports to a port-
channel. Most of these commands are the same as the commands in the Ethernet interface mode, and are
used to manage the member ports as a single entity. The interface port-channel Global Configuration mode
command is used to enter the Port Channel Interface Configuration mode.
• SSH Public Key-chain — Contains commands to manually specify other device SSH public keys. The
crypto key pubkey-chain ssh Global Configuration mode command is used to enter the SSH Public Key-
chain Configuration mode.
• QoS — Contains commands related to service definitions. The qos Global Configuration mode command is
used to enter the QoS services configuration mode.
Page 14

• MAC Access-List — Configures conditions required to allow traffic based on MAC addresses. The mac
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 13
access-list Global Configuration mode command is used to enter the MAC access-list configuration mode..
1.2 Starting the CLI
The device can be managed over a direct connection to the device console port or via a Telnet connection. The
device is managed by entering command keywords and parameters at the prompt. Using the device commandline interface (CLI) is very similar to entering commands on a UNIX system.
If access is via a Telnet connection, ensure that the device has a defined IP address, corresponding management
access is granted, and the workstation used to access the device is connected to the device prior to using CLI
commands.
Note
The following steps are for use on the console line only.
To start using the CLI, perform the following steps:
1. Connect the DB9 null-modem or cross over cable to the RS-232 serial port of the device to the RS-232 serial
port of the terminal or computer running the terminal emulation application.
Note
The default data rate is 38400.
a) Set the data format to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity.
b) Set Flow Control to none.
c) Under Properties, select VT100 for Emulation mode.
d) Select Terminal keys for Function, Arrow, and Ctrl keys. Ensure that the setting is for Terminal keys
(not Windows keys).
Note
When using HyperTerminal with Microsoft® Windows 2000,ensure that Windows® 2000 Service Pack 2
or later is installed.With Windows 2000 Service Pack 2, the arrow keys function properly in
HyperTerminal’s VT100 emulation. Go to www.microsoft.com for information on Windows 2000 service
packs.
2. Enter the following commands to begin the configuration procedure:
Console>
Console#
enable
configure
Console(config)#
3. Configure the device and enter the necessary commands to complete the required tasks.
4. When finished, exit the session with the exit command.
When a different user is required to log onto the system, use the login Privileged EXEC mode command. This
effectively logs off the current user and logs on the new user.
Page 15
1.3 Editing Features
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 14
1.3.1 Entering Commands
A CLI command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify
configuration parameters. For example, in the command show interfaces status ethernet e8, show, interfaces
and status are keywords, ethernet is an argument that specifies the interface type, and 8 specifies the port.
To enter commands that require parameters, enter the required parameters after the command keyword. For
example, to set a password for the administrator, enter:
Console(config)#
When working with the CLI, the command options are not displayed. The command is not selected from a menu,
but is manually entered. To see what commands are available in each mode or within an interface configuration,
the CLI does provide a method of displaying the available commands, the command syntax requirements and in
some instances parameters required to complete the command. The standard command to request help is ?.
There are two instances where help information can be displayed:
• Keyword lookup — The character ? is entered in place of a command. A list of all valid commands and cor-
responding help messages are is displayed.
• Partial keyword lookup — If a command is incomplete and or the character ? is entered in place of a
parameter. The matched keyword or parameters for this command are displayed.
To assist in using the CLI, there is an assortment of editing features. The following features are described:
• Terminal Command Buffer
• Command Completion
• Keyboard Shortcuts
username
admin
password
smith
1.3.1.1 Terminal Command Buffer
Every time a command is entered in the CLI, it is recorded on an internally managed Command History buffer.
Commands stored in the buffer are maintained on a First In First Out (FIFO) basis. These commands can be
recalled, reviewed, modified, and reissued. This buffer is not preserved across device resets.
Keyword Description
Up-arrow key
Ctrl+P
Down-arrow key Returns to more recent commands in the history buffer after recalling com-
By default, the history buffer system is enabled, but it can be disabled at any time. For information about the command syntax to enable or disable the history buffer, see history.
There is a standard default number of commands that are stored in the buffer. The standard number of 10 commands can be increased to 216. By configuring 0, the effect is the same as disabling the history buffer system. For
information about the command syntax for configuring the command history buffer, see history size.
To display the history buffer, see show history.
Recalls commands in the history buffer, beginning with the most recent command. Repeats the key sequence to recall successively older commands.
mands with the up-arrow key. Repeating the key sequence will recall successively more recent commands.
Page 16
1.3.1.2 Negating the Effect of Commands
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 15
For many configuration commands, the prefix keyword no can be entered to cancel the effect of a command or
reset the configuration to the default value. This guide describes the negation effect for all applicable commands.
1.3.1.3 Command Completion
If the command entered is incomplete, invalid or has missing or invalid parameters, then the appropriate error
message is displayed. This assists in entering the correct command. By pressing the <Tab> button, an incomplete
command is entered. If the characters already entered are not enough for the system to identify a single matching
command, press ? to display the available commands matching the characters already entered.
1.3.1.4 Keyboard Shortcuts
The CLI has a range of keyboard shortcuts to assist in editing the CLI commands. The following table describes
the CLI shortcuts.
Keyboard Key Description
Up-arrow key Recalls commands from the history buffer, beginning with the most recent command.
Repeat the key sequence to recall successively older commands.
Down-arrow key Returns the most recent commands from the history buffer after recalling commands with
the up arrow key. Repeating the key sequence will recall successively more recent commands.
Ctrl+A Moves the cursor to the beginning of the command line.
Ctrl+E Moves the cursor to the end of the command line.
Ctrl+Z / End Returns back to the Privileged EXEC mode from any configuration mode.
Backspace key Deletes one character left to the cursor position.
1.3.1.5 CLI Command Conventions
When entering commands there are certain command entry standards that apply to all commands. The following
table describes the command conventions.
Convention Description
[ ] In a command line, square brackets indicates an optional entry.
{ } In a command line, curly brackets indicate a selection of compulsory parameters sepa-
rated by the | character. One option must be selected. For example: flowcontrol
{auto|on|off} means that for the flowcontrol command either auto, on or off must be
selected.
Italic font Indicates a parameter.
<Enter> Any individual key on the keyboard. For example click <Enter>.
Ctrl+F4 Any combination keys pressed simultaneously on the keyboard.
Page 17
Screen Display
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 16
Indicates system messages and prompts appearing on the console.
all When a parameter is required to define a range of ports or parameters and all is an
option, the default for the command is all when no parameters are defined. For example, the command interface range port-channel has the option of either entering a
range of channels, or selecting all. When the command is entered without a parameter,
it automatically defaults to all.
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Page 18
Section 2. AAA Commands
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 17
aaa authentication login
The aaa authentication login Global Configuration mode command defines login authentication. To return to the
default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
aaa authentication login {default | list-name} method1 [method2...]
no aaa authentication login {default | list-name}
Parameters
default — Uses the listed authentication methods that follow this argument as the default list of methods
•
when a user logs in.
• list-name — Character string used to name the list of authentication methods activated when a user logs in.
(Range: 1-12 characters).
• method1 [method2...] — Specify at least one from the following table:
Keyword Description
enable Uses the enable password for authentication.
line Uses the line password for authentication.
local Uses the local username database for authentication.
none Uses no authentication.
radius Uses the list of all RADIUS servers for authentication.
Default Configuration
The local user database is checked. This has the same effect as the command aaa authentication login list-
name local.
Note
On the console, login succeeds without any authentication check if the authentication method is not
defined.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
Page 19

User Guidelines
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 18
The default and optional list names created with the aaa authentication login command are used with the login
authentication command.
Create a list by entering the aaa authentication login list-name method command for a particular protocol, where
list-name is any character string used to name this list. The method argument identifies the list of methods that the
authentication algorithm tries, in the given sequence.
The additional methods of authentication are used only if the previous method returns an error, not if it fails. To
ensure that the authentication succeeds even if all methods return an error, specify none as the final method in
the command line.
Example
The following example configures the authentication login.
Console(config)#
aaa authentication login default radius local enable none
Page 20

aaa authentication enable
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 19
The aaa authentication enable Global Configuration mode command defines authentication method lists for
accessing higher privilege levels. To return to the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
aaa authentication enable {default | list-name} method1 [method2...]
no aaa authentication enable {default | list-name}
Parameters
default — Uses the listed authentication methods that follow this argument as the default list of methods,
•
when using higher privilege levels.
• list-name — Character string used to name the list of authentication methods activated, when using access
higher privilege levels (Range: 1-12 characters).
• method1 [method2...] — Specify at least one from the following table:
Keyword Description
enable Uses the enable password for authentication.
line Uses the line password for authentication.
none Uses no authentication.
radius Uses the list of all RADIUS servers for authentication. Uses username $enabx$.,
where x is the privilege level.
Default Configuration
If the default list is not set, only the enable password is checked. This has the same effect as the command aaa
authentication enable default enable.
On the console, the enable password is used if it exists. If no password is set, the process still succeeds. This has
the same effect as using the command aaa authentication enable default enable none.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
The default and optional list names created with the aaa authentication enable command are used with the
enable authentication command.
The additional methods of authentication are used only if the previous method returns an error, not if it fails. To
ensure that the authentication succeeds even if all methods return an error, specify none as the final method in
the command line.
All aaa authentication enable default requests sent by the device to a RADIUS server include the username
$enabx$., where x is the requested privilege level.
Page 21

Example
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 20
The following example sets the enable password for authentication when accessing higher privilege levels.
Console(config)#
aaa authentication enable default enable
Page 22

login authentication
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 21
The login authentication Line Configuration mode command specifies the login authentication method list for a
remote telnet or console. To return to the default configuration specified by the aaa authentication login command, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
login authentication {default | list-name}
no login authentication
Parameters
default — Uses the default list created with the aaa authentication login command.
•
• list-name — Uses the indicated list created with the aaa authentication login command.
Default Configuration
Uses the default set with the command aaa authentication login.
Command Mode
Line Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Changing login authentication from default to another value may disconnect the telnet session.
Example
The following example specifies the default authentication method for a console.
Console(config)#
Console(config-line)#
line console
login authentication default
Page 23
enable authentication
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 22
The enable authentication Line Configuration mode command specifies the authentication method list when
accessing a higher privilege level from a remote telnet or console. To return to the default configuration specified
by the aaa authentication enable command, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
enable authentication {default | list-name}
no enable authentication
Parameters
default — Uses the default list created with the aaa authentication enable command.
•
• list-name — Uses the indicated list created with the aaa authentication enable command.
Default Configuration
Uses the default set with the aaa authentication enable command.
Command Mode
Line Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example specifies the default authentication method when accessing a higher privilege level from a
console.
Console(config)#
Console(config-line)#
line console
enable authentication default
Page 24
ip http authentication
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 23
The ip http authentication Global Configuration mode command specifies authentication methods for HTTP
server users. To return to the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
ip http authentication method1 [method2...]
no ip http authentication
Parameters
method1 [method2...] — Specify at least one from the following table:
•
Keyword Description
local Uses the local username database for authentication.
none Uses no authentication.
radius Uses the list of all RADIUS servers for authentication.
Default Configuration
The local user database is checked. This has the same effect as the command ip http authentication local.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
The additional methods of authentication are used only if the previous method returns an error, not if it fails. To
ensure that the authentication succeeds even if all methods return an error, specify none as the final method in
the command line.
Example
The following example configures the HTTP authentication.
Console(config)#
ip http authentication radius local
Page 25
ip https authentication
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 24
The ip https authentication Global Configuration mode command specifies authentication methods for HTTPS
server users. To return to the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
ip https authentication method1 [method2...]
no ip https authentication
Parameters
method1 [method2...] — Specify at least one from the following table:
•
Keyword Source or destination
local Uses the local username database for authentication.
none Uses no authentication.
radius Uses the list of all RADIUS servers for authentication.
Default Configuration
The local user database is checked. This has the same effect as the command ip https authentication local.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
The additional methods of authentication are used only if the previous method returns an error, not if it fails. To
ensure that the authentication succeeds even if all methods return an error, specify none as the final method in
the command line.
Example
The following example configures HTTPS authentication.
Console(config)#
ip https authentication radius local
Page 26
show authentication methods
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 25
The show authentication methods Privileged EXEC mode command displays information about the authentication methods.
Syntax
show authentication methods
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example displays the authentication configuration.
Console#
Login Authentication Method Lists
---------------------------------
Default: Radius, Local, Line
Console_Login:
Enable Authentication Method Lists
----------------------------------
Default: Radius, Enable
Console_Enable:
Line Login Method List Enable Method List
-------------- ----------------- ------------------
Console Console_Login Console_Enable
Telnet Default Default
SSH Default Default
http: Radius, Local
https: Radius, Local
dot1x: Radius
show authentication methods
Line, None
Enable, None
Page 27
password
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 26
The password Line Configuration mode command specifies a password on a line. To remove the password, use
the no form of this command.
Syntax
password password [encrypted]
no password
Parameters
password — Password for this level (Range: 1-159 characters).
•
• encrypted — Encrypted password to be entered, copied from another device configuration.
Default Configuration
No password is defined.
Command Mode
Line Configuration mode
User Guidelines
If a password is defined as encrypted, the required password length is 32 characters.
Example
The following example specifies password secret on a console.
Console(config)#
Console(config-line)#
line console
password
secret
Page 28

enable password
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 27
The enable password Global Configuration mode command sets a local password to control access to user and
privilege levels. To remove the password requirement, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
enable password [level level] password [encrypted]
no enable password [level level]
Parameters
password — Password for this level (Range: 1-159 characters).
•
• level — Level for which the password applies. If not specified the level is 15
(Range: 1-15).
• encrypted — Encrypted password entered, copied from another device configuration.
Default Configuration
No enable password is defined.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example sets local level 15 password secret to control access to user and privilege levels.
Console(config)#
enable password level
15 secret
Page 29

username
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 28
The username Global Configuration mode command creates a user account in the local database. To remove a
user name, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
username name [password password] [level level] [encrypted]
no username name
Parameters
name — The name of the user (Range: 1- 20 characters).
•
• password — The authentication password for the user (Range: 1-159 characters).
• level — The user level (Range: 1-15).
• encrypted — Encrypted password entered, copied from another device configuration.
Default Configuration
No user is defined.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
User account can be created without a password.
Example
The following example configures user bob with password lee and user level 15 to the system.
Console(config)#
username
bob
password
lee
level
15
Page 30

Section 3. Address Table Commands
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 29
bridge address
The bridge address Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode command adds a MAC-layer station source address to
the bridge table. To delete the MAC address, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
bridge address mac-address {ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number} [permanent | delete-on-
reset | delete-on-timeout | secure]
no bridge address [mac-address]
Parameters
mac-address — A valid MAC address.
•
• interface — A valid Ethernet port.
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
• permanent — The address can only be deleted by the no bridge address command.
• delete-on-reset — The address is deleted after reset.
• delete-on-timeout — The address is deleted after "age out" time has expired.
• secure — The address is deleted after the port changes mode to unlock learning (no port security com-
mand). This parameter is only available when the port is in the learning locked mode.
Default Configuration
No static addresses are defined. The default mode for an added address is permanent.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode
User Guidelines
Using the no form of the command without specifying a MAC address deletes all static MAC addresses belonging
to this VLAN).
Example
The following example adds a permanent static MAC-layer station source address 3aa2.64b3.a245 on port 7 to
the bridge table.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface vlan
bridge address
2
3aa2.64b3.a245
ethernet
e7
permanent
Page 31

bridge multicast filtering
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 30
The bridge multicast filtering Global Configuration mode command enables filtering multicast addresses. To disable filtering multicast addresses, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
bridge multicast filtering
no bridge multicast filtering
Default Configuration
Filtering multicast addresses is disabled. All multicast addresses are flooded to all ports.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
If multicast routers exist on the VLAN, do not change the unregistered multicast addresses state to drop on the
switch ports.
If multicast routers exist on the VLAN and IGMP-snooping is not enabled, the bridge multicast forward-all command should be used to enable forwarding all multicast packets to the multicast switches.
Example
In this example, bridge multicast filtering is enabled.
Console(config)#
bridge multicast filtering
Page 32

bridge multicast address
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 31
The bridge multicast address Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode command registers a MAC-layer multicast
address in the bridge table and statically adds ports to the group. To unregister the MAC address, use the no form
of this command.
Syntax
bridge multicast address {mac-multicast-address | ip-multicast-address}
bridge multicast address {mac-multicast-address | ip-multicast-address} [add | remove] {ethernet interface-list
| port-channel port-channel-number-list}
no bridge multicast address {mac-multicast-address | ip-multicast-address}
Parameters
add — Adds ports to the group. If no option is specified, this is the default option.
•
• remove — Removes ports from the group.
• mac-multicast-address — A valid MAC multicast address.
• ip- multicast-address — A valid IP multicast address.
• interface-list — Separate nonconsecutive Ethernet ports with a comma and no spaces; a hyphen is used to
designate a range of ports.
• port-channel-number-list — Separate nonconsecutive port-channels with a comma and no spaces; a hyphen
is used to designate a range of ports.
Default Configuration
No multicast addresses are defined.
Command Mode
Interface configuration (VLAN) mode
User Guidelines
If the command is executed without add or remove, the command only registers the group in the bridge database.
Static multicast addresses can only be defined on static VLANs.
Examples
The following example registers the MAC address:
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
The following example registers the MAC address and adds ports statically.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface vlan
bridge multicast address
interface vlan
bridge multicast address
8
8
01:00:5e:02:02:03
01:00:5e:02:02:03
add ethernet
e1-4, e7
Page 33

bridge multicast forbidden address
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 32
The bridge multicast forbidden address Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode command forbids adding a specific multicast address to specific ports. Use the no form of this command to return to the default configuration.
Syntax
bridge multicast forbidden address {mac-multicast-address | ip-multicast-address} {add | remove} {ethernet
interface-list | port-channel port-channel-number-list}
no bridge multicast forbidden address {mac-multicast-address | ip-multicast-address}
Parameters
add — Adds ports to the group.
•
• remove — Removes ports from the group.
• mac-multicast-address — A valid MAC multicast address.
• ip- multicast-address — A valid IP multicast address.
• interface-list — Separate nonconsecutive Ethernet ports with a comma and no spaces; hyphen is used to
designate a range of ports.
• port-channel-number-list — Separate nonconsecutive valid port-channels with a comma and no spaces; a
hyphen is used to designate a range of port-channels.
Default Configuration
No forbidden addresses are defined.
Command Modes
Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode
User Guidelines
Before defining forbidden ports, the multicast group should be registered.
Examples
In this example, MAC address 0100.5e02.0203 is forbidden on port 7 within VLAN 8.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
interface vlan
bridge multicast address
bridge multicast forbidden address
8
0100.5e.02.0203
0100.5e02.0203
add ethernet
e7
Page 34

bridge multicast forward-all
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 33
The bridge multicast forward-all Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode command enables forwarding all multicast packets on a port. To restore the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
bridge multicast forward-all {add | remove} {ethernet interface-list | port-channel port-channel-number-list}
no bridge multicast forward-all
Parameters
add — Force forwarding all multicast packets.
•
• remove — Do not force forwarding all multicast packets.
• interface-list — Separate nonconsecutive Ethernet ports with a comma and no spaces; a hyphen is used to
designate a range of ports.
• port-channel-number-list — Separate nonconsecutive port-channels with a comma and no spaces; a hyphen
is used to designate a range of port-channels.
Default Configuration
This setting is disabled.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, all multicast packets on port 8 are forwarded.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface vlan 2
bridge multicast forward-all add ethernet e8
Page 35

bridge multicast forbidden forward-all
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 34
The bridge multicast forbidden forward-all Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode command forbids a port to be
a forward-all-multicast port. To restore the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
bridge multicast forbidden forward-all {add | remove} {ethernet interface-list | port-channel port-channel-
number-list}
no bridge multicast forbidden forward-all
Parameters
add — Forbids forwarding all multicast packets.
•
• remove — Does not forbid forwarding all multicast packets.
• interface-list — Separates nonconsecutive Ethernet ports with a comma and no spaces; a hyphen is used to
designate a range of ports.
• port-channel-number-list — Separates nonconsecutive port-channels with a comma and no spaces; a
hyphen is used to designate a range of port-channels.
Default Configuration
This setting is disabled.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (VLAN) mode
User Guidelines
IGMP snooping dynamically discovers multicast router ports. When a multicast router port is discovered, all the
multicast packets are forwarded to it unconditionally.
This command prevents a port from becoming a multicast router port.
Example
In this example, forwarding all multicast packets to port 1 with VLAN 2 is forbidden.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface vlan
bridge multicast forbidden forward-all add ethernet
2
e1
Page 36

bridge aging-time
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 35
The bridge aging-time Global Configuration mode command sets the address table aging time. To restore the
default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
bridge aging-time seconds
no bridge aging-time
Parameters
seconds — Time in seconds. (Range: 10-630 seconds)
•
Default Configuration
The default setting is 300 seconds.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example the bridge aging time is set to 250.
Console(config)#
bridge aging-time
250
Page 37

clear bridge
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 36
The clear bridge Privileged EXEC mode command removes any learned entries from the forwarding database.
Syntax
clear bridge
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, the bridge tables are cleared.
Console#
clear bridge
Page 38

port security
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 37
The port security Interface Configuration mode command locks the port, thereby, blocking unknown traffic and
preventing the port from learning new addresses. To return to the default configuration, use the no form of this
command.
Syntax
port security [forward | discard | discard-shutdown] [trap seconds]
no port security
Parameters
forward — Forwards packets with unlearned source addresses, but does not learn the address.
•
• discard — Discards packets with unlearned source addresses. This is the default if no option is indicated.
• discard-shutdown — Discards packets with unlearned source addresses. The port is also shut down.
• seconds — Sends SNMP traps and defines the minimum amount of time in seconds between consecutive
traps. (Range: 1-1000000)
Default Configuration
This setting is disabled.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, port 1 forwards all packets without learning addresses of packets from unknown sources and
sends traps every 100 seconds if a packet with an unknown source address is received.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
port security forward trap
e1
100
Page 39

port security routed secure-address
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 38
The port security routed secure-address Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command adds
a MAC-layer secure address to a routed port. Use the no form of this command to delete a MAC address.
Syntax
port security routed secure-address mac-address
no port security routed secure-address mac-address
Parameters
mac-address — A valid MAC address.
•
Default Configuration
No addresses are defined.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode. Cannot be configured for a range of interfaces (range context).
User Guidelines
The command enables adding secure MAC addresses to a routed port in port security mode. The command is
available when the port is a routed port and in port security mode. The address is deleted if the port exits the security mode or is not a routed port.
Example
In this example, the MAC-layer address 66:66:66:66:66:66 is added to port 1.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
port security routed secure-address
e1
66:66:66:66:66:66
Page 40

show bridge address-table
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 39
Use the show bridge address-table Privileged EXEC command to view entries in the bridge-forwarding database.
Syntax
show bridge address-table [vlan vlan] [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number] ] [address mac-
address]
Parameters
vlan — Specific VLAN, such as VLAN 1.
•
• interface — Ethernet port.
• port-channel-number — Port-channel number.
• mac-address— MAC address.
Parameters Range
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC
User Guidelines
Internal usage VLANs (VLANs that are automatically allocated on routed ports) are presented in the VLAN column
by a port number and not by a VLAN ID.
Example
Console#
Aging time is 300 sec
vlan mac address Port Type
--------- -------------- ---- -------
3 00:00:00:55:55:66 3 dynamic
3 00:03:47:cc:01:ce 3 dynamic
3 00:06:1b:c9:6f:c5 3 dynamic
3 00:11:11:6b:3a:32 3 dynamic
3 00:80:92:0b:80:80 3 dynamic
show bridge address-table
Page 41

show bridge address-table static
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 40
The show bridge address-table static Privileged EXEC mode command displays statically created entries in the
bridge-forwarding database.
Syntax
show bridge address-table static [vlan vlan] [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
vlan — Specifies a valid VLAN, such as VLAN 1.
•
• interface — A valid Ethernet port.
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, all static entries in the bridge-forwarding database are displayed.
Console#
Aging time is 300 sec
vlan mac address port type
---- ----------------- ---- -----------------
1 00:60:70:4C:73:FF 8 Permanent
1 00:60.70.8C.73:FF 8 delete-on-timeout
200 00:10:0D:48:37:FF 9 delete-on-reset
show bridge address-table static
Page 42

show bridge address-table count
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 41
The show bridge address-table count Privileged EXEC mode command displays the number of addresses
present in the Forwarding Database.
Syntax
show bridge address-table count [vlan vlan][ ethernet interface-number | port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
vlan — Specifies a valid VLAN, such as VLAN 1.
•
• interface — A valid Ethernet port.
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, the number of addresses present in all VLANs are displayed.
Console#
Capacity: 8192
Free: 8083
Used: 109
Secure addresses: 2
Static addresses: 1
Dynamic addresses: 97
Internal addresses: 9
show bridge address-table count
Page 43

show bridge multicast address-table
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 42
The show bridge multicast address-table User EXEC mode command displays multicast MAC address or IP
address table information.
Syntax
show bridge multicast address-table [vlan vlan-id] [address mac-multicast-address | ip-multicast-address]
[format ip | format mac]
Parameters
vlan-id — A valid VLAN ID value.
•
• mac-multicast-address — A valid MAC multicast address.
• ip-multicast-address — A valid IP multicast address.
• format ip|mac — Multicast address format. Can be ip or mac. If the format is unspecified, the default is mac.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
A MAC address can be displayed in IP format only if it is in the range of 0100.5e00.0000-0100.5e7f.ffff.
Example
In this example, multicast MAC address and IP address table information is displayed.
Console#
Vlan MAC Address Type Ports
---- -------------- ------- ----------
1 01:00:5e:02:02:03 static 1, 2
18 01:00:5e:02:02:08 static 1-3
19 00:00:5e:02:02:08 dynamic 5-7
Forbidden ports for multicast addresses:
Vlan MAC Address Ports
---- -------------- -----
1 01:00:5e:02:02:03 8
19 01:00:5e:02:02:08 8
show bridge multicast address-table
Page 44

Console#
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 43
show bridge multicast address-table format ip
Vlan IP/MAC Address Type Ports
---- ----------------- ------ ---------
1 224-239.130|2.2.3 static 1,2
18 224-239.130|2.2.8 static 1-3
19 224-239.130|2.2.8 dynamic 5-7
Forbidden ports for multicast addresses:
Vlan IP/MAC Address Ports
---- ----------------- ------
1 224-239.130|2.2.3 8
19 224-239.130|2.2.8 8
Note
A multicast MAC address maps to multiple IP addresses as shown above.
Page 45

show bridge multicast filtering
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 44
The show bridge multicast filtering User EXEC mode command displays the multicast filtering configuration.
Syntax
show bridge multicast filtering vlan-id
Parameters
vlan-id — VLAN ID value.
•
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
User EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, the multicast configuration for VLAN 1 is displayed.
Console#
Filtering: Enabled
VLAN: 1
Port Forward-Unregistered Forward-All
---- --------- --------- --------- ----------
1 Forbidden Filter Forbidden Filter
2 Forward Forward(s) Forward Forward(s)
3 - Forward(d) - Forward(d)
show bridge multicast filtering
Static Status Static Status
1
Page 46

show ports security
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 45
The show ports security Privileged EXEC mode command displays the port-lock status.
Syntax
show ports security [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
interface — A valid Ethernet port.
•
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In this example, all classes of entries in the port-lock status are displayed:
Console#
Port Action Trap Frequency
1 Disabled - -
2 Disabled Discard Disabled -
3 Disabled - - -
4 Disabled - - -
5 Disqbled - - -
6 Disabled - - -
7 Disabled - - -
8 Disabled - - -
9 Disabled - - -
10 Disabled - - -
ch1 Disabled
ch2 Disabled
ch3 Disabled
ch4 Disabled
ch5 Disabled
ch6 Disabled
show ports security
Page 47

ch7 Disabled
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 46
ch8 Disabled
The following tables describes the fields shown above.
Field Description
Port Port number
Status Locked/Unlocked
Action Action on violation
Trap Indicates if traps are sent in case of a violation
Frequency Minimum time between consecutive traps
Page 48

Section 4. Clock
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 47
clock set
The clock set Privileged EXEC mode command manually sets the system clock.
Syntax
clock set hh:mm:ss day month year
or
clock set hh:mm:ss month day year
Parameters
hh:mm:ss — Current time in hours (military format), minutes, and seconds (hh: 0 - 23, mm: 0 - 59, ss: 0 - 59).
•
• day — Current day (by date) in the month (1 - 31).
• month — Current month using the first three letters by name (Jan, …, Dec).
• year — Current year (2000 - 2097).
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example sets the system time to 13:32:00 on the 7th March 2002.
Console# clock set 13:32:00 7 Mar 2002
Page 49

clock source
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 48
The clock source Global Configuration mode command configures an external time source for the system clock.
Use no form of this command to disable external time source.
Syntax
clock source {sntp}
no clock source
Parameters
sntp — SNTP servers
•
Default Configuration
No external clock source
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example configures an external time source for the system clock.
Console(config)# clock source sntp
Page 50

clock timezone
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 49
The clock timezone Global Configuration mode command sets the time zone for display purposes. To set the
time to the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), use the no form of this command.
Syntax
clock timezone hours-offset
no clock timezone
Parameters
hours-offset — Hours difference from UTC. (Range: -12 – +13)
•
Default Configuration
Clock set to UTC.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
The system internally keeps time in UTC, so this command is used only for display purposes and when the time is
manually set.
Examples
The following example sets the timezone to 6 hours difference from UTC.
Console(config)# clock timezone -6 zone CST
Page 51

clock summer-time
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 50
The clock summer-time Global Configuration mode command configures the system to automatically switch to
summer time (daylight saving time). To configure the software not to automatically switch to summer time, use the
no form of this command.
Syntax
clock summer-time recurring { | {week day month hh:mm week day month hh:mm}} [offset offset] [zone acro-
nym]
clock summer-time date date month year hh:mm date month year hh:mm [offset offset] [zone acronym]
clock summer-time date month date year hh:mm month date year hh:mm [offset offset] [zone acronym]
no clock summer-time recurring
Parameters
recurring — Indicates that summer time should start and end on the corresponding specified days every
•
year.
• date — Indicates that summer time should start on the first specific date listed in the command and end on
the second specific date in the command.
• week — Week of the month. (Range: 1 - 5, first, last)
• day — Day of the week (Range: first three letters by name, like sun)
• date — Date of the month. (Range:1 - 31)
• month — Month. (Range: first three letters by name, like Jan)
• year — year - no abbreviation (Range: 2000 - 2097)
• hh:mm — Time in military format, in hours and minutes. (Range: hh: 0 - 23, mm:0 - 59)
• offset — Number of minutes to add during summer time. (Range: 1 - 1440)
• acronym — The acronym of the time zone to be displayed when summer time is in effect. (Range: Up to 4
characters)
Default Configuration
Summer time is disabled.
offset — Default is 60 minutes.
acronym — If unspecified default to the timezone acronym.
If the timezone has not been defined, the default is UTC.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
Page 52

User Guidelines
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 51
In both the date and recurring forms of the command, the first part of the command specifies when summer time
begins, and the second part specifies when it ends. All times are relative to the local time zone. The start time is
relative to standard time. The end time is relative to summer time. If the starting month is chronologically after the
ending month, the system assumes that you are in the southern hemisphere.
Examples
The following example sets summer time starting on the first Sunday in April at 2 am and finishing on the last Sunday in October at 2 am.
Console(config)# clock summer-time recurring first sun apr 2:00 last sun oct 2:00
Page 53

sntp authentication-key
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 52
The sntp authentication-key Global Configuration mode command defines an authentication key for Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP). To remove the authentication key for SNTP, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp authentication-key number md5 value
no sntp authentication-key number
Parameters
number — Key number (Range: 1-4294967295)
•
• value — Key value (Range: 1-8 characters)
Default Configuration
No authentication key is defined.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Multiple keys can be generated.
Examples
The following example defines the authentication key for SNTP.
Console(config)#
sntp authentication-key
8
md5
ClkKey
Page 54

sntp authenticate
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 53
The sntp authenticate Global Configuration mode command grants authentication for received Simple Network
Time Protocol (SNTP) traffic from servers. To disable the feature, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp authenticate
no sntp authenticate
Default Configuration
No authentication
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
The command is relevant for both unicast and broadcast.
Examples
The following example defines the authentication key for SNTP and grants authentication.
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
sntp authentication-key
sntp trusted-key
sntp authenticate
8
8
md5
ClkKey
Page 55

sntp trusted-key
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 54
The sntp trusted-key Global Configuration mode command authenticates the identity of a system to which Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) will synchronize. To disable authentication of the identity of the system, use the
no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp trusted-key key-number
no sntp trusted-key key-number
Parameters
key-number — Key number of authentication key to be trusted. (Range: 1 - 4294967295)
•
Default Configuration
No keys are trusted.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
The command is relevant for both received unicast and broadcast.
If there is at least 1 trusted key, then unauthenticated messages will be ignored.
Examples
The following example authenticates key 8.
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
sntp authentication-key
sntp trusted-key
sntp authenticate
8
8
md5
ClkKey
Page 56

sntp client poll timer
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 55
The sntp client poll timer Global Configuration mode command sets the polling time for the Simple Network
Time Protocol (SNTP) client. To return to default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp client poll timer seconds
no sntp client poll timer
Parameters
seconds — Polling interval in seconds (Range: 60-86400)
•
Default Configuration
Polling interval is 1024 seconds.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example sets the polling time for the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) client to 120 seconds.
Console(config)#
sntp client poll timer
120
Page 57

sntp broadcast client enable
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 56
The sntp broadcast client enable Global Configuration mode command enables Simple Network Time Protocol
(SNTP) broadcast clients. To disable SNTP broadcast clients, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp broadcast client enable
no sntp broadcast client enable
Default Configuration
The SNTP broadcast client is disabled.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Use the sntp client enable (Interface) Interface Configuration mode command to enable the SNTP client on a
specific interface.
Examples
The following example enables the SNTP broadcast clients.
Console(config)# sntp broadcast client enable
Page 58

sntp anycast client enable
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 57
The sntp anycast client enable Global Configuration mode command enables SNTP anycast client. To disable
the SNTP anycast client, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp anycast client enable
no sntp anycast client enable
Default Configuration
The SNTP anycast client is disabled.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Polling time is determined by the sntp client poll timer Global Configuration mode command.
Use the sntp client enable (Interface) Interface Configuration mode command to enable the SNTP client on a
specific interface.
Examples
The following example enables SNTP anycast clients.
console(config)#
sntp anycast client enable
Page 59

sntp client enable (Interface)
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 58
The sntp client enable Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel, VLAN) mode command enables the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) client on an interface. This applies to both receive broadcast and anycast
updates. To disable the SNTP client, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp client enable
no sntp client enable
Default Configuration
The SNTP client is disabled on an interface.
Command Mode
Interface configuration (Ethernet, port-channel, VLAN) mode
User Guidelines
Use the sntp broadcast client enable Global Configuration mode command to enable broadcast clients globally.
Use the sntp anycast client enable Global Configuration mode command to enable anycast clients globally.
Examples
The following example enables the SNTP client on Ethernet port 3.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
e3
sntp client enable
Page 60

sntp unicast client enable
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 59
The sntp unicast client enable Global Configuration mode command enables the device to use the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) to request and accept SNTP traffic from servers. To disable requesting and accepting
SNTP traffic from servers, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp unicast client enable
no sntp unicast client enable
Default Configuration
The SNTP unicast client is disabled.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Use the sntp server Global Configuration mode command to define SNTP servers.
Examples
The following example enables the device to use the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) to request and accept
SNTP traffic from servers.
Console(config)#
sntp unicast client enable
Page 61

sntp unicast client poll
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 60
The sntp unicast client poll Global Configuration mode command enables polling for the Simple Network Time
Protocol (SNTP) predefined unicast servers. To disable the polling for SNTP client, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp unicast client poll
no sntp unicast client poll
Default Configuration
Polling is disabled.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Polling time is determined by the sntp client poll timer Global Configuration mode command.
Examples
The following example enables polling for Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) predefined unicast clients.
Console(config)#
sntp unicast client poll
Page 62

sntp server
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 61
The sntp server Global Configuration mode command configures the device to use the Simple Network Time
Protocol (SNTP) to request and accept SNTP traffic from a specified server. To remove a server from the list of
SNTP servers, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
sntp server {ip-address | hostname}[poll] [key keyid]
no sntp server host
Parameters
ip-address — IP address of the server.
•
• hostname — Hostname of the server. (Range: 1-158 characters)
• poll — Enable polling.
• keyid — Authentication key to use when sending packets to this peer.
(Range:1-4294967295)
Default Configuration
No servers are defined.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Up to 8 SNTP servers can be defined.
Use the sntp unicast client enable Global Configuration mode command to enable predefined unicast clients
globally.
To enable polling you should also use the sntp unicast client poll Global Configuration mode command for glo-
bal enabling.
Polling time is determined by the sntp client poll timer Global Configuration mode command.
Examples
The following example configures the device to accept SNTP traffic from the server on 192.1.1.1.
Console(config)#
sntp server
192.1.1.1
Page 63

show clock
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 62
The show clock User EXEC mode command displays the time and date from the system clock.
Syntax
show clock [detail]
Parameters
detail — Shows timezone and summertime configuration.
•
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
User EXEC mode
User Guidelines
The symbol that precedes the show clock display indicates the following:
Symbol Description
* Time is not authoritative.
(blank) Time is authoritative.
. Time is authoritative, but SNTP is not synchronized.
Example
The following example displays the time and date from the system clock.
Console> show clock
15:29:03 PDT(UTC-7) Jun 17 2002
Time source is SNTP
Console>
15:29:03 PDT(UTC-7) Jun 17 2002
Time source is SNTP
Time zone:
Acronym is PST
Offset is UTC-8
Summertime:
Acronym is PDT
Recurring every year.
Begins at first Sunday of April at 2:00.
Ends at last Sunday of October at 2:00.
Offset is 60 minutes.
show clock detail
Page 64

show sntp configuration
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 63
The show sntp configuration Privileged EXEC mode command shows the configuration of the Simple Network
Time Protocol (SNTP).
Syntax
show sntp configuration
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example displays the current SNTP configuration of the device.
Console#
Polling interval: 7200 seconds
MD5 Authentication keys: 8, 9
Authentication is required for synchronization.
Trusted Keys: 8, 9
Unicast Clients: Enabled
Unicast Clients Polling: Enabled
Server Polling Encryption Key
----------- ------- --------------
176.1.1.8 Enabled 9
176.1.8.179 Disabled Disabled
Broadcast Clients: Enabled
Anycast Clients: Enabled
Broadcast and Anycast Interfaces: 1, 3
show sntp configuration
Page 65

show sntp status
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 64
The show sntp status Privileged EXEC mode command shows the status of the Simple Network Time Protocol
(SNTP).
Syntax
show sntp status
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example shows the status of the SNTP.
Console# show sntp status
Clock is synchronized, stratum 4, reference is 176.1.1.8, unicast
Reference time is AFE2525E.70597B34 (00:10:22.438 PDT Jul 5 1993)
Unicast servers:
Server Status Last response Offset
[mSec]
----------- ------- ---------------------------- ------ ------
176.1.1.8 Up 19:58:22.289 PDT Feb 19 2002 7.33 117.79
176.1.8.179 Unknown 12:17.17.987 PDT Feb 19 2002 8.98 189.19
Anycast server:
Server Interface Status Last response Offset Delay
[mSec] [mSec]
--------- ------- ----- ----------------------------- ------ -----
176.1.11.8 VLAN 118 Up 9:53:21.789 PDT Feb 19 2002 7.19 119.89
Broadcast:
Interface IP address Last response
--------- --------- ----------------------------
176.9.1.1 VLAN 119 19:17:59.792 PDT Feb 19 2002
Delay
[mSec]
Page 66

Section 5. Configuration and Image Files
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 65
copy
The copy Privileged EXEC mode command copies files from a source to a destination.
Syntax
copy source-url destination-url
Parameters
source-url — The source file location URL or reserved keyword of the source file to be copied.
•
(Range: 1-160 characters)
• destination-url — The destination file URL or reserved keyword of the destination file.
(Range: 1-160 characters)
The following table displays keywords and URL prefixes:
Keyword Source or Destination
flash: Source or destination URL for flash memory. It’s the default in case a URL is specified
without a prefix.
running-config Represents the current running configuration file.
startup-config Represents the startup configuration file.
image If the source file, represents the active image file. If the destination file, represents the
non-active image file.
boot Boot file.
tftp:// Source or destination URL for a TFTP network server. The syntax for this alias is tftp://
host/[directory]/filename. The host can be represented by its IP address or hostname.
xmodem: Source for the file from a serial connection that uses the Xmodem protocol.
null: Null destination for copies or files. A remote file can be copied to null to determine its size.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
Up to five backup configuration files are supported on the device.
The location of a file system dictates the format of the source or destination URL.
The entire copying process may take several minutes and differs from protocol to protocol and from network to
network.
Understanding Invalid Combinations of Source and Destination
Page 67

Some invalid combinations of source and destination exist. Specifically, you cannot copy if one of the following
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 66
conditions exist:
The source file and destination file are the same file.
xmodem: is the destination file. The source file can be copied to image, boot and null: only.
tftp:// is the source file and destination file on the same copy.
The following table describes copy characters:
Character Description
! For network transfers, indicates that the copy process is taking place. Each exclamation
point indicates successful transfer of ten packets (512 bytes each).
. For network transfers, indicates that the copy process timed out. Generally, many peri-
ods in a row means that the copy process may fail.
Copying an Image File from a Server to Flash Memory
To copy an image file from a server to flash memory, use the copy source-url image command.
Copying a Boot File from a Server to Flash Memory
To copy a boot file from a server to flash memory, enter the copy source-url boot command.
Copying a Configuration File from a Server to the Running Configuration File
To load a configuration file from a network server to the running configuration file of the device, enter the copy
source-url running-config command. The commands in the loaded configuration file are added to those in the
running configuration file as if the commands were typed in the command-line interface (CLI). Thus, the resulting
configuration file is a combination of the previous running configuration and the loaded configuration files with the
loaded configuration file taking precedence.
Copying a Configuration File from a Server to the Startup Configuration
To copy a configuration file from a network server to the startup configuration file of the device, enter copy source-
url startup-config. The startup configuration file is replaced by the copied configuration file.
Storing the Running or Startup Configuration on a Server
Use the copy running-config destination-url command to copy the current configuration file to a network server
using TFTP. Use the copy startup-config destination-url command to copy the startup configuration file to a network server.
Saving the Running Configuration to the Startup Configuration
To copy the running configuration to the startup configuration file, enter the copy running-config startup-config
command.
Backing up the Running or Startup Configuration to a backup file
To copy the running configuration file to a backup configuration file, enter the copy running-config file command.
To copy the startup configuration file to a backup configuration file, enter the copy startup-config file command.
Page 68

Example
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 67
The following example copies system image file1 from the TFTP server 172.16.101.101 to a
non-active image file.
Console#
copy tftp://
172.16.101.101/file1
image
Accessing file 'file1' on 172.16.101.101...
Loading file1 from 172.16.101.101:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [OK]
Copy took 0:01:11 [hh:mm:ss]
Page 69

delete
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 68
The delete Privileged EXEC mode command deletes a file from a flash memory device.
Syntax
delete url
Parameters
url — A reserved keyword of the file to be deleted. (Range: 1-160 characters)
•
The following table displays the reserved keyword:
Keyword Source or Destination
startup-config Represents the startup configuration file.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
*.sys, image file cannot be deleted.
Examples
The following example deletes file test from flash memory.
Console#
Delete startup-config [y/n]?
delete startup-config
Page 70

delete startup-config
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 69
The delete startup-config Privileged EXEC mode command deletes the startup-config file.
Syntax
delete startup-config
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example deletes the startup-config file.
Console#
delete startup-config
Page 71

show running-config
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 70
The show running-config Privileged EXEC mode command displays the contents of the currently running configuration file.
Syntax
show running-config
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example displays the contents of the running configuration file.
Console#
no spanning-tree
interface ethernet e3
ip address 10.6.39.150 255.255.255.0
exit
username ews password d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e level 15 encrypted
snmp-server engineID local 8000005903001325387800
snmp-server v3-host 10.6.39.23 testUser informs auth
snmp-server group testgroup v3 noauth notify DefaultSuper read DefaultSuper w
rite DefaultSuper
show running-config
Page 72

show startup-config
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 71
The show startup-config Privileged EXEC mode command displays the contents of the startup configuration file.
Syntax
show startup-config
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example displays the contents of the running configuration file.
Console#
console# show startup-config
no spanning-tree
interface ethernet e3
ip address 10.6.39.150 255.255.255.0
exit
username ews password d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e level 15 encrypted
snmp-server engineID local 8000005903001325387800
snmp-server v3-host 10.6.39.23 testUser informs auth
snmp-server group testgroup v3 noauth notify DefaultSuper read DefaultSuper w
rite DefaultSuper
show startup-config
Page 73

Section 6. Ethernet Configuration Commands
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 72
interface ethernet
The interface ethernet Global Configuration mode command enters the interface configuration mode to configure
an Ethernet type interface.
Syntax
interface ethernet interface
Parameters
interface — Valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example enables configuring Ethernet port 7.
Console(config)#
interface ethernet
e7
Page 74

interface range ethernet
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 73
The interface range ethernet Global Configuration mode command configures multiple Ethernet type interfaces
at the same time.
Syntax
interface range ethernet {port-range | all}
Parameters
port-range — List of valid ports. Where more than one port is listed, separate nonconsecutive ports with a
•
comma and no spaces, use a hyphen to designate a range of ports and group a list seperated by commas in
brackets.
• all — All Ethernet ports.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
Commands under the interface range context are executed independently on each active interface in the range. If
the command returns an error on one of the active interfaces, it does not stop executing commands on other
active interfaces.
Example
The following example shows how ports 1 to 5 and 6 to 8 are grouped to receive the same command.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface range ethernet
e1-5, e6-8
Page 75

shutdown
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 74
The shutdown Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command disables an interface. To restart a
disabled interface, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
shutdown
no shutdown
Default Configuration
The interface is enabled.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example disables Ethernet port 5 operations.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
The following example restarts the disabled Ethernet port.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet e
shutdown
interface ethernet
no shutdown
5
e5
Page 76

description
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 75
The description Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command adds a description to an interface. To remove the description, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
description string
no description
Parameters
string — Comment or a description of the port to enable the user to remember what is attached to the port.
•
(Range: 1-64 characters)
Default Configuration
The interface does not have a description.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example adds a description to Ethernet port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet e
description
5
"RD SW#3"
Page 77

speed
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 76
The speed Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command configures the speed of a given
Ethernet interface when not using auto-negotiation. To restore the default configuration, use the no form of this
command.
Syntax
speed {10 | 100 | 1000 |}
no speed
Parameters
10 — Forces10 Mbps operation.
•
• 100 — Forces 100 Mbps operation.
• 1000 — Forces 1000 Mbps operation.
Default Configuration
Maximum port capability
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
The no speed command in a port-channel context returns each port in the port-channel to its maximum capability.
Example
The following example configures the speed operation of Ethernet port 5 to 100 Mbps operation.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
speed 100
e5
Page 78

duplex
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 77
The duplex Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command configures the full/half duplex operation of a given
Ethernet interface when not using auto-negotiation. To restore the default configuration, use the no form of this
command.
Syntax
duplex {half | full}
Parameters
no duplex
•
• half — Forces half-duplex operation
• full — Forces full-duplex operation
Default Configuration
The interface is set to full duplex.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode
User Guidelines
When configuring a particular duplex mode on the port operating at 10/100 Mbps, disable the auto-negotiation on
that port.
Half duplex mode can be set only for ports operating at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps.
Example
The following example configures the duplex operation of Ethernet port 5 to full duplex operation.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
duplex full
e5
Page 79

negotiation
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 78
The negotiation Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command enables auto-negotiation operation for the speed and duplex parameters of a given interface. To disable auto-negotiation, use the no form of this
command.
Syntax
negotiation [capability1 [capability2…capability5]]
no negotiation
Parameters
capability — Specifies the capabilities to advertise. (Possible values: 10h, 10f, 100h,100f, 1000f)
•
Default Configuration
Auto-negotiation is enabled.
If unspecified, the default setting is to enable all capabilities of the port.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
If capabilities were specified when auto-negotiation was previously entered, not specifying capabilities when currently entering auto-negotiation overrides the previous configuration and enables all capabilities.
Example
The following example enables auto-negotiation on Ethernet port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
negotiation
e5
Page 80

flowcontrol
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 79
The flowcontrol Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command configures flow control on a
given interface. To disable flow control, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
flowcontrol {auto | on | off}
no flowcontrol
Parameters
auto — Indicates auto-negotiation
•
• on — Enables flow control.
• off — Disables flow control.
Default Configuration
Flow control is off.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
Negotiation should be enabled for flow control auto.
Example
In the following example, flow control is enabled on port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet e
5
flowcontrol on
Page 81

mdix
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 80
The mdix Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command enables cable crossover on a given interface. To disable cable crossover, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
mdix {on | auto}
no mdix
Parameters
on — Manual mdix
•
• auto — Automatic mdi/mdix
Default Configuration
The default setting is on.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode
User Guidelines
Auto: All possibilities to connect a PC with cross or normal cables are supported and are automatically detected.
On: It is possible to connect to a PC only with a normal cable and to connect to another device only with a cross
cable.
No: It is possible to connect to a PC only with a cross cable and to connect to another device only with a normal
cable.
Example
In the following example, automatic crossover is enabled on port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
mdix auto
e5
Page 82

back-pressure
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 81
The back-pressure Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command enables back pressure on a
given interface. To disable back pressure, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
back-pressure
no back-pressure
Default Configuration
Back pressure is enabled.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In the following example back pressure is enabled on port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)# back-pressure
interface ethernet
e5
Page 83

clear counters
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 82
The clear counters User EXEC mode command clears statistics on an interface.
Syntax
clear counters [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
interface — Valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — Valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
User EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
In the following example, the counters for interface 1 are cleared.
Console>
clear counters ethernet
e1
Page 84

set interface active
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 83
The set interface active Privileged EXEC mode command reactivates an interface that was shutdown.
Syntax
set interface active {ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number}
Parameters
interface — Valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — Valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
This command is used to activate interfaces that were configured to be active, but were shutdown by the system
for some reason (e.g., port security).
Example
The following example reactivates interface 5.
Console# set interface active ethernet e5
Page 85

show interfaces advertise
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 84
The show interfaces advertise Privileged EXEC mode command displays autonegotiation data.
Syntax
show interfaces advertise [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number ]
Parameters
interface — Valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — Valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following examples display autonegotiation information.
Console#
Port Type Neg Operational Link Advertisement
---- ----------- ------- ------------------------------
1 100M-Copper Enabled --
2 100M-Copper Enabled --
3 100M-Copper Enabled --
4 100M-Copper Enabled --
5 100M-Copper Enabled 100f, 100h, 10f, 10h
6 100M-Copper Enabled --
7 100M-Copper Enabled --
8 100M-Copper Enabled --
9 1G-Copper Enabled
19 1G-Fiber Enabled
Port Type Neg Operational Link Advertisement
---- ----------- ------- ------------------------------
ch1 Enabled
ch2 Enabled
show interfaces advertise
Page 86

ch3 Enabled
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 85
ch4 Enabled
ch5 Enabled
ch6 Enabled
Page 87

show interfaces configuration
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 86
The show interfaces configuration Privileged EXEC mode command displays the configuration for all configured interfaces.
Syntax
show interfaces configuration [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number ]
Parameters
interface — Valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — Valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example displays the configuration of all configured interfaces:
Console#
Port Type Duplex Speed Neg Flow
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------- ---- ----- -------- ----
1 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
2 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
3 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
4 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
5 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
6 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
7 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
8 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
9 1G-Copper Full 1000 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
10 100M-Fiber Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
show interfaces configuration
Ctrl
Link
State
Back
Pressure
Mdix
Mode
Page 88

show interfaces status
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 87
The show interfaces status Privileged EXEC mode command displays the status of all configured interfaces.
Syntax
show interfaces status [ethernet interface| port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
interface — A valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Mode
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example displays the status of all configured interfaces:
Console#
Port Type Duplex Speed Neg Flow
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------- ---- ----- -------- ----
1 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
2 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
3 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
4 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
5 100M-Copper Full 100 Enabled Off Up Disabled Auto
6 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
7 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
8 100M-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
9 1G-Copper -- -- -- -- Down -- --
10 1G-Fiber -- -- -- -- Down -- --
Port Type Duplex Speed Neg Flow
---- ----------- ------ ----- ------- ---- -----
show interfaces status
Ctrl
Ctrl
Link
State
Link
State
Back
Pressure
Mdix
Mode
Page 89

ch1 Not Present
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 88
ch2 Not Present
ch3 Not Present
ch4 Not Present
ch5 Not Present
ch6 Not Present
Page 90

show interfaces description
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 89
The show interfaces description Privileged EXEC mode command displays the description for all configured
interfaces.
Syntax
show interfaces description [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
interface — Valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example displays descriptions of configured interfaces.
Console#
Port Description
---- -----------
1 lab
2
3
4
5
6
ch1
ch2
show interfaces description
Page 91

show interfaces counters
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 90
The show interfaces counters User EXEC mode command displays traffic seen by the physical interface.
Syntax
show interfaces counters [ethernet interface | port-channel port-channel-number]
Parameters
interface — A valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
• port-channel-number — A valid port-channel number.
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Modes
User EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Examples
The following example displays traffic seen by the physical interface:
Console#
Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts
---- -------- ----------- ----------- -----------
1 183892 0 0 0
20 0 0 0
3 123899 0 0 0
40 0 0 0
50 0 0 0
60 0 0 0
7 9188 0 0 0
80 0 0 0
9 8789 0 0 0
10 0 0 0 0
Ch OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts
--- --------- ------------ ------------ ------------
10 0 0 0
2 27889 0 0 0
show interfaces counters
Page 92

30 0 0 0
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 91
40 0 0 0
50 0 0 0
60 0 0 0
7 23739 0 0 0
The following example displays counters for Ethernet port 1.
Console#
show interfaces counters ethernet
e1
Port InOctets InUcastPkts InMcastPkts InBcastPkts
------ ----------- -------------- ----------- -----------
1 183892 0 0 0
Port OutOctets OutUcastPkts OutMcastPkts OutBcastPkts
------ ----------- -------------- ------------ ------------
19188 0 0 0
FCS Errors: 0
Single Collision Frames: 0
Late Collisions: 0
Excessive Collisions: 0
Oversize Packets: 0
Internal MAC Rx Errors: 0
Received Pause Frames: 0
Transmitted Pause Frames: 0
The following table describes the fields shown in the display:
Field Description
InOctets Counted received octets.
InUcastPkts Counted received unicast packets.
InMcastPkts Counted received multicast packets.
InBcastPkts Counted received broadcast packets.
OutOctets Counted transmitted octets.
OutUcastPkts Counted transmitted unicast packets.
OutMcastPkts Counted transmitted multicast packets.
OutBcastPkts Counted transmitted broadcast packets.
FCS Errors Counted received frames that are an integral number of octets in length but do
not pass the FCS check.
Page 93

Single Collision Frames Counted frames that are involved in a single collision, and are subsequently
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 92
transmitted successfully.
Late Collisions Number of times that a collision is detected later than one slotTime into the
transmission of a packet.
Oversize Packets Counted frames received that exceed the maximum permitted frame size.
Internal MAC Rx Errors Counted frames for which reception fails due to an internal MAC sublayer
receive error.
Received Pause Frames Counted MAC Control frames received with an opcode indicating the PAUSE
operation.
Transmitted Pause Frames Counted MAC Control frames transmitted on this interface with an opcode indi-
cating the PAUSE operation.
Page 94

port storm-control include-multicast
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 93
The port storm-control include-multicast Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command counts multicast
packets in broadcast storm control. To disable counting multicast packets, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
port storm-control include-multicast [unknown-unicast]
no port storm-control include-multicast
Parameters
unknown-unicast — Specifies also counting unknown unicast packets.
•
Default Configuration
Multicast packets are not counted.
Command Modes
Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode
User Guidelines
To control multicasts storms, use the port storm-control broadcast enable and port storm-control broadcast
rate commands.
Example
The following example enables counting broadcast and multicast packets on Ethernet port 3.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
e3
port storm-control include-multicast
Page 95

port storm-control broadcast enable
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 94
The port storm-control broadcast enable Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command enables broadcast
storm control. To disable broadcast storm control, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
port storm-control broadcast enable
no port storm-control broadcast enable
Default Configuration
Broadcast storm control is disabled.
Command Modes
Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode
User Guidelines
Use the port storm-control broadcast rate Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command, to set the maximum allowable broadcast rate.
Use the port storm-control include-multicast Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command to enable
counting multicast packets and optionally unknown unicast packets in the storm control calculation.
The command can be enabled on a specific port only if rate-limit interface configuration command is not enabled
on that port.
Example
The following example enables broadcast storm control on Ethernet port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
port storm-control broadcast enable
e5
Page 96

port storm-control broadcast rate
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 95
The port storm-control broadcast rate Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode command configures the maximum broadcast rate. To return to the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
port storm-control broadcast rate rate
no port storm-control broadcast rate
Parameters
rate — Maximum kilobits per second of broadcast and multicast traffic on a port
•
Possible values are:
– 70K - 1M in steps of at least 10K
– 1M-10M in steps of at least 1M
– 10M-250M in steps based on the requested rate
Default Configuration
The default storm control broadcast rate is 100 Kbits/Sec.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet) mode
User Guidelines
Use the port storm-control broadcast enable Interface Configuration mode command to enable broadcast
storm control.
Since granularity depends on the requested rate, the software displays the actual rate.
Example
The following example configures the maximum storm control broadcast rate at 900 Kbits/Sec on Ethernet
port 5.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet
port storm-control broadcast rate
e5
900
Page 97

show ports storm-control
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 96
The show ports storm-control Privileged EXEC mode command displays the storm control configuration.
Syntax
show ports storm-control [interface]
Parameters
interface — A valid Ethernet port. (Full syntax: port)
•
Default Configuration
This command has no default configuration.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example displays the storm control configuration.
Console#
Port State Rate [Kbits/Sec] Included
---- -------- ---------------- --------------------------------------
1 Enabled 100 Broadcast
2 Enabled 100 Broadcast
3 Enabled 100 Broadcast
4 Enabled 100 Broadcast
5 Enabled 100 Broadcast
6 Enabled 100 Broadcast
7 Enabled 100 Broadcast
8 Enabled 100 Broadcast
9 Enabled 1000 Broadcast
10 Disabled 1000 Broadcast
show ports storm-control
Page 98

Section 7. GVRP Commands
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 97
gvrp enable (Global)
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) is an industry-standard protocol designed to propagate VLAN information from device to device. With GVRP, a single device is manually configured with all desired VLANs for the network, and all other devices on the network learn these VLANs dynamically.
The gvrp enable Global Configuration mode command enables GVRP globally. To disable GVRP on the device,
use the no form of this command.
Syntax
gvrp enable
no gvrp enable
Default Configuration
GVRP is globally disabled.
Command Mode
Global Configuration mode
User Guidelines
There are no user guidelines for this command.
Example
The following example enables GVRP globally on the device.
Console(config)#
gvrp enable
Page 99

gvrp enable (Interface)
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 98
The gvrp enable Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode command enables GVRP on an interface.
To disable GVRP on an interface, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
gvrp enable
no gvrp enable
Default Configuration
GVRP is disabled on all interfaces.
Command Mode
Interface Configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
An access port does not dynamically join a VLAN because it is always a member in only one VLAN.
Membership in an untagged VLAN is propagated in the same way as in a tagged VLAN. That is, the PVID is manually defined as the untagged VLAN VID.
Example
The following example enables GVRP on Ethernet port 6.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet e
6
gvrp enable
Page 100

garp timer
TL-SG3109/TL-SL3428/TL-SL3452 Gigabit Managed Switch Family CLI Reference Guide
Page 99
The garp timer Interface Configuration (Ethernet, Port channel) mode command adjusts the values of the join,
leave and leaveall timers of GARP applications. To return to the default configuration, use the no form of this command.
Syntax
garp timer {join | leave | leaveall} timer_value
no garp timer
Parameters
{join | leave | leaveall} — Indicates the type of timer.
•
• timer_value — Timer values in milliseconds in multiples of 10. (Range: 10-2147483647)
Default Configuration
Following are the default timer values:
• Join timer — 200 milliseconds
• Leave timer — 600 milliseconds
• Leavall timer — 10000 milliseconds
Command Mode
Interface configuration (Ethernet, port-channel) mode
User Guidelines
The following relationship must be maintained between the timers:
Leave time must be greater than or equal to three times the join time.
Leave-all time must be greater than the leave time.
Set the same GARP timer values on all Layer 2-connected devices. If the GARP timers are set differently on Layer
2-connected devices, the GARP application will not operate successfully.
Example
The following example sets the leave timer for Ethernet port 6 to 900 milliseconds.
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
interface ethernet e
garp timer leave
6
900
 Loading...
Loading...