Page 1

User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB
9-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch
TL-SL2210WEB
8-Port 10/100Mbps + 2-Port Gigabit Web
Smart Switch
TL-SL2218WEB
16-Port 10/100Mbps + 2-Port Gigabit
Web Smart Switch
TL- SL2428WEB
24-Port 10/100Mbps + 4-Port Gigabit
Web Smart Switch
TL-SL2452WEB
48-Port 10/100Mbps + 4-Port Gigabit Web
Smart Switch
Rev: 1.0.3
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Specifications are subject to change without notice. is
a registered trademark of TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Other
brands and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
No part of the specifications may be reproduced in any form or by any
means or used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation,
or adaptation without permission from TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © 2010 TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
FCC STATEMENT
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
This device may not cause harmful interference.1)
This device must accept any interference received, including 2)
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Page 3

Any changes or modications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
In compliance with the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, Low Voltage Directive
73/23/EEC, this product meets the requirements of the following standards:
EN55022
¾
EN55024
¾
EN60950
¾
(EUROPE)
SAFETY NOTICES
Caution:
Do not use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a
swimming pool.
Avoid using this product during an electrical storm. There may be a remote
risk of electric shock from lightning.
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Package contents .................................................................................1
Chapter 1: Introduction .......................................................................2
1.1 Intended Audience ..................................................................................2
1.2 Agreement ...............................................................................................2
1.3 Guide Overview ......................................................................................2
Chapter 2: Device Description ...........................................................4
2.1 Introduction to the Device .......................................................................4
2.2 Features and Technical Specications ..................................................4
2.2.1 Features ...............................................................................................4
2.2.2 Technical Specications .......................................................................5
Chapter 3: Mounting Device ............................................................... 7
3.1 Install the Device .....................................................................................7
3.1.1 Desktop or Shelf Installation ................................................................7
3.1.2 Rack Installation ...................................................................................7
3.1.3 AC Power ............................................................................................8
3.2 Switch Aspect Description ......................................................................8
3.2.1 Front Panel...........................................................................................8
3.2.2 Back Panel .........................................................................................10
3.2.3 SFP Module .......................................................................................10
3.3 Note ....................................................................................................... 11
Chapter 4: Function Description .....................................................12
4.1 System Setting ......................................................................................12
Page 5

4.1.1 System Information ............................................................................12
4.1.2 File Transfer .......................................................................................12
4.1.3 Reboot & Reset ..................................................................................12
4.1.4 User ....................................................................................................13
4.2 Port Setting ...........................................................................................13
4.2.1 Port Parameter ...................................................................................13
4.2.1.1 Duplex Mode ...................................................................................13
4.2.1.2 Flow Control ....................................................................................13
4.2.1.3 Port Security ...................................................................................13
4.2.2 Port Statistic and Port Status ............................................................. 14
4.2.3 Storm Control .....................................................................................14
4.2.4 Port Description .................................................................................15
4.3 Network Setting .....................................................................................15
4.3.1 Switch IP Address ..............................................................................15
4.3.2 Aging Time and Dynamic Address Table ...........................................16
4.3.3 Static MAC Address Table .................................................................16
4.3.4 Filtering MAC Address Table .............................................................17
4.3.5 Dynamic Binding ................................................................................17
4.3.6 Ping ....................................................................................................18
4.4 VLAN Setting ........................................................................................18
4.4.1 VLAN Mode .......................................................................................19
4.5 Port Trunking .........................................................................................20
4.6 Priority Setting .......................................................................................20
4.6.1 Priority Mode ......................................................................................20
4.6.2 Port-Based Priority .............................................................................21
4.6.3 Port Default Priority ............................................................................21
Page 6

4.6.4 802.1p Priority ....................................................................................21
4.7 Port Mirroring ........................................................................................21
4.8 Virtual Cable Test ..................................................................................22
Chapter 5: WEB Management ..........................................................23
5.1 Overview ...............................................................................................23
5.2 Connecting to the Device ......................................................................23
5.2.1 Getting Started ..................................................................................23
5.2.2 Login the Switch .................................................................................27
5.3 Setting the Device .................................................................................27
5.3.1 System Setting ..................................................................................32
5.3.1.1 System Information .........................................................................32
5.3.1.2 File Transfer ...................................................................................33
5.3.1.3 Reboot & Reset ...............................................................................34
5.3.1.4 User .................................................................................................35
5.3.2 Port Setting ........................................................................................36
5.3.2.1 Port Parameter ................................................................................36
5.3.2.2 Port Statistic ....................................................................................37
5.3.2.3 Port Status ......................................................................................39
5.3.2.4 Storm Control ..................................................................................40
5.3.2.5 Port Description ..............................................................................41
5.3.3 Network Setting ..................................................................................41
5.3.3.1 Switch IP Address ...........................................................................42
5.3.3.2 Static MAC Address ........................................................................43
5.3.3.3 Filtering MAC Address ....................................................................45
5.3.3.4 Dynamic Binding .............................................................................46
5.3.3.5 Bound MAC Address ......................................................................48
Page 7

5.3.3.6 Aging Time .....................................................................................49
5.3.3.7 Ping .................................................................................................50
5.3.4 VLAN Setting .....................................................................................51
5.3.4.1 VLAN Mode .....................................................................................51
5.3.4.2 Port VLAN Setting ...........................................................................51
5.3.4.3 Tag VLAN Global Setting ................................................................53
5.3.4.4 Tag VLAN Setting ............................................................................54
5.3.4.5 MTU VLAN Setting .........................................................................56
5.3.5 Port Trunking ......................................................................................56
5.3.6 Priority Setting ....................................................................................57
5.3.6.1 Priority Mode ...................................................................................58
5.3.6.2 Port-Based Priority ..........................................................................58
5.3.6.3 Port Default Priority .........................................................................59
5.3.6.4 802.1p Priority Class .......................................................................59
5.3.7 Port Mirroring .....................................................................................60
5.3.8 Virtual Cable Test ...............................................................................61
Appendix A Pin Explain For RJ-45 Connector ..............................63
Appendix B Table of Factory Defaults ............................................ 65
Appendix C Table of Function Differences of Switch Family ....67
Page 8

TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
Package contents
The following contents should be found in your box:
One Web Smart Switch
¾
One AC power cord
¾
User Guide
¾
Two mounting brackets and other ttings
¾
Note:
If any of the listed contents are damaged or missing, please contact the
retailer from whom you purchased the TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-
SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch for
assistance.
1
Page 9

2
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Chapter 1: Introduction
Thanks for choosing the TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/
TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch! The switch
family provides friendly management interface and excellent performance.
1.1 Intended Audience
This guide is intended for network administrators familiar with IT concepts and
network terminology.
1.2 Agreement
Due to the similarity in function of the TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-
SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch,
the TL-SL2210WEB model is selected to illustrate the usage of this switch
family. The “switch” referred in this guide indicates the TL-SG2109WEB/TL-
SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/ TL-SL2452WEB Gigabit Web
Smart Switch.
1.3 Guide Overview
This user guide is divided into the following sections to provide concise
information for conguring, and managing the TP-Link device:
Section 1: Introduction.
Section 2: Device Description -- Provides an overview about the switch family.
Section 3: Mounting Device -- Describes the mounting procedure of the
switch.
Section 4: Function Description -- Describes the functions supported by the
switch family and presents the network concepts referred in this guide.
Page 10

3
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Section 5: WEB Management -- Give an explanation to the terms in WEB
interface and describes the conguring suggestions of the switch.
Appendix A: Pin Explain For RJ-45 Connector
Appendix B: Table of Factory Defaults
Appendix C: Table of Function Differences of Switch Family
Page 11

4
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Chapter 2: Device Description
2.1 Introduction to the Device
TheTL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/
TL-SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch is compliant with the IEEE802.3
Ethernet protocols. The EIA-standardized framework and smart conguration
capacity can provide exible solutions for variable scale of networks.
This switch family is equipped with powerful management interface, via which
system, port, network, VLAN, truck and priority can be congured.
TheTL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-
SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch provides 0/8/16/24/48 10/100M Fast
Ethernet ports, 8/1/1/2/2 10/100/1000M Gigabit Ethernet ports and 1/1/1/2/2
SFP ports respectively, which extends the connecting area and increases the
networking exibility.
2.2 Features and Technical Specications
2.2.1 Features
Compliant with IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, IEEE802.3ab and IEEE802.3z
¾
Standards
IEEE 802.3x ow control for full-duplex
¾
Back pressure ow control for half-duplex
¾
Store-and-Forward switching method
¾
(0/8/16/24/48) 10/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet ports (Auto MDI/MDI-X
¾
support)
(8/1/1/2/2) 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet ports (Auto MDI/MDI-X support)
¾
(1/1/1/2/2) SFP ports
¾
Page 12
5
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Support N-Way adaptive mode
¾
Support up 200 meters of Cat. 5 cables at the transmission speed of 10M
¾
Support MAC address table of 8K entries
¾
Support MAC address learning and aging time
¾
Support port-based VLAN and IEEE802.1Q tag VLAN
¾
Support trunks
¾
Support management via WEB browser
¾
Support port-based priority and IEEE 802.1p priority
¾
Support static MAC address and ltering MAC address
¾
Support dynamic binding of MAC address
¾
Support port security, storm control and port monitoring
¾
Support virtual cable test
¾
Support static switch IP address and dynamic switch IP address through
¾
DHCP client
Support system upgrading, conguration uploading and backup through
¾
TFTP server
2.2.2 Technical Specications
IEEE802.3 10Base-T Ethernet
IEEE802.3u 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet
Standards
Port
VLAN Mode
IEEE802.3ab 1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE802.3z 1000Base-X Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE802.3x Flow Control
RJ-45 ports, which support MDI/MDIX, and some SFP ports are
provided (Appendix C can be referred for details)
IEEE802.1Q Tag VLAN Mode
Port-based VLAN Mode
MTU VLAN Mode
Page 13
6
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Transmission
Medium
Power Indicates whether power is supplied or not
LED
Dimensions
(L×W×H)
Operating
Environment
Power Supply AC 100-240V~ 50-60Hz
Port
10Base-T: UTP/STP of Cat. 3 or above
100Base-TX: UTP/STP of Cat. 5
1000Base-X: MMF or SMF SFP Module (OPTIONAL)
10/100Mbps RJ-45 port: Link/Act LED and 10/100Mbps LED
10/100/ 1000Mbps RJ-45 port: Link/Act and 10/100/1000Mbps LED
SFP port: 1000Mbps Link/Act LED
294mm×180mm×44mm (TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB)
440mm×180mm×44mm (TL-SL2218WEB)
440mm×220mm×44mm (TL-SL2428WEB)
440mm×260mm×44mm (TL-SL2452WEB)
Operating Temperature: 0
Storage Temperature: -40
Operating Humidity: 10% ~ 90% RH
Storage Humidity: 5% ~ 90% RH
O
C ~ 40OC
O
C ~ 70OC
Page 14
7
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
1
3
5
7
2
4
6
8
G
I
G
A S
F
P
1
0
/
1
0
0
M
b
p
s
10/100/1000Mbps
1
0
0
0
M
b
p
s
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TL-SL2210WEB
R
E
S
E
T
8
+
2
G
W
e
b
S
m
a
r
t
S
w
i
t
c
h
P
o
w
e
r
1
0
0
M
L
i
n
k
A
c
t
S
y
s
t
e
m
1000M
GIGA
L
i
n
k
/
A
c
t
L
i
n
k
/
A
c
t
Chapter 3: Mounting Device
3.1 Install the Device
Installation Precautions:
1. Ensure the surface on which the device is placed is adequately secured to
prevent it from becoming unstable and/or falling over.
2. Ensure the power outlet is placed within 1.5 m (5 feet) of the device.
3. Ensure the device is connected safely to the power outlet with the AC
power cable.
4. Ensure the device is placed in a ventilated enviroment.
3.1.1 Desktop or Shelf Installation
1. Place the switch on the desktop with its bottom upturned.
2. Attach the supplied rubber feet on the bottom at each corner of the switch.
3. Turnover the switch and place it on the desktop.
3.1.2 Rack Installation
The device can be mounted in an EIA standard-sized, 19-inch rack, which can
be placed in a wiring closet with other equipment.
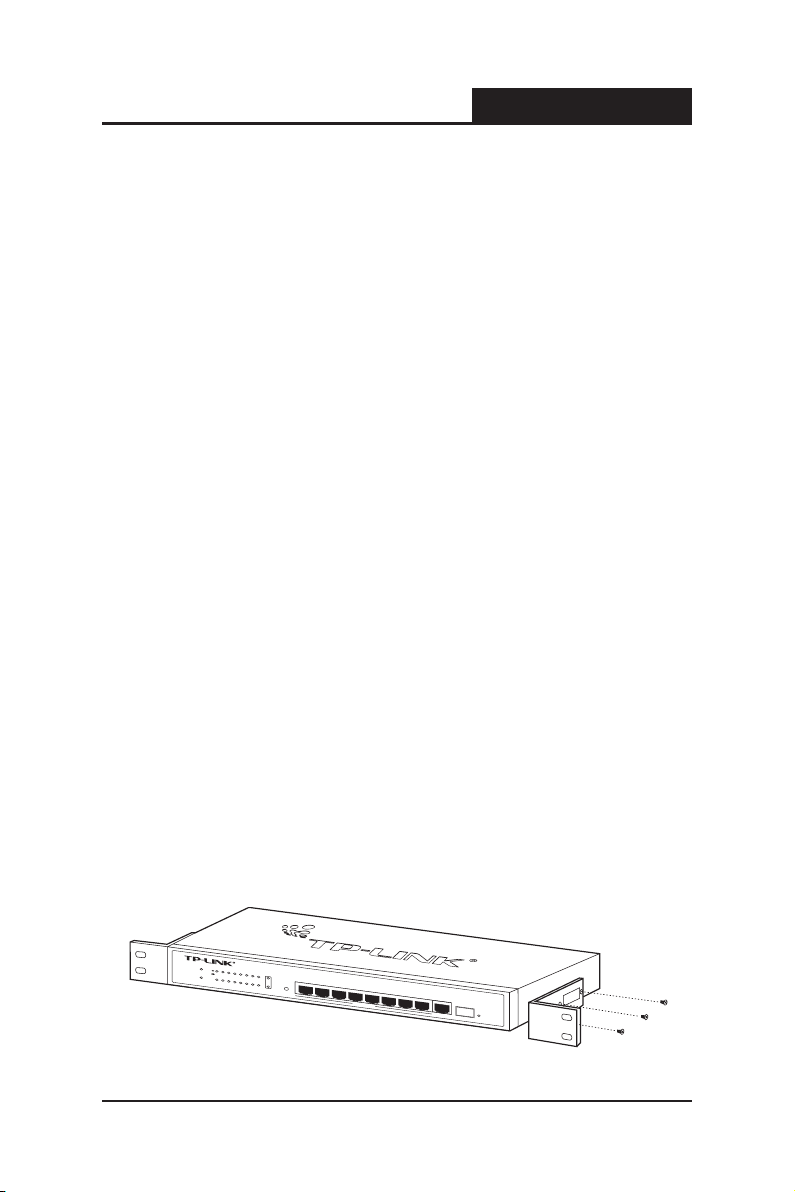
1. Install the supplied rack-mounting bracket on each side of the device, using
the supplied screws. The following figure illustrates where to mount the
brackets.
Figure 3-1 Mounting Brackets
Page 15

8
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
1 3
5 7
2 4 6 8 GIGA SFP
10/100Mbps
10/100/1000Mbps
1000Mbps
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
TL-SL2210WEB
RESET
8+2G W eb-Sm art Swi tch
Power
100M
Link
Act
System
1000M
GIGA
Link/Act
Link/Act
R
2. Insert the switch into the rack.
3. Fix the switch to the rack with the rack screws (not provided).
3.1.3 AC Power
The switch can be used with AC power supply 100 to 240V AC,50 to 60Hz.
The switch’s power supply will adjust to the local power source automatically.
The electrical outlet shall be installed near the device and shall be easily
accessible.
3.2 Switch Aspect Description
3.2.1 Front Panel
The front panel of TL-SL2210WEB is congured as follows:
Figure 3-2. TL-SL2210WEB Front Panel
8 10/100Mbps RJ-45 ports
¾
: designed to connect to the device with the
bandwidth of 10M or 100M.Each port has a corresponding Link/Act and
10/100Mbps LED.
1 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports
¾
: designed to connect to the device with
the bandwidth of 10M, 100M or 1000M. It has a corresponding Link/Act
and 10/100/1000Mbps LED.
1 SFP ports
¾
: designed to install SFP module. It has a corresponding
1000Mbps Link/Act LED.
Reset Button
¾
: Press this button for three seconds to the reset software
setting back to factory default setting.
Page 16

9
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
1 3 5 7
2 4
6 8
SFP
1 2 3 456 7 8
8+1 Giga bit SwitchWeb-Sm art
TL-SG2109WEB
10/100/100 0Mbps
1000Mbps
RESET
Power
System
Link
Act
1000M
Link/Act
R
10 12 14 16
91113 15
1
3 5 7
2 4 6 8
SFP
16+2G Giga bit Web-Smar t Switch
Power
1000Mbps
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15
Link/Ac t
GIGA
System
TL-SL2218WEB
GIGA
Link/Act
RESET
Link
Act
100Mbps
R
LEDS
¾
1) LEDs lie at the left side of the panel (1000Mbps Link/Act LED of the SFP
lie at right side of the SFP).
2) Power LED: solid red when power is supplied to the switch and is
operating normally.
3) System LED: solid green when CPU of the switch works normally.
4) 10/100Mbps LED: When a 10/100Mbps port connect to a 100Mbps
device, the corresponding LED turns on in solid green; When the port
connects to a 10Mbps device, the LED turns off.
5) 10/100/1000Mbps LED: When a 10/100/1000Mbps port connect to a
1000Mbps device, the corresponding LED turns on in solid green; When
the port connect to a 10/100Mbps device, the LED turns off.
6) Link/Act LED: Solid green when a valid link is established on the port;
Flashes green when packet transmission or reception is occurring on the
port. (SFP port has Link/Act LED only and must connect to 1000Mbps
device.)
The following shows the front panel of TL-SG2109WEB, TL-SL2218WEB, TL-
SL2428WEB and TL-SL2452WEB:
Figure 3-3 TL-SG2109WEB Front Panel
Figure 3-4 TL-SL2218WEB Front Panel
Page 17

10
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
GIGA1
GIGA2
9 11 13 151 357 17 19 21 23
10
12 14
16
2 4
6 8 18 20
22 24
SFP 1
Power
1 357
9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
GIGA1
2 4
6 8 10
12 14
16 18 20
22 24
GIGA2
System
100M 1000M
SFP 2
ActLink
SFP 2
SFP 1
Reset
TL-SL2428WEB
24+4G Gigabit Web-Smart Swi tch
RESET
Power
System
48+4G Gigabit Web-SmartSwitch
TL-SL2452W EB
SFP 1
SFP 2
29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 482 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 25 26 27 281 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 GIGA1GIGA2
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48
GIGA2
27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47251 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
GIGA1
SFP 1 SFP 2
Link/Act
R
Figure 3-5 TL-SL2428WEB Front Panel
Figure 3-6 TL-SL2452WEB Front Panel
3.2.2 Back Panel
The back panel of the switch is congured as follows:
Figure 3-7 TL-SG2109WEB/SL2210WEB Back Panel
Figure 3-9 TL-SL2218WEB/SL2428WEB/SL2452WEB Back Panel
AC Power Connector
¾
: This is a three-pronged connector that supports
the power cable. Plug in the female connector of the provided power cable
into this connector, and the male into a power outlet.
3.2.3 SFP Module
The SFP port accommodates a standard SFP module. Small Form Factor
Pluggable (SFP) Optical Show as follow.
Page 18

11
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
SFP module support hot-plugging, plug the SFP module into the SFP port and
the switch can identify it automatically.
3.3 Note
The surface on which the switch is placed should be adequately secured
¾
to prevent it from becoming unstable and/or falling over.
Ensure the power source circuits are properly grounded.
¾
Ensure the power cable, extension cable, and/or plug is not damaged.
¾
Ensure the switch is not exposed to water.
¾
Ensure the switch is not exposed to radiators and/or heat sources.
¾
Do not push foreign objects into the switch, as it may cause a fire or
¾
electric shock.
Allow the switch to cool before removing covers or touching internal
¾
equipment.
Use the switch only with approved equipment. If the switch is connected to
¾
other network devices with UTP cable, ensure that the cable is not more
than 100 meters .
Page 19

12
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Chapter 4: Function Description
This section presents the network concepts referred in switch function
description.
4.1 System Setting
System setting contains the following topics: displaying and configuring the
switch information, upgrading rmware, backing up and loading conguration,
rebooting and soft-resetting, conguring username and password.
4.1.1 System Information
The system information contains hardware version, software version, system
description, system name, system location, contact information and run time.
4.1.2 File Transfer
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-
SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch is equipped with the function of
conguration backup, conguration loading and system upgrading.
The configuration file and executive file are transferred in TFTP protocol.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is dedicated to transferring les between
two network stations. It’s based on UDP protocol.
4.1.3 Reboot & Reset
The “Reset” indicates “Soft-reset” here. Soft-resetting restores the switch
conguration to default except the switch IP address.
Page 20

13
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
4.1.4 User
The username and password can be modied in order to exclude illegal users.
4.2 Port Setting
4.2.1 Port Parameter
4.2.1.1 Duplex Mode
Ports have the duplex modes: 10M HD, 10M FD, 100M HD, 100M FD and
1000M FD (Giga port support).
The First part indicates the transmission rate and the second part indicates the
duplex mode.
HD ¾: half-duplex, the port supports transmission between the device and
the client in only one direction at a time.
FD ¾: full-duplex, the port supports transmission between the device and its
link partner in both directions simultaneously.
Switch support auto negotiation is a protocol between two link partners that
enables a port to advertise its transmission rate and duplex mode to its
partner.
4.2.1.2 Flow Control
Flow control enables lower speed devices to communicate with higher speed
devices. This is implemented by the higher speed device refraining from
sending packets.
4.2.1.3 Port Security
Page 21

14
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
If the port security is enabled, it will not learn new MAC address and only
transmit the frames from the MAC address list in the port’s static MAC address
table.
4.2.2 Port Statistic and Port Status
Port Statistic calculates the statistics of each port, such as how many frames,
error frames, broadcast frames it has received, and so on.
Port Status indicates whether the port is linked, not linked or disabled, what
speed and duplex mode it is working on, and whether ow control is enabled
or disabled.
4.2.3 Storm Control
Storm control limits the amount of multicast, broadcast and UL (the address
hasn't been learned) frames accepted and forwarded by the device. When
Layer 2 frames are forwarded, broadcast, multicast and UL frames are ooded
to all ports on the relevant VLAN. This occupies bandwidth, and loads all
nodes on all ports.
A Storm is a result of an excessive amount of these frames simultaneously
transmitted across a network by a single port. Forwarded message responses
are heaped onto the network, straining network resources or causing the
network to time out. Storm control is enabled for all ports by defining the
packet type and the rate at which the packets are transmitted. The system
measures the incoming dened frame rates on each port, and discards the
frames when the rate exceeds a user-dened rate.
Page 22

15
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
4.2.4 Port Description
Use a description word to indicate the port.
4.3 Network Setting
The network module provides the function of setting switch IP address,
dynamic binding and aging time, conguring static MAC address and ltering
MAC address, displaying dynamic bound address and ping.
4.3.1 Switch IP Address
An IP address is indispensable for a switch to be accessed. TheTL-
SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-
SL2452WEB Gigabit Web Smart Switch provides the conguration interface
of IP address, netmask and default gateway.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol) is dedicated for the DHCP client
to obtain IP configuration information from the DHCP server. Two types of
information are included in IP conguration information. One type is specic
conguration information; another is IP address parameter. DHCP is based
on client-server mode. The network station that offers the IP configuration
information is called DHCP server.
Make sure that a DHCP server is correctly connected to the network, enable
the DHCP client function of the switch, then the switch will automatically obtain
IP address, netmask and default gateway from the DHCP server.
If more than one DHCP servers are available in the network, the switch will
choose one according to a specic algorithm.
Page 23

16
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Notice:
If no DHCP server is present in the network, the DHCP client fails to get IP
conguration information, the switch then restores the IP parameters to default
in several minutes to ensure a valid IP address being equipped.
4.3.2 Aging Time and Dynamic Address Table
A dynamic MAC address table is maintained inside the switch. A MAC address
is the physical address of a network device; it is six-bytes long and should be
hole in a subnet. A network device can be identied by its MAC address.
A dynamic address table entry contains two items: MAC address and its
corresponding switch port. The dynamic address table is volatile. The dynamic
address entry begins to age once it has been added; it will be purged if it isn’t
renewed in a specied length of time, which is dened as aging time.
The aging time ranges from 0 to 3825 seconds for this switch family.
The default value is 300 seconds. Dynamic address table entry won’t age if 0
is set. The aging time precision is 15 seconds.
4.3.3 Static MAC Address Table
A static MAC address table entry contains a MAC address and its
corresponding switch port. All the packets taking that MAC address as their
destination will be forwarded to the corresponding switch port.
The static MAC address won’t age, which differs from the dynamic MAC
address. The static MAC address table entry is always valid before it is
deleted.
Page 24

17
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Supposing an entry, whose MAC address is 000AEB000001 and
corresponding port number is 1, it is added to the static MAC address table.
All the packets routing to the address of 000AEB000001 egress for the switch
port 1. This static entry obliges the device of 000AEB000001 to be connected
to port 1; otherwise, that device cannot be accessed. Static MAC addresses
are free of MAC learning, which enhances the efciency of packets forwarding.
The MAC addresses already congured in static MAC address table cannot
be added to ltering MAC address table.
The static MAC address table capacity of different types of switches may be
different. Appendix C lists the difference.
4.3.4 Filtering MAC Address Table
A ltering MAC address excludes a device from being accessed through the
switch. All the packets taking the ltering MAC address as their destination will
be discarded. The ltering MAC address is applicable to all the switch ports.
The configured filtering MAC address can neither be added to static MAC
address table, nor be bound by switch ports.
4.3.5 Dynamic Binding
A switch port in dynamic binding state can bind a specied number of MAC
address. Once the specied number is reached, the port transfers into secure
state automatically and stops binding MAC addresses. The bound MAC
addresses won’t age, they can be removed by disabling the dynamic binding
or rebooting the switch.
The function of dynamic binding causes the switch port to acknowledge the
devices connecting to it after startup, and stores the connections (through
Page 25

18
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
binding MAC addresses) in static state. This enhances the efficiency of
packets forwarding and limits the connecting device number of the switch port.
Reboot the switch after conguring the dynamic binding function. The switch
will acknowledge and bind the latest connecting devices. If the switch is
managed through remote connection, please add the MAC address of the
management computer or that of the default gateway to the static MAC
address table; otherwise, the management channel may break down.
4.3.6 Ping
The ping function is to test the connectedness of the link between the switch
and destination.
4.4 VLAN Setting
VLANs are logical subgroups with a Local Area Network (LAN) that combine
user stations and network devices into a single unit, regardless of the physical
LAN segment to which they are attached. VLANs allow network trafc to ow
more efciently within subgroups.
VLANs use software to reduce the amount of time it takes for network
changes, additions, and moves to be implemented.
VLANs can be created per unit, per device, or through any other logical
connection combination, since they are software-based and not defined by
physical attributes. VLANs function at Layer 2. Since VLANs isolate traffic
within the VLAN, a Layer 3 router working at a protocol level is required to
allow traffic flow between VLANs. Layer 3 routers identify segments and
coordinate with VLANs. VLANs are Broadcast and Multicast domains.
Broadcast and Multicast trafc is transmitted only in the VLAN in which the
Page 26

19
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
trafc is generated.
4.4.1 VLAN Mode
There are 3 types of VLAN mode support in the switch:
1) Port VLAN
VLANs are divided basic on ports.
2) IEEE802.1Q Tag VLAN
The IEEE802.1Q protocol define a new format of the frame, it add a tag
header in the original Ethernet frame, as follow:
Figure 4-1. IEEE802.1Q frame
IEEE802.1Q Tag VLAN is divided by VLAN ID (VID). On receiving a frame,
switch check the VID in the tag header of the frame to decide which VLAN it
belongs to. If the receiving frame doesn’t contain the tag header, switch will
assign a tag to the frame, using the PVID of the port as its VID.
3) MTU VLAN
MTU VLAN(Multi-Tenant Unit VLAN)dene an uplink port, the uplink port will
buildup several VLANs with each of the other ports. Each VLAN contains two
ports, the uplink port and one of the other ports in the switch, so the uplink port
Page 27

20
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
can communicate with any other ports but other ports can’t communicate with
each other.
4.5 Port Trunking
Trunk is Link Aggregation. It optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports
together to form a single trunk (aggregated groups).Bandwidth of the Trunk is
the sum of bandwidth of its member port.
There are some rules on using Trunk:
1) Before setting the Trunk, its member ports should be divided to the same
VLAN, and have the same PVID and drop untagged frame rule. Change
of the Trunk setting will not affect the VLAN setting. Trunks can not be set
if the switch is in MTU VLAN mode
2) The Trunk member ports can’t enable port security and can’t be set as
mirror or mirrored port.
3) All of the Trunk member ports should be connected correctly; otherwise
some ports will not be able to work.
4.6 Priority Setting
The priority mode of the switch can be set to “Disable”, “Port-Based” or
“IEEE802.1p”.
4.6.1 Priority Mode
Three priority modes (disable, port-based and IEEE802.1p) are provided for
this switch family.
The priority rule can be set to “Weighted” or “Fixed”. When priority rule is
Page 28

21
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
congured as "weighted", a 1,2,4,8 weighting is applied to forward packets.
When "xed" is selected, all packets with top priority egress for a switch port
until that priority's queue is empty, then the packets with next lower priority.
4.6.2 Port-Based Priority
Four priority classes (lowest, lower, higher and highest) are available for a
switch port in port-based priority mode. The priority class of the port is applied
to the all packets entering from the port.
4.6.3 Port Default Priority
If IEEE802.1p priority mode is configured, when a switch port receives an
untagged frame (a frame without priority tag), the port's default priority tag will
be inserted into the frame before any other process.
4.6.4 802.1p Priority
In IEEE802.1p priority mode, all packets are classied into four priority classes
(lowest, lower, higher and highest) according to the embedded priority tag.
If an untagged frame is received, the default priority tag of the port will be
attached.
4.7 Port Mirroring
Port mirroring monitors and mirrors network traffic by forwarding copies
of incoming and outgoing packets from one port to a monitoring port. Port
mirroring enables switch performance monitoring.
Network administrators can congure port mirroring by selecting a specic port
from which to copy all packets, and other ports to which the packets copied.
Page 29

22
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
4.8 Virtual Cable Test
The virtual cable test feature uses Time Domain Reectometry (TDR) to test
the quality of the cables connected to the port. Some of the possible problems
than can be diagnosed include opens, shorts, cable impedance mismatch,
bad connectors, termination mismatch, and bad magnetics. It can also test the
distance to the problem location, with the precision of ±1 meter.
Page 30

23
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Chapter 5: WEB Management
5.1 Overview
The Web-Smart switch is managed via WEB pages. The smart and friendly
interfaces make the switch management an easy job.
5.2 Connecting to the Device
5.2.1 Getting Started
Before connecting to the WEB server (switch), the installation of WEB browser,
which supports JavaScript, must be completed in the computer.
Due to the difference of parsing syntax, the WEB page display may differ
between variable WEB browsers. Microsoft Internet Explorer of version 5.0
or higher is recommended. If Netscape is selected, please ensure the latest
version. To obtain excellent display quality, a screen resolution of 1024 x 768
or higher is necessary.
The appropriate conguration of WEB browser must be ensured before switch
management. An example of conguration using IE on Windows XP is given
below.
Firstly, select “Tool->Internet Options” on the menu, a dialog will pop up:
Page 31

24
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Figure 5-1 Internet Options Dialog
Secondly, click the “Settings” button hinted in gure 5-1, a new dialog will
display:
Figure 5-2 Settings Dialog
Page 32

25
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
In the case of IE5.0, please check the option “Every visit to the page”;
otherwise, some wrong information may display in WEB pages. If the
IE version is 6.0, “Every visit to the page” or “Automatically” are both
appropriate.
Click the “OK” button and complete this setting.
Thirdly, click the “Security” label of “Internet Options” dialog; press the
“Custom Level” button hinted in gure 5-3.
Figure 5-3 Internet Options Dialog
A dialog will display as below.
Page 33

26
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Figure 5-4 Security Settings
Fourthly, Select the “Medium” option of the combo box indicated in gure 5-4,
click the “Reset” button, and click “OK” to quit.
Fifthly, right-click the mouse on desktop, select the “Display Properties” in the
popup menu, a new dialog will display:
Figure 5-5 Resolution Settings
Page 34

27
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Click the “Settings” label, set the screen resolution to 1024 x 768 and click “OK”.
All the necessary IE conguration is completed.
5.2.2 Login the Switch
Supposing the switch IP address is set as 192.168.0.1, open a web browser
and enter http://192.168.0.1 in the address location, and then the following
dialog page appears:
Figure 5-6 Login Dialog
Enter username and password (default value are both "supervisor") to login
the switch conguration main page.
5.3 Setting the Device
After logging into the switch, the main page appears as the following. It
contains three parts:
Page 35

28
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Figure 5-7 TL-SL2210WEB Main Page
1) The main part of the page is the main window to display the
conguration page.
2) The Port Led Indicator table lies at the top of the page. It provides a
visual representation of the ports on the switch front panel to display
the status of the ports. The ports, signed with number are the normal
ports, signed with GIGA are the Giga ports, signed with SFP are the
SFP ports. The green icon indicates that the port is linked; the gray icon
indicates that the port is not linked; a gray icon with a black bar indicates
that the port is disabled; for the SFP port, a blue icon indicates that the
SFP module hasn’t been installed.
Figure 5-8 Port Led Indicator Table (SFP uninstalled)
Figure 5-9 Port Led Indicator Table (SFP installed)
Page 36

29
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Click on the icon of the port to open a new window, which shows the status
details of the port, as shown below:
Figure 5-10a Port Status Table
Figure 5-10b SFP Status Table (uninstalled)
Figure 5-10c SFP Status Table (installed)
Page 37

30
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
3) On the left side of the page is the menu table. It contains 8 main menus.
Each menu has some submenu. Click on a menu, it will open its
submenu and the main window display the configuration page of the
submenu list rst, click on the submenu you want to congure to open
the corresponding conguration page. The menu structure is as follows:
Figure 5-11 Main Menu
System Setting
¾
User.
Port Setting
¾
and Port Description.
Network Setting
¾
Address, Dynamic Binding, Bound MAC Address, Aging Time, and Ping.
VLAN Setting
¾
Tag VLAN Setting, and MTU VLAN Setting.
Port Trunking
¾
Priority Setting
¾
and 802.1p Priority Class.
Port Mirroring
¾
Virtual Cable Test
¾
: System Information, File Transfer, Reboot & Reset, and
: Port Parameter, Port Statistic, Port Status, Storm Control,
: Switch IP Address, Static MAC Address, Filtering MAC
: VLAN Mode, Port VLAN Setting, Tag VLAN Global Setting,
: Port Trunking.
: Priority Mode, Port-Based Priority, Port Default Priority,
: Port Mirroring.
: Virtual Cable Test.
Page 38

31
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
The following shows main page of the TL-SG2109WEB, TL-SL2218WEB,
TL-SL2428WEB and TL-SL2452WEB:
Figure 5-12 TL-SG2109WEB Main Page
Figure 5-13 TL-SL2218WEB Main Page
Page 39

32
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Figure 5-14 TL-SL2428WEB Main Page
Figure 5-15 TL-SL2452WEB Main Page
5.3.1 System Setting
System setting contains four topics: system information, le transfer, reboot
& reset and user.
5.3.1.1 System Information
Page 40

33
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
This page contains the following elds:
Figure 5-16 System Information
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
Software Version
Hardware Version
number.
System Description
System Name
System Location
running.
Contact Information
Run time
: Shows the run time since last startup.
: Displays the installed software version number.
: Displays the installed device hardware version
: Displays the device model number and name.
: Denes the user-dened device name.
: Defines the location where the system is currently
: Denes the contact information of switch manager.
5.3.1.2 File Transfer
This page contains the following elds:
Figure 5-17 File Transfer
Page 41

34
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Transfer Type
¾
File Name
¾
server.
TFTP Server IP
¾
Further explanation
File transfer types:
System Upgrading
¾
server to switch and upgrading the system.
Configuration Backup
¾
the switch to TFTP server.
Conguration Loading
¾
server to the switch and update it.
Notice:
1) Please make sure the target file exits on TFTP server before
downloading.
2) Please make sure the TFTP server in operation.
3) Breaks should be avoided during le transfer; otherwise, the switch may
get damaged.
: Lists three types of le transfer supported by the switch.
: Identies the le to be loaded or to be backed up on TFTP
: Indicates the IP address of TFTP server.
: Means downloading the executable le from TFTP
: Means backing up the current configuration of
: Means downloading the conguration from TFTP
5.3.1.3 Reboot & Reset
This page is showed as below.
Figure 5-18 Reboot & Reset
Page 42

35
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
A prompt will display if a button is pressed. For example, if the button “Soft-
reset” is pressed, a message box will be activated as showed in gure 5-19.
Figure 5-19 Message Box
5.3.1.4 User
This page provides the interface of conguring username and password.
Figure 5-20 User Conguration
You are kindly suggested to retype the new password in "Confirm new
password" box instead of copying in order to avoid typing mistakes.
Notice:
1) Only letters, numbers and punctuations can be input into username and
password eld, the other characters are considered illegal. The length of
username and password ranges from 1 to 16 characters.
2) The initial username and password is supervisor/supervisor.
Page 43

36
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5.3.2 Port Setting
5.3.2.1 Port Parameter
This page contains the following elds:
Figure 5-21 Port Parameter
Port Status
¾
Enable" Indicates the port is operational and "Disable" Indicates the port
is non-operational. If a port is unused for a long time, it can be set it to be
non-operational to cut down energy costs.
Notice:
You can't manage the switch via the port, which is non-operational, please set
the value of the management port to “enable”.
Port Security
¾
and only transmit the frames from the MAC address it has learned.”
Disable" Indicates it will learn new MAC address.
: Indicates whether the port is operational or non-operational.”
: "Enable" Indicates the port will not learn new MAC address
Page 44

37
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Notice:
If you haven’t set the static MAC address, you can't enable all of the port
security, which will result in an inability to manage the switch.
Flow Control
¾
Duplex Mode
¾
HD, 100M FD and 1000M FD (Giga port support), "HD" stands for half-
duplex and "FD" stands for full-duplex. “Auto” means auto negotiation.
Further explanation:
1) By operating on fields in the All Ports line expediently, you can set the
values of all ports in the corresponding field. Some other setting pages
offer the same function.
2) Parameters of Trunk member ports are congured with default value (see
the Appendix B table) and cannot be congured here (see port 5 and 6 in
the gure for example). For SFP, the Duplex Mode is set to “1000M FD”
and cannot be modied.
: Indicates whether the ow control is enabled or disabled.
: Possible led values are Auto, 10M HD, 10M FD, 100M
5.3.2.2 Port Statistic
This page displays the port statistic, it contains the following entries:
Figure 5-22 Port Statistic
Page 45

38
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Tx Collisions
¾
counter is applicable in half-duplex only.
Tx Ucast
¾
address.
Tx Mcast
¾
MAC address.
Tx Bcast
¾
MAC address.
Rx (G Pkts)
¾
Rx Ucast
¾
MAC address.
Rx Mcast
¾
destination MAC address.
Rx Bcast
¾
destination MAC address.
Rx (B Bytes)
¾
The frames with the length more than 1522 octets are counted as 1522
octets ones.
Rx UnderSz
¾
with a valid FCS.
Rx OverSize
¾
octets but with a valid FCS.
Rx Jabber
¾
octets but with an invalid FCS.
RX64 B
¾
those with errors.
RX 65 to 127 B
¾
: The number of collision events seen by the MAC. This
: The number of frames sent that have a unicast destination MAC
: The number of frames sent that have a multicast destination
: The number of frames sent that have a broadcast destination
: The number of good frames received.
: The number of frames received that have a unicast destination
: The number of frames received that have a multicast
: The number of frames received that have a broadcast
: The sum of bytes of frames received with an invalid length.
: Total frames received with a length of less than 64 octets but
: Total frames received with a length of more than max size
: Total frames received with a length of more than max size
: Total frames received with a length of exactly 64 octets, including
: Total frames received with a length of between 65 and
Page 46

39
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
127 octets inclusive, including those with errors.
RX 128 to 255 B
¾
255 octets inclusive, including those with errors.
RX 256 to 511 B
¾
511 octets inclusive, including those with errors.
RX 512 to 1023 B
¾
and 1023 octets inclusive, including those with errors.
RX Bytes
¾
errors.
Notice:
Each statistic counter has the max numerical value of about 1.8e+19,in excess
of this value, the counter will reset to zero. You can also click on the “Reset”
button to reset all of the statistic counters to zero.
: Total frames received with a length of between 128 and
: Total frames received with a length of between 256 and
: Total frames received with a length of between 512
: The sum of bytes of frames received, not including those with
5.3.2.3 Port Status
This page display the port status, it contains the following elds:
Figure 5-23 Port Status
Page 47

40
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
¾
¾
¾
¾
Port Status
Speed (Mbps)
Duplex Mode
Flow Control
disable.
: Indicates whether the port is linked, not linked, or disabled.
: Indicates the port speed with the unit of Mbps.
: Indicates the port duplex mode.
: Indicates whether flow control of the port is enable or
5.3.2.4 Storm Control
This page contains the following elds:
Figure 5-24 Storm Control
Broadcast Control
¾
broadcast frames.
Multicast Control
¾
multicast frames, enabling multicast control will also enable broadcast
control.
UL Control
¾
enabling UL control will also enable broadcast control and multicast
control.
: Enable or disable the UL control to limit the UL packets,
: Enable or disable the broadcast control to limit the
: Enable or disable the multicast control to limit the
Page 48

41
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Limit Rate
¾
the controlled packets configured above are forwarded. For the 1000M
port, if set the value of 64K, the actual value is about 70Kbps.
Notice:
Parameters of Trunk member ports display the parameters of the Trunk they
belong to and cannot be congured here (see port 5 and 6 in the gure for
example). You can congure parameters of the Trunk in the “Port Trunking”
page.
: Indicates the maximum rate (kilobytes per second) at which
5.3.2.5 Port Description
This page congures the description to indicate the ports.
Input description words in the Description filed for each port. Notice that at
most 15 letters or numbers can be held in each eld.
Figure 5-25 Port Description
5.3.3 Network Setting
This page contains the following topics: switch IP address, static MAC
address, ltering MAC address, dynamic binding, bound MAC address, aging
time and ping.
Page 49

42
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5.3.3.1 Switch IP Address
This page is showed as below:
Figure 5-26 Switch IP Address
MAC Address
¾
sole and unchangeable.
DHCP Client
¾
client is enabled, the switch will obtain the IP address, netmask and default
gateway from the DHCP server automatically; otherwise, these three items
should be congured manually.
IP Address
¾
switch IP address must be compliant with the subnet layout.
Default Gateway
¾
destination IP address is not within the switch’s subnet is to be forwarded.
Notice:
1) When DHCP client is enabled, the IP parameters are obtained
automatically from the DHCP server, so the “IP Address”, “Netmask” and
“Default Gateway” elds are disabled. These parameters can be queried
on the DHCP server.
2) The initial state of DHCP client is disabled and the initial IP address is
192.168.0.1.
: Is firmed into switch in the manufacturing process; it is
: Indicates whether the DHCP function is enabled. If DHCP
: Is necessary for switch management. The configuration of
: Serves as the default destination when a packet whose
Page 50

43
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5.3.3.2 Static MAC Address
This page provides the function of adding, searching a static MAC address
and changing the entry state, as shown in gure 5-27.
Figure 5-27 Static MAC address
A MAC address and its corresponding switch port should be provided when
adding a static MAC address entry.
Search
¾
: Input the MAC address in “Mac Address” eld and click “Search”
button. If that MAC address exists, the following page will display:
Figure 5-28 A Successful Searching
Index
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
A searching can be also executed in this page.
: Stands for entry index of the MAC address in the table.
Port
: Stands for the switch port number.
State
: Indicates the entry in enabled state or disabled state.
Operation
entry.
Return
: Provides the function of enabling, disabling or deleting an
: Return to the “Static MAC Address” page.
Page 51

44
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
If the static MAC address doesn’t be found in a searching, then the following
page will display:
Figure 5-29 A Failed Searching
Add
¾
1) That MAC address doesn’t exist in static MAC address;
2) That MAC address doesn’t exist in ltering MAC address;
3) There is enough space in static MAC address table (the capacity of the
: Input the MAC address in “MAC Address” field and select a port
number in “Corresponding Port” combo box, click the “Add” button, that
MAC address is added to the static MAC address table if the following
conditions are met:
static MAC address table is shown in “Appendix C”).
The static MAC address table is divided into several pages. At most 10 entries
can be held in one page. The buttons “First”, “Previous” and “Next” can be
used to browse the whole table.
Notice:
1) The capacity of the static MAC address is showed in “Appendix C”.
2) If an incorrect port number is selected when adding an entry, or the port
number is modied unexpectedly later, then the entries must be renewed;
otherwise, the packets cannot be forwarded correctly.
3) If a device, whose MAC address is added to static MAC address table, it
is connected to a wrong switch port (not the port congured in static MAC
Page 52

45
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
address entry), all the packets routing to the device cannot reach the
device.
4) A MAC address cannot be added to static MAC address table and ltering
MAC address table simultaneously.
5.3.3.3 Filtering MAC Address
All the packets taking the filtering MAC address as their destination are
discarded by the switch no matter which port they enter from.
This page provides the function of adding, searching a ltering MAC address
and changing the entry state. The ltering MAC address entry is applicable to
all switch ports. The operating instruments, which are similar to “Static MAC
Address”, are omitted here.
Figure 5-30 Filtering MAC Address
Index: Indicates the entry index of ltering MAC address table.
¾
MAC Address: Indicates the ltering MAC address to be congured or to
¾
be searched.
State: Indicates the entry in enabled state or disabled state.
¾
Notice:
The capacity of ltering MAC address table is showed in “Appendix C”.
Page 53

46
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5.3.3.4 Dynamic Binding
This page provides the function of enabling or disabling dynamic binding.
If dynamic binding is disabled, the switch port learns MAC address unlimitedly
(at most 8000 entries can be learned).
A switch port with dynamic binding enabled can bind a specied number of
MAC address. The MAC addresses bound by the switch port are always valid
and won’t age. If the specied number is reached, the port stops binding and
transfers into secure state.
The bound MAC addresses can be queried in the “Bound MAC Address“
page.
If the dynamic binding is disabled or the switch restarts, the bound MAC
address entries are cleared.
There are 5 items in this page:
Figure 5-31 Dynamic Binding
Page 54

47
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Port
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
Options of dynamic binding:
1) Disable: Cause this port to learn MAC address freely.
2) Enable: Cause the port to bind MAC addresses until the specied number
3) --: This option is available only if the port is in a secure state, when this
: Indicates switch port number.
Binding
Number of MAC Address to Bind
addresses that one switch port can bind.
Number of Bound MAC Address
addresses that already bind to a switch port.
State
port, unplugged or "--". A further explanation is stated below.
is reached.
option is selected, the port state keeps unchanged.
: Three options are available. A further explanation is stated below.
: Indicates the max number of MAC
: Indicates the switch port state that may be binding, free port, secure
Further explanation
: Indicates the number of MAC
Port states:
1) Free Port: The binding function is disabled, and the port can learn MAC
address freely.
2) Binding: The port is in binding state, and its bound MAC address number
is still less than the max number.
3) Secure Port: The port has already bound the max number of MAC
address in dynamic binding mode, or it was set to secure port manually in
"Port Parameter" page.
4) Unplugged: The port is a SFP port and unplugged. The dynamic binding
function cannot be congured now.
Page 55

48
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5) --: The port is a trunk member and its binding function cannot be
congured.
Further Explanation
1) If the port is set to secure port manually in "Port Parameter " page, the
dynamic binding cannot be configured here. If the port with dynamic
binding enabled transfers into secure state automatically because the
port has bound the specied number MAC address, the dynamic binding
function of the port can be enabled or disabled again.
2) The combo box in "All Ports " entry is used to change the selections of
corresponding combo boxes of all ports simultaneously.
3) A "Refresh" button is provided to look up the latest number of bound MAC
address.
Notice:
If the switch port is a trunk member or an unplugged SFP port, the binding
function of the port cannot be congured here.
5.3.3.5 Bound MAC Address
This page is shown below:
Figure 5-32 Bound MAC Address
Index
¾
: Indicates the entry index in dynamic binding MAC address table.
Page 56

49
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
MAC Address
¾
ports.
Port
¾
1) The bound MAC address table contains all the MAC addresses bound
2) The bound MAC address table is divided into several pages. At most 10
: Indicates the switch port number corresponding to the bound MAC
address.
Further Explanation
by the switch ports. Every entry contains one MAC address and its
corresponding port number.
entries can be held in one page. The buttons “First”, “Previous” and “Next”
can be used to browse the whole table.
: Indicates MAC addresses already bound to the switch
5.3.3.6 Aging Time
This page is showed as below:
Figure 5-33 Aging Time
Aging Time (0~3825)
¾
switch, it will be added to the dynamic MAC address table and a relative
timer will be generated immediately. If no packet taking the MAC address
as its source passes through the switch in a specied length of time, that
MAC address will be removed from the MAC address table. This process
is called "aging", and the specified time length referred above is called
: When a new MAC address is learned by the
Page 57

50
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
"aging time".
Further Explanation
1) The aging time ranges from 0 to 3825 seconds. An appropriate aging
time should be congured here. An aging time that is too long lengthens
the time of the dynamic MAC address being deleted and further causes
the packets to be forwarded incorrectly. An aging time that is too short
causes the table entries to be deleted quickly. Some packets have to be
broadcasted because no corresponding entries can be abided by. The
efciency of packet forwarding is reduced.
2) The MAC addresses in static MAC address table, ltering MAC address
table and bound MAC address table are free of the aging time.
5.3.3.7 Ping
The ping function is to test the connectedness of the link between the switch
and destination. This page is showed as below:
Figure 5-34 Ping
Destination IP Address
¾
Ping Count
¾
Data Size
¾
Ping Interval
¾
: Indicates the ping times in one submission.
: Indicates the data eld length of ping packet.
: Indicates the time interval between two continuous pings.
: Indicates the IP Address of the test destination.
Page 58

51
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5.3.4 VLAN Setting
5.3.4.1 VLAN Mode
This page selects the VLAN Mode, possible eld values are:
Figure 5-35 VLAN Mode
VLAN Disable
¾
can communicate with each other.
Port VLAN (Port-Based VLAN)
¾
Tag VLAN (802.1Q Tag VLAN)
¾
MTU VLAN
¾
Trunk has be set.
: Do not set any VLAN in the switch, all ports of the switch
: Set the Port-Based VLAN mode.
: Set the 802.1Q Tag VLAN mode.
: Set the MTU VLAN mode. This mode cannot be set if any
5.3.4.2 Port VLAN Setting
This page displays when the switch is in Port VLAN mode, it contains the
following elds:
Figure 5-36 Port VLAN Setting
Page 59

52
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
VLAN
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
: The VLAN number. Select the number of the VLAN you want to
congure here.
Port
: The switch port number.
Member
indicates the port belongs to the current VLAN.
Description
All VLAN
: Select the member of the VLAN here. If this eld is checked, it
: Display the user-dened port description.
: Display all dened Port VLANs.
Figure 5-37 All Port VLAN
Select All
¾
Clean Up
¾
Submit
¾
1) Any VLAN cannot be the subset or superset of other VLANs.
2) At least two port members should be included to add a VLAN group. (If the
page is submitted with 0 VLAN member, it indicates to delete the VLAN.)
3) If any Trunk has been set, the Trunk can be configured as a VLAN
member, and the member ports of the Trunk cannot be congured (see
Port 1 and 2 in the gure for example).
4) For the first time the Port VLAN mode is set, a default VLAN, which is
indexed as NO. 1 and contains all switch ports, will be built up.
5) The ports haven’t be assigned to any VLAN manually will be assigned to a
hidden VLAN automatically to make sure they can communicate with each
: Select all ports to be the VLAN member.
: Clean up all members of the VLAN.
: Submit to buildup a VLAN with the selected members.
Notice:
Page 60

53
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
other.
6) The number of Port VLAN can be set is the same as the switch port
number.
5.3.4.3 Tag VLAN Global Setting
This page display when the switch is in Tag VLAN mode, the global setting of
the ports will affect all Tag VLANs. It contains the following elds:
Figure 5-38 Tag VLAN Global Setting
Port
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
: The switch port number.
PVID
: while receiving an untagged frame from the port, the switch will
assign a tag to the frame, using the PVID of the port as its VID.
Untag Frame
drop the frame and "Pass" will transmit the frame in the VLAN with the VID
the same as the PVID of the port.
All Ports
all ports in the corresponding eld.
Notice
member ports of the Trunk are not able to be congured and in the elds it
displays the parameters of the Trunk they belong to.(see port1 and 2 in the
gure for example).
: The solution to the untagged frame received. "Drop" will
: By operating on this eld expediently, you can set the values of
: If any Trunk has been set, the Trunk can be configured, but
Page 61

54
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
5.3.4.4 Tag VLAN Setting
This page is displayed when the switch is in Tag VLAN mode, it congures
each VLAN and is affected by the global setting of the ports, it contains the
following elds:
Figure 5-39 Tag VLAN Setting
VLAN
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
: The VLAN number. Select the number of the VLAN you want to
congure here.
VLAN ID
Port
Member
indicates the port belongs to the current VLAN.
Egress Frame
drop the tag header before sending the frame. "Add Tag" indicates add the
tag header before sending the frame. "Unmodify” indicates not to modify
the tag header before sending the frame.
Description
: congure the VLAN ID.
: The switch port number.
: Select the member of the VLAN here. If this eld is checked, it
: The solution to the egress frame. "Drop Tag" indicates
: Display the user-dened port description.
Page 62

55
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
All Ports
¾
all ports in the corresponding eld.
All VLAN
¾
Select All
¾
Clean Up
¾
Submit
¾
1) VID of the VLAN must be unique and within the range of 1 to 4094.
2) At least two port members should be included to add a VLAN group. (If the
page is submitted with 0 VLAN member, it indicates to delete the VLAN.)
3) If any Trunk has been set, the Trunk can be configured as a VLAN
member and member ports of the Trunk cannot be congured (see Port 1
and 2 in the gure for example).
4) If the port is connected to a device that doesn’t support IEEE802.1Q (e.g.
HUB and some network adapter), value of the Egress Frame eld should
be set to “Drop Tag”.
5) For the first time the Port VLAN mode is set, a default VLAN, which is
indexed as NO. 1 and contains all switch ports, will be built up.
6) The ports haven’t been assigned to any VLAN manually cannot
communicate with each other or other VLAN. That’s different from the Port
VLAN.
: By operating on this eld expediently, you can set the values of
: Display all dened Tag VLANs.
Figure 5-40 All Tag VLAN
: Select all ports to be the VLAN member.
: Clean up all members of the VLAN.
: Submit to buildup a VLAN with the selected members.
Notice:
Page 63

56
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
7) The number of Port VLAN that can be set depends on the switch type.
See the Appendix C for details.
5.3.4.5 MTU VLAN Setting
This page, which is designed to congure the uplink port, displays when the
switch is in MTU VLAN mode.
Figure 5-41 MTU VLAN Setting
Notice:
1) The uplink port will buildup several VLANs with each of the other ports.
Each VLAN contains two ports, the uplink port and one of the other ports
in the switch, so the uplink port can communicate with any other port but
other ports can’t communicate with each other.
2) First time the MTU VLAN mode is set, it set port 1 to be the uplink port by
default.
5.3.5 Port Trunking
This page contains the following elds:
Figure 5-42 Port Trunking
Page 64

57
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Trunk
¾
¾
¾
¾
¾
1) Each Trunk should contains 2 to 4 ports (If a Trunk is submitted with 0
2) SFP and 1000M port in TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-
3) Trunks cannot be set if the switch is in MTU VLAN mode.
: The Trunk number.
Member
ports to compose a Trunk.
Storm Control
ports of the Trunk share the same settings. Subeld of the Storm Control
are the same as that of the port storm control, see phase 5.3.2.4 for
details.
Select All
Clean Up
member port, it indicates to delete the Trunk).
SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB, is not able to be the Trunk member.
: Select the member of the Trunk here. Each group has 4 optional
: congure the storm control for the Trunk here. All member
: Select all Trunk members in the list.
: Clean up the Trunk member list.
Notice:
5.3.6 Priority Setting
Priority setting contains four topics: priority mode, port-based priority, port
default priority and 802.1p priority.
Because dynamic menu is adopted, only the pages corresponding to current
priority mode are revealed. If the parameters of other priority modes are to be
congured, select the corresponding priority mode in “Priority Mode” page rst.
5.3.6.1 Priority Mode
This page is shown below:
Page 65

58
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Figure 5-43 Priority Mode
Priority Mode
¾
Priority Rule
¾
to “Disable”, the priority rule cannot be congured.
: Contains “Disable”, “Port-Based” and “IEEE802.1p”.
: Contains “Weighted” and “Fixed”. If the priority mode is set
5.3.6.2 Port-Based Priority
This page is revealed when the “Port-Based” mode is congured. As shown
below.
Figure 5-44. Port-Based priority
Port
¾
¾
: Indicates the switch port number.
Priority Class
into four priority classes: lowest, lower, higher and highest. All the packets
entering from the port of the switch are forwarded in the corresponding
priority queue.
: In port-based priority mode, the switch ports are classied
Page 66

59
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Further Explanation
When priority rule is congured as "weighted", a 1,2,4,8 weighting is applied to
forward these four classes of packets.
5.3.6.3 Port Default Priority
This page is revealed when the “IEEE802.1p” mode is congured. When a
switch port receives an untagged frame (a frame without priority tag), the port's
default priority tag will be inserted into the frame before any other process.
Figure 5-45 Port Default Priority
Port
¾
¾
: Indicates the switch port number.
Default Priority Tag
frames.
: Indicates 802.1p tag being inserted into untagged
5.3.6.4 802.1p Priority Class
This page is revealed when the “IEEE802.1p” mode is congured as shown
below:
Page 67

60
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Figure 5-46 802.1p Priority
Priority Tag
¾
Corresponding Priority Class
¾
switch. The tagged frames are classified into four classes inside the
switch: lowest, lower, higher and highest. When the “Weighted” priority rule
is congured, a 1,2,4,8 weighting is applied to forward these four classes
of packets.
Further explanation
In IEEE802.1p priority mode, when a switch port receives an untagged frame (a
frame without priority tag), the port's default priority tag will be inserted into the
frame before any other process.
: The priority tag dened in IEEE802.1p.
: Indicates the inner priority classes of
5.3.7 Port Mirroring
This page contains the following elds:
Figure 5-47 Port Mirroring
Page 68
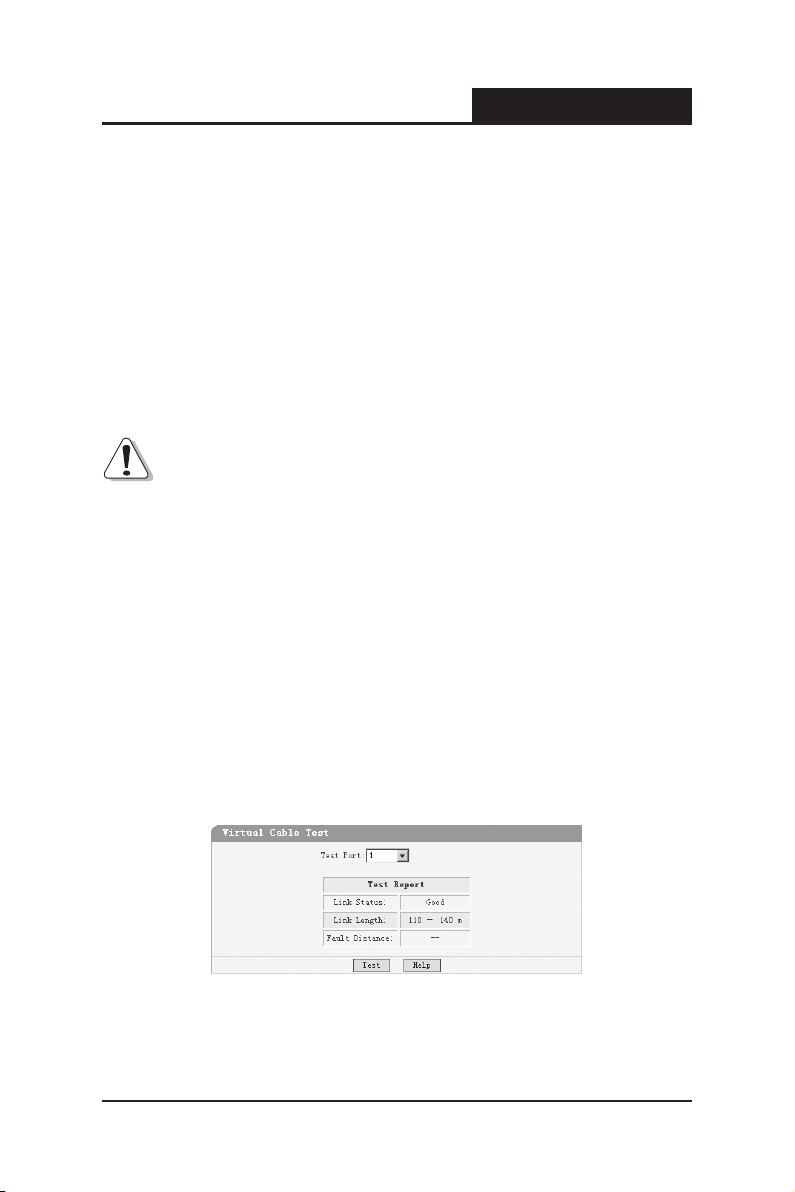
61
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Mirror Mode
¾
egress trafc, or both. You can also disable port mirroring.
Mirror Port
¾
dened here.
Mirrored Port
¾
Trunk member can't be defined here. At most 4 ports can be mirrored
simultaneously.
Clean Up
¾
Notice:
1) Trunk member port can be neither Mirror Port nor Mirrored Port.
2) The Mirror Port can’t be the Mirrored Port at the same time.
3) At most 4 Mirrored Ports can be set.
4) While setting the 100M ports as Mirror Port, it’s not able to select SFP
and 1000M ports in the Mirrored Port list. It’s suggested to set the SFP or
1000M ports as Mirror Port.
: You can set the mirror mode to monitor the ingress trafc,
: Denes the port to monitor the trafc, Trunk member can't be
: Indicates the port from which the packets are mirrored,
: Clean Up the Mirrored Port list.
5.3.8 Virtual Cable Test
The virtual cable test feature lets you test the continuity of the cable circuit. It
contains the following elds:
Figure 5-48 Virtual Cable Test
Page 69

62
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Test Port
¾
Link Status
¾
shorts or any impedance mismatch in the cable.
Link Length
¾
good.
Fault Distance
¾
Test
¾
Cable connected to the SFP cannot be tested.
: Select the port you want to test.
: Reports good status or issues such as cable opens, cable
: Reports the range of the cable length if the link status is
: Reports the distance to the open/short location.
: Test the cable via the selected port.
Notice:
Page 70

63
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Appendix A Pin Explain For RJ-45 Connector
The switching port can connect to stations wired in standard RJ-45 Ethernet
station mode using straight cables. Transmission devices connected to each
other use crossed cables. The following gure illustrates the pin allocation:
Figure RJ-45 connector
The following shows the way to make the cable use to connect switch to
network adapter, and cable use to connect switch to switch/hub/bridge.
Pin signal allocation for RJ-45 connector
Pin MDI-II MDI-X
1 TX+ (send) RX+ (receive)
2 TX- (send) RX- (receive)
3 RX+ (receive) TX+ (send)
4 No use No use
5 No use No use
6 RX- (receive) TX- (send)
7 No use No use
8 No use No use
Straight cable: use to connect switch (uplink port) or network adapter to switch/
hub/other device (normal port).
Page 71

64
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
1 TX+
2 TX-
3 RX+
6 RX-
RX+ 1
RX- 2
TX+ 3
TX- 6
MDI-II
MDI-X
1 RX+
2 RX-
3 TX+
6 TX-
RX+ 1
RX- 2
TX+ 3
TX- 6
MDI-XMDI-X
Figure straight cable
Crossed cable: use to connect switch (normal port) to switch/hub/other
device(normal port).
Figure crossed cable
Page 72

65
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Appendix B Table of Factory Defaults
Table of Factory Defaults:
System Name Null
System Setting
Port Setting
Network Setting
System Information
File Transfer
User
Port Parameter
Port Statistic All 0
Storm Control
Port Description Null
Switch IP Address
Static MAC Address Null
Filtering MAC Address Null
Dynamic Binding
Bound MAC Address Null
System Location Null
Contact Information Null
Transfer Type System Upgrading
File Name
User Name supervisor
Password supervisor
Port Status Enable
Port Security Disable
Flow Control Disable
Duplex Mode Auto
Broadcast Control Disable
Multicast Control Disable
UL Control Disable
Limit Rate 64K
DHCP client Disable
IP Address 192.168.0.1
Netmask 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway Null
Binding Disable
Number of MAC
Address to Bind
SysSL2210WEB.bin
5
Page 73

66
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Aging Time Aging Time 300
Destination IP Address
Network Setting
VLAN Setting
Port Trunking No congured Trunk
Priority Setting
Port Mirroring Port Mirroring
Ping
VLAN Mode Disable
Port VLAN Setting All ports belong to VLAN 1
Tag VLAN
Global Setting
Tag VLAN Setting
MTU VLAN Setting Uplink port 1
Priority Mode
Port-Based Priority Priority Class Lowest
Port Default Priority
802.1P Priority
Ping Count 4
Data Size 64
Ping Interval 1000
PVID 1
Untag Frame Pass
All ports belong to VLAN 1; the VID is 1 and
“Egress Frame” is "Drop Tag"
Priority Mode Disable
Priority Rule Weighted
Port Default Priority Tag
Priority Tag 0,1 Lowest
Priority Tag 2,3 Lower
Priority Tag 4,5 Higher
Priority Tag 6,7 Highest
Mirror Mode Disable
Mirror Port 1
Mirrored Port Null
192.168.0.1
0
Page 74

67
Gigabit Web Smart Switch User's Guide
TL-SG2109WEB/TL-SL2210WEB/TL-SL2218WEB/TL-SL2428WEB/TL-SL2452WEB
Appendix C Table of Function Differences of
Switch Family
Table of Function Differences of Switch Family
Function
Port 9 10 18 28 52
Giga Port 9 2 2 4 4
SFP Port 1 1 1 2 2
Trunk 2 2 4 6 8
Port VLAN 9 10 18 28 52
Tag VLAN 64 64 64 128 256
Static MAC 64 64 128 128 128
Filtering MAC
Dynamic
Binding MAC
Power
Consumption
TL-SG2109WEB TL-SL2210WEB TL-SL2218WEB TL-SL2428WEB TL-SL2452WEB
64 64 128 128 128
128 128 256 384 544
20W MAX 9W MAX 13W MAX 20W MAX 35W MAX
Models
Page 75

7106503155
TP-LINK TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
http://www.tp-link.com
 Loading...
Loading...