
.
RAV4 EV
Electric
2012 Model
2nd Generation
© 2012 Toyota Motor Corporation
All rights reserved. This document may not be
altered without the written permission of Toyota Motor Corporation.
12 Toyota RAV4 EV ERG REV – (05/28/12)

-i-
Foreword
In 1997, Toyota released the 1st generation Toyota RAV4 EV electric
vehicle in North America. To educate and assist emergency responders
in the safe handling of RAV4 EV technology, Toyota published the
1998 RAV4 EV Emergency Response Guide.
With the release of the 2nd generation Toyota RAV4 EV in July 2012, a
new 2012 Toyota RAV4 EV Emergency Response Guide was
published for emergency responders. While many features from the 1st
generation model are similar, emergency responders should recognize
and understand the new, updated features of the 2nd generation RAV4
EV covered in this guide.
High voltage electricity powers the electric motor, DC/DC converter,
battery coolant heater, air conditioning (A/C) compressor, cabin
coolant heater and inverter. All other automotive electrical devices
such as the head lights, radio, and gauges are powered from a separate
12 Volt auxiliary battery. Numerous safeguards have been designed
into the RAV4 EV to help ensure the high voltage, approximately 230
to 386 Volt, Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Electric Vehicle (EV) battery
assembly is kept safe and secure in an accident.
The RAV4 EV utilizes the following electrical systems:
Maximum 450 Volts AC
Nominal 230 to 386 Volts DC
Nominal 120/240 Volts AC
Nominal 12 Volts DC
2nd generation RAV4 EV features:
Complete model change with a new exterior and interior design.
A high voltage Electric Vehicle (EV) battery assembly rated at 230
to 386 Volts.
A high voltage motor driven Air Conditioning (A/C) compressor
rated at 230 to 386 Volts.
A high voltage battery coolant heater and cabin coolant heater rated
at 230 to 386 Volts.
An electric vehicle charge cable rated at 120/240 Volts.
An onboard battery charger with AC 120/240 Volt input and DC
230 to 386 Volt output.
A DC/DC Converter with a 230 to 386 Volt input and a 12 Volt
output.
A body electrical system rated at 12 Volts with a negative chassis
ground.
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – dual stage frontal airbags,
front seat side airbags, side curtain airbags and front seat belt
pretensioners.
High voltage electrical safety remains an important factor in the
emergency handling of the RAV4 EV Electric Vehicle. It is important
to recognize and understand the disabling procedures and warnings
throughout the guide.
Additional topics in the guide include:
RAV4 EV identification.
Major Electric Vehicle component locations and descriptions.
Extrication, fire, recovery, and additional emergency response
information.
Roadside assistance information.
2012 Model Year RAV4 EV 1998 - 2003 Model Year RAV4 EV
This guide is intended to assist emergency responders in the safe
handling of a RAV4 EV vehicle during an incident.
NOTE:
Emergency Response Guides for Toyota electric, hybrid and alternative
fuel vehicles may be viewed at http://techinfo.toyota.com.

-ii-
Table of Contents Page
About the RAV4 EV 1
RAV4 EV Identification 2
Electric Vehicle Component Locations & Descriptions 5
Plug-in Charging System Component Locations & Descriptions 7
Smart Key System 8
Electronic Shift Selector 10
Electric Vehicle Operation 11
Electric Vehicle (EV) Battery Assembly 12
Plug-in Charging System 13
Remote Climate Control System 15
Low Voltage Battery 17
High Voltage Safety 18
Plug-in Charging Safety 19
SRS Airbags & Seat Belt Pretensioners 21
Emergency Response 23
Extrication 23
Fire 30
Overhaul 31
Recovering of Li-ion EV Battery Assembly 32
Spills 32
First Aid 32
Submersion 33
Table of Contents Page
Roadside Assistance 34

-1-
About the RAV4 EV
The RAV4 EV continues into its 2nd generation as an electric vehicle.
Electric Vehicle means that the vehicle contains only an electric motor
and does not have a gasoline engine for power. Electricity stored in a
high voltage Electric Vehicle (EV) battery assembly for the electric
motor.
The following illustration demonstrates how the RAV4 EV operates in
various driving modes.
Utilizing the charge cable assembly connected to a 120/240 Volt
outlet, the vehicle’s EV battery assembly can be fully charged
within 40 hours (when charging at 120 Volt / 15 Amp) or 6 hours
(when charging at 240 Volt / 40 Amp) from a fully discharged state.
During driving, when the Li-ion battery is sufficiently charged, the
vehicle will drive using electric only power for approximately 152
miles (245 km).
During deceleration, such as when braking, the vehicle regenerates
kinetic energy from the front wheels to produce electricity that
recharges the EV battery assembly.
While the vehicle is stopped, the electric motor is off, however the
vehicle remains on and operational.
Deceleration
Driving Stopped Plug-in Charging
Plug-in Charging
Electricity
Charging Batteries
-2-
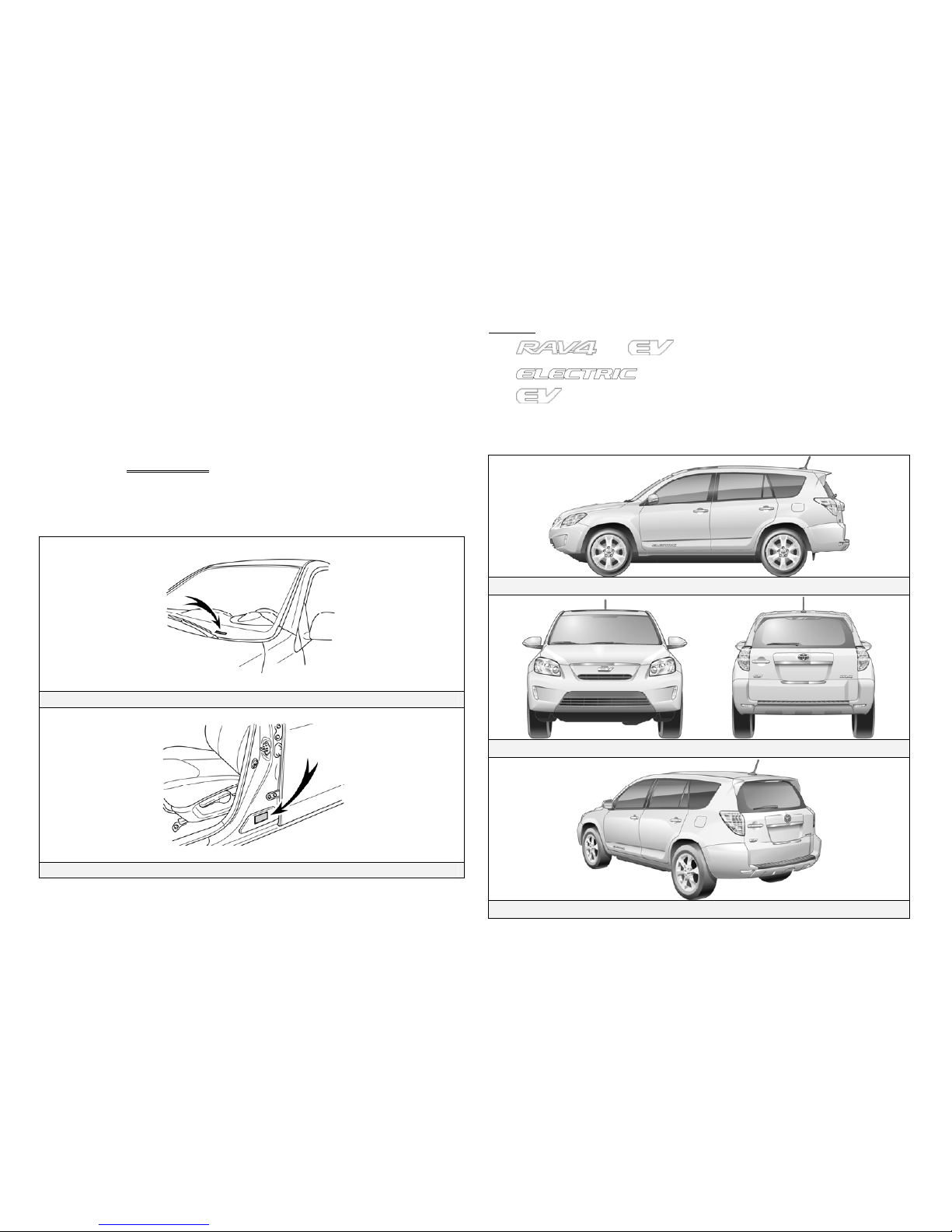
RAV4 EV Identification
In appearance, the 2012 model year RAV4 EV is nearly identical to the
conventional, non-electric Toyota RAV4. The RAV4 EV is a 5-door
SUV. Exterior, interior, and motor compartment illustrations are
provided to assist in identification.
The alphanumeric 17 character Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is
provided in the front windshield cowl and on the driver side B pillar.
Example VIN: 2T3YL4DV0C2020211
A RAV4 EV is identified by the first 8 alphanumeric characters
2T3YL4DV.
Driver Side Windshield
Driver Side B Pillar
Exterior
and logos on the back door.
logo on the driver and front passenger door.
logo on the front upper grille.
Charge inlet door located on the driver side rear quarter panel.
Exterior Driver Side View
Exterior Front and Rear View
Exterior Rear and Driver Side View

-3-
RAV4 EV Identification (Continued)
Interior
The instrument cluster (power meter, driving range & battery gauge,
READY indicator, plug-in indicator and warning lights) located in the dash
behind the steering wheel, is different than the one on the conventional,
non-electric RAV4.
NOTE:
If the vehicle is shut off, the instrument cluster gauges will be “blacked
out”, not illuminated.
Interior View
Instrument Cluster View
Power Meter, Driving Range & Battery Gauge
READY Indicator
Plug-in Indicator

-4-
RAV4 EV Identification (Continued)
Motor Compartment
Logo on the plastic cover.
Motor Compartment View
-5-
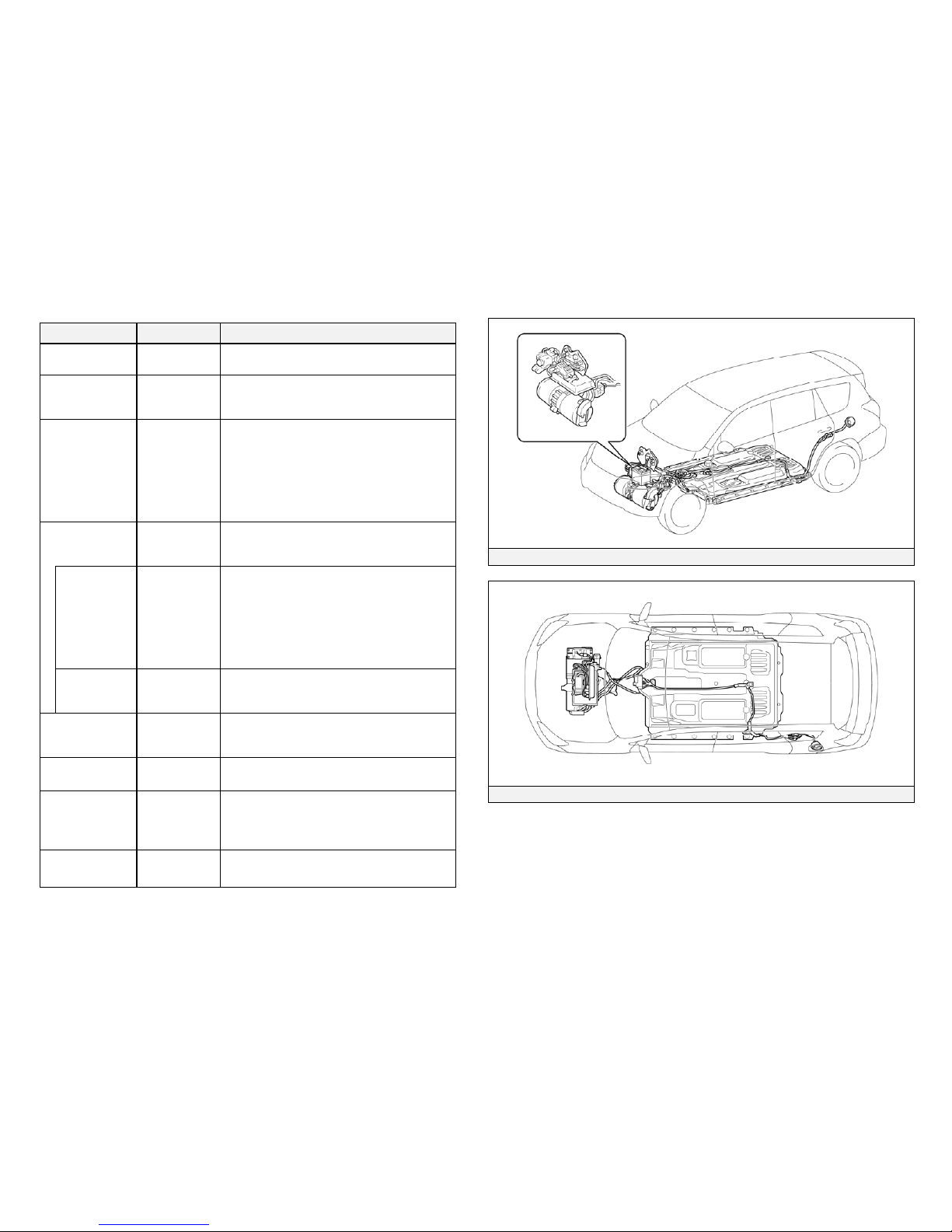
Electric Vehicle Component Locations & Descriptions
Component Location Description
12 Volt Auxiliary
Battery
Motor
Compartment
A lead-acid battery that supplies power to
the low voltage devices.
Electric Vehicle
(EV) Battery
Assembly
Under the
Floor
230 to 386 Volt Lithium-ion (Li-ion)
battery assembly consisting of 3.6 Volt
cells connected in a series-parallel circuit.
Power Cables Undercarriage,
Motor
Compartment
and Driver Side
behind Rear
Quarter Panel
Orange colored power cables carry high
voltage Alternating Current (AC) between
the charge port and on-board charger, and
high voltage Direct Current (DC) between
the EV battery assembly, DC/DC converter,
inverter, A/C compressor, battery coolant
heater and cabin coolant heater.
Drive Unit Motor
Compartment
The drive unit integrates the inverter,
electric motor, differential and p-lock
actuator.
Inverter Drive Unit Inverts the high voltage electricity from the
EV battery to 3-phase AC electricity that
drive the electric motor. Also converts the
high voltage AC power generated by the
electric motor during regeneration to high
voltage DC power to charge the EV battery
assembly.
Electric Motor Drive Unit 3-phase high voltage AC inductive electric
motor contained in the drive unit. It is used
to power the front wheels.
On-Board
Charger
Motor
Compartment
Boosts the AC power supplied from an
external power source and converts it to DC
to charge the EV battery assembly.
A/C Compressor
(with Inverter)
Motor
Compartment
3-phase high voltage AC electrically driven
motor compressor.
DC/DC
Converter for 12
Volt Auxiliary
Battery
Motor
Compartment
Converts 230 to 386 Volts from the EV
battery assembly to 12 Volts for low
voltage vehicle power.
Cabin Coolant
Heater
Motor
Compartment
Heats the coolant used for the cabin heater.
Electric Vehicle Components
Components (Top View) and High Voltage Power Cables

-6-
Electric Vehicle Component Locations & Descriptions
(Continued)
Key Specifications:
Electric Motor: 154 hp (115 kW), AC Inductive Motor
Transaxle: Automatic Only
EV Battery Assembly: 230 to 386 Volt Sealed Li-ion Battery
Curb Weight: 4,032 lbs/1,829 kg
Frame Material: Steel Unibody
Body Material: Steel Panels
Seating Capacity: 5 passengers
Steel Unibody

-7-
Plug-in Charging System Component Locations &
Descriptions
Component Location Description
Charge Inlet Driver Side
Rear Quarter
Panel
Connects to the charge cable assembly
charge connector. Supplies the electrical
power from an external power source to
the vehicle.
Power Cable for
Charging
Driver Side
behind Rear
Quarter Panel
and
Undercarriage
Connects the charge inlet and on-board
charger.
On-board
Charger
Motor
Compartment
Boosts the AC power supplied from an
external power source and converts it to
DC to charge the EV battery assembly.
Charge Cable
Assembly
Driver Side
Rear Quarter
Panel
Connects to the charge inlet and supplies
power from an external power source to
the vehicle.
Plug-in Indicator Instrument
Cluster in
Dash behind
Steering
Wheel
Illuminates in green to indicate that the
power cable is correctly plugged in.
Illuminates in yellow to indicate a
malfunction.
Charge Indicator Driver Side
Rear Quarter
Window
Displays the charging status by
illuminating, flashing or turning off.
Plug-in Charging System Components
Plug-in Charging System Components (Top View) and Charge Inlet Power Cables
-8-
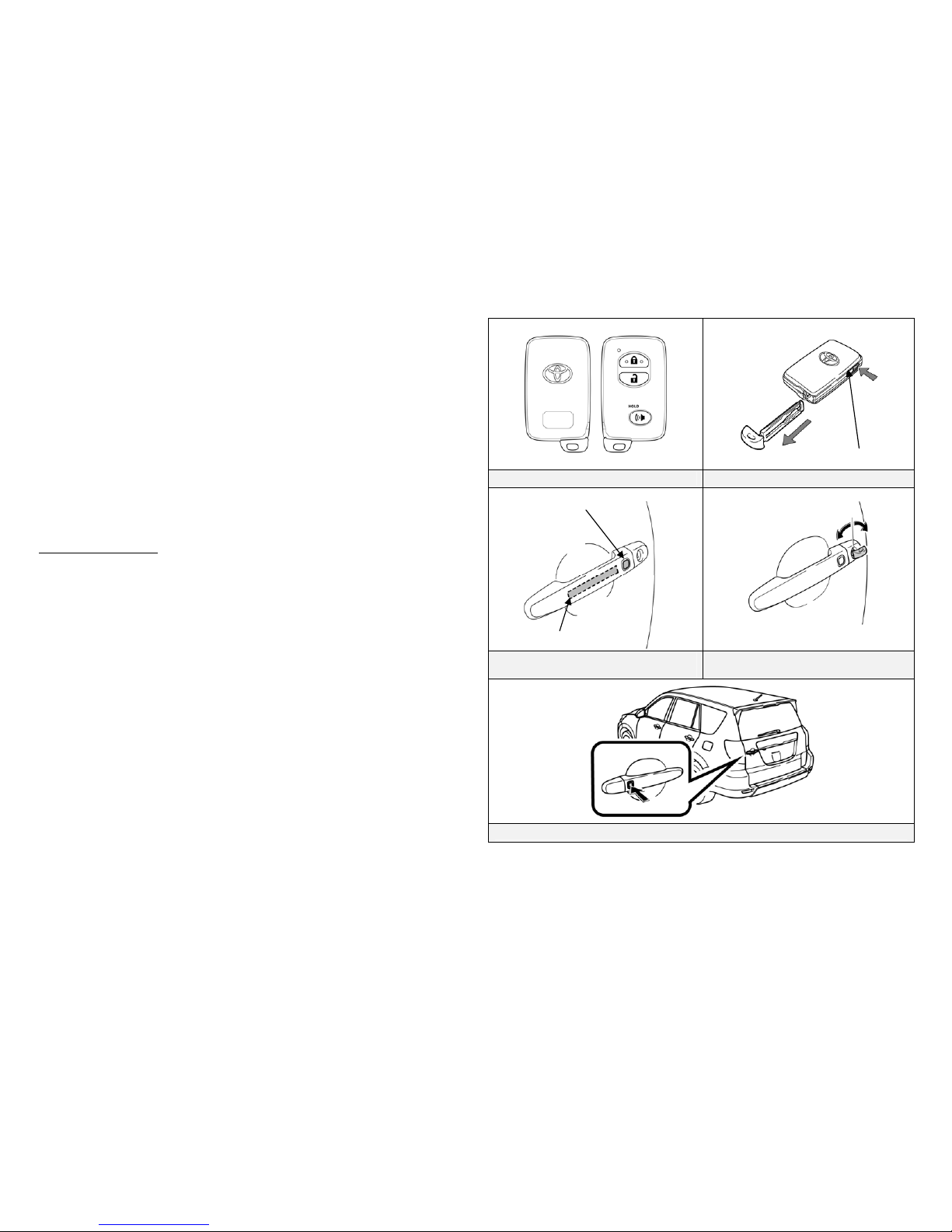
Smart Key System
The RAV4 EV smart key system consists of a smart key transceiver that
communicates bi-directionally, enabling the vehicle to recognize the
smart key in proximity to the vehicle. Once recognized, the smart key
will allow the user to lock and unlock the doors without pushing smart
key buttons, and start the vehicle without inserting it into an ignition
switch.
Smart key features:
Passive (remote) function to lock/unlock the doors and start the
vehicle.
Wireless transmitter buttons to lock/unlock all 5 doors.
Hidden metal cut key to lock/unlock the doors.
Door (Lock/Unlock)
There are several methods available to lock/unlock the doors.
Pushing the smart key lock button will lock all the doors including
the back door. Pushing the smart key unlock button once unlocks the
driver door, twice unlocks all doors.
Touching the unlock touch sensor on the backside of the driver door
exterior handle, with the smart key in close proximity to the vehicle,
unlocks the driver door. Touching the unlock touch sensor on the
backside of the front passenger door exterior handle, with the smart
key in close proximity to the vehicle, unlocks all the doors. Pushing
the lock button on either front door will lock all the doors, or pushing
the back door lock button will lock all doors.
Inserting the hidden metal cut key in the driver door lock and turning
it clockwise once unlocks the driver door, twice unlocks all doors.
To lock all doors turn the key counterclockwise once. Only the
driver door contains an exterior door lock for the metal cut key.
Smart Key (Fob) Hidden Metal Cut Key for Door Lock
Driver Door Unlock Touch Sensor and
Lock Button
Front Driver Door Lock
Back Door Lock Button
Release Button
Use the Hidden Metal Cut Key
Lock Button
Unlock Touch Sensor
-9-
Smart Key System (Continued)
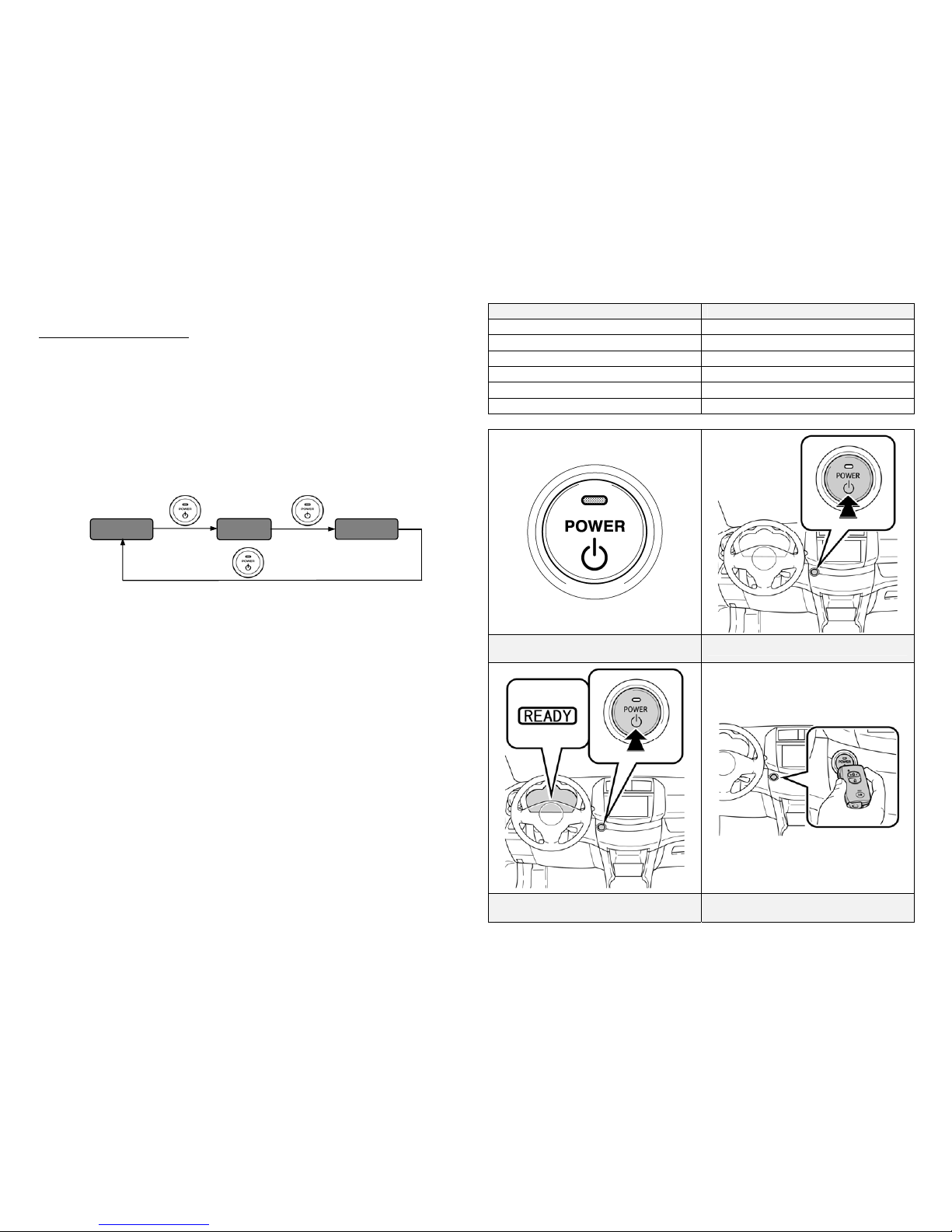
Vehicle Starting/Stopping
The smart key has replaced the conventional metal cut key, and the power
button with an integrated status indicator light has replaced the ignition switch.
The smart key only needs to be in proximity to the vehicle to allow the system
to function.
With the brake pedal released, the first push of the power button operates
the accessory mode, the second push operates the ignition-on mode, and the
third push turns the ignition off again.
Ignition Mode Sequence (brake pedal released):
Starting the vehicle takes priority over all other ignition modes and is
accomplished by depressing the brake pedal and pushing the power button
once. To verify the vehicle has started, check that the power button status
indicator light is off and the READY indicator is illuminated in the
instrument cluster.
If the internal smart key battery is dead, use the following method to start
the vehicle.
1. Touch the Toyota emblem side of the smart key to the power button.
2. Within the 10 seconds after the buzzer sounds, push the power button
with the brake pedal depressed (the READY indicator will illuminate).
Once the vehicle has started and is on and operational (READY-ON), the
vehicle is shut off by bringing the vehicle to a complete stop and then
depressing the power button once.
To shut off the vehicle before coming to a stop in an emergency, push and
hold down the power button for more than 2 seconds or push the power
button 3 times or more in a row. This procedure may be useful at an
accident scene in which the READY indicator is on, Park (P) cannot be
selected, and the drive wheels remain in motion.
Ignition Mode Power Button Indicator Light
Off Off
Accessory Amber
Ignition-On Amber
Brake Pedal Depressed Green
Vehicle Started (READY-ON) Off
Malfunction Blinking Amber
Power Button with Integrated Status
Indicator Light
Ignition Modes (Brake Pedal Released)
Starting Sequence
(Brake Pedal Depressed)
Smart Key Recognition
(When Smart Key Battery is Dead)
Vehicle Off
Accessory
Ignition-On
Button Push
Button Push
Button Push
