Texas Instruments TL1454IDR, TL1454EVM-085, TL1454ID, TL1454CPWR, TL1454CPWLE Datasheet
...
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
D
T wo Complete PWM Control Circuits
D
Outputs Drive MOSFETs Directly
D
Oscillator Frequency...50 kHz to 2 MHz
D
3.6-V to 20-V Supply-Voltage Range
D
Low Supply Current...3.5 mA Typ
D
Adjustable Dead-Time Control, 0% to 100%
D
1.25-V Reference
description
The TL1454 is a dual-channel pulse-width-modulation (PWM) control circuit, primarily intended for
low-power, dc/dc converters. Applications include
LCD displays, backlight inverters, notebook computers, and other products requiring small, high-frequency , dc/dc converters. Each PWM channel has its own
error amplifier, PWM comparator, dead-time control comparator, and MOSFET driver. The voltage reference,
oscillator, undervoltage lockout, and short-circuit protection are common to both channels.
Channel 1 is configured to drive n-channel MOSFETs in step-up or flyback converters, and channel 2 is
configured to drive p-channel MOSFETs in step-down or inverting converters. The operating frequency is set
with an external resistor and an external capacitor, and dead time is continuously adjustable from 0 to 100%
duty cycle with a resistive divider network. Soft start can be implemented by adding a capacitor to the dead-time
control (DTC) network. The error-amplifier common-mode input range includes ground, which allows the
TL1454 to be used in ground-sensing battery chargers as well as voltage converters.
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGED DEVICES
†
T
A
SMALL OUTLINE
(D)
PLASTIC DIP
(N)
TSSOP
(PW)
CHIP FORM
(Y)
–20°C to 85°C TL1454CD TL1454CN TL1454CPWLE TL1454Y
–40°C to 85°C TL1454ID TL1454IN — —
†
The D package is available taped and reeled. Add the suffix R to the device name (e.g., TL1454CDR). The
PW package is available only left-end taped and reeled (indicated by the LE suffix on the device type; e.g.,
TL1454CPWLE).
Copyright 1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
CT
RT
DTC1
IN1+
IN1–
COMP1
GND
OUT1
D, N OR PW PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
REF
SCP
DTC2
IN2+
IN2–
COMP2
V
CC
OUT2
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
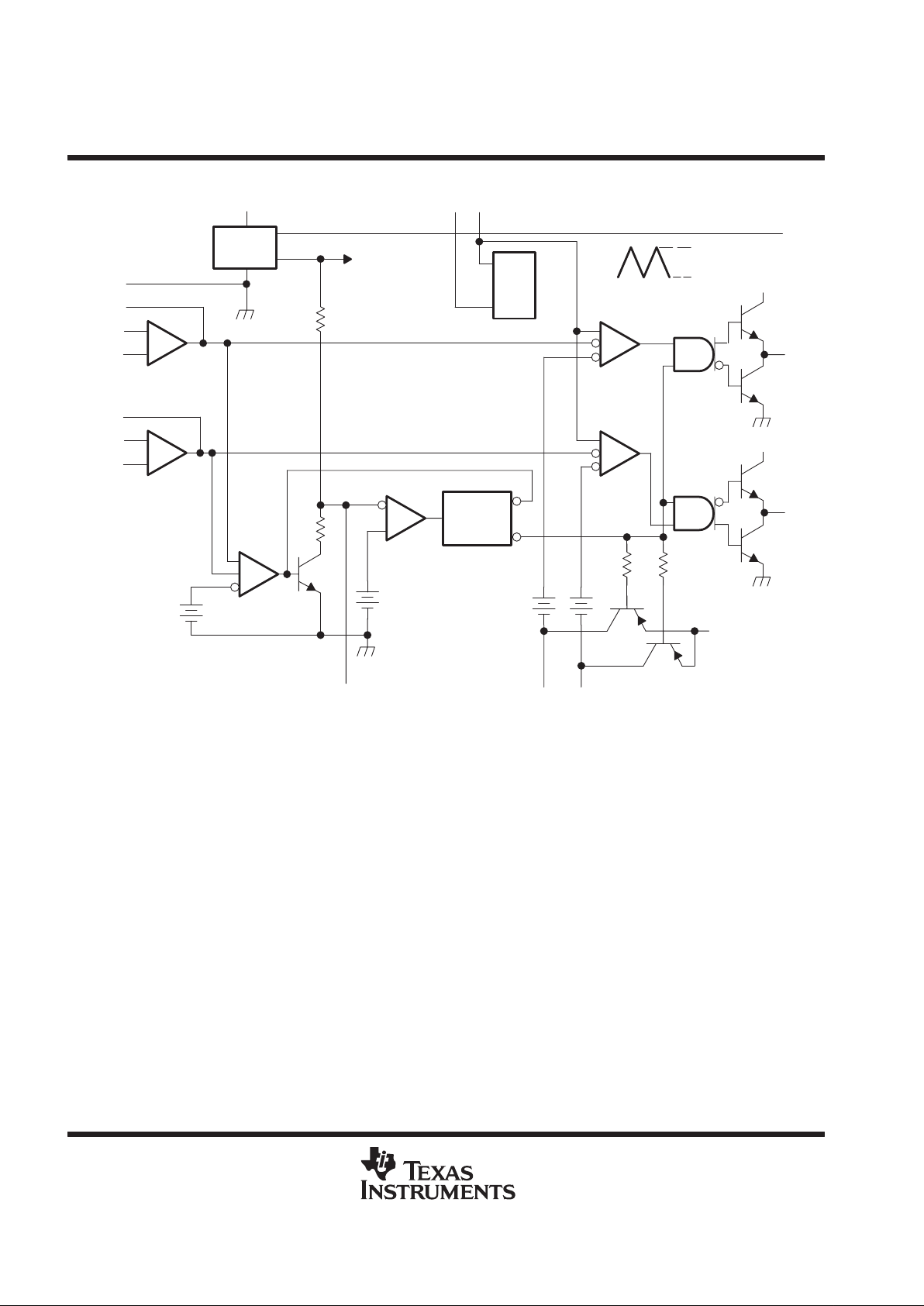
functional block diagram
_
+
_
+
OSC
PWM
Comparator 1
Error
Amplifier 1
To Internal
Circuitry
2.5 V
1.25 V
1 V
1 V
SCP
V
CC
GND
DTC1 DTC2
143
15
7
16
4
5
13
12
6
11
10
21
CTRT
OUT1
OUT2
8
V
CC
UVLO
and
SCP Latch
IN1+
IN1–
IN2+
IN2–
COMP1
COMP2
REF
1.8 V
1.2 V
SCP
Comparator 1
Voltage
REF
9
V
CC
0.65 V
0.65 V
1.25 V
PWM
Comparator 2
Error
Amplifier 2
SCP
Comparator 2
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
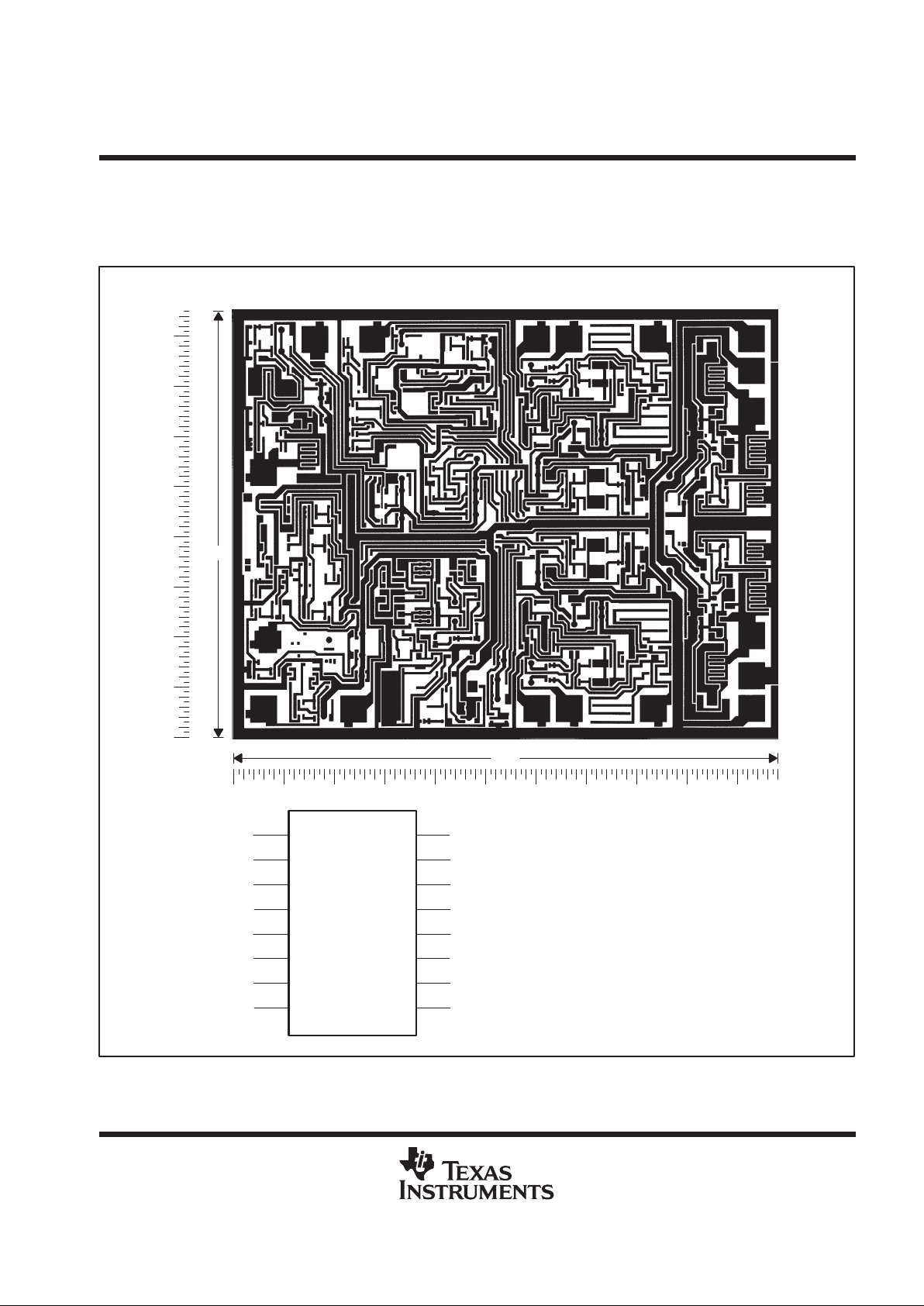
TL1454Y chip information
This chip, when properly assembled, displays characteristics similar to the TL1454C. Thermal compression or
ultrasonic bonding may be used on the doped aluminum bonding pads. The chips may be mounted with
conductive epoxy or a gold-silicon preform.
BONDING PAD ASSIGNMENTS
CHIP THICKNESS: 15 TYPICAL
BONDING PADS: 4 × 4 MINIMUM
TJmax = 150°C
TOLERANCES ARE ±10%.
ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILS.
TL1454Y
(2)
(14)
(1)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(16)
(13)
(12)
(11)
(10)
(9)
REF
DTC2
IN2+
IN2–
COMP2
V
CC
OUT2OUT1
COMP1
IN1–
IN1+
RT
CT
GND
86
108
(1)
(2) (3)
(4) (5) (6) (7)
(10)(11)
(12)(13)(14)(15)
(16)
(8)
(9)
(15)
SCP
DTC1
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
theory of operation
reference voltage
A linear regulator operating from V
CC
generates a 2.5-V supply for the internal circuits and the 1.25-V reference,
which can source a maximum of 1 mA for external loads. A small ceramic capacitor (0.047 µF to 0.1 µF) between
REF and ground is recommended to minimize noise pickup.
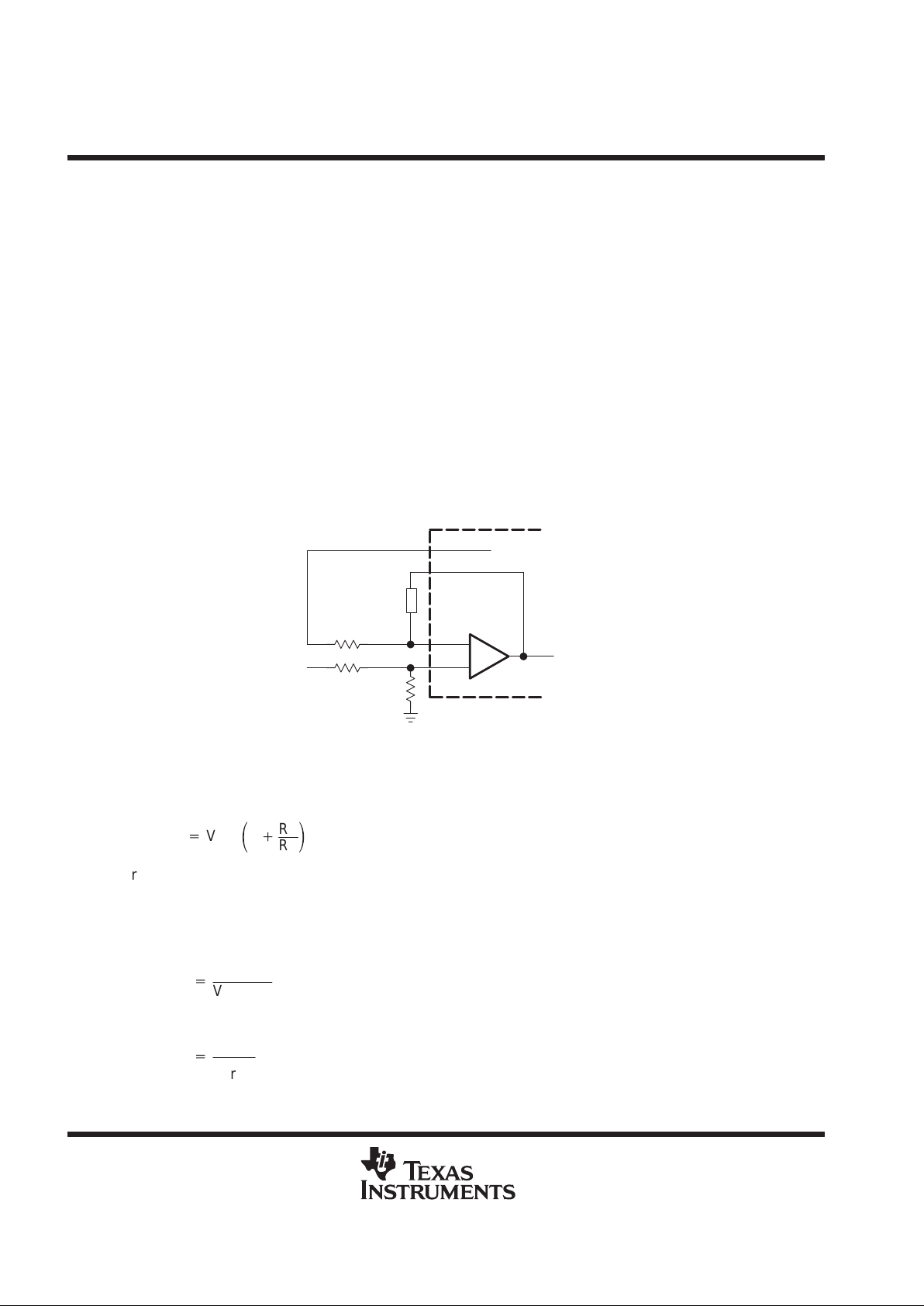
error amplifier
The error amplifier generates the error signal used by the PWM to adjust the power-switch duty cycle for the
desired converter output voltage. The signal is generated by comparing a sample of the output voltage to the
voltage reference and amplifying the difference. An external resistive divider connected between the converter
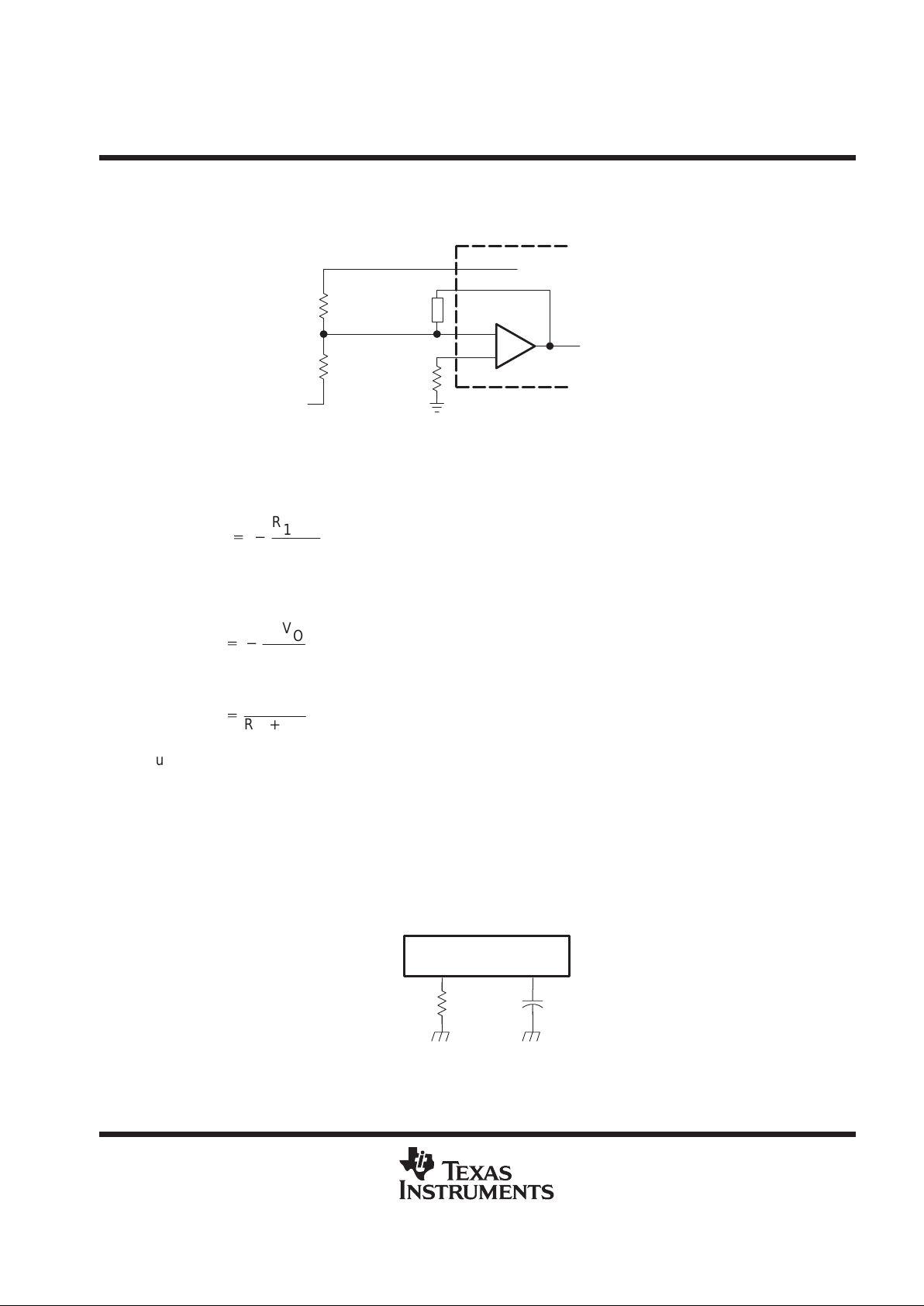
output and ground, as shown in Figure 1, is generally required to obtain the output voltage sample.
The amplifier output is brought out on COMP to allow the frequency response of the amplifier to be shaped with
an external RC network to stabilize the feedback loop of the converter. DC loading on the COMP output is limited
to 45 µA (the maximum amplifier source current capability).
Figure 1 illustrates the sense-divider network and error-amplifier connections for converters with positive output
voltages. The divider network is connected to the noninverting amplifier input because the PWM has a phase
inversion; the duty cycle decreases as the error-amplifier output increases.
_
+
IN–
IN+
R3
R1
R2
COMP
To PWM
V
O
Compensation
Network
REF
Converter
Output
TL1454
Figure 1. Sense Divider/Error Amplifier
Configuration for Converters with Positive Outputs
The output voltage is given by:
VO+
V
ref
ǒ
1
)
R1
R2
Ǔ
where V
ref
= 1.25 V.
The dc source resistance of the error-amplifier inputs should be 10 kΩ or less and approximately matched to
minimize output voltage errors caused by the input-bias current. A simple procedure for determining appropriate
values for the resistors is to choose a convenient value for R3 (10 kΩ or less) and calculate R1 and R2 using:
R1+
R3V
O
VO–V
ref
R2+
R3V
O
V
ref
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
error amplifier
R1 and R2 should be tight-tolerance (±1% or better) devices with low and/or matched temperature coefficients
to minimize output voltage errors. A device with a ±5% tolerance is suitable for R3.
_
+
IN–
IN+
R2
COMP
To PWM
V
O
Compensation
Network
REF
R1
R3
Converter
Output
Figure 2. Sense Divider/Error Amplifier Configuration for Converters with Negative Outputs
Figure 2 shows the divider network and error-amplifier configuration for negative output voltages. In general,
the comments for positive output voltages also apply for negative outputs. The output voltage is given by:
VO+*
R1V
ref
R
2
The design procedure for choosing the resistor value is to select a convenient value for R2 (instead of R3 in
the procedure for positive outputs) and calculate R1 and R3 using:
R1+*
R2V
O
V
ref
R3+
R1R
2
R1)
R
2
V alues in the 10-kΩ to 20-kΩ range work well for R2. R3 can be omitted and the noninverting amplifier connected
to ground in applications where the output voltage tolerance is not critical.
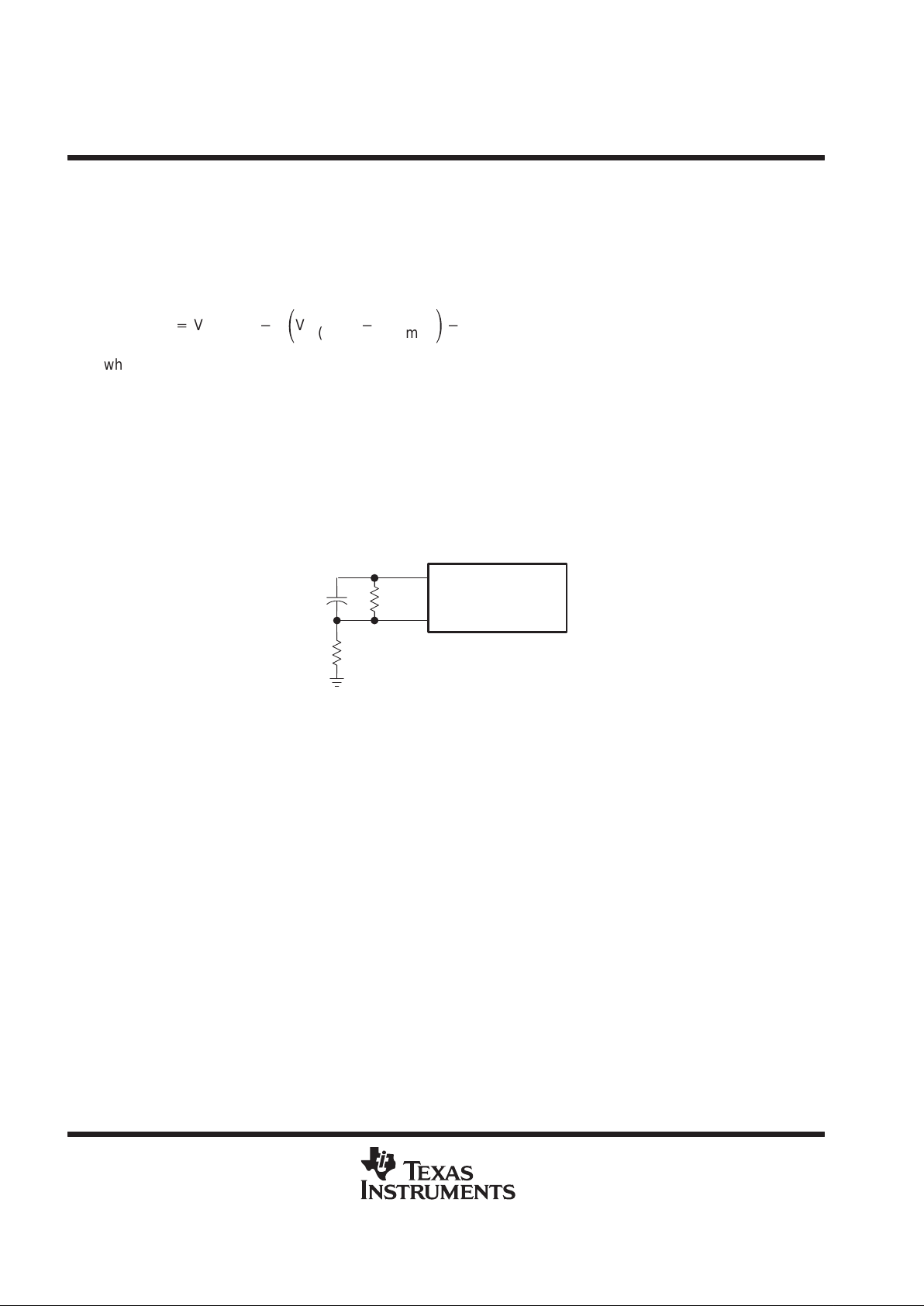
oscillator
The oscillator frequency can be set between 50 kHz and 2 MHz with a resistor connected between RT and GND
and a capacitor between CT and GND (see Figure 3). Figure 6 is used to determine R
T
and CT for the desired
operating frequency. Both components should be tight-tolerance, temperature-stable devices to minimize
frequency deviation. A 1% metal-film resistor is recommended for R
T
, and a 10%, or better, NPO ceramic
capacitor is recommended for C
T
.
R
T
C
T
RT CT
TL1454
21
Figure 3. Oscillator Timing
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
dead-time control (DTC) and soft start
The two PWM channels have independent dead-time control inputs so that the maximum power-switch duty
cycles can be limited to less then 100%. The dead-time is set with a voltage applied to DTC; the voltage is
typically obtained from a resistive divider connected between the reference and ground as shown in Figure 4.
Soft start is implemented by adding a capacitor between REF and DTC.
The voltage, V
DT
, required to limit the duty cycle to a maximum value is given by:
VDT+
V
O(max)
*
D
ǒ
V
O(max)
*
V
O(min)
Ǔ
*
0.65
where V
O(max)
and V
O(min)
are obtained from Figure 9, and D is the maximum duty cycle.
Predicting the regulator startup or rise time is complicated because it depends on many variables, including:
input voltage, output voltage, filter values, converter topology , and operating frequency. In general, the output
will be in regulation within two time constants of the soft-start circuit. A five-to-ten millisecond time constant
usually works well for low-power converters.
The DTC input can be grounded in applications where achieving a 100% duty cycle is desirable, such as a buck
converter with a very low input-to-output differential voltage. However, grounding DTC prevents the
implementation of soft start, and the output voltage overshoot at power-on is likely to be very large. A better
arrangement is to omit R
DT1
(see Figure 4) and choose R
DT2
= 47 kΩ. This configuration ensures that the duty
cycle can reach 100% and still allows the designer to implement soft start using C
SS
.
C
SS
REF
TL1454
R
DT1
DTC
R
DT2
16
Figure 4. Dead-Time Control and Soft Start
PWM comparator
Each of the PWM comparators has dual inverting inputs. One inverting input is connected to the output of the
error amplifier; the other inverting input is connected to the DTC terminal. Under normal operating conditions,
when either the error-amplifier output or the dead-time control voltage is higher than that for the PWM triangle
wave, the output stage is set inactive (OUT1 low and OUT2 high), turning the external power stage off.
undervoltage-lockout (UVLO) protection
The undervoltage-lockout circuit turns the output circuit off and resets the SCP latch whenever the supply
voltage drops too low (to approximately 2.9 V) for proper operation. A hysteresis voltage of 200 mV eliminates
false triggering on noise and chattering.
short-circuit protection (SCP)
The TL1454 SCP function prevents damage to the power switches when the converter output is shorted to
ground. In normal operation, SCP comparator 1 clamps SCP to approximately 185 mV. When one of the
converter outputs is shorted, the error amplifier output (COMP) will be driven below 1 V to maximize duty cycle
and force the converter output back up. When the error amplifier output drops below 1 V, SCP comparator 1
releases SCP, and capacitor, C
SCP
, which is connected between SCP and GND, begins charging. If the
error-amplifier output rises above 1 V before C
SCP
is charged to 1 V , SCP comparator 1 discharges C
SCP
and
normal operation resumes. If C
SCP
reaches 1 V , SCP comparator 2 turns on and sets the SCP latch, which turns
off the output drives and resets the soft-start circuit. The latch remains set until the supply voltage is lowered
to 2 V or less, or C
SCP
is discharged externally.

TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
7
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
short-circuit protection (SCP) (continued)
The SCP time-out period must be greater than the converter start-up time or the converter will not start. Because
high-value capacitor tolerances tend to be ±20% or more and IC resistor tolerances are loose as well, it is best
to choose an SCP time-out period 10-to-15 times greater than the converter startup time. The value of C
SCP
may be determined using Figure 6, or it can be calculated using:
C
SCP
+
T
SCP
80.3
where C
SCP
is in µF and T
SCP
is the time-out period in ms.
output stage
The output stage of the TL1454 is a totem-pole output with a maximum source/sink current rating of 40 mA and
a voltage rating of 20 V . The output is controlled by a complementary output AND gate and is turned on (sourcing
current for OUT1, sinking current for OUT2) when all the following conditions are met: 1) the oscillator triangle
wave voltage is higher than both the DTC voltage and the error-amplifier output voltage, 2) the
undervoltage-lockout circuit is inactive, and 3) the short-circuit protection circuit is inactive.
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
†
Supply voltage, V
CC
(see Note 1) 23 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Error amplifier input voltage: IN1+, IN1–, IN2+, IN2– 23 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output voltage: OUT1, OUT2 20 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous output current: OUT1, OUT2 ±200 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Peak output current: OUT1, OUT2 1 A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous total dissipation See Dissipation Rating Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature range, T
A
: C suffix –20°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I suffix –40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE 1: All voltage values are with respect to network GND.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE
TA ≤ 25°C
POWER RATING
DERATING FACTOR
ABOVE TA = 25°C
TA = 70°C
POWER RATING
TA = 85°C
POWER RATING
D 950 mW 7.6 mW/°C 608 mW 494 mW
N 1250 mW 10.0 mW/°C 800 mW 650 mW
PW 500 mW 4.0 mW/°C 320 mW 260 mW
TL1454, TL1454Y
DUAL-CHANNEL PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION (PWM)
CONTROL CIRCUIT
SLVS086B – APRIL 1995 – REVISED NOVEMBER 1997
8
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
• HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251–1443
recommended operating conditions
MIN MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
CC
3.6 20 V
Error amplifier common-mode input voltage –0.2 1.45 V
Output voltage, V
O
20 V
Output current, I
O
±40 mA
COMP source current –45 µA
COMP sink current 100 µA
Reference output current 1 mA
COMP dc load resistance 100 kΩ
Timing capacitor , C
T
10 4000 pF
Timing resistor , R
T
5.1 100 kΩ
Oscillator frequency 50 2000 kHz
p
p
TL1454C –20 85
°
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
TL1454I –40 85
°C
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range, VCC = 6 V,
f
osc
= 500 kHz (unless otherwise noted)
reference
TL1454
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNIT
p
IO = 1 mA, TA = 25°C 1.23 1.25 1.28
V
ref
Output voltage, REF
IO = 1 mA 1.2 1.31
V
Input regulation VOC = 3.6 V to 20 V, IO = 1 mA 2 6 mV
Output regulation IO = 0.1 mA to 1 mA 1 7.5 mV
p
p
TA = T
A(min)
to 25°C, IO = 1 mA –12.5 –1.25 12.5
Output voltage change with temperature
TA = 25°C to 85°C, IO = 1 mA –12.5 –2.5 12.5
mV
I
OS
Short-circuit output current V
ref
= 0 V 30 mA
undervoltage lockout (UVLO)
TL1454
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNIT
V
IT+
Positive-going threshold voltage 2.9 V
V
IT–
Negative-going threshold voltage
TA = 25°C
2.7 V
V
hys
Hysteresis, V
IT+
– V
IT–
100 200 mV
short-circuit protection (SCP)
TL1454
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN TYP MAX
UNIT
V
IT
Input threshold voltage TA = 25°C 0.95 1 1.05 V
V
stby
†
Standby voltage
p
p
140 185 230 mV
V
I(latched)
Latched-mode input voltage
No pullup
60 120 mV
V
IT(COMP)
Comparator threshold voltage COMP1, COMP2 1 V
Input source current TA = 25°C, V
O(SCP)
= 0 –5 –15 –20 µA
†
This symbol is not presently listed within EIA/JEDEC standards for semiconductor symbology.
 Loading...
Loading...