Page 1
TANDBERG
Gatekeeper/Border Controller
API User Guide
D14172.01
July 2008
Page 2

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Table of Contents
The TANDBERG API............................................................................................ ..................... 3
1
1.1 Introduction to XML..................................................................................................................... 4
1.2 Introduction to XML Path Language (XPath) .............................................................................. 6
1.3 The TANDBERG XML Engine.................................................................................................... 8
1.4 The XML Documents...................................................................................................... ............ 9
1.5 Introduction to TANDBERG XML API Service (TXAS).............................................................. 14
1.6 Exercises........................................... ....................................................................................... 19
2 The XML-based Advanced Command Line Interface...................... ......... ..... .... ..... .... .......... 21
2.1 XACLI.................................................................. ..................................................................... 21
2.2 The Status-type root commands – xstatus / xhistory................................................................ 24
2.3 The Configuration-type root commands - xconfiguration........................................................... 26
2.4 The Command-type root commands - xcommand........ ....................................................... ..... 29
2.5 XML Output - xgetxml............................................... .... ..... ......... .... ..... ..... ......... .... ..... ......... ..... 32
2.6 Special Commands................................................................................................................... 33
3 API - Configurations............................................................................................................... 37
3.1 configuration.xml – xconfiguration............................................................................................ 37
4 API - Commands....................................................................................................... .............. 48
4.1 command.xml – xcommand................................. ..................................................................... 48
5 API - Status ............................................... .............................................................................. 60
5.1 status.xml – xstatus.................................................................................................................. 60
5.2 history.xml – xhistory................................................................................................................ 71
5.3 event.xml – xevent.................................................................................................................... 74
D14172.01 page 2 of 84
Page 3

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
1 The TANDBERG API
This document is a guide to the API interface of the TANDBERG Gatekeeper and Border Controller
products. All rights reserved. This document contains information that is proprietary to TANDBERG.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form,
or by any means, electronically, mechanically, by photocopying, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of TANDBERG. Nationally and internationally recognized trademarks and trade names are
the property of their respective holders and are hereby acknowledged.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is furnished for informational purposes only, is subject to change
without prior notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by TANDBERG. The in formation in
this document is believed to be accurate and reliable; however TANDBERG assumes no responsibility
or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this document, nor for any infringements of
patents or other rights of third parties resulting from its use. No license is granted under any patents or
patent rights of TANDBERG.
This document was written by the Research and Development Department of TANDBERG, United
Kingdom. We are committed to maintaining a high level of quality in all our documentation. Towards
this effort, we welcome your comments and suggestions regarding the content and structure of this
document. Please fax or mail your comments and suggestions to the attention of:
Research and Development Department
TANDBERG
Philip Pedersen vei 22
1366 Lysaker
Norway
Tel: +47 67 125 125
Fax: +47 67 125 234
COPYRIGHT © 2008, TANDBERG
D14172.01 page 3 of 84
Page 4

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
1.1 Introduction to XML
XML is a markup language for documents containing structured information.
All information elements in an XML document are marked by a tag and a corresponding end-tag. The
end-tag has the same name as the tag, but is prefixed with a slash ( / ). All tags are put within
angular brackets ( < > ).
Example 1.1
Below is an example of how the configuration for SNMP could be represe nted using XML.
<Configuration>
<SNMP item="1">
<Mode item="1">On</Mode>
<CommunityName item="1">public</CommunityName>
<SystemContact item="1">Administrator</SystemContact>
<SystemLocation item="1"></SystemLocation>
</SNMP>
</Configuration>
From the tree structure of this example we can see that Mode, CommunityName, SystemContact
and SystemLocation are properties of the SNMP configuration. We can distinguish between
container-elements and value-elements. Container-elements contain one or more sub-elements, while
value-elements contain a value. This is analogous to files and folders on a computer. Containerelements are folders that can contain sub-folders and files, while value-elements are files containing
data.
In the XML str ucture for the SNMP configuration we see that the container-element SNMP contains four
sub-elements. All these sub-elements are value-elements, each holding values for the properties:
Mode, CommunityName, SystemContact and SystemLocation.
Example 1.2
In this example we will look at element attributes. Attributes are used to add meta information to an
element. Attributes are placed within the start tag of an element and different attributes are separated
by space.
An XML structure representing the status of a connection to an NTP server is shown below:
<Status>
<NTP item="1" status="Inactive"/>
</Status>
We can see from the status attribute of the NTP element that the NTP connection is Inactive. This
is because it has yet to be configured. There is no further relevant information when the NTP status is
inactive therefore the sub-structure of the NTP element is empty.
D14172.01 page 4 of 84
Page 5

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.3
If we now look at the NTP element once NTP has been correctly configured we see that it now
contains more sub-structure:
<Status>
<NTP item="1" status="Active">
<Address item="1">10.0.0.2</Address>
<Port item="1">123</Port>
<LastUpdate item="1">2008-01-01 12:00:00</LastUpdate>
<LastCorrection item="1">1</LastCorrection>
</NTP>
</Status>
In this example, the att ributes are used to provide valuable information in ad dition to establishing a
dependency to the underlying sub-structure of the element.
Example 1.4
In the above examples, all elements have an attribute named item. This attribute specifies the
instance number of the ele ment. If we exam ine the DNS configuration f or a system which has two
DNS servers configured then the XML structure would look like this:
<Configuration>
<IP item="1">
<DNS item="1">
<Server item="1">
<Address item="1">10.0.0.3</Address>
</Server>
<Server item="2">
<Address item="1">10.0.0.4</Address>
</Server>
<Domain item="1">
<Name item="1">example.com</Name>
</Domain>
</DNS>
</IP>
</Configuration>
D14172.01 page 5 of 84
Page 6

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
1.2 Introduction to XML Path Language (XPath)
XPath is a comprehensive language to address data in XML documents. It is, however, very simple to
understand the basics. If you are able to specify the path to a file on your computer, you are able to
specify the path to an element in a XML structure.
Example 1.5
Let us go back to the SNMP configuration of Example 1.1:
<Configuration>
<SNMP item="1">
<Mode item="1">On</Mode>
<CommunityName item="1">public</CommunityName>
<SystemContact item="1">Administrator</SystemContact>
<SystemLocation item="1"></SystemLocation>
</SNMP>
</Configuration>
To specify the path to the SNMP element we simply start at the root level and separate the levels in the
tree structure by a slash ( / ):
Configuration/SNMP
The path to the CommunityName element is:
Configuration/SNMP/CommunityName
Example 1.6
To address a specific item of an element, the item number is added within brackets ( [ ] ) after the
element name.
The path to the Address element of Server item 2 in Example 1.4 is:
Configuration/IP/DNS/Server[2]/Address
If the item number is omitted for an element, all items of this element will be addressed. The following
expression addresses the Address element of all DNS servers:
Configuration/IP/DNS/Server/Address
D14172.01 page 6 of 84
Page 7

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.7
When using XPath it is possible to omit specifying intermediate levels in the address expression. By
using the powerful “double slash" you can address elements without having to specify the complete
path.
To show all the aliases registered on the system, the complete path would be:
Status/Registrations/Registration/Aliases/Alias
Using the “double slash" syntax this can be simplified to:
Status//Alias
Example 1.8
XPath also supports addressing by putting constraints on element attributes. The below expression
will address the Name element of all Failed zones in a system:
Status/Zones/Zone[@status="Failed"]/Name
D14172.01 page 7 of 84
Page 8

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
1.3 The TANDBERG XML Engine
The TANDBERG XML engine is optimized for advanced machine-machine interaction between a
TANDBERG system and an external control application. The main features can be summarized as:
• Structuring of information
• Addressing using XPath
• Feedback
1.3.1 Structuring of Information
An application programming interface can be seen as a gate where information is exchanged between
two systems: a control application and a target system. The control application transmits instructions
to the target system, while the target system supplies information about how these instructions are
executed, in addition to other system related information.
Thus, the exchange of information can be divided into:
1. information flowing from target, hereby called read information (r)
2. information flowing to target, hereby called write information (w)
If we now look at the TANDBERG systems we can identify three main types of information, either
being read information (r), write information (w) or read-write information (rw):
1. (r) Read information – Status Information.
Informati on about the system and sys tem processes, i.e. infor mation generated by the sy stem.
For example: status about registered systems, ongoing calls, network status etc.
All status information is structured in a hierarchy, making up a database constantly being
updated by the system to reflect process changes.
2. (w) Write information – Command Information.
Information supplied by the user to initiate an action.
For example: instructing the system to place a call, disconnect an existing call, remove a
registration etc.
A command is usually followed by a set of parameters to specify how the given action is to be
executed.
3. (rw) Read-Write information – Configuration Information. Information defining system
settings. This information can both be supplied and read by the user. For example: IP settings,
bandwidth settings, enabling/disabling of various features etc.
All configuration information is structured in a hierarchy making up a database of system
settings. But for the Configuration information, the data in the database can only be updated by
the user/control application.
1.3.2 Addressing using XPath
To address information in th e hierarchic s tructure of Status and Configuration information the
TANDBERG systems support abbreviated XML Path Language (XPath). This allows the user/control
application to address everything from a single element of data (for example the source address of a
specific call), to larger parts of the hierarchy (for example all information available for a given call).
The structuring of information together with XPath for addressing makes up powerful features like
searching an d s etting of multiple instances of a con f i gu r ation.
1.3.3 Feedback
Feedback is an extremely powerful feature where the TANDBERG system actively returns updated
status and configuration information to the user/control application whenever changes occur. The
user/control application can specify what parts of the status and configuration hierarchies it wants to
D14172.01 page 8 of 84
Page 9

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
monitor by using XPath. The user/control application can therefore limit the amount of information it
receives f rom the target system to only those parts being of interest for the given application.
1.4 The XML Documents
1.4.1 Documents
The XML Data in the TANDBERG systems are divided into three main types of documents. The
division is based on whether the information is Read Information, Write Information or Read-Write
information:
1. Status documents (r): Documents holding all available Status Information in the system.
Supported documents:
a. status.xml
b. history.xml
2. Configuration documents (rw): Documents holding all system configurations.
Supported documents:
a. configuration.xml
3. Command documents (w): Documents def ining the supported system commands used to
initiate system processes. This is write data, i.e. the parameter values for a given command are
defined by the user and posted to the system. The posted values will not be returned when
reading the document from the system. Reading a command document from the system returns
descriptions of the supported commands with empty parameter values.
Supported documents:
a. command.xml
4. Meta Documents: Meta documents contain information that can be referenced by other
documents, e.g. value domains of configurations or command parameters. Supported Meta
Documents:
a. valuespace.xml
1.4.2 Status Documents (r)
The Status Documents are characterised by an extensive use of XML attributes. In addition to holding
information, the attributes are used to reflect the structure of the sub-elements, which are dependent
on the state of the system.
D14172.01 page 9 of 84
Page 10

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.9
The element Zone will contain different sub elements depending on the zone status:
<Status>
<Zones item="1">
<Zone item="2" status="Failed">
<Cause item="1">No gatekeeper reachable</Cause>
<Name item="1">MyNeighbor</Name>
<Gatekeeper item="1" status="Failed">
<Cause item="1">DNS Resolution Failed</Cause>
<Address >baddns.example.com</Address>
<Port item="1">1719</Port>
</Gatekeeper>
<Calls item="1"/>
<Bandwidth item="1">
<Total item="1">Unlimited</Total>
<PerCall item="1">Unlimited</PerCall>
<Used item="1">0</Used>
</Bandwidth>
</Zone>
</Zones>
</Status>
<Status>
<Zones item="1">
<Zone item="1" status="Active">
<Name item="1">MyNeighbor</Name>
<Gatekeeper item="1" status="Active">
<Address >10.0.0.10</Address>
<Port item="1">1719</Port>
</Gatekeeper>
<Calls item="1"/>
<Bandwidth item="1">
<Total item="1">Unlimited</Total>
<PerCall item="1">Unlimited</PerCall>
<Used item="1">0</Used>
</Bandwidth>
</Zone>
</Zones>
</Status>
In the above example we see that the Cause element is only present if the zone status is Failed.
1.4.3 Configuration documents (rw)
The structure of the Configuration documents is independent of system state, i.e. the structure will be
constant in time. In addition to holding the values for the various configurations, each configuration
value-elem ent includes an attribute, valueSpaceRef
configuration.
D14172.01 page 10 of 84
, referencing the value domain for the
Page 11

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.10
From the XML structure below we see that the Speed element of Ethernet[1] is configured to Auto.
The Speed element references the EthernetSpeed element in the ValueSpace document,
showing the value domain for this configuration.
<Configuration>
<Ethernet item="1">
<Speed item="1" valueSpaceRef="/ValueSpace/EthernetSpeed[@item='1']">
Auto</Speed>
</Ethernet>
</Configuration>
---
<ValueSpace>
<EthernetSpeed item="1" type="Literal">
<Value >Auto</Value>
<Value >10half</Value>
<Value >10full</Value>
<Value >100half</Value>
<Value >100full</Value>
</EthernetSpeed>
</ValueSpace>
To change configurations, the part(s) of the document containing the configurations to be updated
should be posted back to the system with the new values. Posting configuration to the system is
described in section 1.5 Introduction to TANDBERG XML API Service (TXAS).
1.4.4 Command documents (w)
Command documents contain descriptions of the supported commands for the system. A Command
consists of a Command name and a set of Command parameters. The parameter elements have
attributes to denote whether the parameter is optional or required, in addition to referencing the value
domain for the given parameter.
Command parameters do not contain any values when read from the system.
D14172.01 page 11 of 84
Page 12

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.11
The command Dial is defined to take five parameters. Only the callSrc and callDst parameters
are required; this is specified by the attribute required. The value domain for the parameters is
referenced by the attribute valueSpaceRef.
<Command>
<Dial item="1">
<callSrc item="1" required="True"
valueSpaceRef="/ValueSpace/MandatoryAlias[@item='1']"></callSrc>
<callDst item="1" required="True"
valueSpaceRef="/ValueSpace/MandatoryAlias[@item='1']"></callDst>
<Bandwidth item="1" required="False"
valueSpaceRef="/ValueSpace/BandwidthPerCall[@item='1']"></Bandwidth>
<EncryptionMode item="1" required="False"
valueSpaceRef="/ValueSpace/EncryptionModes[@item='1']"> </EncryptionMode>
<EncryptionType item="1" required="False"
valueSpaceRef="/ValueSpace/EncryptionTypesSpace[@item='1']">
</EncryptionType>
</Dial>
</Command>
To issue a command, the command structure is posted back to the system together with values for the
various parameters. Optional parameters can be omitted when posting the structure back to the
system.
Example 1.12
To place a call from Alice to Bob the user can simply post the following XML structure to the system:
<Command>
<Dial item="1">
<callSrc item="1">alice@example.com</CallSrc>
<callDst item="1">bob@example.com</CallDst>
</Dial>
</Command>
When issuing commands, the system will return an XML structure in response. The response structure
will have the same name as the command issued, but it will be suffixed with Result. All commands
will have an attribute named status, stating whether the command was accepted or not. If a
command is not accepted, the response structure will contain a Cause code. If the command is
accepted, the response structure may contain information relevant for the specific command.
D14172.01 page 12 of 84
Page 13
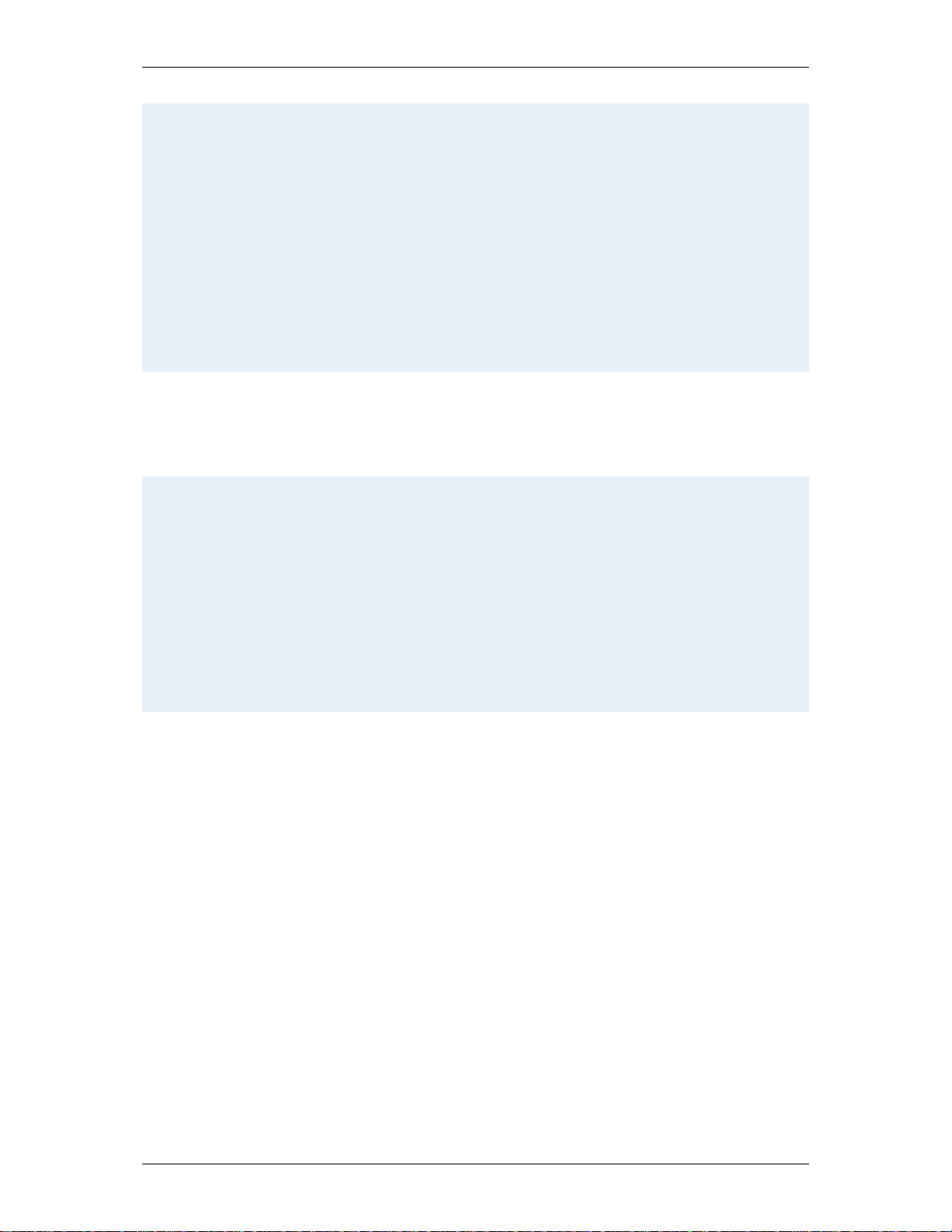
TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.13
The Dial command in the above example may return the following response structure:
<Command>
<DialResult item="1" status="OK">
<callSrc item="1">alice@example.com</callSrc>
<callDst item="1">bob@example.com</callDst>
<Bandwidth item="1">384</Bandwidth>
<CallSerialNumber item="1">1</CallSerialNumber>
<EncryptionMode item="1">Auto</EncryptionMode>
<EncryptionType item="1">Auto</EncryptionType>
</DialResult>
</Command>
The response structure for the Dial command, DialResult, states that the command was accepted
by the system. In addition to stating that the command was accepted, the Dial command returns the
element CallSerialNumber. This lets the user identify/trace the call in the Status documents
(status.xm l and hi s tory.xml).
Example 1.14
Below is an example of the Dial command not being accepted by the system because the same alias
has been specified for both the callSrc and callDst:
<Command>
<DialResult item="1" status="Error">
<Cause item="1">89</Cause >
<Description item="1"> callSrc and callDst must have different
aliases</Description>
</DialResult>
</Command>
D14172.01 page 13 of 84
Page 14

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
1.5 Introduction to TANDBERG XML API Service
(TXAS)
TXAS is a service provided by TANDBERG units for transmitting and receiving information encoded in
XML format.
The API uses HTTP(S) as the transport mechanism and connects to the normal web port (80). TXAS
can be accessed in two ways:
• bare-bone HTTP requests where URLs uniquely identify the request, and
• SOAP, where a single URI is used but the request itself is encoded with XML.
1.5.1 Bare-bone HTTP(S) access
The bare-bone HTTP(S) mode uses a unique URL to identify the specific request. The contents of the
HTTP body will be a XML document (or part of it).
Bare-bone HTTP(S) access is accomplished by passing arguments in the query string (after '?' in a
URI) in a GET request, or using the "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" content-type method of
POSTing form data.
getxml
Request URI: /getxml
Request parameter: location = XPath expression
The getxml request returns an XML document based on the location parameter passed to the request.
The elements (or complete document) matching the expression will be returned.
If an invalid XPath expression is supplied, a <Fault> element with a <XPathError> element will be
returned.
Example 1.15
Using the Unix curl command, the up time of a system can be retrieved from the Status document:
curl –k –u admin:<password> \
https://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Status/SystemUnit/Uptime
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<Status>
<SystemUnit item="1">
<Uptime item="1">604800</Uptime>
</SystemUnit>
</Status>
formputxml
Request URI: /formputxml
Request parameter: xmldoc = "an XML document of Configuration or a Command"
This is most useful in a POST (to extend character limit of 255 of GET urls). It posts a Configuration or
Command document to set some configuration values or issue a command.
D14172.01 page 14 of 84
Page 15

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Like getxml, it has the data URL form-data encoded with one single parameter. The Content-Type of
the document must be of type “application/x-www-form-urlencoded" and the body must be encoded
accordingly (e.g. first line will be xmldoc=<then the document>).
Example 1.16
Using the Unix curl command, the systems SNMP contact can be set in the Configuration document:
curl –k –u admin:<password> -d \
'<Configuration><SNMP><SystemContact>Alice</SystemContact></SNMP></Configur
ation>' https://10.0.0.1/formputxml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<Configuration>
<Success/>
</Configuration>
The new configuration value can be confirmed using the getxml request:
curl –k –u admin:<password> \
https://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Configuration/SNMP/SystemContact
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<Configuration>
<SNMP item="1">
<SystemContact item="1">Alice</SystemContact>
</SNMP>
</Configuration>
Example 1.17
Using the Unix curl command, the dial co mmand can be invoked on the target system to place a call
between Alice and Bob:
curl –k –u admin:<password> -d \
'<Command><Dial><callSrc>Alice</callSrc><callDst>Bob</callDst></Dial></Comm
and>' https://10.0.0.1/formputxml
<?xml version=“1.0"?>
<Command>
<DialResult item="1" status="OK">
<callSrc item="1">Alice</callSrc>
<callDst item="1">Bob</callDst>
<Bandwidth item="1">384</Bandwidth>
<CallSerialNumber item="1">00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
</CallSerialNumber>
<EncryptionMode item="1">Auto</EncryptionMode>
<EncryptionType item="1">Auto</EncryptionType>
</DialResult>
</Command>
D14172.01 page 15 of 84
Page 16
TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
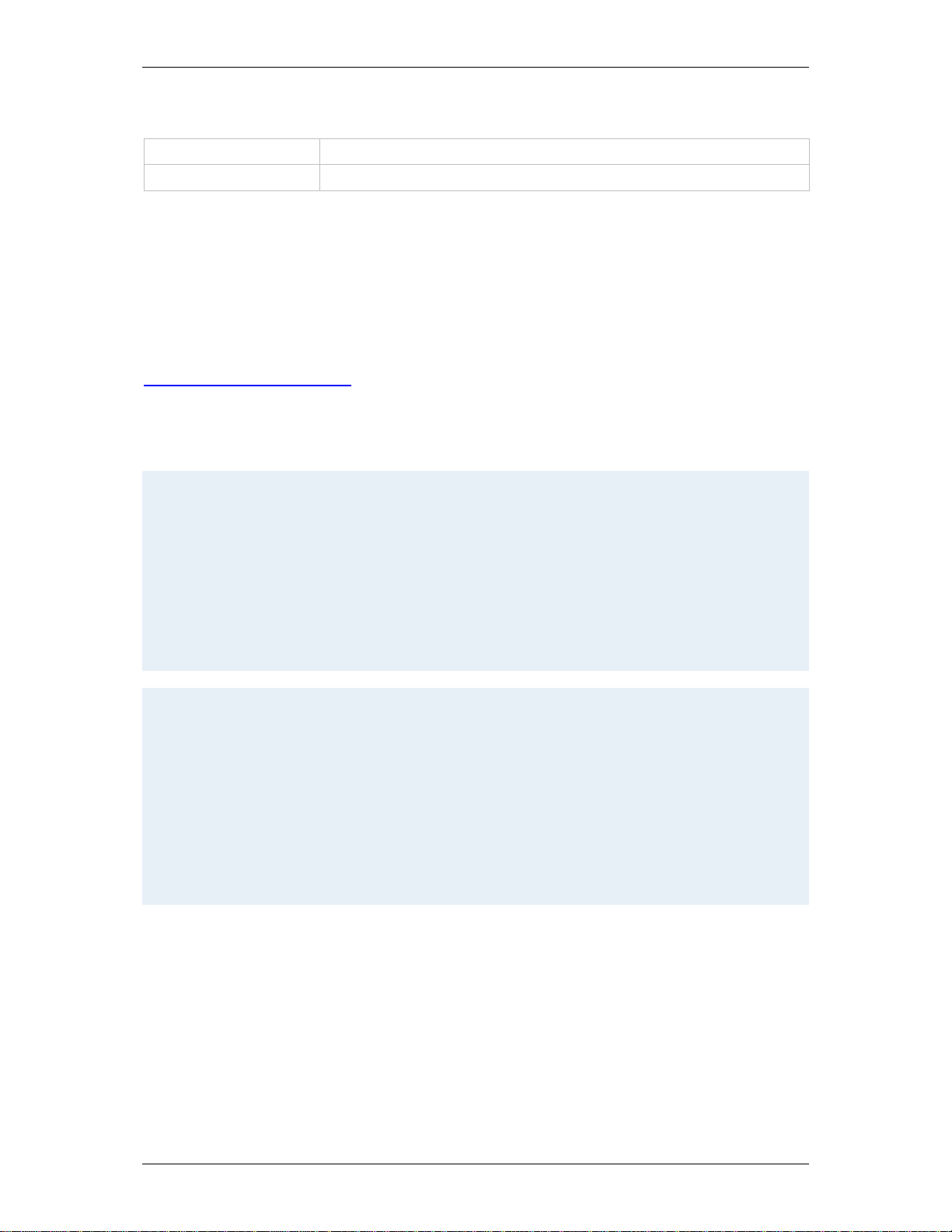
putxml
Request URI: /putxml
Request parameter: HTTP BODY as argument
Putxml is like formputxml, but uses the complete BODY as the argument (i.e. the content of the
xmldoc parameter). The Content-type should be set to either "text/xml", "application/xml" or
"text/plain".
1.5.2 SOAP
The command and configuration interface is also available over SOAP. The syntax for the interface is
specified using the Web Services Description Language (WSDL). The WSDL file is located at the root
of the system’s web server at the URL “/webservices.wsdl": e.g.
http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl
Most programming environments have built in support for developing web service clients or else third
party libraries are available. The following examples use the PHP scripting language to illustrate how
to develop a client web service for the Gatekeeper and Border Controller.
Example 1.18
The example below shows how to reboot the system using the boot command:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$client->Boot();
?>
Example 1.19
The example below shows how to use the dial command which requires parameters to be passed as
part of the operation:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$client->Dial( array('callSrc' => 'Alice', 'callDst' => 'Bob') );
?>
D14172.01 page 16 of 84
Page 17

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
The SOAP interface has a number of operations for dealing with Status and Configuration:
GetXML
Returns sta tus or configuration information for a specified XPath expression. The returned
value is an XML document.
GetConfiguration
Returns configuration information for a specified XPath expression. The returned value is a
strongly typed SOAP value as defined in the WSDL document.
GetConfigurationXML
Returns configuration information for a specified XPath expression. The returned value is an
XML document.
SetConfiguration
Sets configuration. The configuration parameter is passed as an XML document.
SetConfigurationXML
Sets configu ration. The configuration p arameter is passed as strongly typed SOAP
parameters as defined in the WSDL document.
Example 1.20
The example below shows how to use GetXML to retrieve information about the system unit from the
status document and extract the up time:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$result = $client->GetXML( array('Location' => '/Status/SystemUnit') );
$xml_result = SimpleXMLElement( $result->GetXMLResult->any );
echo $xml_result->SystemUnit->Uptime;
?>
Example 1.21
The example below shows how to use GetConfigurationXML to retrieve information about the SNMP
configuration and extract the system contact:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$result = $client->GetConfigurationXML( array('Location' => '/SNMP') );
$xml_result = new SimpleXMLElement(
$result->GetConfigurationXMLResult->any );
echo $xml_result->SNMP->SystemContact;
?>
D14172.01 page 17 of 84
Page 18

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 1.22
The example below performs the same task as Example 1.21 but uses GetConfiguration:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$result = $client->GetConfiguration( array('Location' => '/SNMP') );
echo $result->GetConfigurationResult->Configuration->SNMP->SystemContact;
?>
Example 1.23
The example below shows how to use SetConfigurationXML to modify the SNMP system contact
configuration:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$config_xml = '<Configuration xmlns="http://www.tandberg.no/XML/CUIL/1.0">
<SNMP><SystemContact>Alice</SystemContact></SNMP></Configuration>';
$params = array( 'Document' => array('any' => $config_xml) );
$client->SetConfigurationXML( $params );
?>
Example 1.24
The example below shows performs the same task as Example 1.23 but uses SetConfiguration:
<?php
$client = new SoapClient('http://10.0.0.1/webservices.wsdl',
array('login' => '<username>', 'password' => '<password>'));
$params->Document->Configuration->SNMP->SystemContact = 'Alice';
$client->SetConfiguration( $params );
?>
D14172.01 page 18 of 84
Page 19

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
1.6 Exercises
The exercises in this section are based on using a TANDBERG Gatekeeper and Microsoft Internet
Explorer. Some of the examples may however also apply to other systems and other browsers.
NOTE! Replace the IP address 10.0.0.1 in the below examples with the IP address of your system.
Exercise 1
The example in this exercise shows how to read the supported XML documents from the system using
a web browser.
Enter the following address in the browsers address field:
http://10.0.0.1/status.xml
http://10.0.0.1/history.xml
http://10.0.0.1/configuration.xml
http://10.0.0.1/command.xml
http://10.0.0.1/valuespace.xml
Exercise 2
This exercise shows how to use getxml to read the supported XML documents from the system. Enter
the following expressions in the browser’s address field.
(NOTE! The first letter in the document names is uppercase):
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Status
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=History
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Configuration
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Command
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=ValueSpace
Exercise 3
This exercis e shows how to use XPath expressions to read sub sets of the XM L documents.
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Status/SystemUnit
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Configuration/SNMP/SystemContact
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=ValueSpace/SNMPCommunityName[@item='1’]
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Configuration/IP//Address
http://10.0.0.1/getxml?location=Command/Dial
D14172.01 page 19 of 84
Page 20

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Exercise 4
The address: http://10.0.0.1/xmlput.ssi contains an editor where XML data can be edited and then
posted to the system by pressing the save button. Below are examples of XML structures to be posted
to the system:
<Configuration>
<SNMP>
<SystemContact>Administrator</SystemContact>
</SNMP>
</Configuration>
---
<Configuration>
<SNMP>
<SystemContact>Administrator</SystemContact>
</SNMP>
<NTP>
<Address>10.0.0.2</Address>
</NTP>
</Configuration>
---
<Command>
<Dial>
<callSrc>Alice</callSrc>
<callDst>Bob</callDst>
</Dial>
</Command>
---
<Command>
<Boot/>
</Command>
D14172.01 page 20 of 84
Page 21

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2 The XML-based
Advanced Command Line Interface
The XML-based Advanced Command Line Interface, XACLI, is a very flexible interface optimized for
both machine-machine interaction and man-machine interaction. It is based on the powerful
TANDBERG XML engine and offers many of the same features as the TANDBERG XML interface.
The main distinction between XACLI and the TANDBERG XML interface is the input format. As XACLI
is a command-line interface, all inputs from the user/control application have to be put on one line, as
opposed to the XML interface where a complete XML document can be posted to the system in one
operation.
A basic understanding of the information structuring in the TANDBERG XML engine is important in
order to get the most out of the XACLI interface. We therefore recommend you read the TANDBERG
XML API section of this document prior to reading this section.
2.1 XACLI
2.1.1 Accessing XACLI
XACLI can be accessed through Telnet via the LAN interface or through RS-232 by connecting a
serial cable to the serial interface connector, referred to as the Dataport.
UP to 48 Telnet sessions can be active at the same time in addition to the RS-232 connection.
2.1.2 Root commands
For each of the XML documents supported by the system, there is a corresponding XACLI root
command. The root command has the same name as the corresponding XML document, except that
the root command is prefixed by an “x":
XML document XACLI root command
status.xml xstatus
history.xml xhistory
configuration.xml xconfiguration
command.xml xcommand
The information in the TANDBERG XML engine is divided into three main types: Status Information,
Configuration Information and Command Information, ref. the documentation of the TANDBERG XML
API.
As there is a fundamental difference in these three main types of information, there is also three
different ways of working with the information using XACLI.
2.1.3 Addressing
XACLI supports XPath for addressing Status Information and Configuration Information.
In addition there is support for the proprietary TANDBERG SimplePath notation. With SimplePath
notation an element or a group of elements are addressed by supplying a space-separated list of
element names (elemName) and optional element instance numbers (item):
<elemName> [item] <elemName> [item] ...
D14172.01 page 21 of 84
Page 22
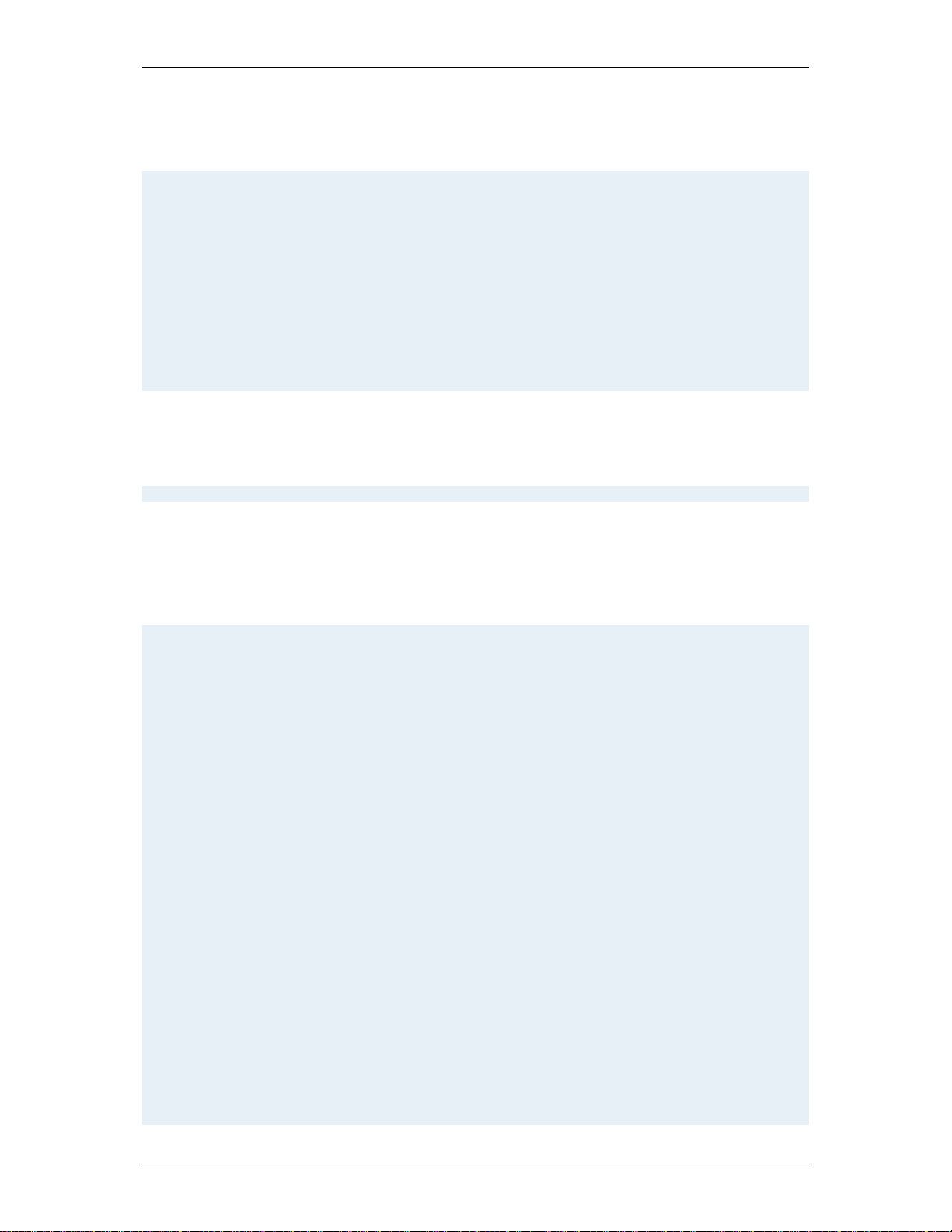
TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
If the instance number of a given element is omitted, the expression addresses all instances of this
element
Example 2.1
To address the Address sub-element of DNS Server 2:
XPath: IP/DNS/Server[2]/Address
SimplePath: IP DNS Server 2 Address
To address the Address sub-element of all DNS Server elements:
XPath: IP/DNS/Server/Address
SimplePath: IP DNS Server Address
2.1.4 Exposure options
By adding an exposure option after the address (XPath or SimplePath) expression, the system can be
instructed to return only parts of the information within an element structure.
<root command> <address expression> <exposure option>
Supported exposure options:
• “-“ hides all value elements
• “--" hides all sub-elements
Example 2.2
Request for Zone 1 element with no exposure option:
xstatus zones zone 1
*s Zones:
Zone 1 (status=Active):
Name: "MyNeighbor"
Gatekeeper (status=Active):
Address: "10.0.0.10"
Port: 1719
Calls: /
Bandwidth:
Total: "Unlimited"
PerCall: "Unlimited"
Used: 0
*s/end
Request for Zone1 element with exposure option “-“:
xstatus zones zone 1 -
*s Zones:
Zone 1 (status=Active):
Gatekeeper (status=Active):
Calls: /
Bandwidth:
*s/end
D14172.01 page 22 of 84
Page 23

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Request for Zone1 element with exposure option “--“:
xstatus zones zone 1 --
*s Zones:
Zone 1 (status=Active):
*s/end
2.1.5 Misc
• The XACLI interface is not case sensitive.
• XACLI allows using only partial names.
D14172.01 page 23 of 84
Page 24

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.2 The Status-type root commands –
xstatus / xhistory
The information accessible through these commands is the exact same information that is available in
the corresponding XML documents.
To get an overview of accessible top-level elements within a status-type root command, type ? or
help after the status-type root command.
Example 2.3
xstatus ?
- Status -
Calls NTP
Ethernet Options
ExternalManager Pipes
Feedback [1..3] Registrations
Gatekeeper ResourceUsage
IP SubZones
LDAP SystemUnit
Links Zones
OK
xhistory ?
- History -
Calls Registrations
OK
To access status-type data, simply type the status-type root command (xstatus or xhistory) and
then an XPath address expression or a TANDBERG SimplePath expression:
<status-type root command> <address expression>
Example 2.4
xstatus registrations registration 1 aliases alias 1
*s Registrations:
Registration 1:
Aliases:
Alias 1 (type=H323Id, origin=Endpoint): "alice@example.com"
*s/end
OK
D14172.01 page 24 of 84
Page 25

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.2.1 Format
Status information is presented by a mark-up notation, similar to XML. The main differences are:
• all braces ar e removed in the XACLI format
• XACLI does not use end-tags, except for a tag to mark end of the top element
• XACLI does not use indent spaces to present the data structure
• XACLI hides the instance number (item number in XML) of an element if only one instance of a
given element exists
• A status top level element starts with “*s"
Example 2.5 shows XML formatting and XACLI formatting for the same status element, NTP.
Example 2.5
XML:
<Status>
<NTP item="1" status="Active">
<Address item="1">10.0.0.2</Address>
<Port item="1">123</Port>
<LastUpdate item="1">2008-01-01 12:00:00</LastUpdate>
<LastCorrection item="1">1</LastCorrection>
</NTP>
</Status>
XACLI:
*s NTP (status=Active):
Address: "10.0.0.2"
Port: 123
LastUpdate: "2008-01-01 12:00:00"
LastCorrection: 1
*s/end
NOTE! To write a parser for the XACLI format, the parser must keep track of the levels by counting
white spaces. The indent is increased by two whitespaces for each level.
D14172.01 page 25 of 84
Page 26

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.3 The Configuration-type root commands -
xconfiguration
The information accessible through these commands is exactly the same information that is available
in the corresponding XML documents.
To get an overview of accessible top-level configuration elements, type ? or help after the
configuration-type root command:
<configuration-type root command> ?
Example 2.6
?
- User Configurations -
Authentication LDAP SNMP
Ethernet Links SSH
ExternalManager Log SubZones
Gatekeeper NTP SystemUnit
HTTP Option [1..64] Telnet
HTTPS Pipes TimeZone
IP Services Traversal
IPProtocol Session Zones
OK
2.3.1 Configuration help
To get help on configurati ons, type the c onfiguration-type root command, follo wed by an addres s
expression, followed by ? or help. The possible values for the elements matching the address
expression will be returned.
<configuration-type root command> <address expr> ?/help
Example 2.7
User wants to configure IP:
ip ?
*h IPProtocol: <Both/IPv4/IPv6>
*h IP Address: <IPAddr>
*h IP SubnetMask: <IPAddr>
*h IP Gateway: <IPAddr>
*h IP V6 Address: <S: 0, 39>
*h IP V6 Gateway: <S: 0, 39>
*h IP DNS Server [1..5] Address: <S: 0, 39>
*h IP DNS Domain Name: <S: 0, 128>
D14172.01 page 26 of 84
Page 27

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
NOTE! Only typing ? actually addresses all configuration ele ments within t he root command. One
would therefore expect that help on all configurations would be returned. But as described above, this
is a special case and only listings of the top level elements are returned. To get help on all
configurations supported by the system, type:
// ?
or
??
2.3.2 Configuration read
To read configurations, type the configuration-type root command followed by an address expression:
<configuration-type root command> <address expr>
Example 2.8
User wants to read IP configurations:
ip
*c IPProtocol: IPv4
*c IP Address: "10.0.0.1"
*c IP SubnetMask: "255.255.255.0"
*c IP Gateway: "10.0.0.254"
*c IP V6 Address: ""
*c IP V6 Gateway: ""
*c IP DNS Server 1 Address: "10.0.0.3"
*c IP DNS Server 2 Address: "10.0.0.4"
*c IP DNS Server 3 Address: ""
*c IP DNS Server 4 Address: ""
*c IP DNS Server 5 Address: ""
*c IP DNS Domain Name: "example.com"
OK
2.3.3 Configuration set (write)
To set confi gurations, the address expression follo wing the configuration-type root command must end
with a colon. The value to be set must be added after the colon:
<configuration-type root command> <address expr>: value
D14172.01 page 27 of 84
Page 28

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Example 2.9
User wants to set IP address:
ip address: "10.0.0.1"
or
ip/address: "10.0.0.1"
D14172.01 page 28 of 84
Page 29

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.4 The Command-type root commands -
xcommand
To get an overview of the supported commands within a command-type root command, type ? or
help after the command-type root command.
<command-type root command> ?
Example 2.10
xcommand ?
- User Commands -
AdHocConference DenyListDelete PipeAdd
AllowListAdd Dial PipeDelete
AllowListDelete DisconnectCall RemoveRegistration
Boot FeedbackDeregister SubZoneAdd
CallTransfer FeedbackRegister SubZoneDelete
CheckBandwidth FindRegistration TransformAdd
CredentialAdd LinkAdd TransformDelete
CredentialDelete LinkDelete TraversalZoneAdd
DefaultLinksAdd Locate TraversalZoneDelete
DefaultValuesSet OptionKeyAdd ZoneAdd
DenyListAdd OptionKeyDelete ZoneDelete
OK
To list usage for all commands with parameters, type a double question mark after the command-type
root command.
<command root command> ??
Example 2.11
xcommand dial ??
*h xCommand AdHocConference
Registration(r): <1..3750>
*h xCommand AllowListAdd
Pattern(r): <S: 1, 60>
*h xCommand AllowListDelete
AllowListId(r): <1..2500>
*h xCommand Boot
*h xCommand CallTransfer
Call(r): <1..900>
Leg(r): <1..2>
Alias(r): <S: 1, 60>
…
D14172.01 page 29 of 84
Page 30

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.4.1 Command help
To get help on a specific command, type the command-type root command, followed by a command
name, followed by ? or help:
<command-type root command> <command name> ?
Example 2.12
xcommand Dial ?
xcomm dial ?
*h xCommand Dial
callSrc(r): <S: 1, 60>
callDst(r): <S: 1, 60>
Bandwidth: <1..100000000>
EncryptionMode: <Auto/On/Off>
EncryptionType: <DES/AES-128/Auto>
OK
NOTE! Required parameters are identified by an “(r)" behind the parameter name.
2.4.2 Issuing a command
A command must start with a command-type root command, followed by a command name, followed
by a set of parameters. Parameters values can either be specified by a mark-up notation or by placing
the parameter values in the sequence specified by the help text – or a combination of these methods.
Markup notation
<command-type root command> <command> <parameter:value>
<parameter:value>...
When using this notation, the sequence in which the parameters are entered is not essential:
Example 2.13
xcommand dial Bandwidth:384 callDst:bob callSrc:alice
Abbreviations can be used for the parameter names as long as the parameter names are unique
within the command:
Example 2.14
xcommand dial B:384 callD:bob callS:alice
D14172.01 page 30 of 84
Page 31

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Sequence notation
<command-type root command> <command> <value> <value>...
When using this notation, the parameter values must be entered in the sequence as stated in the help
text:
Example 2.16
xcommand dial alice bob 384
Combination
A combination of mark-up notation and sequence are also supported. The marked parameters will be
assigned the user -entered values first, and then the system will assign the sequence entered
parameters for the parameters not yet having been assigned a value:
Example 2.17
xcommand dial alice B:384 bob
Command response
When issuing a command, the system will return a set of return values (refer to the section
TANDBERG XML API). The response will be on the same format as the standard XACLI Status
format.
Example 2.18
xcommand dial alice bob
*r Result (status=OK):
callSrc: "alice"
callDst: "bob"
Bandwidth: 384
CallSerialNumber: 1
EncryptionMode: Auto
EncryptionType: Auto
*r/end
OK
NOTE! When using XACLI as a machine-machine interface it is recommended to use markup notation
and always supply complete tag names.
D14172.01 page 31 of 84
Page 32
TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.5 XML Output - xgetxml
As an alternative to the standard XACLI output format, XML format is supported through the root
command xgetxml. xgetxml takes an XPath expression as parameter and the elements (or complete
document) matching the expression will be returned.
Example 2.19
xgetxml status/ntp
<Status>
<NTP item="1" status="Active">
<Address item="1">10.0.0.2</Address>
<Port item="1">123</Port>
<LastUpdate item="1">2008-01-01 12:00:00</LastUpdate>
<LastCorrection item="1">1</LastCorrection>
</NTP>
</Status>
OK
D14172.01 page 32 of 84
Page 33

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.6 Special Commands
In addition to the root commands described above, XACLI support a set of root commands that only
applies to the Telnet session or RS232 session from where they are issued. This lets the user/control
application individually configure the session(s) in use.
Supported special commands:
• xfeedback (not supported on all platforms)
• xpreferences
2.6.1 xfeedback
The special command xfeedback lets the user register user-defined XPath expressions (with possible
exposure options) to monitor changes in the XML/XACLI data. Whenever there is a change in one or
more elements addressed by a registered XPath expression, the part of the element structure
containing these changes will be returned. The system supports a total of 20 registered expressions,
with a total of 15 expressions for one session.
xfeedback ?
usage: xfeedback register <XPathExpression>
or: xfeedback deregister <index>
or: xfeedback list
or: xfeedback paths
-
(note: deregistration with index=0 will deregister all registered
expressions)
OK
Example 2.20
User wants to monitor changes in the aliases registered to the system:
xfeedback register status/Registrations/Registration/Aliases/Alias
To view registered expressions:
xfeedback list
*xf 1 status/Registrations/Registration/Aliases/Alias
OK
When the endpoint for Alice registers:
*s Registrations:
Registration 1:
Aliases:
Alias 1 (type=H323Id, origin=Endpoint): "alice@example.com"
*s/end
*s Registrations:
Registration 1:
Aliases:
D14172.01 page 33 of 84
Page 34

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Alias 2 (type=E164, origin=Endpoint): "441184960001"
*s/end
Example 2.21
User wants to monitor for when a zone fails:
xfeedback register status/zones/zone[@status="Failed"]
OK
When a problem with a zone occurs:
*s Zones:
Zone 1 (status=Failed):
Cause: No gatekeeper reachable
Name: "MyNeighbor"
Gatekeeper (status=Failed):
Cause: No response from gatekeeper
Address: "10.0.0.10"
Port: 1719
Calls: /
Bandwidth:
Total: "Unlimited"
PerCall: "Unlimited"
Used: 0
*s/end
D14172.01 page 34 of 84
Page 35

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
2.6.2 xpreferences
The special command xpreferences lets the user/control application individually configure the
Telnet/RS-232 session in use.
xpreferences ?
usage: xpreferences xpathwrite <on/off>
or: xpreferences detaillevel <1..2>
or: xpreferences xmlconfigfeedback <on/off>
or: xpreferences xmlstatusfeedback <on/off>
or: xpreferences xmlcommandresult <on/off>
OK
xpreferences xpathwrite <on/off>
This command disables/enables the XPath engine when issuing configurations. When the XPath
engine is disabled, the user/control application must supply the complete path to the configurations to
be set (no “double slashes" allowed). This will improve the perf ormance of th e system when issuing
many consecutive configurations.
NOTE! It is always recommended to supply the complete path for configurations to be set when
issuing commands from an external control application.
xpreferences detaillevel <1..2>
This command has no effect on the Gatekeeper and Border Controller.
xpreferences xmlconfigfeedback <on/off>
If xmlconfigfeedback is set to on, feedback on configurations will be returned in XML-format instead of
the standard XACLI configuration format.
Example 2.25
XACLI-format:
*c SNMP SystemContact: Administrator
XML-format:
<Configuration>
<SNMP item="1">
<SystemContact item="1">Administrator</SystemContact>
</SNMP>
</Configuration>
D14172.01 page 35 of 84
Page 36

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
xpreferences xmlstatusfeedback <on/off>
If xmlstatusfeedback is set to on, all status feedback will be returned in XML-format instead of the
standard XACLI status format.
Example 2.26
XACLI-format:
*s NTP (status=Active):
Address: "10.0.0.2"
Port: 123
LastUpdate: "2008-01-01 12:00:00"
LastCorrection: 1
*s/end
XML-format:
<Status>
<NTP item="1" status="Active">
<Address item="1">10.0.0.2</Address>
<Port item="1">123</Port>
<LastUpdate item="1">2008-01-01 12:00:00</LastUpdate>
<LastCorrection item="1">1</LastCorrection>
</NTP>
</Status>
xpreferences xmlcommandresult <on/off>
If xmlcommandresult is set to on, response for commands will be returned in XML-format.
Example 2.27
XACLI-format:
xcommand dial alice bob
*r Result (status=OK):
callSrc: "alice"
callDst: "bob"
Bandwidth: 384
CallSerialNumber: 1
EncryptionMode: Auto
EncryptionType: Auto
*r/end
XML-format:
xcommand dial alice bob
<Command>
<DialResult item="1" status="OK">
<callSrc item="1">alice@example.com</callSrc>
<callDst item="1">bob@example.com</callDst>
<Bandwidth item="1">384</Bandwidth>
<CallSerialNumber item="1">1</CallSerialNumber>
<EncryptionMode item="1">Auto</EncryptionMode>
<EncryptionType item="1">Auto</EncryptionType>
</DialResult>
</Command>
D14172.01 page 36 of 84
Page 37

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
3 API - Configurations
This section gives an overview of the Configuration Information available in the Configuration XML
document (configuration.xml).
All examples are presented using the standard XACLI format.
3.1 configuration.xml – xconfiguration
SystemUnit Name: <S: 0, 50>
Defines the name of the system. Choose a name that uniquely identifies the system.
SystemUnit Password: <S: 0, 16>
Defines the password of the system. The password is used to login with Telnet, HTTP(S),
SSH, SCP, and on the serial port.
Option [1..64] Key: <S: 0, 90>
Specifies the option key of the option you wish to add. Option keys are added to the system
in order to add extra functionality, such as increasing the system's capacity. Contact your
TANDBERG representativ e for further information.
Ethernet Speed: <Auto/10half/10full/100half/100full>
Specifies the setting of the Ethernet link. Use Auto to automatically configure the speed.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
IPProtocol: <Both/IPv4/IPv6>
Selects whether the system is operating in IPv4, IPv6 or dual stack mode.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
IP Address: <IPAddr>
Specifies the IPv4 address of the system.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
IP SubnetMask: <IPAddr>
Specifies the IPv4 subnet mask of the system.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
IP Gateway: <IPAddr>
Specifies the IPv4 gateway of the system.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
IP V6 Address: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies the IPv6 address of the system.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
IP V6 Gateway: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies the IPv6 gateway of the system.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
D14172.01 page 37 of 84
Page 38

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
IP DNS Server [1..5] Address: <S: 0, 39>
Sets the IP Address of up to 5 DNS servers to be queried when resolving domain names.
IP DNS Domain Name: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies the name to be appended to the host name before a query to the DNS server is
executed. Used only when attempting to resolve a domain name which is not fully qualified.
NTP Address: <S: 0, 128>
Sets the IP Address or FQDN of the NTP server to be used when synchronizing system
time.
TimeZone Name: <S: 0, 64>
Sets the local time zone of the system. Time zone names follow the POSIX naming
convention e.g. Europe/London or America/New_York.
LDAP Server Address: <S: 0, 128>
Sets the IP Address or FQDN of the LDAP server to be used when making LDAP queries.
LDAP Server Port: <1..65534>
Sets the IP port of the LDAP server to be used when making LDAP queries.
LDAP UserDN: <S: 0, 255>
Sets the user distinguished name to be used when binding to the LDAP server.
LDAP Password: <S: 0, 25>
Sets the password to be used when binding to the LDAP server.
LDAP Encryption: <Off/TLS>
Sets the encryption to be used for the connection to the LDAP server. Off: no encryption is
used. TLS: TLS encryption is used.
SNMP Mode: <On/Off>
Enables or disables SNMP support.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
SNMP CommunityName: <S: 0, 16>
Specifies the system's SNMP community name.
SNMP SystemContact: <S: 0, 70>
Specifies the name of the person who can be contacted regarding issues with the system.
SNMP SystemLocation: <S: 0, 70>
Specifies the physical location of the system.
Session TimeOut: <0..65534>
Sets the number of minutes that an administration session (HTTPS, Telnet or SSH) may be
inactive before the session is timed out. A value of 0 turns session time outs off.
Telnet Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether the system can be accessed via telnet.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
D14172.01 page 38 of 84
Page 39

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
SSH Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether the system can be accessed via SSH and SCP.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
HTTP Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether the system can be accessed via the web server over HTTP.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
HTTPS Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether the system can be accessed via the web server over HTTPS.
Note: You must restart the system for any changes to take effect.
ExternalManager Address: <S: 0, 128>
Sets the IP Address or FQDN of the External Manager.
ExternalManager Path: <S: 0, 255>
Sets the URL of the External Manager.
Log Level: <1..3>
Controls the granularity of event logging. 1 is the least verbose, 3 the most.
Log Server Address: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the server to which the log will be written.
Gatekeeper CallRouted: <On/Off>
Specifies whether the signaling of a non-traversal call will be routed via the system. On: Call
signaling is routed via the system. Off: Call signaling goes directly between endpoints.
Note: Applies only to non-traversal calls; the signaling of traversal calls will always be routed
via the system regardless of this setting.
Gatekeeper LocalPrefix: <S: 0, 60>
Sets the local zone prefix of the system.
Gatekeeper TimeToLive: <60..65534>
Specifies the interval (in seconds) at which an endpoint must re-register with the system in
order to confirm that it is still functioning.
Gatekeeper CallTimeToLive: <60..65534>
Specifies the interval (in seconds) at which the system polls the endpoints in a call to verify
that they are st i ll in th e c all .
Gatekeeper AutoDiscovery: <On/Off>
Determines whether or not the system responds to gatekeeper discovery requests from
endpoints.
Gatekeeper CallsToUnknownIPAddresses: <Off/Direct/Indirect>
Determines the way in which the system will attempt to call systems which are not registered
with it or one of its neighbor s. Direct: Allows an endpoint to make a call to an unknown IP
Address without the system querying any neighbors. Indirect: Upon receiving a call to an
unknown IP Address, the system will query its neighbors for the remote address and if
permitted will route the call through the neighbor. Off: Endpoints registered directly to the
system may only call an IP Address of a system also registered directly to that system.
D14172.01 page 39 of 84
Page 40

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Gatekeeper ForwardLocationRequests: <On/Off>
Determines the behavior of the system when it receives from another Gatekeeper a location
request (LRQ) that it cannot resolve locally. On: the request will be forwarded to neighbor
Gatekeepers. Off: the request will not be forwarded.
Gatekeeper DNSResolution Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether or not DNS lookup of H.323 URIs is enabled on this system.
Gatekeeper ENUM Mode: <On/Off>
Specifies whether the system will attempt ENUM resolution for E.164 numbers.
Gatekeeper ENUM DNSSuffix [1..5]: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies a DNS domain to use when attempting ENUM resolution.
Gatekeeper LocalDomain DomainName: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies the DNS name of the domain that the system is responsible for. Used when
searching for matching endpoint registrations.
Gatekeeper Registration RestrictionPolicy: <None/AllowList/DenyList>
Specifies the policy to be used when determining which endpoints may register with the
system.
Gatekeeper Registration AllowList [1..2500] Pattern: <S: 0, 60>
Specifies an entry to be added to the Allow List. If one of an endpoint's aliases matches one
of the patterns in the Allow List, the registration will be permitted.
Gatekeeper Registration DenyList [1..2500] Pattern: <S: 0, 60>
Specifies an entry to be added to the Deny List. If one of an endpoint's aliases matches one
of the patterns in the Deny List, the registration will not be permitted.
Gatekeeper Registration ConflictMode: <Overwrite/Reject>
Determines how the system will behave if an endpoint attempts to register an alias currently
registered from another IP Address. Reject: denies the registration. Overwrite: deletes the
original registration and replaces it with the new registration.
Gatekeeper Alternates Monitor: <On/Off>
Controls whether or not alternate gatekeepers are periodically interrogated to ensure that
they are still functioning. In order to prevent delays during call setup, non-functional
alternates will not receive Location Requests.
Gatekeeper Alternates Alternate [1..5] Address: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies the IP Address of an alternate system. Up to 5 Alternates may be configured.
When the system receives a Location Request, all Alternates will also be queried.
Gatekeeper Alternates Alternate [1..5] Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the IP Port of an alternate system.
Gatekeeper Policy Mode: <On/Off>
Enables and disables use of Administr ator Policy.
D14172.01 page 40 of 84
Page 41

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Gatekeeper Downspeed PerCall Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether or not the system will attempt to downspeed a call if there is insufficient
per-call bandwidth available to fulfill the request. On: the system will attempt to place the call
at a lower bandwidth. Off: the call will be rejected.
Gatekeeper Downspeed Total Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether or not the system will attempt to downspeed a call if there is insufficient
total bandwidth available to fulfill the request. On: the system will attempt to place the call at
a lower bandwidth. Off: the call will be rejected.
Gatekeeper Unregistered Caller Mode: <On/Off>
Specifies whether the system will accept incoming calls from endpoints that are not
registered to any other system.
Gatekeeper Unregistered Caller Fallback: <S: 0, 60>
Specifies the alias to which incoming calls are placed for calls where the IP Address or
domain name of the system has been given but no callee alias has been specified.
Gatekeeper Transform [1..200] Pattern: <S: 0, 60>
Specifies the pattern against which the alias is compared.
Gatekeeper Transform [1..200] Priority: <0..65534>
Assigns a priority to the specified t r ansform. Transforms are applied in order of priority, and
the priority must be unique for each transform.
Gatekeeper Transform [1..200] Type: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
Determines the way in which t he string must match the alias. Prefix: the stri ng must appear
at the beginning of the alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the
string will be treated as a regular expression.
Gatekeeper Transform [1..200] Behavior: <Strip/Replace>
Determines how the matched part of the alias will be modified. Strip: the matching prefix or
suffix will removed from the alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted
with the text in the Replace string.
Gatekeeper Transform [1..200] Replace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if pattern behavior is set to Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Traversal RetryInterval: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the interval in seconds with which a
failed attempt to establish a connection to the traversal server should be retried.
Traversal AllowMediaDirect: <On/Off>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Determines whether endpoints must route their
media through the Gatekeeper or may, if capable, send media directly to the Border
Controller.
Traversal UDPProbe RetryInterval: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Sets the interval with which a failed
attempt to establish a UDP channel should be repeated.
D14172.01 page 41 of 84
Page 42

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Traversal UDPProbe RetryCount: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the syste m is a Border Controller.) Specifies the nu mber of attempts at reestablishing a failed UDP channel.
Traversal UDPProbe KeepAliveInterval: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the syste m is a Border Controller.) Specifies the interval with which a UDP
channel should be refreshed.
Traversal TCPProbe RetryInterval: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Specifies the interval with which a failed
attempt to establish a TCP channel should be repeated.
Traversal TCPProbe RetryCount: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the syste m is a Border Controller.) Specifies the nu mber of attempts at reestablishing a failed TCP channel.
Traversal TCPProbe KeepAliveInterval: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Specifies the interval with which a TCP
channel should be refreshed.
Traversal Media RTP Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Specifies the UDP port to which media
should be sent.
Traversal Media RTCP Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Specifies the UDP port to which media
control information should be sent.
Traversal AssentEnabled: <On/Off>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Determines whether or not the Border
Controller will allow firewall traversal using TANDBERG's proprietary Assent protocol.
Traversal H46018Enabled: <On/Off>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Determines whether or not the Border
Controller will allow firewall traversal using the ITU H.460.18/19 protocols.
Traversal Preference: <Assent/H46018>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) Determines which of the two protocols to
use when given a choice.
Traversal H46019Demultiplexing: <On/Off>
(Applies only if the system is a Border Controller.) H.460.19 optionally allows all media to be
sent to the same ports on the Border Controller and demultiplexed there.
Authentication Mode: <On/Off>
Determines whether or not to enforce authentication for registrations.
Authentication UserName: <S: 0, 25>
Specifies the user name to be used by the system when authenticating with another system.
Authentication Password: <S: 0, 25>
Specifies the password to be used by the system when authenticating with another system.
D14172.01 page 42 of 84
Page 43

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Authentication Database: <LocalDatabase/LDAPDatabase>
Selects between a local database and a remote LDAP repository for the storage of password
information for authentication.
Authentication LDAP BaseDN: <S: 0, 255>
Specifies the Distinguished Name to use when connecting to an LDAP server.
Authentication LDAP AliasOrigin: <LDAP/Endpoint/Combined>
Determines which aliases (i.e. from the LDAP database or the endpoint) should be used to
register the endpoint. Combined: the endpoint will be registered both with the aliases which it
has presented and with those configured in the LDAP repository.
Authentication Credential [1..2500] Name: <S: 0, 25>
Defines the name for this entry in the local authentication database.
Authentication Credential [1..2500] Password: <S: 0, 25>
Defines the password for this entry in the local authentication database.
Zones DefaultZone HopCount: <1..255>
Specifies the hop count to be used when sending an alias search request to a system that is
not configured as a neighbor zone or traversal zone.
Zones Zone [1..100] Name: <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this zone.
Zones Zone [1..100] Gatekeeper [1..6] Address: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
Zones Zone [1..100] Gatekeeper [1..6] Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
Zones Zone [1..100] HopCount: <1..255>
Specifies the hop count to be used when sending an alias search request to this zone.
Note: If the search request was received from another zone and already has a hop count
assigned, the lower of the two values will be used.
Zones Zone [1..100] Monitor: <On/Off>
If zone monitoring is enabled, an LRQ will be periodically sent to the zone gatekeeper. If it
fails to respond, that gatekeeper will be marked as inactive.
Zones Zone [1..100] Match [1..5] Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always be
queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Zones Zone [1..100] Match [1..5] Pattern String: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which the
alias is compared.
D14172.01 page 43 of 84
Page 44

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Zones Zone [1..100] Match [1..5] Pattern Type: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the string
must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the alias. Suffix: the
string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be treated as a regular
expression.
Zones Zone [1..100] Match [1..5] Pattern Behavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched part of
the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the alias will be
unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the alias. Replace: the
matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the Replace string.
Zones Zone [1..100] Match [1..5] Pattern Replace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Name: <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Mode: <Assent/H46018>
Determines which H.323 traversal protocol to use, either Assent or H.460.18.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] AccountName: <S: 0, 50>
Specifies the account name to be used when connecting to an Assent Traversal Zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Address: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server to
connect to.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] HopCount: <1..255>
Specifies the hop count to be used when sending an alias search request to this zone.
Note: If the search request was received from another zone and already has a hop count
assigned, the lower of the two values will be used.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Match [1..5] Mode:
<AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always be
queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Match [1..5] Pattern String: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which the
alias is compared.
D14172.01 page 44 of 84
Page 45

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Match [1..5] Pattern Type:
<Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the string
must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the alias. Suffix: the
string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be treated as a regular
expression.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Match [1..5] Pattern Behavior:
<Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched part of
the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the alias will be
unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the alias. Replace: the
matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the Replace string.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Match [1..5] Pattern Replace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth Total Mode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether the Default Subzone has a limit on the total bandwidth being used by its
endpoints at any one time. None corresponds to no bandwidth available.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth Total Limit: <1..100000000>
Sets the total bandwidth limit (in kbps) of the Default Subzone (applies only if Mode is set to
Limited).
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth PerCall Inter Mode:
<None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth for any one call to or from an endpoint
in the Default Subzone.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth PerCall Inter Limit: <1..100000000>
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) for any one call to or from an endpoint in the Default
Subzone (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth PerCall Intra Mode:
<None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth for any one call between two endpoints
within the Default Subzone.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth PerCall Intra Limit: <1..100000000>
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) for any one call between two endpoints within the
Default Subzone (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth Total Mode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether or not there is a limit to the total bandwidth of all traversal calls being
handled by the system.
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth Total Limit: <1..100000000>
Specifies the total bandwidth (in kbps) allowed for all traversal calls being handled by the
system (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
D14172.01 page 45 of 84
Page 46

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth PerCall Mode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth of any one traversal call being handled
by the system.
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth PerCall Limit: <1..100000000>
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) applied to any one traversal call being handled by the
system (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Name: <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this subzone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth Total Mode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether this subzone has a limit on the total bandwidth of calls being used by its
endpoints at any one time.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth Total Limit: <1..100000000>
Sets the total bandwidth limit (in kbps) of this subzone (applies only if Mode is set to
Limited).
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall Inter Mode:
<None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth for any one call to or from an endpoint
in this subzone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall Inter Limit: <1..100000000>
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) on any one call to or from an endpoint in this subzone
(applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall Intra Mode:
<None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth for any one call between two endpoints
within this subzone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall Intra Limit: <1..100000000>
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) for any one call between two endpoints within this
subzone (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Subnet [1..5] IP Address: <S: 0, 128>
Specifies an IP Address used (in conjunction with the IP Prefix Length) to identify a subnet to
be assigned to this subzone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Subnet [1..5] IP PrefixLength: <0..128>
Specifies the number of bits of the Subnet IP Address which must match for an IP Address
to belong in this subzone.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Name: <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this pipe.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth Total Mode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether or not this pipe is enforcing total bandwidth restrictions. None: no
bandwidth available.
D14172.01 page 46 of 84
Page 47

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth Total Limit: <1..100000000>
If this pipe has limited bandwidth, sets the maximum bandwidth (in kbps) available at any
one time on the pipe.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall Mode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether or not this pipe is limiting the bandwidth of individual calls. None: no
bandwidth available.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall Limit: <1..100000000>
If this pipe has limited per-call bandwidth, sets the maximum amount of bandwidth (in kbps)
available for any one call.
Links Link [1..100] Name: <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this link.
Links Link [1..100] Node1 Name: <S: 0, 50>
Specifies the first zone or subzone to which this link will be applied.
Links Link [1..100] Node2 Name: <S: 0, 50>
Specifies the second zone or subzone to which this link will be applied.
Links Link [1..100] Pipe1 Name: <S: 0, 50>
Specifies the first pipe to be associated with this link.
Links Link [1..100] Pipe2 Name: <S: 0, 50>
Specifies the second pipe to be associated with this link.
Services CallTransfer Mode: <On/Off>
Controls whether or not third party call transfer is enabled.
Note: The Gatekeeper must be operating in call routed mode in order for calls to be
transfered.
Services AdHocConferencing Mode: <On/Off>
Controls whether or not Multiway is enabled.
Services AdHocConferencing ID: <S: 3, 3>
Specifies the unique 3-digit ID for this system. This ID is used by the MCU to distinguish
between conference requests from different gatekeepers.
Services AdHocConferencing Prefix: <S: 0, 30>
Specifies the prefix to be used for unencrypted conference requests.
Services AdHocConferencing Encryption Prefix: <S: 0, 30>
Specifies the prefix to be used for encrypted conference requests.
D14172.01 page 47 of 84
Page 48

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
4 API - Commands
This section gives an overview of the supported system Commands.
All examples are presented using the standard XACLI format.
4.1 command.xml – xcommand
AdHocConference
Transfers all calls for the specified endpoint to the configured ad hoc conference.
Registration(r): <1..3750>
The index of the registration to be transferred.
AllowListAdd
Adds an entry to the Allow List.
Pattern(r): <S: 1, 60>
Specifies an entry to be added to the Allow List. If one of an endpoint's aliases
matches one of the patterns in the Allow List, the registration will be permitted.
AllowListDelete
Deletes an entry from the Allow List.
AllowListId(r): <1..2500>
The index of the entry to be deleted.
Boot
Reboots the system.
This command has no parameters.
CallTransfer
Transfers t he specified call from one call party to the en dpoint specified by the supplied
alias.
Call(r): <1..900>
The index of the call to be transferred.
Leg(r): <1..2>
The index of the call leg to be transferred.
Alias(r): <S: 1, 60>
The alias for the call to be transferred to.
CheckBandwidth
A diagnostic tool that returns the status and route (as a list of nodes and links) that a call of
the specified type and bandwidth would take between two nodes. Note that this command
does not change any existing system configuration.
Node1(r): <S: 1, 50>
The subzone or zone from which the call originates.
Node2(r): <S: 1, 50>
The subzone or zone at which the call terminates.
D14172.01 page 48 of 84
Page 49

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Bandwidth( r): <1..10000 0 0 00 >
The requested bandwidth of the call (in kbps).
CallType(r): <Traversal/Routed/Direct>
Whether the call type is Traversal, Routed or Direct.
CredentialAdd
Adds an entry to the local authentication database.
CredentialN a me ( r) : <S: 1, 25>
Defines the name for this entry in the local authentication database.
CredentialPassword(r): <S: 1, 25>
Defines the password for this entry in the local authentication database.
CredentialDelete
Deletes an entry from the local authentication database.
CredentialId(r): <1..2500>
The index of the credential to be deleted.
DefaultLinksAdd
Restores links between the Default Subzone, Traveral Subzone and the Default Zone.
DefaultValuesSet
Resets system parameters to default values. Level 1 will reset most parameters. There are
currently no level 2 parameters, so setting that level has the same effect as setting level 1.
Level 3 resets all level 1 and 2 parameters as well as additional parameters. See the
Administrator Guide for full details.
Level(r): <1..3>
The level of system parameters to be reset.
DenyListAdd
Adds an entry to the Deny List.
Pattern(r): <S: 1, 60>
Specifies an entry to be added to the Deny List. If one of an endpoint's aliases
matches one of the patterns in the Deny List, the registration will not be permitted.
DenyListDelete
Deletes an entry from the Deny List.
DenyListId(r): <1..2500>
The index of the entry to be deleted.
Dial
Places a call between two endpoints.
callSrc(r): <S: 1, 60>
The alias of the first endpoint to be placed in the call.
callDst(r): <S: 1, 60>
The alias of the second endpoint to be placed in the call.
Bandwidth: <1..100000000>
The requested bandwidth of the call (in kbps).
EncryptionMode: <Auto/On/Off>
Specifies whether the call will be encrypted.
D14172.01 page 49 of 84
Page 50

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
EncryptionType: <DES/AES-128/Auto>
The type of encryption that will be used for the call.
DisconnectCall
Disconnects a call.
Call: <1..900>
The index of the call to be disconnected..
CallSerialNumber: <S: 0, 255>
The serial number of the call to be disconnected.
FeedbackRegister
Activates notifications on the event or status change(s) described by the Expression(s).
Notifications are sent in XML format to the specified URL. Up to 15 Expressions may be
registered for each of 3 feedback IDs.
ID: <1..3>
The ID of this particular feedback request.
URL(r): <S: 1, 256>
The URL to which notifications are to be sent.
Expression.1..15: <S: 1, 256>
The events or status change to be notified. See the Administrator Guide for a full list of
valid Expressions.
FeedbackDeregister
Deactivates a particular feedback request.
ID: <1..3>
The ID of the feedback request to be deactivated.
FindRegistration
Returns information about the registration associated with the specified alias. The alias must
be registered on the system on which the command is issued.
Alias(r): <S: 1, 60>
The alias that you wish to find out about.
LinkAdd
Adds and configures a new link.
LinkName(r): <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this link.
Node1: <S: 1, 50>
Specifies the first zone or subzone to which this link will be applied.
Node2: <S: 1, 50>
Specifies the second zone or subzone to which this link will be applied.
Pipe1: <S: 1, 50>
Specifies the first pipe to be associated with this link.
Pipe2: <S: 1, 50>
Specifies the second pipe to be associated with this link.
LinkDelete
Deletes a link.
LinkId(r): < 1..100>
The index of the link to be deleted.
D14172.01 page 50 of 84
Page 51

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Locate
Runs the system's location algorithm to locate the endpoint identified by the given alias,
searching locally, on neighbors, and on systems discovered through the DNS system, within
the specified number of 'hops'. Results are reported back through the xFeedback
mechanism, which must therefore be activated before issuing this command (e.g. xFeedback
register event/locate).
Alias(r): <S: 1, 60>
The alias associated with the endpoint you wish to locate.
HopCount(r): <0..255>
The hop count to be used in the search.
OptionKeyAdd
Adds a new option key to the system.
Key(r): <S: 0, 90>
Specifies the option key of the option you wish to add. Option keys are added to the
system in order to add extra functionality, such as increasing the system's capacity.
Contact your TANDBERG representative for further information.
OptionKeyDelete
Deletes a software option key from the system.
OptionKeyId(r): <1..64>
Specifies the ID of the software option to be deleted.
PipeAdd
Adds and configures a new pipe.
PipeName(r): <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this pipe.
TotalMode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether or not this pipe is enforcing total bandwidth restrictions. None: no
bandwidth available.
Total: <1..100000000>
If this pipe has limited bandwidth, sets the maximum bandwidth (in kbps) available at
any one time on the pipe.
PerCallMode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether or not this pipe is limiting the bandwidth of individual calls. None:
no bandwidth available.
PerCall: <1..100000000>
If this pipe has limited per-call bandwidth, sets the maximum amount of bandwidth (in
kbps) available for any one call.
PipeDelete
Deletes a pipe.
PipeId(r): <1..100>
The index of the pipe to be deleted.
RemoveRegistration
Removes a registration from the system.
Registration: <1..375 0>
The index number of the registration to be removed.
D14172.01 page 51 of 84
Page 52

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
RegistrationSerialNumber: <S: 0, 255>
The serial number of the registration to be removed.
SubZoneAdd
Adds and configures a new subzone.
SubZoneName(r): <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this subzone.
Address1: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies an IP Address used (in conjunction with the IP Prefix Length) to identify a
subnet to be assigned to this subzone.
PrefixLength1: <0..128>
Specifies the number of bits of the Subnet IP Address which must match for an IP
Address to belong in this subzone.
Address2: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies an IP Address used (in conjunction with the IP Prefix Length) to identify a
subnet to be assigned to this subzone.
PrefixLength2: <0..128>
Specifies the number of bits of the Subnet IP Address which must match for an IP
Address to belong in this subzone.
Address3: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies an IP Address used (in conjunction with the IP Prefix Length) to identify a
subnet to be assigned to this subzone.
PrefixLength3: <0..128>
Specifies the number of bits of the Subnet IP Address which must match for an IP
Address to belong in this subzone.
Address4: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies an IP Address used (in conjunction with the IP Prefix Length) to identify a
subnet to be assigned to this subzone.
PrefixLength4: <0..128>
Specifies the number of bits of the Subnet IP Address which must match for an IP
Address to belong in this subzone.
Address5: <S: 0, 39>
Specifies an IP Address used (in conjunction with the IP Prefix Length) to identify a
subnet to be assigned to this subzone.
PrefixLength5: <0..128>
Specifies the number of bits of the Subnet IP Address which must match for an IP
Address to belong in this subzone.
TotalMode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether this subzone has a limit on the total bandwidth of calls being used
by its endpoints at any one time.
Total: <1..100000000>
Sets the total bandwidth limit (in kbps) of this subzone (applies only if Mode is set to
Limited).
PerCallInterMode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth for any one call to or from an
endpoint in this subzone.
PerCallInter: <1..100000000>
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) on any one call to or from an endpoint in this
subzone (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
D14172.01 page 52 of 84
Page 53

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
PerCallIntraMode: <None/Limited/Unlimited>
Determines whether there is a limit on the bandwidth for any one call between two
endpoints within this subzone.
PerCallInt ra: <1..10000 0 0 00 >
Specifies the bandwidth limit (in kbps) for any one call between two endpoints within
this subzone (applies only if Mode is set to Limited).
SubZoneDelete
Deletes a subzone.
SubZoneId(r): <1..100>
The index of the subzone to be deleted.
TransformAdd
Adds a new destination alias transform.
Pattern(r): <S: 1, 60>
Specifies the pattern against which the alias is compared.
Type: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
Determines the way in which the string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must
appear at the beginning of the alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the
alias. Regex: the string will be treated as a regular expression.
Behavior: <Strip/Replace>
Determines how the matched part of the alias will be modified. Strip: the matching
prefix or suffix will removed from the alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will
be substituted with the text in the Replace string.
Replace: <S: 1, 60 >
(Applies only if pattern behavior is set to Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Priority: <0..65534>
Assigns a priority to the specified t r ansform. Transforms are applied in order of
priority, and the priority must be unique for each transform.
TransformDelete
Deletes a transform.
TransformId(r): <1..200>
The index of the transform to be deleted.
TraversalZoneAdd
Adds a new traversal zone.
TraversalZoneName(r): <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this traversal zone.
Mode(r): <Assent/H46018>
Determines which H.323 traversal protocol to use, either Assent or H.460.18.
AccountName: <S: 1, 50>
Specifies the account name to be used when connecting to an Assent Traversal Zone.
Gatekeeper1Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Gatekeeper1Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server
to connect to.
D14172.01 page 53 of 84
Page 54

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Gatekeeper2Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Gatekeeper2Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server
to connect to.
Gatekeeper3Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Gatekeeper3Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server
to connect to.
Gatekeeper4Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Gatekeeper4Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server
to connect to.
Gatekeeper5Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Gatekeeper5Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server
to connect to.
Gatekeeper6Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQDN of the traversal server. Up to five alternate traversal
servers can also be specified.
Gatekeeper6Port: <1..65534>
(Applies only if the system is a Gatekeeper.) Specifies the port on the traversal server
to connect to.
HopCount: <1..255>
Specifies the hop count to be used when sending an alias search request to this zone.
Note: If the search request was received from another zone and already has a hop
count assigned, the lower of the two values will be used.
Match1Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match1PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match1PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match1PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
D14172.01 page 54 of 84
Page 55

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Match1PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match2Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match2PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match2PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match2PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match2PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match3Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match3PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match3PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match3PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match3PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match4Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match4PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
D14172.01 page 55 of 84
Page 56

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Match4PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match4PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match4PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match5Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match5PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match5PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match5PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match5PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
TraversalZoneDelete
Deletes a traversal zone.
TraversalZoneId(r): <1..50>
The index of the traversal zone to be deleted.
ZoneAdd
Adds a new zone.
ZoneName(r): <S: 1, 50>
Assigns a name to this zone.
Gatekeeper1Address(r): <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
Gatekeeper1Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
Gatekeeper2Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
D14172.01 page 56 of 84
Page 57

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Gatekeeper2Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
Gatekeeper3Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
Gatekeeper3Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
Gatekeeper4Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
Gatekeeper4Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
Gatekeeper5Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
Gatekeeper5Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
Gatekeeper6Address: <S: 1, 128>
Specifies the IP Address or FQD N of this neighbor.
Gatekeeper6Port: <1..65534>
Specifies the port on the neighbor to be used.
HopCount: <1..255>
Specifies the hop count to be used when sending an alias search request to this zone.
Note: If the search request was received from another zone and already has a hop
count assigned, the lower of the two values will be used.
Monitor: <On/Off>
If zone monitoring is enabled, an LRQ will be periodically sent to the zone gatekeeper.
If it fails to respond, that gatekeeper will be marked as inactive.
Match1Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match1PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match1PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match1PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match1PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match2Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
D14172.01 page 57 of 84
Page 58

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Match2PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match2PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match2PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match2PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match3Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match3PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match3PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match3PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match3PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match4Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match4PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match4PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
D14172.01 page 58 of 84
Page 59

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Match4PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match4PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
Match5Mode: <AlwaysMatch/PatternMatch/Disabled>
Determines if and when a query will be sent to this zone. Always: the zone will always
be queried. Pattern: the zone will only be queried if the alias queried for matches the
corresponding pattern. Disabled: the zone will never be queried.
Match5PatternString: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Specifies the pattern against which
the alias is compared.
Match5PatternType: <Prefix/Suffix/Regex>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines the way in which the
string must match the alias. Prefix: the string must appear at the beginning of the
alias. Suffix: the string must appear at the end of the alias. Regex: the string will be
treated as a regular expression.
Match5PatternBehavior: <Strip/Leave/Replace>
(Applies only if the Match mode is Pattern Match.) Determines whether the matched
part of the alias should be modified before an LRQ is sent to this zone. Leave: the
alias will be unmodified. Strip: the matching prefix or suffix will be removed from the
alias. Replace: the matching part of the alias will be substituted with the text in the
Replace string.
Match5PatternReplace: <S: 0, 60>
(Applies only if the Pattern Behavior is Replace.) Specifies the string to be used as a
substitution for the part of the alias that matched the pattern.
ZoneDelete
Deletes a zone.
ZoneId(r): <1..100>
The index of the zone to be deleted.
D14172.01 page 59 of 84
Page 60

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
5 API - Status
This section gives an overview of the Status Information available in the Status XML documents
(status.xml / history.xml / event.xml) and the Status root commands (xstatus / xhistory) of the XACLI
interface.
All examples are presented using the standard XACLI format.
5.1 status.xml – xstatus
SystemUnit
SystemUnit Product: <String>
Shows the product name.
SystemUnit Uptime: <Integer>
Shows the uptime in seconds.
SystemUnit SystemTime: <String>
Shows the system time.
SystemUnit TimeZone: <String>
Shows the time zone.
SystemUnit TimeZone: <String>
Shows the time zone.
SystemUnit LocalTime: <String>
Shows the local time.
SystemUnit Software Version: <String>
Shows the software version.
SystemUnit Software Build: <String>
Shows the software build.
SystemUnit Software Name: <String>
Shows the software name.
SystemUnit Software ReleaseDate: <String>
Shows the software release date.
SystemUnit Software ReleaseKey: <String>
Shows the software rele ase key.
SystemUnit Software Configuration NonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the systems non traversal call capacity.
D14172.01 page 60 of 84
Page 61

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
SystemUnit Software Configuration TraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the systems traversal call capacity.
SystemUnit Software Configuration Registrations: <Integer>
Shows the systems registration capacity.
SystemUnit Software Configuration Encryption: <True/False>
Shows whether AES encryption is present.
SystemUnit Software Configuration Multiway: <True/False>
Shows whether Multiway is available.
SystemUnit Hardware Version: <String>
Shows the hardware version.
SystemUnit Hardware SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the serial number.
Options
Options Option [1..64] Key: <String>
Shows an installed option key.
Options Option [1..64] Description: <String>
Shows a description of the option key.
Ethernet
Ethernet MacAddress: <String>
Shows the MAC address of the Ethernet in terface.
Ethernet Speed: <10half/10full/100half/100full>
Shows the speed of the Ethernet interf ace.
IP
IP Protocol: <Both/IPv4/IPv6>
Shows the IP protocols.
IP Address: <IPv4Addr>
Shows the systems IPv4 address. Only present if the Protocol is IPv4 or Both.
IP SubnetMask: <IPv4Addr>
Shows the systems IPv4 subnet mask. Only present if the Protocol is IPv4 or Both.
IP Gateway: <IPv4Addr>
Shows the IPv4 address of the default gateway. Only present if the Protocol is IPv4 or Both.
IP IPv6 Address: <IPv4Addr>
Shows the IPv6 address of the system. Only present if the Protocol is IPv6 or Both.
D14172.01 page 61 of 84
Page 62

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
IP IPv6 Gateway: <IPv4Addr>
Shows the IPv6 address of the default gateway. Only present if the Protocol is IPv6 or Both.
IP DNS Server [1..5] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address of a configured DNS server.
IP DNS Domain Name: <IPv4Addr>
Shows the DNS domain to which the system belongs.
NTP
NTP [status = <Inactive/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the NTP server.
NTP Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to connect to the NTP server. Only present if the NTP
status is Failed.
NTP Address: <String>
Shows the address of the NTP server. Only present if the NTP status is Active or Failed.
NTP Port: <String>
Shows the port of the NTP server. Only present if the NTP status is Active or Failed.
NTP LastUpdate: <String>
Shows the time at which the last NTP update occurred. Only present if the NTP status is
Active.
NTP LastCorrection: <String>
Shows the last correction to the time that occurred. Only present if the NTP status is Active.
LDAP
LDAP [status = <Inactive/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the LDAP server.
LDAP Reason: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to connect to the LDAP server. Only present if the LDAP
status is Failed or Inactive.
LDAP Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to connect to the LDAP server. Only present if the LDAP
status is Failed or Inactive and the Reason is not "Not configured".
LDAP Address: <String>
Shows the address of the LDAP server. Only present if the LDAP status is Active or Failed.
LDAP Port: <String>
Shows the port of the LDAP server. Only present if the LDAP status is Active or Failed.
D14172.01 page 62 of 84
Page 63

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
ExternalManager
ExternalManager [status = <Inactive/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the external manager.
ExternalManager Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to connect to the external manager. Only present if the
external manager status is Failed.
ExternalManager Address: <String>
Shows the address of the external manager. Only present if the external manager status is
Active.
ExternalManager Protocol: <String>
Shows the prot o c o l be i ng used to communi c ate with the external manager. Only present if
the external manager status is Active.
ExternalManager URL: <String>
Shows the URL on the external manager being connected to. Only present if the external
manager status is Active or Failed.
Feedback
Feedback [1..3] [status = <On/Off>]
Shows whether feedback is configured.
Feedback [1..3] URL: <String>
Shows the URL of a system which has registered for feedback. Only present if the Feedback
status is On.
Feedback [1..3] Expression [1..15]: <String>
Shows the URL of a system which has registered for feedback. Only present if the Feedback
status is On.
ResourceUsage
ResourceUsage Registrations: <Integer>
Shows the current number of registrations on the system.
ResourceUsage MaxRegistrations: <Integer>
Shows the max imum number of concurrent registrations on the system.
ResourceUsage NonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the current number of non traversal calls on the system. Only pres ent if the system is
a Gatekeeper.
ResourceUsage MaxNonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the maximum number of concurrent non traversal calls on the system. Only present if
the system is a Gatekeeper.
D14172.01 page 63 of 84
Page 64

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
ResourceUsage TotalNonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the total number of non traversal calls that have been placed on the system. Only
present if the system is a Gatekeeper.
ResourceUsage TraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the current number of traversal calls on the system.
ResourceUsage MaxTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the maximum number of concurrent traversal calls on the system.
ResourceUsage TotalTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the total number of traversal calls placed on the system.
Gatekeeper
Gatekeeper Alternates Alternate [1..5] [status = <Unknown/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to an alternate system.
Gatekeeper Alternates Alternate [1..5] Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to connect to the alternate system. Only present if the
alternate status if Failed.
Gatekeeper Alternates Alternate [1..5] Address: <String>
Shows the address of the alternate system.
Gatekeeper Alternates Alternate [1..5] Port: <String>
Shows the port of the alternate system.
Calls
Calls Call [1..900] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
Calls Call [1..900] State: <Unknown/Connecting/Connected/Disconnected
/ConnectionFailed/Parked/Parking/Unparking/ParkFailed>
Shows the state of the call.
Calls Call [1..900] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
Calls Call [1..900] Transferable: <On/Off>
Shows whether this call is capable of being transferred.
Calls Call [1..900] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps for the call.
Calls Call [1..900] Route Zone: <String>
Shows the name of a zone that is part of the route the call takes.
Calls Call [1..900] Route Link: <String>
Shows the name of a link that is part of the route the call takes.
D14172.01 page 64 of 84
Page 65

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] RegistrationID: <String>
Shows the registration ID of the call party if it is locally registered.
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the serial number of the call party registrat ion. Only present if the call party is locally
registered.
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email
/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party.
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption [status = <On/Off>]
Shows the status of encryption on the call leg.
Calls Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption CheckCode: <String>
Shows the check code for the encrypted call leg. Only present if encryption status is On.
Calls Call [1..900] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
Calls Call [1..900] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
Calls Call [1..900] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
Calls Call [1..900] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
Calls Call [1..900] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
Calls Call [1..900] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party.
D14172.01 page 65 of 84
Page 66

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Registrations
Registrations Registration [1..3750] CallSignalAddresses Address [1..10]:
<String>
Shows the IP address and port to use for call signaling.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] RASAddresses Address [1..10]: <String>
Shows the IP address and port to use for RAS signaling.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Endpoint:
Shows that the registration is an endpoint. Only present if the registration is an endpoint.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Gatekeeper:
Shows that the registration is a gatekeeper. Only present if the registration is a gatekeeper.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Gateway:
Shows that the registration is a gateway. Only present if the registration is a gateway.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Gateway Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered gateway service. Only present if the registration is a
gateway.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] MCU:
Shows that the registration is an MCU. Only present if the registration is an MCU.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] MCU Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered MCU service. Only present if the registration is an MCU.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] OutOfResources: <On/Off>
Shows the resource usage of a gateway or an MCU. Only present if the registered system is
a gateway or an MCU.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Traversal: <Assent/H46018>
Shows the traversal type of the registration. Only present if the registered system supports
firewall traversal.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200] [type =
<IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the alias.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200]: <String>
Shows the alias value.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] SubZone: <String>
Shows the subzone to which this regis tration belongs.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the registration.
Registrations Registration [1..3750] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration was created.
D14172.01 page 66 of 84
Page 67

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Zones
Zones DefaultZone Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call in the Default Zone.
Zones DefaultZone Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed in the Default Zone.
Zones DefaultZone Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call in the Default Zone.
Zones DefaultZone Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps being used in the Default Zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] [status = <Warning/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to communicate with the traversal zone. Only present if
the traversal zone status is Failed or Warning.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Name: <String>
Shows the name of the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Traversal: <Assent/H46018>
Shows the traversal type of the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] AccountName: <String>
Shows the account name for the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] [status = <Unknown/Active
/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the gatekeeper in the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to communicate with the gatekeeper. Only present if the
gatekeeper status is Failed.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Address: <String>
Shows the address for a gatekeeper in the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Port: <String>
Shows the port for a gatekeeper in the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call in the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed in the traversal zone.
D14172.01 page 67 of 84
Page 68

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call in the traversal zone.
Zones TraversalZone [1..50] Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps being used in the traversal zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] [status = <Warning/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to communicate with the zone. Only present if the zone
status is Failed or Warning.
Zones Zone [1..50] Name: <String>
Shows the name of the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] [status = <Unknown/Active/Failed>]
Shows the status of the connection to the gatekeeper.
Zones Zone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Cause: <String>
Shows an error reason for a failure to communicate with the gatekeeper. Only present if the
gatekeeper status is Failed.
Zones Zone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Address: <String>
Shows the address for a gatekeeper in the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Gatekeeper [1..6] Port: <String>
Shows the port for a gatekeeper in the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call in the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed in the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call in the zone.
Zones Zone [1..50] Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps being used in the zone.
D14172.01 page 68 of 84
Page 69

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Subzones
SubZones DefaultSubZone Registrations Registration [1..3750]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a registration in the Default SubZone.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call in the Default SubZone.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed in the Default SubZone.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call in the Default SubZone.
SubZones DefaultSubZone Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps being used in the Default SubZone.
SubZones TraversalSubZone Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call in the Traversal SubZone.
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed in the Traversal SubZone.
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the ba ndwidth in kbps allowed per call in the Traversal SubZone.
SubZones TraversalSubZone Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the ba ndwidth in kbps being used in the Traversal SubZone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Name: <Integer>
Shows the name of the SubZone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Registrations Registration [1..3750]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a registration in the SubZone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call in the SubZone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed in the SubZone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call in the SubZone.
SubZones SubZone [1..100] Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps being used in the SubZone.
D14172.01 page 69 of 84
Page 70

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Links
Links Link [1..100] Name: <Integer>
Shows the name of the link.
Links Link [1..100] Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call using the link.
Links Link [1..100] Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed on the link.
Links Link [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call on the link.
Links Link [1..100] Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps being used on the link.
Pipes
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Name: <Integer>
Shows the name of the pipe.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Calls Call [1..900]: <Integer>
Shows the index of a call using the pipe.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth Total: <String>
Shows the total bandwidth in kbps allowed on the pipe.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth PerCall: <String>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps allowed per call on the pipe.
Pipes Pipe [1..100] Bandwidth Used: <String>
Shows the ba ndwidth in kbps being used on the pipe.
D14172.01 page 70 of 84
Page 71

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
5.2 history.xml – xhistory
Calls
Calls Call [1..255] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
Calls Call [1..255] State: <Disconnected/ConnectionFailed>
Shows the state of the call.
Calls Call [1..255] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
Calls Call [1..255] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps for the call.
Calls Call [1..255] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email
/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
Calls Call [1..255] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
Calls Call [1..255] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party.
Calls Call [1..255] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
Calls Call [1..255] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
Calls Call [1..255] DisconnectCauseValue: <String>
Shows the reason the call was disconnected.
Calls Call [1..255] DisconnectCause: <String>
Shows a description of the reason the call was disconnected.
Calls Call [1..255] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
Calls Call [1..255] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
Calls Call [1..255] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
Calls Call [1..255] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party.
D14172.01 page 71 of 84
Page 72

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Registrations
Registrations Registration [1..255] CallSignalAddresses Address [1..10]:
<String>
Shows the IP address and port used for call signaling.
Registrations Registration [1..255] RASAddresses Address [1..10]: <String>
Shows the IP address and port used for RAS signaling.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Endpoint:
Shows that the registration was endpoint. Only present if the registration was an endpoint.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Gatekeeper:
Shows that the registration was a gatekeeper. Only present if the registration was a
gatekeeper.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Gateway:
Shows that the registration was a gateway. Only present if the registration was a gateway.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Gateway Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered gateway service. Only present if the registration was a
gateway.
Registrations Registration [1..255] MCU:
Shows that the registration was an MCU. Only present if the registration was an MCU.
Registrations Registration [1..255] MCU Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered MCU service. Only present if the registration was an MCU.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Aliases Alias [1..200] [type =
<IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the alias.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Aliases Alias [1..200]: <String>
Shows the alias value.
Registrations Registration [1..255] SubZone: <String>
Shows the subzone to which this registration belonged.
Registrations Registration [1..255] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the registration.
Registrations Registration [1..255] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration was created.
Registrations Registration [1..255] EndTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration ended.
Registrations Registration [1..255] Reason: <String>
Shows the reason for the registration ending.
D14172.01 page 72 of 84
Page 73

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Registrations Registration [1..255] RegistrationRejectionCause: <String>
Shows the ca use for the regi stration being rejected. Only present if the reason is
RegistrationRejected.
Registrations Registration [1..255] RegistrationRejectionDescription:
<String>
Shows a description of the cause for the registration being rejected. Only present if the
reason is RegistrationRejected.
D14172.01 page 73 of 84
Page 74

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
5.3 event.xml – xevent
CallAttempt
CallAttempt Call [1..900] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] State: <Initializing>
Shows the state of the call.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Transferable: <On/Off>
Shows whether this call is capable of being transferred.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps for the call.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Route Zone: <String>
Shows the name of a zone that is part of the route the call takes.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Route Link: <String>
Shows the name of a link that is part of the route the call takes.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] RegistrationID: <String>
Shows the registration ID of the call party if it is locally registered.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the serial number of the call party registration. Only present if the call party is locally
registered.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id/
Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption [status = <On/Off>]
Shows the status of encryption on the call leg.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption CheckCode: <String>
Shows the check code for the encrypted call leg. Only present if encryption status is On.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
D14172.01 page 74 of 84
Page 75

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
CallAttempt Call [1..900] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
CallAttempt Call [1..900] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party.
Connected
Connected Call [1..900] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
Connected Call [1..900] State: <Connected>
Shows the state of the call.
Connected Call [1..900] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
Connected Call [1..900] Transferable: <On/Off>
Shows whether this call is capable of being transferred.
Connected Call [1..900] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps for the call.
Connected Call [1..900] Route Zone: <String>
Shows the name of a zone that is part of the route the call takes.
Connected Call [1..900] Route Link: <String>
Shows the name of a link that is part of the route the call takes.
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] RegistrationID: <String>
Shows the registration ID of the call party if it is locally registered.
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the serial number of the call party registration. Only present if the call party is locally
registered.
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id/
Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
D14172.01 page 75 of 84
Page 76

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party.
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption [status = <On/Off>]
Shows the status of encryption on the call leg.
Connected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption CheckCode: <String>
Shows the check code for the encrypted call leg. Only present if encryption status is On.
Connected Call [1..900] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
Connected Call [1..900] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
Connected Call [1..900] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
Connected Call [1..900] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
Connected Call [1..900] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
Connected Call [1..900] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party.
Disconnected
Disconnected Call [1..900] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
Disconnected Call [1..900] State: <Disconnected>
Shows the state of the call.
Disconnected Call [1..900] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
Disconnected Call [1..900] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps for the call.
Disconnected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id
/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
Disconnected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
Disconnected Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party.
D14172.01 page 76 of 84
Page 77

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Disconnected Call [1..900] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
Disconnected Call [1..900] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
Disconnected Call [1..900] DisconnectCauseValue: <String>
Shows the reason the call was disconnected.
Disconnected Call [1..900] DisconnectCause: <String>
Shows a description of the reason the call was disconnected.
Disconnected Call [1..900] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
Disconnected Call [1..900] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
Disconnected Call [1..900] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
Disconnected Call [1..900] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party.
ConnectionFailure
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] State: <ConnectionFailed>
Shows the state of the call.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the bandwidth in kbps for the call.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164
/H323Id/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party. Only present if the address could be
determined.
D14172.01 page 77 of 84
Page 78

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] DisconnectCauseValue: <String>
Shows the reason the call failed.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] DisconnectCause: <String>
Shows a description of the reason the call failed.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
ConnectionFailure Call [1..900] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party. Only present if the destination
address could be determined.
Registration
Registration Registration [1..3750] CallSignalAddresses Address [1..10]:
<String>
Shows the IP address and port to use for call signaling.
Registration Registration [1..3750] RASAddresses Address [1..10]: <String>
Shows the IP address and port to use for RAS signaling.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Endpoint:
Shows that the registration is an endpoint. Only present if the registration is an endpoint.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Gatekeeper:
Shows that the registration is a gatekeeper. Only present if the registration is a gatekeeper.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Gateway:
Shows that the registration is a gateway. Only present if the registration is a gateway.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Gateway Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered gateway service. Only present if the registration is a
gateway.
Registration Registration [1..3750] MCU:
Shows that the registration is an MCU. Only present if the registration is an MCU.
D14172.01 page 78 of 84
Page 79

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Registration Registration [1..3750] MCU Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered MCU service. Only present if the registration is an MCU.
Registration Registration [1..3750] OutOfResources: <On/Off>
Shows the resource usage of a gateway or an MCU. Only present if the registered system is
a gateway or an MCU.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Traversal: <Assent/H46018>
Shows the traversal type of the registration. Only present if the registered system supports
firewall traversal.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200] [type =
<IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the alias.
Registration Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200]: <String>
Shows the alias value.
Registration Registration [1..3750] SubZone: <String>
Shows the subzone to which this regis tration belongs.
Registration Registration [1..3750] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the registration.
Registration Registration [1..3750] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration was created.
Unregistration
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] CallSignalAddresses Address [1..10]:
<String>
Shows the IP address and port used for call signaling.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] RASAddresses Address [1..10]:
<String>
Shows the IP address and port used for RAS signaling.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Endpoint:
Shows that the registration was endpoint. Only present if the registration was an endpoint.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Gatekeeper:
Shows that the registration was a gatekeeper. Only present if the registration was a
gatekeeper.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Gateway:
Shows that the registration was a gateway. Only present if the registration was a gateway.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Gateway Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered gateway service. Only present if the registration was a
gateway.
D14172.01 page 79 of 84
Page 80

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] MCU:
Shows that the registration was an MCU. Only present if the registration was an MCU.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] MCU Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered MCU service. Only present if the registration was an MCU.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200] [type =
<IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the alias.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200]: <String>
Shows the alias value.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] SubZone: <String>
Shows the subzone to which this registration belonged.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the registration.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration was created.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] EndTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration ended.
Unregistration Registration [1..3750] Reason: <String>
Shows the reason for the registration ending.
RegistrationFailure
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] CallSignalAddresses Address
[1..10]: <String>
Shows the IP address and port used for call signaling.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] RASAddresses Address [1..10]:
<String>
Shows the IP address and port used for RAS signaling.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Endpoint:
Shows that the registration was endpoint. Only present if the registration was an endpoint.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Gatekeeper:
Shows that the registration was a gatekeeper. Only present if the registration was a
gatekeeper.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Gateway:
Shows that the registration was a gateway. Only present if the registration was a gateway.
D14172.01 page 80 of 84
Page 81

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Gateway Prefix [1..200]:
<String>
Shows the prefix of a registered gateway service. Only present if the registration was a
gateway.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] MCU:
Shows that the registration was an MCU. Only present if the registration was an MCU.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] MCU Prefix [1..200]: <String>
Shows the prefix of a registered MCU service. Only present if the registration was an MCU.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200] [type =
<IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the alias.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Aliases Alias [1..200]: <String>
Shows the alias value.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] SubZone: <String>
Shows the subzone to which this registration belonged.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the registration.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration was created.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] EndTime: <String>
Shows the time at which this registration ended.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] Reason: <String>
Shows the reason for the registration ending.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750] RegistrationRejectionCause:
<String>
Shows the cause for the re gistration being reject ed.
RegistrationFailure Registration [1..3750]
RegistrationRejectionDescription: <String>
Shows a description of the cause for the registration being rejected.
D14172.01 page 81 of 84
Page 82

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Bandwidth
Bandwidth Call [1..900] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] State: <Unknown/Connecting/Connected/Disconnected
/ConnectionFailed/Parked/Parking/Unparking/ParkFailed>
Shows the state of the call.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] CallType: <Traversal/Direct/Routed>
Shows the type of the call.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Transferable: <On/Off>
Shows whether this call is capable of being transferred.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Bandwidth: <Integer>
Shows the updated bandwidth in kbps for the call.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Route Zone: <String>
Shows the name of a zone that is part of the route the call takes.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Route Link: <String>
Shows the name of a link that is part of the route the call takes.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] RegistrationID: <String>
Shows the registration ID of the call party if it is locally registered.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] SerialNumber: <String>
Shows the serial number of the call party registration. Only present if the call party is locally
registered.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id
/Email/Url/Prefix/Suffix>]
Shows the type of the call party alias.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Alias: <String>
Shows the alias of the call party.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the call party.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption [status = <On/Off>]
Shows the status of encryption on the call leg.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Leg [1..2] Encryption CheckCode: <String>
Shows the check code for the encrypted call leg. Only present if encryption status is On.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] StartTime: <String>
Shows the time at which the call was initiated.
D14172.01 page 82 of 84
Page 83

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
Bandwidth Call [1..900] Duration: <String>
Shows the duration of the call in seconds.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] SourceAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the source call party.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] SourceAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the source call party.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] DestinationAlias: <String>
Shows the alias of the destination call party.
Bandwidth Call [1..900] DestinationAddress: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the destination call party.
Locate
LocateResult Result: <Success/Failed>
Shows the result of the search.
LocateResult Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url>]
Shows the ty pe of the alias being searched for.
LocateResult Alias: <String>
Shows the value of the alias being searched for.
LocateResult CallSerialNumber: <String>
Shows the unique serial number of the call
LocateResult Location Type: <Local Database/Neighbor/Traversal>
Shows the type of locatio n being searched.
LocateResult Location Alias [type = <IPAddress/E164/H323Id/Email/Url>]
Shows the type of the alias this location is being searched with.
LocateResult Location Alias: <String>
Shows the alias this location is being searched with.
Note: The alias may be different from the original search alias if transforms have been
applied.
LocateResult Location Address: <String>
Shows the IP address and port of the location being searched. Only present if the Location
Type is Neighbor or Traversal.
LocateResult Location Result: <Success/Failed>
Shows the result of searching this location
LocateResult Location Reason: <Success/Failed>
Shows a description of the reason the search of this location failed. Only present if the
Location Result is Failed and the Location Type is Neighbor or Traversal.
D14172.01 page 83 of 84
Page 84

TANDBERG Gatekeeper/Border Controller API User Guide
ResourceUsage
ResourceUsage Registrations: <Integer>
Shows the current number of registrations on the system.
ResourceUsage MaxRegistrations: <Integer>
Shows the max imum number of concurrent registrations on the system.
ResourceUsage NonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the current number of non traversal calls on the system. Only pres ent if the system is
a Gatekeeper.
ResourceUsage MaxNonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the maximum number of concurrent non traversal calls on the system. Only present if
the system is a Gatekeeper.
ResourceUsage TotalNonTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the total number of non traversal calls that have been placed on the system. Only
present if the system is a Gatekeeper.
ResourceUsage TraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the current number of traversal calls on the system.
ResourceUsage MaxTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the maximum number of concurrent traversal calls on the system.
ResourceUsage TotalTraversalCalls: <Integer>
Shows the total number of traversal calls placed on the system.
D14172.01 page 84 of 84
 Loading...
Loading...