SEW Eurodrive MOVITRAC 31 User Manual

0922 6818 / 0498
MOVITRAC®31..
Frequency Inverter
PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
(FFP 31.. Option and Size 0/DP)
Manual
Edition 04/98
08/198/96

Important Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
• Read this User Manual carefully before you start installation and commissioning work on
®
MOVITRAC
frequency inverters with fieldbus options.
This User Manual assumes that the user is familiar with and has at his disposal all relevant
®
documentation on the MOVITRAC
system, in particular the Installation and Operating Instruc-
tions.
• Safety notes:
Always follow the safety notes contained in this User Manual.
Safety notes are marked as follows:
Electrical hazard, e.g. during live working
Mechanical hazard, e.g. when working on hoists
Important Instructions for the safe and fault-free operation of the system, e.g.
pre-setting before commissioning. Failure to follow these instructions may
result in injury to people and damage to property.
• General safety notes for bus systems:
The fieldbus option gives you a communications system which allows you to match the
®
MOVITRAC
31.. drive system to the specifics of your application to a very high degree. As
with all bus systems there is, however, the risk of a programming error in the program which
may result in unexpected (not uncontrolled, though) system behaviour.
• In this manual, cross-references are marked with a →, e.g.,
(→ MC_SHELL) means: Please refer to the MC_SHELL User Manual for detailed in formation or
information on how to carry out this instruction.
(→ section x.x) means: Further information can be found in section x.x of this User Manual.
• Each unit is manufactured and tested to current SEW-EURODRIVE technical standards and
specifications.
The manufacturer reserves the right to make changes to the technical data and designs as well
as the user interface herein described, which are in the interest of technical progress.
A requirement for fault-free operation and fulfilment of any rights to claim under guarantee is
that these instructions and notes are followed.
These instructions contain important information for servicing, they should therefore be kept in
the vicinity of the unit.
2
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface

Preface
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Preface
This manual for the PROFIBUS interface describes the procedure for installing the FFP 31C PROFI-
®
BUS option pcb in the inverter, for installing the MOVITRAC
®
BUS-DP interface and for commissi oning MOVITRA C
31.. frequency inverter when connect ed to
31.. size 0 with integrated PROFIa PROFIBUS-FMS fieldbus system.
In addition to describing all the settings on the fieldbus option pcb, this manual further discusses
the various options for connecting the inverter to PROFIBUS-DP or PROFIBUS-FMS in the form of
brief commissioning examples.
In addition to this PROFIBUS Option User Manual, the following more detailed documentation on
®
fieldbuses is also necessary in order to enable the MOVITRAC
31.. to be connected simply and
efficiently to the fieldbus system (e.g. PROFIBUS):
®
– User Manual Fieldbus Unit Profile MOVITRAC
– User Manual Communications Interfaces and Parameter List MOVITRAC
31.., part number 0922 7016
®
31..
part number 0923 0580
®
The MOVITRAC
31.. Fieldbus Unit Profile Manual gives a detailed description of the fieldbus
parameters and their codes and discusses various control concepts and application options in the
form of brief commissioning examples.
®
The MOVITRAC
31.. Parameter List c ontains a lis t of all the i nverter parameters that can be read
or written via the various communications interfaces such as the RS-232, RS-485, and via the
fieldbus interface.
Note:
®
These instructions also apply to the inver ter MOVITRAC
31.. size 0 with integra ted PROFIBUS- DP
interface. Functions, which are not supported by this unit, are labeled with the note “(Not with
®
MOVITRAC
31.. size 0)”.
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
3

Contents
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1 Introducti on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Assembly / Installation Instructions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Installing the FFP 31.. Option pcb. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
2.1.1 Scope of delivery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
2.1.2 Supported inverter types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
2.1.3 Assembly instructions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
®
2.2 Installation of the MOVITRAC
2.3 Pin Assignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
2.4 Screening and Laying of the Bus Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.5 Bus Termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2.6 Setting the Station Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.7 Setting the Bus Parameters (not for MOVITRAC
2.8 Display Elements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
2.9 Commissioning the Inverter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
31.. size 0/DP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
®
31.., size 0). . . . . . . .13
Page
3 The PROFIBUS-DP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.1 Configuration of the DP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
3.1.1 Description of the Configuration Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
3.1.2 Configuring for 1 Process Data Word (1 PD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3.1.3 Configuring for 2 Process Data Words (2 PD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
3.1.4 Configuring for 3 Process Data Words (3 PD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.1.5 Configuring for 1 PD + Parameter Channel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.1.6 Configuring for 2 PD + Parameter Channel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
3.1.7 Configuring for 3 PD + Parameter Channel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
3.2 Ident Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
3.3 Watchdog Timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
3.4 Diagnostic Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
3.4.1 Data in Octet 1: Station Status 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
3.4.2 Data in Octet 2: Station Status 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
3.4.3 Data in Octet 3: Station Status 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
3.4.4 DP Master Address in Octet 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
3.4.5 Ident Number in Octet 5/6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
3.4.6 Unit Related Diagnosis using Octet 7/8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
3.5 Sync and Freeze Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
3.6 Control via PROFIBUS-DP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
3.7 Parameter setting via PROFIBUS-DP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
3.7.1 Structure of the Parameter Channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
3.7.2 Reading a Parameter via PROFIBUS-DP (Read) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
3.7.3 Writing a Parameter via PROFIBUS-DP (Write). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
3.7.4 Sequence of Parameter Adjustment via PROFIBUS-DP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
3.7.5 Parameter Data Format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
3.8 The GSD File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
4
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface

4 The PROFIBUS-FMS Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 7
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4.1 FMS Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.1.1 Initiate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.1.2 Abort . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.3 Reject. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.4 Identify. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.5 Get-OV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.6 Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.7 Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.8 Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.2 Object List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.2.1 Object Description of the Drive Parameter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.2.2 Objects for Process Data Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4.2.3 “Min Tsdr” Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
4.2.4 “DP Station Diagnosis” Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
4.2.5 “Download Parameter Block” Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
4.2.6 “Universal Write Parameter” Object. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
4.2.7 “Universal Read” Functionality Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
4.3 Communications Relationship List (CRL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
4.3.1 CRL Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
4.3.2 Communications Relationship Lists of the Inverter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
4.4 Communications Relationship List of the Master. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Contents
5 Parameter Adjustment Return Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
5.1 Incorrect Service Code in the Parameter Channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
5.2 Incorrect Specification of the Data Length in the Parameter Channel . . . 56
5.3 Internal Communications Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
6 Program Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
7 Technical Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
7.1 Technical Data FFP 31.. Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
®
7.2 Technical data MOVITRAC
31C.. size 0/DP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Appendix A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
MOVITRAC ® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
5

1 Introduction
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1 Introduction
Thanks to its high-per formance, uni versal fi eldbus in terface , the MOVITRAC® 31.. inverter with the
FFP 31C option enables connecti ons to be made with hig her-l evel automa tion sy stems vi a the open
and standardized serial PROFIBUS-FMS and PROFIBUS-DP bus system.
In addition MOVITRAC
full inverter functionality with extremely compact design.
PROFIBUS-FMS
PROFIBUS-FMS (Fieldbus Message Specification) is designed for non-time-critical applications in
automation engineering such as, for example, networking different automation systems of various
manufacturers. In drive engineering the PROFIBUS-FMS is mainly used for visualization and
parameter adjustment of d rives, as larger, non-time-cr it i cal amou nts of da ta can be exc hanged in a
simple way. PROFIBUS-FMS is defined in EN 50170 Volume 2 / DIN 19245 Part 2.
PROFIBUS-DP
PROFIBUS-DP (Decentralized Periphery) is mainly used for communication with decentralized
peripherals, i.e. in the sensor/actuator field, where short system reaction times are required. The
main task of PROFIBUS-DP is the fast cyclic data exchange between central automation units
(PROFIBUS master) and decentralized peripherals, such as inverters. PROFIBUS-DP is defined in
EN 50170 Volume 2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3.
PROFIBUS-FMS and PROFIBUS-DP can gene ral l y be ope rat ed on a joint transmission medium. If a
joint transmission medium is used, however, the units which are to communicate directly with
each other must be able to understand the same protocol option.
®
31.. size 0 with PROFIBUS-DP with standard integ rated DP Interface offer s
®
MOVITRAC
With the FFP 31C PROFIBUS opt ion pcb the MOVITRAC
3 1.. with FFP 3 1 = Combislave
®
31.. inverter as Combislave uni t supports
both PROFIBUS-FMS and PROFIBUS-DP. This allows the inverter to be controlled via PLC and
PROFIBUS-DP, for example, wh il e at the same time a vi sua li z ati on system can read out a nd d is pl ay
on a PC screen actual values from the inverter using PROFIBUS-FMS. Of course the inverter may
be controlled and parameters set using only PROFIBUS-DP or only PROFIBUS-FMS, too.
®
MOVITRAC
The MOVITRAC
3 1.. size 0 with integrated PROFIBUS-DP Interface
®
31.. size 0/DP inverter is already standard equipped with a PROFIBUS-DP interface. This allows the inverter to be controlled and parameters set via PROFIBUS-DP in the same
way as the larger unit sizes with the option FFP 31.
®
MOVITRAC
3 1.. and PROFIBUS
The inverter unit profile for PROFIBUS mode, i.e. the way the invert er ope ra tes and responds when
in PROFIBUS mode, is independent of the type of fieldbus, and thus consistent for all fieldbus
types. This allows the user to develop his drive applications independent of a particular fieldbus or
change to another bus system, e.g. the open standardized INTERBUS-S (FFI 11A option) sensor/
actuator bus.
6
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
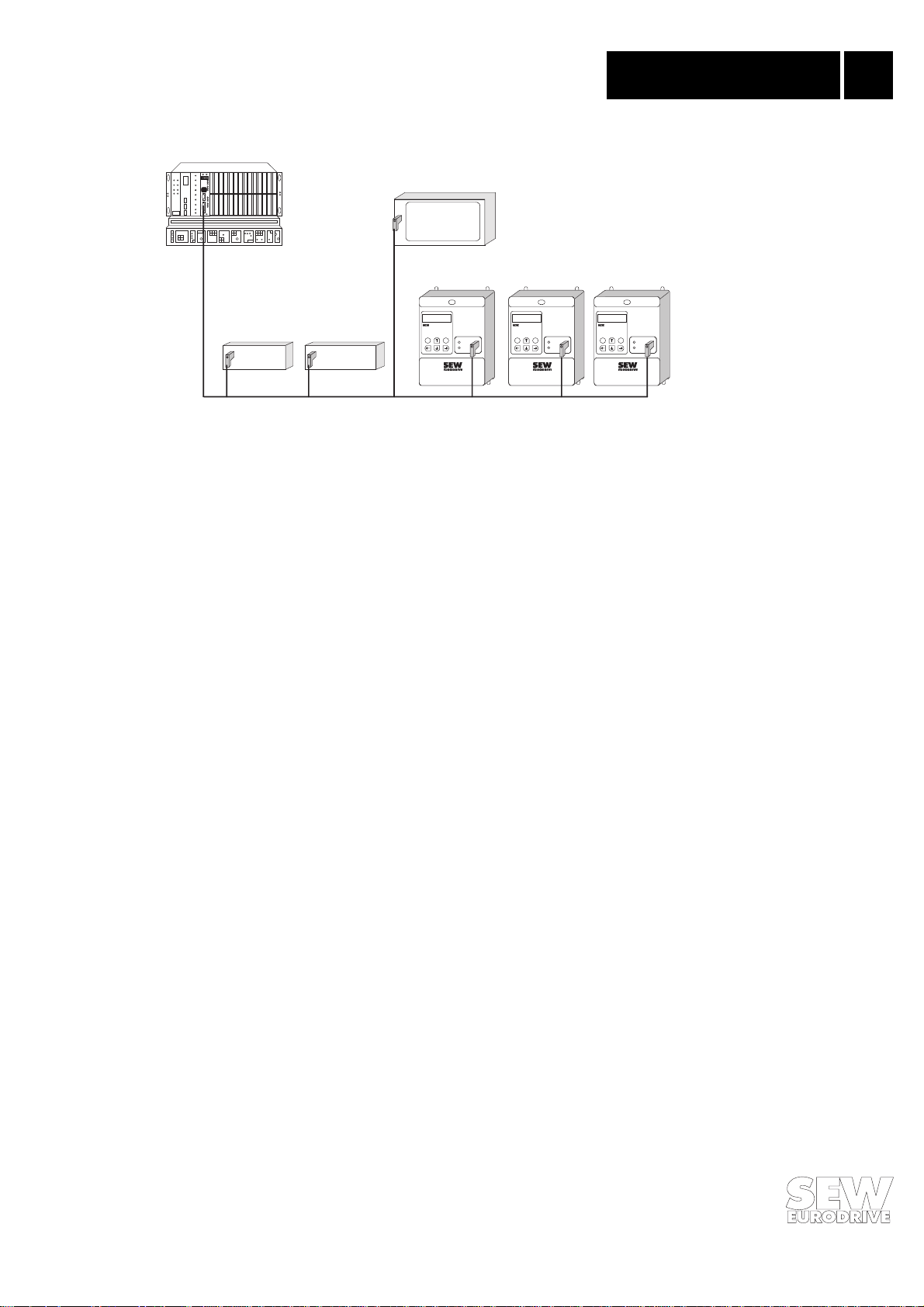
Controller
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Introduction 1
Visualization
PROFIBUS-FMS masterPROFIBUS-DP master
Frequency inverter
®
Fieldbus
MOVITRAC
RUN
BUS
FAULT
00942AEN
Digital I/O
Analog I/O
Fig. 1: PROFIBUS- DP and/or FMS with MOVITR AC
841
CONTROL MODE
EQ
PROFIBUS-DP/FMS
®
®
Fieldbus
RUN
BUS
FAULT
841
CONTROL MODE
MOVITRAC
EQ
®
Fieldbus
RUN
BUS
FAULT
841
CONTROL MODE
MOVITRAC
EQ
MOVITRAC® 31.. offers digital access to all drive parameters and functions via the PROFIBUS
interface. The inverter is controlled by the high-speed cyclic process data. This process data
channel provides the facility to specify setpoints, such as setpoint speeds, ramp generator times
for acceleration and deceleration etc., as well as various drive functions such as enable, controller
inhibit, stop, rapid stop, etc. to be triggered. This channel can also be used to read back actual
values from the inverter, such as actual speed, current, unit status, error number or reference
messages.
Whereas process data are generally exchanged in cycles, the drive parameters can be read and
written acyclically via the READ and WRITE services or the parameter channel. This exchange of
parameter data enables applicatio ns wh ere all major drive parameters are stor ed i n the higher-level
automation unit to be implemented, thus avoiding manual adjustment of parameters on the
inverter itself, which can be very time-consuming.
The PROFIBUS option pcb is designed so that all fieldbus specific settings, such as the station
address or the default parameters, can be made by the option pcb by means of a hardware switch.
These manual settings enable the inverter to be integrated into the PROFIBUS environment and
switched on in a very short space of time. Parameters can be set fully automatically by the higherlevel PROFIBUS master (parameter download). This forward-looking version offers the benefits of
a shorter commissioning period for the plant as well as simpler documentation of the application
program, as all major drive parameter data can now be recorded directly in the control program.
The use of a fieldbus system in drive technology requires additional monitoring functions, such as
fieldbus timeout or speci al emergenc y stop concep ts. The monito ring funct ions of the MOVITRAC
31.. can be matched to the specific application for which it is to be used. This feature enables you,
for instance, to specify which fault response the inverter should trigger if an error should occur in
the bus. A rapid stop wil l be pr actical for many applic at io ns, but it is also possibl e t o fr eeze the last
setpoints, so that the drive can continue with the last valid setpoints (e.g. conveyor belt). As the
functionality of the control terminals is also ensured when the inverter is operated in the fieldbus
mode, fieldbus-independent emergency stop concepts can still be implemented via the inverter's
terminals.
®
The MOVITRAC
31.. inverter offers numerous diagnostic fa cili ties for commis sioni ng and servicing. For instance, both the setpoints transmitted from the higher-level control unit as well as the
actual values can be checked with the fieldbus monitor in the hand-held keypad. It also provides
you with a lot of additional information on the status of the fieldbus option pcb. The PC software
MC_SHELL offers even mo re convenient diagnosti c facilities in t hat i t provides a detailed display of
the fieldbus and unit s tatus infor matio n as wel l as t he f acil ity to set all the dr ive pa rame ters ( incl uding the fieldbus parameters).
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
®
7

2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly / Installation
Instructions
2 Assembly / Installation Instructions
The following secti on descr ibes t he a ssembly and in stal lation of th e MOVITRAC® 31.. inverters for
the integration in a PROFIBUS network.
For MOVITRAC
option pcb. MOVITRAC
integrated in the basic unit. They only support the DP-option, whereas the FFP 31.. option pcb as
combislave option supports PROFIBUS-DP as well as PROFIBUS-FMS.
2.1 Installing the FFP 3 1.. Option pcb
For size 1-4 the in verte rs ar e conne cted to the PROFIBUS via t he FFP 31 o ption pcb. The opti on pcb
is either supplied separately, so that you can fit yourself or, if specified when ordering an inverter,
with the FFP 31 option pcb already installed inside the unit.
2.1.1 Scope of delivery
Unless the FFP 31 option pc b is al ready installed in th e MOV ITRAC
scope of delivery. The scope of delivery consists of the following components:
– 1 FFP 31 (PROFIBUS FMS/DP) option pcb
– 3 fastening screws
– 1 housing cover
®
31.. size 1-4 the inverter is generally connected to the PROFIBUS via the FFP 31
®
31.. size 0 with PROFIBUS-DP have the PROFIBUS-DP interface already
®
31.. inverter, please che ck t he
2.1.2 Supported inverter types
The FFP 31.. option pcb for connection to a PROFIBUS-FMS/DP system can be operated with
®
MOVITRAC
Option FFP 3 1A: With the inverters MOVITRAC
31.. size 1-4 as follows:
®
31B with service code of component 4 great er
or equal 14 (→ Installation and Operating Instructions MOVITRAC
®
31B
section 4).
Option FFP 3 1C: With all inverters MOVITRAC
To adjust the fieldbus parameters you need a keypad for MOVITRAC
®
31C size 1-4.
®
31.. and/or the current PC
program MC_SHELL !
8
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
Assembly / Installation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Instructions
2.1.3 Assembly instructions
The FFP 31.. must only be installed by electronic equipment specialists, observing the following
ESD protection measures:
• Before touching the pcb, make sure you have taken appropriate e.s.d. measures (wrist strap,
conductive shoes etc.)
• Earth the units and work bench.
• Store the option pcb in its original packaging and only take it out shortly before installation.
• Hold the option pcb by its edge and do not touch unnecessarily.
Procedure for Fitting the Option PCB:
1. Ensure that the enti re inverter system is vol tage-free. Switch off t he mai ns po wer and, if appli-
cable, the external 24 V supply.
2. Take off the housing cover after removing the three recessed head screws.
3. Remove the right upper option pcb or the system EPROM pcb after undoing the screws.
(→ see Fig. 2).
4. Fit the FFP 31 option pcb and fasten with three screws.
5. Remove cover strip above the option pcb slot from the housing cover.
6. Refit the housing cover and secure with the three recessed head screws.
7. Push on new cover for the PROFIBUS option pcb slot.
The FFP 31 option pcb is now completely fitted.
2
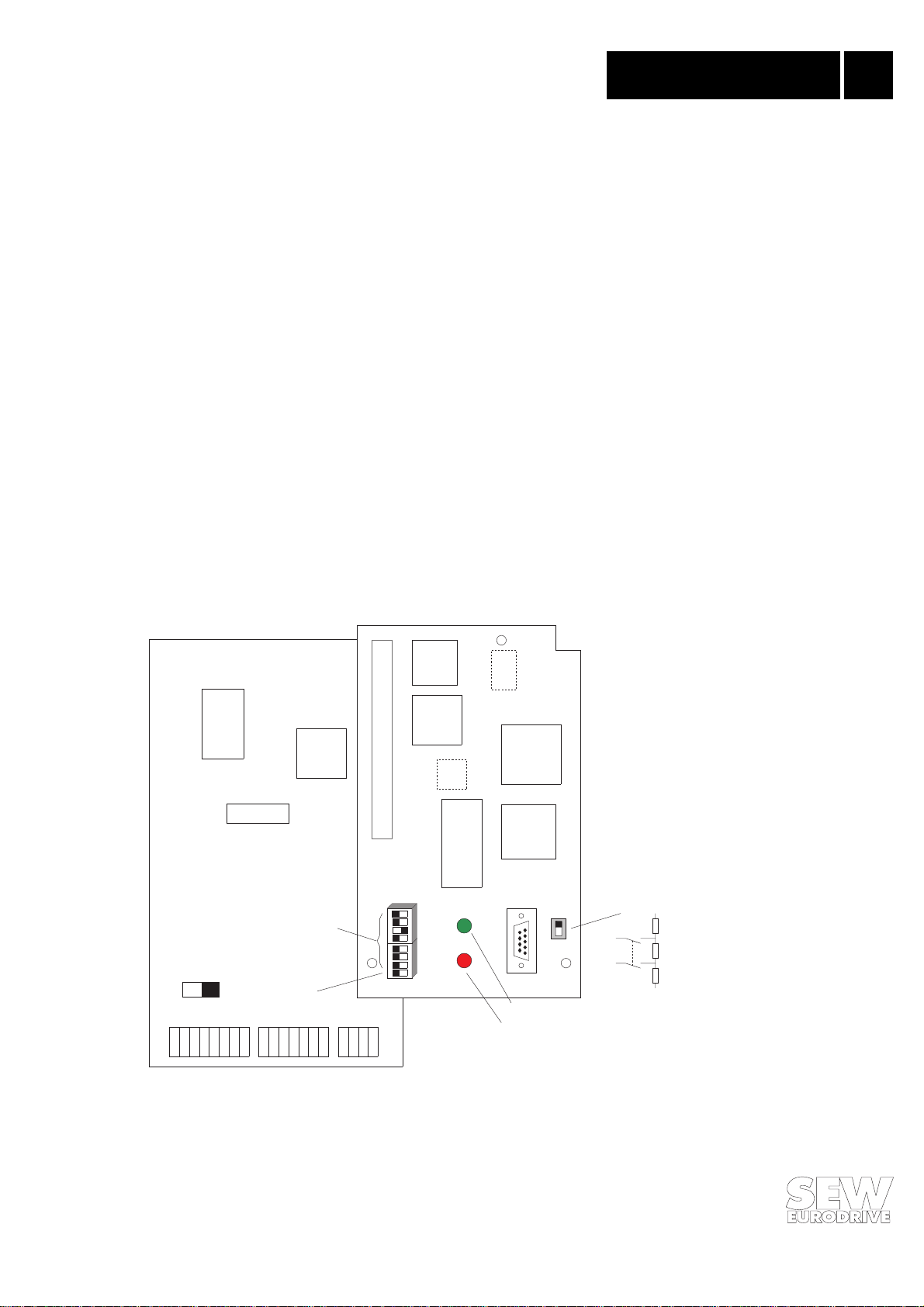
MOVITRAC 31.. control pcb
®
Address
S1
X2: X3: X14:
Bus parameter
X20:
S2
EPROM
DPRAM
H1
H2
Flash EPROM
LED red:
Processor
SPC
X15:
LED green:
BUS FAULT
S1
on
off
Bus termination
RUN
Fig. 2: The FFP 31 option
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
00301BEN
9
2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly / Installation
Instructions
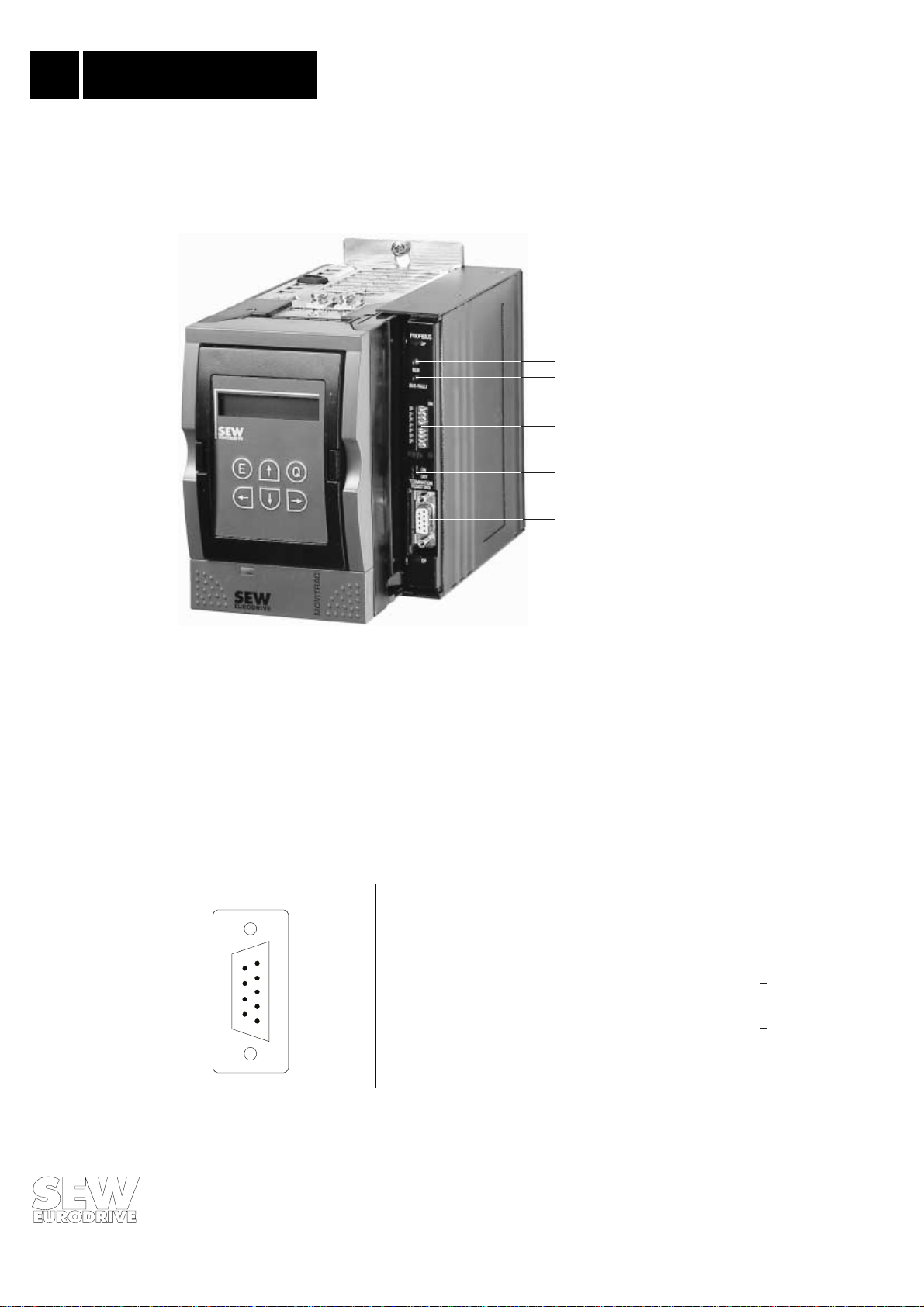
2.2 Installation of the MOVITRAC
The size 0 inverters (MOVITRAC
®
®
3 1.. size 0/DP
31.. size 0/DP) have the PROFIBUS-DP interface already inte-
grated in the basic unit. They only support the DP-option! Fig. 3 shows the general design of the
®
MOVITRAC
31.. size 0/DP.
1 LED green: RUN
2 LED red: BUS FAULT
1
2
3 DIP switch for setting of the
station address
4 DIP switch for connecting/
3
disconnecting the bus
terminating resistor
5 9-pin type D-socket for the
4
5
bus connection
Fig. 3: Unit with PROFIBUS-DP interface and option FBG 31
00924AXX
2.3 Pin Assignment
®
The MOVITRAC
31.. frequency inve rt er i s c onne ct ed t o t he PROFIBUS network via a 9 -pi n t yp e D
connector in accordance with EN 50170 V2 / DIN 19245 Part 3. Connection to the T bus is with an
appropriately designed connector or a bus terminal. Fig. 4 shows the pin assignment. As the bus
terminating resistors on the option pcb can be connected, it is not necessary to use a type D
connector with integrated terminating resistors.
9-pin type D
connector
12345
6
7
8
9
Pin no. Signal RS-485
1:
2:
3
:
4:
5:
6:
7:
8
:
9:
Connector
housing
-
-
RxD / TxD-P
CTNR-P
DGND
VP
-
RxD / TxD-N
DGND
Shield of the twisted two-wire cable
not assigned
not assigned
receive/send data P
repeater control signal (TTL)
data reference potential (M5V)
supply voltage plus (P5V)
not assigned
receive/send data N
data reference potential (M5V)
reference
B/A/B
C/C
A
Fig. 4: Assignment of the 9 pin type D connector to EN 50170 V2 / DIN 19245 Part 3
10
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
00302AEN

Assembly / Installation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Instructions
The MOVITRAC® 31.. frequency inverter is connected to the PROFIBUS system via a twisted,
screened two-wire cable. The connection of the two-wire cable to the PROFIBUS connector is via
pin 8 (A/A
A/A
via the bus will not be possible.
Via pin 4 (CNTR-P) the PROFIBUS option pcb supplies a TTL control signal for a repeater (reference = pin 9).
2.4 Screening and Laying of the Bus Cables
The FFP 31 option pcb supports the RS-485 transmission technology and requires as a physical
medium a screened, two-wire twisted-pair cable (cable type A) specified for PROFIBUS in accordance with EN 50170 V2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3 (→ Appendix).
Technically correct screening of the bus cable absorbs the electrical interference that can occur in
an industrial environment. You will achieve the best screening results if you adopt the following
measures:
• Hand-tighten the fixing screws of plugs, modules and equipotential bonding conductors.
• Only use plugs with metal or metal-plated housings.
• Connect the screening in the plug over as large an area as possible.
• Connect the screening at both ends of the bus cable
• Do not lay signal an d bus c ables paral lel to power cables (motor l eads), but wherever possibl e in
separate cable conduits.
• In an industrial environment use metallic, earthed cable trays.
• Run signal cables and the associated equipotential bonding conductor as close as possible to
each other, using the shortest route.
• Avoid extending bus cables through the use of connectors.
• Run the bus cables close to existing earthed surfaces.
) and pin 3 (B/B). These two contacts are used for communication. The RS-485 signals
and B/B must be contacted the same on all PROFIBUS stations, as otherwise communication
2
Important!
In the event of fluctuations in the earth potential, a circulating current may flow through any
screening which may be connected at both ends and connected to the earth potential (PE). In this
case, ensure there is adequate equipotential bonding in accordance with the relevant VDE provisions.
2.5 Bus Termination
®
If the MOVITRAC
connection to the PROFIBUS network, as a rule, is not via a T bus with an incoming and outgoing
PROFIBUS cable but dir ectly with only on e PROFIBUS cab le. To avoid in terf erence s on th e bus s ystem caused by reflections etc., the PROFIBUS segment must be terminated with bus terminating
resistors on the physically first and last stations (→ Fig. 5).
31.. frequency inverter is at the beginning or the end of a PROFIBUS segment,
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
11
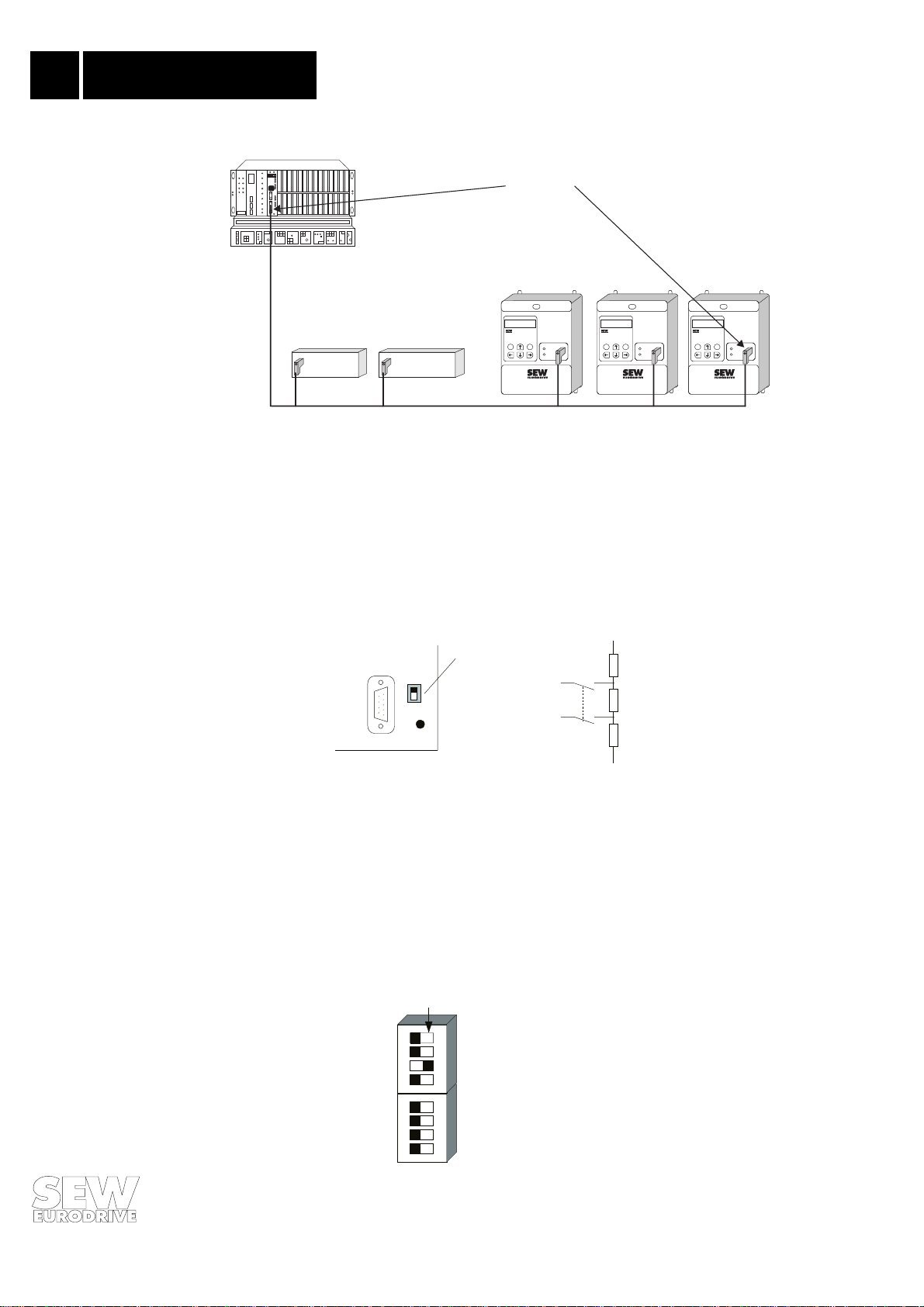
2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly / Installation
Instructions
Bus termination
PROFIBUS-DP master
®
Fieldbus
MOVITRAC
RUN
BUS
FAULT
Digital I/O
Analog I/O
841
Fieldbus
CONTROL MODE
EQ
®
841
CONTROL MODE
MOVITRAC
RUN
BUS
FAULT
EQ
®
Fieldbus
RUN
BUS
FAULT
841
CONTROL MODE
MOVITRAC
EQ
PROFIBUS-DP/FMS
00943AEN
Fig. 5: Bus terminat ion at the beginning and end of a PROFIBUS segment
As the bus terminating resistors can be connected on the FFP 31 of the frequency inverter, it is not
necessary to use a type D connector with integrated terminating resistors. With the appropriate
DIP switch on the option pcb (→ Fig. 6) set to the “on” position the bus terminating resistors (in
accordance with EN 50170 V2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3) can be connected.
The bus termination for cable type A is implemented in accordance with EN 5170 V2 /DIN E 19245
Part 3.
VP
Bus terminated
on
on = connected
off = not connected
off
on
off
R = 390 Ohm
u
R = 220 Ohm
t
R = 390 Ohm
d
DGND
00303AEN
Fig. 6: Activating the bus terminating resistors
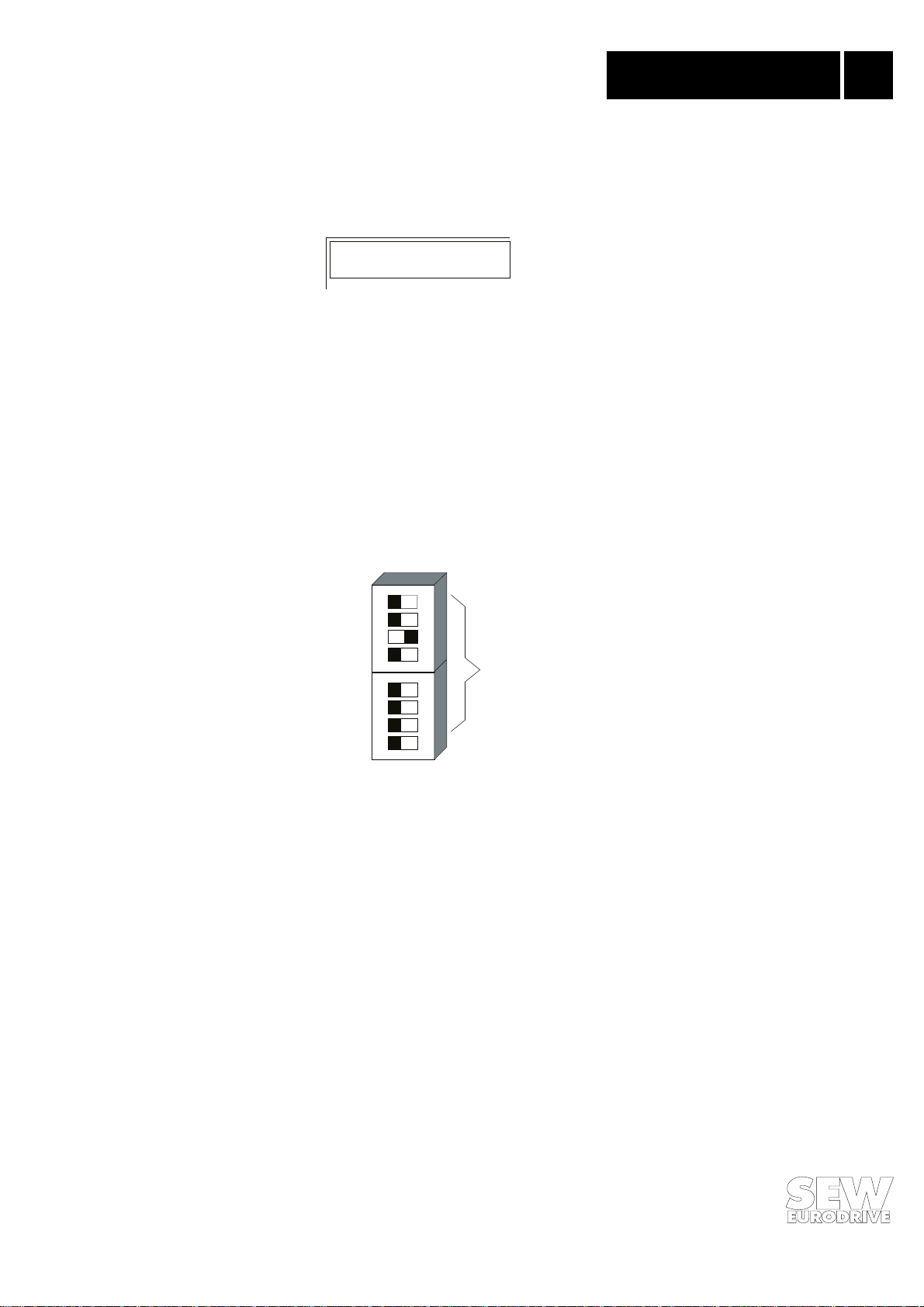
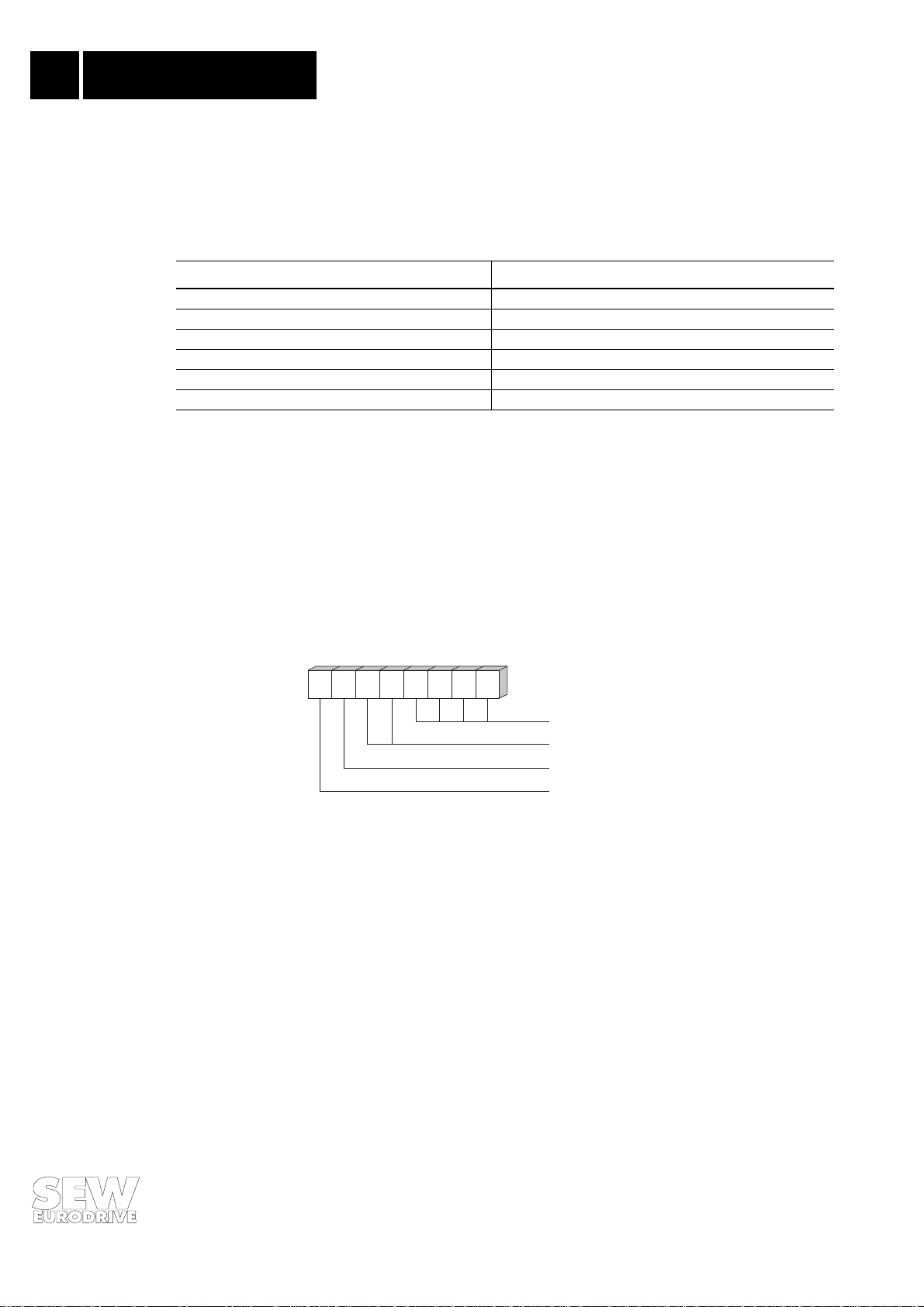
2.6 Setting the Station Address
The PROFIBUS station address i s set with the DIP switche s on the opti on pcb. PRO FIBUS suppor ts
the address range from 0 - 125. The address 126 is reserved for PROFIBUS-DP and is for setting
®
the address via the bus interface. This feature is, however, not supported by the MOVITRAC
31...
The address 127 is reserved for the broadcast service. Fig. 7 shows how the station address is set
with the DIP switches.
Significance on
112244
33
Fig. 7: Setting the PROFIBUS station addre ss
OPENOPEN
Significance 1:
Significance 2:
Significance 4:
Significance 8:
Significance 16:
Significance 32:
Significance 64:
x 0 =
0
x 0 =
+ 0
x 1 =
+ 4
x 0 =
+ 0
x 0 =
+ 0
x 0 =
+ 0
x 0 =
+ 0
________
Address 4 = factory setting
00304BEN
12
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
Assembly / Installation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Instructions
It is not possible to chang e the PROFIBUS st ation address via th e DIP swit ches whi le the inverter is
running. If the station address is changed, the new station address will only be effective after the
inverter has been switched off (including the 24 V supply) and then switched on again. The station
address set on the frequency inverter can be displayed in the fieldbus monitor parameter P073
Fieldbus Address (see Fig. 7).
073 4
FIELDBUS ADDRESS
2
Fig. 8: Displaying the current PROFIBUS stat ion address
01156AEN
2.7 Setting the Bus Parameters (not for MOVITRAC® 3 1.., size 0)
The setting of the protocol option FMS/DP is not possible for MOVITRAC
®
31.. size 0/DP, as the
unit only supports PROFIBUS-DP. The corresponding DIP switch below the address setting is not
assigned.
The default value for the bus parameters depends on the protocol option used. For straight
PROFIBUS-DP mode the DIP switch must be set to DP. This will activate the default bus parameters (in particular the min. TSDR) in accordance with EN 50170 V2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3 for timeoptimized DP mode. For mixed mode (FMS/DP) or straight FMS mode the DIP switch must be set
to FMS (→ Fig. 9).
Address
112244
Example: FMS/DP active
FMS DP
Default bus parameter for
- FMS mode or
- FMS/DP mixed mode
OPENOPEN
33
Default bus parameter for
straight DP PROFIBUS mode
Fig. 9: Setting the default-bus parame ter s to DIN 1924 5
00944AEN
This switch only serves to select the default bus parameters. Independent of the setting of this
switch the inverter at any time supports simultaneous use of the PROFIBUS protocol options FMS
and DP (Combislave functionality).
Any change to this DIP switch setting will only become effective after the inverter has been
switched off (including the 24 V supply) and switched on again.
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
13
2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly / Installation
Instructions
2.8 Display Elements
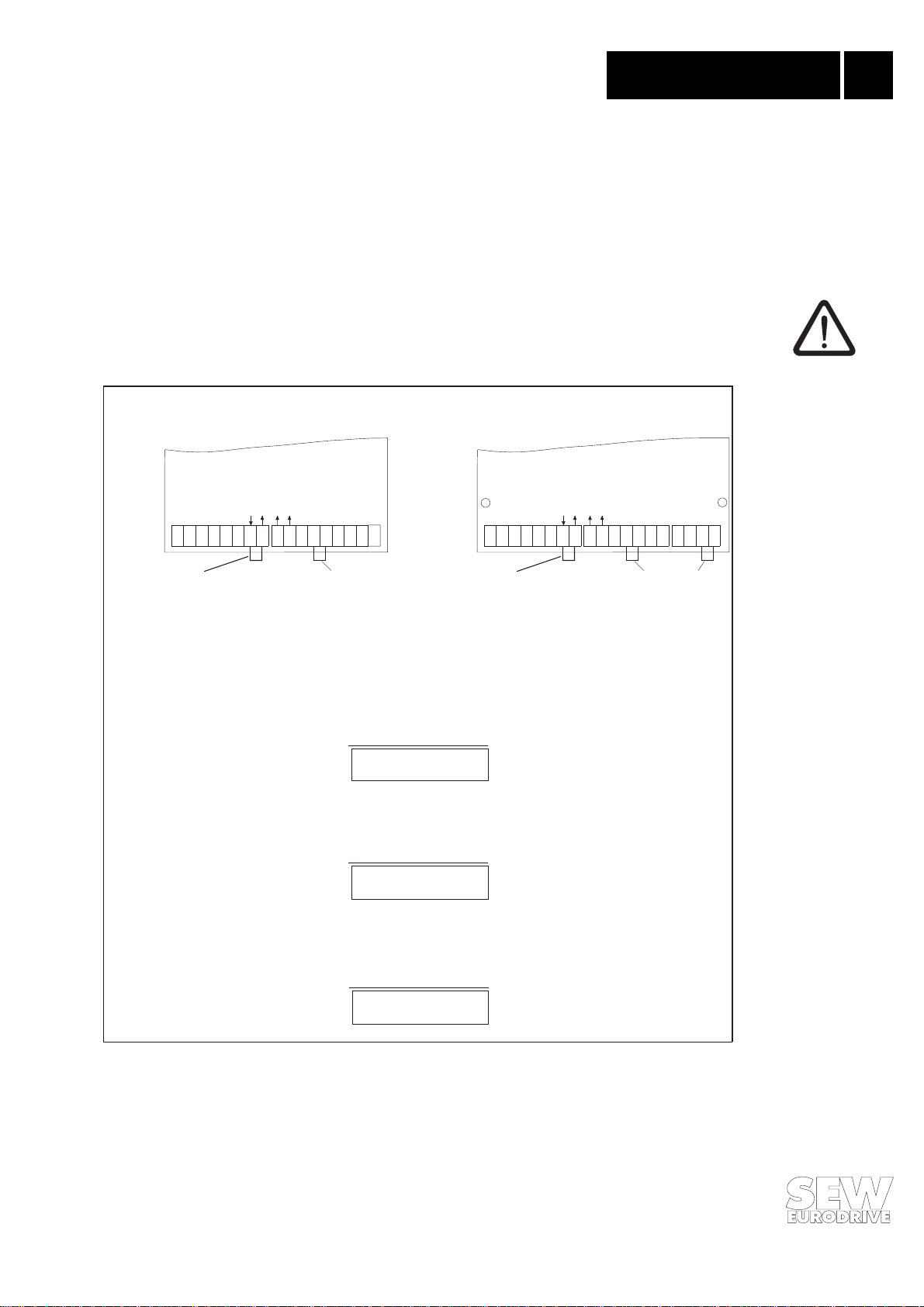
LED Green RUN LED Red BUS FAULT Meaning
Flashing at approx. 3 Hz Off Inverter is in initialization phase (only occurs immediately after switching on or
On Fla shing at approx. 0.5 Hz Co nf ig ure d st ation address is not within the permitte d range (0...125) ⇒ set
On Irrelevant Normal operation – the unit is working correctly
On On DP mode:
On Of f D P m ode:
On / Flickering Off The inverte r is parameterized via P ROFIBUS-DP or FMS
Off On Hardware fault on the bus connection
Flashing at approx. 1 Hz Flashing at approx. 1 Hz Hardware fault on the bus conn ection
resetting inverter)
correct station address and switch the unit on again.
a) During commissioning / accelerating: The inverter has not yet been set to
data exchange mode by the DP ma ster.
b) The timeout period has elapsed without the inverter being addressed by the
DP master.
FMS mode:
There is no acti ve FMS-connecti on between FMS m aster and inverter.
Mixed mode FMS/DP:
Combination of the above.
The inverter is set to data exchange mode.
FMS mode:
There is an active FMS-connecti on between FMS mast er and inverter.
Mixed mode FMS/DP:
Combination of the above.
(read/write access).
*)
*)
*)
*)
*)
*)
*) not for MOVITRAC® 31... size 0
The option pcb has two LEDs for status and fault indication of the option pcb and the connected
bus system (Fig. 2). The table shows the meaning of the visual signals of these LEDs. While the
green LED “RUN” indicates the operational status of the option pcb, the red LED “BUS FAULT”
indicates the status of the PROFIBUS connection.
2.9 Commissioning the Inverter
After installing the PROFIBUS option pcb and setting the station address and bus parameters
®
(using the DIP switches), the MOVITRAC
31.. inverter can be immediately parameterized via the
fieldbus system without any further manual intervention. This means, for example, that after
switching on the inverter, all drive parameters can be downloaded directly from the higher-level
control via the PROFIBUS system.
To control the in verter via PROFIBUS, however, it must f ir st be switched to the appropriate contro l
mode. This is possible using the parameter P841 Cont rol Mode . The factory setting for this parameter is STANDARD (control and se tpo int pr ocess ing vi a inpu t ter minals ). Usi ng the p aramet er P841
Control Mode = FIELDBUS, the inverter is programmed to accept setpoints from the fieldbus.
®
MOVITRAC
31.. now responds to process data sent from the higher-level control.
The activation of the fieldbus control mode is signalled to the higher-level control by the Fieldbus
Mode Active bit in the status word.
14
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
Assembly / Installation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Instructions
For safety reasons the inverter must also be enabled on the terminal side as well to permit control
via the fieldbus system. The terminals are therefore to be wired or programmed in such a way that
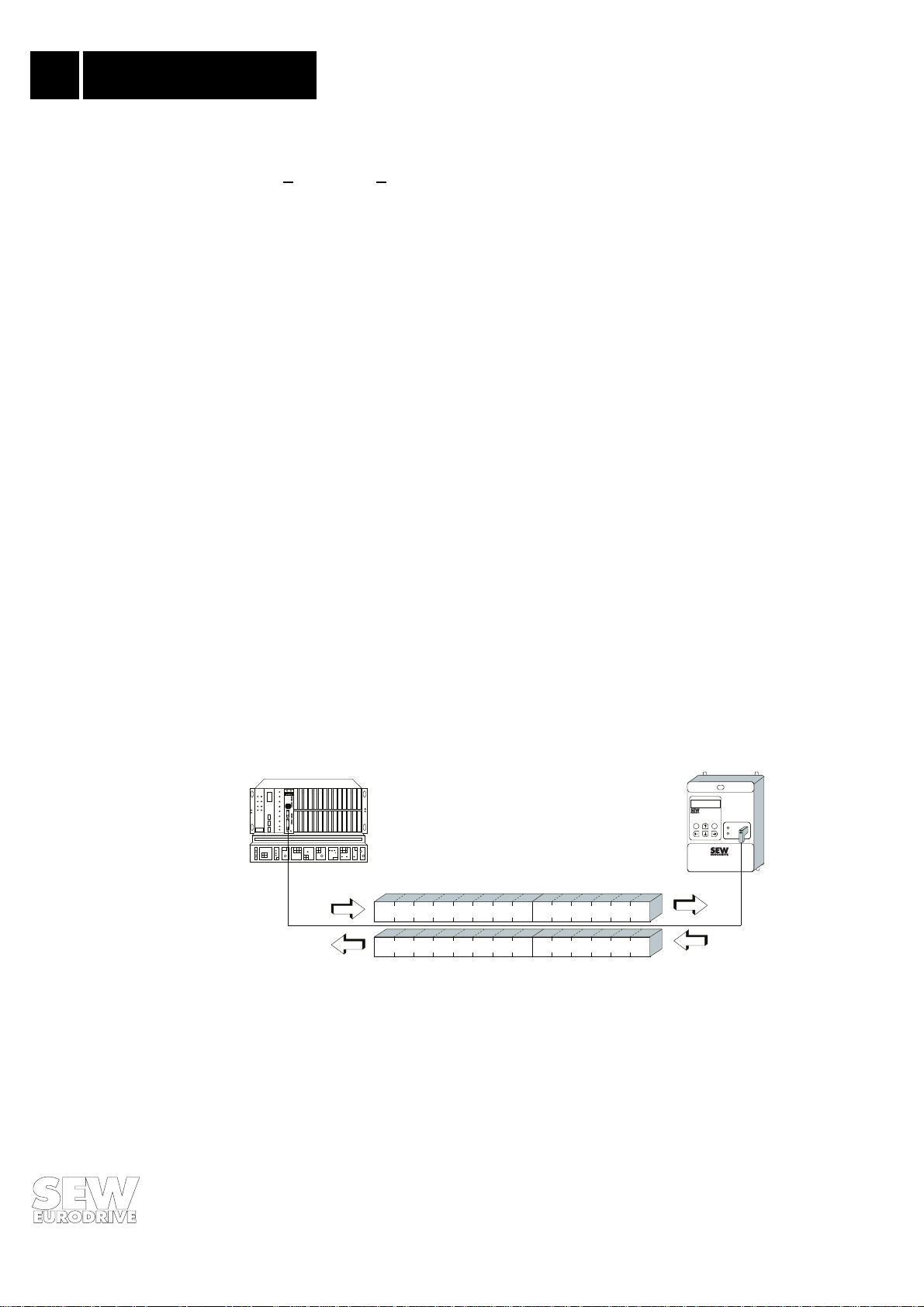
the inverter i s enab led v ia th e i nput t ermina ls. The ea siest way of enabl ing t he inver ter o n t he ter minal side is, for example, to connect input terminal 41 (CW/STOP function) to a +24 V signal and
program input terminals 42 and 43 to NO FUNCTION. Fig. 10 shows an example of the commissioning procedure for the MOVITRAC
Attention!
Carry out commissioning with mains voltage switched off and with the external 24 V-supply only.
This prevents the drive from starting to move automatically during reprogramming. Switch on
mains voltage only after completed setting of parameters.
1. ENABLE the inverter on the terminal side
Apply a +24 V signal on input terminal 41 (Function CW/STOP) (e.g. set jumper as shown below).
1/0 CW/STOP
no function
X2 X3
31
35065
34
+24 V
41
42
44
40
®
31.. inverter with a fieldbus interface.
Size 0 Size 1 - 4
no function
no function
no function
43
47
60
X2 X3 X14
61
62
48
30
49
31
35065
34
+24 V
44
40
1/0 CW/STOP
41
42
43
47
60
61
62
48
30
49
60
30
2
Use this jumper to enable the
inverter via terminal side
Jumper installed when supplied
Use this jumper to enable the
inverter via terminal side
Jumper installed when supplied
2. For setting inverter parameter only switch on 24 V supply (no mains voltage!)
3 . Control mode = fieldbus
Set control and setpoint processing of the drive inverter to FIELDBUS in parameter P841.
841 FIELDBUS
CONTROL MODE
4. Input terminal 42 = NO FUNCTION:
Program functionality of input terminal 42 to NO FUNCTION in parameter P600.
600 NO FUNCT.
TERMINAL 42
5. Input terminal 43 = NO FUNCTION:
Program functionality of input terminal 43 to NO FUNCTION in parameter P601.
601 NO FUNCT.
TERMINAL 43
Fig. 10: Commissioning the inverter
For more information on commi ssionin g an d contr olling the MOVITRAC® 31.. inverter plea se ref er
to the Fieldbus Unit Profile User Manual documentation.
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
00312BEN
15
3
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The PROFIBUS-DP
Interface
3 The PROFIBUS-DP Interface
PROFIBUS-DP (Decentralized P erip hery) is t he spee d-opti mized PROFIBUS o ption desig ned in particular for fast data exchange at the sensor/actuator level. DP is used by central automation systems (e.g. programmable lo gi c controllers) to communi cat e wi th de ce ntralized peripherals such as
sensors and actuators, among them inverters, via a fast serial link. Data exchange with these
decentralized units is mainly cyclic. The central control system sends new process output data to
all slaves in a message and reads in all process input data from the slaves (sensors, actuators) in
the same message.
The considerable incr ease in speed of PROFIBUS-D P compar ed to PROF IBUS-FMS is pr imari ly due
to the fact that DP has no application layer (layer 7) and I/O data are transferred between the master and a slave in a single message cycle. A maximum of 246 bytes of I/O data can be transferred
between the DP master and a DP slave. Normally, however, shorter data blocks (of up to 32 bytes)
are used to increase effici ency still further. Consequently, the e xchange of data via PROFIBUS-DP
can be seen as a straight process communications procedure.
To enable the DP master to communicate with the DP slaves, it has to be given some important
information regarding the DP interface o f the connected slave. In add ition to data re lating to the
type and amount of I/O data to be transferred, it also requires additional information regarding the
identity of each DP slave.
3 .1 Configuration of the DP Interface
To be able to define the type and amount of I/O data to be transferred, the DP master has to pass a
®
certain configurat ion to the inve rter. The MOVITRAC
31.. inverter can g enerall y be operat ed usi ng
six different configurations. You have the option of only controlling the inverter by exchanging
process data, or, in addition to controlling the inverter via process data, of reading or writing
parameters using an additional para meter channel at the s ame time.
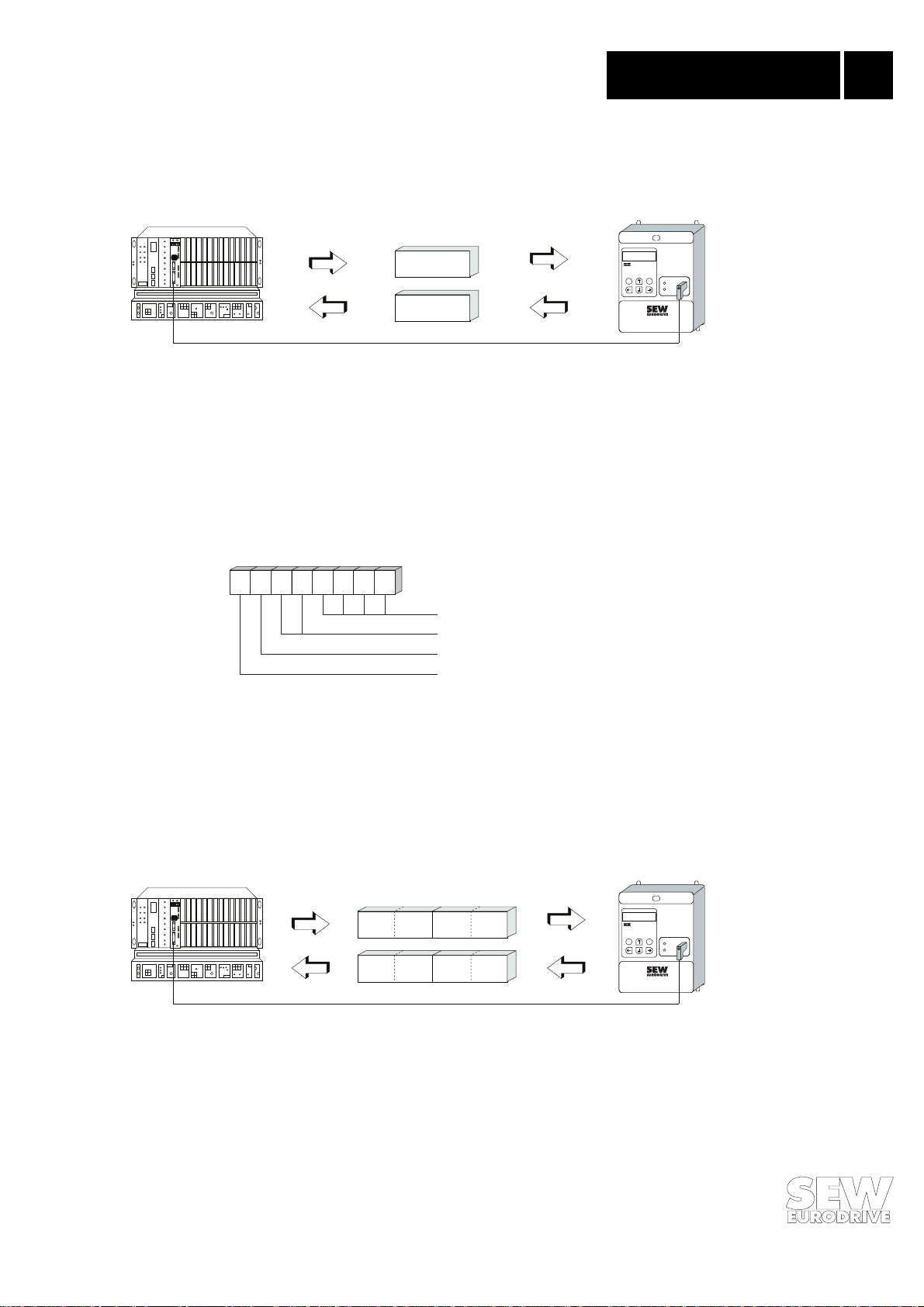
Fig. 11 provides a schematic representation of the exchange of data between the programmable
®
automation unit (DP master) and the MOVITRAC
31.. inverter (DP slave) using process data and
parameter channels.
841 FIELDBUS
Fig. 11: Communication via PROFIBUS-DP
Parameter channel
Parameter channel
ControlMode
EQ
Process data channel
Process data channel
MOVITRAC
RUN
BUS
FAULT
00945AEN
16
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface

The PROFIBUS-DP
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Interface
When commissioning the DP master, you have to specify which configuration is going to be used
to operate the inverter. This configuration is then transferred to the inverter when the DP master is
started up (with the DDLM_Chk_Cfg service). The inverter checks the transferred configuration
data for plausibility before going into data transfer mode. The configuration data are coded in
accordance with EN 50170 V2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3 and are discussed in the following section.
3 .1.1 Description of the Configuration Data
The format of the configuration data is described in EN 50170 V2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3. Fig. 12
shows the Cfg_Data identifier byte which, according to EN 50170 V2 / DIN E 19245 Part 3, is used
to describe which I/O data are to be transferred between master and slave using PROFIBUS-DP.
In addition to specifying the data length in bits 0-3, you have to use bits 4 and 5 to define whether
the transfer i nvo lves input and/or output data. Bit 6 i ndicates whether the data are to be t ransferred
in byte or word format and bit 7 is used to specify the consistency with which the data are to be
handled by the bus system. For example , position values of th e MOVITRAC
transferred in a consistent manner, i.e. it has to be ensured that contiguous data are also transferred together a nd not, for examp le, tha t the le ast si gnifi cant part of the po siti on is tr ansfe rred one
bus cycle ahead of the more significant part.
®
31.. inverter should be
3
LSBMSB
7
6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Data length
0000 = 1 byte/word
1111 = 16 bytes/word
Input/output
00 = special identifier formats
01 = input
10 = output
11 = input/output
Format
0 byte structure
1 word structure
Consistency over
0 byte or word
1 complete length
Fig. 12: Format of identifier byte Cfg_Data according to EN 50170 V2 / DI N E 19245 Part 3
00949AEN
The MOVITRAC® 31.. inverter supports six different process data configurations. To control the
inverter, you can define the amount of process data to be transferred using 1, 2 or 3 process data
words and also enable/disable a parameter channel for read/write access to all drive parameters.
This produces the following process data configurations:
1 process data word (1 PD)
2 process data words (2 PD)
3 process data words (3 PD)
1 process data word + parameter channel (1 PD + Param)
2 process data words + parameter channel (2 PD + Param)
3 process data words + parameter channel (3 PD + Param)
This configuration is set up solely via the DP master as the bus system is started up, so that no
additional manual parameterizing of the inverter is required. This automatic configuring mechanism enables download applications to be implemented where the inverter can be completely
controlled and parameterized via the bus system.
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
17
3
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The PROFIBUS-DP
Interface
To set these process data configurations, the inverter supports a number of different codes for the
Cfg_Data identifier byte. The process data configuration is allocated based on the amount of input
and output data. A valid DP configuration sent from the DP master to the inverter must conform to
the following conventions:
– The amount of input or output data must correspond to the contents of the following table.
– The number of input bytes and output bytes must be the same.
Length of the input/output data Meaning
2 bytes or 1 word 1 process data word
4 bytes or 2 words 2 process data words
6 bytes or 3 words 3 process data words
10 bytes or 5 words 1 process data words + parameter channel
12 bytes or 6 words 2 process data words + parameter channel
14 bytes or 7 words 3 process data words + parameter channel
The inverter interpr ets the length of the DP configu rati on passed to it as sho wn in the table. The si x
different process data configurations for PROFIBUS-DP are described below.
3 .1.2 Configuring for 1 Process Data Word (1 PD)
®
Control of the MOVITRAC
31.. inverter using only one process data word requires, for example,
that the Cfg_Data identifier byte is coded as shown in Fig. 13. This code must be sent to the
inverter by the DP master when PROFIBUS-DP is started so that the DP master and DP slave can
exchange a process data word.
Cfg_Data identifier byte
LSBMSB
1
1 1 1 0 0 0 0
Fig. 13: Configuration data example for setting 1 input/output word (1 PD)
= F0 = 240
hex dez
Data length: 1 word
Input/output
Word structure
Consistency over the complete length
01164AEN
18
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
The PROFIBUS-DP
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Interface
3
Fig. 14 shows the communication between the automation unit (DP master) and the MOVITRAC
31.. frequency inver ter via on e p rocess data word on ly. Th is con figur atio n coul d be us ed, fo r e xample, to control the inverter with control word 1 and status word 1 (see SEW documentation
bus Unit Profile User Manual
Fig. 14: Control of the inverter via 1 process data word
).
PD1
PD1
PD1
PD1
841
Feldbus
841
Fieldbus
STEUERMODE
CONTROL MODE
EQ
EQ
Field-
®
®
MOVITRAC
MOVITRAC
RUN
RUN
BUS
BUS
FAULT
FAULT
01165AEN
3 .1.3 Configuring for 2 Process Data Words (2 PD)
Control of the MOVITRAC
®
31.. inverter using two process data words requires that the Cfg_Data
identifier byte is coded as shown in Fig. 15. This code must be sent to the inverter by the DP master when PROFIBUS-DP is started so that the DP master and DP slave can exchange two process
data words.
Cfg_Data identifier byte
LSBMSB
1
1 1 1 0 0 0 1
= F1 = 241
hex dez
Data length: 2 words
Input/output
Word structure
Consistency over the complete length
®
Fig. 15: Configurat ion data example for settin g 2 input/output words (2PD)
01168A
Fig. 16 shows the communication between the automation unit (DP master) and the MOVITRAC
31.. frequency inverter via two process data words. The higher-level control system could use this
configuration, for example, to send the process output data
and read in the process input da ta
Fieldbus Unit Profile User Manual
Status Word 1
).
PD1
PD1
Fig. 16: Control of the inverter via 2 process data words
Speed Actual Va lu e
and
PD2
PD2
Control Word 1
(see SEW documentation
Speed Setpoint
and
841
Fieldbus
CONTROL MODE
EQ
®
MOVITRAC
RUN
BUS
FAULT
01166AEN
®
MOVITRAC® 31.. PROFIBUS Fieldbus Interface
19
 Loading...
Loading...