Page 1
Gearmotors \ Industrial Gear U nits \ Dri ve Ele ctroni cs \ Dr ive Aut omat ion \ Servi ces
DFE32B PROFINET IO
Fieldbus Interface
Edition 09/2007
11614226 / EN
M
anual
Page 2

SEW-EURODRIVE – Driving the world
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Page 3

1 General Notes.........................................................................................................6
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.1 Structure of the safety notes .......................................................................... 6
1.2 Right to claim under warranty ........................................................................ 6
1.3 Exclusion of liability ........................................................................................ 6
2 Safety Notes ...................................... ................................................................. ... . 7
2.1 Other applicable documentation .................................................................... 7
2.2 General safety notes for bus systems............................................................ 7
2.3 Safety functions ............................................................................................. 7
2.4 Hoist applications ........................................................................................... 7
2.5 Product names and trademarks ..................................................................... 7
2.6 Waste disposal............................................................................................... 8
3 Introduction ............................................................................................................ 9
3.1 Content of the manual.................................................................................... 9
3.2 Additional documentation............................................................................... 9
3.3 Features ......................................................................................................... 9
3.3.1 MOVIDRIVE
®
B, MOVITRAC®B and PROFINET ............................. 9
3.3.2 Access to all information ................................................................... 10
3.3.3 Monitoring functions .......................................................................... 10
3.3.4 Diagnostics ....................................................................................... 10
3.3.5 Fieldbus monitor ............................................................................... 10
4 Assembly and Installation Notes........................................................................ 11
®
4.1 Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE
MDX61B ..................... 11
4.1.1 Before you begin ............................................................................... 12
4.1.2 Basic procedure for installing and removing an option card
(MDX61B, BG 1 - 6) .......................................................................... 13
®
4.2 Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE
4.2.1 Connecting a system bus (SBus 1) between a MOVITRAC
B ................................. 14
®
B
and the DFE32B option .................................................................... 14
4.2.2 Connecting system bus (SBus 1) between several
®
MOVITRAC
B units ......................................................................... 15
4.3 Installing the DFE32B/UOH11B gateway..................................................... 17
4.4 Connection and terminal description DFE32B option .................................. 18
4.5 Pin assignment ............................................................................................ 19
4.6 Shielding and routing bus cables ................................................................. 20
4.7 TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks......................................................... 21
4.8 Setting the IP address parameters via DCP ................................................ 23
4.9 Procedure after device replacement ............................................................ 24
4.9.1 Device replacement MOVIDRIVE
4.9.2 Device replacement MOVITRAC
®
B ............................................... 24
®
B / gateway ................................ 24
4.10 Operating display DFE32B option................................................................ 25
4.10.1 PROFINET-LEDs ............................................................................. 25
4.10.2 Gateway LED ................................................................................... 26
5 Project Planning with PROFINET............................ ...... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .. 28
5.1 Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller ........................................ 28
5.1.1 Assigning the PROFINET device name ............................................ 29
5.1.2 Project planning for the PROFINET interface for MOVIDRIVE
5.1.3 Project planning for MOVITRAC
®
B or gateway with
DFE32B option ................................................................................. 37
5.1.4 Project planning for the PROFINET interface for MOVITRAC
®
B ... 31
®
B .... 38
5.2 Auto setup for gateway operation ................................................................ 44
5.3 Setting the MOVIDRIVE
®
MDX61B drive inverter ....................................... 46
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
3
Page 4

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.4 Setting the MOVITRAC® B frequency inverter............................................. 47
5.5 Startup procedure for MDX61B with DFE32B option ................................... 48
5.5.1 Preliminary work ............................................................................... 48
5.5.2 Starting up MOVIDRIVE
®
B with DC 24 V or AC 400 V ................... 48
5.6 Startup procedure for the DFE32B option as gateway................................. 50
5.6.1 Preliminary work ............................................................................... 50
5.6.2 Starting up units with DC 24 V or AC 400 V ..................................... 51
6 PROFINET Operating Behavior........................................................................... 53
6.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 53
6.2 The integrated Ethernet switch .................................................................... 55
6.3 Process data configuration .......................................................................... 56
6.4 Controlling the MOVIDRIVE
6.4.1 Control example SIMATIC S7 with MOVIDRIVE
6.4.2 PROFINET timeout (MOVIDRIVE
6.4.3 Fieldbus timeout response (MOVIDRIVE
6.5 Controlling the MOVITRAC
6.5.1 Control example for SIMATIC S7 with MOVITRAC
®
MDX61B drive inverter ................................. 57
®
MDX61B) .................................. 58
®
®
B (gateway) frequency inverter...................... 59
®
MDX61B ............. 58
MDX61B) ....................... 58
®
B (gateway) .... 60
6.5.2 SBus timeout .................................................................................... 60
6.5.3 Unit error ........................................................................................... 60
6.5.4 Fieldbus timeout response of the DFE32B in gateway operation ..... 60
6.6 SIMATIC S7 Sample program...................................................................... 61
®
6.7 PROFINET alarms using the example of MOVIDRIVE
B .......................... 62
7 Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47......................................................... 64
7.1 Introducing PROFINET data sets................................................................. 64
7.1.1 Features of the SEW-EURODRIVE PROFINET units ...................... 65
7.2 Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel .......................................... 66
7.2.1 Parameter setting procedure via data set 47 .................................... 67
7.2.2 Controller processing sequence ....................................................... 68
7.2.3 Addressing connected inverters ........................................................ 69
7.2.4 MOVILINK
®
parameter requests ...................................................... 70
7.2.5 PROFIdrive parameter requests ....................................................... 75
7.3 Read or write parameters via data set 47 .................................................... 80
7.3.1 Sample program for SIMATIC S7 ..................................................... 80
7.3.2 Technical data PROFINET for MOVIDRIVE
®
DFE32B .................... 80
7.3.3 Error codes of the PROFINET services ............................................ 81
8 Integrated Web Server.........................................................................................82
8.1 Software requirements ................................................................................. 82
8.2 Security settings........................................................................................... 82
8.3 Homepage layout MOVIDRIVE
®
MDX61B with DFE32B option ................. 82
8.4 Structure of the diagnostics applet............................................................... 83
8.5 Access protection......................................................................................... 87
9 MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio via Ethernet.......................................................... 88
9.1 Overview ...................................................................................................... 88
9.2 Procedure for configuring units .................................................................... 89
9.3 Communication with external units .............................................................. 92
10 Error Diagnostics.............................. ...................................................................94
10.1 Diagnostic procedures ................................................................................. 94
10.2 Error list in gateway operation...................................................................... 97
4
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 5

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
11 Technical Data...................................................................................................... 98
11.1 DFE32B for MOVIDRIVE
gateway housing .......................................................................................... 98
11.2 Dimension DFE32B via UOH11B gateway housing..................................... 99
12 Index.................................................................................................................... 100
®
B, MOVITRAC® B and UOH11B
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
5
Page 6
1
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
General Notes
Structure of the safety notes
1 General Notes
1.1 Structure of the safety notes
The safety notes in this manual are designed as follows:
Symbol SIGNAL WORD
Nature and source of hazard.
Possible consequence(s) if disregarded.
• Measure(s) to avoid the hazard.
Symbol Signal Word Meaning Consequences if
Example:
HAZARD Imminent hazard Severe or fatal injuries
disregarded
WARNING Possible hazardous situation Severe or fatal injuries
General hazard
CAUTION Possible hazardous situation Minor injuries
Specific hazard,
e.g. electric shock
STOP Possible damage to property Damage to the drive system or its environ-
NOTE Useful information or tip.
Simplifies drive system handling
1.2 Right to claim under warranty
A requirement of fault-free operation and fulfillment of any rights to claim under limited
warranty is that you adhere to the information in the documentation. Therefore, read the
manual before you start operating the device!
Make sure that the manual is available to persons responsible for the plant and its operation, as well as to person who work independently on the device. You must also ensure that the documentation is legible.
ment
1.3 Exclusion of liability
You must comply with the information contained in the MOVIDRIVE®- / MOVITRAC
documentation to ensure safe operation and to achieve the specified product characteristics and performance requirements. SEW-EURODRIVE assumes no liability for injury
to persons or damage to equipment or property resulting from non-observance of these
operating instructions. In such cases, any liability for defects is excluded.
6
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
®
Page 7

Other applicable documentation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2 Safety Notes
2.1 Other applicable documentation
• Installation and startup only by trained personnel observing the relevant accident
prevention regulations and the following documents:
– "MOVIDRIVE
– "MOVITRAC
• Read through this manual carefully before you commence installation and startup of
the DFE32B option.
• As a prerequisite to fault-free operation and fulfillment of warranty claims, you must
adhere to the information in the documentation.
2.2 General safety notes for bus systems
This communication system allows you to match the MOVIDRIVE® drive inverter to the
specifics of your application. As with all bus systems, there is a danger of invisible, external (as far as the inverter is concerned) modifications to the parameters which give
rise to changes in the unit behavior. This may result in unexpected (not uncontrolled)
system behavior.
®
MDX60B / 61B operating instructions
®
B" operating instructions
Safety Notes
2
2.3 Safety functions
The MOVIDRIVE® MDX60B/61B and MOVITRAC® B drive inverters may not perform
safety functions without higher-level safety systems. Use higher-level safety systems to
ensure protection of equipment and personnel.
For safety applications, refer to the information in the following publications.
• Safe disconnection for MOVIDRIVE
Use only those components in safety applications that were explicitly designed and delivered for this purpose by SEW-EURODRIVE.
2.4 Hoist applications
MOVIDRIVE® MDX60B/61B and the MOVITRAC® B are not designed for use as a
safety device in hoist applications..
Use monitoring systems or mechanical protection devices as safety equipment to avoid
possible damage to property or injury to people.
2.5 Product names and trademarks
The brands and product names in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks
of the titleholders.
®
/ MOVITRAC® B
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
7
Page 8

2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2.6 Waste disposal
Safety Notes
Waste disposal
Please follow the current national regulations.
Dispose of the following materials separately in accordance with the country-specific
regulations in force, as:
• Electronics scrap
• Plastics
• Sheet metal
• Copper
etc.
8
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 9

3 Introduction
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.1 Content of the manual
This user manual describes
• Install the DFE32B PROFINET IO option card in the MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B drive
inverter.
• Use the DFE32B PROFINET IO option card in the MOVITRAC
and in the UOH11B gateway housing
• Start up the MOVIDRIVE
• Start up the MOVITRAC
• Configuring the PROFINET using GSD files
• Operating MOVITOOLS
• Diagnostics via integrated web server
Introduction
Content of the manual
®
B with the PROFINET fieldbus system
®
B with the PROFINET gateway
®
MotionStudio via PROFINET.
®
B frequency inverter
3
3.2 Additional documentation
For information on how to connect MOVIDRIVE® / MOVITRAC® B straightforwardly and
effectively to the PROFINET IO fieldbus system, you should request the following additional publications about fieldbus technology:
•MOVIDRIVE
•MOVITRAC
The manual for the MOVIDRIVE
manual describes the fieldbus parameters and their coding, as well as explaining the
whole range of various control concepts and application options in the form of brief examples.
The MOVIDRIVE
drive inverter that can be read and written via the several communication interfaces such
as Systembus, RS485 and via the field bus interface.
®
®
B / MOVIDRIVE® B system manual
3.3 Features
With the DFE32B PROFINET IO option and their powerful universal fieldbus interface,
the MOVIDRIVE
low for a connection to higher-level automation systems.
®
Fieldbus Unit Profile manual
®
Fieldbus Unit Profile and MOVITRAC® B system
®
fieldbus unit profile manual provides a list of all parameters of the
MDX61B drive inverter and the MOVITRAC®B frequency inverter al-
3.3.1 MOVIDRIVE
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
®
B, MOVITRAC®B and PROFINET
The behavior of the inverter which forms the basis of PROFINET operation is referred
to as the unit profile. It is independent of any particular fieldbus and is therefore a uniform feature. This feature allows the user to develop fieldbus-independent drive applications. This makes it much easier to change to other bus systems, such as DeviceNet
(option DFD).
9
Page 10

3
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.3.2 Access to all information
Introduction
Features
MOVIDRIVE
and functions via the PROFINET interface. The drive inverter is controlled via fast, cyclic
process data. Via this process data channel, you can enter setpoints such as the setpoint speed, ramp generator time for acceleration/deceleration, etc. as well as trigger
various drive functions such as enable, control inhibit, normal stop, rapid stop, etc. At
the same time you can also use this channel to read back actual values from the drive
inverter, such as actual speed, current, unit status, error number or reference signals.
3.3.3 Monitoring functions
Using a fieldbus system requires additional monitoring functions for the drive technology, for example, time monitoring of the fieldbus (fieldbus timeout) or rapid stop concepts.
You can, for example, adapt the monitoring functions of MOVIDRIVE
specifically to your application. You can determine, for instance, which of the drive inverter’s error responses should be triggered in the event of a bus error. It is a good idea
to use a rapid stop function for many applications. However you can also freeze the last
setpoints so that the drive continues to operate with the most recently valid setpoints (for
example, conveyor belt). As the range of functions for the control terminals is also guaranteed in fieldbus mode, you can continue to implement rapid stop concepts using the
terminals of the drive inverter, irrespective of the fieldbus used.
®
MDX61B and MOVITRAC® B offer digital access to all drive parameters
®
/ MOVITRAC
®
3.3.4 Diagnostics
The MOVIDRIVE
numerous diagnostics options for startup and service. For example, you can use the integrated fieldbus monitor to control setpoint values sent from the higher-level controller
as well as the actual values. The integrated Web server allows you to access the diagnostic values using a standard browser.
3.3.5 Fieldbus monitor
Furthermore, you are supplied with a variety of additional information about the status
of the fieldbus interface. The fieldbus monitor function in conjunction with the
MOVITOOLS
setting all drive parameters (including the fieldbus parameters) and for displaying the
fieldbus and device status information in detail.
®
drive inverter and the MOVITRAC® B frequency inverter offer you
®
MotionStudio PC software offers you an easy-to-use diagnostic tool for
10
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 11

Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B
4 Assembly and Installation Notes
4
This section contains information about assembly and installation of the DFE32B
PROFINET IO option card in the MOVIDRIVE
gateway housing.
®
MDX61B, MOVITRAC® B and UOH11B
4.1 Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B
NOTES
• Only SEW-EURODRIVE engineers are allowed to install or remove option
cards for MOVIDRIVE
• Option cards can only be installed or removed by users for MOVIDRIVE
MDX61B sizes 1 to 6.
• You have to connect the DFE32B PROFINET IO option to fieldbus slot 1.
• Only use connectors and cables approved for PROFINET IO when cabling.
[1]
®
MDX61B size 0.
®
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
62179AXX
11
Page 12

4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4.1.1 Before you begin
Assembly and Installation Notes
Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B
Read the following notes before installing or removing an option card:
• Disconnect the inverter from the power. Switch off the 24 V DC and the supply voltage.
• Take appropriate measures to protect the option card from electrostatic charge (use
discharge strap, conductive shoes, and so on) before touching it.
• Before installing the option card, remove the keypad and the front cover (→ oper-
ating instructions MOVIDRIVE
• After installing the option card, replace the keypad and the front cover (→ operating
instructions MOVIDRIVE
• Keep the option card in its original packaging until immediately before you are ready
to install it.
• Hold the option card by its edges only. Do not touch any components.
®
MDX60B/61B, section 'Installation').
®
MDX60B/61B, section 'Installation').
12
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 13
Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B
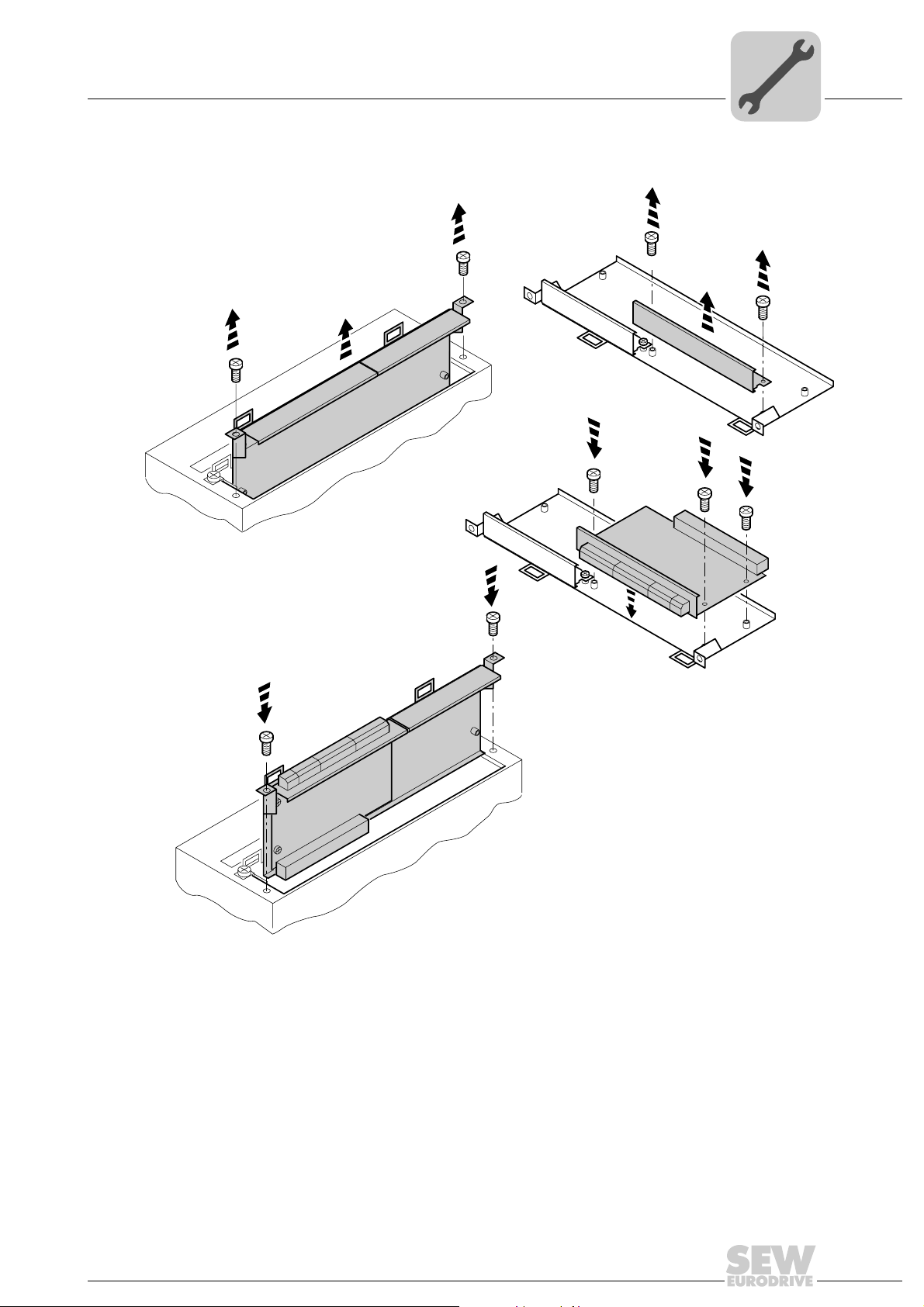
4.1.2 Basic procedure for installing and removing an option card (MDX61B, BG 1 - 6)
2.
1.
1.
3.
3.
4
2.
3.
4.
4.
60039AXX
1. Remove the two retaining screws holding the card retaining bracket. Pull the card retaining bracket out evenly from the slot (do not twist!).
2. Remove the two retaining screws of the black cover plate on the card retaining bracket. Remove the black cover plate.
3. Position the option card onto the retaining bracket so that the three retaining screws
fit into the corresponding bores on the card retaining bracket.
4. Insert the retaining bracket with installed option card into the slot, pressing slightly so
it is seated properly. Secure the card retaining bracket with the two retaining screws.
5. To remove the option card, follow the instructions in reverse order.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
13
Page 14
4
Assembly and Installation Notes
Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® B
4.2 Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® B
NOTES
•MOVITRAC® B does not require special firmware status.
• Only SEW-EURODRIVE engineers are allowed to install or remove option cards for
MOVITRAC
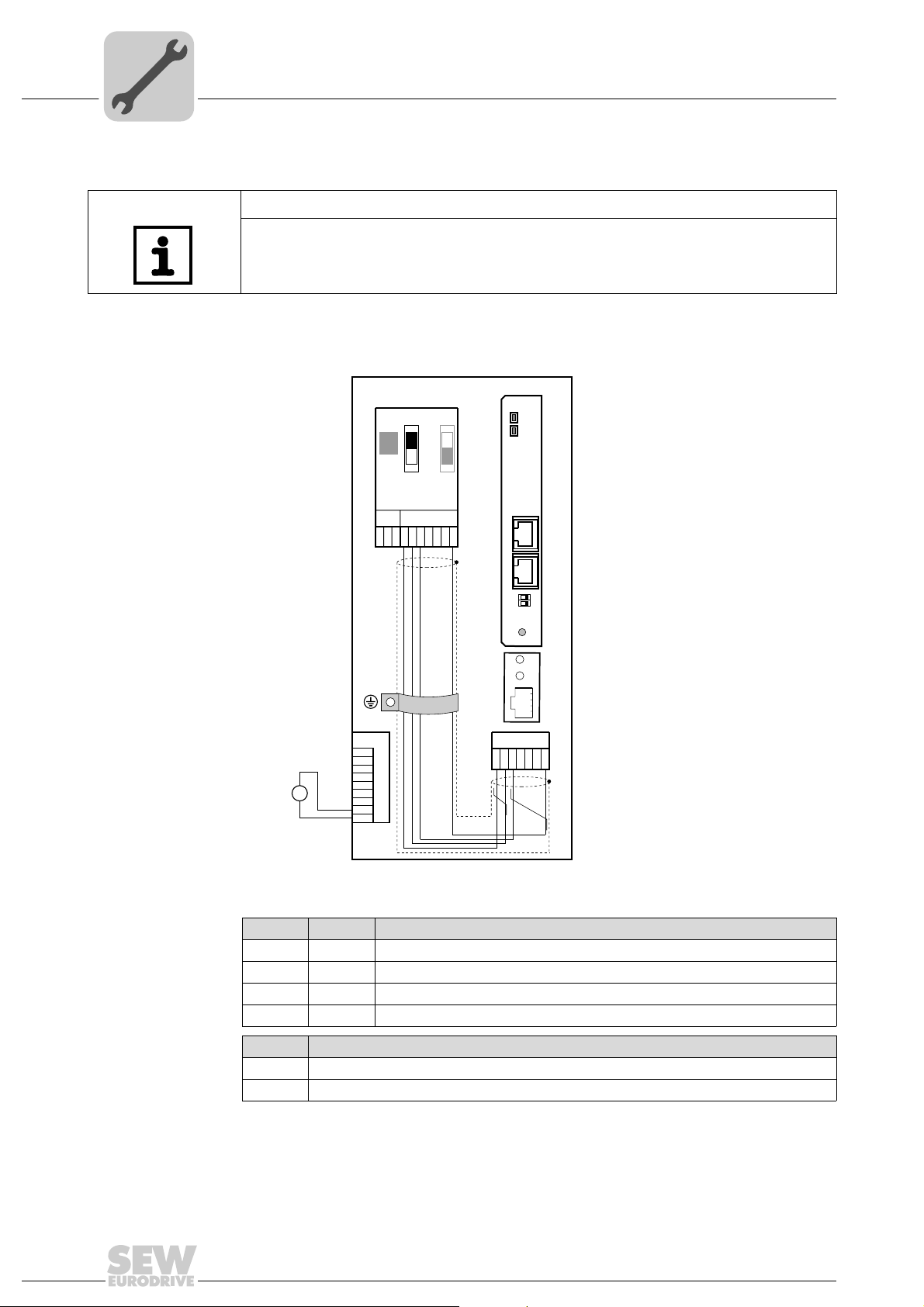
4.2.1 Connecting a system bus (SBus 1) between a MOVITRAC® B and the DFE32B option
®
B.
DFE 32B
RUN
BUS
FAULT
X44
S1
S2
ON
OFF
FSC11B
X46
X45
7
23456HL ⊥
1
X30X32
X12
1
DC 24 V
2
3
+
=
24V IO
–
GND
4
5
6
7
8
9
1234567
X46 X26 Terminal assignment
X46:1 X26:1 SC11 SBus +, CAN high
X46:2 X26:2 SC12 SBus –, CAN low
X46:3 X26:3 GND, CAN GND
X46:7 X26:7 DC 24 V
Def IP
AS
01
PROFINET IO
X24
X26
H1
H2
61633AXX
14
X12 Terminal assignment
X12:8 DC+24 V input
X12:9 GND reference potential for the binary inputs
To simplify cabling, the DFP32B can be supplied with DC 24 V from X46.7 of the
MOVITRAC
®
to X26.7.
MOVITRAC® B must be supplied with DC 24 V at terminals X12.8 and X12.9 when it
supplies the DFE32B option.
Activate the system bus terminating resistor at the FSC11B option (S1 = ON).
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 15
Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® B
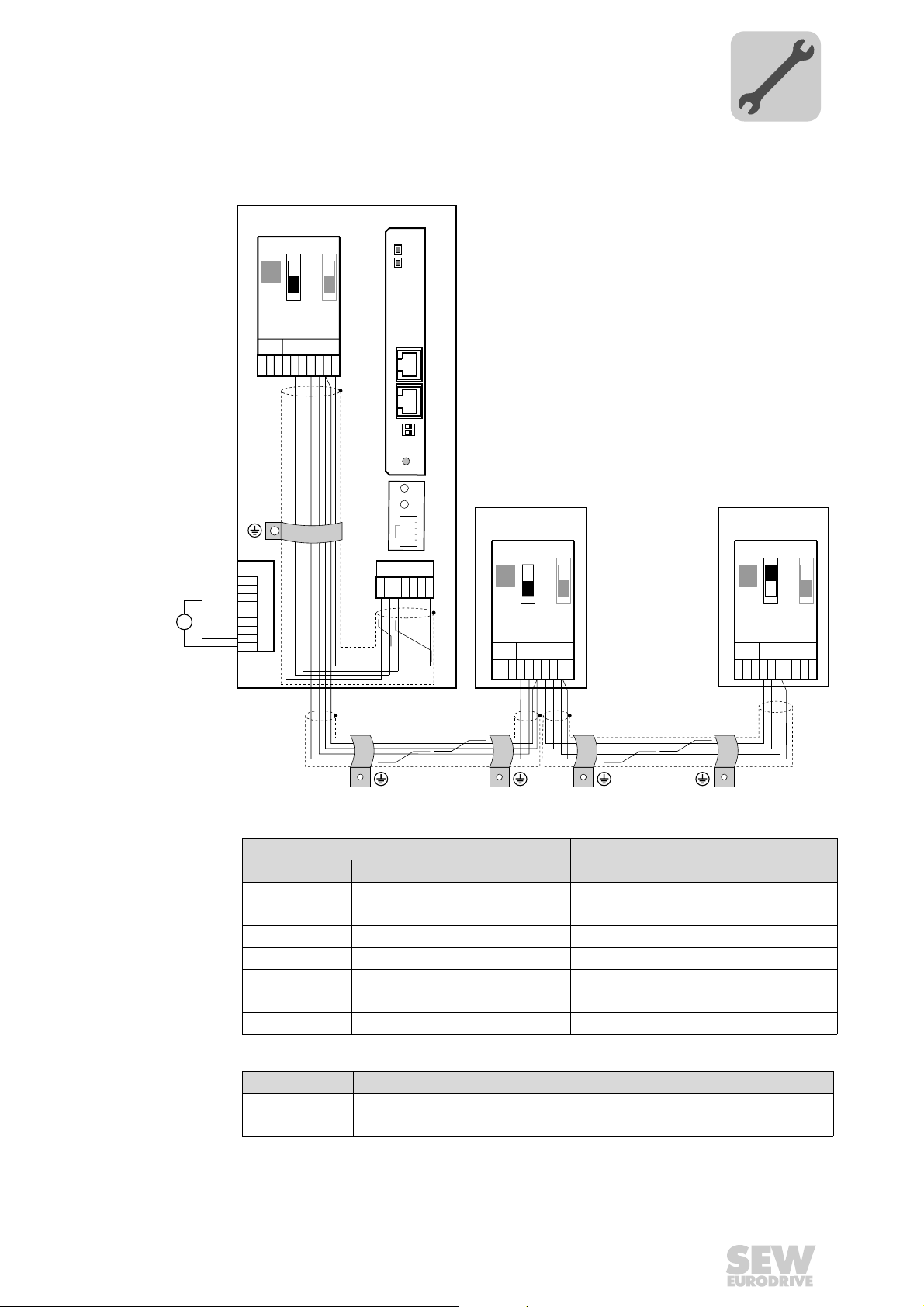
4.2.2 Connecting system bus (SBus 1) between several MOVITRAC® B units
4
DC 24 V
MOVITRAC® B
DFE 32B
RUN
BUS
FAULT
X44
S1
S2
ON
OFF
FSC11B
X46
X45
7
23456HL⊥
1
X12
1
2
3
+
=
-
24V IO
GND
4
5
6
7
8
9
X30X32
Def IP
AS
01
PROFINET IO
H1
H2
X24
X26
1234567
MOVITRAC® B
S1
ON
OFF
X44
FSC11B
X46
X45
23456HL ⊥
1
S2
MOVITRAC® B
S1
S2
ON
OFF
X44
FSC11B
X46
X45
7
23456HL ⊥
1
7
61635AXX
MOVITRAC® B DFE32B via UOH11B gateway housing
X46 Terminal assignment X26 Terminal assignment
X46:1 SC11 (System bus high, incoming) X26:1 SC11 SBus +, CAN High
X46:2 SC12 (System bus low, incoming) X26:2 SC12 SBus –, CAN Low
X46:3 GND (System bus reference) X26:3 GND, CAN GND
X46:4 SC21 (System bus high, outgoing)
X46:5 SC22 (System bus low, outgoing)
X46:6 GND (System bus reference)
X46:7 DC 24 V X26:7 DC 24 V
X12 Terminal assignment
X12:8 DC+24 V input
X12:9 GND reference potential for the binary inputs
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
15
Page 16
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Notes
Installing the DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE® B
Please note:
• Use a 2x2 core twisted pair and shielded copper cable (data transmission cable with
braided copper shield). Connect the shield flatly on both sides of the electronics
shield clamp of MOVITRAC
ble must meet the following specifications:
– Cable cross section 0.25 mm
– Line resistance 120 Ω at 1 MHz
– Capacitance per unit length ≤ 40 pF/m at 1 kHz
Suitable cables are CAN bus or DeviceNet cables.
• The permitted total cable length depends on the baud rate setting of the SBus:
– 250 kBaud: 160 m
– 500 kBaud: 80 m
– 1000 kBaud: 40 m
• Connect the system bus terminating resistor (S1 = ON) at the end of the system bus
connection. Switch off the terminating resistor on the other units (S1 = OFF). The
DFE32B gateway must always be connected either at the beginning or the end of the
system bus connection and feature a permanently installed terminating resistor.
®
B. Also connect the ends of the shield to GND. The ca-
2
(AWG18) ... 0,75 mm2 (AWG23)
NOTES
• There must not be any potential displacement between the units connected with the
SBus. Take suitable measures to avoid a potential displacement, e.g. by connecting the unit ground connectors using a separate lead.
• Point-to-point wiring is not permitted.
16
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 17
Assembly and Installation Notes
V
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Installing the DFE32B/UOH11B gateway
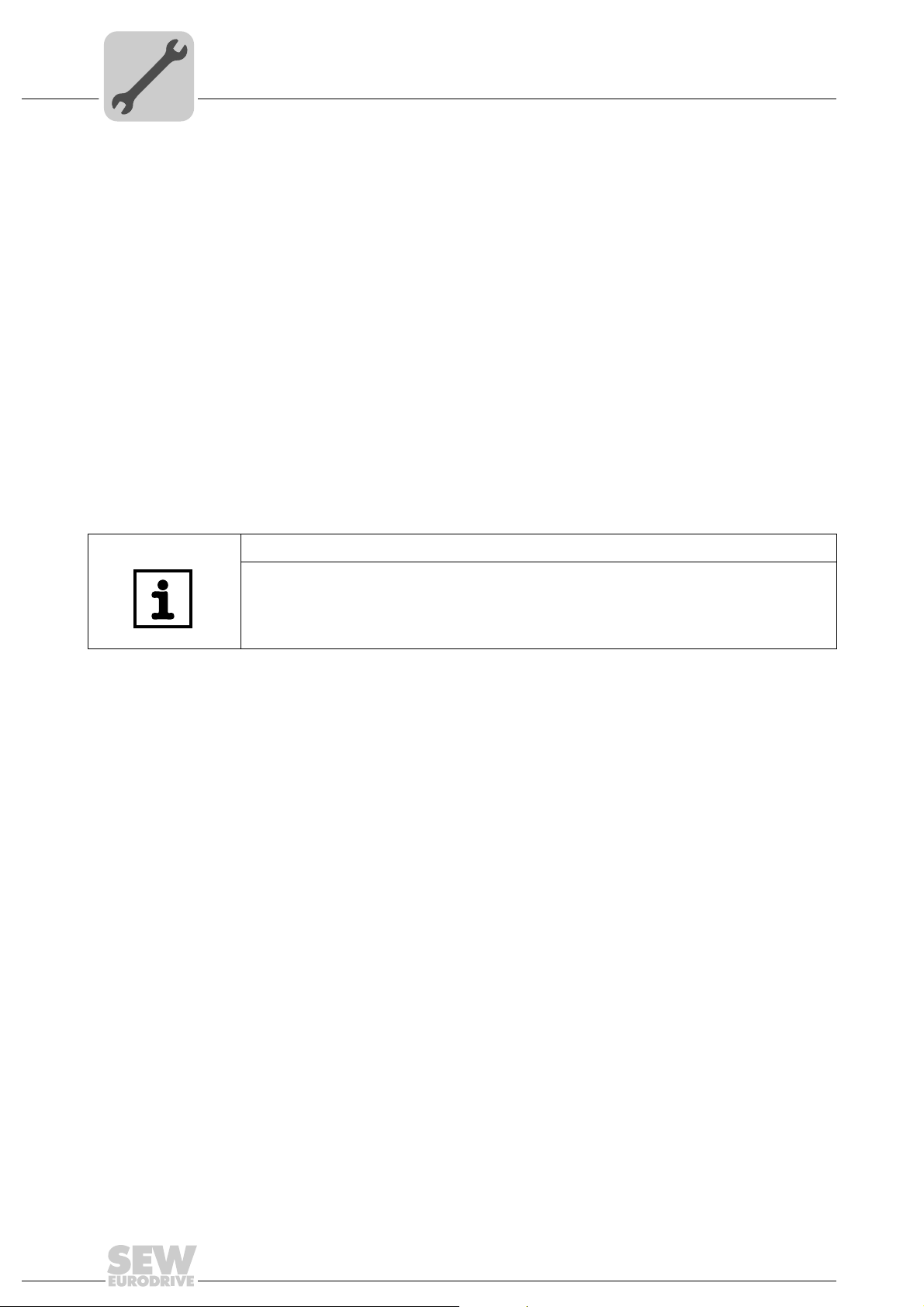
4.3 Installing the DFE32B/UOH11B gateway
The following figure shows the connection of the DFE32B option via the UOH11B:X26
gateway housing.
NOTE
• Only SEW-EURODRIVE engineers are allowed to install or remove option cards
in/from the UOH11B gateway housing.
UOH11B
DFE 32B
RUN
BUS
FAULT
X30X32
4
SEW Drive
SC11 Systembus +, CAN high
SC12 Systembus -, CAN low
GND, CAN GND
UOH11B gateway housing
X26 Terminal assignment
X26:1 SC11 system bus +, CAN high
X26:2 SC12 system bus, CAN low
X26:3 GND, CAN GND
X26:4 Reserved
X26:5 Reserved
X26:6 GND, CAN GND
X26:7 DC 24 V
Def IP
AS
PROFINET IO
X26
23456
1
X24
01
H1
H2
7
DC+24
GND
61636AXX
The gateway housing has a power supply of DC 24 V that is connected to X26.
Connect the system bus terminating resistor at the end of the system bus connection.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
17
Page 18
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Notes
Connection and terminal description DFE32B option
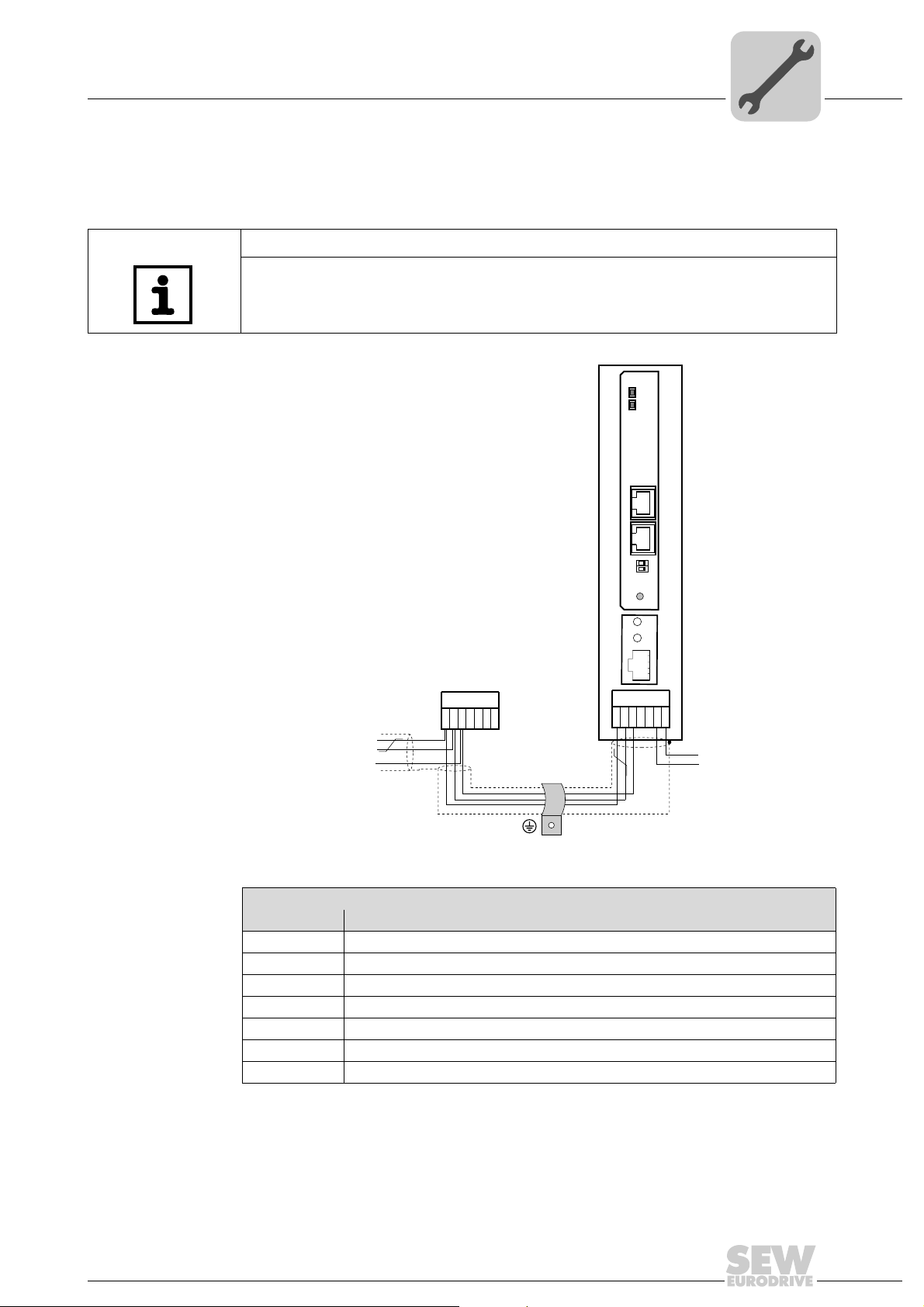
4.4 Connection and terminal description DFE32B option
Part number DFE32B PROFINET IO fieldbus interface option: 1821 345 6
NOTES
• The "DFE32B PROFINET IO fieldbus interface " is only possible in conjunction with
MOVIDRIVE
• Plug the DFE32B option into the fieldbus slot.
®
MDX61B, not with MDX60B.
Front view of
DFE32B
DFE 32B
RUN
BUS
FAULT
X30X32
Description
LED RUN (red/yellow/green)
LED BUS FAULT (red/yellow/green)
X30: Ethernet connection
LED Link (green)
LED Activity (yellow)
DIP
switches
Function
Shows the current status of the DFE32B.
Shows the status of the PROFINET IO connection.
X32: Ethernet connection
LED Link (green)
LED Activity (yellow)
Def IP
AS
01
PROFINET IO
61630AXX
Front view of MOVITRAC® B, DFE32B and
UOH11B
H1
H2
X24
DIP switches AS
58129axx
DEF IP
Description Function
LED H1 (red)
LED H2 (green)
X24 X terminal
Auto setup for gateway operation
Resets the address parameters to the following default values:
• IP address: 192.168.10.4
• Subnetwork mask: 255.255.255.0
• Gateway: 1.0.0.0
• PROFINET device name: PNETDeviceName_MACID
System error (only for gateway functions)
Reserved
RS485 interface for diagnostics via PC and MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio (only for MOVITRAC
®
®
B)
18
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 19
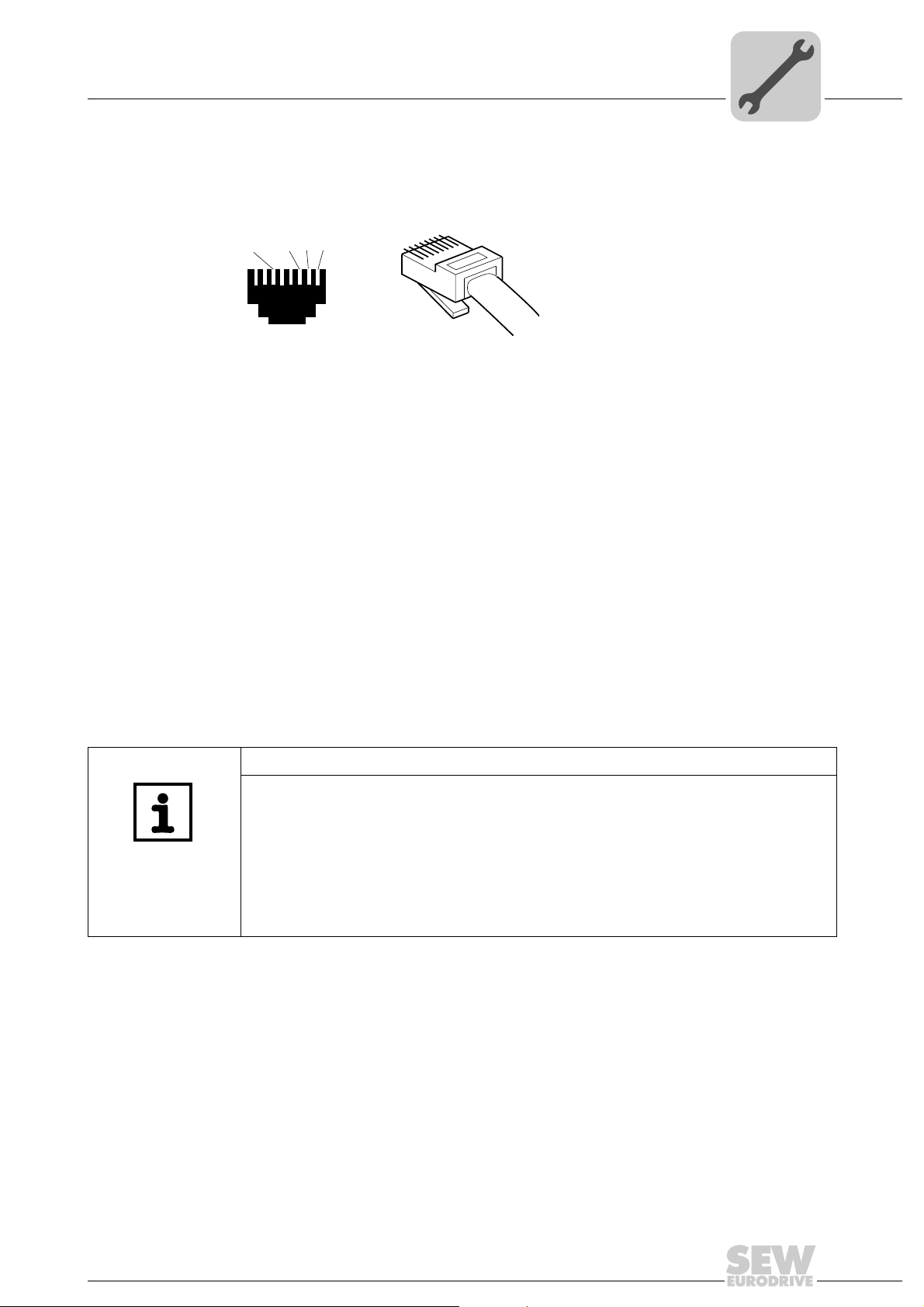
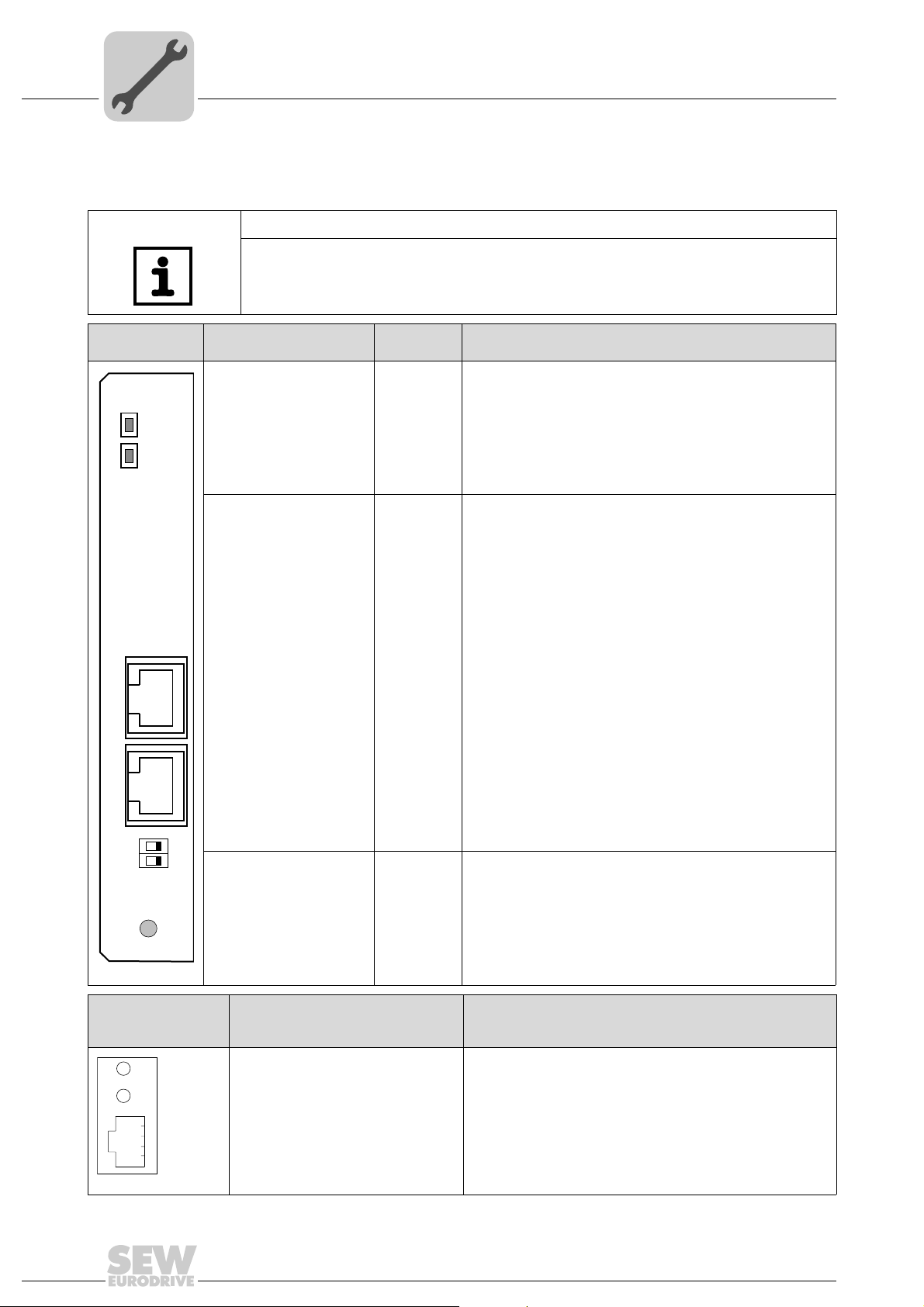
4.5 Pin assignment
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Use prefabricated, shielded RJ45 plug connectors compliant with IEC 11801, edition
2.0, category 5.
[6]
Figure 1: Pin assignment of an RJ45 plug connector
A = Front view
B = View from back
[1] Pin 1 TX+ Transmit Plus
[2] Pin 2 TX– Transmit Minus
[3] Pin 3 RX+ Receive Plus
[6] Pin 6 RX– Receive Minus
Assembly and Installation Notes
Pin assignment
[1]
[2]
[3]
AB
6
3
2
1
4
54174AXX
Connection MOVIDRIVE
To connect the DFE32B, connect the Ethernet interface X30 or X32 (RJ45 connector)
using a category 5, class D shielded twisted-pair cable in compliance with IEC 11801
edition 2.0. The integrated switch provides support for realizing a line topology.
NOTES
• According to IEC 802.3, the maximum cable length for 10 / 100 MBaud Ethernet
• VLAN tag prioritized Ethernet frames with the frame identification 8892
®
B / MOVITRAC® B / Ethernet
(10BaseT / 100BaseT), e.g. between DFE32B and switch, is 100 m.
are used
hex
for the real-time data exchange with PROFINET IO. This requires switched networks. The switches must support prioritization. Hubs are not permitted. Data transmission takes place using the full duplex process with 100 MBit. Detailed information on cabling can be found in the 'PROFINET installation guideline' publication
that was issued by the PROFINET user organization.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
19
Page 20

4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Notes
Shielding and routing bus cables
4.6 Shielding and routing bus cables
Only use shielded cables and connection elements that also meet the requirements of
category 5, class 2 in compliance with IEC 11801 edition 2.0.
Correct shielding of the bus cable attenuates electrical interference that may occur in
industrial environments. The following measures ensure the best possible shielding:
• Manually tighten the mounting screws on the connectors, modules, and equipotential
bonding conductors.
• Use only connectors with a metal housing or a metallized housing.
• Connect the shielding in the connector over a wide surface area.
• Apply the shielding of the bus cable on both ends.
• Route signal and bus cables in separate cable ducts. Do not route them parallel to
power cables (motor leads).
• Use metallic, grounded cable racks in industrial environments.
• Route the signal cable and the corresponding equipotential bonding close to each
other using the shortest possible route.
• Avoid using plug connectors to extend bus cables.
• Route the bus cables closely along existing grounding surfaces.
STOP
In case of fluctuations in the ground potential, a compensating current may flow via the
bilaterally connected shield that is also connected to the protective earth (PE). Make
sure you supply adequate equipotential bonding according in accordance with relevant
VDE regulations in such a case.
20
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 21
Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks
4.7 TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks
Introduction The settings for the address of the IP protocol are made using the following parameters:
• IP address
• Subnetwork mask
• Standard gateway
The addressing mechanisms and subdivision of the IP networks into subnetworks are
explained in this chapter to help you set the parameters correctly.
IP address The IP address is a 32 bit value that uniquely identifies a station in the network. An IP
address is represented by four decimal numbers separated by decimal points.
Example: 192.168.10.4
Each decimal number stands for one byte (= 8 bits) of the address and can also be represented using binary code (→ following table).
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
11000000 . 10101000 . 00001010 . 00000100
4
The IP address comprises a network address and a station address (→ following table).
Network address Station address
192.168.10 4
The part of the IP address that denotes the network and the part that identifies the station is determined by the network class and the subnetwork mask.
Station addresses cannot consist of only zeros or ones (binary) because they represent
the network itself or a broadcast address.
Network classes The first byte of the IP address determines the network class and as such represents
the division into network addresses and station addresses.
Value range
Byte 1
0 ... 127 A 10.1.22.3 10 = Network address
128 ... 191 B 172.16.52.4 172.16 = Network address
192 ... 223 C 192.168.10.4 192.168.10 = Network address
Network class
Complete network address
(Example)
Meaning
1.22.3 = Station address
52.4 = Station address
4 = Station address
This rough division is not sufficient for a number of networks. They also use an explicit,
adjustable subnet mask.
Subnet mask A subnet mask is used to divide the network classes into even finer sections. Like the
IP address, the subnet mask is represented by four decimal numbers separated by decimal points. Every decimal number stands for one byte.
Example: 255.255.255.128
Each decimal number stands for one byte (= 8 bits) of the subnet mask and can also be
represented using binary code (→ following table).
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
11111111 . 11111111 . 11111111 . 10 000000
If you compare the IP addresses with the subnet masks, you see that in the binary representation of the subnet mask all ones determine the network address and all the zeros
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
21
Page 22
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Notes
TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks
determine the station address (→ following table).
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
IP address
Subnetwork mask
The class C network with the address 192.168.10. is further subdivided into
255.255.255.128 using the subnetwork mask. Two networks are created with the ad-
dress 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.10.128.
The following station addresses are permitted in the two networks:
• 192.168.10.1 ... 192.168.10.126
• 192.168.10.129 ... 192.168.10.254
The network stations use a logical AND operation for the IP address and the subnetwork
mask to determine whether there is a communication partner in the same network or in
a different network. If the communication partner is in a different network, the standard
gateway is addressed.
decimal 192 . 168. . 10 . 128
Binary 11000000 . 10101000 . 00001010 . 10000000
decimal 255 . 255 . 255 . 128
Binary 11111111 . 11111111 . 11111111 . 10000000
Standard gateway The standard gateway is also addressed via a 32-bit address. The 32-bit address is rep-
resented by four decimal numbers separated by decimal points.
Example: 192.168.10.1
The standard gateway establishes a connection to other networks. In this way, a network station that wants to address another station can use a logical AND operation with
the IP address and the subnetwork mask to decide whether the desired station is located
in the same network. If this is not the case, the station addresses the standard gateway
(router), which must be part of the actual network. The standard gateway then takes on
the job of transmitting the data packages.
22
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 23

Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Setting the IP address parameters via DCP
4.8 Setting the IP address parameters via DCP
Initial startup For PROFINET IO, the IP address parameters are determined via the "DCP" protocol
(Discovery and Configuration Protocol). DCP operates with device names (Device
Name). The device name uniquely identifies a PROFINET IO station in the network. It
is identified with the PROFINET IO controller for the project planning of the station and
also set using the project planning software on the PROFINET IO device. With the aid
of the device name, the controller identifies the device during startup and transfers the
corresponding IP address parameters. Settings directly on the slave are no longer required. The basic procedure is described with SIMATIC STEP 7 as an example in chapter "Project Planning with PROFINET" (→ section "Assigning the PROFINET device
name").
4
Resetting the IP
address parameters
If you do not know the IP address parameters and cannot access the inverter using the
serial interface or the DBG60B keypad, you can reset the IP address parameters to the
default values using the DIP switch "Def IP".
This action resets the DFE32B option to the following default values:
• IP address: 192.168.10.4
• Subnetwork mask: 255.255.255.0
• Default gateway: 1.0.0.0
• PROFINET device name: PNETDeviceName_MACID
Proceed as follows to reset the IP address parameters to the default values:
• Switch off the 24 V DC supply voltage and the mains voltage.
• Set the DIP switch "Def IP" on the DFE32B option to "1."
• Switch the 24 V DC supply voltage and the mains voltage back on.
• Wait until the DFE32B option boots up. The "RUN" LED is green when the option is
ready.
You can now access the inverter via the IP address 192.168.10.4. Proceed as follows
to set new IP address parameters:
• Start a web browser and access the homepage of the DFE32B option or start
MOVITOOLS
• Select the address parameters you want.
• Set the DIP switch "Def IP" on the DFE32B option to "0."
• The new address parameters are adopted after the device is switched off and
switched on again.
®
MotionStudio.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
23
Page 24
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Notes
Procedure after device replacement
4.9 Procedure after device replacement
4.9.1 Device replacement MOVIDRIVE® B
If you insert the memory card of the replaced MOVIDRIVE
B, the new device is recognized by the PROFINET IO controller without any additional
measures.
NOTE
If you do not install the memory card of the replaced MOVIDRIVE® B in the new
MOVIDRIVE
load the saved parameter set into the new MOVIDRIVE
the PROFINET IO device name again using the project planning software. Proceed as
with an initial startup (→ chapter "Project Planning with PROFINET").
There are no measures required if only the DFE32B option is replaced.
4.9.2 Device replacement MOVITRAC
• Only for device replacement MOVITRAC
the saved parameter set into the new MOVITRAC
plete startup of the inverter (→ operating instructions MOVITRAC
• You have to set the PROFINET IO device name again using the project planning
software. Proceed as with an initial startup (→ chapter "Project Planning with PROFINET").
• Prior to the auto setup, check the parameters P884 SBus Baud Rate and P831
Reaction Fieldbus Timeout. The baud rate of the devices connected to the SBus has
to correspond to the baud rate of the gateway (DFE32B). Use the parameter tree of
the gateway in MOVITOOLS
• Now activate the auto setup function. Set the DIP switch "AS" on the DFE32B option
to "1."
®
B, you have to perform a complete startup of the inverter or you have to
®
B / gateway
®
MotionStudio.
®
B in the new MOVIDRIVE
®
B. Further, you have to set
®
B with fieldbus option: You have to load
®
B or you have to perform a com-
®
B).
®
24
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 25
Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Operating display DFE32B option
4.10 Operating display DFE32B option
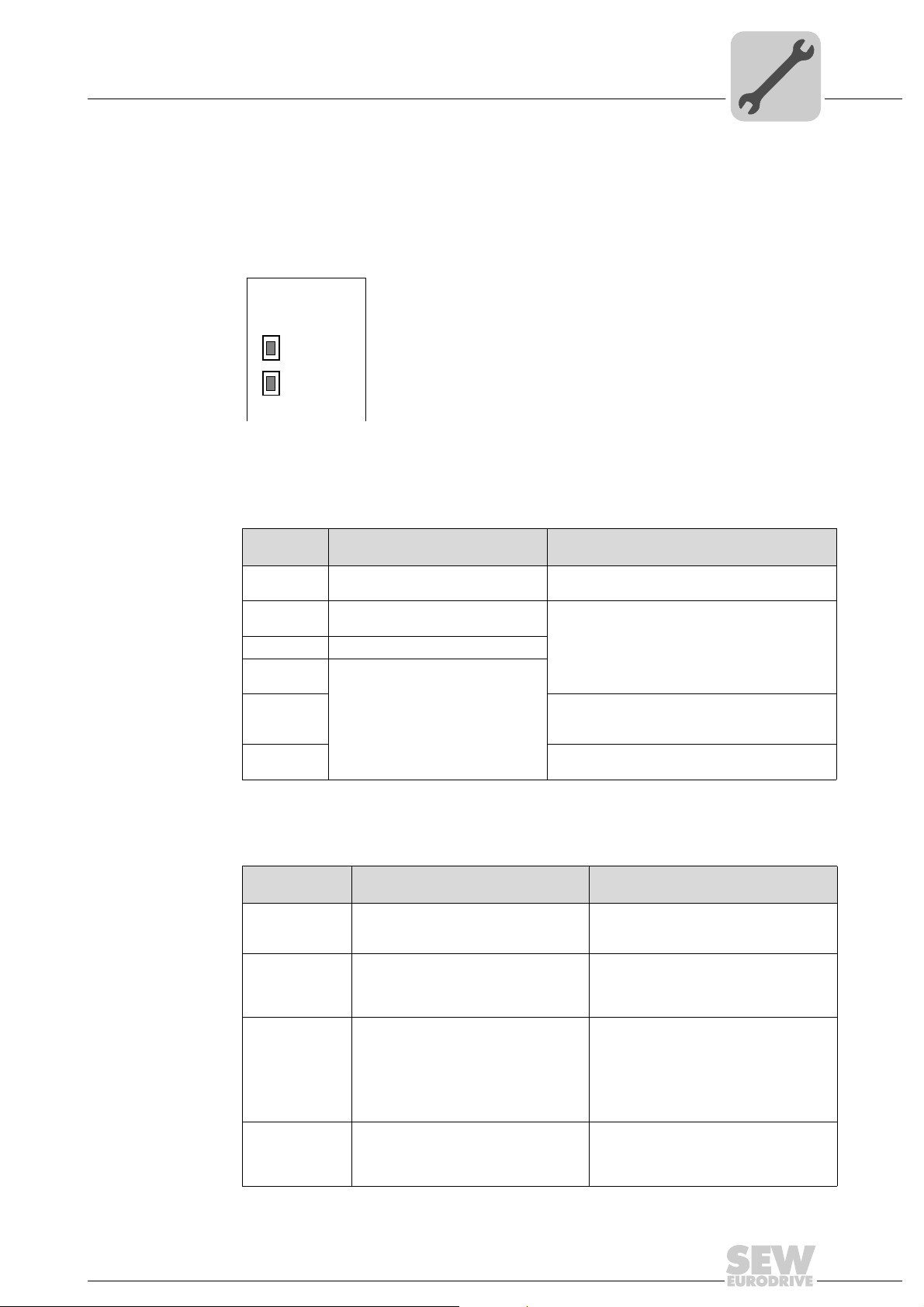
4.10.1 PROFINET-LEDs
There are two LEDs on the DFE32B option card that display the current status of the
DFE32B option and the PROFINET system.
DFE32B
RUN
BUS
FAULT
RUN LED The RUN LED indicates that the bus electronics are operating correctly
4
61629AXX
States of the
RUN LED
Green • DFE32B hardware OK.
Off • DFE32B is not ready for opera-
Red • Error in the DFE32B hardware
Flashing
green
Flashing
yellow
Yellow • Switch the unit on again. Consult SEW service
Cause of error Remedy
• Proper operation
tion
• Hardware of the DFE32B does
not boot up.
–
• Switch the unit on again. Consult SEW service
if the error occurs again.
• Switch the unit on again. Set default IP
addressparameter via DIP switch "DEF IP" .
Consult SEW service if the error occurs again.
if the error occurs again.
BUS FAULT LED The BUS FAULT LED displays the status of the PROFINET.
Status of the
BUS FAULT LED
Off • PROFINET IO device is currently
Flashing green
Flashing
green/red
Red • Connection to the PROFINET IO
Yellow
Flashing yellow
Cause of error Remedy
exchanging data with the PROFINET
IO controller (Data Exchange).
• The flashing function in the PROFINET IO controller project planning is
activated to visually localize the stations.
controller has failed.
• PROFINET IO device does not
detect a link
• Bus interruption
• PROFINET IO controller is not in
operation
• The STEP 7 hardware configuration
contains a module that is not permitted.
-
-
• Check the PROFINET connection of
the DFE32B option
• Check the PROFINET IO controller
• Check the cabling of your PROFINET
network
• Switch the STEP 7 hardware configuration to ONLINE and analyze the status of the components of the slots in
the PROFINET IO device.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
25
Page 26
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Notes
Operating display DFE32B option
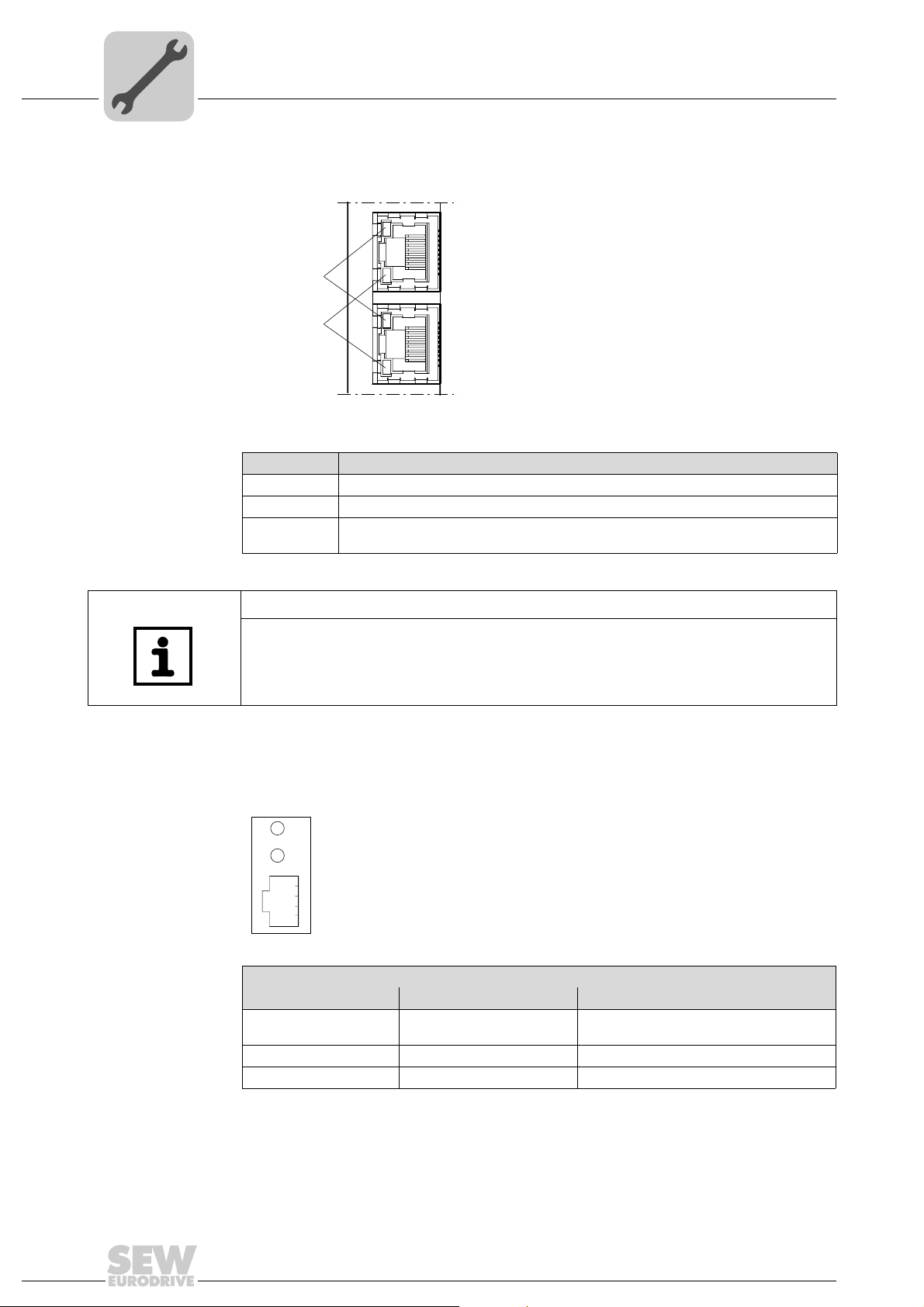
Link / Activity
LED
The two LEDs, Link (green) and Activity (yellow), integrated in the RJ45 plug connec-
tors (X30, X32) display the status of the Ethernet connection.
LED "Link"
LED "Activity"
LED / Status Meaning
Link / Green There is an Ethernet connection.
Link / Off There is no Ethernet connection.
Activity / Yel-
low
X30
X32
61880AXX
Data is currently being exchanged via Ethernet.
NOTES
• As the firmware of the DFE32B option card requires approximately 10 seconds for
initialization, the status "0" (inverter not ready) is displayed in the 7-segment display
of MOVIDRIVE
• The Run LED on the DFE32B option card lights up green.
®
during this time.
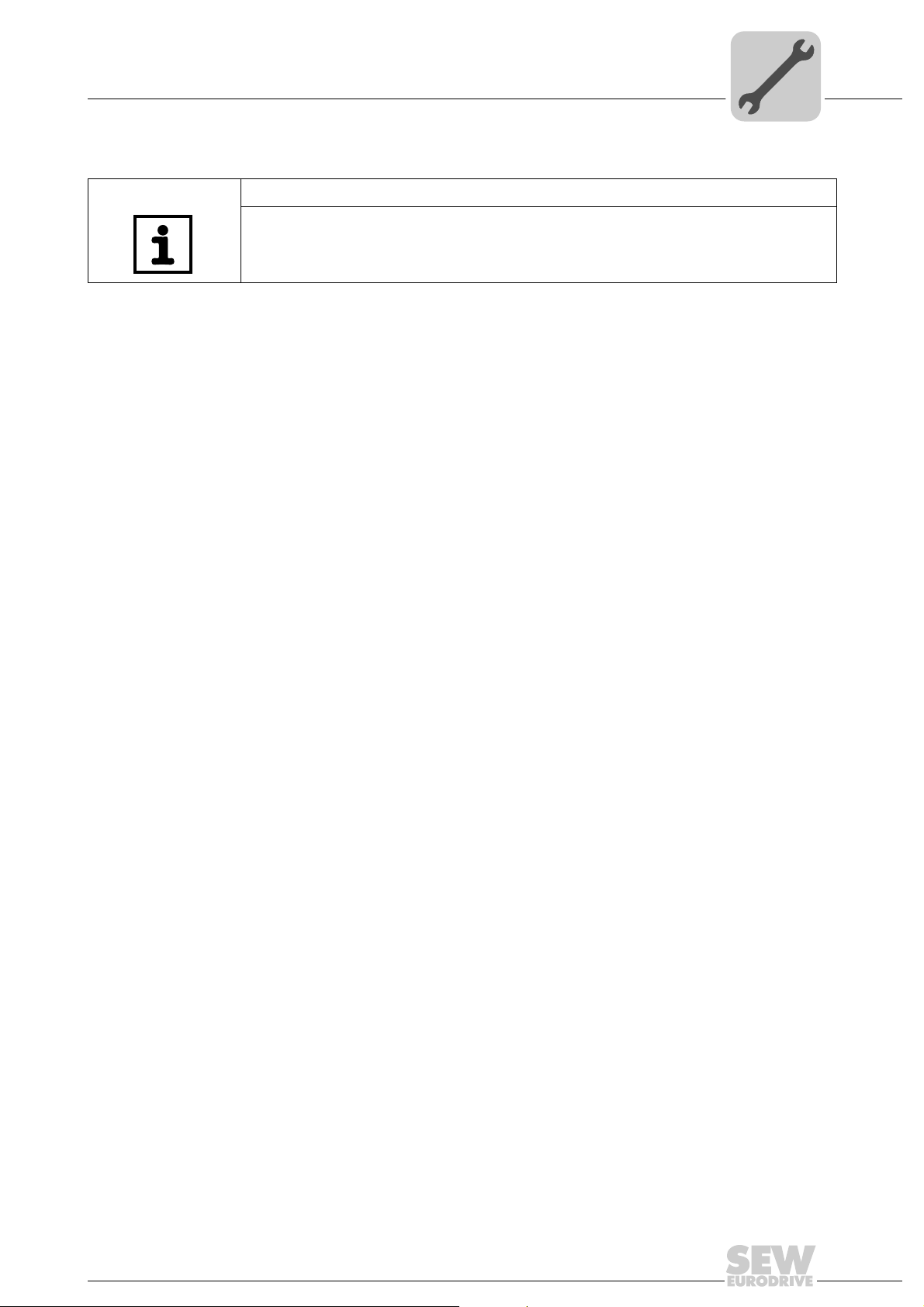
4.10.2 Gateway LED
LEDs H1 and H2 indicate the communication status in gateway operation.
H1
H2
X24
58129axx
LED H1 Sys-fault (red) Only for gateway function
Status State Description
Red System error Gateway is not configured or one of the
drives is inactive.
Off SBus ok Gateway is configured correctly
Flashes Bus scan Bus is being checked by the gateway
26
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 27
Assembly and Installation Notes
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Operating display DFE32B option
NOTES
•LED H2 H2 (green) is currently reserved.
• X-terminal X24 is the RS-485 interface for diagnostics via PC and MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio.
4
®
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
27
Page 28
5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
5 Project Planning with PROFINET
This Chapter describes the project planning for the MOVIDRIVE® B and
MOVITRAC
used for the project planning of the DFE32B with MOVIDRIVE
GSDML-V2.1-SEW-DFE-DFS-2Ports-jjjjmmtt.xml
This GSD file contains the unit description for the operation of the DFE32B in
MOVIDRIVE
®
B / gateway inverters with the DFE32B option. The following GSD file is
®
B or as fieldbus gateway for MOVITRAC® B.
5.1 Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
This chapter describes the project planning for MOVIDRIVE® B or MOVITRAC® B with
PROFINET using the current GSD(ML) file. The configuration is described using the example of the SIMATIC Manager project planning software with a SIMATIC CPU 315F 2
PN/DP.
Initializing the
GSD file
• Start STEP7 HWCONFIG and select the [Install new GSD file] menu item in the [Extras] menu.
• Select the file "GSDML-V2.1-SEW-DFE-DFS-2Ports-JJJJMMTT.xml" on the "Software ROM 7" CD as in the following dialog. "JJJJMMTT" [YYYYMMDD] represents
the date of the file. You can navigate to the required directory using the 'Browse' button. Confirm your selection with [OK].
• You will find the SEW PROFINET IO DFE32B interface under [Other field devices] /
[Drives] / [SEW] / [DFE/DFS(2Ports)].
®
B or in MOVITRAC® B:
NOTE
The latest GSD file version is also available for download on the SEW website
in the "Software" section.
28
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 29
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.1.1 Assigning the PROFINET device name
The general procedure is described with SIMATIC STEP 7 as an example .
• In STEP 7 HWKONFIG, select [PLC] / [Ethernet] / [Edit Ethernet Node ...].
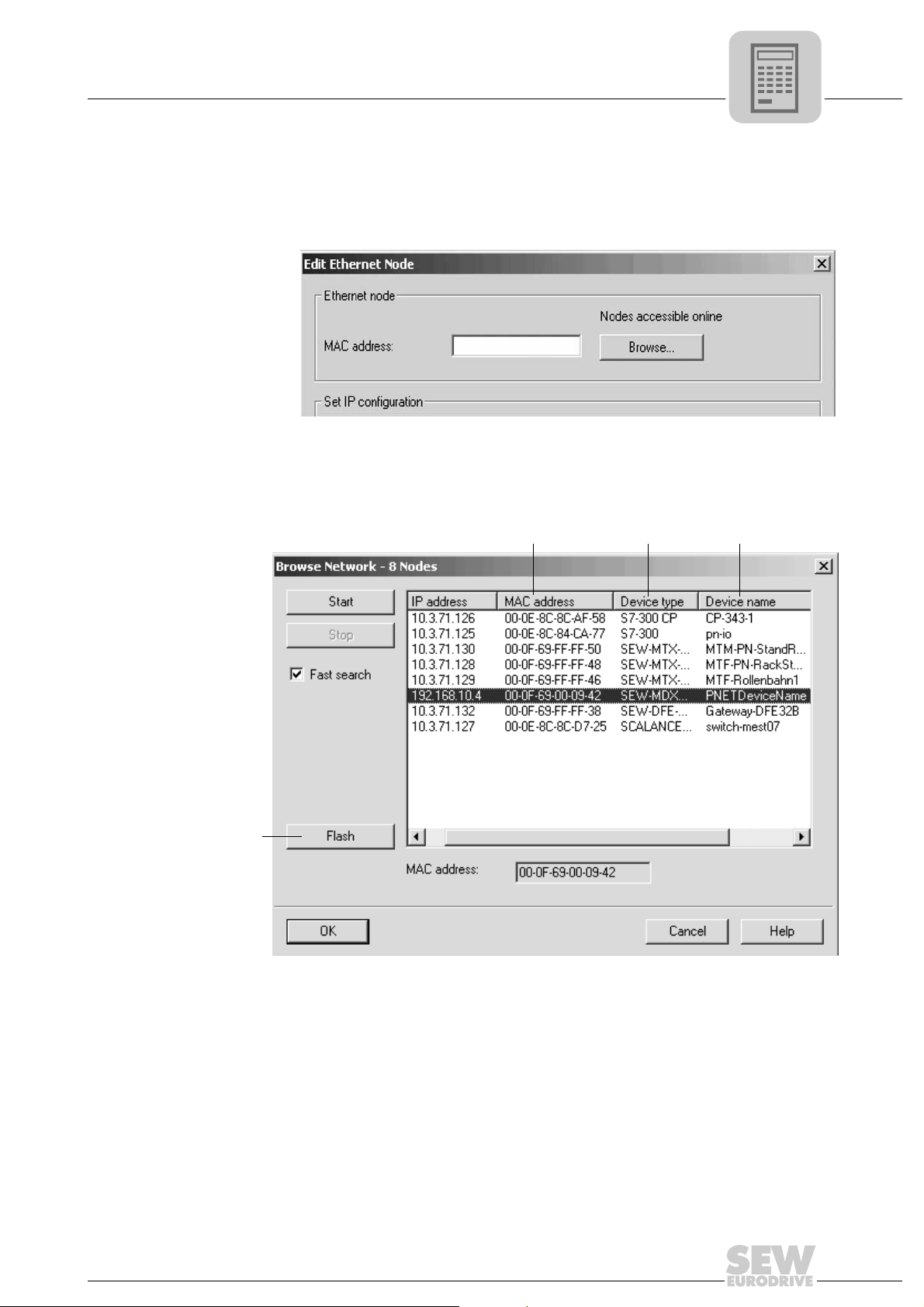
• Click on "Browse". You receive an overview of all PROFINET IO nodes that you can
reach online with your project planning tool (→ following figure).
Project Planning with PROFINET
5
11727AEN
[2]
[1]
• Choose the required station. The SEW node appears as "SEW-MDX61B+DFE32B"
under Device type [3]. The device name [4] is set to 'PNETDeviceName' ex works
and must be adapted to your system conditions. Several MDX61B units can be distinguished between by the MAC addresses [2] displayed. The MAC address [2] is attached to the DFE32B option. Use the [Flash] button [1] to enable the Status LED to
flash green for the selected DFE32B in order to check your selection.
[3] [4]
62340AEN
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
29
Page 30
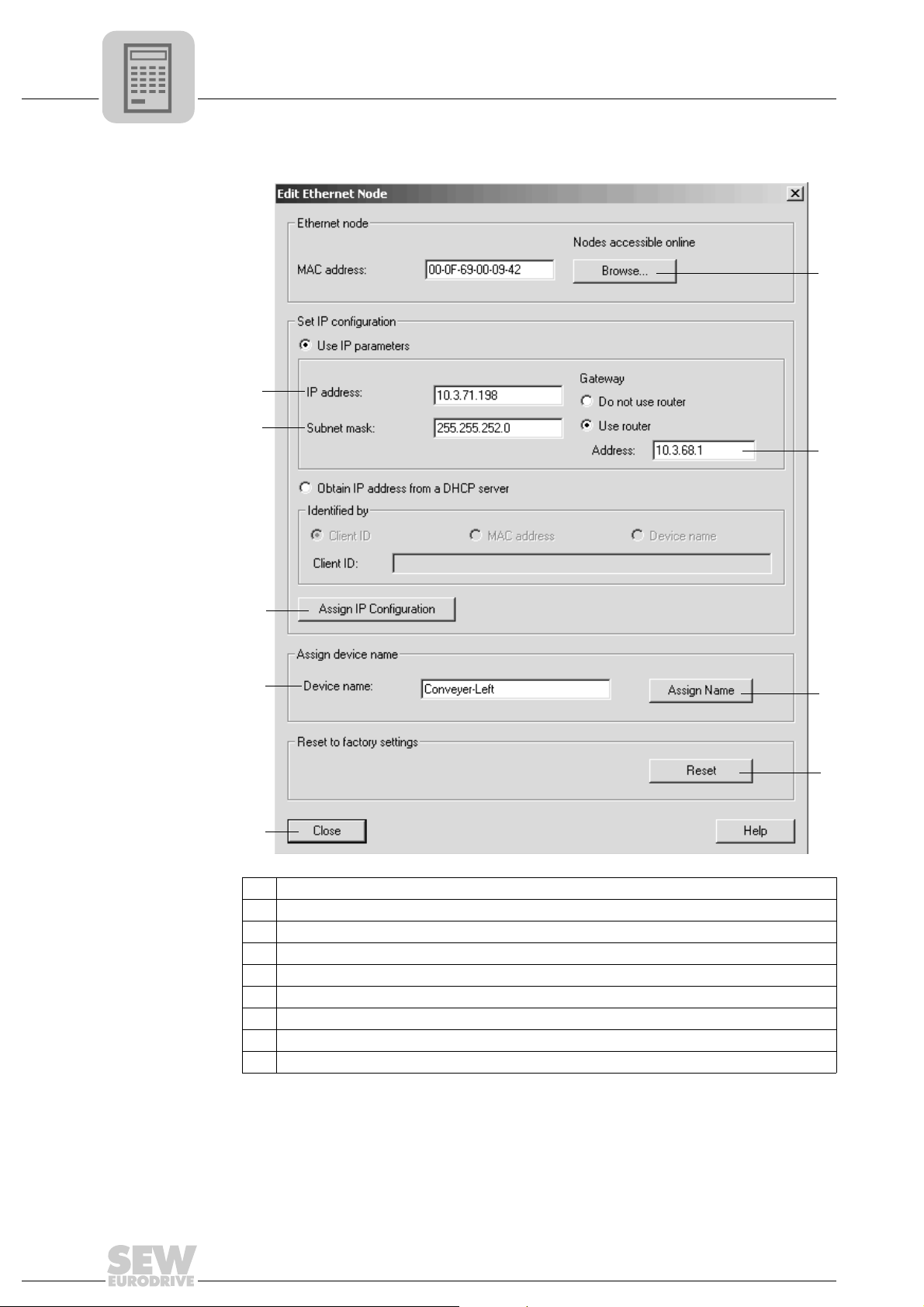
5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
[6]
[5]
[4]
[7]
[3]
[2]
[1]
[1] "Close" button.
[2] "Device name" input field
[3] "Assign IP Configuration" button
[4] "Subnet mask" input field
[5] " IP address" input field
[6] "Browse" button
[7] " Router address" Input field
[8] "Assign name" button
[9] " Reset" button
[8]
[9]
62330AEN
• Enter the device name in the "Device name" input field [2] and click the [Assign
name] button [8]. The device name is now transferred to the station and saved there.
It can be up to 255 characters long.
• Specify an IP address [5] and a subnet mask [4] as well as a router address [7] if required. Click the [Assign IP Configuration] button [3].
30
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 31

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
NOTE
The IO controller must not yet be in a cyclic data transmission with the IO devices.
• Click the [Browse] button [6] again to check whether your settings were adopted.
Click the [Close] button [1].
• You can reset the device name of the DFE32B online via the [Reset] button. Now
you need to restart the DFE32B.
5
5.1.2 Project planning for the PROFINET interface for MOVIDRIVE
Creating a new
project
Start the SIMATIC Manager and create a new project. Select your control type and add
the required modules. The OB82, OB86 and OB122 modules are particularly useful.
The OB82 module makes sure that the controller does not go to 'STOP' for so-called diagnostic alarms. The OB86 module indicates the failure of the decentralized periphery.
The OB122 module is called up if the controller cannot access data of a station of the
decentralized periphery. This can occur, for example, when the DFE32B is ready for operation later than the control system.
• Start STEP7 HWCONFIG and select the PN-IO slot in the control rack.
• Add a PROFINET IO system by right-clicking the context menu with your mouse.
Specify an IP address for the PROFINET IO controller when doing this. Add a new
PROFINET subsystem using the [Ethernet] button.
• Open [PROFINET IO] / [ADDITIONAL FIELD UNITS ] / [Drives] / [SEW] /
[DFE/DFS(2Ports)] [1] in the hardware catalog.
®
B
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
[1]
[2]
62334AEN
31
Page 32

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
• Move the entry "MDX61B+DFE32B" [2] to the PROFINET IO/ system with the mouse
and assign a PROFINET station name.
This name must later correspond to the PROFINET unit name specified in the
DFE32B.
• Delete the entry on slot 2 in to perform the project planning for your application. Select the process data configuration required for your application.
• Specify the I/O and periphery addresses for the configured data widths and save
your configuration.
The slot model is used for project planning with PROFINET. Each slot is assigned to
a DFE32B communication interface.
[1]
[2]
62335AEN
Slot 1: Must be indicated as Slot not used [1]
Slot 2: Process data channel [2]. Number of process data periodically exchanged between PROFINET IO controller and PROFINET IO device.
• Add data exchange with the new units to your program.
• Process data transfer is consistent. SFC14 and SFC15 can be used to transfer process data.
32
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 33

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
5
Configuring the
nodes
When the individual slots are configured, the new node has to be configured with further
settings. The following dialog appears by double-clicking on the new node’s unit symbol.
[2]
[1]
[3]
[4]
62255AEN
[1] "General" tab page
[2] "IO Cycle" tab page
[3] "Device name" input field
[4] "Ethernet" button.
• Enter the previously specified device name in the "Device name" input field [3] on the
"General" tab page [1] . Observe the coding.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
33
Page 34

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
• To enter the previously specified IP address (→ following figure), click the [Ethernet]
button [4] in the "Node / PN IO system" field.
11728AEN
• On the "IO Cycle" tab page [2], you can specify an update time for the node to update
its process data. The DFE32B option in MOVIDRIVE
time of 2 ms (→ following figure).
®
B supports a minimum update
11729AEN
34
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 35

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
5
Starting thecontroller
Load the configuration in the SIMATIC S7 and start the module. The Error LED of the
controller should now go out.
The LEDs of the DFE32B option should have the following statuses:
• RUN LED Lights up green
• BUS FAULT LED: Off
• Link / Activity LED: flicker
If this is not the case, check the configuration, especially the device name and the IP
address of the participant.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
35
Page 36

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
Project planningexample for theprocess data configuration of
MOVIDRIVE
®
B
®
This example is to show the positioning of the drive via MOVIDRIVE
positioning via bus" application module can be used.
The information between PLC and inverter is exchanged via 6 process data.
IO controller:
e.g. PLC
De-
celeration
Stat us –
Stat us –
Stat us –
Status
Wort
Wort
Wort
word
The following figure shows the corresponding PROFINET parameter settings.
Beschleu-
- Be schleu-
Beschleu-
Accelera nigung
nigung
nigung
tion
Ist –
Ist –
Ist –
Actual
position
position
position
position
Outputs
Inputs
6 process output data
Soll-
Soll-
Soll-
Setpoint
drehzahl
drehzahl
drehzahl
speed
Ist –
Ist –
Ist –
Actual
position
position
position
position
6 process input data
Ziel-
Ziel-
Ziel-
Target
position
position
position
position
Ist –
Ist –
Ist –
Actual
drehzahl
drehzahl
drehzahl
speed
IO device:
e.g. drive inverter
Target
position
position
position
position
Output
Ausgangs –
Ausgangs –
Ausgangs –
strom
strom
strom
current
B. The "Extended
Ziel-
Ziel-
T-
–
Ger äte –
Ger äte –
Ger äte –
utilization
auslastung
auslastung
auslastung
Control
Control
Control
Control
Wort
Wort
Wort
word
Unit
62347AEN
36
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
11730AEN
Page 37

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
5.1.3 Project planning for MOVITRAC® B or gateway with DFE32B option
5
General information
The inverter must be given a specific PROFINET configuration by the IO controller to
define type and number of input and output data used for the transmission. You have
the opportunity to control the drives via process data and to read and write all parameters of the fieldbus interface in an acyclic way.
The following figure describes the data exchange between the programmable controller
(IO controller), the fieldbus interface (IO device) and an inverter with process data channel.
Configuring the
process data
62258AXX
The PROFINET interface allows for different configurations for the data exchange between IO controller and IO device. The configurations are determined by the default process data width for SEW inverters of three process data words. The fieldbus interface
then distributes these process data words to the individual devices. The PROFINET interface accepts 1×3 to 8×3 process data words.
NOTE
3 PDs are always assigned to any SBus station.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
37
Page 38

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.1.4 Project planning for the PROFINET interface for MOVITRAC® B
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
Creating a new
project
Start the SIMATIC Manager and create a new project. Select your control type and add
the required modules. The OB82, OB86 and OB122 modules are particularly useful.
The OB82 module makes sure that the controller does not go to 'STOP' for so-called diagnostic alarms. The OB86 module indicates the failure of the decentralized periphery.
The OB122 module is called up if the controller cannot access data of a station of the
decentralized periphery. This can occur, for example, when the DFE32B is ready for operation later than the control system.
• Start STEP7 HWCONFIG and select the PROFINET IO slot in the control rack.
• Add a PROFINET IO system by right-clicking the context menu with your mouse.
Specify an IP address for the PROFINET IO controller when doing this. Add a new
PROFINET subsystem using the [Ethernet] button.
• Open [PROFINET IO] / [ADDITIONAL FIELD UNITS ] / [Drives] / [SEW] /
[DFE/DFS(2Ports)] [1] in the hardware catalog.
62338AEN
• Move the entry "Gateway DFE32B" [2] to the PROFINET IO/ system with the mouse
and assign a PROFINET station name.
This name must later correspond to the PROFINET unit name specified in the
DFE32B.
• The inverters connected to the gateway are represented in PROFINET as of slot 2.
Delete the entries for the respective slots depending on the number of connected inverters (e.g. slot 2 to slot 7 for a configuration of 5 inverters).
• Move the entry "AS 1 Drive (1x3PD)" to the free slots.
• Specify the I/O and periphery addresses for the configured drives and save your configuration.
[1]
[2]
38
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 39

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
The slot model is used for project planning with PROFINET. Each slot is assigned to
a DFE32B fieldbus interface. The following segmentation is used for the gateway
function of the DFE32B.
11731AEN
Slot 1 is not currently not used. Slots 2 ... 9 are assigned process data channels for
connected devices and and 3 process data per drive.
• Add data exchange with the new units to your program.
• Process data transfer is consistent. SFC14 and SFC15 can be used to transfer process data.
5
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
39
Page 40

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
Configuring the
nodes
When the individual slots are configured, the new node has to be configured with further
settings. The following dialog appears by double-clicking on the new node’s unit symbol.
[2]
[1]
[3]
[4]
62336AEN
[1] [General] tab page
[2] "IO Cycle" tab page
[3] "Device name" input field
[4] "Ethernet" button.
• Enter the previously specified device name in the "Device name" input field [3] on the
"General" tab page [1] . Observe the coding.
40
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 41

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
• To enter the previously specified IP address (→ following figure), click the [Ethernet]
button [4] in the "Node / PN IO system" field.
5
11732AEN
• On the "IO Cycle" tab page [2], you can specify an update time for the node to update
its process data. The DFE32B option in MOVITRAC
time of 4 ms (→ following figure).
®
B supports a minimum update
11733AEN
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
41
Page 42

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
Starting thecontroller
Application
example
Load the configuration in the SIMATIC S7 and start the module. The Error LED of the
controller should now go out.
The LEDs of the DFE32B option should have the following statuses:
• RUN LED Lights up green
• BUS FAULT LED: Off
• Link / Activity LED: flicker
If this is not the case, check the configuration, especially the device name and the IP
address of the participant.
8 MOVITRAC
ample. The information between PLC and the individual inverters is exchanged via 3
process data.
®
B frequency inverters are to be operated at a variable speeds in this ex-
42
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
62260AXX
Page 43

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning for the PROFINET IO controller
The following figure shows the corresponding PROFINET parameter settings.
5
11734AEN
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
43
Page 44

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Auto setup for gateway operation
5.2 Auto setup for gateway operation
The Auto setup function enables startup of the DFE32B as gateway to be performed
without a PC. It is activated via the auto setup DIP switch (see chapter "Installing the
DFE32B / UOH11B gateway page 17).
NOTE
Switching on the Auto setup DIP switch causes the function to be performed once. The
Auto setup DIP switch must then remain in the ON position.The function can be
reactivated by turning the DIP switch off and back on again.
As a first step, the DFE32B searches for drive inverters on the SBus below its hierarchi-
cal level. This process is indicated by the H1 LED (system error) flashing briefly. For this
purpose, different SBus addresses must be set for the drive inverters (P813). We recommend assigning the addresses beginning with address 1 in ascending order based
on the arrangement of inverters in the switch cabinet. The process image on the fieldbus
side is expanded by three words for each detected drive inverter.
The H1 LED remains lit if no drive inverter was located. A total of up to eight drive invert-
ers is taken into account. The following figure shows the process image for three drive
inverters with three words each of process output data and process input data.
After the search is completed, the DFE32B periodically exchanges three process data
words with each connected drive inverter. The process output data are fetched from the
fieldbus, divided into blocks of three and transmitted. The drive inverters read the process input data, put them together and send them to the fieldbus master.
The cycle time of the SBus communication is 2 ms per node at a baud rate of 500 kBit/s
without any additional engineering activities.
Thus, for an application with 8 inverters on the SBus, the cycle time of the process data
update is then 8 x 2 ms = 16 ms.
NOTE
Perform auto setup again in the following cases, since the DFE32B stores these values
once during auto setup. All devices installed at the SBus must be switched on. At the
same time, the process data assignments of the connected drive inverters may not be
changed dynamically after Auto setup.
• If you change the process data assignment of the drive inverters connected to the
DFE32B.
• If you changed the SBus address of one of the connected devices.
• If you add or remove devices.
44
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 45

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Auto setup for gateway operation
The following illustration shows the data exchange between the PLC, the DFE32B option and the inverter.
5
IO-Controller
PROFINET
DFE
62322AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
45
Page 46

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Setting the MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B drive inverter
5.3 Setting the MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B drive inverter
11638AEN
To control the drive inverter via PROFINET, you must first switch the drive inverter to
control signal source (P101) and setpoint source (P100) = FIELDBUS. The FIELDBUS
setting means the drive inverter parameters are set for control and setpoint entry via
PROFINET. The MOVIDRIVE
transmitted from the master programmable controller.
The parameters of the MOVIDRIVE
NET without any further settings once the PROFINET option card has been installed.
For example, all parameters can be set by the master programmable controller after
power-on.
Activation of the control signal source and setpoint source FIELDBUS is signaled to the
machine controller using the "Fieldbus mode active" bit in the status word.
For safety reasons, you must also enable the drive inverter at the terminals for control
via the fieldbus system. Therefore, you must wire and program the terminals in such a
way that the drive inverter is enabled via the input terminals. For example, the simplest
way of enabling the drive inverter at the terminals is to connect the DIØØ
(function / CONTROLLER INHIBIT) input terminal to a DC +24 V signal and to program
input terminals DIØ1 ... DIØ3 to NO FUNCTION.
®
drive inverter then responds to the process output data
®
drive inverter can be set straight away via PROFI-
46
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 47

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Setting the MOVITRAC® B frequency inverter
5.4 Setting the MOVITRAC® B frequency inverter
5
11736AEN
To control the frequency inverter via PROFINET, you must switch the drive inverter to
control signal source (P101) and setpoint source (P100) = SBus beforehand. The SBus
setting means the inverter parameters are set for control and setpoint entry via gateway.
The MOVITRAC
ted from the master programmable controller.
It is necessary to set the SBus1 timeout interval (P815) to a value other than 0 ms for
the MOVITRAC
tered. We recommend a value in the range 50 ... 200 ms.
Activation of the control signal source and setpoint source SBus is signaled to the higher-level controller using the "SBus mode active" bit in the status word.
For safety reasons, you must also enable the inverter at the terminals for control via the
fieldbus system. Therefore, you must wire and program the terminals in such a way that
the inverter is enabled via the input terminals. The simplest way of enabling the frequency inverter at the terminals is, for example, to connect the DIØ1 (function CW/STOP) input terminal to a DC +24-V signal and to set the remaining input terminals to NO FUNCTION.
®
frequency inverter then responds to the process output data transmit-
®
frequency inverter to stop if faulty SBus communication is encoun-
NOTES
• Set the parameter P881 SBus address to values between 1 to 8 in ascending order.
• The SBus address 0 is used by DFE32B gateway and therefore must not be used.
•Set P883 SBus timeout to values between 50 ... 200 ms
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
47
Page 48

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Startup procedure for MDX61B with DFE32B option
5.5 Startup procedure for MDX61B with DFE32B option
The following sections will describe the the startup procedure for a MOVIDRIVE® B with
the DFE32B PROFINET IO option step-by-step.
5.5.1 Preliminary work
Step 1: Installing the required software
1. FTDI Driver for USB11A programming interface
– Connect USB11A to the PC. Windows hardware detection installs the required
FTDI driver.
– the FTDI driver is available on the Software ROM 7 or on the SEW website.
2. GSD file: SEW-DFE32B-2-Port_V2.1-JJJJ.MM.TT.xml
3. MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio version 5.40 and higher.
Step 2: Installing the devices
1. Install MOVIDRIVE
– Supply system cable
– Motor cable
– Brake resistor
– DC 24 V backup voltage
2. Install PROFINET and connect DFE32B to PROFINET.
5.5.2 Starting up MOVIDRIVE
Step 1: Configuring MOVIDRIVE
1. Start MOVITOOLS
Specify a project name and assign USB11A programming interface according to serial COM interface.
– When the USB11A programming interface is connected to the PC for the first
time, Windows hardware detection installs the required FTDI driver
– If USB11A is not recognized, check the assignment to the COM interface. The
suitable COM port is marked by "USB"
2. Connect the PC to MOVIDRIVE
3. Perform a unit scan. Mark the unit with the mouse button and select [Startup] / [Parameter tree] via the right mouse button.
4. Set P100 setpoint source and P101 control signal source to "Fieldbus".
5. For simple control via fieldbus, the binary inputs can be set to "No Function" via the
parameters P601 ... P608.
6. Check the parameter setting for the process data (P87x). The parameters for control
word and status word must be set. Set P876 PO data enable to "Yes".
®
MDX60B/61B according to operating instructions:
®
B with DC 24 V or AC 400 V
®
B
®
MotionStudio and open a new project.
®
B via USB11A programming interface.
48
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 49

Startup procedure for MDX61B with DFE32B option
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Step 2: Configuring PROFINET
1. Start the control manufacturer’s software to configure the hardware (e.g. STEP 7HWKONFIG).
2. Install the GSD file if necessary (→ chapter "Preliminary work")
3. Check whether PC and control are in the same subnetwork:
– Are the IP addresses of PC and CPU identical up to the lowest byte?
– Is the subnet mask identical?
4. Check whether a TCP/IP communication can be set up.
5. Carry out the PROFINET configuration according to this manual.
– Assign PROFINET device name
– Assign IP configuration if necessary
– Perform process data configuration
– Load the configuration to the controller
6. The BUS FAULT LED of the DFE32B option is off when PROFINET is successfully
configured. Process data is now being exchanged.
7. Extent control program and set up process data exchange to MOVIDRIVE
8. Start MOVITOOLS
communication interface.
– Alternatively, MOVITOOLS
cation with USB11A. Connect PC with MOVIDRIVE
9. Perform a unit scan.
10.Mark MOVIDRIVE
button. Check whether the project data exchange between control and MOVIDRIVE
is working.
11.Switch on the supply voltage and enable MOVIDRIVE
Activate unit enable via control word 1 = 0x0006 .
– If MOVIDRIVE
group P60x) and supply further binary inputs with DC 24 V if required.
Project Planning with PROFINET
®
B.
®
MotionStudio and open a new project. Set up "Ethernet" as
®
MotionStudio can be operated via serial communi-
®
B and select [Diagnostics] / [Bus monitor] with the right mouse
®
B remains in "No Enable", check terminal assignment (parameter
®
B.
®
B at the terminals (DI00=1).
5
®
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
49
Page 50

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project Planning with PROFINET
Startup procedure for the DFE32B option as gateway
5.6 Startup procedure for the DFE32B option as gateway
The following sections will describe the the startup procedure for a MOVITRAC® B with
the DFE32B PROFINET IO option as gateway step-by-step.
5.6.1 Preliminary work
Step 1: Installing the required software
1. FTDI Driver for USB11A programming interface
– Connect USB11A to the PC. Windows hardware detection installs the required
FTDI driver.
– the FTDI driver is available on the Software ROM 7 or on the SEW website.
2. GSD file: SEW-DFE32B-2-Port_V2.1-JJJJ.MM.TT.xml
3. MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio version 5.40 and higher.
Step 2: Installing the devices
1. Install MOVITRAC
– Supply system cable
– Motor cable
– Brake resistor
– DC 24 V backup voltage
2. Install PROFINET and connect gateway to PROFINET.
3. Install the system bus according to this manual.
4. Activate terminating resistor at final node.
®
B according to operating instructions:
50
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 51

Project Planning with PROFINET
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure for the DFE32B option as gateway
5.6.2 Starting up units with DC 24 V or AC 400 V
5
Step 1: Configure MOVITRAC
1. Start MOVITOOLS
Specify a project name and assign USB11A programming interface according to serial COM interface.
– When the USB11A programming interface is connected to the PC for the first
time, Windows hardware detection installs the required FTDI driver
– If USB11A is not recognized, check the assignment to the COM interface. The
suitable COM port is marked by "USB"
2. Connect the PC to MOVITRAC
3. Perform a unit scan. Mark the unit with the mouse button and select [Startup] / [Parameter tree] via the right mouse button.
4. Set the parameters for P881 SBus address in ascending order (1 ... 8) unequal to 0
Set P883 SBus timeout interval to 50 ... 200 ms
5. Set P100 setpoint source to "SBus1 / fixed setpoint" and P101 control signal source
to"SBus1".
6. For simple control via fieldbus, the binary inputs can be set to "No Function" via the
parameters P601 ... P608.
7. Check the parameter setting for the process data (P87x). The parameters for control
word and status word must be set. Set P876 PO data enable to "Yes".
8. Repeat steps 2 to 7 for the individual units connected to the SBus.
9. Activate "Auto setup" function via DIP switch "AS" of the DFx gateway. Set DIP
switch "AS" to "1". H1 LED flashes during the scan and goes out after successful
completion.
10.Connect the PC to DFx gateway via USB11A programming interface.
11.Perform a unit scan. Now, the DFx gateway and all units installed at the SBus must
be accessible.
12.Mark DFx gateway and select [Diagnostics] / [Monitor Fieldbus Gateway DFx] with
the right mouse button. Go to the "Gateway Configuration" tab page and check
whether the "Auto setup" function has recognized all units. If not, check
– the SBus installation
– whether the terminating resistor is connected to the final unit
– the SBus addresses of the individual units
®
B
®
MotionStudio and open a new project.
®
B via USB11A programming interface.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
51
Page 52

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Step 2: Configuring PROFINET
Project Planning with PROFINET
Startup procedure for the DFE32B option as gateway
1. Start the control manufacturer’s software to configure the hardware (e.g. STEP 7HWKONFIG).
2. Install the GSD file if necessary (→ chapter "Preliminary work")
3. Check whether PC and control are in the same subnetwork:
– Are the IP addresses of PC and CPU identical up to the lowest byte?
– Is the subnet mask identical?
4. Check whether a TCP/IP communication can be set up.
5. Carry out the PROFINET configuration according to this manual.
– Assign PROFINET device name
– Assign IP configuration if necessary
– Perform process data configuration
– Load the configuration to the controller
6. The BUS FAULT LED of the DFE32B option is off when PROFINET is successfully
configured. Process data is now being exchanged.
7. Extend control program and set up process data exchange to DFx gateway.
8. Start MOVITOOLS
communication interface.
– Alternatively, MOVITOOLS
cation with USB11A. Connect PC with DFx gateway.
9. Perform a unit scan. DFx gateway and all units installed at the SBus must now be
accessible if the MOVITRAC
10.Activate DFx gateway with the mouse button start the "Monitor DFx Fieldbus Gateway" tool with the right mouse button. Switch to the "Process data monitor" window
and check whether the process data exchange between control and gateway is working.
11.Switch on the supply voltage and enable MOVITRAC
Activate unit enable via control word 1 = 0x0006
– If MOVITRAC
group P60x) and supply further binary inputs with DC 24 V if required.
®
MotionStudio and open a new project. Set up "Ethernet" as
®
MotionStudio can be operated via serial communi-
®
B units have been configured beforehand.
®
B at the terminals (DI01=1).
®
B remains in "No Enable", check terminal assignment (parameter
52
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 53

PROFINET Operating Behavior
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6 PROFINET Operating Behavior
6.1 Introduction
Classic fieldbus communication is enhanced by fast Ethernet technology as a physical
transmission medium using PROFINET IO. Profinet supports real-time capable process
communication as well as open communication via Ethernet TCP/IP. PROFINET distinguishes between three communication classes that differentiate in terms of efficiency
and functionality.
Introduction
I
6
00
Three communication classes
Three unit
classes
• TCP/IP
Open Ethernet TCP / IP communication without real-time requirements (e.g. web
technology)
• RT (Real-Time)
IO data exchange between automation units in real-time (> 1 ms).
• IRT (Isochronous Real-Time)
Isochronous real-time communication for synchronized IO data exchange (e.g. for
motion control applications - not for DFE32B option).
The DFE32B option meets the requirements of the PROFINET RT class and provides
open communication via TCP / IP or UDP / IP.
PROFINET IO differentiates between three unit types - 'IO controller', 'IO device' and 'IO
supervisor'.
• IO controller
The IO controller undertakes the master function for the cyclic IO data exchange with
the decentralized field units and is usually implemented as a communication interface of a controller. It is similar to a PROFIBUS DP master class 1. A PROFINET IO
system can have several IO controllers.
• IO device
All field units of PROFINET IO that are controlled by an IO controller are designated
as IO devices, e.g. I/O, drives, valve terminals, etc. IO devices are comparable with
PROFIBUS DP slave participants. The DFE32B option is a PROFINET IO device.
• IO supervisor
Programming devices / PC with corresponding engineering / diagnostic tools are
designated as IO supervisors. IO supervisors have access to process and parameter
data as well as alarm and diagnostic information.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
53
Page 54

6
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
PROFINET Operating Behavior
Introduction
00
Communication
model
Unit model The known decentralized periphery of PROFIBUS DP was enhanced for the device
The communication model of PROFINET IO is based on the many years of experience
with PROFIBUS DP-V1. The master slave access procedure was mapped on a provider-consumer model.
Several communication channels are used for the data exchange between IO controller
and IO devices. The cyclic IO data and the event-driven alarms are transferred via realtime channels. The standard channel based on UDP / IP is used for parameter settings,
configuration and diagnostic information.
model. The device model is based on slot and subslot mechanisms where modular devices with slots can be implemented for modules and submodules. In this way, the slot
and submodules are represented by subslots for the modules. These mechanisms also
enable logical modularization, e.g. for a drive system (→ following figure).
54
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
58645AXX
Page 55

A single drive axle is represented as a module under PROFINET IO. Several submod-
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
ules can be plugged into this module. The submodules determine the process data interface to the IO controller or the data traffic partner. Thus they have provider or consumer quality. The model provides the option to plug several modules into an IO device
for multi-axis systems that have a common PROFINET IO interface. In this way, each
module again represents a single axis. Slot 0 is used as a Device Access Point (DAP)
and usually represents the IO device.
6.2 The integrated Ethernet switch
You can use the integrated Ethernet switch to achieve line topologies known from the
fieldbus technology. There are other possible bus topologies such as star or tree, of
course. Ring topologies are not supported.
NOTES
The number of industrial Ethernet switches connected to the line affects the telegram
runtime. If a telegram passes through the units, the telegram runtime is delayed by the
Store & Forward function of the Ethernet switch:
• for a telegram length of 64 Byte by approximately 10 µs (at 100 Mbit/s)
• for a telegram length of 1500 Byte by approximately 130 µs (at 100/Mbit/s)
This means that the more units a telegram has to pass through, the higher the telegram
runtime is.
PROFINET Operating Behavior
The integrated Ethernet switch
I
6
00
Autocrossing The two ports leading out of the Ethernet switch have autocrossing functionality. This
means you can use patch or cross-over cables to connect the next Ethernet node.
Autonegotiation The baud rate and the duplex mode is negotiated by both Ethernet nodes when estab-
lishing the connection. The two Ethernet ports of the PROFINET interface support autonegotiation functionality and operate at a baud rate of 100 Mbit or 10 Mbit in full duplex
or half duplex mode.
NOTE
PROFINET IO networks must be operated at a baud rate of 100 Mbit in full duplex
mode.
Monitoring the
LINK status
Both ports allow for a monitoring of the LINK status. You can set up this function via the
STEP 7 hardware configuration as follows:
• Select slot 0 in STEP 7.
• Select [Object properties] from the context menu.
• Select the tab "Parameters".
Only set the monitoring for the port that sends data packages to other nodes and not to
the control. If a LINK DOWN is detected when the monitoring function is switched on,
the PROFINET device sends a diagnostics alarm to the control via the other port
(→ chapter "PROFINET alarms using the example of MOVIDRIVE
®
B")
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
55
Page 56

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6
PROFINET Operating Behavior
Process data configuration
00
6.3 Process data configuration
For the DFE32B option, Slot 1 must be configured as 'slot not used'. Modules with 1 to
10 I/O words can be plugged into slot 2. After the unit sis switched on and before the IO
controller establishes the communication, the configuration is set to 3 process data
words I/O. It can be changed by the IO controller while the communication is estab-
lished. The current configuration is shown in P090 PD configuration.
Permitted
configurations
ID Process data length
101 1 process data word I/O
102 2 process data words I/O
103 3 process data words I/O
104 4 process data words I/O
105 5 process data words I/O
106 6 process data words I/O
107 7 process data words I/O
108 8 process data words I/O
109 9 process data words I/O
110 10 process data words I/O
The DAP (Device Access Point) is designated as ID 100 (slot 0, subslot 1)
NOTE
The configuration of the DFE32B option is compatible to the DFE12B option. That
means that you do not have to change the configuration when you replace the DFE12B
option with the DFE32B option. The DFE32B option then accepts 1 ... 10 process data
words on slot 1.
56
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 57

PROFINET Operating Behavior
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Controlling the MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B drive inverter
6.4 Controlling the MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B drive inverter
The drive inverter is controlled via the process data channel which is up to 10 I/O words
in length. These process data words may be mapped in the I/O or peripheral area of the
controller if a programmable controller is used as IO controller and can be addressed as
usual.
I
6
00
PW160
PW158
PW156
[1]
PW160
PW158
PW156
Figure 2: Mapping PROFINET data in the PLC address range
[1] PLC address range
PI1 ... PE10 Process input data
PO1 ... PO10 Process output data
PA 3
PA 2
PA 1
PE 3
PE 2
PE 1
PA 1
PE 1
PA 2
PE 2
PA 3
PE 3
PA 10
PE 10
B
®
MOVIDRIVE
62321AXX
NOTES
For more information about controlling via the process data channel, in particular regarding the coding of the control and status word, refer to the Fieldbus Unit Profile
manual.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
57
Page 58

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6
PROFINET Operating Behavior
Controlling the MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B drive inverter
00
6.4.1 Control example SIMATIC S7 with MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B
The drive inverter is controlled using Simatic S7 in accordance with the selected process
data configuration either directly using load and transfer commands or by means of spe-
cial system functions, SFC 14 DPRD_DAT and SFC15 DPWR_DAT.
In principle, S7 data lengths of 3 bytes or more than 4 bytes must be transmitted using
system functions SFC14 and SFC15.
Consequently, the data in the following table applies:
Process data configuration STEP 7 access via
1 PD Load / transfer commands
2 PD Load / transfer commands
3 PD System functions SFC14/15 (length 6 bytes)
6 PD System functions SFC14/15 (length 12 bytes)
10 PD System functions SFC14/15 (length 20 bytes)
6.4.2 PROFINET timeout (MOVIDRIVE
If the data transfer via PROFINET is faulty or interrupted, the response monitoring time
in MOVIDRIVE
up or flashes to indicate that no new user data is being received. At the same time,
MOVIDRIVE
®
®
MDX61B)
®
elapses (if configured in the IO control). The BUS FAULT LED lights
performs the error response selected with P831 Fieldbus timeout re-
sponse.
P819 Fieldbus timeout displays the response monitoring time specified by the IO con-
troller during the PROFINET startup. The timeout can only be changed via the IO controller. Although modifications made via the keypad or MOVITOOLS
displayed, they do not have any effect and are overwritten when the PROFINET is next
started up.
6.4.3 Fieldbus timeout response (MOVIDRIVE
Parameter P831 Response Fieldbus Timeout is used to set the error response that is
triggered via the fieldbus timeout monitoring function. The setting made here must correspond to the setting in the master system (S7: response monitoring).
®
MDX61B)
®
MotionStudio are
58
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 59

PROFINET Operating Behavior
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Controlling the MOVITRAC® B (gateway) frequency inverter
6.5 Controlling the MOVITRAC® B (gateway) frequency inverter
The inverter is controlled via the process data channel, which is up to 3 I/O words in
length. These process data words are reproduced in the I/O or peripheral area of the
controller, for example when a programmable logic controller is used as the IO controller. As a result, they can be addressed in the usual manner.
I
6
00
PO 3
PO 2
PO 1
PO 3
PO 2
PO 1
PO 1
PO 2
PO 3
PO 1
[1]
[2]
POW318
POW316
POW314
POW312
POW310
POW308
MOVITRAC® B 1 MOVITRAC® B 2
PI 2
PI 3
PI 1
PIW318
PIW316
PIW314
PIW312
PIW310
PIW308
PI 1
PI 3
PI 2
PI 1
PI 3
PI 2
PI 1
Figure 3: Mapping PROFINET data in the PLC address range
[1] Address range MOVITRAC®B, device 2
[2] Address range MOVITRAC
®
B, device 1
PO 2
PI 2
PO 3
PI 3
58612AXX
PO = process output data PI / PI = process input data
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
59
Page 60

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6
PROFINET Operating Behavior
Controlling the MOVITRAC® B (gateway) frequency inverter
00
6.5.1 Control example for SIMATIC S7 with MOVITRAC® B (gateway)
The inverter is controlled using SIMATIC S7 in accordance with the selected process
data configuration either directly using load and transfer commands or by means of special system functions SFC 14 DPRD_DAT and SFC15 DPWR_DAT.
In principle, S7 data lengths of 3 bytes or more than 4 bytes must be transmitted using
system functions SFC14 and SFC15.
Process data configuration STEP 7 access via
3 PD ... 24 PD System functions SFC14/15
Param + 3 PD ... 24 PD System functions SFC14/15
6.5.2 SBus timeout
(length: 6 ... 48 bytes)
(length 6 ... 48 bytes for PD + 8 bytes for parameter)
If one or more drive inverters on the SBus can no longer be addressed by the DFE32B,
the gateway enters error code F11 System fault, in status word 1 of the corresponding
inverter. The H1 LED (system fault) lights up, and the error is also displayed via the diagnostics interface. It is necessary to set the SBus timeout interval (P815) of the
®
MOVITRAC
B system error to a value other than 0 for the inverter to stop. The error
resets itself in the gateway. In other words, the current process data is exchanged immediately after restarting the communication.
6.5.3 Unit error
The gateways detect a series of errors during the self test and respond by locking themselves. For the exact error responses and according measures please refer to the error
list (→ chapter "Error list in gateway operation"). A hardware defect causes error F111
system fault to be displayed on the fieldbus process input data for status words 1 of all
drive inverters. The H1 LED (system fault) at the DFE is lit. The exact error code of the
gateway status can be displayed via the diagnostics interface with MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio (Tool "Status").
6.5.4 Fieldbus timeout response of the DFE32B in gateway operation
®
You can set how the gateway should respond in case of timeout using the P831 Fieldbus
timeout response parameter.
No response The drives on the subordinate SBus continue with the last setpoint value.
PA_ DATA = 0
(factory setting)
60
These drives cannot be controlled when the PROFIBUS communication is
interrupted.
The rapid stop is activated for all drives that have a process data configuration
with control word 1 or 2 when a PROFINET timeout is detected. For this, the
gateway sets the bits 0 ... 2 of the control word to 0.
The drives are stopped with the rapid stop ramp.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 61

6.6 SIMATIC S7 Sample program
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
NOTE
This example is a special and free service that demonstrates only the basic approach
to generating a PLC program as a non-binding sample. We are not liable for the contents of the sample program.
In this example, the project planning for MOVIDRIVE® B or MOVITRAC® B has the process data configuration "3 PD" on input addresses PIW576... and output addresses
POW576....
A data block DB3 is created with about 50 data words.
When SFC14 is called, the process input data is copied to data block DB3, data words
0, 2 and 4. When SFC15 is called after the control program has been processed, the
process output data are copied from data words 20, 22 and 24 to the output address
POW 576 ...
Note the length specification in bytes for the RECORD parameter. The length information must correspond to the configured length.
Refer to the online help for STEP 7 for further information about the system functions.
PROFINET Operating Behavior
SIMATIC S7 Sample program
I
6
00
//Start of cyclical program processing in OB1
BEGIN
NETWORK
TITLE =Copy PI data from servo drive to DB3, word 0/2/4
CALL SFC 14 (DPRD_DAT) //READ IO DeviceRecord
LADDR := W#16#240 //Input address 576
RET_VAL:= MW 30 //Result in flag word 30
RECORD := P#DB3.DBX 0.0 BYTE 6 //Pointer
NETWORK
TITLE =PLC program with drive application
// PLC program uses the process data in DB3 for
// drive control
L DB3.DBW 0//Load PI1 (status word 1)
L DB3.DBW 2 //Load PI2 (actual speed value)
L DB3.DBW 4 //Load PI3 (no function)
L W#16#0006
T DB3.DBW 20//Write 6hex to PO1 (control word = enable)
L 1500
T DB3.DBW 22//Write 1500dec to PO2 (speed setpoint = 300 1/min)
L W#16#0000
T DB3.DBW 24//Write 0hex to PO3 (has no function)
//End of cyclical program processing in OB1
NETWORK
TITLE =Copy PO data from DB3, word 20/22/24 to the inverter
CALL SFC 15 (DPWR_DAT) //WRITE IO Device Record
LADDR := W#16#240 //Output address 576 = 240hex
RECORD := P#DB3.DBX 20.0 BYTE 6 //Pointer to DB/DW
RET_VAL:= MW 32 //Result in flag word 32
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
61
Page 62

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6
PROFINET Operating Behavior
PROFINET alarms using the example of MOVIDRIVE® B
00
6.7 PROFINET alarms using the example of MOVIDRIVE® B
The DFE32B supports diagnostics alarms in case of a unit error. These diagnostic
alarms are switched off at the factory. Proceed as follows to enable the diagnostics
alarms in STEP 7 HWKONFIG (→ following figure).
62269AEN
Diagnostics
alarm of the
MOVIDRIVE
Diagnostics
alarm of the integrated switch
®
• Select slot 2 of DFE32B.
• Press the right mouse button and select [Object properties] or double-click on the
slot. The "DFE32B properties" window opens.
• Select the "Parameters" tab.
• Set the diagnostics alarm to "ON" and confirm with [OK]
In case of an error of the MOVIDRIVE
can read the error message of the MOVIDRIVE
• Select slot 0 of DFE32B.
• Press the right mouse button and select [Object properties] or double-click on the
slot. The "DFE32B properties" window opens.
• Select the "Parameters" tab. Set "Alarm Port 1" or "Alarm Port 2" to "ON" and confirm
with [OK]. In a line topology, the respective port of the Ethernet node must be monitored that leads to the subsequent Ethernet node (coming from the PLC).
The DFE32B uses this setting to monitor the unit communication with adjacent
nodes. A diagnostics alarm is generated if the DFE32B detects an inactive partner at
port 1 or 2.
®
, a diagnostics alarm is generated and you
®
in plain text.
62
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 63

PROFINET Operating Behavior
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
PROFINET alarms using the example of MOVIDRIVE® B
00
A unit error of the MOVIDRIVE® B or the integrated switch results in a diagnostics alarm
being sent to the SIMATIC control as a so-called "incoming event". The "SF" LED lights
up red. You can determine the cause of the error in STEP 7 HWKONFIG. Go to ONLINE, mark the symbol of the DFE32B and check the module information via the context
menu (right mouse button).
6
58647AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
63
Page 64

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Introducing PROFINET data sets
00
7 Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
7.1 Introducing PROFINET data sets
With "Read Record" and "Write Record", PROFINET offers acyclic services that can be
used to transfer parameter data between PROFINET controller (master) and a PROFINET device (slave). Via UDP (User Datagram Protocol), the priority of this data exchange is lower than the priority of the process data exchange.
PROFINET
Controller
PO
Read/Write Record
The user data transported via an acyclic PROFINET service is grouped in a data set.
Each data set is clearly addressed by the following characteristics:
• API
•Slot number
• Subslot number
• Index
The structure of data set 47 is used for the parameter exchange with SEW-EURODRIVE
PROFINET units. The structure of data set 47 is specified in the PROFIdrive profile drive
technology of the PROFIBUS user organization as of V4.0 as PROFINET parameter
channel. Different procedures for accessing parameter data of the SEW-EURODRIVE
PROFINET unit are provided via this parameter channel.
PI
SEW
PROFINET
Device
62204AXX
64
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 65

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Introducing PROFINET data sets
7.1.1 Features of the SEW-EURODRIVE PROFINET units
The SEW-EURODRIVE PROFINET units that support acyclic Read Record and Write
Record services all have the same communication characteristics. The units are basically controlled via a PROFINET controller with cyclic process data. Additionally, this
controller (usually a PLC) can set the parameters for the SEW-EURODRIVE PROFINET
unit via Read Record and Write Record.
PROFINET
Controller
Read / Write Record
PD
I
7
00
PROFINET
Interface
SEW PROFINET
Cyclic IN/Out
Parameterbuffer 1
ParameterbufferProcess Data
Drive System
62205AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
65
Page 66

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
7.2 Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
Generally, the parameter setting of the drives to the PROFIdrive-Base Mode Parameter
Access of profile version 4.0 is implemented via data set 47. The Request ID entry is
used to distinguish between parameter access based on PROFIdrive profile or via SEWMOVILINK
ements. The data set structure is the same for PROFIdrive and MOVILINK
®
services. The following table shows the possible codes of the individual el-
®
access.
READ/WRITE
Record
The following MOVILINK
• 8-byte MOVILINK
PROFIdrive
Parameter Channel
SEW MOVILINK
®
DS47
®
services are supported:
®
parameter channel with all the services supported by the inverter
such as
– READ parameters
– WRITE parameter
– WRITE parameter volatile
–etc.
Box Data type Values
Unsigned8 0x00 Reserved
Request ID Unsigned8 0x40 SEW MOVILINK® service
Response ID Unsigned8 Response (+):
Unsigned8 0x00 ... 0xFF Number of axes 0 ... 255
No. of parameters Unsigned8 0x01 ... 0x13 1 ... 19 DWORDs (240 DP-V1 data bytes)
Attributes Unsigned8 For SEW MOVILINK® (Request ID = 0x40):
0x01 ... 0xFF
0x41 SEW Data Transport
0x00 Reserved
0x40 SEW MOVILINK® service (+)
0x41 SEW Data Transport
Response (–):
0xC0 SEW MOVILINK® service (–)
0x41 SEW Data Transport
0x00 No service
0x10 READ parameters
0x20 WRITE parameter
0x40 Read Minimum
0x50 Read Maximum
0x60 Read Default
0x80 Read Attribute
0x90 Read EEPROM
0xA0 ... 0xF0 Reserved
62206AXX
SEW Data Transport:
0x10 Value
No. of elements Unsigned8 0x00 For parameters that are not indexed
Parameter Number Unsigned16 0x0000 ... 0xFFFF MOVILINK
Subindex Unsigned16 0x0000 SEW: always 0
Format Unsigned8 0x43 Double word
No. of Values Unsigned8 0x00 ... 0xEA Quantity 0 ... 234
Error Value Unsigned16 0x0080 + MOVILINK
66
0x01 ... 0x75 Quantity 1 ... 117
®
parameter index
0x44 Error
®
For SEW MOVILINK® 16 Bit error value
-Additional Code Low
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 67

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
7.2.1 Parameter setting procedure via data set 47
Parameter access takes place with the combination of the WRITE RECORD and READ
RECORD PROFINET services. The parameter setting order is transferred to the IO de-
vice using the WRITE.req, whereupon it is processed internally.
The controller now sends a READ.req to pick up the parameter setting response. The
device sends a positive response READ.res. The user data now contain the parameter
setting response of the parameter setting order that was previously sent with WRITE.req
(see the following figure). This mechanism applies to a PROFINET controller.
I
7
00
Controller
Parameter
Request
Parameter
Response
PROFINET
WRITE.req DS47
with data (parameter request)
WRITE.res
without data
READ.req DS47
without data
READ.res(+)
with data (parameter response)
Figure 4: Telegram sequence for parameter access via Read/Write Record
SEW-Device
Parameter
Request
Parameter
Processing
Parameter
Response
62208AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
67
Page 68

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
7.2.2 Controller processing sequence
If the bus cycles are very short, the request for the parameter response arrives before
the SEW device has concluded the parameter access in the device. This means that the
response data from the SEW device is not yet available. In this state, the device delays
the response to the Read Record Request.
Send Write.request
with parameter data
Check Write.
response
Write.response
positive
Send Read.request
Read.response
negative or
timeout
No
Parameter transfer
ok, data available
Write.response
negative
Yes
Parameter transfer
aborted with ERROR
62209AEN
68
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 69

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
7.2.3 Addressing connected inverters
The structure of the DS47 data set defines an axis element. This element is used to
reach multi-axis drives that are operated via one PROFINET interface. The axis element
addresses one of the units connected via the PROFINET interface.
I
7
00
Addressing a
MOVIDRIVE
®
B
on the PROFINET
With the setting Axis = 0, the parameters of the MOVIDRIVE
®
B drive inverter are ac-
cessed. Since there are no drive units connected to the MOVIDRIVE
Axis > 0 is returned with an error code.
PROFINET
Controller
Cyclic OUT Data
PD
PD
Cyclic IN Data
Read / Write
Record
Axis = 0
®
B, an access with
PROFINET
62210AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
69
Page 70

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
7.2.4 MOVILINK® parameter requests
Example for reading a parameter
via MOVILINK
®
The MOVILINK
ture of data set 47. The Request ID 0x40 (SEW MOVILINK
change of MOVILINK
®
parameter channel of the SEW inverter is directly mapped in the struc-
®
parameter setting orders. Parameter access with MOVILINK
®
service) is used for the ex-
services usually takes place according to the structure described below. The typical telegram sequence for data set 47 is used.
Request ID: 0x40 SEW MOVILINK
The actual service is defined by the data set element Attribute in the MOVILINK
rameter channel. The high nibble of the element corresponds to the MOVILINK
®
service
®
®
service
pa-
code.
The following tables give an example of the structure of the WRITE.request and
READ.response user data for reading an individual parameter via the MOVILINK
®
pa-
rameter channel.
Sending parameter request
The table shows the coding of the user data for the WRITE.request PROFINET service.
The WRITE.request service is used to transfer the parameter setting request to the in-
verter. The firmware version is read.
The following table shows the WRITE request header for transferring the parameter request.
®
Service WRITE. request Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 10 10byte user data for parameter request
®
The following table shows the WRITE.request user data for MOVILINK
"Read param-
eters".
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Individual reference number for the parameter setting
1 Request ID 0x40 SEW MOVILINK
2 0x00 Axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Attributes 0x10 MOVILINK
5 No. of elements 0x00 0 = access to direct value, no subelement
6, 7 Parameter Number 0x206C MOVILINK
8, 9 Subindex 0x0000 Subindex 0
request is mirrored in the parameter response
®
service
®
service “READ parameter”
®
index 8300 = “Firmware version”
70
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 71

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
Query parameter response
The following table shows the coding of the READ.request user data including the
PROFINET header.
Service READ. request Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 240 Maximum length of response buffer in the master
7
Positive MOVILINK
®
parameter setting response
The table shows the READ.response user data with the positive response data of the
parameter setting request. The parameter value for index 8300 (firmware version) is returned as an example.
Service READ. request Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 10 Maximum length of response buffer in the master
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Reflected reference number from the parameter set-
1 Response ID 0x40 Positive MOVILINK
2 0x00 Reflected axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Format 0x43 Parameter format: Double word
5 No. of values 0x01 1 value
6, 7 Value High 0x311C Higher-order part of the parameter
8, 9 Value Low 0x7289 Lower-order part of the parameter
ting request
®
response
Decoding:
0x 311C 7289 = 823947913 dec
>> firmware version 823 947 9.13
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
71
Page 72

7
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
Example for writing a parameter
via MOVILINK
®
The following tables show the sequence of the WRITE and READ services for non-vol-
plus®
atile writing of the value 12345 to IPOS
®
example. The MOVILINK
service Write Parameter volatile is used for this purpose.
variable H0 (parameter index 11000) as an
Send „WRITE parameter volatile“ request
Service WRITE. request Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 16 16 byte user data for order buffer
®
The following table shows the WRITE.request user data for MOVILINK
"Write param-
eters volatile.
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Individual reference number for the parameter setting
1 Request ID 0x40 SEW MOVILINK
2 0x00 Axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Attributes 0x30 MOVILINK
5 No. of elements 0x00 0 = access to direct value, no subelement
6, 7 Parameter Number 0x2AF8 Parameter index 11000 = ’IPOS variable H0’
8, 9 Subindex 0x0000 Subindex 0
10 Format 0x43 Double word
11 No. of values 0x01 Change 1 parameter value
12, 13 Value High word 0x0000 Higher-order part of the parameter value
14, 15 Value Low word 0x0BB8 Lower-order part of the parameter value
order is reflected in the parameter response
®
service
®
service “WRITE parameter volatile”
72
After sending this WRITE.request, the WRITE.response is received. If there was no status conflict in processing the parameter channel, a positive WRITE.response occurs.
Otherwise, the status error is located in Error_code_1.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 73

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
Query parameter response
The following table shows the coding of the READ.req user data including the
PROFINET- header.
Service READ. request Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 240 Maximum length of response buffer in the master
Positive response to “WRITE Parameter volatile”
Service READ. response Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 4 4 byte user data in response buffer
7
Negative parameter response
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Reflected reference number from the parameter setting
1 Response ID 0x40 Positive MOVILINK
2 0x00 Reflected axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
The following table shows the coding of a negative response of a MOVILINK
request
®
response
®
service.
Bit 7 is entered in the the response ID if the response is negative.
Service WRITE. response Description
API 0 Fixed setting = 0
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Subslot_Number 1 Fixed setting = 1
Index 47 Index of the data set for the parameter request; constant index 47
Length 8 8 byte user data in response buffer
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Reflected reference number from the parameter setting order
1 Response ID 0xC0 Negative MOVILINK
2 0x00 Reflected axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Format 0x44 Error
5 No. of values 0x01 1 error code
6, 7 Error value 0x0811 MOVILINK
e. g. ErrorClass 0x08, add. code 0x11
(see section "MOVILINK
NET" on page 73 page 74)
®
®
response
return code
®
configuration return codes for PROFI-
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
73
Page 74

7
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
MOVILINK®
configuration
return codes for
PROFINET
The following table shows the return codes that are returned by the SEW PROFINET
interface module in case of an error in the PROFINET parameter access.
MOVILINK®
Return codes (hex)
0x0810 Invalid index, parameter index does not exist in the unit
0x0811 Function / parameter not implemented
0x0812 Read access only
0x0813 Parameter lock activated
0x0814 Factory setting is active
0x0815 Value for parameter too large
0x0816 Value for parameter too small
0x0817 Required option card not installed
0x0818 Error in system software
0x0819 Parameter access only via RS-485 process interface
0x081A Parameter access only via RS-485 diagnostics interface
0x081B Parameter is access-protected
0x081C Controller inhibit is required
0x081D Invalid value for parameter
0x081E Factory setting was activated
0x081F Parameter was not saved in EEPROM
0x0820 Parameter cannot be changed with output stage enabled/reserved
0x0821 Reserved
0x0822 Reserved
0x0823 Parameter may only be changed at IPOS program stop
0x0824 Parameter may only be changed when auto setup is deactivated
0x0505 Incorrect coding of management and reserved byte
0x0602 Communication error between inverter system and fieldbus interface
0x0502 Timeout of secondary connection (e.g. during reset or with Sys-Fault)
0x0608 Incorrect coding of the format field
Description
74
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 75

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
7.2.5 PROFIdrive parameter requests
The PROFIdrive parameter channel of SEW inverters is directly mapped in the structure
of data set 47. Parameter access with PROFIdrive services usually takes place according to the structure described below. The typical telegram sequence for data set 47 is
used. PROFIdrive only defines the two request IDs
Request ID: 0x01request parameter (PROFIdrive)
Request ID: 0x02change parameter (PROFIdrive)
This means there is restricted data access in comparison with the MOVILINK
NOTE
The request ID 0x02 Change Parameter (PROFIdrive) results in remanent write ac-
cess to the selected parameter. Consequently, the internal flash/EEPROM of the inverter is written with each write access. Use the MOVILINK
eter volatile“ if parameters must be written cyclically at short intervals. With this service, you only alter the parameter values in the RAM of the inverter.
I
00
®
services.
®
service „WRITE Param-
7
Example for reading a parameter
via PROFIdrive
The following tables show an example of the structure of the WRITE.request and
READ.res user data for reading an individual parameter via the MOVILINK
®
parameter
channel.
Sending parameter request
The table shows the coding of the user data for the WRITE.req service specifying the
PROFINET header. The WRITE.req service is used to transfer the parameter setting request to the inverter.
Service: WRITE.request Description
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Index 47 Index of the data set; constant index 47
Length 10 10 byte user data for parameter request
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Individual reference number for the parameter setting order that is
1 Request ID 0x01 Request parameter (PROFIdrive)
2 0x00 Axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Attributes 0x10 Access to parameter value
5 No. of elements 0x00 0 = access to direct value, no subelement
6, 7 Parameter Number 0x206C MOVILINK
8, 9 Subindex 0x0000 Subindex 0
reflected in the parameter response
®
index 8300 = “Firmware version”
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
75
Page 76

7
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
Query parameter response
The following table shows the coding of the READ.req user data including the
PROFINET header.
Service: READ.request Description
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Index 47 Index of the data set; constant index 47
Length 240 Maximum length of response buffer in the PN controller
Positive PROFIdrive parameter response
The table shows the READ.res user data with the positive response data of the parameter setting request. The parameter value for index 8300 (firmware version) is returned
as an example.
Service: READ.request Description
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Index 47 Index of the data set; constant index 47
Length 10 10 byte user data in response buffer
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Reflected reference number from the parameter setting order
1 Response ID 0x01 Positive response for „Request Parameter“
2 0x00 Reflected axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Format 0x43 Parameter format: Double word
5 No. of values 0x01 1 value
6, 7 Value Hi 0x311C Higher-order part of the parameter
8, 9 Value Lo 0x7289 Lower-order part of the parameter
Decoding:
0x 311C 7289 = 823947913 dec
>> firmware version 823 947 9.13
76
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 77

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
I
7
00
Example for writing a parameter
via PROFIdrive
The following tables show an example of the structure of the WRITE and READ services
for the remanent writing of the internal setpoint n11 (see section "Example for writing a
®
parameter via MOVILINK
"). page 72). The PROFIdrive service change parameter is
used for this purpose.
Send "WRITE parameter" request
The following table shows the PROFINET header of the WRITE request with parameter
request.
Service: WRITE.request Description
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Index 47 Index of the data set; constant index 47
Length 16 16 byte user data for order buffer
The following table shows the WRITE.req user data for the PROFINET service "Change
Parameter".
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Individual reference number for the parameter setting order is
1 Request ID 0x02 Change parameter (PROFIdrive)
2 0x01 Axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Attributes 0x10 Access to parameter value
5 No. of elements 0x00 0 = access to direct value, no subelement
6, 7 Parameter Number 0x7129 Parameter index 8489 = P160 n11
8, 9 Subindex 0x0000 Subindex 0
10 Format 0x43 Double word
11 No. of values 0x01 Change 1 parameter value
12, 13Value HiWord 0x0000 Higher-order part of the parameter value
reflected in the parameter response
14, 15Value LoWord 0x0BB8 Lower-order part of the parameter value
After sending this WRITE.request, the WRITE.response is received. If there was no status conflict in processing the parameter channel, a \positive WRITE.response occurs.
Otherwise, the status error is located in Error_code_1.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
77
Page 78

7
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
I
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
00
Query parameter response
The following table shows the coding of the WRITE.req user data including the PROFINET header.
Field Value Description
Function_Num READ.req
Slot_Number X Slot number not used
Index 47 Index of the data set
Length 240 Maximum length of response buffer in the PN controller
Positive response to "WRITE Parameter"
The following table shows the PROFINET header of the positive READ.response with
parameter setting response.
Service: READ.response Description
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Index 47 Index of the data set; constant index 47
Length 4 4 byte user data in response buffer
Negative parameter response
The following table shows the positive response for the PROFINET service "Change Parameter".
Byte Box Value Description
0 0x01 Reflected reference number from the parameter setting order
1 Response ID 0x02 Positive PROFIdrive response
2 0x01 Reflected axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
The following table shows the coding of a negative response of a PROFIdrive service.
Bit 7 is entered in the response ID if the response is negative.
Service: READ.response Description
Slot_Number 0 Random, (is not evaluated)
Index 47 Index of the data set; constant index 47
Length 8 8 byte user data in response buffer
Byte Box Value Description
0 Response refer-
ence
1 Response ID 0x810x82 Negative response for Request Parameter Negative response for
2 0x00 Reflected axis number; 0 = single axis
3 No. of parameters 0x01 1 parameter
4 Format 0x44 Error
5 No. of values 0x01 1 error code
6, 7 Error value 0x0811 MOVILINK
0x01 Reflected reference number from the parameter setting order
Change Parameter
®
e. g. ErrorClass 0x08, add. code 0x11
(see section "MOVILINK
NET" on page 74)
return code
®
configuration return codes for PROFI-
78
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 79

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Structure of the PROFINET parameter channel
I
7
00
PROFIdrive
return codes for
PROFINET
The following table shows the coding of the error number in the PROFIdrive parameter
response according to PROFIdrive profile V3.1. This table applies if you use the
PROFIdrive services "Request Parameter" and/or "Change Parameter"
Error no. Meaning Used for
0x00 Invalid parameter number. Access to non-existent parameters
0x01 Parameter value cannot be
changed
0x02 Minimum or maximum value
exceeded
0x03 Incorrect subindex Access to non-existent subindex
0x04 No assignment Access with subindex to parameter that is not indexed
0x05 Incorrect data type An attempt was made to change a replace a value with one
0x06 Setting not permitted (can
only be reset)
0x07 Description element cannot
be changed
0x08 Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: PPO write query for IR not available)
0x09 Description does not exist Access to description that is not accessible (parameter value
0x0A Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: incorrect access group)
0x0B No operation priority An attempt was made to change a parameter without change
0x0C Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: incorrect password)
0x0D Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: text cannot be read in cyclic data
0x0E Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: name cannot be read in cyclic data
0x0F No text assignment avail-
able
0x10 Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: no PPO write)
0x11 Request cannot be exe-
cuted due to the operating
mode
0x12 Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: other error)
0x13 Reserved (PROFIdrive Profile V2: data cannot be read in cyclic
0x14 Illegal value An attempt was made to change a value to one that is in the
0x15 Response is too long The length of the current response exceeds the maximum
0x16 Invalid parameter address Invalid value or value that is not valid for this attribute, num-
0x17 Incorrect format Write request: Invalid format or parameter data format that is
0x18 Number of values is not
consistent
0x19 Axis does not exist Access to an axis that does not exist
up to 0x64 Reserved –
0x65..0xFF Depends on the manufac-
turer
An attempt was made to change a parameter value that cannot be changed
An attempt was made to change a value to one that is outside
of the limit values
that does not correspond to the data type of the parameter
An attempt was made to set a value to one larger than 0
where this is not permitted
Access to description element that cannot be changed
is exists)
rights
transfer)
transfer)
Access to text assignment that is not accessible (parameter
value exists)
Access is currently not possible and the reason is not
explained
exchange)
permitted range but is not permitted due to other long-term
reasons (parameter with specified individual values)
transmittable length
ber of elements, parameter number, subindex or a combination of these factors.
not supported
Write request: Number of values of parameter data does not
correspond to the number of elements in the parameter
address
–
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
79
Page 80

I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
7
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Read or write parameters via data set 47
00
7.3 Read or write parameters via data set 47
7.3.1 Sample program for SIMATIC S7
The STEP 7 code stored in the GSD file shows how parameters are accessed via the
STEP 7 system function modules SFB 52/53. You can copy the STEP 7 code and import/compile it as a STEP 7 source.
NOTES
• There is an example of a function module for SIMATIC S7 controls available for
download in the "Software" section on the SEW website.
• This example is a special and free service that demonstrates only the basic approach to generating a PLC program as a non-binding sample. We are not liable for
the contents of the sample program.
7.3.2 Technical data PROFINET for MOVIDRIVE
GSD file for PROFINET:GSDML-V2.1-SEW-DFE-DFS-2Ports-jjjj.mm.tt.xml
Module name for project planning: MOVIDRIVE DFE32B
Supported data set: Index 47
Supported slot number: Recommendation: 0
Manufacturer code: 10A hex (SEW-EURODRIVE)
Profile ID: 0
C2 response timeout 1 s
Max. length C1 channel: 240 byte
Max. length C2 channel: 240 byte
®
DFE32B
80
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 81

Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Read or write parameters via data set 47
7.3.3 Error codes of the PROFINET services
The following table shows possible error codes of PROFINET services that may occur
in the event of an error in the communication on PROFINET telegram level. This table
is relevant if you want to write your own parameter assignment block based on the
PROFINET services because the error codes are reported directly back on the telegram
level.
7 6 5 4 3 3 2 0
Bit:
I
7
00
Error_Class
Error_Class (from
PROFINET-Specification)
0x0 ... 0x9 hex = reserved
0xA = application 0x0 = read error
0xB = access 0x0 = invalid index 0xB0 = No data block Index 47 (DB47);
0xC = resource 0x0 = read constraint conflict
0xD...0xF = user specific
Error_Code (from
PROFINET-Specification)
0x2 = module failure
0x3 to 0x7 = reserved
0x8 = version conflict
0xA to 0xF = user specific
0x1 = write length error
0x2 = invalid slot
0x3 = type conflict
0x4 = invalid area
0x5 = state conflict 0xB5 = Access to DB 47 temporarily not pos-
0x6 = access denied
0x7 = invalid range 0xB7 = WRITE DB 47 with error in the DB 47
0x8 = invalid parameter
0x9 = invalid type
0xA to 0xF = user specific
0x1 = write constraint conflict
0x2 = resource busy
0x3 = resource unavailable
0x4..0x7 = reserved
0x8..0xF = user specific
Error_Code
PROFINET Parameter channel
parameter requests are not supported
sible due to internal processing status
header
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
81
Page 82

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Integrated Web Server
Software requirements
8 Integrated Web Server
The DFE32B option card has a homepage for simple web diagnostics of MOVIDRIVE
and MOVITRAC®. Enter the configured IP address to access the homepage.
You can use the web page to access information about service and diagnostics.
8.1 Software requirements
The website has been tested with Microsoft® Internet Explorer 5.0 and Mozilla® Firefox
2.0. To display dynamic elements you will need the Java 2 Runtime Environment SE,
v1.5.0 or above.
If the Java 2 Runtime Environment is not installed on your system, the program will connect to Java and start an automatic download, if you allow it. Should you encounter any
problems, you can also download Java 2 Runtime SUN website and install it locally.
8.2 Security settings
If you are using a firewall or if you have a personal firewall installed on your system, they
could prevent you from accessing the Ethernet units. In this situation, you should allow
outgoing TCP/IP and UDP/IP traffic.
• An applet 'sewAppletsMoviEWeb.JAppletWeb' will prompt you to accept a certificate.
Click <Execute>. the certificate will be imported to the certificate list of the Java 2
Runtime Environment
• Click the check box 'Always trust content from this publisher' in order to avoid this
dialog for future executions.
®
8.3 Homepage layout MOVIDRIVE® MDX61B with DFE32B option
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
62223AXX
[1] Navigation bar
[2] Main window (Home) Button for starting the diagnostics applet
[3] Main window (Home) Button for displaying website help
[4] Main window (Home) Link to the MOVIDRIVE
82
®
B documentation page (Internet access required)
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 83

Structure of the diagnostics applet
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
8.4 Structure of the diagnostics applet
[1]
[2]
Integrated Web Server
8
[3]
[4]
[1] Tree view / Overview The tree displays the MOVIDRIVE
[2] Popup menu when you
right-click on a unit in the
tree
[3] Toolbar
(Quick selection using buttons)
[4] Plugin window ee section "Plugin window"
[5] Status table and unit sta-
tus
'My Network Tree'. Individual subsystems of the corresponding unit versions are displayed below that; they may contain additional units.
You can navigate to the plugins of an individual unit by right-clicking a unit
in the tree. A popup window appears, which leads you to that unit’s plugins. Further, you can adjust the access settings for a MOVIDRIVE
(see chapter "Access protection" Right-click on the network node and
select "Scan" to detect new units and display them in the tree.
[a] [b] [d] [e] [f] [g]
[a] Rescan unit tree and display it in the tree
[b] Open plugin for selected unit in unit tree
[c] Overview plugin for selected unit in unit tree, see section "Plugin window (Overview)"
[d] Close the selected plugin
[e] Settings for Ethernet communication and scanner
[f] Change to window mode or applet mode
[g] Display information dialog box
The table is visible by default. It lists all units and subunits found during a
scan. Since the status table sends cyclical parameter requests to the unit,
you can also close the table using the status button (bottom right).
[c]
62225AXX
®
B Ethernet unit in the network node
®
B
[5]
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
83
Page 84

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Plugin window
Integrated Web Server
Structure of the diagnostics applet
[1]
[2]
[3]
62226AXX
[1] Tab for open plugins If you have opened multiple plugins (e.g. plugins of various units), they
[2] Tab within the plugin
(shows parameter displays
being implemented)
[3] Main window with display
values and figures
are listed in the tab.
If the selected unit has several display columns, the tab will display
those columns.
The main window gives a visualization of the parameters.
84
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 85

Integrated Web Server
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Structure of the diagnostics applet
8
Example: Busmonitor plugin forMOVIDRIVE
®
This plugin is used to display the process data between the control and the
MOVIDRIVE
®
B and also for diagnosing the process data assignment.
62229AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
85
Page 86

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Integrated Web Server
Structure of the diagnostics applet
Example: Busmonitor plugin forMOVITRAC
®
This plugin is used to display the process data between the control and the MOVITRAC
B and also for diagnosing the process data assignment.
®
62230AXX
86
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 87

8.5 Access protection
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Access to the drive parameters and diagnostics information can be protected by a password. The access protection is deactivated as standard. You can activate the access
protection function by assigning a password [2]. To deactivate the function again, delete
the password (blank password).
If access protection is activated, a login dialog [1] will appear to request the saved password.
Integrated Web Server
Access protection
[1]
[2]
61662AXX
8
[1] Login [2] Config Login
Under "User" in the login dialog, you can select "Observer" or "Maintenance".
• Observer
– The drive unit parameters can be read with MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio but not
changed.
– The current parameter settings can be uploaded from the unit to the PC (param-
eter set upload).
plus®
– It is not possible to download a parameter set or an IPOS
®
– Diagnostics via MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio is possible, the scope settings, how-
program.
ever, cannot be changed.
• Maintenance
– MOVITOOLS
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
®
MotionStudio can be operated without any limitations.
87
Page 88

9
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
Overview
9 MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
9.1 Overview
The MOVITOOLS® software (version 5.40 or above) enables straightforward parameter
setting, visualization and diagnostics for your drive application. With MOVITOOLS
tionStudio, you can communicate with the MOVIDRIVE
DFE32B gateway and the SEW units connected to the gateway via Ethernet via the
DFE32B option card.
®
MDX61B drive inverter, the
®
Mo-
STOP
Before starting MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio, you must add exceptions to your firewall
for the installed software components.
• In your firewall, enter all the executable programs that belong to the software components you have installed.
• Check your firewall settings. It is possible that the firewall prevents the execution of
a program in the background. In other words, the user does not receive a message.
• Check whether an Ethernet communication can be established between the PC and
the DFE32B. To do so, you can use the "ping" command of the Windows command
prompt (Example: ping 10.3.71.15).
The MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio user interface comprises a central framework and the
individual tools. These are started as separate applications from the framework, or they
are integrated into the framework as plugins. The following figure shows the areas within
the framework.
88
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
11721AEN
Page 89

MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Procedure for configuring units
9
Areas and their
functions
The following table describes the areas within the framework and their function.
[1] Menu bar The main menu and toolbar contain all the important commands for
[2] Toolbar
[3] Area for project views Information about the units in a project. The information is visualized
[4] Area for plugins The tools are displayed in the form of plugins in this area. The plugins
[5] Unit status area You can display the status information of units that are accessible
[6] Status bar You can view the current communication status of the MOVITOOLS
navigating the framework.
using the following types of project views:
• Network View
• Project Planning View
are displayed either using tabs or as a separate window.
The display depends on the selected tool. In this example, the "Parameter tree" tool has been selected for a MOVIDRIVE
online in the "Status bar". You can also hide the "unit status" area.
MotionStudio in the status bar. This is where progress information is
displayed during a unit scan.
®
.
9.2 Procedure for configuring units
Overview The following figure shows the main steps to configure units with MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio.
1. Create the project and the network
®
®
2. Configure the communication channel(s)
3. Scan the network (Unit scan)
4. Switch to online mode
5. Configure the units with tools
6. Upload the inverter parameters,
then save the project
62348AEN
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
89
Page 90

9
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
Procedure for configuring units
Step 1: Create the
project and the
network
• Make sure that 'New project' is selected and confirm. The "New project" window
opens.
• Enter a name and directory for the new project and confirm your entries. The "New
network" window opens.
• Enter a name for the new network and confirm your entries. The main screen opens
and the 'Configure communication plugs' window opens.
Step 2: Configure
the communication channel
11723AEN
• Set the first or an additional communication channel to "Ethernet".
90
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
11724AEN
Page 91

MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Procedure for configuring units
9
Step 3: Scan the
network (unit
scan)
Step 4: Configure
units with tools
• Scan the network with (unit scan).
• Activate the online mode with .
• Select the unit you want to configure.
• Right-click to open the context menu and display the tools for configuring the unit.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
11737AEN
91
Page 92

9
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
Communication with external units
9.3 Communication with external units
If you want to establish an Ethernet communication with units outside the local network
segment, click "Configure SMLP".
11726AEN
• Open the context menu [1] by clicking on the button or via the key combination
[Ctrl-A] to add an IP address.
• Enter the respective IP address of the DFE32 units in the "IP address" field.
92
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 93

MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio via Ethernet
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Communication with external units
9
Parameters for
SMLP
The following table describes the parameters for SMLP (Simple MOVILINK® Protocol).
Parameters Description Note
Timeout Waiting time in [ms] that the client waits
Broadcast IP address IP addresses of the local network seg-
IP address
SMLP server
for a reply from the server after it has
made a request.
ment within which the unit scan is carried out
IP address of the SMLP server or of
other units that are to be included in the
unit scan but are outside the local network segment
Default setting: 1000 ms
Increase the value as required if a delay
in communication is causing malfunctions.
In the default setting, the unit scan only
retrieves units that are in the local network segment.
Enter the following IP address:
• the IP address of the SIMATIC S7
control if you run a direct communication from Ethernet to PROFIBUS
via SIMATIC S7.
• the IP address of units that are to
be included in the unit scan but are
outside the local network segment.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
93
Page 94

10
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Error Diagnostics
Diagnostic procedures
10 Error Diagnostics
10.1 Diagnostic procedures
The diagnostic procedures described in the following section demonstrate the error
analysis methods for the most frequent problems:
• Inverter does not work on PROFINET IO
• Inverter cannot be controlled using the IO controller
For more information dealing specifically with the inverter parameter settings for various
fieldbus applications, refer to the Fieldbus Unit Profile manual and the MOVIDRIVE
rameter list.
®
pa-
94
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 95

Error Diagnostics
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnostic problem 1: Inverter does not work on PROFINET IO.
Initial status:
• Inverter is connected to PROFINET IO
• Inverter configured in IO controller and bus communication is active
↓
Is the bus connector plugged in? No →
Yes
↓
Response of the Link
LED?
OFF → [C]
Response of the
BUS FAULT LED?
Yes
↓
Yellow →
Red →
10
[A]
[B]
[C]
Green
↓
Inverter has no connection to Ethernet
Check the configured and set PROFINET name.
PROFINET names identical? No → [D]
Yes
You may have configured an incorrect unit type or defined the configuration incorrectly.
Delete configuration for the inverter from the PROFINET IO network.
Perform project planning for the inverter again, choosing the unit designation "MOVIDRIVE+DFE32B".
Assign the address range for your control system.
Now load the configuration in the PROFINET IO controller and start the bus communication again.
[A] Check the bus cabling.
Off
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
[B] The DFE32B option was not yet configured or configured incorrectly.
Check the configuration, particularly the device name and the IP
address.
↓
[C] The DFE32B option indicates that the PROFINET IO controller has not
yet established communication.
↓
The PROFINET IO controller is switched off or has not yet been
started up.
[D] Adapt PROFINET names!
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
95
Page 96

10
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Error Diagnostics
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnostic problem 2:
Inverter cannot be controlled via the IO controller
Initial status:
• Bus communication with inverter OK (LED BUS FAULT off)
• Inverter running with 24 V (no supply voltage)
↓
The problem is either caused by incorrect parameter settings in the inverter or a
faulty control program in the PROFINET IO controller.
↓
Use P094 ... P097 (setpoint description PO1 ... PO3) to check whether the setpoints sent by the controller are received correctly.
To do so, send a setpoint other than 0 as a test in each output word.
↓
Setpoints received? Yes → [A]
No
↓
Check that the correct settings have been made for the following drive parameters:
• P100 SETPOINT SOURCE FIELDBUS
• P101 CONTROL SIGNAL SOURCEFIELDBUS
• P876 ENABLE PO DATA YES
↓
Settings OK? No → [B]
Yes
↓
The problem may be caused by your control program in the IO controller.
↓
Check that the address used in the program is the same as the address for
project planning.
Note that the inverter requires consistent data and access must take place
within the control program, if necessary, via special system functions (for example, SIMATIC S7, SFC 14 / 15).
96
[A] Setpoints are transferred.
Check whether the drive inverter has been enabled at the terminals.
[B] Correct settings.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 97

10.2 Error list in gateway operation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Error Diagnostics
Error list in gateway operation
10
Error
code
25 EEPROM SBus communication
28 Fieldbus timeout Default: PO data = 0
37 Watchdog error SBus communication
38 Internal error SBus communication
45 Error
111 System error
Designation Response Cause Measure
stopped
Error response
adjustable via P831
stopped
stopped
Initialization
device timeout
SBus communication
stopped
None Check the red system error LED (H1) of
Error while accessing EEPROM Activate factory settings, perform
No communication between master
and slave within the projected response
monitoring.
Error during execution of system software
Inverter electronics is faulted, possibly
due to EMC influence
Error after self-test during reset Perform a reset. Consult SEW service
the DFE. If this LED is on, one or several participants on the SBus could not
be addressed within the timeout interval. If the red system error LED (H1)
flashes, the DFE itself is in an error
state. In this case, error F111 was
reported to the control only via fieldbus.
reset and set parameters for DFE
again. Contact SEW service if the
error occurs again
• Check communications routine of
the master
• Extend the fieldbus timeout interval (response monitoring) in the
master configuration or deactivate
monitoring
Contact SEW Service.
Check ground connections and
shielding and correct, if necessary.
Contact SEW service if this error
occurs again.
if the error occurs again.
Check voltage supply and SBus
cabling, check SBus terminating
resistors. Check the project planning
if the DFE was configured with the
PC. Switch DFE off and on again. If
the error is still present, query the
error via diagnostic interface and perform the action described in this table.
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
97
Page 98

11
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
kVA
i
n
f
Technical Data
DFE32B for MOVIDRIVE® B, MOVITRAC® B and UOH11B gateway hou-
Hz
P
11 Technical Data
11.1 DFE32B for MOVIDRIVE® B, MOVITRAC® B and UOH11B gateway housing
DFE32B option
Part number 1821 345 6
Power consumption P = 3 W
Voltage supply (only in
gateway operation)
Application protocols • PROFINET IO (Ethernet frames with frame identification 8892
Port numbers used • 300 (SMLP)
EtherNet services •ARP
ISO / OSI layer 2 EtherNet II
Baud rate 100 Mbaud in full duplex process
Connection technology RJ45
Addressing 4 byte IP address or MAC-ID (00:0F:69:xx:xx:xx)
Manufacturer ID
(Vendor ID)
Tools for startup • MOVITOOLS
Firmware status of
MOVIDRIVE
®
MDX61B
U = DC 24 V (–15 %, +20 %)
= DC 200 mA
I
max
= 3.4 W
P
max
-control and set parameters for the drive inverter.
• HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) for diagnostics using a Web browser.
• SMLP (Simple Movilink Protocol), protocol used by MOVITOOLS
• 80 (HTTP)
• ICMP (Ping)
010A
hex
®
• DBG60B keypad
Firmware status 824 854 0.17 or above (→ Display with P076)
MotionStudio version 5.40 and higher.
hex
) to
®
.
98
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
Page 99

Dimension DFE32B via UOH11B gateway housing
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
11.2 Dimension DFE32B via UOH11B gateway housing
4.5
5.5
DFE 32B
RUN
BUS
FAULT
X30X32
224
Def IP
AS
PROFINET IO
01
257.5
234.5
Technical Data
185
kVA
i
P
f
Hz
n
11
30
28
22.5
100
62286AXX
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
99
Page 100

12
Index
12 Index
A
Access protection
Addressing
Assembly and Installation Notes
DFE32B option card in MOVIDRIVE
MDX61B .......................................................11
DFE32B option card in MOVITRAC
Installing and removing an option card
Assembly and Installation Notes
DFE32B / UOH11B gateway
Auto setup for gateway operation
B
Baud rate
Bus cables
BUS FAULT LED
C
Configuration via PROFIdrive Data Set 47
Connection
Connection MOVIDRIVE
Ethernet
Connection technology
Control
Control example
D
DFE32B
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnostics
..................................................... 16, 98
Shielding and routing
Addressing connected inverters
Controller processing sequence
Error codes of the PROFINET services
Features of the SEW-EURODRIVE
PROFINET units
Introducing PROFINET data sets
MOVILINK
Parameter setting procedure via record 47
PROFIdrive parameter requests
Read or write parameters via data set 47
Sample program for SIMATIC S7
Structure of the PROFINET parameter
channel
Technical data PROFINET for
MOVIDRIVE
DFE32B option
System bus (SBus 1) between a
MOVITRAC
System bus (SBus 1) between several
MOVITRAC
..............................................................19
MOVIDRIVE
MOVITRAC
Connection
Operating display
Terminal description
................................................87
..........................................................98
.........................11
®
®
B ........14
........................17
.......................44
....................................20
................................................25
...................69
...................68
...........................................65
®
parameter requests ..................70
.................64
..................75
.................80
.........................................................66
®
DFE32B .................................80
.............................................18
®
B unit and DFE32B .................14
®
B units ....................................15
®
/MOVITRAC®
.......................................98
®
MDX61B ................................57
®
B .............................................59
..................................................58
...................................................18
.........................................25
.....................................18
........................................94
.........................................................10
.........13
.........64
.......81
..67
....80
E
Error Diagnostics
Diagnostic procedures
Error list in gateway operation
Exclusion of liability
F
Fieldbus monitor
G
Gateway operation, error list
General Information
Exclusion of liability
General notes
right to claim under warranty
Structure of the safety notes
H
Homepage layout
I
IP address
L
Link / Activity LED
M
Monitoring functions
MOVIDRIVE
Control
Setting the drive inverter
MOVITOOLS
MOVITRAC
Control
Setting the frequency inverter
N
Network classes
O
Operating display DFE32B
BUS FAULT LED
Link / Activity LED
RUN LED
Option card
Installation and removal
Other applicable documentation
P
Part number
Pin assignment of an RJ45 plug connector
Plugin window
Sample plugin busmonitor for MOVITRAC
Sample plugin busmonitor for
MOVIDRIVE
Procedure after device replacement
Device replacement MOVIDRIVE
............................................... 94
................................. 94
........................... 97
.............................................. 6
................................................ 10
.............................. 97
....................................... 6
...................................................... 6
......................... 6
.......................... 6
............................................... 82
.......................................................... 21
.............................................. 26
........................................... 10
®
MDX61B
......................................................... 57
.............................. 46
®
MotionStudio via PROFINET ..... 88
®
B
......................................................... 59
...................... 47
................................................. 21
................................ 25
......................................... 25
........................................ 26
..................................................... 25
............................... 13
.......................... 7
....................................................... 98
.................................................... 84
®
.............................................. 85
.................. 24
®
B .......... 24
....... 19
®
86
100
Manual – DFE32B PROFINET IO Fieldbus Interface
 Loading...
Loading...