Page 1

MODELLING & ENGRAVING SET PMGS 12 B2
MODELLING & ENGRAVING SET
Operation and Safety Notes
Translation of original operation manual
KOMPLET ZA MODELIRANJE IN GRAVIRANJE
Navodila za upravljanje in varnostna opozorila
Prevod originalnega navodila za uporabo
MODELÁRSKA A GRAVÍROVACIA SÚPRAVA
Pokyny pre obsluhu a bezpečnostné pokyny
Preklad originálneho návodu na obsluhu
IAN 89959
ZESTAW MODELARSKI I GRAWERSKI
Wskazówki dotyczące obsługi i bezpieczeństwa
Tłumaczenie oryginalnej instrukcji obsługi
MODELÁŘSKÁ A GRAVÍROVACÍ SADA
Pokyny pro obsluhu a bezpečnostní pokyny
Překlad originálního provozního návodu
MODELLBAU- UND GRAVIERSET
Bedienungs- und Sicherheitshinweise
Originalbetriebsanleitung
Page 2

Before reading, unfold the page containing the illustrations and familiarise yourself with all functions of the
device.
Przed przeczytaniem proszę rozłożyć stronę z ilustracjami, a następnie proszę zapoznać się z wszystkimi
funkcjami urządzenia.
Pred branjem odprite stran s slikami in se nato seznanite z vsemi funkcijami naprave.
Před čtením si otevřete stranu s obrázky a potom se seznamte se všemi funkcemi přístroje.
Pred čítaním si odklopte stranu s obrázkami a potom sa oboznámte so všetkými funkciami prístroja.
Klappen Sie vor dem Lesen die Seite mit den Abbildungen aus und machen Sie sich anschließend mit allen
Funktionen des Gerätes vertraut.
GB Operation and Safety Notes Page 5
PL Wskazówki dotyczące obsługi i bezpieczeństwa Strona 17
SI Navodila za upravljanje in varnostna opozorila Stran 31
CZ Pokyny pro obsluhu a bezpečnostní pokyny Strana 43
SK Pokyny pre obsluhu a bezpečnostné pokyny Strana 55
DE / AT / CH Bedienungs- und Sicherheitshinweise Seite 67
Page 3
321
5
8
2
„AUS (OFF)“
„EIN (ON)“
76
45
A
8 9
11
B
10
23
22
21
20
19
18
C
8 10
E
F
12
13
14
15
16
17
4
D
G
Page 4

Page 5

Table of contents
Introduction
Proper use ............................................................................................................................................ Page 6
Features and equipment ..................................................................................................................... Page 6
Included items .....................................................................................................................................Page 6
Technical information .......................................................................................................................... Page 6
General safety advice for electrical power tools
1. Workplace safety ........................................................................................................................... Page 7
2. Electrical safety ............................................................................................................................... Page 7
3. Personal safety ................................................................................................................................ Page 8
4. Careful handling and use of electrical power tools ..................................................................... Page 8
5. Service ............................................................................................................................................. Page 9
Safety advice for all uses .................................................................................................................... Page 9
Safety advice relating to kickback ..................................................................................................... Page 10
Special safety advice relating to grinding and disc-cutting .............................................................. Page 11
Further special safety advice for disc-cutting ..................................................................................... Page 11
Special safety advice for abrading using sandpaper ......................................................................Page 11
Special safety advice for polishing .................................................................................................... Page 12
Special safety advice for working with wire brushes ........................................................................ Page 12
Device-specific safety instructions for small drill PMGS 12 B2 and
mains adapter-PMGS 12 B2-1 ..........................................................................................................Page 12
Operation .......................................................................................................................................Page 12
Inserting or replacing a tool / collet ...................................................................................................Page 13
Switching on and off / Setting the speed range ................................................................................Page 13
Advice on working with materials / Tools / Speed ranges ............................................................... Page 13
Tips and tricks ...................................................................................................................................... Page 14
Maintenance and cleaning ............................................................................................... Page 14
Service ............................................................................................................................................... Page 14
Warranty ......................................................................................................................................... Page 14
Disposal ............................................................................................................................................ Page 15
Conformity Declaration / Manufacturer ................................................................ Page 15
5 GB
Page 6
Modelling and engraving set
PMGS 12 B2
Q
Introduction
We congratulate you on the purchase of your new
device. You have chosen a high quality product. The
instructions for use are part of the product. They
contain important information concerning safety,
use and disposal. Before using the product, please
familiarise yourself with all of the safety information
and instructions for use. Only use the unit as de
and for the specified applications. If you pass the
product on to anyone else, please ensure that you
also pass on all the documentation with it.
scribed
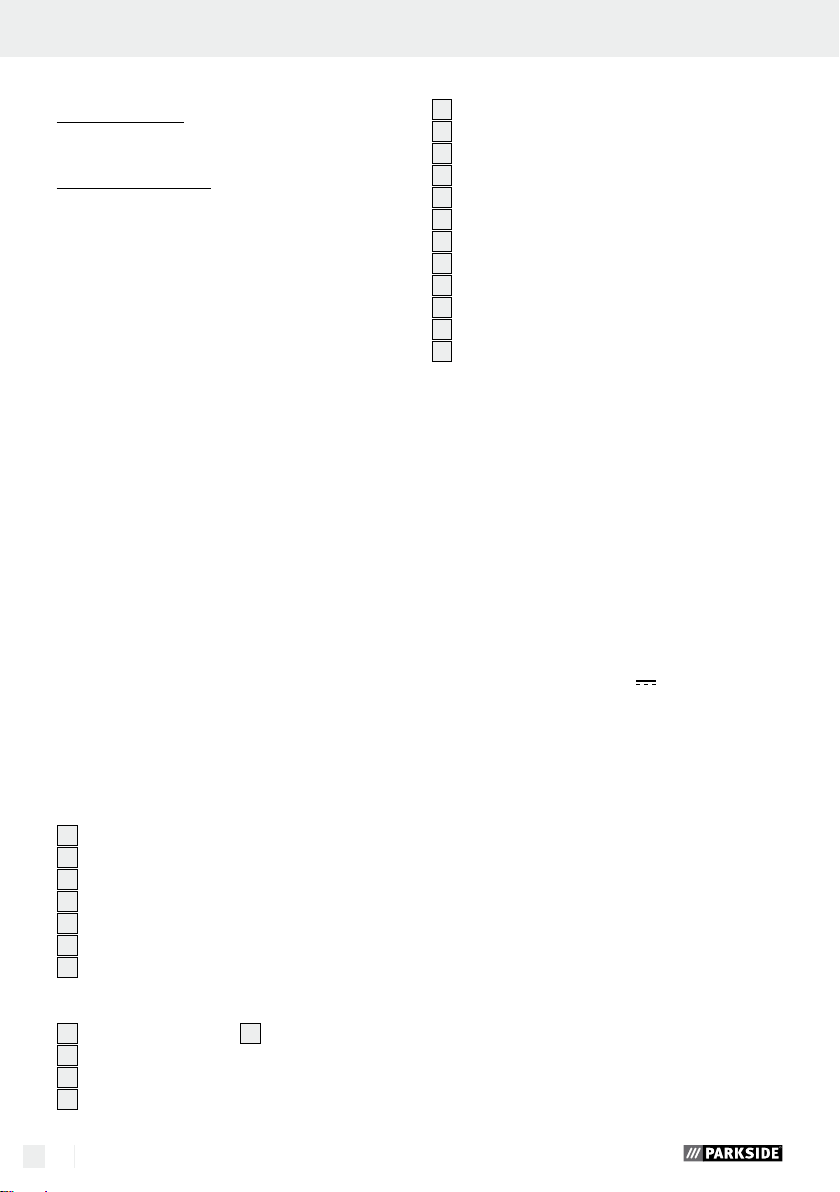
Accessories (see Fig. B):
12
6 HSS drills
13
2 Mandrels for mounting tools
14
3 Polishing wheels
15
4 Grinding wheels
16
1 Metal brush
17
16 Cutting wheels
18
5 Collets
19
2 Plastic brushes
20
3 Milling bits
21
2 Engraving bits
22
5 Grinding bits
23
1 Combination tool
Q
Included items
Q
Proper use
The small drill is to be used for drilling, milling, engraving, polishing, cleaning up, grinding, separating
and sawing of wood, metal, plastic, ceramic or stone
in dry rooms. Any other use or modification to the
drill / grinder shall be considered as improper use
and could give rise to considerable dangers. The
manufacturer will not accept liability for loss or
damage arising from improper use. Not intended
for commercial use.
Q
Features and equipment
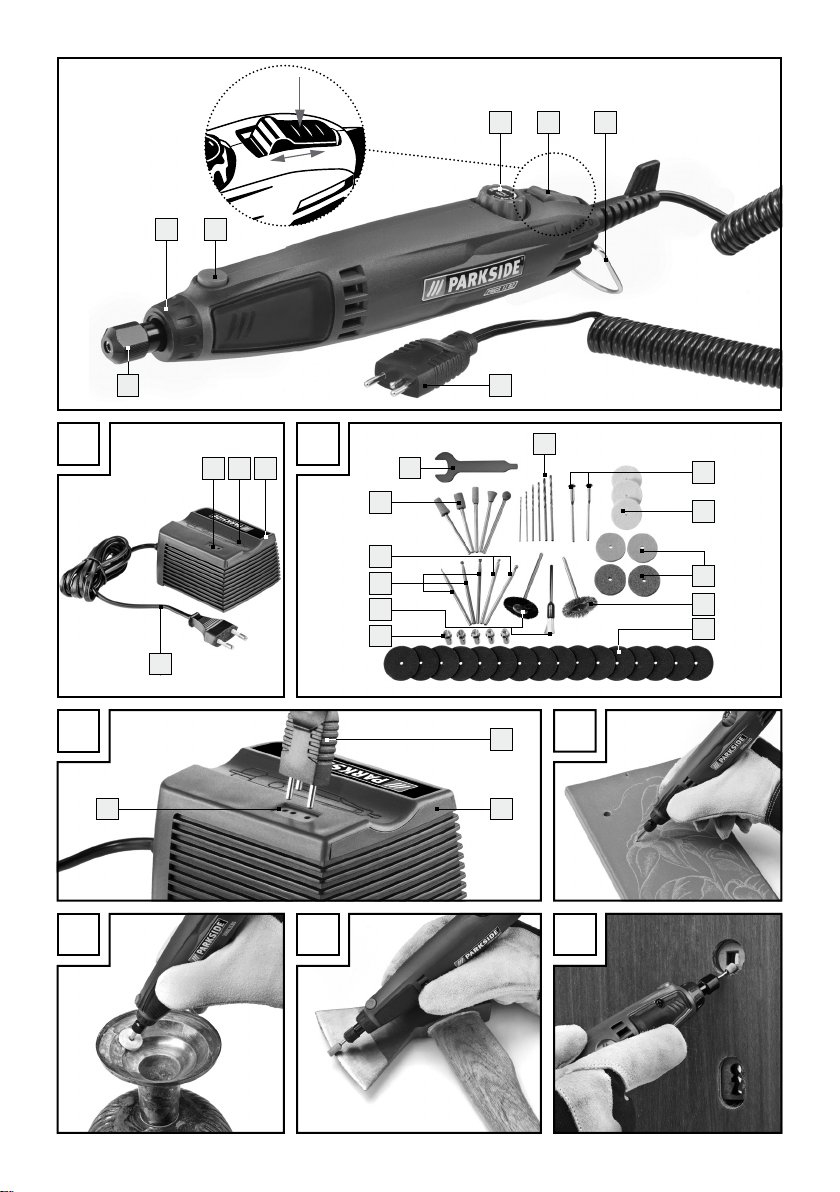
Small drill:
1
Rotational speed control
2
ON / OFF switch
3
Metal stirrup hanger
4
Plug for mains adapter
5
Clamping nut
6
Spigot nut
7
Spindle lock
Mains adapter (see Fig. A):
8
Plug-in device for plug
9
Tray
10
Mains adapter
11
Power cable (with mains plug)
4
1 Small drill
1 Mains adapter
1 Plastic case
1 Accessory kit (50-piece)
1 Operating instructions
Q
Technical information
Small drill PMGS 12 B2:
Nominal voltage: 12 V
Nominal input power: 22 W
Idle-running speed: n
5000–20000 min
0
-1
Drill bit diameter: max. ø 3.2 mm
Disc: max. ø 25 mm
Certified acc. to:
EN60745-1; EN60745-2-1
EN60745-2-3
Noise and vibration data:
Measured values for noise are determined in accordance with EN 60745. The A-weighted noise level
of the electrical power tool are typically:
Sound pressure level: 54.70 dB(A)
Sound power level: 65.70 dB(A)
Uncertainty K: 3 dB
Evaluated acceleration, typical:
Hand / arm vibration: 1.868 m / s
Uncertainty K = 1.5 m / s
2
2
6 GB
Page 7

Introduction / General safety advice for electrical power tools
The vibration level specified in
these instructions was measured in accordance with
an EN 60745 standardised measurement process
and can be used to compare equipment. The vibration emission value specified can also serve as a
preliminary assessment of the exposure.
The vibration level will change according to the application of the electrical tool an in some cases may
exceed the value specified in these instructions. Regularly using the electric tool in such a way may
make it easy to underestimate the vibration.
Note: If you wish to make an accurate assessment
of the vibration loads experienced during a particular
period of working, you should also take into account
the intervening periods of time when the device is
switched off or is running but is not actually in use.
This can result in a much lower vibration load over
the whole of the period of working.
Mains adapter PMGS 12 B2-1:
INPUT:
Rated voltage: 230 V∼ 50 Hz
OUTPUT:
Nominal voltage: 12 V
Nominal current: 1 A
Protection class: II /
Certified acc. to: EN61558
General safety advice for
electrical power tools
Read all the safety
advice and instructions! Failure to
observe the safety advice and instructions
may result in electric shock, fire and / or serious injury.
Keep all the safety advice and instructions
in a safe place for future reference!
The term “electrical tool” used in the safety advice
refers to electrical tools powered by mains electricity
(by means of a mains lead) and electrical tools
powered by rechargeable batteries (without a
mains lead).
1. Workplace safety
a) Keep your working area clean and
well lit. Untidy or poorly lit working areas
can lead to accidents.
b) Do not work with the device in poten-
tially explosive environments in which
there are inflammable liquids, gases
or dusts. Electrical power tools create sparks,
which can ignite dusts or fumes.
c) Keep children and other people away
while you are operating the electrical
tool. Distractions can cause you to lose control
of the device.
2. Electrical safety
a)
The mains plug on the device must match
the mains socket. The plug must not be
modified in any way. Do not use an
adapter plug with devices fitted with
a protective earth. Unmodified plugs and
matching sockets reduce the risk of electric shock.
b) Avoid touching earthed surfaces such
as pipes, radiators, ovens and refrigerators with any part of your body.
There is an increased risk of electric shock if
your body is earthed
c) Keep the device away from rain or
moisture. Water entering an electrical device
increases the risk of electric shock.
d) Do not use the mains lead for any pur-
pose for which it was not intended, e.g.
to carry the device, to hang up the device or to pull the mains plug out of the
mains socket. Keep the mains lead
away from heat, oil, sharp edges or
moving parts of the device. Damaged
or tangled mains leads increase the risk of
electric shock.
e) When working outdoors with an
electrical power tool always use extension cables that are also approved
for use outdoors. The use of an extension
cable suitable for outdoor use reduces the risk
of electric shock.
.
7 GB
Page 8

f) Use a residual current device (RCD)
for protection if operating the electrical power tool in a moist environment
is unavoidable. The use of an RCD reduces
the risk of electric shock.
correctly used. The use of these devices
reduces the hazard presented by dust.
4.
Careful handling and use
of electrical power tools
3. Personal safety
a) Remain alert at all times, watch what
you are doing and always proceed
with caution. Do not use the device if
you are tired or under the influence of
drugs, alcohol or medication. One mo
of carelessness when using the device can lead
to serious injury.
b)
personal protective equipment such as dust
masks, non-slip safety shoes, safety helmets or
ear protectors, appropriate to the type of electrical power tool used and work undertaken,
reduces the risk of injury.
c) Avoid unintentional operation of the
device. Check that the electrical power
tool is switched off before you connect
it to the mains, pick it up or carry it.
Accidents can happen if you carry the device
with your finger on the ON / OFF switch or with
the device switched on.
d) Remove any setting tools or spanners
before you switch the device on. A tool
or spanner left attached to a rotating part of a
device can lead to injury.
e) Avoid placing your body in an unnat-
ural position. Keep proper footing
and balance at all times. By doing this
you will be in a better position to control the
device in unforeseen circumstances.
f) Wear suitable clothing. Do not wear
loose clothing or jewellery. Keep your
hair, clothing and gloves clear of moving parts. Loose clothing, jewellery or long
hair can become trapped in moving parts.
g) If vacuum dust extraction and collection
devices are fitted do not forget to
that they are properly connected and
8 GB
Wear personal protective
equipment and always wear
safety glasses. The wearing of
ment
check
a) Do not overload the device. Always
use an electrical power tool that is
intended for the task you are undertaking. By using the right electrical power
tool for the job you will work more safely and
achieve a better result.
b) Do not use an electrical power tool if
its switch is defective. An electrical power
tool that can no longer be switched on and off
is dangerous and must be repaired.
c) Pull the mains plug from the socket
before you make any adjustments to
the device, change accessories or when
the device is put away. This precaution is
intended to prevent you from unintentionally
starting the device.
d) When not in use always ensure that
electrical power tools are kept out of
reach of children. Do not let anyone use
the device if he or she is not familiar
with it or has not read the instructions
and advice. Electrical power tools are dan-
gerous when they are used by inexperienced
people.
e) Look after the device carefully. Check
that moving parts are working properly and move freely. Check for any parts
that are broken or damaged enough
to detrimentally affect the functioning
of the device. Have damaged parts
repaired before you use the device.
Many accidents have their origins in poorly
maintained electrical power tools.
f) Keep cutting tools clean and sharp.
Carefully maintained cutting tools with sharp
cutting edges are less likely to jam and are
easier to control.
g) Use the electrical power tool, accesso-
ries, inserted tools etc. in accordance
with these instructions and advice, and
the stipulations drawn up for this par-
Page 9

General safety advice for electrical power tools
ticular type of device. In doing this, take
into account the working conditions
and the task in hand. The use of electrical
power tools for purposes other than those intended can lead to dangerous situations.
5. Service
a) Have your device repaired at the ser-
vice centre or by qualified specialist
personnel using original manufacturer
parts only. This will ensure that your device
remains safe to use.
Q
Safety advice for all uses
General safety advice for grinding,
sanding (with sandpaper), wire brushing,
polishing and disc-cutting:
a) This electrical power tool is intended
for use as a grinding, sanding, wirebrushing, and disc-cutting machine.
Observe all the safety advice, instructions, information in figures and all
other information you received with
this device. If you do not observe the following
advice it could lead to electric shock, fire and /
or serious injury.
b) Normative statement / advice for this tool is not
applicable.
c) Do not use any accessory not specifi-
cally intended by the manufacturer for
this electrical power tool. Although an
accessory may fit on your electrical power tool,
this does not on its own guarantee that it can
be safely used.
d) The maximum permitted speed of an
attachment must be at least as high as
the maximum speed indicated for the
electrical power tool. An accessory rotating
faster than its permitted speed could disintegrate
or fly off.
e) The external diameter and the thickness
of the attachment must be compatible
with the dimensions of your electrical
power tool. Attachments that are not dimen-
sionally compatible cannot be adequately
guarded or controlled.
f) Grinding discs, flanges, grinding
wheels or other accessories must fit
exactly on to the spindle of your electrical power tool. Attachments that do not
exactly fit on the spindle turn unevenly, vibrate
severely and could lead to loss of control.
g) Do not use damaged attachments.
Before every use check attachments
such as grinding discs for loose fragments and cracks, grinding wheels for
cracks, deterioration or excessive wear
and wire brushes for loose or broken
wires. If the electrical power tool or
attachment is dropped, inspect for
damage or change the attachment for
an undamaged one. When you have
inspected and inserted the attachment,
position yourself and bystanders away
from the plane of the rotating attachment and run the device at maximum
speed for one minute. Damaged attach-
ments will usually break apart during this test.
h)
glasses, depending on the application.
Wear a dust mask, hearing protectors,
safety gloves or special apron capable
of stopping particles of the grinding
medium or workpiece, as appropriate
for the task. Eyes must be protected from the
flying debris which can arise from some operations. Dust or breathing masks must be capable
of filtering out the dust generated by the application. Prolonged exposure to loud noise can
lead to hearing loss.
i) Keep bystanders at a safe distance
from your work area. Anyone entering
the work area must wear personal
protective equipment. Fragments of the
workpiece or of a broken attachment could fly
off and cause injury beyond the immediate
working area.
j) Hold the device by the insulated han-
dle surfaces when you are undertaking work where there is the danger
Wear personal protective
equipment. Use a full face visor, safety goggles or safety
9 GB
Page 10

of the attachment striking hidden
electricity cables or the device’s mains
lead. Contact with a live wire could cause
metal parts of the device to become live and
lead to electric shock.
k) Keep the mains lead away from rotat-
ing attachments. If you lose control of the
device the mains lead may become severed or
trapped and your hand or arm may be pulled
into the rotating attachment.
l) Never lay the electrical power tool
down until after the attachment has
come to a complete standstill. The rotat-
ing attachment may snag when it comes into
contact with the surface and cause you to lose
control of the device.
m) Do not have the electrical power tool
running while you are carrying it. Your
clothing could become trapped by unintentional contact with the rotating attachment and the
tool could be pulled into your body.
n) Clean the ventilation slots on your
electrical power tool regularly. The motor’s fan draws dust into the housing. A build-up
of metal dust could give rise to an electrical
hazard.
o) Never use the electrical power tool
near inflammable materials. Sparks
could ignite these materials.
p) Do not use attachments that require
the use of coolants. The use of water or
other liquid coolants could result in electric shock.
Q
Safety advice
relating to kickback
Kickback is the sudden reaction to a pinched or
snagged rotating attachment, such as a grinding
disc, grinding pad, wire brush etc. Pinching or
snagging results in the rotating attachment coming
to an abrupt stop. This causes the electrical power
tool (if not controlled) to move in the opposite direction to the direction of rotation of the attachment
at the point of constraint.
If, for example, a grinding disc is pinched or snags
in a workpiece, this can cause the edge of the
grinding disc to penetrate the workpiece, become
trapped there and either free itself or kickback. The
grinding disc moves towards or away from the operator, depending on the direction of movement of
the disc at the point of constraint. The grinding disc
could also break.
Kickback occurs as a result of incorrect use or misuse of the electrical power tool. It can be prevented
by taking the appropriate precautions as described
below.
a) Maintain a firm grip on the electrical
power tool and position your body
and arms to allow you to resist kickback forces. Always use the auxiliary
handle, if provided, to exercise the
greatest possible control over kickback forces or reaction torques as the
device builds up to full speed. By taking
suitable precautions the operator can control
kickback and reaction forces.
b) Do not place your hands near a rotat-
ing attachment. If kickback occurs the attachment could move over your hand.
c) Avoid positioning your body in the
area into which the electrical power
tool would move in the event of a
kickback. A kickback moves the electrical
power tool in the opposite direction to the direction of movement of the grinding disc at the
point of constraint.
d) Work particularly carefully in the area
of corners, sharp edges etc. to avoid
the attachment bouncing or snagging
on the workpiece. Corners, sharp edges or
bouncing have a tendency to snag the rotating
attachment. This causes loss of control or kickback.
e) Do not use saw-chain woodcarving
discs or toothed discs. Such attachments
create frequent kickback and loss of control of
the electrical power tool.
10 GB
Page 11

General safety advice for electrical power tools
Q
Special safety advice relating
to grinding and disc-cutting
a) Always use the guard designed for
the type of abrasive consumable you
are using. Always use abrasive consumables
approved for use with your electrical power
tool. Abrasive consumables not approved for
use with your electrical power tool cannot be
adequately guarded and are unsafe.
b) To ensure the highest level of opera-
tional safety, the disc guard cover must
be attached to the electrical power tool
and set in such a way that the smallest
possible area of the abrasive consumable is exposed to the operator. The disc
guard cover is there to protect the operator from
pieces breaking off and accidental contact with
the abrasive consumable.
c) Abrasive consumables must be used
only for their recommended purposes, For example: never grind with the
side face of a cutting disc. Cutting discs
are intended for removing material using the
edge of the disc. Sideways forces on these
abrasive consumables can cause them to break.
d) Always use an undamaged mounting
flange of the correct size and shape
for your selected grinding disc. Suitable
flanges support the grinding disc and reduce the
chance of it breaking. Flanges for cutting discs
different from the flanges for other abrasive discs.
e) Never use worn down abrasive con-
sumables intended for larger electrical
power tools. Abrasive consumables intended
for larger electrical power tools are not designed
for the faster rotational speeds of these smaller
electrical power tools and could break.
are
creases the load and the tendency of the disc
to twist or snag in the cut, making kickback or
disc breakage more likely.
b) Avoid the area in front of or behind
the rotating cutting disc. If the cutting disc
is moving away from you at the point of constraint in the workpiece, then, in the event of
a kickback, the electrical power tool and the
rotating disc may be thrown towards you.
c) If the cutting disc jams or you stop
work for a while, switch the device
off and hold it until the disc comes to
a complete stop. Never attempt to
pull the still rotating cutting disc out of
the cut as this could cause kickback.
Determine and rectify the reason for the jamming.
d) Do not switch on the device if the cut-
ting disc is in the workpiece. Allow
the cutting disc to reach full speed before carefully continuing with the cut.
Otherwise the disc could snag, jump out of the
workpiece or cause a kickback.
e) Support boards or workpieces whilst
cutting to reduce the risk of kickback
caused by a jammed cutting disc. Large
workpieces may bend under their own weight.
The workpiece must be supported to both sides
of the cutting disc and particularly near the
cutting disc and at the workpiece edge.
f) B
e particularly careful when pocket
cutting in existing walls or other areas
where you cannot see what you are cut
t
ing into. The cutting disc plunged into the surface
could cut through gas or water pipes, electricity
cables or other objects and cause kickback.
Q
Special safety advice for
abrading using sandpaper
-
Q
Further special safety
advice for disc-cutting
a) Avoid snagging the cutting disc and
do not use too much contact pressure.
Do not attempt to make excessively
deep cuts. Overloading the cutting disc in-
Do not use over-sized sanding sheets.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for sanding sheet size. Sanding
sheets that project beyond the backing pad
could cause injury in addition to jamming,
tearing of the sheet or kickback.
11 GB
Page 12
Q
Special safety
advice for polishing
Do not use the polishing bonnet if it
has any loose parts, in particular the
fastening cords. Tuck the fastening cords
away or trim them. Loose fastening cords rotating with the attachment could catch your fingers
or become trapped in the workpiece.
Q
Special safety advice for
working with wire brushes
a) Bear in mind that wire brushes lose
pieces of wire during normal use. Do
not overload the wires by applying too
much pressure. Flying pieces of wire can very
easily penetrate thin clothing and / or skin.
b) U
se a guard, if recommended, but m
sure that the wire brush does not come
into contact with the guard. The diameters
of disc brushes and cup brushes can increase
due to contact pressure and centripetal forces.
Q
D
evice-specific safety instructi
for small drill PMGS 12 B2 and
mains adapter-PMGS 12 B2-1
When you use the drill / grinder wear
the following protective equipment:
safety glasses and protective gloves.
For indoor use only!
CAUTION! The tool continues to rotate
after it has been switched off! Avoid
contact with rapidly rotating drill / grinder components.
Securely support the
workpiece. Use clamps or a vice to grip the
workpiece firmly. This is much safer than holding
it in your hand.
Never support your-
self by placing your hands near or in
front of the device or the workpiece
surface. A slip can result in injury.
12 GB
ake
ons
Avoid contact with moving sanding or
grinding tools.
DANGER OF FIRE FROM FLYING
Abrading metal creates flying sparks. For this
reason, always make sure that nobody is placed
in any danger and that there are no inflamma
materials near the working area.
DUST HAZARD! Any
harmful / noxious dusts generated from machining represent a risk to the health of the person
operating the device and to anyone near the
work area.
Wear a dust mask!
NOXIOUS FUMES!
Ensure that there is adequate ventilation when
machining surfaces containing plastic or covered with paint, varnish etc.
Do not soak the materials or the sur-
face you are about to work on with
liquids containing solvents.
Avoid abrading paints containing lead
or other substances hazardous to
Do not machine materials containing
asbestos. Asbestos is a known carcinogen.
Do not machine moist materials or
damp surfaces.
NOTE! Do not allow the tool to come to a
standstill by overloading it!
Switch the device off
and allow it to come to a standstill before you put it down.
Always keep the de
clean, dry and free of oil or grease.
Children or persons who lack the knowledge or
experience to use the device or whose physical,
sensory or intellectual capacities are limited
must never be allowed to use the device without
supervision or instruction by a person responsible
for their safety. Children must never be allowed
to play with the device.
Q
Operation
Never use the device for a purpose
for which it was not intended or with
non-original parts / accessories. The use
of tools or accessories other than those recom-
SPARKS!
health.
vice
ble
Page 13
Operation
mended in the operating instructions could lead
to you suffering an injury.
Q
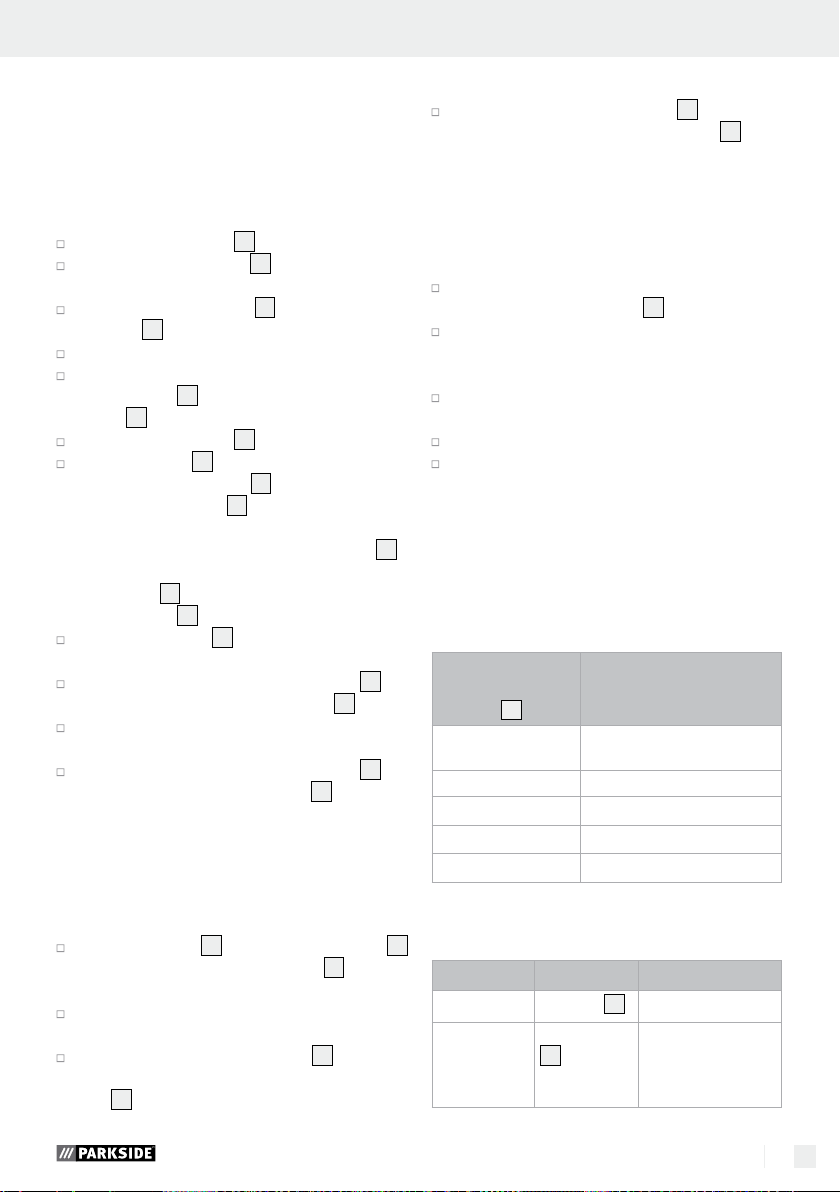
Inserting or replacing
a tool / collet
Press the spindle lock 7 and keep it pressed.
Rotate the clamping nut 5 until the lock
engages.
Loosen the clamping nut 5 with the combina-
23
tion key
.
If a tool is already inserted, remove it.
First insert the tool you wish to use though the
clamping nut
collet
5
before you insert it into the
18
suitable for the tool shaft.
Press the spindle lock 7 and keep it pressed.
Insert the collet 18 into the threaded insert and
tighten the clamping nut
the combination key
Using the Insertion tool with mandrel
5
on the thread using
23
.
13
NOTE: Use the screwdriver end of the combi-
nation key
the mandrels
23
to release or tighten the screw of
13
.
Insert the mandrel 13 into the electrical tool as
described.
With the aid of the combination wrench 23,
unscrew the screw from the mandrel
13
.
Place the insertion tool you wish to have onto
the screw between the two washers.
With the aid of the combination wrench 23,
tighten the screw on the mandrel
Q
Switching on and off /
13
.
Setting the speed range
Switching off:
Set the rotational speed control 1 to position
“5”. Press down the ON / OFF switch
then move it in direction of the cable.
Q
Advice on working with
materials / Tools / Speed ranges
Use the highest speed when working on steel
or iron with the milling bits
Use a short trial on a test piece to determine the
optimum rotational speed range for working on
zinc, zinc alloy, aluminium, copper and lead.
Use the low speed range for working on plastics
and low-melting point materials.
Use high speeds on wood.
Use the medium speed range for cleaning,
polishing and buffing.
The following information shall be considered as
recommendatory only. Learn by practical experience
:
which tools and settings are the best for the materials you work with.
Setting the appropriate speed:
Numeral on the
rotational speed
control
1
5
8
12
16
20
20
.
Material to be
worked on
Plastics and low melting
point materials
Stone, Ceramics
Softwood, metal
Hardwood
Steel
2
and
Switching on / Setting the speed range:
Connect the plug 4 to the power supply unit 10
by inserting it into the plug-in device
8
provided
for such purposes (see Fig. C).
Connect the device to the power supply by
inserting the mains plug into the socket.
Press down the ON / OFF switch 2 and then
move it in direction of the rotational speed con-
1
trol
. Then set the rotational speed control to
a position between “5” and “20”.
Examples of appropriate tool selection
Function:
Function Accessory Application
Drilling
HSS drill
Milling Milling bits
20
Drilling wood
12
Various tasks, e.g.
hollowing out,
gouging, shaping,
grooving or slotting
13 GB
Page 14
Function Accessory Application
Engraving Engraving
bits
21
Making marks,
craft projects
(see Fig. D)
Polishing,
derusting
CAUTION!
Use only the
lightest contact pressure
of the tool on
Metal brush
16
Polishing
wheel
14
Derusting
Working on various metals and
plastics, in particular noble metals
like gold or silver
(see Fig. E)
the workpiece.
Cleaning Plastic brush
19
E.g. cleaning complex plastic housings or the area
around a door lock
Grinding Grinding
wheels
grinding bits
22
Grinding work on
stone, wood; fine
,
15
work on hard materials such as ceram
or alloyed steel
(see Figs. F, G)
Cutting and
sawing
Q
Tips and tricks
Cutting discs
17
Cutting metal,
plastic or wood
If you use press too hard you run the risk of breaking the tool or damaging the workpiece. You will
achieve the best results by operating the tool at a
constant rotational speed and using a low contact
pressure on the workpiece.
Q
Maintenance and cleaning
The device is maintenance-free.
Clean all the dirt off the drill / grinder. Use a
dry cloth for cleaning.
Q
Service
Have your device
repaired at the service centre or by
qualified specialist personnel using
original manufacturer parts only. This
will ensure that your device remains safe to use.
If the plug or lead
needs to be replaced, always have
the replacement carried out by the
manufacturer or its service centre. This
will ensure that your device remains safe to use.
Q
Warranty
The warranty for this appliance is for 3
years from the date of purchase. The appliance has been manufactured with care
and meticulously examined before delivery. Please retain your receipt as proof of
purchase. In the event of a warranty claim,
ic
please make contact by telephone with our
Service Department. Only in this way can a
p
ost-free despatch for your goods be assured.
The warranty covers only claims for material and
maufacturing defects, but not for transport damage,
for wearing parts or for damage to fragile components, e.g. buttons or batteries. This product is for private use only and is not intended for commercial use.
The warranty is void in the case of abusive and improper handling, use of force and internal tampering not carried out by our authorized service branch.
Your statutory rights are not restricted in any way
by this warranty.
The warranty period will not be extended by repairs
made unter warranty. This applies also to replaced
and repaired parts. Any damage and defects extant
on purchase must be reported immediately after
unpacking the appliance, at the latest, two days after
the purchase date. Repairs made after the expiration
of the warranty period are subject to payment.
14 GB
Page 15

Warranty / Disposal / Conformity Declaration / Manufacturer
GB
Service Great Britain
Tel.: 0871 5000 720
(0,10 GBP/Min.)
e-mail: kompernass@lidl.co.uk
IAN 89959
Q
Disposal
The packaging is wholly composed of
environmentally-friendly materials that can
be disposed of at a local recycling centre.
Do not dispose of electric tools
in the household waste!
In accordance with European Directive 2002 / 96 / EC
about waste electrical and electronic equipment
and its transposition into national legislation, worn
out electric tools must be collected separately and
taken for environmentally compatible recycling.
Please contact your municipal or city council to ask
about how to dispose of old electrical tools.
Q
Conformity Declaration /
Manufacturer
We, KOMPERNASS GMBH, the person responsible
for documents: Mr Semi Uguzlu, BURGSTR. 21,
44867 BOCHUM, GERMANY, hereby declare that
this product complies with the following standards,
normative documents and EU directives:
Machinery Directive
(2006 / 42 / EC)
EU Low Voltage Directive
(2006 / 95 / EC)
Electromagnetic Compatibility
(2004 / 108 / EC)
RoHS Directive
(2011 / 65 / EU)
Applicable harmonized standards
EN 60745-1/A11:2010, EN 60745-2-1:2010
EN 60745-2-3:2011
EN 55014-1/A2:2011, EN 55014-2/A2:2008
EN 61000-3-2/A2:2009, EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61558-1/A1:2009, EN 61558-2-6:2009
Type / Device description:
Modelling and engraving set PMGS 12 B2
Date of manufacture (DOM): 04–2013
Serial number: IAN 89959
Bochum, 30.04.2013
Semi Uguzlu
- Quality Manager -
We reserve the right to make technical modifications
in the course of further development.
15 GB
Page 16

16
Page 17

Spis zawartości
Wstęp
Użytkowanie zgodnie z przeznaczeniem ...................................................................................... Strona 18
Wyposażenie ................................................................................................................................... Strona 18
Zakres dostawy ................................................................................................................................ Strona 18
Dane techniczne .............................................................................................................................. Strona 18
Ogólne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dla elektronarzędzi
1. Bezpieczeństwo miejsca pracy ..................................................................................................Strona 19
2. Bezpieczeństwo elektryczne .......................................................................................................Strona 19
3. Bezpieczeństwo osób ................................................................................................................. Strona 20
4. Staranne obchodzenie się i użytkowanie narzędzi elektrycznych .......................................... Strona 21
5. Serwis ........................................................................................................................................... Strona 21
Wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dla wszystkich zastosowań ............................................................ Strona 21
Odrzut i odpowiednie wskazówki bezpieczeństwa......................................................................Strona 23
Szczególne wskazówki odnośnie szlifowania i cięcia .................................................................. Strona 23
Dalsze szczególne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dotyczące tarcz tnących ................................. Strona 24
Szczególne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dotyczące szlifowania papierem ściernym ................Strona 24
Szczególne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dotyczące polerowania .............................................. Strona 24
Szczególne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dotyczące pracy przy użyciu szczotek drucianych ...... Strona 25
Wskazówki dotyczące bezpieczeństwa użytkowania mini-wiertarki PMGS 12 B2 i
zasilacza-PMGS 12 B2-1 ...............................................................................................................Strona 25
Uruchomienie
Zakładanie / wymiana uchwytu mocującego ................................................................................ Strona 26
Załączanie i wyłączanie / Nastawianie zakresu prędkości obrotowej .......................................Strona 26
Wskazówki dotyczące obróbki materiału / Narzędzia / Prędkości obrotowych ........................ Strona 26
Dobre rady i triki .............................................................................................................................. Strona 27
Konserwacja i czyszczenie............................................................................................Strona 27
Serwis ............................................................................................................................................. Strona 27
Gwarancja .................................................................................................................................. Strona 28
Usuwanie ..................................................................................................................................... Strona 28
Deklaracja zgodności / Producent ..........................................................................Strona 29
17 PL
Page 18
Zestaw modelarski i grawerski
PMGS 12 B2
Q
Wstęp
Zasilacz (patrz ilustracja A):
8
Wejście kabla z wtyczką
9
Półka
10
Zasilacz
11
Kabel sieciowy (z wtyczką)
4
Gratulujemy zakupu nowego urządzenia. Tym samym zdecydowali się Państwo na zakup produktu
wysokiej jakości. Instrukcja obsługi jest częścią tego
produktu. Zawiera ona ważne wskazówki dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa, użytkowania iutylizacji. Przed
pierwszym użyciem produktu należy zapoznać się
ze wszystkimi wskazówkami dotyczącymi obsługi
ibezpieczeństwa. Używać produktu wyłącznie
zgodnie zjego poniżej opisanym przeznaczeniem.
Wprzypadku przekazania produktu innej osobie
należy dołączyć do niego całą jego dokumentację.
Q
Użytkowanie zgodnie
z przeznaczeniem
Mini-wiertarka jest przeznaczona do wiercenia, frezowania, grawerowania, polerowania, czyszczenia,
szlifowania, cięcia i piłowania drewna, metalu, tworzywa sztucznego, ceramiki lub kamienia, w suchych
pomieszczeniach. Każde inne zastosowanie urządzenia lub zmiana dokonana w urządzeniu są
uznawane za niezgodne z przeznaczeniem i kryją
w sobie poważne zagrożenie nieszczęśliwym wypadkiem. Za szkody powstałe wskutek użytkowania
urządzenia sprzecznego z przeznaczeniem producent nie ponosi żadnej odpowiedzialności. Urządzenie nie jest przeznaczone do celów zarobkowych.
Q
Wyposażenie
Mini-wiertarka:
1
Regulacja prędkości obrotowej
2
Łącznik ZAŁ. / WYŁ.
3
Kabłąk metalowy
4
Wtyczka do zasilacza
5
Nakrętka mocująca
6
Nakrętka kołpakowa
7
Blokada wrzeciona
18 PL
Osprzęt (patrz Rysunek B):
12
6 Wierteł ze stali szybkotnącej o
podwyższonej wydajności skrawania
13
2 Trzpienie do mocowania narzędzi
14
3 Tarcze polerskie
15
4 Tarcze szlifierskie
16
1 Szczotka metalowa
17
16 Ściernic tarczowych do cięcia
18
5 Tuleje zaciskowe
19
2 Szczotki z tworzywa sztucznego
20
3 Nasadki frezowe
21
2 Nasadki grawerskie
22
5 Nasadek szlifierskich
23
1 Klucz uniwersalny
Q
Zakres dostawy
1 Mini-wiertarka
1 Zasilacz sieciowy
1 Walizka z tworzywa sztucznego
1 Zestaw osprzętu (50 części)
1 Instrukcja obsługi
Q
Dane techniczne
Mini-wiertarka PMGS 12 B2:
Napięcie nominalne: 12 V
Nominalny pobór mocy: 22 W
Prędkość obrotowa
biegu jałowego: n
5000–20000 min
0
-1
Wiertło: maks. ø 3,2 mm
Tarcz: maks. ø 25 mm
Certyfikacja wg: EN60745-1;
EN60745-2-1
EN60745-2-3
Informacje dotyczące hałasu i wibracji:
Wartość pomiarowa hałasu wyznaczona zgodnie
z EN 60745. Poziom hałasu elektronarzędzia wg
oceny A wynosi typowo:
Page 19

Wstęp / Ogólne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dla elektronarzędzi
Poziom ciśnienia hałasu: 54,70 dB(A)
Pozom mocy hałasu: 65,70 dB(A)
Niepewność pomiaru K: 3 dB
Określone przyśpieszenie, typowe:
Przenoszenie wibracji: 1,868 m / s
Niepewność K = 1,5 m / s
Podany w niniejszych instrukcjach poziom drgań wyznaczony został za
pomocą metody pomiarowej określonej w normie
EN 60745 i może zostać użyty do porównania
urządzeń. Podany poziom emisji drgań może być
wykorzystywany również do wstępnego oszacowania przerw w działaniu.
Poziom drgań będzie się różnił w zależności od
zastosowania elektronarzędzia i w niektórych
przypadkach może przekroczyć wartość podaną
w niniejszej instrukcji. Obciążenie drganiami może
wydawać się mniejsze niż w rzeczywistości, jeśli
elektronarzędzie będzie regularnie używane ten
sposób.
Wskazówka: Celem dokładnego oszacowania
obciążenia wibracjami w okresie określonego okresu
czasu pracy należy uwzględnić również te okresy, w
których urządzenie jest wyłączone lub wprawdzie
jest włączone, ale w rzeczywistości nie pracuje.
Może to przyczynić się do znacznej redukcji obciążenia wibracjami w całym okresie czasu pracy.
Zasilacz PMGS 12 B2-1:
WEJŚCIE / Input:
Napięcie znamionowe: 230 V∼ 50 Hz
WYJŚCIE / Output:
Napięcie nominalne: 12 V
Prąd znamionowy: 1A
Klasa ochronna: II /
Certyfikacja wg: EN61558
2
2
Ogólne wskazówki bezpie-
czeństwa dla elektronarzędzi
Przeczytaj
wszystkie wskazówki dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa oraz instrukcje!
Zaniedbania w przestrzeganiu wskazówek dotyczących bezpieczeństwa oraz w przestrzeganiu
instrukcji mogą spowodować porażenie prądem
elektrycznym, pożar i / lub ciężkie obrażenia ciała.
Przechowuj na przyszłość wszystkie
wskazówki dotyczące bezpieczeństwa
oraz instrukcje!
Używany we wskazówkach dotyczących bezpieczeństwa termin „narzędzie elektryczne“ odnosi się
do narzędzi elektrycznych zasilanych z sieci (z kablem sieciowym) oraz do narzędzi elektrycznych
zasilanych
z akumulatorów (bez kabla sieciowego).
1. Bezpieczeństwo miejsca pracy
a) Utrzymywać stanowisko pracy w czy-
stości i dobrze oświetlone. Nieporządek
i nieoświetlone obszary robocze mogą prowadzić do wypadków.
b) Nie pracuj przy użyciu urządzenia w
otoczeniu zagrożonym eksplozją, w
którym znajdują się palne ciecze, gazy
lub pyły. Urządzenia elektryczne wytwarza-
ją iskry, które mogą zapalić pył lub pary.
c) Podczas użytkowania urządzenia
elektrycznego trzymaj dzieci i inne
osoby z daleka od urządzenia. Przy
odchyleniu możesz stracić kontrolę nad urządzeniem.
2. Bezpieczeństwo elektryczne
a) Wtyk sieciowy urządzenia musi
pasować do wtykowego gniazdka
sieciowego. W żaden sposób nie
wolno zmieniać wtyku sieciowego
urządzenia. Nie używaj żadnych wty-
19 PL
Page 20

ków adapterowych razem z urządzeniami
wyposażonymi w uziemienie
ochron
ne. Niezmienione wtyki sieciowe i pa-
sujące wtykowe gniazdka sieciowe zmniejszają
ryzyko porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
b) Unikaj kontaktu fizycznego z powier-
zchniami uziemionymi takimi jak
powierzchnie rur, grzejników, kuchni
elektrycznych i lodówek. Istnieje podwyż-
szone niebezpieczeństwo porażenia prądem
elektrycznym, gdy twoje ciało jest uziemione.
c) Trzymaj urządzenie z daleka od desz-
czu i wilgoci. Wniknięcie wody do urządzenia
elektrycznego zwiększa ryzyko porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
d)
Nie używaj kabla sieciowego w
sprzeczny z jego przeznaczeniem, tj.
do noszenia urządzenia, zawieszania
urzą dzenie lub do wyciągania wtyku
sieciowego z wtykowego gniazdka
sieciowego. Trzymaj kabel z daleka
od gorąca, oleju, ostrych krawędzi lub
poruszających się części urządzeń.
Uszkodzone lub poplątane kable zwiększają
ryzyko porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
e)
Gdy pracujesz z urządzeniem elektrycznym na dworze używaj wyłącznie
przedłużaczy, które są dopuszczone
również do pracy na dworze. Użycie
przedłużacza przystosowanego do stosowania
na dworze zmniejsza ryzyko porażenia prądem
elektrycznym.
f) Jeśli praca elektronarzędzia w otocze-
niu wilgotnym jest nie do uniknięcia,
należy zastosować wyłącznik prądu
uszkodzeniowego. Zastosowanie wyłącz-
nika prądu uszkodzeniowego zapobiega niebezpieczeństwu porażenia prądem elektrycz
sposób
nym.
3. Bezpieczeństwo osób
a) Bądź stale uważny, zwracaj uwagę
na to co robisz i postępuj rozsądnie w
trakcie pracy z narzędziem elektrycznym. Nie używaj narzędzia, gdy jesteś
zmęczony lub znajdujesz się pod
wpływem narkotyków, alkoholu lub
lekarstw. Chwila nieuwagi przy użytkowaniu
urządzenia może prowadzić do poważnych
obrażeń ciała.
b)
wyposażenia ochronnego takiego jak maska
c) Unikaj niezamierzonego uruchomienia.
d) Usuń narzędzia do nastawiania urzą-
e) Unikaj nienormalnej postawy ciała.
f) Noś odpowiednią odzież. Nie noś ob-
g) Jeżeli zostaną zamontowane urzą-
Noś osobiste wyposażenie
ochronne i zawsze okulary
ochronne. Noszenie osobistego
przeciwpyłowa, buty antypoślizgowe, kask
ochronny lub ochrona słuchu stosownie do
sposobu użytkowania narzędzia elektrycznego
zmniejsza ryzyko obrażeń ciała.
Upewnij się, że narzędzie elektryczne
jest wyłączone zanim podłączysz je
do zasilania prądowego, uchwycisz je
lub będziesz je przenosił. Jeżeli podczas
przenoszenia urządzenia będziesz trzymał
palec na przełączniku WŁĄCZ. / WYŁĄCZ.
lub jeżeli urządzenie jest włączone, to może
to prowadzić do nieszczęśliwych wypadków.
dzenia lub klucze płaskie zanim włączysz urządzenie. Narzędzie lub klucz,
który znajduje się w obracającej się części
urządzenia może prowadzić do obrażeń ciała.
Zadbaj o pewne stanowisko i w każdej chwili utrzymuj równowagę.
Dzięki temu będziesz mógł lepiej kontrolować
urządzenie, zwłaszcza w nieoczekiwanych
sytuacjach.
szernej odzieży ani biżuterii. Trzymaj
włosy, odzież i rękawice z daleka od
poruszających się części. Luźna odzież,
biżuteria lub długie włosy mogą zostać uchwycone przez poruszające się części.
dzenia do odsysania i wychwytywania
pyłu, to upewnij się, że są one podłączone i że będą prawidłowo używane.
Używanie tych urządzeń zmniejsza zagrożenie
wywoływane pyłem.
20 PL
Page 21

Ogólne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dla elektronarzędzi
4.
Staranne obchodzenie
się i użytkowanie narzędzi
elektrycznych
a) Nie przeciążaj urządzenia. Używaj
do swojej pracy przeznaczonego do
niej narzędzia elektrycznego. Za pomo-
cą odpowiedniego narzędzia elektrycznego
pracujesz lepiej i bezpieczniej w danym zakresie robót.
b) Nie używaj żadnego narzędzia elek-
trycznego, którego przełącznik jest
uszkodzony. Narzędzie elektryczne, które
nie daje się już więcej włączyć lub wyłączyć,
jest niebezpieczne i musi zostać naprawione.
c) Zanim przeprowadzisz nastawy urzą-
dzenia, wymienisz części osprzętu lub
odłożysz urządzenie wyciągnij wtyczkę sieciową z sieciowego gniazdka
wtykowego. Ten środek ostrożności zapo-
biega niezamierzonemu startowi urządzenia.
d) Przechowuj nieużywane narzędzia
elektryczne poza zasięgiem dzieci. Nie
pozwól na użytkowanie urządzenia
osobom, które nie są z nim obznajomione lub nie przeczytały niniejszych
instrukcji. Narzędzia elektryczne są niebez-
pieczne, gdy są używane przez osoby niedoświadczone.
e) Pielęgnuj starannie urządzenie.
Sprawdź, czy ruchome części urządzenia funkcjonują nienagannie i nie
zakleszczają się, czy części urządzenia
nie są złamane lub uszkodzone w takim stopniu, że funkcjonowanie urządzenia jest uszczuplone. Zleć naprawę
uszkodzonych części przed użyciem
urządzenia. Przyczyną wielu wypadków są
źle konserwowane narzędzia elektryczne.
f) Utrzymuj narzędzia tnące w stanie
ostrym i czystym. Starannie pielęgnowane
narzędzia tnące o ostrych krawędziach tnących mniej zakleszczają się i dają się łatwiej
prowadzić.
g) Używaj narzędzia elektrycznego,
osprzętu, narzędzi wymiennych itp.
odpowiednio do niniejszych instrukcji
i w taki sposób, jaki jest zalecany dla
tego specjalnego typu urządzenia.
Uwzględniaj przy tym warunki robocze i wykonywane czynności. Użycie
narzędzi elektrycznych do innych zastosowań
niż to przewidziano może prowadzić do niebezpiecznych sytuacji.
5.
Serwis
a) Urządzenie oddawać do naprawy tyl-
ko wykwalifikowanemu personelowi
fachowemu i tylko z użyciem oryginalnych części zamiennych. To sposób na
zapewnienie bezpieczeństwa urządzenia.
Q
Wskazówki bezpieczeństwa
dla wszystkich zastosowań
Wspólne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa
dla szlifowania, szlifowanie papierem
ściernym, praca ze szczotkami drucianymi,
polerowanie i cięcie tarczą tnącą:
a) Niniejsze elektronarzędzie można
używać jako szlifierkę, szlifierkę do
szlifowania papierem ściernym, szczotkę drucianą, polerkę i szlifierkę do
cięcia tarczą tnącą. Prosimy o przestrzeganie wszelkich wskazówek bezpieczeństwa, instrukcji, ilustracji i danych
otrzymanych wraz z urządzeniem.
W przypadku nieprzestrzegania poniższych
instrukcji może dojść do porażenia prądem
elektrycznym, pożaru lub ciężkich obrażeń ciała.
b) Normatywne zwroty / wskazówki nie dotyczą
tego narzędzia.
c) Nie należy używać żadnego wyposa-
żenia, które nie zostało przewidziane
specjalnie przez producenta dla tego
elektronarzędzia. To, że dane wyposażenie
można zamocować na elektronarzędziu, nie
gwarantuje jego bezpiecznego użycia.
d)
Dopuszczalna liczba obrotów narzędzia
roboczego winna być przynajmniej
tak duża, jak maksymalna liczba obrotów podana na elektronarzędziu.
21 PL
Page 22

Wyposażenie, obracające się szybciej niż to
jest dopuszczalne może się rozpaść lub oderwać.
e) Średnice zewnętrzne oraz grubość
narzędzia roboczego winny odpowiadać danym wymiarowym elektronarzędzia. Narzędzia robocze o niewłaści-
wych wymiarach nie mogą być dostatecznie
osłonięte lub kontrolowane.
f) Ściernice, kołnierze, ściernice talerzowe
lub inne wyposażenie winny dokładnie odpowiadać średnicy wrzeciona
elektronarzędzia. Narzędzia robocze, które
nie są dokładnie dostosowane do średnicy
wrzeciona szlifierki obracają się nierównomiernie, wpadają w bardzo mocne wibracje i mogą
prowadzić do utraty kontroli nad narzędziem.
g) Nie należy nigdy stosować uszkodzo-
nych narzędzi roboczych. Przed każdy
użyciem narzędzi roboczych takich
jak ściernice należy sprawdzić pod
kątem odprysków i pęknięć, ściernice
talerzowe pod kątem pęknięć, stępienia lub dużego zużycia, szczotki druciane pod kątem popękanych drutów.
Po upadku elektronarzędzia lub narzędzia roboczego należy sprawdzić,
czy nie jest ono uszkodzone; używać
tylko nieuszkodzonych narzędzi roboczych. Po sprawdzeniu narzędzia
roboczego przed przystąpieniem do
pracy upewnić się, czy osoby będące
w pobliżu znajdują się poza płaszczyzną wirowania narzędzia roboczego,
to samo dotyczy osoby obsługującej,
następnie włączyć urządzenie na kilka minut na najwyższych obrotach.
Uszkodzone narzędzia robocze najczęściej
ulegną pęknięciu w czasie tego testowania.
h)
Zakładać osobiste wyposażenie ochronne. W zależności
od rodzaju pracy należy
stosować pełną ochronę twarzy, ochro-
nę oczu lub okulary ochronne. Jeśli to
jest potrzebne, zakładać maskę przec
iwpyłową, ochronniki słuchu, rękawice
ochronne, specjalny fartuch chroniący
przed cząstkami ściernicy i materiału
obrabianego. Oczy należy chronić przed
22 PL
odpryskującymi ciałami obcymi powstającymi
przy różnych pracach, maski przeciwpyłowe
lub maski do ochrony dróg oddechowych winny filtrować pył powstający w czasie pracy. W
przypadku narażenia osoby na hałas przez
dłuższy okres czasu może dojść do utraty słuchu.
i) Zwracać uwagę, aby osoby postronne
przebywały w bezpiecznej odległości
od obszaru pracy. Każdy, kto wchodzi w
obszar pracy winien zakładać osobiste wyposażenie ochronne. Odłamki obrabianego
przedmiotu lub połamane narzędzia robocze
mogą się oderwać i spowodować obrażenia
również poza bezpośrednim obszarem pracy.
j) W czasie robót, przy których można
natrafić na ukryte przewody elektryczne lub kabel sieciowy urządzenie
m
należy trzymać za izolowane powierzchnie uchwytów. Zetknięcie z prze-
wodami będącymi pod napięciem może spowodować przepływ prądu również do metalowych
elementów urządzenia i doprowadzić do porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
k) Trzymać kabel zasilający z dala od
wirujących narzędzi roboczych. W
przypadku utraty kontroli nad urządzeniem,
kabel zasilający może zostać przecięty lub
porwany, a dłoń lub ręka może dostać się do
obracającego narzędzia roboczego.
l) Nie należy nigdy odkładać elektrona-
rzędzia dopóki nie przestanie się ono
całkowicie obracać. Obracające się narzę-
dzie robocze może zetknąć się z powierzchnią
odkładania, przez co można utracić nad nim
kontrolę.
m) Podczas przenoszenia elektronarzę-
dzia nie może być ono włączone i się
obracać. Na skutek przypadkowego zetknię-
cia z obracającym się narzędziem roboczym
ubranie robocze obsługującego może zostać
porwane, a narzędzie robocze może spowodować obrażenia ciała.
n) Należy regularnie czyścić szczeliny
wentylacyjne elektronarzędzia. Wentylatorek silnika zasysa pył do środka, a duże
nagromadzenie pyłu metalowego może spowodować zagrożenia elektryczne.
Page 23

Ogólne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dla elektronarzędzi
o) Nie wolno używać elektronarzędzia
w pobliżu materiałów palnych. Iskry
mogą spowodować zapalenie się tych materiałów.
p)
Nie używać żadnych narzędzi roboczyc
wymagających płynnego chłodziwa.
Użycie wody lub innego chłodziwa płynnego
może prowadzić do porażenia prądem elektrycznym.
Q
Odrzut i odpowiednie
wskazówki bezpieczeństwa
Odrzut jest gwałtowną reakcją na skutek zakleszczenia lub zablokowania obracających się narzędzi
roboczych, takich jak ściernice, ściernice talerzowe,
szczotki druciane itd. Zakleszczenie lub zablokowanie powoduje natychmiastowe zatrzymanie się
narzędzia roboczego. Wskutek tego niekontrolowane
elektronarzędzie zostaje gwałtownie obrócone w
kierunku przeciwnym do kierunku jego obracania
się wokół miejsca zablokowania.
Jeśli na przykład ściernica zostanie zakleszczona
lub zablokowana w przedmiocie obrabianym, krawędź ściernicy, która zagłębiona jest w materiale
zostaje zatrzymana, a na skutek tego ściernica może
się wyłamać i spowodować odrzut. Ściernica wtedy
porusza się od lub w kierunku obsługującego w zależności od kierunku obrotów ściernicy na miejscu
zablokowania. W tym wypadku ściernica może
również się połamać.
Odrzut jest skutkiem niewłaściwego lub błędnego
użycia narzędzia roboczego. Można mu zapobiec
poprzez zastosowanie środków opisanych poniżej.
a) Trzymać elektronarzędzie pewnie, a
korpus i ręce ułożyć w takim położeniu, w którym można przeciwstawić
się siłom odrzutu. Należy zawsze używać uchwytu dodatkowego, jeśli on
jest, aby mieć jak największe panowanie nad siłami odrzutu lub momentami
reakcyjnymi podczas uruchomienia.
Obsługujący może opanować siły odrzutu lub
siły reakcji poprzez podjęcie odpowiednich
środków ostrożności.
b) Nie wkładać nigdy ręki w pobliże
h
obracających się narzędzi roboczych.
W przypadku odrzutu narzędzie robocze może
uderzyć w rękę.
c) Unikać wchodzenia do obszaru, w któ-
rym w czasie odrzutu może się porus
elektronarzędzie. Odrzut powoduje cofnię-
cie elektronarzędzia w kierunku przeciwnym
do ruchu ściernicy na miejscu zablokowania.
d) Szczególnie ostrożnie należy pracować
w obrębie naroży, ostrych krawędzi
itd., unikać odrzucenia lub zakleszczenia się narzędzi roboczych na obrabianym przedmiocie. Obracające się
narzędzie robocze ma skłonności przy odskoczeniu do zakleszczania się na narożach i
ostrych krawędziach. Powoduje to utratę panowania nad narzędziem lub jego odrzut.
e) Nie należy stosować kół łańcuchowych
ani uzębionych brzeszczotów. Takie
narzędzia robocze powodują często odrzut i
utratę kontroli nad elektronarzędziem.
Q
Szczególne wskazówki
odnośnie szlifowania i cięcia
a) Używać wyłącznie ściernic dopusz-
czonych do posiadanego elektronarzędzia oraz osłon przewidzianych dla
tych ściernic. Ściernice, nieprzewidziane do
danego elektronarzędzia, nie mogą być dostatecznie osłonięte i są niebezpieczne.
b) Osłona winna być należycie zamoco-
wana na elektronarzędziu i być tak
ustawiona, aby móc osiągnąć najwyższy stopień bezpieczeństwa, tzn. aby
możliwie najmniejsza część ściernicy
była odsłonięta w kierunku obsługującego. Osłona winna chronić obsługującego
przed odłamkami i przed przypadkowym zetknięciem się ze ściernicą.
c) Ściernic można używać tylko dla zale-
canych możliwości zastosowania. Na
zać
23 PL
Page 24

przykład, nigdy nie należy szlifować
powierzchnią boczną tarczy tnącej. Tar-
cze tnące są przeznaczone do zdejmowania materiału krawędzią tarczy. Boczne działanie siły
na tę tarcze może spowodować ich połamanie.
d) Używać zawsze tylko nieuszkodzonych
kołnierzy mocujących o prawidłowej
wielkości i kształcie dla wybranej
ściernicy. Odpowiednie kołnierze podpierają
ściernice i zmniejszają niebezpieczeństwo pęknięcia ściernicy. Kołnierze tarcz tnących mogą
się różnić od kołnierzy dla innych ściernic.
e) Nie należy używać zużytych ściernic
od większych elektronarzędzi. Ściernice
dla większych elektronarzędzi nie są przystosowane do wyższych liczb obrotów mniejszych
elektronarzędzi i mogą ulec pęknięciu.
Q
Dalsze szczególne wskazówki
bezpieczeństwa dotyczące
tarcz tnących
a) Unikać blokowania tarczy tnącej lub
zbyt dużej siły docisku. Nie należy
dokonywać zbyt głębokich cięć. Prze-
ciążenie tarczy tnącej zwiększa jej obciążenie
i skłonności do zakleszczania się lub blokowania,
a tym samym możliwości odrzutu lub pęknięcia
tarczy.
b) Unikać obszaru przed i za obracającą
się tarczą tnącą. Jeśli tarcza tnąca odskoczy
od przecinanego przedmiotu, to w przypadku
odrzutu elektronarzędzie wraz z obracającą
się tarczą może zostać odrzucone bezpośrednio na obsługującego.
c) W przypadku zakleszczenia się tarczy
tnącej lub przerwania pracy przez
obsługującego należy odłączyć urządzenie i trzymać spokojnie aż tarcza
się zatrzyma. Nie należy nigdy próbować wyrywać obracającej się tarczy
tnącej z przecinanego materiału, ponieważ może to spowodować odrzut
elektronarzędzia. Ustalić i wyeliminować
przyczynę zakleszczania.
d) Nie należy nigdy włączać z powrotem
elektronarzędzia tkwiącego jeszcze
24 PL
w obrabianym materiale. Najpierw
należy pozwolić by tarcza tnąca osiągnęła pełną liczbę obrotów zanim
przystąpi się ostrożnie do kontynuowania cięcia. W przeciwnym razie tarcza
może się zahaczyć, wyskoczyć z obrabianego
materiału lub spowodować odrzut.
e) Płyty lub przedmioty obrabiane winny
być podparte lub zamocowane, aby
zmniejszyć ryzyko odrzutu na skutek
zakleszczonej tarczy tnącej. Duże
przedmioty obrabiane mogą się wygiąć pod
działaniem własnego ciężaru. Obrabiany
przedmiot winien być podparty po obydwu
stronach tarczy i to zarówno w pobliżu tarczy
tnącej, jak również na krawędzi.
f) Należy zachować szczególną ostroż-
ność podczas wykonywania „cięć kieszeniowych” w istniejących ścianach
lub w obszarach niewidocznych. Zagłę-
biająca się tarcza tnąca może spowodować
odrzut przy natrafieniu na przewody gazowe
lub wodne, przewody elektryczne lub na inne
obiekty.
Q
Szczególne wskazówki
bezpieczeństwa dotyczące
szlifowania papierem ściernym
Nie należy używać za dużych krążków
papieru ściernego, lecz przestrzegać
zaleceń producenta odnośnie wielkości krążków papieru ściernego. Krążki
papieru ściernego wystające poza tarczę
wsporczą mogą powodować obrażenia, jak
również prowadzić do blokowania, ich rozrywania lub do spowodowania odrzutu.
Q
Szczególne wskazówki
bezpieczeństwa dotyczące
polerowania
Nie pozostawiać żadnych luźnych części
nasadki polerskiej, w szczególności
sznurów mocujących. Sznury mocujące
należy związać lub skrócić. Luźne obracające
Page 25

Ogólne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dla elektronarzędzi
się sznury mocujące mogą pochwycić palce i
lub zaplątać się w polerowanym przedmiocie.
Q
Szczególne wskazówki bezpieczeństwa dotyczące pracy
przy użyciu szczotek drucianych
a) Należy pamiętać o tym, iż szczotka
druciana w trakcie normalnego używania gubi kawałki drutu. Nie należy
przeciążać drutów zbyt dużą siłą docisku. Odrywające się i wylatujące kawałki drutu mogą
łatwo przebić się przez cienkie ubranie i
utkwić w ciele.
b) Jeśli stosowana jest osłona, należy
zapobiegać ocieraniu się szczotki drucianej o osłonę. Szczotki talerzowe i garn-
kowe mogą zwiększać swoją średnicę na skutek
działania siły docisku i sił odśrodkowych.
Q
Wskazówki dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa użytkowania
mini-wiertarki PMGS 12 B2 i
zasilacza-PMGS 12 B2-1
W trakcie pracy należy stosować na-
stępujące wyposażenie ochronne:
okulary ochronne i rękawice ochronne.
Tylko do użytku wewnątrz pomiesz-
czeń!
OSTROŻNIE! Po wyłączeniu urządzenia
następuje wybieg narzędzia! Należy
unikać jakiegokolwiek kon taktu z szybko obracającymi się narzędziami.
przedmiot obrabiany. Używaj urządzeń
mocujących / imadła, aby przytrzymać przedmiot obrabiany. W ten sposób jest on pewniej
trzymany niż twoją ręką.
nie opieraj rąk obok lub przed urządzeniem i obrabianą powierzchnią,
ponieważ w przypadku ześlizgnięcia
się istnieje niebezpieczeństwo obrażeń ciała.
Zabezpieczaj
W żadnym wypadku
Unikać zetknięcia się z wirującym
narzędziem szlifierskim.
ZAGROŻENIE POŻAROWE WSKUTEK
WYRZUCANIA ISKIER! Gdy szlifowane są
metale powstaje wyrzut iskier. Dlatego też należy bezwzględnie zwracać uwagę na to, żeby
nie zostały zagrożone żadne osoby oraz żeby
w pobliżu obszaru roboczego nie znajdowały
się żadne palne materiały.
ZAGROŻENIE
PRZEZ PYŁ! Powstające w trakcie obróbki
szkodliwe / trujące pyły stanowią zagrożenie
zdrowotne dla obsługujących osób lub dla
osób znajdujących się w pobliżu.
Zakładać maskę przeciwpyłową!
TRUJĄCE OPARY!
Podczas obróbki tworzyw sztucznych, farb, lakierów, itp. zadbać o wystarczającą wentylację.
Nie nasączać materiałów lub obrabia-
nych powierzchni cieczami zawierającymi rozpuszczalniki.
Unikać szlifowania farb z zawartością
ołowiu lub innymi materiałami szkodliwymi dla zdrowia.
Nie wolno szlifować materiału zawie-
rającego azbest. Azbest uważany jest jako
czynnik wywołujący raka.
Nie należy obrabiać zwilżonych po-
wierzchni ani materiałów.
WSKAZÓWKA! Nie należy obciążać urzą-
dzenia w czasie pracy do tego stopnia, iż
zostanie ono zatrzymane!
Odczekać do za-
trzymania się wyłączonego urządze
zanim zostanie ono odłożone.
Urządzenie winno
być zawsze czyste, suche niezanieczyszczone olejem ani smarem.
Dzieciom lub osobom, którym brak wiedzy lub
doświadczenia w obchodzeniu się z urządzeniem oraz osobom, które są ograniczone pod
względem ich fizycznych, sensorycznych lub
duchownych zdolności, nie wolno obsługiwać
urządzenia bez nadzoru lub wskazówek osoby
odpowiedzialnej za ich bezpieczeństwo. Dzieci
muszą być nadzorowane, aby nie bawiły się
urządzeniem.
nia,
25 PL
Page 26

Q
Uruchomienie
Nie należy używać urządzenia nie-
zgodnie z przeznaczeniem, stosować
tylko oryginalne części zamienne /
wyposażenie. Użycie części innych niż za-
lecanych w instrukcji obsługi lub innego wyposażenia może oznaczać dla użytkownika
powstania zagrożenia odniesienia obrażeń.
Q
Zakładanie / wymiana
uchwytu mocującego
Nacisnąć blokadę wrzeciona 7 i przytrzymać
ja w stanie naciśniętym.
Pokręcić nakrętkę mocującą 5 aż blokada
wzębi się zapadkowo.
Odkręcić nakrętkę mocującą 5 kluczem uni-
wersalnym
Wyjąć w razie potrzeby założone narzędzie.
Wsunąć najpierw przewidziane narzędzie
przez nakrętkę mocującą
je do uchwytu mocującego
trzpienia narzędzia.
Nacisnąć i przytrzymać naciśniętą blokadę
wrzeciona
Włożyć uchwyt mocujący 18 gwintu i dokręcić
nakrętkę mocującą
wersalnego
Stosować narzędzia z trzpieniem do
mocowania
WSKAZÓWKA: Używać stronę śrubokrętową
klucza uniwersalnego
przykręcenia śruby trzpieni mocujących
Włożyć trzpień do mocowania 13 do
elektronarzędzia w sposób jak opisano.
Za pomocą klucza uniwersalnego 23 odkręcić
śrubę od trzpienia do mocowania
Nałożyć żądane narzędzie na śrubę pomiędzy
obydwie podkładki.
Za pomocą klucza uniwersalnego 23 dokręcić
śrubę na trzpieniu do mocowania
23
z gwintu.
7
.
23
w gwincie.
13
:
5
zanim włoży się
18
pasującego do
5
za pomocą klucza uni-
23
do odkręcenia i
13
.
13
.
13
.
Q
Załączanie i wyłączanie /
Nastawianie zakresu
prędkości obrotowej
Załączanie / Nastawianie zakresu
prędkości obrotowej:
Podłączyć wtyczkę 4do zasilacza 10, wkła-
dając ją do przewidzianego do tego celu
urządzenia wtykowego
8
(patrz Rys. C).
Podłączyć urządzenie do źródła zasilania, wtyka-
jąc wtyczkę zasilacza do gniazdka sieciowego.
Wcisnąć wyłącznik główny 2 do dołu i przesu-
nąć w kierunku regulatora obrotów
1
. Ustawić
regulator w pozycji między „5” a „20”.
Wyłączanie:
Ustawić regulator obrotów 1 w pozycji „5”.
Wcisnąć wyłącznik główny
2
do dołu i prze-
sunąć w kierunku przewodu.
Q
Wskazówki dotyczące obróbki
materiału / Narzędzia /
Prędkości obrotowych
Nasadki frezowe
róbki stali i żelaza przy prędkościach obrotowych
poniżej maksymalnej prędkości obrotowej.
Zakres prędkości obrotowych do obróbki cynku,
stopów cynku, aluminium, miedzi i ołowiu należy
wyznaczyć metodą prób i błędów na próbkach.
Tworzywa sztuczne i materiały o niskiej tempe-
raturze topnienia należy obrabiać przy niskim
zakresie prędkości obrotowych.
Drewno należy obrabiać przy wysokich pręd-
kościach obrotowych.
Prace związane z czyszczeniem, polerowaniem
oraz polerowaniem za pomocą wielowarstwowej
płóciennej tarczy polerskiej należy wykonywać
przy średnim zakresie prędkości obrotowych.
Poniższe dane są niezobowiązującymi zaleceniami.
W trakcie praktycznej pracy należy również samemu
przetestować, jakie narzędzie i jakie ustawienie
nadaje się optymalnie do obrabianego materiału.
20
należy stosować do ob-
26 PL
Page 27

Uruchomienie / Konserwacja i czyszczenie / Serwis
Nastawianie odpowiedniej prędkości
obrotowej:
Cyfry na regu-
Obrabiany materiał
latorze liczby
obrotów
1
5
Tworzywa sztuczne i materiały
o niskiej temperaturze topnie
8
12
16
20
Kamień, ceramika
Drewno miękkie, metal
Drewno twarde
Stal
Przykłady zastosowania / wybór
odpowiedniego narzędzia:
Funkcja Osprzęt Zastosowanie
Wiercenie Wiertła ze
Obróbka drewna
stali szybkotnącej o podwyższonej
wydajności
skrawania
Frezowanie Nasadki
frezowe
12
Prace wielostronne,
na przykład obrób-
20
ka wnęk, drążenie,
kształtowanie, wy-
konywanie rowków
lub szczelin.
Grawerowanie
Nasadki grawerskie
21
Wykonywanie
oznakowania, maj-
sterkowanie (patrz
ilustracja D)
Polerowanie,
usuwanie
rdzy
OSTROŻ
-
NIE!
Na przedmiot
obrabiany na
l
eży wywierać
narzędziem
Szczotka metalowa
Tarcze
polerskie
-
Usuwanie rdzy
16
Obróbka różnych
metali i tworzyw
14
sztucznych,
zwłaszcza metali
szlachetnych takich
jak złoto lub srebro
(patrz Rysunek E).
tylko niewielki
nacisk.
Funkcja Osprzęt Zastosowanie
Czyszczenie Szczotki z
tworzywa
sztucznego
19
Na przykład czyszczenie trudno dostępnych obudów z
tworzywa sztucznego lub czyszczenie
obszaru otaczają-
nia
cego zamek
drzwiowy.
Szlifowanie Tarcze szli-
fierskie
nasadki szlifierskie
Szlifowanie kamienia, drewna, prace
,
15
precyzyjne na materiałach twardych,
22
jak ceramika lub
stal stopowa (patrz
ilustracja F, G)
Cięcie i piłowanie
Q
Dobre rady i triki
Ściernice tarczowe do
cięcia
17
Obróbka metalu,
tworzywa sztucznego i drewna
Jeżeli będzie wywierany zbyt duży nacisk, to
zamocowane narzędzie może złamać się i / lub
może zostać uszkodzony przedmiot obrabiany.
Optymalne wyniki pracy można osiągnąć prowadząc
narzędzie w stałym zakresie prędkości obrotowych i
przy niewielkim nacisku na przedmiot obrabiany.
Q
Konserwacja i czyszczenie
Urządzenie nie wymaga konserwacji.
Usunąć zanieczyszczenia z urządzenia.
Do tego celu należy użyć suchej szmatki.
Q
Serwis
Zlecaj naprawę
urządzeń punktowi serwisowemu lub
fachowcowi-elektrykowi i wyłącznie
przy użyciu oryginalnych części zamiennych. W ten sposób będzie zapewnione, że
pieczeństwo urządzenia pozostanie zachowane.
Wymianę wtyczki
lub przewodu sieciowego zawsze zlecaj producentowi urządzenia lub jego
służbie serwisowej. W ten sposób będzie
bez-
27 PL
Page 28

zapewnione, że bezpieczeństwo urządzenia
pozostanie zachowane.
Q
Gwarancja
Urządzenie objęte jest 3-letnią gwarancją,
licząc od daty zakupu. Urządzenie zostało
starannie wyprodukowane i poddane
skrupulatnej kontroli przed wysyłką. Paragon należy zachować jako dowód dokonania zakupu. W przypadku roszczeń
gwarancyjnych należy skontaktować się
telefonicznie z serwisem. Tylko w ten sposób można zagwarantować bezpłatną
wysyłkę zakupionego produktu.
Gwarancja obejmuje wyłącznie wady materiałowe
i fabryczne, natomiast nie obejmuje szkód powstałych podczas transportu, części ulegających zużyciu
ani uszkodzeń części łatwo łamliwych / podatnych
na uszkodzenia mechaniczne, np. wyłączników,
akumulatorów. Produkt przeznaczony jest wyłącznie do użytku domowego, a nie do zastosowań
profesjonalnych.
Gwarancja traci ważność w przypadku niewłaściwego używania urządzenia, używania niezgodnego z
przeznaczeniem, użycia siły lub ingerencji w urządzenie dokonywanej poza naszymi autoryzowany
punktami serwisowymi. Niniejsza gwarancja nie
ogranicza ustawowych praw nabywcy urządzenia.
mi
Q
Usuwanie
Opakowanie składa się z materiałów
nieszkodliwych dla środowiska, które
można usuwać w miejscowych firmach
recyklingowych.
Nie wyrzucać elektronarzędzi
do śmieci domowych!
Zgodnie z dyrektywą 2002 / 96 / EC o zużytych
urządzeniach elektrycznych i elektronicznych oraz
w oparciu o prawo narodowe, zużyte elektronarzędzia muszą być zbierane oddzielnie i przekazywane do proekologicznego recyklingu.
W sprawie możliwości utylizacji wysłużonych elektronarzędzi proszę informować się w Państwa
urzędzie gminy lub miasta.
Okres gwarancji nie ulega wydłużeniu o czas trwania usługi gwarancyjnej. Dotyczy to również wymienionych i naprawionych części. Szkody i wady
zauważone już w chwili zakupu należy zgłosić od
razu po rozpakowaniu, nie później niż po upływie
dwóch dni od daty zakupu. Po upływie okresu
gwarancyjnego wszystkie naprawy będą wykonywane płatnie.
PL
Serwis Polska
Tel.: 22 397 4996
e-mail: kompernass@lidl.pl
IAN 89959
28 PL
Page 29

Q
Deklaracja zgodności /
Producent
Deklaracja zgodności / Producent
My, KOMPERNASS GMBH, osoba odpowiedzialn
za dokumentację: pan Semi Uguzlu, BURGSTR. 21,
44867 BOCHUM, GERMANY, niniejszym oświadczamy, iż produkt ten spełnia wymagania następujących
norm, dokumentów normatywnych i dyrektyw WE:
Dyrektywa maszynowa
(2006 / 42 / EC)
Wytyczna WE dla niskiego napięcia
(2006 / 95 / EC)
Odpowiedniość elektromagnetyczna
(2004 / 108 / EC)
RoHS Dyrektywa
(2011 / 65 / EU)
Stosowane normy zharmonizowane
EN 60745-1/A11:2010, EN 60745-2-1:2010
EN 60745-2-3:2011
EN 55014-1/A2:2011, EN 55014-2/A2:2008
EN 61000-3-2/A2:2009, EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61558-1/A1:2009, EN 61558-2-6:2009
Typ /Określenie urządzenia:
Zestaw modelarski i grawerski PMGS 12 B2
a
Date of manufacture (DOM): 04–2013
Numer seryjny: IAN 89959
Bochum, 30.04.2013
Semi Uguzlu
- Menadżer jakości -
Zmiany techniczne w sensie dalszego rozwoju są
zastrzeżone.
29 PL
Page 30

30
Page 31

Kazalo
Uvod
Uporaba v skladu z določili .............................................................................................................. Stran 32
Oprema .............................................................................................................................................. Stran 32
Obseg dobave ................................................................................................................................... Stran 32
Tehnični podatki ................................................................................................................................. Stran 32
Splošna varnostna navodila za električno orodje
1. Varnost na delovnem mestu .......................................................................................................... Stran 33
2. Električna varnost ........................................................................................................................... Stran 33
3. Varnost oseb .................................................................................................................................. Stran 34
4. Skrbno ravnanje in uporaba električnega orodja ....................................................................... Stran 34
5. Servis .............................................................................................................................................. Stran 35
Varnostna opozorila za vse vrste uporabe ...................................................................................... Stran 35
Povratni udarec in ustrezna varnostna opozorila ............................................................................ Stran 36
Posebna varnostna opozorila za brušenje in ločevanje.................................................................. Stran 37
Dodatna posebna varnostna opozorila za ločevanje ..................................................................... Stran 37
Posebna varnostna opozorila za brušenje s smirkovim papirjem ................................................... Stran 37
Posebna varnostna opozorila za poliranje ...................................................................................... Stran 38
Posebna varnostna opozorila za delo z žičnimi ščetkami .............................................................. Stran 38
Za majhen vrtalni stroj PMGS 12 B2 in napajalnik PMGS 12 B2-1 specifična
varnostna navodila ............................................................................................................................ Stran 38
Začetek uporabe ..................................................................................................................... Stran 38
Uporaba / zamenjava orodja / zateznih klešč ................................................................................ Stran 39
Vklop / Izklop / Nastavitev števila vrtljajev ....................................................................................... Stran 39
Navodila za obdelovanje materiala / Orodje / Nastavitev števila vrtljajev .................................. Stran 39
Nasveti in triki ..................................................................................................................................... Stran 40
Vzdrževanje in čiščenje ...................................................................................................... Stran 40
Servis ................................................................................................................................................. Stran 40
Garancija ........................................................................................................................................ Stran 40
Odstranjevanje ......................................................................................................................... Stran 41
Izjava o skladnosti / Izdelovalec ................................................................................ Stran 41
Garancijski list ........................................................................................................................... Stran 42
31 SI
Page 32

Uvod Uvod / Splošna varnostna navodila za električno orodje
Komplet za modeliranje in
graviranje PMGS 12 B2
Q
Uvod
Iskrene čestitke ob nakupu vaše nove naprave.
Odločili ste se za zelo kakovosten izdelek. To navodilo za uporabo je sestavni del tega izdelka. Vsebuje pomembna navodila za varnost, uporabo in
odstranitev. Preden začnete izdelek uporabljati, se
seznanite z vsemi navodili za uporabo in varnostnimi napotki. Izdelek uporabljajte samo tako, kot je
opisano, in samo za navedena področja uporabe.
Če izdelek odstopite novemu lastniku, mu zraven
izročite tudi vse dokumente.
Q
Uporaba v skladu z določili
Majhen vrtalni stroj se uporablja za vrtanje, rezkanje,
graviranje, poliranje, čiščenje, brušenje, rezanje in
žaganje lesa, kovine, plastike, keramike ali kamna
v suhih prostorih. Kakršnakoli drugačna uporaba ali
sprememba naprave ni v skladu z določili in predstavlja znatno nevarnost nesreč. Za škodo, nastalo
pri uporabi, ki ni v skladu z določili, izdelovalec ne
prevzame jamstva. Naprava ni namenjena za profesionalno uporabo.
Q
Oprema
Majhen vrtalni stroj:
1
Regulator števila vrtljajev
2
Stikalo za VKLOP / IZKLOP
3
Kovinsko obešalo
4
Vtič za napajalnik
5
Natezna matica
6
Prekrivna matica
7
Gumb za aretiranje vretena
Napajalnik (glejte sl. A):
8
vtična priprava za vtič
9
odlagalna površina
10
napajalnik
11
priključni kabel (z električnim vtičem)
4
Oprema (glejte sl. B):
12
6 HSS Svedrov
13
2 Nastavka za vpenjanje orodja
14
3 Polirne ploščice
15
4 Brusilne ploščice
16
1 Kovinska ščetka
17
16 Ločilnih ploščic
18
5 Vpenjalne klešče
19
2 Plastični ščetki
20
3 Biti za rezkanje
21
2 Bita za graviranje
22
5 Bitov za brušenje
23
1 Kombinirani ključ
Q
Obseg dobave
1 Majhen vrtalni stroj
1 Naprava za priključitev na omrežje
1 Plastični kovček
1 Komplet opreme (50 delov)
1 Navodilo za uporabo
Q
Tehnični podatki
Majhen vrtalni stroj PMGS 12 B2:
Nazivna napetost: 12 V
Nazivna moč: 22 W
Število vrtljajev v
prostem teku: n
5000–20000 min
0
-1
Svedri: maks. ø 3,2 mm
Ploščic: maks. ø 25 mm
Testirano skladno z: EN60745-1; EN60745-2-1
EN60745-2-3
Podatki o hrupu in vibracijah:
Izmerjena vrednost za hrup določena v skladu z
EN 60745. Raven hrupa električnega orodja po
A-vrednotenju tipično znaša:
Nivo zvočnega tlaka: 54,70 dB(A)
Nivo hrupa: 65,70 dB(A)
Negotovost K: 3 dB
Ocenjeni pospešek, tipično:
Vibracije na dlani in roki: 1,868 m / s
Negotovost K = 1,5 m / s
2
2
32 SI
Page 33

Uvod / Splošna varnostna navodila za električno orodje
Nivo nihanja, ki je naveden
v teh navodilih, je bil merjen skladno z merilnim
postopkom, normiranim po standardu EN 60745
in se ga lahko uporablja za primerjavo naprav.
Navedeno vrednost emisije nihanja lahko uporabite
tudi za uvodno ocene izpostavitve.
Nivo nihanja se bo spreminjal skladno z uporabo
električnega orodja in lahko v nekaterih primerih
leži nad vrednostjo, navedeno v teh navodilih. Kadar se električno orodje redno uporablja na tak
način, bi nihajno obremenitev lahko podcenili.
Opozorilo: Za natančno oceno nihajne obremenitve med določenim delovnim obdobjem je treba
upoštevati tudi čase, v katerih je naprava izklopljena
in sicer teče, vendar pa ni dejansko v uporabi. To
lahko nihajno obremenitev preko celotnega časov-
-nega obdobja občutno zmanjša.
Napajalnik PMGS 12 B2-1:
VHOD / Input:
Nazivna napetost: 230 V∼ 50 Hz
IZHOD / Output:
Nazivna napetost: 12 V
Nazivni tok: 1A
Zaščitni razred: II /
Testirano skladno z: EN61558
Splošna varnostna navodila
za električno orodje
Preberite var-
nostna opozorila in navodila!
Neupoštevanje varnostnih opozoril in
navodil lahko vodi do povzročitve električnega
udara, požara in / ali hudih poškodb.
Vsa varnostna opozorila in navodila shranite za uporabo v prihodnje!
V varnostnih navodilih uporabljeni pojem „električno
orodje“ se nanaša na električno orodje na omrežni
pogon (s kablom za priključitev na omrežje) in na
električno orodje na akumulatorski pogon (brez
kabla za priključitev na omrežje).
1. Varnost na delovnem mestu
a) Delovno območje naj bo vedno čisto
in dobro osvetljeno. Nered in neosvetljena
delovna področja so lahko vzrok za nezgode.
b) Z orodjem ne delajte v okolici, kjer ob-
staja nevarnost eksplozije in v kateri
se nahajajo vnetljive tekočine, plini ali
prah. Električna orodja proizvajajo iskrice, ki
bi lahko povzročile vžig prahu ali pare.
c) Poskrbite, da bodo otroci in druge ose-
be med uporabo električnega orodja
dovolj oddaljene od mesta uporabe.
Če vaša pozornost ni v celoti usmerjena na delo,
lahko izgubite nadzor nad orodjem.
2. Električna varnost
a)
Priključni vtič mora ustrezati električni
vtičnici. Vtiča v nobenem primeru ne
smete spreminjati. Skupaj z ozemljenimi
stroji ne uporabljajte dodatnih nastav
kov vtiča. Originalen nespremenjen vtič in
ustrezna vtičnica zmanjšata tveganje električnega udara.
b) Preprečite telesni stik z ozemljenimi
površinami, kot so cevi, grelci, štedilniki in hladilniki. Obstaja povečano tveganje
električnega udara, če je vaše telo ozemljeno.
c) Preprečite stik orodja z vodo ali vlago.
Vdor vode v električno orodje poveča tveganje
električnega udara.
d) Kabla ne uporabljajte za nošenje
orodja, za obešanje orodja ali za vlečenje vtiča iz vtičnice. Kabel zavarujte
pred vročino, olji, ostrimi robovi ali
gibljivim delom orodja. Poškodovani ali
zavozlani kabli povečajo tveganje električnega udara.
e) Kadar z električnim orodjem delate na
prostem, uporabljajte samo električne
podaljške, ki so primerni in namenjeni
uporabi na prostem. Uporaba električnega
podaljška, ki je izdelan za uporabo na prostem,
zmanjša tveganje električnega udara.
f) Če se uporabi električnega orodja v
vlažnem okolju ne da izogniti, upora-
-
33 SI
Page 34

bljajte zaščitno stikalo za okvarni tok.
Uporaba zaščitnega stikala za okvarni tok
zmanjša tveganje električnega udara.
3. Varnost oseb
pravilno uporabljena. Uporaba opreme
zmanjša ogrožanje zaradi prahu.
4.
Skrbno ravnanje in uporaba
električnega orodja
a) Ves čas bodite pozorni, pazite, kaj de-
late in pri delu z električnim orodjem
ravnajte razumno. Orodja ne uporabljajte, če ste utrujeni ali če ste
vplivom droge, alkohola ali zdravil
Trenutek nepozornosti med uporabo orodja
lahko povzroči resne poškodbe.
b)
zaščitne opreme kot so maska za prah, delovni
c) Preprečite nenameren vklop naprave.
d) Pred vklopom orodja odstranite vsa
e) Izogibajte se abnormalni telesni drži.
f) Oblečeni bodite v primerna oblačila.
g) Kadar je vgrajena oprema za odsesa-
34 SI
Vedno uporabljajte osebno
zaščitno opremo in vedno
zaščitna očala. Uporaba osebne
čevlji z zaščito proti drsenju, zaščitna čelada
ali zaščita sluha, odvisno od načina uporabe
električnega orodja, zmanjšuje tveganje nastanka poškodb.
Prepričajte se, da je električno orodje
izklopljeno, preden ga priključite na
oskrbo s tokom, dvignete ali nosite.
Če imate pri nošenju naprave prst na stikalu
za VKLOP / IZKLOP ali je naprava vklopljena,
to lahko vodi do povzročitve nesreč.
orodja, ki jih potrebujete za nastavitve
in vse vijačne ključe. Orodje ali ključ v
vrtečem se delu orodja bi lahko povzročil
poškodbe.
Skrbite za varno stojišče in pazite na
ravnotežje. Na ta način lahko napravo, še
posebno v nepričakovanih situacijah, bolje
kontrolirate.
Ne nosite širokih oblačil ali nakita.
Poskrbite, da v bližino vrtečih se delov stroja ne pridejo lasje, oblačila in
rokavice. Ohlapna oblačila, nakit ali dolgi
lasje bi se lahko ujeli v premikajoče se dele.
vanje ali prestrezanje prahu, se prepričajte, da je oprema priključena in
pod
.
a) Naprave ne preobremenjujte. Za vaše
delo uporabljajte za to namenjeno
električno orodje. Z ustreznim električnim
orodjem boste v določenem območju zmogljivosti delali bolje in bolj varno.
b) Ne uporabljajte električnega orodja,
čigar stikalo je defektno. Električno orod
ki se ne da več vklopiti ali izklopiti, je nevarno
in ga je treba dati v popravilo.
c) Preden izvajate nastavitve na napravi,
zamenjujete dele opreme ali napravo
date iz rok, izvlecite električni vtič iz
vtičnice. Ti previdnosti ukrepi preprečujejo nenameren zagon električnega
orodja. Ti previdnosti ukrepi preprečujejo
nenameren zagon naprave.
d) Neuporabljano električno orodje hra-
nite zunaj dosega otrok. Osebam, ki z
napravo niso seznanjene ali niso prebrale teh navodil, uporabe naprave ne
dovolite. Električno orodje je nevarno, če ga
uporabljajo neizkušene osebe.
e)
Napravo skrbno negujte. Kontrolirajte,
če premikajoči se deli naprave brezhibno delujejo in se ne zatikajo, če so deli
naprave odlomljeni ali poškodovani,
ter da delovanje naprave ni ovirano.
Poškodovane dele dajte pred ponovno
uporabo naprave v popravilo. Vzrok za
mnoge nesreče je slabo vzdrževano električno
orodje.
f) Poskrbite, da bodo rezalna orodja
vedno ostra in čista. Skrbno vzdrževana
rezalna orodja z ostrimi rezili se ne zatikajo in
so lažje vodljiva.
g) Električna orodja, dodatno opremo,
nastavke itd. uporabljajte v skladu z
navodili za uporabo in na način, ki je
predpisan posebej za ta specialni tip
stroja. Vedno upoštevajte delovne pogoje in vrsto dela, ki ga želite opraviti.
je,
Page 35

Splošna varnostna navodila za električno orodje
Uporaba električnih orodij v namene, ki se
razlikujejo od namenov, ki jih je predvidel
proizvajalec, lahko povzroči nastanek nevarnih situacij.
5. Servis
a) Vaše naprave dajte vpopravilo servi-
sni službi ali strokovnjaku za električne naprave, popravilo pa naj poteka
samo z originalnimi nadomestnimi
Na ta način se zagotovi, da varnost naprave
ostane ohranjena.
Q
Varnostna opozorila
deli.
za vse vrste uporabe
Skupna varnostna opozorila za brušenje,
brušenje s smirkovim papirjem, dela z
žičnimi ščetkami, poliranje in ločevanje:
a) To električno orodje se uporablja kot
brusilnik, brusilnik na smirkov papir,
žično ščetko, polirni stroj in stroj za
ločevanje. Upoštevajte vsa varnostna
opozorila, navodila, slike in podatke,
ki jih dobite skupaj z napravo. Če nave-
denih navodil ne upoštevate, lahko pride udara
električnega toka, požar in / ali hudih poškodb.
b) Normativni stavek / normativno opozorilo za to
orodje ni uporabno.
c) Ne uporabljajte opreme, ki je izdelo-
valec ni predvidel posebej za to električno orodje. Le zaradi tega, ker lahko
opremo pritrdite na vaše električno orodje, to
še ne garantira varne uporabe.
d) Dovoljeno število vrtljajev vstavnega
orodja mora biti vsaj tako visoko kot
je najvišje število vrtljajev, navedeno
na električnem orodju. Oprema, ki se vrti
hitreje kot je dovoljeno, se lahko prelomi ali leti
naokrog.
e) Zunanji premer in debelina vstavnega
orodja morata ustrezati podatkom o
merah vašega električnega orodja.
Napačno dimenzioniranega vstavnega orodja
se ne da zadostno zavarovati ali kontrolirati.
f) Brusilni koluti, prirobnice, brusilne
plošče ali druga oprema se morajo
natančno prilegati brusilnemu vretenu
vašega električnega orodja. Vstavno
orodje, ki se natančno ne prilega brusilnemu
vretenu, se vrti neenakomerno, zelo močno
vibrira in lahko vodi do izgube kontrole.
g) Ne uporabljajte poškodovanega
vstavnega orodja. Pred vsako uporabo kontrolirajte vstavno orodje kot so
brusilni koluti, ali kažejo vidne znake
luščenja in razpoke, ter brusilne plošče,
ali kažejo vidne znake razpok, obrabe
ali močne izrabe. Kontrolirajte žične
ščetke, ali imajo razrahljane ali odlomljene žice. Če električno orodje ali
vstavna oprema pade na tla, prekontrolirajte, ali je poškodovano, ali pa
uporabite nepoškodovano vstavno
orodje. Ko ste vstavno orodje prekontrolirali in ga vstavili, pazite, da se vi
sami in pa osebe v vaši bližini zadržujete zunaj ravni vrtečega vstavnega
orodja in napravo pustite teči ene
minuto z najvišjim številom obratov.
Poškodovano vstavno orodje se v fazi testiranja
večinoma zlomi.
h)
celega obraza, zaščito za oči ali zašči-
tna očala. V kolikor je primerno, nosite proti-
prašno zaščitno masko, opremo za zaščito sluha,
zaščitne rokavice ali posebni predpasnik, ki
vas ščitijo pred obruski in drugimi koščki materiala. Oči je treba zaščititi pred letečimi tujki, ki
nastajajo pri različnih vrstah uporabe, protiprašne zaščitne maske in dihalne maske pa morajo
filtrirati prah, ki nastaja pri uporabi orodja. Če
ste dlje časa izpostavljeni glasnemu hrupu, lahko utrpite zgubo sluha.
i) Pazite na to, da se druge osebe zadr-
žujejo v varni razdalji od vašega delovnega območja. Vsak, ki vstopi v
delovno območje, mora nositi osebno
zaščitno opremo. Odlomljeni delci obdelo-
vanca ali zlomljeno vstavno orodje lahko odleti
Nosite osebno zaščitno opremo. Odvisno od vrste uporabe
nosite primerno zaščito preko
35 SI
Page 36

in povzroči poškodbe tudi zunaj direktnega
delovnega območja.
j) Kadar izvajate dela, pri katerih vstavno
orodje lahko zadane ob skrito električno napeljavo ali lastni priključni kabel,
napravo držite samo za izolirane površine za prijemanje. Kontakt z vodnikom,
ki je pod napetostjo, lahko premosti napetost
na kovinske dele naprave in povzroči udar električnega toka.
k) Priključni kabel vedno držite stran od
vrtečega vstavnega orodja. Če izgubite
nadzor nad napravo, se priključni kabel lahko
pretrga ali ga naprava zagrabi in vaša dlan ali
roka lahko zaide v vrteče vstavno orodje.
l) Električnega orodja nikoli ne odložite,
dokler se vstavno orodje popolnoma
ne zaustavi. Vrteče vstavno orodje lahko
pride v stik z odlagalno površino, pri čemer
lahko izgubite nadzor nad električnim orodjem.
m) Električnega orodja ne pustite teči,
medtem ko ga nosite. Vaša oblačila lahko
pri naključnem stiku vrteče vstavno orodje zagrabi in vstavno orodje se lahko zarije v vaše telo.
n) Prezračevalne odprtine vašega elek-
tričnega orodja redno čistite. Ventilator
motorja sesa prah v ohišje in močno nabiranje
kovinskega prahu lahko predstavlja nevarnosti
zaradi električnega toka.
o) Električnega orodja ne uporabljajte v
bližini vnetljivih materialov. Iskre lahko
te materiale zanetijo.
p) Ne uporabljajte vstavnega orodja,
za katera so potrebna tekoča hladilna
sredstva. Uporaba vode ali drugih tekočih
hladilnih sredstev lahko vodi do udara električnega toka.
Q
Povratni udarec in ustrezna
varnostna opozorila
Povratni udarec je nenadna reakcija kot posledica
zataknjenega ali zablokiranega vrtečega vstavnega
orodja, kot so brusilni koluti, brusilne plošče, žične
ščetke itn. Zatikanje ali blokiranje vodi do nenadne
zaustavitve vrtečega vstavnega orodja. Zaradi tega
36 SI
se nekontrolirano električno orodje na mestu blokade
pospeši v nasprotno smer vrtenja vstavnega orodja.
Kadar se npr. brusilni kolut zatakne v obdelovanec
ali zablokira, se lahko rob brusilnega koluta, ki je
vtaknjen v obdelovanec, zatakne in s tem se brusilni kolut lahko odlomi ali povzroči povratni udarec.
Brusilni kolut se takrat premika proti upravljavcu ali
stran od njega, odvisno od smeri vrtenja koluta na
mestu blokade. Pri tem se brusilni koluti lahko tudi
prelomijo.
Povratni udarec je posledica napačne ali pomanjkljive uporabe električnega orodja. Lahko se ga
prepreči s primernimi previdnostnimi ukrepi, kot je
opisano v nadaljevanju.
a) Električno orodje dobro držite in vaše
telo in roke namestite v položaj, v
katerem lahko prestrežete sile povratnega udarca. Vedno uporabljajte
dodatni ročaj, če je na voljo, da imate
najboljši možen nadzor nad silo povratnega udarca ali reakcijski moment
pri zagonu. Upravljavec lahko s primernimi
previdnostnimi ukrepi sile povratnega udarca
in reakcijske sile obvlada.
b) Vaših rok nikoli ne približujte vrtečemu
vstavnemu orodju. Vstavno orodje se lahko
pri povratnem udarcu premika čez vašo roko.
c) S telesom se izogibajte območju, v
katero se električno orodje v primeru
povratnega udarca premakne. Povratni
udarec električno orodje požene v nasprotno
smer od premikanja brusilnega koluta na mestu
blokade.
d) Še posebno previdno delajte v območju
kotov, ostrih robov itn.Preprečite, da
bi se vstavno orodje odbilo od obdelovanca in zataknilo. Vrteče vstavno orodje
je nagnjeno k temu, da se pri kotih, ostrih robovih ali, kadar se odbije, zatakne. To povzroči
izgubo nadzora ali povratni udarec.
e) Ne uporabljajte žaginih listov za mo-
torne žage ali nazobčanih žaginih listov. Takšno vstavno orodje pogosto povzroči
povratni udarec ali izgubo nadzora nad električnim orodjem.
Page 37

Splošna varnostna navodila za električno orodje
Q
Posebna varnostna opozorila
za brušenje in ločevanje
a) Uporabljajte izključno brusilna telesa,
ki so dovoljena za uporabo na vašem
električnem orodju, in za ta brusilna
telesa predvidene zaščitne pokrove.
Brusilnih teles, ki niso predvidena za uporabo
na električnem orodju, se ne da zadostno zaščititi in niso varna.
b) Zaščitni pokrov je treba varno pritrditi
na električno orodje in ga nastaviti
tako, da je dosežena najvišja stopnja
varnosti, to pomeni, da je proti upravljavcu naprave odprto usmerjen najmanjši možni del brusilnega telesa.
Zaščitni pokrov naj bi upravljavca ščitil pred
odlomljenimi delci in naključnim stikom z brusilnim telesom.
c) Brusilna telesa se sme uporabljati samo
za priporočene možnosti uporabe.
Na primer: Nikoli ne brusite s stransko
površino ločevalnega koluta. Ločevalni
koluti so namenjeni za odstranjevanje materiala
z robom koluta. Delovanje sil s strani na ta brusilna telesa jih lahko prelomi.
d) Vedno uporabljajte nepoškodovano
napenjalno prirobnico prave velikosti
in oblike za brusilni kolut, ki ste ga izbrali. Ustrezne prirobnice podpirajo brusilni
kolt in zmanjšujejo nevarnost preloma brusilnega koluta. Prirobnica za ločevalne kolute se
lahko razlikuje od prirobnic za druge brusilne
kolute.
e) Ne uporabljajte obrabljenih brusilnih
kolutov večjega električnega orodja.
Brusilni koluti za večje električno orodje niso
konstruirani za višja števila vrtljajev manjših
električnih orodij in se lahko prelomijo.
ta zviša obremenitev in dovzetnost za zatikanje
ali blokiranje in s tem za možnost povratnega
udarca ali prelom brusilnega telesa.
b) Izogibajte se območju pred vrtečim
ločevalnim kolutom ali za njim. Kadar
ločevalni kolut v obdelovancu premikate stran od
sebe, lahko električno orodje z vrtečim kolutom
v primeru povratnega udarca zabriše direktno
proti vam.
c) Če se ločevalni kolut zatakne ali delo
prekinete, napravo izklopite in jo mirno držite, dokler se kolut ne zaustavi.
Ločevalnega koluta, ki se še vrti, nikoli ne poskušajte potegniti iz obdelovanca, v nasprotnem
primeru lahko pride od povratnega udarca.
Ugotovite vzrok za zatikanje in ga odpravite.
d) Električnega orodja ne vklopite po-
novno, dokler se kolut nahaja v obdelovancu. Pustite ločevalni kolut, da najprej
doseže končno število vrtljajev, preden nadaljujete z rezanjem. V nasprotnem se kolut lahko
zatakne, skoči ven iz obdelovanca ali povzroči
povratni udarec.
e) Plošče ali obdelovance podprite, da
zmanjšate tveganje za povratni udarec
zaradi zataknjenega ločevalnega koluta. Veliki obdelovanci se lahko pod lastno
težo upognejo. Obdelovanec mora biti podprt
na obeh straneh koluta in sicer tako v bližini
ločevalnega koluta kot tudi na robu.
f) Bodite še posebno previdni pri »rezanju
žepov« v obstoječe stene ali v druga
območja, ki niso vidna. Ločevalni kolut, ki
se zarezuje v globino, lahko pri zarezu v plinsko
ali vodovodno napeljavo, električno napeljavo
ali v druge predmete povzroči povratni udarec.
Q
Posebna varnostna opozorila za
brušenje s smirkovim papirjem
Q
Dodatna posebna varnostna
opozorila za ločevanje
a) Izogibajte se blokiranju ločevalnega
koluta ali prevelikemu pritisku ob obdelovanec. Ne izvajajte preveč globokih rezov. Preobremenitev ločevalnega kolu-
Ne uporabljajte predimenzioniranih
brusilnih kolutov, temveč upoštevajte
podatke izdelovalca za velikost brusilnega koluta. Brusilni koluti, ki segajo pre-
ko brusilne plošče, lahko povzročijo poškodbe
kot tudi blokiranje, raztrganje brusilnih kolutov
ali vodijo do povzročitve povratnega udarca.
37 SI
Page 38

Q
Posebna varnostna
opozorila za poliranje
Ne pustite nobenih ohlapnih delov
polirnih nastavkov, še posebno ne
pritrdilnih vrvic. Pritrdilne vrvice spravite ali jih skrajšajte. Ohlapne pritrdilne
vrvice, ki se vrtijo skupaj s kolutom, lahko zagrabijo vaše prste ali se zataknejo v obdelovanec.
Q
Posebna varnostna opozorila
za delo z žičnimi ščetkami
a) Upoštevajte, da lahko žična ščetka
tudi med običajno uporabo izgubi
kose žice. Žic ne preobremenjujte s
premočnim pritiskanjem ob obdelovanec. Kosi žic, ki odletijo stran, se lahko zelo
enostavno zarinejo skozi tanka oblačila in / ali
v kožo.
b) Če je priporočljiva uporaba zaščitnega
pokrova, preprečite, da bi se zaščitni
pokrov in žična ščetka dotaknila. Pri
krožnih in lončastih ščetkah se lahko zaradi pritiska in centrifugalnih sil poveča premer.
Q
Za majhen vrtalni stroj PMGS
12 B2 in napajalnik PMGS 12
B2-1 specifična varnostna navodila
Pri uporabi naprave uporabljajte na-
slednjo zaščitno opremo: Zaščitna
očala in zaščitne rokavice.
Samo za uporabo v notranjih
prostorih!
PREVIDNOST! Po izklopu se orodje še
premika! Izogibajte se stiku z orodjem, ki se
hitro vrti.
rujte. Za fiksiranje obdelovanca uporabljajte
vpenjalne priprave / primež. Tako je bolj varno
fiksiran, kot v vaši roki.
ne opirajte pred ali za napravo in na
38 SI
Obdelovanec zava-
Z rokami se nikoli
površino, ki jo nameravate obdelovati,
ker v primeru zdrsa obstaja nevarnost
poškodb.
Izogibajte se stiku z brusilnim orodjem,
med delovanjem.
NEVARNOST POŽARA ZARA
ISKER! Kadar brusite kovine nastajajo iskre.
Zaradi tega obvezno pazite na to, da ne ogrožate oseb in se v bližini delovnega območja ne
nahajajo vnetljivi materiali.
NEVARNOST PRAHU!
Škodljiva / strupen prah, ki nastaja pri obdelavi,
predstavlja nevarnost za zdravje osebe, ki rokuje z napravo ali osebo, ki je v bližini.
Nosite masko za zaščito pred prahom!
STRUPENE PARE!
Pri obdelavi plastike, barv, lakov itd., poskrbite
za zadostno zračenje.
Materiale ali površine, ki jih je potreb-
no obdelati ne močite s tekočinami, ki
vsebujejo topila.
Izogibajte se brušenju barv, ki vsebu-
jejo svinec ali druge materiale, ki so
škodljive za zdravje.
Material, ki vsebuje azbest se ne sme
obdelovati. Azbest je karcenogen.
Ne obdelujte navlaženih ali vlažnih
površin.
NAVODILO! Naprave med delovanjem ne
obremenjujte tako, da se ustavi!
Preden napravo od
žite, jo izključite in pustite, da se ustavi.
Naprava mora biti
vedno čista, suha in brez olja in maziva.
Otroci ali osebe, ki jih primanjkuje znanja ali
izkušenj v ravnanju z napravo, ali ki so omejeni
v telesnih, senzoričnih ali duševnih zmogljivostih,
naprave ne smejo uporabljati brez nadzora
oziroma samo pod vodstvom druge osebe, odgovorne za njihovo varnost. Otroke je treba
nadzorovati, da se ne igrajo z napravo.
Q
Začetek uporabe
Naprave nikoli ne uporabljajte nena-
mensko in jo vedno uporabljajte z originalnimi deli / priborom. Uporaba drugih
DI LETENJA
lo-
Page 39

Začetek uporabe
delov ali drugega pribora, razen tistega, ki je
priporočen v Navodilih za rokovanje, lahko za
Vas predstavlja nevarnost poškodb.
Q
Uporaba / zamenjava orodja /
zateznih klešč
Pritisnite gumb za aretiranje vretena 7 in ga
držite pritisnjenega.
Zavrtite natezno matico 5, dokler se aretirni
mehanizem ne zaskoči.
S kombiniranim ključem 23 sprostite zatezno
5
matico
iz navoja.
Po potrebi odstranite uporabljeno orodje.
Najprej predvideno orodje potisnite skozi zatez-
no matico
klešče
5
preden ga vtaknete v zatezne
18
, ki ustrezajo telesu orodja.
Aktivirajte vretenasto zapiralo 7 in ga kratek
čas držite.
Zatezne klešče 18 položite v navojni vložek in
nato zatezno matico
23
ključem
zavijte na navoj.
5
s kombiniranim
Uporaba vpenjalnega orodja z vpenjalnim
13
trnom
NAVODILO: Izvijač na kombiniranem ključu
:
23
uporabite za rahljanje in zatezanje vijakov
zateznih trnov
13
.
Vpenjalni trn 13 vstavite v električno orodje kot
je opisano.
S pomočjo kombiniranega ključa 23 odvijte
vijak z vpenjalnega trna
13
.
Med obe podložki na vijak nataknite želeno
vpenjalno orodje.
S pomočjo kombiniranega ključa 23 privijte
vijak na vpenjalni trn
Q
Vklop / Izklop / Nastavitev
13
.
števila vrtljajev
Vklop / Izklop / Nastavitev števila
vrtljajev:
Vtič 4 priključite na napajalnik 10, tako da
ga vtaknete v za to predvideno vtično
pripravo
8
(glejte sl. C).
Napravo priključite na oskrbo z energijo, tako
da električni vtič vtaknete v vtičnico.
Stikalo za VKLOP/IZKLOP 2 pritisnite navzdol
in ga nato potisnite v smer regulatorja števila
vrtljajev
1
. Regulator števila vrtljajev nastavite
na pozicijo med „5“ in „20“.
Izklop:
Regulator števila vrtljajev 1 nastavite na pozi-
cijo „5“. Sikalo za VKLOP / IZKLOP
2
pritisnite
navzdol in ga nato potisnite v smer kabla.
Q
Navodila za obdelovanje
materiala / Orodje / Nasta vitev
števila vrtljajev
Za obdelovanje jekla in železa pri najvišjem
številu vrtljajev uporabljajte bite za rezkanje
Za obdelovanje cinka, cinkovih zlitin, aluminija,
bakra in svinca s poskusi na testnih kosih ugotovite primerno število vrtljajev.
Za obdelovanje plastike in materialov z nizkim
tališčem uporabljajte nizko število vrtljajev.
Za obdelovanje lesa uporabljajte visoko število
vrtljajev.
Za čiščenje in poliranje in uporabljajte srednje
število vrtljajev.
Sledeči podatki so neobvezujoči priporočeni podatki.
Pri praktičnem delu tudi sami testirajte, katero orodje
in katera nastavitev sta najbolj optimalno primerna za
določeni material, ki ga želite obdelovati.
Nastavitev primernega števila vrtljajev:
Številka na regulatorju števila
vrtljajev
1
5
8
12
16
20
Material za
obdelovanje
Plastika in materiali z
nizkim tališčem
Kamnine, Keramika
Mehek les, Kovina
Trd les
Jeklo
20
.
39 SI
Page 40

Primeri uporabe / izbira primernega orodja:
Funkcija Oprema Uporaba
Vrtanje HSS Svedri
12
Rezkanje Biti za
rezkanje
Obdelovanje lesa
Vsestranska dela;
npr. širjenje, izvotlje-
20
vanje, oblikovanje,
izdelava utorov ali
zarez
Graviranje Biti za gravi-
ranje
21
Izdelava oznake,
ročna dela (glejte
sl. D)
Poliranje,
Odstranjevanje rje
PREVI-
DNOST!
Z orodjem izvajajte le ra-
Kovinska
ščetka
16
Polirne
ploščice
Odstranjevanje rje
Obdelava različnih
kovin in plastike,še
14
posebno žlahtnih
kovin kot sta zlato in
srebro (glejte sl. E)
hel pritisk na
obdelovanec.
Čiščenje Plastične
ščetke
npr. čiščenje težko
dostopnih plastičnih
19
ohišij ali čiščenje
okolice ključavnice
na vratih
Brušenje Brusilne
ploščice
Biti a brušenje
22
Brušenje kamna,
lesa, natančna
,
15
dela na trdih materialih, kot so keramika ali legirano jeklo
(glejte sl. F, G)
Ločevanje in
žaganje
Q
Nasveti in triki
Ločilne
ploščice
Obdelava kovin,
plastike in lesa
17
Kadar izvajate prevelik pritisk, se lahko vpeto orodje zlomi in / ali obdelovanec poškoduje. Optimalne
delovne rezultate lahko dosežete, če orodje vodite
z enakomernim številom vrtljajev in majhnim pritiskom na obdelovanec.
Q
Vzdrževanje in čiščenje
Naprava ne terja vzdrževanja.
Z naprave odstranite umazanijo. V ta namen
uporabljajte suho krpo.
Q
Servis
Vaše naprave dajte
v popravilo servisni službi ali strokovnjaku za električne naprave, popravilo
pa naj poteka samo z originalnimi nadomestnimi deli. Na ta način se zagotovi,
da varnost naprave ostane ohranjena.
Zamenjavo vtiča ali
priključne napeljave naj vedno opravi izdelovalec naprave ali njegova
služba za pomoč strankam. Na ta način
s
e zagotovi, da varnost naprave ostane ohranjena.
Q
Garancija
Ta naprava ima 3 leta garancije od datuma
nakupa. Naprava je bila skrbno izdelana
in pred dobavo natančno preverjena.
Prosimo, da blagajniški račun shranite
kot dokazilo o nakupu. V primeru uveljavljanja garancije se po telefonu obrnite
na svojo servisno službo. Samo tako je
zagotovljeno brezplačno pošiljanje
vašega izdelka.
Garancija velja le za napake pri materialu ali izdelavi, ne pa tudi za poškodbe pri transportu, potrošne
dele ali za poškodbe lomljivih delov, npr. stikal ali
akumulatorjev. Izdelek je namenjen izključno za
zasebno in ne za poslovno uporabo.
V primeru zlorabe ali nepravilnega ravnanja, pri
uporabi sile ter pri posegih, ki jih ni izvedla naša
pooblaščena servisna poslovalnica, garancija preneha veljati. Vaših zakonskih pravic ta garancija ne
omejuje.
40 SI
Page 41

Garancija / Odstranjevanje / Izjava o skladnosti / Izdelovalec
Jamstvo ne podaljša garancijske dobe. To velja tudi
za zamenjane in popravljene dele. Morebitne po
be in pomanjkljivosti, ki obstajajo že pri nakupu, je
treba javiti takoj po razpakiranju, najpozneje pa dva
dni po datumu nakupa.Popravila po preteku garancijske dobe je treba plačati.
SI
Servis Slovenija
Phone: 080080917
e-mail: kompernass@lidl.si
škod-
IAN 89959
Q
Odstranjevanje
Embalaža sestoji iz naravi prijaznih ma-
terialov, ki jih lahko odvržete v lokalne
zbiralnike za recikliranje odpadkov.
Električnega orodja ne mečite
med hišne odpadke!
V skladu z evropsko direktivo 2002 / 96 / EC o starih
električnih napravah in njenim izvajanjem v narodnem pravu je treba električno orodje zbirati ločeno
in vrniti v naravi primerno ponovno predelavo.
Q
Izjava o skladnosti /
Izdelovalec
Mi, podjetje KOMPERNASS GMBH, za dokumente odgovorna oseba: gospod Semi Uguzlu,
BURGSTR. 21, 44867 BOCHUM, GERMANY,
izjavljamo, da je ta izdelek skladen z naslednjimi
normativi, normativnimi dokumenti in direktivami ES:
Direktiva o strojih
(2006 / 42 / EC)
Direktiva EC o nizkonapetostni
električni opremi
(2006 / 95 / EC)
Elektromagnetna kompatibilnost
(2004 / 108 / EC)
RoHS Direktiva
(2011 / 65 / EU)
Uporabljeni harmonizirani standardi
EN 60745-1/A11:2010, EN 60745-2-1:2010
EN 60745-2-3:2011
EN 55014-1/A2:2011, EN 55014-2/A2:2008
EN 61000-3-2/A2:2009, EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61558-1/A1:2009, EN 61558-2-6:2009
O možnostih za odstranjevanje odsluženega
električnega orodja se prosimo informirajte pri
vaši občinski ali mestni upravi.
Oznaka tipa / Naprave:
Komplet za modeliranje in graviranje PMGS 12 B2
Date of manufacture (DOM): 04–2013
Serijska številka: IAN 89959
Bochum, 30.04.2013
Semi Uguzlu
- Vodja kakovosti -
Pridržujemo si pravico do tehničnih sprememb.
41 SI
Page 42

Garancijski list
KOMPERNASS GMBH
BURGSTRASSE 21
44867 BOCHUM
GERMANY
080080917
Garancijski list
1. S tem garancijskim listom jamčimo Kompernaß
GmbH, da bo izdelek v garancijskem roku ob
normalni in pravilni uporabi brezhibno deloval
in se zavezujemo, da bomo ob izpolnjenih spodaj navedenih pogojih odpravili morebitne pomanjkljivosti in okvare zaradi napak v materialu
ali izdelavi oz. po svoji presoji izdelek zamenjali
ali vrnili kupnino.
2. Garancija je veljavna na ozemlju Republike
Slovenije.
3. Garancijski rok za proizvod je 3 leta od dneva
izročitve balga. Dan izročitve blaga je enak
dnevom prodaje, ki je razviden iz računa.
4. Kupec je dolžan okvaro javiti pooblaščenemu
servisu oz. se informirati o nadaljnjih postopkih
na zgoraj navedeni telefonski številki. Svetujem
vam, da pred tem natančno preberete navodila
o sestavi in uporabi izdelka.
5. Kupec je dolžan pooblaščenemu servisu predložiti garancijski list in račun, kot potrdilo in
dokazilo o nakupu.
6. V primeru, da proizvod popravlja nepooblaščeni servis ali oseba, kupec ne more uveljavljati
zahtevkov iz te garancije.
7. Vzroki za okvaro oz. nedelovanje izdelka morajo biti lastnosti stvari same, in ne vzroki, ki so
zunaj proizvajalčeve oz. prodajalčeve sfere. Kupe
c ne more uveljavljati zahtevkov iz te garancije
če se ni držal priloženih navodil za sestavo in
uporabo izdelka ali, če je izdelek kakorkoli
spremenjen ali nepravilno vzdrževan.
8. Jamčimo servisiranje in rezervne dele za minimalno dobo, ki je zahtevana s strani zakonodaje.
9. Obrabni deli oz. potrošni material so izvzeti iz
garancije.
10. Vsi potrebni podatki za uveljavljanje garancije
o
se nahajajo na dveh ločenih dokumentih (gar
cijski list, račun).
11. Ta garancija proizvajalca ne izključuje pravic
potrošnika, ki izhajajo iz odgovornosti prodajalca za napake na blagu.
,
an-
Prodajalec:
Lidl d.o.o.k.d., Pod lipami 1, SI-1218 Komenda
42 SI
Page 43

Seznam obsahu
Úvod
Předpokládané použití ....................................................................................................................Strana 44
Výbava .............................................................................................................................................Strana 44
Rozsah dodávky ..............................................................................................................................Strana 44
Technické údaje ............................................................................................................................... Strana 44
Všeobecné bezpečnostní pokyny pro elektrické nářadí
1. Bezpečnost na pracovišti ............................................................................................................ Strana 45
2. Elektrická bezpečnost ..................................................................................................................Strana 45
3. Bezpečnost osob ......................................................................................................................... Strana 46
4. Používání a zacházení s elektrickým nářadím ...........................................................................Strana 46
5. Servis ............................................................................................................................................ Strana 47
Bezpečnostní pokyny pro všechna použití ..................................................................................... Strana 47
Zpětný ráz a příslušné bezpečnostní pokyny .................................................................................Strana 48
Zvláštní pokyny k broušení a rozbrušování .................................................................................... Strana 48
Další zvláštní bezpečnostní pokyny k rozbrušování ......................................................................Strana 49
Zvláštní bezpečnostní pokyny k broušení brusným papírem .........................................................Strana 49
Zvláštní bezpečnostní pokyny k leštění ........................................................................................... Strana 49
Zvláštní bezpečnostní pokyny k práci s drátěnými kartáči ............................................................ Strana 49
Specifické bezpečnostní pokyny pro minivrtačku PMGS 12 B2 anapájecí
zdroj PMGS 12 B2-1 ......................................................................................................................Strana 50
Uvedení do provozu
Vložení / výměna nástroje / upínací kleštiny ...................................................................................Strana 50
Zapnutí a vypnutí / nastavení rozsahu otáček ................................................................................Strana 51
Pokyny k obrábění materiálu / nástrojům / rozsahu otáček .......................................................... Strana 51
Tipy a triky ........................................................................................................................................ Strana 52
Údržba a čištění ...................................................................................................................... Strana 52
Servis ............................................................................................................................................... Strana 52
Záruka ............................................................................................................................................Strana 52
Likvidace .......................................................................................................................................Strana 52
Prohlášení o shodě / Výrobce ..................................................................................... Strana 53
43 CZ
Page 44

Modelářská a gravírovací sada
PMGS 12 B2
Úvod
Blahopřejeme vám ke koupi nového výrobku. Roz
li jste se pro kvalitní produkt. Návod kobsluze je
součástí tohoto výrobku. Obsahuje důležité pokyny
pro bezpečnost, použití a likvidaci. Před použitím
výrobku se seznamte se všemi pokyny k obsluze a
bezpečnostními pokyny. Používejte výrobek jen
popsaným způsobem a na uvedených místech. Při
předání výrobku třetí osobě předejte i všechny podklady.
hod-
Příslušenství (viz obr. B):
12
6 HSS vrtáky
13
2 upínací trny pro uchycení obrobku
14
3 lešticí kotouče
15
4 brusné kotouče
16
1 kovový kartáček
17
16 řezacích kotoučů
18
5 upínacích kleštin
19
2 plastové kartáčky
20
3 frézovací bity
21
2 gravírovací bity
22
5 brusných bitů
23
1 kombinovaný klíč
Rozsah dodávky
Předpokládané použití
Minivrtačka je určena k vrtání, frézování, gravírování, polírování, čištění, broušení, řezání dřeva, kovu,
plastů, keramiky nebo kameniva v suchých prostorách. Jakékoli jiné použití nebo úpravy přístroje je v
rozporu s předpokládaným použitím a skrývá
značné nebezpečí zranění. Za škody vzniklé při
používání v rozporu s předpokládaným využitím
výrobce neručí. Není určeno pro řemeslné použití.
Výbava
Minivrtačka:
1
Regulace otáček
2
Vypínač přístroje
3
Kovový třmen
4
Zástrčka síťového zdroje
5
Upínací matice
6
Přesuvná matice
7
Aretace vřetene
Síťový zdroj (viz obr. A):
8
Zásuvka pro zástrčku
9
Odkládací plocha
10
Síťový zdroj
11
Přívodní elektrický kabel (se zástrčkou)
4
1 minivrtačka
1 napájecí díl
1 plastový kufřík
1 sada příslušenství (50 dílů)
1 návod k obsluze
Technické údaje
Minivrtačka PMGS 12 B2:
Jmenovité napětí: 12 V
Jmenovitý příkon: 22 W
Volnoběžné otáčky:
Vrtáku: max. ø 3,2 mm
Kotouče: max. ø 25 mm
zkoušeno podle: EN60745-1;
Informace o hlučnosti a vibracích:
Naměřené hodnoty zjištěny podle EN 60745. Hladina akustické intenzity, filtr A, pro elektrické nářadí je:
Hladina akustického tlaku: 54,70 dB(A)
Hladina akustického výkonu: 65,70 dB(A)
Nepřesnost K: 3 dB
Efektivní hodnota zrychlení je:
Vibrace na ruku / paži: 1,868 m / s
Nepřesnost K = 1,5 m / s
n0 5000–20000 min
EN60745-2-1
EN60745-2-3
2
2
-1
44 CZ
Page 45

Úvod / Všeobecné bezpečnostní pokyny pro elektrické nářadí
Hladina vibrací uvedená v tom-
to návodu k obsluze byla měřena postupem v souladu se standardizovanou zkouškou popsanou v
normě EN 60745 a může se použít pro srovnávání
přístrojů. Hodnotu emise vibrací je možné použít k
počátečnímu posouzení jejich vyloučení.
Hladina vibrací se mění podle použití elektrického
nástroje a v některých případech může přesahovat
hodnotu udanou v těchto návodech. Zátěž vibracemi
by mohla být podceněna, používá-li se elektrický
nástroj pravidelně tímto způsobem.
Upozornění: Pro přesný odhad zatížení vibracemi
během určitého časového období práce s nářadím
by se měly zohlednit i doby, kdy je přístroj vypnutý
nebo sice běží, ale ve skutečnosti se nepoužívá. To
může zatížení vibracemi po celou dobu práce
značně snížit.
Síťový zdroj PMGS 12 B2-1:
VSTUP / Input:
Jmenovité napětí: 230 V∼ 50 Hz
VÝSTUP / Output:
Jmenovité napětí: 12 V
Jmenovitý proud: 1 A
Třída ochrany: II /
zkoušeno podle: EN61558
Všeobecné bezpečnostní poky-
ny pro elektrické nářadí
Přečtěte si bezpečnostní pokyny a návod k obsluze. Nedodržení bezpečnostních
pokynů a návodu k obsluze může způsobit úraz
elektrickým proudem, požár a / nebo vážná zranění.
Bezpečnostní pokyny a návod k obsluze
si uložte pro budoucí použití!
Pojem „elektrické nářadí“ používaný v bezpečnostních pokynech se vztahuje na ruční nářadí s elektrickým pohonem (se síťovým kabelem) a na ruční
nářadí s elektrickým pohonem z akumulátorové
baterie (bez síťového kabelu).
1. Bezpečnost na pracovišti
a) Udržujte své pracoviště v čistotě a dob-
ře osvětlené. Nepořádek a neosvětlené
pracovní prostory mohou vést k úrazu.
b) S elektrickým nářadím nepracujte v
prostředí s nebezpečím výbuchu, ve
kterém jsou hořlavé kapaliny, plyny
nebo prach. Elektrické nářadí vytváří jiskry,
které mohou zapálit prach nebo výpary.
c) Děti a jiné osoby by se během použí-
vání elektrického nářadí neměly přibližovat. V případě nepozornosti můžete
ztratit kontrolu nad přístrojem.
2. Elektrická bezpečnost
a) Připojovací zástrčka elektrického ná-
řadí musí sedět do zásuvky. Zástrčka
se v žádném případě nesmí měnit.
Pro připojení elektrického nářadí s
ochranným uzemněním nepoužívejte
adaptéry. Neupravené zástrčky a odpovída-
jící zásuvky zmenšují riziko úrazu elektrickým
proudem.
b) Zamezte kontaktu těla s uzemněnými
povrchy, jako jsou trubky, topení,
ohřívače a chladničky. Když je vaše tělo
uzemněné, hrozí větší nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým proudem.
c) Elektrické nářadí chraňte před deštěm
a vlhkostí. Vniknutí vody do elektrického pří-
stroje zvyšuje nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým
proudem.
d) Nepoužívejte kabel k přenášení elek-
trického nářadí, k jeho zavěšení ani k
vytažení zástrčky ze zásuvky. Kabel
chraňte před teplem, olejem, ostrými
hranami nebo pohybujícími se díly
přístroje. Poškozené nebo zamotané kabely
zvyšují riziko úrazu elektrickým proudem.
e) Když s elektrickým nářadím pracujete
venku, používejte pouze prodlužovací
kabely, které jsou rovněž vhodné pro
venkovní prostředí. Použití prodlužovacího
kabelu vhodného pro venkovní prostředí zmenšuje nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým proudem.
45 CZ
Page 46

f) Pokud nelze provoz elektrického nářa-
dí ve vlhkém prostředí vyloučit, použijte proudový chránič. Použití proudového
chrániče zmenšuje nebezpečí úrazu elektrickým
proudem.
3. Bezpečnost osob
a) Buďte stále opatrní, dávejte pozor na
to, co děláte a k práci s elektrickým
nářadím přistupujte s rozumem. Elektrické nářadí nepoužívejte, když jste
unavení nebo pod vlivem drog, alkoholu či některých léků. Moment nepozor-
nosti při používání elektrického nářadí může
vést k vážným zraněním.
b)
ních ochranných prostředků jako masky proti
prachu, neklouzavé bezpečnostní obuvi, ochranné přílby nebo ochrany sluhu, podle druhu a používání elektrického nářadí, snižuje riziko zranění.
c) Zamezte neúmyslnému uvedení do
provozu. Dříve než elektrické nářadí
připojíte k napájecímu zdroji, uchopíte
ho nebo přenášíte, ujistěte se že je
vypnuté. Když při přenášení elektrického
nářadí držíte prst na spínači nebo přístroj připojujete k elektrickému zdroji již zapnutý, může
to vést ke zranění.
d) Před zapnutím elektrického nářadí
odstraňte seřizovací nástroje a šroubovací klíč. Nástroj nebo klíč, který je v
rotující části přístroje, může vést ke zranění.
e) Zamezte nepřirozenému držení těla.
Zajistěte bezpečný postoj a vždy udržujte rovnováhu. Můžete tak elektrické ná-
řadí lépe kontrolovat v neočekávaných situacích.
f) Noste vhodné oblečení. Nenoste volné
oblečení ani různé ozdoby. Vlasy, oblečení ani rukavice se nesmí dostat do
pohybujících se dílů. Volné oblečení, oz-
doby nebo dlouhé vlasy mohou být otáčejícími
se díly zachyceny.
g) Když jsou namontována zařízení na
odsávání a zachycování prachu, ujis-
46 CZ
Používejte osobní ochranné
prostředkya vždy noste
ochranné brýle. Používání osob-
těte se, že jsou připojená a správně se
používají. Používání odsávání prachu může
snížit ohrožení zdraví způsobované prachem.
4. Používání a zacházení s
elektrickým nářadím
a) Přístroj nepřetěžujte. Používejte elek-
trické nářadí určené pro daný typ
S vhodným elektrickým nářadím pracujete lépe
a bezpečněji v uvedeném rozsahu výkonu.
b) Nepoužívejte elektrické nářadí, jehož
spínač je vadný. Elektrické nářadí, které
nejde zapnout nebo vypnout, je nebezpečné
a musí se nechat opravit.
c) Před prováděním nastavování přístro
výměnou součástí příslušenství nebo
před odložením přístroje vytáhněte
zástrčku ze zásuvky. Toto preventivní
opatření zamezí neočekávanému spuštění
elektrického nářadí.
d) Nepoužívané elektrické nářadí uložte
mimo dosah dětí. Nenechte s přístro
pracovat osoby, které s ním nejsou
seznámeny nebo si nepřečetly tento
návod k obsluze. Elektrické nářadí je ne
pečné, když ho používají nezkušené osoby.
e) Pečujte o elektrické nářadí pečlivě.
Zkontrolujte, jestli pohyblivé části fungují bezvadně a neváznou, jestli nejsou
zlomené nebo poškození části, jestli
funkce elektrického nářadí není omezena. Poškozené části přístroje nechte
opravit před jeho používáním. Mnoho
nehod má příčinu ve špatně prováděné údržbě
elektrického nářadí.
f) Řezné nářadí udržujte ostré a čisté.
Pečlivě ošetřované řezné nářadí s ostrými břity
méně vázne a lépe se vede.
g) Používejte elektrické nářadí, příslušen-
ství, nasazovací nástroje atd. podle
tohoto návodu k obsluze. Přitom mějte
na zřeteli pracovní podmínky a prováděnou činnost. Používání elektrického
nářadí k jiným účelům než k předpokládanému
použití může vést k nebezpečným situacím.
práce.
je,
jem
bez-
Page 47

Všeobecné bezpečnostní pokyny pro elektrické nářadí
5. Servis
a) Zařízení nechejte opravit jen místem
servisu nebo odbornou elektrickou
dílnou a jen s originálními náhradními
díly. Tím se zajistí, že bezpečnost zařízení zů-
stane zachována.
Q
Bezpečnostní pokyny
pro všechna použití
Společné bezpečnostní pokyny k broušení,
broušení brusným papírem, práce s drátěnými kartáči, leštění a rozbrušování:
a) Tento elektrický nástroj lze použít jako
brusku, brusku s brusným papírem,
drátěný kartáč, leštičku a rozbrušovací zařízení. Dbejte všech bezpečnostních
pokynů, návodů, zobrazení a údajů,
které obdržíte se zařízením. Nedbáte-li
následujících instrukcí, může dojít k úrazu elektrickým proudem, požáru a / nebo závažným
poraněním.
b) Normativní větu / upozornění pro tento nástroj
nelze použít.
c) Nepoužívejte příslušenství, které ne-
bylo speciálně pro tento elektrický
nástroj stanoveno. Skutečnost, že příslu-
šenství můžete na svém elektrickém nástroji
upevnit, nezaručuje bezpečné použití.
d) Přípustný počet otáček vloženého ná-
stroje musí být aspoň tak velký, jako je
maximální počet otáček udaný na elektrickém nástroji. Příslušenství, které rychleji točí
než je povoleno, se může zlomit nebo odletět.
e) Vnější průměr a tloušťka vloženého
nástroje musí souhlasit s údaji rozměrů
vašeho elektrického nástroje. Chybně
dimenzované vložené nástroje nemohou být
dostatečně odstíněny nebo kontrolovány.
f) Brusné kotouče, příruby, brusné talíře
nebo jiné příslušenství musí přesně
lícovat s vřetenem brusného kotouče
vašeho elektrického nástroje. Vložené
nástroje, které přesně nelícují s vřetenem brusného kotouče, se otáčejí nerovnoměrně, velmi
silně vibrují a mohou vést ke ztrátě kontroly.
g) Nepoužívejte poškozené vložené
nástroje. Zkontrolujte před každým
použitím vložené nástroje, jako jsou
brusné kotouče vzhledem k odštěpení
a trhlinám, brusné talíře vzhledem k
trhlinám, otěru nebo silnému opotřebení. Dřevěné kartáče vzhledem k
volným nebo zlomeným drátům.
Spadne-li elektrický nástroj nebo vložený nástroj dolů, přezkoušejte, není-li
poškozen, nebo použijte nepoškozený
vložený nástroj. Zkontrolovali-li a vložili-li jste nástroj, nevyskytujte se vy a
v blízkosti se nacházející osoby v rovině otáčejícího se vloženého nástroje a
nechejte zařízení po dobu jedné minuty běžet na nejvyšší otáčky. Poškozené
vložené nástroje se většinou zlomí v testovací době.
h)
ochranu očí nebo ochranné brýle.
Pokud lze, noste masku proti prachu,
ochranu sluchu, ochranné rukavice
nebo speciální zástěru, která vás chrání
před brusnými a materiálovými částicemi. Oči by se měli chránit před poletujícími
cizími tělesy, které vznikají při různých použitích,
masky proti prachu nebo masky pro ochranu
dýchacích cest musí filtrovat prach vzniklý při
použití Jste-li po delší dobu vystaveni hluku, můžete utrpět ztrátu sluchu.
i) Dbejte u jiných osob na bezpečný od-
stup k pracovní oblasti. Každý, kdo
vstoupí do pracovní oblasti, musí nosit
osobní ochranné vybavení. Úlomky ob-
robků nebo zlomené vložené nástroje mohou
odletět a způsobit poranění i mimo přímou
pracovní oblast.
j) Držte zařízení na izolovaných plochách
k uchopení při konání prací, při nichž
vložený nástroj se může strefit do vodičů vedoucích proud nebo do síťového
kabelu. Kontakt s vodičem pod napětím může
uvést pod napětí i kovové vodiče a vést k úrazu
elektrickém proudem.
k) Chraňte síťový kabel před otáčejícími
se vloženými nástroji. Ztratíte-li kontrolu
Noste osobní ochranné vy-
bavení! Použijte vždy podle
p
oužití ochranu celého obličej
e,
47 CZ
Page 48

zařízení, může se síťový kabel proříznout nebo
být zachycen a vaše ruka nebo paže se může
dostat do otáčejícího se vloženého nástroje.
l) Elektrický nástroj nikdy neodložte,
nedostane-li se předtím vložený nástroj
úplně do klidového stavu. Otáčející se
vložený nástroj může přijít do styku s opěrnou
plochou, čímž můžete ztratit kontrolu elektrického nástroje.
m) Elektrický nástroj nenechte běžet, no-
síte-li jej. Váš oděv se může zachytit náhodným
kontaktem otáčejícím se vloženým nástrojem a
vložený nástroj se může zavrtat do vaší hlavy.
n) Pravidelně čistěte větrací štěrbinu
svého elektrického nástroje. Ventilátor
motoru vtáhne prach do pouzdra, a silné nahromadění kovového prachu může způsobit
nebezpečí elektřinou.
o) Elektrický nástroj nepoužívejte v blíz-
kosti hořlavých materiálů. Jiskry mohou
tyto materiály zapálit.
p) Nepoužívejte vložené nástroje, které
vyžadují kapalná chladiva. Použití vody
a jiných kapalných chladiv může vést k úrazu
elektrickým proudem.
Q
Zpětný ráz a příslušné
bezpečnostní pokyny
Zpětný ráz je náhlá reakce v důsledku zaháknutého
nebo zablokovaného otáčejícího se vloženého nástroje, jako brusný kotouč, brusný talíř, drátěný kartáč
atd. Zaháknutí nebo zablokování vedou k trhavému
zastavení otáčejícího se vloženého nástroje. Tím se
nekontrolovaný elektrický nástroj zrychlí proti směru otáčení vloženého nástroje k blokovacímu místu.
Je-li např. brusný kotouč v obrobku zaháknutý nebo
zablokovaný, může se hrana brusného kotouče, která
vnikla do obrobku, zachytit a tím brusný kotouč vylomit nebo způsobit zpětný ráz. Brusný kotouče se
pohybuje směrem k obsluhující osobě nebo od ní,
vždy podle směru otáčení kotouče na zablokovaném
místě. Přitom se mohou brusné kotouče také vylomit.
48 CZ
pak
Zpětný ráz je následkem chybného nebo vadného
použití elektrického nástroje. Lze mu následujícími
vhodnými preventivními opatřeními zabránit.
a) Držte elektrický nástroj pevně a
své tělo a paže do polohy, v níž můžete
síly zpětného rázu zachytit. Použijte
vždy přídavné rukojeti, je-li k dispozici,
abyste měli největší možnou kontrolu
sil zpětného rázu nebo reakčních mo
tů při běhu s vyššími otáčkami. Obsluhujíc
osoba může ovládat síly zpětného rázu a reakční
síly prostřednictvím vhodných preventivních opat
b) Neuveďte ruku do blízkosti otáčejících
se vložených nástrojů. Vložený nástroj se
může při zpětném rázu pohybovat přes vaši ruku.
c) Vyhněte se svým tělem oblasti, v níž
se pohybuje elektrický nástroj se zpětným rázem. Zpětný ráz pohání elektrický
nástroj do směru proti pohybu brusného kotouče
na zablokovaném místě.
d) Obzvlášť opatrně pracujte v oblasti
rohů, ostrých hran atd. Zabraňte tomu, aby
se vložené nástroje od obrobku odrazily zpět a
uvízly. Otáčející se vložený nástroj má sklon k
uvíznutí u rohů, ostrých hran nebo odrazí-li se.
To způsobuje ztrátu kontroly nebo zpětný ráz.
e) Nepoužívejte řetězový nebo ozubený
pilový list. Takové vložené nástroje často
způsobí zpětný ráz nebo ztrátu kontroly elektrického nástroje.
Q
Zvláštní pokyny k
uveďte
men-
ření.
broušení a rozbrušování
a) Používejte výhradně brusná tělíska
povolená pro váš elektrický nástroj
a ochranný poklop určený pro tato
brusná tělíska. Brusná tělíska, která nejsou
určena pro elektrický nástroj, nelze dostatečně
odstínit a jsou nejistá.
b) Ochranný poklop se musí bezpečně
umístit na elektrickém nástroji a nastavit tak, aby bylo dosaženo nejvyšší
bezpečnosti, tzn. aby nejmenší možný
díl brusného tělíska směřoval otevřeně k obsluhující osobě. Ochranný poklop
í
Page 49

Všeobecné bezpečnostní pokyny pro elektrické nářadí
má obsluhující osobu chránit před úlomky a
náhodným stykem s brusným tělískem.
c) Brusná tělíska se smí používat jen pro
doporučené možnosti použití. Například: Nikdy nebruste s boční plochou
rozbrušovacího kotouče. Rozbrušovací
kotouče jsou určeny k úběru materiálu hranou
kotouče. Boční působení síly na tato brusná
tělíska je může zlomit.
d) Používejte vždy nepoškozenou upína-
cí přírubu o správné velikosti a tvaru
pro brusný kotouč, který jste zvolili.
Vhodné příruby podpírají brusný kotouč a snižují
nebezpečí zlomení brusného kotouče. Příruby
pro rozbrušovací kotouče se mohou lišit od přírub pro jiné brusné kotouče.
e) Nepoužívejte opotřebované brusné
kotouče od velkých elektrických nástrojů. Brusné kotouče pro větší elektrické ná-
stroje nejsou dimenzovány pro vysoké počty
otáček menších elektrických nástrojů a mohou
se zlomit.
Q
Další zvláštní bezpečnostní
pokyny k rozbrušování
a) Vyhněte se zablokování brusného
kotouče nebo příliš vysokému přítlačnému tlaku. Neprovádějte nadměrně
hluboké řezy. Přetížení brusného kotouče
zvyšuje jeho namáhání a náchylnost ke zkroucení nebo zablokování a tím možnost zpětného
rázu nebo zlomení brusného tělíska.
b) Vyhněte se oblasti před a za otáčejícím
se brusným kotoučem. Pohybuje-li se brusný
kotouč od sebe v obrobku, může elektrický
nástroj s otáčejícím se kotoučem v případě
zpětného rázu přímo na vás odstředit.
c) V případě, že brusný kotouč uvázl
nebo jste ukončili práci, zařízení vypněte a držte je klidně, až kotouč přejde do klidového stavu. Nikdy se nepokoušejte ještě běžící rozbrušovací
kotouč z řezu vytáhnout, jinak může
nastat zpětný ráz. Vyšetření a odstranění
příčiny pro uváznutí.
d) Pokud se v obrobku nachází obrobek,
elektrický nástroj znovu nezapněte.
Nechejte brusný kotouč nejprve dosáhnout svých plných otáček, předtím
než opatrně budete pokračovat v řezu.
Jinak se může kotouč zaháknout, vyskočit z obrobku nebo způsobit zpětný ráz.
e) Desky nebo obrobky podepřete, aby
se zmenšilo riziko zpětného rázu uvíznutým rozbrušovacím kotoučem. Velké
obrobky se mohou pod svou vlastní hmotností
prohnout. Obrobek se musí na obou stranách
kotouče podepřít. A sice jak v blízkosti rozbrušovacího kotouče tak i na hraně.
f) Buďte obzvlášť opatrní u „kapesních
řezů“ do existujících stěn nebo jiných
nepředvídaných oblastí. Ponořený roz-
brušovací kotouč může při řezání do plynových
a vodovodních potrubí, elektrických vodičů
nebo jiných objektů způsobit zpětný ráz.
Q
Zvláštní bezpečnostní pokyny
k broušení brusným papírem
Nepoužívejte předimenzované brusné
listy, nýbrž se řiďte údaji výrobce k
velikosti brusných listů. Brusné listy, které
vyčnívají přes brusný talíř. Mohou způsobit poraněním jakož i vést k zablokování, přetržení
brusných listů a ke zpětnému rázu.
Q
Zvláštní bezpečnostní
pokyny k leštění
Nepřipusťte volné díly lešticího víka,
zejména upevňovací šňůry. Upevňovací
šňůry uskladněte nebo zkraťte. Volné, spolu se
otáčející upevňovací šňůry mohou zachytit
vaše prsty nebo uvíznout ve výrobku.
Q
Zvláštní bezpečnostní pokyny
k práci s drátěnými kartáči
a) Mějte na paměti, že drátěný kartáč
ztrácí i během běžného použití kusy
49 CZ
Page 50

drátů. Nepřetěžujte dráty příliš vysokým přítlačným tlakem. Odletující kusy
drátů mohou velmi snadno proniknout tenkým
oděvem a / nebo pokožkou.
b) Doporučuje-li se ochranný poklop, za-
braňte tomu, aby se ochranný poklop
a drátěný kartáč dotýkaly. Kartáče na
talíře a hrnce mohou přítlačným tlakem a odstředivými silami svůj průměr zvětšit.
Specifické bezpečnostní pokyny
pro minivrtačku PMGS 12 B2
anapájecí zdroj PMGS 12 B2-1
Při provozu používejte toto ochranné
vybavení: ochranné brýle a ochranné
pracovní rukavice.
POZOR! Nástroj má po vypnutí doběh!
Zamezte styku s rychle se otáčejícími nástroji.
Obrobek zajistěte. Pro
upnutí obrobku použijte upínací přípravky nebo
svěrák. Obrobek je tak uchycen pevněji než ve
Vaší ruce.
V žádném případě si
neopírejte ruce vedle nebo před pří
jem a obráběnou plochou, protože při
sklouznutí hrozí nebezpečí zranění.
Zamezte kontaktu s běžícím brusným
nástrojem.
NEBEZPEČÍ POŽÁRU Z ODLÉTAJÍCÍCH
JISKER! Při broušení kovů odlétají jiskry. Proto
bezpodmínečně dávejte pozor, aby nebyly
ohroženy osoby a v blízkosti pracovního prostoru nebyly žádné hořlavé materiály.
OHROŽENÍ PRACHEM!
Zdraví škodlivý či jedovatý prach vznikající při
obrábění představuje ohrožení zdraví pro ob
jící osobu a pro osoby zdržující se v blízkosti.
Používejte masku proti prachu!
JEDOVATÉ VÝPARY! Při
obrábění plastů, barev, laků atd. zajistěte dostatečné větrání.
50 CZ
Používejte pouze ve vnitřním prostředí!
stro-
sluhu-
Obráběné materiály neboplochy ne-
impregnujte kapalinamiobsahujícími
rozpouštědla.
Zamezte broušení barev obsahujících
olovo nebo jiných zdraví škodlivých
materiálů.
Materiál obsahující azbest se nesmí
obrábět. Azbest způsobuje rakovinu.
Neobrábějte navlhčené materiály
mokré plochy.
UPOZORNĚNÍ! Přístroj během provozu ne-
zatěžujte tak silně, že dojde k jeho zastavení!
Před odložením vy-
pnutého přístroje počkejte, až se úplně zastaví.
Povrch přístroje musí
být stále čistý, suchý a bez oleje nebo
mazacího tuku.
Tento přístroj není určen k tomu, aby byl použí-
ván osobami (včetně dětí) s omezenými psychickými, smyslovými nebo duševními schopnostmi
nebo nedostatečnými zkušenostmi a / nebo nedostatečnými vědomostmi, ledaže by byly pod
dozorem osoby zodpovědné za jejich bezpečn
nebo od ní obdržely pokyny, jak přístroj správně používat. Děti by měly být pod dozorem, aby
bylo zajištěno, že si s přístrojem nebudou hrát.
nebo
Uvedení do provozu
Nepoužívejte přístroj k jiným než
předpokládaným účelům a vždy pouze s originálními díly a příslušenstvím.
Používání jiných dílů nebo jiného příslušenství,
než je doporučeno v tomto návodu k obsluze,
může znamenat nebezpečí úrazu.
Vložení /výměna nástroje /
upínací kleštiny
Stiskněte aretaci vřetene 7 a držte stisknuté.
Otáčejte upínací maticí 5, až se aretace za-
klesne.
Uvolněte upínací matici 5 kombinovaným
23
klíčem
Vyjměte vložený nástroj.
ze závitu.
ost
Page 51

Uvedení do provozu
Nejdříve zvolený nástroj prostrčte přes upínací
5
matici
, než jej zastrčíte do upínací kleštiny 18
vhodné pro daný nástroj.
Stiskněte aretaci vřetena 7 a držte je stisknuté.
Vložte upínací kleštinu 18 do závitové vložky a
na závit.
5
pomocí
13
pak našroubujte upínací matici
kombinovaného klíče
23
Používání nástroje s upínacím trnem
UPOZORNĚNÍ: Používejte stranu kombinova-
ného klíče
a dotažení šroubů upínacích trnů
23
ve tvaru šroubováku k povolení
13
.
Upínací trn 13 vložte do elektrického nářadí
podle popisu.
Pomocí kombinovaného klíče 23 povolte šroub
na upínacím trnu
13
.
Nasaďte požadovaný nasazovací nástroj na
šroub mezi obě podložky.
Pomocí kombinovaného klíče 23 dotáhněte
šroub na upínacím trnu
13
.
Zapnutí a vypnutí /
nastavení rozsahu otáček
Zapnutí / nastavení rozsahu otáček:
Připojte zástrčku 4 k napájecímu zdroji 10 tak,
že zástrčku zasunete do příslušné zásuvky
8
(viz obr. C).
Přístroj připojte k elektrickému napájení tak, že
síťovou zástrčku zasunete do zásuvky.
Stiskněte spínač ZAP / VYP 2 dolů a posuňte
jej pak ve směru regulace otáček
1
. Nastavte
regulaci otáček do polohy mezi „5“ a „20.“.
Vypínání:
Nastavte regulaci otáček 1 do polohy „5“.
Stiskněte spínač ZAP / VYP
2
dolů a posuňte
jej ve směru kabelu.
Pokyny k obrábění materiálu /
nástrojům / rozsahu otáček
Frézovací bity 20 používejte k obrábění oceli
a železa s maximálními otáčkami.
Rozsah otáček pro obrábění zinku, slitin zinku,
hliníku, mědi a olova zjistěte na zkušebních
vzorcích.
Plasty a materiály s nízkým bodem tavení obrá-
bějte při nízkých otáčkách.
Dřevo obrábějte s vysokými otáčkami.
Čištění, leštění a práce s látkovými kotouči pro-
vádějte se středními otáčkami.
:
Následující údaje jsou nezávazná doporučení. Při
praktické práci si také sami vyzkoušejte, který nástroj a které nastavení je pro obráběný materiál
nejvhodnější.
Nastavení vhodných otáček:
Číslice na regulaci otáček
5
obráběnýmateriál
1
Plast a materiály s nízkým
bodem tavení
8
12
16
20
Kamenina, keramika
Měkké dřevo, kov
Tvrdé dřevo
Ocel
Příklady použití / volba správného nástroje:
Funkce Příslušen-
Použití
ství
Vrtání
HSS vrták
Frézování Frézovací
20
bity
Obrábění dřeva
12
Různé práce;např.
vybrání, vyhloubení, tvarování, žlábkování nebo vytváření drážek a čepů
Gravírování Gravírovací
21
bity
Leštěnízbavení rzi
POZOR!
Vyvíjejte pou-
Kovovýkartáč
16
Lešticíkotouče
14
ze lehký tlak
nástroje na
obrobek.
Rytí nápisůkutilské
práce(viz obr. D)
Zbavení rzi
Obrábění různých
kovů a plastů, zvláště ušlechtilých kovů
jako zlata nebo
stříbra (viz obr. E)
51 CZ
Page 52

Funkce Příslušen-
ství
Čištění Plastovékartá-
Broušení Brusné kotou-
Řezání Řeznékotou-
19
če
15
če
né bity
17
če
, brus-
Použití
např. čištění špatně
přístupných plastových krytů nebo čištění okolí zámku dveří
Broušení kameniny,
dřeva, jemné práce
22
na tvrdých materiálech jako keramice
nebo legované
oceli (viz obr. F, G)
Obrábění kovu,
plastů a dřeva
Tipy a triky
Když vyvíjíte příliš velký tlak, může upnutý nástroj
prasknout a /nebo se může poškodit obrobek. Optimálních výsledků práce můžete dosáhnout tak, že
nástroj vedete na obrobku s konstantními otáčkami
a malým tlakem.
Údržba a čištění
Přístroj nevyžaduje údržbu.
Z přístroje odstraňte nečistoty. Použijte k tomu
suchou utěrku.
Servis
Přístroje nechte opra-
vovat servisním střediskem nebo odborným elektrotechnikem a pouze s
originálními náhradními díly. Tím se za-
ručí, že bezpečnost přístroje zůstane zachová
Výměnu zástrčky
nebo přívodního kabelu nechte vždy
provést u výrobce přístroje nebo v
jeho servisní dílně. Tím se zaručí, že bez-
pečnost přístroje zůstane zachována.
na.
Q
Záruka
Na tento přístroj platí tříletá záruka od
data zakoupení. Přístroj byl vyroben s
nejvyšší pečlivostí a před odesláním prošel výstupní kontrolou. Uschovejte si,
prosím, pokladní lístek jako doklad o nákupu. V případě uplatňování záruky kontaktujte telefonicky Vaší servisní službu.
Pouze tak může být zajištěno bezplatné
zaslání Vašeho zboží.
Záruka se vztahuje pouze na chyby materiálu nebo
výrobní závady, ale ne na škody,vzniklé při přepravě, ne na součásti, podléhající rychlému opotřebení
nebo na poškození křehkých dílů, jako jsou např.
spínače nebo akumulátory. Výrobek je určen pouze pro privátní použití, ne průmyslové.
Při nesprávném a neodborném využívání, při použití
násilí a při zásazích, které nebyly provedeny našimi
autorizovanými servisními provozovnami, záruční
nároky zanikají. Vaše práva vyplývající ze zákona
touto zárukou nejsou omezena.
Záruční doba se zárukou neprodlouží. Toto platí také
pro náhradní díly a opravené součásti. Případné
škody a vady, existující už při koupi, se musí hlásit
ihned po vybalení, nejpozději však do dvou dnů
od data nákupu. Po uplynutí záruční doby se provedené opravy musí zaplatit.
CZ
Servis Česko
Hotline: 800 143873
e-mail: kompernass@lidl.cz
IAN 89959
Likvidace
Obal se skládá z ekologických materiálů, které můžete likvidovat prostřednictvím
místních sběren recyklovatelných materiálů.
52 CZ
Page 53

Likvidace / Prohlášení o shodě / Výrobce
Elektrické nářadí nevyhazujte
do komunálního odpadu!
Podle evropské směrnice 2002 / 96 / EC o odpad
elektrických a elektronických zařízeních (OEEZ) a
podle jejího převedení do národního práva se musí
opotřebené elektrické nářadí shromažďovat odděleně a odevzdat k ekologickému zpracování.
O možnostech likvidace vysloužilého elektrického
nářadí se informujte na svém obecním nebo městském úřadě.
ních
Q
Prohlášení o shodě / Výrobce
My, KOMPERNASS GMBH, pracovník zodpovědný
za dokumentaci: pan Semi Uguzlu, BURGSTR. 21
448
67 BOCHUM, GERMANY, tímto prohlašujeme
pro tento výrobek shodu s následujícími normami,
normativními dokumenty a směrnicemi ES:
Směrnice o strojích
(2006 / 42 / EC)
ES směrnice o elektrických zařízeních nízkého napětí (2006 / 95 / EC)
Elektromagnetická kompatibilita
(2004 / 108 / EC)
RoHS Směrnice
(2011 / 65 / EU)
Použité sladěné normy
EN 60745-1/A11:2010, EN 60745-2-1:2010
EN 60745-2-3:2011
EN 55014-1/A2:2011, EN 55014-2/A2:2008
EN 61000-3-2/A2:2009, EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61558-1/A1:2009, EN 61558-2-6:2009
,
Typ / Označení přístroje:
Modelářská a gravírovací sada PMGS 12 B2
Date of manufacture (DOM): 04–2013
Sériové číslo: IAN 89959
Bochum, 30.04.2013
Semi Uguzlu
- Manager jakosti -
Technické změny ve smyslu dalšího vývoje jsou
vyhrazeny.
53 CZ
Page 54

54
Page 55

Zoznam obsahu
Úvod
Určený účel použitia ........................................................................................................................ Strana 56
Výbava .............................................................................................................................................Strana 56
Rozsah dodávky ..............................................................................................................................Strana 56
Technické údaje ............................................................................................................................... Strana 56
Všeobecné bezpečnostné pokyny pre elektrické nástroje
1. Bezpečnosť na pracovnom mieste ............................................................................................. Strana 57
2. Elektrická bezpečnosť ................................................................................................................. Strana 57
3. Bezpečnosť osôb ......................................................................................................................... Strana 58
4. Používanie a zaobchádzanie s elektrickým nástrojom ............................................................. Strana 58
5. Servis ............................................................................................................................................ Strana 59
Bezpečnostné upozornenia pre všetky použitia ............................................................................ Strana 59
Spätný ráz a príslušné bezpečnostné upozornenia ...................................................................... Strana 60
Osobitné bezpečnostné upozornenia k brúseniu a rozbrusovaniu .............................................. Strana 61
Ďalšie osobitné bezpečnostné upozornenia k rozbrusovaniu ...................................................... Strana 61
Osobitné bezpečnostné upozornenia k brúseniu brúsnym papierom ..........................................Strana 62
Osobitné bezpečnostné upozornenia k lešteniu ............................................................................Strana 62
Osobitné bezpečnostné upozornenia k prácam s drôtenými kefami ...........................................Strana 62
Špecifické bezpečnostné pokyny pre malú vŕtačku PMGS 12 B2 a sieťový
diel PMGS 12 B2-1 ......................................................................................................................... Strana 62
Uvedenie do prevádzky
Nástroj / nasadenie / výmena upínacej klieštiny ............................................................................Strana 63
Zapnutie a vypnutie / nastavenie rozsahu otáčok .........................................................................Strana 63
Pokyny pre spracovanie materiálu / nástroj / rozsah otáčok ........................................................ Strana 63
Tipy a triky ........................................................................................................................................ Strana 64
Údržba a čistenie ................................................................................................................... Strana 64
Servis ............................................................................................................................................... Strana 64
Záruśná lehota ........................................................................................................................ Strana 64
Likvidácia ..................................................................................................................................... Strana 65
Vyhlásenie o zhode / Vyhlásenie výrobcu ...................................................... Strana 65
55 SK
Page 56

Modelárska a gravírovacia
súprava PMGS 12 B2
Úvod
Blahoželáme vám ku kúpe nového výrobku. Rozhodli
ste sa pre veľmi kvalitný výrobok. Návod na obsluhu je súčasťou tohto výrobku. Obsahuje dôležité
upozornenia týkajúce sa bezpečnosti, používania
a likvidácie. Skôr ako začnete výrobok používať,
oboznámte sa so všetkými pokynmi k obsluhe a
bezpečnosti. Výrobok používajte iba v súlade s
popisom a v uvedených oblastiach používania. V
prípade postúpenia výrobku ďalším osobám odovzdajte aj všetky dokumenty patriace k výrobku.
Určený účel použitia
Malá vŕtačka je určená na vŕtanie, frézovanie, gravírovanie, leštenie, čistenie, brúsenie, rezanie dreva,
kovu, plastov, keramiky alebo kameniny v suchých
priestoroch. Akékoľvek iné použitie alebo zmena
prístroja sa považuje za použitie alebo zmenu v
rozpore s určeným účelom použitia a skrýva v sebe
veľké nebezpečenstvo úrazu. Výrobca neručí za
škody vzniknuté použitím v rozpore s určeným účelom použitia. Prístroj nie je určený na profesionálne
použitie.
Výbava
Malá vŕtačka:
1
Regulácia otáčok
2
Vypínač ZAP / VYP
3
Kovový strmeň
4
Vidlica pre sieťový napájací zdroj
5
Upínacia matica
6
Prevlečná matica
7
Aretácia vretena
Sieťový diel (pozri obr. A):
8
Zásuvka pre napájanie vŕtačky
9
Odkladacia plocha
10
Sieťový diel
11
Sieťový kábel (so sieťovou vidlicou)
56 SK
4
Príslušenstvo (pozri obr. B):
12
6 ks Vrták HSS
13
2 ks Upínacie tŕne pre upnutie nástroja
14
3 ks Leštiaci kotúč
15
4 ks Brúsny kotúč
16
1 ks Drôtená kefa
17
16 ks Rezný kotúč
18
5 ks Klieština
19
2 ks Plastová kefa
20
3 ks Frézovací bit
21
2 ks Gravírovací bit
22
5 ks Brúsny bit
23
1 ks Kľúč
Rozsah dodávky
1 ks Malá vŕtačka
1 sieťový diel
1 plastový kufor
1 súprava príslušenstva (50 dielov)
1 návod na obsluhu
Technické údaje
Malá vŕtačka PMGS 12 B2:
Menovité napätie: 12 V
Menovitý príkon: 22 W
Otáčky naprázdno: n
Vrták: max. ø 3,2 mm
Kotúčov
: max. ø 25 mm
Vyhovuje skúškam podľa: EN60745-1;
Informácie o hlučnosti a vibráciách:
Nameraná hodnota hluku stanovená podľa
EN 60745. Stanovená hladina hluku elektrického
nástroja triedy A má nasledujúce typické hodnoty:
Akustická hladina: 54,70 dB(A)
Hladina akustického tlaku: 65,70 dB(A)
Presnosť K: 3 dB
Stanovené zrýchlenie, typické:
Vibrácia ruky / ramena: 1,868 m / s
Presnosť K = 1,5 m / s
0
EN60745-2-1;
EN60745-2-3
2
5000–20000 min
2
-1
Page 57

Úvod / Všeobecné bezpečnostné pokyny pre elektrické nástroje
Hladina oscilácií uvedená v
tomto návode bola stanovená podľa normalizovanéh
postupu EN 60745 a môže sa použiť na porovnávanie prístrojov. Zadaná emisná hodnota oscilácií môže
byť použitá i pre úvodné vyhodnotenie prerušenia.
Hladina oscilácií sa mení závisle od použitého elektrického prístroja a v niektorých prípadoch môže byť
vyššia ako hodnota stanovená v týchto pokynoch.
Môže dôjsť k podceneniu vibračnej záťaže, ak sa
elektrické náradie bežne používa týmto spôsobom.
Upozornenie: Na presný odhad oscilačného
zaťaženia počas určitej pracovnej doby treba zohľadniť aj čas vypnutia prístroja a čas, keď je prístroj síce
zapnutý, ale v skutočnosti sa nepoužíva. Tým sa
môže oscilačné zaťaženie počas celej pracovnej
doby výrazne znížiť.
Sieťový diel PMGS 12 B2-1:
VSTUP / Input:
Menovité napätie: 230 V∼ 50 Hz
VÝSTUP / Output:
Menovité napätie: 12 V
Menovitý prúd: 1A
Trieda ochrany: II /
vyhovuje skúškam podľa: EN61558
Všeobecné bezpečnostné po-
kyny pre elektrické nástroje
Prečítajte všetky bezpečnostné pokyny a nariadenia. Opomenutie dodržiavania
bezpečnostných pokynov a nariadení môže mať
za následok vznik úrazu elektrickým prúdom, požiaru a / alebo ťažkého zranenia.
Uschovajte všetky bezpečnostné pokyny
a nariadenia pre budúce použitie!
V bezpečnostných pokynoch uvedený pojem „elektrický nástroj“ sa vzťahuje na elektrické nástroje
napájané sieťovým prúdom (so sieťovým káblom)
a na elektrické nástroje s akumulátorom (bez sieťového kábla).
1. Bezpečnosť na
o
pracovnom mieste
a) Udržujte svoj pracovný priestor čistý
a dobre osvetlený. V pracovných priesto-
roch s neporiadkom a bez osvetlenia môže
dôjsť k úrazom.
b) S elektrickým nástrojom nepracujte v
prostredí s nebezpečenstvom výbuchu, v ktorom sa nachádzajú horľavé
kvapaliny, plyny alebo horľavý prach.
Pri používaní elektrických nástrojov vznikajú iskry, ktoré môžu zapáliť prach alebo výpary.
c) Počas používania nedovoľte, aby sa
deti a iné osoby dostali do blízkosti
elektrického nástroja. Ak sa budete roz-
ptyľovať, môžete stratiť kontrolu nad prístrojom.
2. Elektrická bezpečnosť
a) Vidlica napájania elektrického nástroja
musí byť v elektrickej zásuvke dobre
zasunutá. Vidlica napájania sa nesmie
v žiadnom prípade zmeniť. Nepoužívajte adaptéry pre elektrické nástroje
zemnené ochranným vodičom. Nezmene-
né napájacie vidlice a vhodné zásuvky znižujú
riziko úrazu elektrickým prúdom.
b) Vyvarujte sa telesného kontaktu so
zemnenými povrchmi ako potrubie,
vykurovacie telesá, šporáky a chladničky. Existuje zvýšené riziko úrazu elektrickým
prúdom, keď sa vaše telo uzemní.
c) Chráňte elektrické nástroje pred daž-
ďom a vlhkosťou. Vniknutie vody do elektric-
kého prístroja zvyšuje riziko úrazu elektrickým
prúdom.
d) Nepoužívajte kábel na iné účely, ako
je určený, t.j. elektrický nástroj nenoste zavesený za kábel, nevešajte ho
na kábel, ani nevyťahujte vidlicu zo
zásuvky ťahaním za kábel. Chráňte
kábel pre teplom, olejom, ostrými
hranami a pohybujúcimi sa dielmi prístroja. Poškodené alebo zamotané káble
zvyšujú riziko úrazu elektrickým prúdom.
57 SK
Page 58

e) Keď pracujete s elektrickým nástrojom
vonku, používajte len predlžovací
kábel určený pre vonkajšie použitie.
Používanie vhodného predlžovacieho kábla
pre vonkajšie použitie znižuje riziko úrazu
elektrickým prúdom.
f) Keď sa nedá vyhnúť použitiu elektric-
kého nástroja vo vlhkom prostredí,
použite prúdový ochranný spínač. Po-
užitie prúdového ochranného spínača znižuje
riziko úrazu elektrickým prúdom.
3. Bezpečnosť osôb
nástroj v neočakávaných situáciách lepšie kontrolovať.
f) Noste vhodné oblečenie. Nenoste širo-
ké oblečenie a šperky. Nepribližujte
sa vlasmi, oblečením a rukavicami k
pohybujúcim sa dielom. Voľné oblečenie,
šperky alebo dlhé vlasy sa môžu zachytiť do
pohybujúcich sa dielov.
g) Keď sa môžu namontovať zariadenia
na odsávanie a zachytávanie prachu,
uistite sa, že sú pripojené a správne
používané. Používanie odsávania prachu
môže znížiť ohrozovanie prachom.
a) Buďte vždy pozorný, dávajte pozor na
to, čo robíte, a s elektrickým nástrojom pracujte rozvážne. Nepoužívajte
elektrický nástroj, keď ste unavený
alebo pod vplyvom drog, alkoholu
alebo liekov. Chvíľa nepozornosti pri pou-
žívaní elektrického nástroja môže spôsobiť
závažné poranenia.
b)
pomôcok ako protiprachová maska, nekĺzavej
bezpečnostnej obuvi, ochrannej prilby alebo
ochrany sluchu v závislosti od spôsobu použitia
elektrického nástroja znižuje riziko poranení.
c) Vyvarujte sa náhodnému uvedeniu do
prevádzky. Uistite sa, že elektrický
nástroj je vypnutý ešte pred pripojením napájania, pred jeho zdvihnutím
alebo prenesením. Keď máte pri prenáša-
ní elektrického nástroja prst na vypínači alebo
už zapnutý prístroj pripájate na napájanie,
môže dôjsť k úrazom.
d) Pred zapnutím elektrického nástroja
odložte nastavovacie nástroje alebo
kľúče. Nástroj alebo kľúč, ktorý sa nachá-
dza v otáčajúcom sa dieli prístroja môže spôsobiť zranenie.
e) Vyvarujte sa nenormálnemu držaniu
tela elektrického nástroja. Dbajte vždy
na bezpečný postoj a vždy zachovávajte rovnováhu. Tak môžete elektrický
58 SK
Noste osobné ochranné pomôcky a vždy ochranné okuliare. Nosenie osobných ochranných
4. Používanie a zaobchádzanie
s elektrickým nástrojom
a) Prístroj nepreťažujte. Pri svojej práci
používajte len elektrický nástroj určený
na daný účel. S vhodným elektrickým nástro-
jom budete pracovať lepšie a bezpečnejšie pri
danom výkone.
b) Elektrický nástroj nepoužívajte, ak má
pokazený vypínač. Elektrický nástroj, ktorý
sa nedá zapnúť alebo vypnúť, je nebezpečný
a musí sa opraviť.
c) Vidlicu napájania vytiahnite zo zásuv-
ky ešte predtým, než začnete prístroj
nastavovať, vymienať príslušenstvo
alebo prístroj odložíte. Tieto opatrenia z
obozretnosti zabraňujú neúmyselnému spusteniu
elektrického nástroja.
d) Nepoužívané elektrické nástroje ucho-
vávajte mimo dosahu detí. Osobám,
ktoré toto nevedia alebo ktoré tieto
pokyny nečítali, nedovoľte, aby prí
používali. Elektrické nástroje sú nebezpečné,
keď ich používajú neskúsené osoby.
e) Starostlivo sa starajte o elektrické ná-
stroje. Kontrolujte, či pohyblivé diely
bezchybne fungujú a nezasekávajú
sa, či diely nie sú zlomené alebo tak
poškodené, že narušujú funkčnosť
elektrického nástroja. Poškodené
diely nechajte pred použítím prístroja
opraviť. Príčinou mnoných úrazov je zle udr-
žiavaný elektrický nástroj.
stroj
Page 59

Všeobecné bezpečnostné pokyny pre elektrické nástroje
f) Rezné nástroje udržiavajte ostré a čis
Starostlivo udržiavané rezné nástroje s ostrými
reznými hranami sa menej zasekávajú a dajú
sa ľahšie viesť.
g) Používajte elektrický nástroj, príslušen-
stvo, zásahové nástroje atď. podľa
týchto pokynov. Pritom zohľadňujte
pracovné podmienky a vykonávanú
činnosť. Používanie elektrických nástrojov na
iné než určené účely použitia môže viesť k
vzniku nebezpečných situácií.
5.
Servis
a) Prístroje nechajte opraviť vservisnom
stredisku alebo odborníkom zoblasti
elektrotechniky, ktorí používajú na
opravy len originálne náhradné diely.
Tým zabezpečíte, že zostane zachovaná bezpečnosť prístroja.
Q
Bezpečnostné upozornenia
té.
pre všetky použitia
Spoločné bezpečnostné upozornenia pre
brúsenie, brúsenie brúsnym papierom,
práce s drôtenými kefami, leštenie a rozbrusovanie:
a) Toto elektrické náradie sa používa na
brúsenie, brúsenie brúsnym papierom,
práce s drôtenými kefami, leštenie a
rozbrusovanie. Dodržiavajte všetky
bezpečnostné upozornenia, pokyny,
vyobrazenia a údaje, ktoré získate
spolu s náradím. Ak nebudete dodržiavať
nasledujúce pokyny, môže dôjsť k zásahu elektrickým prúdom, k požiaru a / alebo k závažným
poraneniam.
b) Normatívny predpis / normatívny pokyn pre
tento nástroj nie sú aplikovateľné.
c) Nepoužívajte príslušenstvo, ktoré vý-
robcom nebolo špeciálne určené pre
toto elektrické náradie. Samotná možnosť
pripevnenia príslušenstva k vášmu elektrickému
náradiu ešte nie je zárukou bezpečného používania.
d) Povolené otáčky vloženého nástroja
musia byť minimálne také vysoké ako
údaj o maximálnych otáčkach uvedený
na elektrickom náradí. Príslušenstvo, ktoré
sa otáča rýchlejšie, než je povolené, sa môže
zlomiť alebo odletieť.
e) Vonkajší priemer a hrúbka vloženého
nástroja musí zodpovedať rozmerovým údajom vášho elektrického náradia. Vložené nástroje s nesprávnymi rozmermi
sa nedajú dostatočne chrániť alebo kontrolovať.
f) Brúsne kotúče, príruby, brúsne taniere
alebo iné príslušenstvo musí presne
prekryť brúsne vreteno vášho elektrického náradia. Vložené nástroje, ktoré
presne neprekrývajú brúsne vreteno, sa otáčajú
nepravidelne, veľmi silno vibrujú a môžu viesť
k strate kontroly.
g) Nepoužívajte poškodené nástroje.
Pred každým použitím skontrolujte
vložené nástroje, napr. brúsne kotúče,
či sa neodlupujú a či na nich nie sú trhliny, u brúsnych tanierov výskyt trhlín,
opotrebovanie alebo silné opotrebenie.
U drôtených kefiek kontrolujte výskyt
uvoľnených alebo zlomených drôtov.
Ak elektrické náradie alebo vložený
nástroj spadne na zem, skontrolujte,
či nie je poškodený, alebo použite
nepoškodený nástroj. Ak ste nástroj
skontrolovali a vložili, zdržiavajte sa
vy i osoby nablízku mimo roviny rotujúceho vloženého nástroja a náradie
nechajte bežať jednu minútu pri maximálnych otáčkach. Poškodené vložené ná-
stroje sa väčšinou zlomia počas doby testovania.
h)
ochranu, ochranu očí alebo ochranné
okuliare. Ak je to vhodné, noste protiprachovú masku, ochranu sluchu, ochranné rukavice alebo špeciálne zástery, ktoré vás uchránia pred brúsnymi
časticami a časticami materiálov. Oči
treba chrániť pred odletujúcimi cudzími telesami,
ktoré vznikajú pri rôznych použitiach, protiprachové alebo ochranné dýchacie masky musia
Noste osobný ochranný výstroj. V závislosti od použitia
používajte celotvárovú
59 SK
Page 60

pri použití filtrovať vznikajúci prach. Ak ste dlhší
čas vystavený veľkému hluku, môžete utrpieť
stratu sluchu.
i) Dbajte na bezpečnú vzdialenosť iných
osôb od pracovnej oblasti. Každý, kto
vstupuje do pracovnej oblasti, musí
nosiť osobný ochranný výstroj. Úlomky
nástroja alebo zlomené vložené nástroje môžu
odlietavať a spôsobiť poranenia aj mimo priamej pracovnej oblasti.
j) Ak vykonávate práce, pri ktorých môže
vložený nástroj naraziť na ukryté
elektrické vedenia alebo na sieťový
kábel, držte náradie len za izolované
plochy rukovätí. Kontakt s vedením, ktoré
je pod napätím, môže uviesť pod napätie aj
kovové časti náradia a viesť k zásahu elektrickým prúdom.
k) Sieťový kábel držte mimo dosahu
otáčajúcich sa vložených nástrojov.
Ak stratíte kontrolu nad náradím, môže dôjsť k
pretrhnutiu alebo zachyteniu sieťového kábla a
k zachyteniu ruky alebo ramena do otáčajúceho sa vloženého nástroja.
l) Elektrické náradie nikdy neodkladajte
skôr, než sa vložený nástroj úplne nezastaví. Otáčajúci sa vložený nástroj sa môže
dostať do kontaktu s odkladacou plochou, v
dôsledku čoho môžete stratiť kontrolu nad elektrickým náradím.
m) Keď elektrické náradie prenášate,
nenechávajte ho zapnuté. Váš odev sa v
dôsledku náhodného kontaktu s otáčajúcim sa
vloženým nástrojom môže zachytiť a vložený
nástroj sa môže zavŕtať do vášho tela.
n) Pravidelne čistite vetracie štrbiny
elektrického náradia. Ventilátor motora
vťahuje prach do krytu a silné nahromadenie
kovového prachu môže zapríčiniť elektrické riziká.
o) Elektrické náradie nepoužívajte v
blízkosti horľavých materiálov. Iskry
môžu tieto materiály zapáliť.
p) Nepoužívajte nástroje, ktoré si vyža-
dujú kvapalné chladiace prostriedky.
Používanie vody alebo iných kvapalných chladiacich prostriedkov môže viesť k zásahu elektrickým
prúdom.
60 SK
Q
Spätný ráz a príslušné
bezpečnostné upozornenia
Spätný ráz je náhla reakcia v dôsledku zaseknutia
alebo zablokovania otáčajúceho sa vloženého nástroja, ako napr. brúsneho kotúča, brúsneho taniera,
drôtenej kefy, atď. Zaseknutie alebo zablokovanie
vedie k náhlemu zastaveniu rotujúceho vloženého
nástroja. V dôsledku toho sa zrýchli pohyb nekontrolovaného elektrického náradia proti smeru otáčania vloženého nástroja na zablokované miesto.
Keď sa napríklad v obrábanom predmete zasekne
alebo zablokuje brúsny kotúč, môže sa zachytiť hrana
brúsneho kotúča, ktorá sa vnára do obrábaného
predmetu, v dôsledku čoho sa brúsny kotúč vylomí
alebo vyvolá spätný ráz. Brúsny kotúč sa následne
pohybuje smerom k obsluhe alebo od nej, v závislosti od smeru otáčania kotúča na zablokovanom
mieste. Brúsne kotúče sa pritom môžu aj zlomiť.
S
pätný ráz je dôsledkom nesprávneho alebo chybného
použitia elektrického náradia. Dá sa mu vyhnúť vhodný
mi preventívnymi opatreniami, ktoré sú opísané nižšie.
a) Elektrické náradie držte pevne a telo i
ramená uveďte do polohy, v ktorej
dokážete zachytiť silu spätného rázu.
Vždy používajte prídavnú rukoväť,
aby ste dosiahli čo najvyšší stupeň
kontroly nad silou spätného rázu alebo nad reakčným momentom pri zvýšení otáčok. Personál obsluhy dokáže prija-
tím vhodných preventívnych opatrení ovládať
silu spätného rázu alebo reakčnú silu.
b) Ruku nikdy neklaďte do blízkosti otá-
čajúcich sa vložených nástrojov. Vložený
nástroj môže pri spätnom ráze prejsť cez vašu
ruku.
c) Vyhýbajte sa telom oblasti, do ktorej
sa elektrické náradie presúva pri
spätnom ráze. Spätný ráz ženie elektrické
náradie do smeru oproti pohybu brúsneho
kotúča na zablokovanom mieste.
d) Obzvlášť opatrne pracujte v oblasti
rohov, ostrých hrán, atď. Zabráňte
odrazeniu vložených nástrojov od obrábaného predmetu a ich zaseknutiu.
-
Page 61

Všeobecné bezpečnostné pokyny pre elektrické nástroje
Rotujúci vložený nástroj má na rohoch, ostrých hranách alebo po odrazení sklon k zaseknutiu. Dôsledkom toho je strata kontroly alebo spätný ráz.
e) Nepoužívajte list reťazovej píly alebo
ozubený pílový list. Takéto vložené nástroje často zapríčiňujú spätný ráz alebo stratu
kontroly nad elektrickým náradím.
Q
Osobitné bezpečnostné
upozornenia k brúseniu
a rozbrusovaniu
a) Používajte výlučne brúsne nástroje
schválené pre vaše elektrické náradie
a ochranný kryt určený na tieto brúsne
nástroje. Brúsne nástroje, ktoré nie sú určené
pre elektrické náradie, sa nedajú dostatočne
chrániť a sú nespoľahlivé.
b) Ochranný kryt musí byť na elektrickom
náradí namontovaný bezpečne a musí
byť nastavený tak, aby sa dosiahla
maximálna miera bezpečnosti, t. j. aby
čo najmenšia časť brúsneho nástroja
smerovala odkrytá k personálu obslu
Ochranný kryt má chrániť personál obsluhy pred
úlomkami a náhodným kontaktom s brúsnym
nástrojom.
c) Brúsne nástroje sa smú používať len
na odporúčané účely. Napríklad: Nikdy
nebrúste bočnou plochou rozbrusovacieho kotúča. Rozbrusovacie kotúče sú
určené na uberanie materiálu hranou kotúča.
Bočné pôsobenie síl na tieto brúsne nástroje
ich môže zlomiť.
d) Vždy používajte nepoškodenú upínaciu
prírubu správnej veľkosti a tvaru pre
vami zvolený brúsny kotúč. Vhodné
príruby podopierajú brúsny kotúč a znižujú nebezpečenstvo zlomenia brúsneho kotúča. Príruby pre rozbrusovacie kotúče sa môžu líšiť od
prírub pre iné brúsne kotúče.
e) Nepoužívajte opotrebované brúsne
kotúče z väčšieho elektrického náradia.
Brúsne kotúče pre väčšie elektrické náradie nie
sú uspôsobené na vyššie otáčky menšieho elektrického náradia a môžu sa zlomiť.
hy.
Q
Ďalšie osobitné bezpečnostné
upozornenia k rozbrusovaniu
a) Vyhýbajte sa zablokovaniu rozbruso-
vacieho kotúča alebo nadmernému
pritláčaniu. Nevykonávajte nadmerne
hlboké rezy. Preťaženie brúsneho kotúča
zvyšuje jeho namáhanie a náchylnosť na spriečenie alebo zablokovanie, a tým možnosť spätného rázu alebo zlomenia brúsneho nástroja.
b) Vyhýbajte sa oblasti pred a za rotujú-
cim rozbrusovacím kotúčom. Ak rozbrusovací kotúč presúvate v obrábanom predmete
smerom od seba, môže sa elektrické náradie v
prípade spätného rázu vymrštiť s otáčajúcim sa
kotúčom priamo na vás.
c) Ak sa rozbrusovací kotúč zasekne,
alebo ak prácu prerušíte, vypnite náradie a pokojne ho držte, až kým sa
kotúč nezastaví. Nikdy sa nepokúšajte
vyťahovať pohybujúci sa rozbrusovací kotúč z rezu, inak môže dôjsť k
spätnému rázu. Zistite príčinu zaseknutia a
odstráňte ju.
d) Elektrické náradie nezapínajte znovu
dovtedy, kým sa nachádza v obrábanom predmete. Skôr než budete opatrne pokračovať v reze, počkajte, kým
rozbrusovací kotúč nedosiahne maximálne otáčky. V opačnom prípade sa kotúč
môže zaseknúť, vyskočiť z obrábaného predmetu, alebo zapríčiniť spätný ráz.
e) Dosky alebo obrábané predmety po-
doprite, aby sa znížilo riziko spätného
rázu v dôsledku zaseknutého rozbrusovacieho kotúča. Veľké obrábané predmety
sa pod ťarchou vlastnej hmotnosti môžu prehnúť.
Obrábaný predmet musí byť podoprený po
oboch stranách kotúča, a to tak v blízkosti rozbrusovacieho kotúča, ako aj na hrane.
f) Buďte mimoriadne opatrný pri zare-
závaní do existujúcich stien alebo do
iných oblastí bez možnosti nahliadnutia. Vnárajúci sa rozbrusovací kotúč môže pri
zarezaní do plynového alebo vodovodného
potrubia, do elektrických vedení či iných objektov zapríčiniť spätný ráz.
61 SK
Page 62

Q
Osobitné bezpečnostné
upozornenia k brúseniu
brúsnym papierom
Nepoužívajte predimenzované brúsne
listy, ale riaďte sa údajmi výrobcu
týkajúcimi sa veľkosti brúsnych listov.
Brúsne listy, ktoré prečnievajú cez brúsny tanier,
môžu spôsobiť poranenia a taktiež viesť k zablokovaniu, roztrhnutiu brúsnych listov, alebo
k spätnému rázu.
Q
Osobitné bezpečnostné
upozornenia k lešteniu
Zabráňte uvoľneniu častí leštiaceho
krytu, najmä upevňovacích šnúr. Upevňovacie šnúry vyrovnajte, alebo ich
skráťte. Voľné otáčajúce sa upevňovacie šnúry
môžu zachytiť vaše prsty alebo sa môžu zachytiť
v obrábanom predmete.
Q
Osobitné bezpečnostné
upozornenia k prácam
s drôtenými kefami
a) Nezabúdajte, že drôtená kefa stráca
časti drôtu aj počas bežného používania.
Nepreťažujte drôty nadmerným pritláčaním. Odletujúce kúsky drôtu môžu veľmi ľahko
preniknúť cez tenký odev a / alebo cez pokožku
b) Ak sa odporúča použitie ochranného
krytu, zabráňte možnému dotýkaniu
ochranného krytu s drôtenou kefou.
Tanierové a hrncové kefy môžu v dôsledku pritláčania a odstredivých síl zväčšiť svoj priemer.
Q
Špecifické bezpečnostné pokyny pre malú vŕtačku PMGS 12
B2 a sieťový diel PMGS 12 B2-1
Pri prevádzke používajte nasledujúcu
ochrannú výbavu: ochranné okuliare
a ochranné rukavice.
Len pre použitie v interiéri!
P
OZOR! Nástroj sa po vypnutí zastavuj
dobehom! Nedotýkajte sa rýchlo sa otáčajú-
cich nástrojov.
Obrobok zabezpečte
proti pohybu. Na uchytenie obrobku použite
upínacie zariadenie / zverák. Tam je bezpeč
uchytený než vašou rukou.
V žiadnom prípade
nepodopierajte ruky vedľa alebo pred
prístrojom a opracovávanou plochou,
pretože pri skĺznutí hrozí nebezpečenstvo zranenia.
Nedotýkajte sa brúsneho nástroja v
chode.
NEBEZPEČENSTVO POŽIARU V DÔSLED-
KU ODLIETAVANIA ISKIER! Pri brúsení kovov vzniká prúd iskier. Preto bezpodmienečne
dbajte na to, aby sa žiadne osoby nezranili a
aby sa v blízkosti pracovného priestoru nenachádzali horľavé materiály.
OHROZENIE PRA-
CHOM! Škodlivý / jedovatý prach vznikajúci
počas opracovávania predstavuje ohrozenie
zdravia pre obsluhujúcu osobu alebo v blízkosti nachádzajúce sa osoby.
Noste ochrannú masku proti prachu!
JEDOVATÉ VÝPARY!
Pri opracovávaní plastov, farieb, lakov atď. zabezpečte dostatočné vetranie.
.
Materiály alebo opracovávané plochy
nenechávajte nasiaknuť kvapalinami
obsahujúcimi organické rozpúšťadlá.
Vyvarujte sa obrusovaniu farieb ob-
sahujúcich olovo alebo iných materiálov so zdraviu škodlivým účinkom.
Materiál obsahujúci azbest sa nesmie
opracovávať. Azbest je rakovinotvorný.
Neopracovávajte navlhčené materiály
ani vlhké plochy.
UPOZORNENIE! Prístroj pri prevádzke ne-
zaťažujte tak silno, až sa zastaví!
Pred odložením poč-
kajte, kým sa vypnutý prístroj úplne
nezastaví.
e
nejšie
62 SK
Page 63

Všeobecné bezpečnostné pokyny pre elektrické nástroje / Uvedenie do prevádzky
Prístroj musí byť
vždy čistý, suchý a bez oleja alebo
mazacích tukov.
Tento prístroj nie je určený na tom, aby ho pou-
žívali osoby (vrátane detí) s obmedzenými fyzickými, zmyslovými alebo duševnými schopnosťami alebo nedostatočnými skúsenosťami, a /
alebo nedostatočnými poznatkami. V takom
prípade musia byť pod dozorom osoby zodpovednej za ich bezpečnosť alebo musia dostávať
od nej pokyny, ako prístroj používať. Deti musi
byť pod dozorom, aby sa zabezpečilo, že sa s
prístrojom nehrajú.
Uvedenie do prevádzky
Používajte prístroj vždy len na určený
účel použitia a len s originálnymi dielmi
a originálnymi príslušenstvom. Používa-
nie iných ako v návode na obsluhu uvedených
dielov alebo iného príslušenstva môže pre vás
znamenať nebezpečenstvo zranenia.
Nástroj/ nasadenie/výmena
upínacej klieštiny
Upínací tŕň 13 nasadzujte tak, ako je uvedené
v elektrickom nástroji.
Pomocou skrutkovača kľúča uvoľnite 23 skrut-
ku upínacieho tŕňa
Nasaďte požadovaný nasadzovací nástroj
medzi dve podložky na skrutke.
Pomocou kľúča utiahnite 23 skrutku na upína-
com tŕni
13
13
.
.
Zapnutie a vypnutie /
nastavenie rozsahu otáčok
Zapnutie/ nastavenie rozsahu otáčok:
Pripojte vidlicu 4 na sieťový diel 10 zasunutím
do zásuvky určenej na tento účel
obr. C).
Pripojte prístroj na napájanie elektrickým prúdom
zasunutím sieťovej vidlice do sieťovej zásuvky.
Stlačte spínač ZAP / VYP 2 nadol a posuňte
potom v smere regulácie otáčok
reguláciu otáčok do polohy medzi „5“ a „20“.
Vypnutie:
Nastavte reguláciu otáčok 1 do polohy „5“.
Stlačte spínač ZAP / VYP
ho v smere kábla.
8
(pozri
1
. Nastavte
2
nadol a posuňte
ho
Stlačte aretáciu vretena 7 a držte ju stlačenú.
Otáčajte upínaciu maticu, 5 kým aretácia ne-
zapadne.
Kľúčom odskrutkujte 5 upínaciu maticu 23 zo
závitu.
Vyberte nástroj, ktorý ste v v prípade potreby
použili.
Pretlačte najprv určený nástroj cez upínaciu
5
maticu
nacej klieštiny
Stlačte aretáciu vretena 7 a držte ju stlačenú.
Nasaďte upínaciu klieštinu 18 na závitovú
vložku a potom pevne priskrutkujte upínaciu
maticu
Použite nasadzovacieho nástroja s upínacím tŕňom
UPOZORNENIE: Používajte časť kľúča so
skrutkovačom
skrutky upínacích tŕňov
a potom ho zasuňte do vhodnej upí-
18
na hriadeli nástroja.
5
kľúčom 23 na závit.
13
:
23
na uvoľnenie a upevnenie
13
.
Pokyny pre spracovanie mate-
riálu / nástroj / rozsah otáčok
Frézovacie bity používajte 20 na obrábanie
ocele a železa pri najvyšších otáčkach.
Rozsah otáčok pre obrábanie zinku, zliatin
zinku, hliníka, medi a olova zistite pokusne na
skúšobných vzorkách.
Plasty a materiály s nízkou teplotou topenia
obrábajte pri nízkom rozsahu otáčok.
Drevo obrábajte pri vysokých otáčkach.
Čistiace, leštiace a uhladzovacie práce vyko-
návajte v strednom rozsahu otáčok.
Nasledujúce údaje sú nezáväzné odporúčania.
Aj sami si prakticky odskúšajte, ktorý nástroj a ktoré
nastavenia sú najoptimálnejšie pre opracovávaný
materiál.
63 SK
Page 64

Nastavenie vhodných otáčok:
Číslo na regulácii otáčok
5
Obrábaný materiál
1
plasty a materiály s nízkou
teplotou topenia
8
12
16
20
kamenina, keramika
mäkké drevo, kov
tvrdé drevo
oceľ
Príklady použitia / výber vhodného
nástroja:
Funkcia Príslušen-
Použitie
stvo
vŕtanie
vrták HSS
opracovávanie
12
dreva
frézovanie frézovacie
20
bity
rozmanité práce;
napr. rozširovanie
otvorov, dlabanie,
tvarovanie, drážkovanie, vyrezávanie
gravírovanie gravírovacie
21
bity
zhotovovanie označení, majstrovanie
(pozri obr. D)
leštenie,
zbavovanie
hrdze
POZOR!
S nástrojom
vyvíjajte na
obrobok len
slabý tlak.
čistenie plastové kefy
drôtená kefa
16
leštiacekotú-
14
če
19
zbavovanie hrdze
opracovávanie
rôznych kovov a
plastov, hlavne drahých kovov ako
zlato a striebro
(pozri obr. E)
napr. čistenie zle prístupných plastových
schránok alebo okolia dverného zámku
brúsenie brúsne kotú-
15
če
, brús-
ne bity
brúsenie kameniny,
dreva, jemné práce
22
na tvrdých materiáloch ako keramika
alebo legovaná oceľ
(pozri obr. F, G)
rezanie reznékotúče
17
opracovávanie
plastov a dreva
kovu,
Tipy a triky
Keď vyvíjate príliš vysoký tlak, môže sa upnutý obrobok zlomiť a / alebo nástroj poškodiť. Optimálne
výsledky práce môžete dosiahnuť použitím ustáleného rozsahu otáčok a slabého tlaku na obrobok.
Údržba a čistenie
Prístroj nevyžaduje údržbu.
Z prístroja odstráňte nečistoty. Použite na to
suchú handru.
Servis
Svoje nástroje si
nechajte opraviť v elektrických opravovňach alebo u kvalifikovaných odborníkov len s použitím originálnych
náhradných dielov. Tým sa zabezpečí
zachovanie bezpečnosti prístroja.
Výmenu vidlice alebo
sieťového vodiča si nechajte vykonať
vždy len u výrobcu alebo v jeho popredajnom servise. Tým sa zabezpečí
zachovanie bezpečnosti prístroja.
Q
Záruśná lehota
Na tento prístroj máte trojročnú záruku od
dátumu nákupu. Prístroj bol starostlivo
vyrobený a pred expedíciou dôkladne
vyskúšaný. Uschovajte si, prosím, účtenku
ako dôkaz o nákupe. V prípade uplatňovania záruky sa spojte s opravovňou
telefonicky. Len tak sa dá zabezpečiť
bezplatné zaslanie tovaru.
Záruka platí len na chyby materiálu a výroby, nie
na poškodenia spôsobené prepravou, opotrebením
ani na poškodenia krehkých častí, ako sú spínače
alebo akumulátory. Výrobok je určený výlučne na
súkromné používanie a nie na komerčné účely.
64 SK
Page 65

Záruśná lehota / Likvidácia / Vyhlásenie o zhode / Vyhlásenie výrobcu
Záruka prestáva platiť pri zaobchádzaní nezodpovedajúcom účelu, pri neprimeranom zaobchádzaní,
pri používaní násilia a pri zásahoch, ktoré neurobil
nami autorizovaný servis. Práva vyplývajúce zo zákona nie sú touto zárukou obmedzené.
Záručná doba sa nepredlžuje o dobu trvania záručných opráv. To platí aj na vymenené alebo opravené
diely. Prípadné poškodenia a nedostatky zistené už
pri nákupe musíte ohlásiť ihneď po vybalení, najneskoršie však do dvoch dní od dátumu zakúpenia. V
prípade opráv spadajúcich do obdobia po uplynutí záručnej doby ste povinní uhradiť vzniknuté náklady.
SK
Servis Slovensko
Tel. 0850 232001
e-mail: kompernass@lidl.sk
IAN 89959
Likvidácia
Obal pozostáva z materiálov neohrozujúcich životné prostredie, ktoré sa môžu
likvidovať v miestnych zariadeniach.
Elektrické nástroje neodhadzujte
do domového odpadu!
Podľa európskej smernice 2002 / 96 / EC pre staré
elektrické a elektronické prístroje a jej uplatnení v
národnom práve sa musia použité elektrické nástroje
zberať oddelene a odpad z nich sa musí zhodnocovať v súlade s predpismi pre ochranu životného
prostredia.
Vyhlásenie o zhode /
Vyhlásenie výrobcu
My, KOMPERNASS GMBH, osoba zodpovedná
za dokumenty: pán Semi Uguzlu, BURGSTR. 21,
44867 BOCHUM, GERMANY, týmto vyhlasujeme,
že tento výrobok sa zhoduje s nasledujúcimi normami, normatívnymi dokumentmi a smernicami ES:
Smernica o strojoch
(2006 / 42 / EC)
Smernica ES onízkonapäťových strojoch
(2006 / 95 / EC)
Elektromagnetická znášanlivosť
(2004 / 108 / EC)
RoHS Smernica (2011 / 65 / EU)
RoHS Smernica
(2011 / 65 / EU)
Aplikované harmonizované normy
EN 60745-1/A11:2010, EN 60745-2-1:2010
EN 60745-2-3:2011,
EN 55014-1/A2:2011, EN 55014-2/A2:2008
EN 61000-3-2/A2:2009, EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61558-1/A1:2009, EN 61558-2-6:2009
Typ / Názov prís troja:
modelárska a gravírovacia súprava PMGS 12 B2
Date of manufacture (DOM): 04–2013
Sériové číslo: IAN 89959
Bochum, 30.04.2013
O možnostiach likvidácie doslúžených elektrických
nástrojov sa informujte na svojom obecnom alebo
mestskom úrade.
Semi Uguzlu
- Manažér kvality -
Technické zmeny v súvislosti s ďalším vývojom sú
vyhradené.
65 SK
Page 66

66
Page 67

Inhaltsverzeichnis
Einleitung
Bestimmungsgemäßer Gebrauch ....................................................................................................... Seite 68
Ausstattung .......................................................................................................................................... Seite 68
Lieferumfang ........................................................................................................................................ Seite 68
Technische Daten ................................................................................................................................ Seite 68
Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge
1. Arbeitsplatzsicherheit .....................................................................................................................Seite 69
2. Elektrische Sicherheit ...................................................................................................................... Seite 69
3. Sicherheit von Personen ................................................................................................................. Seite 70
4. Verwendung und Behandlung des Elektrowerkzeugs .................................................................. Seite 70
5. Service ............................................................................................................................................. Seite 71
Sicherheitshinweise für alle Anwendungen ....................................................................................... Seite 71
Rückschlag und entsprechende Sicherheitshinweise ........................................................................Seite 72
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise zum Schleifen und Trennschleifen .................................................. Seite 73
Weitere besondere Sicherheitshinweise zum Trennschleifen ........................................................... Seite 73
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise zum Sandpapierschleifen ............................................................... Seite 74
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise zum Polieren .................................................................................... Seite 74
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise zum Arbeiten mit Drahtbürsten ....................................................... Seite 74
Gerätespezifische Sicherheitshinweise für Kleinbohrmaschine PMGS 12 B2
und Netzteil-PMGS 12 B2-1 .............................................................................................................. Seite 74
Inbetriebnahme
Werkzeug / Spannzange einsetzen / wechseln ................................................................................ Seite 75
Ein- und ausschalten / Drehzahlbereich einstellen ............................................................................Seite 76
Hinweise zu Material- bearbeitung / Werkzeug / Drehzahlbereich ................................................ Seite 76
Tipps und Tricks ................................................................................................................................... Seite 77
Wartung und Reinigung ..................................................................................................... Seite 77
Service ............................................................................................................................................... Seite 77
Garantie ........................................................................................................................................... Seite 77
Entsorgung ..................................................................................................................................... Seite 78
Konformitätserklärung / Hersteller ..........................................................................Seite 78
67 DE/AT/CH
Page 68

Einleitung
Modellbau- und Gravierset
PMGS 12 B2
Einleitung
Wir beglückwünschen Sie zum Kauf Ihres neuen
Gerätes. Sie haben sich damit für ein hochwertiges
Produkt entschieden. Die Bedienungsanleitung ist
Teil dieses Produkts. Sie enthält wichtige Hinweise
für Sicherheit, Gebrauch und Entsorgung. Machen
Sie sich vor der Benutzung des Produkts mit allen
Bedien- und Sicherheitshinweisen vertraut. Benutzen
Sie das Produkt nur wie beschrieben und für die
angegebenen Einsatzbereiche. Händigen Sie alle
Unterlagen bei Weitergabe des Produkts an Dritte
mit aus.
Bestimmungsgemäßer Gebrauch
Die Kleinbohrmaschine ist zum Bohren, Fräsen,
Gravieren, Polieren, Säubern, Schleifen, Trennen von
Holz, Metall, Kunststoff, Keramik oder Gestein in
trockenen Räumen zu verwenden. Jede andere Verwendung oder Veränderung des Gerätes gilt als nicht
bestimmungsgemäß und birgt erhebliche Unfallgefahren. Für aus bestimmungswidriger Verwendung
entstandene Schäden übernimmt der Hersteller keine
Haftung. Nicht für gewerblichen Einsatz bestimmt.
Ausstattung
Kleinbohrmaschine:
1
Drehzahlregulierung
2
EIN- / AUS-Schalter
3
Metallbügel
4
Stecker für Netzteil
5
Spannmutter
6
Überwurfmutter
7
Spindelarretierung
Zubehör (siehe Abb. B):
12
6 HSS-Bohrer
13
2 Spanndornen zur Werkzeugaufnahme
14
3 Polierscheiben
15
4 Schleifscheiben
16
1 Metallbürste
17
16 Trennscheiben
18
5 Spannzangen
19
2 Kunststoffbürsten
20
3 Fräsbits
21
2 Gravierbits
22
5 Schleifbits
23
1 Kombischlüssel
Lieferumfang
1 Kleinbohrmaschine
1 Netzteil
1 Kunststoffkoffer
1 Zubehör-Set (50 Teile)
1 Bedienungsanleitung
Technische Daten
Kleinbohrmaschine PMGS 12 B2:
Nennspannung: 12 V
Nennaufnahmeleistung: 22 W
Leerlaufdrehzahl: n
5000–20000 min
0
Bohrer: max. ø 3,2 mm
Scheiben: max. ø 25 mm
geprüft nach: EN60745-1; EN60745-2-1
EN60745-2-3
Geräusch und Vibrationsinformationen:
Messwert für Geräusch ermittelt entsprechend
EN 60745. Der A-bewertete Geräuschpegel des
Elektrowerkzeugs beträgt typischerweise:
Schalldruckpegel: 54,70 dB(A)
Schallleistungspegel: 65,70 dB(A)
Unsicherheit K: 3 dB
-1
Netzteil (siehe Abb. A):
8
Einsteckvorrichtung für Stecker
9
Ablage
10
Netzteil
11
Netzkabel (mit Netzstecker)
68 DE/AT/CH
Bewertete Beschleunigung, typischerweise:
4
Hand- / Armvibration: 1,868 m / s
Unsicherheit K = 1,5 m / s
2
2
Page 69

Einleitung / Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge
Der in diesen Anweisungen
angegebene Schwingungspegel ist entsprechend
einem in EN 60745 genormten Messverfahren gemessen worden und kann für den Gerätevergleich
verwendet werden. Der angegebene Schwingungsemissionswert kann auch zu einer einleitenden Einschätzung der Aussetzung verwendet werden.
Der Schwingungspegel wird sich entsprechend dem
Einsatz des Elektrowerkzeugs verändern und kann in
manchen Fällen über dem in diesen Anweisungen
angegebenen Wert liegen. Die Schwingungsbelastung könnte unterschätzt werden, wenn das Elektrowerkzeug regelmäßig in solcher Weise verwendet wird.
Hinweis: Für eine genaue Abschätzung der
Schwingungsbelastung während eines bestimmten
Arbeitszeitraumes sollten auch die Zeiten berücksichtigt werden, in denen das Gerät abgeschaltet
ist oder zwar läuft, aber nicht tatsächlich im Einsatz
ist. Dies kann die Schwingungsbelastung über den
gesamten Arbeitszeitraum deutlich reduzieren.
Netzteil PMGS 12 B2-1:
EINGANG / Input:
Nennspannung: 230 V∼ 50 Hz
AUSGANG / Output:
Nennspannung: 12 V
Nennstrom: 1A
Schutzklasse: II /
geprüft nach: EN61558
Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise
für Elektrowerkzeuge
Lesen Sie alle
Sicherheitshinweise und Anweisungen. Versäumnisse bei der Einhaltun
der Sicherheitshinweise und Anweisungen können
elektrischen Schlag, Brand und / oder schwere Verletzungen verursachen.
Bewahren Sie alle Sicherheitshinweise
und Anweisungen für die Zukunft auf!
Der in den Sicherheitshinweisen verwendete Begriff
„Elektrowerkzeug“ bezieht sich auf netzbetriebene
Elektrowerk
triebene Elektrowerkzeuge (ohne Netzkabel).
zeuge (mit Netzkabel) und auf akkube-
1. Arbeitsplatzsicherheit
a) Halten Sie Ihren Arbeitsbereich sauber
und gut beleuchtet. Unordnung und unbeleuch-
tete Arbeitsbereiche können zu Unfällen führen.
b) Arbeiten Sie mit dem Elektrowerkzeug
nicht in explosionsgefährdeter Umgebung, in der sich brennbare Flüssigkeiten, Gase oder Stäube befinden.
Elektrowerkzeuge erzeugen Funken, die den
Staub oder die Dämpfe entzünden können.
c) Halten Sie Kinder und andere Per-
sonen während der Benutzung des
Elektrowerkzeugs fern. Bei Ablenkung
können Sie die Kontrolle über das Gerät verlieren.
2. Elektrische Sicherheit
a) Der Anschlussstecker des Elektrowerk-
zeuges muss in die Steckdose passen.
Der Stecker darf in keiner Weise verändert werden. Verwenden Sie keine
Adapterstecker gemeinsam mit
schutzgeerdeten Elektrowerkzeugen.
Unveränderte Stecker und passende Steckdosen
verringern das Risiko eines elektrischen Schlages.
b) Vermeiden Sie Körperkontakt mit ge-
erdeten Oberflächen, wie von Rohren,
Heizungen, Herden und Kühlschränken.
Es besteht ein erhöhtes Risiko durch elektrischen
Schlag, wenn Ihr Körper geerdet ist.
c) Halten Sie Elektrowerkzeuge von Re-
g
gen oder Nässe fern. Das Eindringen von
Wasser in ein Elektrogerät erhöht das Risiko
eines elektrischen Schlages.
d) Zweckentfremden Sie das Kabel nicht,
um das Elektrowerkzeug zu tragen,
aufzu-hängen oder um den Stecker
aus der Steckdose zu ziehen. Halten
69 DE/AT/CH
Page 70

Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge
Sie das Kabel fern von Hitze, Öl, scharfen Kanten oder sich bewegenden
Geräteteilen. Beschädigte oder verwickelte
Kabel erhöhen das Risiko eines elektrischen
Schlages.
e) Wenn Sie mit einem Elektrowerkzeug
im Freien arbeiten, verwenden Sie nur
Verlängerungskabel, die auch für den
Außenbereich zugelassen sind. Die
Anwendung eines für den Außenbereich
geeigneten Verlängerungskabels verringert
das Risiko eines elektrischen Schlages.
f) Wenn der Betrieb des Elektrowerk-
zeuges in feuchter Umgebung nicht
vermeidbar ist, verwenden Sie einen
Fehlerstromschutzschalter. Der Einsatz
eines Fehlerstromschutzschalters vermindert
das Risiko eines elektrischen Schlages.
3. Sicherheit von Personen
a)
Seien Sie stets aufmerksam, achten Sie
darauf, was Sie tun und gehen Sie mit
Vernunft an die Arbeit mit einem Elek
trowerkzeug. Benutzen Sie kein Elektrowerkzeug, wenn Sie müde sind oder
unter dem Einfluss von Drogen, Alkohol oder Medikamenten stehen. Ein
Moment der Unachtsamkeit beim Gebrauch
des Elektrowerkzeuges kann zu ernsthaften
Verletzungen führen.
b)
Schutzausrüstung wie Staubmaske, rutschfeste
Sicherheitsschuhe, Schutzhelm oder Gehörschut
je nach Art und Einsatz des Elektrowerkzeuges,
verringert das Risiko von Verletzungen.
c) Vermeiden Sie eine unbeabsichtigte
Inbetriebnahme. Vergewissern Sie sich,
dass das Elektrowerkzeug ausgeschaltet ist, bevor Sie es an die Stromversorgung anschließen, es aufnehmen
oder tragen. Wenn Sie beim Tragen des
Elektrowerkzeuges den Finger am Schalter ha
oder das Gerät bereits eingeschaltet an die
Tragen Sie persönliche Schutzausrüstung und immer eine
Schutzbrille. Das Tragen persönlicher
-
ben
Stromversorgung anschließen, kann dies zu
Unfällen führen.
d) Entfernen Sie Einstellwerkzeuge oder
Schraubenschlüssel, bevor Sie das
Elektrowerkzeug einschalten. Ein Werk-
zeug oder Schlüssel, der sich in einem drehenden
Geräteteil befindet, kann zu Verletzungen führen.
e) Vermeiden Sie eine abnormale Körper-
haltung. Sorgen Sie für einen sicheren
Stand und halten Sie jederzeit das
Gleichgewicht. Dadurch können Sie das
Elektrowerkzeug in unerwarteten Situationen
besser kontrollieren.
f) Tragen Sie geeignete Kleidung. Tragen
Sie keine weite Kleidung oder Schmuck.
Halten Sie Haare, Kleidung und Handschuhe fern von sich bewegenden
Teilen. Lockere Kleidung, Schmuck oder lange
Haare können von sich bewegenden Teilen
erfasst werden.
g) Wenn Staubabsaug- und -auffangein-
richtungen montiert werden können,
vergewissern Sie sich, dass diese
angeschlossen sind und richtig verwendet werden. Die Verwendung einer
Staubabsaugung kann Gefährdungen durch
Staub verringern.
4. Verwendung und Behandlung
des Elektrowerkzeugs
a) Überlasten Sie das Gerät nicht. Ver-
wenden Sie für Ihre Arbeit das dafür
bestimmte Elektrowerkzeug. Mit dem
passenden Elektrowerkzeug arbeiten Sie besser
z,
und sicherer im angegebenen Leistungsbereich.
b) Benutzen Sie kein Elektrowerkzeug,
dessen Schalter defekt ist. Ein Elektrowerk-
zeug, das sich nicht mehr ein- oder ausschalten
lässt, ist gefährlich und muss repariert werden.
c) Ziehen Sie den Stecker aus der Steck-
dose, bevor Sie Geräteeinstellungen
vornehmen, Zubehörteile wechseln
oder das Gerät weglegen. Diese Vorsichts-
maßnahme verhindert den unbeabsichtigten
Start des Elektrowerkzeuges.
70 DE/AT/CH
Page 71

Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge
d) Bewahren Sie unbenutzte Elektrowerk-
zeuge außerhalb der Reichweite von
Kindern auf. Lassen Sie Personen das
Gerät nicht benutzen, die mit diesem
nicht vertraut sind oder diese Anweisungen nicht gelesen haben. Elektrowerk-
zeuge sind gefährlich, wenn sie von unerfahrenen
Personen benutzt werden.
e) Pflegen Sie Elektrowerkzeuge mit
Sorgfalt. Kontrollieren Sie, ob bewegliche Teile einwandfrei funktionieren
und nicht klemmen, ob Teile gebrochen
oder so beschädigt sind, dass die Funktion des Elektrowerkzeuges beeinträchtigt ist. Lassen Sie beschädigte Teile vor
dem Einsatz des Gerätes reparieren.
Viele Unfälle haben ihre Ursache in schlecht
gewarteten Elektrowerkzeugen.
f) Halten Sie Schneidwerkzeuge scharf
und sauber. Sorgfältig gepflegte Schneid-
werkzeuge mit scharfen Schneidkanten verklemmen sich weniger und sind leichter zu führen.
g) Verwenden Sie Elektrowerkzeug,
Zubehör, Einsatzwerkzeuge usw.
entsprechend diesen Anweisungen.
Berücksichtigen Sie dabei die Arbeitsbedingungen und die auszuführende
Tätigkeit. Der Gebrauch von Elektrowerkzeu-
gen für andere als die vorgesehenen Anwendungen kann zu gefährlichen Situationen führen.
5. Service
a) Lassen Sie Ihr Elektrowerkzeug nur von
qualifiziertem Fachpersonal und nur
mit Original-Ersatzteilen reparieren.
Damit wird sichergestellt, dass die Sicherheit
des Elektrowerkzeugs erhalten bleibt.
Sicherheitshinweise für alle
Anwendungen
Gemeinsame Sicherheitshinweise zum
Schleifen, Sandpapierschleifen, Arbeiten
mit Drahtbürsten, Polieren und Trennschleifen:
a) Dieses Elektrowerkzeug ist zu verwen-
den als Schleifer, Sandpapierschleifer,
Drahtbürste, Polierer und Trennschleifmaschine. Beachten Sie alle Sicherheitshinweise, Anweisungen, Darstellungen
und Daten, die Sie mit dem Gerät erhalten. Wenn Sie die folgenden Anweisungen
nicht beachten, kann es zu elektrischem Schlag,
Feuer und / oder schweren Verletzungen kommen.
b) Normativer Satz / Hinweis für dieses Werkzeug
nicht anwendbar.
c) Verwenden Sie kein Zubehör, das vom
Hersteller nicht speziell für dieses
Elektrowerkzeug vorgesehen und
empfohlen wurde. Nur weil Sie das Zubehör
an Ihrem Elektrowerkzeug befestigen können,
garantiert das keine sichere Verwendung.
d) Die zulässige Drehzahl des Einsatz-
werkzeugs muss mindestens so hoch
sein wie die auf dem Elektrowerkzeug
angegebene Höchstdrehzahl. Zubehör,
das sich schneller als zulässig dreht, kann zerbrechen oder umherfliegen.
e) Außendurchmesser und Dicke des Ein-
satzwerkzeugs müssen den Maßangaben Ihres Elektrowerkzeugs entsprechen
Falsch bemessene Einsatzwerkzeuge können
nicht ausreichend abgeschirmt oder kontrolliert
werden.
f) Schleifscheiben, Flansche, Schleifteller
oder anderes Zubehör müssen genau
auf die Schleifspindel Ihres Elektrowerkzeugs passen. Einsatzwerkzeuge, die nicht
genau auf die Schleifspindel passen, drehen
sich ungleichmäßig, vibrieren sehr stark und
können zum Verlust der Kontrolle führen.
g) Verwenden Sie keine beschädigten
Einsatzwerkzeuge. Kontrollieren Sie
vor jeder Verwendung Einsatzwerkzeuge
wie Schleifscheiben auf Absplitte-
rungen und Risse, Schleifteller auf R
isse,
.
71 DE/AT/CH
Page 72

Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge
Verschleiß oder starke Abnutzung,
Drahtbürsten auf lose oder gebrochene
Drähte. Wenn das Elektrowerkzeug
oder das Einsatzwerkzeug herunterfällt, überprüfen Sie, ob es beschädigt
ist, oder verwenden Sie ein unbeschädigtes Einsatzwerkzeug. Wenn Sie
das Einsatzwerkzeug kontrolliert und
eingesetzt haben, halten Sie und in
der Nähe befindliche Personen sich
außerhalb der Ebene des rotierenden
Einsatzwerkzeuges auf und lassen Sie
das Gerät eine Minute lang mit Höchstdrehzahl laufen. Beschädigte Einsatzwerk-
zeuge brechen meist in der Testzeit.
h)
schutz, Augenschutz oder Schutzbrille.
Soweit angemessen, tragen Sie Staubmaske,
o
der Spezialschürze, die kleine Schleifund Materialpartikel von Ihnen fernhält. Die Augen sollen vor herumfliegenden
Fremdkörpern geschützt werden, die bei verschiedenen Anwendungen entstehen, Stauboder Atemschutzmasken müssen den bei der
Anwendung entstehenden Staub filtern. Wenn
Sie länger lautem Lärm ausgesetzt sind, können
Sie einen Hörverlust erleiden.
i) Achten Sie bei anderen Personen auf
sicheren Abstand zu Ihrem Arbeitsbereich. Jeder, der den Arbeitsbereich
betritt, muss persönliche Schutzausrüstung tragen. Bruchstücke des Werkstücks
oder gebrochene Einsatzwerkzeuge können
wegfliegen und Verletzungen auch außerhalb
des direkten Arbeitsbereichs verursachen.
j) Halten Sie das Gerät nur an den iso-
lierten Griffflächen, wenn Sie Arbeiten
ausführen, bei denen das Einsatzwerkzeug verborgene Stromleitungen oder
das Netzkabel treffen kann. Der Kontakt
mit einer spannungsführenden Leitung kann
metallene Geräteteile unter Spannung setzen
und zu einem elektrischen Schlag führen.
k) Halten Sie das Netzkabel von sich
drehenden Einsatzwerkzeugen fern.
72 DE/AT/CH
Tragen Sie persönliche Schutzausrüstung. Verwenden Sie je
nach Anwendung Vollgesichts-
Gehörschutz, Schutzhandschuhe
auch
Wenn Sie die Kontrolle über das Gerät verlieren,
kann das Netzkabel durchtrennt oder erfasst
werden und Ihre Hand oder Arm in das sich
drehende Einsatzwerkzeug geraten.
l) Legen Sie das Elektrowerkzeug niemals
ab, bevor das Einsatzwerkzeug völlig
zum Stillstand gekommen ist. Das sich
drehende Einsatzwerkzeug kann in Kontakt mit
der Ablagefläche geraten, wodurch Sie die Kontrolle über das Elektrowerkzeug verlieren können.
m) Lassen Sie das Elektrowerkzeug nicht
laufen, während Sie es tragen. Ihre
Kleidung kann durch zufälligen Kontakt mit dem
sich drehenden Einsatzwerkzeug erfasst werden
und das Einsatzwerkzeug sich in Ihren Körper
bohren.
n) Reinigen Sie regelmäßig die Lüftungs-
schlitze Ihres Elektrowerkzeugs. Das
Motorgebläse zieht Staub in das Gehäuse,
und eine starke Ansammlung von Metallstaub
kann elektrische Gefahren verursachen.
o) Verwenden Sie das Elektrowerkzeug
nicht in der Nähe brennbarer Materialien. Funken können diese Materialen entzünden.
p)
Verwenden Sie keine Einsatzwerkzeuge
die flüssige Kühlmittel erfordern. Die
Verwendung von Wasser oder anderen flüssigen Kühlmitteln kann zu einem elektrischen
Schlag führen.
Rückschlag und entsprechende
Sicherheitshinweise
Rückschlag ist die plötzliche Reaktion infolge eines
hakenden oder blockierten drehenden Einsatzwerkzeuges, wie Schleifscheibe, Schleifteller, Drahtbürste
usw. Verhaken oder Blockieren führen zu einem
abrupten Stopp des rotierenden Einsatzwerkzeugs.
Dadurch wird ein unkontrolliertes Elektrowerkzeug
gegen die Drehrichtung des Einsatzwerkzeugs an
die Blockierstelle beschleunigt.
Wenn z.B. eine Schleifscheibe im Werkstück hakt
oder blockiert, kann sich die Kante der Schleifscheibe,
die in das Werkstück eintaucht, verfangen und dadurch
die Schleifscheibe ausbrechen oder einen Rückschlag
verursachen. Die Schleifscheibe bewegt sich dann
,
Page 73

Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge
auf die Bedienperson zu oder von ihr weg, je nach
Drehrichtung der Scheibe an der Blockierstelle. Hierbei können Schleifscheiben auch brechen.
Ein Rückschlag ist die Folge eines falschen oder
fehlerhaften Gebrauchs des Elektrowerkzeugs. Er
kann durch geeignete Vorsichtsmaßnahmen, wie
nachfolgend beschrieben, verhindert werden.
a) Halten Sie das Elektrowerkzeug gut
fest und bringen Sie Ihren Körper und
Ihre Arme in eine Position, in der Sie
die Rückschlagkräfte abfangen kön
Verwenden Sie immer den Zusatzgriff,
falls vorhanden, um die größtmögliche
Kontrolle über Rückschlagkräfte oder
Reaktionsmomente beim Hochlauf zu
haben. Die Bedienperson kann durch geeig-
nete Vorsichtsmaßnahmen die Rückschlag- und
Reaktionskräfte beherrschen.
b) Bringen Sie Ihre Hand nie in die Nähe
sich drehender Einsatzwerkzeuge. Das
Einsatzwerkzeug kann sich beim Rückschlag
über Ihre Hand bewegen.
c) Meiden Sie mit Ihrem Körper den Be-
reich, in den das Elektrowerkzeug bei
einem Rückschlag bewegt wird. Der
Rückschlag treibt das Elektrowerkzeug in die
Richtung entgegengesetzt zur Bewegung der
Schleifscheibe an der Blockierstelle.
d) Arbeiten Sie besonders vorsichtig im
Bereich von Ecken, scharfen Kanten
usw. Verhindern Sie, dass Einsatzwerkzeuge vom Werkstück zurückprallen
und verklemmen. Das rotierende Einsatz-
werkzeug neigt bei Ecken, scharfen Kanten oder
wenn es abprallt dazu, sich zu verklemmen. Dies
verursacht einen Kontrollverlust oder Rückschlag.
e) Verwenden Sie kein Ketten- oder ge-
zähntes Sägeblatt. Solche Einsatzwerkzeuge
verursachen häufig einen Rückschlag oder den
Verlust der Kontrolle über das Elektrowerkzeug.
nen.
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise
zum Schleifen und Trennschleifen
a) Verwenden Sie ausschließlich die für
Ihr Elektrowerkzeug zugelassenen
Schleifkörper und die für diese Schleifkörper vorgesehene Schutzhaube.
Schleifkörper, die nicht für das Elektrowerkzeug
vorgesehen sind, können nicht ausreichend
abgeschirmt werden und sind unsicher.
b) Die Schutzhaube muss sicher am
Elektrowerkzeug angebracht und so
eingestellt sein, dass ein Höchstmaß
an Sicherheit erreicht wird, d.h. der
kleinstmögliche Teil des Schleifkörpers
zeigt offen zur Bedienperson. Die Schutz-
haube soll die Bedienperson vor Bruchstücken
und zufälligem Kontakt mit dem Schleifkörper
schützen.
c) Schleifkörper dürfen nur für die emp-
fohlenen Einsatzmöglichkeiten verwendet
werden. Zum Beispiel: Schleifen Sie
mit der Seitenfläche einer Trennscheibe.
Trennscheiben sind zum Materialabtrag mit der
Kante der Scheibe bestimmt. Seitliche Krafteinwirkung auf diese Schleifkörper kann sie zerbrechen.
d) Verwenden Sie immer unbeschädigte
Spannflansche in der richtigen Größe
und Form für die von Ihnen gewählte
Schleifscheibe. Geeignete Flansche stützen
die Schleifscheibe und verringern so die Gefahr eines Schleifscheibenbruchs. Flansche für
Trennscheiben können sich von den Flanschen
für andere Schleifscheiben unterscheiden.
e) Verwenden Sie keine abgenutzten
Schleifscheiben von größeren Elektrowerkzeugen. Schleifscheiben für größere
Elektrowerkzeuge sind nicht für die höheren
Drehzahlen von kleineren Elektrowerkzeugen
ausgelegt und können brechen.
nie
Weitere besondere Sicherheits-
hinweise zum Trennschleifen
a) Vermeiden Sie ein Blockieren der
Trennscheibe oder zu hohen Anpressdruck. Führen Sie keine übermäßig
73 DE/AT/CH
Page 74

Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge / Inbetriebnahme
tiefen Schnitte aus. Eine Überlastung der
Trennscheibe erhöht deren Beanspruchung und
die Anfälligkeit zum Verkanten oder Blockieren
und damit die Möglichkeit eines Rückschlags
oder Schleifkörperbruchs.
b) Meiden Sie den Bereich vor und hinter
der rotierenden Trennscheibe. Wenn
Sie die Trennscheibe im Werkstück von sich
wegbewegen, kann im Falle eines Rückschlags
das Elektrowerkzeug mit der sich drehenden
Scheibe direkt auf Sie zugeschleudert werden.
c) Falls die Trennscheibe verklemmt oder
Sie die Arbeit unterbrechen, schalten
Sie das Gerät aus und halten Sie es
ruhig, bis die Scheibe zum Stillstand
gekommen ist. Versuchen Sie nie, die
noch laufende Trennscheibe aus dem
Schnitt zu ziehen, sonst kann ein Rückschlag erfolgen. Ermitteln und beheben Sie
die Ursache für das Verklemmen.
d) Schalten Sie das Elektrowerkzeug nicht
wieder ein, solange es sich im Werk
befindet. Lassen Sie die Trennscheibe
erst ihre volle Drehzahl erreichen, bevor Sie den Schnitt vorsichtig fortset
Andernfalls kann die Scheibe verhaken, aus
dem Werkstück springen oder einen Rückschlag
verursachen.
e) Stützen Sie Platten oder Werkstücke
ab, um das Risiko eines Rückschlags
durch eine eingeklemmte Trennscheibe
zu vermindern. Große Werkstücke können
sich unter ihrem eigenen Gewicht durchbiegen.
Das Werkstück muss auf beiden Seiten der Scheibe abgestützt werden, und zwar sowohl in der
Nähe der Trennscheibe als auch an der Kante.
f) Seien Sie besonders vorsichtig bei
„Taschenschnitten“ in bestehende
Wände oder andere nicht einsehbare
Bereiche. Die eintauchende Trennscheibe
kann beim Schneiden in Gas- oder Wasserleitungen, elektrische Leitungen oder andere
Objekte einen Rückschlag verursachen.
stück
zen.
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise
zum Sandpapierschleifen
Benutzen Sie keine überdimensionier
Schleifblätter, sondern befolgen Sie die
Herstellerangaben zur Schleifblattgröß
Schleifblätter, die über den Schleifteller hinausragen, können Verletzungen verursachen sowie
zum Blockieren, Zerreißen der Schleifblätter
oder zum Rückschlag führen.
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise
ten
e.
zum Polieren
Lassen Sie keine losen Teile der Polier-
haube, insbesondere Befestigungsschnüre, zu. Verstauen oder kürzen
Sie die Befestigungsschnüre. Lose, sich
mitdrehende Befestigungsschnüre können Ihre
Finger erfassen oder sich im Werkstück verfangen.
Besondere Sicherheitshinweise
zum Arbeiten mit Drahtbürsten
a) Beachten Sie, dass die Drahtbürste auch
während des üblichen Gebrauchs Draht
stücke verliert. Überlasten Sie Drähte
nicht durch zu hohen Anpressdruck.
Wegfliegende Drahtstücke können sehr leicht
durch
dünne Kleidung und / oder Haut dringen.
b) Wird eine Schutzhaube empfohlen,
verhindern Sie, dass sich Schutzhaube
und Drahtbürste berühren können. Tel
und Topfbürsten können durch Anpressdruck und
Zentrifugalkräfte ihren Durchmesser vergrößern.
ler-
Gerätespezifische Sicherheits-
hinweise für Kleinbohrmaschine
PMGS 12 B2 und NetzteilPMGS 12 B2-1
-
74 DE/AT/CH
Verwenden Sie beim Betrieb folgende
Schutzausrüstung: Schutzbrille und
Schutzhandschuhe.
Page 75

Allgemeine Sicherheitshinweise für Elektrowerkzeuge / Inbetriebnahme
VORSICHT! Das Werkzeug läuft nach
dem Ausschalten nach! Vermeiden Sie je
Kontakt zu den schnell drehenden Werkzeugen.
Sichern Sie das
stück. Benutzen Sie Spannvorrichtungen /
Schraubstock, um das Werkstück festzuhalten.
Es ist damit sicherer gehalten, als mit Ihrer Hand.
Stützen Sie auf keinen
Fall die Hände neben oder vor dem
Gerät und der zu bearbeitenden Fläche
ab, da bei einem Abrutschen Verletzungsgefahr besteht.
Vermeiden Sie den Kontakt mit dem
laufenden Schleifwerkzeug.
BRANDGEFAHR DURCH FUNKENFLUG!
Wenn Sie Metalle schleifen, entsteht Funkenflug.
Achten Sie deshalb unbedingt darauf, dass keine
Personen gefährdet werden und sich keine
brennbaren Materialien in der Nähe des
Arbeitsbereiches befinden.
DURCH STAUB! Die durch die Bearbeitung
entstehenden schädlichen / giftigen Stäube stelle
eine Gesundheitsgefährdung für die Bedienperson oder in der Nähe befindliche Personen dar.
Tragen Sie eine Staubschutzmaske!
GIFTIGE DÄMPFE!
Sorgen Sie bei der Bearbeitung von Kunststoffen,
Farben, Lacken, etc. für ausreichende Belüftung.
Tränken Sie Materialien oder zu
bearbeitende Flächen nicht mit
lösungsmittelhaltigen Flüssigkeiten.
Vermeiden Sie das Schleifen von
bleihaltigen Farben oder anderen
gesundheitsschädlichen Materialien.
Asbesthaltiges Material darf nicht bear-
beitet werden. Asbest gilt als krebserregend.
Bearbeiten Sie keine angefeuchteten
Materialien oder feuchte Flächen.
HINWEIS! Belasten Sie das Gerät im Betrieb
nicht derart stark, dass Stillstand eintritt!
Lassen Sie das ausge-
schaltete Gerät zum Stillstand komm
bevor Sie es ablegen.
Nur zur Verwendung in Innenräumen!
den
Werk-
GEFÄHRDUNG
en,
Das Gerät muss stets
sauber, trocken und frei von Öl oder
Schmierfetten sein.
Dieses Gerät ist nicht dafür bestimmt, durch Per-
sonen (einschließlich Kinder) mit eingeschränkten
physischen, sensorischen oder geistigen Fähigkeiten oder mangels Erfahrung und / oder
mangels Wissen benutzt zu werden, es sei
denn, sie werden durch eine für ihre Sicherheit
zuständige Person beaufsichtigt oder erhielten
von ihr Anweisungen, wie das Gerät zu benutzen
ist. Kinder sollten beaufsichtigt werden, um si
zustellen, dass sie nicht mit dem Gerät spielen.
Inbetriebnahme
Verwenden Sie das Gerät niemals
zweckentfremdet und nur mit Originalteilen / -zubehör. Der Gebrauch anderer
als in der Bedienungsanleitung empfohlener
Teile oder anderen Zubehörs kann eine Verletzungsgefahr für Sie bedeuten.
n
Werkzeug / Spannzange
einsetzen / wechseln
Betätigen Sie die Spindelarretierung 7 und
halten Sie diese gedrückt.
Drehen Sie die Spannmutter 5 bis die
Arretierung einrastet.
Lösen Sie die Spannmutter 5 mit dem Kombi-
schlüssel
Entnehmen Sie ggf. ein eingesetztes Werkzeug.
Schieben Sie zuerst das vorgesehene Werkzeug
durch die Spannmutter
zum Werkzeugschaft passende Spannzange
stecken.
Betätigen Sie die Spindelarretierung 7 und
halten Sie diese gedrückt.
Stecken Sie die Spannzange 18 in den Gewinde-
einsatz und schrauben Sie dann die Spannmutter
23
vom Gewinde.
5
bevor Sie es in die
5
mit dem Kombischlüssel 23 am Gewinde fest.
cher-
18
75 DE/AT/CH
Page 76

Inbetriebnahme Inbetriebnahme / Wartung und Reinigung / Service / Garantie
Einsatzwerkzeug mit Spanndorn 13
verwenden:
HINWEIS: Verwenden Sie die Schraubendre-
herseite des Kombischlüssels
Festziehen der Schraube der Spanndornen
Setzen Sie den Spanndorn 13 wie beschrieben
in das Elektrowerkzeug ein.
Lösen Sie mit Hilfe des Kombischlüssels 23 die
Schraube vom Spanndorn
Stecken Sie das gewünschte Einsatzwerkzeug
zwischen die beiden Unterlegscheiben auf die
Schraube auf.
Ziehen Sie mit Hilfe des Kombischlüssels 23
die Schraube am Spanndorn
23
zum Lösen und
13
.
13
fest.
13
Ein- und ausschalten /
Drehzahlbereich einstellen
Einschalten / Drehzahlbereich einstellen:
Schließen Sie den Stecker 4 an das Netzteil 10
an, indem Sie ihn in die dafür vorgesehene Einsteckvorrichtung
Schließen Sie das Gerät an die Stromversorgung
an, indem Sie den Netzstecker in die Steckdose
stecken.
Drücken Sie den EIN- / AUS-Schalter 2 nach
unten und schieben Sie ihn dann in Richtung
der Drehzahlregulierung
auf eine Position zwischen „5“ und „20“.
Ausschalten:
Stellen Sie die Drehzahlregulierung 1 auf
die Position „5“. Drücken Sie den EIN- / AUSSchalter
Richtung des Kabels.
8
stecken (siehe Abb. C).
1
. Stellen Sie diese
2
nach unten und schieben Sie ihn in
Hinweise zu Material-
bearbeitung / Werkzeug /
Drehzahlbereich
Bearbeiten Sie Kunststoffe und Materialien mit
niedrigem Schmelzpunkt im niedrigen Dreh-
zahlbereich.
Bearbeiten Sie Holz mit hohen Drehzahlen.
.
Führen Sie Reinigungs-, Polier- und Schwabbel-
arbeiten im mittleren Drehzahlbereich durch.
Die nachfolgenden Angaben sind unverbindliche
Empfehlungen. Testen Sie beim praktischen Arbeiten
auch selbst, welches Werkzeug und welche Einstellung für das zu bearbeitende Material optimal geeignet sind.
Geeignete Drehzahl einstellen:
Ziffer an der
Drehzahlregulierung
Anwendungsbeispiele / geeignetes
Werkzeug auswählen:
Funktion Zubehör Verwendung
Bohren HSS-Bohrer
Fräsen
Gravieren Gravierbits
1
5
8
12
16
20
zu bearbeitendes
Material
Kunststoff und Werkstoffe mit
niedrigem Schmelzpunkt
Gestein, Keramik
Weichholz, Metall
Hartholz
Stahl
12
Fräsbits
21
Holz bearbeiten
Vielseitige Arbeiten;
20
z.B. Ausbuchten,
Aushöhlen, Formen,
Nuten oder Schlitze
erstellen
Kennzeichnung
anfertigen, Bastelarbeiten
(siehe Abb. D)
Verwenden Sie die Fräsbits 20 zur Bearbeitung
von Stahl und Eisen unter Höchstdrehzahl.
Ermitteln Sie den Drehzahlbereich zur Bearbei-
tung von Zink, Zinklegierungen, Aluminium,
Kupfer und Blei durch Versuche an Probestücken.
76 DE/AT/CH
Page 77

Inbetriebnahme / Wartung und Reinigung / Service / Garantie
Funktion Zubehör Verwendung
Polieren,
Entrosten
VORSICHT!
Üben Sie nur
leichten Druck
mit dem Werk
zeug auf das
Werkstück
aus.
Säubern Kunststoff-
Schleifen Schleifschei-
Trennen Trenn-
Metallbürste 16
Polierscheiben
-
bürsten
ben
Schleifbits
scheiben
Entrosten
Verschiedene
14
Metalle und Kunststoffe, insbesondere
Edelmetalle wie
Gold oder Silber
bearbeiten (siehe
Abb. E)
z.B. schlecht zu-
19
gängliche Kunststoffgehäuse
säubern oder den
Umgebungsbereich
eines Türschlosses
säubern
15
Schleifarbeiten an
Gestein, Holz, feine
,
22
Arbeiten an harten
Materialien, wie
Keramik oder legiertem Stahl
(siehe Abb. F, G)
Metall, Kunststoff
17
und Holz bearbeiten
Tipps und Tricks
Wenn Sie zu hohen Druck ausüben, kann das
eingespannte Werkzeug zerbrechen und / oder
das Werkstück beschädigt werden. Sie können
optimale Arbeitsergebnisse erzielen, indem Sie das
Werkzeug mit gleich bleibendem Drehzahlbereich
und geringem Druck an das Werkstück führen.
Wartung und Reinigung
Das Gerät ist wartungsfrei.
Entfernen Sie Verschmutzungen vom Gerät.
Verwenden Sie dazu ein trockenes Tuch.
Service
Lassen Sie Ihre Gerät
von der Servicestelle oder einer Elektrofachkraft und nur mit Original-Ersatzteilen reparieren. Damit wird sichergestellt,
dass die Sicherheit des Gerätes erhalten bleibt.
Lassen Sie den Aus-
tausch des Steckers oder der Netzleitung immer vom Hersteller des Gerätes
oder seinem Kundendienst ausführen.
Damit wird sichergestellt, dass die Sicherheit
des Gerätes erhalten bleibt.
Garantie
Sie erhalten auf dieses Gerät 3 Jahre Garantie ab Kaufdatum. Das Gerät wurde
sorgfältig produziert und vor Anlieferung
gewissenhaft geprüft. Bitte bewahren Sie
den Kassenbon als Nachweis für den Kauf
auf. Bitte setzen Sie sich im Garantiefall mit
Ihrer Servicestelle telefonisch in Verbin
Nur so kann eine kostenlose Einsendung
Ihrer Ware gewährleistet werden.
Die Garantieleistung gilt nur für Material- oder Fabrikationsfehler, nicht aber für Transportschäden,
Verschleißteile oder für Beschädigungen an zerbrechlichen Teilen, z. B. Schalter oder Akkus.
Das Produkt ist lediglich für den privaten und nicht
für den gewerblichen Gebrauch bestimmt.
Bei missbräuchlicher und unsachgemäßer Behandlung, Gewaltanwendung und bei Eingriffen, die nicht
von unserer autorisierten Service-Niederlassung
vorgenommen wurden, erlischt die Garantie. Ihre
gesetzlichen Rechte werden durch diese Garantie
nicht eingeschränkt.
Die Garantiezeit wird durch die Gewährleistung nicht
verlängert. Dies gilt auch für ersetzte und reparierte
Teile. Eventuell schon beim Kauf vorhandene Schäden
und Mängel müssen sofort nach dem Auspacken
gemeldet werden, spätestens aber zwei Tage nach
Kaufdatum. Nach Ablauf der Garantiezeit anfallende
Reparaturen sind kostenpflichtig.
e
dung.
77 DE/AT/CH
Page 78

Garantie / Entsorgung / Konformitätserklärung / Hersteller
DE
Service Deutschland
Tel.: 0800 5435 111
E-mail: kompernass@lidl.de
IAN 89959
AT
Service Österreich
Tel.: 0820 201 222
(0,15 EUR/Min.)
E-mail: kompernass@lidl.at
IAN 89959
CH
Service Schweiz
Tel.: 0842 665566
(0,08 CHF/Min., Mobilfunk
max. 0,40 CHF/Min.)
E-mail: kompernass@lidl.ch
IAN 89959
Entsorgung
Die Verpackung besteht aus umweltfreundlichen Materialien, die Sie über die örtlichen Recyclingstellen entsorgen können.
Werfen Sie Elektrowerkzeuge
nicht in den Hausmüll!
Gemäß Europäischer Richtlinie 2002 / 96 / EC
über Elektro- und Elektronik-Altgeräte und Umsetzung
in nationales Recht müssen verbrauchte Elektrowerkzeuge getrennt gesammelt und einer umweltgerechten Wiederverwertung zugeführt werden.
Konformitätserklärung /
Hersteller
Wir, KOMPERNASS GMBH, Dokumentenverantwortlicher: Herr Semi Uguzlu, BURGSTR. 21,
44867 BOCHUM, DEUTSCHLAND, erklären hiermit, dass dieses Produkt mit den folgenden Normen,
normativen Dokumenten und EG-Richtlinien übereinstimmt:
Maschinenrichtlinie
(2006 / 42 / EC)
EG-Niederspannungsrichtlinie
(2006 / 95 / EC)
Elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit
(2004 / 108 / EC)
RoHS Richtlinie
(2011 / 65 / EU)
angewandte harmonisierte Normen
EN 60745-1/A11:2010, EN 60745-2-1:2010
EN 60745-2-3:2011
EN 55014-1/A2:2011, EN 55014-2/A2:2008
EN 61000-3-2/A2:2009, EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61558-1/A1:2009, EN 61558-2-6:2009
Typ / Gerätebezeichnung:
Modellbau- und Gravierset PMGS 12 B2
Herstellungsjahr: 04–2013
Seriennummer: IAN 89959
Bochum, 30.04.2013
Über Entsorgungsmöglichkeiten für ausgediente
Elektrowerkzeuge informieren Sie sich bitte bei
Ihrer Gemeinde- oder Stadtverwaltung.
78 DE/AT/CH
Semi Uguzlu
- Qualitätsmanager -
Technische Änderungen im Sinne der Weiterentwicklung sind vorbehalten.
Page 79

KOMPERNASS GMBH
BURGSTRASSE 21
44867 BOCHUM
GERMANY
Last Information Update · Stan informacji
Stanje informacij · Stav informací · Stav
informácií · Stand der Informationen: 04 / 2013
Ident.-No.: PMGS12B2042013-PL / SI / CZ / SK
IAN 89959
 Loading...
Loading...