Page 1

Electronic user’s guide released subject to "Nokia User’s Guides Terms and Conditions, 7th June, 1998
Nokia 22 Operator’s Guide
9353070
Issue 1
Page 2

DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
We, NOKIA MOBILE PHONES Ltd declare under our sole responsibility that the product
TME-1 is in conformity with the following Council Directive: 1999/5/EC.
Copyright © Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd 2001. All rights reserved.
Reproduction, transfer, distribution or storage of part or all of the contents in this document in any form without the prior written permission of Nokia is prohibited.
Nokia and Nokia Connecting People are registered trademarks of Nokia Corporation. Other product and company names mentioned herein may be trademarks or tradenames of
their respective owners.
Nokia operates a policy of continuous development. Nokia reserves the right to make
changes and improvements to any of the products described in this document without
prior notice.
Under no circumstances shall Nokia be responsible for any loss of data or income or any
special, incidental, consequential or indirect damages howsoever caused.
The contents of this document are provided “as is”. Except as required by applicable law,
no warranties of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the
implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, are made in
relation to the accuracy, reliability or contents of this document. Nokia reserves the right
to revise this document or withdraw it at any time without prior notice.
The availability of particular products may vary by region. Please check with the Nokia
dealer nearest to you.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Product overview......... 5
Package contents ...................... 6
System requirements ............... 7
Network services ....................... 7
Operating environment ........... 7
2. Product features.......... 9
GSM terminal ............................. 9
Application module ................10
Light indicators .......................12
Power supply ............................ 14
Supplementary services ........15
Short Message Service
(SMS) ..........................................15
Voice mail ................................. 15
High Speed Circuit Switched
Data (HSCSD) ...........................16
Calling Line Identification
(CLI) ............................................. 16
Automatic Area Code (AAC)
and routing ............................... 16
Intensity of Field (IOF) ........... 17
Faster call setup ...................... 17
AutoPIN security feature ......17
3. Setting up
the terminal ...................18
Installing the SIM card .......... 18
Mounting the GSM terminal 19
Connecting the power
supply .........................................19
Connecting a telephone ........19
Entering the PIN code ...........19
Terminal tone indicators ....... 20
Checking the signal strength 20
Making test calls .....................22
Installing the antenna
adapter .......................................23
4. PBX installation.........24
Functionality in trunk mode 24
Functionality in extension
mode ...........................................25
Connecting the Nokia 22
to a trunk line of a PBX ........26
Connecting the Nokia 22
to an extension line of a PBX 28
5. Configuration ............30
Methods ..................................... 30
Basic settings ........................... 30
Advanced settings ..................31
6. Accessories.................34
Nokia 22 Data Packet ............ 34
Nokia 22 Configurator
Software .................................... 34
Antenna adapter .....................35
Backup battery set .................35
7. Technical
specifications .................36
GSM terminal ........................... 36
Application module ................ 36
Terminal data transfer
modes .........................................36
Factory default values ........... 38
Terminal connectors ............... 40
8. Security
information ....................43
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 3
Page 4

9. Care and
maintenance...................44
10. Troubleshooting ......46
First things to check ..............46
Light indicator 3 is blinking .46
No tone can be heard when
you lift the receiver ................ 46
Call is disconnected
immediately after answering 47
Appendix: Supplementary
services ......................... 48
How the supplementary
services work ............................48
Number identification ...........48
Call forwarding
(Call offering) ...........................49
Call waiting
(Call completion) .....................50
In-call handling .......................50
Call restriction ......................... 51
Security options ......................53
Call transfer ..............................53
Abbreviations ............... 54
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 4
Page 5

Product overview
1. Product overview
The Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal is a GSM terminal that can be used for
both digital and analogue Private Branch Exchange (PBX) connections. The terminal is composed of a GSM terminal and an application module for PBX connections. The application module features PBX connection interfaces for both
trunk (public side) and extension (private side) connections.
In addition to PBX connectivity solutions, the terminal can also be used in conjunction with other GSM applications and various data solutions, for example
High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD), PC fax, Short Message Service (SMS)
and GSM Phase 2+ supplementary services.
Important! In addition to this guide, refer to the Nokia 22 User’s Guide
which provides information about the use of the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal including safety information.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 5
Page 6
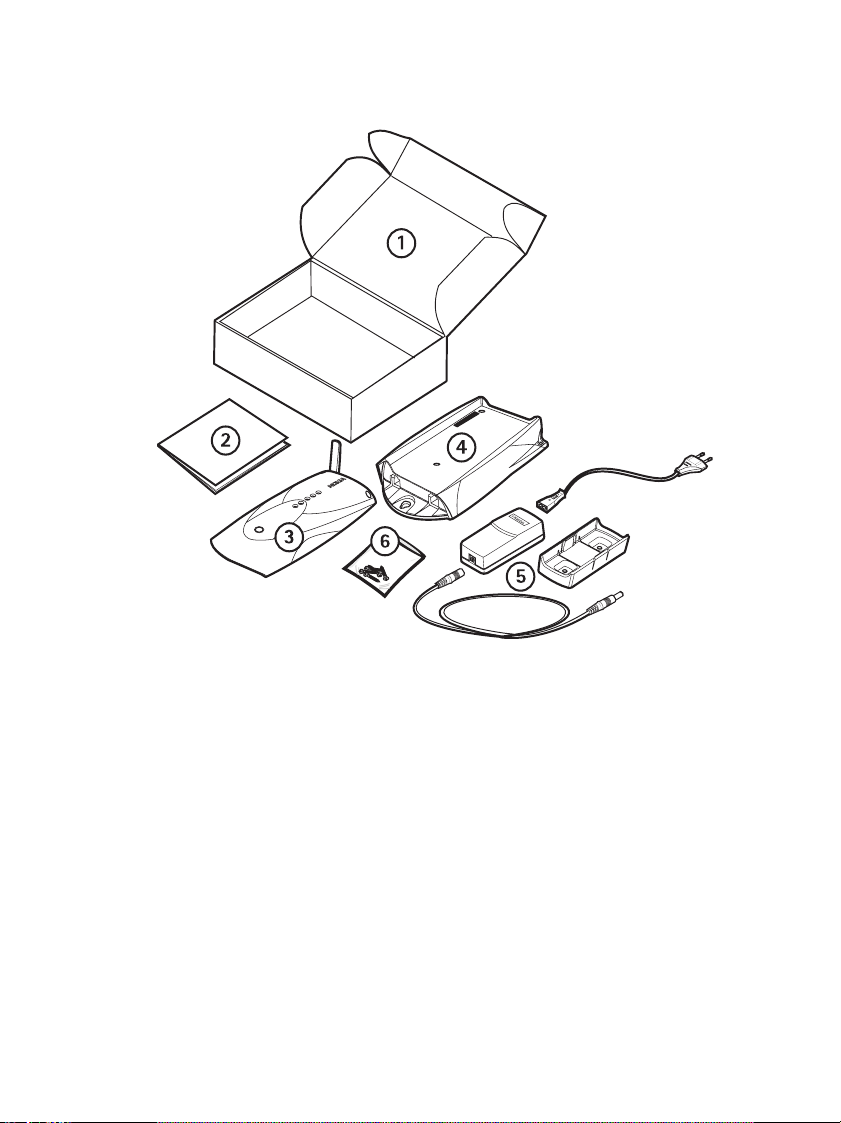
Package contents
Product overview
The Nokia 22 basic sales package
1 Nokia 22 sales package
2 Nokia 22 User’s Guide
3 Nokia 22 GSM terminal
4 Application module
5 Power source with a wall rack, AC and DC cables
6 Screws
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 6
Page 7

Product overview
System requirements
The Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal can be connected to a digital or analogue PBX. The terminal can be connected either to the trunk connector or the
extension connector of the PBX. The application module has two RJ-11 connectors for both type of connections. Only one of the connectors can be used at a
time.
The terminal can be configured using a DTMF telephone or with the Nokia 22
Configurator Software. For further information , see “6. Accessories” on page 34.
The Nokia 22 supports both DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) and pulse dialling.
Normal telephone sets and answering machines can be connected directly to the
application module’s trunk connector.
Note: Standard land line telefaxes and modems are not compatible with
the terminal. Only a PC fax application can be used with the Nokia 22
Data Packet. For further information, see “6. Accessories” on page 34.
Important! Do not connect the Nokia 22 to a digital (ISDN) interface of
a PBX.
Network services
The cellular device described in this guide is approved for use on the GSM900,
GSM1800 and GSM900/1800 dual-band networks.
Note that Dual band functionality is a network-dependent feature. Check with
your local service provider if you can subscribe to and use the dual band
functionality.
A number of features included in this guide are called network services. They are
special services provided by wireless service providers. Before you can take
advantage of any of these network services, you must subscribe to these
service(s) from your home service provider and obtain instructions for their use.
Operating environment
Operating of any radio transmitting equipment may interfere with the functionality of inadequately protected medical devices. Consult a physician or the manufacturer of the medical device if you have any questions. Other electronic
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 7
Page 8

Product overview
equipment may also be subject to interference. The terminal should not be installed outdoors.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 8
Page 9
Product features
2. Product features
GSM terminal
The GSM terminal features a dual band transceiver with built-in data capabilities, a SIM card reader, an antenna, a RS-232 data connector, a power supply
and an application interface connector. The GSM terminal provides access to the
data functionality of the GSM system including Short Message System (SMS)
and High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD). The GSM terminal provides the
subscriber data transmission, one connection at a time.
The Nokia 22 supports only small size SIM
cards. The SIM card should have the PIN
code request activated.
GSM terminal basic features:
• Dual Band GSM 900 MHz & GSM 1800 MHz
• Voice codecs EFR, FR, HR
• PC fax support
• HSCSD (High Speed Circuit Switched Data)
• V24 interface with auto baud rate
• Data compression (V42 bis)
• Mobile Originated and Mobile Terminated SMS with the help of AT
commands
• SIM lock support
• ETS GSM 07.07 and 07.05 compatible AT command set
• GSM Phase 2+ supplementary services
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 9
Page 10
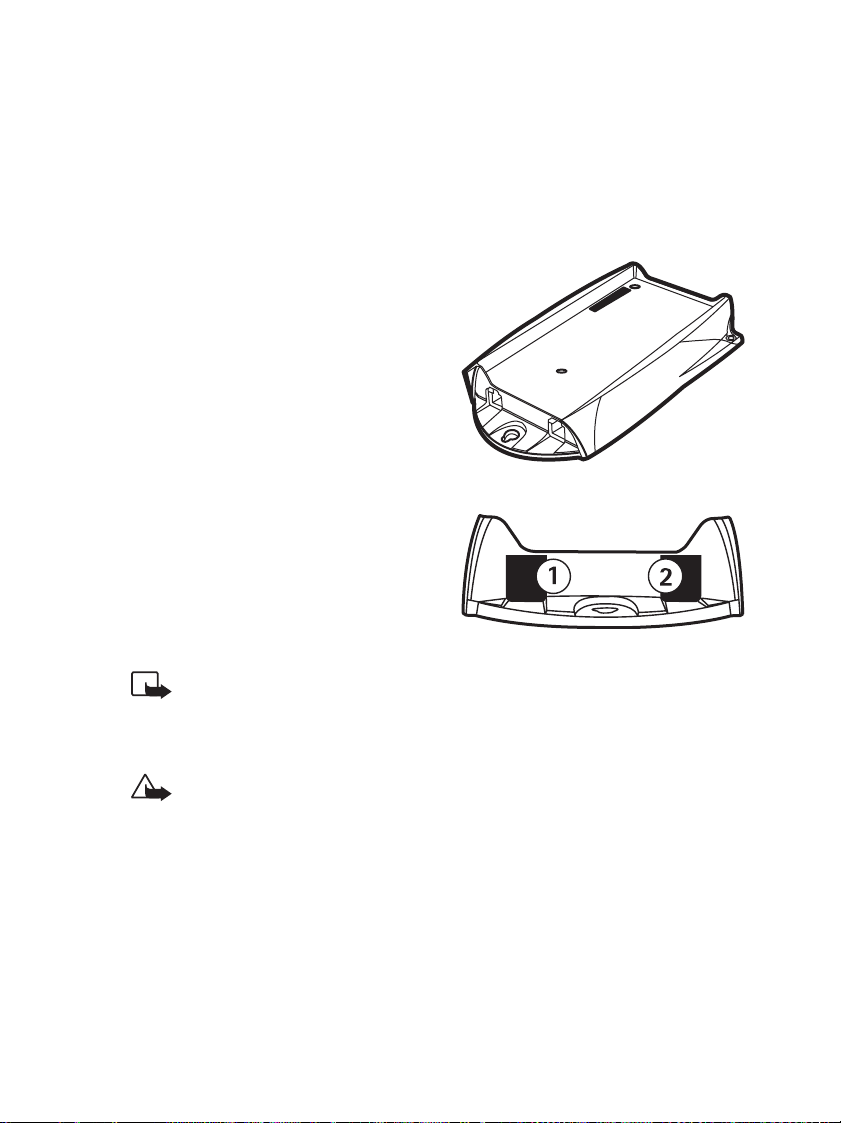
Product features
Application module
The application module has two operating modes: extension mode and trunk
mode. In extension mode the application module is connected to the analogue
extension (private) interface of the PBX. In trunk mode the application module
is connected to the analogue trunk (public) interface of the PBX. The application
module complies with the ETS 300-001 standards for PBX trunk and extension
connections.
The application module can also be connected directly to a normal telephone set.
The telephone can be used like a normal
landline telephone , for example to make
and receive calls.
1. Extension connector
2. Trunk connector
Note: Some telephones sets and PBXs are more sensitive to radio interference than others and there may occur some audible interference. If
this problem occurs, increase the distance between the terminal and the
PBX or the telephone set.
Warning! To avoid damage to the devices, the telephone set must be
connected to the terminal’s trunk connector with a standard 4-pin RJ11 cable that has only its two middle pins connected.
Application module basic features:
• ITU-T standard
• Pulse/DTMF dialling
• Calling Line Identification (CLI)
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 10
Page 11

Product features
• Support for analogue extension and trunk interfacing
• Loop reversal and loop interruption (detection and generating)
• Country specific R-key settings
Application module functionality
The application module can function in different modes when the Nokia 22 is
connected to a PBX. For further information, see “ Functionality in trunk mode”
on page 24 and “ Functionality in extension mode” on page 25.
Call creation
When the PBX or the telephone set connected to the Nokia 22 switches over to
the OFF-HOOK state, the terminal generates a local dial tone.
When the user makes a call, dialled digits are first saved in the memory of the
Nokia 22. The dial tone stops after the first digit is dialled. A four seconds waiting time follows after the last dialled digit. After that the terminal assumes the
telephone number is fully dialled, and a call request is sent to the network. The
call is processed.
A local busy tone will be heard after 30 seconds and a howler tone after 60 seconds if digits are not dialled. In such a situation before a number can be dialled,
the PBX or the telephone set must switch over to the ON-HOOK state and after
that again to the OFF-HOOK state.
Note: When making a call, an area code must be dialled for both local
calls and long distance calls if the network system does not support local area dialling or the AAC (Automatic Area Code) feature is not in use.
For further information about the AAC feature, see section “ Automatic
Area Code (AAC) and routing” on page 16.
Note: The generating of dial tones does not depend on the service state
of the GSM terminal. Even if the GSM terminal is not connected to the
GSM network (that is light indicator 3 is blinking on the terminal) the
application module tries to connect the call. Thus, emergency calls can
be made using any network service provider available or even without a
SIM card in the terminal. For a description of the terminal light indicators, see “ Light indicators”on page 12.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 11
Page 12
Product features
Call termination
When the PBX or the telephone set connected to the Nokia 22 terminates the
call by switching over to the ON-HOOK state, the Nokia 22 terminates the GSM
connection immediately.
When the B subscriber terminates the call, the GSM connection of the terminal
is terminated as the PBX or the telephone set connected to the terminal switches over to the ON-HOOK state.
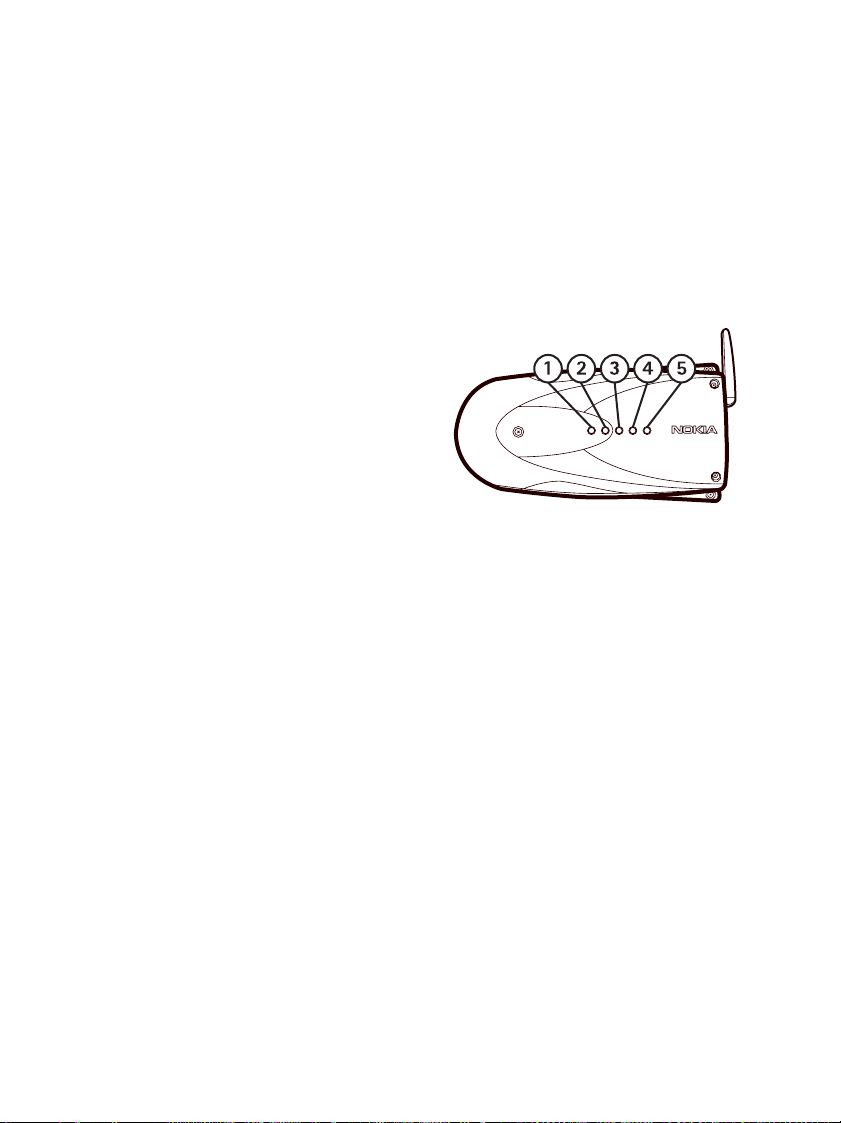
Light indicators
There are five light indicators on the
Nokia 22.
Light indicators 1 and 2 indicate the
state of the application module and light
indicators 3, 4 and 5 indicate the state of
the GSM terminal.
The terminal is ready for use when the
light indicator 3 is lit.
The use of light indicators is described in Table 1: Application module light
indicators and Table 2: GSM terminal light indicators.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 12
Page 13
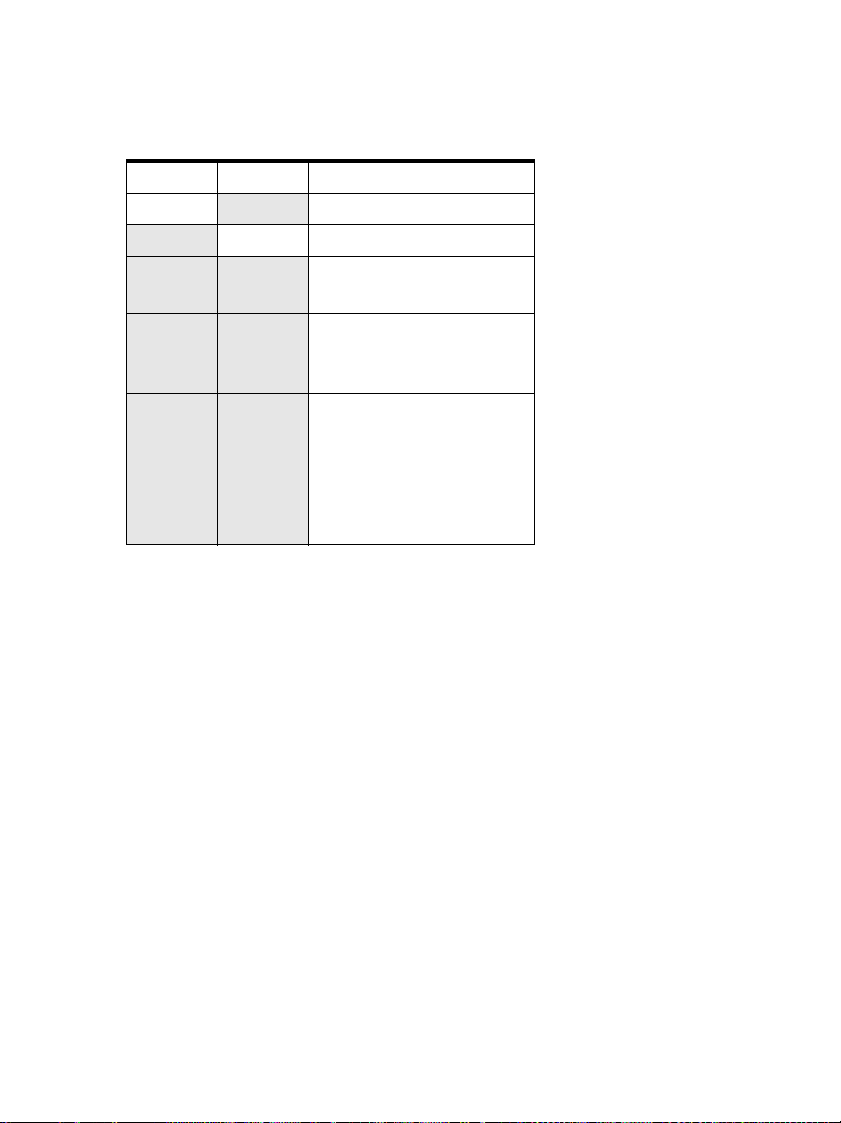
Table 1: Application module light indicators
1 2 Description
-
On - Trunk mode is active.
On On Advanced setup mode is
OnBlinkingOn
OnBlinking_
BlinkingBlinkingBlinkingOn
On Extension mode is active.
active.
OnBlinkingOn
OnBlinking_
BlinkingBlinkingBlinkingOn
OK
An error has occured.
Contact service personnel.
Product features
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 13
Page 14
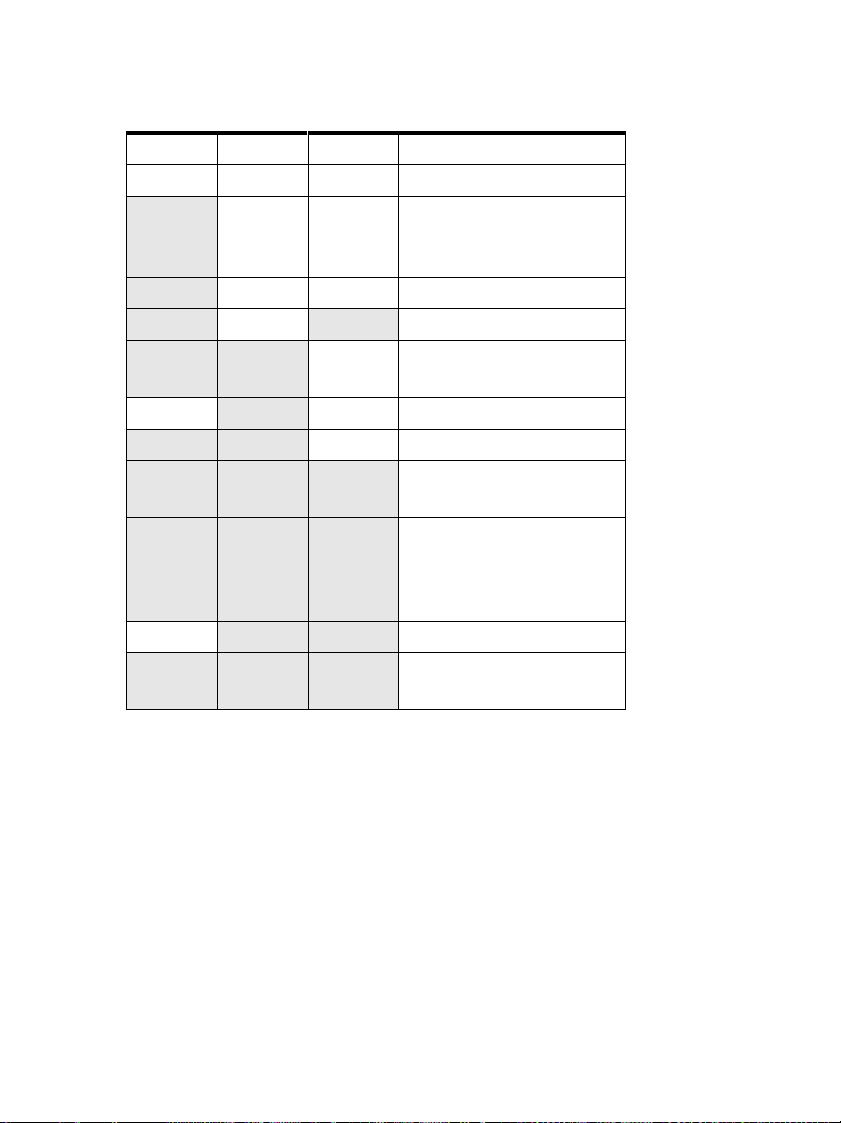
Table 2: GSM terminal light indicators
345Description
---Power is off.
Blinking - - Power is on. The terminal is
attempting to connect to
the telephone network.
On - - In service.
On - On Call in progress.
On Blinking - The terminal has received a
call.
-
Blinking Blinking - Enter the PUK code.
On On On The terminal has received an
On On Blinking The terminal has no space
-
Blinking Blinking Blinking An error has occured.
Blinking - Enter the PIN code.
SMS message or voice mail.
for new SMS messages. The
oldest message is
automatically deleted.
Blinking Blinking Install the SIM card.
Contact service personnel.
Product features
Power supply
The ACW-3 power supply is supplied with the terminal.
A backup battery set with its own power supply is also available, see “ Backup
battery set” on page 35.
Connect the power supply to the DC jack connector on the left side of the terminal. After that, connect the power supply to the AC wall outlet.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 14
Page 15

Product features
Note: The DC connector’s middle contact has negative (-) polarity and
the outer contact has positive (+) polarity.
Supplementary services
These features are network services. They are special services provided by wireless network service providers and differ from one network and country to another. For details, check with the local network service provider.
The Nokia 22 supports the GSM Phase 2+ Supplementary Services
1 Number identification
2 Call offering
3 Call completion
4 In-call handling
5 Call transfer
6 Call restriction
7 High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD)
8 Security Options
For more specific information about the supplementary services supported by
the terminal, see “ Appendix: Supplementary services” on page 48.
Short Message Service (SMS)
The Nokia 22 supports both Mobile Originated (MO) and Mobile Terminated (MT)
short message services with the help of AT commands.
A PC and the Nokia 22 Data Packet are needed when using the SMS feature.
When an SMS message is received the light indicators 3, 4 and 5 light up and a
tone indicator (--- --- ---) is heard through the telephone set’s receiver.
Note: SMS message received signals are reset when the receiver is lifted
off-hook.
Voice mail
The Nokia 22 supports the GSM network voice mail service. If the network sends
an SMS of received voice mail, the terminal will indicate the received SMS by
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 15
Page 16

Product features
means of light indicators and also by means of tone in the telephone set’s receiver. For further information, see “ Short Message Service (SMS)”on page 15.
High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD)
The GSM terminal supports High Speed Circuit Switched Data that enables a
data transmission speed of up to 43.2 kbps. The High Speed Circuit Switched
Data (HSCSD) relies on the simultaneous use of multiple GSM timeslots.
For the terminal data transfer modes, see “7. Technical specifications” on page
36. The Nokia 22 Data Packet is required to use this feature.
The HSCSD is a network service. For details, contact your service provider.
Calling Line Identification (CLI)
The Calling Line Identification (CLI) feature displays the caller’s number with an
external calling line display device.
Two signalling methods are available, ETSI FSK (European Telecommunications
Standards Institute Frequency Shift Keying) and DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency).
The signalling mode varies depending on the operator and the country. The default mode is ETSI FSK. For information about changing the CLI mode, see “
Changing Calling Line Identification (CLI) mode” on page 32.
Note: The CLI devices are not provided by Nokia. For details and availability, contact your service provider.
Automatic Area Code (AAC) and routing
The Automatic Area Code (AAC) feature allows the user to dial local numbers
without a local area code in the GSM network. Before the number is sent a preprogrammed local area code is added automatically by the Nokia 22.
The user can also specify that the terminal changes certain prefixes automatically, for example to provide a cost-effective route. The AAC and routing settings
can be modified using the Nokia 22 Configurator Software.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 16
Page 17

Product features
Intensity of Field (IOF)
The Intensity of Field (IOF) feature indicates the strength of the received radio
signal. The IOF is indicated by the light indicators. The feature can be activated
with a DTMF telephone connected to the terminal’s trunk connector. To activate
the feature, key in 777**#. The feature is automatically deactivated when the
DTMF telephone’s receiver is replaced on the hook. For further information on
the IOF feature, see “3. Setting up the terminal” on page 18.
Faster call setup
Faster call setup allows a faster call establishment. The last 10 different dialled
numbers are stored in the memory of the Nokia 22. If the dialled number matches one of the stored numbers, there is no delay before the terminal sends the
number and the call is established immediately.
Note: Only successful (answered) calls are stored in the terminal’s
memory.
AutoPIN security feature
The Nokia 22 has an AutoPIN security feature. It saves the PIN code in the
terminal’s memory when the code is entered for the first time or when the code
is changed. In addition, the AutoPIN feature enables device recovery after
occasional power cuts without on-site intervention. The terminal enters the PIN
code automatically the next time it switches on and requests the PIN code. For
changing the PIN code, see “ Security options” on page 53.
Use of the SIM card in other GSM terminals or mobile phones can be prevented.
The user does not have to know the PIN code. However, other SIM cards can be
used with the terminal. The AutoPIN feature can be deactivated using the Nokia
22 Configurator Software.
The default value is that the AutoPIN feature is active.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 17
Page 18

Setting up the terminal
3. Setting up the terminal
Before the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal can be used it must be installed
properly.
In the following instructions it is assumed that the PIN code request and the
AutoPIN feature are active.
To use the Nokia 22 for the first time, proceed as follows:
1 Install the SIM card.
2 Mount the GSM terminal on the application module.
3 Connect the power supply to the terminal and to an AC wall outlet.
4 Connect a DTMF telephone to the terminal.
5 Enter the PIN code if your SIM card requires it.
6 Check the signal strength.
7 Install the external antenna.
8 Make test calls.
Warning! Do not connect the power supply to an AC wall outlet before
you have installed the SIM card and mounted the GSM terminal on the
application module.
Installing the SIM card
If the SIM card has not been installed, install it.
Insert the SIM card ensuring that the golden
contact area is facing downwards.
Note: Keep SIM cards always out of the reach of small children.The card
can be damaged by scratching or bending so it must be handled
carefully.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 18
Page 19

Mounting the GSM terminal
Mount the GSM terminal on the application
module using the three screws supplied with
the terminal.
Connecting the power supply
1 Connect the power cord from the power sup-
ply to the GSM terminal.
2 Connect the power supply to an AC wall out-
let.
Setting up the terminal
Connecting a telephone
Connect the DTMF telephone to the application module’s trunk connector (RJ11 ).
Warning! To avoid damage to the devices, the telephone set must be
connected to the trunk connector with a standard 4-pin RJ-11 cable
that has only its two middle pins connected.
Entering the PIN code
The PIN (Personal Identification Number) code protects your SIM card against
unauthorised use. It is usually supplied with the SIM card. Use the DTMF
telephone connected to the Nokia 22 to enter the PIN code.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 19
Page 20

Setting up the terminal
When light indicator 4 blinks, lift the receiver. When the enter PIN code tone is
heard, enter the PIN code followed by #. The OK tone is heard and light indicator
3 lights up. If the operation fails, see “ Entering PIN code does not succeed” on
page 30.
When the terminal is being connected for the first time or after a power cut, it
takes 20-30 seconds before the terminal is connected to the network. Light
indicator 3 on the GSM terminal lights up and indicates that the connection is
active. The terminal is now ready for installing.
If the AutoPIN feature is active, the terminal automatically enters the PIN code
the next time the power is switched on.
Terminal tone indicators
The following tone signals indicate the state of the Nokia 22.
Table 3: Terminal tone indicators
Tones Description
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Enter SIM card
- _ _ - _ _ - _ _ Enter PIN code
- - Enter PUK code
- - - - Error
OK
SMS received
Checking the signal strength
The (IOF) feature indicates the strength of the received radio signal.
To check the signal strength, lift the receiver of the DTMF telephone connected
to the Nokia 22 and key in 777**#.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 20
Page 21

Setting up the terminal
The signal strength is indicated by the light indicators until the receiver is replaced on the hook.
For the use of light indicators in the Intensity of Field, see Table 4: IOF light indicators.
Note: Only emergency calls can be established when the terminal is in
the IOF state.
Note: The installation location must be clean and dry. The terminal must
be installed indoors. The terminal operating temperature range is
-10C...+55C.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 21
Page 22

Setting up the terminal
Table 4: IOF light indicators
12345Signal
strength
Blinking----No signal.
On----Approx. -
105dBm
On Blinking---Approx. -
100dBm
On On---Approx. -
95dBm
On On Blinking - - Approx. -
90dBm
On On On - - Approx. -
85dBm
On On On Blinking - Approx. -
80dBm
On On On On - Approx. -
75dBm
On On On On Blinking Approx. -
70dBm
On On On On On Approx. -
65dBm
• If the required values are not obtained, move the terminal to another location.
• If you cannot find a place where the signal is stronger than -95 dBm, that is
light indicators 1 and 2 are lit, you can install an external antenna to achieve
proper signalling (See section “ Installing the antenna adapter” on page 23).
• Place the terminal in the desired location.
Making test calls
Make test calls to and from the Nokia 22 using the telephone set connected to
the terminal. To adjust the volume, key in 0**x during the call, the x representing
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 22
Page 23

Setting up the terminal
a value between 1(the lowest volume level) and 10 (the highest volume
level).
The terminal is now ready for connecting to the PBX.
Installing the antenna adapter
An external antenna improves signal reception and transmission. An antenna
adapter for use between the Nokia 22 and a standard FME connector is provided
by Nokia (See “6. Accessories” on page 34).
Distance, large obstacles (for example hills, buildings) or installing the device
below ground level can reduce the signal strength. Installing an external antenna may help.
The installation procedure:
1 Pull out the antenna from the GSM
terminal.
2 Connect the antenna adapter to the
antenna connector.
3 Install the antenna adapter in the ex-
ternal FME antenna connector.
For specifications for the external antenna, antenna adapter and connectors, see
“7. Technical specifications” on page 36.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 23
Page 24

PBX installation
4. PBX installation
The application module can be connected to an analogue or digital PBX’s analogue trunk or extension line complying with ETS 300-001 standards. The applicati on m odul e has two RJ-1 1 co nnec tor s for both kind s o f con nect ion s. On ly o ne
connector can be used at a time.
Warning! Inappropriate installation of the Nokia 22 to a PBX may damage the PBX or the Nokia 22.
Light indicators 1 and 2 in the terminal indicate the state of the application
module. For further information about the application module light indicators,
see Table 1: Application module light indicators, “ Light indicators” on page 12.
Functionality in trunk mode
Outgoing call on the trunk line
1 A PBX is configured to route mobile calls via the Nokia 22. The user enters the
number using his/her extension telephone.
2 The PBX processes the number and discovers if the number is a mobile net-
work number and sends the number sequence to the line where the terminal
is connected.
3 The terminal processes the call.
Incoming call on the trunk line
1 The Nokia 22 receives a call.
1 The terminal sends a ring tone to the PBX.
2 The switching centre answers.
3 The switching centre redirects the call to an extension.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 24
Page 25

PBX installation
Functionality in extension mode
Outgoing call on the extension line, mode A
1 The user keys in the number of the extension where the Nokia 22 is connect-
ed.
2 The terminal answers the call and provides a dial tone.
3 The user keys in the number of the B subscriber.
4 The terminal establishes the call.
Outgoing call on the extension line, mode B
1 The user keys in the number of the extension where the Nokia 22 is connect-
ed.
2 The terminal answers the call and provides silence.
3 The user keys in the number of the B subscriber.
4 The terminal establishes the call.
The terminal can be configured to change or add a mobile prefix to the number.
Thus, it can provide for example cost-effective routing. For further information
about the AAC, see “ Automatic Area Code (AAC) and routing” on page 16.
Note: Some exceptions like emergency numbers have to be taken into
account. For details, see “8. Security information” on page 43.
Incoming call on the extension line, mode A
1 The Nokia 22 answers the incoming call and opens the extension line.
2 The PBX provides a dial tone.
3 The user enters an extension number or outgoing number.
4 The PBX routes the call as it would come from an extension telephone.
Incoming call on the extension line, mode B
1 The Nokia 22 answers the incoming call and opens the extension line.
2 The terminal sends a pre-defined number to the PBX extension.
3 The B subscriber answers.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 25
Page 26

PBX installation
4 The call is established.
For further information on how to change the mode, see “ Changing application
module extension modes” on page 32.
Connecting the Nokia 22 to a trunk line of a PBX
1 Disconnect the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal power supply from the AC
wall outlet.
2 Connect the Nokia 22 to a free PBX trunk line with an RJ-11 cable.
3 Connect the power supply to the terminal.
If the AutoPIN feature is active, the Nokia 22 automatically connects to the network. In 20-30 seconds, light indicator 3 lights up to indicate the network connection and light indicator 1 to indicate the PBX trunk connection.
If the AutoPIN feature is not active, you have to enter your PIN code. For information about entering the PIN code, see “ Entering the PIN code” on page 19.
For details, contact your PBX supplier.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 26
Page 27

PBX installation
Warning! Inappropriate installation of the Nokia 22 to a PBX may
damage the PBX or the Nokia 22. If an extension line of the PBX is
connected to the trunk connector of the Nokia 22, the devices attempt
to feed current to each other and they can be damaged.
To avoid damage to the devices, an analogue trunk line of the PBX must
be connected to the terminal’s trunk connector with a standard 4-pin
RJ-11 cable that has only its two middle pins connected.
Note that the terminal’s trunk and extension connectors cannot be used
at the same time to connect a device.
Important! Do not connect the Nokia 22 to a digital (ISDN) interface of
a PBX.
Making test calls
Incoming call
Make a call to the Nokia 22 GSM number. For details, contact your service provider. The Nokia 22 redirects the call and sends a ring tone to the PBX trunk line.
The switching centre answers and redirects the call.
Outgoing call
PBX has to be configured to route certain outgoing numbers (for example numbers with mobile prefix) to the trunk line the Nokia 22 is connected before an
outgoing call can be made. When a number is sent by the PBX to the terminal,
the terminal connects the call.
For terminal functionality in trunk mode, see section “ Functionality in trunk
mode” on page 24.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 27
Page 28

PBX installation
Connecting the Nokia 22 to an extension line of a PBX
1 Disconnect the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal power supply from the AC
wall outlet.
2 Connect the Nokia 22 to a free PBX extension line with an RJ-11 cable.
3 Reconnect the power supply to the terminal.
If the AutoPIN feature is active, the terminal automatically connects the network. In 20-30 seconds, light indicator 3 lights up to indicate the network connection and light indicator 2 to indicate the PBX extension connection.
If the AutoPIN feature is not active, you have to enter your PIN code. For information about entering the PIN code, see “ Entering the PIN code” on page 19.
For details, contact your PBX supplier.
Warning! Inappropriate installation of the Nokia 22 to a PBX may
damage the PBX or the Nokia 22. If an extension line of the PBX is
connected to the trunk connector of the Nokia 22, the devices attempt
to feed current to each other and they can be damaged.
To avoid damage to the devices, an analogue extension line of the PBX
must be connected to the terminal’s extension connector with a standard 4-pin RJ-11 cable that has only its two middle pins connected.
Note that the terminal’s trunk and extension connectors cannot be used
at the same time to connect a device.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 28
Page 29

PBX installation
Important! Do not connect the Nokia 22 to a digital (ISDN) interface of
a PBX.
Making Test Calls
Incoming call
Make a call to the Nokia 22 GSM number. For details, contact your service provider. The Nokia 22 answers the call and places the PBX extension line off-hook.
The PBX provides a dial tone and you can dial the desired extension or outgoing
number. The PBX connects the call.
Outgoing call
Make a call to the PBX extension number where the Nokia 22 is connected. The
Nokia 22 answers the call. You hear either a dial tone or silence depending on
the settings of the terminal. Dial the desired number. The terminal connects the
call.
The PBX can also be configured to route certain numbers automatically.
For terminal functionality in the extension connection, see “ Functionality in extension mode” on page 25.
Some PBXs are more sensitive to radio interference than others
Note:
and there may be some audible interference. If this problem occurs, increase the distance between the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal
and the PBX. If there are other problems with the product or with connecting the product to the PBX, please consult your local dealer, service
provider or Nokia Mobile Phones for further information.
Note: When the Nokia 22 is connected to an extension line of a PBX,
some precautions must be taken into account. If no calling restrictions
have been set up, any caller calling the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity
terminal’s GSM number gains access to the outgoing PBX trunk line and
can make phone calls that are charged to the PBX owner.
To prevent this situation, the PBX must be configured to deny any outgoing calls coming from the extension line the Nokia 22 is connected to.
If the PBX cannot be configured in such a way, it is possible to configure
the Nokia 22 to automatically call a predefined extension number when
it receives a GSM call. For further information, see “5. Configuration” on
page 30. For more information about PBX configuration, see your PBX
User’s Guide.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 29
Page 30

Configuration
5. Configuration
Methods
The Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal can be configured using a DTMF telephone connected to the application module or using the Nokia 22 Configurator
Software. The Nokia 22 Configurator Software is a tool for the configuration of
the terminal. For further information, see “6. Accessories” on page 34.
The settings can also be modified via a PBX.
Note: When multiple Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminals are connected to a single PBX, the PBX may treat them as a pool of devices. As a
result, it is not possible to change the settings of a specific Nokia 22
connectivity terminal via the PBX. For further information, contact your
service provider.
For terminal tone indicators, see “ Terminal tone indicators” on page 20.
Basic settings
Basic settings include PIN and PUK code input, the speaker volume control and
activation of the Intensity of Field (IOF) feature.
Entering PIN and PUK code
To enter the PIN code, key in PINCode#.
To enter the PUK code, key in PUKCode#.
Entering PIN code does not succeed
If entering the PIN code fails three times, the code is blocked. You can unblock
it by entering your PUK (Personal Unblocking Key) code. The PUK code may be
supplied with the SIM card. If not, contact your local service provider for the
code. If you lose the code, contact your service provider. When the PIN code is
blocked, light indicators 3 and 4 blink. To unblock the code, proceed as follows:
1 Lift the receiver of the DTMF telephone connected to the Nokia 22. When the
enter PUK code tone is heard, enter the PUK code followed by #.
2 Enter a new PIN code (4-8 digits) followed by # when light indicator 4 blinks
and the enter PIN code tone is heard.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 30
Page 31

Configuration
3 Confirm the new PIN by re-entering the code followed by #.
Adjusting telephone speaker volume
To adjust the telephone set’s speaker volume, key in 0**x during the call, the x
representing a value between 1 (the lowest volume level) and 10 (the highest
volume level). The default value is 5.
Activating IOF
To activate the IOF (Intensity of Field) feature, key in 777**#. Placing the receiver on the hook completes the function.
Advanced settings
The more advanced settings can be modified when the Nokia 22 is in configuration mode.
The following settings are available in configuration mode:
• Loop interruption time in milliseconds
• Polarity reversal time in milliseconds
• CLI mode
• Network selection
• PBX application module extension mode change
• Terminal restart
Activating configuration mode
To activate configuration mode, key in **####**.
The configuration mode is protected with a four-digit access code. When configuration mode has been activated, the Nokia 22 requires an access code for
changing the settings. The default code is 1234. To change the default access
code, use the Nokia 22 Configurator Software.
To enter the access code, key in AccessCode#.
Note: After changing the configuration mode values the Nokia 22 must
be restarted in order to save the new settings. Restart the terminal in
the configuration mode by keying in 555**#.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 31
Page 32

Configuration
Changing the loop interruption time
The default loop interruption time is 300 milliseconds. Key in a zero to disable
the loop interruption. After you have keyed in the interruption time the Nokia
22 returns to configuration mode.
To change the loop interruption time, key in 2**Interruption_Time#.
Changing the polarity reversal time
After you have keyed in the polarity reversal time the Nokia 22 returns to configuration mode.
To change the polarity reversal time, key in 3**Polarity_Reversal_Time#.
Changing Calling Line Identification (CLI) mode
The following CLI modes can be selected in the configuration mode:
000=ETSI FSK (Default setting)
001=DTMF
010=DTMF-DK
To change a CLI mode, key in 4**CLI_Mode#.
A more detailed configuation of the CLI functionality can be made using the
Nokia 22 Configurator Software.
Selecting network
To select a certain network operator a five digit operator code must be keyed in.
To select a network, key in 5**Operator_Code#.
For automatic network selection, key in 5**000#.
Changing application module extension modes
Outgoing call
To change extension mode to the outgoing call mode A, key in 6**#.
To change extension mode to the outgoing call mode B, key in 7**#.
Incoming call
To change extension mode to the incoming call mode A, key in 8**#.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 32
Page 33

Configuration
To change extension mode to the incoming call mode B, key in
9**Pre-Defined_Extension_Number#.
For further information about the application module functionality in different
outgoing and incoming modes, see “ Functionality in trunk mode” on page 24
and “ Functionality in extension mode” on page 25.
Restarting the terminal
To restart the Nokia 22, key in 555**#.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 33
Page 34

Accessories
6. Accessories
A range of accessories is available for the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal.
Contact your local dealer for information about availability of accessories.
Note: Use only accessories approved by the terminal manufacturer for
use with this particular terminal model. The use of any other types will
invalidate any approval or warranty applying to the terminal, and may
be dangerous.
When you disconnect the power cord of any accessory, grasp and pull the plug,
not the cord.
Please check with your local dealer for information about availability of approved accessories.
Nokia 22 Data Packet
Use the Nokia 22 Data Packet to send and receive SMS, PC fax, file transfer, email and Internet access at data rates of up to 43.2 kbps. For more information,
contact your local dealer, service provider or Nokia Mobile Phones.
The data packet includes:
• RS-232 data cable
• AT command set CD rom
Nokia 22 Configurator Software
Using this PC software you can configure all the Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal related settings in a Win95/Win98/Win 2000/Win NT compatible format.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 34
Page 35

Antenna adapter
The antenna adapter allows an external
antenna to be connected to the Nokia 22.
For further information, see “7. Technical
specifications” on page 36 and “ Installing
the antenna adapter” on page 23.
Backup battery set
You can connect an external backup battery BBW-4 with the power supply ACW4 to the Nokia 22.
Use the backup battery to provide terminal functionality, for example during a
power cut.
Accessories
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 35
Page 36

Technical specifications
7. Technical specifications
GSM terminal
• Dual Band GSM 900/1800
• Transmitting power max 2.0 W (GSM 900), 1.0 W (GSM 1800)
• HSCSD multi-slot data (up to 43.2 kbps)
• Small-size SIM cards supported
• D9 female connector for RS-232
• Power input range:
• Nominal 7.2 V DC
• Absolute min. 6.5 V DC
• Absolute max. 15.6 V DC
Application module
Trunk interface:
• Line voltage 50 V
• Ringing voltage 48 V
• Line impedance 600 Ohm
Extension interface:
• Off-hook AC impedance 600 Ohm
• On-hook AC impedance 150 kOhm
• On-hook DC resistance 10 MOhm
• Loop DC current min 15 mA, max 120 mA
Terminal data transfer modes
The GSM terminal supports non-transparent and transparent data connections
(HSCSD in non-transparent mode only).
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 36
Page 37

Technical specifications
Table 5: Data transfer modes
Data transfer mode Mode Data rate
Non-transparent data Asynchronous data 9600 bps
Asynchronous data 14400 bps
Asynchronous data
HSCSD
Transparent data Asynchronous data 2400 bps
Asynchronous data 4800 bps
Asynchronous data 9600 bps
Asynchronous data 14400 bps
Multi-slot (1+1, 2+2,
3+1)
• 14.4 kbps + 14.4
kbps
• 28.8 kbps + 28.8
kbps
• 43.2 + 14.4 kbps
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 37
Page 38

Technical specifications
Factory default values
Table 6: Terminal factory default values
Feature State Remarks
Short Message Service Always on Can be used with help
of AT commands
Radio Local Net Always on Network requires
maintenance software
Calling Line
Identification
User Data Always on Requires Nokia 22 Data
Intensity Of Field
strength
Automatic Local Area
Code adding
GSM Phase 2+
Supplementary Services
Dimensions 182 x 101 x 46 mm withouth dual-band antenna
Weight 420 g
On, ETSI FSK mode Nokia 22 Configurator
Software for settings
Packet
Always available To activate, dial 777**#
using DTMF telephone
Off Nokia 22 Configurator
Software for settings
Always on Depends on network
services available
Operating time with optional backup battery BBW- 4 (3 Ah)
Standby time
Talktime
Battery voltage
Power supply ACW-3
Charger type Switched mode power supply
AC mains plug type Europe, UK, US
Input voltage 100-240 V AC
DC connector 5.5. mm DC plug
Weight 75 g + cables
Volume 115 c m
Cable length AC 1500 mm, DC 1500 mm
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 38
20 h
8 h
12 V
3
Page 39

Environmental specifications
Normal operating
+15C...+35C
conditions
Extreme operating
-10C...+55C
conditions
Storage conditions
Relative humidity range under normal operating conditions
-40C...+70C
20...75% non-condensing. Relative humidity range in
storage 5...95% non-condensing. The terminal is not
protected against ingress of water or liquids of any type.
External antenna adapter specifications
Operating
frequency range
Invertion loss in
890 - 960 MHz and 1710 - 1880
MHz
1.5 dB
GSM 900 band
max.
Invertion loss in
2.0 dB
GSM 1800 band
max.
Nominal antenna
50 Ohm
cable impedance
Length 600 mm
Diameter 2.7 mm
Antenna cable
Standard fme male connector
connector
Technical specifications
External antenna specifications
Operating
frequency range
890 - 960 MHz and 1710 - 1880
MHz
Antenna gain Over 5 dBm
Electro-magnetic compatibility (Europe)
The GSM terminal is tested for electro-magnetic
compatibility (EMC) according to the ETS 300 342-1/13/
standards.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 39
Page 40

Technical specifications
The application module fullfils the ITU-T standard and the
ETS 300-001 specifications for PBX extension and trunk
connections. The module supports also ETS 300-659 Calling
Line Identification (FSK and DTMF).
If the antenna is directional, direct it towards the nearest base station. The antenna should be mounted in such a position that no part of a human body rests
too close to any part of it.
The shorter the antenna cable, the smaller the attenuation and the better the
performance of the antenna. Use a quality coaxial cable for antenna connections.
Note: External antennas or antenna cables are not provided by Nokia.
For details and availability, contact your local dealer or service provider.
Terminal connectors
GSM terminal
The GSM terminal has an RS-232 data
connector.
For the data connector pin signals and
names, see Table 7: RS-232 data connector pin signals and names.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 40
Page 41

Technical specifications
Table 7: RS-232 data connector pin signals and names
Pin Signal Name
1 DCD Carried Detect
2 RxD Received Data
3TxDTransmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal
Ready
5 GND Signal Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8CTSClear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicator
Application module
The application module has an RJ-11
trunk connector and an RJ-11 extension
connector.
For the pin functions of the trunk connector, see Table 8: RJ-11 trunk connector
pin functions.
For the pin functions of the extension
connector, see Table 9: RJ-11 extension
connector pin functions.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 41
Page 42

Technical specifications
Table 8: RJ-11 trunk connector pin functions
Pin Function
1Ground
2Service use
3RING
4TIP
5Service use
6Service use
Note: In normal use, do not connect any device to the pins 2, 5 or 6 in
order to avoid damaging the terminal.
Table 9: RJ-11 extension connector pin functions
Pin Function
1Not connected
2Not connected
3B
4A
5Not connected
6Not connected
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 42
Page 43

Security information
8. Security information
The Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal operates using wireless and land line
networks, radio signals and an electrical network. Not all connections can be
guaranteed in all conditions. Therefore, you should never rely solely on any mobile phone or radio device similar to the GSM terminal for essential communications, for example medical emergencies.
National service and emergency numbers differ from one country to another.
Emergency calls may not be possible on all wireless telephone networks or when
certain network services/product features are in use. For details, check from your
local telephone operator.
Important! For further information about the use of the Nokia 22 including important safety information, refer to the Nokia 22 User’s
Guide.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 43
Page 44

Care and maintenance
9. Care and maintenance
7KH1RNLD3%;FRQQHFWLYLW\WHUPLQDOLVDSURGXFWRIVXSHULRUGHVLJQDQG
FUDIWVPDQVKLSDQGVKRXOGEHWUHDWHGZLWKFDUH7KHVXJJHVWLRQVEHORZZLOOKHOS
\RXWRIXOILODQ\ZDUUDQW\REOLJDWLRQVDQGWRHQMR\WKLVSURGXFWIRUPDQ\\HDUV
:KHQXVLQJWKHWHUPLQDORUDQ\DFFHVVRU\
.HHSLWDQGDOOLWVSDUWVDQGDFFHVVRULHVRXWRIWKHVPDOOFKLOGUHQ©VUHDFK
.HHSLWGU\3UHFLSLWDWLRQKXPLGLW\DQGOLTXLGVFRQWDLQPLQHUDOVWKDWZLOOFRU
URGHHOHFWURQLFFLUFXLWV
'RQRWXVHRUVWRUHLWLQGXVW\GLUW\DUHDV
'RQRWVWRUHLWLQKRWDUHDV+LJKWHPSHUDWXUHVFDQVKRUWHQWKHOLIHRIHOHF
WURQLFGHYLFHVDQGZDUSRUPHOWFHUWDLQSODVWLFV
'RQRWVWRUHLWLQFROGDUHDV:KHQWKHWHUPLQDOZDUPVXSWRLWVQRUPDOWHP
SHUDWXUHPRLVWXUHFDQIRUPLQVLGHWKHWHUPLQDOZKLFKPD\GDPDJHHOHF
WURQLFFLUFXLWERDUGV
'RQRWDWWHPSWWRRSHQLW1RQH[SHUWKDQGOLQJRIWKHGHYLFHPD\GDPDJHLW
'RQRWGURSNQRFNRUVKDNHLW5RXJKKDQGOLQJFDQEUHDNLQWHUQDOFLUFXLW
ERDUGV
'RQRWXVHKDUVKFKHPLFDOVFOHDQLQJVROYHQWVRUVWURQJGHWHUJHQWVWRFOHDQ
LW:LSHLWZLWKDVRIWFORWKVOLJKWO\GDPSHQHGLQDPLOGVRDSDQGZDWHUVR
OXWLRQ
'RQRWSDLQWLW3DLQWFDQFORJWKHGHYLFHDQGSUHYHQWSURSHURSHUDWLRQ
Use only the supplied or an approved replacement or external antenna. Unauthorised antennas, modifications or attachments could damage the terminal and may violate regulations governing radio devices.
When dismounting the GSM terminal from the application module, first dis-
connect the power supply from the terminal.
'RQRWXVHLWLQDQHQYLURQPHQWZKHUHVWURQJUDGLDWLRQRUPDJQHWLFILHOGV
PD\H[LVW
'RQRWFRYHUWKHWHUPLQDORUSRZHUVXSSO\
• If the terminal or any of its accessories are not working properly, take them
to your nearest qualified service facility. The personnel will assist you, and if
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 44
Page 45

necessary and make arrangements for service
Care and maintenance
.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 45
Page 46

10. Troubleshooting
Always check light indicators when problems are encountered. For the use of
light indicators, see “ Light indicators” on page 12.
First things to check
1 Check that all line cables are connected properly.
2 Check that the power supply is firmly connected to the Nokia 22 and the AC
wall outlet.
3 Check that the antenna is firmly connected to the terminal.
Light indicator 3 is blinking
The Nokia 22 is not in service. The terminal is not connected to the network, the
signal is too weak or the antenna is not connected to the terminal.
Replace the receiver and wait for a while, then try again. You can also move the
terminal to another location and then try again. See also “ No tone can be heard
when you lift the receiver” on page 46.
No tone can be heard when you lift the receiver
Disconnect the power supply from the Nokia 22. Wait for 10 seconds. Reconnect
the power supply to the terminal. Operation succeeds when light indicator 3 is
lit continuously and you hear the dial tone.
Note: If the AutoPIN feature is disabled or the SIM card is installed for
the first time, the enter PIN code tone is heard. Enter the PIN code. After
that you should hear a dial tone within 30 seconds.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 46
Page 47

Troubleshooting
Call is disconnected immediately after answering
Check that the antenna is properly connected to the Nokia 22. If the terminal is
still not working, contact the local dealer, service provider or the nearest Nokia
Mobile Phones representative.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 47
Page 48

Appendix: Supplementary
services
Supplementary services are network services. They are cellular services provided
by network operators and therefore differ from one network to another.
Supplementary services provide the subscriber with an opportunity to control
incoming and outgoing phone calls. The Nokia 22 PBX connectivity terminal
supports the following GSM Phase 2 + supplementary services.
• Number identification
• Call offering
• Call completion
• In-call handling
• Call restriction
• Security options
• Call transfer
Note: The call offering supplementary service and the call restriction
supplementary service cannot be deactivate at the same time.
How the supplementary services work
The activation, deactivation, request and registration of a supplementary service
function in the same way as in a mobile phone. The dialled supplementary service sequence will be executed after 4 second’s dial time-out. The Nokia 22 responds to a supplementary service activation, deactivation, request and
registration by sending OK or error tones from the telephone set’s receiver.
Number identification
Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP)
The CLIP (Calling Line Identification Presentation) feature displays the caller’s
number on an external CLI (Calling Line Identity) device. The CLI device must be
connected between the Nokia 22 and the DTMF telephone. In order to connect
the CLI, signalling mode must be activated.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 48
Page 49

Troubleshooting
Note that the CLIP function usually has to be activated by the network operator.
To request this function, key in *#30#.
Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR)
The CLIR (Calling Line Identification Restriction) feature offers the user an opportunity to prevent his/her number from being shown to the B subscriber.
The network operator sets the CLIR either to ON or OFF state for the subscriber.
It is also possible to revert to the CLIR status for one call at a time.
If, for example the CLIR is disabled (that is a phone number will be shown to the
called person), invoke the CLIR by keying in #31#PhoneNumber
The phone makes a normal call to the PhoneNumber but the B subscriber will
not be able to see the Nokia 22 phone number.
If the CLIR has been set permanently to the ON state (that is the phone number
is normally never shown to the B subscriber), key in *#31# to show the number.
.
Call forwarding (Call offering)
These functions allow the user to forward incoming calls.
Table 10: Call forwarding functions
Function Request Activation Deactivation
Call forwarding:
Unconditional (CFU)
Call forwarding:
Busy (CFB)
Call Forwarding:
No reply (CFNRy)
Call Forwarding:
Not reachable
(CFNRc)
• Unconditional call forwarding, also called call offering, allows incoming calls
to be directed to another number (network service).
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 49
*#21# *21*PhoneNumber# ##21#
*#67# *67*PhoneNumber# ##67#
*#61# *61*PhoneNumber# ##61#
*#62# *62*PhoneNumber# ##62#
Page 50

• Busy call forwarding allows the subscriber to direct incoming calls to another
number when the telephone set is busy. Usually, the CFB service has to be
first activated by calling the operator’s service number (network service).
• No reply call forwarding enables the subscriber to direct incoming calls to
another number when the calls are not answered. Usually the CFNRy service
has to be first activated by calling the operator’s service number (network
service).
• Not reachable call forwarding allows the subscriber to direct incoming calls
to another number when the network is not in service or the terminal is powered off. Usually the CFNRy service has to be first activated by calling to the
operator service number (network service).
Call waiting (Call completion)
Call waiting, also called call completion, alerts the subscriber of another incoming call during a phone call (network service).
To request call waiting, key in *#43#.
To activate call waiting, key in *43#.
To deactivate call waiting, key in #43#.
In-call handling
These functions allow the user to switch between phone calls. The service is controlled by the R (register recall) button.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 50
Page 51

Troubleshooting
Table 11: In-call handling functions
Function Action
Call in progress, release call waiting 0R
Answer call waiting, release active call 1R
Answer call waiting, hold active call 2R
Switch between active and held call R
Release active call 1R
Release held call 0R
Release all calls but waiting call On-hook
Hold active call and set up new call R number
Call restriction
To activate or deactivate the barring of supplementary services, the user needs
the network password from the network operator.
Table 12: Call restriction functions
Function Request Activation Deactivation
Barring of all
outgoing calls
Barring of all
international
calls
Barring of all
incoming calls
*#33# *33*NetworkPassword# #33*NetworkPassword#
*#331# *331*NetworkPassword# #331*NetworkPassword#
*#35# *35*NetworkPassword# #35*NetworkPassword#
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 51
Page 52

Important!
Restricting calls in some networks may restrict the ability to make
emergency calls. If this is the case in your network, ALL USERS OF
THE TERMINAL MUST BE INFORMED by appropriate warning signs
on ALL phones connected to the terminal.
The effect of call restriction varies among networks so each operator must provide its own warning signs that accurately describe any
emergency restrictions.
Test the effect of call restriction on calls to your local emergency
number(s) and warn as needed.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 52
Page 53

Security options
These functions provide the user with security options.
Table 13: Functions of security options
Security function Action
Change PIN **04*Old_PIN*New_PIN*New_PIN#
Change PIN2 **042*Old_PIN2*New_PIN2*New_PIN2#
Troubleshooting
Change PIN2 when
PIN2 is not known
To unblock PIN Enter PUK code and press #. Enter a new PIN code and press #.
To change registration
password
To change all barring
service password
To change outgoing
barring service
password
To change incoming
barring service
password
1) The Password Control Code (PCC) is needed to change the password. The PCC code can
1
1
1
be requested from the network operator.
**052*PUK2*New_PIN2*New_PIN2#
Verify the new PIN code and press #.
*03*PCC*Old_NetworkPassword*New_NetworkPassword*
New_NetworkPassword#
*03*330*PCC*Old_NetworkPassword*New_NetworkPassword*
1
New_NetworkPasswd#
*03*333*PCC*Old_NetworkPassword*New_NetworkPassword*
New_NetworkPassword#
*03*353*PCC*Old_NetworkPassword*New_NetworkPassword*
New_NetworkPassword#
If entering the PIN code does not succeed, refer to “ Entering PIN code does not
succeed” on page 30 for further information.
Call transfer
To transfer a call to a different number:
1 Hold the active call by pressing R (register recall).
2 Dial the new number to which the call is to be transferred.
3 Press 4 and the R (register recall) button.
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 53
Page 54

Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
AAC Automatic Area Code
AC Alternating Current
CLI Calling Line Identification
DC Direct Current
DTMF Dual Tone Multi Frequency
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
ETSI European Telecommunications
Standards Institute
FSK Frequency Shifting Keying
FR Full Rate
GSM Global System Mobile
HR Half Rate
HSCSD High Speed Circuit Switched Data
IOF Intensity of Field
MO Mobile Originated
MT Mobile Terminated
PBX Private Branch Exchange
PC Personal Computer
PIN Personal Identification Number
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
PUK PIN Unblocking Key
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SMS Short Message Service
©2001 Nokia Mobile Phones. All rights reserved. 54
 Loading...
Loading...