Page 1

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Serial Communications Protocol Definition
Project: MC-12/MC-12B
Updated: June 10, 2003
Software Version 3.0
Lexicon, Inc.
3 Oak Park
Bedford, MA 01730-1413
(781) 280-0300
Protocol Version:
Major rev 1
Minor rev 5
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 of 94
Page 2

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories. “Dolby”, “Pro Logic”, and the double-D
symbol are trademarks of Dolby laboratories.
Lucasfilm and THX are trademarks or registered trademarks of Lucasfilm, Ltd.
© Lucasfilm, Ltd. & TM. Surround EX is a jointly developed technology of THX and Dolby
Laboratories, Inc. and is a trademark of Dolby Laboratories, Inc. All rights reserved. Used under
authorization.
Manufactured under license from Digital Theater Systems, Inc. U.S. Pat. No. 5,451,942;
5,956,674; 5,974,380; 5,978,762 and other world-wide patents issued and pending. “DTS”, “DTSES Extended Surround” and “Neo:6” are trademarks of Digital Theater Systems, Inc. © 1996,
2000 Digital Theater Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
“LOGIC7” and the LOGIC7 symbol are registered trademarks of Lexicon, Inc., a Harman
International Company.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved.
This document should not be construed as a commitment on the part of Lexicon, Inc. The
information it contains is subject to change without notice. Lexicon, Inc. assumes no responsibility
for errors that may appear within this document.
Lexicon, Inc.
3 Oak Park
Bedford, MA 01730-1413 USA
Tel 781-280-0300
Fax 781-280-0490
www.lexicon.com
Customer Support
Tel 781-280-0300
Fax 781-280-0495 (Sales)
Fax 781-280-0499 (Service)
Lexicon Part No. 070-15859 REV 3
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 2 of 94
Page 3

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1Documents 6
1.1 Change List 6
2 Definitions 6
2.1 Protocol Version Cross-reference 6
3 Abbreviations 6
4 General Description 7
5 Physical Layer 8
DB-9 RS232 Connector 8
5.2 Serial Port Driver 8
5.3 Errors 8
5.4 MC-12 Receive Buffer 8
5.5 MC-12 Hardware Verification (V1.10, Not Supported in MC-12 V1.00, V1.01) 8
6 Data Link Layer 9
6.1 Errors 9
7 Application Layer 10
7.1 MC-12 Asynchronous Notification Packets 10
7.1.1 Wakeup Notification (MC-12, MC-1) 10
7.1.2 Sleep Notification (MC-12, MC-1) 10
7.1.3 Front Panel Display (MC-12, MC-1) 10
7.1.4 MC-1 Parameter Change (MC-12, MC-1) 11
7.1.5 MC-12 Parameter Notification by Id (MC-12) 13
7.2 Acknowledgment Packets 14
7.2.1 Acknowledge (MC-12, MC-1) 14
7.2.2 No Acknowledge (MC-12, MC-1) 15
7.3 Host Initiated Command Packets 15
7.3.1 Reset Unit (MC-12, MC-1) 15
7.3.2 Restore (MC-12, MC-1) 15
7.3.3 MC-1 Send IR Command (MC-12, MC-1) 16
7.3.4 Get Unit Configuration (MC-12, MC-1) 16
7.3.5 Get System Status (MC-12, MC-1) 19
7.3.6 Get Zone 2 Status (MC-12, MC-1) 21
7.3.7 Get System Parameter Definition (MC-1) 22
7.3.8 Get System Parameter Values (MC-1) 22
7.3.9 Get Effect Definition by Id (MC-1) 22
7.3.10 Get Effect Parameter Definition (MC-1) 22
7.3.11 Get Effect Parameter Values (MC-1) 22
7.3.12 Get Custom Name (MC-12, MC-1) 22
7.3.13 Get Input Name by Id (MC-12, MC-1) 23
7.3.14 Get FPD Control Registers (MC-1) 23
7.3.15 Set System Parameter Values (MC-1) 24
7.3.16 Set Effect Parameter Values (MC-1) 24
7.3.17 Set Effect Name by Effect Id (MC-1) 24
7.3.18 Set System Volume (MC-12, MC-1) 24
7.3.19 Set Main Balance (MC-12, MC-1) 24
7.3.20 Set Front/Back Balance (MC-12, MC-1) 25
7.3.21 Set Active Effect by Id (MC-12, MC-1) 26
7.3.22 Set Record Input (MC-12, MC-1) 26
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 of 94
Page 4

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.23 Clear Record Input (MC-12, MC-1) 27
7.3.24 Set Zone2 Volume (MC-12, MC-1) 27
7.3.25 Set Zone2 Left/Right Balance (MC-12, MC-1) 28
7.3.26 Set Custom Name (MC-12, MC-1) 29
7.3.27 Set Input Name by Id (MC-12, MC-1) 29
7.3.28 Set FPD Control Registers (MC-1) 30
7.3.29 Host Wakeup (MC-12, MC-1) 30
7.3.30 Host Sleep (MC-12, MC-1) 31
7.3.31 Get Communication Configuration (MC-12, MC-1) 31
7.3.32 Set Communication Configuration (MC-12, MC-1) 32
7.3.33 Set Mute (MC-12, MC-1) 32
7.3.34 Set Output Level Adjustments (MC-1) 33
7.3.35 Send Display String Command (MC-12, MC-1) 33
7.3.36 MC-12 Get Parameter Definition by Id (MC-12) 34
7.3.37 MC-12 Set Parameter Value by Id (MC-12) 36
7.3.38 MC-12 Set Parameter Value by Id, No Run (MC-12) 38
7.3.39 MC-12 Get Unit Configuration (MC-12) 38
7.3.40 MC-12 Send IR Command (MC-12) 41
7.3.41 MC-12 Get Parameter Value by Id (MC-12) 41
7.3.42 MC-12 Set Parameter Notification by Id (MC-12) 42
7.3.43 MC-12 Parameter Get Value String by Id (MC-12) 43
7.3.44 MC-12 Clear All Parameter Notifications (MC-12) 44
7.3.45 MC-12 Get System Status (MC-12) 44
7.3.46 MC-12 Get Record Status (MC-12) 46
7.3.47 MC-12 Set System Volume (MC-12) 47
7.3.48 MC-12 Set Main Balance (MC-12) 47
7.3.49 MC-12 Set Front/Back Balance (MC-12) 48
7.3.50 MC-12 Set Active Effect by Id (MC-12) 48
7.3.51 MC-12 Set Record Input (MC-12) 49
7.3.52 MC-12 Set Zone2 Volume (MC-12) 50
7.3.53 MC-12 Set Zone2 Left/Right Balance (MC-12) 50
7.3.54 MC-12 Get Input Name by Id (MC-12) 51
7.3.55 MC-12 Set Input Name by Id (MC-12) 52
Appendix A Command Codes 53
Appendix B Error Codes 55
Appendix C DC-2, MC-1 IR-Codes 57
Appendix D MC-12 IR Codes 58
Appendix E MC-1 Input Id’s 59
Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids 59
Appendix G Protocol Constants 59
Appendix H MC-12 to MC-1 Effect Map 60
Appendix I MC-1 to MC-12 Effect ID Map 61
Appendix J MC-12 Mode Ids 62
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 4 of 94
Page 5

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Application Notes and Examples 63
1.1 Box initializations: 63
1.1.1 MC-12: 63
1.1.2 HOST: 63
1.2 Getting System Wide Status and Setup: 63
1.1 Downloading the System Setup to the 63
1.3 MC-12: 63
1.4 Simple System Control & System Status: 63
1.5 Examples: 65
1.5.1 MC-12 Get Unit Configuration 65
1.5.2 Send MC-1 IR Command Example 66
1.5.3 Send MC-12 IR Command Example 67
1.6 MC12 V2.00 Parameter ID List 67
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 5 of 94
Page 6

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1 Documents
The following documents should also be used with this document to understand how this protocol can be
used with an MC-12.
070-13227 MANUAL,OWNER'S,DC2
070-13278 MANUAL,OWNER'S,MC1
MC1/DC2 Serial Port Definition, Protocol Version 0.5
070-14773 Manual, Owner’s, MC12/MC12B
1.1 Change List
9/23/02 Added this paragraph.
9/23/02 Changed “7.9 MC12 V1.10 Parameter ID List” to “7.9 MC12 V2.00 Parameter ID List”
9/23/02 Updated Parameter Id Reference Table 7.9 MC12 V2.00 Parameter ID List for V2.00 s/w.
9/23/02 Updated Appendix J MC-12 Mode Ids for new V2.00 modes.
9/24/02 Updated 7.3.36.4 Parameter Definition Response Packet for correct CurrentValue length.
9/24/02 The range of the PARAM_TYPE_UINT32 parameter type has been corrected.
9/24/02 Updated Appendix H MC-12 to MC-1 Effect Map to reflect added modes in V2.0.
9/24/02 Updated Appendix I MC-1 to MC-12 Effect Map to reflect added modes in V2.0.
10/2/02 Updated Appendix D MC-12 IR Codes to reflect added button functionality for V2.0.
6/10/03 Updated Parameter Id Reference Table 7.9 MC12 V3.00 Parameter ID List for V3.00 s/w.
6/10/03 Updated Appendix J MC-12 Mode Ids for new V3.00 modes.
6/10/03 Updated 7.1.4 MC-1 Parameter Change (MC-12, MC-1) to reflect the disabled default state.
6/10/03 Added paragraph 7.1.5.4 Defaults to show parameters that are defaulted for notification.
2 Definitions
User Parameter: A user changeable variable that stores a specific value that describes an
operating condition for the MC-12 system.
HOST: The device initiating or receiving the serial communication packets to/from the
MC-12.
MC-12 ,MC-1,DC-2: The Lexicon product receiving or transmitting the serial communication packets
to/from the HOST.
Nonvolatile RAM: The area of memory in an MC-12 that stores users adjustable parameters. The
Nonvolatile RAM is battery backed, to maintain values during MC-12 power
down.
2.1 Protocol Version Cross-reference
All references to MC-12 shall be valid for both the MC-12 and SDP-40 products unless specifically
documented otherwise. All references to MC-1 shall be valid for the MC-1, DC-2 and SDP-3 products
unless specifically documented otherwise.
3 Abbreviations
SOP Start of Packet
EOP End of Packet
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 6 of 94
Page 7
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
ACK Acknowledge
NAK No Acknowledge
FPD Front Panel Display
4 General Description
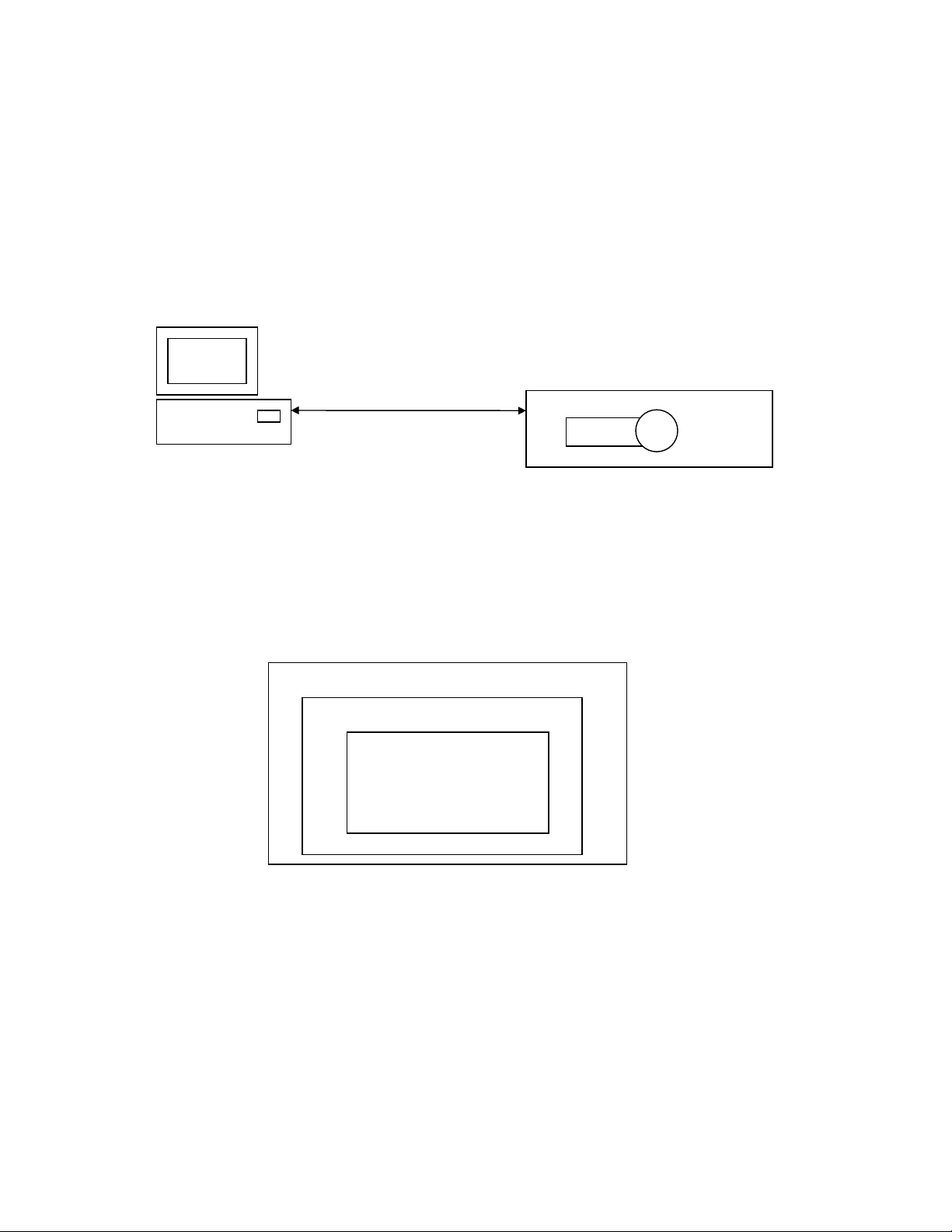
The intention of the MC-12 serial port and protocol communication is for an external connected HOST to
control and obtain status from the MC-12. The protocol has been designed to focus on two specific goals.
The first is HOST uploading and downloading of MC-12 configuration, and system/effect setups. The
second is HOST control of basic user adjustable parameters.(i.e. input, volume, balance…)
Rs-232 Serial Link
HOST
The MC-12 uses simple notification, command, response and acknowledgment packets to have
communication transactions with a given HOST. This protocol is designed for point to point
communication between a HOST and MC-12. The MC-12 Protocol is a 3 layered system. The MC-12
serial protocol allows for the MC-12, or the HOST, to initiate a communication transaction. Most
transactions are initiated by the HOST. MC-12 then responds to the HOST command with either a response
or acknowledgment packet. There are a few asynchronous notifications that MC-12 initiates indicating
system changes. Each transaction initiated must wait for a corresponding response before initiating the next
transmission.
The 3 protocol layers are: Physical, Data Link, and Application Layers.
Physical Layer (RS232)
Data Link Layer
Application Layer
Lexicon MC-12
CD VOL
The MC-12 Serial Protocol attempts to be as backward compatible with the MC-1 as possible. This
document will try to inform the user/programmer of the consistencies and differences between the MC-1
protocol and the MC-12 protocol. The basic structure of the protocol has not changed. A number of
command/responses/notifications packets have been implemented exactly as they were in the MC-1. These
commands may not fully exercise the functionality of the MC-12 (i.e. Mc-1 has 8 inputs that have been
mapped to 8 of the 12 inputs on the MC-12, MC-1 IR codes are not the same as MC-12 IR codes) In the
case of these commands additional MC-12 commands have been added to fully implement the MC-12
functionality. In addition, some the internal structure of the MC-12 has forced the protocol to be unable to
support some MC-1 commands. These commands have been totally replaced with new commands that
provide more control over the MC-12 than was capable in the MC-1. (Parameter Set/Get commands)
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 7 of 94
Page 8
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
5 Physical Layer
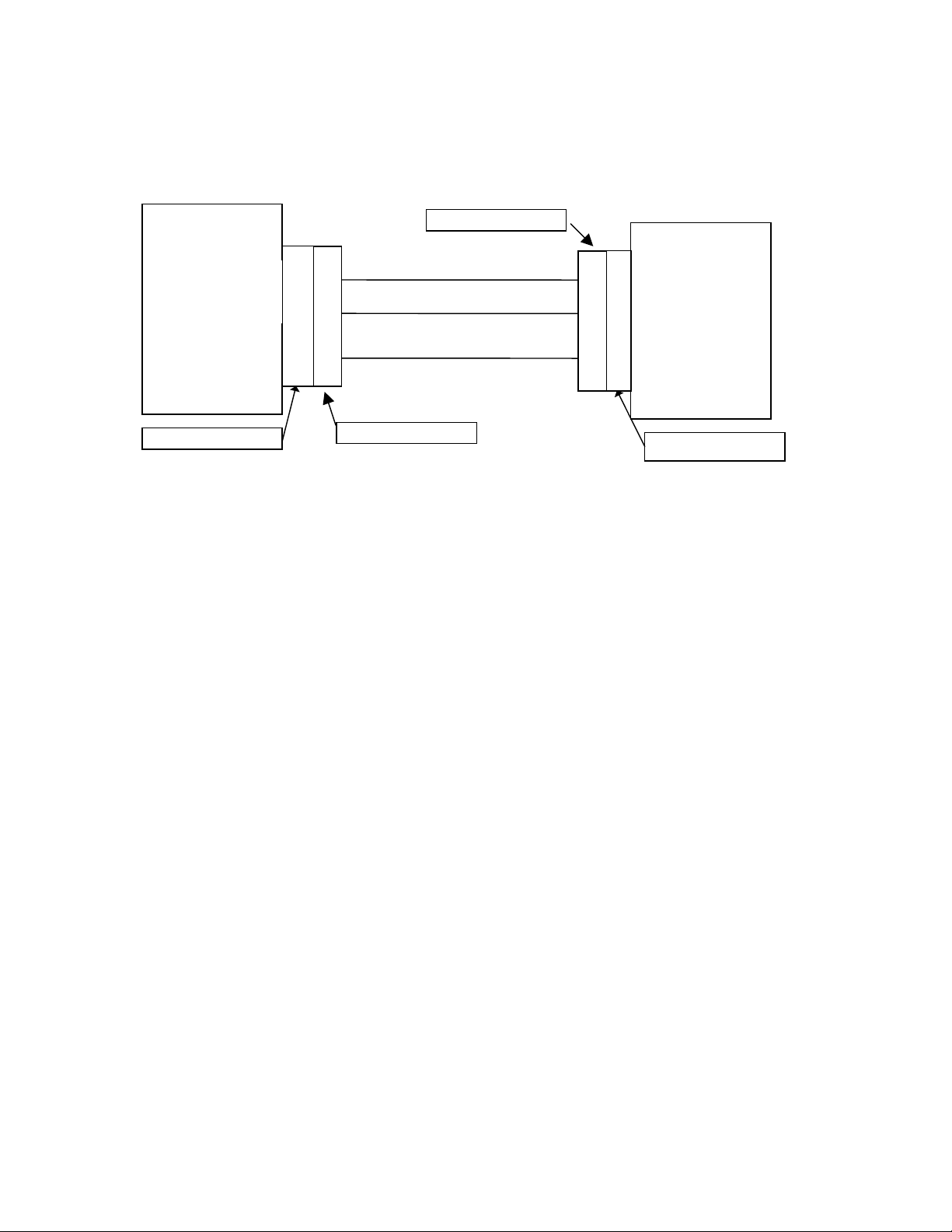
5.1 DB-9 RS232 Connector
MC-12
COM1
Transmit Data
Receive Data
Ground
9 Pin D-Shell (female)
Note: The wiring requirements for a 9 pin to 9 pin serial connection, are a male to female straight through
cable.
2
2
3
3
5
5
9 Pin D-Shell (male)
9 Pin D-Shell (female)
2
2
3
3
5
5
Host
Receive Data
Transmit Data
Ground
9 Pin D-Shell (male)
5.2 Serial Port Driver
MC-12 serial port has been setup to operate as follows:
Operating Mode: Full Duplex
Baud rate: 19.2K baud
Data Size: 8 bits (1 byte)
Parity: Odd
Stop Bits: 1
Hardware Handshaking: None
5.3 Errors
The MC-12 will detect parity, framing and data overrun errors. If any of the physical layer errors are
detected, the complete packet is corrupted and the MC-12 will reset the transaction and begin to look for a
start of packet byte.
5.4 MC-12 Receive Buffer
The MC-12 has an internal receive buffer. The buffer is 256 Bytes and will transmit a NAK packet with an
error code of DC_ERR_BUFFER_FULL to the HOST if the buffer is full. If the buffer is full, all data
transmitted to the MC-12 will be ignored. Therefore, making the currently transmitted packet, if partially
transmitted invalid.
5.5 MC-12 Hardware Verification (V1.10, Not Supported in MC-12 V1.00, V1.01)
This test verifies the RS232 ports are working by comparing the transmitted signal (at pin 2) to the received
signal (at pin 3). The MC-12 transmits a known test signal just following a power up. The MC-12 monitors
the serial port receivers while transmitting the test signal. If the signals are the same, the test passes. In
order to test this circuit, RS232 Wraparound plug(s) are needed and must be installed at the female D9
connector(s) on the rear panel of the MC-12 labeled “RS232”. The wraparound plug shorts pins 2 to 3,
allowing for the MC-12 to receive the signal it is transmitting. Once installed, power cycle the MC-12 and
verify the following message is displayed on the FPD:
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 8 of 94
Page 9

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
SERIAL PORT A PASSED
SERIAL PORT B PASSED
This message is displayed for about 2 seconds before entering normal operating mode. If no messages are
displayed, then both wrap tests failed.
6 Data Link Layer
The data link layer is used to define a transmission packet. The layer appends a header and tail that
encloses the transmitted application packet data. The data link header will contain the start of packet byte
and count of bytes to follow. The data link tail will contain the end of packet byte.
Data Link Header:
Byte Number Description Value
First Byte(0) Start of Packet (SOP) 0xF1
Byte(1) DLL Data Count nn
Application Header:
Byte(2) Command nn
Byte(3)
Application Data:
Byte(4) Data[0] nn
Byte(5) Data[1] nn
… Data[…] nn
Last Data Byte -1 Data[Data Count -1] nn
Data Link Tail:
Last Byte End of Packet (EOP) 0xF2
APP Data Count (number of application data bytes to
Follow) nn
6.1 Errors
If the number of DLL data bytes received is the same as the data count and an EOP has not been received,
the MC-12 responds by transmitting a NAK packet with an error code DC_ERR_INVALID_PACKET.
The MC-12 then continues to look for a SOP byte and will not process the erroneous application packet.
The HOST can use this as an indicator to retransmit the corrupted packet.
In addition, each byte of a packet must be received sequentially and within the INTER_PACKET_TIME. If
any of the bytes within a packet transmission exceeds the INTER_PACKET_TIME, the MC-12 will
respond by transmitting a NAK packet with an error code DC_ERR_INVALID_PACKET. The MC-12
then continues to look for a SOP byte and will not process the erroneous application packet. The HOST
can use this as an indicator to retransmit the corrupted packet.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 9 of 94
Page 10

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7 Application Layer
7.1 MC-12 Asynchronous Notification Packets
MC-12 has been designed to transmit the asynchronous notification packets following these system
changes:
1. Power On
2. Entering Standby
3. Front Panel Display update
4. Parameter Value Changes.
The notification packets are defined as follows:
7.1.1 Wakeup Notification (MC-12, MC-1)
By transmitting the Wakeup Notification, MC-12 indicates the unit has just “powered on” or reset and is
ready to receive host commands. This notification is primarily for the HOST to know the status of the MC-
12.
7.1.1.1 Notification Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_WAKEUP 0x01
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.1.1.2 Host Response
The MC-12 does not expect any response from the HOST.
7.1.2 Sleep Notification (MC-12, MC-1)
By transmitting the Sleep Notification, MC-12 indicates the unit is shutting down into a standby mode.
Because the hard power switch could be activated independently of the MC-12 system software, hard power
down will not be notified. Acknowledgment of the Sleep Notification is not required. This notification is
primarily for the HOST to know the operating status of the MC-12.
7.1.2.1 Notification Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_SLEEP 0x02
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.1.3 Front Panel Display (MC-12, MC-1)
MC-12 will transmit the front panel display buffer following the update to the MC-12 front panel display.
The MC-12 front panel display is 2 X 20 ASCII character display. The HOST can enable transmission of
this notification message by sending Host Wakeup (7.3.29). To disable transmission the HOST can send
Host Sleep (7.3.30). Transmission of the display buffer is asynchronous to other host/MC-12
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 10 of 94
Page 11

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
communication and will only transmit following the completion of any communication exchanges in
progress or pending.
7.1.3.1 Notification Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_FPD 0x03
Data Count 42 0x2A
Application Data:
Data[0] - Data[20] Line1 ch ch ch… 0x00
Data[21] - Data[41] Line2 ch ch ch … 0x00
7.1.3.2 Data Description
Line1
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: DISP_LINE_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
Line2
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: DISP_LINE_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
The MC-12 includes 8 custom characters that are defined to display increments of a display block. (i.e.
Volume Bar) The custom characters are ASCII character codes 8E - 93(hex). The codes are used as
follows:
'8E' - empty cell
'8F' - left 1 bar
'90' - left 2 bars
'91' - left 3 bars
'92' - left 4 bars
'93' - full cell
7.1.3.3 HOST Response
The MC-12 does not expect any response from the HOST.
7.1.4 MC-1 Parameter Change (MC-12, MC-1)
MC-12 will transmit predetermined parameter change notifications. If a parameter value is changed due to
any user action or system action the MC-12 will transmit the current value of the parameter that is changing.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in the
Supported System Parameters table listed below.
The MC-12 with s/w V3.0 will disable this notification by default.
This notifications can be enabled and disabled by using the commands described in 7.3.31 Get
Communication Configuration (MC-12, MC-1) and 7.3.32 Set Communication Configuration (MC-12,
MC-1).
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 11 of 94
Page 12
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.1.4.1 Notification Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_PARAM_CHG_MSG 0x04
Data Count 2 0x02
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId nn
Data[1] Value nn
7.1.4.2 Data Description
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Max: 255.
Value:
The Current Value for this system parameter.
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Max: Set by the Max Value per the Parameter Definition response Packet for
the Parameter Id of this packet.
7.1.4.3 HOST Response
The MC-12 does not expect any response from the HOST.
7.1.4.4 Supported System Parameters
The following parameters will be supported by this Parameter Change Notification:
Parameter MC-12 Parameter
Name
Current Effect PROGRAM 1
Mute MUTE 3
System Volume VOLUME 5
Balance LR_BALANCE 6
Input Selection INPUT 7
Record/Zone 2 On/Off RECORD_ENABLED 18
Zone 2 Volume Z2_VOL 154
Zone 2 Balance Z2_BAL 156
Zone 2 Mute Z2_MUTE 157
Bass BASS 167
Treble TREBLE 168
Loudness LOUDNESS 169
Tilt TILT 174
Menu Background On/Off MENU_BKGND 190
Note: The Record/Zone 2 On/Off only applies to the MC-12 Record zone. The Zone 2 Volume, Zone 2
Balance and Zone 2 Mute only apply to the MC-12 Zone-2.
For Input Parameter Change Notifications the Input Value is a MC-12 to MC-1 input mapping, as shown in
Appendix F MC-12 Input Id's.
MC-1
ParamId(V4.00)
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 12 of 94
Page 13

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.1.5 MC-12 Parameter Notification by Id (MC-12)
MC-12 will transmit parameter change notifications if they are enabled using the command described in
7.3.42 (MC12_Set_Parameter_Notification_By_Id). If a parameter value is changed due to any user action
or system action the MC-12 will transmit the current value of the parameter that is changing.
7.1.5.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_PARAM_NOTIFICATION_BY_ID 0x05
Data Count 24 0x18
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId(LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId(MSB) nn
Data[2] ParamType nn
Data[3-23] Value[0 -20]
7.1.5.2 Data Description
Same as Paragraph 7.3.37.2
7.1.5.3 HOST Response
The MC-12 does not expect any response from the HOST.
nn nn
nn…
7.1.5.4 Defaults
The following Parameters Notifications are Enabled in the MC-12 default state:
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 13 of 94
Page 14
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Parameter MC-12 Parameter Name
Current Mode
PARAM.MAIN.EFFECT
Main Zone Mute
Main Zone Volume
Main Zone Balance
Main Zone Input Selection
Zone 2 Input
Zone 2 Volume
Zone 2 Balance
Zone 2 Mute
Bass
Treble
Loudness
Tilt
Menu Background On/Off
PARAM.MAIN.MUTE
PARAM.MAIN.VOLUME
PARAM.MAIN.BALANCE
PARAM.MAIN.INPUT
PARAM.ZONE.INPUT
PARAM.ZONE.VOLUME
PARAM.ZONE.BALANCE
PARAM.ZONE.MUTE
PARAM.MAIN.BASS
PARAM.MAIN.TREBLE
PARAM.MAIN.LOUDNESS
PARAM.MAIN.TILT
PARAM.OSD.BACKGND
See MC12 V3.00 Parameter ID List for the Parameter ID definitions.
7.2 Acknowledgment Packets
Acknowledge and No Acknowledge packets are used to communicate transmission, packet and data
validation status. Both the HOST and MC-12 can transmit and receive these packets.
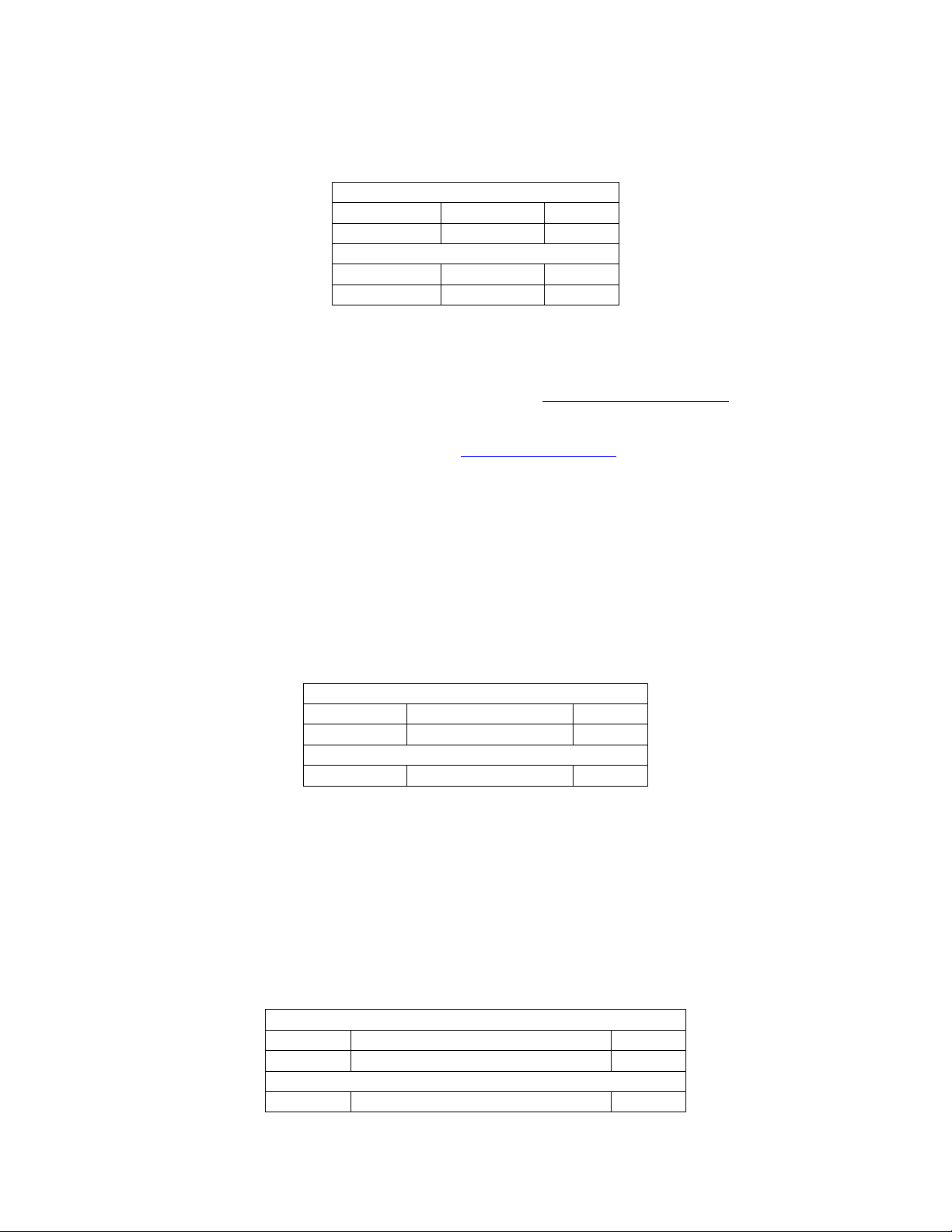
7.2.1 Acknowledge (MC-12, MC-1)
7.2.1.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_ACK 0xE0
Data Count 10x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Command nn
7.2.1.2 Data Description
Command:
DataType: Valid MC-12 command as defined in Appendix A Command Codes.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 14 of 94
Page 15
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.2.2 No Acknowledge (MC-12, MC-1)
7.2.2.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_NACK 0xE1
Data Count 20x02
Application Data:
Data[0] Command nn
Data[1] ErrorCode nn
7.2.2.2 Data Description
Command:
DataType: Valid MC-12 command as defined in Appendix A Command Codes.
ErrorCode:
DataType: Error code as defined in Appendix B Error Codes.
7.3 Host Initiated Command Packets
The MC-12 serial communication protocol has been designed to respond to the following commands as
described below. Each command is transmitted to the MC-12 with the identified parameters. If the
command is successfully received and processed by the MC-12, the unit will respond with the described
response packet or action.
7.3.1 Reset Unit (MC-12, MC-1)
Commands the MC-12 to soft reset.
7.3.1.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_RESET 0x10
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.1.2 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will perform an internal reset. After reset the MC-12 will go through a soft power-up
initialization. This includes transmitting the “Wakeup Notification Packet”. A soft reset does not
reinitialize the MC-12. Nonvolatile RAM is maintained.
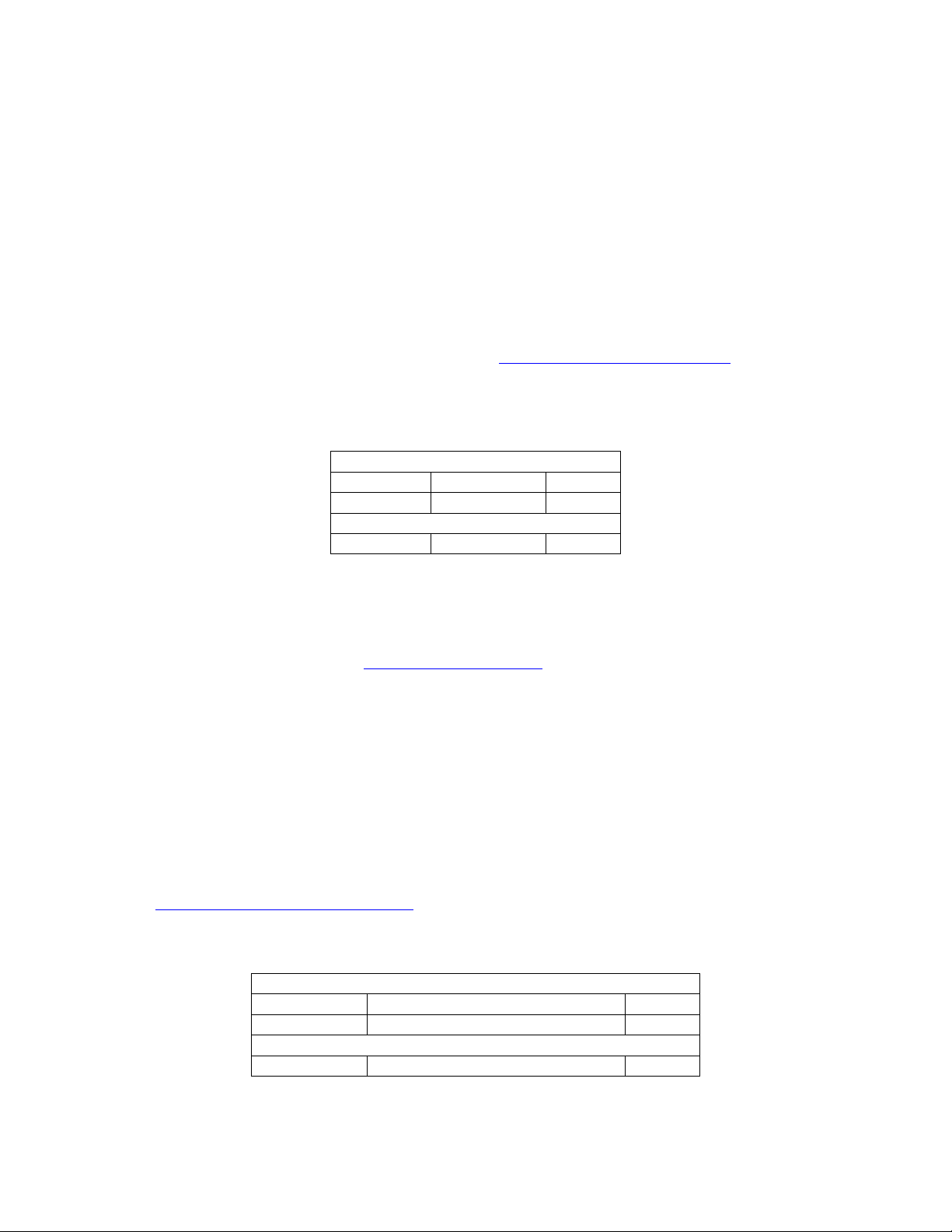
7.3.2 Restore (MC-12, MC-1)
Commands the MC-12 to restore the system and effect parameters to the factory defaults.
7.3.2.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_RESTORE_DEFAULTS 0x13
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 15 of 94
Page 16
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.2.2 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will reset, clear any saved system and effect parameters in Nonvolatile RAM, and restore the
factory default system and effect parameters. After reset the MC-12 will go through a soft power-up
initialization. This includes transmitting the “Wakeup Notification Packet”.
7.3.3 MC-1 Send IR Command (MC-12, MC-1)
Transmits MC-1 IR command key codes to the MC-12.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility to the MC-1. The MC-1 IR code
functionality has been mapped to the MC-12 IR code functionality as per the MC-1 to MC-12 IR code
table. MC-12 users should use the command described in 7.3.40 (MC-12_Send_IR_Command).
7.3.3.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_IR 0x14
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] KeyCode nn
7.3.3.2 Data Description
KeyCode:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Valid Values: Appendix C MC-1 IR-Codes
7.3.3.3 MC-12 Response
The KeyCode is processed as a valid IR code. No acknowledgment will be sent from MC-12.
7.3.3.4 Data Validation
The KeyCode data will be verified as a legal IR code. If the Code is not valid the MC-12 will not respond.
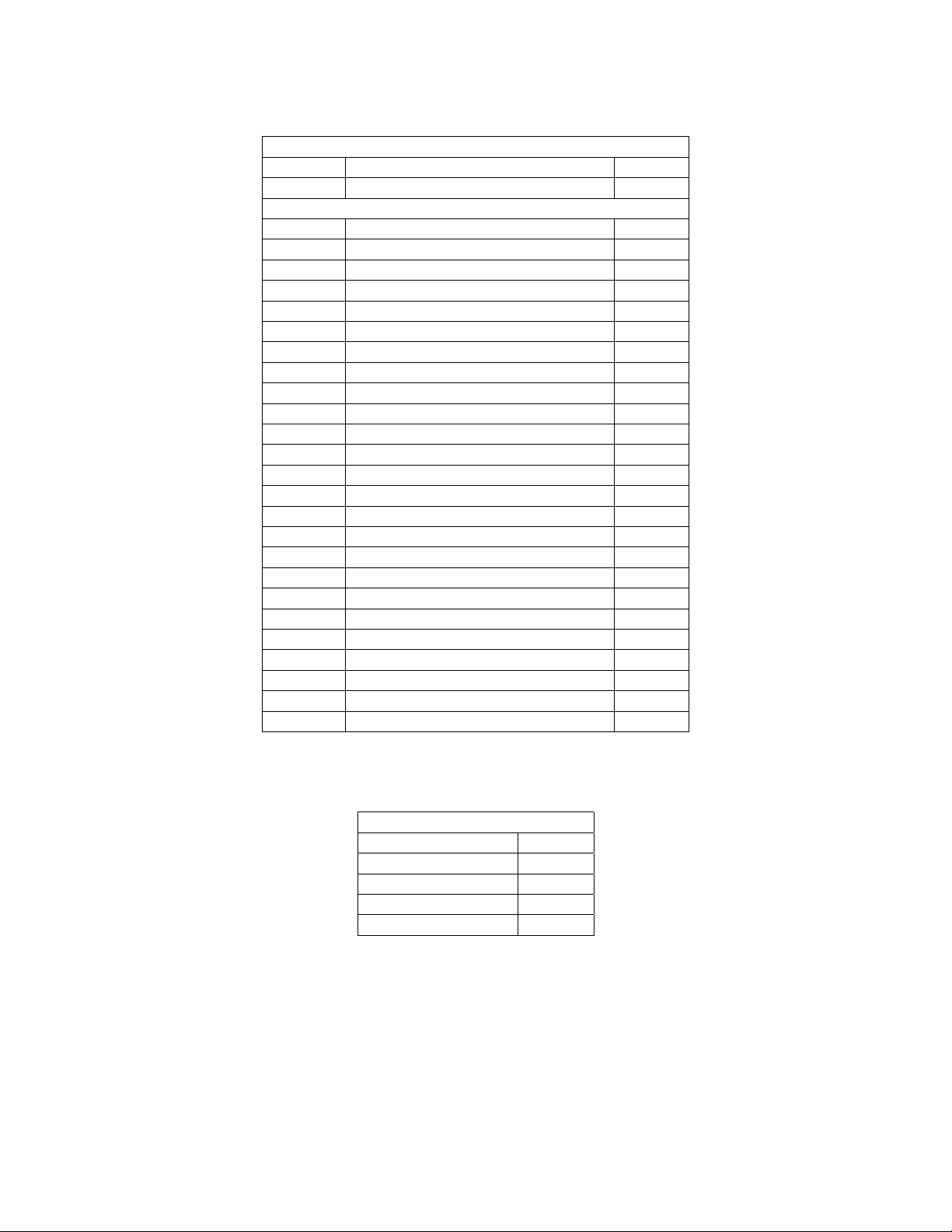
7.3.4 Get Unit Configuration (MC-12, MC-1)
Request to MC-12 for its current unit configuration.
This command is supported for backward compatibility. MC-12 users should use the command described
in 7.3.39 (MC-12_Get_Unit_Configuration). MC-12 will respond with “Unit Configuration Packet”. The
HOST should use this information to determine if any information saved by the HOST is current.
7.3.4.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_GET_CONFIG 0x15
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 16 of 94
Page 17
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.4.2 MC-12 Unit Configuration Response Packet
Application Header:
Command DC_RESP_UNIT_CONFIG 0x80
Data Count 25 0x19
Application Data:
Data[0] ProductId nn
Data[1] Software Type nn
Data[2] Software Level nn
Data[3] Software Major Revision nn
Data[4] Software Minor Revision nn
Data[5] Protocol Major Revision nn
Data[6] Protocol Minor Revision nn
Data[7] N/A nn
Data[8] Total Number of Effects nn
Data[9] TimeStamp[0] ch
Data[10] TimeStamp[1] ch
Data[11] TimeStamp[2] ch
Data[12] TimeStamp[3] ch
Data[13] TimeStamp[4] ch
Data[14] TimeStamp[5] ch
Data[15] TimeStamp[6] ch
Data[16] TimeStamp[7] ch
Data[17] TimeStamp[8] ch
Data[18] TimeStamp[9] ch
Data[19] TimeStamp[10] ch
Data[20] TimeStamp[11] ch
Data[21] TimeStamp[12] ch
Data[22] TimeStamp[13] ch
Data[23] TimeStamp[14] ch
Data[24] TimeStamp[15] 0x00
7.3.4.3 Data Description
ProductId: This unsigned 8 bit value describes the product.
Product ID
Lexicon DC-2 1
Lexicon MC-1 2
JBL Synthesis SDP-3 3
Lexicon MC-12 4
JBL Synthesis SDP-40 5
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 17 of 94
Page 18
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
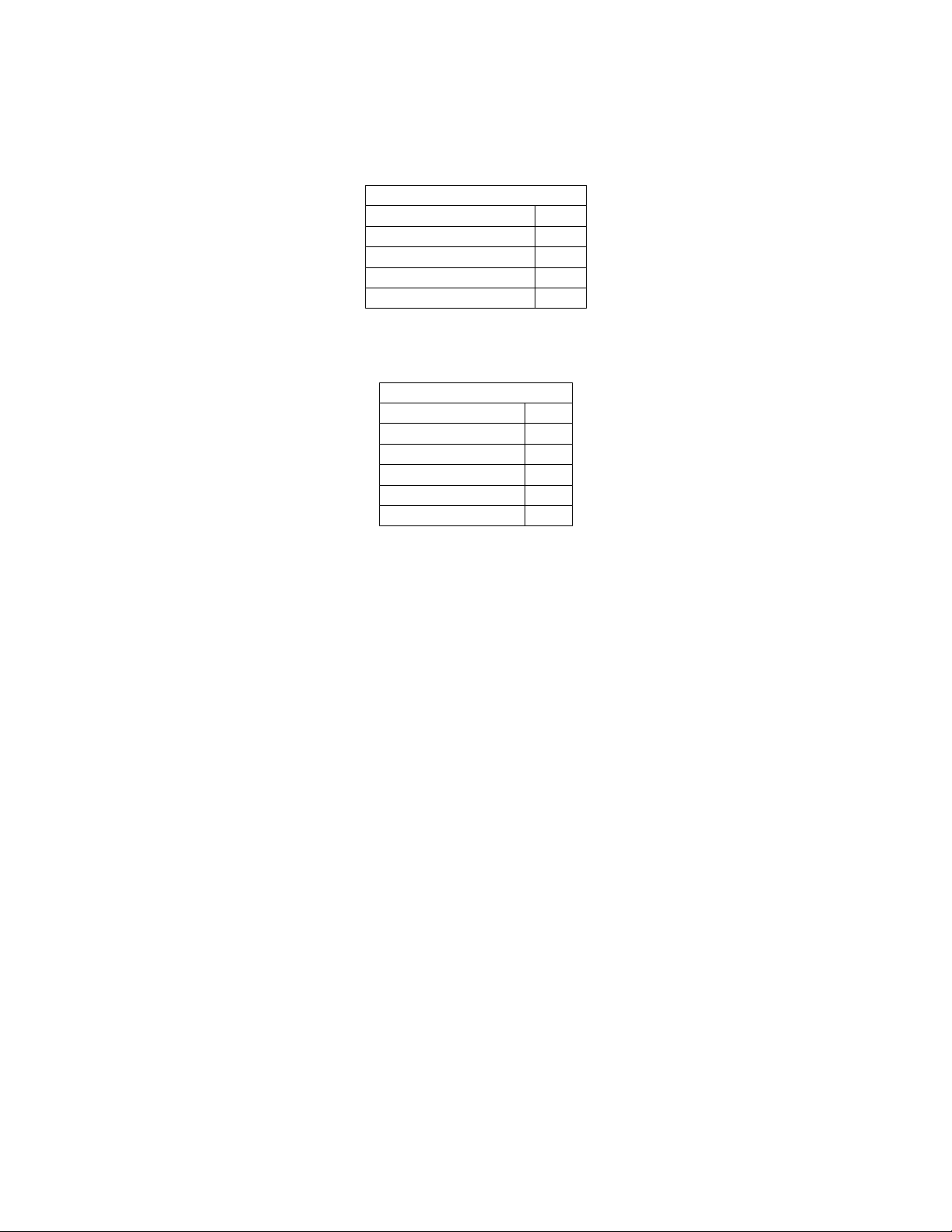
Software Type: An unsigned 8 bit value indicating the current configuration of the unit’s
software. The following table shows the values assigned to the available types:
SW Type
THX 1
AC3 2
DTS 3
COMPLETE 4
BOOTROM 5
Software Level: The following table shows the values assigned to the possible software levels:
SW Level
RELEASED 0
PRE_ALPHA 1
ALPHA 2
BETA 3
GAMMA 4
UNSUPPORTED 5
*Note: SW level indicates the status of the MC-12 internal application software.
Software Major Revision: An unsigned integer value indicating the unit’s major software version. The host
should use this information to determine if new effects, effect parameters, or
system parameters have been added or removed.
Software Minor Revision: An unsigned integer value indicating this unit’s minor software version.
Indicates the units software operation has changed but effects, effect parameters,
or system parameters have not changed.
Protocol Major Revision: An unsigned integer value indicating the serial communication protocol major
version. The host should use this value to determine if new commands,
notifications, or response packets have been added or deleted from this
specification.
Protocol Minor Revision: An unsigned integer value indicating the serial communication protocol minor
version. The host should use this value to determine if the existing commands,
notifications, or response packets have changed in this specification
Total Number of Effects: An unsigned integer value indicating the maximum number of effects available
for this version of software. This should be used to determine the maximum
EffectId used in the “Get Effect Definition Packet”, “Get Effect Parameter
Definition Packet”, “Set Effect Name Packet”, and “Set Effect Parameter
Values Packet”.
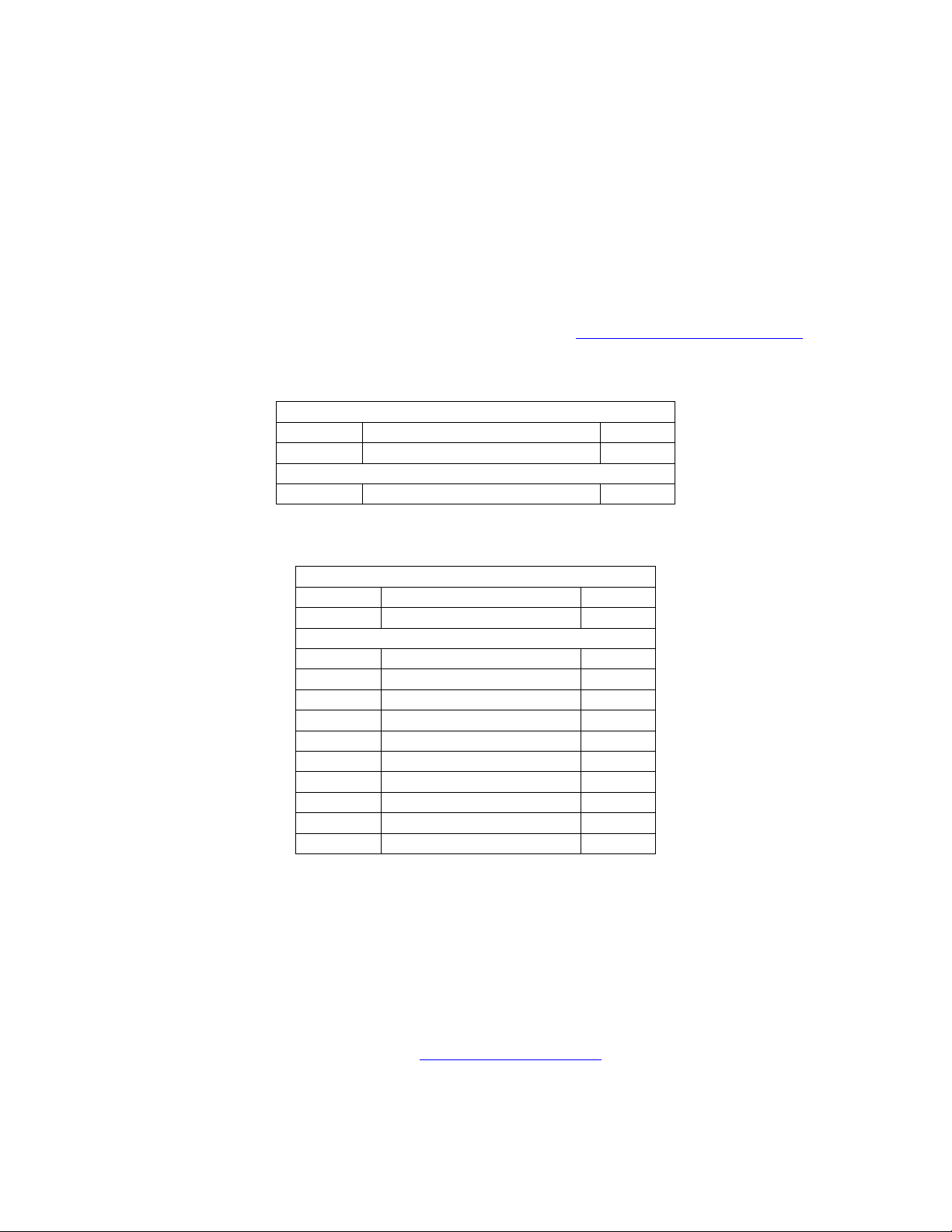
TimeStamp: Is a null terminated ASCII text string describing the build date and time of the
current software build. The Format of this text string is:
“yy/mm/dd(sp)hh:mm”
yy- is the last two digits of the year (i.e. year 1999 = 99, year 2000 = 00)
mm - is the month
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 18 of 94
Page 19
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
dd- is the day
(sp) - is an ASCII space character (0x20)
hh - is the hour
mm - is the minute
7.3.5 Get System Status (MC-12, MC-1)
Request to MC-12 for its current system status. MC-12 will respond with “System Status Packet”.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.45 (MC-12_Get_System_Status).
7.3.5.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_GET_SYS_STATUS 0x16
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.5.2 System Status Response Packet
Application Header:
Command DC_RESP_SYS_STATUS 0x81
Data Count 10 0x0A
Application Data:
Data[0] System Volume nn
Data[1] Current Input nn
Data[2] Current Effect Id nn
Data[3] Current Input Sample Rate nn
Data[4] Current Input Format nn
Data[5] Mute Active nn
Data[6] Effect Bypass nn
Data[7] Left/Right Balance nn
Data[8] Front/Back Balance nn
Data[9] Video Synch nn
7.3.5.3 Data Description
System Volume:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Maximum Value: 92
Conversion: 0 = -80 dB
92 = +12 dB
Current Input:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
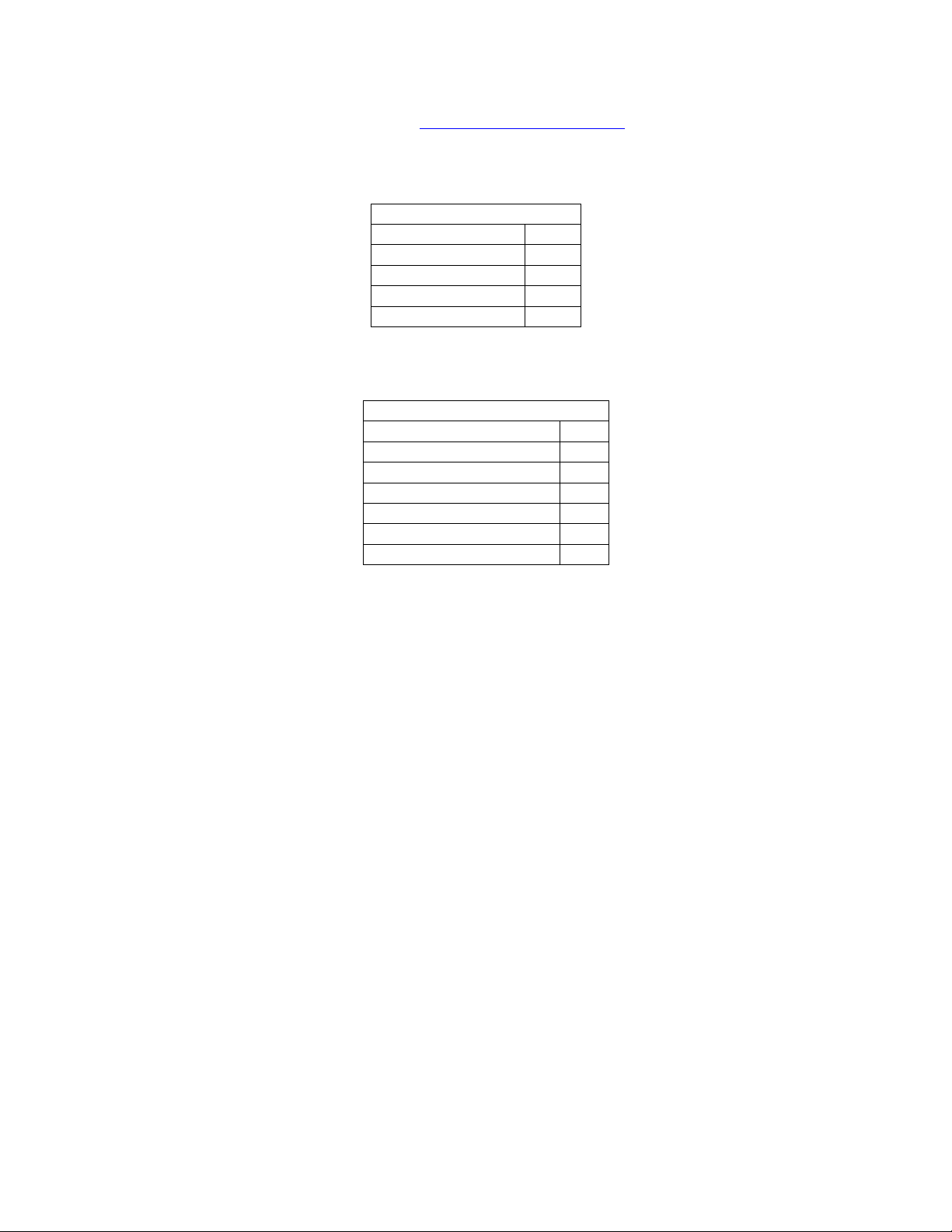
Current Effect Id:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 19 of 94
Page 20
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Definition/Conversion: Appendix_H_MC-12_Effect_Ids
Current Input Sample Rate:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
SAMPLE RATE
RATE_UNKNOWN 0
RATE_44 1
RATE_48 2
RATE_88 3
RATE_96 4
Current Input Format:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
DATA STREAM TYPE
DATA_TYPE_UNKNOWN 0
DATA_TYPE_BYPASS 1
DATA_TYPE_ANALOG 2
DATA_TYPE_PCM 3
DATA_TYPE_DD 4
DATA_TYPE_DTS 5
DATA_TYPE_NOISE 6
Mute Active:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: System Mute is Active
FALSE: System is unmuted.
Effect Bypass:
Data Type: Boolean
TRUE: Effect Bypass is Active
FALSE: Effect Bypass is Inactive
Left/Right Balance:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Maximum Value: 32
Conversion: 0 = Left
Front/Back Balance:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Maximum Value: 32
Conversion: 0 = Front
Video Synch:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: MC-12 has detected Video Sync for current video input
FALSE: MC-12 can not detect Video Sync for the current video input
16 = Center
32 = Right
16 = Center
32 = Back
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 20 of 94
Page 21
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
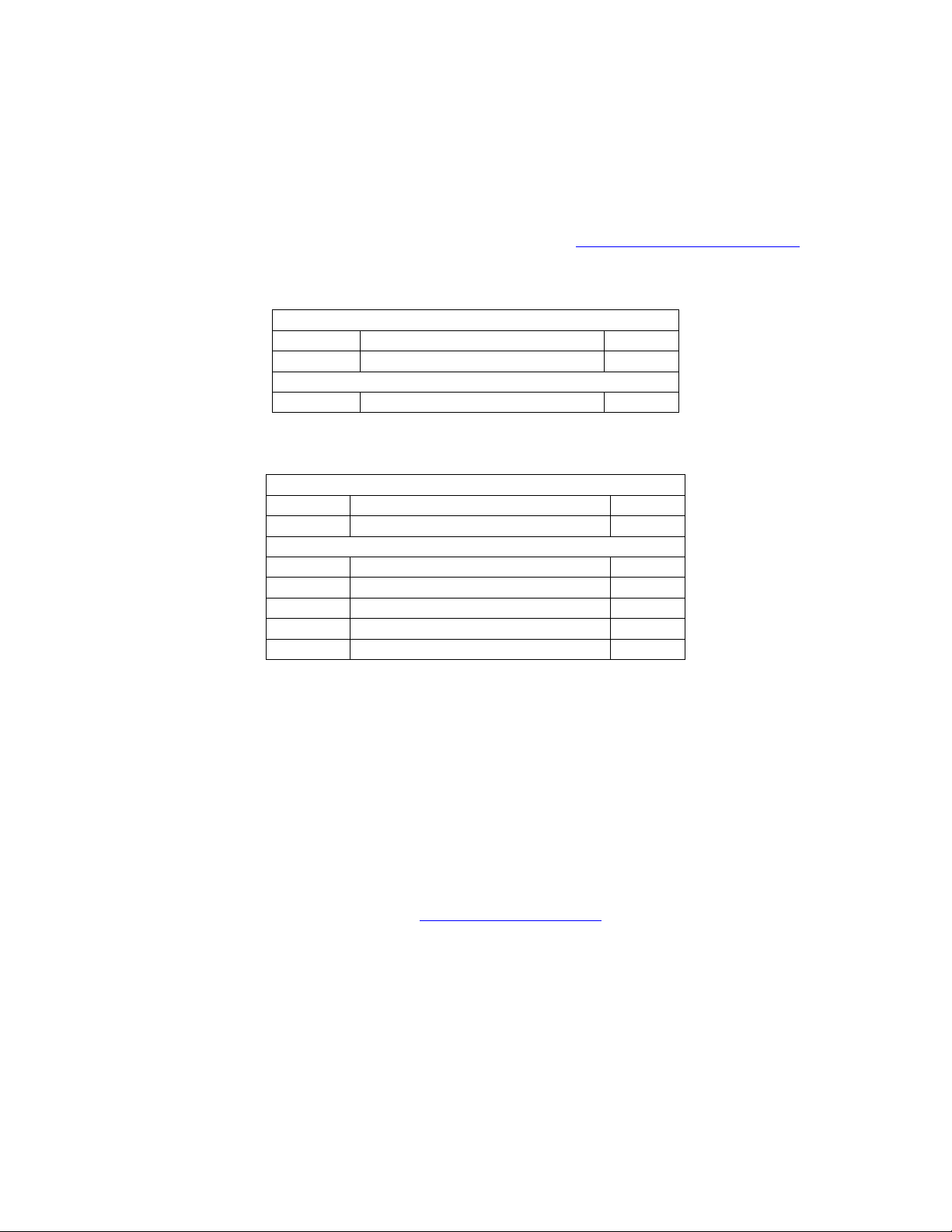
7.3.6 Get Zone 2 Status (MC-12, MC-1)
This command is a request to MC-12 for current Zone 2 Status. MC-12 will respond with “Zone2 Status
Packet”.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.46 (MC12_Get_Zone_2_Status).
7.3.6.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_GET_ZONE2_STATUS 0x17
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.6.2 Zone2 Status Response Packet
Application Header:
Command DC_RESP_ZONE2_STATUS 0x82
Data Count 5 0x05
Application Data:
Data[0] Zone2 Volume nn
Data[1] Assigned Zone 2 Input nn
Data[2] Zone2 Mute Active nn
Data[3] Record Active nn
Data[4] Zone2 Balance nn
7.3.6.3 Data Description
Zone2 Volume:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Maximum Value: 92
Conversion: 0 = -80 dB
Assigned Zone 2 Input:
Indicates the Zone 2 input that is currently assigned for the zone 2 outputs.
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
Zone2 Mute Active:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: Zone2 Outputs are active.
FALSE: Zone 2 Outputs are not active.
Record Active:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: Record Zone Output is active
FALSE: Record Zone Output is not Active.
92 = +12 dB
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 21 of 94
Page 22
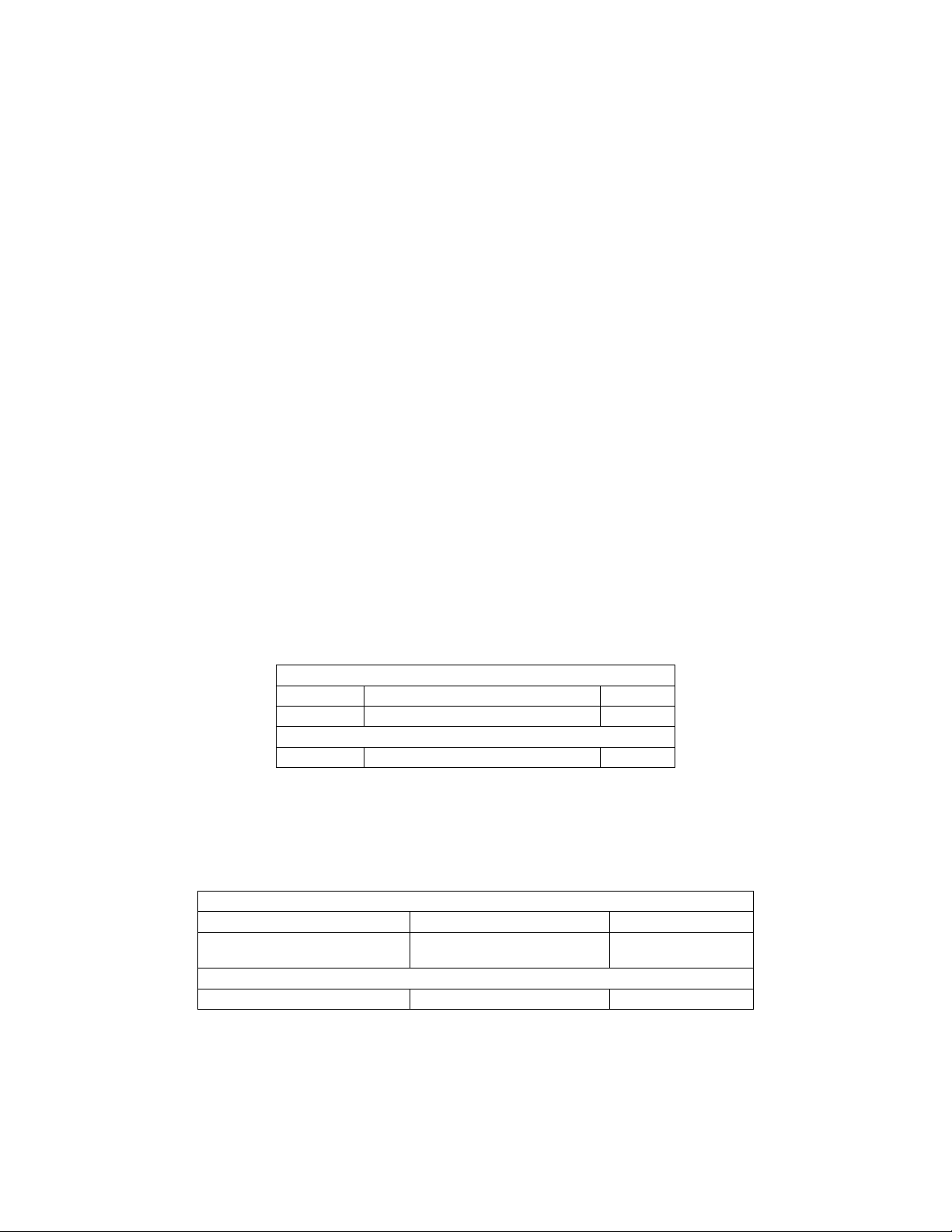
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Zone 2 Balance:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Maximum Value: 32
Conversion: 0 = Left
32 = Right
7.3.7 Get System Parameter Definition (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.8 Get System Parameter Values (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.9 Get Effect Definition by Id (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.10 Get Effect Parameter Definition (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.11 Get Effect Parameter Values (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.12 Get Custom Name (MC-12, MC-1)
Request to MC-12 for an effect definition. MC-12 will respond with “Custom Name Packet”.
7.3.12.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_GET_CUST_NAME 0x2B
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.12.2 Data Description
N/A
7.3.12.3 Custom Name Response Packet
Application Header:
Command DC_RESP_CUST_NAME 0x89
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0]- Data[DataCount-1] CustomName ch ch ch … 0x00
Number of Characters in
CustomName + 1 nn
7.3.12.4 Data Description
CustomName:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 22 of 94
Page 23
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Max Length: CUSTOM_NAME_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
7.3.13 Get Input Name by Id (MC-12, MC-1)
This command is a request to MC-12 for the custom input name. MC-12 will respond with “Input Name
Packet”.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.54
(MC12_Get_Input_Name_By_Id).
7.3.13.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_GET_INPUT_NAME 0x2D
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId nn
7.3.13.2 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
7.3.13.3 Data Validation:
The InputId must be a valid Input number. If it is not the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error
code DC_INVALID_INPUT.
7.3.13.4 Input Name Response Packet
Application Header:
Command DC_RESP_INPUT_NAME 0x8A
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId Nn
Data[1]- Data[DataCount-1] InputName ch ch ch … 0x00
Number of Characters in
InputName + 2 Nn
7.3.13.5 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
InputName:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: INPUT_NAME_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
7.3.14 Get FPD Control Registers (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 23 of 94
Page 24
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.15 Set System Parameter Values (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.16 Set Effect Parameter Values (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.17 Set Effect Name by Effect Id (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.18 Set System Volume (MC-12, MC-1)
This command is a request to the MC-12 to set the system volume with the value in this packet.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.47 (MC12_Set_System_Volume).
7.3.18.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_SYS_VOLUME 0x21
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.18.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Max: 92
Conversion: 0 = -80 dB
92 = +12 dB
7.3.18.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the system volume.
7.3.18.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.19 Set Main Balance (MC-12, MC-1)
Commands MC-12 to set the system balance to the value in this packet.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.48 (MC12_Set_Main_Balance).
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 24 of 94
Page 25
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.19.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_SYS_BALANCE 0x22
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.19.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Maximum Value: 32
Conversion: 0 = Left
16 = Center
32 = Right
7.3.19.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the system balance.
7.3.19.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.20 Set Front/Back Balance (MC-12, MC-1)
Commands MC-12 to set the front/back balance to the value in this packet.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.49
(MC12_Set_Front_Back_Balance).
7.3.20.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_FRONT_BACK_BALANCE 0x23
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.20.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Max: 32
Conversion: 0 = Front
16 = Center
32 = Back
7.3.20.3 MC-12 Response
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 25 of 94
Page 26
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the front/back balance.
7.3.20.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.21 Set Active Effect by Id (MC-12, MC-1)
This command requests the MC-12 to set the active effect to the value in this packet.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.50
(MC12_Set_Active_Effect_By_Id).
7.3.21.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_EFFECT 0x24
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] EffectId nn
7.3.21.2 Data Description
EffectId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix I MC-1 to MC-12 Effect ID Map.
7.3.21.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will load the desired effect.
7.3.21.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.22 Set Record Input (MC-12, MC-1)
Sets the Record input.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.51 (MC12_Set_Record_Input).
7.3.22.1 Command Packet Description
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 26 of 94
Page 27
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_REC_INPUT 0x25
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId nn
7.3.22.2 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Description/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
7.3.22.3 MC-12 Response:
If the Input Id is a valid MC-12 input then the MC-12 will make the request Input the active record input.
7.3.22.4 Data Validation:
The InputId must be a valid Input Id. If it is not the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error code
DC_INVALID_INPUT. If the input is assigned the MC-12 will respond with an ACK Packet.
7.3.23 Clear Record Input (MC-12, MC-1)
Clears or unassigns the Record input. If Record is active, this command will set the Record Input to OFF
7.3.23.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_CLEAR_REC_INPUT 0x26
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId nn
7.3.23.2 Data Description
InputId:
This value is not used by MC-12.
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
7.3.23.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will set the active record input to OFF.
7.3.23.4 Data Validation
The InputId is not used.
7.3.24 Set Zone2 Volume (MC-12, MC-1)
Commands MC-12 to set the Zone 2 volume with the value in this packet.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.52 (MC12_Set_Zone2_Volume).
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 27 of 94
Page 28
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.24.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_ZONE2_VOLUME 0x27
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.24.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Max: 92
Conversion: 0 = -80 dB
92 = +12 dB
7.3.24.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the Zone 2 volume.
7.3.24.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.25 Set Zone2 Left/Right Balance (MC-12, MC-1)
Commands MC-12 to set the Zone 2 balance to the value in this packet.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.53
(MC12_Set_Zone2_Left_Right_Balance).
7.3.25.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_ZONE2_BALANCE 0x28
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.25.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Max: 32
Conversion: 0 = Left
32 = Right
7.3.25.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the Zone 2 balance.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 28 of 94
Page 29
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.25.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.26 Set Custom Name (MC-12, MC-1)
Sets the Custom Name that can be displayed when the unit powers up.
7.3.26.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_CUST_NAME 0x2C
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0] CustomNameEnable nn
Data[1]-Data[DataCount-1] CustomName ch ch ch … 0x00
7.3.26.2 Data Description
CustomNameEnable: Enables/Disables the Custom Name Display.
DataType: Boolean
TRUE: CustomName Enabled
FALSE: CustomName Disabled
Number of characters in
CustomName + 2 nn
CustomName:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: CUSTOM_NAME_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
7.3.26.3 MC-12 Response
If the custom name enable is TRUE then the custom name banner is display on “power on”. If the Custom
Name Enable is FALSE the custom name is not displayed. The CustomName string is copied to
Nonvolatile RAM. The MC-12 will ACK when completed with this command.
7.3.26.4 Data Validation:
No data validation is done on the transmitted data.
7.3.27 Set Input Name by Id (MC-12, MC-1)
Sets an Input Name to the transmitted value for a given input.
This command has been maintained for backward compatibility with MC-1. In order to maintain backward
compatibility, the MC-12 Parameters have been mapped to the MC-1 parameters as described in each Data
Description. MC-12 users should be using the command described in 7.3.55
(MC12_Set_Input_Name_By_Id).
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 29 of 94
Page 30

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.27.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_INPUT_NAME 0x2E
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId 0 to 7
Data[1]-Data[DataCount-1] InputName ch ch ch ... 0x00
Number of characters in
InputName + 2 nn
7.3.27.2 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Description/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Id's
InputName:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: INPUT_NAME_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
7.3.27.3 MC-12 Response
MC-12 will copy the InputName to the given input.
7.3.27.4 Data Validation:
The InputId must be a valid Input Id. If it is not the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error code
DC_INVALID_INPUT. If the InputName string exceeds the INPUT_NAME_LENGTH, the MC-12 will
truncate the string to the INPUT_NAME_LENGTH.
7.3.28 Set FPD Control Registers (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.29 Host Wakeup (MC-12, MC-1)
By transmitting the Wakeup Notification, the Host indicates it has just “powered on” or reset and is ready to
receive MC-12 Notifications or Responses. The Host is assumed to be asleep upon power up of the MC-
12. Host status is maintained during standby.
7.3.29.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command HOST_WAKEUP 0x11
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.29.2 Data Description
N/A
7.3.29.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will respond to this command with an ACK.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 30 of 94
Page 31

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.30 Host Sleep (MC-12, MC-1)
By transmitting the Sleep command, the Host indicates it has just “powered down” and will no longer
respond to MC-12 Notifications. No Acknowledgment is expected. The Host is assumed to be asleep upon
power up of the MC-12. Host status is maintained during standby.
7.3.30.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command HOST_SLEEP 0x12
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.30.2 Data Description
N/A
7.3.31 Get Communication Configuration (MC-12, MC-1)
This command is a request to the MC-12 for the current communications configuration for the serial port
and protocol. The MC-12 responds to this command with a Communication Configuration Packet.
7.3.31.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_GET_COM_CONFIG 0x2F
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.31.2 Communication Configuration Response Packet
Application Header:
Command DC_RESP_COM_CONFIG 0x8C
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Configuration Register 0 nn
7.3.31.3 Data Description
Data Word Bit Definition
0 0 Acknowledge Enable
0 1 Parameter Change Enable
Acknowledge Enable:
TRUE Indicates the MC-12 will transmit Acknowledge Notification’s to the Host.
FALSE Indicates the MC-12 will not transmit any positive Acknowledge Notification
messages. The MC-12 will always transmit NAK error notification messages.
Parameter Change Enable:
TRUE Indicates the MC-12 will transmit any parameter change Notification as
specified in the Parameter Change Notification Message.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 31 of 94
Page 32

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
FALSE Indicates the MC-12 will not transmit parameter change Notifications.
7.3.32 Set Communication Configuration (MC-12, MC-1)
The Set Communication Configuration Command allows the serial port user to set up the various serial
port/ protocol configuration parameters.
7.3.32.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_COM_CONFIG 0x30
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Configuration Register 0 nn
7.3.32.2 Data Description
Data Word Bit Definition
0 0 Acknowledge Enable
0 1 Parameter Change Enable
Acknowledge Enable:
TRUE Indicates the MC-12 will transmit Acknowledge Notification’s to the Host.
FALSE Indicates the MC-12 will not transmit any positive Acknowledge Notification
messages. The MC-12 will always transmit NAK error notification messages.
Parameter Change Enable:
TRUE Indicates the MC-12 will transmit any parameter change Notification as
specified in the Parameter Change Notification Message.
FALSE Indicates the MC-12 will not transmit parameter change Notifications.
7.3.32.3 MC-12 Response
The data values transmitted will be copied over to the registers stored in nonvolatile RAM. The MC-12
will respond with an ACK Packet.
7.3.33 Set Mute (MC-12, MC-1)
The Set Mute Command message allows the RS232 users to set/clear the MC-12 mute state directly.
7.3.33.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_MUTE 0x31
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Mute State nn
7.3.33.2 Data Description
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 32 of 94
Page 33

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
MUTE State:
Value Definition Description
0 UNMUTE The user mute state is set to unmuted. The MC-12 may
still be muted for other internal reasons.
1 USER MUTE The system volume decrements by the specified user
amount as set in the OUTPUT LEVELS Menu.
2 FULL MUTE The system is fully muted.
7.3.33.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will set the mute state according to the value transmitted. The MC-12 may still be full muted if
other conditions require the audio path to be muted. This is only a direct access to the user mute state.
7.3.33.4 Data Validation
The data value transmitted to the MC-12 will be verified as a valid value. If it is valid the MC-12 will
set/clear the mute and respond with an ACK Packet. If the data value is invalid the MC-12 will respond
with a DC_INVALID_DATA error NAK.
7.3.34 Set Output Level Adjustments (MC-1)
This command is not supported by the MC-12.
7.3.35 Send Display String Command (MC-12, MC-1)
This command allows the Host to send a 40 character string to the MC-12 for display on the OSD and Front
Panel Display.
7.3.35.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_DISPLAY_STR 0x33
Data Count Number of characters in the
DisplayStr + 2
Application Data:
Data[0] DisplayFlags nn
Data[1]-Data[DataCount-1] DisplayStr ch ch ch … 0x00
7.3.35.2 Data Description
Display Command Flags:
Word Bit Definition
0 0 FPD only: If set TRUE, the display string will only be sent to the FPD device for display.
0 1 Undefined.
0 2 Undefined.
0 3 Undefined.
0 4 Undefined.
0 5 Undefined.
0 6 Undefined.
0 7 Undefined.
nn
Display String:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 33 of 94
Page 34

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Max Length: 40 Characters.
7.3.35.3 MC-12 Response
The display string is sent to the OSD and Front Panel Display. The MC-12 will ACK when completed with
this command.
7.3.35.4 Data Validation:
If a string length exceeds the 40 character maximum the string will be truncated before displaying and the
MC-12 transmit a DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.36 MC-12 Get Parameter Definition by Id (MC-12)
Request to MC-12 for a Parameter Definition by Parameter Id. MC-12 will respond with “MC-12 Parameter
Definition Packet”.
7.3.36.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_GET_PARAM_BY_ID 0x35
Data Count 2 0x02
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId(LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId(MSB) nn
7.3.36.2 Data Description
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 16 bit Integer
Max Value: Max Parameter Count as reported by the MC-12 Unit Configuration Response
Packet in 7.3.39.2
7.3.36.3 Data Validation:
If the ParamId is not a valid Id the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error code DC_
INVALID_PARAM_ID.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 34 of 94
Page 35

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.36.4 Parameter Definition Response Packet
The following Packet has been defined as follows for MC-12 V1.00. Future releases may modify this
definition.
Application Header:
Command MC_SYS_PARAM_DEF_PKT 0x8F
Data Count 110 0x6E
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId(LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId(MSB) nn
Data[2] ParamType nn
Data[3] MAX Value(LSB) nn
Data[4] MAX Value(MSB) nn
Data[5] MIN Value(LSB) nn
Data[6] MIN Value(MSB) nn
Data[7-27] CurrentValue[0 -20] nn nn nn…
Data[28]-Data[108] Parameter Path
Data[108] Read Only nn
7.3.36.5 Data Description
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 16 bit Integer
Max Value: Max Parameter Count as reported by the MC-12 Unit Configuration Response
Packet in 7.3.39.2
ch ch ch …
0x00
ParamType:
Param Type Name ParamTy
pe ID
PARAM_TYPE_UINT8 0 Unsigned 8 bit integer(0 to
PARAM_TYPE_UINT16 1 Unsigned 16 bit integer(0 to
PARAM_TYPE_CSTR8 2 Zero terminated string of 8
PARAM_TYPE_CSTR13 3 Zero terminated string of 13
PARAM_TYPE_UINT32 4 Unsigned 32 bit integer (0 to
PARAM_TYPE_BOOLEAN 5 Boolean( 0 to 1) 1
PARAM_TYPE_INT8 6 Signed 8 bit integer
PARAM_TYPE_BRANCH 7 Parameter Branch N/A
PARAM_TYPE_INT16 8 Signed 16 bit integer
PARAM_TYPE_CSTR20 9 Zero terminated string of 20
Data:
Type Description Data Size
255)
65535)
ascii characters
ascii characters
4,294,967,295 )
(-127 to 128)
(-32,767 to 32,768)
ascii characters
(Bytes)
1
2
9
14
4
1
2
21
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 35 of 94
Page 36

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
The data value transmitted is dependent on the ParamType, as described above. The
CurrentValue is always packed starting at the CurrentValue [0] byte in the packet. For
multi-byte data, the values are packed LSB first(CurrentValue [0]) to MSB(CurrentValue
[0+(num bytes-1)]). For example: Setting a given signed 16 bit parameter to a value of 300 the data array would be packed as follows:
Data[0] = 0xd4
Data[1] = 0xfe
Data[2 - 13] = don't care.
If a parameter's current value is a signed 16 bit parameter with a value of -3 the data array
would be packed as follows:
Data[0] = 0xfd
Data[1] = 0xff
Data[2 - 13] = don't care.
All signed values are in the 2's compliment format.
Max Value:
This is a 16 bit value representing the maximum value for a parameter. Parameter values
exceeding the maximum will be limited to the maximum. This may be a signed or
unsigned value depending on the Parameter Type.
Min Value:
This is a 16 bit value representing the minimum value for a parameter. Parameter values
exceeding the minimum will be limited to the minimum. . This may be a signed or
unsigned value depending on the Parameter Type.
Parameter Path:
This is a zero terminated ASCII character string describing the parameter's name and path
in the units parameter tree structure.
Read Only:
Data Type: Boolean
TRUE: Parameter is read only
FALSE: Parameter is writeable
7.3.37 MC-12 Set Parameter Value by Id (MC-12)
MC-12 Set Parameter by Id command sets the parameter value equal to the value sent in the command
packet and then runs the appropriate functional changes associated with changing the given parameter.
7.3.37.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_SYS_PARAM_VALUE_BY_ID 0x36
Data Count 24 0x18
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId(LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId(MSB) nn
Data[2] ParamType nn
Data[3-23] Value[0 -20] nn nn nn…
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 36 of 94
Page 37

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.37.2 Data Description
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 16 bit Integer
Max Value: Max Parameter Count as reported by the MC-12 Unit Configuration Response
Packet in 7.3.39.2
ParamType:
Param Type Name Param
Type
ID
PARAM_TYPE_UINT8 0 Unsigned 8 bit integer(0 to
PARAM_TYPE_UINT16 1 Unsigned 8 bit integer(0 to
PARAM_TYPE_CSTR8 2 Zero terminated string of 8
PARAM_TYPE_CSTR13 3 Zero terminated string of 13
PARAM_TYPE_UINT32 4 Unsigned 32 bit integer (0 to
PARAM_TYPE_BOOLEAN 5 Boolean (0 to 1) 1
PARAM_TYPE_INT8 6 Signed 8 bit integer
PARAM_TYPE_BRANCH 7 Parameter Branch N/A
PARAM_TYPE_INT16 8 Signed 16 bit integer
PARAM_TYPE_CSTR20 9 Zero terminated string of 20
Type Description Data
Size
(Bytes)
1
255)
2
65535)
9
ascii characters
14
ascii characters
4
4,294,967,295 )
1
(-127 to 128)
2
(-32,767 to 32,768)
21
ascii characters
Value:
The data value transmitted is dependent on the ParamType, as described above. The Data
Value is always packed starting at the Value[0] byte in the packet. For multi-byte data,
the values are packed LSB first(Value[0]) to MSB(Value[0+(num bytes-1)]). For
example: Setting a given signed 16 bit parameter to a value of -300 the data array would
be packed as follows:
Value[0] = 0xd4
Value[1] = 0xfe
Value[2 - 13] = don't care.
All signed values are in the 2's compliment format.
7.3.37.3 Data Validation:
The ParamId must be a valid Parameter. The ParamType must be valid for the given ParamId. If either of
these condition is not true the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error code DC _
INVALID_PARAM_ID. The data value size cannot exceed the size of a given data type. A value that does
exceed the size of a give data type will be truncated to the appropriate size. The ParamType transmitted
must match the ParamType for the Parameter being transmitted, as per the Parameter Definition as
transmitted by the MC_SYS_PARAM_DEF_PKT . If the types do not match The MC-12 will transmit a
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 37 of 94
Page 38
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
NAK packet with a DC_INVALID_INPUT error code. The MC-12 will transmit a NAK packet with a
DC_ERR_READ_ONLY error code for read only parameters.
7.3.38 MC-12 Set Parameter Value by Id, No Run (MC-12)
MC-12 Set Parameter by Id command sets the parameter value equal to the value sent in the command
packet and does not run the appropriate functional changes associated with changing the given parameter.
7.3.38.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_SYS_PARAM_VALUE_BY_ID_NO_RUN 0x37
Data Count 24 0x18
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId(LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId(MSB) nn
Data[2] ParamType nn
Data[3-23] Value[0 -20]
7.3.38.2 Data Description
Same as Paragraph 7.3.37.2
nn nn
nn…
7.3.39 MC-12 Get Unit Configuration (MC-12)
Request to MC-12 for its current unit configuration. MC-12 will respond with “Unit Configuration Packet”.
The HOST should use this information to determine if any information saved by the HOST is current.
7.3.39.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_GET_CONFIG 0x38
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 38 of 94
Page 39

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.39.2 MC-12 Unit Configuration Response Packet
Application Header:
Command MC_RESP_UNIT_CONFIG 0x91
Data Count 30 0x1E
Application Data:
Data[0] ProductId nn
Data[1] Software Type nn
Data[2] Software Level nn
Data[3] Software Major Revision nn
Data[4] Software Minor Revision nn
Data[5] Protocol Major Revision nn
Data[6] Protocol Minor Revision nn
Data[7] Parameter Count Low(LSB) nn
Data[8] Parameter Count High(MSB) nn
Data[9] Effect Count nn
Data[10] TimeStamp[0] ch
Data[11] TimeStamp[1] ch
Data[12] TimeStamp[2] ch
Data[13] TimeStamp[3] ch
Data[14] TimeStamp[4] ch
Data[15] TimeStamp[5] ch
Data[16] TimeStamp[6] ch
Data[17] TimeStamp[7] ch
Data[18] TimeStamp[8] ch
Data[19] TimeStamp[9] ch
Data[20] TimeStamp[10] ch
Data[21] TimeStamp[11] ch
Data[22] TimeStamp[12] ch
Data[23] TimeStamp[13] ch
Data[24] TimeStamp[14] ch
Data[25] TimeStamp[15] 0x00
Data[26] SerialNumber(LSB) nn
Data[27] SerialNumber nn
Data[28] SerialNumber nn
Data[29] SerialNumber(MSB) nn
7.3.39.3 Data Description
ProductId: This unsigned 8 bit value describes the product.
Product ID
Lexicon DC-2 1
Lexicon MC-1 2
JBL Synthesis SDP-3 3
Lexicon MC-12 4
JBL Synthesis SDP-40 5
Software Type: An unsigned 8 bit value indicating the current configuration of the unit’s
software. The following table shows the values assigned to the available types:
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 of 94
Page 40

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
SW Type
THX 1
AC3 2
DTS 3
COMPLETE 4
BOOTROM 5
Software Level: The following table shows the values assigned to the possible software levels:
SW Level
RELEASED 0
PRE_ALPHA 1
ALPHA 2
BETA 3
GAMMA 4
UNSUPPORTED 5
*Note: SW level indicates the status of the MC-12 internal application software.
Software Major Revision: An unsigned 8 bit integer value indicating the unit’s major software version.
The host should use this information to determine if new effects, effect
parameters, or system parameters have been added or removed.
Software Minor Revision: An unsigned 8 bit integer value indicating this units minor software version.
Indicates the units software operation has changed but effects, effect parameters,
or system parameters have not changed.
Protocol Major Revision: An unsigned 8 bit integer value indicating the serial communication protocol
major version. The host should use this value to determine if new commands,
notifications, or response packets have been added or deleted from this
specification.
Protocol Minor Revision: An unsigned 8 bit integer value indicating the serial communication protocol
minor version. The host should use this value to determine if the existing
commands, notifications, or response packets have changed in this specification
Parameter Count: An unsigned 16 bit integer value indicating the maximum number of parameters
for this version of software. All Parameters are sequential ordered with in the
unit so cycling from ParamId 0 to ParamId = Parameter Count -1 allows for the
host system to learn the Parameter definitions for all Parameters defined for a
given software version. The 16 bit value is packed LSB followed by the MSB.
Total Number of Effects: An unsigned 8 bit integer value indicating the maximum number of effects
available for this version of software.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 40 of 94
Page 41

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
TimeStamp: Is a null terminated ASCII text string describing the build date and time of the
current software build. The Format of this text string is:
“yy/mm/dd(sp)hh:mm”
yy- is the last two digits of the year (i.e. year 2001=01, year 2002 = 02)
mm - is the month
dd- is the day
(sp) - is an ASCII space character (0x20)
hh - is the hour
mm - is the minute
SerialNumber: The Serial Number is an unsigned 32 bit integer holding the unique value of the
current unit.
7.3.40 MC-12 Send IR Command (MC-12)
This command allows the HOST to transmit IR command key codes to the MC-12.
7.3.40.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_IR 0x39
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] KeyCode nn
7.3.40.2 Data Description
KeyCode:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Valid Values: Appendix D MC-12 IR-Codes
7.3.40.3 MC-12 Response
The KeyCode is processed as a valid IR code. No acknowledgment will be sent from MC-12.
7.3.40.4 Data Validation
The KeyCode data will be verified as a legal IR code. If the Code is not valid the MC-12 will not respond.
7.3.41 MC-12 Get Parameter Value by Id (MC-12)
Request to MC-12 for the current value of a given parameter. The MC-12 will respond with a “Parameter
Value Packet”.
7.3.41.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_GET_PARAM_VALUE_BY_ID 0x3A
Data Count 2 0x02
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId (LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId (MSB) nn
7.3.41.2 Data Description
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 41 of 94
Page 42

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 16 bit integer.
Max: Max Parameter Count as reported by the MC-12 Unit Configuration
Response Packet in 7.3.39.2
7.3.41.3 Data Validation
If ParamId exceeds the its maximum value, the MC-12 will ignore the command and transmit a
DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_PARAM_ID.
7.3.41.4 MC-12 Value String Response Packet
Application Header:
Command MC_RESP_PARAM_VALUE 0x92
Data Count 24 0x18
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId (LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId (MSB) nn
Data[2] ParamType nn
Data[3-23] Value[0 -20]
nn nn
nn…
7.3.41.5 Data Description
Same as Paragraph 7.3.37.2
7.3.42 MC-12 Set Parameter Notification by Id (MC-12)
Request to MC-12 to enable or disable transmission of the MC-12 parameter change notification for a given
parameter.
7.3.42.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_PARAM_NOTIFICATION_BY_ID 0x3B
Data Count 3 0x03
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId (LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId (MSB) nn
Data[2] Enable/Disable nn
7.3.42.2 Data Description
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 16 bit integer.
Max: Max Parameter Count as reported by the MC-12 Unit Configuration
Response Packet in 7.3.39.2
Enable/Disable:
Data Type: Boolean
TRUE: Enable transmission of parameter notification
FALSE: Disable transmission of parameter notification
7.3.42.3 Data Validation
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 42 of 94
Page 43

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
If ParamId exceeds the its maximum value, the MC-12 will ignore the command and transmit a
DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_PARAM_ID.
7.3.42.4 MC-12 Response
If a parameter has been enabled for notification the MC-12 will transmit its current value whenever
it has been changed due to any user or system action. For the details of the MC-12 notification
packet, see 7.1.5 (MC12_Parameter_Notification_By_Id).
7.3.43 MC-12 Parameter Get Value String by Id (MC-12)
Request to MC-12 for the string representation of a given value for a given parameter. The MC-12 will
respond with a “Value String Response Packet”.
7.3.43.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_PARAM_GET_VALUE_STRING_BY_ID 0x3C
Data Count 23 0x17
Application Data:
Data[0] ParamId (LSB) nn
Data[1] ParamId (MSB) nn
Data[2] - Data[22] Value[0] - Value[20]
nn nn
nn ..
7.3.43.2 Data Description
ParamId:
Data Type: Unsigned 16 bit integer.
Max: Max Parameter Count as reported by the MC-12 Unit Configuration
Response Packet in 7.3.39.2
Value:
See MC12_Value_Union_Description.
7.3.43.3 Data Validation
If ParamId exceeds the its maximum value, the MC-12 will ignore the command and transmit a
DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_PARAM_ID.
7.3.43.4 MC-12 Value String Response Packet
Application Header:
Command MC_RESP_VALUE_STRING 0x93
Number of Characters in Value
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0] - Data[20] Value String
String + 1 nn
ch ch ch
… 0x00
7.3.43.5 Data Description
Value String:
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 43 of 94
Page 44

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII string.
Max Length: 21 (20 characters plus terminating Null)
7.3.44 MC-12 Clear All Parameter Notifications (MC-12)
Request to the MC-12 to disable all MC-12 parameter notifications.
7.3.44.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_CLEAR_ALL_PARAM_NOTIFICATIONS 0x3D
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.45 MC-12 Get System Status (MC-12)
Request to MC-12 for its current system status. MC-12 will respond with “System Status Packet”.
7.3.45.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_GET_SYS_STATUS 0x3E
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.45.2 System Status Response Packet
Application Header:
Command MC_RESP_SYS_STATUS 0x94
Data Count 10 0x0A
Application Data:
Data[0] System Volume nn
Data[1] Current Input nn
Data[2] Current Effect Id nn
Data[3] Current Input Sample Rate nn
Data[4] Current Input Format nn
Data[5] Mute Active nn
Data[6] Effect Bypass nn
Data[7] Left/Right Balance nn
Data[8] Front/Back Balance nn
Data[9] Video Sync nn
7.3.45.3 Data Description
System Volume:
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 44 of 94
Page 45

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +12 (0x0C) (12 dB)
Min: -80 (0xB0) (-80 dB)
Current Input:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
Current Effect Id:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix_H_MC-12_Effect_Ids
Current Input Sample Rate:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
SAMPLE RATE
RATE_UNKNOWN 0
RATE_44 1
RATE_48 2
RATE_88 3
RATE_96 4
Current Input Format:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Mute Active:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: System Mute is Active
FALSE: System is unmuted.
Effect Bypass:
Data Type: Boolean
TRUE: Effect Bypass is Active
FALSE: Effect Bypass is Inactive
Left/Right Balance:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: 16 (0x10) (Full Right)
Min: -16 (0xF0) (Full Left)
DATA STREAM TYPE
DATA_TYPE_UNKNOWN 0
DATA_TYPE_BYPASS 1
DATA_TYPE_ANALOG 2
DATA_TYPE_PCM 3
DATA_TYPE_DD 4
DATA_TYPE_DTS 5
DATA_TYPE_NOISE 6
Front/Back Balance:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: 16 (0x10) (Full Front)
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 45 of 94
Page 46

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Min: -16 (0xF0) (Full Back)
Video Sync:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: MC-12 has detected Video Sync for current video input
FALSE: MC-12 can not detect Video Sync for the current video input
7.3.46 MC-12 Get Record Status (MC-12)
This command is a request to MC-12 for current Zone 2 Status. MC-12 will respond with “Zone2 Status
Packet”.
7.3.46.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_GET_REC_STATUS 0x3F
Data Count 0 0x00
Application Data:
N/A
7.3.46.2 Zone2 Status Response Packet
Application Header:
Command MC_RESP_REC_STATUS 0x95
Data Count 5 0x05
Application Data:
Data[0] Zone2 Volume nn
Data[1] Assigned Zone 2 Input nn
Data[2] Zone2 Mute Active nn
Data[3] Record Active nn
Data[4] Zone2 Balance nn
7.3.46.3 Data Description
Zone2 Volume:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +12 (0x0C) (12 dB)
Min: -80 dB (0xB0) (-80 dB)
Assigned Zone 2 Input:
Indicates the Zone 2 input that is currently assigned for the zone 2 outputs.
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer.
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
Zone2 Mute Active:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: Zone2 Outputs are active.
FALSE: Zone 2 Outputs are not active.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 46 of 94
Page 47

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Record Active:
Data Type: Boolean.
TRUE: Record Zone Output is active
FALSE: Record Zone Output is not Active.
Zone 2 Balance:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: 16 (0x10) (Full Right)
Min: -16 (0xF0) (Full Left)
7.3.47 MC-12 Set System Volume (MC-12)
This command is a request to the MC-12 to set the system volume with the value in this packet.
7.3.47.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_SYS_VOLUME 0x40
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.47.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +12 (0x0C) (12 dB)
Min: -80 (0xB0) (-80 dB)
7.3.47.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the system volume.
7.3.47.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.48 MC-12 Set Main Balance (MC-12)
Commands MC-12 to set the system balance to the value in this packet.
7.3.48.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command DC_CMD_SET_SYS_BALANCE 0x41
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 47 of 94
Page 48

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.48.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +16 (0x10) (Full Right)
Min: -16 (0xF0) (Full Left)
7.3.48.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the system balance.
7.3.48.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a DC_NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.49 MC-12 Set Front/Back Balance (MC-12)
Commands MC-12 to set the front/back balance to the value in this packet.
7.3.49.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_FRONT_BACK_BALANCE 0x42
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.49.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +16 (0x10) (Full Front)
Min: -16 (0xF0) (Full Back)
7.3.49.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the front/back balance.
7.3.49.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.50 MC-12 Set Active Effect by Id (MC-12)
This command requests the MC-12 to set the active effect to the value in this packet.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 48 of 94
Page 49

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.50.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_EFFECT 0x43
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] EffectId nn
7.3.50.2 Data Description
EffectId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix I MC-1 to MC-12 Effect ID Map.
7.3.50.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will load the desired effect.
7.3.50.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.51 MC-12 Set Record Input (MC-12)
Sets the Record input.
7.3.51.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_REC_INPUT 0x44
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId nn
7.3.51.2 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Description/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
7.3.51.3 MC-12 Response:
If the Input Id is a valid MC-12 input then the MC-12 will make the request Input the active record input.
7.3.51.4 Data Validation:
The InputId must be a valid Input Id. If it is not the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error code
DC_INVALID_INPUT. If the input is assigned the MC-12 will respond with an ACK Packet.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 49 of 94
Page 50

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.52 MC-12 Set Zone2 Volume (MC-12)
Commands MC-12 to set the Zone 2 volume with the value in this packet.
7.3.52.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_ZONE2_VOLUME 0x45
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.52.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +12 (0x0C) (12dB)
Min: -80 (0xB0) (-80 dB)
7.3.52.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the Zone 2 volume.
7.3.52.4 Data Validation
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.53 MC-12 Set Zone2 Left/Right Balance (MC-12)
Commands MC-12 to set the Zone 2 balance to the value in this packet.
7.3.53.1 Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_ZONE2_BALANCE 0x46
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] Value nn
7.3.53.2 Data Description
Value:
Data Type: Signed 8 bit integer (2’s compliment)
Max: +16 (0x10) (Full Right)
Min: -16 (0xF0) (Full Left)
7.3.53.3 MC-12 Response
The MC-12 will assign the value from the packet to the Zone 2 balance.
7.3.53.4 Data Validation
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 50 of 94
Page 51
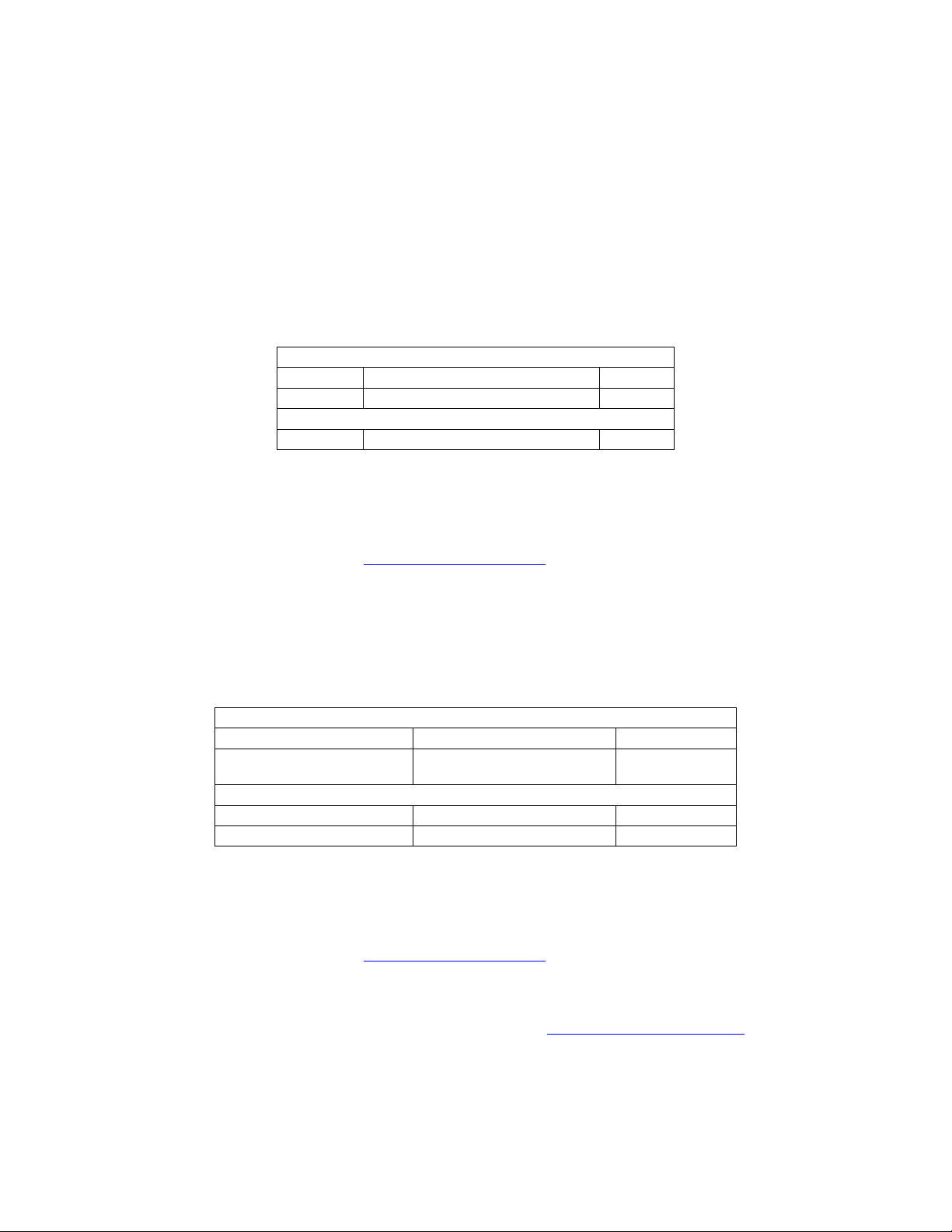
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
If a value is passed that exceeds the maximum value of that parameter the MC-12 will ignore the command
and transmit a NAK command with an error code DC_INVALID_DATA.
7.3.54 MC-12 Get Input Name by Id (MC-12)
This command is a request to MC-12 for the custom input name. MC-12 will respond with “Input Name
Packet”.
7.3.54.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_GET_INPUT_NAME 0x47
Data Count 1 0x01
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId nn
7.3.54.2 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
7.3.54.3 Data Validation:
The InputId must be a valid Input number. If it is not the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error
code DC_INVALID_INPUT.
7.3.54.4 Input Name Response Packet
Application Header:
Command MC_RESP_INPUT_NAME 0x96
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId nn
Data[1]- Data[DataCount-1] InputName ch ch ch … 0x00
Number of Characters in
InputName + 2 nn
7.3.54.5 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Definition/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
InputName:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: INPUT_NAME_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 51 of 94
Page 52

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
7.3.55 MC-12 Set Input Name by Id (MC-12)
Sets an Input Name to the transmitted value for a given input.
7.3.55.1 Command Packet Description
Application Header:
Command MC_CMD_SET_INPUT_NAME 0x48
Data Count
Application Data:
Data[0] InputId 0 to 7
Data[1]-Data[DataCount-1] InputName ch ch ch ... 0x00
7.3.55.2 Data Description
InputId:
Data Type: Unsigned 8 bit Integer
Description/Conversion: Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
InputName:
Data Type: Null (0x00) terminated ASCII character string.
Max Length: INPUT_NAME_LENGTH defined in Appendix G Protocol Constants.
Number of characters in
InputName + 2 nn
7.3.55.3 MC-12 Response
MC-12 will copy the InputName to the given input.
7.3.55.4 Data Validation:
The InputId must be a valid Input Id. If it is not the MC-12 will respond with a NAK packet and error code
DC_INVALID_INPUT. If the InputName string exceeds the INPUT_NAME_LENGTH, the MC-12 will
truncate the string to the INPUT_NAME_LENGTH.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 52 of 94
Page 53

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix A Command Codes
Notifications:
DC_WAKEUP 0x01
DC_SLEEP 0x02
DC_FPD 0x03
DC_PARAM_CHG_MSG 0x04
DC_NO_CMD 0x00
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 53 of 94
Page 54

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Host Commands:
HOST_WAKEUP 0x11
HOST_SLEEP 0x12
DC_CMD_RESTORE_DEFAULTS 0x13
DC_CMD_IR 0x14
DC_CMD_GET_CONFIG 0x15
DC_CMD_GET_SYS_STATUS 0x16
DC_CMD_GET_REC_STATUS 0x17
DC_CMD_GET_SYS_PARAM_BY_ID 0x18
DC_CMD_GET_SYS_PARAM_BY_NAME 0x19
DC_CMD_GET_SYS_PARAM_VALUES 0x1A
DC_CMD_GET_EFFECT 0x1B
DC_CMD_GET_EFFECT_PARAM_DEF 0x1C
DC_CMD_GET_EFFECT_PARAM_VALUES 0x1D
DC_CMD_SET_SYS_PARAM_VALUES 0x1E
DC_CMD_SET_EFFECT_PARAM_VALUES 0x1F
DC_CMD_SET_EFFECT_NAME 0x20
DC_CMD_SET_SYS_VOLUME 0x21
DC_CMD_SET_SYS_BALANCE 0x22
DC_CMD_SET_FRONT_BACK_BALANCE 0x23
DC_CMD_SET_EFFECT 0x24
DC_CMD_SET_REC_INPUT 0x25
DC_CMD_CLEAR_REC_INPUT 0x26
DC_CMD_SET_ZONE2_VOLUME 0x27
DC_CMD_SET_ZONE2_BALANCE 0x28
DC_CMD_GET_FPD_CTRL 0x29
DC_CMD_SET_FPD_CTRL 0x2A
DC_CMD_GET_CUST_NAME 0x2B
DC_CMD_SET_CUST_NAME 0x2C
DC_CMD_GET_INPUT_NAME 0x2D
DC_CMD_SET_INPUT_NAME 0x2E
DC_CMD_GET_COM_CONFIG 0x2F
DC_CMD_SET_COM_CONFIG 0x30
DC_CMD_SET_MUTE 0x31
DC_CMD_SET_OUTPUT_ADJ 0x32
DC_CMD_SEND_DISPLAY_STR 0x33
DC_CMD_RESET 0x10
MC_CMD_GET_SYS_PARAM_BY_ID 0x35
MC_CMD_SET_SYS_PARAM_VALUE_BY_ID 0x36
MC_CMD_SET_SYS_PARAM_VALUE_BY_ID_NO_RUN 0x37
MC_CMD_GET_CONFIG 0x38
MC_CMD_IR 0x39
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 54 of 94
Page 55

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Responses
DC_RESP_UNIT_CONFIG 0x80
DC_RESP_SYS_STATUS 0x81
DC_RESP_REC_ZONE2_STATUS 0x82
DC_RESP_SYS_PARAM_DEF 0x83
DC_RESP_SYS_PARAM_VALUES 0x84
DC_RESP_EFFECT_DEF 0x85
DC_RESP_EFFECT_PARAM_DEF 0x86
DC_RESP_EFFECT_PARAM_VALUES 0x87
DC_RESP_FPD_CTRL_STATUS 0x88
DC_RESP_CUST_NAME 0x89
DC_RESP_INPUT_NAME 0x8A
DC_RESP_PEEK_VALUE 0x8B
DC_RESP_COM_CONFIG 0x8C
Acknowledgments
DC_ACK 0xE0
DC_NAK 0xE1
MC_RESP_SYS_PARAM_DEF 0x8F
MC_RESP_UNIT_CONFIG 0x91
Appendix B Error Codes
Error Code(Hex)
NO_ACK 0x00
DC_NO_ERROR 0x01
DC_ERR_PARITY 0x02
DC_ERR_FRAMING 0x03
DC_ERR_OVERRUN 0x04
DC_ERR_INVALID_PACKET 0x05
DC_ERR_TIME_OUT 0x06
DC_ERR_BUFFER_FULL 0x07
DC_INVALID_COUNT 0x10
DC_INVALID_CMD 0x11
DC_INVALID_DATA 0x12
DC_INVALID_ADDRESS 0x13
DC_INVALID_EFFECT_ID 0x14
DC_INVALID_PARAM_ID 0x15
DC_INVALID_NAME 0x16
DC_INVALID_INPUT 0x17
DC_ERR_READ_ONLY 0x18
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 55 of 94
Page 56

Page 57

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix C DC-2, MC-1 IR-Codes
MC-1
Function
Off STANDBY 19 Trigger Off TRIGGER1_OFF 99 Zone-2: Off ZONE_OFF 59
On ON 18 Trigger On TRIGGER1_ON 98 Zone-2: On ZONE_DVD_2 58
OSD Off OSD 02 Menu Back Off BLUE 82 Reserved 42
FrontPanel Off FP 03 reserved 83 Reserved 43
LIGHT N/A N/A N/A
FrontPanel On FP 04 reserved 84 Reserved 44
OSD On OSD 05 Menu Back On BLUE 85 Status Menu INPUT_STATUS 45
Menu Up UP_ARROW 01 Fade Front 81 Reserved 41
Done
SPARE 06 SPARE 86 SPARE 46
Select
Menu Down DN_ARROW 1D Fade Rear FADER_REAR 9D Reserved 5D
Mute MUTE 15 Full Mute FULL_MUTE 95 Z-2: Mute ZONE_MUTE 55
Effect + MODE_INCR 1A Center Bal/Fad BAL_CENTER 9A Lock the LOCK 5A
Effect - MODE_DECR 1B EQ Off EQ_OFF 9B Reserved 5B
Volume + VOL_INCR 17 Volume +5dB VOL_03DB 97 Z-2: Volume + ZONE_VOL_INCR 57
Volume - VOL_DECR 16 Volume –5dB VOL_N03DB 96 Z-2: Volume - ZONE_VOL_DECR 56
VCR MAIN_VCR 13 Bass + BASS_INCR 93 R/Z-2: VCR ZONE_VCR 53
DVD MAIN_DVD_1 12 Treble + TREBLE_INCR 92 R/Z-2: DVD ZONE_DVD_1 52
V-DISC MAIN_LD 11 Tilt + TILT_INCR 91 R/Z-2: V-DISC ZONE_LD 51
TV MAIN_TV 10 Loudness On 90 R/Z-2: TV ZONE_TV 50
AUX MAIN_AUX 0F Bass - BASS_DECR 8F R/Z-2: AUX ZONE_AUX 4F
CD MAIN_CD 0E Treble - TREBLE_DECR 8E R/Z-2: CD ZONE_CD 4E
TUNER MAIN_TUNER 0D Tilt - TILT_DECR 8D R/Z-2: TUNER ZONE_TUNER 4D
TAPE MAIN_TAPE 0C Loudness Off 8C R/Z-2: TAPE ZONE_TAPE 4C
Dolby DOLBY_LOGO 20 Nightclub A0 Z-2 Vol: -30dB ZONE_VOL_N30DB 60
THX THX_LOGO 21 Concert Hall A1 Z-2 Vol: -20dB ZONE_VOL_N30DB 61
Logic7 LOGIC7_LOGO 22 Church A2 Z-2 Vol: -10dB ZONE_VOL_N30DB 62
dts DTS_LOGO 23 Cathedral A3 Z-2 Vol: +00dB ZONE_VOL_00DB 63
2-Chan On/Off MAIN_2_CHANNEL 24 Expansion Ports* A4 Volume: -30dB VOL_N30DB 64
Party 25 Panorama A5 Volume: -20dB VOL_N30DB 65
TV Matrix TV_L_LOGO 26 Mono Logic A6 Volume: -10dB VOL_N30DB 66
Music MUSIC 27 Music Surround MUSIC A7 Volume: +00dB VOL_00DB 67
SPARE 28 SPARE A8 SPARE 68
SPARE 29 SPARE A9 SPARE 69
SPARE 2A SPARE AA SPARE 6A
SPARE 2B SPARE AB SPARE 6B
SPARE 2C SPARE AC SPARE 6C
SPARE 2D SPARE AD SPARE 6D
SPARE 2E SPARE AE SPARE 6E
SPARE 2F SPARE AF SPARE 6F
Null 30 null B0 null 70
Mapped to MC-12
Function
LEFT_ARROW_DO
NE 0A Balance Left
RIGHT_ARROW_S
ELECT 08 Balance Right
Hex
Code
MC-1 Shift
Functions
Mapped to MC-
12 Function
BAL_LEFT
BAL_RIGHT
Hex
MC-1 Rec
Code
Function
8A Z-2: Bal Left
88 Z-2: Bal Right
Mapped to MC-12
Function
ZONE_BAL_LEFT
ZONE_BAL_RIGHT
Hex
Code
4A
48
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 57 of 94
Page 58

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix D MC-12 IR Codes
Button2
Main
KEY
Setup LIGHT None LIGHT None LIGHT None LIGHT None
1 MAIN_ON_STDBY 0x05 ZONE_ON_STDBY 0x05 REC_ON_STDBY 0x05 SHIFT_STDBY 0x05
2 MAIN None MAIN None MAIN None MAIN None
3 ZONE None ZONE None ZONE None ZONE None
4 REC None REC None REC None REC None
5 Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None
6 Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None
7 Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None
8 Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None
9 SHIFT None SHIFT None SHIFT None SHIFT None
10 MAIN_DVD_1 0x20 ZONE_DVD_1 0x60 REC_DVD_1 0xE0 MAIN_OFF 0xA0
11 MAIN_DVD_2 0x21 ZONE_DVD_2 0x61 REC_DVD_2 0xE1 ZONE_OFF 0xA1
12 MAIN_LD 0x22 ZONE_LD 0x62 REC_LD 0xE2 REC_OFF 0xA2
13 MAIN_TV 0x23 ZONE_TV 0x63 REC_TV 0xE3 LOUDNESS_ON 0xA3
14 MAIN_SAT 0x24 ZONE_SAT 0x64 REC_SAT 0xE4 LOUDNESS_OF F 0xA4
15 MAIN_VCR 0x25 ZONE_VCR 0x65 REC_VCR 0xE5 Reserved 0xA5
16 MAIN_CD 0x26 ZONE_CD 0x66 REC_CD 0xE6 BASS_INCR 0xA6
17 MAIN_PVR 0x27 ZONE_PVR 0x67 REC_PVR 0xE7 TREBLE_INCR 0xA7
18 MAIN_GAME 0x28 ZONE_GAME 0x68 REC_GAME 0xE8 TILT_INCR 0xA8
19 MAIN_TAPE 0 x29 ZONE_TAPE 0x69 REC_TAPE 0xE9 BASS_DECR 0xA9
20 MAIN_TUNER 0x2A ZONE_TUNER 0x6A REC_TUNER 0xEA TREBLE_DECR 0xAA
21 MAIN_AUX 0x2B ZONE_AUX 0x6B REC_AUX 0xEB TILT_DECR 0xAB
22 MODE_INCR 0x1A TRIGGER1_ON 0x5A TRIGGER2_On 0xDA ON 0x9A
23 MODE_DECR 0x1B TRIGGER1_OFF 0x5B TRIGGER2_OFF 0xDB STANDBY 0x9B
24 FP 0x04 ZONE_VOL_N15DB 0x44 REC_VOL_N15DB 0xC4 VOL_N15DB 0x84
25 BLUE 0x03 ZONE_VOL_N30DB 0x43 REC_VOL_N30DB 0xC3 VOL_N30DB 0x83
26 OSD 0x02 Reserved 0x42 Reserved 0xC2 EQ_OFF 0x82
27 VOL_INCR 0x17 ZONE_VOL_INCR 0x57 REC_VOL_INCR 0xD7 VOL_03DB 0x97
28 VOL_DECR 0x16 ZONE_VOL_DECR 0x56 REC_VOL_DECR 0xD6 VOL_N03DB 0x96
29 STAT 0x1C ZONE_STATUS 0x5C REC_STATUS 0xDC INPUT_STATUS 0x9C
30 MUTE 0x15 ZONE_MUTE 0x55 REC_MUTE 0xD5 FULL_MUTE 0x95
31 UP_ARROW 0x01 SUB_ADJ_INCR 0x41 Reserved 0xC1 FADER_F RONT 0x81
32 DN_ARROW 0x1D SUB_ADJ_DECR 0x5D Reserved 0xDD FADER_REAR 0x9D
33 LEFT_ARROW_DONE 0x0A ZONE_BAL_LEFT 0x4A REC_BAL_LEFT 0xCA BAL_LEFT 0x8A
34 RIGHT_ARROW _SELECT0x08 ZONE_BAL_RIGHT 0x48 REC_BAL_RIGHT 0xC8 BAL_RIGHT 0x88
35 MENU 0x09 ZONE_BAL_CENTER 0x49 REC_BAL_CENTER 0xC9 BAL_CENTER 0x89
36 MAIN_TOGGLE_7_5 0x1E Reserved 0x5E Reserved 0xDE MAIN_SRC_MODE 0x9E
37 MAIN_2_CHANNEL 0x1F Reserved 0x5F Reserved 0xDF BYPASS 0x9F
38 THX_LOGO 0x0B Reserved 0x4B Reserved 0xCB THX_EX_TOGGLE 0x8B
39 DOLBY_LOGO 0x0C Reserved 0x4C Reserved 0xCC DOLBY_EX_TOGGLE 0x8C
40 LOGIC7_LOGO 0x0D Reserved 0x4D Reserved 0xCD Reserved 0x8D
41 TV_L_LOGO 0x0E Reserved 0x4E Reserved 0xCE MONO_LOGIC 0x8E
42 DTS_LOGO 0x0F Reserved 0x4F Reserved 0xCF DTS_ES_TOGGLE 0x8F
43 MUSIC 0x10 Reserved 0x50 Reserved 0xD0 MUSIC_SURROUND 0x90
44-55 Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None Deleted None
LABEL DATA
(hex)
Zone-2
FUNCTION DATA
Button3
(hex)
Record
FUNCTION DATA
Button4
(hex)
Button9
Shift
FUNCTION DATA (hex)
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 58 of 94
Page 59

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix E MC-1 Input Id’s
Input Name
Tape
Tuner
Cd
Aux
TV
V-Disc
DVD
VCR
Input Id
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Appendix F MC-12 Input Ids
Mapped
MC-12
Input Name
OFF 0
DVD1 1
DVD2 2
LD 3
TV 4
SAT 5
VCR 6
CD 7
PVR 8
GAME 9
TAPE 10
TUNER 11
AUX 12
MC-12
Input Id
MC-1
Input Name
N/A
Aux
Aux
V-Disc
TV
Aux
VCR
CD
Aux
Aux
TAPE
TUNER
AUX
Appendix G Protocol Constants
Constant Value (Dec)
FPD_LINE_LENGTH 20Chars
PARAM_NAME_LENGTH 13Chars
CUSTOM_NAME_LENGTH 20Chars
INPUT_NAME_LENGTH 8Chars
PARAM_PATH_LENGTH 80Chars
INTER_PACKET_TIME 200mSec
SOP 0xF1 Hex
EOP 0xF2 Hex
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 59 of 94
Units
Page 60

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix H MC-12 to MC-1 Effect Map
MC-12 Effect Name MC-12
Effect ID
NONE 0 Bypass
N/A 1 Bypass
Internal Noise 2
L7 Film 3 Logic 7
L7 TV 4 TV Logic
L7 Music 5 Music Logic
2-Ch Surround 6 Music Surround
2-Channel 7 2-Channel
Mono Logic 8 Mono Logic
Mono Surround 9 Mono Logic
Mono 10 Mono Logic
Pro Logic 11 Prologic
Prologic II 12 Prologic
PLII Music 13 Prologic
THX Cinema 14 THX Cinema
Reserved 15 Logic 7
Reserved 16 Music Logic
5.1 L7 Film 17 5.1 Logic 7
5.1 L7 TV 18 5.1 Logic 7
5.1 L7 Music 19 5.1 Music
5.1 THX(ex) 20 THX 5.1
Dolby Digital 21 Dolby Digital
5.1 2-Channel 22 5.1 2-Channel
5.1 Mono Logic 23 Mono Logic
5.1 Mono Surround 24 Mono Logic
5.1 Mono 25 Mono Logic
dts L7 Film 26 dts Logic 7
dts L7 Music 27 dts Music
dts 2-Channel 28 dts 2-Channel
dts Film 29 dts Film
dts THX 30 dts THX 5.1
2ch Analog Bypass 31 Bypass
5.1 Analog Bypass 32 Bypass
External Noise PLII 33 Prologic
External Noise Dolby Digital 34 Dolby Digital
External Noise dts 35 dts Film
5.1a L7 Film 36 5.1 Logic 7
5.1a L7 Music 37 5.1 Music
5.1a 2-Channel 38 5.1 2-Channel
5.1a Standard 39 Dolby Digital
5.1a THX 40 THX 5.1
Nightclub 41 Nightclub
Concert Hall 42 Concert Hall
Church 43 Church
Cathedral 44 Cathedral
L7 Music Surround 45 Music Surround
MC-1 Effect Name
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 60 of 94
Page 61

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix I MC-1 to MC-12 Effect ID Map
MC-1
Effect
ID
0 Bypass Analog Bypass
1 Church Church
2 THX Cinema PL II THX
3 TV Logic L7 TV
4 Mono Logic Mono Logic
5 Panorama L7 Film
6 Nightclub Nightclub
7 Prologic Prologic II
8 Music Logic L7 Music
9 Party 2-Ch Surround
10 N/A none
11 N/A none
12 Concert Hall Concert Hall
13 Cathedral Cathedral
14 Music Surround L7 Music Surround
15 Logic 7 L7 Film
16 2-Channel 2-Channel
17 DD 2.0 Prologic Prologic II
18 DD 2.0 THX Cinema PL II THX
19 DD 2.0 Logic 7 L7 Film
20 DD 2.0 Music Surround L7 Music
21 DD 2.0 2-Channel 2-Channel
22 Dolby Digital Dolby Digital
23 THX 5.1 5.1 THX
24 5.1 Logic 7 5.1 L7 Film
25 5.1 Music 5.1 L7 Music
26 5.1 2-Channel 5.1 2-Channel
27 dts Film dts
28 dts THX 5.1 dts THX
29 dts Logic 7 dts L7 Film
30 dts Music dts L7 Music
31 dts 2-Channel dts 2-Chan
32 dts 2-Channel dts
33 N/A none
34 N/A none
35 N/A none
36 N/A none
37 N/A none
MC-1 Effect Name MC-12 Effect Name
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 61 of 94
Page 62

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Appendix J MC-12 Mode Ids
MC-12 Mode ID MC-12 Mode Name
0NONE
1N/A
2 Internal Noise
3 L7 Film
4 L7 TV
5 L7 Music
6 2-Ch Surround
7 2-Channel
8 Mono Logic
9 Mono Surround
10 Mono
11 Pro Logic
12 Prologic II
13 PLII Music
14 THX Cinema
15 Dts Neo6 Film
16 Dts Neo6 Music
17 5.1 L7 Film
18 5.1 L7 TV
19 5.1 L7 Music
20 5.1 THX(ex)
21 Dolby Digital(Ex)
22 5.1 2-Channel
23 5.1 Mono Logic
24 5.1 Mono Surround
25 5.1 Mono
26 dts L7 Film
27 dts L7 Music
28 dts 2-Channel
29 dts Film
30 dts THX
31 2ch Analog Bypass
32 5.1 Analog Bypass
33 External Noise PLII
34 External Noise Dolby Digital
35 External Noise dts
36 5.1a L7 Film
37 5.1a L7 Music
38 5.1a 2-Channel
39 5.1a Standard
40 5.1a THX
41 NightClub
42 Concert Hall
43 Church
44 Cathedral
45 L7 Music Surround
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 62 of 94
Page 63

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Application Notes and Examples
1.1 Box initializations:
1.1.1 MC-12:
When the MC-12 is powered on it will initialize the serial port and then transmit the DC_WAKEUP Packet,
and look for an ACK from the HOST. Currently, if an ACK is not received, the MC-12 continues to
operate. This message is mostly for the HOST to know if the MC-12 is in an operational state.
1.1.2 HOST:
When the HOST issues a HOST_WAKEUP Packet the MC-12 responds with an ACK and then transmits
the current FPD buffer with a DC_FPD notification. If the Host issues a HOST_WAKEUP command and
does not receive the ACK it should assume it is not connected or the MC-12 is not capable of responding
on the RS232 and therefore further serial communications will not be possible. If the MC-12 RS232 is
capable of communicating, the MC-12 will respond to a HOST_WAKEUP Command in any “Powered up”
state including standby.
1.2 Getting System Wide Status and Setup:
TBD
1.3 Downloading the System Setup to the MC-12:
TBD
1.4 Simple System Control & System Status:
The HOST can control the system via the IR commands thus making any direct IR code a direct command.
Because of some limitations in the IR codes the HOST also has direct control over the system volume,
balance, fader, effect selection, zone 2 volume, balance and input selection through dedicated commands.
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 63 of 94
Page 64

Page 65
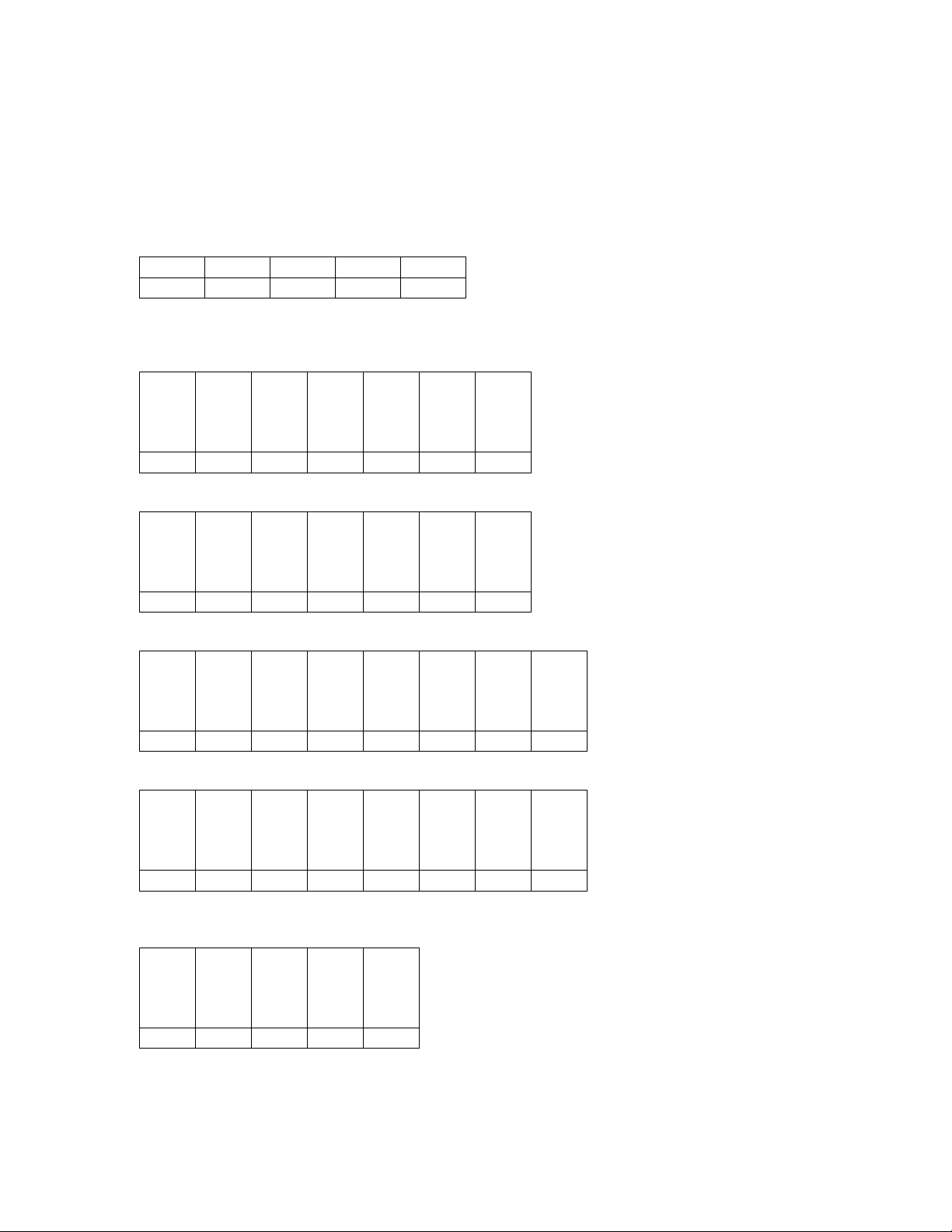
Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1.5 Examples:
The following examples show the byte’s transmitted for the MC-12 Get Unit Configuration, and Send MC-1
IR, and Send MC-12 IR Commands . They are shown as they should be transmitted from left to right.
1.5.1 MC-12 Get Unit Configuration
The HOST initiates by sending the GET_UNIT_CONFIG command packet:
SOP DLL DC CMD AppDC EOP
F1 03 38 00 F2
If the command is received without error the MC-12 responds with the UNIT_CONFIG response packet:
SOP DLL DC CMD App DC DATA0 DATA1 DATA2
REV
ProductIdSW
PARAM
COUNT
(LSB)
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
TYPE SW LVL
PARAM
COUNT
(MSB)
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
EFFECT
COUNT
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
F1 1E 91 19 04 04 00
DATA3 DATA4 DATA5 DATA6 DATA7 DATA8 DATA9
SW MJ
REV
DATA10 DATA11 DATA12 DATA13 DATA14 DATA15 DATA16 DATA17
Time
Stamp
DATA18 DATA19 DATA20 DATA21 DATA22 DATA23 DATA24 DATA25
Time
Stamp
SW MN
01 00 01 01 EF 03 23
Stamp
30 31 2f 30 37 2f 32 37
01 / 07 / 27
Stamp
20 31 37 3A 30 37 00 00
(sp) 1 7 : 0 7
REV
Time
Time
PTCL MJ
REV
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
PTCL MN
Time
Stamp
Time
Stamp
DATA26 DATA27 DATA28 DATA29 EOP
Serial
Number
(LSB)
Serial
Number
68 04 00 00 F2
Serial
Number
Serial
Number
(MSB)
From the response packet we can see that the MC-12 is configured as a
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 65 of 94
Page 66

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
Product Id is Lexicon MC-12
Software type COMPLETE
Software level of RELEASED
Software Version 1.00
Protocol Version 1.01
with 1007 parameters
and 25 effects,
and the software image was built
“01/07/27 17:07”
and has an internal serial number of
1128 (0x00 00 04 68)
1.5.2 Send MC-1 IR Command Example
SOP DLL DC CMD AppDC DATA0 EOP
IR Key
F1 04 14 01 17 F2
This example shows how to transmit the MC-1 IR command for “Volume Up”. The bytes are transmitted
from left to right and they are defined as:
Byte 0: Start of Packet(F1 hex)
Byte 1: Data Link Layer(DLL) Data Count(DC); for an IR command this would be 4 bytes to
follow
Byte 2: The Application Layer Command, in this case it is 14 hex indicating this is an IR
command packet.
Byte 3: The Application Layer Data Count(DC); for this packet it is 1 data byte to follow.
Byte 4: The Application Command Data: This IR Command Packet is transmitting Key Code
“Volume Up”(17 hex). To transmit other IR Key Codes the user would replace this byte
with other IR key codes as found in Appendix C MC-12 IR-Codes.
Byte 5: End of Packet (F2 hex)
Code
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 66 of 94
Page 67

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1.5.3 Send MC-12 IR Command Example
SOP DLL DC CMD AppDC DATA0 EOP
IR Key
F1 04 39 01 28 F2
Code
This example shows how to transmit the IR command for “
MAIN_GAME
”. This example command will select
the GAME input for the Main Zone. The bytes are transmitted from left to right and they
are defined as:
Byte 0: Start of Packet(F1 hex)
Byte 1: Data Link Layer(DLL) Data Count(DC); for an IR command this would be 4 bytes to
follow
Byte 2: The Application Layer Command, in this case it is 39 hex indicating this is an IR
command packet.
Byte 3: The Application Layer Data Count(DC); for this packet it is 1 data byte to follow.
Byte 4: The Application Command Data: This IR Command Packet is transmitting Key Code
MAIN_GAME
“
”(28 hex). To transmit other IR Key Codes the user would replace this byte
with other IR key codes as found in Appendix D MC-12 IR Codes.
Byte 5: End of Packet (F2 hex)
1.6 MC12 V3.00 Parameter ID List
The following table is for
V3.00 reference only
Protocol version changes. The MC12 can always be queried for the correct Parameter Id numbers and
Parameter Definition Packets.
ParamId
(dec)
ParamId
(hex)
ParamName
0 0x0000
1 0x0001 PARAM.INPUTS
2 0x0002 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF
3 0x0003 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.INPNAME
4 0x0004 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.DIGIN
5 0x0005 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.ANLGIN
6 0x0006 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.ANLGTRIM
7 0x0007 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.TRIMMODE
8 0x0008 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.VIDEOIN
9 0x0009 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.CH2EFFCT
10 0x000A PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.DDEFFCT
11 0x000B PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.DTSEFFCT
12 0x000C PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.MSRCMODE
13 0x000D PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.RSRCMODE
14 0x000E PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.ZSRCMODE
15 0x000F PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.RECTRIM
16 0x0010 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.SPDIF
17 0x0011 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.ANLGBYPASS
18 0x0012 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.DIGBYPASS
19 0x0013 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.TRIGGER1
20 0x0014 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.TRIGGER2
21 0x0015 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.COMPONENTIN
22 0x0016 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.SVID_16_9
. These Parameter Id Values will change with S/W and
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 67 of 94
Page 68

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
23 0x0017 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.RECBLOCK
24 0x0018 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.SVIDOSD_4_3
25 0x0019 PARAM.INPUTS.OFF.COMPNTOSD
26 0x001A PARAM.INPUTS.OFF._51_AD_EFFECT
27 0x001B PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1
28 0x001C PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.INPNAME
29 0x001D PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.DIGIN
30 0x001E PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.ANLGIN
31 0x001F PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.ANLGTRIM
32 0x0020 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.TRIMMODE
33 0x0021 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.VIDEOIN
34 0x0022 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.CH2EFFCT
35 0x0023 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.DDEFFCT
36 0x0024 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.DTSEFFCT
37 0x0025 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.MSRCMODE
38 0x0026 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.RSRCMODE
39 0x0027 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.ZSRCMODE
40 0x0028 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.RECTRIM
41 0x0029 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.SPDIF
42 0x002A PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.ANLGBYPASS
43 0x002B PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.DIGBYPASS
44 0x002C PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.TRIGGER1
45 0x002D PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.TRIGGER2
46 0x002E PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.COMPONENTIN
47 0x002F PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.SVID_16_9
48 0x0030 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.RECBLOCK
49 0x0031 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.SVIDOSD_4_3
50 0x0032 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1.COMPNTOSD
51 0x0033 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD1._51_AD_EFFECT
52 0x0034 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2
53 0x0035 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.INPNAME
54 0x0036 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.DIGIN
55 0x0037 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.ANLGIN
56 0x0038 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.ANLGTRIM
57 0x0039 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.TRIMMODE
58 0x003A PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.VIDEOIN
59 0x003B PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.CH2EFFCT
60 0x003C PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.DDEFFCT
61 0x003D PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.DTSEFFCT
62 0x003E PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.MSRCMODE
63 0x003F PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.RSRCMODE
64 0x0040 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.ZSRCMODE
65 0x0041 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.RECTRIM
66 0x0042 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.SPDIF
67 0x0043 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.ANLGBYPASS
68 0x0044 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.DIGBYPASS
69 0x0045 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.TRIGGER1
70 0x0046 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.TRIGGER2
71 0x0047 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.COMPONENTIN
72 0x0048 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.SVID_16_9
73 0x0049 PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.RECBLOCK
74 0x004A PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.SVIDOSD_4_3
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 68 of 94
Page 69

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
75 0x004B PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2.COMPNTOSD
76 0x004C PARAM.INPUTS.DVD2._51_AD_EFFECT
77 0x004D PARAM.INPUTS.LD
78 0x004E PARAM.INPUTS.LD.INPNAME
79 0x004F PARAM.INPUTS.LD.DIGIN
80 0x0050 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.ANLGIN
81 0x0051 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.ANLGTRIM
82 0x0052 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.TRIMMODE
83 0x0053 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.VIDEOIN
84 0x0054 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.CH2EFFCT
85 0x0055 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.DDEFFCT
86 0x0056 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.DTSEFFCT
87 0x0057 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.MSRCMODE
88 0x0058 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.RSRCMODE
89 0x0059 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.ZSRCMODE
90 0x005A PARAM.INPUTS.LD.RECTRIM
91 0x005B PARAM.INPUTS.LD.SPDIF
92 0x005C PARAM.INPUTS.LD.ANLGBYPASS
93 0x005D PARAM.INPUTS.LD.DIGBYPASS
94 0x005E PARAM.INPUTS.LD.TRIGGER1
95 0x005F PARAM.INPUTS.LD.TRIGGER2
96 0x0060 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.COMPONENTIN
97 0x0061 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.SVID_16_9
98 0x0062 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.RECBLOCK
99 0x0063 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.SVIDOSD_4_3
100 0x0064 PARAM.INPUTS.LD.COMPNTOSD
101 0x0065 PARAM.INPUTS.LD._51_AD_EFFECT
102 0x0066 PARAM.INPUTS.CD
103 0x0067 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.INPNAME
104 0x0068 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.DIGIN
105 0x0069 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.ANLGIN
106 0x006A PARAM.INPUTS.CD.ANLGTRIM
107 0x006B PARAM.INPUTS.CD.TRIMMODE
108 0x006C PARAM.INPUTS.CD.VIDEOIN
109 0x006D PARAM.INPUTS.CD.CH2EFFCT
110 0x006E PARAM.INPUTS.CD.DDEFFCT
111 0x006F PARAM.INPUTS.CD.DTSEFFCT
112 0x0070 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.MSRCMODE
113 0x0071 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.RSRCMODE
114 0x0072 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.ZSRCMODE
115 0x0073 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.RECTRIM
116 0x0074 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.SPDIF
117 0x0075 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.ANLGBYPASS
118 0x0076 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.DIGBYPASS
119 0x0077 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.TRIGGER1
120 0x0078 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.TRIGGER2
121 0x0079 PARAM.INPUTS.CD.COMPONENTIN
122 0x007A PARAM.INPUTS.CD.SVID_16_9
123 0x007B PARAM.INPUTS.CD.RECBLOCK
124 0x007C PARAM.INPUTS.CD.SVIDOSD_4_3
125 0x007D PARAM.INPUTS.CD.COMPNTOSD
126 0x007E PARAM.INPUTS.CD._51_AD_EFFECT
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 69 of 94
Page 70

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
127 0x007F PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE
128 0x0080 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.INPNAME
129 0x0081 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.DIGIN
130 0x0082 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.ANLGIN
131 0x0083 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.ANLGTRIM
132 0x0084 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.TRIMMODE
133 0x0085 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.VIDEOIN
134 0x0086 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.CH2EFFCT
135 0x0087 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.DDEFFCT
136 0x0088 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.DTSEFFCT
137 0x0089 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.MSRCMODE
138 0x008A PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.RSRCMODE
139 0x008B PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.ZSRCMODE
140 0x008C PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.RECTRIM
141 0x008D PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.SPDIF
142 0x008E PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.ANLGBYPASS
143 0x008F PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.DIGBYPASS
144 0x0090 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.TRIGGER1
145 0x0091 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.TRIGGER2
146 0x0092 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.COMPONENTIN
147 0x0093 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.SVID_16_9
148 0x0094 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.RECBLOCK
149 0x0095 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.SVIDOSD_4_3
150 0x0096 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE.COMPNTOSD
151 0x0097 PARAM.INPUTS.TAPE._51_AD_EFFECT
152 0x0098 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER
153 0x0099 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.INPNAME
154 0x009A PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.DIGIN
155 0x009B PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.ANLGIN
156 0x009C PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.ANLGTRIM
157 0x009D PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.TRIMMODE
158 0x009E PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.VIDEOIN
159 0x009F PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.CH2EFFCT
160 0x00A0 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.DDEFFCT
161 0x00A1 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.DTSEFFCT
162 0x00A2 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.MSRCMODE
163 0x00A3 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.RSRCMODE
164 0x00A4 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.ZSRCMODE
165 0x00A5 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.RECTRIM
166 0x00A6 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.SPDIF
167 0x00A7 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.ANLGBYPASS
168 0x00A8 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.DIGBYPASS
169 0x00A9 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.TRIGGER1
170 0x00AA PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.TRIGGER2
171 0x00AB PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.COMPONENTIN
172 0x00AC PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.SVID_16_9
173 0x00AD PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.RECBLOCK
174 0x00AE PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.SVIDOSD_4_3
175 0x00AF PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER.COMPNTOSD
176 0x00B0 PARAM.INPUTS.TUNER._51_AD_EFFECT
177 0x00B1 PARAM.INPUTS.TV
178 0x00B2 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.INPNAME
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 70 of 94
Page 71

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
179 0x00B3 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.DIGIN
180 0x00B4 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.ANLGIN
181 0x00B5 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.ANLGTRIM
182 0x00B6 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.TRIMMODE
183 0x00B7 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.VIDEOIN
184 0x00B8 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.CH2EFFCT
185 0x00B9 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.DDEFFCT
186 0x00BA PARAM.INPUTS.TV.DTSEFFCT
187 0x00BB PARAM.INPUTS.TV.MSRCMODE
188 0x00BC PARAM.INPUTS.TV.RSRCMODE
189 0x00BD PARAM.INPUTS.TV.ZSRCMODE
190 0x00BE PARAM.INPUTS.TV.RECTRIM
191 0x00BF PARAM.INPUTS.TV.SPDIF
192 0x00C0 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.ANLGBYPASS
193 0x00C1 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.DIGBYPASS
194 0x00C2 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.TRIGGER1
195 0x00C3 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.TRIGGER2
196 0x00C4 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.COMPONENTIN
197 0x00C5 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.SVID_16_9
198 0x00C6 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.RECBLOCK
199 0x00C7 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.SVIDOSD_4_3
200 0x00C8 PARAM.INPUTS.TV.COMPNTOSD
201 0x00C9 PARAM.INPUTS.TV._51_AD_EFFECT
202 0x00CA PARAM.INPUTS.VCR
203 0x00CB PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.INPNAME
204 0x00CC PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.DIGIN
205 0x00CD PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.ANLGIN
206 0x00CE PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.ANLGTRIM
207 0x00CF PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.TRIMMODE
208 0x00D0 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.VIDEOIN
209 0x00D1 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.CH2EFFCT
210 0x00D2 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.DDEFFCT
211 0x00D3 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.DTSEFFCT
212 0x00D4 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.MSRCMODE
213 0x00D5 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.RSRCMODE
214 0x00D6 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.ZSRCMODE
215 0x00D7 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.RECTRIM
216 0x00D8 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.SPDIF
217 0x00D9 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.ANLGBYPASS
218 0x00DA PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.DIGBYPASS
219 0x00DB PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.TRIGGER1
220 0x00DC PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.TRIGGER2
221 0x00DD PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.COMPONENTIN
222 0x00DE PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.SVID_16_9
223 0x00DF PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.RECBLOCK
224 0x00E0 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.SVIDOSD_4_3
225 0x00E1 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR.COMPNTOSD
226 0x00E2 PARAM.INPUTS.VCR._51_AD_EFFECT
227 0x00E3 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR
228 0x00E4 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.INPNAME
229 0x00E5 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.DIGIN
230 0x00E6 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.ANLGIN
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 71 of 94
Page 72

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
231 0x00E7 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.ANLGTRIM
232 0x00E8 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.TRIMMODE
233 0x00E9 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.VIDEOIN
234 0x00EA PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.CH2EFFCT
235 0x00EB PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.DDEFFCT
236 0x00EC PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.DTSEFFCT
237 0x00ED PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.MSRCMODE
238 0x00EE PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.RSRCMODE
239 0x00EF PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.ZSRCMODE
240 0x00F0 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.RECTRIM
241 0x00F1 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.SPDIF
242 0x00F2 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.ANLGBYPASS
243 0x00F3 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.DIGBYPASS
244 0x00F4 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.TRIGGER1
245 0x00F5 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.TRIGGER2
246 0x00F6 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.COMPONENTIN
247 0x00F7 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.SVID_16_9
248 0x00F8 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.RECBLOCK
249 0x00F9 PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.SVIDOSD_4_3
250 0x00FA PARAM.INPUTS.PVR.COMPNTOSD
251 0x00FB PARAM.INPUTS.PVR._51_AD_EFFECT
252 0x00FC PARAM.INPUTS.SAT
253 0x00FD PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.INPNAME
254 0x00FE PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.DIGIN
255 0x00FF PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.ANLGIN
256 0x0100 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.ANLGTRIM
257 0x0101 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.TRIMMODE
258 0x0102 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.VIDEOIN
259 0x0103 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.CH2EFFCT
260 0x0104 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.DDEFFCT
261 0x0105 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.DTSEFFCT
262 0x0106 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.MSRCMODE
263 0x0107 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.RSRCMODE
264 0x0108 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.ZSRCMODE
265 0x0109 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.RECTRIM
266 0x010A PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.SPDIF
267 0x010B PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.ANLGBYPASS
268 0x010C PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.DIGBYPASS
269 0x010D PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.TRIGGER1
270 0x010E PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.TRIGGER2
271 0x010F PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.COMPONENTIN
272 0x0110 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.SVID_16_9
273 0x0111 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.RECBLOCK
274 0x0112 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.SVIDOSD_4_3
275 0x0113 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT.COMPNTOSD
276 0x0114 PARAM.INPUTS.SAT._51_AD_EFFECT
277 0x0115 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME
278 0x0116 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.INPNAME
279 0x0117 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.DIGIN
280 0x0118 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.ANLGIN
281 0x0119 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.ANLGTRIM
282 0x011A PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.TRIMMODE
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 72 of 94
Page 73

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
283 0x011B PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.VIDEOIN
284 0x011C PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.CH2EFFCT
285 0x011D PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.DDEFFCT
286 0x011E PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.DTSEFFCT
287 0x011F PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.MSRCMODE
288 0x0120 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.RSRCMODE
289 0x0121 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.ZSRCMODE
290 0x0122 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.RECTRIM
291 0x0123 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.SPDIF
292 0x0124 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.ANLGBYPASS
293 0x0125 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.DIGBYPASS
294 0x0126 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.TRIGGER1
295 0x0127 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.TRIGGER2
296 0x0128 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.COMPONENTIN
297 0x0129 PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.SVID_16_9
298 0x012A PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.RECBLOCK
299 0x012B PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.SVIDOSD_4_3
300 0x012C PARAM.INPUTS.GAME.COMPNTOSD
301 0x012D PARAM.INPUTS.GAME._51_AD_EFFECT
302 0x012E PARAM.INPUTS.AUX
303 0x012F PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.INPNAME
304 0x0130 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.DIGIN
305 0x0131 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.ANLGIN
306 0x0132 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.ANLGTRIM
307 0x0133 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.TRIMMODE
308 0x0134 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.VIDEOIN
309 0x0135 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.CH2EFFCT
310 0x0136 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.DDEFFCT
311 0x0137 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.DTSEFFCT
312 0x0138 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.MSRCMODE
313 0x0139 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.RSRCMODE
314 0x013A PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.ZSRCMODE
315 0x013B PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.RECTRIM
316 0x013C PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.SPDIF
317 0x013D PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.ANLGBYPASS
318 0x013E PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.DIGBYPASS
319 0x013F PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.TRIGGER1
320 0x0140 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.TRIGGER2
321 0x0141 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.COMPONENTIN
322 0x0142 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.SVID_16_9
323 0x0143 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.RECBLOCK
324 0x0144 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.SVIDOSD_4_3
325 0x0145 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX.COMPNTOSD
326 0x0146 PARAM.INPUTS.AUX._51_AD_EFFECT
327 0x0147 PARAM.INPUTS.ANLGCONFIG
328 0x0148 PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS
329 0x0149 PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.INLEFT
330 0x014A PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.INRIGHT
331 0x014B PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.INCENTER
332 0x014C PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.INLFE
333 0x014D PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.SIDELEFT
334 0x014E PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.SIDERIGHT
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 73 of 94
Page 74

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
335 0x014F PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.REARLEFT
336 0x0150 PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.REARRIGHT
337 0x0151 PARAM.INPUTS.LEVELS.PEAK
338 0x0152 PARAM.INPUTS.AUTOTRIM
339 0x0153 PARAM.MAIN
340 0x0154 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS
341 0x0155 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT
342 0x0156 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.HP_XOVER
343 0x0157 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.LEFT
344 0x0158 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.LEFT.DISTANCE
345 0x0159 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.LEFT.OUTLEVEL
346 0x015A PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.RIGHT
347 0x015B PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.RIGHT.DISTANCE
348 0x015C PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.FRONT.RIGHT.OUTLEVEL
349 0x015D PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA
350 0x015E PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_FRONT_HP_XOVER
351 0x015F PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_FRONT_L_DIST
352 0x0160 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_FRONT_L_LEVEL
353 0x0161 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_FRONT_R_DIST
354 0x0162 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_FRONT_R_LEVEL
355 0x0163 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_CNTR_HP_XOVER
356 0x0164 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_CNTR_DIST
357 0x0165 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_CNTR_LEVEL
358 0x0166 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SIDE_HP_XOVER
359 0x0167 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SIDE_L_DIST
360 0x0168 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SIDE_L_LEVEL
361 0x0169 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SIDE_R_DIST
362 0x016A PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SIDE_R_LEVEL
363 0x016B PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_REAR_HP_XOVER
364 0x016C PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_REAR_L_DIST
365 0x016D PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_REAR_L_LEVEL
366 0x016E PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_REAR_R_DIST
367 0x016F PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_REAR_R_LEVEL
368 0x0170 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SUB_LP_XOVER
369 0x0171 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SUB_L_DIST
370 0x0172 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SUB_L_LEVEL
371 0x0173 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SUB_R_DIST
372 0x0174 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_SUB_R_LEVEL
373 0x0175 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_LFE_DIST
374 0x0176 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOCAL_DATA.AC_LFE_LEVEL
375 0x0177 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.CENTER
376 0x0178 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.CENTER.HP_XOVER
377 0x0179 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.CENTER.DISTANCE
378 0x017A PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.CENTER.OUTLEVEL
379 0x017B PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE
380 0x017C PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.HP_XOVER
381 0x017D PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.LEFT
382 0x017E PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.LEFT.DISTANCE
383 0x017F PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.LEFT.OUTLEVEL
384 0x0180 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.RIGHT
385 0x0181 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.RIGHT.DISTANCE
386 0x0182 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SIDE.RIGHT.OUTLEVEL
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 74 of 94
Page 75

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
387 0x0183 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR
388 0x0184 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.HP_XOVER
389 0x0185 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.LEFT
390 0x0186 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.LEFT.DISTANCE
391 0x0187 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.LEFT.OUTLEVEL
392 0x0188 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.RIGHT
393 0x0189 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.RIGHT.DISTANCE
394 0x018A PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.REAR.RIGHT.OUTLEVEL
395 0x018B PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB
396 0x018C PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.LP_XOVER
397 0x018D PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.LEFT
398 0x018E PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.LEFT.DISTANCE
399 0x018F PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.LEFT.OUTLEVEL
400 0x0190 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.RIGHT
401 0x0191 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.RIGHT.DISTANCE
402 0x0192 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.RIGHT.OUTLEVEL
403 0x0193 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.CONFIG
404 0x0194 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.LIMITEN
405 0x0195 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUB.LIMITADJ
406 0x0196 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.LFE
407 0x0197 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.LFE.DISTANCE
408 0x0198 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.LFE.OUTLEVEL
409 0x0199 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.LFE.LIMITEN
410 0x019A PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.LFE.LIMITADJ
411 0x019B PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.LFE.PRESENT
412 0x019C PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.DISTUNITS
413 0x019D PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.SUBNOISE
414 0x019E PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.THX_ULTRA2_SUB
415 0x019F PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.THX_BGC
416 0x01A0 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.THX_ASA
417 0x01A1 PARAM.MAIN.OUTPUTS.AUTOEQENABLED
418 0x01A2 PARAM.MAIN.DATA_STREAM
419 0x01A3 PARAM.MAIN.DATA_STREAM.SAMPLE_RATE
420 0x01A4 PARAM.MAIN.DATA_STREAM.DATA_TYPE
421 0x01A5 PARAM.MAIN.DATA_STREAM.CHANNELS
422 0x01A6 PARAM.MAIN.INPUT
423 0x01A7 PARAM.MAIN.EFFECT
424 0x01A8 PARAM.MAIN.VOLUME
425 0x01A9 PARAM.MAIN.BALANCE
426 0x01AA PARAM.MAIN.FADER
427 0x01AB PARAM.MAIN.PWRONVOL
428 0x01AC PARAM.MAIN.MUTEBY
429 0x01AD PARAM.MAIN.BASS
430 0x01AE PARAM.MAIN.TREBLE
431 0x01AF PARAM.MAIN.TILT
432 0x01B0 PARAM.MAIN.MUTE
433 0x01B1 PARAM.MAIN.MODE
434 0x01B2 PARAM.MAIN.LOUDNESS
435 0x01B3 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA
436 0x01B4 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.DD_CHAN
437 0x01B5 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.ENCODING
438 0x01B6 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.REF_OFFSET
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 75 of 94
Page 76

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
439 0x01B7 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.DDBITRATE
440 0x01B8 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.EXDETECT
441 0x01B9 PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.ROOMTYPE
442 0x01BA PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.CLEV
443 0x01BB PARAM.MAIN.DOLBYDATA.SLEV
444 0x01BC PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA
445 0x01BD PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA.DTS_CHAN
446 0x01BE PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA.ES_FLAG
447 0x01BF PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA.DTSBITRATE
448 0x01C0 PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA.WORDLEN
449 0x01C1 PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA.SFREQ
450 0x01C2 PARAM.MAIN.DTSDATA._9624FLAG
451 0x01C3 PARAM.RECORD
452 0x01C4 PARAM.RECORD.DATA_STREAM
453 0x01C5 PARAM.RECORD.DATA_STREAM.SAMPLE_RATE
454 0x01C6 PARAM.RECORD.DATA_STREAM.DATA_TYPE
455 0x01C7 PARAM.RECORD.DATA_STREAM.CHANNELS
456 0x01C8 PARAM.RECORD.INPUT
457 0x01C9 PARAM.RECORD.VOLUME
458 0x01CA PARAM.RECORD.BALANCE
459 0x01CB PARAM.RECORD.PWRONVOL
460 0x01CC PARAM.RECORD.MUTE
461 0x01CD PARAM.RECORD.TRIGGER1
462 0x01CE PARAM.RECORD.TRIGGER2
463 0x01CF PARAM.ZONE
464 0x01D0 PARAM.ZONE.DATA_STREAM
465 0x01D1 PARAM.ZONE.DATA_STREAM.SAMPLE_RATE
466 0x01D2 PARAM.ZONE.DATA_STREAM.DATA_TYPE
467 0x01D3 PARAM.ZONE.DATA_STREAM.CHANNELS
468 0x01D4 PARAM.ZONE.INPUT
469 0x01D5 PARAM.ZONE.VOLUME
470 0x01D6 PARAM.ZONE.BALANCE
471 0x01D7 PARAM.ZONE.PWRONVOL
472 0x01D8 PARAM.ZONE.MUTE
473 0x01D9 PARAM.ZONE.TRIGGER1
474 0x01DA PARAM.ZONE.TRIGGER2
475 0x01DB PARAM.EFFECTS
476 0x01DC PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE
477 0x01DD PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.NAME
478 0x01DE PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.OUTPUTLEVELS
479 0x01DF PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
480 0x01E0 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
481 0x01E1 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
482 0x01E2 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
483 0x01E3 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
484 0x01E4 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.TRIGGER1
485 0x01E5 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.TRIGGER2
486 0x01E6 PARAM.EFFECTS.INT_NOISE.FRONTOUTLEVEL
487 0x01E7 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7
488 0x01E8 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.NAME
489 0x01E9 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS
490 0x01EA PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 76 of 94
Page 77

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
491 0x01EB PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
492 0x01EC PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
493 0x01ED PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
494 0x01EE PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
495 0x01EF PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.AUTOAZIMUTH
496 0x01F0 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.VOCALENH
497 0x01F1 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.FRONTSTEER
498 0x01F2 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.REEQ
499 0x01F3 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.SOUNDSTAGE
500 0x01F4 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.FIVESPKRENH
501 0x01F5 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.BASSENH
502 0x01F6 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.SURRROLLOFF
503 0x01F7 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.REARDLYOFF
504 0x01F8 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.CENTERONOFF
505 0x01F9 PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.SEVENCHANNEL
506 0x01FA PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.MONODETECT_ON
507 0x01FB PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.SURRONOFF
508 0x01FC PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.TRIGGER1
509 0x01FD PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.TRIGGER2
510 0x01FE PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.HIFRONT_REARROLLOFF
511 0x01FF PARAM.EFFECTS.LOGIC7.AUTOBALON
512 0x0200 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC
513 0x0201 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.NAME
514 0x0202 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
515 0x0203 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
516 0x0204 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
517 0x0205 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
518 0x0206 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
519 0x0207 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
520 0x0208 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.AUTOAZIMUTH
521 0x0209 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.VOCALENH
522 0x020A PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.FRONTSTEER
523 0x020B PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.REEQ
524 0x020C PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.SOUNDSTAGE
525 0x020D PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.FIVESPKRENH
526 0x020E PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.BASSENH
527 0x020F PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.SURRROLLOFF
528 0x0210 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.REARDLYOFF
529 0x0211 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.CENTERONOFF
530 0x0212 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.SEVENCHANNEL
531 0x0213 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.MONODETECT_ON
532 0x0214 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.SURRONOFF
533 0x0215 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.TRIGGER1
534 0x0216 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.TRIGGER2
535 0x0217 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.HIFRONT_REARROLLOFF
536 0x0218 PARAM.EFFECTS.TV_LOGIC.AUTOBALON
537 0x0219 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC
538 0x021A PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.NAME
539 0x021B PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
540 0x021C PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
541 0x021D PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
542 0x021E PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 77 of 94
Page 78

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
543 0x021F PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
544 0x0220 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
545 0x0221 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.AUTOAZIMUTH
546 0x0222 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.VOCALENH
547 0x0223 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.FRONTSTEER
548 0x0224 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.REEQ
549 0x0225 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.SOUNDSTAGE
550 0x0226 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.FIVESPKRENH
551 0x0227 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.BASSENH
552 0x0228 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.SURRROLLOFF
553 0x0229 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.REARDLYOFF
554 0x022A PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.CENTERONOFF
555 0x022B PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.SEVENCHANNEL
556 0x022C PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.MONODETECT_ON
557 0x022D PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.SURRONOFF
558 0x022E PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.TRIGGER1
559 0x022F PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.TRIGGER2
560 0x0230 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.HIFRONT_REARROLLOFF
561 0x0231 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_LOGIC.AUTOBALON
562 0x0232 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA
563 0x0233 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.NAME
564 0x0234 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.OUTPUTLEVELS
565 0x0235 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
566 0x0236 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
567 0x0237 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
568 0x0238 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
569 0x0239 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
570 0x023A PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.TWO_CH_MUX
571 0x023B PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.TWOCHCNTRMIX
572 0x023C PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.CENTERDELAY
573 0x023D PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.MONOREARON
574 0x023E PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.DECORRELATE
575 0x023F PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.VOCALENH
576 0x0240 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.REEQ
577 0x0241 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.SURDLY10_25
578 0x0242 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.TIMBRE
579 0x0243 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.THXMODEON
580 0x0244 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.TRIGGER1
581 0x0245 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.TRIGGER2
582 0x0246 PARAM.EFFECTS.THX_CINEMA.REARTIMBRE
583 0x0247 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC
584 0x0248 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.NAME
585 0x0249 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
586 0x024A PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
587 0x024B PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
588 0x024C PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
589 0x024D PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
590 0x024E PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
591 0x024F PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.TWO_CH_MUX
592 0x0250 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
593 0x0251 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.CENTERDELAY
594 0x0252 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.MONOREARON
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 78 of 94
Page 79

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
595 0x0253 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.DECORRELATE
596 0x0254 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.VOCALENH
597 0x0255 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.REEQ
598 0x0256 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.SURDLY10_25
599 0x0257 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.TRIGGER1
600 0x0258 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC.TRIGGER2
601 0x0259 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2
602 0x025A PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.NAME
603 0x025B PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.OUTPUTLEVELS
604 0x025C PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
605 0x025D PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
606 0x025E PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
607 0x025F PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
608 0x0260 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
609 0x0261 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.SURDLY10_25
610 0x0262 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.TW O_CH_MUX
611 0x0263 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.TWOCHCNTRMIX
612 0x0264 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.CENTERDELAY
613 0x0265 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.MONOREARON
614 0x0266 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.DECORRELATE
615 0x0267 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.VOCALENH
616 0x0268 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.REEQ
617 0x0269 PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.TRIGGER1
618 0x026A PARAM.EFFECTS.PROLOGIC2.TRIGGER2
619 0x026B PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC
620 0x026C PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.NAME
621 0x026D PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
622 0x026E PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
623 0x026F PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
624 0x0270 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
625 0x0271 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
626 0x0272 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
627 0x0273 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.SURROUNDDELAY
628 0x0274 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
629 0x0275 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
630 0x0276 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
631 0x0277 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.MONOREARON
632 0x0278 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.DECORRELATE
633 0x0279 PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.VOCALENH
634 0x027A PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.REEQ
635 0x027B PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.PL2PAN
636 0x027C PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.CNTRWIDTH
637 0x027D PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.DIMENSION
638 0x027E PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.TRIGGER1
639 0x027F PARAM.EFFECTS.PL2MUSIC.TRIGGER2
640 0x0280 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY
641 0x0281 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.NAME
642 0x0282 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.OUTPUTLEVELS
643 0x0283 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
644 0x0284 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
645 0x0285 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
646 0x0286 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 79 of 94
Page 80

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
647 0x0287 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
648 0x0288 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.AUTOAZIMUTH
649 0x0289 PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.VOCALENH
650 0x028A PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.REEQ
651 0x028B PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.MONOCNTR
652 0x028C PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.TRIGGER1
653 0x028D PARAM.EFFECTS.PARTY.TRIGGER2
654 0x028E PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO
655 0x028F PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.NAME
656 0x0290 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.OUTPUTLEVELS
657 0x0291 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
658 0x0292 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
659 0x0293 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
660 0x0294 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
661 0x0295 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
662 0x0296 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.AUTOAZIMUTH
663 0x0297 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.VOCALENH
664 0x0298 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.REEQ
665 0x0299 PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.MONOCNTR
666 0x029A PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.TRIGGER1
667 0x029B PARAM.EFFECTS.STEREO.TRIGGER2
668 0x029C PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC
669 0x029D PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.NAME
670 0x029E PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.MONOENH
671 0x029F PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.MAINLEVEL
672 0x02A0 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.ACADEMY
673 0x02A1 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.SURRROLLOFF
674 0x02A2 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.EFFECTLEVEL
675 0x02A3 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
676 0x02A4 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
677 0x02A5 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
678 0x02A6 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
679 0x02A7 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
680 0x02A8 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
681 0x02A9 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.VOCALENH
682 0x02AA PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.REEQ
683 0x02AB PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.USEREVERB
684 0x02AC PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.TRIGGER1
685 0x02AD PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_LOGIC.TRIGGER2
686 0x02AE PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO
687 0x02AF PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.NAME
688 0x02B0 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS
689 0x02B1 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
690 0x02B2 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
691 0x02B3 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
692 0x02B4 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
693 0x02B5 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
694 0x02B6 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.USEREVERB
695 0x02B7 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.FRONTOUTLEVEL
696 0x02B8 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.TRIGGER1
697 0x02B9 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO.TRIGGER2
698 0x02BA PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 80 of 94
Page 81

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
699 0x02BB PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.NAME
700 0x02BC PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS
701 0x02BD PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEV
EL
702 0x02BE PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVE
L
703 0x02BF PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEV
EL
704 0x02C0 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVE
L
705 0x02C1 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVE
L
706 0x02C2 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.USEREVERB
707 0x02C3 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.TRIGGER1
708 0x02C4 PARAM.EFFECTS.MONO_SURROUND.TRIGGER2
709 0x02C5 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7
710 0x02C6 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.NAME
711 0x02C7 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS
712 0x02C8 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
713 0x02C9 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
714 0x02CA PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
715 0x02CB PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
716 0x02CC PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
717 0x02CD PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.VOCALENH
718 0x02CE PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.FIVESPKRENH
719 0x02CF PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.BASSENH
720 0x02D0 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.REEQ
721 0x02D1 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.REARDLYOFF
722 0x02D2 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.COMPRESSION
723 0x02D3 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.LFEMIX
724 0x02D4 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.TWO_CH_MUX
725 0x02D5 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.TWOCHCNTRMIX
726 0x02D6 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.CENTERDELAY
727 0x02D7 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.SOUNDSTAGE
728 0x02D8 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.FRONTSTEER
729 0x02D9 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.SURREX
730 0x02DA PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.SEVENCHANNEL
731 0x02DB PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.TRIGGER1
732 0x02DC PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.TRIGGER2
733 0x02DD PARAM.EFFECTS._51_LOGIC7.MONOREARON
734 0x02DE PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC
735 0x02DF PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.NAME
736 0x02E0 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
737 0x02E1 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
738 0x02E2 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
739 0x02E3 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
740 0x02E4 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
741 0x02E5 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
742 0x02E6 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.VOCALENH
743 0x02E7 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.FIVESPKRENH
744 0x02E8 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.BASSENH
745 0x02E9 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.REEQ
746 0x02EA PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.REARDLYOFF
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 81 of 94
Page 82

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
747 0x02EB PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.COMPRESSION
748 0x02EC PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.LFEMIX
749 0x02ED PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
750 0x02EE PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
751 0x02EF PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
752 0x02F0 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.SOUNDSTAGE
753 0x02F1 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.FRONTSTEER
754 0x02F2 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.SURREX
755 0x02F3 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.SEVENCHANNEL
756 0x02F4 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
757 0x02F5 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
758 0x02F6 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MUSIC.MONOREARON
759 0x02F7 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC
760 0x02F8 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.NAME
761 0x02F9 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
762 0x02FA PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
763 0x02FB PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
764 0x02FC PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
765 0x02FD PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
766 0x02FE PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
767 0x02FF PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.VOCALENH
768 0x0300 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.FIVESPKRENH
769 0x0301 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.BASSENH
770 0x0302 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.REEQ
771 0x0303 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.REARDLYOFF
772 0x0304 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.COMPRESSION
773 0x0305 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.LFEMIX
774 0x0306 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.TWO_CH_MUX
775 0x0307 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.TW OCHCNTRMIX
776 0x0308 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.CENTERDELAY
777 0x0309 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.SOUNDSTAGE
778 0x030A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.FRONTSTEER
779 0x030B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.SURREX
780 0x030C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.SEVENCHANNEL
781 0x030D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.TRIGGER1
782 0x030E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.TRIGGER2
783 0x030F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_TV_LOGIC.MONOREARON
784 0x0310 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX
785 0x0311 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.NAME
786 0x0312 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS
787 0x0313 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
788 0x0314 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
789 0x0315 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
790 0x0316 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
791 0x0317 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
792 0x0318 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.COMPRESSION
793 0x0319 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.LFEMIX
794 0x031A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.TWO_CH_MUX
795 0x031B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.TWOCHCNTRMIX
796 0x031C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.CENTERDELAY
797 0x031D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.MONOREARON
798 0x031E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.DECORRELATE
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 82 of 94
Page 83

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
799 0x031F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.VOCALENH
800 0x0320 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.REEQ
801 0x0321 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.TIMBRE
802 0x0322 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.SURREX
803 0x0323 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.THXMODEON
804 0x0324 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.TRIGGER1
805 0x0325 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.TRIGGER2
806 0x0326 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX.REARTIMBRE
807 0x0327 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL
808 0x0328 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.NAME
809 0x0329 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.OUTPUTLEVELS
810 0x032A PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
811 0x032B PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
812 0x032C PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
813 0x032D PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
814 0x032E PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
815 0x032F PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.COMPRESSION
816 0x0330 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.LFEMIX
817 0x0331 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.TWO_CH_MUX
818 0x0332 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.TWOCHCNTRMIX
819 0x0333 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.CENTERDELAY
820 0x0334 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.DECORRELATE
821 0x0335 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.VOCALENH
822 0x0336 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.REEQ
823 0x0337 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.TRIGGER1
824 0x0338 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.TRIGGER2
825 0x0339 PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.MONOREARON
826 0x033A PARAM.EFFECTS.DOLBY_DIGITAL.EX
827 0x033B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL
828 0x033C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.NAME
829 0x033D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS
830 0x033E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
831 0x033F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
832 0x0340 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
833 0x0341 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
834 0x0342 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
835 0x0343 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.COMPRESSION
836 0x0344 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.LFEMIX_2CH
837 0x0345 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.TWO_CH_MUX
838 0x0346 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.TWOCHCNTRMIX
839 0x0347 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.CENTERDELAY
840 0x0348 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.DECORRELATE
841 0x0349 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.VOCALENH
842 0x034A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.REEQ
843 0x034B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.SURRMIX
844 0x034C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.MASTERLEVEL
845 0x034D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.TRIGGER1
846 0x034E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.TRIGGER2
847 0x034F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_2CHANNEL.MONOREARON
848 0x0350 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND
849 0x0351 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.NAME
850 0x0352 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 83 of 94
Page 84

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
851 0x0353 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROU
TLEVEL
852 0x0354 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUT
LEVEL
853 0x0355 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROU
TLEVEL
854 0x0356 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTL
EVEL
855 0x0357 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTL
EVEL
856 0x0358 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.USEREVERB
857 0x0359 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.TRIGGER1
858 0x035A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_SURROUND.TRIGGER2
859 0x035B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC
860 0x035C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.NAME
861 0x035D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
862 0x035E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEV
EL
863 0x035F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVE
L
864 0x0360 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVE
L
865 0x0361 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
866 0x0362 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
867 0x0363 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.EFFECTLEVEL
868 0x0364 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.ACADEMY
869 0x0365 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.SURRROLLOFF
870 0x0366 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.USEREVERB
871 0x0367 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.TRIGGER1
872 0x0368 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO_LOGIC.TRIGGER2
873 0x0369 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM
874 0x036A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.NAME
875 0x036B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS
876 0x036C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
877 0x036D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
878 0x036E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
879 0x036F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
880 0x0370 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
881 0x0371 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.VOCALENH
882 0x0372 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.FIVESPKRENH
883 0x0373 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.BASSENH
884 0x0374 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.REEQ
885 0x0375 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.REARDLYOFF
886 0x0376 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.LFEMIX
887 0x0377 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.TWO_CH_MUX
888 0x0378 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.TWOCHCNTRMIX
889 0x0379 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.CENTERDELAY
890 0x037A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.SOUNDSTAGE
891 0x037B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.FRONTSTEER
892 0x037C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.SURREX
893 0x037D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.SEVENCHANNEL
894 0x037E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.TRIGGER1
895 0x037F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.TRIGGER2
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 84 of 94
Page 85

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
896 0x0380 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_FILM.MONOREARON
897 0x0381 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS
898 0x0382 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.NAME
899 0x0383 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS
900 0x0384 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTL
EVEL
901 0x0385 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTL
EVEL
902 0x0386 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTL
EVEL
903 0x0387 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLE
VEL
904 0x0388 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLE
VEL
905 0x0389 PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.TRIGGER1
906 0x038A PARAM.EFFECTS._20_ANALOG_BYPASS.TRIGGER2
907 0x038B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS
908 0x038C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.NAME
909 0x038D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS
910 0x038E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTL
EVEL
911 0x038F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTL
EVEL
912 0x0390 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTL
EVEL
913 0x0391 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLE
VEL
914 0x0392 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLE
VEL
915 0x0393 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.TRIGGER1
916 0x0394 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_ANALOG_BYPASS.TRIGGER2
917 0x0395 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO
918 0x0396 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.NAME
919 0x0397 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS
920 0x0398 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
921 0x0399 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
922 0x039A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
923 0x039B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
924 0x039C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
925 0x039D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.USEREVERB
926 0x039E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.FRONTOUTLEVEL
927 0x039F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.TRIGGER1
928 0x03A0 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_MONO.TRIGGER2
929 0x03A1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS
930 0x03A2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.NAME
931 0x03A3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.OUTPUTLEVELS
932 0x03A4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
933 0x03A5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
934 0x03A6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
935 0x03A7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
936 0x03A8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
937 0x03A9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.LFEMIX
938 0x03AA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.TWO_CH_MUX
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 85 of 94
Page 86

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
939 0x03AB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.TWOCHCNTRMIX
940 0x03AC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.CENTERDELAY
941 0x03AD PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.MONOREARON
942 0x03AE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.DECORRELATE
943 0x03AF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.VOCALENH
944 0x03B0 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.REEQ
945 0x03B1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.TRIGGER1
946 0x03B2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.TRIGGER2
947 0x03B3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS.DTS_ES_DETECT
948 0x03B4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7
949 0x03B5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.NAME
950 0x03B6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS
951 0x03B7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
952 0x03B8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
953 0x03B9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
954 0x03BA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
955 0x03BB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
956 0x03BC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.VOCALENH
957 0x03BD PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.FIVESPKRENH
958 0x03BE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.BASSENH
959 0x03BF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.REEQ
960 0x03C0 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.REARDLYOFF
961 0x03C1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.LFEMIX
962 0x03C2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.TWO_CH_MUX
963 0x03C3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.TWOCHCNTRMIX
964 0x03C4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.CENTERDELAY
965 0x03C5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.SOUNDSTAGE
966 0x03C6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.FRONTSTEER
967 0x03C7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.SURREX
968 0x03C8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.SEVENCHANNEL
969 0x03C9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.TRIGGER1
970 0x03CA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.TRIGGER2
971 0x03CB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.MONOREARON
972 0x03CC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_LOGIC7.DTS_ES_DETECT
973 0x03CD PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX
974 0x03CE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.NAME
975 0x03CF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS
976 0x03D0 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
977 0x03D1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
978 0x03D2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
979 0x03D3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
980 0x03D4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
981 0x03D5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.LFEMIX
982 0x03D6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.TWO_CH_MUX
983 0x03D7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.TWOCHCNTRMIX
984 0x03D8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.CENTERDELAY
985 0x03D9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.MONOREARON
986 0x03DA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.DECORRELATE
987 0x03DB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.VOCALENH
988 0x03DC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.REEQ
989 0x03DD PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.TIMBRE
990 0x03DE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.SURREX
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 86 of 94
Page 87

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
991 0x03DF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.THXMODEON
992 0x03E0 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.TRIGGER1
993 0x03E1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.TRIGGER2
994 0x03E2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.REARTIMBRE
995 0x03E3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX.DTS_ES_DETECT
996 0x03E4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC
997 0x03E5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.NAME
998 0x03E6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
999 0x03E7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1000 0x03E8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1001 0x03E9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1002 0x03EA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1003 0x03EB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1004 0x03EC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.VOCALENH
1005 0x03ED PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.FIVESPKRENH
1006 0x03EE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.BASSENH
1007 0x03EF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.REEQ
1008 0x03F0 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.REARDLYOFF
1009 0x03F1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.LFEMIX
1010 0x03F2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
1011 0x03F3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1012 0x03F4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
1013 0x03F5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.SOUNDSTAGE
1014 0x03F6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.FRONTSTEER
1015 0x03F7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.SURREX
1016 0x03F8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.SEVENCHANNEL
1017 0x03F9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
1018 0x03FA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
1019 0x03FB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.MONOREARON
1020 0x03FC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_MUSIC.DTS_ES_DETECT
1021 0x03FD PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL
1022 0x03FE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.NAME
1023 0x03FF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS
1024 0x0400 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1025 0x0401 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1026 0x0402 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1027 0x0403 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1028 0x0404 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1029 0x0405 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.LFEMIX_2CH
1030 0x0406 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.TWO_CH_MUX
1031 0x0407 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1032 0x0408 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.CENTERDELAY
1033 0x0409 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.MONOREARON
1034 0x040A PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.DECORRELATE
1035 0x040B PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.VOCALENH
1036 0x040C PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.REEQ
1037 0x040D PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.SURRMIX
1038 0x040E PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.MASTERLEVEL
1039 0x040F PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.TRIGGER1
1040 0x0410 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.TRIGGER2
1041 0x0411 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_2CHANNEL.DTS_ES_DETECT
1042 0x0412 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 87 of 94
Page 88

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1043 0x0413 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.NAME
1044 0x0414 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
1045 0x0415 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVE
L
1046 0x0416 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1047 0x0417 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVE
L
1048 0x0418 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1049 0x0419 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1050 0x041A PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
1051 0x041B PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
1052 0x041C PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.DECORRELATE
1053 0x041D PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_MUSIC.MONOREARON
1054 0x041E PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM
1055 0x041F PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.NAME
1056 0x0420 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS
1057 0x0421 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1058 0x0422 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1059 0x0423 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1060 0x0424 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1061 0x0425 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1062 0x0426 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.TRIGGER1
1063 0x0427 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.TRIGGER2
1064 0x0428 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.DECORRELATE
1065 0x0429 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_NEO_FILM.MONOREARON
1066 0x042A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC
1067 0x042B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.NAME
1068 0x042C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
1069 0x042D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1070 0x042E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1071 0x042F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1072 0x0430 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1073 0x0431 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1074 0x0432 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.VOCALENH
1075 0x0433 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.FIVESPKRENH
1076 0x0434 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.BASSENH
1077 0x0435 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.REEQ
1078 0x0436 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.REARDLYOFF
1079 0x0437 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.LFEMIX
1080 0x0438 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
1081 0x0439 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1082 0x043A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
1083 0x043B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.SOUNDSTAGE
1084 0x043C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.FRONTSTEER
1085 0x043D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.SURREX
1086 0x043E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.SEVENCHANNEL
1087 0x043F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
1088 0x0440 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
1089 0x0441 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_MUSIC.MONOREARON
1090 0x0442 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL
1091 0x0443 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.NAME
1092 0x0444 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 88 of 94
Page 89

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1093 0x0445 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEV
EL
1094 0x0446 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEV
EL
1095 0x0447 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEV
EL
1096 0x0448 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVE
L
1097 0x0449 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVE
L
1098 0x044A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.LFEMIX_2CH
1099 0x044B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.TWO_CH_MUX
1100 0x044C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1101 0x044D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.CENTERDELAY
1102 0x044E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.DECORRELATE
1103 0x044F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.VOCALENH
1104 0x0450 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.REEQ
1105 0x0451 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.SURRMIX
1106 0x0452 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.MASTERLEVEL
1107 0x0453 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.TRIGGER1
1108 0x0454 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.TRIGGER2
1109 0x0455 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_2CHANNEL.MONOREARON
1110 0x0456 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD
1111 0x0457 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.NAME
1112 0x0458 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.OUTPUTLEVELS
1113 0x0459 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1114 0x045A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1115 0x045B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1116 0x045C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1117 0x045D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1118 0x045E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.VOCALENH
1119 0x045F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.REEQ
1120 0x0460 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.TRIGGER1
1121 0x0461 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD.TRIGGER2
1122 0x0462 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX
1123 0x0463 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.NAME
1124 0x0464 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS
1125 0x0465 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1126 0x0466 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1127 0x0467 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1128 0x0468 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1129 0x0469 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1130 0x046A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.LFEMIX
1131 0x046B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.TWO_CH_MUX
1132 0x046C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1133 0x046D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.CENTERDELAY
1134 0x046E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.MONOREARON
1135 0x046F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.DECORRELATE
1136 0x0470 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.VOCALENH
1137 0x0471 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.REEQ
1138 0x0472 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.TIMBRE
1139 0x0473 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.SURREXA
1140 0x0474 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.THXMODEON
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 89 of 94
Page 90

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1141 0x0475 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.TRIGGER1
1142 0x0476 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.TRIGGER2
1143 0x0477 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX.REARTIMBRE
1144 0x0478 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC
1145 0x0479 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.NAME
1146 0x047A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
1147 0x047B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLE
VEL
1148 0x047C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEV
EL
1149 0x047D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLE
VEL
1150 0x047E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEV
EL
1151 0x047F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVE
L
1152 0x0480 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.LFEMIX
1153 0x0481 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
1154 0x0482 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1155 0x0483 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
1156 0x0484 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.MONOREARON
1157 0x0485 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.DECORRELATE
1158 0x0486 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.VOCALENH
1159 0x0487 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.REEQ
1160 0x0488 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.TIMBRE
1161 0x0489 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.SURREX
1162 0x048A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.THXMODEON
1163 0x048B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
1164 0x048C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
1165 0x048D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_AD_THX_MUSIC.REARTIMBRE
1166 0x048E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC
1167 0x048F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.NAME
1168 0x0490 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
1169 0x0491 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1170 0x0492 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1171 0x0493 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1172 0x0494 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1173 0x0495 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1174 0x0496 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.COMPRESSION
1175 0x0497 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.LFEMIX
1176 0x0498 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
1177 0x0499 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.TWOCHCNTRMIX
1178 0x049A PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
1179 0x049B PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.MONOREARON
1180 0x049C PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.DECORRELATE
1181 0x049D PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.VOCALENH
1182 0x049E PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.REEQ
1183 0x049F PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.TIMBRE
1184 0x04A0 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.SURREX
1185 0x04A1 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.THXMODEON
1186 0x04A2 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
1187 0x04A3 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
1188 0x04A4 PARAM.EFFECTS._51_THX_MUSIC.REARTIMBRE
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 90 of 94
Page 91

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1189 0x04A5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC
1190 0x04A6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.NAME
1191 0x04A7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS
1192 0x04A8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1193 0x04A9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1194 0x04AA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1195 0x04AB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1196 0x04AC PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1197 0x04AD PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.LFEMIX
1198 0x04AE PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.TWO_CH_MUX
1199 0x04AF PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.TW OCHCNTRMIX
1200 0x04B0 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.CENTERDELAY
1201 0x04B1 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.MONOREARON
1202 0x04B2 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.DECORRELATE
1203 0x04B3 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.VOCALENH
1204 0x04B4 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.REEQ
1205 0x04B5 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.TIMBRE
1206 0x04B6 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.SURREX
1207 0x04B7 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.THXMODEON
1208 0x04B8 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.TRIGGER1
1209 0x04B9 PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.TRIGGER2
1210 0x04BA PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.REARTIMBRE
1211 0x04BB PARAM.EFFECTS.DTS_THX_MUSIC.DTS_ES_DETECT
1212 0x04BC PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL
1213 0x04BD PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.NAME
1214 0x04BE PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.OUTPUTLEVELS
1215 0x04BF PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1216 0x04C0 PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1217 0x04C1 PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1218 0x04C2 PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1219 0x04C3 PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1220 0x04C4 PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.TRIGGER1
1221 0x04C5 PARAM.EFFECTS.AUTO_CAL.TRIGGER2
1222 0x04C6 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB
1223 0x04C7 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.NAME
1224 0x04C8 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.OUTPUTLEVELS
1225 0x04C9 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1226 0x04CA PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1227 0x04CB PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1228 0x04CC PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1229 0x04CD PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1230 0x04CE PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.TRIGGER1
1231 0x04CF PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.TRIGGER2
1232 0x04D0 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.EFFECTLEVEL
1233 0x04D1 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.SURRROLLOFF
1234 0x04D2 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.SIZE
1235 0x04D3 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.PREDELAY
1236 0x04D4 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.MIDRT
1237 0x04D5 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.SPEECHDETECT
1238 0x04D6 PARAM.EFFECTS.NIGHTCLUB.CENTERDRYLEVEL
1239 0x04D7 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL
1240 0x04D8 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.NAME
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 91 of 94
Page 92

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1241 0x04D9 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.OUTPUTLEVELS
1242 0x04DA PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1243 0x04DB PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1244 0x04DC PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1245 0x04DD PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1246 0x04DE PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1247 0x04DF PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.TRIGGER1
1248 0x04E0 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.TRIGGER2
1249 0x04E1 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.EFFECTLEVEL
1250 0x04E2 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.SURRROLLOFF
1251 0x04E3 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.SIZE
1252 0x04E4 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.PREDELAY
1253 0x04E5 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.MIDRT
1254 0x04E6 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.SPEECHDETECT
1255 0x04E7 PARAM.EFFECTS.CONCERT_HALL.CENTERDRYLEVEL
1256 0x04E8 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH
1257 0x04E9 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.NAME
1258 0x04EA PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.OUTPUTLEVELS
1259 0x04EB PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1260 0x04EC PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1261 0x04ED PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1262 0x04EE PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1263 0x04EF PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1264 0x04F0 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.TRIGGER1
1265 0x04F1 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.TRIGGER2
1266 0x04F2 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.EFFECTLEVEL
1267 0x04F3 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.SURRROLLOFF
1268 0x04F4 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.SIZE2
1269 0x04F5 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.PREDELAY
1270 0x04F6 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.MIDRT
1271 0x04F7 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.SPEECHDETECT
1272 0x04F8 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.MONOLOGICFRONTEND
1273 0x04F9 PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.STEREORVB
1274 0x04FA PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.BASSRT
1275 0x04FB PARAM.EFFECTS.CHURCH.CENTERDRYLEVEL
1276 0x04FC PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL
1277 0x04FD PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.NAME
1278 0x04FE PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.OUTPUTLEVELS
1279 0x04FF PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1280 0x0500 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1281 0x0501 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1282 0x0502 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1283 0x0503 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1284 0x0504 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.TRIGGER1
1285 0x0505 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.TRIGGER2
1286 0x0506 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.EFFECTLEVEL
1287 0x0507 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.SURRROLLOFF
1288 0x0508 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.SIZE2
1289 0x0509 PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.PREDELAY
1290 0x050A PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.MIDRT
1291 0x050B PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.SPEECHDETECT
1292 0x050C PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.MONOLOGICFRONTEND
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 92 of 94
Page 93

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1293 0x050D PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.STEREORVB
1294 0x050E PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.BASSRT
1295 0x050F PARAM.EFFECTS.CATHEDRAL.CENTERDRYLEVEL
1296 0x0510 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR
1297 0x0511 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.NAME
1298 0x0512 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.OUTPUTLEVELS
1299 0x0513 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1300 0x0514 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1301 0x0515 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1302 0x0516 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1303 0x0517 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1304 0x0518 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.AUTOAZIMUTH
1305 0x0519 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.VOCALENH
1306 0x051A PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.FRONTSTEER
1307 0x051B PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.REEQ
1308 0x051C PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.SOUNDSTAGE
1309 0x051D PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.FIVESPKRENH
1310 0x051E PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.BASSENH
1311 0x051F PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.SURRROLLOFF
1312 0x0520 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.REARDLYOFF
1313 0x0521 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.CENTERONOFF
1314 0x0522 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.SEVENCHANNEL
1315 0x0523 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.MONODETECT_ON
1316 0x0524 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.SURRONOFF
1317 0x0525 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.TRIGGER1
1318 0x0526 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.TRIGGER2
1319 0x0527 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.HIFRONT_REARROLLOFF
1320 0x0528 PARAM.EFFECTS.MUSIC_SURR.AUTOBALON
1321 0x0529 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA
1322 0x052A PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.NAME
1323 0x052B PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.PANINPUTBAL
1324 0x052C PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.EFFECTLEVEL
1325 0x052D PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.SURRROLLOFF
1326 0x052E PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.OUTPUTLEVELS
1327 0x052F PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.CNTROUTLEVEL
1328 0x0530 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.SIDEOUTLEVEL
1329 0x0531 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.REAROUTLEVEL
1330 0x0532 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.SUBOUTLEVEL
1331 0x0533 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.OUTPUTLEVELS.LFEOUTLEVEL
1332 0x0534 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.BASSWIDTH
1333 0x0535 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.TRIGGER1
1334 0x0536 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.TRIGGER2
1335 0x0537 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.REARDLYOFF
1336 0x0538 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.BASSCONTENT
1337 0x0539 PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.SPEAKERANGLE
1338 0x053A PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.FINETIMEALIGN
1339 0x053B PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.CALSOURCE
1340 0x053C PARAM.EFFECTS.PANORAMA.CALIBRATEACTIVE
1341 0x053D PARAM.OSD
1342 0x053E PARAM.OSD.STATUS
1343 0x053F PARAM.OSD.POSITION
1344 0x0540 PARAM.OSD.FORMAT
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 93 of 94
Page 94

Lexicon, Inc.
MC-12 Serial Communications Protocol Printed on: 08/18/03
1345 0x0541 PARAM.OSD.BACKGND
1346 0x0542 PARAM.OSD.COMPONENTON
1347 0x0543 PARAM.OSD.SHOWREMOTE
1348 0x0544 PARAM.FPD
1349 0x0545 PARAM.FPD.STATUS
1350 0x0546 PARAM.FPD.BRIGHT
1351 0x0547 PARAM.LOCKS
1352 0x0548 PARAM.LOCKS.FXLOCK
1353 0x0549 PARAM.LOCKS.AUDIOLCK
1354 0x054A PARAM.LOCKS.SETUPLCK
1355 0x054B PARAM.STANDBY
1356 0x054C PARAM.CNAME
1357 0x054D PARAM.CNAMEEN
1358 0x054E PARAM.AVSYNC
1359 0x054F PARAM.PRESETEN
1360 0x0550 PARAM.TRIGGER1MODE
1361 0x0551 PARAM.TRIGGER2MODE
1362 0x0552 PARAM.USERMESSAGE
1363 0x0553 PARAM.COM
1364 0x0554 PARAM.COM.CONFIGREG0
1365 0x0555 PARAM.TMPKEY
1366 0x0556 PARAM.ERRORS
1367 0x0557 PARAM.ERRORS.ERROR1
1368 0x0558 PARAM.ERRORS.ERROR2
1369 0x0559 PARAM.LANGUAGE
© 2003 Lexicon, Inc. All rights reserved. 94 of 94
 Loading...
Loading...