Page 1

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI
Revision 1.0
June, 2012
Enterprise Platforms and Services Division
Technical Product Specification
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 2

Revision History Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
ii
Date
Revision
Number
Modifications
April, 2012
0.5
Initial release.
June, 2012
1.0
Corrected BMC LAN settings.
Revision History
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied, by
estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel®’s
Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel® assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel® disclaims any
express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel® products including liability or warranties relating to
fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel® products are not intended for use in medical, lifesaving, or life sustaining applications. Intel® may make
changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or
“undefined”. Intel® reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or
incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the
product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel Corporation server baseboards support peripheral components and contain a number of high-density VLSI and
power delivery components that need adequate airflow to cool. Intel®’s own chassis are designed and tested to meet
the intended thermal requirements of these components when the fully integrated system is used together. It is the
responsibility of the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel® developed server building blocks to consult
vendor datasheets and operating parameters to determine the amount of air flow required for their specific application
and environmental conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible if components fail or the compute module
does not operate correctly when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating limits.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2012.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 3

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Chapter Outline ...................................................................................................... 1
2. Product Overview ............................................................................................................... 2
2.1 Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI Feature Set.................................................... 2
2.2 Compute Module Layout ........................................................................................ 3
2.2.1 Connector and Component Locations .................................................................... 3
2.2.2 External I/O Connector Locations ........................................................................... 4
3. Functional Architecture ..................................................................................................... 5
3.1 Intel® Xeon® processor ........................................................................................... 5
3.1.1 Processor Support ................................................................................................. 5
3.1.2 Processor Initialization Error Summary................................................................... 7
3.2 Processor Functions Overview ................................ ............................................... 9
3.2.1 Intel® QuickPath Interconnect ............................................................................... 10
3.2.2 Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology ...................................................................... 10
3.3 Processor Integrated I/O Module (IIO) ................................................................ .. 10
3.3.1 PCI Express Interfaces ......................................................................................... 10
3.3.2 DMI2 Interface to the PCH ................................................................................... 11
3.3.3 Integrated IOAPIC ................................................................................................ 11
3.3.4 Intel® QuickData Technology ................................................................................ 11
3.4 Memory Subsystem.............................................................................................. 11
3.4.1 Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) and Memory Subsystem .............................. 11
3.4.2 Publishing Compute Module Memory ................................................................... 15
3.4.3 Memory Map and Population Rules ...................................................................... 15
3.4.4 Memory RAS ........................................................................................................ 19
3.5 Intel® C602-J Chipset Overvew ............................................................................ 20
3.5.1 Digital Media Interface (DMI) ................................................................................ 21
3.5.2 PCI Express* Interface ......................................................................................... 21
3.5.3 Serial ATA (SATA) Controller ............................................................................... 21
3.5.4 Low Pin Count (LPC) Interface ................................................................ ............. 21
3.5.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) ........................................................................... 21
3.5.6 Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) ........................................... 21
3.5.7 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controllers ................................................................ 22
3.6 Integrated Baseboard Management Controller Overview ..................................... 22
3.6.1 Super I/O Controller ............................................................................................. 22
3.6.2 Graphics Controller and Video Support ................................................................ 23
3.6.3 Baseboard Management Controller ...................................................................... 24
3.7 Network Interface Controller (NIC) ....................................................................... 25
3.8 Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d) ............................... 26
Revision 1.0 iii
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 4

Table of Contents Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
iv
4. System Security ................................................................................................................ 27
4.1 BIOS Password Protection ................................................................................... 27
4.2 Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Support .............................................................. 28
4.2.1 TPM security BIOS ............................................................................................... 28
4.2.2 Physical Presence ................................................................................................ 29
4.2.3 TPM Security Setup Options ................................................................................ 29
4.3 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology .................................................................... 30
5. Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs .................................................................... 31
5.1 Board Connector Information ............................................................................... 31
5.2 Power Connectors ................................................................................................ 31
5.3 I/O Connector Pin-out Definition ........................................................................... 32
5.3.1 VGA Connector .................................................................................................... 32
5.3.2 I/O Mezzanine Card Connector ............................................................................ 32
5.3.3 Midplane Signal Connector .................................................................................. 36
5.3.4 Serial Port Connector ........................................................................................... 37
5.3.5 USB 2.0 Connectors............................................................................................. 37
5.3.6 Low Profile eUSB SSD Support ........................................................................... 38
6. Jumper Block Settings ..................................................................................................... 39
6.1 CMOS Clear and Password Clear Usage Procedure ............................................ 40
6.2 Integrated BMC Force Update Procedure ............................................................ 41
6.3 Integrated BMC Initialization ................................................................................. 41
6.4 ME Force Update Jumper .................................................................................... 41
6.5 BIOS Recovery Jumper ........................................................................................ 42
7. Product Regulatory Requirements .................................................................................. 43
7.1 Product Regulatory Requirements ........................................................................ 43
7.2 Product Regulatory Compliance and Safety Markings .......................................... 43
7.3 Product Environmental/Ecology Requirements ..................................................... 43
Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips .............................................................................. 44
Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder .............................................................. 45
Appendix C: POST Error Code ............................................................................................... 50
Appendix D: Supported Intel® Modular Server System ........................................................ 56
Glossary .................................................................................................................................. 57
Reference Documents ............................................................................................................ 60
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 5

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1. Component and Connector Location Diagram .............................................................. 3
Figure 2. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI Front Panel Layout .............................................. 4
Figure 3. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI Functional Block Diagram .................................... 5
Figure 4. Processor Socket Assembly ......................................................................................... 6
Figure 5. Intergrated Memory Controller (IMC) and Memory Subsystem ................................... 11
Figure 6. DIMM Slot Order ........................................................................................................ 18
Figure 7. Integrated BMC Functional Block Diagram ................................................................. 22
Figure 8. eUSB SSD Support .................................................................................................... 38
Figure 9. Recovery Jumper Blocks ............................................................................................ 39
Figure 10. POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder ................................................................ ...... 45
Figure 11. Intel® Modular Server System MFSYS25V2 ............................................................. 56
Revision 1.0 v
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 6

List of Tables Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
vi
List of Tables
Table 1. Intel® compute module MFS2600KI Feature Set ........................................................... 2
Table 2. Mixed Processor Configurations .................................................................................... 8
Table 3. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI PCIe Bus Segment Characteristics ..................... 11
Table 4. UDIMM Support Guidelines (Preliminary. Subject to Change) ..................................... 13
Table 5. RDIMM Support Guidelines (Preliminary. Subject to Change) ..................................... 14
Table 6. LRDIMM Support Guidelines (Preliminary. Subject to Change) ................................... 14
Table 7. DDR3 RDIMM Population within a Channel................................................................. 16
Table 8. DDR3L Low Voltage RDIMM Population within a Channel .......................................... 16
Table 9. DDR3 UDIMM Population within a Channel................................................................. 17
Table 10. DDR3L Low Voltage UDIMM Poplulation within a Channel ....................................... 17
Table 11. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI DIMM Nomenclature ......................................... 18
Table 12. Video Modes ............................................................................................................. 23
Table 13. Video mode ............................................................................................................... 24
Table 14. NIC LED BEHAVIOR ................................................................................................. 25
Table 15. Board Connector Matrix............................................................................................. 31
Table 16. Power Connector Pin-out (J1A1) ............................................................................... 31
Table 17. VGA Connector Pin-out (J2K1) .................................................................................. 32
Table 18. 120-pin I/O Mezzanine Card Connector Pin-out ........................................................ 33
Table 19. 120-pin I/O Mezzanine Card Connector Signal Definitions ........................................ 34
Table 20. 40-pin I/O Mezzanine Card Connector Pin-out .......................................................... 36
Table 21. 96-pin Midplane Signal Connector Pin-out................................................................. 36
Table 22. Internal 9-pin Serial Header Pin-out (J4K1) ............................................................... 37
Table 23. External USB Connector Pin-out ............................................................................... 38
Table 24. Pin-out of Internal USB Connector for low-profile Solid State Drive (J1K1) ................ 38
Table 25. Recovery Jumpers .................................................................................................... 40
Table 26. POST Progress Code LED Example ......................................................................... 45
Table 27. POST Progress Codes .............................................................................................. 46
Table 28. MRC Progress Codes ............................................................................................... 48
Table 29. MRC Fatal Error Codes ............................................................................................. 48
Table 30. POST Error Codes and Messages ............................................................................ 50
Table 31. POST Error Beep Codes ........................................................................................... 55
Table 32. Integrated BMC Beep Codes ..................................................................................... 55
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 7

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS List of Tables
< This page intentionally left blank.>
Revision 1.0 vii
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 8

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Introduction
1. Introduction
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) provides board-specific information detailing the
features, functionality, and high-level architecture of the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI.
1.1 Chapter Outline
This document is divided into the following chapters:
Chapter 1 – Introduction
Chapter 2 – Product Overview
Chapter 3 – Functional Architecture
Chapter 4 – System Security
Chapter 5 – Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Chapter 6 – Jumper Block Settings
Chapter 7 – Product Regulatory Requirements
Appendix A – Integration and Usage Tips
Appendix B – POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
Appendix C – Post Error Code
Appendix D – Supported Intel® Modular Server System
Glossary
Reference Documents
Revision 1.0 1
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 9
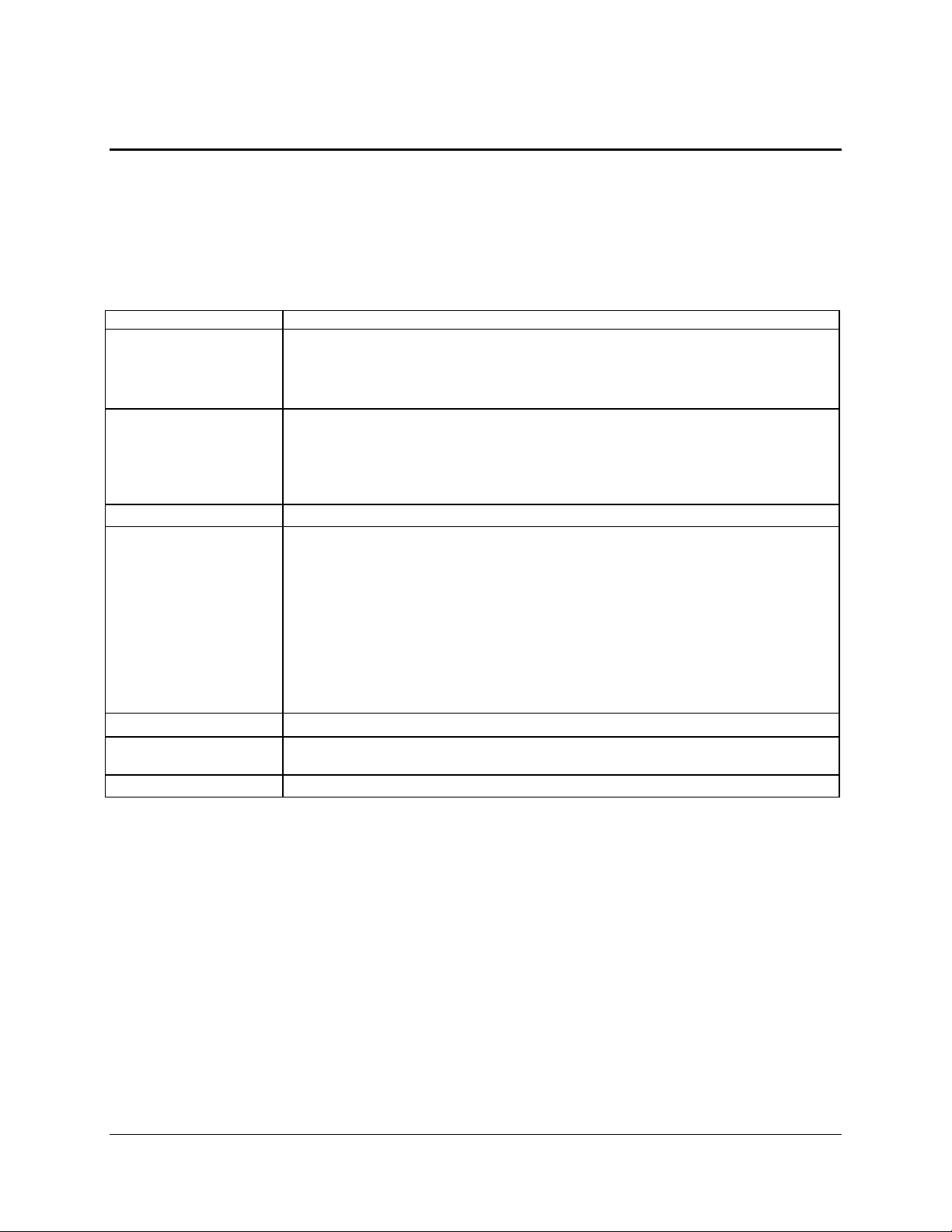
Product Overview Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
2
Feature
Description
Processors
Support for one or two Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-2600 series with up to 95W Thermal
Design Power (TDP).
8.0 GT/s, and 6.4 GT/s Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (Intel® QPI)
Enterprise Voltage Regulator-Down (EVRD) 12.0
Memory
Support for 1067/1333/1600 MT/s ECC registered (RDIMM), unbuffered (UDIMM)
and LRDIMM DDR3 memory.
16 DIMMs total across 8 memory channels (4 channels per processor).
Note: Mixed memory is not tested or supported. Non-ECC memory is not tested and is
not supported in a server environment.
Chipset
Intel® C602-J Chipset
On-board
Connectors/Headers
External connections:
Four USB 2.0 ports
DB-15 Video connector
Internal connectors/headers:
One low-profile USB Type-A connector to support low-profile USB solid state drives
One internal 7pin SATA connector for embedded SATA Flash Drive
One eUSB for embedded USB device
Intel® I/O Mezzanine connectors supporting Dual Gigabit NIC Intel® I/O Expansion
Module (Optional)
On-board Video
Integrated Matrox* G200 Core, one DB15 Video port (Front)
On-board Hard Drive
Controller
LSI* 1064e SAS controller
LAN
Intel® I350 Dual 1GbE Network Controller
2. Product Overview
The Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI is a monolithic printed circuit board with features that
were designed to support the high-density compute module market.
2.1 Intel
®
Compute Module MFS2600KI Feature Set
Table 1. Intel® compute module MFS2600KI Feature Set
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 10
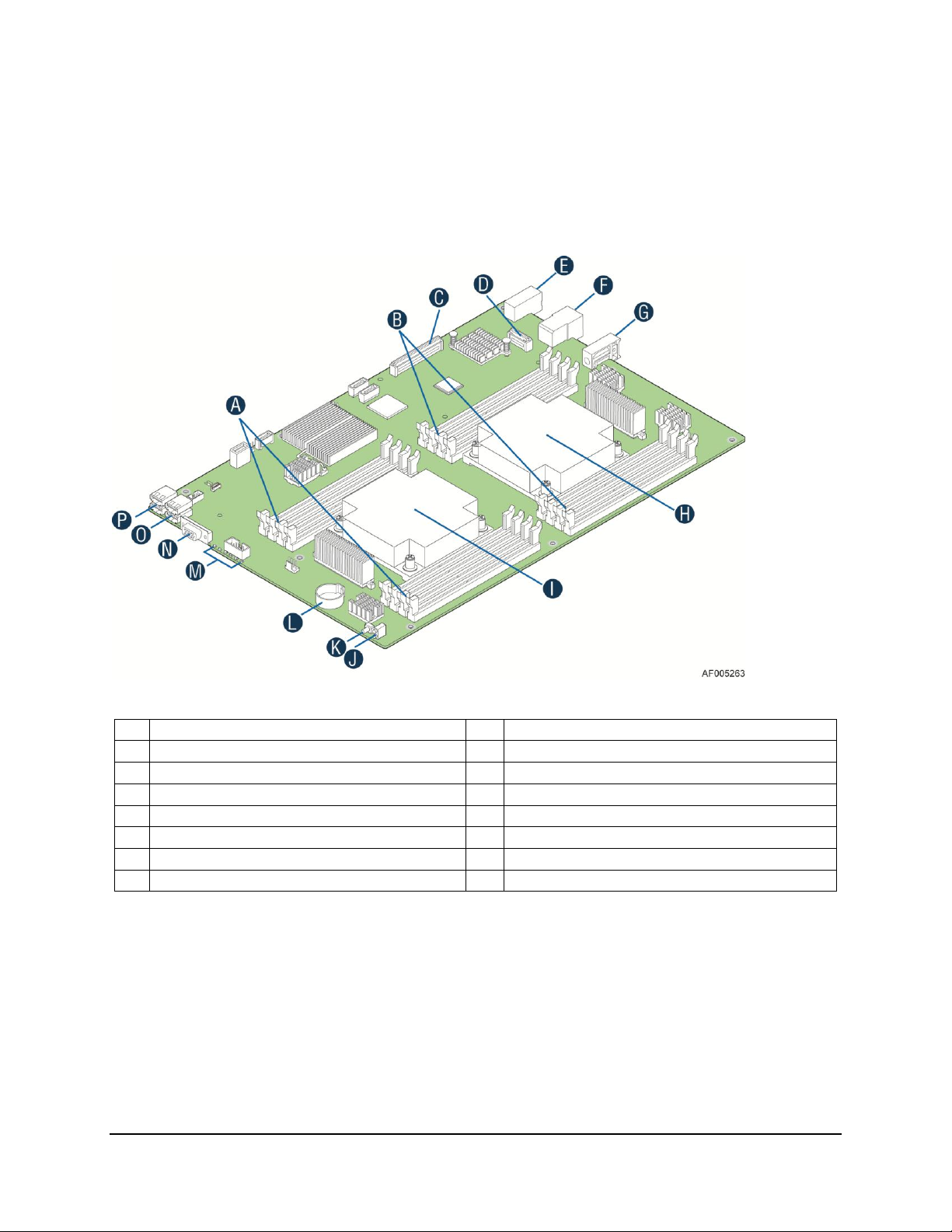
Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Product Overview
A
CPU 1 DIMM Slots
I
CPU 1 Socket
B
CPU 2 DIMM Slots
J
Power/Fault LEDs
C
Mezzanine Card Connector 1
K
Power Button
D
Mezzanine Card Connector 2
L
Battery
E
Midplane Power Connector
M
Activity and ID LEDs
F
Midplane Signal Connector
N
Video Connector
G
Midplane Guide Pin Receptacle
O
USB Ports 2 and 3
H
CPU 2 Socket
P
USB1 Ports 0 and 1
2.2 Compute Module Layout
2.2.1 Connector and Component Locations
The following figure shows the board layout of the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI. Each
connector and major component is identified by a number or letter. A description of each
identified item is provided below the figure.
Figure 1. Component and Connector Location Diagram
Revision 1.0 3
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 11
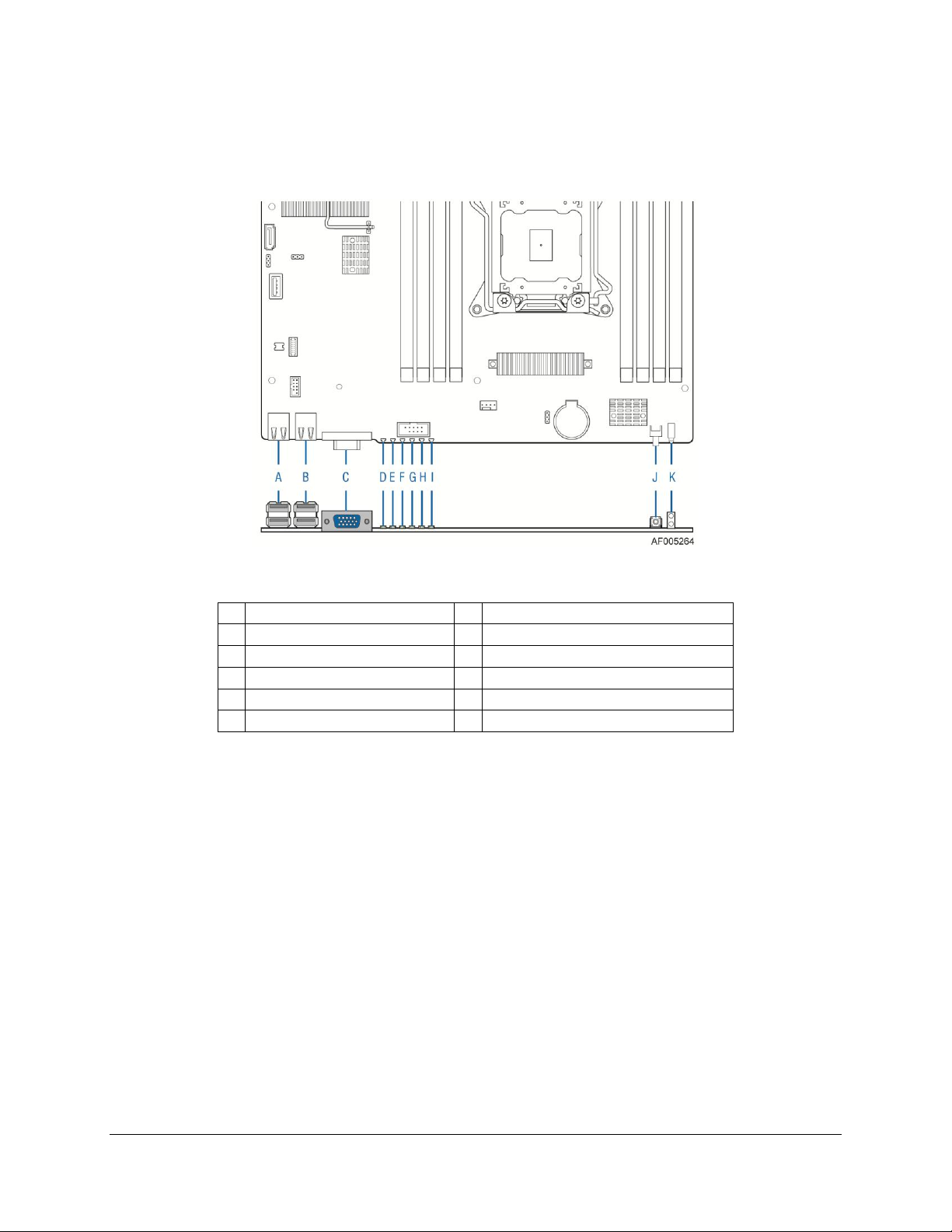
Product Overview Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
4
A
USB ports 0 and 1
G
NIC 1 LED
B
USB ports 2 and 3
H
Hard Drive Activity LED
C
Video
I
ID LED
D
I/O Mezzanine NIC 4 LED
J
Power button
E
I/O Mezzanine NIC 3 LED
K
Power and Fault LEDs
F
NIC 2 LED
2.2.3 External I/O Connector Locations
The following drawing shows the layout of the external I/O components for the Intel® Compute
Module MFS2600KI.
Figure 2. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI Front Panel Layout
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 12
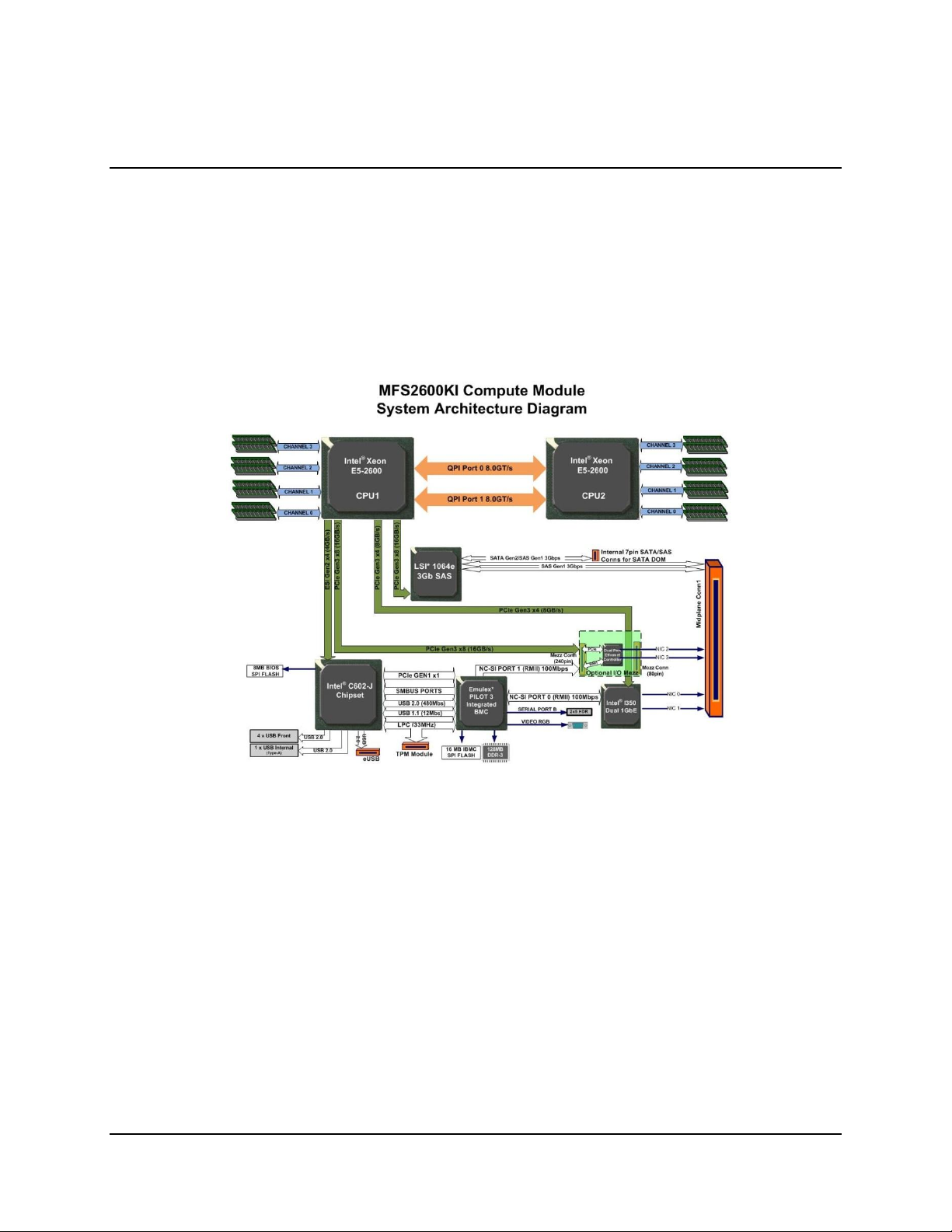
Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
3. Functional Architecture
The architecture of the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI is developed around the integrated
features and functions of the Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 product family the Intel® C602-J
chipset, the Intel® Ethernet Controller I350 GbE controller chip and the Baseboard
Management Controller.
The following diagram provides an overview of the compute module architecture, showing the
features and interconnects of each of the major sub-system components.
Figure 3. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI Functional Block Diagram
3.1 Intel
®
Xeon® processor
3.1.1 Processor Support
The compute module includes two Socket-R (LGA2011) processor sockets and can support one
or two of the Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 product family, with a Thermal Design Power
(TDP) of up to 95W processors.
Revision 1.0 5
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 13
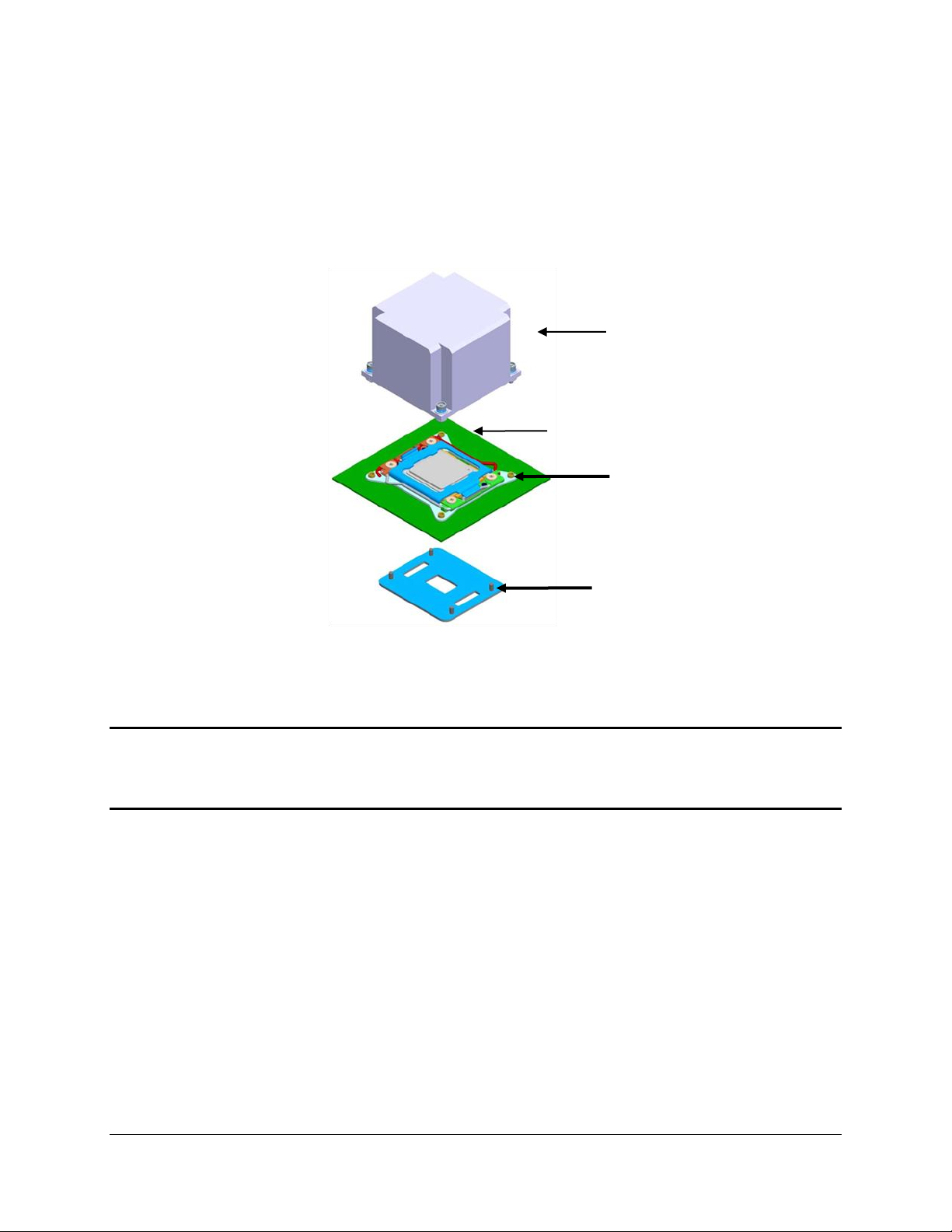
Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
6
Heat Sink
Server Board
Independent Latching
Mechanism (ILM)
Back Plate
3.1.1.1 Processor Socket Assembly
Each processor socket of the server board is pre-assembled with an Independent Latching
Mechanism (ILM) and Back Plate which allow for secure placement of the processor and
processor heat to the server board.
The illustration below identifies each sub-assembly component.
Figure 4. Processor Socket Assembly
3.1.1.2 Processor Population Rules
Note: Although the Compute Module does support dual-processor configurations consisting of
different processors that meet the defined criteria below, Intel® does not perform validation
testing of this configuation. For optimal performance in dual-processor configurations, Intel®
recommends that identical processors be installed.
When using a single processor configuration, the processor must be installed into the processor
socket labeled CPU1.
When two processors are installed, the following population rules apply:
Both processors must be of the same processor family.
Both processors must have the same number of cores.
Both processors must have the same cache sizes for all levels of processor cache
memory.
Processors with different core frequencies can be mixed in a system, given the prior
rules are met. If this condition is detected, all processor core frequencies are set to the
lowest common denominator (highest common speed) and an error is reported.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 14

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
Processors which have different Intel
®
Quickpath (QPI) Link Frequencies may operate
together if they are otherwise compatible and if a common link frequency can be
selected. The common link frequency would be the highest link frequency that all
installed processors can achieve.
Processor stepping within a common processor family can be mixed as long as it is
listed in the processor specification updates published by Intel Corporation.
3.1.2 Processor Initialization Error Summary
The following table describes mixed processor conditions and recommended actions for the
MFS2600KIdesigned around the Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 product family and Intel®
C602-J chipset product family architecture. The errors fall into one of the following categories:
Fatal: If the system can boot, it pauses at a blank screen with the text “Unrecoverable
fatal error found. System will not boot until the error is resolved” and “Press <F2>
to enter setup”, regardless of whether the “Post Error Pause” setup option is enabled or
disabled.
When the operator presses the <F2> key on the keyboard, the error message is
displayed on the Error Manager screen, and an error is logged to the System Event Log
(SEL) with the POST Error Code.
The system cannot boot unless the error is resolved. The user needs to replace the
faulty part and restart the system.
For Fatal Errors during processor initialization, the System Status LED will be set to a
steady Amber color, indicating an unrecoverable system failure condition.
Major: If the “Post Error Pause” setup option is enabled, the system goes directly to the
Error Manager to display the error, and logs the POST Error Code to SEL. Operator
intervention is required to continue booting the system.
Otherwise, if “POST Error Pause” is disabled, the system continues to boot and no
prompt is given for the error, although the Post Error Code is logged to the Error
Manager and in a SEL message.
Minor: The message is displayed on the screen or on the Error Manager screen, and
the POST Error Code is logged to the SEL. The system continues booting in a degraded
state. The user may want to replace the erroneous unit. The POST Error Pause option
setting in the BIOS setup does not have any effect on this error.
Revision 1.0 7
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 15
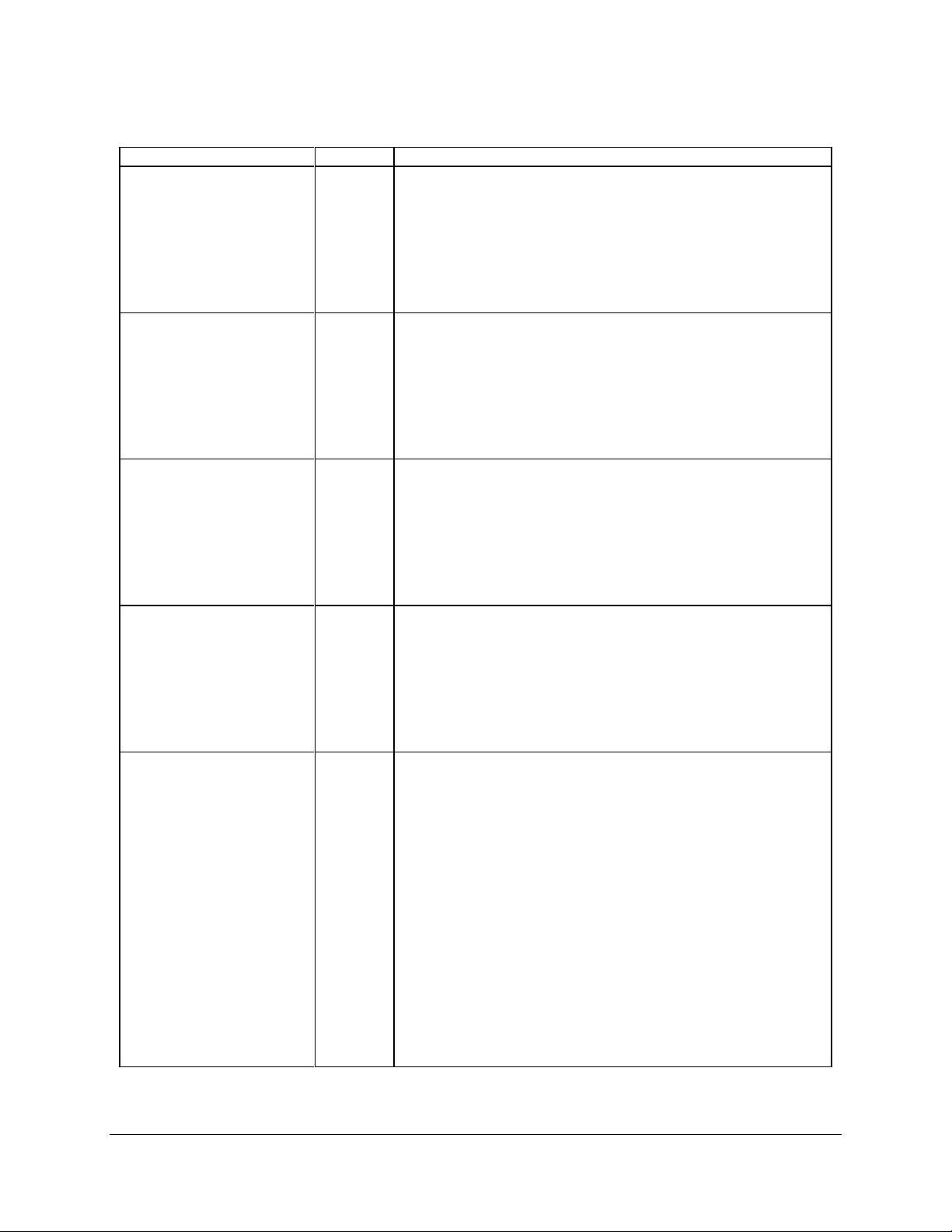
Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
8
Error
Severity
System Action
Processor family not
Identical
Fatal
The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows:
Logs the POST Error Code into the System Event Log (SEL).
Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber.
Displays “0194: Processor family mismatch detected”
message in the Error Manager.
Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the
fault condition is remedied.
Processor model not
Identical
Fatal
The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows:
Logs the POST Error Code into the System Event Log (SEL).
Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber.
Displays “0196: Processor model mismatch detected”
message in the Error Manager.
Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the
fault condition is remedied.
Processor cores/threads not
identical
Fatal
The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows:
Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL.
Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber.
Displays “0191: Processor core/thread count mismatch
detected” message in the Error Manager.
Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the
fault condition is remedied.
Processor cache not
identical
Fatal
The BIOS detects the error condition and responds as follows:
Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL.
Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber.
Displays “0192: Processor cache size mismatch detected
message in the Error Manager.
Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the
fault condition is remedied.
Processor frequency (speed)
not identical
Fatal
The BIOS detects the processor frequency difference, and responds
as follows:
Adjusts all processor frequencies to the highest common
frequency.
No error is generated – this is not an error condition.
Continues to boot the system successfully.
If the frequencies for all processors cannot be adjusted to be the
same, then this is an error, and the BIOS responds as follows:
Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL.
Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber.
Does not disable the processor.
Displays “0197: Processor speeds unable to synchronize”
message in the Error Manager.
Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault
condition is remedied.
Table 2. Mixed Processor Configurations
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 16

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
Error
Severity
System Action
Processor Intel® QuickPath
Interconnect link frequencies
not identical
Fatal
The BIOS detects the QPI link frequencies and responds as follows:
Adjusts all QPI interconnect link frequencies to highest common
frequency.
No error is generated – this is not an error condition.
Continues to boot the system successfully.
If the link frequencies for all QPI links cannot be adjusted to be the
same, then this is an error, and the BIOS responds as follows:
Logs the POST Error Code into the SEL.
Alerts the BMC to set the System Status LED to steady Amber.
Displays “0195: Processor Intel® QPI link frequencies unable
to synchronize” message in the Error Manager.
Does not disable the processor.
Takes Fatal Error action (see above) and will not boot until the fault
condition is remedied.
3.2 Processor Functions Overview
With the release of the Intel® Xeon® processor E5-2600 product family, several key system
components, including the CPU, Integrated Memory Controller (IMC), and Integrated IO Module
(IIO), have been combined into a single processor package and feature per socket; two Intel®
QuickPath Interconnect point-to-point links capable of up to 8.0 GT/s, up to 40 lanes of Gen 3
PCI Express* links capable of 8.0 GT/s, and 4 lanes of DMI2/PCI Express* Gen 2 interface with
a peak transfer rate of 5.0 GT/s. The processor supports up to 46 bits of physical address space
and 48-bit of virtual address space.
The following sections will provide an overview of the key processor features and functions that
help to define the architecture, performance and supported functionality of the server board. For
more comprehensive processor specific information, refer to the Intel® Xeon® processor E52600 product family documents listed in the Reference Document list in Chapter 1.
Processor Core Features:
Up to 8 execution cores
Each core supports two threads (Intel
per socket
46-bit physical addressing and 48-bit virtual addressing
1 GB large page support for server applications
A 32-KB instruction and 32-KB data first-level cache (L1) for each core
A 256-KB shared instruction/data mid-level (L2) cache for each core
Up to 20 MB last level cache (LLC): up to 2.5 MB per core instruction/data last level
cache (LLC), shared among all cores
Supported Technologies:
Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
Revision 1.0 9
Intel order number: G51989-002
®
Hyper-Threading Technology), up to 16 threads
Page 17

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
10
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
Intel® 64 Architecture
Intel® Streaming SIMD Extensions 4.1 (Intel® SSE4.1)
Intel® Streaming SIMD Extensions 4.2 (Intel® SSE4.2)
Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel® AVX)
Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
Execute Disable Bit
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
Intel® Intelligent Power Technology
Enhanced Intel® SpeedStep Technology
3.2.1 Intel
®
QuickPath Interconnect
The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) is a high speed, packetized, point-to-point interconnect
used in the processor. The narrow high-speed links stitch together processors in distributed
shared memory and integrated I/O platform architecture. It offers much higher bandwidth with
low latency. The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect has an
efficient architecture
allowing more
interconnect performance to be achieved in real systems. It has a snoop protocol optimized for
low latency and high scalability, as well as packet and lane structures enabling quick
completions of transactions. Reliability, availability, and serviceability features (RAS) are built into
the architecture.
The physical connectivity of each interconnect link is made up of twenty differential signal pairs
plus a differential forwarded clock. Each port supports a link pair consisting of two uni-directional
links to complete the connection between two components. This supports traffic in both
directions simultaneously. To facilitate flexibility and longevity, the interconnect is defined as
having five layers: Physical, Link, Routing, Transport, and Protocol.
The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect includes a cache coherency protocol to keep the distributed
memory and caching structures coherent during system operation. It supports both low-latency
source snooping and a scalable home snoop behavior. The coherency protocol provides for
direct cache-to-cache transfers for optimal latency.
3.2.2 Intel
®
Hyper-Threading Technology
Most Intel® Xeon® processors support Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology. The BIOS detects
processors that support this feature and enables the feature during POST.
If the processor supports this feature, the BIOS Setup provides an option to enable or disable
this feature. The default is enabled.
3.3 Processor Integrated I/O Module (IIO)
The processor’s integrated I/O module provides features traditionally supported through chipset
components. The integrated I/O module provides the following features:
3.3.1 PCI Express Interfaces
The integrated I/O module incorporates the PCI Express interface and supports up to 40 lanes
of PCI Express. The following tables list the CPU PCIe port connectivity of the Intel® Compute
Module MFS2600KI.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 18
Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
CPU#
Device
Physical Connector
Electrical
Width
CPU1
Intel® C602-J
N/A
x4 Gen2
CPU1
IO Mezzanine Card
120 pin
Mezzanine Card
Connector
x8 Gen2
CPU1
Intel® I350 NIC
N/A
x4 Gen2
CPU1
LSI* 1064e SAS
N/A
x8 Gen1
CPU 2
CPU 1
2 DIMMs/Ch
2 DIMMs/Ch
Table 3. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI PCIe Bus Segment Characteristics
3.3.2 DMI2 Interface to the PCH
The platform requires an interface to the legacy Southbridge (PCH) which provides basic,
legacy functions required for the server platform and operating systems. Since only one PCH is
required and allowed for the system, CPU2 which does not connect to PCH would use this port
as a standard x4 PCI Express 2.0 interface.
3.3.3 Integrated IOAPIC
Provides support for PCI Express devices implementing legacy interrupt messages without
interrupt sharing.
3.3.4 Intel
®
QuickData Technology
Used for efficient, high bandwidth data movement between two locations in memory or from
memory to I/O.
3.4 Memory Subsystem
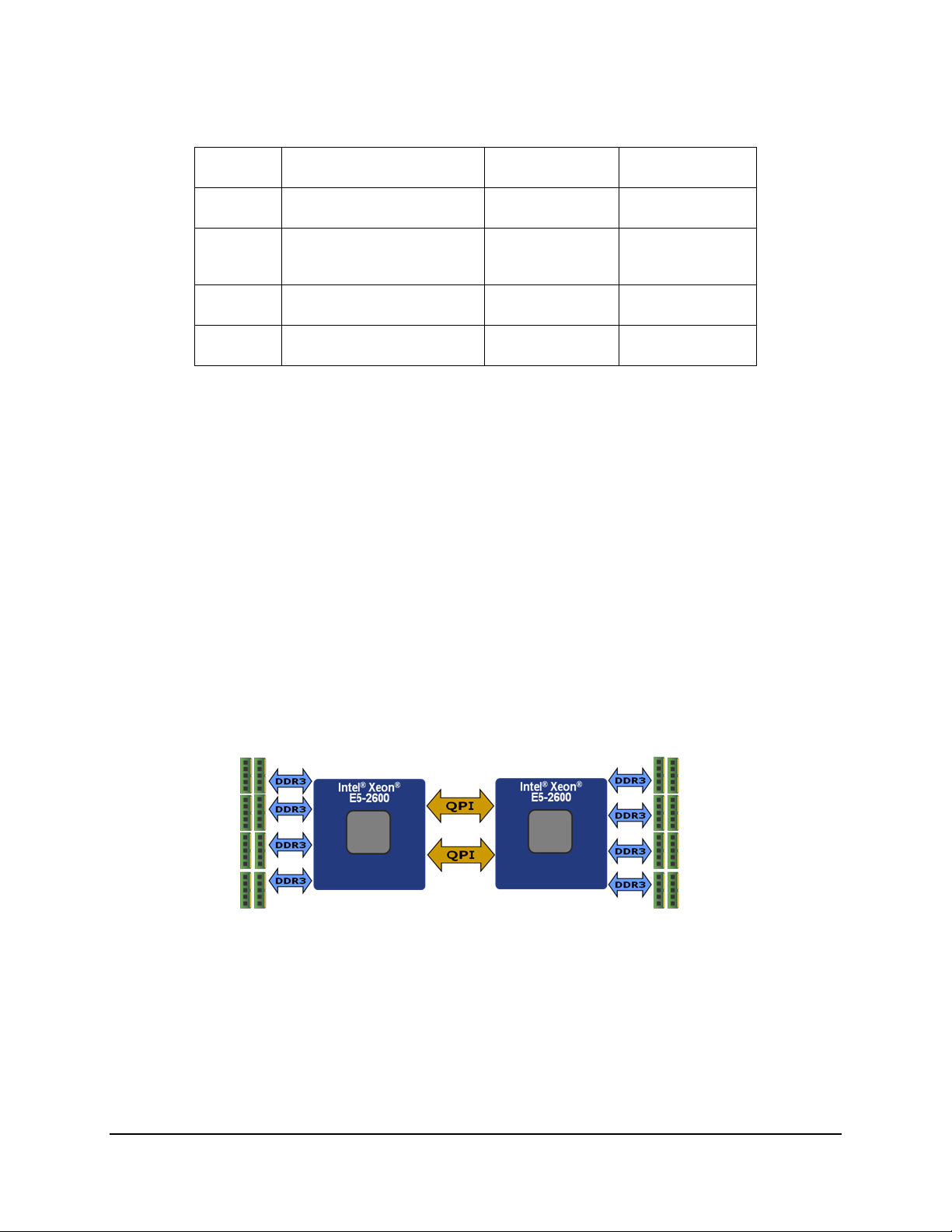
3.4.1 Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) and Memory Subsystem
Figure 5. Intergrated Memory Controller (IMC) and Memory Subsystem
Integrated into the processor is a memory controller. Each processor provides four DDR3
channels that support the following:
Unbuffered DDR3 and registered DDR3 DIMMs
LR DIMM (Load Reduced DIMM) for buffered memory solutions demanding higher
capacity memory subsystems
Revision 1.0 11
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 19

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
12
Independent channel mode or lockstep mode
Data burst length of eight cycles for all memory organization modes
Memory DDR3 data transfer rates of 800, 1066, 1333, and 1600 MT/s
64-bit wide channels plus 8-bits of ECC support for each channel
DDR3 standard I/O Voltage of 1.5 V and DDR3 Low Voltage of 1.35 V
1-Gb, 2-Gb, and 4-Gb DDR3 DRAM technologies supported for these devices:
o UDIMM DDR3 – SR x8 and x16 data widths, DR – x8 data width
o RDIMM DDR3 – SR,DR, and QR – x4 and x8 data widths
o LRDIMM DDR3 – QR – x4 and x8 data widths with direct map or with rank
multiplication
Up to eight ranks supported per memory channel, 1, 2 or 4 ranks per DIMM
Open with adaptive idle page close timer or closed page policy
Per channel memory test and initialization engine can initialize DRAM to all logical zeros
with valid ECC (with or without data scrambler) or a predefined test pattern
Isochronous access support for Quality of Service (QoS)
Minimum memory configuration: independent channel support with 1 DIMM populated
Integrated dual SMBus* master controllers
Command launch modes of 1n/2n
RAS Support:
o Rank Level Sparing and Device Tagging
o Demand and Patrol Scrubbing
o DRAM Single Device Data Correction (SDDC) for any single x4 or x8 DRAM
device. Independent channel mode supports x4 SDDC. x8 SDDC requires
lockstep mode
o Lockstep mode where channels 0 and 1 and channels 2 and 3 are operated in
lockstep mode
o Data scrambling with address to ease detection of write errors to an incorrect
address.
o Error reporting through Machine Check Architecture
o Read Retry during CRC error handling checks by iMC
o Channel mirroring within a socket
CPU1 Channel Mirror Pairs (A,B) and (C,D)
CPU2 Channel Mirror Pairs (E,F) and (G,H)
o Error Containment Recovery
Improved Thermal Throttling with dynamic Closed Loop Thermal Throttling (CLTT)
Memory thermal monitoring support for DIMM temperature
3.4.1.1 Intel
®
Compute Module MFS2600KI Supported Memory
Each processor provides four banks of memory, each capable of supporting up to two DIMMs.
DIMMs are organized into physical slots on DDR3 memory channels that belong to
processor sockets.
The memory channels from processor socket 1 are identified as Channel A, B, C, and D.
The memory channels from processor socket 2 are identified as Channel E, F, G, and H.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 20
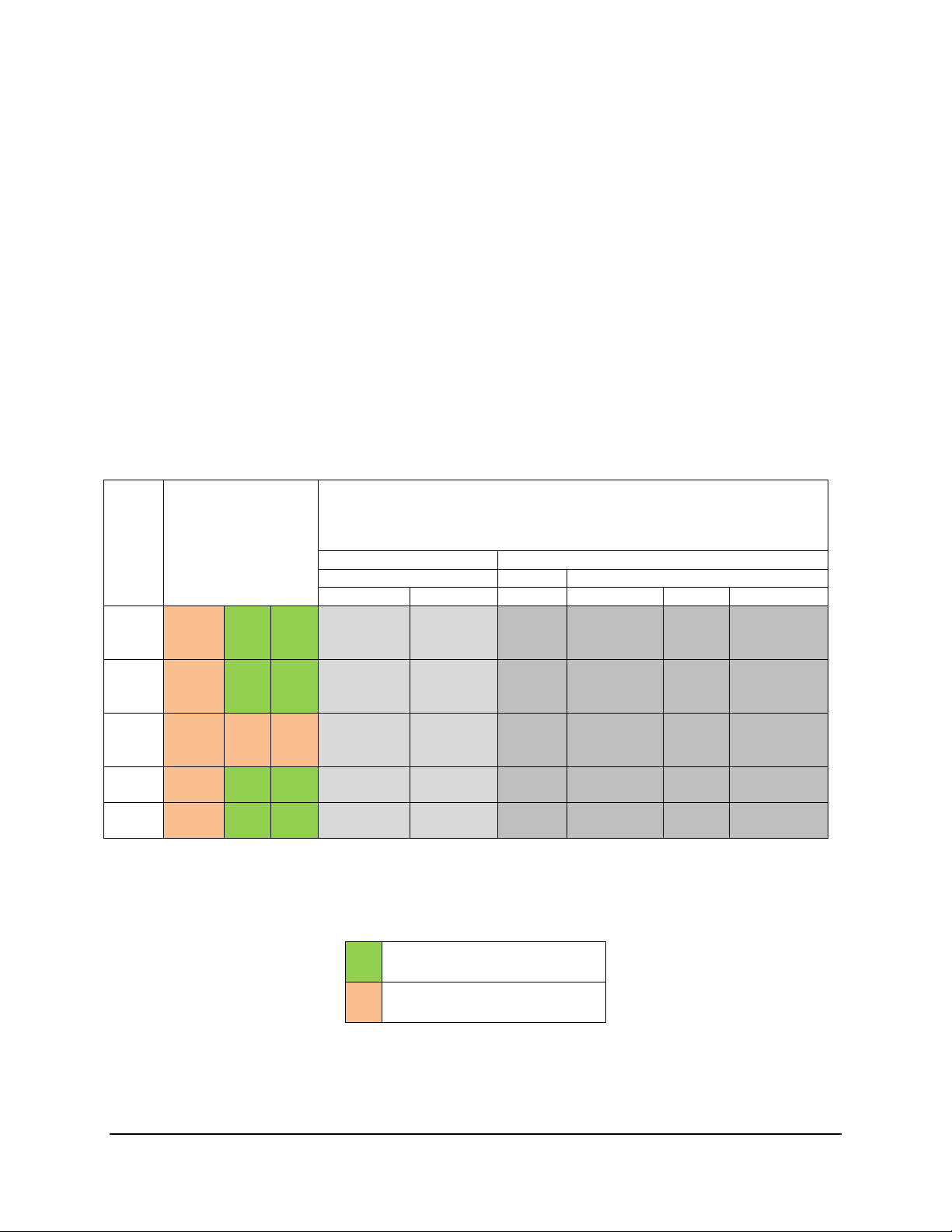
Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
Ranks
Per
DIMM
and
Data
Width
Memory Capacity Per
DIMM1
Speed (MT/s) and Voltage Validated by
Slot per Channel (SPC) and DIMM Per Channel (DPC)2,3
1 Slot per Channel
2 Slots per Channel
1DPC
1DPC
2DPC
1.35V
1.5V
1.35V
1.5V
1.35V
1.5V
SRx8
Non-
ECC
1GB
2GB
4GB
n/a
1066,
1333, 1600
n/a
1066, 1333
n/a
1066, 1333
DRx8
Non-
ECC
2GB
4GB
8GB
n/a
1066,
1333, 1600
n/a
1066, 1333
n/a
1066, 1333
SRx16
Non-
ECC
512MB
1GB
2GB
n/a
1066,
1333, 1600
n/a
1066, 1333
n/a
1066, 1333
SRx8
ECC
1GB
2GB
4GB
1066, 1333
1066,
1333, 1600
1066
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
DRx8
ECC
2GB
4GB
8GB
1066, 1333
1066,
1333, 1600
1066
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
Supported and Validated
Supported but not Validate
The silk screened DIMM slot identifiers on the board provide information about the
channel, and therefore the processor to which they belong. For example, DIMM_A1 is
the first slot on Channel A on processor 1; DIMM_E1 is the first DIMM socket on
Channel E on processor 2.
The memory slots associated with a given processor are unavailable if the
corresponding processor socket is not populated.
A processor may be installed without populating the associated memory slots provided
and a second processor is installed with associated memory. In this case, the memory is
shared by the processors. However, the platform suffers performance degradation and
latency due to the remote memory.
Processor sockets are self-contained and autonomous. However, all memory subsystem
support (such as Memory RAS, Error Management,) in the BIOS setup are applied
commonly across processor sockets.
For a complete list of supported memory for the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI, refer to the
Tested Memory List published in the Intel® Server Configurator Tool.
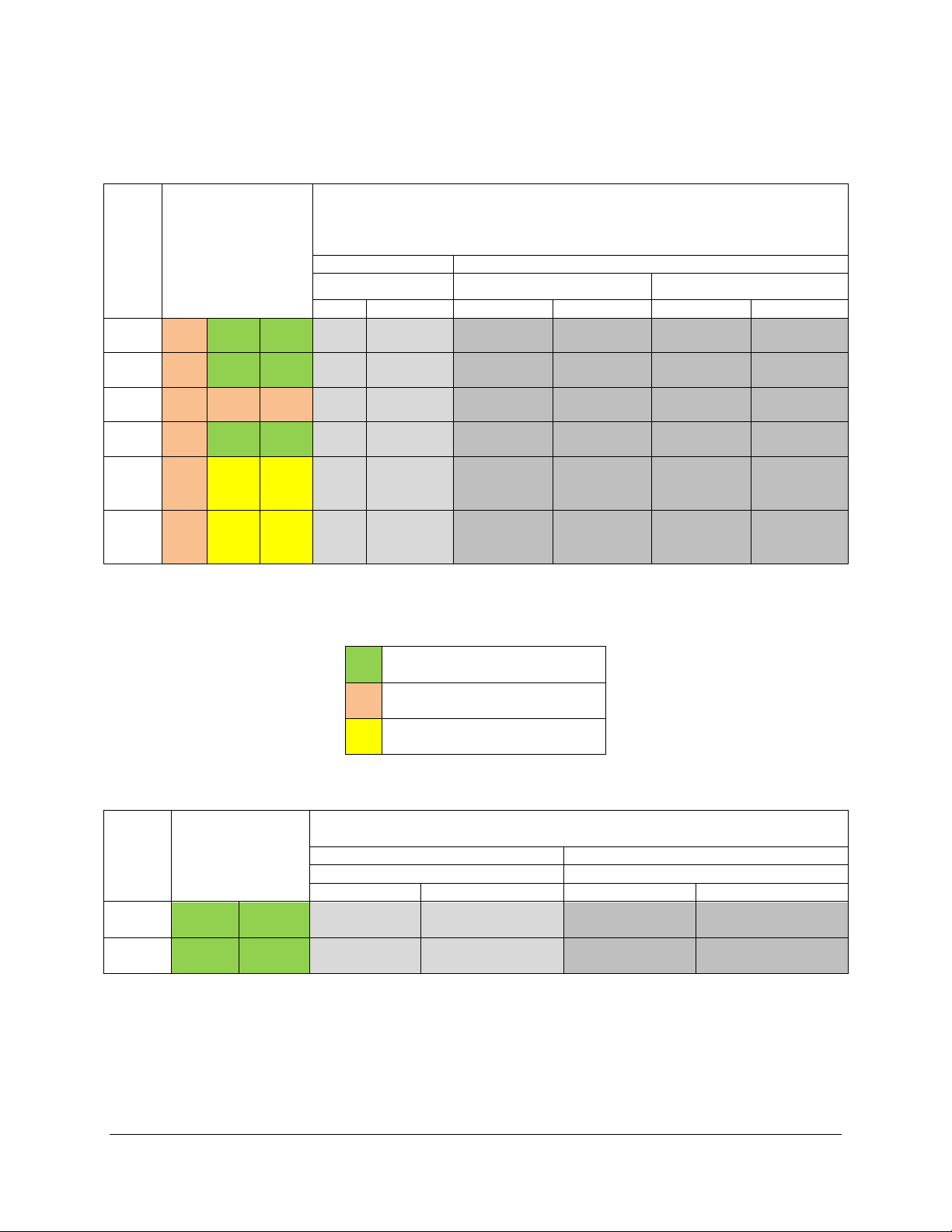
Table 4. UDIMM Support Guidelines (Preliminary. Subject to Change)
Notes:
1. Supported DRAM Densities are 1Gb, 2Gb, and 4Gb. Only 2Gb and 4Gb are validated by Intel®
2. Command Address Timing is 1N for 1DPC and 2N for 2DPC
3. No Support for 3DPC when using UDIMMs
Revision 1.0 13
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 21
Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
14
Ranks
Per
DIMM
and
Data
Width
Memory Capacity Per
DIMM1
Speed (MT/s) and Voltage Validated by
Slot per Channel (SPC) and DIMM Per Channel (DPC)2
1 Slot per Channel
2 Slots per Channel
1DPC
1DPC
2DPC
1.35V
1.5V
1.35V
1.5V
1.35V
1.5V
SRx8
1GB
2GB
4GB
1066,
1333
1066,
1333, 1600
1066, 1333
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
DRx8
2GB
4GB
8GB
1066,
1333
1066,
1333, 1600
1066, 1333
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
SRx4
2GB
4GB
8GB
1066,
1333
1066,
1333, 1600
1066, 1333
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
DRx4
4GB
8GB
16GB
1066,
1333
1066, 1333
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
QRx4
8GB
16GB
32GB
800
1066
800
1066
800
800
QRx8
4GB
8GB
16GB
800
1066
800
1066
800
800
Supported and Validated
Supported but not Validate
TBD
Ranks
Per
DIMM
and Data
Width1
Memory Capacity Per
DIMM2
Speed (MT/s) and Voltage Validated by
Slot per Channel (SPC) and DIMM Per Channel (DPC)3,4,5
1 Slot per Channel
2 Slots per Channel
1DPC
1DPC and 2DPC
1.35V
1.5V
1.35V
1.5V
QRx4
(DDP)6
16GB
32GB
1066, 1333
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
QRx8
(P)6
8GB
16GB
1066, 1333
1066, 1333
1066
1066, 1333
Table 5. RDIMM Support Guidelines (Preliminary. Subject to Change)
Notes:
1. Supported DRAM Densities are 1Gb, 2Gb, and 4Gb. Only 2Gb and 4Gb are validated by Intel®.
2. Command Address Timing is 1N
Notes:
1. Physical Rank is used to calculate DIMM Capacity
2. Supported and validated DRAM Densities are 2Gb and 4Gb
3. Command address timing is 1N
4. The speeds are estimated targets and will be verified through simulation
5. For 3SPC/3DPC – Rank Multiplication (RM) >=2
6. DDP – Dual Die Package DRAM stacking. P – Planar monolithic DRAM Dies.
Revision 1.0
Table 6. LRDIMM Support Guidelines (Preliminary. Subject to Change)
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 22

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
Supported and Validated
3.4.2 Publishing Compute Module Memory
The BIOS displays the “Total Memory” of the compute module during POST if Display
Logo is disabled in the BIOS setup. This is the total size of memory discovered by the
BIOS during POST, and is the sum of the individual sizes of installed DDR3 DIMMs in
the system.
The BIOS displays the “Effective Memory” of the compute module in the BIOS setup.
The term Effective Memory refers to the total size of all DDR3 DIMMs that are active (not
disabled) and not used as redundant units.
The BIOS provides the total memory of the compute module in the main page of the
BIOS setup. This total is the same as the amount described by the first bullet above.
If Display Logo is disabled, the BIOS displays the total system memory on the diagnostic
screen at the end of POST. This total is the same as the amount described by the first
bullet above.
3.4.3 Memory Map and Population Rules
The following are generic DIMM population requirements that generally apply to the Intel®
Compute Module MFS2600KI.
DIMM slots on any memory channel must be filled following the “farthest fill first” rule.
A maximum of eight ranks can be installed on any one channel, counting all ranks in
each DIMM on the channel.
DIMM types (UDIMM, RDIMM, LRDIMM) must not be mixed within or across processor
sockets.
Mixing ECC with non-ECC DIMMs (UDIMMs) is not supported within or across
processor sockets.
Mixing Low Voltage (1.35V) DIMMs with Standard Voltage (1.5V) DIMMs is not
supported within or across processor sockets.
Mixing DIMMs of different frequencies and latencies is not supported within or across
processor sockets.
LRDIMM Rank Multiplication Mode and Direct Map Mode must not be mixed within or
across processor sockets.
Only ECC UDIMMs support Low Voltage 1.35V operation.
QR RDIMMs may only be installed in DIMM Slot 1 or 2 on a channel.
Two DPC QR Low Voltage RDIMMs are not supported.
In order to install 3 QR LRDIMMs on the same channel, they must be operated with
Rank Multiplication as RM = 2.
RAS Modes Lockstep, Rank Sparing, and Mirroring are mutually exclusive in this BIOS.
Only one operating mode may be selected, and it will be applied to the entire system.
If a RAS Mode has been configured, and the memory population will not support it
during boot, the system will fall back to Independent Channel Mode and log and
display errors
Revision 1.0 15
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 23

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
16
Configuration
Number Speed
1N or 2N
DIMM 2
DIMM 1
(Blue Slot)
1
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Empty
Single-rank
2
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Empty
Dual-rank
3
DDR3-1066
1N
Empty
Quad-rank
4
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Single-rank
Single-rank
5
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Single-rank
Dual-rank
6
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Dual-rank
Dual-rank 7 DDR3-800
1N
Single-rank
Quad-rank 8 DDR3-800
1N
Dual-rank
Quad-rank 9 DDR3-800
1N
Quad-rank
Quad-rank
10
DDR3-800
1N
Single-rank
Single-rank
11
DDR3-800
1N
Single-rank
Dual-rank
12
DDR3-800
1N
Dual-rank
Dual-rank
13
DDR3-800
1N
Dual-rank
Dual-rank
14
DDR3-800
1N
Single-rank
Quad-rank
15
DDR3-800
1N
Dual-rank
Quad-rank
16
DDR3-800
1N
Dual-rank
Quad-rank
Configuration
Number Speed
1N or 2N
DIMM 2
DIMM 1
(Blue Slot)
1
DDR3L-1333, 1066
1N
Empty
Single-rank
2
DDR3L-1333, 1066
1N
Empty
Dual-rank 3 DDR3L-800
1N
Empty
Quad-rank
4
DDR3L-1066
1N
Single-rank
Single-rank
5
DDR3L-1066
1N
Single-rank
Dual-rank
6
DDR3L-1066
1N
Dual-rank
Dual-rank
7
DDR3L- 800
1N
Single-rank
Quad-rank
Rank Sparing Mode is only possible when all channels that are populated with memory
meet the requirement of having at least two SR or DR DIMM installed, or at least one
QR DIMM installed, on each populated channel.
Lockstep or Mirroring Modes require that for any channel pair that is populated with
memory, the memory population on both channels of the pair must be identically sized.
DIMM population rules require that DIMMs within a channel be populated starting with the BLUE
DIMM slot or DIMM farthest from the processor in a “fill-farthest” approach. In addition, when
populating a Quad-rank DIMM with a Single- or Dual-rank DIMM in the same channel, the
Quad-rank DIMM must be populated farthest from the processor.
Table 7. DDR3 RDIMM Population within a Channel
Revision 1.0
Table 8. DDR3L Low Voltage RDIMM Population within a Channel
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 24

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
Configuration
Number Speed
1N or 2N
DIMM 2
DIMM 1
(Blue Slot)
1
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Empty
Single-rank
2
DDR3-1333, and 1066
1N
Empty
Dual-rank
3
DDR3-1333, and 1066
2N
Single-rank
Single-rank
4
DDR3-1333, and 1066
2N
Single-rank
Dual-rank
5
DDR3-1333, and 1066
2N
Dual-rank
Dual-rank
Configuration
Number Speed
1N or 2N
DIMM 2
DIMM 1
(Blue Slot)
1
DDR3-1333,1066
1N
Empty
Single-rank
2
DDR3-1333, 1066
1N
Empty
Dual-rank
3
DDR3-1066
2N
Single-rank
Single-rank
4
DDR3-1066
2N
Single-rank
Dual-rank
5
DDR3-1066
2N
Dual-rank
Dual-rank
Table 9. DDR3 UDIMM Population within a Channel
Table 10. DDR3L Low Voltage UDIMM Poplulation within a Channel
Revision 1.0 17
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 25

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
18
Processor Socket 1
Processor Socket 2
(0)
Channel A
(1)
Channel B
(2)
Channel C
(3)
Channel D
(0)
Channel E
(1)
Channel F
(2)
Channel G
(3)
Channel H
A1
A2
B1
B2
C1
C2
D1
D2
E1
E2
F1
F2
G1
G2
H1
H2
Figure 6. DIMM Slot Order
3.4.3.1 Memory Subsystem Nomenclature
The nomenclature for DIMM sockets implemented on the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI is
detailed in the following table.
Table 11. Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI DIMM Nomenclature
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 26

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
3.4.3.2 Publishing System Memory
The BIOS displays the “Total Memory” of the system during POST if Quite Boot is disabled in
the BIOS setup. This is the total size of memory discovered by the BIOS during POST, and is
the sum of the individual sizes of installed DDR3 DIMMs in the system.
The BIOS displays the “Effective Memory” of the system in the BIOS setup. The term Effective
Memory refers to the total size of all DDR3 DIMMs that are active (not disabled) and not used
as redundant units.
The BIOS provides the total memory of the system in the main page of the BIOS setup. This
total is the same as the amount described by the first bullet above.
If Quite Boot is disabled, the BIOS displays the total system memory on the diagnostic screen at
the end of POST. This total is the same as the amount described by the first bullet above.
3.4.4 Memory RAS
3.4.4.1 RAS Features
The Compute Module supports the following memory RAS features:
Independent Channel Mode
Rank Sparing Mode
Mirrored Channel Mode
Lockstep Channel Mode
Regardless of RAS mode, the requirements for populating within a channel given in the section
3.3.3 must be met at all times. Note that support of RAS modes that require matching DIMM
population between channels (Mirrored and Lockstep) require that ECC DIMMs be populated.
Independent Channel Mode is the only mode that supports non-ECC DIMMs in addition to ECC
DIMMs.
For RAS modes that require matching populations, the same slot positions across channels
must hold the same DIMM type with regards to size and organization. DIMM timings do not
have to match but timings will be set to support all DIMMs populated (that is, DIMMs with slower
timings will force faster DIMMs to the slower common timing modes).
3.4.4.2 Independent Channel Mode
Channels can be populated in any order in Independent Channel Mode. All four channels may
be populated in any order and have no matching requirements. All channels must run at the
same interface frequency but individual channels may run at different DIMM timings (RAS
latency, CAS Latency, and so forth).
3.4.4.3 Rank Sparing Mode
In Rank Sparing Mode, one rank is a spare of the other ranks on the same channel. The spare
rank is held in reserve and is not available as system memory. The spare rank must have
identical or larger memory capacity than all the other ranks (sparing source ranks) on the same
channel. After sparing, the sparing source rank will be lost.
Revision 1.0 19
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 27

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
20
3.4.4.4 Mirrored Channel Mode
In Mirrored Channel Mode, the memory contents are mirrored between Channel 0 and Channel 2
and also between Channel 1 and Channel 3. As a result of the mirroring, the total physical
memory available to the system is half of what is populated. Mirrored Channel Mode requires
that Channel 0 and Channel 2, and Channel 1 and Channel 3 must be populated identically with
regards to size and organization. DIMM slot populations within a channel do not have to be
identical but the same DIMM slot location across Channel 0 and Channel 2 and across Channel
1 and Channel 3 must be populated the same.
3.4.4.5 Lockstep Channel Mode
In Lockstep Channel Mode, each memory access is a 128-bit data access that spans Channel 0
and Channel 1, and Channel 2 and Channel 3. Lockstep Channel mode is the only RAS mode
that allows SDDC for x8 devices. Lockstep Channel Mode requires that Channel 0 and Channel
1, and Channel 2 and Channel 3 must be populated identically with regards to size and
organization. DIMM slot populations within a channel do not have to be identical but the same
DIMM slot location across Channel 0 and Channel 1 and across Channel 2 and Channel 3 must
be populated the same.
3.5 Intel
®
C602-J Chipset Overvew
The Intel® C602-J chipset in the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI provide a connection point
between various I/O components and Intel® Xeon E5-2600 processors, which includes the
following core platform functions:
Digital Media Interface (DMI)
PCI Express* Interface
Serial ATA (SATA) Controller
Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)/SATA Controller
AHCI
Rapid Storage Technology
PCI Interface
Low Pin Count (LPC) Interface
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Compatibility Modules (DMA Controller, Timer/Counters, Interrupt Controller)
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC)
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controllers
Gigabit Ethernet Controller
RTC
GPIO
Enhanced Power Management
Intel
Manageability
System Management Bus (SMBus* 2.0)
Integrated NVSRAM controller
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel
®
Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT)
®
VT-d)
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 28

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
JTAG Boundary-Scan
KVM/Serial Over LAN (SOL) Function
3.5.1 Digital Media Interface (DMI)
Digital Media Interface (DMI) is the chip-to-chip connection between the processor and Intel®
C602-J chipset. This high-speed interface integrates advanced priority-based servicing allowing
for concurrent traffic and true isochronous transfer capabilities. Base functionality is completely
software-transparent, permitting current and legacy software to operate normally.
3.5.2 PCI Express* Interface
The Intel® C602-J chipset provides up to eight PCI Express Root Ports, supporting the PCI
Express Base Specification, Revision 2.0. Each Root Port x1 lane supports up to 5 Gb/s
bandwidth in each direction (10 Gb/s concurrent). PCI Express Root Ports 1-4 or Ports 5-8 can
independently be configured to support four x1s, two x2s, one x2 and two x1s, or one x4 port
widths.
3.5.3 Serial ATA (SATA) Controller
The Intel® C602-J chipset has two integrated SATA host controllers that support independent
DMA operation on up to six ports and supports data transfer rates of up to 6.0 Gb/s (600 MB/s)
on up to two ports (Port 0 and 1 Only) while all ports support rates up to 3.0 Gb/s (300 MB/s)
and up to 1.5 Gb/s (150 MB/s). The SATA controller contains two modes of operation – a legacy
mode using I/O space, and an AHCI mode using memory space. Software that uses legacy
mode will not have AHCI capabilities.
The Intel® C602-J chipset supports the Serial ATA Specification, Revision 3.0. The Intel® C602J also supports several optional sections of the Serial ATA II: Extensions to Serial ATA 1.0
Specification, Revision 1.0 (AHCI support is required for some elements).
3.5.4 Low Pin Count (LPC) Interface
The Intel® C602-J chipset implements an LPC Interface as described in the LPC 1.1
Specification. The Low Pin Count (LPC) bridge function of the Intel® C602-J resides in PCI
Device 31: Function 0. In addition to the LPC bridge interface function, D31:F0 contains other
functional units including DMA, interrupt controllers, timers, power management, system
management, GPIO, and RTC.
3.5.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
The Intel® C602-J chipset implements an SPI Interface as an alternative interface for the BIOS
flash device. The SPI flash is required to support Gigabit Ethernet and Intel® Active
Management Technology. The Intel® C602-J chipset supports up to two SPI flash devices with
speeds up to 50 MHz.
3.5.6 Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC)
In addition to the standard ISA compatible Programmable Interrupt controller (PIC) described in
the previous section, the Intel® C602-J incorporates the Advanced Programmable Interrupt
Controller (APIC).
Revision 1.0 21
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 29

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
22
3.5.7 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controllers
The Intel® C602-J chipset has up to two Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) host
controllers that support USB high-speed signaling. High-speed USB 2.0 allows data transfers up
to 480 Mb/s which is 40 times faster than full-speed USB. The Intel® C602-J chipset supports up
to fourteen USB 2.0 ports. All fourteen ports are high-speed, full-speed, and low-speed capable.
Four external connectors are located on the front of the compute module.
One internal 2x5 header is provided, capable of supporting a low-profile USB solid
state drive.
Two ports are routed to the Integrated BMC to support rKVM.
3.6 Integrated Baseboard Management Controller Overview
The Intel® Computer Module MFS2600KI utilizes the I/O controller, Graphics Controller, and
Baseboard Management features of the Emulex* Pilot-III Management Controller. The following
is an overview of the features as implemented on the server board from each
embedded controller.
Figure 7. Integrated BMC Functional Block Diagram
3.6.1 Super I/O Controller
The integrated super I/O controller provides support for the following features as implemented
on the server board:
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 30

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
2D Mode
2D Video Mode Support
8 bpp
16 bpp
24 bpp
32 bpp
640x480
X X X
X
800x600
X X X
X
1024x768
X X X
X
1152x864
X X X
X
1280x1024
X X X
X
1600x1200**
X
X
Two Fully Functional Serial Ports, compatible with the 16C550
Serial IRQ Support
Up to 16 Shared direct GPIO’s
Serial GPIO support for 80 general purpose inputs and 80 general purpose outputs
available for host processor
Programmable Wake-up Event Support
Plug and Play Register Set
Power Supply Control
Host SPI bridge for system BIOS support
3.6.1.1 Keyboard and Mouse Support
The Intel® Computer Module MFS2600KI does not support PS/2 interface keyboards and mice.
However, the system BIOS recognizes USB specification-compliant keyboard and mice.
3.6.1.2 Wake-up Control
The super I/O contains functionality that allows various events to power on and power off
the system.
3.6.2 Graphics Controller and Video Support
The integrated graphics controller provides support for the following features as implemented on
the server board:
Integrated Graphics Core with 2D Hardware accelerator
DDR-3 memory interface with 16 MB of memory allocated and reported for graphics
memory
High speed Integrated 24-bit RAMDAC
Single lane PCI-Express host interface running at Gen 1 speed
The integrated video controller supports all standard IBM VGA modes. The following table
shows the 2D modes supported for both CRT and LCD:
Table 12. Video Modes
Revision 1.0 23
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 31

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
24
On-board Video
Enabled
Disabled
Dual Monitor Video
Enabled
Disabled
Shaded if on-board video is set to "Disabled"
** Video resolutions at 1600x1200 and higher are only supported through the
external video connector located on the rear I/O section of the server board.
Utilizing the optional front panel video connector may result in lower video
resolutions.
The server board provides two video interfaces. The primary video interface is accessed using a
standard 15-pin VGA connector found on the back edge of the server board. In addition, video
signals are routed to a 14-pin header labeled “FP_Video” on the leading edge of the server
board, allowing for the option of cabling to a front panel video connector. Attaching a monitor to
the front panel video connector will disable the primary external video connector on the back
edge of the board.
The BIOS supports dual-video mode when an add-in video card is installed.
In the single mode (dual monitor video = disabled), the on-board video controller is
disabled when an add-in video card is detected.
In the dual mode (on-board video = enabled, dual monitor video = enabled), the on-
board video controller is enabled and is the primary video device. The add-in video card
is allocated resources and is considered the secondary video device. The BIOS Setup
utility provides options to configure the feature as follows:
Table 13. Video mode
3.6.3 Baseboard Management Controller
The server board utilizes the following features of the embedded baseboard management
controller.
IPMI 2.0 Compliant
400MHz 32-bit ARM9 processor with memory management unit (MMU)
Two independent10/100/1000 Ethernet Controllers with RMII/RGMII support
DDR2/3 16-bit interface with up to 800 MHz operation
12 10-bit ADCs
Fourteen fan tachometers
Eight Pulse Width Modulators (PWM)
Chassis intrusion logic
JTAG Master
Eight I2C interfaces with master-slave and SMBus* timeout support. All interfaces are
SMBus* 2.0 compliant.
Parallel general-purpose I/O Ports (16 direct, 32 shared)
Serial general-purpose I/O Ports (80 in and 80 out)
Three UARTs
Platform Environmental Control Interface (PECI)
Six general-purpose timers
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 32

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Functional Architecture
LED Color
LED State
NIC State
Green
On
Link
Blinking
Transmit / Receive activity
Interrupt controller
Multiple SPI flash interfaces
NAND/Memory interface
Sixteen mailbox registers for communication between the BMC and host
LPC ROM interface
BMC watchdog timer capability
SD/MMC card controller with DMA support
LED support with programmable blink rate controls on GPIOs
Port 80h snooping capability
Secondary Service Processor (SSP), which provides the HW capability of off-loading
time critical processing tasks from the main ARM core.
3.6.3.1 Remote Keyboard, Video, Mouse, and Storage (KVMS) Support
USB 2.0 interface for Keyboard, Mouse and Remote storage such as CD/DVD ROM
and floppy
USB 1.1/USB 2.0 interface for PS2 to USB bridging, remote Keyboard and Mouse
Hardware Based Video Compression and Redirection Logic
Supports both text and Graphics redirection
Hardware assisted Video redirection using the Frame Processing Engine
Direct interface to the Integrated Graphics Controller registers and Frame buffer
Hardware-based encryption engine
3.6.3.2 Integrated BMC Embedded LAN Channel
The Integrated BMC hardware includes two dedicated 10/100 network interfaces. These
interfaces are not shared with the host system. At any time, only one dedicated interface may
be enabled for management traffic. The default active interface is the NIC 1 port.
3.7 Network Interface Controller (NIC)
Network interface support is provided from the on-board Intel® I350 NIC, which is a single,
compact component with two fully integrated GbE Media Access Control (MAC) and Physical
Layer (PHY) ports. The on-board Intel® I350 NIC provides the Compute Module with support for
dual LAN ports designed for 1000 Mbps operation.
The Intel® I350 device provides two standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet interface through its
SERDES interfaces. Each network interface controller (NIC) drives two LEDs (1 per port)
located on the front panel. The LED indicates transmit/receive activity when blinking.
Table 14. NIC LED BEHAVIOR
Revision 1.0 25
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 33

Functional Architecture Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
26
Intel® I350 NIC will be used in conjunction with the Emulex* Pilot-III Management Controller for
out of band Management traffic. The BMC will communicate with Intel® I350 NIC over a NC-SI
interface (RMII physical). Intel® I350 NIC will be on standby power so that the BMC can send
management traffic over the NC-SI interface to the network during sleep state S5.
3.8 Intel
®
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
The Intel® C602-J chipset provides hardware support for implementation of Intel® Virtualization
Technology with Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d). Intel® VT-d consists of technology components that
support the virtualization of platforms based on Intel® Architecture Processors. Intel® VT-d
Technology enables multiple operating systems and applications to run in independent
partitions. A partition behaves like a virtual machine (VM) and provides isolation and protection
across partitions. Each partition is allocated its own subset of host physical memory.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 34

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS System Security
4. System Security
4.1 BIOS Password Protection
The BIOS uses passwords to prevent unauthorized tampering with the server setup. Passwords
can restrict entry to the BIOS Setup, restrict use of the Boot Popup menu, and suppress
automatic USB device reordering.
There is also an option to require a Power On password entry in order to boot the system. If the
Power On Password function is enabled in Setup, the BIOS will halt early in POST to request a
password before continuing POST.
Both Administrator and User passwords are supported by the BIOS. An Administrator password
must be installed in order to set the User password. The maximum length of a password is
14 characters. A password can have alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters and it is case
sensitive. Certain special characters are also allowed, from the following set:
! @ # $ % ^ & * ( ) - _ + = ?
The Administrator and User passwords must be different from each other. An error message will
be displayed if there is an attempt to enter the same password for one as for the other.
The use of “Strong Passwords” is encouraged, but not required. In order to meet the criteria for
a “Strong Password”, the password entered must be at least 8 characters in length, and must
include at least one each of alphabetic, numeric, and special characters. If a “weak” password is
entered, a popup warning message will be displayed, although the weak password will
be accepted.
Once set, a password can be cleared by changing it to a null string. This requires the
Administrator password, and must be done through BIOS Setup or other explicit means of
changing the passwords. Clearing the Administrator password will also clear the
User password.
Alternatively, the passwords can be cleared by using the Password Clear jumper if necessary.
Resetting the BIOS configuration settings to default values (by any method) has no effect on the
Administrator and User passwords.
Entering the User password allows the user to modify only the System Time and System Date in
the Setup Main screen. Other setup fields can be modified only if the Administrator password
has been entered. If any password is set, a password is required to enter the BIOS setup.
The Administrator has control over all fields in the BIOS setup, including the ability to clear the
User password and the Administrator password.
It is strongly recommended that at least an Administrator Password be set, since not having set
a password gives everyone who boots the system the equivalent of Administrative access.
Unless an Administrator password is installed, any User can go into Setup and change BIOS
settings at will.
In addition to restricting access to most Setup fields to viewing only when a User password is
entered, defining a User password imposes restrictions on booting the system. In order to
simply boot in the defined boot order, no password is required. However, the F6 Boot popup
Revision 1.0 27
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 35

System Security Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
28
prompts for a password, and can only be used with the Administrator password. Also, when a
User password is defined, it suppresses the USB Reordering that occurs, if enabled, when a
new USB boot device is attached to the system. A User is restricted from booting in anything
other than the Boot Order defined in the Setup by an Administrator.
As a security measure, if a User or Administrator enters an incorrect password three times in a
row during the boot sequence, the system is placed into a halt state. A system reset is required
to exit out of the halt state. This feature makes it more difficult to guess or break a password.
In addition, on the next successful reboot, the Error Manager displays a Major Error code 0048,
which also logs a SEL event to alert the authorized user or administrator that a password
access failure has occurred.
4.2 Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Support
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) option is a hardware-based security device that addresses
the growing concern on boot process integrity and offers better data protection. TPM protects
the system start-up process by ensuring it is tamper-free before releasing system control to the
operating system. A TPM device provides secured storage to store data, such as security keys
and passwords. In addition, a TPM device has encryption and hash functions. The compute
module implements TPM as per TPM PC Client Specifications revision 1.2 by the Trusted
Computing Group (TCG).
A TPM device is optionally installed onto a high density 14-pin connector labeled “TPM” on the
compute module, and is secured from external software attacks and physical theft. A pre-boot
environment, such as the BIOS and operating system loader, uses the TPM to collect and store
unique measurements from multiple factors within the boot process to create a system
fingerprint. This unique fingerprint remains the same unless the pre-boot environment is
tampered with. Therefore, it is used to compare to future measurements to verify the integrity of
the boot process.
After the system BIOS completes the measurement of its boot process, it hands off control to
the operating system loader and in turn to the operating system. If the operating system is TPMenabled, it compares the BIOS TPM measurements to those of previous boots to make sure the
system was not tampered with before continuing the operating system boot process. Once the
operating system is in operation, it optionally uses TPM to provide additional system and data
security (for example, Microsoft Vista* supports Bitlocker drive encryption).
4.2.1 TPM security BIOS
The BIOS TPM support conforms to the TPM PC Client Implementation Specification for
Conventional BIOS and to the TPM Interface Specification, and the Microsoft Windows
BitLocker* Requirements. The role of the BIOS for TPM security includes the following:
Measures and stores the boot process in the TPM microcontroller to allow a TPM
enabled operating system to verify system boot integrity.
Produces EFI and legacy interfaces to a TPM-enabled operating system for using TPM.
Produces ACPI TPM device and methods to allow a TPM-enabled operating system to
send TPM administrative command requests to the BIOS.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 36

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS System Security
Verifies operator physical presence. Confirms and executes operating system TPM
administrative command requests.
Provides BIOS Setup options to change TPM security states and to clear TPM
ownership.
For additional details, refer to the TCG PC Client Specific Implementation Specification, the
TCG PC Client Specific Physical Presence Interface Specification, and the Microsoft BitLocker*
Requirement documents.
4.2.2 Physical Presence
Administrative operations to the TPM require TPM ownership or physical presence indication by
the operator to confirm the execution of administrative operations. The BIOS implements the
operator presence indication by verifying the setup Administrator password.
A TPM administrative sequence invoked from the operating system proceeds as follows:
1. User makes a TPM administrative request through the operating system’s security software.
2. The operating system requests the BIOS to execute the TPM administrative command
through TPM ACPI methods and then resets the system.
3. The BIOS verifies the physical presence and confirms the command with the operator.
4. The BIOS executes TPM administrative command(s), inhibits BIOS Setup entry and boots
directly to the operating system which requested the TPM command(s).
4.2.3 TPM Security Setup Options
The BIOS TPM Setup allows the operator to view the current TPM state and to carry out
rudimentary TPM administrative operations. Performing TPM administrative options through the
BIOS setup requires TPM physical presence verification.
Using BIOS TPM Setup, the operator can turn ON or OFF TPM functionality and clear the TPM
ownership contents. After the requested TPM BIOS Setup operation is carried out, the option
reverts to No Operation.
The BIOS TPM Setup also displays the current state of the TPM, whether TPM is enabled or
disabled and activated or deactivated. Note that while using TPM, a TPM-enabled operating
system or application may change the TPM state independent of the BIOS setup. When an
operating system modifies the TPM state, the BIOS Setup displays the updated TPM state.
The BIOS Setup TPM Clear option allows the operator to clear the TPM ownership key and
allows the operator to take control of the system with TPM. You use this option to clear security
settings for a newly initialized system or to clear a system for which the TPM ownership security
key was lost.
Revision 1.0 29
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 37

System Security Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
30
4.3 Intel
®
Trusted Execution Technology
The Intel® Xeon® Processor E5-2600 support Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT),
which is a robust security environment. Designed to help protect against software-based
attacks, Intel® Trusted Execution Technology integrates new security features and capabilities
into the processor, chipset and other platform components. When used in conjunction with Intel®
Virtualization Technology, Intel® Trusted Execution Technology provides hardware-rooted trust
for your virtual applications.
This hardware-rooted security provides a general-purpose, safer computing environment
capable of running a wide variety of operating systems and applications to increase the
confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information without compromising the usability of
the platform.
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology requires a computer system with Intel® Virtualization
Technology enabled (both VT-x and VT-d), an Intel® Trusted Execution Technology-enabled
processor, chipset and BIOS, Authenticated Code Modules, and an Intel® Trusted Execution
Technology compatible measured launched environment (MLE). The MLE could consist of a
virtual machine monitor, an OS or an application. In addition, Intel® Trusted Execution
Technology requires the system to include a TPM v1.2, as defined by the Trusted Computing
Group TPM PC Client Specifications, Revision 1.2.
When available, Intel® Trusted Execution Technology can be enabled or disabled in the
processor by a BIOS Setup option.
For general information about Intel® TXT, visit the Intel® Trusted Execution Technology website,
http://www.intel.com/technology/security/.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 38

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Connector
Quantity
Reference Designators
Power Connector
1
J1A1
Midplane Signal Connector
1
J3A1
CPU
2
CPU1(U6H1), CPU2(U7C1)
Main Memory
16
J9J2, J9J1, J8J2, J8J1, J5F1,J4F3,
J4F2,J4F1, J4B1, J4B2, J4B3, J5B1, J8E1,
J9E1, J9E2, and J9E3
I/O Mezzanine
2
J1D2, J2A1
Battery
1
BT7K1
TypeA USB
1
J1H3
Serial Port A
1
J4K1
Video connector
1
J2K1
USB connector
1
J1K2, J1K3
eUSB
1
J1K1
TPM
1
J1J2
SATA DOM
1
J1G1
Power button
1
S9K1
Position
Signal
1
+12 Vdc
2
GND
3
GND
4
+12 Vdc
5. Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
5.1 Board Connector Information
The following section provides detailed information regarding all connectors, headers, and
jumpers on the compute module. The following table lists all connector types available on the
board and the corresponding reference designators printed on the silkscreen.
Table 15. Board Connector Matrix
5.2 Power Connectors
The power connection is obtained using a 2x2 FCI Airmax* power connector. The following
table defines the power connector pin-out.
Revision 1.0 31
Table 16. Power Connector Pin-out (J1A1)
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 39

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
32
Pin
Signal Name
Description
1
V_IO_R_CONN
Red (analog color signal R)
2
V_IO_G_CONN
Green (analog color signal G)
3
V_IO_B_CONN
Blue (analog color signal B)
4
TP_VID_CONN_B4
No connection
5
GND
Ground
6
GND
Ground
7
GND
Ground
8
GND
Ground
9
P5V_VID_CONN_9
P5V
10
GND
Ground
11
TP_VID_CONN_B11
No connection
12
V_IO_DDCDAT
DDCDAT
13
V_IO_HSYNC_CONN
HSYNC (horizontal sync)
14
V_IO_VSYNC_CONN
VSYNC (vertical sync)
15
V_IO_DDCCLK
DDCCLK
5.3 I/O Connector Pin-out Definition
5.3.1 VGA Connector
The following table details the pin-out definition of the VGA connector (J2K1).
Table 17. VGA Connector Pin-out (J2K1)
5.3.2 I/O Mezzanine Card Connector
The compute module provides an internal 120-pin Tyco dual-row receptacle (J1D2) and a Tyco
40-pin dual-row receptacle (J2A1) to accommodate high-speed I/O expansion modules, which
expands the I/O capabilities of the compute module. The following table details the pin-out of
the Intel® I/O expansion module connector.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 40

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
P5V 1 P5V
2
GND
3
GND
4
P3V3
5
P3V3
6
P3V3
7
P3V3
8
P3V3
9
P3V3
10
GND
11
GND
12
P3V3AUX
13
P3V3AUX
14
P3V3AUX
15
P3V3AUX
16
SMB_SDA
17
SMB_SCL
18
HSC0_LNK_LED
19
HSC0_ACT_LED
20
HSC1_LNK_LED
21
HSC1_ACT_LED
22
HSC2_LNK_LED
23
HSC2_ACT_LED
24
HSC3_LNK_LED
25
HSC3_ACT_LED
26
GND
27
WAKE_N
28
Rsvd
29
GND
30
Rsvd
31
GND
32
GND
33
PCIe_0_A_TXP
34
GND
35
PCIe_0_A_TXN
36
PCIe_0_A_RXP
37
GND
38
PCIe_0_A_RXN
39
GND
40
GND
41
PCIe_0_B_TXP
42
GND
43
PCIe_0_B_TXN
44
PCIe_0_B_RXP
45
GND
46
PCIe_0_B_RXN
47
GND
48
GND
49
PCIe_0_C_TXP
50
GND
51
PCIe_0_C_TXN
52
PCIe_0_C_RXP
53
GND
54
PCIe_0_C_RXN
55
GND
56
GND
57
PCIe_0_D_TXP
58
GND
59
PCIe_0_D_TXN
60
PCIe_0_D_RXP
61
GND
62
PCIe_0_D_RXN
63
GND
64
GND
65
PCIe_1_A_TXP
66
GND
67
PCIe_1_A_TXN
68
PCIe_1_A_RXP
69
GND
70
PCIe_1_A_RXN
71
GND
72
GND
73
PCIe_1_B_TXP
74
GND
75
PCIe_1_B_TXN
76
PCIe_1_B_RXP
77
GND
78
PCIe_1_B_RXN
79
GND
80
GND
81
PCIe_1_C_TXP
82
GND
83
PCIe_1_C_TXN
84
PCIe_1_C_RXP
85
GND
86
PCIe_1_C_RXN
87
GND
88
Table 18. 120-pin I/O Mezzanine Card Connector Pin-out
Revision 1.0 33
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 41

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
34
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
GND
89
PCIe_1_D_TXP
90
GND
91
PCIe_1_D_TXN
92
PCIe_1_D_RXP
93
GND
94
PCIe_1_D_RXN
95
GND
96
GND
97
Mezz_Present
98
GND
99
Reset_N
100
Clk0_100M_PCIE_P
101
GND
102
Clk0_100M_PCIE_N
103
GND
104
GND
105
Rsvd
106
GND
107
Rsvd
108
Rsvd
109
GND
110
Rsvd
111
Rsvd
112
Rsvd
113
Rsvd
114
P12V
115
P12V
116
P12V
117
P12V
118
P12V
119
P12V
120
Signal Name
Signal Description
Purpose
Connector Location
PCIe_0_A_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane A Link 0
Host connect
34
PCIe_0_A_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane A Link 0
Host connect
36
PCIe_0_A_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane A Link 0
Host connect
37
PCIe_0_A_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane A Link 0
Host connect
39
PCIe_0_B_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane B Link 0
Host connect
42
PCIe_0_B_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane B Link 0
Host connect
44
PCIe_0_B_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane B Link 0
Host connect
45
PCIe_0_B_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane B Link 0
Host connect
47
PCIe_0_C_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane C Link 0
Host connect
50
PCIe_0_C_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane C Link 0
Host connect
52
PCIe_0_C_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane C Link 0
Host connect
53
PCIe_0_C_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane C Link 0
Host connect
55
PCIe_0_D_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane D Link 0
Host connect
58
PCIe_0_D_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane D Link 0
Host connect
60
PCIe_0_D_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane D Link 0
Host connect
61
PCIe_0_D_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane D Link 0
Host connect
63
PCIe_1_A_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane A Link 1
Host connect
66
PCIe_1_A_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane A Link 1
Host connect
68
PCIe_1_A_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane A Link 1
Host connect
69
PCIe_1_A_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane A Link 1
Host connect
71
PCIe_1_B_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane B Link 1
Host connect
74
PCIe_1_B_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane B Link 1
Host connect
76
PCIe_1_B_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane B Link 1
Host connect
78
PCIe_1_B_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane B Link 1
Host connect
79
PCIe_1_C_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane C Link 1
Host connect
82
Table 19. 120-pin I/O Mezzanine Card Connector Signal Definitions
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 42

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Signal Name
Signal Description
Purpose
Connector Location
PCIe_1_C_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane C Link 1
Host connect
84
PCIe_1_C_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane C Link 1
Host connect
85
PCIe_1_C_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane C Link 1
Host connect
87
PCIe_1_D_TXP
PCIe TX+ of Lane D Link 1
Host connect
90
PCIe_1_D_TXN
PCIe TX- of Lane D Link 1
Host connect
92
PCIe_1_D_RXP
PCIe RX+ of Lane D Link 1
Host connect
93
PCIe_1_D_RXN
PCIe RX- of Lane D Link 1
Host connect
95
Clk0_100M_PCIe_P
100MHz clk +
PCIe Clk
101
Clk0_100M_PCIe_N
100MHz clk -
PCIe Clk
103
SMB_SCL
SMBus* Clock
Mngt connect
18
SMB_SDA
SMBus* Data
Mngt connect
17
HSC_0_LNK_LED
HSC 0 Link LED driver
LED control
19
HSC_1_LNK_LED
HSC 1 Link LED driver
LED control
21
HSC_2_LNK_LED
HSC 2 Link LED driver
LED control
23
HSC_3_LNK_LED
HSC 3 Link LED driver
LED control
25
HSC_0_ACT_LED
HSC 0 Activity LED driver
LED control
20
HSC_1_ACT_LED
HSC 1 Activity LED driver
LED control
22
HSC_2_ACT_LED
HSC 2 Activity LED driver
LED control
24
HSC_3_ACT_LED
HSC 3 Activity LED driver
LED control
26
WAKE_N
PCIe WAKE_N signal
Wake on LAN
28
Reset_N
Reset signal (Active Low)
Mezz Reset
100
Mezz_PRES_N
Mezzanine Present signal (active
Low)
Present
indication
98
P12V
12V power
Power
115, 116, 117, 118, 119,
120
P3V3
3.3V Power
power
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
P5V
5V power
power
1, 2
P3V3AUX
Auxiliary power
Aux power
13, 14, 15, 16
Rsvd
Reserved pins
Future use
29, 31, 106, 108, 109,
111, 112, 113, 114
GND
Ground
3, 4, 11, 12, 27, 30, 32,
33, 35, 38, 40, 41, 43,
46, 48, 49, 51, 54, 56,
57,59, 62, 64, 65, 67, 70,
72, 73, 75, 78, 80, 81,
83, 86, 88, 89, 91, 94,
96, 97, 99, 102, 104,
105, 107, 110
Revision 1.0 35
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 43

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
36
Signal Name
Connector Location
Signal Name
Connector Location
TP 1 GND
2
RMII_IBMC_IOMEZZ
_CRS_DV
3
XE_B1_TXP
4
GND
5
XE_B1_TXN
6
XE_B1_RXP
7
GND
8
XE_B1_RXN
9
GND
10
GND
11
XE_B2_TXP
12
GND
13
XE_B2_TXN
14
XE_B2_RXP
15
GND
16
XE_B2_RXN
17
GND
18
GND
19
XE_D2_TXP
20
GND
21
XE_D2_TXN
22
XE_D1_RXP
23
GND
24
XE_D1_RXN
25
GND
26
GND
27
XE_D1_TXP
28
GND
29
XE_D1_TXN
30
XE_D2_RXP
31
GND
32
XE_D2_RXN
33
RMII_IBMC_IOME
ZZ_TX_EN
34
GND
35
RMII_IBMC_IOME
ZZ_TXD1
36
RMII_IBMC_IOMEZZ
_RXD1
37
RMII_IBMC_IOME
ZZ_TXD0
38
RMII_IBMC_IOMEZZ
_RXD0
39
CLK_IOMEZZ_RMI
I
40
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
A1
XE_P1_A_RXP
E1
XE_P2_D_RXN
I1
GND
A2
GND
E2
XE_P2_D_TXP
I2
SAS_P1_TXN
A3
XE_P1_B_RXP
E3
SMB_SDA_B
I3
GND
A4
GND
E4
FM_BL_X_SP
I4
XE_P2_C_TXN
A5
XE_P1_C_RXP
E5
XE_P2_B_RXN
I5
GND
A6
GND
E6
XE_P2_B_TXP
I6
SAS_P2_TXN
A7
XE_P1_D_RXP
E7
XE_P2_A_RXN
I7
GND
A8
GND
E8
XE_P2_A_TXP
I8
Fm_bl_slot_id5
B1
XE_P1_A_RXN
F1
GND
J1
SMB_SCL_A
B2
XE_P1_A_TXP
F2
XE_P2_D_TXN
J2
GND
B3
XE_P1_B_RXN
F3
GND
J3
FM_BL_SLOT_ID2
Table 20. 40-pin I/O Mezzanine Card Connector Pin-out
5.3.3 Midplane Signal Connector
The compute module connects to the midplane through a 96-pin Airmax* connector (J3A1)
(power is J1A1) to connect the various I/O, management, and control signals of the system.
Table 21. 96-pin Midplane Signal Connector Pin-out
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 44

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
B4
XE_P1_B_TXP
F4
12V (BL_PWR_ON)
J4
GND
B5
XE_P1_C_RXN
F5
GND
J5
reserved
B6
XE_P1_C_TXP
F6
XE_P2_B_TXN
J6
GND
B7
XE_P1_D_RXN
F7
GND
J7
reserved
B8
XE_P1_D_TXP
F8
XE_P2_A_TXN
J8
GND
C1
GND
G1
SAS_P1_RXP
K1
SMB_SDA_A
C2
XE_P1_A_TXN
G2
GND
K2
FM_BL_SLOT_ID0
C3
GND
G3
XE_P2_C_RXP
K3
FM_BL_SLOT_ID3
C4
XE_P1_B_TXN
G4
GND
K4
FM_BL_SLOT_ID4
C5
GND
G5
SAS_P2_RXP
K5
reserved
C6
XE_P1_C_TXN
G6
GND
K6
reserved
C7
GND
G7
spare
K7
reserved
C8
XE_P1_D_TXN
G8
GND
K8
reserved
D1
XE_P2_D_RXP
H1
SAS_P1_RXN
L1
GND
D2
GND
H2
SAS_P1_TXP
L2
FM_BL_SLOT_ID1
D3
SMB_SCL_B
H3
XE_P2_C_RXN
L3
GND
D4
GND
H4
XE_P2_C_TXP
L4
FM_BL_PRES_N
D5
XE_P2_B_RXP
H5
SAS_P2_RXN
L5
GND
D6
GND
H6
SAS_P2_TXP
L6
reserved
D7
XE_P2_A_RXP
H7
spare
L7
GND
D8
GND
H8
spare
L8
reserved
Pin
Signal Name
Description
1
SPA_DCD
DCD (carrier detect)
2
SPA_DSR
DSR (data set ready)
3
SPA_SIN_L
RXD (receive data)
4
SPA_RTS
RTS (request to send)
5
SPA_SOUT_N
TXD (transmit data)
6
SPA_CTS
CTS (clear to send)
7
SPA_DTR
DTR (data terminal ready)
8
SPA_RI
RI (ring Indicate)
9
GND
Ground
5.3.4 Serial Port Connector
The compute module provides one internal 9-pin Serial port header (J4K1). The following table
defines the pin-out.
Table 22. Internal 9-pin Serial Header Pin-out (J4K1)
5.3.5 USB 2.0 Connectors
The following table details the pin-out of the external USB connectors (J1K2, J1K3) found on the
front edge of the compute module.
Revision 1.0 37
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 45

Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
38
Pin
Signal Name
Description
1
+5V
USB_PWR
2
USB_N
Differential data line paired with DATAH0
3
USB_P
(Differential data line paired with DATAL0
4
GND
Ground
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
+5V 2 NC 3 USB_N
4
NC 5 USB_P
6
NC 7 GND
8
NC 9 Key Pin
10
LED#
Table 23. External USB Connector Pin-out
5.3.6 Low Profile eUSB SSD Support
The system provides support for a low profile eUSB SSD storage device through a 2mm 2x5-pin
connector (J1K1). The pin-out of the connector is detailed in the following table.
Table 24. Pin-out of Internal USB Connector for low-profile Solid State Drive (J1K1)
eUSB features include:
Two wire small form factor Universal Serial Bus 2.0 (Hi-Speed USB) interface to host.
Read Speed up to 35 MB/s and write Speed up to 24 MB/s.
Capacity range from 256GB to 32GB.
Support USB Mass Storage Class requirements for Boot capability.
Figure 8. eUSB SSD Support
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 46

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Jumper Block Settings
6. Jumper Block Settings
The compute module has several 3-pin jumper blocks that can be used to configure, protect, or
recover specific features of the server board. Pin 1 on each jumper block is denoted by
an “*” or “▼”.
Figure 9. Recovery Jumper Blocks
Revision 1.0 39
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 47

Jumper Block Settings Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
40
Jumper Name
Pins
What happens at system reset …
J1F3: BMC Force
Update
1-2
BMC Firmware Force Update Mode – Disabled (Default)
2-3
BMC Firmware Force Update Mode – Enabled
J1F4: BIOS
R
e
c
o
v
e
r
1-2
These pins should have a jumper in place for normal operation. (Default)
2-3
If these pins are jumpered, the compute module boots from the emergency BIOS
image. These pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
J1F5: ME Force
U
p
d
a
t
e
1-2
ME Firmware Force Update Mode – Disabled (Default)
2-3
ME Firmware Force Update Mode – Enabled
J1F8: CMOS Clear
1-2
These pins should have a jumper in place for normal operation. (Default)
2-3
If these pins are jumpered, the CMOS settings are cleared on the next boot. These
pins should not be jumpered for normal operation
J1F9: Password
C
l
e
a
r
1-2
These pins should have a jumper in place for normal operation. (Default)
2-3
To clear administrator and user passwords, power on the system with pins 2-3
connected. The administrator and user passwords clear in 5-10
seconds after power on. Pins 2-3 should not be connected for
normal system operation..
Table 25. Recovery Jumpers
6.1 CMOS Clear and Password Clear Usage Procedure
The CMOS Clear (J1F8) and Password Clear (J1F9) recovery features are designed such that
the desired operation can be achieved with minimal system downtime. The usage procedure for
these two features has changed from previous generation Intel® server boards. The following
procedure outlines the new usage model.
1. Power down the compute module.
2. Remove the compute module from the modular server chassis.
3. Open the compute module.
4. Move jumper from the default operating position (pins 1-2) to the Clear position
(pins 2-3).
5. Wait 5 seconds.
6. Move jumper back to the default position (pins 1-2).
7. Close the compute module.
8. Reinstall the compute module in the modular server chassis.
9. Power up the compute module.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 48

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Jumper Block Settings
Password and/or CMOS are now cleared and can be reset by going into the BIOS setup.
6.2 Integrated BMC Force Update Procedure
When performing a standard Integrated BMC firmware update procedure, the update utility
places the Integrated BMC into an update mode, allowing the firmware to load safely onto the
flash device. In the unlikely event that the Integrated BMC firmware update process fails due to
the Integrated BMC not being in the proper update state, the compute module provides a BMC
Force Update jumper (J1F3), which will force the Integrated BMC into the proper update state.
The following procedure should be followed in the event the standard Integrated BMC firmware
update process fails.
1. Power down the compute module.
2. Remove the compute module from the modular server chassis.
3. Open the compute module.
4. Move jumper from the default operating position (pins 1-2) to the “Enabled” position
(pins 2-3)
5. Close the compute module.
6. Reinstall and power up the compute module.
7. Perform Integrated BMC firmware update procedure.
8. Power down the compute module.
9. Remove the compute module from the server system.
10. Move jumper from the “Enabled” position (pins 2-3) to the “Disabled” position (pins 1-2).
11. Close the compute module.
12. Reinstall the compute module into the modular server chassis.
13. Power up the compute module.
Note: Normal Integrated BMC functionality (for example, KVM, monitoring, and remote media)
is disabled with the force BMC update jumper set to the “Enabled” position. The server should
never be run with the BMC force update jumper set in this position and should only be used
when the standard firmware update process fails. This jumper should remain in the default –
disabled position when the server is running normally.
6.3 Integrated BMC Initialization
When the DC power is first applied to the compute module by installing it into a chassis, 5VSTBY is present, the Integrated BMC on the compute module requires 15-30 seconds to
initialize. During this time, the power button functionality of the control panel is disabled,
preventing the compute module from powering up.
6.4 ME Force Update Jumper
When performing the standard ME force update procedure, the update utility places the ME into
an update mode, allowing the ME to load safely onto the flash device. In the unlikely event ME
firmware update process fails due to ME not being in the proper update state, the compute
module provides an Integrated BMC Force Update jumper, which forces the ME into the proper
update state. The following procedure should be completed in the event the standard ME
firmware update process fails.
Revision 1.0 41
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 49

Jumper Block Settings Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
42
1. Power down and remove the compute module from chassis.
2. Open the compute module enclosure
3. Move jumper from the default operating position (covering pins 1 and 2) to the enabled
position (covering pins 2 and 3).
4. Close the compute module enclosure.
5. Reinsert the compute module and power up.
6. Perform the ME firmware update procedure as documented in the README.TXT file
that is included in the given ME firmware update package (same package as BIOS).
7. Power down and remove the compute module.
8. Open the compute module enclosure.
9. Move jumper from the enabled position (covering pins 2 and 3) to the disabled position
(covering pins 1 and 2).
10. Close the compute module enclosure.
11. Reinsert the compute module and power up.
6.5 BIOS Recovery Jumper
The following procedure boots the recovery BIOS and flashes the normal BIOS:
1. Turn off the system power.
2. Move the BIOS recovery jumper to the recovery state.
3. Insert a bootable BIOS recovery media containing the new BIOS image files.
4. Turn on the system power.
The BIOS POST screen will appear displaying the progress, and the system will boot to the EFI
shell. The EFI shell then executes the Startup.nsh batch file to start the flash update process.
The user should then switch off the power and return the recovery jumper to its normal position.
The user should not interrupt the BIOS POST on the first boot after recovery.
When the flash update completes:
1. Remove the recovery media.
2. Turn off the system power.
3. Restore the jumper to its original position.
4. Turn on the system power.
5. Re-flash any custom blocks, such as user binary or language blocks.
The system should now boot using the updated system BIOS.
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 50

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Product Regulatory Requirements
7. Product Regulatory Requirements
7.1 Product Regulatory Requirements
The Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI is evaluated as part of the Intel® Modular Server
System MFSYS25V2, which requires meeting all applicable system component regulatory
requirements. Refer to the Intel® Modular Server System Technical Product Specification for a
complete listing of all system and component regulatory requirements.
7.2 Product Regulatory Compliance and Safety Markings
No markings are required on the Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI itself as it is evaluated as
part of the Intel® Modular Server System MFSYS25V2.
7.3 Product Environmental/Ecology Requirements
The Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI is evaluated as part of the Intel® Modular Server
System MFSYS25V2, which requires meeting all applicable system component environmental
and ecology requirements. For a complete listing of all system and component environment and
ecology requirements and markings, refer to the Intel® Modular Server System Technical
Product Specification.
Revision 1.0 43
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 51

Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
44
Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips
When two processors are installed, both must be of identical revision, core voltage, and
bus/core speed. Mixed processor steppings are supported as long as they are listed in
the processor specification updates published by Intel Corporation. However, the
stepping of one processor cannot be greater than one stepping back of the other.
This server board supports The Intel
Thermal Design Power (TDP) of up to and including 95 Watts. Previous generations of
the Intel® Xeon® processors are not supported.
Processors must be installed in order. CPU 1 must be populated for the Compute
Module to operate.
On the front edge of the Compute Module are eight diagnostic LEDs that display a
sequence of amber POST codes during the boot process. If the server board hangs
during POST, the LEDs display the last POST event run before the hang.
This server board only supports registered DDR3 DIMMs (RDIMMs) and unbuffered
DDR3 DIMMs (UDIMMs). Mixing of RDIMMs and UDIMMs is not supported.
For the best performance, the number of DDR3 DIMMs installed should be balanced
across both processor sockets and memory channels. For example, a two-DIMM
configuration performs better than a one-DIMM configuration. In a two-DIMM
configuration, DIMMs should be installed in DIMM sockets A1 and E1. An eight-DIMM
configuration (DIMM sockets A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1, G1, and H1) performs better than a
four-DIMM configuration (DIMM sockets A1, B1, C1, and D1).
Normal Integrated BMC functionality (for example, KVM, monitoring, and remote media)
is disabled with the BMC Force Update jumper set to the “enabled” position (pins 2-3).
The Compute Module should never be run with the BMC Force Update jumper set in this
position and should only be used when the standard firmware update process fails. This
jumper should remain in the default (disabled) position (pins 1-2) when the server is
running normally.
When performing a normal BIOS update procedure, the BIOS recovery jumper must be
set to its default position (pins 1-2).
®
Xeon® Processor E5-2600 product family with a
Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 52

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
45
LEDs
Upper Nibble AMBER LEDs
Lower Nibble GREEN LEDs
MSB
LSB
LED #7
LED #6
LED #5
LED #4
LED #3
LED #2
LED #1
LED #0
8h
4h
2h
1h
8h
4h
2h
1h
Status
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
Results
1 0 1 0 1 1 0
0
Ah
Ch
Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
During the system boot process, the BIOS executes a number of platform configuration
processes, each of which is assigned a specific hex POST code number. As each configuration
routine is started, the BIOS displays the POST code to the POST Code Diagnostic LEDs on the
back edge of the server board. To assist in troubleshooting a system hang during the POST
process, the Diagnostic LEDs can be used to identify the last POST process that was executed.
Each POST code is represented by a sequence of eight amber diagnostic LEDs. The POST
codes are divided into two nibbles, an upper nibble and a lower nibble. The upper nibble bits are
represented by diagnostic LEDs #4, #5, #6, and #7. The lower nibble bits are represented by
diagnostics LEDs #0, #1, #2, and #3. If the bit is set in the upper and lower nibbles, then the
corresponding LED is lit. If the bit is clear, then the corresponding LED is off.
The diagnostic LED #7 is labeled as “MSB”, and the diagnostic LED #0 is labeled as “LSB”.
Figure 10. POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
In the following example, the BIOS sends a value of ACh to the diagnostic LED decoder. The
LEDs are decoded as follows:
Table 26. POST Progress Code LED Example
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 53

Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
46
Checkpoint
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Description
1 = LED On, 0 = LED Off
Upper Nibble
Lower Nibble
MSB
LSB
8h
4h
2h
1h
8h
4h
2h
1h
LED #
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
#1
#0
SEC Phase
01h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 First POST code after CPU reset
02h
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Microcode load begin
03h
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 CRAM initialization begin
04h
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 Pei Cache When Disabled
05h
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 SEC Core At Power On Begin.
06h
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 Early CPU initialization during Sec Phase.
07h
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 Early SB initialization during Sec Phase.
08h
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 Early NB initialization during Sec Phase.
09h
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 End Of Sec Phase.
0Eh
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 Microcode Not Found.
0Fh
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 Microcode Not Loaded.
PEI Phase
10h
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 PEI Core
11h
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 CPU PEIM
15h
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 NB PEIM
19h
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 SB PEIM
MRC Process Codes – MRC Progress Code Sequence is executed - See Table 28
PEI Phase continued…
31h
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 Memory Installed
32h
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 CPU PEIM (Cpu Init)
33h
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 CPU PEIM (Cache Init)
34h
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 CPU PEIM (BSP Select)
35h
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 CPU PEIM (AP Init)
36h
0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 CPU PEIM (CPU SMM Init)
4Fh
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 Dxe IPL started
DXE Phase
60h
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 DXE Core started
61h
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 DXE NVRAM Init
62h
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 SB RUN Init
63h
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 Dxe CPU Init
68h
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 DXE PCI Host Bridge Init
69h
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 DXE NB Init
6Ah
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 DXE NB SMM Init
70h
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 DXE SB Init
71h
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 DXE SB SMM Init
72h
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 DXE SB devices Init
78h
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 DXE ACPI Init
79h
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 DXE CSM Init
90h
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 DXE BDS Started
91h
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 DXE BDS connect drivers
92h
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 DXE PCI Bus begin
93h
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 DXE PCI Bus HPC Init
94h
1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 DXE PCI Bus enumeration
Upper nibble bits = 1010b = Ah; Lower nibble bits = 1100b = Ch; the two are concatenated as
ACh
The following table provides a list of all POST progress codes.
Table 27. POST Progress Codes
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 54

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
47
Checkpoint
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Description
1 = LED On, 0 = LED Off
Upper Nibble
Lower Nibble
MSB
LSB
8h
4h
2h
1h
8h
4h
2h
1h
LED #
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
#1
#0
95h
1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 DXE PCI Bus resource requested
96h
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 DXE PCI Bus assign resource
97h
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 DXE CON_OUT connect
98h
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 DXE CON_IN connect
99h
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 DXE SIO Init
9Ah
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 DXE USB start
9Bh
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 DXE USB reset
9Ch
1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 DXE USB detect
9Dh
1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 DXE USB enable
A1h
1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 DXE IDE begin
A2h
1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 DXE IDE reset
A3h
1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 DXE IDE detect
A4h
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 DXE IDE enable
A5h
1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 DXE SCSI begin
A6h
1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 DXE SCSI reset
A7h
1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 DXE SCSI detect
A8h
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 DXE SCSI enable
A9h
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 DXE verifying SETUP password
ABh
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 DXE SETUP start
ACh
1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 DXE SETUP input wait
ADh
1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 DXE Ready to Boot
AEh
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 DXE Legacy Boot
AFh
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 DXE Exit Boot Services
B0h
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 RT Set Virtual Address Map Begin
B1h
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 RT Set Virtual Address Map End
B2h
1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 DXE Legacy Option ROM init
B3h
1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 DXE Reset system
B4h
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 DXE USB Hot plug
B5h
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 DXE PCI BUS Hot plug
B6h
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 DXE NVRAM cleanup
B7h
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 DXE Configuration Reset
00h
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 INT19
S3 Resume
E0h
1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 S3 Resume PEIM (S3 started)
E1h
1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 S3 Resume PEIM (S3 boot script)
E2h
1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 S3 Resume PEIM (S3 Video Repost)
E3h
1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 S3 Resume PEIM (S3 OS wake)
BIOS Recovery
F0h
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 PEIM which detected forced Recovery condition
F1h
1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 PEIM which detected User Recovery condition
F2h
1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 Recovery PEIM (Recovery started)
F3h
1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 Recovery PEIM (Capsule found)
F4h
1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 Recovery PEIM (Capsule loaded)
POST Memory Initialization MRC Diagnostic Codes
There are two types of POST Diagnostic Codes displayed by the MRC during memory
initialization; Progress Codes and Fatal Error Codes.
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 55

Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
48
Checkpoint
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Description
1 = LED On, 0 = LED Off
Upper Nibble
Lower Nibble
MSB
LSB
8h
4h
2h
1h
8h
4h
2h
1h
LED
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
#1
#0
MRC Progress Codes
B0h
1 0 1 1 0 0 0
0
Detect DIMM population
B1h
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 Set DDR3 frequency
B2h
1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 Gather remaining SPD data
B3h
1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 Program registers on the memory controller level
B4h
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 Evaluate RAS modes and save rank information
B5h
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 Program registers on the channel level
B6h
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 Perform the JEDEC defined initialization sequence
B7h
1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 Train DDR3 ranks
B8h
1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 Initialize CLTT/OLTT
B9h
1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 Hardware memory test and init
BAh
1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 Execute software memory init
BBh
1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 Program memory map and interleaving
BCh
1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 Program RAS configuration
BFh
1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 MRC is done
Checkpoint
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Description
1 = LED On, 0 = LED Off
Upper Nibble
Lower Nibble
MSB
LSB
8h
4h
2h
1h
8h
4h
2h
1h
LED
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
#1
#0
MRC Fatal Error Codes
E8h
1 1 1 0 1 0 0
0
No usable memory error
E9h
1 1 1 0 1 0 0
1
Memory is locked by Intel® Trusted Execuiton Technology and is
inaccessible
EAh
1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 DDR3 channel training error
The MRC Progress Codes are displays to the Diagnostic LEDs that show the execution point in
the MRC operational path at each step.
Table 28. MRC Progress Codes
Memory Initialization at the beginning of POST includes multiple functions, including: discovery,
channel training, validation that the DIMM population is acceptable and functional, initialization
of the IMC and other hardware settings, and initialization of applicable RAS configurations.
When a major memory initialization error occurs and prevents the system from booting with data
integrity, a beep code is generated, the MRC will display a fatal error code on the diagnostic
LEDs, and a system halt command is executed. Fatal MRC error halts do NOT change the state
of the System Status LED, and they do NOT get logged as SEL events. The following table lists
all MRC fatal errors that are displayed to the Diagnostic LEDs.
Table 29. MRC Fatal Error Codes
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 56

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Appendix B: POST Code Diagnostic LED Decoder
49
Checkpoint
Diagnostic LED Decoder
Description
1 = LED On, 0 = LED Off
Upper Nibble
Lower Nibble
MSB
LSB
8h
4h
2h
1h
8h
4h
2h
1h
LED
#7
#6
#5
#4
#3
#2
#1
#0
EBh
1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 Memory test failure
EDh
1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 DIMM configuration population error
EFh
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 Indicates a CLTT table structure error
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 57

Appendix C: POST Error Code Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
50
Error Code
Error Message
Response
0012
System RTC date/time not set
Major
0048
Password check failed
Major
0140
PCI component encountered a PERR error
Major
0141
PCI resource conflict
Major
0146
PCI out of resources error
Major
0191
Processor core/thread count mismatch detected
Fatal
0192
Processor cache size mismatch detected
Fatal
0194
Processor family mismatch detected
Fatal
0195
Processor Intel® QPI link frequencies unable to synchronize
Fatal
0196
Processor model mismatch detected
Fatal
0197
Processor frequencies unable to synchronize
Fatal
5220
BIOS Settings reset to default settings
Major
5221
Passwords cleared by jumper
Major
5224
Password clear jumper is Set
Major
8130
Processor 01 disabled
Major
8131
Processor 02 disabled
Major
8132
Processor 03 disabled
Major
8133
Processor 04 disabled
Major
8160
Processor 01 unable to apply microcode update
Major
8161
Processor 02 unable to apply microcode update
Major
8162
Processor 03 unable to apply microcode update
Major
Appendix C: POST Error Code
Most error conditions encountered during POST are reported using POST Error Codes. These
codes represent specific failures, warnings, or informational messages that are identified with
particular hardware units. These POST Error Codes may be displayed in the Error Manager
display screen, and are always automatically logged to the System Event Log (SEL). The table
below lists the supported POST Error Codes, with a descriptive Error Message text. For each,
There is also a Response listed, which classifies the error as Minor, Major, or Fatal depending
on how serious the error is and what action the system should take. The Response section in
the following table indicates one of these actions:
Minor: The message is displayed on the screen or on the Error Manager screen, and an
error is logged to the SEL. The system continues booting in a degraded state. The user
may want to replace the erroneous unit. The POST Error Pause option setting in the
BIOS setup does not have any effect on this error.
Major: The message is displayed on the Error Manager screen, and an error is logged
to the SEL. The POST Error Pause option setting in the BIOS setup determines whether
the system pauses to the Error Manager for this type of error so the user can take
immediate corrective action or the system continues booting.
Fatal: The system halts during post at a blank screen with the text “Unrecoverable
fatal error found. System will not boot until the error is resolved” and “Press <F2>
to enter setup” The POST Error Pause option setting in the BIOS setup does not have
any effect with this class of error.
Table 30. POST Error Codes and Messages
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 58

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Appendix C: POST Error Code
51
Error Code
Error Message
Response
8163
Processor 04 unable to apply microcode update
Major
8170
Processor 01 failed Self Test (BIST)
Major
8171
Processor 02 failed Self Test (BIST)
Major
8172
Processor 03 failed Self Test (BIST)
Major
8173
Processor 04 failed Self Test (BIST)
Major
8180
Processor 01 microcode update not found
Minor
8181
Processor 02 microcode update not found
Minor
8182
Processor 03 microcode update not found
Minor
8183
Processor 04 microcode update not found
Minor
8190
Watchdog timer failed on last boot
Major
8198
OS boot watchdog timer failure
Major
8300
Baseboard management controller failed self-test
Major
8305
Hot Swap Controller failure
Major
83A0
Management Engine (ME) failed Selftest
Major
83A1
Management Engine (ME) Failed to respond.
Major
84F2
Baseboard management controller failed to respond
Major
84F3
Baseboard management controller in update mode
Major
84F4
Sensor data record empty
Major
84FF
System event log full
Minor
8500
Memory component could not be configured in the selected RAS mode
Major
8501
DIMM Population Error
Major
8520
DIMM_A1 failed test/initialization
Major
8521
DIMM_A2 failed test/initialization
Major
8522
DIMM_A3 failed test/initialization
Major
8523
DIMM_B1 failed test/initialization
Major
8524
DIMM_B2 failed test/initialization
Major
8525
DIMM_B3 failed test/initialization
Major
8526
DIMM_C1 failed test/initialization
Major
8527
DIMM_C2 failed test/initialization
Major
8528
DIMM_C3 failed test/initialization
Major
8529
DIMM_D1 failed test/initialization
Major
852A
DIMM_D2 failed test/initialization
Major
852B
DIMM_D3 failed test/initialization
Major
852C
DIMM_E1 failed test/initialization
Major
852D
DIMM_E2 failed test/initialization
Major
852E
DIMM_E3 failed test/initialization
Major
852F
DIMM_F1 failed test/initialization
Major
8530
DIMM_F2 failed test/initialization
Major
8531
DIMM_F3 failed test/initialization
Major
8532
DIMM_G1 failed test/initialization
Major
8533
DIMM_G2 failed test/initialization
Major
8534
DIMM_G3 failed test/initialization
Major
8535
DIMM_H1 failed test/initialization
Major
8536
DIMM_H2 failed test/initialization
Major
8537
DIMM_H3 failed test/initialization
Major
8538
DIMM_I1 failed test/initialization
Major
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 59

Appendix C: POST Error Code Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
52
Error Code
Error Message
Response
8539
DIMM_I2 failed test/initialization
Major
853A
DIMM_I3 failed test/initialization
Major
853B
DIMM_J1 failed test/initialization
Major
853C
DIMM_J2 failed test/initialization
Major
853D
DIMM_J3 failed test/initialization
Major
853E
DIMM_K1 failed test/initialization
Major
853F
(Go to
85C0)
DIMM_K2 failed test/initialization
Major
8540
DIMM_A1 disabled
Major
8541
DIMM_A2 disabled
Major
8542
DIMM_A3 disabled
Major
8543
DIMM_B1 disabled
Major
8544
DIMM_B2 disabled
Major
8545
DIMM_B3 disabled
Major
8546
DIMM_C1 disabled
Major
8547
DIMM_C2 disabled
Major
8548
DIMM_C3 disabled
Major
8549
DIMM_D1 disabled
Major
854A
DIMM_D2 disabled
Major
854B
DIMM_D3 disabled
Major
854C
DIMM_E1 disabled
Major
854D
DIMM_E2 disabled
Major
854E
DIMM_E3 disabled
Major
854F
DIMM_F1 disabled
Major
8550
DIMM_F2 disabled
Major
8551
DIMM_F3 disabled
Major
8552
DIMM_G1 disabled
Major
8553
DIMM_G2 disabled
Major
8554
DIMM_G3 disabled
Major
8555
DIMM_H1 disabled
Major
8556
DIMM_H2 disabled
Major
8557
DIMM_H3 disabled
Major
8558
DIMM_I1 disabled
Major
8559
DIMM_I2 disabled
Major
855A
DIMM_I3 disabled
Major
855B
DIMM_J1 disabled
Major
855C
DIMM_J2 disabled
Major
855D
DIMM_J3 disabled
Major
855E
DIMM_K1 disabled
Major
855F
(Go to
85D0)
DIMM_K2 disabled
Major
8560
DIMM_A1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8561
DIMM_A2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8562
DIMM_A3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8563
DIMM_B1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 60

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Appendix C: POST Error Code
53
Error Code
Error Message
Response
8564
DIMM_B2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8565
DIMM_B3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8566
DIMM_C1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8567
DIMM_C2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8568
DIMM_C3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8569
DIMM_D1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
856A
DIMM_D2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
856B
DIMM_D3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
856C
DIMM_E1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
856D
DIMM_E2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
856E
DIMM_E3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
856F
DIMM_F1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8570
DIMM_F2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8571
DIMM_F3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8572
DIMM_G1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8573
DIMM_G2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8574
DIMM_G3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8575
DIMM_H1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8576
DIMM_H2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8577
DIMM_H3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8578
DIMM_I1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8579
DIMM_I2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
857A
DIMM_I3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
857B
DIMM_J1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
857C
DIMM_J2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
857D
DIMM_J3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
857E
DIMM_K1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
857F
(Go to
85E0)
DIMM_K2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85C0
DIMM_K3 failed test/initialization
Major
85C1
DIMM_L1 failed test/initialization
Major
85C2
DIMM_L2 failed test/initialization
Major
85C3
DIMM_L3 failed test/initialization
Major
85C4
DIMM_M1 failed test/initialization
Major
85C5
DIMM_M2 failed test/initialization
Major
85C6
DIMM_M3 failed test/initialization
Major
85C7
DIMM_N1 failed test/initialization
Major
85C8
DIMM_N2 failed test/initialization
Major
85C9
DIMM_N3 failed test/initialization
Major
85CA
DIMM_O1 failed test/initialization
Major
85CB
DIMM_O2 failed test/initialization
Major
85CC
DIMM_O3 failed test/initialization
Major
85CD
DIMM_P1 failed test/initialization
Major
85CE
DIMM_P2 failed test/initialization
Major
85CF
DIMM_P3 failed test/initialization
Major
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 61

Appendix C: POST Error Code Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
54
Error Code
Error Message
Response
85D0
DIMM_K3 disabled
Major
85D1
DIMM_L1 disabled
Major
85D2
DIMM_L2 disabled
Major
85D3
DIMM_L3 disabled
Major
85D4
DIMM_M1 disabled
Major
85D5
DIMM_M2 disabled
Major
85D6
DIMM_M3 disabled
Major
85D7
DIMM_N1 disabled
Major
85D8
DIMM_N2 disabled
Major
85D9
DIMM_N3 disabled
Major
85DA
DIMM_O1 disabled
Major
85DB
DIMM_O2 disabled
Major
85DC
DIMM_O3 disabled
Major
85DD
DIMM_P1 disabled
Major
85DE
DIMM_P2 disabled
Major
85DF
DIMM_P3 disabled
Major
85E0
DIMM_K3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E1
DIMM_L1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E2
DIMM_L2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E3
DIMM_L3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E4
DIMM_M1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E5
DIMM_M2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E6
DIMM_M3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E7
DIMM_N1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E8
DIMM_N2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85E9
DIMM_N3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85EA
DIMM_O1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85EB
DIMM_O2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85EC
DIMM_O3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85ED
DIMM_P1 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85EE
DIMM_P2 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
85EF
DIMM_P3 encountered a Serial Presence Detection (SPD) failure
Major
8604
POST Reclaim of non-critical NVRAM variables
Minor
8605
BIOS Settings are corrupted
Major
92A3
Serial port component was not detected
Major
92A9
Serial port component encountered a resource conflict error
Major
A000
TPM device not detected.
Minor
A001
TPM device missing or not responding.
Minor
A002
TPM device failure.
Minor
A003
TPM device failed self-test.
Minor
A100
BIOS ACM Error
Major
A421
PCI component encountered a SERR error
Fatal
A5A0
PCI Express component encountered a PERR error
Minor
A5A1
PCI Express component encountered an SERR error
Fatal
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 62

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Appendix C: POST Error Code
55
Beeps
Error Message
POST Progress Code
Description
3
Memory error
See Table 64
System halted because a fatal error related to the memory
was detected.
1 long
Intel® TXT security
violation
0xAE, 0xAF
System halted because Intel® Trusted Execution
Technology detected a potential violation of system
security.
Code
Reason for Beep
Associated Sensors
1-5-2-1
No CPUs installed or first CPU socket is
empty.
CPU Missing Sensor
1-5-2-4
MSID Mismatch.
MSID Mismatch Sensor.
1-5-4-2
Power fault: DC power is unexpectedly
lost (power good
dropout).
Power unit – power unit failure
offset.
1-5-4-4
Power control fault (power good assertion
timeout).
Power unit – soft power control
failure
offset.
1-5-1-2
VR Watchdog Timer sensor assertion
VR Watchdog Timer
1-5-1-4
The system does not power on or
unexpectedly
powers off and a
power supply unit
(PSU) is present
that is an
incompatible model
with one or more
other PSUs in the
system
PS Status
The following table lists the POST error beep codes. Prior to system video initialization, the
BIOS uses these beep codes to inform users on error conditions. The beep code is followed by
a user-visible code on the POST Progress LEDs
Table 31. POST Error Beep Codes
POST Error Beep Code
The Integrated BMC may generate beep codes upon detection of failure conditions. Beep codes
are sounded each time the problem is discovered, such as on each power-up attempt, but are
not sounded continuously. Codes that are common across all Intel® server boards and systems
that use same generation chipset are listed in the following table. Each digit in the code is
represented by a sequence of beeps whose count is equal to the digit.
Table 32. Integrated BMC Beep Codes
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 63

Appendix D: Supported Intel® Modular Server System Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
56
A
Shared hard drive storage bay
B
I/O cooling fans
C
Empty compute module bay
D
Compute module cooling fans
E
Compute module midplane connectors
Appendix D: Supported Intel® Modular Server System
The Intel® Compute Module MFS5520VI is supported in the following chassis:
Intel
®
Modular Server System MFSYS25V2
This section provides a high-level pictorial overview of the Intel® Modular Server System
MFSYS25V2. For more details, refer to the Intel® Modular Server System Technical Product
Specification (TPS).
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Figure 11. Intel® Modular Server System MFSYS25V2
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 64

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Glossary
57
Term
Definition
ACPI
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
AP
Application Processor
APIC
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Control
ASIC
Application Specific Integrated Circuit
ASMI
Advanced Server Management Interface
BIOS
Basic Input/Output System
BIST
Built-In Self Test
BMC
Baseboard Management Controller
Bridge
Circuitry connecting one computer bus to another, allowing an agent on one to access the other
BSP
Bootstrap Processor
byte
8-bit quantity.
CBC
Chassis Bridge Controller (A microcontroller connected to one or more other CBCs, together they
bridge the IPMB buses of multiple chassis.
CEK
Common Enabling Kit
CHAP
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
CMOS
In terms of this specification, this describes the PC-AT compatible region of battery-backed 128 bytes
of memory, which normally resides on the server board.
DPC
Direct Platform Control
EEPROM
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
EHCI
Enhanced Host Controller Interface
EMP
Emergency Management Port
EPS
External Product Specification
ESB2
Enterprise South Bridge 2
FBD
Fully Buffered DIMM
FMB
Flexible Mother Board
FRB
Fault Resilient Booting
FRU
Field Replaceable Unit
FSB
Front-Side Bus
GB
1024MB
GPIO
General Purpose I/O
GTL
Gunning Transceiver Logic
HSC
Hot-Swap Controller
Hz
Hertz (1 cycle/second)
I2C
Inter-Integrated Circuit Bus
IA
Intel® Architecture
IBF
Input Buffer
ICH
I/O Controller Hub
ICMB
Intelligent Chassis Management Bus
IERR
Internal Error
Glossary
This appendix contains important terms used in the preceding chapters. For ease of use,
numeric entries are listed first (for example, “82460GX”) followed by alpha entries (for example,
“AGP 4x”). Acronyms are followed by non-acronyms.
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 65

Glossary Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
58
Term
Definition
IFB
I/O and Firmware Bridge
INTR
Interrupt
IP
Internet Protocol
IPMB
Intelligent Platform Management Bus
IPMI
Intelligent Platform Management Interface
IR
Infrared
ITP
In-Target Probe
KB
1024 bytes
KCS
Keyboard Controller Style
LAN
Local Area Network
LCD
Liquid Crystal Display
LED
Light Emitting Diode
LPC
Low Pin Count
LUN
Logical Unit Number
MAC
Media Access Control
MB
1024KB
MCH
Memory Controller Hub
MD2
Message Digest 2 – Hashing Algorithm
MD5
Message Digest 5 – Hashing Algorithm – Higher Security
ms
milliseconds
MTTR
Memory Type Range Register
Mux
Multiplexor
NIC
Network Interface Controller
NMI
Non-maskable Interrupt
OBF
Output Buffer
OEM
Original Equipment Manufacturer
Ohm
Unit of electrical resistance
PEF
Platform Event Filtering
PEP
Platform Event Paging
PIA
Platform Information Area (This feature configures the firmware for the platform hardware)
PLD
Programmable Logic Device
PMI
Platform Management Interrupt
POST
Power-On Self Test
PSMI
Power Supply Management Interface
PWM
Pulse-Width Modulation
RAM
Random Access Memory
RASUM
Reliability, Availability, Serviceability, Usability, and Manageability
RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing
ROM
Read Only Memory
RTC
Real-Time Clock (Component of ICH peripheral chip on the server board)
SDR
Sensor Data Record
SECC
Single Edge Connector Cartridge
SEEPROM
Serial Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
SEL
System Event Log
SIO
Server Input/Output
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 66

Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS Glossary
59
Term
Definition
SMBus*
System Management Bus
SMI
Server Management Interrupt (SMI is the highest priority non-maskable interrupt)
SMM
Server Management Mode
SMS
Server Management Software
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol
TBD
To Be Determined
TIM
Thermal Interface Material
UART
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
UHCI
Universal Host Controller Interface
UTC
Universal time coordinate
VID
Voltage Identification
VRD
Voltage Regulator Down
Word
16-bit quantity
ZIF
Zero Insertion Force
Revision 1.0 Intel Confidential
Intel order number: G51989-002
Page 67

Reference Documents Intel® Compute Module MFS2600KI TPS
60
Reference Documents
For additional information, refer to the Intel® Modular Server System Technical
Product Specification.
Intel Confidential Revision 1.0
Intel order number: G51989-002
 Loading...
Loading...