Page 1
Intel® Desktop Board
D845GVSR Product Guide
Order Number: C45520-001
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
-001 First release of the Intel® Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide. July 2003
If an FCC declaration of conformity marking is present on the board, the following statement applies:
FCC Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
For questions related to the EMC performance of this product, contact:
Intel Corporation
5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway
Hillsboro, OR 97124
1-800-628-8686
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct
the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit other than the one to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Intel Corporation could void the user’s authority
to operate the equipment.
Canadian Department of Communications Compliance Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the
Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le présent appareil numerique német pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils
numériques de la classe B prescrites dans le Réglement sur le broullage radioélectrique édicté par le ministére des
Communications du Canada.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or
otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel’s Terms and
Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied
warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular
purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not
intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications. Intel may make changes to specifications and
product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Desktop Board D845GVSR may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate
from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product
order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be
obtained from Intel Corporation by going to the World Wide Web site at: http://www.intel.com/ or by calling
1-800-548-4725.
Intel, Celeron and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United
States and other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2003, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Preface
This Product Guide gives information about board layout, component installation, BIOS Setup
menus, and regulatory requirements for Intel
®
Desktop Board D845GVSR.
Intended Audience
The Product Guide is intended for technically qualified personnel. It is not intended for general
audiences.
Information Layout
The chapters in this Product Guide are arranged as follows:
1 Desktop Board Features
2 Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
board and other hardware components.
3 Updating the BIOS
4 Using the BIOS Setup Program
5 Desktop Board Resources
A Error Messages and Indicators
B Regulatory Compliance
: a summary of product features.
: instructions on how to install the desktop
: instructions on how to update the BIOS.
: contents of the BIOS Setup menus and submenus
: information about desktop board resources.
: information about BIOS error messages and beep codes.
: safety and EMC regulations, product certification.
Conventions
The following conventions are used in this manual:
WARNING
Warnings indicate conditions that, if not observed, can cause personal injury.
CAUTION
Cautions warn the user about how to prevent damage to hardware or loss of data.
NOTE
Notes call attention to important information.
iii
Page 4

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Terminology
The table below gives descriptions to some common terms used in the product guide.
Term Description
GB Gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes)
GHz Gigahertz (one billion hertz)
KB Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
MB Megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
Mbit Megabit (1,048,576 bits)
MHz Megahertz (one million hertz)
Box Contents
• Intel Desktop Board
• I/O shield
• One IDE cable
• One diskette drive cable
• Quick Reference Guide
• Configuration and battery caution statement label
®
• Intel
Express Installer CD-ROM
iv
Page 5
Contents
1 Desktop Board Features
Desktop Board Components ...............................................................................................11
Processor............................................................................................................................13
Main Memory ......................................................................................................................14
Intel® 845GV Chipset ..........................................................................................................15
Audio Subsystem ................................................................................................................15
LAN Subsystem (Optional)..................................................................................................16
LAN Subsystem Software...........................................................................................16
RJ-45 LAN Connector LEDs.......................................................................................16
Hi-Speed USB 2.0 Support..................................................................................................16
Enhanced IDE Interface ......................................................................................................17
Expansion Slots...................................................................................................................17
BIOS ...................................................................................................................................17
PCI Auto Configuration...............................................................................................17
IDE Auto Configuration...............................................................................................17
Security Passwords ....................................................................................................18
Power Management Features .............................................................................................18
Speaker...............................................................................................................................20
Battery.................................................................................................................................20
Real-Time Clock..................................................................................................................20
2 Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
Before You Begin ................................................................................................................21
Installation Precautions .......................................................................................................22
Installation Instructions........................................................................................................22
Installing the I/O Shield .......................................................................................................24
Installing and Removing the Desktop Board........................................................................25
Installing and Removing a Processor ..................................................................................26
Installing a Processor .................................................................................................26
Installing the Processor Fan Heatsink ........................................................................26
Connecting the Processor Fan Heatsink Cable ..........................................................27
Removing a Processor ...............................................................................................27
Installing and Removing Memory ........................................................................................28
Installing DIMMs.........................................................................................................28
Removing DIMMs.......................................................................................................29
Connecting the IDE Cable...................................................................................................30
Connecting Internal Headers...............................................................................................31
Connecting the Front Panel Header ...........................................................................32
Installing a Front Panel Audio Solution .......................................................................32
Installing a USB 2.0 Solution ......................................................................................33
Connecting Hardware Control and Power Cables ...............................................................34
Connecting Hardware Control Cables.........................................................................35
Connecting Power Cables ..........................................................................................35
v
Page 6

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Connecting Add-In Card and Peripheral Interface Connectors ............................................36
Setting the BIOS Configuration Jumper Block.....................................................................37
Clearing Passwords ............................................................................................................38
Back Panel Connectors.......................................................................................................39
Replacing the Battery..........................................................................................................40
3 Updating the BIOS
Updating the BIOS with the Intel® Express BIOS Update Utility ..........................................45
Updating the BIOS with the Intel® Iflash BIOS Update Utility...............................................45
Obtaining the BIOS Update File..................................................................................45
Updating the BIOS......................................................................................................46
Recovering the BIOS..................................................................................................46
4 Using the BIOS Setup Program
Maintenance Menu..............................................................................................................50
Main Menu ..........................................................................................................................51
Advanced Menu ..................................................................................................................52
PCI Configuration Submenu .......................................................................................53
Boot Configuration Submenu......................................................................................54
Peripheral Configuration Submenu.............................................................................55
IDE Configuration Submenu .......................................................................................57
Primary/Secondary IDE Master/Slave Submenus.......................................................58
Diskette Configuration Submenu ................................................................................60
Event Log Configuration Submenu.............................................................................61
Video Configuration Submenu....................................................................................62
USB Configuration Submenu......................................................................................63
Chipset Configuration Submenu.................................................................................64
Security Menu .....................................................................................................................66
Power Menu........................................................................................................................67
ACPI Submenu...........................................................................................................68
Boot Menu...........................................................................................................................69
Boot Device Priority Submenu....................................................................................70
Hard Disk Drives Submenu ........................................................................................71
Removable Devices Submenu....................................................................................72
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives ..............................................................................................73
Exit Menu ............................................................................................................................74
5 Desktop Board Resources
Memory Map .......................................................................................................................75
DMA Channels ....................................................................................................................75
Interrupts.............................................................................................................................76
A Error Messages and Indicators
BIOS Beep Codes...............................................................................................................77
BIOS Error Messages .........................................................................................................78
vi
Page 7

B Regulatory Compliance
Safety Regulations ..............................................................................................................81
European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement ........................................................81
Product Ecology Statements ...............................................................................................82
EMC Regulations ................................................................................................................83
Product Certification Markings (Board Level) ......................................................................84
Figures
1. Desktop Board Components.........................................................................................11
2. Location of Standby Power Indicator.............................................................................19
3. Installing the I/O Shield.................................................................................................24
4. Desktop Board Mounting Screw Holes..........................................................................25
5. Installing a Processor....................................................................................................26
6. Connecting the Processor Fan Heatsink Cable to the Processor Fan Header ..............27
7. Installing Memory..........................................................................................................28
8. Connecting the IDE Cable.............................................................................................30
9. Internal Headers ...........................................................................................................31
10. Location of Hardware Control and Power Connectors ..................................................34
11. Add-in Card and Peripheral Interface Connectors.........................................................36
12. Location of the BIOS Configuration Jumper Block ........................................................37
13. Back Panel Connectors ................................................................................................39
14. Removing the Battery from the Desktop Board.............................................................43
Contents
vii
Page 8

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Tables
1. Feature Summary.......................................................................................................... 9
2. Desktop Board Components.........................................................................................12
3. Processors Supported by the Desktop Board ...............................................................13
4. Memory Support ...........................................................................................................14
5. RJ-45 LAN Connector LEDs .........................................................................................16
6. Front Panel Header (J9G1)...........................................................................................32
7. Front Panel Audio Header Signal Names (J8A1)..........................................................32
8. USB 2.0 Header (J9F2) ................................................................................................33
9. Jumper Settings for the BIOS Setup Program Modes (J9H2) .......................................37
10. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar....................................................................................49
11. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys.............................................................................50
12. Maintenance Menu .......................................................................................................50
13. Main Menu....................................................................................................................51
14. Advanced Menu............................................................................................................52
15. PCI Configuration Submenu .........................................................................................53
16. Boot Configuration Submenu........................................................................................54
17. Peripheral Configuration Submenu ...............................................................................55
18. IDE Configuration Submenu .........................................................................................57
19. Primary/Secondary IDE Master/Slave Submenus.........................................................58
20. Diskette Configuration Submenu ..................................................................................60
21. Event Log Configuration Submenu ...............................................................................61
22. Video Configuration Submenu ......................................................................................62
23. USB Configuration Submenu........................................................................................63
24. Chipset Configuration Submenu ...................................................................................64
25. Security Menu...............................................................................................................66
26. Power Menu..................................................................................................................67
27. ACPI Submenu.............................................................................................................68
28. Boot Menu ....................................................................................................................69
29. Boot Device Priority Submenu ......................................................................................70
30. Hard Disk Drives Submenu...........................................................................................71
31. Removable Devices Submenu......................................................................................72
32. ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Submenu.................................................................................73
33. Exit Menu......................................................................................................................74
34. System Memory Map....................................................................................................75
35. DMA Channels..............................................................................................................75
36. Interrupts ......................................................................................................................76
37. Beep Codes ..................................................................................................................77
38. BIOS Error Messages...................................................................................................78
39. Safety Regulations........................................................................................................81
40. EMC Regulations..........................................................................................................83
41. Product Certification Markings ......................................................................................84
viii
Page 9

1 Desktop Board Features
®
Table 1 describes the major features of Intel
Table 1. Feature Summary
Form Factors
Processor
Memory
Chipset
Audio
LAN (Optional)
Graphics
I/O Control
MicroATX at 9.2 inches by 8.2 inches
Support for:
®
• Intel
• Intel
• Two 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMM sockets, 2.5 V
• Support for DDR333/266/200 MHz DIMMs
• Supports up to 2 GB of system memory with DIMMs utilizing 512 Mbit
Intel
• Intel
• Intel
• 4 Mbit Firmware Hub (FWH)
• Intel 845GV chipset (AC ’97)
• Realtek ALC202A codec
Intel
RJ-45 connector
Integrated graphics
SMSC LPC47M172 low pin count (LPC) interface I/O controller
Pentium® 4 processor in an mPGA-478 socket with a 533/400 MHz
system bus
®
Celeron® processor in an mPGA-478 socket with a 400 MHz system
bus
technology DRAM devices
®
845GV chipset, consisting of:
®
82845GV Grahpics and Memory Controller Hub (GMCH)
®
82801DB I/O Controller Hub (ICH4)
®
82562ET 10/100 Mbit/sec Platform LAN Connect (PLC) device and
Desktop Board D845GVSR.
Expansion Capabilities
Peripheral Interfaces
BIOS
Power Management
Three PCI slots
• Up to six USB 2.0 ports
— Four ports routed to the back panel
— Two ports routed to the USB 2.0 header
• Two IDE interfaces with Ultra DMA-33 and ATA-66/100 support
• One diskette drive interface
• One parallel port
• One serial port
• One VGA port
• PS/2* keyboard and mouse ports
• Intel/AMI BIOS
®
• Intel
• Intel
• SMBIOS support
• Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support for power, fan, and chassis intrusion connectors, Suspend
Rapid BIOS Boot
®
Express BIOS Update
to RAM, resume on ring, wake from USB and PS/2 keyboard and mouse, and
PME# wakeup.
9
Page 10

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
NOTE
✏
For information about this Intel desktop board, including the Technical Product Specification
(TPS), BIOS updates, and device drivers, go to the Intel World Wide Web site at:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
Supported Operating Systems
The desktop board supports the following operating systems:
• Microsoft Windows* 98 SE
• Microsoft Windows Me
• Microsoft Windows 2000
• Microsoft Windows XP
10
Page 11
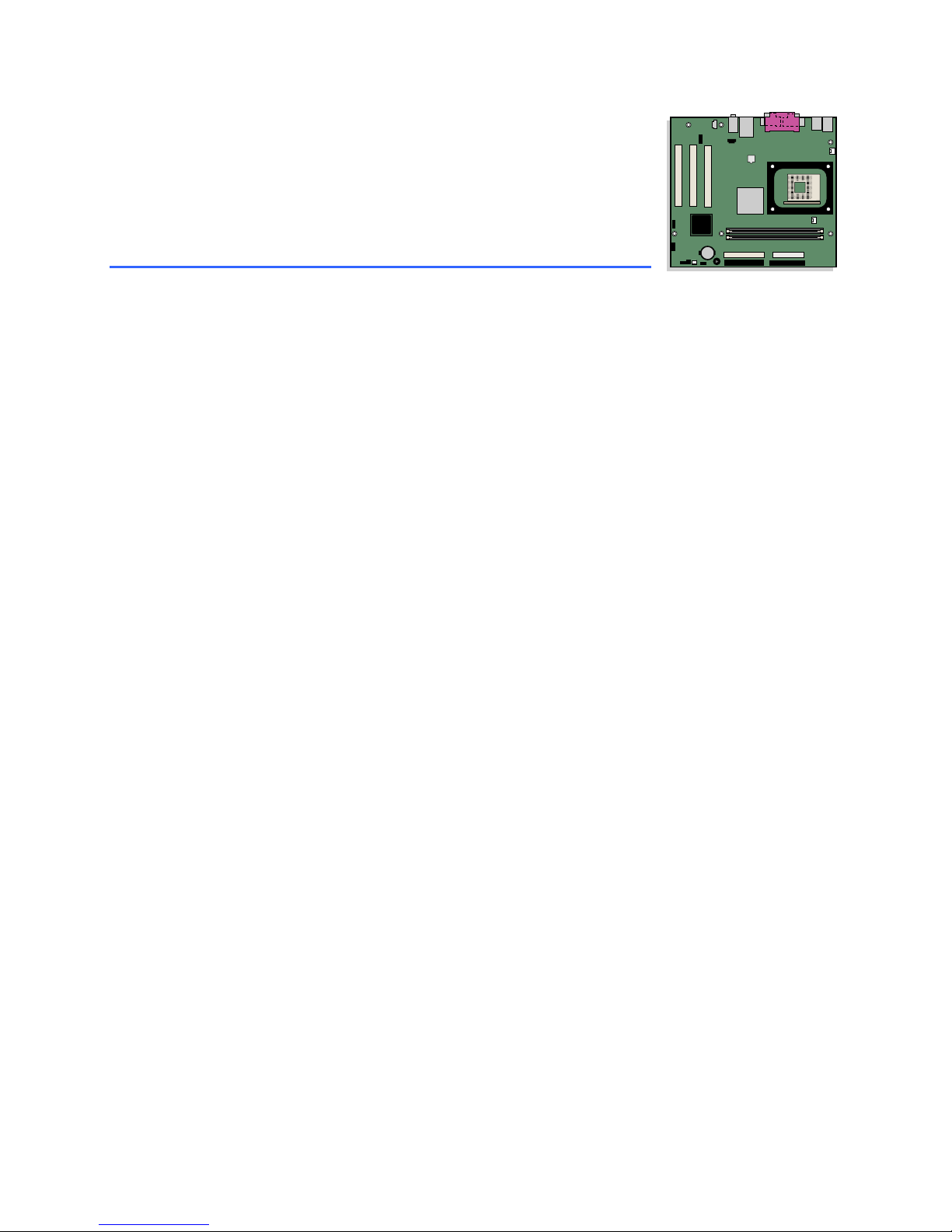
Desktop Board Components
Figure 1 shows the location of the major components on Desktop Board D845GVSR.
Desktop Board Features
USB 2.0
USB 2.0
A
C
B
Line
In
D
E
F
U
T
G
H
S
R
Q
N
P
O
M
L
K
J
I
OM16272
Figure 1. Desktop Board Components
11
Page 12

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Table 2. Desktop Board Components
Item Description
A Front panel audio header
B Auxiliary line-in header
C CD-in (ATAPI) header
D 12 V power connector
E Rear chassis fan header
F Processor socket
G Processor fan header
H DIMM sockets
I Main power connector
J Diskette drive connector
K Secondary IDE connector
L Primary IDE connector
M Speaker
N Battery
O Auxiliary front panel power LED connector
P Front chassis fan header
Q Chassis intrusion header
R BIOS
S Front panel header
T Front panel USB header
U PCI connectors
Related Links:
Go to the following links for more information about Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR:
• http://www.intel.com/design/motherbd
• http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop
12
Page 13
Desktop Board Features
Processor
CAUTION
Failure to use an ATX12V or SFX-12V power supply, or not connecting the additional power
supply lead to Desktop Board D845GVSR may result in damage to the desktop board and/or power
supply.
Desktop Board D845GVSR supports a single Intel Pentium 4 processor or Intel Celeron processor.
Processors are not included with the desktop board and must be purchased separately.
The processor connects to the desktop board through the mPGA-478-pin socket. The Intel
Pentium 4 processor or Intel Celeron processor may be removed and replaced with supported
higher speed processors.
Desktop Board D845GVSR supports the processors listed in Table 3.
Table 3. Processors Supported by the Desktop Board
Type Designation (GHz) System Bus (MHz) L2 Cache (KB)
Intel® Pentium® 4
processor with HT
Technology
Intel Pentium 4 processor
Intel® Celeron® processor 2.60, 2.50, 2.40, 2.30, 2.20, 2.10,
Desktop Board D845GVSR requires an ATX12V compliant power supply to function according to
desktop board specifications. The board has two ATX12V compliant power supply connectors
that are needed to provide extra power to the Intel 845GV chipset and Intel processor.
3.06 533 512
2.80, 2.66, 2.53, 2.40B, and 2.26 533 512
2.60, 2.50, 2.40, 2.20, 2A, 1.80A,
and 1.60A
2, 1.90, 1.80, 1.70, 1.60, and 1.50 400 256
2.0, 1.80, and 1.70
400 512
400 128
Related Links:
Go to the following links or pages for more information about:
• Supported Intel processors for Desktop Board D845GVSR
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
• Instructions on installing or upgrading the processor, see page 26 in Chapter 2
• The location of the two power connectors, see page 34 in Chapter 2.
13
Page 14
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Main Memory
NOTE
✏
To be fully compliant with all applicable Intel® SDRAM memory specification addendums, the
desktop board should be populated with DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD)
data structure. If your memory modules do not support SPD, you will see a notification to this
effect on the screen at power up. The BIOS will attempt to configure the memory controller for
normal operation.
NOTE
✏
All memory components and DIMMs used with the desktop board must comply with the PC
SDRAM specifications. These include the PC SDRAM Specification (memory component specific)
and the PC Unbuffered DIMM Specification.
The desktop board supports single channel memory configurations defined in Table 4.
Table 4. Memory Support
Memory Speed Processor System Bus (MHz) Memory Speed Outcome (MHz)
Pentium 4 processor 533 333 DDR 333
Pentium 4 processor
or Celeron processor
Pentium 4 processor 533 or 400 266 DDR266
Celeron processor 400 266
DDR200 Pentium 4 processor
or Celeron processor
400 266
400 200
• Two 2.5 V 184-pin DDR DIMM sockets with gold-plated contacts
• Serial Presence Detect (SPD)
• Unbuffered, non-ECC RAM (registered memory is not supported)
• Support for 64 Mb, 128 Mb, 256 Mb, and 512 Mb memory technologies for the following
memory configurations:
— 64 MB to 256 MB utilizing 64 Mb technology
— Up to 512 MB utilizing 128 Mb technology
— Up to 1.0 GB utilizing 256 Mb technology
— Up to 2 GB utilizing 512 MB technology
Related Links:
Go to the following links or pages for more information about:
• The latest list of tested memory, http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
• SDRAM specifications, http://www.intel.com/technology/memory/pcsdram/spec/
• Installing memory, page 28 in Chapter 2
14
Page 15

Intel® 845GV Chipset
The Intel 845GV chipset consists of the following:
• Intel 82845GV Graphics and Memory Controller Hub (GMCH) with AHA bus
• Intel 82801DB I/O Controller Hub (ICH4) with AHA bus
• Firmware Hub (FWH)
Related Link:
Go to the following link for more information about the Intel 845GV chipset:
Desktop Board Features
http://developer.intel.com/design/nav/pcserver.htm
Audio Subsystem
The audio subsystem features the following:
• Intel 845GV chipset (AC ’97)
• Realtek ALC202A codec
The audio subsystem supports the following audio interfaces:
• ATAPI-style connectors:
— Auxiliary line in
— CD-ROM
• Front panel audio connector
• Back panel connectors:
— Line out
— Line in
— Mic in
NOTE
✏
The line out connector, located on the back panel, is designed to power either headphones or
amplified speakers only. Poor audio quality may occur if passive (non-amplified) speakers are
connected to this output.
Related Links:
Go to the following link or pages for more information about:
• Audio drivers and utilities, http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
• Installing a front panel audio solution, page 32 in Chapter 2
15
Page 16
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
LAN Subsystem (Optional)
The optional Intel 82562ET (with the Intel 82801DB ICH4) provides a Fast PCI LAN subsystem
providing both 10Base-T and 100Base-TX connectivity. The Intel 82562ET provides the
following functions:
• Basic 10/100 Ethernet LAN connectivity
• Support for RJ-45 connector with status indicator LEDs
• Programmable transit threshold
• Configurable EEPROM that contains the MAC address
LAN Subsystem Software
For LAN software and drivers, refer to the D845GVSR link on Intel’s World Wide Web site at:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
RJ-45 LAN Connector LEDs
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connector. Table 5 describes the LED states when the
desktop board is powered up and the LAN subsystem is operating.
Table 5. RJ-45 LAN Connector LEDs
LED Color LED State Indicates
Off 10 Mbit/sec data rate is selected. Green
On 100 Mbit/sec data rate is selected.
Yellow
Off LAN link is not established.
On (steady state) LAN link is established.
On (brighter and pulsing) The computer is communicating with another computer on
the LAN.
Hi-Speed USB 2.0 Support
NOTE
✏
Computer systems that have an unshielded cable attached to a USB port might not meet FCC
Class B requirements, even if no device or a low-speed USB device is attached to the cable. Use a
shielded cable that meets the requirements for a full-speed USB device.
This desktop board supports up to six USB 2.0 ports via ICH4; four ports routed to the back
panel and two routed to a USB front panel header. USB 2.0 ports are backward compatible with
USB 1.1 devices. USB 1.1 devices will function normally at USB 1.1 speeds.
Disabling Hi-Speed USB in the BIOS reverts all USB 2.0 ports to USB 1.1 operation. This may be
required to accommodate operating systems that do not support USB 2.0.
16
Page 17

Desktop Board Features
Enhanced IDE Interface
The ICH4’s IDE interface handles the exchange of information between the processor and
peripheral devices like hard disks, CD-ROM drives, and Iomega Zip* drives inside the computer.
The interface supports:
• Up to four IDE devices (such as hard drives)
• ATAPI devices (such as CD-ROM drives)
• Older PIO Mode devices
• Ultra DMA-33 and ATA-66/100 protocols
• Laser Servo (LS-120) drives
Expansion Slots
Desktop Board D845GVSR has three PCI bus add-in card connectors.
BIOS
The BIOS provides the Power-On Self-Test (POST), the BIOS Setup program, the PCI and IDE
auto-configuration utilities, and the video BIOS. The BIOS is stored in the firmware hub.
The BIOS can be updated by following the instructions in Chapter 3 on page 45.
PCI Auto Configuration
If you install a PCI add-in card in your computer, the PCI auto-configuration utility in the BIOS
automatically detects and configures the resources (IRQs, DMA channels, and I/O space) for that
add-in card. You do not need to run the BIOS Setup program after you install a PCI add-in card.
IDE Auto Configuration
If you install an IDE device (such as a hard drive) in your computer, the IDE auto-configuration
utility in the BIOS automatically detects and configures the device for your computer. You do not
need to run the BIOS Setup program after installing an IDE device. You can override the
auto-configuration options by specifying manual configuration in the BIOS Setup program.
To use ATA-66/100 features, the following items are required:
• An ATA-66/100 peripheral device
• An ATA-66/100 compatible cable
• ATA-66/100 operating system device drivers
17
Page 18

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Security Passwords
The BIOS includes security features that restrict whether the BIOS Setup program can be accessed
and who can boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be set for the
Setup and for booting the computer, with the following restrictions:
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all Setup options. If
only the supervisor password is set, pressing <Enter> at the password prompt of Setup gives
the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, you must enter either the supervisor
password or the user password to access Setup. Setup options are then available for viewing
and changing depending on whether the supervisor or user password was entered.
• Setting a user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password prompt is
displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor password is set, the computer
boots without asking for a password. If both passwords are set, you can enter either password
to boot the computer.
Power Management Features
• Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support:
— Power connectors
— Fan connectors
— Chassis intrusion
— Suspend to RAM (Instantly Available PC technology)
— Wake from USB
— Wake from PS/2 keyboard/mouse
— PME# wakeup support
ACPI
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug & Play
functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with the desktop board requires an operating system
that provides full ACPI support.
Power Connectors
The desktop board has two power connectors. See Figure 10 on page 34 for the location of the
power connectors.
Fan Connectors
The desktop board has two chassis fan headers and one processor fan header. See Figure 10 on
page 34 for the location of the fan headers.
18
Page 19
Desktop Board Features
Chassis Intrusion
The board supports a chassis security feature that detects if the chassis cover has been removed.
The security feature uses a mechanical switch on the chassis that can be connected to the chassis
intrusion header on the desktop board. See Figure 10 on page 34 for the location of the chassis
intrusion header.
Suspend to RAM (Instantly Available PC Technology)
CAUTION
For Instantly Available PC technology, the 5 V standby line for the power supply must be capable
of delivering adequate +5 V standby current. Failure to provide adequate standby current when
using this feature can damage the power supply and/or effect ACPI S3 sleep state functionality.
Instantly Available PC technology enables the board to enter the ACPI S3 (Suspend-to-RAM)
sleep state. While in the S3 sleep state, the computer will appear to be off. When signaled by a
wake-up device or event, the system quickly returns to its last known awake state.
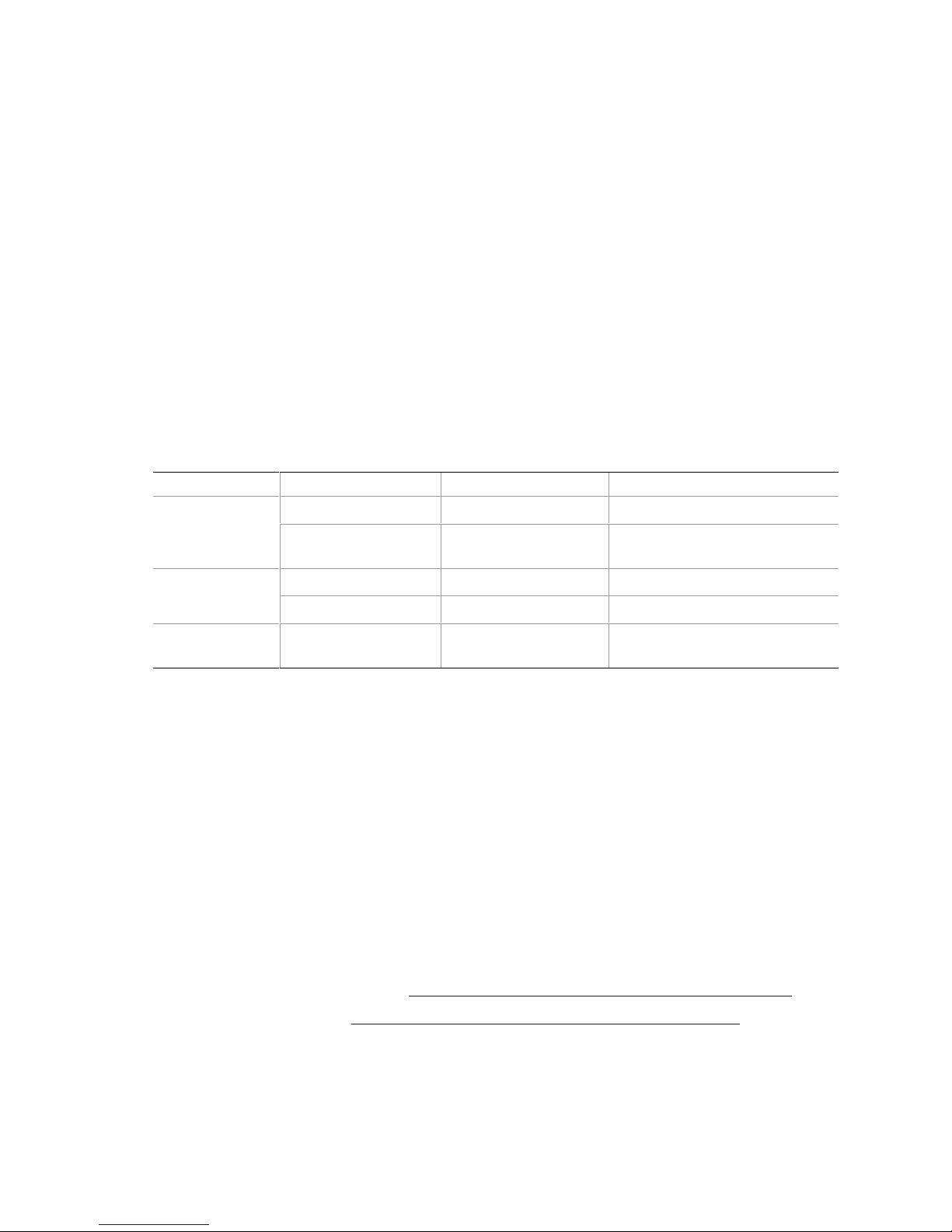
The desktop board’s standby power indicator, shown in Figure 2, is lit when there is standby power
to the system. This includes the memory modules and PCI bus connectors, even when the
computer appears to be off.
If the system has a dual-colored power LED on the front panel, the sleep state is indicated by the
LED turning amber.
OM16273
Figure 2. Location of Standby Power Indicator
CAUTION
Power supplies used with this desktop board must be able to provide enough standby current to
support the standard Instantly Available (ACPI S3 sleep state) configuration. If the standby
current necessary to support multiple wake events from the PCI and/or USB buses exceeds power
supply capacity, the desktop board may lose register settings stored in memory.
Related Links:
For more information on standby current requirements, navigate to the TPS by first selecting the
desktop board from the following link:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
19
Page 20

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Wake from USB
USB bus activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S1 or S3 state.
NOTE
Wake from USB requires the use of a USB peripheral that supports Wake from USB.
Wake from PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse
PS/2 keyboard/mouse activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S1 or S3 state.
PME# Wakeup Support
When the PME# signal on the PCI bus is asserted, the computer wakes from an ACPI S1, S3, or
S5 state.
Speaker
A speaker is mounted on the desktop board. The speaker provides audible error code (beep code)
information during the Power-On Self-Test (POST).
Battery
A battery on the desktop board keeps the values in CMOS RAM and the clock current when the
computer is turned off. See Chapter 2 starting on page 21 for instructions on how to replace the
battery.
Real-Time Clock
The desktop board has a time-of-day clock and 100-year calendar. The battery on the desktop
board keeps the clock current when the computer is turned off.
20
Page 21

2 Installing and Replacing Desktop
Board Components
This chapter tells you how to:
• Install the I/O shield
• Install and remove the desktop board
• Install and remove a processor
• Install and remove memory
• Connect the IDE cable
• Connect internal headers
• Connect hardware control and power cables
• Connect add-in card and peripheral interface connectors
• Set the BIOS configuration jumper block
• Clear passwords
• Connect back panel connectors
• Replace the battery
Before You Begin
WARNINGS
The procedures in this chapter assume familiarity with the general terminology associated with
personal computers and with the safety practices and regulatory compliance required for using
and modifying electronic equipment.
Disconnect the computer from its power source and from any telecommunications links,
networks, or modems before performing any of the procedures described in this chapter.
Failure to disconnect power, telecommunications links, networks, or modems before you open
the computer or perform any procedures can result in personal injury or equipment damage.
Some circuitry on the board can continue to operate even though the front panel power
button is off.
CAUTION
Many of the midboard and front panel connectors provide operating voltage (+5 V dc and
+12 V dc, for example) to devices inside the computer chassis, such as fans and internal
peripherals. These connectors are not overcurrent protected. Do not use these connectors for
powering devices external to the computer chassis. A fault in the load presented by the external
devices could cause damage to the computer, the interconnecting cable, and the external devices
themselves.
21
Page 22

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Follow these guidelines before you begin:
• Always follow the steps in each procedure in the correct order.
• Set up a log to record information about your computer, such as model, serial numbers,
installed options, and configuration information.
• Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components. Perform the procedures described in
this chapter only at an ESD workstation using an antistatic wrist strap and a conductive foam
pad. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD protection by wearing an
antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the computer chassis.
Installation Precautions
When you install and test the Intel desktop board, observe all warnings and cautions in the
installation instructions.
To avoid injury, be careful of:
• Sharp pins on connectors
• Sharp pins on printed circuit assemblies
• Rough edges and sharp corners on the chassis
• Hot components (like processors, voltage regulators, and heat sinks)
• Damage to wires that could cause a short circuit
Observe all warnings and cautions that instruct you to refer computer servicing to qualified
technical personnel.
Installation Instructions
CAUTION
Follow these guidelines to meet safety and regulatory requirements when installing this board.
Read and adhere to all of these instructions and the instructions supplied with the chassis and
associated modules. If the instructions for the chassis are inconsistent with these instructions or
the instructions for associated modules, contact the supplier’s technical support to find out how
you can ensure that your computer meets safety and regulatory requirements. If you do not follow
these instructions and the instructions provided by chassis and module suppliers, you increase
safety risk and the possibility of noncompliance with regional laws and regulations.
Ensure Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Compliance
Before computer integration, make sure that the power supply and other modules or peripherals, as
applicable, have passed Class B EMC testing and are marked accordingly.
Pay close attention to the following when reading the installation instructions for the host chassis,
power supply, and other modules:
• Product certifications or lack of certifications
• External I/O cable shielding and filtering
22
Page 23

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
• Mounting, grounding, and bonding requirements
• Keying connectors when mating the wrong connectors could be hazardous
If the power supply and other modules or peripherals, as applicable, are not Class B EMC
compliant before integration, then EMC testing is required on a representative sample of the newly
completed computer.
Chassis and Component Certifications
Ensure that the chassis and certain components; such as the power supply, peripheral drives,
wiring, and cables; are components certified for the country or market where used. Agency
certification marks on the product are proof of certification. Typical product certifications include:
• In Europe
The CE marking signifies compliance with all applicable European requirements. If the
chassis and other components are not properly CE marked, a supplier’s Declaration of
Conformity statement to the European EMC directive and Low Voltage directive (as
applicable), should be obtained. Additionally, other directives, such as the Radio and
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment (R&TTE) directive may also apply depending on
product features.
• In the United States
A certification mark by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL,
CSA, or ETL signifies compliance with safety requirements. Wiring and cables must also be
UL listed or recognized and suitable for the intended use. The FCC Class B logo for home or
office use signifies compliance with electromagnetic interference (EMI) requirements.
• In Canada
A nationally recognized certification mark such as CSA or cUL signifies compliance with
safety requirements. The Industry Canada statement at the front of this product guide
demonstrates compliance with Canadian EMC regulations. Industry Canada recognizes and
accepts FCC certification as denoting compliance with national electromagnetic interference
(emissions) requirements.
Prevent Power Supply Overload
Do not overload the power supply output. To avoid overloading the power supply, make sure that
the calculated total current loads of all the modules within the computer is less than the output
current rating of each of the power supplies’ output circuits.
Place Battery Marking
There is insufficient space on this Desktop Board to provide instructions for replacing and
disposing of the Lithium ion coin cell battery. For system safety certification, the following
statement or equivalent statement is required to be permanently and legibly marked on the chassis
near the battery.
23
Page 24
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
CAUTION
Risk of explosion if the battery is replaced with an incorrect type. Batteries should be recycled
where possible. Disposal of used batteries must be in accordance with local environmental
regulations.
Related Links:
For information about replacing the battery, go to page 40 in Chapter 2.
Use Only for Intended Applications
All Intel desktop boards are evaluated as Information Technology Equipment (I.T.E.) for use in
personal computers for installation in homes, offices, schools, computer rooms, and similar
locations. The suitability of this product for other applications or environments, such as medical,
industrial, alarm systems, test equipment, etc. may require further evaluation.
Related Links:
For information about regulatory compliance, go to Appendix B on page 81.
Installing the I/O Shield
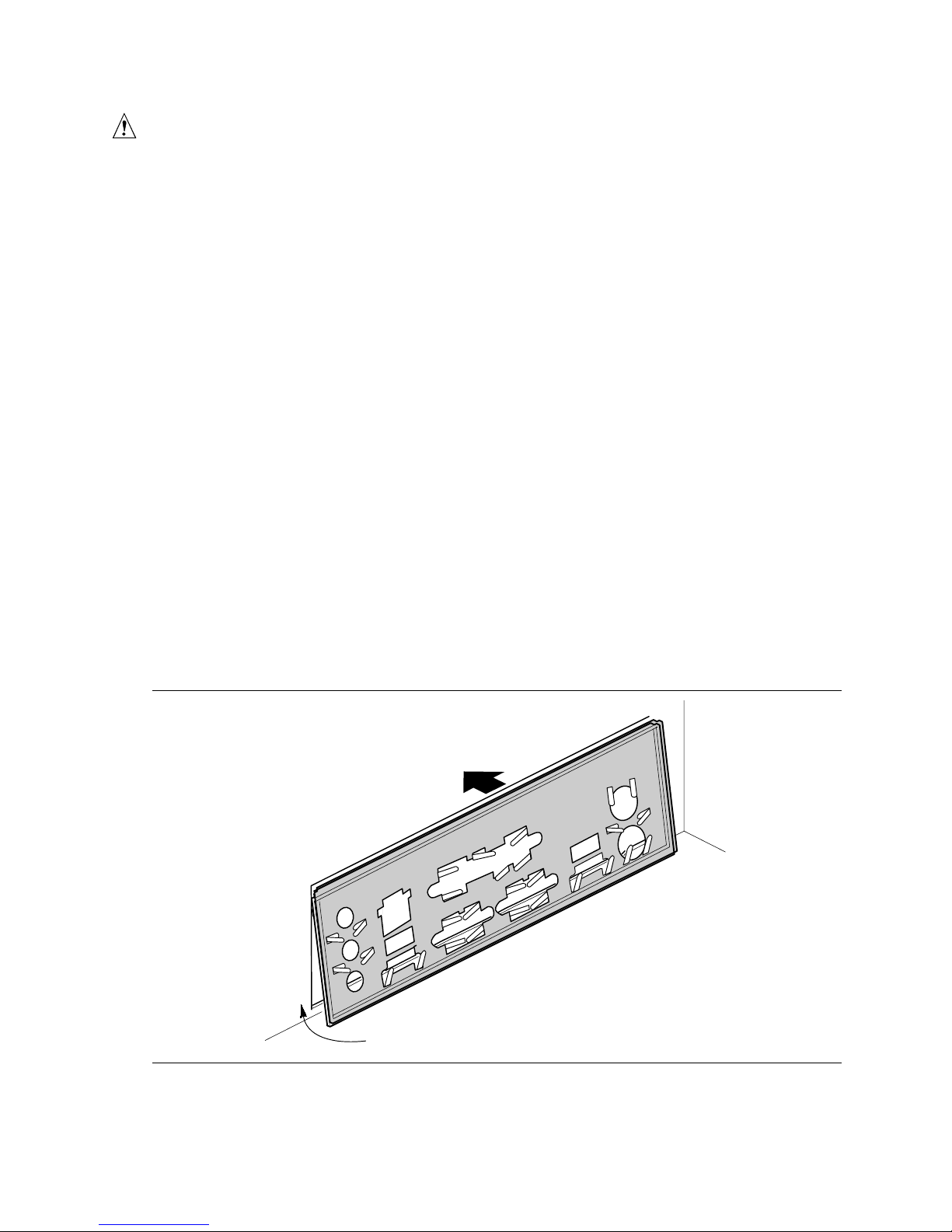
The desktop board comes with an I/O shield. When installed in the chassis, the shield blocks radio
frequency transmissions, protects internal components from dust and foreign objects, and promotes
correct airflow within the chassis.
Install the I/O shield before installing the desktop board in the chassis. Place the shield inside the
chassis as shown in Figure 3. Press the shield into place so that it fits tightly and securely. If the
shield doesn’t fit, obtain a properly-sized shield from the chassis supplier.
24
Figure 3. Installing the I/O Shield
OM16274
Page 25
Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
Installing and Removing the Desktop Board
Refer to your chassis manual for instructions on installing and removing the desktop board.
WARNING
This procedure should be done only by qualified technical personnel. Disconnect the computer
from its power source before performing the procedures described here. Failure to disconnect
the power before you open the computer can result in personal injury or equipment damage.
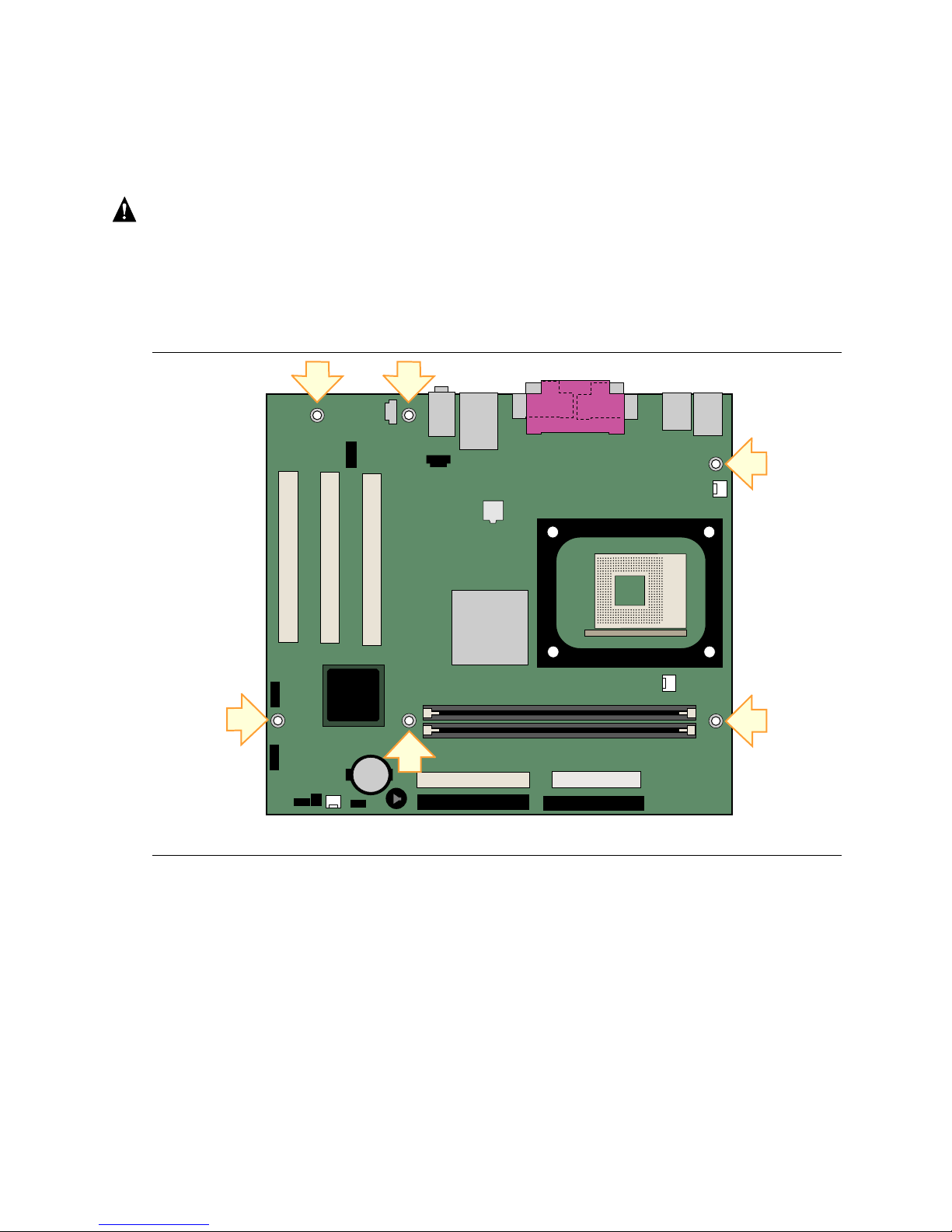
Figure 4 shows the location of the six mounting holes for Desktop Board D845GVSR.
Figure 4. Desktop Board Mounting Screw Holes
OM16275
25
Page 26
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Installing and Removing a Processor
Instructions on how to install the processor to the desktop board are given below.
Installing a Processor
CAUTION
Before installing or removing the processor, make sure that AC power has been removed by
unplugging the power cord from the computer; the standby power LED should not be lit
(see Figure 2 on page 19). Failure to do so could damage the processor and the desktop board.
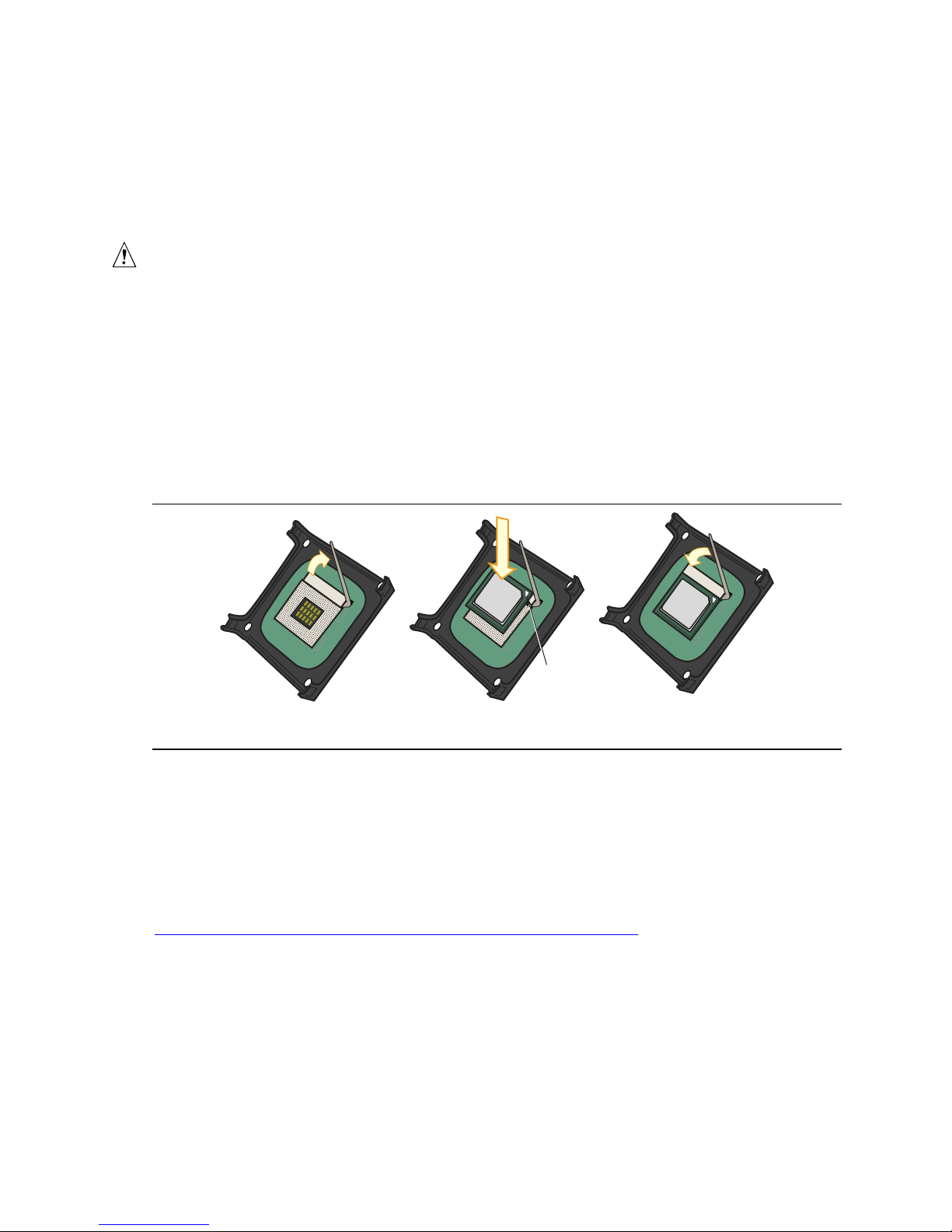
To install a processor, follow these instructions:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Locate the processor socket and raise the socket lever completely.
3. Install the processor so that the corner with the gold triangle marking (A) is aligned with the
corner where the lever is attached to the socket (see Figure 5).
4. Lower the lever to its original position.
mPGA478B
mPGA478B
A
Figure 5. Installing a Processor
mPGA478B
OM15228
Installing the Processor Fan Heatsink
The desktop board has an integrated processor fan heatsink retention mechanism (RM). For
instructions on how to install the processor fan heatsink to the integrated processor fan heatsink
RM, refer to the Intel World Wide Web site at:
http://support.intel.com/support/processors/pentium4/intnotes478.htm
26
Page 27

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
Connecting the Processor Fan Heatsink Cable
Connect the processor fan heatsink cable to the processor fan header (see Figure 6).
OM16276
Figure 6. Connecting the Processor Fan Heatsink Cable to the Processor Fan Header
Removing a Processor
For instruction on how to remove the processor fan heatsink, refer to the Intel World Wide Web
site at:
http://support.intel.com/support/processors/pentium4/intnotes478.htm
27
Page 28

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Installing and Removing Memory
CAUTION
To be fully compliant with all applicable Intel SDRAM memory specification addendums, the
board requires DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data structure. You can
access the PC Serial Presence Detect Specification at:
http://www.intel.com/technology/memory/pcsdram/spec/
The desktop board has two DIMM sockets arranged as DIMM 0 and DIMM 1, as shown in
Figure 7. If installing a single DIMM, install it in DIMM 0.
Refer to the Main Memory heading on page 14 for memory requirements.
Installing DIMMs
To install DIMMs, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer and
disconnect the AC power cord.
3. Remove the computer’s cover and locate the DIMM sockets (see Figure 7).
28
Figure 7. Installing Memory
OM16277
0
1
Page 29

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
4. Make sure the clips at either end of the DIMM socket(s) are pushed outward to the
open position.
5. Position the DIMM above the socket. Align the two small notches in the bottom edge of the
DIMM with the keys in the socket (see inset in Figure 7).
6. Insert the bottom edge of the DIMM into the socket.
7. When the DIMM is inserted, push down on the top edge of the DIMM until the retaining clips
snap into place. Make sure the clips are firmly in place.
8. Replace the computer’s cover and reconnect the AC power cord.
Removing DIMMs
To remove a memory module, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the AC power cord from the computer.
4. Remove the computer’s cover.
5. Remove the AGP card, if necessary.
6. Gently spread the retaining clips at each end of the DIMM socket. The DIMM pops out of
the socket.
7. Hold the DIMM by the edges, lift it away from the socket, and store it in an anti-static package.
8. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the DIMM sockets.
9. Replace the computer’s cover and reconnect the AC power cord.
29
Page 30

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Connecting the IDE Cable
The Intel® boxed desktop board package includes an IDE cable. The cable connects two drives to
the desktop board. The cable supports both ATA-66 and ATA-100 transfer protocols and is
backward compatible with drives using slower IDE transfer protocols. Figure 8 shows the correct
installation of the cable.
NOTE
✏
ATA-66/100 compatible cables are backward compatible with drives using slower IDE transfer
protocols. If an ATA-66/100 disk drive and a disk drive using any other IDE transfer protocol are
attached to the same cable, the maximum transfer rate between the drives may be reduced to that
of the slowest drive.
NOTE
✏
Do not connect an ATA device as a slave on the same IDE cable as an ATAPI master device. For
example, do not connect an ATA hard drive as a slave to an ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
For correct function of the cable:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Attach the cable end with the single blue connector to the desktop board (see Figure 8, A).
3. Attach the cable end with the two closely spaced black and gray connectors to the drives
(see Figure 8, B).
30
A
Figure 8. Connecting the IDE Cable
B
OM16278
Page 31
Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
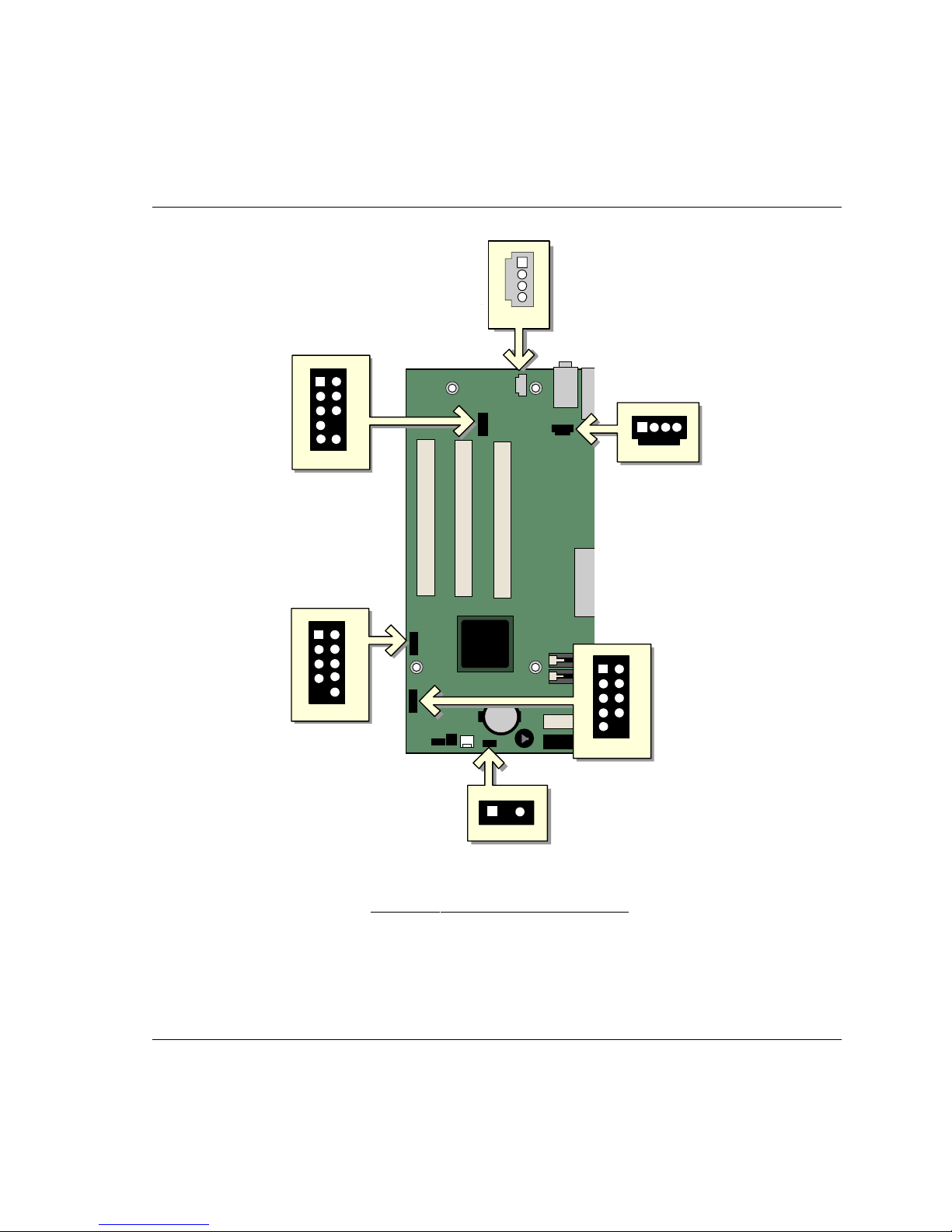
Connecting Internal Headers
Follow the instructions below to connect the USB 2.0 solution, power LED, front panel, and audio
solution. See Figure 9 for pin assignments.
A
J7A1
F
J8A1
2
4
6
10
B
J6B1
1
3
5
7
9
E
C
1
3
5
7
9
2
4
6
8
J9G1
J9F2
2
4
6
8
10
3
1
1
3
5
7
J8H3
D
Item Description
A Auxiliary-in
B CD-in
C Front panel
D Power LED
E Front panel USB 2.0
F Front panel audio
Figure 9. Internal Headers
OM16279
31
Page 32

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Connecting the Front Panel Header
Before connecting the front panel header, observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on
page 21. Table 6 shows the pin assignments for the front panel header.
Table 6. Front Panel Header (J9G1)
Pin Signal In/Out Description Pin Signal In/Out Description
Hard Drive Activity LED Power LED
1 HD_PWR Out Hard disk LED pull-up
(330 Ω) to +5 V
3 HDA# Out Hard disk active LED 4 HDR_BLNK_YEL Out Front panel yellow
Reset Switch On/Off Switch
5 Ground Ground 6 FPBUT_IN In Power switch
7 FP_RESET# In Reset switch 8 Ground Ground
Power Not Connected
9 +5 V Power 10 N/C Not connected
2 HDR_BLNK_GRN Out Front panel green
Installing a Front Panel Audio Solution
Table 7 shows the pin assignments for the front panel audio header.
Table 7. Front Panel Audio Header Signal Names (J8A1)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 AUD-MIC 2 AUD-GND
3 AUD-MIC-BIAS 4 AUD-VCC
LED
LED
5 AUD-FPOUT-R 6 AUD-RET-R
7 NO CONNECTION 8 KEY
9 AUD-FPOUT-L 10 AUD-RET-L
To install the cable that connects a front panel audio solution to the front panel audio header,
follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer and
disconnect the AC power cord.
3. Remove the cover. Locate the front panel audio header (J8A1).
4. Remove the three jumpers from the header (this disables the back panel audio connectors).
5. Install a correctly keyed and shielded front panel audio cable.
6. Connect the audio cable to the front panel audio solution.
7. Replace the cover.
32
Page 33

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
To restore back panel operations, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer and
disconnect the AC power cord.
3. Remove the cover. Remove the front panel audio cable.
4. Install a jumper on pins 5-6 (rear R channel).
5. Install a jumper on pins 9-10 (rear L channel).
6. Install a jumper on pins 1-2 (mic).
7. Replace the cover.
Installing a USB 2.0 Solution
Before installing a USB 2.0 solution, observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
Table 8 shows the pin assignments for the USB 2.0 header.
Table 8. USB 2.0 Header (J9F2)
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 Power 2 Power
3 D- 4 D-
5 D+ 6 D+
7 Ground 8 Ground
9 Key (no pin) 10 Not connected
Note: USB ports may be assigned as needed.
33
Page 34

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Connecting Hardware Control and Power Cables
Figure 10 shows the location of the hardware control headers and power connectors.
A
1
2
B
J1B1
F
J8H1
Figure 10. Location of Hardware Control and Power Connectors
E
J8H2
D
2
1
C
J2F1
OM16280
34
Page 35

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
Connecting Hardware Control Cables
See Figure 10 for fan and chassis intrusion header locations. Connect the processor’s fan heatsink
cable to the processor fan header on the board. Connect chassis fan cables to the board fan
headers. Connect the chassis intrusion cable to the respective header on the board.
Connecting Power Cables
CAUTION
Failure to use an ATX12V power supply, or not connecting the 12 V processor core voltage power
supply connector to the desktop board may result in damage to the desktop board and/or power
supply.
Figure 10 shows the location of the power connectors.
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Connect the 12 V processor core voltage power supply cable to the 2x2 connector.
3. Connect the main power supply cable to the 2x10 connector.
35
Page 36

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Connecting Add-In Card and Peripheral Interface
Connectors
Figure 11 shows the add-in card and peripheral interface connectors.
BC
A
F
Item Description Item Description
A PCI bus connector 3 D Floppy drive
B PCI bus connector 2 (SMBus routed) E Primary IDE
C PCI bus connector 1 F Secondary IDE
Figure 11. Add-in Card and Peripheral Interface Connectors
E
D
OM16281
36
Page 37
Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
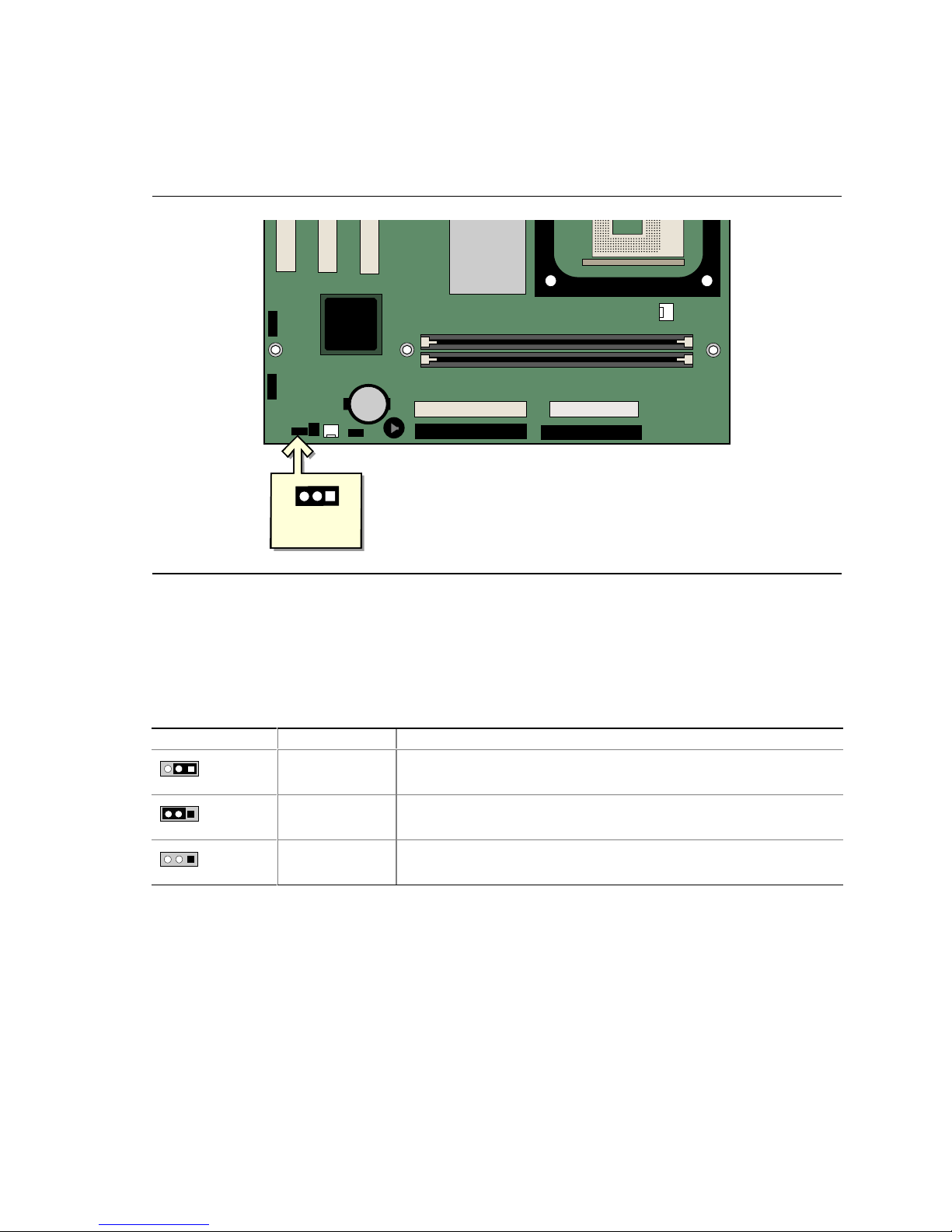
Setting the BIOS Configuration Jumper Block
Figure 12 shows the location of the BIOS configuration jumper block.
1
3
J9H2
OM16282
Figure 12. Location of the BIOS Configuration Jumper Block
The three-pin BIOS jumper block enables all board configurations to be done in BIOS Setup.
Table 9 shows the jumper settings for the Setup program modes.
Table 9. Jumper Settings for the BIOS Setup Program Modes (J9H2)
Jumper Setting Mode Description
3
1
3
1
3
1
Normal (default)
(1-2)
Configure
(2-3)
Recovery
(None)
The BIOS uses the current configuration and passwords for booting.
After the Power-On Self-Test (POST) runs, the BIOS displays the
Maintenance Menu. Use this menu to clear passwords.
Recovers BIOS from a diskette in the event of a failed BIOS update.
37
Page 38

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Clearing Passwords
This procedure assumes that the board is installed in the computer and the configuration jumper
block is set to normal mode.
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer. Disconnect
the computer’s power cord from the AC power source (wall outlet or power adapter).
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Find the configuration jumper block (see Figure 12).
5. Place the jumper on pins 2-3 as shown below.
3
1
6. Replace the cover, plug in the computer, turn on the computer, and allow it to boot.
7. The computer starts the Setup program. Setup displays the maintenance menu.
8. Use the arrow keys to select Clear Passwords. Press <Enter> and Setup displays a pop-up
screen requesting that you confirm clearing the password. Select Yes and press <Enter>.
Setup displays the maintenance menu again.
9. Press <F10> to save the current values and exit Setup.
10. Turn off the computer. Disconnect the computer’s power cord from the AC power source.
11. Remove the computer cover.
12. To restore normal operation, place the jumper on pins 1-2 as shown below.
3
1
13. Replace the cover, plug in the computer, and turn on the computer.
38
Page 39

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
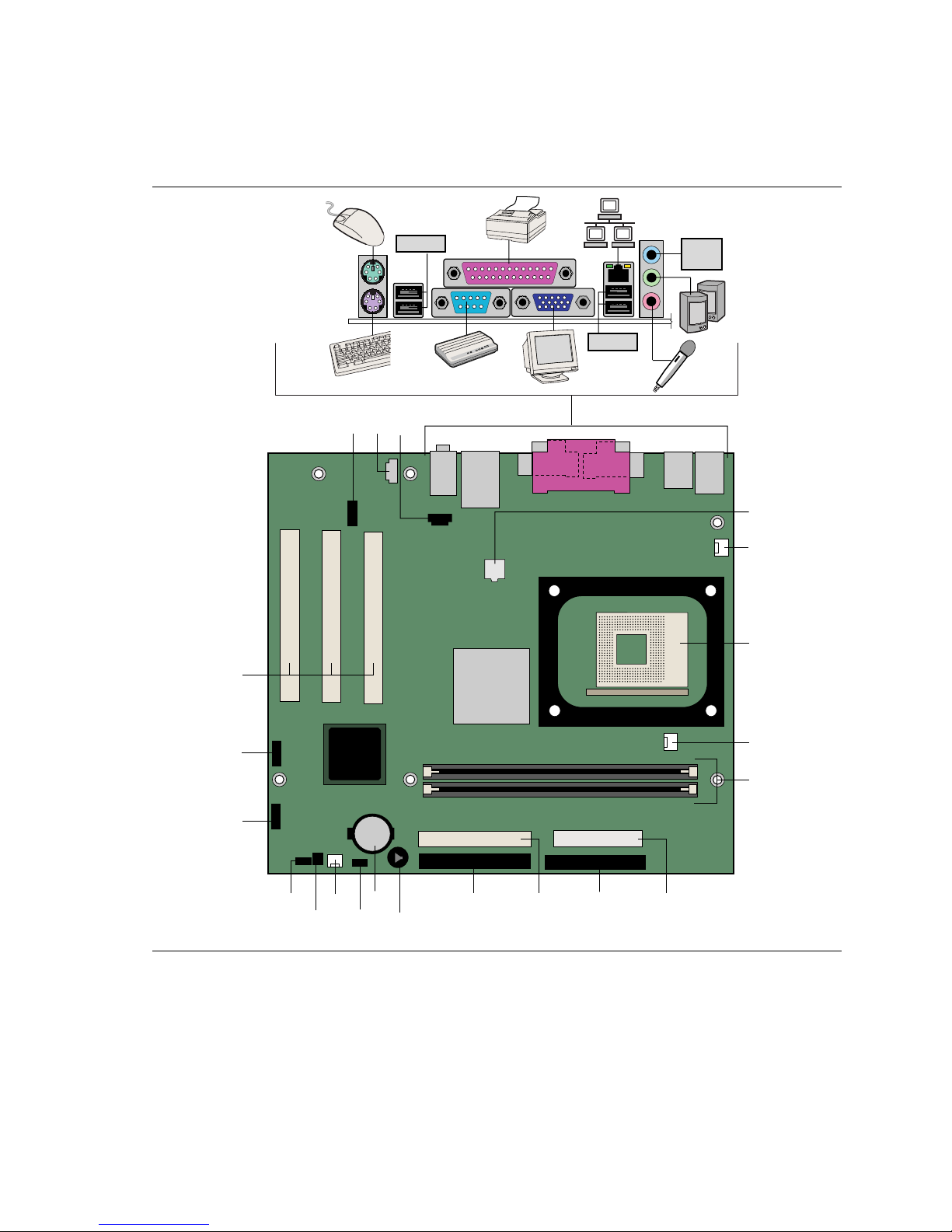
Back Panel Connectors
NOTE
✏
The line out connector, located on the back panel, is designed to power either headphones or
amplified speakers only. Poor audio quality may occur if passive (non-amplified) speakers are
connected to this output.
Figure 13 shows the back panel connectors.
BD
A
C
Item Description
A PS/2 mouse port
B PS/2 keyboard port
C USB 2.0 ports
D Serial port
E Parallel port
F VGA port
G RJ-45 (optional)
H USB 2.0 ports
I Mic in
J Audio line out
K Audio line in
Figure 13. Back Panel Connectors
F
E
H
G
I
K
J
OM16283
39
Page 40

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Replacing the Battery
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the computer
is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of three years. When the
computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends the life of the battery.
The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied.
When the voltage drops below a certain level, the BIOS Setup program settings stored in CMOS
RAM (for example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the battery with an
equivalent one. Figure 14 shows the location of the battery.
&$87,21
Risk of explosion if the battery is replaced with an incorrect type. Batteries should be recycled
where possible. Disposal of used batteries must be in accordance with local environmental
regulations.
35(&$87,21
Risque d’explosion si la pile usagée est remplacée par une pile de type incorrect. Les piles
usagées doivent être recyclées dans la mesure du possible. La mise au rebut des piles usagées doit
respecter les réglementations locales en vigueur en matière de protection de l'environnement.
)25+2/'65(*(/
Eksplosionsfare, hvis batteriet erstattes med et batteri af en forkert type. Batterier bør om muligt
genbruges. Bortskaffelse af brugte batterier bør foregå i overensstemmelse med gældende
miljølovgivning.
2%6
Det kan oppstå eksplosjonsfare hvis batteriet skiftes ut med feil type. Brukte batterier bør kastes i
henhold til gjeldende miljølovgivning.
9,.7,*7
Risk för explosion om batteriet ersätts med felaktig batterityp. Batterier ska kasseras enligt de
lokala miljövårdsbestämmelserna.
9$52
Räjähdysvaara, jos pariston tyyppi on väärä. Paristot on kierrätettävä, jos se on mahdollista.
Käytetyt paristot on hävitettävä paikallisten ympäristömääräysten mukaisesti.
9256,&+7
Bei falschem Einsetzen einer neuen Batterie besteht Explosionsgefahr. Die Batterie darf nur durch
denselben oder einen entsprechenden, vom Hersteller empfohlenen Batterietyp ersetzt werden.
Entsorgen Sie verbrauchte Batterien den Anweisungen des Herstellers entsprechend.
40
Page 41

Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
$99(57,0(172
Esiste il pericolo di un esplosione se la pila non viene sostituita in modo corretto. Utilizzare solo
pile uguali o di tipo equivalente a quelle consigliate dal produttore. Per disfarsi delle pile usate,
seguire le istruzioni del produttore.
35(&$8&,1
Existe peligro de explosión si la pila no se cambia de forma adecuada. Utilice solamente pilas
iguales o del mismo tipo que las recomendadas por el fabricante del equipo. Para deshacerse de
las pilas usadas, siga igualmente las instrucciones del fabricante.
:$$56&+8:,1*
Er bestaat ontploffingsgevaar als de batterij wordt vervangen door een onjuist type batterij.
Batterijen moeten zoveel mogelijk worden gerecycled. Houd u bij het weggooien van gebruikte
batterijen aan de plaatselijke milieuwetgeving.
$7(12
Haverá risco de explosão se a bateria for substituída por um tipo de bateria incorreto. As baterias
devem ser recicladas nos locais apropriados. A eliminação de baterias usadas deve ser feita de
acordo com as regulamentações ambientais da região.
$ &,$52 =1$ È
, .
, , .
.
832=2511
9S tSDG YêP Q\EDWHULH]DQHVSUiYQêGUXKP åHGRMtWNYêEXFKX Je-OLWRPRåQpEDWHULHE\P O\
být recyklovány. %DWHULHMHW
HED]OLNYLGRYDWYVRXODGXVPtVWQtPLS HGSLV\RåLYRWQtPSURVW HGt
9,*<=$7
Ha a telepet nem a megfelel WtSXV~WHOHSUHFVHUpOLD]IHOUREEDQKDW$WHOHSHNHWOHKHW VpJV]HULQW
~MUDNHOOKDV]QRVtWDQL$KDV]QiOWWHOHSHNHWDKHO\LN|UQ\H]HWYpGHOPLHO
kiselejtezni.
tUiVRNQDNPHJIHOHO HQNHOO
41
Page 42

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
$:$6
Risiko letupan wujud jika bateri digantikan dengan jenis yang tidak betul. Bateri sepatutnya
dikitar semula jika boleh. Pelupusan bateri terpakai mestilah mematuhi peraturan alam sekitar
tempatan.
2675=( (1,(
,VWQLHMHQLHEH]SLHF]H VWZRZ\EXFKXZSU]\SDGNX]DVWRVRZDQLDQLHZáD FLZHJRW\SXEDWHULL=X \WH
baterLHQDOH
\ZPLDU PR OLZR FLXW\OL]RZDü]JRGQLH]RGSRZLHGQLPLSU]HSLVDPLRFKURQ\
URGRZLVND
35(&$8 ,(
Risc de explo]LHGDF EDWHULDHVWHvQORFXLW FXXQWLSGHEDWHULHQHFRUHVSXQ] WRU%DWHULLOH
WUHEXLHUHFLFODWHGDF
ORFDOHSULYLQGSURWHF
HVWHSRVLELO'HSR]LWDUHDEDWHULLORUX]DWHWUHEXLHV UHVSHFWHUHJOHPHQW ULOH
LDPHGLXOXL
832=251(1,(
$NEDWpULXY\PHQtWH]DQHVSUiYQ\W\SKUR]tQHEH]SHþHQVWYRMHMYêEXFKX
%DWpULHE\VDPDOLSRG
DPRåQRVWLYåG\UHF\NORYD /LNYLGiFLDSRXåLWêFKEDWpULtVDPXVtY\NRQiYD
v súlade s miestnymiSUHGSLVPLQDRFKUDQXåLYRWQpKRSURVWUHGLD
32=25
=DPHQMDYDEDWHULMH]EDWHULMRGUXJDþQHJDWLSDODKNRSRY]URþLHNVSOR]LMR
ýHMHPRJRþHEDWHULMHUHFLNOLUDMWH5DEOMHQHEDWHULMH]DYU]LWHYVNODGX]ORNDOQLPL
okoljevarstvenimi predpisi.
42
Page 43
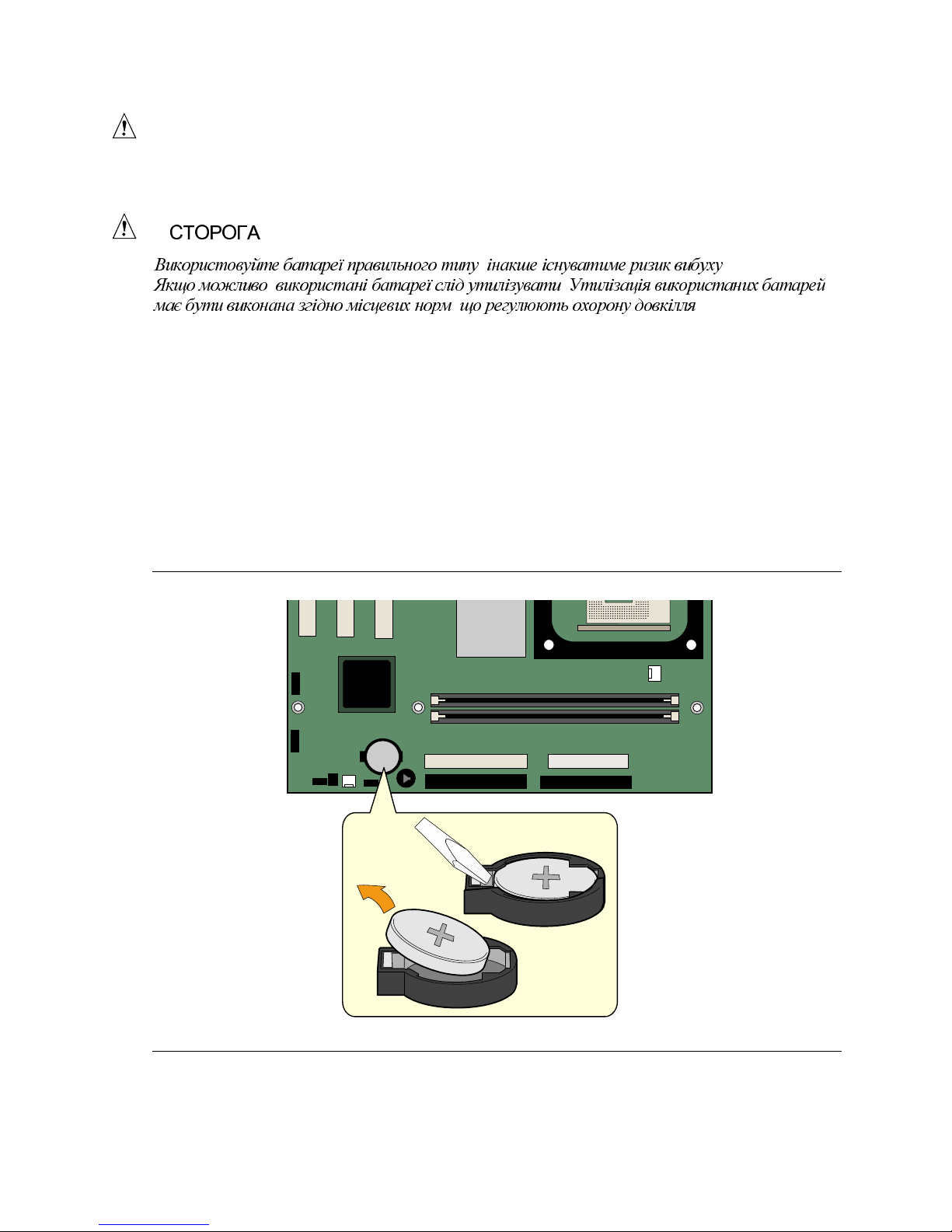
Installing and Replacing Desktop Board Components
8<$5,
<DQOÕúWUGHSLOWDNÕOGÕ÷ÕQGDSDWODPDULVNLYDUGÕU3LOOHUPPNQROGX÷XQGDJHUL
G|QúWUOPHOLGLU.XOODQÕOPÕúSLOOHU\HUHOoHYUH\DVDODUÕQDX\JXQRODUDNDWÕOPDOÕGÕU
2
To replace the battery, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” on page 21.
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Disconnect the computer’s power
cord from the AC power source (wall outlet or power adapter).
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Locate the battery on the board (see Figure 14).
5. Note the orientation of the “+” and “-” on the battery.
6. With a medium flat-bladed screwdriver, gently pry the battery free from its connector.
7. Install the new battery in the connector, orienting the “+” and “-” correctly.
8. Replace the computer cover.
Figure 14. Removing the Battery from the Desktop Board
OM16284
43
Page 44

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
44
Page 45

3 Updating the BIOS
This chapter tells you how to update the BIOS by either using the Intel Express BIOS Update
utility or the Intel
®
Flash Memory Update Utility, and how to recover the BIOS if an update fails.
Updating the BIOS with the Intel® Express BIOS
Update Utility
With the Intel Express BIOS Update utility you can update the system BIOS while in the Windows
environment. The BIOS file is included in an automated update utility that combines the
functionality of the Intel Flash Memory Update Utility and the ease-of use of Windows-based
installation wizards.
To update the BIOS with the Intel Express BIOS Update utility:
1. Go to the Intel World Wide Web site:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
2. Navigate to the D845GVSR page, click “[
Express BIOS Update utility file.
3. Download the file to your hard drive. (You can also save this file to a diskette. This is useful
if you are updating the BIOS for multiple identical systems.)
4. Close all other applications. This step is required. Your system will be rebooted at the last
Express BIOS Update window.
5. Double-click the executable file from the location on your hard drive where it was saved. This
runs the update program.
6. Follow the instructions provided in the dialog boxes to complete the BIOS update.
view] Latest BIOS updates”, and select the
Updating the BIOS with the Intel® Iflash BIOS Update
Utility
With the Intel® Iflash BIOS update utility you can update the system BIOS from a floppy disk or
other bootable media. The utility available from the Web provides a simple method for creating a
bootable flash memory update floppy that will automatically update your BIOS.
Obtaining the BIOS Update File
You can update to a new version of the BIOS by using the BIOS update file. The BIOS update file
is a compressed self-extracting archive that contains all the files you need to update the BIOS. The
BIOS update file contains New BIOS files, BIOS recovery files, and the Intel Flash Memory
Update utility.
You can obtain the BIOS update file through your computer supplier or by navigating to the
D845GVSR page on the Intel World Wide Web site at:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
Navigate to the D845GVSR page, click “[
Intel Iflash BIOS Update utility file.
view] Latest BIOS updates”, and select the
45
Page 46

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
NOTE
✏
Review the instructions distributed with the update utility before attempting a BIOS update.
The Intel Iflash BIOS update utility allows you to:
• Update the BIOS in flash memory
• Update the language section of the BIOS
Updating the BIOS
CAUTION
The AUTOEXEC.BAT file provided with the update files updates the BIOS. Do not interrupt the
process or the system may not function.
1. Boot the computer with the BIOS update diskette in drive A. During system boot, the
AUTOEXEC.BAT file provided with the update files will automatically run the BIOS update
process.
2. When the update process is complete, the monitor will display a message telling you to remove
the diskette and to reboot the system.
3. As the computer boots, check the BIOS identifier (version number) to make sure the update
was successful. If a logo appears, press
<Esc> to view the POST messages.
Recovering the BIOS
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt the BIOS update, however, if an interruption occurs, the
BIOS could be damaged. The following steps explain how to recover the BIOS if an update fails.
The following procedure uses recovery mode for the Setup program. See page 37 for more
information on Setup modes.
NOTE
✏
Because of the small amount of code available in the boot block area, there is no video support.
You will not see anything on the screen during this procedure. Monitor the procedure by listening
to the speaker and looking at the diskette drive LED.
1. Turn off the computer, disconnect the computer’s power cord, and disconnect all external
peripherals.
2. Remove the computer cover and locate the configuration jumper block (J9H2) (see Figure 12).
3. Remove the jumper from all pins as shown below to set recovery mode for Setup.
3
1
4. Insert the bootable BIOS update diskette into diskette drive A.
5. Replace the computer cover, connect the power cord, turn on the computer, and allow it to
boot. The recovery process will take a few minutes.
46
Page 47

Updating the BIOS
6. Listen to the speaker:
• Upon applying power, drive A will begin to show activity. In about a minute, two beeps
are heard and drive A activity ceases (temporarily) indicating the successful recovery of
the BIOS core. Drive A activity will begin again followed by two more beeps indicating
the successful recovery of the boot block. This sequence of events indicates a successful
BIOS recovery.
• A series of continuous beeps indicates a failed BIOS recovery.
7. If recovery fails, return to step 1 and repeat the recovery process.
8. If recovery is successful, turn off the computer, and disconnect its power cord.
9. Remove the computer cover and continue with the following steps.
10. On the jumper block (J9H2), reinstall the jumper back on pins 1-2 as shown below to set
normal mode for Setup.
3
1
11. Leave the update diskette in drive A, replace the computer cover, and connect the computer’s
power cord.
12. Turn on the computer and continue with the BIOS update (see page 46).
47
Page 48

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
48
Page 49

4 Using the BIOS Setup Program
The BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the computer. The
BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <F2> key after the Power-On Self-Test (POST)
memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins.
NOTE
✏
The BIOS Setup menus described in this section may not show the latest settings. For the latest
BIOS settings, refer to the Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Technical Product Specification or the
Intel World Wide Web site at:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/
NOTE
✏
For reference purposes, you should write down the current Setup settings. When you make
changes to the settings, update this record.
NOTE
✏
The Setup menus described in this section apply to the desktop board with BIOS identifier
VA84510A.86A. Desktop boards with other BIOS identifiers might have differences in some of the
Setup menu screens.
Table 10 shows the BIOS Setup program menu bar.
Table 10. BIOS Setup Program Menu Bar
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Clears passwords
and Boot Integrity
Service (BIS)*
credentials, and
configures
extended
configuration
memory settings
* For information about the BIS, refer to the Intel Web site at:
http://developer.intel.com/design/security/index1.htm
Allocates
resources
for
hardware
components
Configures
advanced
features
available
through the
chipset
Sets
passwords
and security
features
Configures
power
management
features
Selects
boot
options
and power
supply
controls
Saves or
discards
changes to
set program
options
49
Page 50

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Table 11 shows the function keys available for menu screens.
Table 11. BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
BIOS Setup Program Function Key Description
<←> or <→> Selects a different menu screen
<↑> or <↓> Moves cursor up or down
<Tab> Moves cursor to the next field
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu
<F9> Load the default configuration values for the current menu
<F10> Save the current values and exits the BIOS Setup program
<Esc> Exits the menu
Maintenance Menu
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Clear All Passwords
Clear BIS credentials
CPU Stepping Signature [F29]
CPU Microcode Update Rev. [<none loaded>]
The menu shown in Table 12 is used to clear the Setup passwords. Setup only displays this menu
in configure mode. See page 37 for information about setting configure mode.
m o
n p
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Select Screen
Select Item
Selecto Sub-Menu
Table 12. Maintenance Menu
Feature Options Description
Clear All Passwords • Ok
Clear BIS Credentials • Ok
CPU Stepping Signature No options Displays processor’s Stepping Signature.
CPU Microcode Update
Revision
* For information about the BIS, refer to the Intel Web site at:
http://developer.intel.com/design/security/index1.htm
50
Clears both the user and supervisor passwords.
• Cancel
Clears the Wired for Management Boot Integrity Service (BIS)
• Cancel
No options Displays processor’s Microcode Update Revision.
credentials.
Page 51

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Main Menu
Maintenance Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
BIOS Version VA84510A.86A.xxxx.xxx
Processor Type Intel(R) XXXXXXXXXXX
Processor Speed X.XX GHz
System Bus Speed XXX MHz
System Memory Speed XXX MHz
Cache RAM XXX KB
Total Memory XXX MB
Memory Bank 0 XXX MB
Memory Bank 1 XXX MB
Enter
Language [English] F1 General Help
System Time [HH.MM.SS] P9 Setup Defaults
System Date [DD.MM.YY] F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Main menu reports processor and memory information and is used to configure the system date and
system time. Table 13 describes this menu.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select f Sub-Menu
Table 13. Main Menu
Feature Options Description
BIOS Version No options Displays the version of the BIOS.
Processor Type No options Displays processor type.
Hyper-Threading
Technology
Processor Speed No options Displays processor speed.
System Bus Speed No options Displays the system bus speed.
System Memory Speed No options Displays the system memory speed.
Cache RAM No options Displays the size of second-level cache and
Total Memory No options Displays the total amount of RAM.
Memory Bank 0
Memory Bank 1
Language • English (default)
System Time Hour, minute, and second Specifies the current time.
System Date Day of week - month/day/year Specifies the current date.
• Enabled (default)
• Disabled
No options Displays the amount and type of RAM in the
• Espanol
Enables or disables Hyper-Threading
Technology.
whether it is ECC-capable.
memory banks.
Selects the current default language used by the
BIOS.
51
Page 52

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Advanced Menu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Setup Warning:
Setting items on this screen to incorrect values
may cause your system to malfunction!
` PCI Configuration
` Boot Configuration
` Peripheral Configuration
` IDE Configuration
` Diskette Configuration
` Event Log Configuration
` Video Configuration
` USB Configuration
` Chipset Configuration
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Enter
Table 14 describes the Advanced Menu. This menu is used to set advanced features that are
available through the chipset.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 14. Advanced Menu
Feature Options Description
PCI Configuration No options Configures individual PCI slot’s IRQ priority. When selected,
displays the PCI Configuration submenu.
Boot Configuration No options Configures Plug & Play and the Numlock key, and resets
configuration data. When selected, displays the Boot
Configuration submenu.
Peripheral Configuration No options Configures peripheral ports and devices. When selected, displays
the Peripheral Configuration submenu.
IDE Configuration No options Specifies type of connected IDE device.
Diskette Configuration No options Configures the floppy drive(s). When selected, displays the
Diskette Configuration submenu.
Event Log Configuration No options Configures event logging. When selected, displays the Event Log
Configuration submenu.
Video Configuration No options Configures video features. When selected, displays the Video
Configuration submenu.
USB Configuration No options Configures USB features. When selected, displays the USB
Configuration submenu.
Chipset Configuration No options Configures chipset features. When selected, displays the Chipset
Configuration submenu.
52
Page 53

Using the BIOS Setup Program
PCI Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
PCI Configuration
PCI Slot 1 IRQ Priority [Auto]
PCI Slot 2 IRQ Priority [Auto]
PCI Slot 3 IRQ Priority [Auto]
The submenu shown in Table 15 is used to configure the IRQ priority of PCI slots individually.
m o
n p
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 15. PCI Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
PCI Slot 1 IRQ Priority • Auto (default)
• 3
• 5
• 9
• 10
• 11
PCI Slot 2 IRQ Priority • Auto (default)
• 3
• 5
• 9
• 10
• 11
PCI Slot 3 IRQ Priority • Auto (default)
• 3
• 5
• 9
• 10
• 11
Allows selection of IRQ priority.
Allows selection of IRQ priority and S5 wake.
Allows selection of IRQ priority.
53
Page 54
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Boot Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Boot Configuration
Plug & Play O/S [No]
Numlock [On]
ASF Support [Enabled]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu shown in Table 16 is used to set the Plug & Play options and the power-on state of
the Numlock key.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 16. Boot Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Plug & Play O/S • No (default)
• Yes
Numlock • Off
• On (default)
ASF Support • Enabled (default)
• Disabled
Specifies if manual configuration is desired.
No lets the BIOS configure all devices in the system. This
setting is appropriate when using a Plug and Play operating
system.
Yes lets the operating system configure Plug & Play (PnP)
devices not required for boot if your system has a Plug & Play
operating system. This option is available for use during lab
testing.
Specifies the power-on state of the Numlock feature on the
numeric keypad of the keyboard.
Configures LAN ASF (Alert Standard Format).
54
Page 55

Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Peripheral Configuration
Serial Port A [Auto]
Parallel Port [Auto]
Audio [Enabled]
LAN Device [Enabled]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
This submenu shown in Table 17 is used for configuring computer peripherals.
m o
n p
Using the BIOS Setup Program
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 17. Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Serial Port A • Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
Base I/O Address
(This feature is present
only when Serial Port A
is set to Enabled)
Interrupt
(This feature is present
only when Serial Port A
is set to Enabled)
Parallel Port • Disabled
• 3F8 (default)
• 2F8
• 3E8
• 2E8
• IRQ 3
• IRQ 4 (default)
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
Configures serial port A.
Auto assigns the first free COM port, normally COM1, the
address 3F8h, and the interrupt IRQ4.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
Specifies the base I/O address for serial port A, if serial
port A is Enabled.
Specifies the interrupt for serial port A, if serial port A is
Enabled.
Configures the parallel port.
Auto assigns LPT1 the address 378h and the
interrupt IRQ7.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
continued
55
Page 56
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Table 17. Peripheral Configuration Submenu (continued)
Feature Options Description
Mode • Output only
• Bi-directional
(default)
• EPP
• ECP
Base I/O Address
(This feature is present
• 378 (default)
• 278
only when Parallel Port
is set to Enabled)
Interrupt
(This feature is present
• IRQ 5
• IRQ 7 (default)
only when Parallel Port
is set to Enabled)
Audio • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
LAN Device
(This feature is present
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
only when there is
onboard LAN)
Selects the mode for the parallel port. Not available if the
parallel port is disabled.
Output Only operates in AT*-compatible mode.
Bi-directional operates in PS/2-compatible mode.
EPP is Extended Parallel Port mode, a high-speed
bi-directional mode.
ECP is Enhanced Capabilities Port mode, a high-speed
bi-directional mode.
Specifies the base I/O address for the parallel port, if
Parallel Port is Enabled.
Specifies the interrupt for the parallel port, if Parallel Port is
Enabled.
Enables or disables the onboard audio subsystem.
Enables or disables the LAN device.
56
Page 57
IDE Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
IDE Configuration
IDE Controller [Both]
PCI IDE Bus Master [Enabled]
Hard Disk Pre-Delay [Disabled]
` Primary IDE Master :
` Primary IDE Slave :
` Secondary IDE Master :
` Secondary IDE Master :
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
This submenu shown in Table 18 is used to configure IDE device options.
[xxxxxxx]
[Not Detected]
[xxxxxxx]
[Xxxxxxx]
Using the BIOS Setup Program
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 18. IDE Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
IDE Controller • Disabled
• Primary
• Secondary
• Both (default)
PCI IDE Bus Master
Hard Disk Pre-Delay • Disabled (default)
Primary IDE Master No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected,
Primary IDE Slave No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected,
Secondary IDE Master No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected,
Secondary IDE Slave No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected,
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• 3 Seconds
• 6 Seconds
• 9 Seconds
• 12 Seconds
• 15 Seconds
• 21 Seconds
• 30 Seconds
Specifies the integrated IDE controller.
Disabled disables the integrated IDE controller.
Primary enables only the primary IDE controller.
Secondary enables only the secondary IDE controller.
Both enables both IDE controllers.
Allows for a PCI device to initiate a transaction as a
master.
Specifies the hard disk drive pre-delay. Causes the BIOS
to insert a delay before attempting to detect IDE drives in
the system.
displays the Primary IDE Master submenu.
displays the Primary IDE Slave submenu.
displays the Secondary IDE Master submenu.
displays the Secondary IDE Slave submenu.
57
Page 58
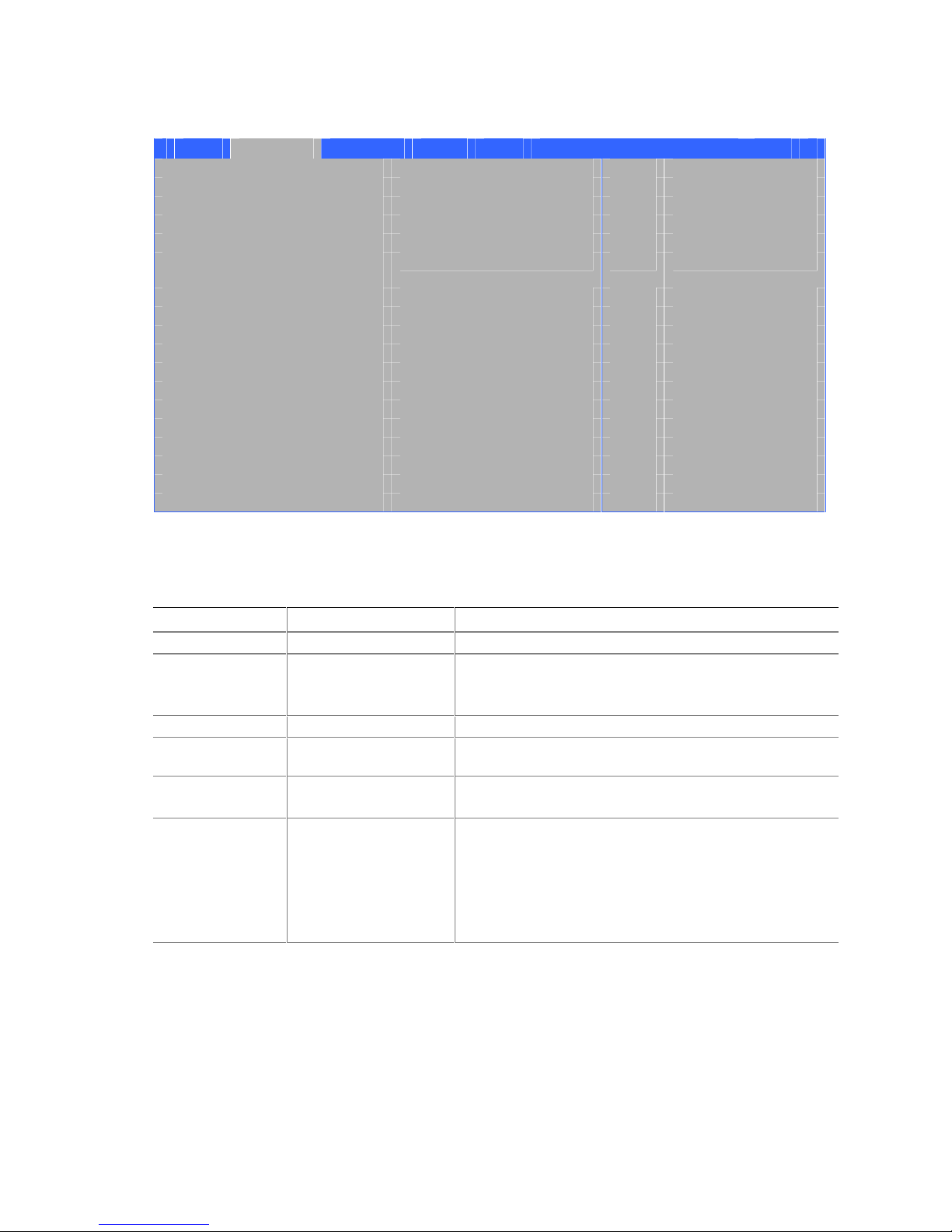
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Primary/Secondary IDE Master/Slave Submenus
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
` [ :
Type [Auto]
Maximum Capacity [Auto]
Configuration Options
Selected By BIOS
LBA Mode : [Supported]
Block Mode : 16 Sectors
PIO Mode : Auto
Ultra DMA : Disabled
Cable Detected : Serial
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Xxxxxxxxx ]
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
There are four IDE submenus: Primary master, primary slave, secondary master, and secondary
slave. Table 19 shows the format of these IDE submenus. For brevity, only one example is shown.
Table 19. Primary/Secondary IDE Master/Slave Submenus
Feature Options Description
Drive Installed • None Displays the type of drive installed.
Type • Auto (default)
• User
Maximum Capacity • None Displays the capacity of the drive.
LBA Mode Control
(Note)
Block Mode
PIO Mode
(Note)
• None Specifies LBA mode control.
• Disabled
• Auto (default)
• Auto (default)
• 0
• 1
• 2
• 3
• 4
Specifies the IDE configuration mode for IDE devices.
Auto fills-in capabilities from ATA/ATAPI device.
User allows capabilities to be changed.
Check the hard disk drive’s specifications for optimum
setting.
Specifies the PIO mode.
continued
58
Page 59

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Table 19. Primary/Secondary IDE Master/Slave Submenus (continued)
Feature Options Description
Ultra DMA
• Disabled (default)
• Mode 0
Specifies the Ultra DMA mode for the drive.
• Mode 1
• Mode 2
• Mode 3
• Mode 4
• Mode 5
Cable Detected
(Note)
Note: These configuration options appear only if an IDE device is installed.
None Displays the type of cable connected to the IDE interface:
40-conductor or 80-conductor (for ATA-66/100 devices).
59
Page 60

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Diskette Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Diskette Configuration
Diskette Controller [Enabled]
Floppy A [1.44/1.25MB 3½"]
Diskette Write Protect [Disabled]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
This submenu shown in Table 20 is used to configure the diskette drive.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 20. Diskette Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Diskette Controller • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Floppy A • Disabled
• 360 KB 5¼”
• 1.2 MB 5¼”
• 720 KB 3½”
• 1.44 MB 3½” (default)
• 2.88 MB 3½”
Diskette Write Protect • Disabled (default)
• Enabled
Configures the integrated diskette controller.
Selects the diskette drive type.
Disables or enables diskette drive write protection.
60
Page 61
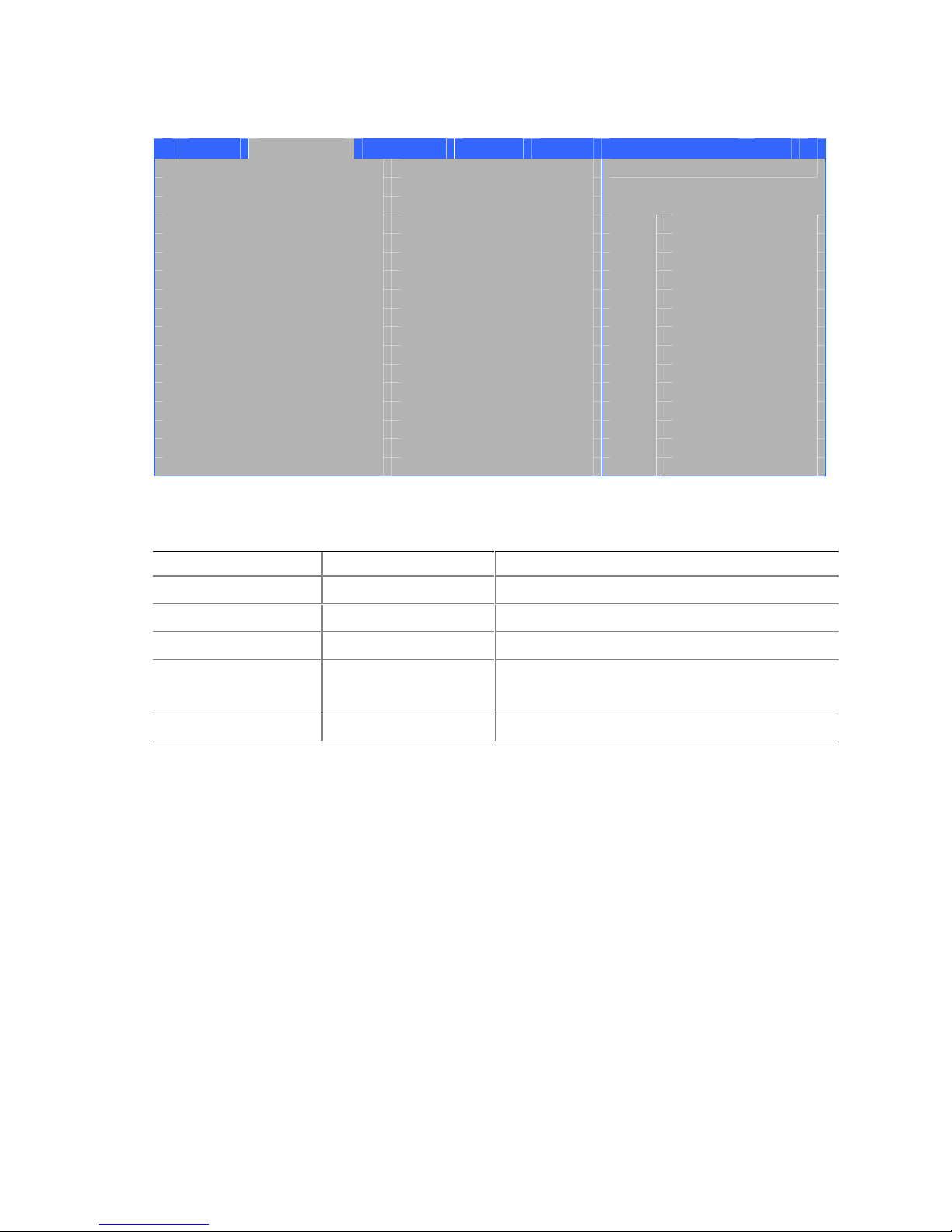
Event Log Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Event Log Configuration
Event Log [Space Available]
View Event Log
Clear Event Log
Event Logging [Enabled]
Mark Events As Read
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu shown in Table 21 is used to configure the event logging features.
m o
n p
Using the BIOS Setup Program
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 21. Event Log Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Event Log No options Indicates if there is space available in the event log.
View Event Log [Enter] Views the contents of the DMI event log.
Clear Event Log No options Discards all events in the event log.
Event Logging • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Mark Events As Read [Enter] Marks all DMI events in the event log as read.
Enabled allows logging of DMI events.
61
Page 62
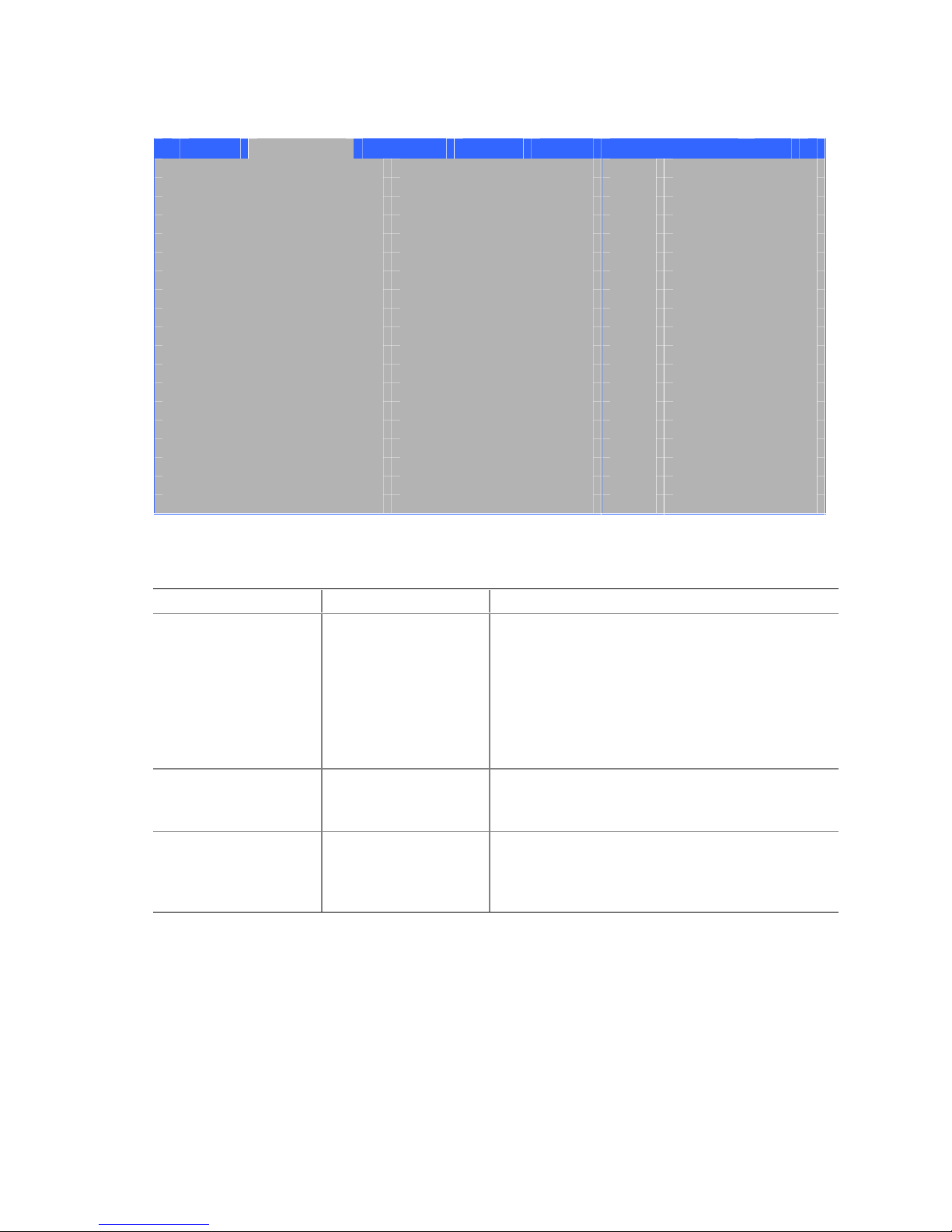
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Video Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Video Configuration
Graphics Aperture Size [ 64MB]
Primary Video Adapter [Integrated]
Frame Buffer Size [1 MB]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu shown in Table 22 is used to configure video features.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 22. Video Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Graphics Aperture Size • 4 MB
• 8 MB
• 16 MB
• 32 MB
• 64 MB (default)
• 128 MB
• 256 MB
Primary Video Adapter • PCI
• Integrated (default)
Frame Buffer Size • 512 KB
• 1 MB (default)
• 8 MB
Amount of system memory available for direct access
by the graphics device.
Allows selecting the PCI video controller as the
display device that will be active when the system
boots.
Controls how much RAM is reserved for use by the
internal graphics device.
62
Page 63

USB Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
USB Configuration
High-Speed USB [Enabled]
Legacy USB Support [Enabled]
USB 2.0 Legacy Support [FullSpeed]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The menu shown in Table 23 is used to configure USB features.
Using the BIOS Setup Program
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 23. USB Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
High Speed USB
Legacy USB Support
USB 2.0 Legacy Support
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Full Speed (default)
• Hi Speed
Disable this option when a USB 2.0 driver is not
available.
Enables support for legacy USB.
Configures Legacy USB transfer rate:
Full Speed: 12 Mbps
Hi Speed: 480 Mbps
63
Page 64

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Chipset Configuration Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Chipset Configuration
Setup Warning:
Setting items on this screen to incorrect values
may cause your system to malfunction!
ISA Enable Bit [Enabled]
PCI Latency Timer [32]
Extended Configuration [Default]
Chipset Memory Timing Control
SDRAM Frequency [Auto]
SDRAM Timing Control [Auto] Enter
SDRAM RAS Act. to Pre. [6] F1 General Help
SDRAM CAS# Latency [2.0] P9 Setup Defaults
SDRAM RAS# to CAS# delay [3] F10 Save and Exit
SDRAM RAS# Precharge [3] ESC Exit
The menu shown in Table 24 is used to configure advanced chipset features.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 24. Chipset Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
ISA Enable Bit • Enabled (default)
• Disabled
PCI Latency Timer • 32 (default)
• 64
• 96
• 128
• 160
• 192
• 224
• 248
Extended Configuration • Default (default)
• User Defined
SDRAM Frequency • Auto (default)
• 200 MHz
• 266 MHz
Some older expansion devices require this to be
enabled.
Set PCI latency time.
Chooses the default or user defined settings for
the extended configuration options.
Allows override of detected memory frequency
value.
continued
64
Page 65

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Table 24. Chipset Configuration Submenu (continued)
Feature Options Description
SDRAM Timing Control • Auto (default)
• Manual – Aggressive
• Manual – User Defined
SDRAM RAS Act. To Pre. • 7
• 6
• 5
• Auto (default)
SDRAM CAS# Latency • 3
• 2
• Auto (default)
SDRAM RAS# to CAS#
delay
SDRAM RAS# Precharge • 3
• 3
• 2
• Auto (default)
• 2
Auto allows timings to be programmed according
to the memory detected.
Manual – Aggressive selects the most aggressive
user defined timings.
Manual – User Defined allows manual override of
detected SDRAM settings.
Selects length of time from read to pre-change.
Selects the number of clock cycles required to
address a column in memory.
Selects the number of clock cycles between
addressing a row and addressing a column.
Selects the length of time required before
accessing a new row.
• Auto (default)
65
Page 66

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Security Menu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Supervisor Password : Not Installed
User Password : Not Installed
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Chassis Intrusion [Disabled]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The menu shown in Table 25 is used to set passwords and security features.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 25. Security Menu
If no password entered previously:
Feature Options Description
Supervisor Password No options Reports if there is a supervisor password set.
User Password No options Reports if there is a user password set.
Set Supervisor Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
Set User Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
Clear User Password
(Note 1)
User access Level
(Note 2)
Chassis Intrusion • Disabled (default)
Notes:
1. This feature appears only if a user password has been set.
2. This feature appears only if both a user password and a supervisor password have been set.
• Yes (default)
• No
• Limited
• No access
• View Only
• Full (default)
• Enabled
Specifies the supervisor password.
Specifies the user password.
Clears the user password.
Sets BIOS Setup Utility access rights for
user level.
Enables and disables the chassis intrusion
feature.
66
Page 67

Power Menu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
ACPI
After Power Failure [Last State]
The options below are not related to ACPI and may
be ignored when shutting down using an ACPI OS.
Wake on PCI PME [Stay Off]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The menu shown in Table 26 is used to set power management features.
Using the BIOS Setup Program
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 26. Power Menu
Feature Options Description
ACPI No Options When selected, displays the ACPI submenu.
After Power Failure • Stay Off
Wake on PCI PME • Stay Off (default)
• Last State (default)
• Power On
• Power-On
Determines the mode of operation if a power loss
occurs.
Stay Off keeps the power off until the power button is
pressed.
Last State restores the previous power state before
power loss occurred.
Power On restores power to the computer.
Determines how the system responds to a PCI-PME
wake up event.
67
Page 68

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
ACPI Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
ACPI Suspend State [S1 State]
Wake on LAN from S5 [Stay Off]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu represented in Table 27 is for setting the ACPI features.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 27. ACPI Submenu
Feature Options Description
ACPI Suspend Mode • S1 (POS) only (default)
• S1 & S3 (STR)
Wake on LAN* from S5 • Stay Off (default)
• Power On
Specifies the ACPI sleep state.
In ACPI soft-off mode only, determines how the
system responds to a LAN wake up event when the
system is in the ACPI soft-off mode.
68
Page 69

Using the BIOS Setup Program
Boot Menu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Silent BOOT [Enabled]
Intel ® Rapid BIOS Boot [Enabled]
Scan User Flash Area [Enabled]
PXE Boot to LAN [Disabled]
USB Boot [Enabled]
` Boot Device Priority
` Hard Disk Drives
` Removable Devices
` ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The menu shown in Table 28 is used to set the boot features and the boot sequence.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 28. Boot Menu
Feature Options Description
Silent Boot • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Intel Rapid BIOS Boot • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Scan User Flash Area • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
PXE Boot to LAN • Disabled (default)
• Enabled
USB Boot • Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Boot Device Priority No options Specifies the boot sequence from the available types of
Hard Disk Drives No options Specifies the boot sequence from the available hard
Removable Devices No options Specifies the boot sequence from the available removable
ATAPI CD-ROM Drives No options Specifies the boot sequence from the available ATAPI
Disabled displays normal POST messages.
Enabled displays OEM logo instead of POST messages.
Allows BIOS to skip certain tests while booting.
Enables the BIOS to scan the flash ROM for user binary
files that are executed at boot time.
Disables or enables PXE boot to LAN.
Disables or enables booting to USB boot devices.
boot devices.
disk drives.
devices.
CD-ROM drives.
69
Page 70

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Boot Device Priority Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
1st Boot Device [1st FLOPPY DRIVE]
2nd Boot Device [xxxxxxxxxxx]
3rd Boot Device [xxxxxxxxxxx]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu represented in Table 29 is for setting boot devices priority.
Specifies the boot
sequence from the
available devices.
A device enclosed in
parenthesis has been
disabled in the
corresponding type
menu.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 29. Boot Device Priority Submenu
Feature
1st Boot Device
nd
Boot Device
2
rd
Boot Device
3
Options Description
• Removable Device
• Hard Drive
• ATAPI CD-ROM
• Disabled
Specifies the boot sequence from the available devices. To
specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the intended boot
device.
The operating system assigns a drive letter to each boot device in
the order listed. Changing the order of the devices changes the
drive lettering. The default settings for the first through final boot
devices are, respectively listed below. The BIOS supports up to
sixteen total boot devices in any combination of the boot device
types below, with respect to these maximums per type.
• Removable Device (maximum of four).
• Hard Drive (maximum of 12).
• ATAPI CD-ROM (maximum of four).
70
Page 71

Hard Disk Drives Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
1st Drive [xxxxxxxxxxxxx]
2nd Drive [xxxxxxxxxxxxx]
3rd Drive [xxxxxxxxxxxxx]
4th Drive [xxxxxxxxxxxxx]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu shown in Table 30 is for setting hard disk drives.
Using the BIOS Setup Program
Specifies the boot
sequence from the
available devices.
Select the boot device
with UpArrow or
DownArrow key. Press
Enter to set the
selections as the
intended boot device.
ARMD = ATAPI Removable
Media Device.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 30. Hard Disk Drives Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st Hard Disk Drive
(Note)
Note: This boot device submenu appears only if at least one boot device of this type is installed. This list will
display up to twelve hard disk drives, the maximum number of hard disk drives supported by the BIOS.
Dependent on installed
hard drives
Specifies the boot sequence from the available hard disk
drives. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the intended
boot device.
71
Page 72

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Removable Devices Submenu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
1st Removable Device [1st FLOPPY DRIVE]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu in shown Table 31 is for setting removable devices.
Specifies the boot
sequence from the
available devices.
Select the boot device
with UpArrow or
DownArrow key. Press
Enter to set the
selections as the
intended boot device.
ARMD = ATAPI Removable
Media Device.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 31. Removable Devices Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st Removable Device
(Note)
Note: This boot device submenu appears only if at least one boot device of this type is installed. This list will
display up to four removable devices, the maximum number of removable devices supported by the BIOS.
Dependent on installed
removable devices
Specifies the boot sequence from the available
removable devices. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the
intended boot device.
72
Page 73

ATAPI CD-ROM Drives
t device submenu appears only if at least one boot device of this type is installed. This list will display up to
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
1st ATAPI CD-ROM Drive [xxxxxxx]
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The submenu shown in Table 32 is for setting ATAPI CD-ROM drives.
Using the BIOS Setup Program
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 32. ATAPI CD-ROM Drives Submenu
Feature Options Description
1st ATAPI CD-ROM Drive
(Note)
Note: This boo
four ATAPI CD-ROM drives, the maximum number of ATAPI CD-ROM drives supported by the BIOS.
Dependent on installed
ATAPI CD-ROM drives
Specifies the boot sequence from the available
ATAPI CD-ROM drives. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <Enter> to set the selection as the
intended boot device.
73
Page 74
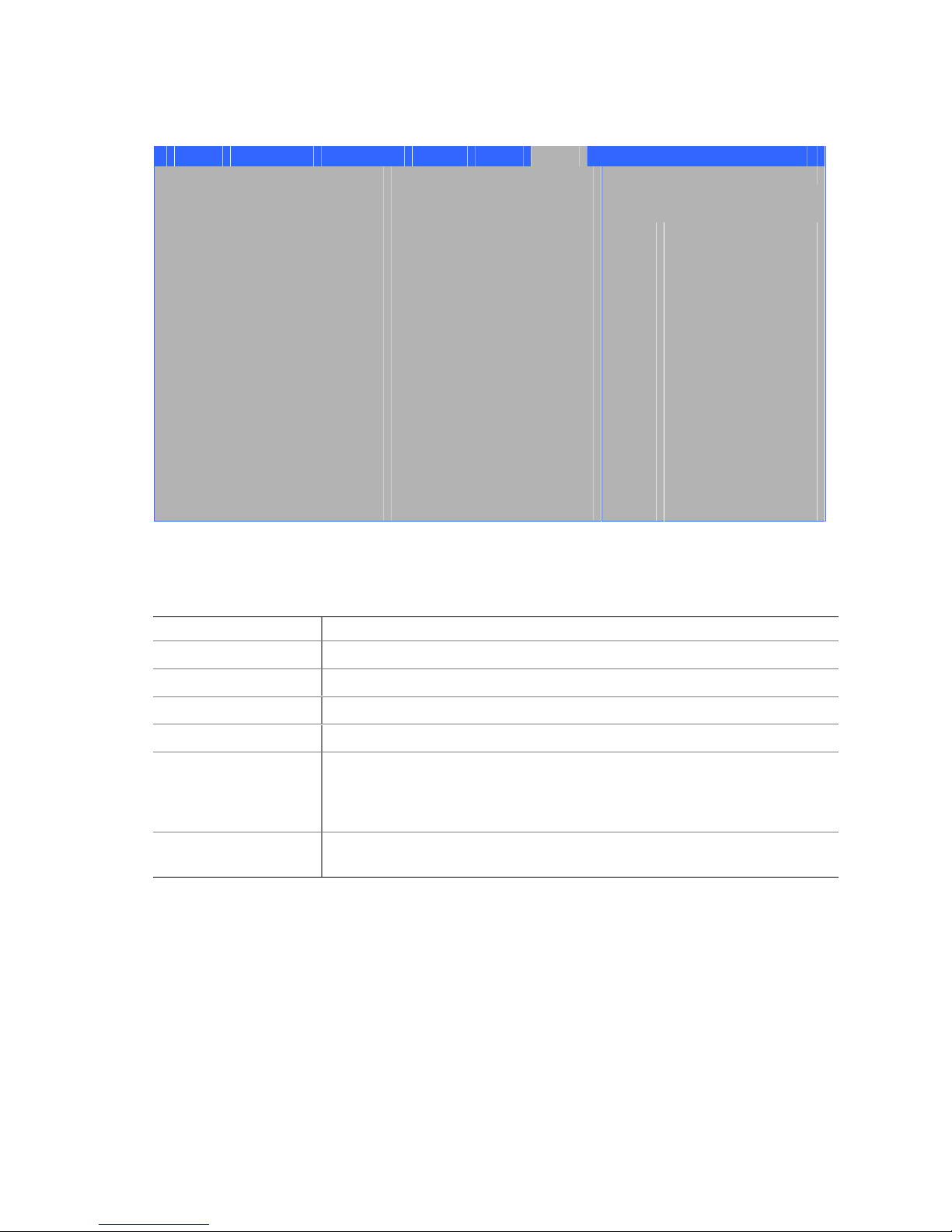
Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Exit Menu
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
Exit Saving Changes
Exit Discarding Changes
Load Optimal Defaults
Load Custom Defaults
Save Custom Defaults
Discard Changes
Enter
F1 General Help
P9 Setup Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
The menu shown in Table 33 is used to exit the BIOS Setup program, saving changes, and loading
and saving defaults.
m o
n p
Select Screen
Select Item
Select ` Sub-Menu
Table 33. Exit Menu
Feature Description
Exit Saving Changes Exits and saves the changes in CMOS SRAM.
Exit Discarding Changes Exits without saving any changes made in the BIOS Setup program.
Load Optimal Defaults Loads optimal defaults.
Load Custom Defaults Loads the custom defaults for Setup options.
Save Custom Defaults Saves the current values as custom defaults. Normally, the BIOS reads the
Setup values from flash memory. If this memory is corrupted, the BIOS reads the
custom defaults. If no custom defaults are set, the BIOS reads the factory
defaults.
Discard Changes Discards changes without exiting Setup. The option values present when the
computer was turned on are used.
74
Page 75
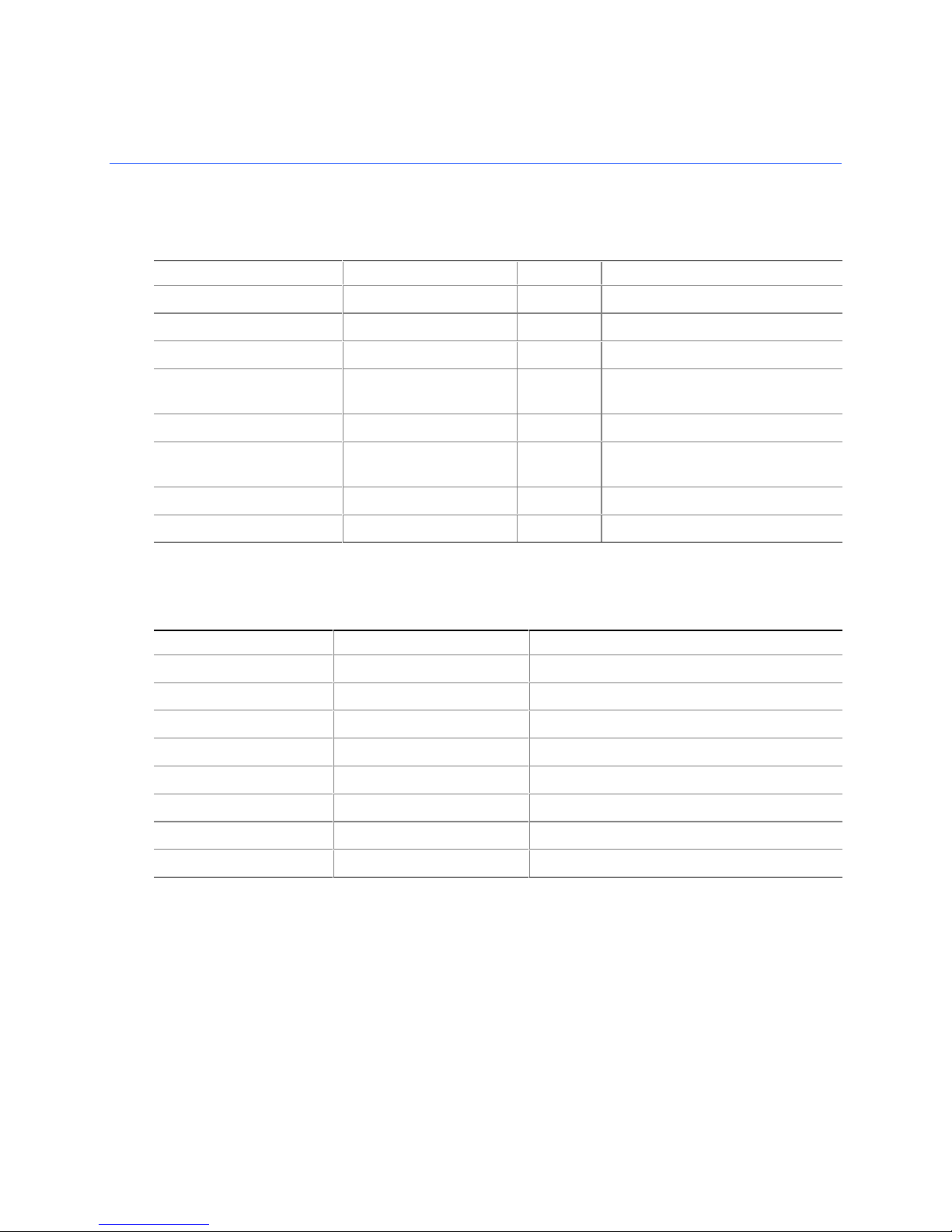
5 Desktop Board Resources
Memory Map
Table 34. System Memory Map
Address Range (decimal) Address Range (hex) Size Description
1024 K - 2097152 K 100000 - 7FFFFFFF 2047 MB Extended Memory
960 K - 1024 K F0000 - FFFFF 64 KB Runtime BIOS
896 K - 960 K E0000 - EFFFF 64 KB Reserved
800 K - 896 K C8000 - DFFFF 96 KB Available high DOS memory (open
to the PCI bus)
640 K - 800 K A0000 - C7FFF 160 KB Video memory and BIOS
639 K - 640 K 9FC00 - 9FFFF 1 KB Extended BIOS data (movable by
memory manager software)
512 K - 639 K 80000 - 9FBFF 127 KB Extended conventional memory
0 K - 512 K 00000 - 7FFFF 512 KB Conventional memory
DMA Channels
Table 35. DMA Channels
DMA Channel Number Data Width System Resource
0 8 or 16 bits
1 8 or 16 bits Parallel port
2 8 or 16 bits Diskette drive
3 8 or 16 bits Parallel port (for ECP or EPP)
4 8 or 16 bits DMA controller
5 16 bits Open
6 16 bits Open
7 16 bits Open
75
Page 76

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Interrupts
Table 36. Interrupts
IRQ System Resource
NMI I/O channel check
0 Reserved, interval timer
1 Reserved, keyboard buffer full
2 Reserved, cascade interrupt from slave PIC
3 COM2*
4 COM1*
5 LPT2 (Plug & Play option) / **
6 Diskette drive controller
7 LPT1*
8 Real time clock
9 **
10 **
11 **
12 Onboard mouse port (if present, else user available)
13 Reserved, math coprocessor
14 Primary IDE (if present, else user available)
15 Secondary IDE (if present, else user available)
* Default, but can be changed to another IRQ.
** Dynamically allocated for all PCI/AGP devices and slots.
76
Page 77

A Error Messages and Indicators
Desktop Board D845GVSR reports POST errors in two ways:
• By sounding a beep code
• By displaying an error message on the monitor
BIOS Beep Codes
The BIOS beep codes are listed in Table 37. The BIOS also issues a beep code (one long tone
followed by two short tones) during POST if the video configuration fails (a faulty video card or
no card installed) or if an external ROM module does not properly checksum to zero.
Table 37. Beep Codes
Number of Beeps Description
1 Refresh failure
2 Parity cannot be reset
3 First 64 K memory failure
4 Timer not operational
5 Processor failure (Reserved; not used)
6 8042 GateA20 cannot be toggled (memory failure or not present)
7 Exception interrupt error
8 Display memory R/W error
9 (Reserved; not used)
10 CMOS Shutdown register test error
11 Invalid BIOS (such as, POST module not found)
77
Page 78

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
BIOS Error Messages
When a recoverable error occurs during the POST, the BIOS displays an error message describing
the problem.
Table 38. BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
GA20 Error An error occurred with Gate-A20 when switching to protected
mode during the memory test.
Pri Master HDD Error
Pri Slave HDD Error
Sec Master HDD Error
Sec Slave HDD Error
Pri Master Drive - ATAPI Incompatible
Pri Slave Drive - ATAPI Incompatible
Sec Master Drive - ATAPI Incompatible
Sec Slave Drive - ATAPI Incompatible
A: Drive Error
B: Drive Error
CMOS Battery Low The battery may be losing power. Replace the battery soon.
CMOS Display Type Wrong The display type is different than what has been stored in CMOS.
CMOS Checksum Bad The CMOS checksum is incorrect. CMOS memory may have been
CMOS Settings Wrong CMOS values are not the same as the last boot. These values
CMOS Date/Time Not Set The time and/or date values stored in CMOS are invalid. Run
DMA Error Error during read/write test of DMA controller.
FDC Failure Error occurred trying to access diskette drive controller.
Could not read sector from corresponding drive.
Corresponding drive is not an ATAPI device. Run Setup to make
sure device is selected correctly.
No response from the diskette drive.
Check Setup to make sure type is correct.
corrupted. Run Setup to reset values.
have either been corrupted or the battery has failed.
Setup to set correct values.
HDC Failure Error occurred trying to access hard disk controller.
Checking NVRAM..... NVRAM is being checked to see if it is valid.
Update OK! NVRAM was invalid and has been updated.
Updated Failed NVRAM was invalid but was unable to be updated.
Keyboard Is Locked The system keyboard lock is engaged. The system must be
Keyboard Error Error in the keyboard connection. Make sure keyboard is
KB/Interface Error Keyboard interface test failed.
78
unlocked to continue to boot.
connected properly.
continued
Page 79

Error Messages and Indicators
Table 38. BIOS Error Messages (continued)
Error Message Explanation
Memory Size Decreased Memory size has decreased since the last boot. If no memory
was removed, then memory may be bad.
Memory Size Increased Memory size has increased since the last boot. If no memory was
added, there may be a problem with the system.
Memory Size Changed Memory size has changed since the last boot. If no memory was
added or removed, then memory may be bad.
No Boot Device Available System did not find a device to boot.
Off Board Parity Error A parity error occurred on an offboard card. This error is followed
by an address.
On Board Parity Error A parity error occurred in onboard memory. This error is followed
by an address.
Parity Error A parity error occurred in onboard memory at an unknown
address.
NVRAM / CMOS / PASSWORD
cleared by Jumper
<CTRL_N> Pressed CMOS is ignored and NVRAM is cleared. User must enter Setup.
NVRAM, CMOS, and passwords have been cleared. The system
should be powered down and the jumper removed.
79
Page 80

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
80
Page 81

B Regulatory Compliance
This appendix contains the following regulatory compliance information for Desktop Board
D845GVSR:
• Safety regulations
• European Union Declaration of Conformity statement
• Product Ecology statements
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) regulations
• Product certification markings
Safety Regulations
Desktop Board D845GVSR complies with the safety regulations stated in Table 39 when correctly
installed in a compatible host system.
Table 39. Safety Regulations
Regulation Title
UL 60950 3rd ed., 2000/CSA
C22.2 No. 60950-00
EN 60950:2000 The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
IEC 60950, 3rd Edition, 1999 The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
Bi-National Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
including Electrical Business Equipment. (USA and Canada)
including Electrical Business Equipment. (European Union)
including Electrical Business Equipment. (International)
European Union Declaration of Conformity Statement
We, Intel Corporation, declare under our sole responsibility that the product Intel® Desktop Board
D845GVSR is in conformity with all applicable essential requirements necessary for CE marking,
following the provisions of the European Council Directive 89/336/EEC (EMC Directive) and
Council Directive 73/23/EEC (Safety/Low Voltage Directive).
The product is properly CE marked demonstrating this conformity and is for distribution within all
member states of the EU with no restrictions.
This product follows the provisions of the European Directives 89/336/EEC and 73/23/EEC.
81
Page 82

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
%BOTL
Dette produkt er i overensstemmelse med det europæiske direktiv 89/336/EEC &
73/23/EEC.
%VUDI
Dit product is in navolging van de bepalingen van Europees Directief 89/336/EEC &
73/23/EEC.
4VPNJ
Tämä tuote noudattaa EU-direktiivin 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC määräyksiä.
'SBOÎBJT
73/23/EEC.
%FVUTDI
73/23/EEC.
*DFMBOEJD
73/23/EEC.
*UBMJBOP
/PSTL
73/23/EEC.
1PSUVHVFTF
73/23/EEC.
&TQB×PM
4WFOTLB
Ce produit est conforme aux exigences de la Directive Européenne 89/336/EEC &
Dieses Produkt entspricht den Bestimmungen der Europäischen Richtlinie 89/336/EEC &
Þessi vara stenst reglugerð Evrópska Efnahags Bandalagsins númer 89/336/ EEC &
Questo prodotto è conforme alla Direttiva Europea 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC.
Dette produktet er i henhold til bestemmelsene i det europeiske direktivet 89/336/ EEC &
Este produto cumpre com as normas da Diretiva Européia 89/336/EEC &
Este producto cumple con las normas del Directivo Europeo 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC.
Denna produkt har tillverkats i enlighet med EG-direktiv 89/336/EEC & 73/23/EEC.
Product Ecology Statements
The following information is provided to address worldwide product ecology concerns and
regulations.
Disposal Considerations
This product contains the following materials that may be regulated upson disposal: lead solder on
the printed wiring board assembly.
Recycling Considerations
Intel encourages its customers to recycle its products and their components (e.g., batteries, circuit
boards, plastic enclosures, etc.) whenever possible. In the U.S., a list of recyclers in your area can
be found at:
http://www.eiae.org
In the absence of a viable recycling option, products and their components must be disposed of in
accordance with all applicable local environmental regulations.
82
Page 83

Regulatory Compliance
EMC Regulations
Desktop Board D845GVSR complies with the EMC regulations stated in Table 40 when correctly
installed in a compatible host system.
Table 40. EMC Regulations
Regulation Title
FCC Class B Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Parts 2 and 15, Subpart B,
Radio Frequency Devices. (USA)
ICES-003 (Class B) Interference-Causing Equipment Standard, Digital Apparatus. (Canada)
EN55022: 1998 (Class B) Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment. (European Union)
EN55024: 1998 Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics Limits and
methods of measurement. (European Union)
AS/NZS 3548 (Class B) Australian Communications Authority, Standard for Electromagnetic
Compatibility. (Australia and New Zealand)
CISPR 22, 3rd Edition,
(Class B)
CISPR 24: 1997 Information Technology Equipment – Immunity Characteristics – Limits and
Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Disturbance Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment. (International)
Methods of Measurement. (International)
Korean Class B statement translated as follows: this is household equipment that is certified to
comply with EMC requirements. You may use this equipment in residential environments and
other non-residential environments.
83
Page 84

Intel Desktop Board D845GVSR Product Guide
Product Certification Markings (Board Level)
Desktop Board D845GVSR has the following product certification markings:
Table 41. Product Certification Markings
Description Mark
UL joint US/Canada Recognized Component mark. Includes adjacent UL file
number for Intel desktop boards: E210882 (component side).
FCC Declaration of Conformity logo mark for Class B equipment; includes Intel
name and D845GVSR model designation (component side).
CE mark. Declares compliance to Euopean Union (EU) EMC directive
(89/336/EEC) and Low Voltage directive (73/23/EEC) (component side). The
CE mark should also be on the shipping container.
Australian Communications Authority (ACA) C-tick mark. Includes adjacent
Intel supplier code number, N-232. The C-tick mark should also be on the
shipping container.
Printed wiring board manufaturer’s recognition mark: consists of a unique UL
recognized manufacturer’s logo, along with a flammability rating (solder side).
94V-0
84
 Loading...
Loading...