Page 1

Before installing or starting this unit for the first time, this
manual should be studied carefully to obtain a working
knowledge of the unit and/or the duties to be performed while
operating and maintaining the unit.
RETAIN THIS MANUAL WITH UNIT. This Technical
manual contains IMPORTANT SAFETY DATA and should
be kept with the unit at all times.
More Than Air Answers.
Online answers: http://www.air.irco.com
Ingersoll Rand
System Automation
VSD V Box MODBUS RTU
User’s Manual
C.C.N. : 80445661
REV. A
DATE: JUNE 2009
Page 2

SECTION 1 – TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 – TABLE OF CONTENTS .................................................................................................................... 2
SECTION 2 - INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................ 3
SECTION 3 - SAFETY PRECAUTIONS .................................................................................................................. 3
SECTION 4 - MODBUS RTU ................................................................................................................................... 5
MODBUS TABLE(S) ............................................................................................................................................. 5
MODBUS RTU ...................................................................................................................................................... 5 U
COMMUNICATION LINK ...................................................................................................................................... 5
RS485 SERIAL DATA FORMAT ........................................................................................................................... 5
MESSAGE DATA FORMAT ................................................................................................................................. 5
SLAVE RESPONSE TIMEOUT ............................................................................................................................ 7
MESSAGE ANSWER FROM SLAVE TO MASTER .............................................................................................. 7
EXCEPTION RESPONSE .................................................................................................................................... 8
TROUBLESHOOTING ......................................................................................................................................... 8
SECTION 5 - MODBUS TABLE DESCRIPTION ..................................................................................................... 9
TABLE ITEM FORMAT ......................................................................................................................................... 9
NAME AND FUNCTION ....................................................................................................................................... 9
CODING ............................................................................................................................................................... 9
MENU REFERENCE .......................................................................................................................................... 10
‘ADV’ ADVISE FUNCTION ................................................................................................................................. 10
‘ADV’ ADVISE FUNCTION – SINGLE ITEM FORMAT OPTION ........................................................................ 10
‘CMD’ COMMAND FUNCTION ........................................................................................................................... 12
‘GET’ FUNCTION ............................................................................................................................................... 13
‘SET’ FUNCTION ................................................................................................................................................ 13
DATA CODING DEFINITIONS: .......................................................................................................................... 14
DATA TYPES ...................................................................................................................................................... 14
DATA UNITS ....................................................................................................................................................... 15
SECTION 6 - X-SERIES AIR SYSTEM .................................................................................................................. 17
SMG BOX ........................................................................................................................................................... 18
GENERAL X-SERIES SYSTEM COMPONENTS .............................................................................................. 18
X-SERIES NETWORK ADDRESSES................................................................................................................. 19
COMMUNICATION LINK .................................................................................................................................... 19
MODBUS TIMING............................................................................................................................................... 19
RS485 MODBUS SERIAL DATA FORMAT ........................................................................................................ 19
SECTION 7 – VSD V BOX MODBUS RTU DEFINITIONS .................................................................................... 20
2
Page 3
SECTION 2 - INTRODUCTION
System MODBUS Gateway (SMG Box) communication is RS485, RTU, Master-Slave configuration. The SMG Box acts as
a transparent interface to enable a remote ‘master’ device to be able to communicate with the X-Series Units and th e
Intellisys Controllers via the ir485 network ‘slave’ device(s). The MODBUS RTU data construction and formatting for a
‘master’ device is the subject of this document. This information is intended for a systems integrator to facilitate set-up of a
‘master’ device in order to communicate successfully with the X-Series Units and the Intellisys Controllers through a SMG
Box.
SECTION 3 - SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING :
!
WARNING :
WARNING :
!
WARNING :
• Before installing or operating the
SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY (SMG)
BOX, take time to carefully read all the
instructions contained in this manual, all
compressor manuals, and all manuals
of any other peripheral devices that may
be installed or connected to the unit.
• Electricity and compressed air have the
potential to cause severe personal injury
or property damage.
• The operator should use common sense
and good working practices while
operating and maintaining this system.
All applicable codes should be strictly
adhered to.
• Maintenance must be performed by
adequately qualified personnel that are
equipped with the proper tools.
INSTALLATION
• Installation work must only be carried
out by a competent person under
qualified supervision.
• A fused isolation switch must be fitted
between the main power supply and the
SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY (SMG)
BOX.
• The SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY
(SMG) BOX should be mounted in such
a location as to allow operational and
maintenance access without obstruction
or hazard and to allow clear visibility of
indicators at all times.
• If raised platforms are required to
provide access to the SYSTEM
MODBUS GATEWAY (SMG) BOX,
they must not interfere with normal
operation or obstruct access. Platforms
and stairs should be of grid or plate
construction with safety rails on all open
sides.
Risk of Danger
Risk of Electric Shock
Risk of High Pressure
Consult Manual
OPERATION
• The SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY
(SMG) BOX must only be operated by
competent personnel under qualified
supervision.
• Never remove or tamper with safety
devices, guards or insulation materials
fitted to the SYSTEM MODBUS
GATEWAY (SMG) BOX.
• The SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY
(SMG) BOX must only be operated at
the supply voltage and frequency for
which it is designed.
• When main power is switched on,
lethal voltages are present in the
electrical circuits and extreme caution
must be exercised whenever it is
necessary to carry out any work on
the unit.
• Do not open access panels or touch
electrical components while voltage is
applied unless it is necessary for
measurements, tests or adjustments.
Such work should be carried out only
by a qualified electrician equipped
with the correct tools and wearing
appropriate protection against
electrical hazards.
• All air compressors and/or other
equipment connected to the unit
should have a warning sign attached
stating “THIS UNIT MAY START
WITHOUT WARNING” next to the
display panel.
• If an air compressor and/or other
equipment connected to the unit is to
be started remotely, attach two
warning signs to the equipment
stating “THIS UNIT CAN BE
STARTED REMOTELY”. Attach one
sign in a prominent location on the
outside of the equipment, and the
other sign inside the equipment
control compartment.
3
Page 4

MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
• Maintenance, repairs or modifications
must only be carried out by competent
personnel under qualified supervision.
• If replacement parts are required, use
only genuine parts from the original
equipment manufacturer, or an
alternative approved source.
• Carry out the following operations
before opening or removing any access
panels or carrying out any work on the
SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY (SMG)
BOX:
i. Isolate the SYSTEM MODBUS
GATEWAY (SMG) BOX from
the main electrical power
supply. Lock the isolator in the
“OFF” position and remove the
fuses.
ii. Attach labels to the isolator
switch and to the unit stating
“WORK IN PROGRESS - DO
NOT APPLY VOLTAGE”. Do
not switch on electrical power
or attempt to start the SYSTEM
MODBUS GATEWAY (SMG)
BOX if such a warning label is
attached.
• Make sure that all instructions
concerning operation and maintenance
are strictly followed and that the
complete unit, with all accessories and
safety devices, is kept in good working
order.
• The accuracy of sensor devices must be
checked on a regular basis. They must
be calibrated when acceptable
tolerances are exceeded. Always
ensure any pressure within the
compressed air system is safely vented
to atmosphere before attempting to
remove or install a sensor device.
• The SYSTEM MODBUS GATEWAY
(SMG) BOX must only be cleaned with
a damp cloth, using mild detergents if
necessary. Avoid the use of any
substances containing corrosive acids
or alkalis.
• Do not paint the control faceplate or
obscure any indicators, controls,
instructions or warnings
4
Page 5

SECTION 4 - MODBUS RTU
MODBUS TABLE(S)
This document discusses generic MODBUS communications and how to implement the software specific ‘MODBUS Table’
information. MODBUS communication formatting may differ from controller to controller and you may require more than one
‘MODBUS Table’.
Always check the software variant identification and version number for a controller or unit with the variant and version of
the ‘MODBUS Table’ supplied. In some instances the information contained in a ‘MODBUS Table’ may not be ap plicable to
a controller or unit installed with the same software variant but a different version number.
MODBUS RTU
MODBUS RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is a master-slave type protocol. An X-Series Automation System Controller or
Intellisys Controller functions as the slave device. Information requests or commands are communicated from master to
slave only through a System Modbus Gateway Box (SMG). The SMG Box will always respond to communications from a
remote master device in accordance with the MODBUS RTU protocol standard.
The MODBUS protocol is used to communicate with personal computers (PC), Programmable Logic Controllers
(PLC’s), or Distributed Control Systems (DCS) over the Network port. The SMG Box only responds to three MODBUS
commands, Read Holding Register 03 (03 Hex), Preset Single Register 06 (06 Hex), and Preset Multip le Registers
command 16 (10 Hex) (See Modicon MODBUS Protocol Reference Guide, PI-MBUS-300 Rev. J, for more details on
MODBUS).
COMMUNICATION LINK
MODBUS is implemented using a two-wire RS485 industry standard communications link operating in master-slave mode.
Polarity of the two RS485 wires (L1+ and L2-) is important; reversal will disrupt communications.
RS485 SERIAL DATA FORMAT
The RS485 MODBUS port is a 2-wire operating with an asynchronous serial data format:
8 data bits / no parity / 1 stop - (8,N, 1) - transmitted at 9600 baud.
MESSAGE DATA FORMAT
The bytes of the MODBUS RTU message must be sent in one message package. The RTU protocol allows for a maximum
pause of 1.5 byte-times between 2 consecutive bytes of a message.
A pause longer than 1.5 byte-times will render the message invalid and it will be ignored.
Message data format is dependant on function and will consist of a combination of the following elements:
1) Destination address (slave network address)
2) Function Code
3) Data start address (slave register start address)
4) Number of registers, number of bytes of data
5) Message data
6) CRC checksum
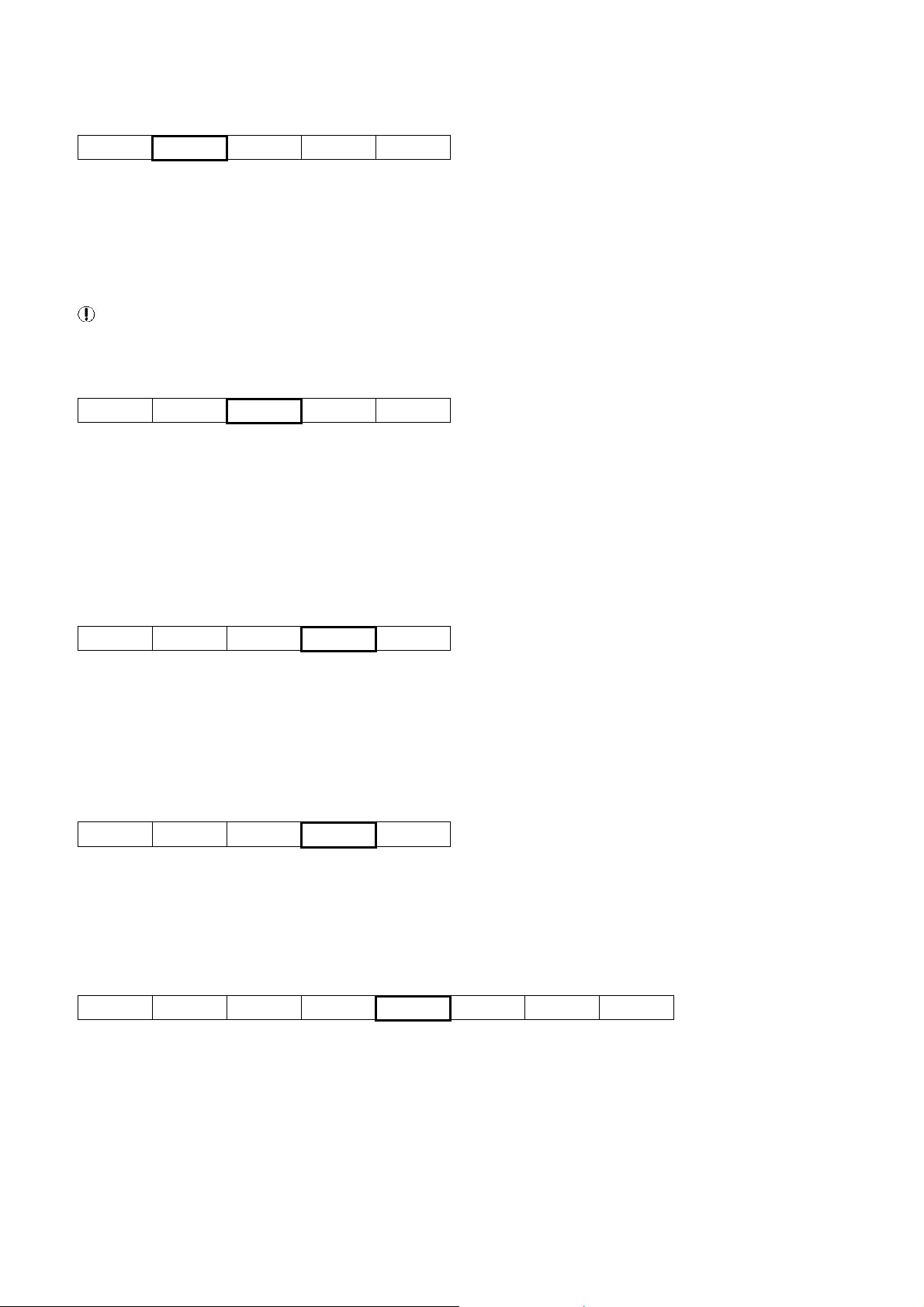
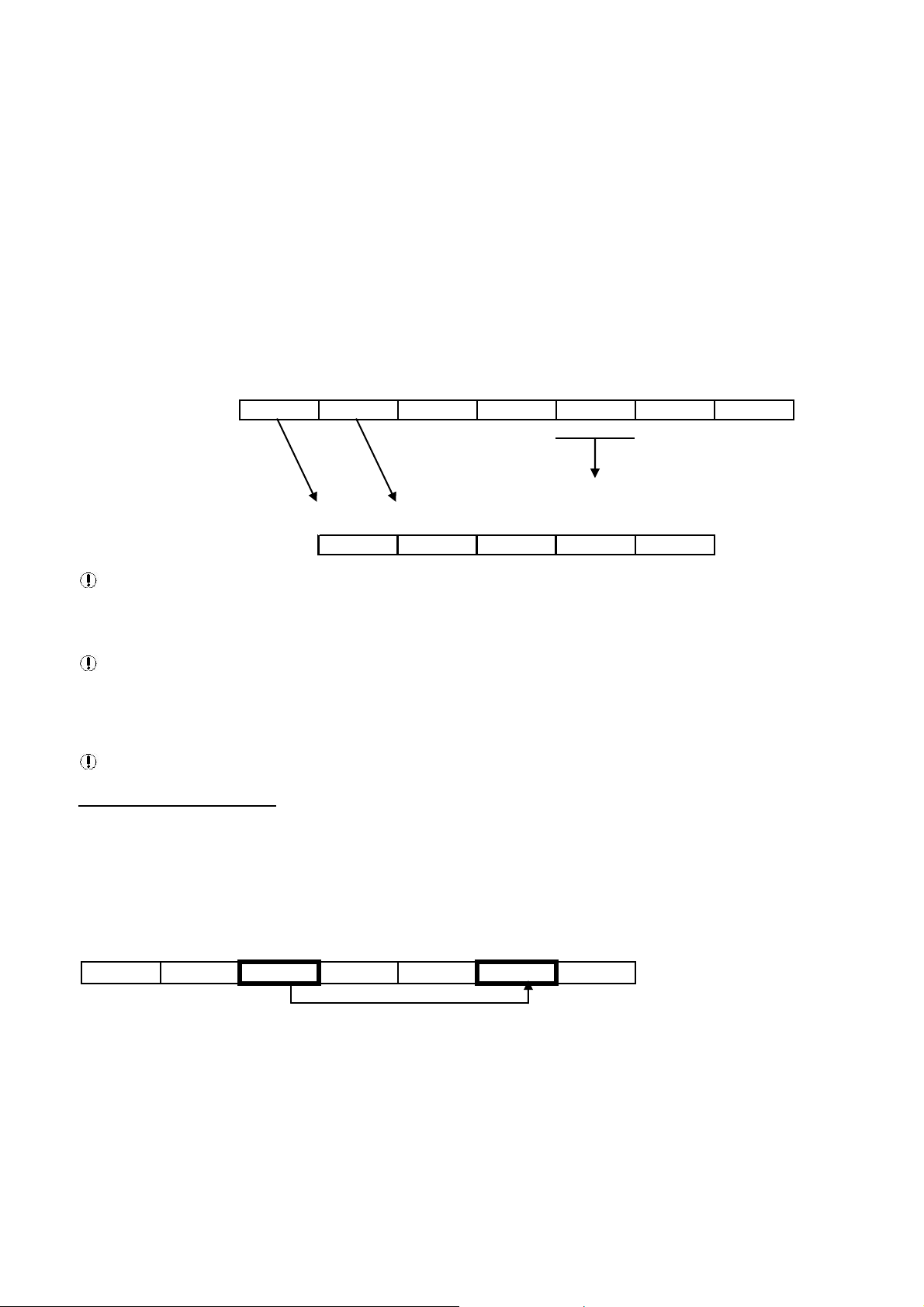
Message Destination Address
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers
CRC Check
Sum
01 03 40 06 00 02 30 CA
The ‘destination address’ must be correct for the ‘slave’ controller device for which the message is inten ded. An address can
be from 01Hex to EFHex. The SMG Box is transparent and addresses must be for the destination ‘slave’ controller or unit.
Each controller or unit must be set with a unique address.
5
Page 6
Message Function Codes
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers
CRC Check
Sum
01 03 40 06 00 02 30 CA
The message function code defines the required data processing operation of the slave controller. Although several types of
message function codes are defined by the MODBUS standard, only the message function code types working directl y with
registers are implemented on controller units:
03H Read Holding Register(s) – Get (Get Data) or Adv (Advise Data) (X-Series) and Read (Intellisys)
06H Preset Single Register - Write (Intellisys Only)
10H Preset Multiple Registers – Set (Set Data) or Cmd (Command Instruction) (X-Series only)
Any other message function code type will result in an EXCEPTION response.
Message Data Start Address
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers
CRC Check
Sum
01 03 40 06 00 02 30 CA
The message data start address (16bit word) designates the initial register address location in the contr oller from which the
data is processed. Start address information is contained in the ‘MODBUS Table’.
Note: high-byte transmitted first followed by low-byte.
Message Data
The message data content depends on the message function code type.
03H Read Holding Register(s) – Get (Get Data), Adv (Advise Data) (X-Series) or Read (Intellisys)
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers
CRC Check
Sum
01 03 40 06 00 02 30 CA
Slave address + function code ’03 Hex’ + start address of registers in slave memory + 16bit integer value that determines
the size (in 16bit ‘word’ registers) of the message data being requested (00 02 = 2 registers of data). This is the number of
16bit registers to read. A maximum of 32 registers can be read at one time. This information is contained in the ‘MODBUS
Table’.
06H Preset Single Register - Write (Intellisys Only)
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
DATA
byte 0 byte 1
CRC Check
Sum
01 06 00 6F 00 5F FE BC
Slave address + function code ’06 Hex’ + start address of register(s) in slave memory to be set then the ‘data’ itself. This
information is contained in the ‘MODBUS Table’.
10H Preset Multiple Registers – Set (Set Data) or Cmd (Command Instruction) (X-Series only)
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers To
Be Set
Number of
Bytes of
Data
DATA
1st Register
byte 0 byte 1
DATA
2nd Register
byte 2 byte 3
CRC Check
Sum
01 10 40 18 00 02 04 00 00 1B 5F 88 0E
Slave address + function code ’10 Hex’ + start address of register(s) in slave memory to be set + 16bit (integer valve of the
number of registers to be set) + 8bit ‘byte’ (integer value for the number of following data bytes) then the ‘data’ itself. This
information is contained in the ‘MODBUS Table’.
Note: A function ’10 Hex’ Set message also requires an additional byte defining the number of ‘data’ bytes in the data
message. This will always be the number of ‘registers’ multiplied by 2 as each ‘data’ register consists of 2 bytes (if number
of ‘data’ registers = 2 then number of ‘data’ bytes = 4).
6
Page 7

Message CRC Checksum
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers
CRC Check
Sum
01 03 40 06 00 02 30 CA
The CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) is a check-sum generated by means of ‘A001H polynomial’.
The CRC is two bytes containing a 16-bit binary value (word). The CRC value is calculated by the transmitting device that
appends the CRC to the end of the message. The receiving device recalculates the CRC value prior to processing of a
received message and compares the result to the actual CRC value appended to the message. If the two values do n ot
match the message is regarded as invalid. The CRC is initiated by first preloading a 16bit register to all 1's (FFFF Hex).
Then a process begins of applying each consecutive 8bit byte of the message to the register contents us ing an exclusive
‘OR’ calculation. The result is shifted one bit in the direction of the least significant bit (LSB), with the most significant bit
(MSB) set at ‘0’. The LSB is then examined; if ‘1’ the register content is applied to the polynomial value ‘A001’ Hex (101 0
0000 0000 0001) using an exclusive ‘OR’ calculation - if ‘0’ no exclusive OR takes place. This process is repeated until eight
‘bit’ shifts have been performed. After the eighth bit shift, the next 8bit message byte is applied to the register contents using
an exclusive ‘OR’ calculation. The bit shift and re-calculation process is then repeated again. When all message bytes have
been processed the final content of the 16bit register is the message CRC value.
Only the 8bits of ‘data’ in each message character is used for generating the CRC; start, stop and parity bits are ignored.
Note: When the 16bit CRC value is appended to a message, the low order byte must be transmitted first followed by the
high order byte. An incorrect or byte reversed check sum will render the message invalid and it will be ignored.
SLAVE RESPONSE TIMEOUT
A slave controller may not answer immediately. Ensure the ‘slave timeout’ setting of the ‘master’ device is set to a value no
less than 500ms. If the ‘slave’ device fails to receive a valid message due to a communication disruption, parity error, CRC
error or other reasons, no response is given and the master must process a timeout condition in this instance. If the ‘slave’
receives a valid message that cannot be processed an exception response will be returned.
MESSAGE ANSWER FROM SLAVE TO MASTER
The format of the ‘slave’ controller answer is similar to the original master request format; the message data content
depends on the message function code type.
The ‘address’ and ‘code’ of the slave answer is identical to the original request message; the address is the ‘slave’ device
address and the ‘code’ is a repeat of received function code type from the master. The remainder of the message is
dependant on the requested function code type. The CRC checksum is re-calculated for the answer message character s
using the specified CRC process.
03Hex – Get: read from register (or ‘Adv’ Advise)
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Bytes of
Data
DATA
1st Register
byte 0 byte 1
DATA
2nd Register
byte 2 byte 3
CRC Check
Sum
01 03 40 18 04 00 00 1B 5F BE 61
1) slave address 1byte
2) function code 1byte
3) bytes of data 1byte (number of bytes in ‘data’ answer)
4) data (high byte of each register transmitted first)
5) CRC checksum 2bytes (low byte first followed by high byte)
06Hex - Preset Single Register: write to single register
Slave Address Function Code Start Address
DATA
byte 0 byte 1
CRC Check Sum
01 06 00 6F 00 5F FE BC
1) slave address 1byte
2) function code 1byte
3) bytes of data 1byte (number of bytes in ‘data’ answer)
4) data (high byte of each register transmitted first)
5) CRC checksum 2bytes (low byte first followed by high byte)
7
Page 8

10H Preset Multiple Registers – Set (Set Data) or Cmd (Command Instruction) (X-Series only)
Slave
Address
Function
Code
Start
Address
Number of
Registers
CRC Check
Sum
01 10 40 18 00 02 D4 0F
1) slave address 1byte
2) function code 1byte
3) number of registers set 2 bytes
4) CRC checksum 2 Bytes (low byte first followed by high byte)
EXCEPTION RESPONSE
If the ‘slave’ device receives a request that cannot be processed an ‘exception response’ is given. An exception response
message consists of the following elements:
1) Slave Network Address (1 byte): Slave address identification
2) Function Code (1 byte): In a normal response, the slave repeats the function code of the original master request. All
function codes have an MSB (most significant bit) of 0 (values are all below 80 hexadecimal). In an exception response,
the slave sets the MSB of the function ‘code’ to 1. This makes the ‘code’ value 80 Hex greater than the received ‘code’
value from the master.
3) Data (1 byte): The ‘data’ response will contain a ‘1 byte’ value exception code.
4) CRC Checksum (2 byte).
CRC Check SumSlave Address Function Code Error Code
01 90 04 4D C3
Exception Codes:
01H Illegal Function Code
The requested ‘code’ function is not supported.
02H Illegal Data Address
The requested ‘data start address’ is not supported.
03H Illegal Data Value
The requested ‘data’ value is not supported.
04H Function Error
The slave cannot execute the request or the request type is inhibited.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Problem: No ‘slave’ response or corrupt MODBUS message
Solution: Check that the ‘slave’ controller is set for the anticipated slave address
Check that all ‘slave’ controllers are set with a unique system address
Check that the controller is set for MODBUS RTU mode (if applicable)
Check that the ‘master’ is operating in MODBUS RTU mode
Check that the ‘master’ baud rate, parity bit and number of s t op bits are correct
Check that the ‘master ‘response timeout is set for a minimum of 500ms
Check that the ‘master’ is implementing the specified CRC check sum process
Check RS485 wiring polarity and security of connections
Problem: Last character of MODBUS message is corrupted
Solution: Add a delay of 2ms after last character received before releasing RTS signal
Problem: The MODBUS master message is reflected in the slave answer
Solution: Inhibit RX/TX echo on ‘master’ device communications port
8
Page 9

SECTION 5 - MODBUS TABLE DESCRIPTION
A ‘MODBUS table’ describes the “items” used to access information in the memory registers of different types of controller,
or similar controllers using different application software variants or versions. The MODBUS Table will contain the valid
message items (“Name”) together with the Function Code (Function), Register Start Address (“Register Address”), Register
Size (“Register Length”) and a definition for coding and decoding the item data (“Coding”). A ‘MODBUS Table’ order form,
detailing the required order information, can be found on the last page of this document.
TABLE ITEM FORMAT
Each ‘item’ of a ‘MODBUS Table’ will define the massage format to read or set the information contained in the slave
controller register(s):-
Name
Descriptive ‘name’ or ‘item tag’ for the data item. The ‘Name’ is not used in code or message
formatting and serves only as a reference for the defined item.
Function
The Hex code required that instructs the slave (Intellisys controller) to perform a GET, ADV
(Advise), CMD (command) or SET function.
Register Address
Register Length
Coding
Menu
The slave controller register start address for the defined processing function.
The number of registers to be processed.
How to construct or interpret the data elements of a message.
Controller menu item reference.
Note: see “MODBUS RTU” for a detailed description of ‘Function’, ‘Register Address’ and ‘Register Length’ formats.
NAME AND FUNCTION
The ‘name’ for each table item will always start with 3 characters that describe the function type:
Adv Advise Function (03Hex) – same format as a Get function, see ‘Advise Function’.
Get Read from register (03Hex)
Set Write to registe r (10Hex)
Cmd Command (10Hex) – same format as a Set function; will instruct the slave to perform a defined action or
process
CODING
Item coding definitions specify the ‘number of data bytes’ and the ‘data conversion type’. In some instances a data message
may contain multiple sets of data items; an ‘Advise’ message for example. In this instance the ‘start location of data’ within
the message is also specified to enable extraction of the required data item from the entire message data.
Number of data bytes:
This specifies the length of the item data in bytes (6 = 6 bytes (3 registers) of data)
Start location of data bytes:
Number of Data
Bytes to Follow
DATA
1st Register byte
0 byte 1
DATA
2nd Register
byte 2 byte 3
DATA
3rd Register byte
4 byte 5
CRC Check SumSlave Address Function Code
01 03 06 09 00 00 65 00 A8 30 4D
If a data message consists of more than one set of data items (multiple item data message) the ‘start location’ specifies
where the first byte of the data associated with in item begins. If, for example, a 6 byte (3 register) answer is returned that
consists of three different ‘2 byte’ item data values, a ‘start location of data bytes’ = ‘2’ indicates that the item data starts with
the 3rd byte (byte 2) of the data message. The 1st byte of a data message is regarded as byte 0(zero). In this instance the
‘number of data bytes’ will be ‘2’ indicating that the data associated with the item is 2 bytes of data in length. A ‘start
location’ of byte ‘2’ and register length of ‘1’ (register = 2 bytes) means the data is contained in the 3rd and 4th bytes of the
data message. If no ‘start location’ is specified then data associated with the item will start with the first byte (byte 0) of the
message data.
Data Conversion Type:
This specifies how to interpret the data; refer to the ‘Data Conversion Type’ list in the Modbus Table.
For example: If the ‘Data Conversion Type’ = CODED, STATUS then the decimal integer value of the data has a defined
meaning; refer to the ‘STATUS’ Coded data list in the ‘MODBUS Table’ for definitions. If the ‘Data Conversion Type’ = PSI
then the decimal integer value of the data is ‘pressure’ in ‘psi’ units.
9
Page 10
MENU REFERENCE
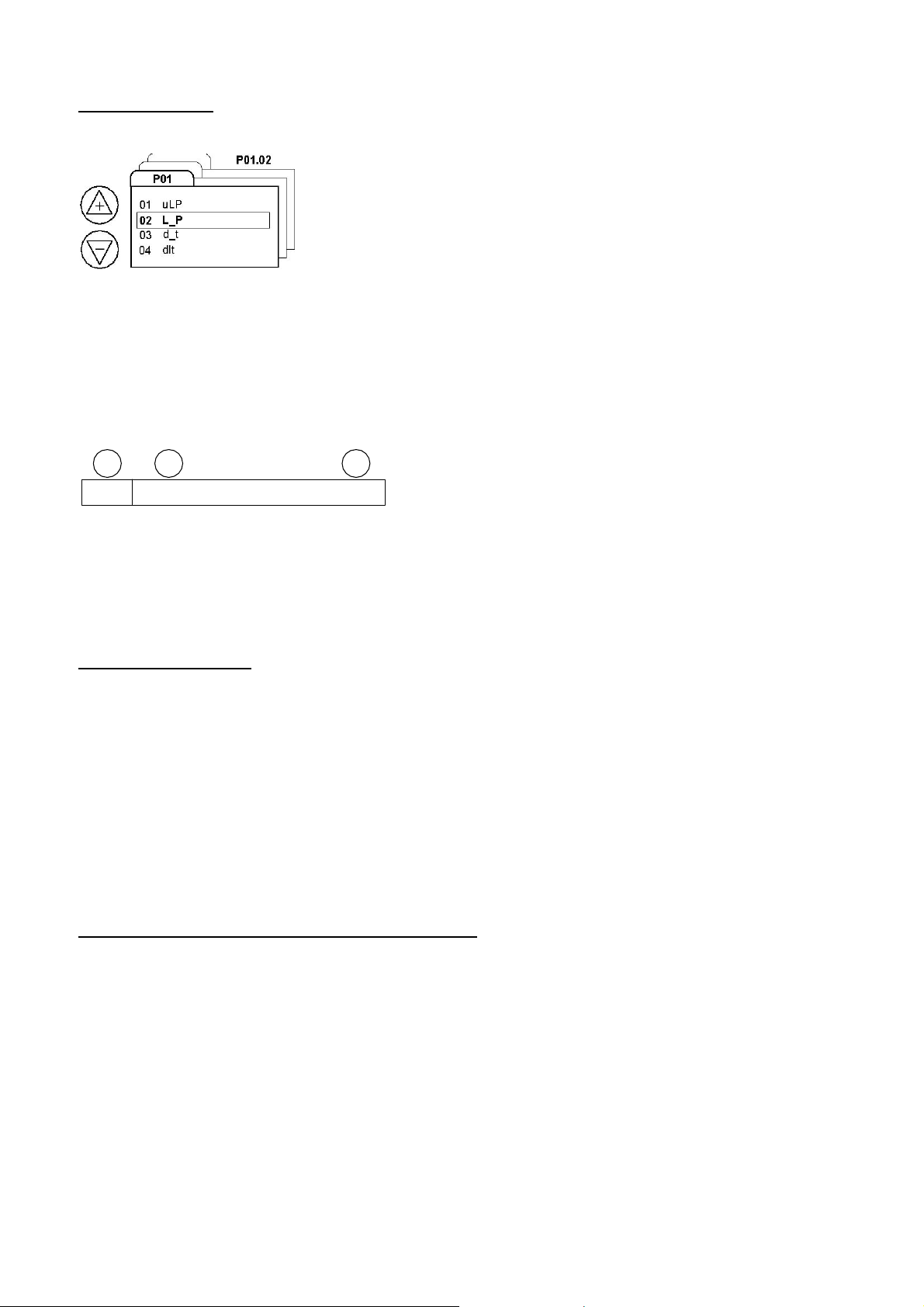
The menu structure of a controller has menu pages that contain a number of menu page ‘items’.
example menu and items
For example: menu pages P00, P01, P02 > P’n’.
Menu page P00 is the normal running list of display items that can be accessed and viewed on the controller displ ay without
access code. These items are ‘read only’ and consist of status, hours run and other general control or monitoring value (s).
Menu pages other than P00 are setup and configuration items that require an ‘access code’ when accessing the items on
the controller display.
Each menu page has a list of items that are referenced ‘1, 2, 3 > ‘n’.
a b c
P01
For example, a menu reference of P01.02 “AB” refers to menu item ‘2’ of menu page P01.
Each menu page item reference also has a two or three alphanumeric character item identification that is displayed by the
controller. With a menu reference the controller manual can be examined to determine the exact function, definition, scope
and limits for the specified item value.
Items that do not have a ‘Menu’ reference are general controller status or menu page P00 items.
‘ADV’ ADVISE FUNCTION
The ‘Advise’ function is a special type of ‘Get’ function. Each ‘Advise’ function item has an equivale nt ‘Get’ function; both
functions will provide a similar result.
Controllers on a Multi485 network will routinely broadcast key value and status specific data to all other controllers on the
network. This information is used, for example, by a system management unit for systems monitoring and control functions.
A SMG Box will automatically capture, store and continuously update these information items for each controller on the
network. Adv are Routine network broadcasts that occur every 2 seconds. Th transmission of this data consumes no
network bandwidth. (The maximum recommended request rate is 1 request every 2 seconds.)
This facility provides a method of retrieving ‘Adv’ data items directly from the SMG Box resulting in a faster response time
for information requests from a master. The method also has the advantage of reducing the amount of data traffic on the
Multi485 network enabling system management controllers to perform there functions without potential communication
delays. For this reason MODBUS ‘Adv’ functions are preferable to ‘Get’ functions when implemented on a Multi485 network
that consists of a system management controller with multiple machine controllers.
‘ADV’ ADVISE FUNCTION – SINGLE ITEM FORMAT OPTION
Controllers or units on a Multi485 network routinely broadcast general status and key per formance information. The SMG
Box will capture and store each ‘Broadcast’ detected. The Gateway ‘Broadcast’ registers will always contain the latest
‘broadcast’ information for each controller or unit on the Multi485 network. When a Modbus ‘Adv’ request is made the SMG
Box will respond immediately with information from it’s own ‘Broadcast’ registers for the unit addr ess specified. This function
reduces network activity and enables a faster Modbus response to commonly requested data.
A standard ‘Advise’ function defined in the ‘MODBUS Table’ will show the entire ‘broadcast’ being returned as a response.
The table will define for each ‘name’ item where in the returned data message the actual requ ested data can be found. The
‘master’ must then extract the required data from the returned data message. This method is very efficient as the master
can extract all ‘broadcast’ data from the single returned data message without the need to perform multiple requests for
each individual data item contained in a single slave controller ‘broadcast’ message.
01.02 AB
10
Page 11
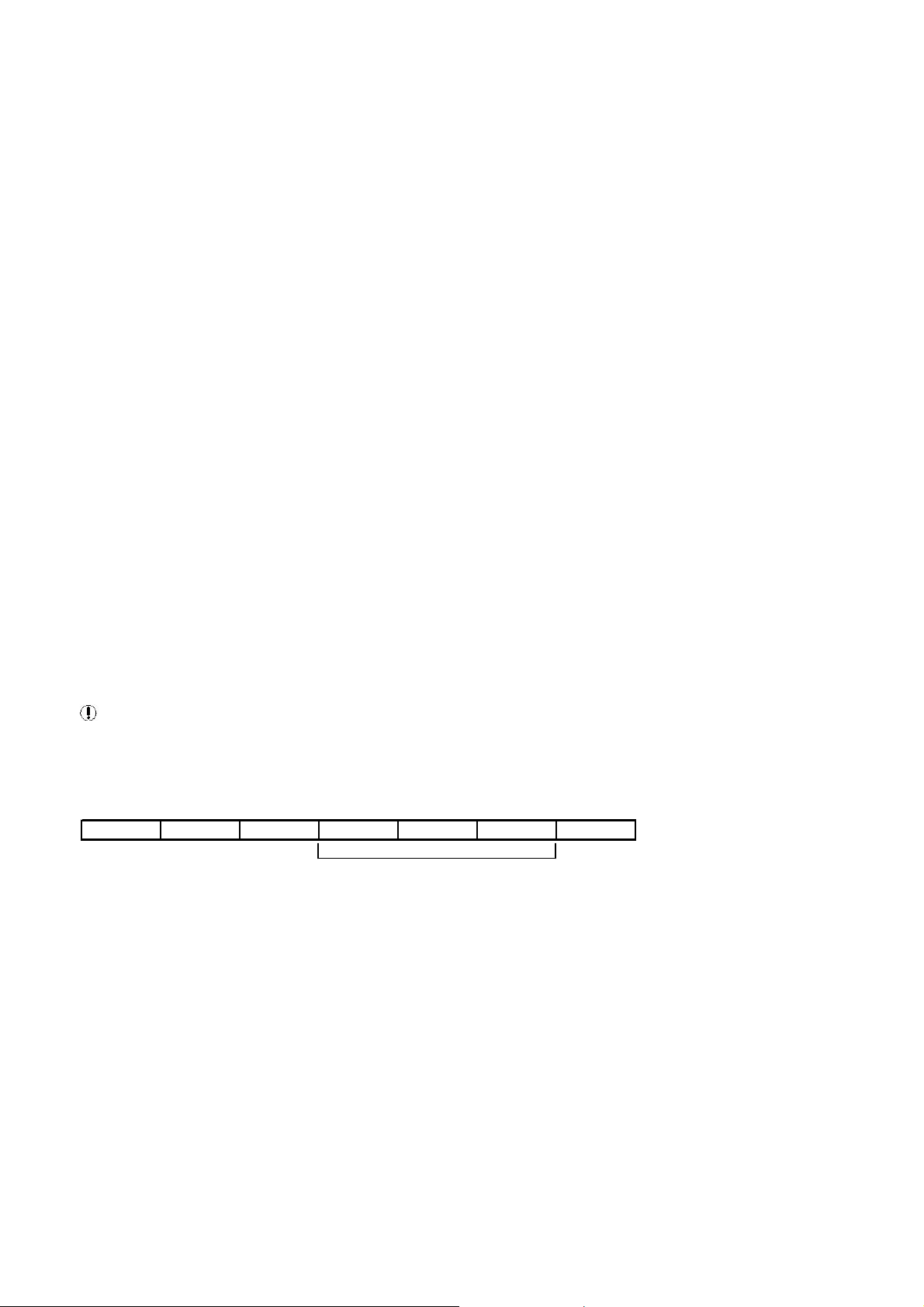
Some ‘master’ devices may not be equipped with the necessary data message memory to handle a large message of many
bytes or have the ability to extract multiple data items from a single data message item. In this instance an alternativ e
‘Advise’ function request method can be implemented.If the ‘Advise’ items of a ‘MODBUS Table’ are examined it will be
seen that the ‘Register Address’ for each individual ‘Advise’ item contained in a single slave controller ‘broadcast’ message
will have the same start address (Register Address). If the entire ‘broadcast’ data message is 7 registers (14 bytes) in length
and only the 2nd register (2 bytes) of item data is required, it is possible to specify a ‘Register Address’ that is 2 bytes higher
(skip the first 2 bytes of the broadcast data message) with a ‘Register Length’ that is consistent with the required item data
length. This will instruct the MODBUS Gateway to extract the 2 bytes of required item data from the entire broadcast data
message and only return the required 2 bytes of data as a response. Using this method an ‘Advise’ fu nction can be handled
by a ‘master’ in exactly the same way as a ‘Get’ function.
For Example: (AdvDeliveryPressure):
The ‘broadcast’ of an example slave controller may be 6 bytes of data (3 registers) in length starting at register address
location ‘F000’ Hex. The 1st byte (byte 0) is 8bits coded status, the 2nd byte (byte 1) is 8bits status flags which together
form a single 16bit status register (1st register). The 3rd and 4th bytes (byte 2 and byte 3) are a single16bit register (2nd
register) containing a ‘delivery pressure’ value. The 5th and 6th b ytes (byte 4 and byte 5) are a single 16bit register (3rd
register) containing a ‘delivery temperature’ value. From an example ‘MODBUS Table’ it may be seen that the ‘Register
Address’ for all four of these separate ‘Adv’ items is ‘F000 Hex’ (the start address of the entire ‘Broadcast’ message that
contains the data specified).
An entire ‘Broadcast’ message may, for example, contain 3 registers (6 bytes) of data. For a particular item the ‘Modbus
Table’ may show the ‘start address’ for the entire broadcast to be ‘F000’ with a length of 3 registers (6 bytes). The Modbus
Table will indicate that the required data is 2 bytes long (number of data bytes) starting at the 2nd byte of data in the entire
broadcast (start location of data bytes).
Name AdvDeliveryPressure
Modbus Function 03
Modbus Register Address F000 (start address of entire Broadcast message)
Modbus Register Length 0003 (length of entire Broadcast message)
Coding Number of data bytes = 2 (length of AdvDeliveryPressure data)
Start location of data bytes = 2 (the 2 data bytes of the AdvDeliveryPressure data item
start at byte 2 in the Broadcast message = bytes 2 and 3 of the message)
Data Conversion Type = PSI
Master Request Message “01 03 F000 00 03 36CB” (36CB = CRC check sum)
Slave Answer Message “01 03 06 09 00 00 65 00 A8 304D” (304D = CRC)
Coding = PSI ‘00 65’Hex = 101 decimal = 101 psi
Register addresses shown are examples only
Status Register
Delivery
Pressure
Delivery
Temperature
Slave Address Function Code
Number of Data
Bytes to Follow
DATA
1st Register byte
0 byte 1
DATA
2nd Register
byte 2 byte 3
DATA
3rd Register byte
4 byte 5
CRC Check Sum
01 03 06 09 00 00 65 00 A8 30 4D
F000 F001 F002
Message Data
11
Page 12
If only the ‘delivery pressure’ (AdvDeliveryPressure) data value is required a new ‘Advise’ req uest message format can be
constructed from the Modbus Table definition:
Name AdvDeliveryPressure
Modbus Function 03
Modbus Register Address F001 (start at the second regi ster, byte 2, of the Broadcast)
Modbus Register Length 0001 (only return one register, 2 bytes, of data)
Using the new ‘Advise’ message format the SMG Box will return only the 2nd Broadcast message register (2 bytes)
containing the ‘delivery pressure’ data value.
Master Request Message “01 03 F001 0001 E6CA” (E6CA = CRC check sum)
Slave Answer Message “01 03 02 00 65 786F” (786F = CRC check sum)
Coding = PSI ’00 6 5’Hex = 101 decimal = 101 psi
Status Register
Delivery
Pressure
Delivery
Temperature
Modbus Register Address F000
Modbus Register Length 0003
Slave Address Function Code
Number of Data
Bytes to Follow
DATA
1st Register byte
0 byte 1
01 03 06 09 00 00 65 00 A8 30 4D
DATA
2nd Register
byte 2 byte 3
DATA
3rd Register byte
4 byte 5
CRC Check Sum
F000 F001 F002
Number of Data
Bytes to Follow
Modbus Register Address F001
Modbus Register Length 0001
Slave Address Function Code
01 03 02 00 65 78 6F
It is only possible to manipulate a Modbus message format using ‘registers’ (1 register = 2 bytes = 1 word = 16bits); it is
not possible to manipulate addresses or register lengths to a single byte of data. At least one register (2 bytes) of data must
be specified even if only one byte of information is required. The ‘master’ must extract the required byte of data from the
returned message.
The data type (the definition of the returned data) may be different when using an ‘Advise’ function than it is when using
a ‘Get’ function for the same information. The ‘delivery pressure’ returned by an ‘Advise’ function will be 2 bytes in length
and will represent pressure as an integer value in ‘psi’ units (PSI). The ‘delivery pressure’ returned by a ‘Get’ function may,
for example, be 4 bytes (2 registers) in length and represent a 32bit signed integer value in miliBar units (mBAR). Always
check the item ‘Coding’ definition to establish the data definition type.
Register addresses shown are examples only
‘CMD’ COMMAND FUNCTION
A ‘Command’ function will instruct the ‘slave’ controller or unit to execute a pre-defined action or process. With a command
type message the content of the ‘message data’ from the ‘master’ must always be the same value as the ‘lower byte’ of the
command register address. For example: if the command item ‘Register Address’ = 3302 then the ‘data’ value must be ’00
02’ Hex.
Slave Address Function Code Start Address
Number of
Registers To Be
Set
Number of Bytes
of Data
DATA
DATA
2nd Register
byte 2 byte 3
CRC Check Sum
CRC Check Sum
01 10 33 02 00 01 02 00 02 25 70
It is the act of setting the specified register in the ‘slave’ controller with the defined ‘data’ value that initiates the action or
process. An incorrect ‘data’ value will result in an exception response. If the ‘command’ is accepted the ‘slave’ will answer
with a normal ‘Set’ register response. If the slave is unable to execute the command it will give a code ‘04’ exception
response.
12
Page 13
Example:
Using a command function item to set the specified item register to the correct value, the ‘slave’ controller is instructed to
perform the defined action or process. In the case of a ‘CmdStart’ item, for example, the ‘slave’ controller is instructed to
start the machine. The implementation of a ‘Cmd’ function message by the ‘master’ is identical to a ‘Set’ function message;
both operations use function code ‘10 Hex’ to write data to a slave controller register.
Name CmdStart
Modbus Function 10
Modbus Register Address 3300
Modbus Register Length 0001
Coding Number of data bytes = 1
CmdStart (to slave at address ‘01’ Hex)
Master Command Message “01 10 3300 0001 02 0000 A553” (A553 = CRC check sum)
Slave Answer Message “01 10 3300 0001 0E8D” if start command executed or “01 90 04 4D C3” exception
response if not executed, ‘90’ = repeat of ‘10’ function code with MSB set to ‘1’ and ‘04’
= exception error code.
Register addresses shown are examples only
Names that begin with CMD are Non-routine. This data must be written to the device. (The maximum recommended
request rate is 2 requests per second up to 32 words per request.)
‘GET’ FUNCTION
Using the MODBUS Table a read data (Get) function message can be constructed:
Name GetDeliveryPressure Modbus
Function 03
Modbus Register Address 4006
Modbus Register Length 0002
Coding Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = mBAR
GetDeliveryPressure (request to slave at address ‘01’ Hex)
Master Request Message “01 03 400 6 0002 31CA” (31CA = CRC check sum)
Slave Answer Message “01 03 04 00 00 1B 58 F139” (F139 = CRC check sum)
Coding = mBAR 1B 58Hex = 7000 decimal = 7000 miliBar (7.0 bar)
Register addresses shown are examples only
Note: Names that begin with Get are Non-routine. This data must be requested from the device. (The maximum
recommended request rate is 2 requests per second up to 32 words per request.)
‘SET’ FUNCTION
Using the MODBUS Table a write data (Set) function message can be constructed:
Name SetLoadPressure Modbus
Function 10
Modbus Register Address 4018
Modbus Register Length 0002
Coding Number of data bytes = 4
SetLoadPressure (to slave at address ‘01’ Hex)
Master Write Message “01 10 4018 0002 04 0000 1B58 C9CC” (C9CC = CRC)
Slave Answer Message “01 10 4018 0002 D40F” (D40F = CRC check sum)
Coding = mBAR 0000 1B58Hex = 7000 decimal = 7000 miliBar (7.0 bar)
Register addresses shown are examples only
Names that begin with Set are Non-routine. This data must be written to the device. (The maximum recommended
request rate is 2 requests per second up to 32 words per request.)
Data Conversion Type = mBAR
13
Page 14

DATA CODING DEFINITIONS:
Definitions for ‘data units’ and ‘data conversion types’ are listed for each ‘item’ in the “MODBUS Table” document.
All ‘data’ values are ‘whole’ numbers (integers); decimal places are not permitted in MODBUS data messages.
All ‘data’ values are unsigned (always positive) unless otherwise stated. Values specified as ‘SIGNED’ in the MODBUS
Table can be negative in accordance to the standard data conventio n for ‘sign ed’ number values.
DATA TYPES
Each standard definition will start with a “key” word that defines the data type:-
The following are selected examples; data types not included below are detaile d in individual ‘Modbus Tables’
Type Description
Coded a decimal value that has a defined definition; see the ‘Coded’ lists in
the ‘MODBUS Table’ for value definitions
Value a ‘whole’ number or value in the specified units
Pressure a ‘whole’ number defining a pressure in the specified units
Temperature a ‘whole’ number defining a temperature in the specified units
Time a ‘whole’ number defining a time period in the specified units
Electrical a ‘whole’ number defining a volt, amp, power, or speed value in the
specified units
Clock Clock values are relevant to real time clock functions; for example
pressure schedules. These ‘whole number’ unsigned values are
‘packaged’ multiple values and must be interpreted as follows.
Clock Data Type Coding
HH_MM 1) Divide the value by 60 = Hours (0 to 23)
2) The remainder (modulus) = Minutes (0 to 59)
Example for a value of ‘1050’
Hours = 1050 / 60 = 17.5 = 17 Hours
Minutes = remainder = 30 = 30 Minutes
Time = 17:30 (5:30pm)
D_HH_MM 1) Divide the value by 10000 = Day (1 = Monday, 7 = Sunday)
2) Divide the remainder (modulus) by 60 = Hours (0 to 23)
3) The remainder (modulus) = Minutes
Example for a value of ‘31050’
Day = 31050 / 10000 = 3.105 = 3 = Wednesday
Hours = = remainder / 60 = 17.5 = 17 Hours
Minutes = remainder = 30 = 30 Minutes
Day/Time = Wednesday 17:30 (5:30pm)
YYYY_DD_MO 1) Divide the value by 10000 = Year
2) Divide the remainder (modulus) by 100 = Day (1 to 31)
3) The remainder (modulus) = Month (1 to 12)
Example for a value of ‘20051605’
Year = 20051605 / 10000 = 2005.1605 = Year 2005
Day = remainder / 100 = 16.05 = Day 16
Month = remainder = 5 = Month 5
Date = 16th May 2005
14
Page 15

DATA UNITS
The ‘MODBUS Table’ will define the ‘data units’ for each item. Data unit definitions are specified in the ‘M ODBUS Table’ as
a separate list; for example:
The following are selected examples; data types not included below are detailed in the ‘Modbus Tables’
Value
The engineering units will differ dependant on unit set-up or item definition.
PSI
BAR
FAH
CEL
HRS
%
BOOLEAN
BINARY
The value must be interpreted in terms of each ‘bit’ as a set of sixteen Boolean (0 or 1) flags. These values
are compressor related or I/O Box Input related. For compressor related items the least significant bit (Bit 0)
represents compressor 1. For unit inputs the least significant bit (Bit 0) generally represents input 1.
The number is the value in the specified engineering units
Pressure in ‘psi’
Pressure in ‘Bar’
Temperature in oF
Temperature in oC
Hours
Percentage 0 to 100
The number will be 0 or greater than 0, (Boolean: 0 = False, 1 = True)
The number represents a 16bit (two byte) binary value of 16bit flags.
16 bit Register
1st Byte (byte 0) 2nd Byte (byte 1)
15141312111098 76543210
Bit
MSB
The example illustrates the bit pattern for a value of ’00 81 Hex’. This value is interpr eted as a ‘true’ condition with respect to
the item definition for compressors 1 and 8. If the ‘item’ definition is ‘Compressors Running’ then com pressors 1 and 8 are in
a ‘running’ condition.
00000000 10000001
Compressor 8 Compressor 1
LSB
15
Page 16

The example illustrates the bit pattern for a value of "1A 04 C2 01" Hex. A reference to ‘Bit 18’ equates to bit ‘2’ of byte ‘1’ in
the answer data message. If the ‘bit’ is ‘1’ then the condition is ‘TRUE’.
2nd Register1st Register
1st Byte (byte 0) 2nd Byte (byte 1) 3rd Byte (byte 2) 4th Byte (byte 3)
3130292827262524 2322212019181716 15141312111098 76543210
Bit
00011010 00000100 11000010 00000000
MSB
BIT ‘n’
Note: The LSB (least significant bit) of a register or byte is regarded as Bit 0(zero)
A Boolean (true/false) can be established from examining the specified ‘bit’ of the
16bit register. If the item specifies ‘Bit 4’ then the 4th bit should be examined:
LSB
16 bit Register
1st Byte (byte 0) 2nd Byte (by te 1)
15141312111098 76543210
Bit
MSB
00011010 10010001
LSB
AND
00000000 00010000
EQUALS
00000000 00010000
= 16 Decimal (Condition is TRUE)
The 4th bit of a register can be extracted by ‘masking’ the register content with “10 Hex”; if the resulting value is greater than
0(zero) then the condition is ‘True’, if the result is 0(zero) then the condition is ‘False’.
Decimal Places:
Numbers with decimal places (eg 20.55) are not permissible in MODBUS data transfer – all numbers must be integer
‘whole’ numbers. To provide ‘decimal place’ accuracy some data values are multiplied by 10, 100 or 1000 and transmitted
as a ‘whole’ number (integer). In this instance the ‘Data Units’ will specify that the number represe nts a value to one or more
decimal places.
For example: PERCENT_DP2 = Percent to 2 decimal places
“2055” divided by 100 = 20.55%
If the ‘Data Units’ specifies “to 1 decimal place”, divide the number by 10 to convert to the correct engineering units. If the
‘Data Units’ specifies “to 2 decimal places”, divide the number by 100; if 3 decimal places divide by 1000.
16
Page 17

SECTION 6 - X-SERIES AIR SYSTEM
Note: example only; systems will differ from installation to installation
17
Page 18

SMG BOX
For Remote Monitoring/Control of X-Series Units and Boxes. The SMG Box provides a RS485 Modbus connection to the
X8I Automation System. A system will only contain one SMG Box.
GENERAL X-SERIES SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The following Components can be monitored by the SMG Box.
X8I Series Controller or X12I Series Controller: Automation System Unit
Monitors and controls the air compressors, all general system and air compressor related information is governed and
available from this unit. A system will only contain one X-Series Automation System controller.
EX Box: Extension to the X-Series Unit
For connection to remote compressor(s) or other specialized compressor integration. All common air compressor status
information is sent to, and available from, the X-Series system management unit. A system may contain multiple EX Boxes.
I/O Box: Monitoring/Control of Auxiliary Equipment and/or Sensors
For monitoring and/or control of auxiliary compressed air equipment (for exam ple: dryer, auto drain, filtration differential,
isolation valves, cooling water towers/pumps, ventilation) or sensors (for example: pressure, pressure differential, dewpoint,
air flow, temperature). A system may contain multiple IO Boxes.
VSD Box: Extension to the X-Series Unit
For connection to variable speed compressor(s) or other specialized compressor integration. All common air compressor
status information is sent to, and available from, the X-Series system management unit. A system may contain multiple VSD
Boxes.
CX Box: Extension to the X-Series Unit
For connection to non-Ingersoll Rand air compressors that are not equipped with any accessible means of remote
connectivity. All common air compressor status information is sent to, and available from, the X-Series system management
unit. A system may contain multiple CX Boxes.
DX Box: Extension to the X-Series Unit
For connection to two fixed speed online/offline air compressors to be seen as one compressor by the X8I or X12I. All
common air compressor status information is sent to, and available from, the X-Series system management unit. A system
may contain multiple DX Boxes.
ir-485 Gateway / irV-485 Gateway
For connection to all Ingersoll Rand Intellisys based compressors. All common air compressor status information is sent to,
and available from, the X-Series system management unit. A system may contain multiple Gateways.
ir-485 Direct
For connection to all Ingersoll Rand R Series (S3) based compressors. All common air compressor status information is
sent to, and available from, the X-Series system management unit. A system may contain multiple R series compressors.
18
Page 19

X-SERIES NETWORK ADDRESSES
UNIT
X8I or X12I
EX, VSD B / mA / V, CX, DX, ir485 / irV485, S3
(As It Relates To The Compressor Number Assigned)
Compressor 1 1 (01)
Compressor 2 2 (02)
Compressor 3 3 (03)
Compressor 4 4 (04)
Compressor 5 5 (05)
Compressor 6 6 (06)
Compressor 7 7 (07)
Compressor 8 8 (08)
Compressor 9 9 (09) X12I ONLY
Compressor 10 10 (0A) X12I ONLY
Compressor 11 11 (0B) X12I ONLY
Compressor 12 12 (0C) X12I ONLY
I/O
I/O Box 1 105(69)
I/O Box 2 112(70)
I/O Box 3 106(6A) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 4 107(6B) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 5 108(6C) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 6 109(6D) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 7 110(6E) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 8 111(6F) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 9 113(71) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 10 114(72) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 11 115(73) X12I ONLY
I/O Box 12 116(74) X12I ONLY
Note: I/O Unit 2 address (70Hex) is intentionally out of sequence; this is not a print error.
DECIMAL (HEX) ADDRESS NOTES
101(65)
COMMUNICATION LINK
To Interface with a X-Series product that is equipped with a Multi485 enabled network port, or to interface with multiple XSeries products operating on a single Multi485 system network, a SMG Box unit is required. The SMG Box forms the
interface between the Multi485 protocol and MODBUS RTU master/slave communications link.
SMG Box connectivity is implemented using a two-wire RS485 industry standard commun ications link operating in point-topoint, master-slave mode. In use the SMG Box is transparent and each X-Series system unit is accessible using individual
system device addresses.
Polarity of the two MODBUS RS485 wires (L1+ or ‘A’ and L2- or ‘B’) is important; reversal will inhibit communications
and result in error.
MODBUS TIMING
The SMG will handle ONE (1) MODBUS request at a time from the customer’s port. The maximum recommended request
rate is 2 requests per second. When a MODBUS request is received for any device connected to the XI Automation System,
that request will be forwarded to the device between sequencer broadcasts and the response from the device will then be
relayed back to the customer’s port. If a second MODBUS command is sent before the first command has been responded
to, the second command will be ignored.
RS485 MODBUS SERIAL DATA FORMAT
The SMG supports only the RTU transmission mode. The user must configure their serial port communication parameters
(baud rate, parity mode, etc.) during configuration to match those of the SMG Box. The SMG Box port operates with an
asynchronous serial data format:
SMG Communication Parameters:
Data Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bit: 1
Baud Rate: 9600
8-N-1-9600
19
Page 20

SECTION 7 – VSD V BOX MODBUS RTU DEFINITIONS
Name : AdvStatusRegister
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : F000
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Data Conversion Type = CODED,STATUS
Conversion table for CODED,STATUS can be found at the end of this
document
Name : AdvStatusFlags
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : F000
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
: Start location of data bytes = 1
Name : AdvDeliveryPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : F000
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
: Start location of data bytes = 2
Data Units = PSI
Name : AdvDeliveryAirTemperature
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : F000
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
: Start location of data bytes = 4
Data Units = FAH
20
Page 21

Name : GetSoftwareVersionIdString
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3400
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 6
Data Conversion Type = STRING
Name : GetSoftwareVersionRevString
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3403
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 6
Data Conversion Type = STRING
Name : CmdStart
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 3300
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Name : CmdStop
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 3301
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Name : CmdLoad
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 3304
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Name : CmdUnload
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 3305
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Name : CmdReset
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 3306
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Name : CmdClearLog
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 3307
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 1
Name : GetStatus
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3406
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 6
Data Conversion Type = CODED,STATUS
Conversion table for CODED,STATUS can be found at the end of this
document
21
Page 22

Name : GetAnalogInput1
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3100
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = ADSTEPS
Name : GetAnalogInput2
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3101
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = ADSTEPS
Name : GetAnalogInput3
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3102
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = ADSTEPS
Name : GetAnalogOutput1
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 310C
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = ADSTEPS
Name : GetDigitalInputs
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 310E
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = BINARY
bitvalue = 0 = digital input INACTIVE
bitvalue = 1 = digital input ACTIVE
bit = Name (Config, Delay in ms)
0 = EMERGENCY_STOP (Normal Closed, 0)
1 = READY_RUN (Pulsed, 0)
2 = SPARE_1 (Normal Open, 0)
3 = SPEED_DETECT (Normal Open, 100)
4 = SPARE_2 (Normal Open, 200)
5 = LOAD_MAINTENANCE (Pulsed, 0)
6 = AUXILIARY_ALARM (Pulsed, 0)
7 = AUXILIARY_TRIP (Normal Closed, 100)
22
Page 23

Name : GetDigitalInputsConfiguration
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 310F
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = BINARY
bitvalue = 0 = digital input NO
bitvalue = 1 = digital input NC
bit = Name
0 = EMERGENCY_STOP
1 = READY_RUN
2 = SPARE_1
3 = SPEED_DETECT
4 = SPARE_2
5 = LOAD_MAINTENANCE
6 = AUXILIARY_ALARM
7 = AUXILIARY_TRIP
Name : GetDigitalOutputs
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3110
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Units = BINARY
bitvalue = 0 = digital output OFF
bitvalue = 1 = digital output ON
bit = Name
0 = RELAY_SEQUENCE
1 = RELAY_SPARE1
2 = RELAY_SPARE2
3 = RELAY_LOAD
4 = RELAY_FUNCTION_1
5 = RELAY_FUNCTION_2
Name : GetDeliveryPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4004
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : GetInternalPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4006
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : GetDiffPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4008
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
23
Page 24

Name : GetRunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 400A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.01 'H1'
Menu = P10.06 'H1'
Name : GetLoadUnloadPressMinDiff
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 400E
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : SetLoadUnloadPressMinDiff
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 400E
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : GetParUnloadPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4010
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P01.01 'Pu'
Name : SetParUnloadPressure
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4010
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P01.01 'Pu'
Name : GetParLoadPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4012
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P01.03 'PL'
Name : SetParLoadPressure
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4012
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P01.03 'PL'
24
Page 25

Name : GetPressureUnitsSel
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4014
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = CODED,P_UNIT
Conversion table for CODED,P_UNIT can be found at the end of this
document
Data Units = LONG_VAL
Menu = P03.01 'P>'
Name : SetPressureUnitsSel
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4014
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = CODED,P_UNIT
Conversion table for CODED,P_UNIT can be found at the end of this
document
Data Units = LONG_VAL
Menu = P03.01 'P>'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog1Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4017
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.02 '01'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog1RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4018
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.02 '01'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog2Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 401B
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.03 '02'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog2RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 401C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.03 '02'
25
Page 26

Name : GetFaultErrorLog3Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 401F
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.04 '03'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog3RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4020
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.04 '03'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog4Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4023
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.05 '04'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog4RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4024
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.05 '04'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog5Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4027
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.06 '05'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog5RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4028
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.06 '05'
26
Page 27

Name : GetFaultErrorLog6Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 402B
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.07 '06'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog6RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 402C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.07 '06'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog7Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 402F
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.08 '07'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog7RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4030
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.08 '07'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog8Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4033
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.09 '08'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog8RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4034
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.09 '08'
27
Page 28

Name : GetFaultErrorLog9Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4037
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.10 '09'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog9RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4038
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.10 '09'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog10Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 403B
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.11 '10'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog10RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 403C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.11 '10'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog11Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 403F
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.12 '11'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog11RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4040
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.12 '11'
28
Page 29

Name : GetFaultErrorLog12Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4043
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.13 '12'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog12RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4044
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.13 '12'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog13Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4047
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.14 '13'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog13RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4048
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.14 '13'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog14Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 404B
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.15 '14'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog14RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 404C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.15 '14'
29
Page 30

Name : GetFaultErrorLog15Fault
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 404F
Modbus Register Length : 0001
Coding : Number of data bytes = 2
Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR
Conversion table for CODED,ERROR can be found at the end of this
document
Menu = P02.16 '15'
Name : GetFaultErrorLog15RunningHours
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4050
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HRS
Menu = P02.16 '15'
Name : GetDeliveryPressureMaxLevel
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4052
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P03.06 'Dm'
Name : SetDeliveryPressureMaxLevel
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4052
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P03.06 'Dm'
Name : GetInternalPressureMaxLevel
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4054
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P03.07 'Im'
Name : SetInternalPressureMaxLevel
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4054
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P03.07 'Im'
Name : GetSelectedLoadEnable
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 407A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
30
Page 31

Name : SetSelectedLoadEnable
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 407A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : GetSelectedStartEnable
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 407C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : SetSelectedStartEnable
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 407C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : GetConfigDigOut5
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4080
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : SetConfigDigOut5
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4080
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : GetConfigDigOut6
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4082
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : SetConfigDigOut6
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4082
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : GetIndicationFieldFunction
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4084
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
31
Page 32

Name : SetIndicationFieldFunction
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4084
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : GetAnalogOutputFunction
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4086
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.04 'Ao'
Name : SetAnalogOutputFunction
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4086
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.04 'Ao'
Name : GetFrequencyHighLimit
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4088
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HZ
Menu = P08.02 'FH'
Name : SetFrequencyHighLimit
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4088
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HZ
Menu = P08.02 'FH'
Name : GetFrequencyLowLimit
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 408A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HZ
Menu = P08.01 'FL'
Name : SetFrequencyLowLimit
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 408A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = HZ
Menu = P08.01 'FL'
32
Page 33

Name : GetVsdSpeedPercentActual
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 408C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = PERCENT_DP2
Name : GetVsdControlPercentActual
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 408E
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = PERCENT_DP2
Menu = P08.03 'C>'
Name : GetDeliveryPressureOffset
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4090
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.01 'do'
Name : SetDeliveryPressureOffset
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4090
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.01 'do'
Name : GetDeliveryPressureRange
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4092
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.02 'dr'
Name : SetDeliveryPressureRange
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4092
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.02 'dr'
Name : GetInternalPressureOffset
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4094
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.03 'Io'
33
Page 34

Name : SetInternalPressureOffset
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4094
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.03 'Io'
Name : GetInternalPressureRange
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4096
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.04 'Ir'
Name : SetInternalPressureRange
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4096
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P04.04 'Ir'
Name : GetErrorLogReset
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 4098
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.05 'Er'
Name : SetErrorLogReset
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 4098
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.05 'Er'
Name : GetInternalPressSensorUsed
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 409A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P03.05 'IP'
Name : SetInternalPressSensorUsed
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 409A
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P03.05 'IP'
34
Page 35

Name : GetVoltagePressSensorUsed
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 409C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : SetVoltagePressSensorUsed
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 409C
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Name : GetDeliveryPressSensRange
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 409E
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : SetDeliveryPressSensRange
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 409E
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : GetInternalPressSensRange
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40A0
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : SetInternalPressSensRange
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40A0
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : GetDeliveryPressureOut
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40A4
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Name : GetInternalPressureOut
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40A6
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
35
Page 36

Name : GetParSetpointPressure
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40A8
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P01.02 'Pt'
Name : SetParSetpointPressure
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40A8
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P01.02 'Pt'
Name : GetDeliveryOutputOffset
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40AA
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.01 'do'
Name : SetDeliveryOutputOffset
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40AA
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.01 'do'
Name : GetDeliveryOutputRange
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40AC
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.02 'dr'
Name : SetDeliveryOutputRange
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40AC
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.02 'dr'
Name : GetInternalOutputOffset
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40AE
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.03 'Io'
36
Page 37

Name : SetInternalOutputOffset
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40AE
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Conversion Type = SIGNED,NUMERIC
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.03 'Io'
Name : GetInternalOutputRange
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40B0
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.04 'Ir'
Name : SetInternalOutputRange
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40B0
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = mBAR
Menu = P05.04 'Ir'
Name : GetAnalogueInputConfig
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40B2
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P03.04 'IC'
Name : SetAnalogueInputConfig
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40B2
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P03.04 'IC'
Name : GetConfigDigIn7
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40B4
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.01 'D7'
Name : SetConfigDigIn7
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40B4
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.01 'D7'
37
Page 38

Name : GetConfigDigIn8
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40B6
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.02 'D8'
Name : SetConfigDigIn8
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40B6
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.02 'D8'
Name : GetHoldSeqControl
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 40BA
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.03 'SQ'
Name : SetHoldSeqControl
Modbus Function : 10
Modbus Register Address : 40BA
Modbus Register Length : 0002
Coding : Number of data bytes = 4
Data Units = UCHAR_VAL
Menu = P10.03 'SQ'
38
Page 39

Name : GetFaultRegister
Modbus Function : 03
Modbus Register Address : 3409
Modbus Register Length : 0003
Coding : Number of data bytes = 6
Data Units = BINARY
bitvalue = 0 = fault INACTIVE
bitvalue = 1 = fault ACTIVE
bit = fault
40 = (E0010) Trip - Emergency Stop
41 = (E0020) Trip - Oil Filter
42 = (E0040) Trip - Air/Oil Separator High DP
43 = (E0080) Trip - Motor Overload
44 = (E0115) Trip - Delivery Pressure Sensor
45 = (E0119) Trip - Delivery Pressure High
46 = (E0125) Trip - Delivery Temperature Sensor
47 = (E0129) Trip - Delivery Temperature High
32 = (E0131) Trip - Internal Rotation Pressure Check
33 = (E0135) Trip - Internal Pressure Sensor
34 = (E0139) Trip - Internal Pressure High
35 = (E0506) Trip - Analog Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module Ai4-1
36 = (E0507) Trip - Analog Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module Ai4-2
37 = (E0508) Trip - Digital Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module
Di8R4-1
38 = (E0509) Trip - Digital Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module
Di8R4-2
39 = (E0809) Trip - Differential Pressure High
24 = (E0814) Trip - Blowdown Timeout
25 = (E0821) Trip – Short Circuit
26 = (E0836) Trip - PLL Unlocked Trip
27 = (E0840) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 1
28 = (E0841) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 2
29 = (E0842) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 3
30 = (E0843) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 4
31 = (E0844) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 5
16 = (E0845) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 6
17 = (E0846) Trip - Delivery Pressure Sensor Problem With Selected
Model
18 = (E0856) Trip - Internal Pressure Sensor Problem With Selected
Model
19 = (E5000) Trip - Parameter Table Index Corrupt
20 = (E5001) Trip - IO-config Table Corrupt
21 = (A2070) Alarm - Auxiliary trip
22 = (A2118) Alarm - Delivery Pressure High
23 = (A2128) Alarm - Delivery Temperature High
8 = (A2138) Alarm - Internal Pressure High
9 = (A2808) Alarm - Differential Pressure High
10 = (A2816) Alarm - Power Failure
11 = (R3123) Run Inhibit - Delivery Temperature Low
12 = (R3137) Run Inhibit - Internal Pressure High
13 = (A4804) Service Alarm - Service Due
14 = 15 = 0 = 1 = 2 = 3 = 4 = 5 = 6 = 7 = -
39
Page 40

Table 1. Conversion table for 'Data Conversion Type = CODED,STATUS'
1 : Shutdown
2 : Initialising
3 : Ready to Start
4 : Standby
5 : Standby
6 : Standby
7 : Running
8 : Not responding
9 : On Load
Table 2. Conversion table for 'Data Conversion Type = CODED,P_UNIT'
0 : Bar
1 : PSI
2 : kPa
Table 3. Conversion table for 'Data Conversion Type = CODED,ERROR'
0 : No Error
10 : (E0010) Trip - Emergency Stop
20 : (E0020) Trip - Oil Filter
40 : (E0040) Trip - Air/Oil Separator High DP
80 : (E0080) Trip - Motor Overload
115 : (E0115) Trip - Delivery Pressure Sensor
119 : (E0119) Trip - Delivery Pressure High
125 : (E0125) Trip - Delivery Temperature Sensor
129 : (E0129) Trip - Delivery Temperature High
131 : (E0131) Trip - Internal Rotation Pressure Check
135 : (E0135) Trip - Internal Pressure Sensor
139 : (E0139) Trip - Internal Pressure High
809 : (E0809) Trip - Differential Pressure High
814 : (E0814) Trip - Blowdown Timeout
821 : (E0821) Trip – Short Circuit
836 : (E0836) Trip - PLL Unlocked Trip
846 : (E0846) Trip - Delivery Pressure Sensor Problem With Selected Model
856 : (E0856) Trip - Internal Pressure Sensor Problem With Selected Model
2070 : (A2070) Alarm - Auxiliary trip
2118 : (A2118) Alarm - Delivery Pressure High
2128 : (A2128) Alarm - Delivery Temperature High
2138 : (A2138) Alarm - Internal Pressure High
2808 : (A2808) Alarm - Differential Pressure High
2816 : (A2816) Alarm - Power Failure
3123 : (R3123) Run Inhibit - Delivery Temperature Low
3137 : (R3137) Run Inhibit - Internal Pressure High
4804 : (A4804) Service Alarm - Service Due
5000 : (E5000) Trip - Parameter Table Index Corrupt
5001 : (E5001) Trip - IO-Config Table Corrupt
506 : (E0506) Trip - Analog Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module Ai4-1
507 : (E0507) Trip - Analog Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module Ai4-2
508 : (E0508) Trip - Digital Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module Di8R4-1
509 : (E0509) Trip - Digital Input Short Circuit On Expansion Module Di8R4-2
840 : (E0840) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 1
841 : (E0841) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 2
842 : (E0842) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 3
843 : (E0843) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 4
844 : (E0844) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 5
845 : (E0845) Trip - Communication Error With Expansion Module 6
40
Page 41

Data Conversion Type
STRING : String of ASCII characters (1 byte represents 1 ASCII character)
SIGNED, NUMERIC : Value is signed numeric
Data Units
mBAR : Pressure in milliBar
HRS : Time in Hours
UCHAR_VAL : Value unsigned byte (8bit)
LONG_VAL : Value signed long (32bit)
BINARY : Value bitwise represented
PERCENT_DP2 : Percentage to 2 decimal places
ADSTEPS : AD-steps
HZ : Frequency in Hertz
PSI : Pressure in PSI
FAH : Temperature in Fahrenheit
41
 Loading...
Loading...