HP LaserJet Pro 100 Color MFP M176n, LaserJet Pro 100 Color MFP M177fw Troubleshooting Manual

COLOR LASERJET PRO MFP
Troubleshooting Manual
OK
X
M176 M177

HP Color LaserJet Pro MFP M176, M177
Troubleshooting Manual

Copyright and License
Trademark Credits
© 2013 Copyright Hewlett-Packard
Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation
without prior written permission is prohibited,
except as allowed under the copyright laws.
The information contained herein is subject to
change without notice.
The only warranties for HP products and
services are set forth in the express warranty
statements accompanying such products and
services. Nothing herein should be construed
as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein.
Part number: CZ165-90944
Edition 1, 9/2013
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows® XP, and
Windows Vista® are U.S. registered trademarks
of Microsoft Corporation.

Conventions used in this guide
TIP: Tips provide helpful hints or shortcuts.
NOTE: Notes provide important information to explain a concept or to complete a task.
CAUTION: Cautions indicate procedures that you should follow to avoid losing data or damaging the
product.
WARNING! Warnings alert you to specific procedures that you should follow to avoid personal injury,
catastrophic loss of data, or extensive damage to the product.
ENWW iii

Table of contents
1 Theory of operation ....................................................................................................................................... 1
Basic operation ...................................................................................................................................................... 2
Major product systems ........................................................................................................................ 2
Sequence of operation ........................................................................................................................ 3
Formatter-control system ..................................................................................................................................... 4
Sleep mode .......................................................................................................................................... 4
Input/output ........................................................................................................................................ 4
CPU ....................................................................................................................................................... 4
Memory ................................................................................................................................................ 4
NAND Flash memory ........................................................................................................................... 4
Firmware .............................................................................................................................................. 5
Memory use ......................................................................................................................................... 5
PJL overview ........................................................................................................................................ 5
LEDM overview .................................................................................................................................... 5
Control panel ....................................................................................................................................... 5
Engine-control system .......................................................................................................................................... 6
DC controller ........................................................................................................................................ 7
Low-voltage power supply ................................................................................................................. 8
High-voltage power supply ................................................................................................................. 9
Fuser control ..................................................................................................................................... 10
Image-formation system .................................................................................................................................... 11
Image-formation process ................................................................................................................. 12
Latent-image formation stage ....................................................................................... 14
Step 1: Primary charging .............................................................................. 14
Step 2: Laser-beam exposure ...................................................................... 14
Developing stage ............................................................................................................ 15
Step 3: Development .................................................................................... 15
Transfer stage ................................................................................................................. 16
Step 4: Primary transfer ............................................................................... 16
Step 5: Secondary transfer .......................................................................... 16
Step 6: Separation from the drum ............................................................... 17
Fusing stage .................................................................................................................... 17
ENWW v

Step 7: Fusing ............................................................................................... 17
Drum cleaning stage ....................................................................................................... 18
Step 8: Drum cleaning .................................................................................. 18
ITB cleaning mechanism ................................................................................................. 18
Pickup, feed, and delivery system ...................................................................................................................... 20
Photo sensors and switches ............................................................................................................. 21
Main-input tray .................................................................................................................................................... 22
Jam detection .................................................................................................................................... 22
Scanner system ................................................................................................................................................... 23
Electrical system ............................................................................................................................... 23
Scanner power-on sequence of events .......................................................................... 23
Copy or scan-to-computer sequence of events ............................................................. 24
Document feeder functions and operation ......................................................................................................... 25
Document feeder operation .............................................................................................................. 25
Document feeder paper path and document feeder sensors .......................................................... 25
Document feeder jam detection ....................................................................................................... 26
Fax functions and operation ............................................................................................................................... 27
Computer and network security features ........................................................................................ 27
PSTN operation ................................................................................................................................. 27
The fax subsystem ............................................................................................................................ 27
Fax card in the fax subsystem .......................................................................................................... 27
Safety isolation ............................................................................................................... 28
Safety-protection circuitry ............................................................................................. 28
Data path ......................................................................................................................... 28
Hook state ....................................................................................................................... 28
Downstream device detection ........................................................................................ 29
Hook switch control ........................................................................................................ 29
Ring detect ...................................................................................................................... 29
Line current control ........................................................................................................ 29
Billing- (metering-) tone filters ...................................................................................... 29
Fax page storage in flash memory ................................................................................................... 29
Stored fax pages ............................................................................................................. 30
Advantages of flash memory storage ............................................................................ 30
2 Solve problems ........................................................................................................................................... 31
Solve problems checklist ..................................................................................................................................... 32
Step 1: Test print functionality ......................................................................................................... 32
Step 2: Test copy functionality ......................................................................................................... 32
Menu map ............................................................................................................................................................ 33
Troubleshooting processes ................................................................................................................................. 34
Determine the problem source ......................................................................................................... 34
vi ENWW

Power subsystem .............................................................................................................................. 35
Power-on checks ............................................................................................................ 35
Tools for troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................... 36
Component diagnostics .................................................................................................................... 36
Engine-test page ............................................................................................................ 36
LCD control-panel tests .................................................................................................. 36
Touchscreen control-panel tests ................................................................................... 36
Diagrams ........................................................................................................................................... 38
Plug/jack locations ......................................................................................................... 38
Locations of connectors ................................................................................................. 39
Locations of major components ..................................................................................... 41
General timing chart ....................................................................................................... 43
General circuit diagram .................................................................................................. 44
Internal print-quality test pages ...................................................................................................... 45
Clean the paper path ....................................................................................................... 45
Print Configuration page ................................................................................................ 45
Print-quality troubleshooting tools ................................................................................................. 46
Repetitive image defects ruler ....................................................................................... 46
Calibrate the product ...................................................................................................... 47
Control panel menus ......................................................................................................................... 48
Touchscreen control panel ............................................................................................. 48
Setup menu .................................................................................................. 48
Fax Menu ....................................................................................................... 55
Copy Menu .................................................................................................... 57
LCD control panel ............................................................................................................ 59
Setup menu .................................................................................................. 59
Interpret control-panel messages .................................................................................................... 66
Control-panel message types ........................................................................................ 66
Control-panel messages ................................................................................................ 66
Clear jams ............................................................................................................................................................ 73
Solve paper feed or jam problems .................................................................................................... 73
The product does not pick up paper ............................................................................... 73
The product picks up multiple sheets of paper .............................................................. 73
Frequent or recurring paper jams .................................................................................. 73
Prevent paper jams ......................................................................................................... 74
Clear jams from the input tray .......................................................................................................... 75
Clear jams in the output bin .............................................................................................................. 79
Clear jams in the document feeder ................................................................................................... 81
Solve paper-handling problems .......................................................................................................................... 83
Solve image-quality problems ............................................................................................................................ 84
General print-quality issues ............................................................................................................. 84
ENWW vii

Color image defects .......................................................................................................................... 88
Copy print-quality problems ............................................................................................................. 93
Scan-quality problems ...................................................................................................................... 94
Prevent scan-quality problems ...................................................................................... 94
Solve scan-quality problems .......................................................................................... 94
Clean the product ................................................................................................................................................ 95
Print a cleaning page ......................................................................................................................... 95
Check the scanner glass for dirt and smudges ................................................................................. 95
Clean the pickup rollers and separation pad in the document feeder ............................................. 96
Solve performance problems .............................................................................................................................. 97
Solve connectivity problems ............................................................................................................................... 98
Solve direct-connect problems ......................................................................................................... 98
Solve wired network problems ......................................................................................................... 98
Poor physical connection ................................................................................................ 98
The computer is using the incorrect IP address for the product ................................... 98
The computer is unable to communicate with the product ........................................... 99
The product is using incorrect link and duplex settings for the network ...................... 99
New software programs might be causing compatibility problems ............................. 99
The computer or workstation might be set up incorrectly ............................................ 99
The product is disabled, or other network settings are incorrect ................................. 99
Solve wireless network problems .................................................................................................... 99
Wireless connectivity checklist .................................................................................... 100
The product does not print after the wireless configuration completes .................... 100
The product does not print, and the computer has a third-party firewall installed ... 101
The wireless connection does not work after moving the wireless router or
product .......................................................................................................................... 101
Cannot connect more computers to the wireless product .......................................... 101
The wireless product loses communication when connected to a VPN ...................... 101
The network does not appear in the wireless networks list ....................................... 101
The wireless network is not functioning ...................................................................... 101
Perform a wireless network diagnostic test ................................................................ 102
Reduce interference on a wireless network ................................................................ 102
Service mode functions ..................................................................................................................................... 103
Secondary service menu ................................................................................................................. 103
Open the secondary service menu ............................................................................... 103
Secondary service menu structure .............................................................................. 103
Product resets ................................................................................................................................. 105
Restore factory settings ............................................................................................... 105
NVRAM initialization ..................................................................................................... 105
Solve fax problems ............................................................................................................................................ 106
Check the hardware setup .............................................................................................................. 106
viii ENWW

Faxes are sending slowly ................................................................................................................ 107
Fax quality is poor ........................................................................................................................... 108
Fax cuts off or prints on two pages ................................................................................................ 109
Product updates ................................................................................................................................................ 110
Appendix A Service and support .................................................................................................................... 111
Hewlett-Packard limited warranty statement ................................................................................................. 112
HP's Premium Protection Warranty: LaserJet toner cartridge limited warranty statement ........................... 113
HP policy on non-HP supplies ........................................................................................................................... 114
HP anticounterfeit Web site .............................................................................................................................. 115
Data stored on the toner cartridge ................................................................................................................... 116
End User License Agreement ............................................................................................................................ 117
OpenSSL ............................................................................................................................................................. 119
Customer self-repair warranty service ............................................................................................................. 120
Customer support .............................................................................................................................................. 121
Appendix B Product specifications ................................................................................................................. 123
Physical specifications ...................................................................................................................................... 124
Power consumption, electrical specifications, and acoustic emissions .......................................................... 124
Environmental specifications ............................................................................................................................ 124
Appendix C Regulatory information ............................................................................................................... 125
FCC regulations .................................................................................................................................................. 126
Environmental product stewardship program ................................................................................................. 127
Protecting the environment ........................................................................................................... 127
Ozone production ............................................................................................................................ 127
Power consumption ........................................................................................................................ 127
Toner consumption ......................................................................................................................... 127
Paper use ......................................................................................................................................... 127
Plastics ............................................................................................................................................ 127
HP LaserJet print supplies .............................................................................................................. 127
Return and recycling instructions ................................................................................................... 128
United States and Puerto Rico ...................................................................................... 128
Multiple returns (more than one cartridge) ............................................... 128
Single returns ............................................................................................. 128
Shipping ...................................................................................................... 128
Non-U.S. returns ........................................................................................................... 129
Paper ............................................................................................................................................... 129
Material restrictions ........................................................................................................................ 129
Disposal of waste equipment by users ........................................................................................... 13 0
ENWW ix

Electronic hardware recycling ........................................................................................................ 130
Chemical substances ....................................................................................................................... 130
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) ................................................................................................ 130
For more information ...................................................................................................................... 130
Declaration of conformity (M176n model) ....................................................................................................... 131
Declaration of conformity (M177fw model) ..................................................................................................... 133
Safety statements ............................................................................................................................................. 135
Laser safety ..................................................................................................................................... 135
Canadian DOC regulations .............................................................................................................. 135
VCCI statement (Japan) ................................................................................................................... 135
Power cord instructions .................................................................................................................. 135
Power cord statement (Japan) ....................................................................................................... 135
EMC statement (Korea) ................................................................................................................... 136
Laser statement for Finland ........................................................................................................... 136
GS statement (Germany) ................................................................................................................ 137
Substances Table (China) ................................................................................................................ 137
Restriction on Hazardous Substances statement (Turkey) ........................................................... 137
Restriction on Hazardous Substances statement (Ukraine) .......................................................... 137
Eurasian Conformity (Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia) ...................................................................... 138
Additional statements for telecom (fax) products ........................................................................................... 139
EU Statement for Telecom Operation ............................................................................................ 139
New Zealand Telecom Statements ................................................................................................. 139
Additional FCC statement for telecom products (US) .................................................................... 139
Telephone Consumer Protection Act (US) ...................................................................................... 140
Industry Canada CS-03 requirements ............................................................................................ 140
Vietnam Telecom wired/wireless marking for ICTQC Type approved products ............................ 141
Additional statements for wireless products ................................................................................................... 142
FCC compliance statement—United States ................................................................................... 142
Australia statement ........................................................................................................................ 142
Brazil ANATEL statement ................................................................................................................ 142
Canadian statements ...................................................................................................................... 142
Products with 5 GHz Operation Industry of Canada ....................................................................... 142
Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation (Canada) ......................................................................... 142
European Union regulatory notice .................................................................................................. 143
Notice for use in France .................................................................................................................. 143
Notice for use in Russia ................................................................................................................... 143
Mexico statement ........................................................................................................................... 143
Taiwan statement ........................................................................................................................... 144
Korean statement ........................................................................................................................... 144
Vietnam Telecom wired/wireless marking for ICTQC Type approved products ............................ 141
x ENWW

Index ........................................................................................................................................................... 145
ENWW xi

List of tables
Table 1-1 Sequence of operation ......................................................................................................................................... 3
Table 1-2 Photo sensors and switches .............................................................................................................................. 21
Table 1-3 Document feeder sensors .................................................................................................................................. 25
Table 2-1 Determine the problem source .......................................................................................................................... 34
Table 2-2 Plug/jack locations ............................................................................................................................................. 38
Table 2-3 Engine control unit PCA connectors .................................................................................................................. 39
Table 2-4 Cross section view .............................................................................................................................................. 41
Table 2-5 External covers and doors (base) ...................................................................................................................... 42
Table 2-6 Repetitive image defects ruler .......................................................................................................................... 46
Table 2-7 HP Web Services menu (touchscreen control panel) ........................................................................................ 48
Table 2-8 Reports menu (touchscreen control panel) ....................................................................................................... 49
Table 2-9 Self Diagnostics menu (touchscreen control panel) ......................................................................................... 49
Table 2-10 Fax Setup menu (touchscreen control panel) ................................................................................................. 49
Table 2-11 System Setup menu (touchscreen control panel) ........................................................................................... 52
Table 2-12 Service menu (touchscreen control panel) ...................................................................................................... 54
Table 2-13 Network Setup menu (touchscreen control panel) ......................................................................................... 55
Table 2-14 Fax Menu (touchscreen control panel) ............................................................................................................ 55
Table 2-15 Copy Menu (touchscreen control panel) .......................................................................................................... 57
Table 2-16 HP Web Services menu (LCD control panel) .................................................................................................... 48
Table 2-17 Copy Setup menu (LCD control panel) ............................................................................................................. 57
Table 2-18 ID Copy menu (LCD control panel) ................................................................................................................... 60
Table 2-19 Reports menu (LCD control panel) .................................................................................................................. 60
Table 2-20 Self Diagnostics menu (LCD control panel) ..................................................................................................... 61
Table 2-21 System Setup menu (LCD control panel) ......................................................................................................... 52
Table 2-22 Service menu (LCD control panel) .................................................................................................................... 54
Table 2-23 Network Setup menu (LCD control panel) ....................................................................................................... 55
Table 2-24 Control-panel messages .................................................................................................................................. 66
Table 2-25 Solve paper-handling problems ...................................................................................................................... 83
Table 2-26 General print-quality issues ............................................................................................................................ 84
Table 2-27 Color image defects ......................................................................................................................................... 88
Table 2-28 Copy print-quality problems ............................................................................................................................ 93
Table 2-29 Scan-quality problems ..................................................................................................................................... 94
ENWW xiii

Table 2-30 Solve performance problems .......................................................................................................................... 97
Table 2-31 Secondary service menu ................................................................................................................................ 103
Table B-1 Physical specifications ..................................................................................................................................... 124
Table B-2 Product dimensions with document feeder opened ....................................................................................... 124
Table B-3 Operating-environment specifications ........................................................................................................... 124
xiv ENWW

List of figures
Figure 1-1 Product systems ................................................................................................................................................. 2
Figure 1-2 Engine control system components ................................................................................................................... 6
Figure 1-3 DC controller circuit diagram .............................................................................................................................. 7
Figure 1-4 Low-voltage power supply ................................................................................................................................. 8
Figure 1-5 High-voltage power supply ................................................................................................................................ 9
Figure 1-6 Image-formation system .................................................................................................................................. 12
Figure 1-7 Image-formation process ................................................................................................................................. 13
Figure 1-8 Primary charging ............................................................................................................................................... 14
Figure 1-9 Laser-beam exposure ....................................................................................................................................... 14
Figure 1-10 Development .................................................................................................................................................. 15
Figure 1-11 Primary transfer ............................................................................................................................................. 16
Figure 1-12 Secondary transfer ......................................................................................................................................... 16
Figure 1-13 Separation from the drum .............................................................................................................................. 17
Figure 1-14 Fusing .............................................................................................................................................................. 17
Figure 1-15 Drum cleaning ................................................................................................................................................. 18
Figure 1-16 ITB cleaning mechanism ................................................................................................................................. 18
Figure 1-17 Pickup, feed, and delivery system block diagram ......................................................................................... 20
Figure 1-18 Photo sensors and switches ........................................................................................................................... 21
Figure 1-19 Document feeder paper path and document feeder sensors ........................................................................ 25
Figure 2-1 Plug/jack locations ........................................................................................................................................... 38
Figure 2-2 Locations of connectors ................................................................................................................................... 39
Figure 2-3 Cross section view ............................................................................................................................................. 41
Figure 2-4 External covers and doors (base) ..................................................................................................................... 42
Figure 2-5 General timing diagram .................................................................................................................................... 43
Figure 2-6 General circuit diagram ..................................................................................................................................... 44
ENWW xv
1 Theory of operation
This chapter presents an overview of the major components of the product, and it includes a detailed
discussion of the image-formation system.
●
Basic operation
●
Formatter-control system
●
Engine-control system
●
Image-formation system
●
Pickup, feed, and delivery system
●
Main-input tray
●
Scanner system
●
Document feeder functions and operation
●
Fax functions and operation
ENWW 1
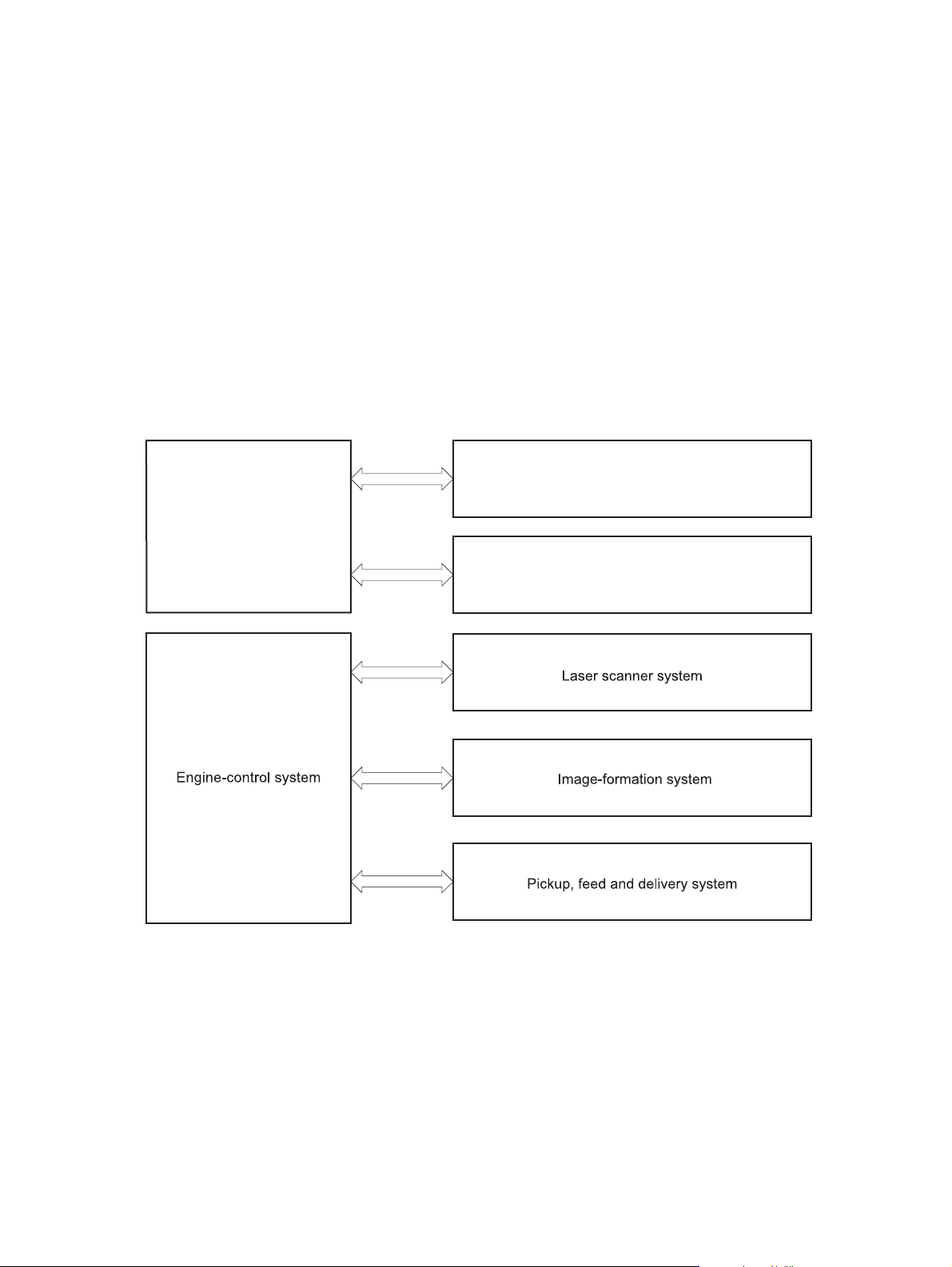
Basic operation
Major product systems
The product includes the following systems:
●
Document feeder
●
Document scanner
●
Engine control system
●
Laser/scanner system
●
Image-formation system
●
Pickup-and-feed system
Figure 1-1 Product systems
Formatter
Document feeder
Document scanner
2 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

Sequence of operation
Table 1-1 Sequence of operation
Period Duration Purpose Remarks
WAIT From the time the power is
turned on or the door is closed
until the drum-phase
adjustment is complete
STBY (Standby period) From end of the WAIT or LSTR
period until either the print
command is received from the
formatter or the power is
turned off
INTR (Initial rotation) From the time the print
command is received until the
paper is picked up
PRINT From the end of INTR period
until the fuser paper sensor
detects the trailing edge of
paper
LSTR (Last rotation) From the end of the PRINT
period until the motor stops
rotating
Clears the potential from the
drum surface, adjusts the drum
phase, and cleans the
intermediate transfer belt (ITB)
Maintains the product in
readiness for a print command
Prepares the photosensitive
drum for printing
Forms the images on the
photosensitive drum and
transfers the toner image to
the paper
Moves the printed sheet out of
the product
Detects the toner level,
cartridge presence, and
environment; completes any
required calibration (color
registration control and image
stability)
The product enters STBY mode
when the formatter sends a
sleep command; the product
performs color registration and
the image stability control
when the formatter sends
those commands
Performs image stabilization at
a specified print interval or at
specified times
The product enters the INTR
period as soon as the formatter
sends another print command
ENWW Basic operation 3

Formatter-control system
The formatter is responsible for the following procedures:
●
Controlling Sleep mode
●
Receiving and processing print data from the various product interfaces
●
Monitoring control-panel functions and relaying product-status information (through the control panel
and the network or bidirectional interface)
●
Developing and coordinating data placement and timing with the DC controller PCA
●
Storing font information
●
Communicating with the host computer through the network or the bidirectional interface
The formatter receives a print job from the network or bidirectional interface and separates it into image
information and instructions that control the printing process. The DC controller PCA synchronizes the imageformation system with the paper-input and -output systems, and then signals the formatter to send the
print-image data.
Sleep mode
After a user-specified time, the Sleep mode feature automatically conserves electricity by substantially
reducing power consumption when the product is not printing. After a user-specified time, the product
automatically reduces its power consumption (Sleep mode). The product returns to the ready state when a
button is pressed, a print job is received, or a door is opened. When the product is in Sleep mode, all of the
control-panel LEDs and the power button backlight LED are off.
Input/output
The product receives print data primarily from the following:
●
Hi-Speed USB 2.0 port
●
10/100/1000 Ethernet LAN connection
●
802.11b/g/n wireless networking
CPU
The formatter incorporates a 600 MHz Arm processor.
Memory
The random access memory (RAM) on the formatter PCA contains the page, I/O buffers, and the font storage
area. RAM stores printing and font information received from the host system, and can also serve to
temporarily store a full page of print-image data before the data is sent to the print engine.
NAND Flash memory
The Smart Install CD image (ISO) is stored in the NAND Flash non-volatile memory. This memory can be
reprogrammed through the firmware.
4 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

Firmware
The product has 128 MB of DDR-2 SDRAM, which is used for run-time firmware imaging and print, scan and
copy job information during printing.
Memory use
The product has a 16 KB EEPROM and 16 MB of SPI NOR Flash Memory, which is used for product
configuration information and print driver firmware.
PJL overview
The print job language (PJL) is an integral part of configuration, in addition to the standard print command
language (PCL). With standard cabling, the product can use PJL to perform a variety of functions such as
these:
●
Two-way communication with the host computer through a network connection or a USB connection.
The product can inform the host about such things as the control-panel settings, and the control-panel
settings can be changed from the host.
●
Dynamic I/O switching. The product uses this switching to be configured with a host on each I/O. The
product can receive data from more than one I/O simultaneously, until the I/O buffer is full. This can
occur even when the product is offline.
●
Context-sensitive switching. The product can automatically recognize the personality (PS or PCL) of
each job and configure itself to serve that personality.
●
Isolation of print environment settings from one print job to the next. For example, if a print job is sent
to the product in landscape mode, the subsequent print jobs print in landscape mode only if they are
formatted for landscape printing.
LEDM overview
The low-end data model (LEDM) provides one consistent data representation method and defines the
dynamic and capabilities tickets shared between clients and devices, as well as the access protocol, event,
security, and discovery methods.
Control panel
The formatter sends and receives product status and command data to and from the control-panel PCA.
ENWW Formatter-control system 5
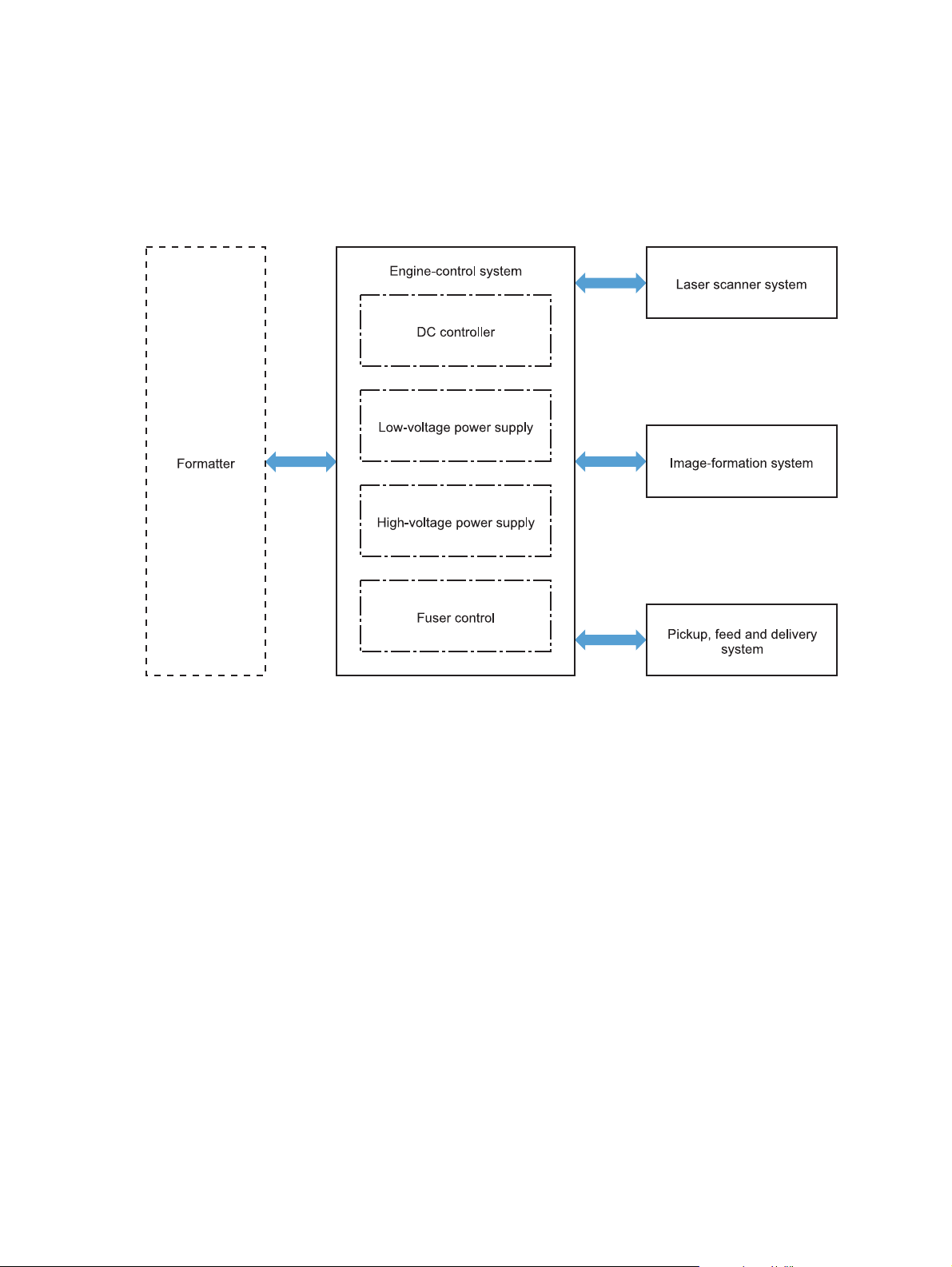
Engine-control system
The engine control system coordinates all product functions and drives the other three systems.
The engine control system contains the DC controller, low-voltage power supply PCA, high-voltage power
supply PCA, and fuser control PCA.
Figure 1-2 Engine control system components
6 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
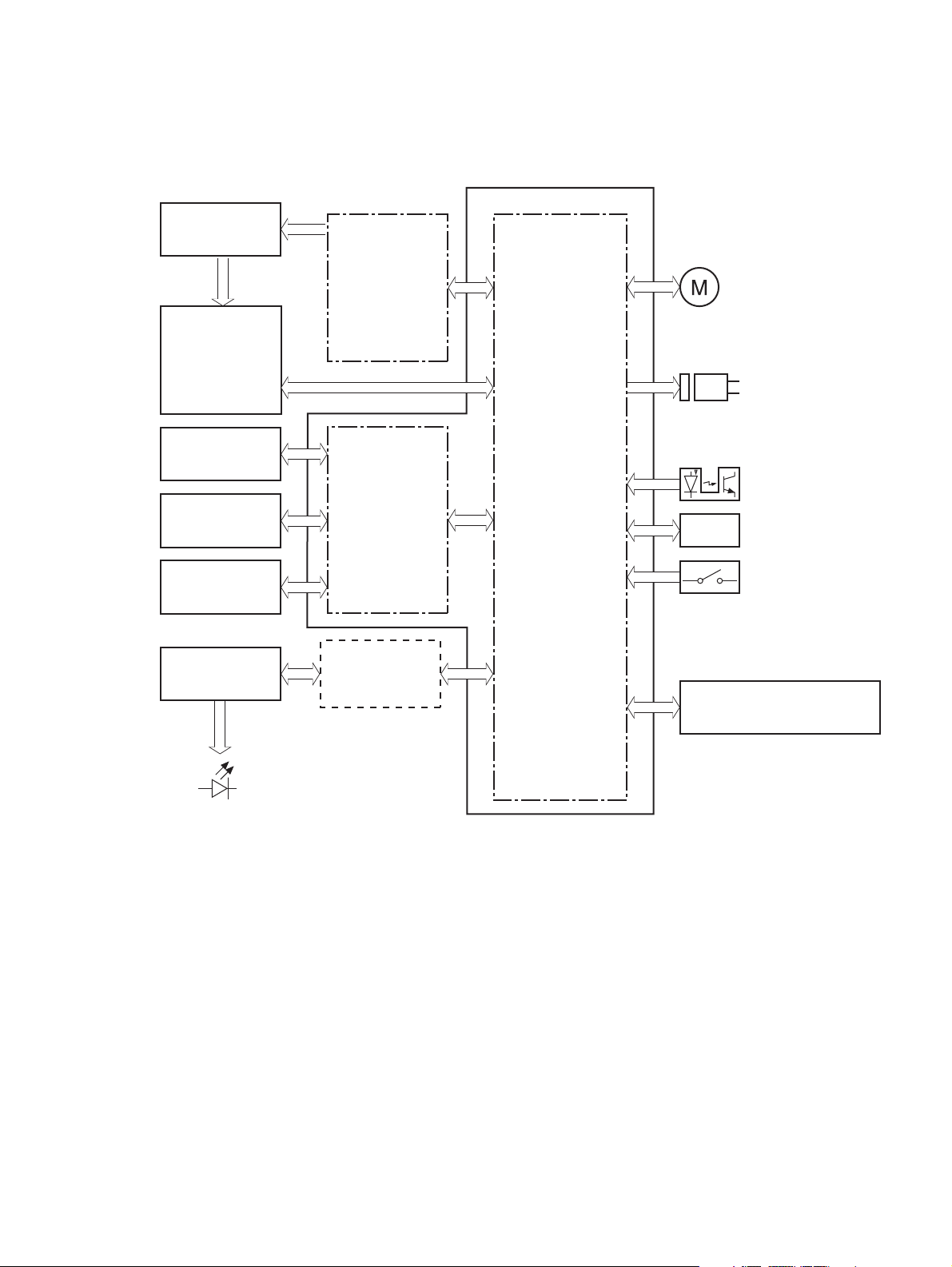
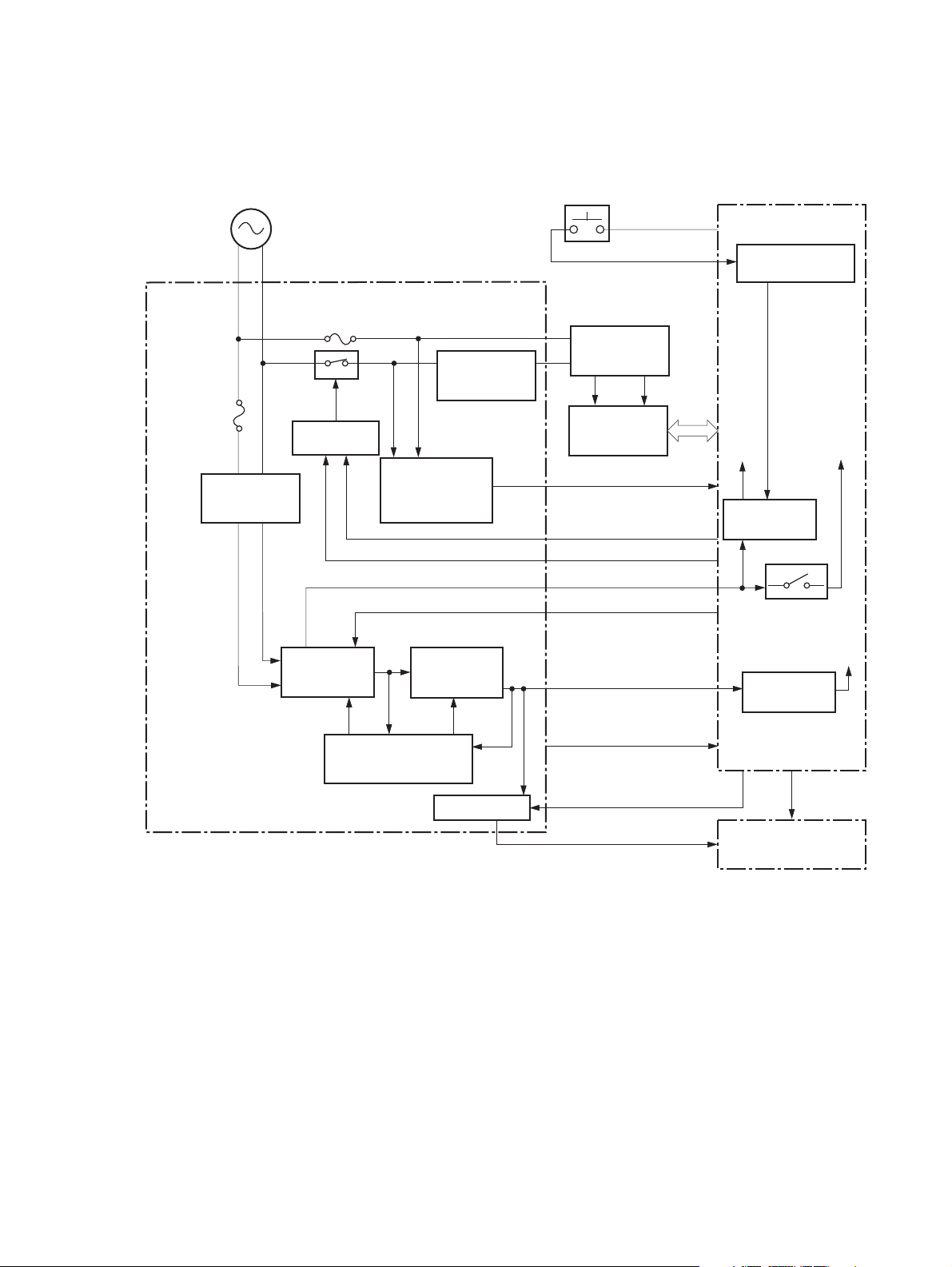
DC controller
The DC controller controls the operational sequences of the product.
Figure 1-3 DC controller circuit diagram
Connector PCA
Engine controller
Fuser
ITB ass’y
T2 roller
Cartridge
Control panel
Low-voltage
power supply
High-voltage
power supply
Formatter
Motor
Solenoid
Photointerruptor
DC controller
Sensor
Switch
Laser scanner ass’y
LED
ENWW Engine-control system 7
Low-voltage power supply
The low-voltage power supply converts AC power from the wall receptacle into DC voltage power.
Figure 1-4 Low-voltage power supply
AC power
Fuse
FU102
Rectifying
Relay
RL401
Relay control
circuit
Fuse
FU101
circuit
Power switch
SW7001
Low-voltage power supply
Fuser control
circuit
Frequency
detection circuit
200V model only
PWSW
Connector
PCA
Fuser
FREQSNS
RLD+
RLD-
+24V
DC controller
Remote switch
control circuit
+24V
Switching
circuit
+24B
+24V
generation
circuit
Protection circuit
+3.3V
generation
circuit
Switch
+24R
PWSV
+3.3R
LVT100V
/REM3V_V
+3.3V
Interlock switch
SW501
+3.3T
Switching
circuit
+24V
Formatter
8 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
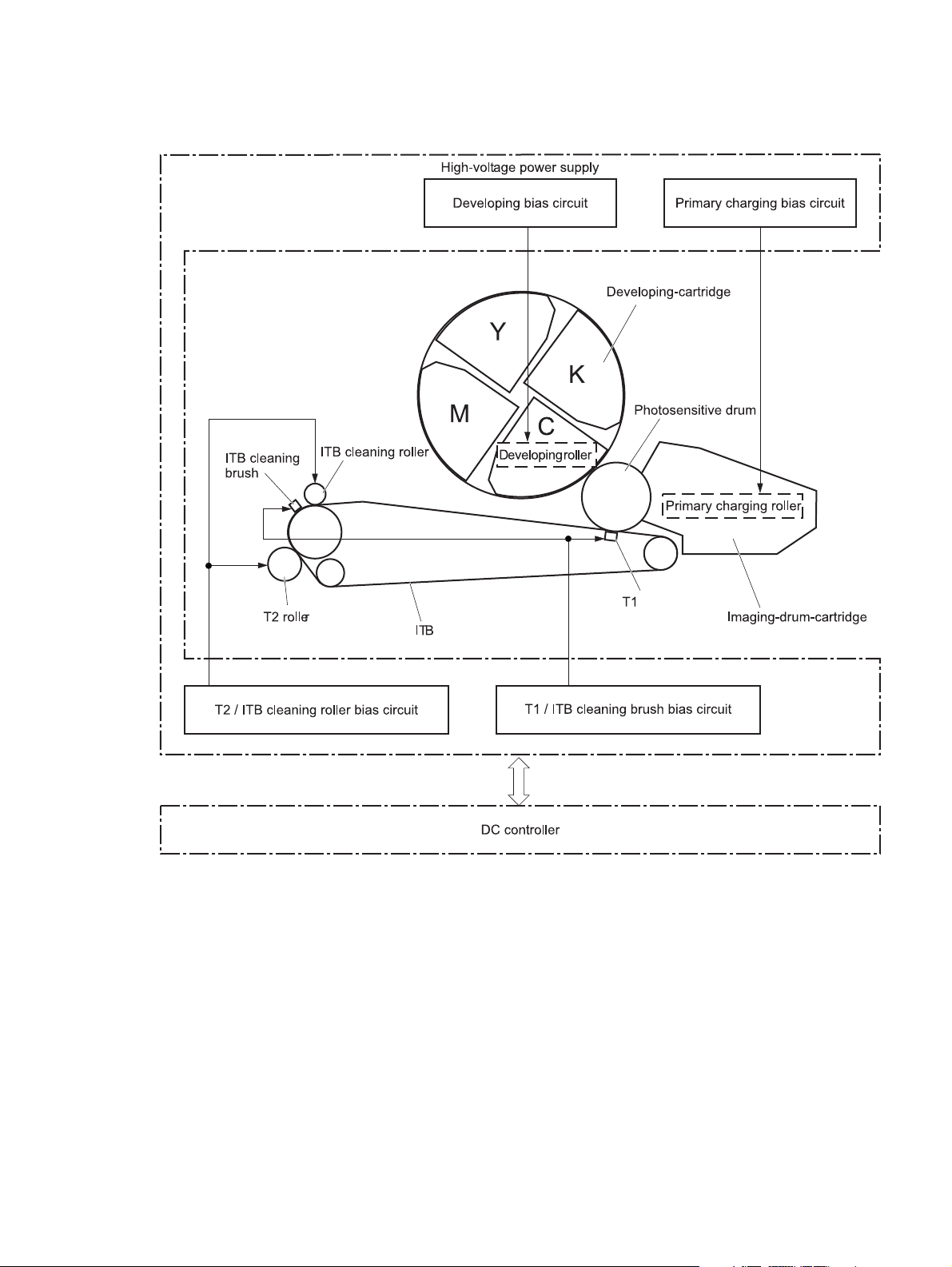
High-voltage power supply
Figure 1-5 High-voltage power supply
brush
ENWW Engine-control system 9
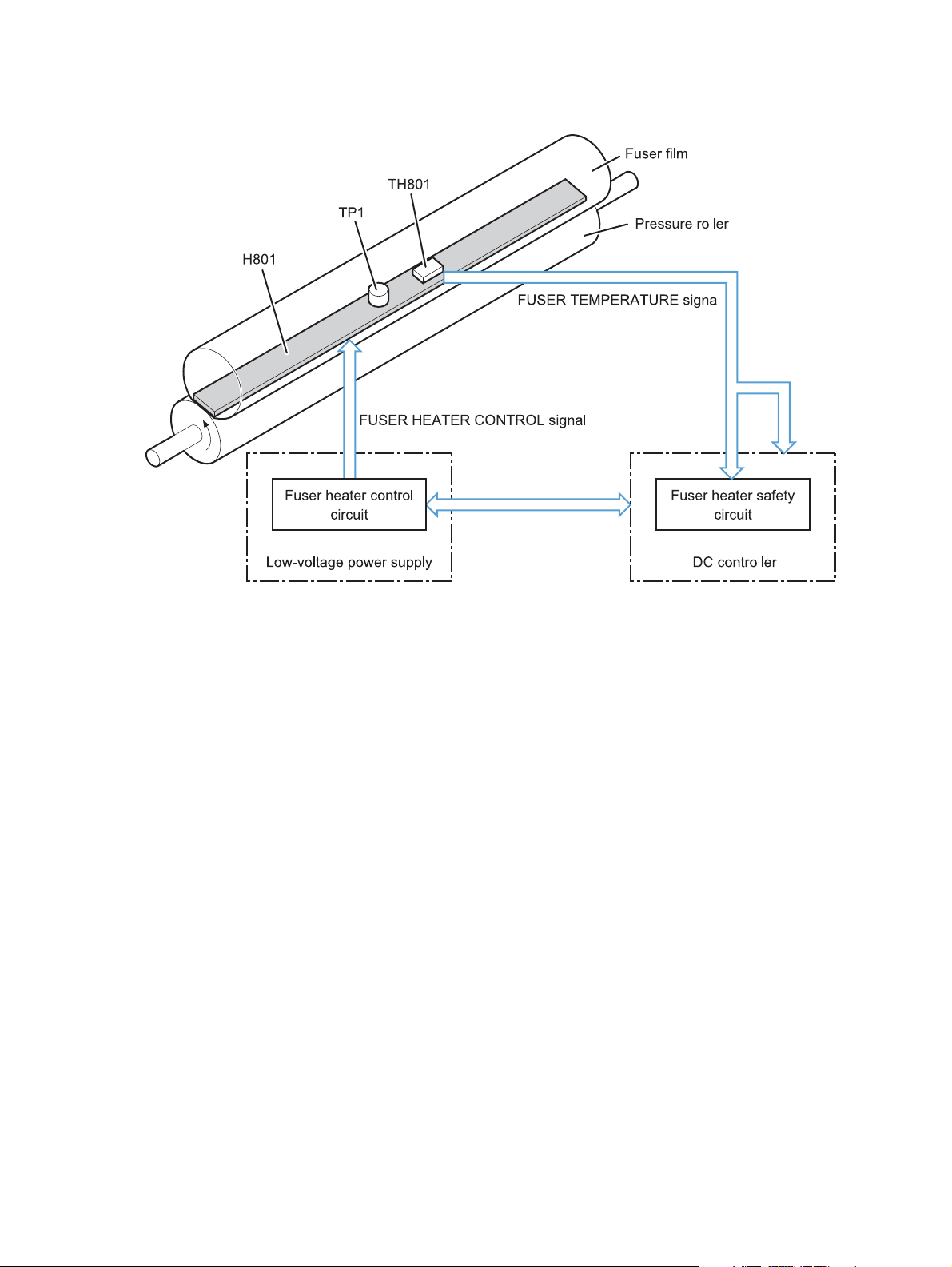
Fuser control
10 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW

Image-formation system
The DC controller controls the image-formation system according to commands from the formatter.
The DC controller controls the internal components of the image scanner system to form the toner image on
the photosensitive drum surface. The toner image is transferred to the paper and fused.
The following are the main components of the image-formation system.
●
Imaging drum
●
Laser scanner assembly
●
Carousel
●
Four toner cartridges
●
ITB
●
ITB drive roller
●
T1 pad
●
ITB cleaning brush
●
ITB cleaning roller
●
T2 roller
●
Fuser film assembly
●
Pressure roller
●
High-voltage power supply
ENWW Image-formation system 11
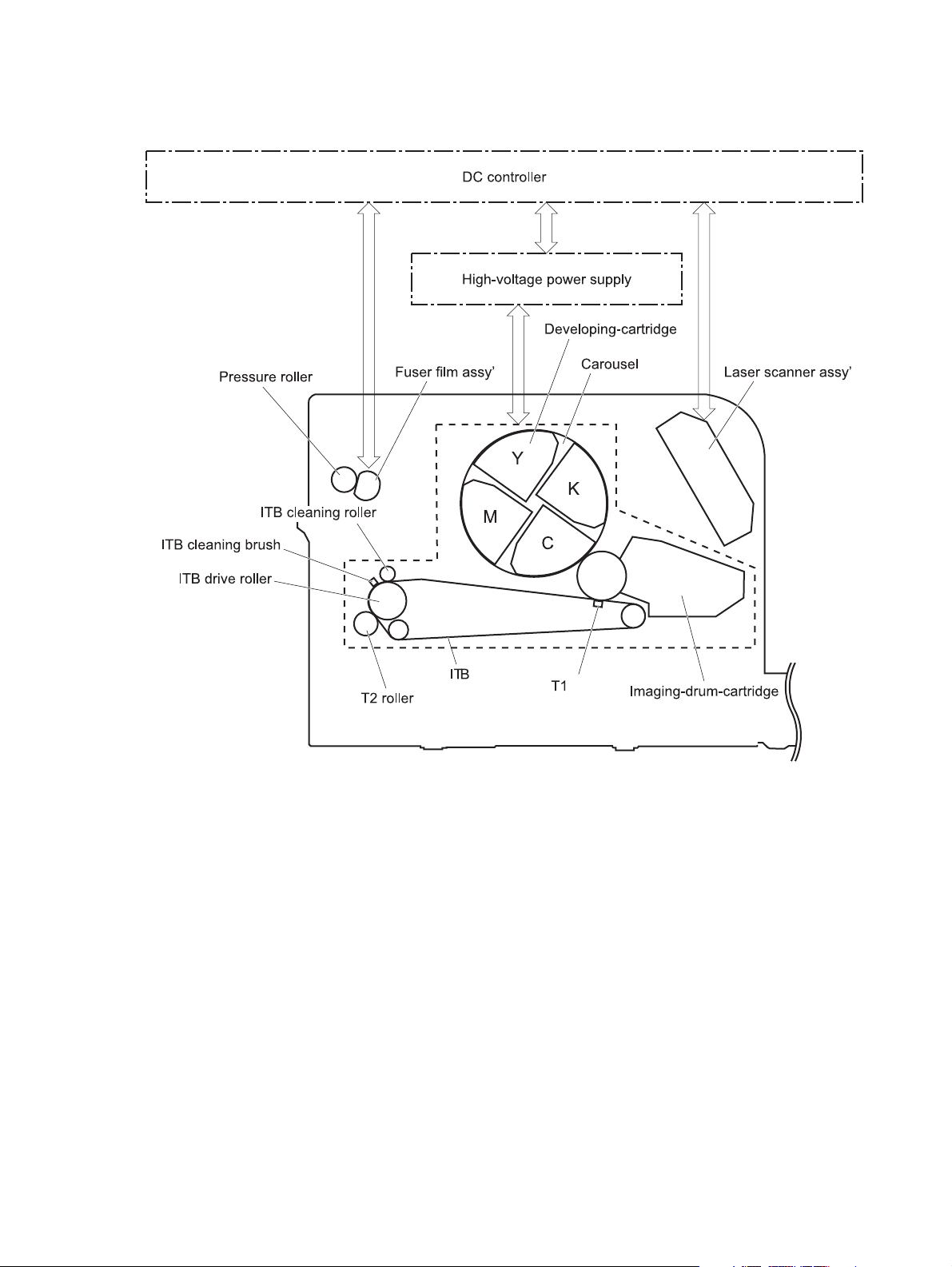
The following image shows the components of the image-formation system.
Figure 1-6 Image-formation system
Image-formation process
The DC controller rotates the following motors to drive each component.
Main motor
●
ITB drive roller
●
ITB (follows the ITB drive roller)
●
T2 roller (follows the ITB)
●
Imaging drum
●
Primary charging roller (part of the imaging drum)
●
Developing roller (part of the toner cartridge)
brush
12 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
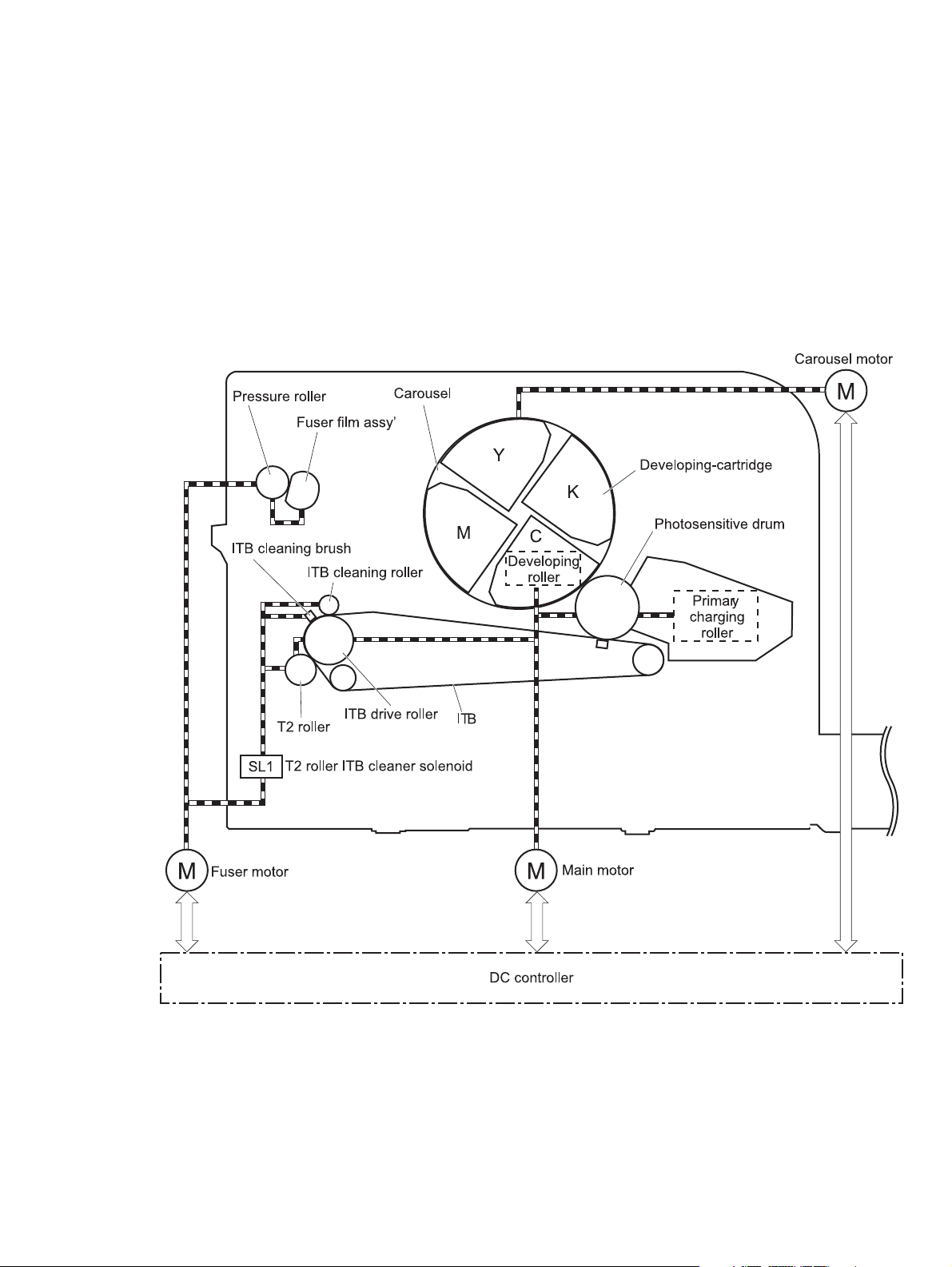
Carousel motor
●
●
Fuser motor
●
●
●
Figure 1-7 Image-formation process
Carousel
Engagement/Disengagement of the developing-cartridge (follows the carousel)
Pressure roller
Fuser film (follows the pressure roller)
Engagement/Disengagement of the T2 roller, ITB cleaning roller and ITB cleaning brush
ENWW Image-formation system 13
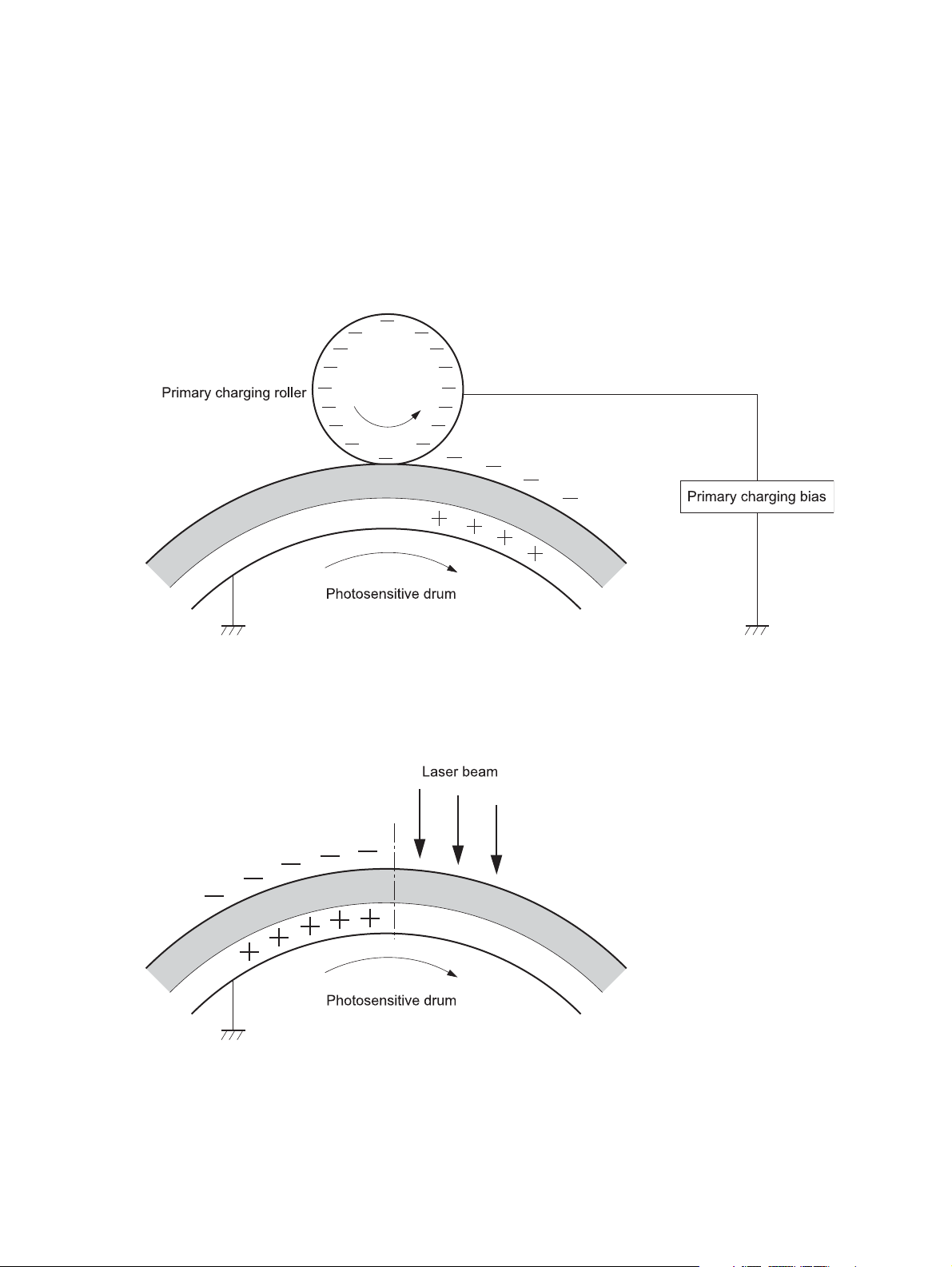
Latent-image formation stage
During the two steps that comprise this stage, a latent image is formed by applying a negative charge to the
photosensitive drum. This image is not visible on the drum.
Step 1: Primary charging
A high-voltage DC bias is applied to the primary charging roller, which is made of conductive rubber and is in
contact with the drum surface. As the roller moves across the drum, it applies the negative charge to that
surface.
Figure 1-8 Primary charging
Step 2: Laser-beam exposure
The laser beam scans the photosensitive drum to neutralize the negative charge on portions of the drum
surface. An electrostatic latent image is formed where the negative charge was neutralized.
Figure 1-9 Laser-beam exposure
14 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
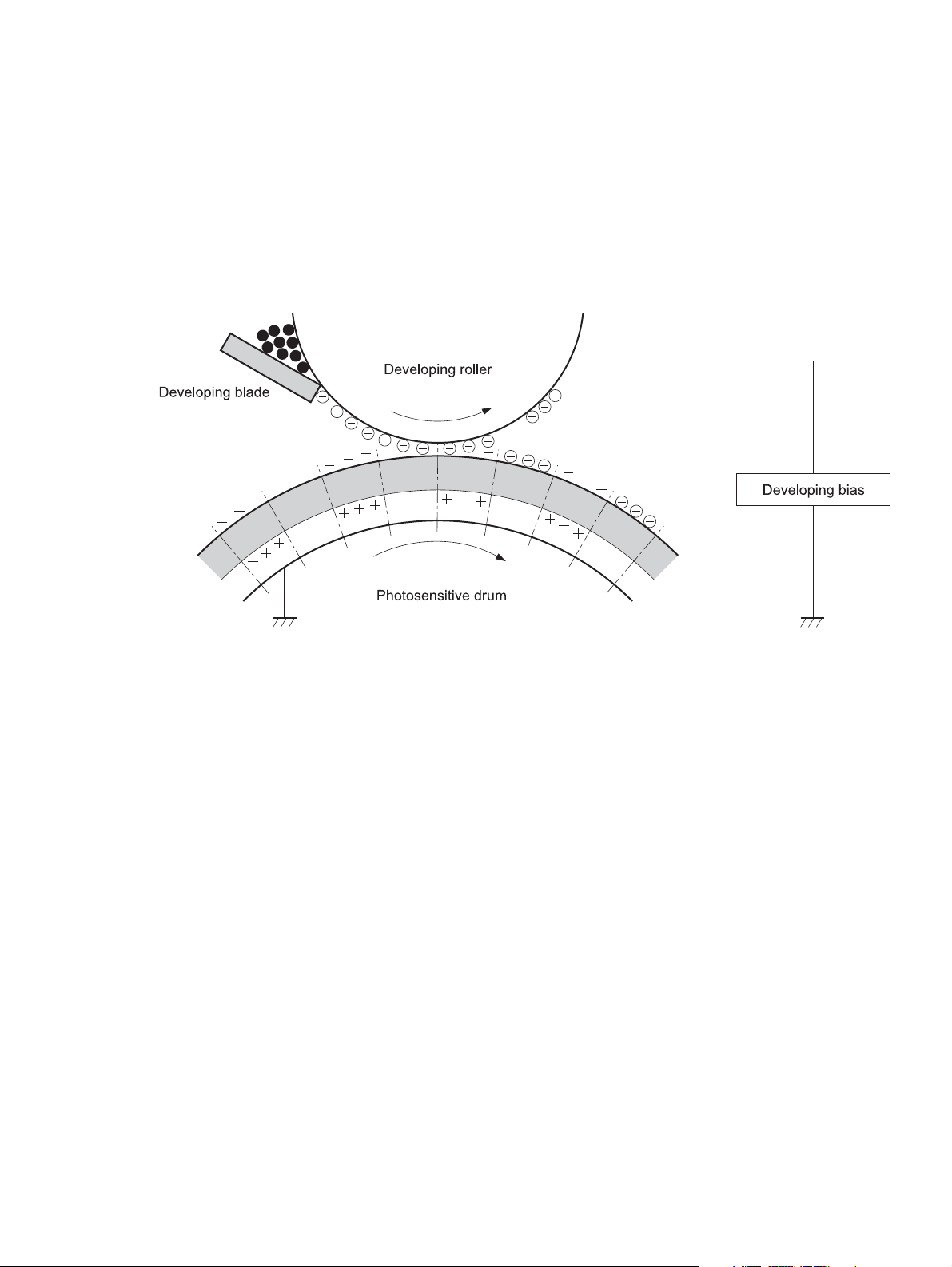
Developing stage
The developing cylinder comes in contact with the photosensitive drum and deposits toner on the
electrostatic latent image.
Step 3: Development
The toner acquires a negative charge as a result of the friction from the developing cylinder rotating against
the developing blade. When the negatively charged toner comes in contact with the drum, it adheres to the
electrostatic latent image. When the toner is on the drum, the image becomes visible.
Figure 1-10 Development
ENWW Image-formation system 15
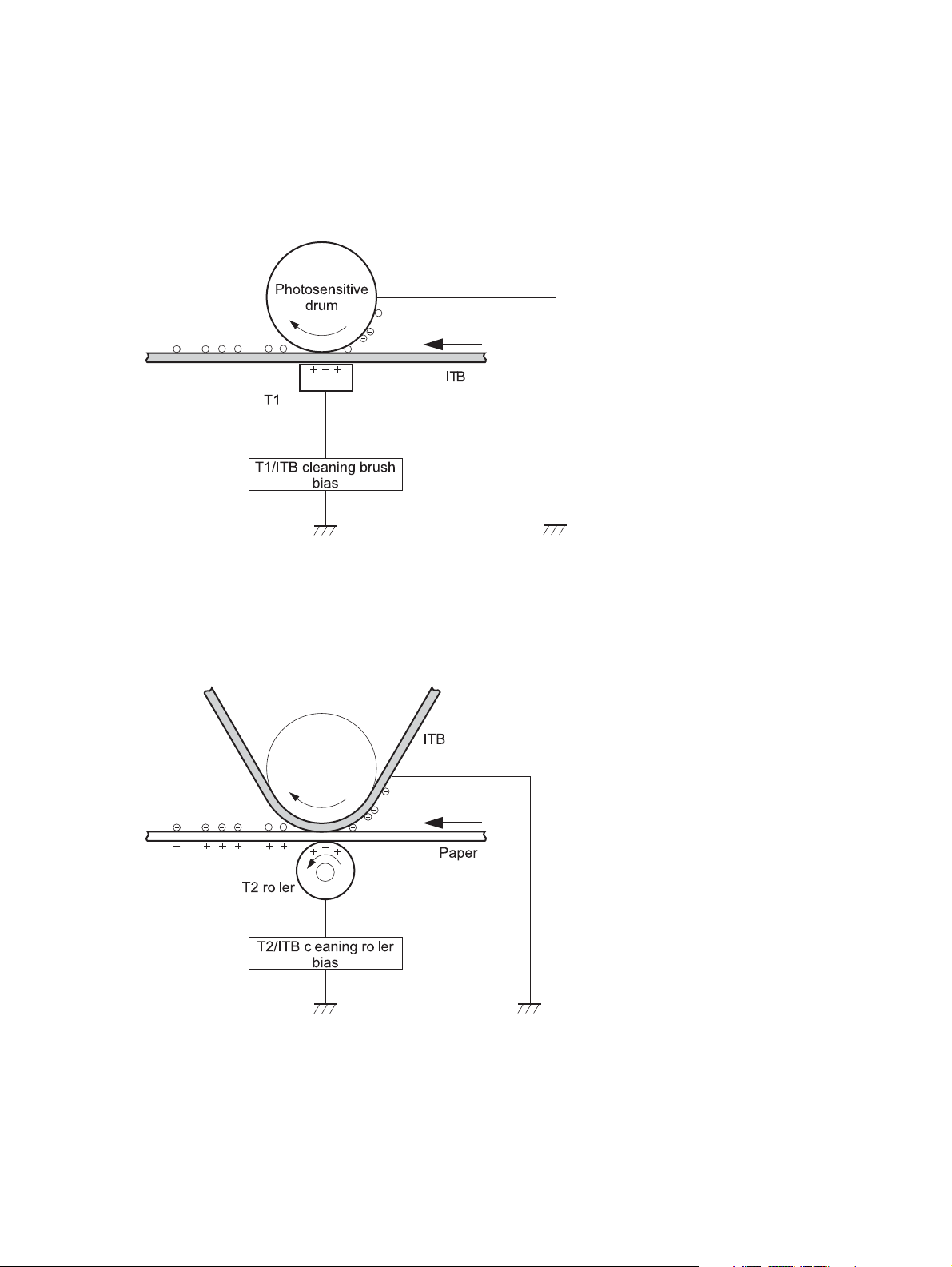
Transfer stage
Step 4: Primary transfer
The toner image on the photosensitive drum is transferred to the ITB. The DC positive bias is applied to the
primary transfer pad. The negatively charged toner transfers to the ITB from the drum surface.
Figure 1-11 Primary transfer
brush
Step 5: Secondary transfer
The toner image on the ITB is transferred to the paper. The DC positive bias is applied to the secondary
transfer roller. As the paper passes between the secondary transfer roller and the ITB, the toner image is
transferred to the paper.
Figure 1-12 Secondary transfer
16 Chapter 1 Theory of operation ENWW
 Loading...
Loading...