Page 1

Page 2

Table of Contents
Manual Overview
This manual contains the following sections:
Section 1 - “Product Overview” describes what is included with the DIR-330 router, and things to consider
before installing (page 1).
Section 2 - “Installation” describes how to install the router on your network (page 6).
Section 3 - “Configuration” describes how to configure the settings on your DIR-330 router (page 11).
Section 4 - “Wireless Security” explains how to setup wireless encryption on your wireless router (page 62).
Section 5 - “Connect to a Wireless Network” explains how to configure your wireless clients to connect to your
router (page 71).
Section 6 - “Troubleshooting” explains how to resolve common issues (page 79).
Appendix - “Appendix” contains wireless and networking basics, technical specifications, technical support
information, warranty, GNU general public license, and registration information (page 83).
iD-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 3

Table of Contents
D-Link reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes in the content hereof without obligation to
notify any person or organization of such revisions or changes.
Manual Revisions
Revision Date Description
1.0 January 15, 2007 • DIR-330 Revision A1 with firmware version 1.00
1.1 September 13, 2007
• Updated for firmware version 1.10
• Added Windows Vista™ support
Trademarks
D-Link and the D-Link logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of D-Link Corporation or its subsidiaries in the
United States or other countries. All other company or product names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
Copyright © 2007 by D-Link Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved. This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior expressed written permission
from D-Link Systems, Inc.
iiD-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 4

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Manual Overview .......................................................... i
Manual Revisions .................................................... ii
Trademarks .............................................................. ii
Product Overview ........................................................1
Package Contents....................................................1
System Requirements ............................................. 2
Features ...................................................................3
Hardware Overview ................................................. 4
Connections .......................................................4
LEDs ..................................................................5
Installation .................................................................... 6
Before you Begin ..................................................... 6
Wireless Installation Considerations ........................7
Connect to Cable/DSL/Satellite Modem .................. 8
Connect to Another Router ...................................... 9
Configuration ............................................................. 11
Web-based Configuration Utility ............................ 11
Setup Wizard ...................................................12
Manual Configuration .......................................17
Dynamic (DHCP) .......................................... 17
PPPoE (DSL) ...............................................18
PPTP ............................................................ 19
L2TP ............................................................. 20
Big Pond .......................................................21
Static IP ........................................................ 22
Russian PPPoE ............................................23
Russian PPTP .............................................. 25
Wireless Settings .............................................26
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WCN 2.0) ................26
Wireless Network Settings ........................... 27
Network Settings ..............................................28
DHCP Server Settings .................................29
DHCP Reservation ....................................... 30
VPN Settings ...................................................31
IPSec Settings .............................................. 32
PPTP/L2TP Settings .................................... 35
Port Forwarding ............................................... 36
Application Rules .............................................37
MAC Filters ......................................................38
Website Filters .................................................39
Firewall Settings ...............................................40
DMZ .............................................................40
Firewall Rules ............................................... 41
Advanced Wireless Settings ............................ 42
Tx Rate ......................................................... 42
DTIM Interval ................................................ 42
Preamble ...................................................... 42
WMM Function ............................................. 42
Advanced Network Settings .............................43
UPnP ............................................................ 43
WAN Ping Respond .....................................43
WAN Port Speed ..........................................43
iiiD-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 5

Table of Contents
Routing ............................................................44
Certificates .......................................................45
User Groups ....................................................46
Administrator Settings ......................................47
Change Password ........................................47
Remote Management ................................... 47
Time and Date Settings ...................................48
System Settings ...............................................49
Update Firmware .............................................50
DDNS ...............................................................51
System Check ..................................................52
Schedules ........................................................53
Log Settings .....................................................54
Device Information ........................................... 55
Log ...................................................................56
Statistics ..........................................................57
Active Session .................................................58
Wireless Clients ...............................................59
LAN Clients ......................................................59
Configure WPA/WPA2-EAP (RADIUS) ..................70
Connect to a Wireless Network ................................ 71
Using Windows Vista
™ .............................................................................. 71
Configure WEP/WPA/WPA2 ............................. 72
Using Windows® XP ............................................... 74
Configure WEP ................................................75
Configure WPA-PSK ........................................ 77
Troubleshooting ......................................................... 79
Wireless Basics ......................................................... 83
What is Wireless? .................................................. 84
Tips ........................................................................ 86
Wireless Modes ..................................................... 87
Networking Basics .................................................... 88
Check your IP address .......................................... 88
Statically Assign an IP address ............................. 89
Technical Specifications ........................................... 91
Routing ............................................................60
VPN .................................................................60
Help .................................................................61
Wireless Security ....................................................... 62
What is WEP? ........................................................62
What is WPA? ........................................................ 63
Wireless Security Setup Wizard ............................ 64
Configure WEP ...................................................... 68
Configure WPA/WPA2-PSK ...................................69
Default Factory Settings ........................................... 92
Contacting Technical Support .................................. 93
Warranty ..................................................................... 94
GNU/Linux GPL ........................................................ 100
GNU General Public License ............................... 101
Registration .............................................................. 107
ivD-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 6
Section 1 - Product Overview
Product Overview
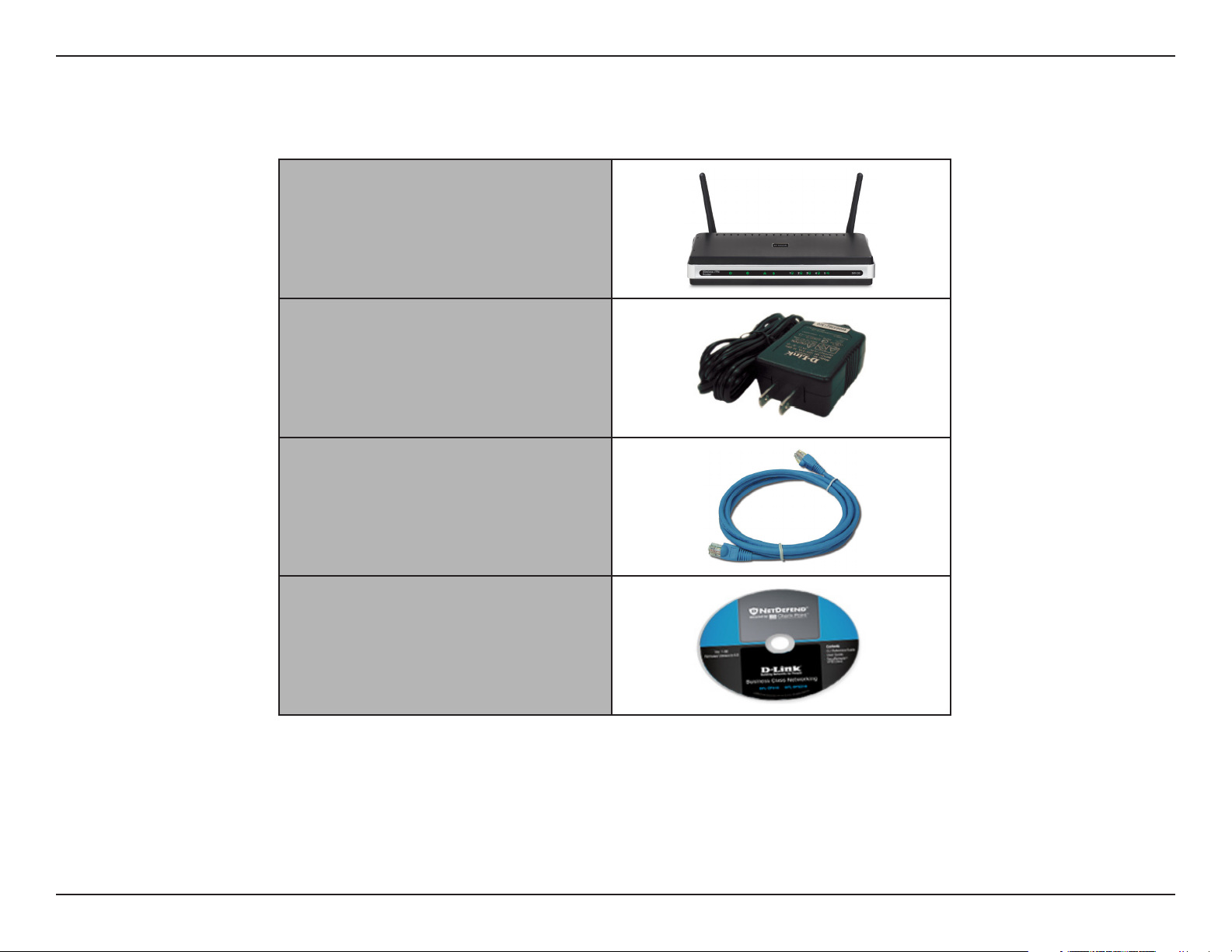
Package Contents
D-Link DIR-330 Wireless
VPN Router
Power Adapter
Ethernet Cable
CD-ROM
Note: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included with the DIR-330 will cause damage and void the warranty for this
product.
1D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 7
Section 1 - Product Overview
System Requirements
Network Requirements
Web-based Configuration
Utility Requirements
• An Ethernet-based Cable or DSL modem
• 802.11g/b wireless clients
• 10/100 Ethernet devices
Computer with the following:
• Windows®, Macintosh, or Linux-based operating
system
• An installed Ethernet adapter
Browser Requirements:
• Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher
• Mozilla 1.7.12 or higher
• Firefox 1.5 or higher
• Safari 1.0 or higher (with Java 1.3.1 or higher)
• Flock 0.7.14 or higher
• Opera 6.0 or higher
Windows® Users: Make sure you have the latest version
of Java installed. Visit www.java.com to download the
latest version.
2D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 8

Section 1 - Product Overview
• Faster Wireless Networking - The DIR-330 provides up to 54Mbps* wireless connection with other
802.11g wireless clients. This capability allows users to participate in real-time activities online, such as
video streaming, online gaming, and real-time audio.
• Compatible with 802.11b Devices - The DIR-330 is still fully compatible with the IEEE 802.11b standard,
so it can connect with existing 802.11b PCI, USB and Cardbus adapters.
• Advanced Firewall Features - The Web-based user interface displays a number of advanced network
management features including:
• Parental Controls - Easily applied content filtering based on MAC Address, URL, and/or
Domain Name.
Features
• Filter Scheduling - These filters can be scheduled to be active on certain days or for a
duration of hours or minutes.
• Secure Multiple/Concurrent Sessions - The DIR-330 can pass through VPN sessions. It
supports multiple and concurrent IPSec and PPTP sessions, so users behind the DIR-330
can securely access corporate networks.
* Maximum wireless signal rate derived from IEEE Standard 802.11g specifications. Actual data throughput will vary. Network conditions and environmental factors,
including volume of network traffic, building materials and construction, and network overhead, lower actual data throughput rate. Environmental conditions will
adversely affect wireless signal range.
3D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 9

Section 1 - Product Overview
Hardware Overview
Connections
Reset
Pressing the Reset button restores the router to
its original factory default settings.
LAN Ports (1-4)
Connect Ethernet devices such as
computers, switches, and hubs.
* The USB port is currently inactive.
Internet Port
The auto MDI/MDIX Internet
port is the connection for the
Ethernet cable to the cable or
DSL modem.
Power Receptor
Receptor for the supplied power
adapter.
4D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 10

Section 1 - Product Overview
Status LED
A blinking light indicates that the
DIR-330 is ready.
Hardware Overview
LEDs
WLAN LED
A solid light indicates that the wireless
segment is ready. This LED blinks
during wireless data transmission.
Power LED
A solid light indicates a
proper connection to the
power supply.
Internet LED
A solid light indicates connection on
the Internet port. This LED blinks
during data transmission.
Local Network LEDs
A solid light indicates a connection to an
Ethernet-enabled computer on ports 1-4.
This LED blinks during data transmission.
5D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 11

Section 2 - Installation
Installation
This section will walk you through the installation process. Placement of the router is very important. Do not place the
router in an enclosed area such as a closet, cabinet, or in the attic or garage.
Before you Begin
Please configure the router with the computer that was last connected directly to your modem. Also, you can only use
the Ethernet port on your modem. If you were using the USB connection before using the router, then you must turn off
your modem, disconnect the USB cable and connect an Ethernet cable to the Internet port on the router, and then turn
the modem back on. In some cases, you may need to call your ISP to change connection types (USB to Ethernet).
If you have DSL and are connecting via PPPoE, make sure you disable or uninstall any PPPoE software such as
WinPoet, Broadjump, or Enternet 300 from your computer or you will not be able to connect to the Internet.
6D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 12

Section 2 - Installation
Wireless Installation Considerations
The D-Link wireless router lets you access your network using a wireless connection from virtually anywhere within
the operating range of your wireless network. Keep in mind, however, that the number, thickness and location of walls,
ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must pass through, may limit the range. Typical ranges vary depending
on the types of materials and background RF (radio frequency) noise in your home or business. The key to maximizing
wireless range is to follow these basic guidelines:
1. Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the D-Link router and other network devices to a minimum
- each wall or ceiling can reduce your adapter’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.) Position your devices
so that the number of walls or ceilings is minimized.
2. Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5 meters), at a
45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet
(14 meters) thick! Position devices so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling (instead
of at an angle) for better reception.
3. Building Materials make a difference. A solid metal door or aluminum studs may have a negative effect on
range. Try to position access points, wireless routers, and computers so that the signal passes through
drywall or open doorways. Materials and objects such as glass, steel, metal, walls with insulation, water
(fish tanks), mirrors, file cabinets, brick, and concrete will degrade your wireless signal.
4. Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical devices or appliances that
generate RF noise.
5. If you are using 2.4GHz cordless phones or X-10 (wireless products such as ceiling fans, lights, and
home security systems), your wireless connection may degrade dramatically or drop completely. Make
sure your 2.4GHz phone base is as far away from your wireless devices as possible. The base transmits
a signal even if the phone in not in use.
7D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 13

Section 2 - Installation
Connect to Cable/DSL/Satellite Modem
If you are connecting the router to a cable/DSL/satellite modem, please follow the steps below:
1. Place the router in an open and central location. Do not plug the power adapter into the router.
2. Turn the power off on your modem. If there is no on/off switch, then unplug the modem’s power adapter. Shut down
your computer.
3. Unplug the Ethernet cable (that connects your computer to your modem) from your computer and place it into the
Internet port on the router.
4. Plug an Ethernet cable into one of the four LAN ports on the router. Plug the other end into the Ethernet port on your
computer.
5. Turn on or plug in your modem. Wait for the modem to boot (about 30 seconds).
6. Plug the power adapter to the router and connect to an outlet or power strip. Wait about 30 seconds for the router
to boot.
7. Turn on your computer.
8. Verify the link lights on the router. The power light, Internet light, and the LAN light (the port that your computer is
plugged into) should be lit. If not, make sure your computer, modem, and router are powered on and verify the cable
connections are correct.
9. Refer to page 11 to configure your router.
8D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 14

Section 2 - Installation
Connect to Another Router
If you are connecting the D-Link router to another router to use as a wireless access point and/or switch, you will have
to do the following before connecting the router to your network:
• Disable UPnP
• Disable DHCP
• Change the LAN IP address to an available address on your network. The LAN ports on the router cannot
accept a DHCP address from your other router.
To connect to another router, please follow the steps below:
1. Plug the power into the router. Connect one of your computers to the router (LAN port) using an Ethernet cable.
Make sure your IP address on the computer is 192.168.0.xxx (where xxx is between 2 and 254). Please see the
Networking Basics section for more information. If you need to change the settings, write down your existing settings
before making any changes. In most cases, your computer should be set to receive an IP address automatically in
which case you will not have to do anything to your computer.
2. Open a web browser and enter http://192.168.0.1 and press Enter. When the login window appears, set the user
name to Admin and leave the password box empty. Click Log In to continue.
3. Click on Advanced and then click Advanced Network. Uncheck the Enable UPnP checkbox. Click Save Settings
to continue.
™
4. Click Setup and then click Network Settings. Uncheck the Enable DHCP Server checkbox. Click Save Settings
to continue.
5. Under Router Settings, enter an available IP address and the subnet mask of your network. Click Save Settings to
save your settings. Use this new IP address to access the configuration utility of the router in the future. Close the
browser and change your computer’s IP settings back to the original values as in Step 1.
9D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 15

Section 2 - Installation
6. Disconnect the Ethernet cable from the router and reconnect your computer to your network.
7. Connect an Ethernet cable in one of the LAN ports of the router and connect it to your other router. Do not plug
anything into the Internet port of the D-Link router.
8. You may now use the other 3 LAN ports to connect other Ethernet devices and computers. To configure your wireless
network, open a web browser and enter the IP address you assigned to the router. Refer to the Configuration and
Wireless Security sections for more information on setting up your wireless network.
10D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 16
Section 3 - Configuration
Configuration
This section will show you how to configure your new D-Link wireless router using the web-based configuration
utility.
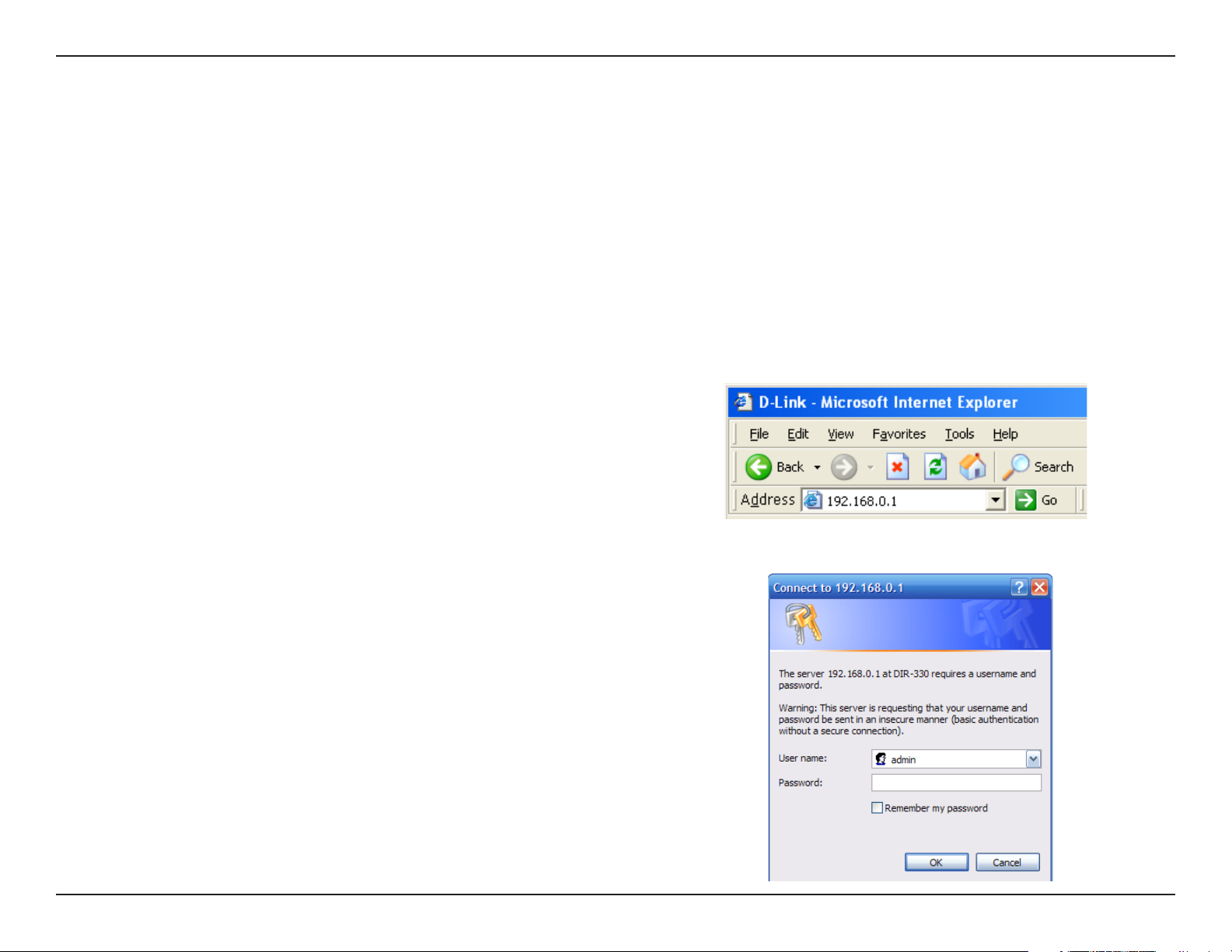
Web-based Configuration Utility
To access the configuration utility, open a web-browser such
as Internet Explorer and enter the IP address of the router
(192.168.0.1).
Enter admin as the User name field and enter the password
in the Password field. Leave the password blank by default.
If you get a Page Cannot be Displayed error, please refer
to the Troubleshooting section for assistance.
11D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 17
Section 3 - Configuration
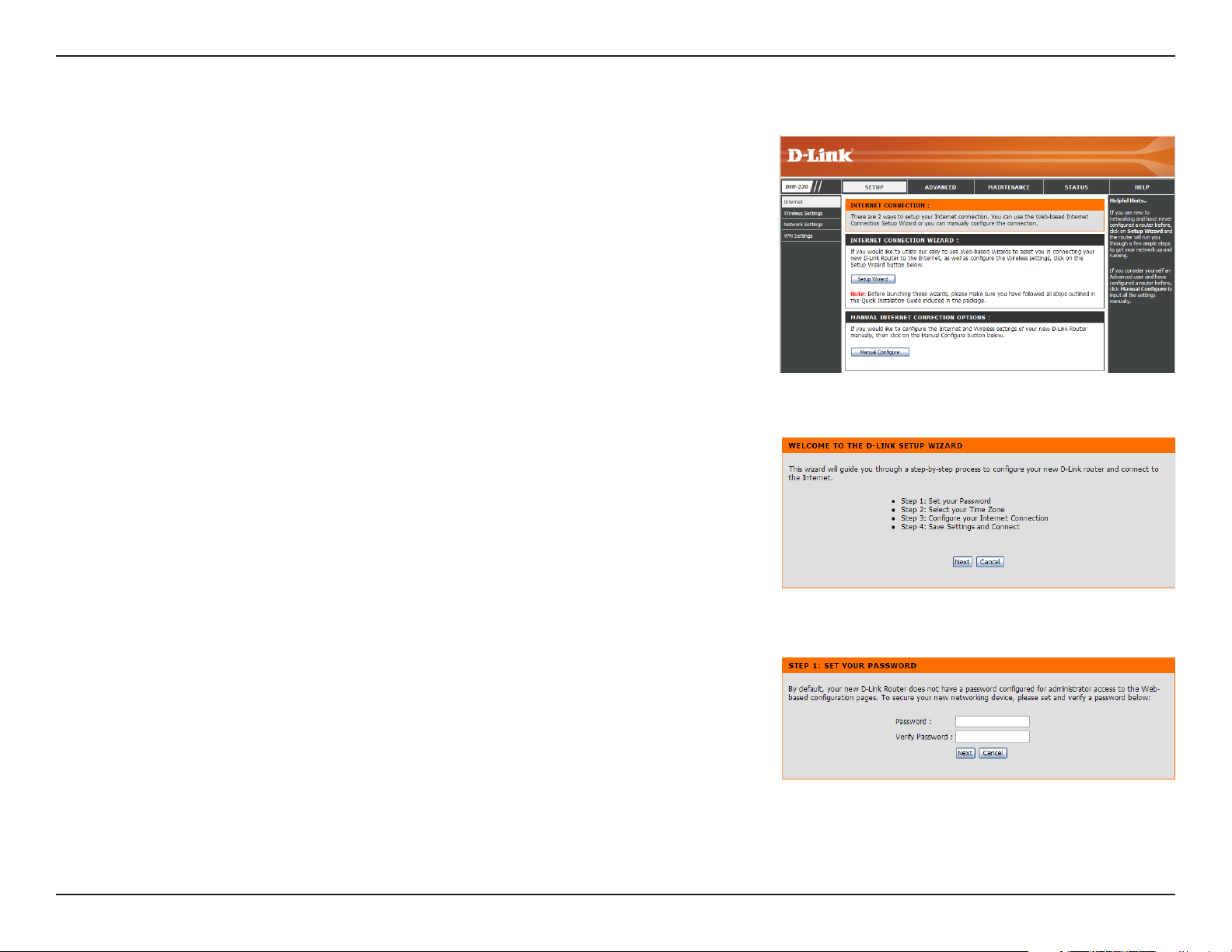
Setup Wizard
You may click Setup Wizard to quickly configure your router.
If you want to enter your settings without running the wizard, click
Manual Configure and skip to page 17.
If you want to configure your wireless settings using the Wireless
Security Setup Wizard, skip to page 64.
Click Next to continue.
Create a new password and then click Next to continue.
12D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 18
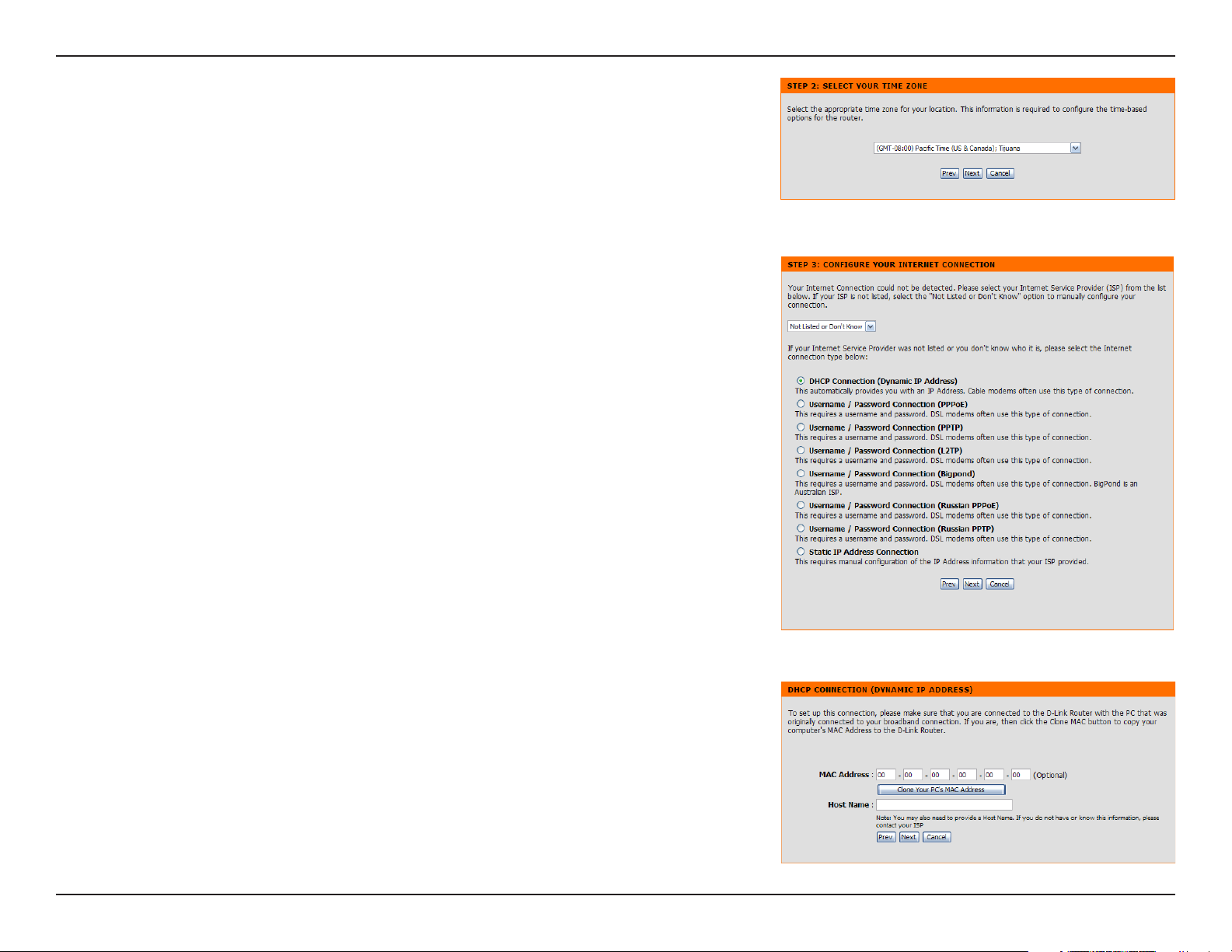
Section 3 - Configuration
Select your time zone from the drop-down menu and then click Next
to continue.
Select the type of Internet connection you use and then click Next
to continue.
If you selected Dynamic, you may need to enter the MAC address of
the computer that was last connected directly to your modem. If you are
currently using that computer, click Clone Your PC’s MAC Address and
then click Next to continue.
The Host Name is optional but may be required by some ISPs. The default
host name is the device name of the Router and may be changed.
13D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 19
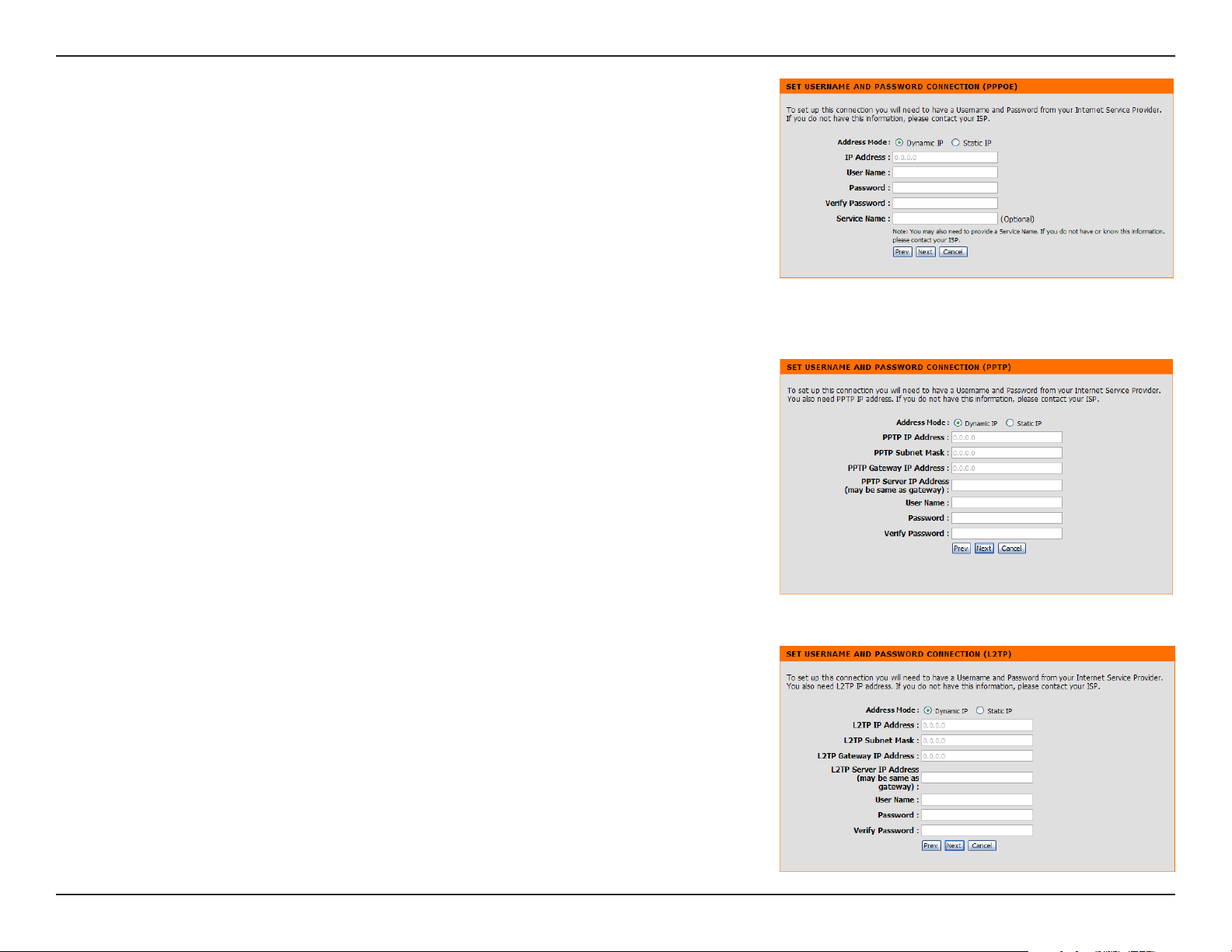
Section 3 - Configuration
If you selected PPPoE, enter your PPPoE username and password. Click
Next to continue.
Select Static if your ISP assigned you the IP address, subnet mask, gateway,
and DNS server addresses.
Note: Make sure to remove your PPPoE software from your computer. The
software is no longer needed and will not work through a router.
If you selected PPTP, enter your PPTP username and password. Click Next
to continue.
If you selected L2TP, enter your L2TP username and password. Click Next
to continue.
14D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 20
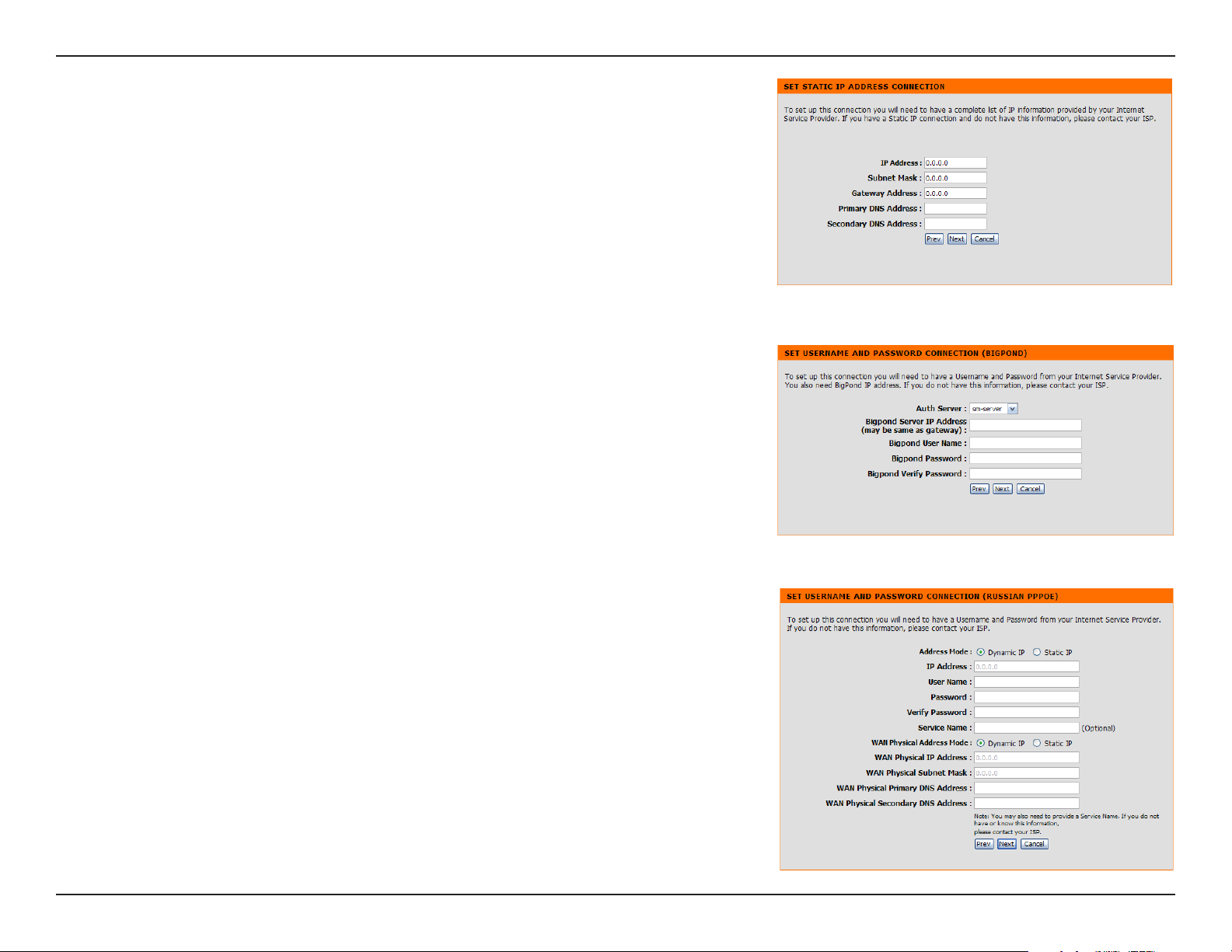
Section 3 - Configuration
If you selected Static, enter your network settings supplied by your Internet
provider. Click Next to continue.
If you selected Big Pond, select your authentication server from the drop
down menu. You will also need to enter your Big Pond username and
password. Click Next to continue.
If you selected PPPoE, enter your PPPoE username and password. Click
Next to continue.
Select Static if your ISP assigned you the IP address, subnet mask, gateway,
and DNS server addresses.
Note: Make sure to remove your PPPoE software from your computer. The
software is no longer needed and will not work through a router.
15D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 21
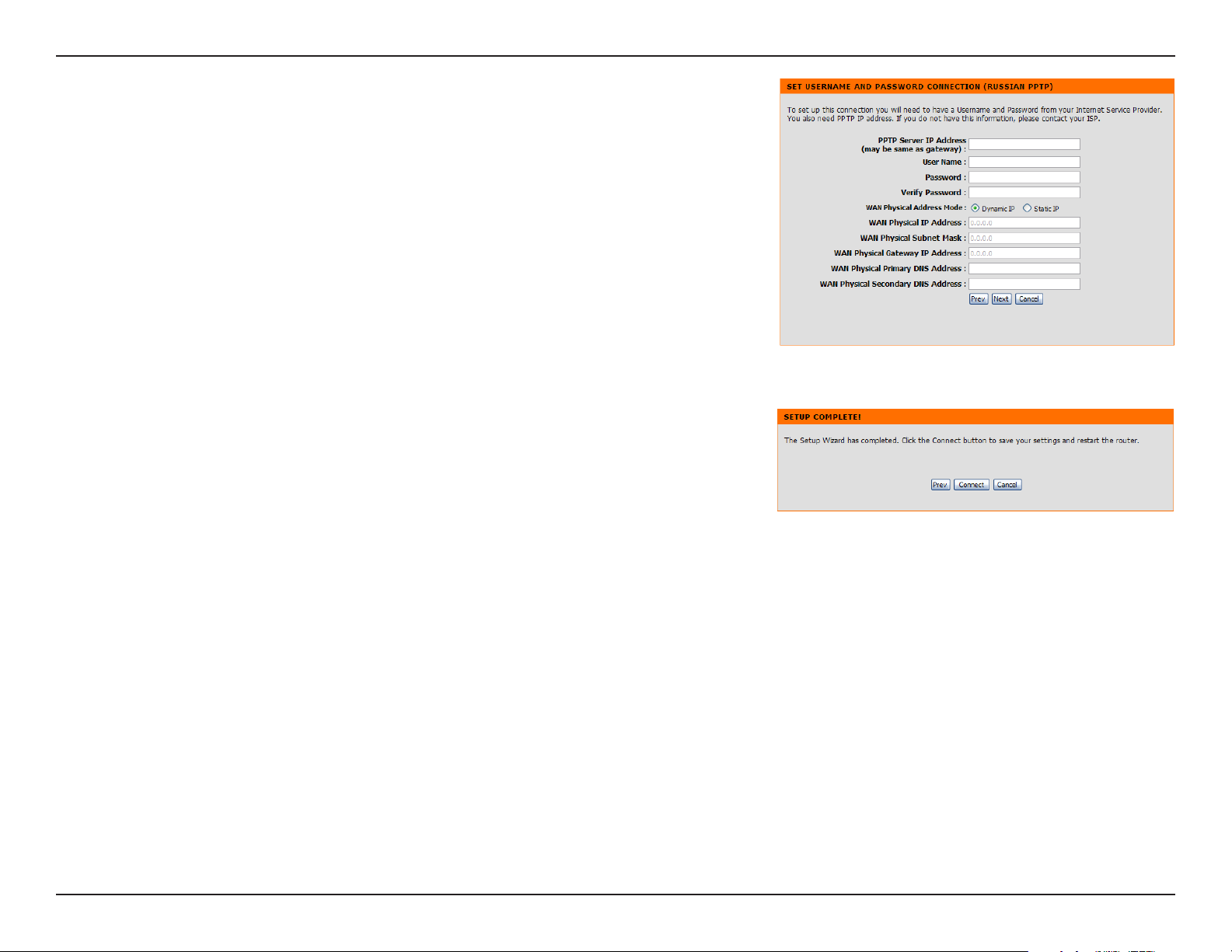
Section 3 - Configuration
If you selected PPTP, enter your PPTP username and password. Click Next
to continue.
Click Connect to save your settings. Once the router is finished rebooting,
click Continue. Please allow 1-2 minutes to connect.
Close your browser window and reopen it to test your Internet connection.
It may take a few tries to initially connect to the Internet.
16D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 22
Section 3 - Configuration
Manual Configuration
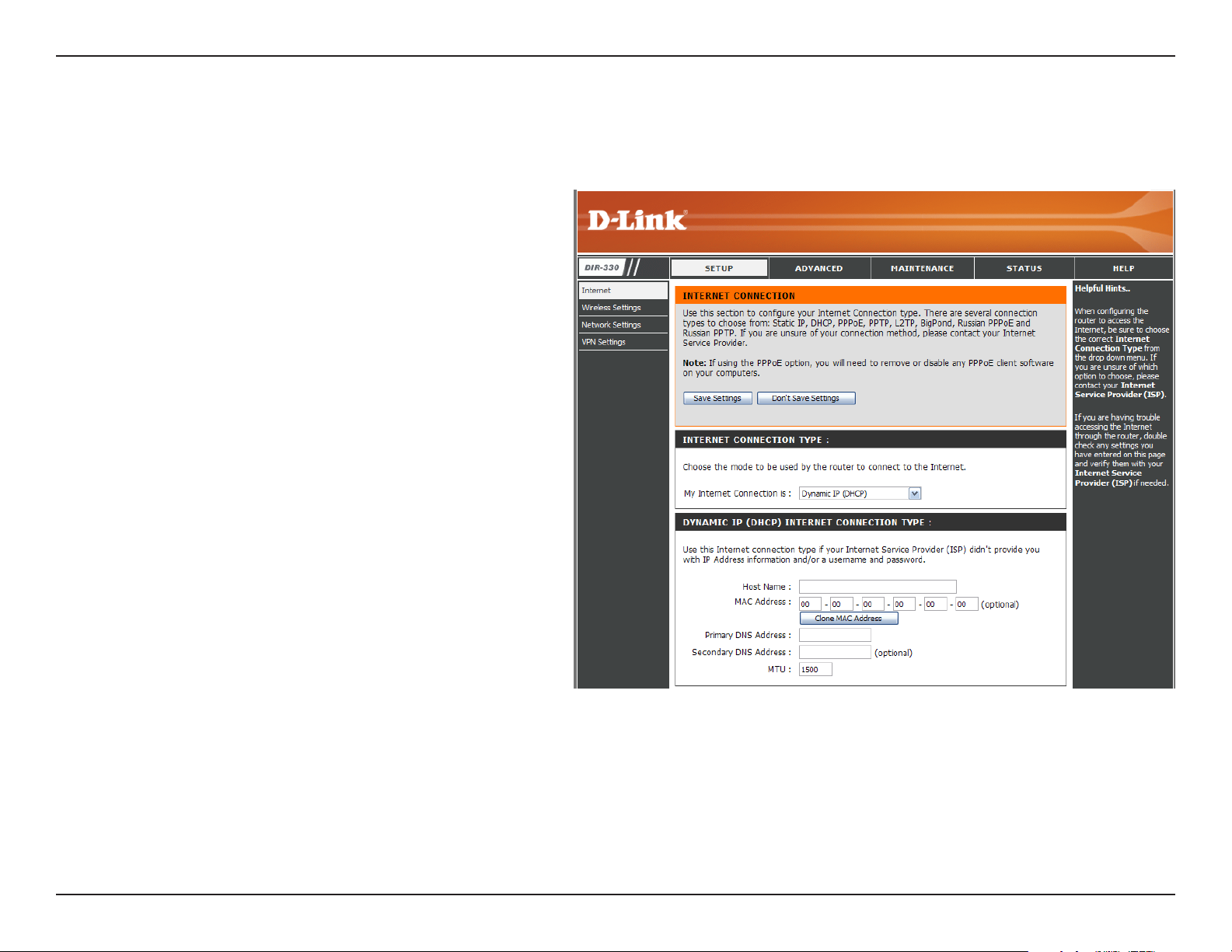
Dynamic (DHCP)
My Internet
Connection:
Host Name:
MAC Address:
DNS Addresses:
Select Dynamic IP (DHCP) to obtain IP Address
information automatically from your ISP. Select
this option if your ISP does not give you any IP
numbers to use. This option is commonly used
for Cable modem services.
The Host Name is optional but may be required
by some ISPs.
The default MAC Address is set to the Internet
port’s physical interface MAC address on the
Broadband Router. It is not recommended that
you change the default MAC address unless
required by your ISP. You can use the Clone
MAC Address button to replace the Internet
port’s MAC address with the MAC address of
your Ethernet card.
Enter the Primary and Secondary DNS server IP
address assigned by your ISP.
MTU:
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum
Transmission Unit) for optimal performance with
your specific ISP. 1500 is the default MTU.
17D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 23
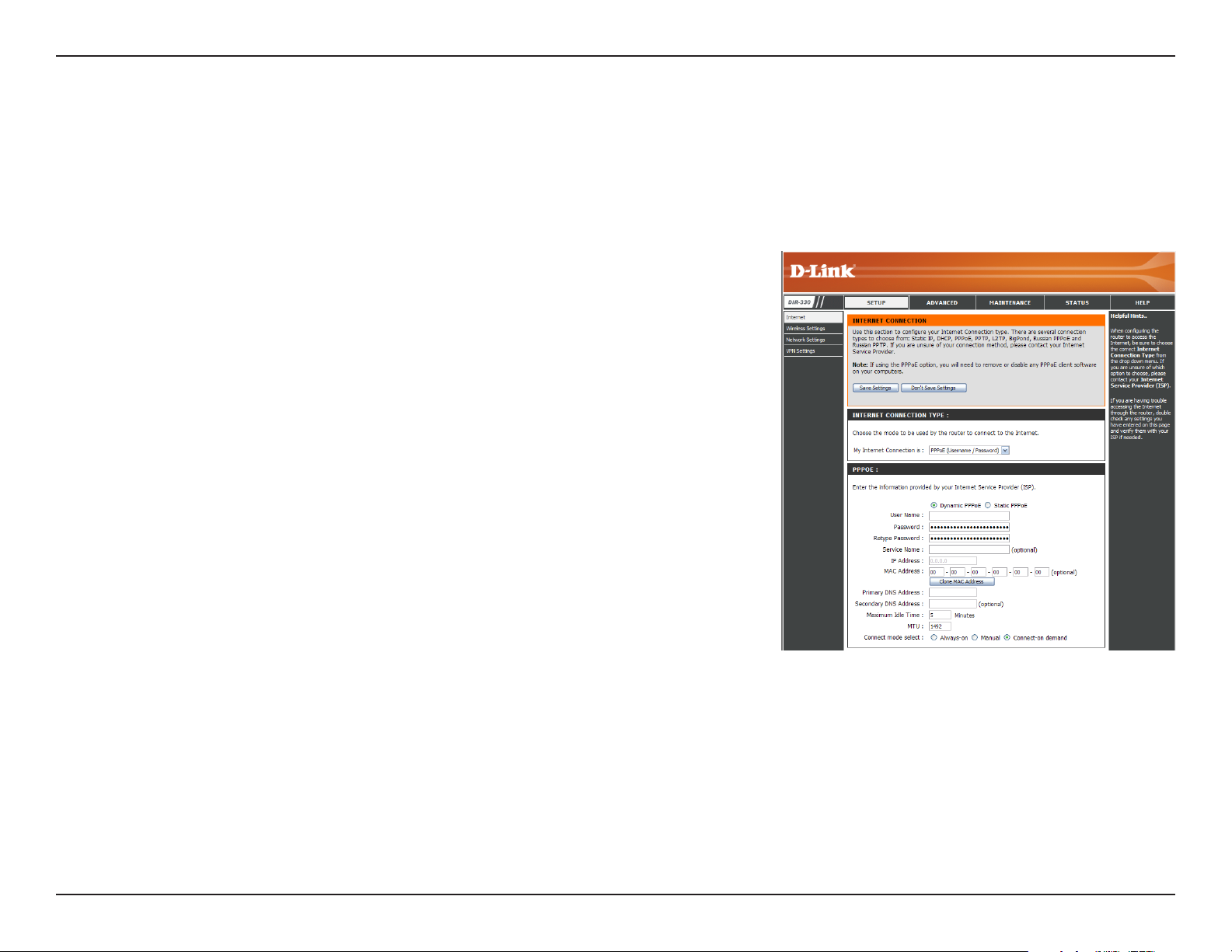
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
PPPoE (DSL)
Choose PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) if your ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP will provide
you with a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services. Make sure to remove your PPPoE
software from your computer. The software is no longer needed and will not work through a router.
My Internet
Connection:
Address Mode:
User Name:
Password:
Service Name:
IP Address:
MAC Address:
DNS Addresses:
Select PPPoE (Username/Password) from the drop-down menu.
In most cases, select Dynamic. Select Static if your ISP assigned you
the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server addresses.
Enter your PPPoE user name.
Enter your PPPoE password and then retype the password in the next
box.
Enter the ISP Service Name (optional).
Enter the IP address (Static PPPoE only).
The default MAC Address is set to the Internet port’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended that you
change the default MAC address unless required by your ISP. You can
use the Clone MAC Address button to replace the Internet port’s MAC
address with the MAC address of your Ethernet card.
Enter the Primary and Secondary DNS Server Addresses (Static PPPoE only).
Maximum Idle Time:
MTU:
Connect Mode:
Enter a maximum idle time during which the Internet connection is maintained during inactivity. To disable this feature,
enable Always-on (Connect Mode option below).
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1492 is
the default MTU.
Select either Always-on, Manual, or Connect On-Demand.
18D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 24
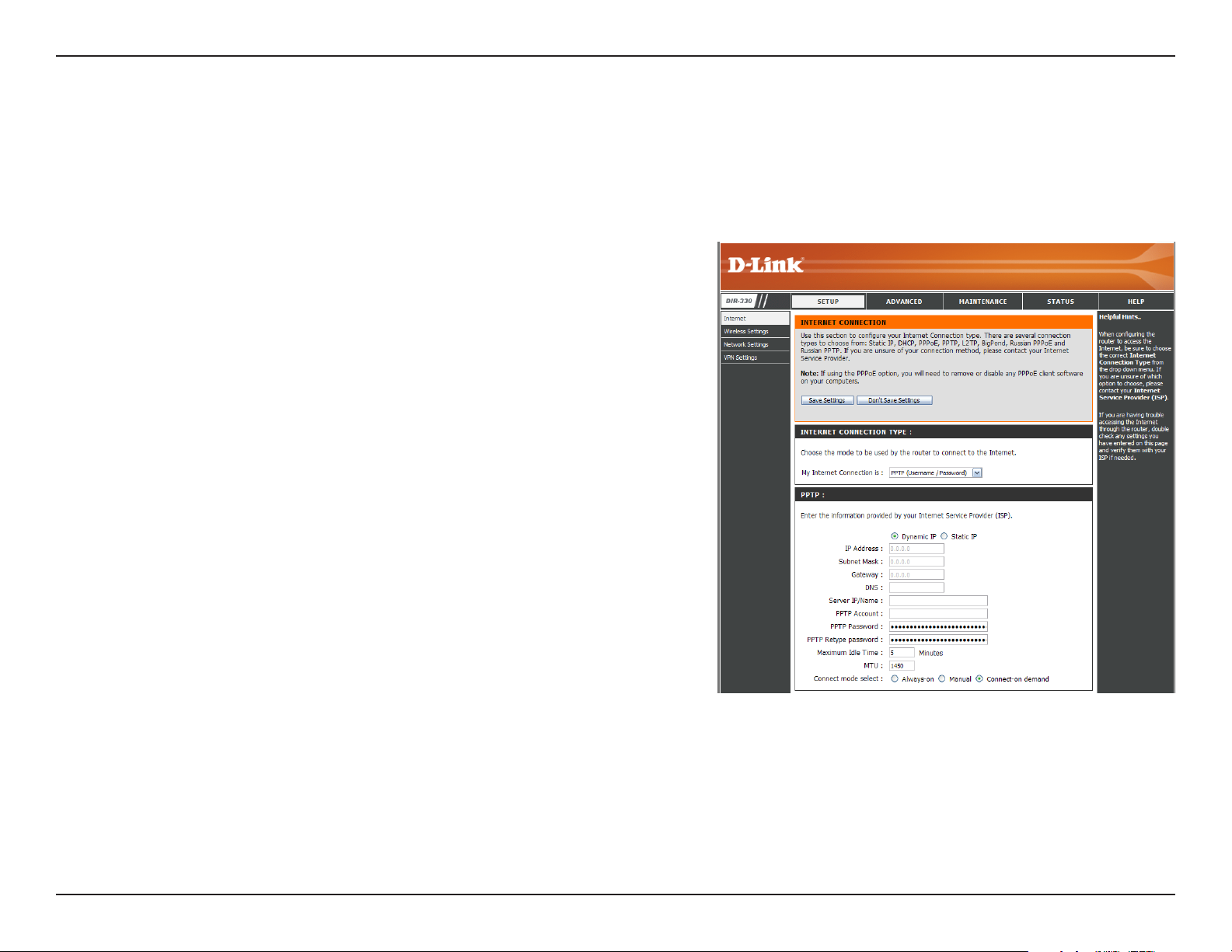
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
PPTP
Choose PPTP (Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol ) if your ISP uses a PPTP connection. Your ISP will provide you with
a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services.
Address Mode:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Gateway:
DNS:
Server IP/Name:
PPTP Account:
PPTP Password:
In most cases, select Dynamic. Select Static if your ISP assigned
you the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server
addresses.
Enter the IP address (Static PPTP only).
Enter the Primary and Secondary DNS Server Addresses (Static
PPTP only).
Enter the Gateway IP Address provided by your ISP.
The DNS server information will be supplied by your ISP (Internet
Service Provider.)
Enter the Server IP provided by your ISP (optional).
Enter your PPTP account (username).
Enter your PPTP password and then retype the password in the
next box.
Maximum Idle
Time:
MTU:
Connect Mode:
Enter a maximum idle time during which the Internet connection is maintained during inactivity. To disable this feature, enable
Always-on (Connect Mode option below).
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1450 is the
default MTU.
Select either Always-on, Manual, or Connect On-Demand.
19D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 25
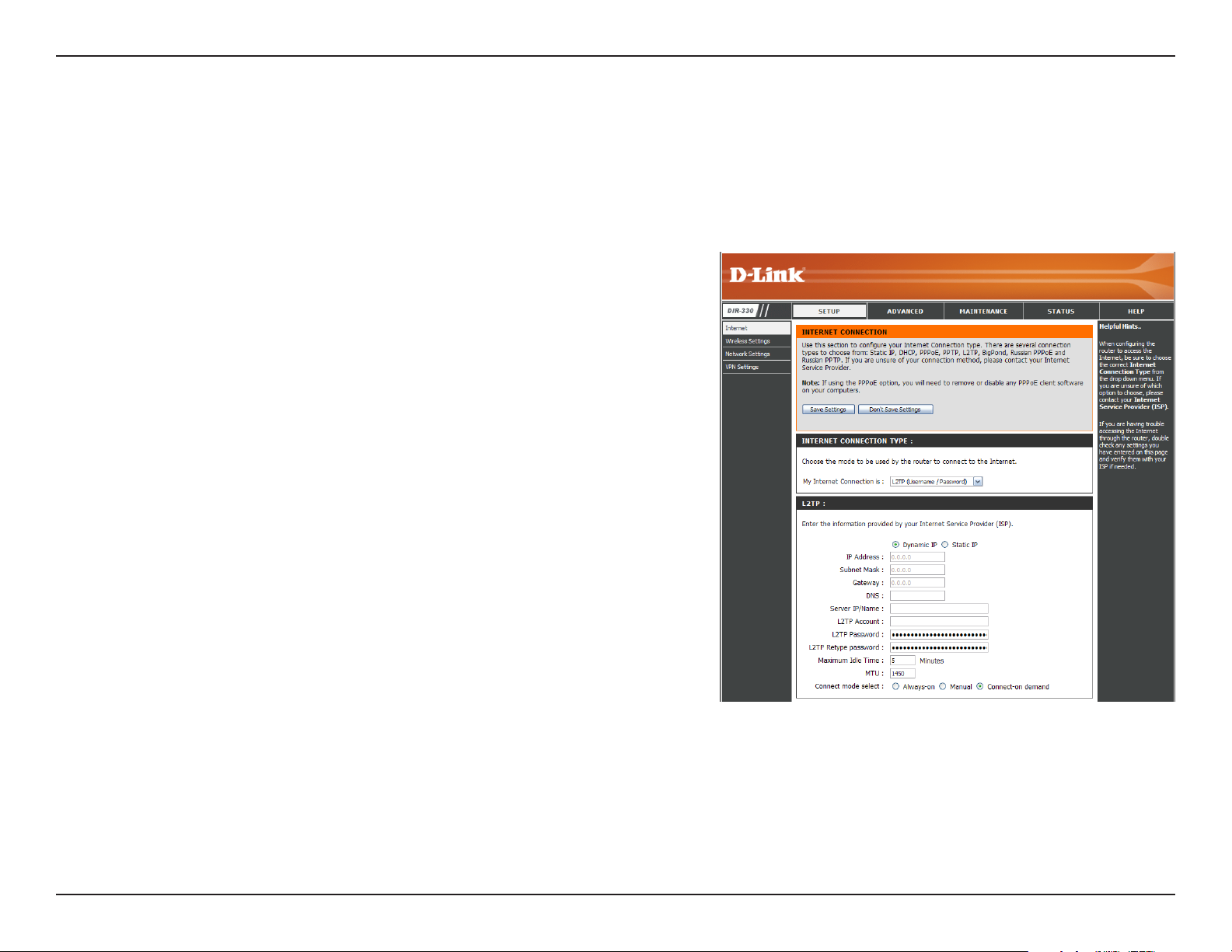
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
L2TP
Choose L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) if your ISP uses a L2TP connection. Your ISP will provide you with a username
and password. This option is typically used for DSL services.
Address Mode:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Gateway:
DNS:
Server IP/Name:
L2TP Account:
L2TP Password:
Maximum Idle Time:
Select Static if your ISP assigned you the IP address, subnet
mask, gateway, and DNS server addresses. In most cases,
select Dynamic.
Enter the L2TP IP address supplied by your ISP (Static only).
Enter the Subnet Mask supplied by your ISP (Static only).
Enter the Gateway IP Address provided by your ISP.
Enter the Primary and Secondary DNS Server Addresses (Static
L2TP only).
Enter the Server IP provided by your ISP (optional).
Enter your L2TP account (username).
Enter your L2TP password and then retype the password in the
next box.
Enter a maximum idle time during which the Internet connection
is maintained during inactivity. To disable this feature, enable Always-on (Connect Mode option below).
MTU:
Connect Mode:
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1450 is
the default MTU.
Select either Always-on, Manual, or Connect On-Demand.
20D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 26
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
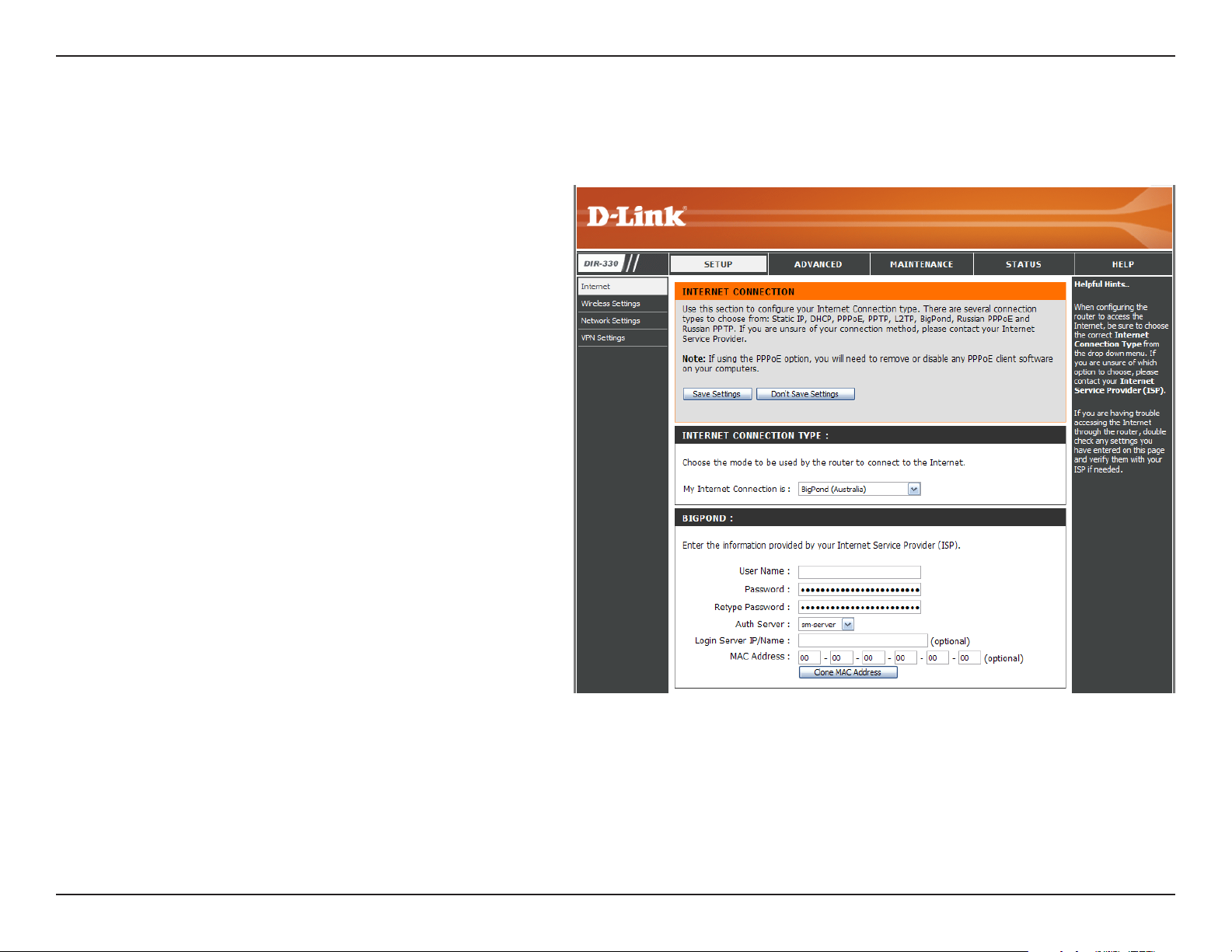
Big Pond
My Internet
Connection:
Username:
Password:
Auth Server:
Login Server IP:
MAC Address:
Select BigPond (Australia) from the drop-down
menu.
Enter your BigPond username.
Enter your BigPond password and then retype
the password in the next box.
Select the type of authentication server being
used from the drop-down menu.
Enter the IP address of the login server.
The default MAC Address is set to the
Internet’s physical interface MAC address on
the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address
unless required by your ISP. You can use the
Clone MAC Address button to replace the
Internet port’s MAC address with the MAC
address of your Ethernet card.
21D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 27
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
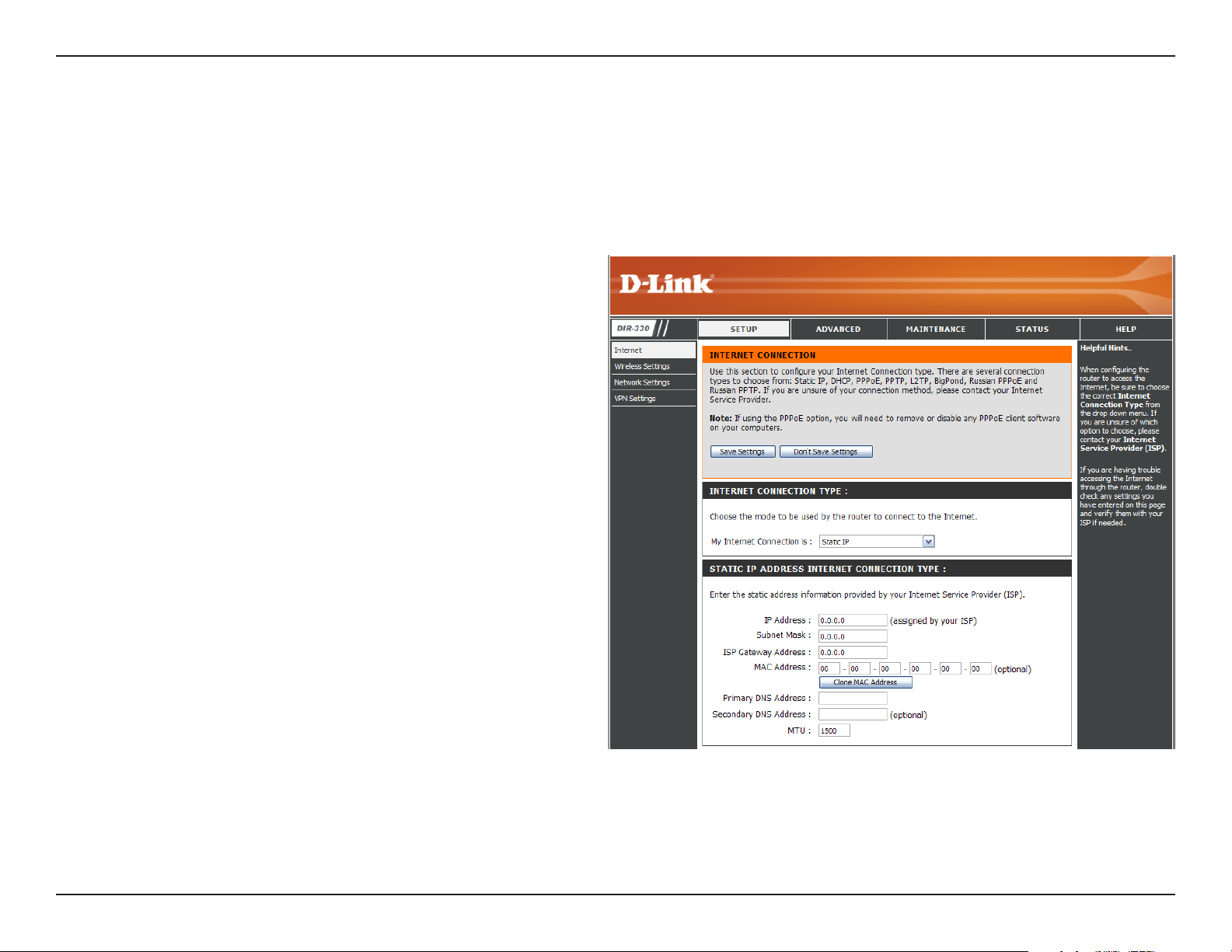
Static IP
Select Static IP Address if all the Internet port’s IP information is provided to you by your ISP. You will need to enter in the IP address,
subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS address(es) provided to you by your ISP. Each IP address entered in the fields must be in the
appropriate IP form, which are four octets separated by a dot (x.x.x.x). The router will not accept the IP address if it is not in this format.
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
ISP Gateway:
MAC Address:
DNS Servers:
MTU:
Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Enter the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
Enter the Gateway assigned by your ISP.
The default MAC Address is set to the Internet port’s
physical interface MAC address on the Broadband
Router. It is not recommended that you change the
default MAC address unless required by your ISP.
You can use the Clone MAC Address button to
replace the Internet port’s MAC address with the
MAC address of your Ethernet card.
The DNS server information will be supplied by your
ISP (Internet Service Provider.)
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum
Transmission Unit) for optimal performance with your
specific ISP. 1500 is the default MTU.
22D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 28
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
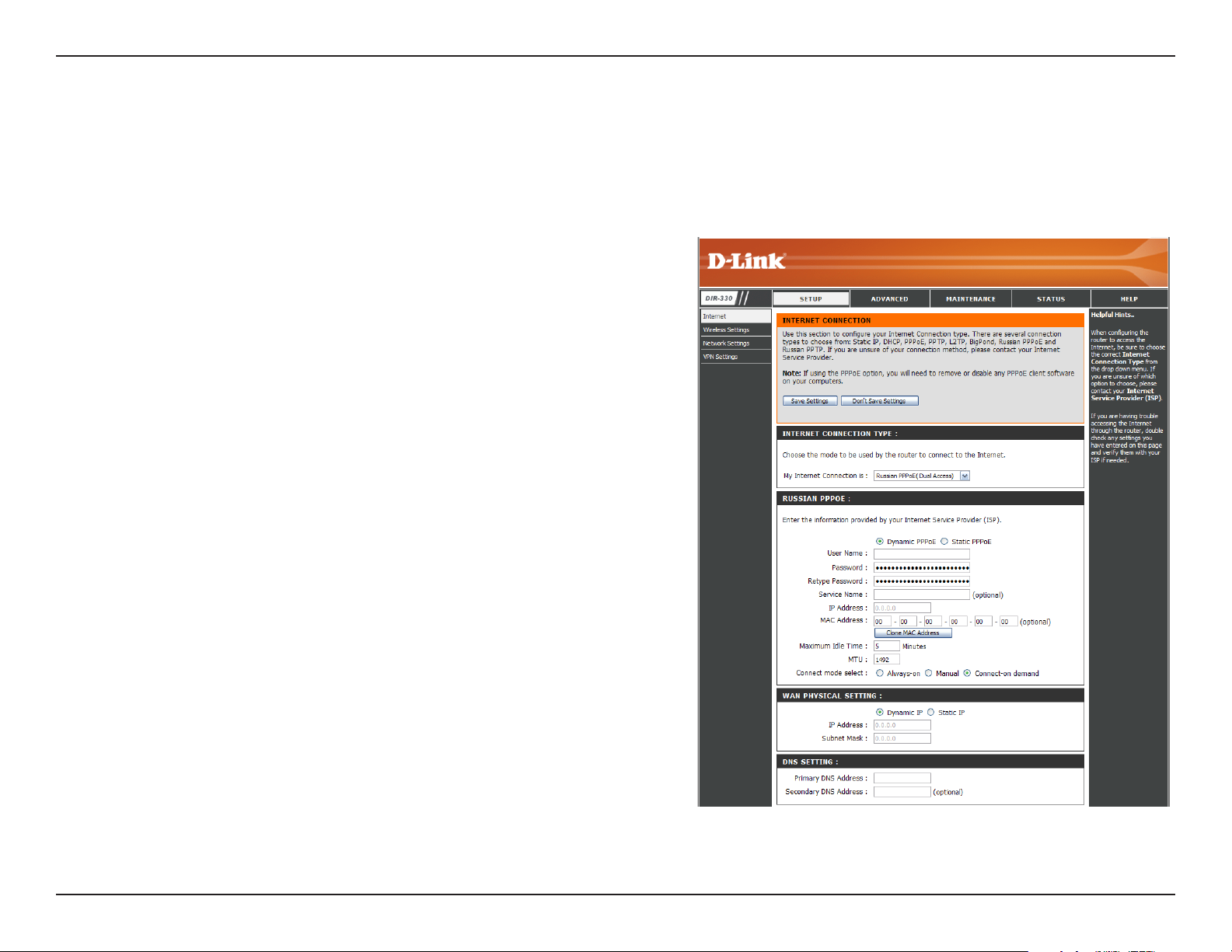
Russian PPPoE
Choose Russian PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) if your ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP will
provide you with a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services. Make sure to remove your
PPPoE software from your computer. The software is no longer needed and will not work through a router.
My Internet
Connection:
Address Mode:
User Name:
Password:
Service Name:
IP Address:
MAC Address:
Select PPPoE (Username/Password) from the drop-down
menu.
In most cases, select Dynamic. Select Static if your ISP
assigned you the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS
server addresses.
Enter your PPPoE user name.
Enter your PPPoE password and then retype the password in
the next box.
Enter the ISP Service Name (optional).
Enter the IP address (Static PPPoE only).
The default MAC Address is set to the Internet port’s physical
interface MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not
recommended that you change the default MAC address unless
required by your ISP. You can use the Clone MAC Address
button to replace the Internet port’s MAC address with the MAC
address of your Ethernet card.
Maximum Idle Time:
MTU:
Enter a maximum idle time during which the Internet connection
is maintained during inactivity. To disable this feature, enable
Always-on (Connect Mode option below).
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum Transmission
Unit) for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1492 is the default MTU.
23D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 29

Section 3 - Configuration
Connect Mode:
WAN Physical
Setting:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
DNS Addresses:
Select either Always-on, Manual, or Connect On-Demand.
In most cases, select Dynamic PPPoE. Select Static PPPoE if your ISP assigned you the IP address, subnet mask,
gateway, and DNS server addresses.
Enter the IP address (Static IP only).
Enter the Subnet Mask supplied by your ISP (Static IP only).
Enter the Primary and Secondary DNS Server Addresses (Static IP only).
24D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 30
Section 3 - Configuration
Internet Setup
Russian PPTP
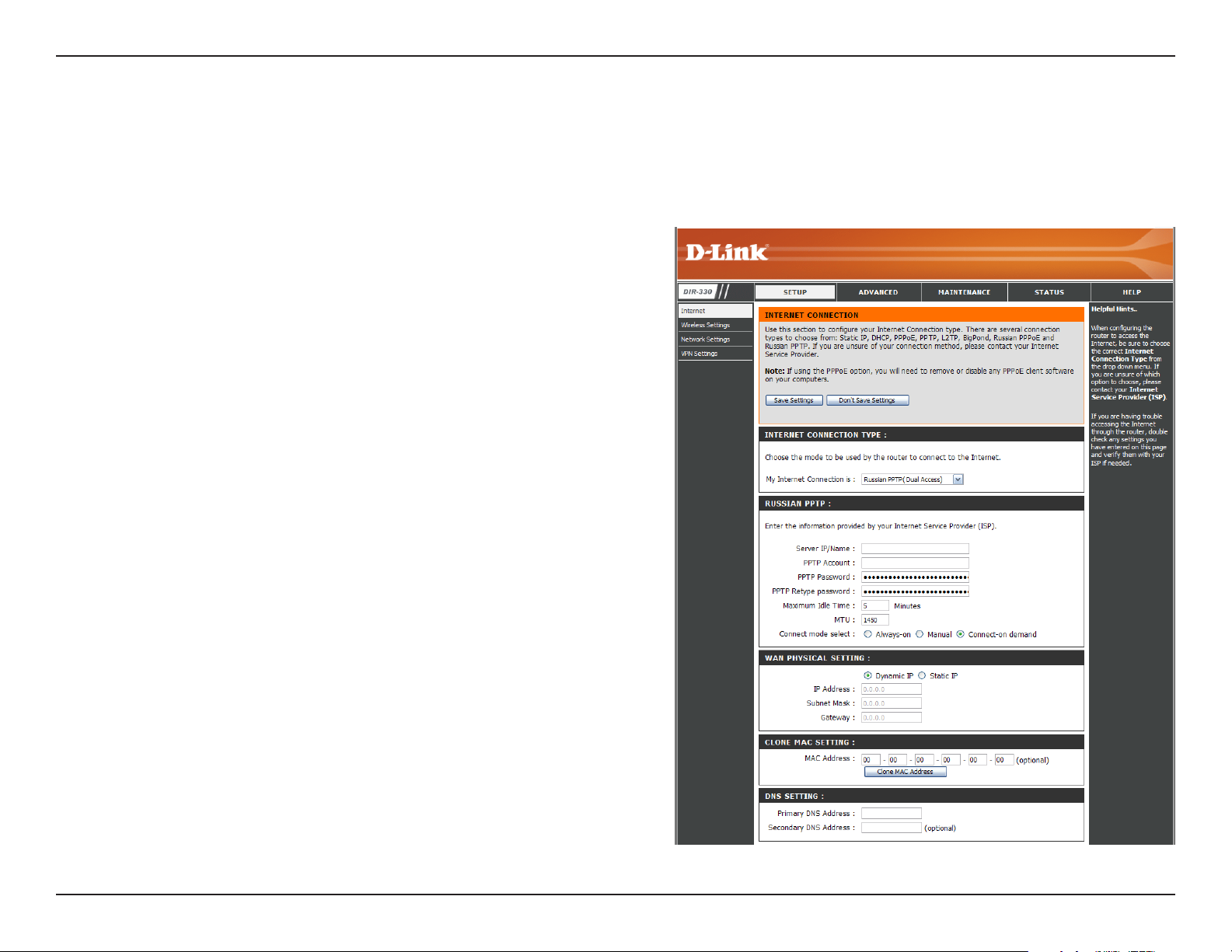
Choose Russian PPTP (Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol ) if your ISP uses a PPTP connection. Your ISP will provide
you with a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services.
Server IP/Name:
PPTP Account:
PPTP Password:
Maximum Idle
Time:
MTU:
Connect Mode:
WAN Physical
Setting:
IP Address:
Enter the Server IP provided with your ISP.
Enter your PPTP account (username).
Enter your PPTP password and then retype the password in
the next box.
Enter a maximum idle time during which the Internet connection
is maintained during inactivity. To disable this feature, enable
Always-on (Connect Mode option below).
You may need to change the MTU (Maximum Transmission
Unit) for optimal performance with your specific ISP. 1450 is
the default MTU.
Click either Always-on, Manual, or Connect-on demand.
In most cases, select either Dynamic IP. Select Static IP if your
ISP assigned you the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and
DNS server addresses.
Enter the IP address (Static IP only).
Subnet Mask:
Gateway:
Clone MAC
Setting:
DNS Setting:
Enter the Subnet Mask supplied by your ISP (Static IP
only).
Enter the Gateway provided by your ISP (Static IP only).
Click the Clone MAC Address button to copy the MAC
Address from your PC.
Enter the Primary and Secondary DNS Server Addresses (Static IP only).
25D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 31

Section 3 - Configuration
Wireless Settings
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WCN 2.0)
Enable:
Current PIN:
Reset to
Unconfigured:
Add Wireless
Device With
WPS:
Check the box to enable WPS.
WPS uses this PIN (Personal Identification
Number) to establish the wireless network. You
can generate a new PIN or reset the PIN to its
default setting.
Click this button if you don’t want to further
configure the settings of WPS and only need to
use one PIN.
Click this button if you want to add a wireless
device with WPS. In the screen that follows, you
can enter the wireless device’s PIN or click a
virtual push button to add a wireless device.
26D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 32

Section 3 - Configuration
Wireless Network Settings
Enable Wirelss:
Wireless Network
Name:
Wireless Channel:
Enable Auto Channel
Selection:
802.11 Mode:
Check the box to enable the wireless connection. If
you do not want to use wireless, uncheck the box
to disable the wireless connection.
The name of your wireless network is also called the
Service Set Identifier (SSID). Create a name using
up to 32 characters. The SSID is case-sensitive.
Indicates the channel setting for the router. The
channel can be changed to fit the channel setting
of an existing wireless network or to customize the
wireless network. If you enable Auto Channel Scan,
this option will be grayed out.
The Enable Auto Channel Scan setting can be
selected to allow the router to choose the channel
with least amount of interference. This feature is
enabled by default.
Select one of the following:
• 802.11b only – Select if all of your wireless
clients are 802.11b.
• 802.11b/g mixed – Select if you are using both
802.11b and 802.11g wireless clients.
• 802.11g only – Select if all of your wireless
clients are 802.11g.
Enable Hidden
Wireless:
Wireless Security
Mode:
Check the box if you do not want the SSID of your wireless network to be broadcasted by the router. If the box is checked,
the SSID will not be seen by site survey utilities so your wireless clients must manually enter the SSID to connect to the
router.
Refer to page 62 for more information regarding wireless security.
27D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 33

Section 3 - Configuration
Network Settings
This section will allow you to change the local network settings of the router and to configure the DHCP settings.
Router IP Address:
Default Subnet Mask:
Local Domain Name:
Enable DNS Relay:
Enter the IP address of the router. The default
IP address is 192.168.0.1. If you change the
IP address, once you click Apply, you will
need to enter the new IP address in your
browser to get back into the configuration
utility.
Enter the subnet mask. The default subnet
mask is 255.255.255.0.
Enter the domain name (Optional).
Uncheck the box to transfer the DNS server
information from your ISP to your computers.
If checked, your computers will use the router
for a DNS server.
28D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 34
Section 3 - Configuration
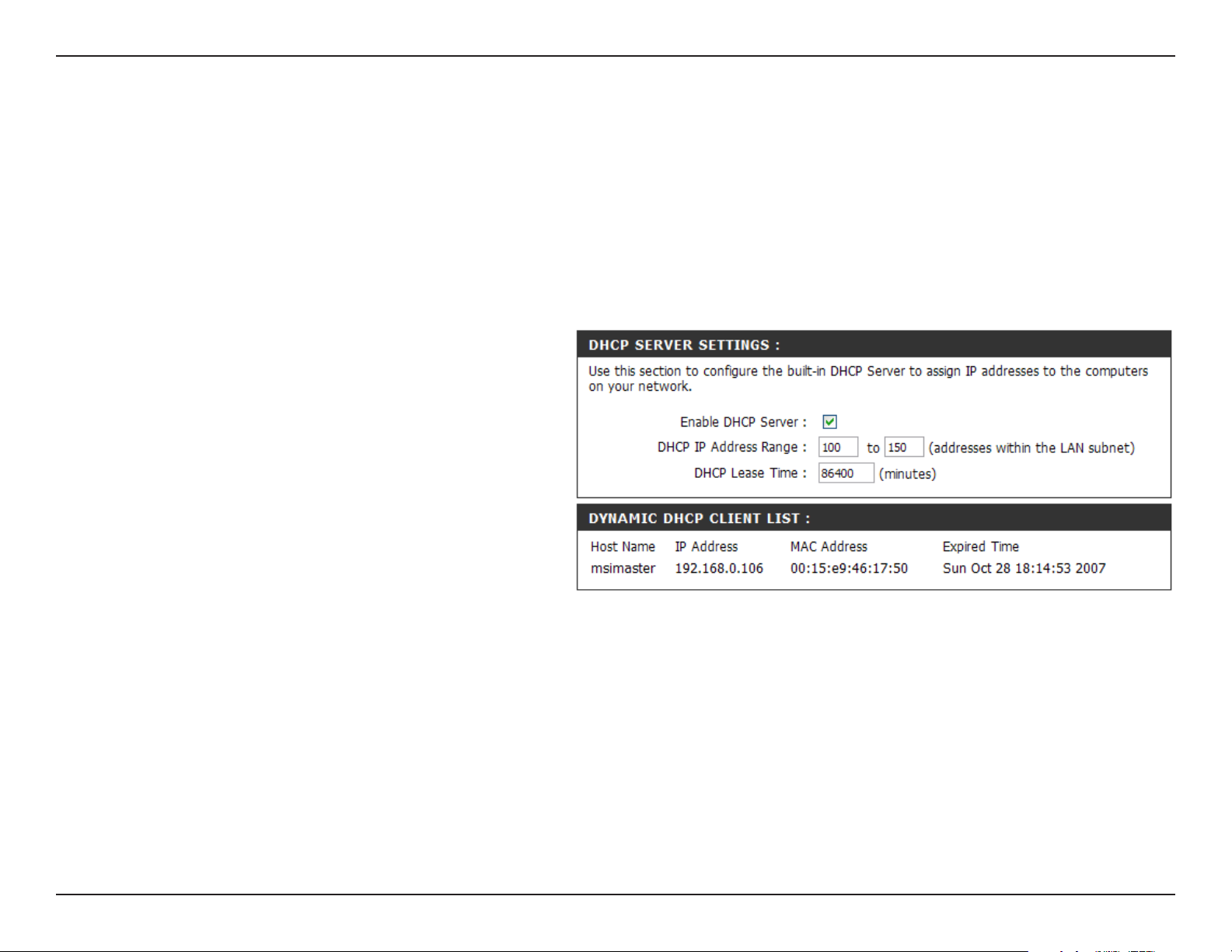
DHCP Server Settings
The router has a built-in DHCP (Dynamic Host Control Protocol) server. The DHCP server will automatically assign an
IP address to the computers on the LAN/private network. Be sure to set your computers to be DHCP clients by setting
their TCP/IP settings to “Obtain an IP Address Automatically.” When you turn your computers on, they will automatically
load the proper TCP/IP settings provided by the DIR-330. The DHCP Server will automatically allocate an unused IP
address from the IP address pool to the requesting computer. You must specify the starting and ending address of the
IP address pool.
Enable DHCP
Server:
DHCP IP Address
Range:
DHCP Lease Time:
Add DHCP
Reservation:
Check this box to enable the DHCP server on
your router. Uncheck to disable this function.
Enter the starting and ending IP addresses for
the DHCP server’s IP assignment.
Note: If you statically (manually) assign IP
addresses to your computers or devices, make
sure the IP addresses are outside of this range
or you may have an IP conflict.
The length of time for the IP address lease.
Enter the Lease time in minutes.
Refer to the next page for the DHCP Reservation
function.
29D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 35

Section 3 - Configuration
DHCP Reservation
If you want a computer or device to always have the same IP address assigned, you can create a DHCP reservation.
The router will assign the IP address only to that computer or device. You may assign up to 50 reservations.
Note: This IP address must be within the DHCP IP Address Range.
Enable:
Computer Name:
IP Address:
MAC Address:
<< Button:
Save Settings:
Check this box to enable the reservation.
Enter the computer name.
Enter the IP address you want to assign to the
computer or device. This IP Address must be
within the DHCP IP Address Range.
Enter the MAC address of the computer or
device.
If you want to assign an IP address to the
computer you are currently on, select a computer
from the last column and click the << button to
populate the fields.
Click Save Settings to save your entry and
activate the reservations.
30D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 36

Section 3 - Configuration
VPN Settings
The DIR-330 supports IPSec or L2TP VPN as the Server Endpoint.
Add VPN Profile:
Select IPSec or PPTP/L2TP VPN from the
drop-down menu and then click Add.
31D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 37

Section 3 - Configuration
IPSec Settings
Enable:
Name:
Local Net/ Mask:
Remote IP:
Check this box to enable IPSec.
Enter a name for your VPN.
Enter the local (LAN) subnet and mask.
(ex. 192.168.0.0/24)
Select Site to Site or Remote User for the
required VPN configuration.
• Site to Site - Network-to-network VPN in
which two entire LAN networks are virtually
connected across the Internet. If selected,
enter the destination gateway IP address in
the box which is the public WAN IP or host
address of the remote VPN server endpoint.
• Remote User – Client-to-server VPN in
which remote VPN clients can to connect to
the router from the Internet and access Local
Network resources.
Remote Local
LAN Net/ Mask:
Authentication:
If Site to Site is selected, enter the Destination
subnet and mask of the remote network.
(ex. 192.168.1.0/24)
Select Pre-shared Key or X.509 Certificate Authentication. One of these two authentication methods must be selected.
• Pre-shared Key - Manually enter ASCII passphrase in box.
• X.509 Certificate - For certificate authentication, certificates must be manually uploaded to the router. See the “Certificates”
section for details.
32D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 38

Section 3 - Configuration
• Additional Authentication Methods (Optional)
XAUTH - Check this box to include additional username and password authentication requirements for the VPN.
Select Server Mode or Client Mode.
• Server Mode - Select a group from the Authentication database drop-down menu containing the list
of user credentials permitted.
• Client Mode - Enter the user name and password if required by the remote VPN server endpoint
configured in xAuth Server Mode.
Local/Remote ID - Check this box to include additional ID authentication requirements for the VPN using a specific
IP Address, FQDN, ASN1, or a Custom String.
• Local ID - Select one of the options from the drop-down menu. Enter an ID to identify and authenticate
the local VPN endpoint.
• Remote ID - Select one of the options from the drop-down menu. Enter an ID to identify and authenticate
the remote VPN endpoint.
Main / Aggressive Mode:
NAT-T Enable:
Select Main Mode or Aggressive Mode for IKE Phase 1 negotiation.
• Main Mode - Select this option to configure the standard negotiation parameters for IKE Phase 1 of
the VPN Tunnel. (Recommended Setting)
• Aggressive Mode - Select this option to configure IKE Phase 1 of the VPN Tunnel to carry out
negotiation in a shorter amount of time. (Not Recommended - Less Secure)
Check this box to enable NAT Traversal. Enabling this option will allow IPSec traffic from this endpoint to traverse
through the translation process during NAT. The remote VPN endpoint must also support this feature and it must
be enabled to function properly over the VPN.
33D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 39

Section 3 - Configuration
Keep Alive / DPD:
DH Group:
IKE Proposal List:
Sel ect None, Kee p Ali ve, or DPD (Dead Pe er
Connection).
• None - Select this option to disable Keep Alive.
• Keep Alive - Select this option to send random ping
requests from this endpoint to the remote endpoint
keeping the tunnel established during long idle
periods of inactivity.
• DPD - Select this option to delete the VPN tunnel if
there is no traffic detected. The VPN will re-establish
once traffic is again sent through the tunnel.
Select a DH Group from the drop-down menu. As the DH
Group number increases, the higher the level of encryption
implemented for Phase 1.
Select the Cipher and Hash from the drop-down menus.
The proposal listing is evaluated in order with #1 being the
first proposal to attempt in IKE negotiation.
IKE Lifetime:
PFS Enable:
PFS DH Group:
IPSec Proposal List:
IPSec Lifetime:
Enter the number of seconds for the IKE Lifetime. The period of time to pass before establishing a new IKE security
association (SA) with the remote endpoint. The default value is 28800.
Check to enable or uncheck to disable. PFS is an additional security protocol.
Select a PFS DH Group from the drop-down menu. As the DH Group number increases, the higher the level of
encryption implemented for PFS.
Select the Cipher and Hash from the drop-down menus. The proposal listing is evaluated in order with #1 being
the first proposal to attempt in IPSec negotiation.
Enter the number of seconds for the IPSec Lifetime. The period of time to pass before establishing a new IPSec
security association (SA) with the remote endpoint. The default value is 3600.
34D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 40

Section 3 - Configuration
PPTP/L2TP Settings
PPTP uses TCP port 1723 for its control connection and uses GRE (IP protocol 47) for the PPP data. PPTP supports
data encryption by used MPPE. L2TP uses UDP protocol to transport the PPP data. This is often encapsulated in IPsec
encryption instead of MPPE.
Enable Setting:
Name:
Connection Type:
VPN Server IP:
Remote IP Range:
Authentication
Protocol:
MPPE Encryption
Mode:
Check this box to enable.
Enter a name for your VPN.
Select PPTP, L2TP, or L2TP over IPsec.
Enter the VPN Server IP address which is the
LAN IP of the router. (i.e. 192.168.0.1).
Assign a range of IP addresses. The assigned IP
range should be on the same IP network but not
the in the same range as your DHCP IP range.
For example, if your network is 192.168.0.xxx
and you set the DHCP range to 192.168.0.100200, the remote IP range cannot be within
192.168.0.100-200.
Select the desired authentication protocol (PAP/
CHAP/MS-CHAP v2).
Select the level of encryption (None/40-bit/128bit).
Authentication
Database:
Select a user group from the drop-down menu.
You can create user groups in the Advanced
> User Group section.
35D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 41

Section 3 - Configuration
Port Forwarding
This will allow you to open a single port or a range of ports.
Name:
IP Address:
Port:
Traffic Type:
Schedule:
Enter a name for the rule or select an application
from the drop-down menu. Select an application
and click << to populate the fields.
Enter the IP address of the computer on your
local network that you want to allow the incoming
service to. If your computer is receiving an IP
address automatically from the router (DHCP), you
computer will be listed in the “Computer Name”
drop-down menu. Select your computer and click
<<.
Enter a port range for the public and private
ports.
Select the type of protocol you would like to assign
to the rule.
The schedule of time when the Port Forward Rule will be enabled. The schedule may be set to Always, which will allow the
particular service to always be enabled. You can create your own times in the Maintenance > Schedules section.
36D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 42

Section 3 - Configuration
Application Rules
Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet gaming, video conferencing, Internet telephony and
others. These applications have difficulties working through NAT (Network Address Translation). Special Applications
makes some of these applications work with the DIR-330. If you need to run applications that require multiple connections,
specify the port normally associated with an application in the “Trigger Port” field, select the protocol type as TCP or
UDP, then enter the firewall (public) ports associated with the trigger port to open them for inbound traffic.
Name:
Trigger:
Firewall:
Traffic Type:
Schedule:
Enter a name for the rule. You may select a
pre-defined application from the drop-down
menu and click <<.
This is the port used to trigger the application. It
can be either a single port or a range of ports.
This is the port number on the Internet side
that will be used to access the application. You
may define a single port or a range of ports.
You can use a comma to add multiple ports or
port ranges.
Select the protocol of the firewall port (TCP,
UDP, or Any).
The schedule of time when the Application Rule
will be enabled. The schedule may be set to
Always, which will allow the particular service
to always be enabled. You can create your own times in the Maintenance > Schedules section.
37D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 43

Section 3 - Configuration
MAC Filters
Use MAC (Media Access Control) Filters to allow or deny LAN (Local Area Network) computers by their MAC addresses
from accessing the Network. You can either manually add a MAC address or select the MAC address from the list of
clients that are currently connected to the router. You may enter up to 25 rules.
Configure MAC
Filtering:
MAC Address:
DHCP Client:
Clear:
Select Turn MAC Filtering Off, Turn MAC
filtering on and ALLOW computers listed to
access the network, or Turn MAC filtering on
and DENY computers listed to access the
network from the drop-down menu.
Enter the MAC address you would like to filter.
To find the MAC address on a computer, please
refer to the Networking Basics section in this
manual.
Select a DHCP client from the drop-down menu
and click << to copy that MAC Address.
Click to delete the settings of the filter rule.
38D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 44

Section 3 - Configuration
Website Filters
Website Filters are used to deny LAN computers from accessing specific web sites by the URL or domain. A URL is a
specially formatted text string that defines a location on the Internet. If any part of the URL contains the blocked word,
the site will not be accessible and the web page will not display. To use this feature, enter the text string to be blocked
and click Save Settings. The text to be blocked will appear in the list. To delete the text, click the Clear the List Below
button.
Configure Website
Filtering:
Website URL/
Domain:
Schedule:
Select Turn Website Filtering Off, Turn
Website filtering on and ALLOW computers
listed to access the network, or Turn Website
filtering on and DENY computers listed
to access the network from the drop-down
menu.
Enter the keywords or URLs that you want to
block (or allow). Any URL with the keyword in it
will be blocked or allowed.
The schedule of time when the selected rule
will be enabled. The schedule may be set to
Always, which will allow the filter to always be
enabled. You can create your own times in the
Maintenance > Schedules section.
39D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 45

Section 3 - Configuration
Firewall Settings
DMZ
A firewall protects your network from the outside world. The router offers a firewall protection such as SPI (Stateful
Packet Inspection) and NAT/PAT (Network Address Translation/Port Address Translation). Sometimes you may want a
computer exposed to the outside world for certain types of applications. If you choose to expose a computer, you can
enable DMZ (Demilitarized Zone). This option will expose the chose computer completely to the outside world.
Enable DMZ Host:
DMZ IP Address:
Schedule:
If an application has trouble working from
behind the router, you can expose one
computer to the Internet and run the application
on that computer.
Note: Placing a computer in the DMZ may
expose that computer to a variety of security
risks. This option is only recommended as a
last resort.
Specify the IP address of the computer on the
LAN that you want to have unrestricted Internet
communication. If this computer obtains its IP
address automatically using DHCP, be sure
to make a static reservation on the Internet >
DHCP page so that the IP address of the DMZ
machine does not change.
The schedule of time when the DMZ will be enabled. The schedule may be set to Always, which will allow the DMZ to always
be enabled. You can create your own times in the Maintenance > Schedules section.
40D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 46

Section 3 - Configuration
Firewall Settings
Firewall Rules
Up to 75 Firewall Rules can be created to control the incoming and outgoing traffic on your router. For each rule you
can create a name and control the direction of traffic. You can also allow or deny a range of IP Addresses, protocol and
a port range. In order to apply a schedule to a Firewall Rule, you must first define a schedule on the Maintenance >
Schedules page. The first 2 Firewall Rules are default and cannot be changed.
Name:
Schedule:
Source/Dest:
IP Address Range:
Protocol:
Enter a name for your Firewall Rule.
Select a schedule from the drop-down menu. In
order to apply a schedule to a Firewall Rule, you
must first define a schedule on the Maintenance >
Schedules page.
This setting controls the direction of traffic. To control
incoming traffic, set the Source Interface to WAN
and the Dest Interface to LAN. To control outgoing
traffic, set the Source Interface to LAN and the Dest
Interface to WAN.
Enter the IP Address Range for both the Source
Interface and Dest Interface. These IP Address
Ranges will be either allowed or denied, depending
on the selected action.
Select a protocol from the drop-down menu. The
protocol that is selected will be either allowed or
denied, depending on the selected action.
Port Range:
Enter a Port Range. The Port Range that is entered
will be either allowed, or denied, depending on the
selected action.
41D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 47

Section 3 - Configuration
Advanced Wireless Settings
Tx Rate:
Beacon Interval:
RTS Threshold:
Fragmentation:
DTIM Interval:
Select the basic transfer rates based on the speed
of wireless adapters on your wireless network. It is
strongly recommended to keep this setting to Auto.
Beacons are packets sent by an Access Point to
synchronize a wireless network. Specify a value. 100
is the default setting and is recommended.
This value should remain at its default setting of 2436.
If inconsistent data flow is a problem, only a minor
modification should be made.
The fragmentation threshold, which is specified
in bytes, deter mines whether packets will be
fragmented. Packets exceeding the 2346 byte setting
will be fragmented before transmission. 2346 is the
default setting.
A DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and
multicast messages. 1 is the default setting.
Preamble Type:
WMM Function:
Select Short or Long Preamble. The Preamble defines the length of the CRC block (Cyclic Redundancy Check is a common
technique for detecting data transmission errors) for communication between the wireless router and the roaming wireless
network adapters. Long is the default setting. Note: High network traffic areas should use the shorter preamble type.
WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) provides QoS (Quality of Service) for your wireless network. Enable this option to improve the quality
of video and voice applications for your wireless clients.
42D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 48

Section 3 - Configuration
Advanced Network Settings
UPnP:
Enable WAN Ping
Respond:
WAN Port Speed:
To use the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP™)
feature click on the checkbox to enable. UPNP
provides compatibility with networking equipment,
software and peripherals.
Unchecking the box will not allow the DIR-330 to
respond to pings. Blocking the Ping may provide
some extra security from hackers. Check the box
to allow the Internet port to be “pinged”.
You may set the port speed of the Internet port to
10Mbps, 100Mbps, or Auto. Some older cable
or DSL modems may require you to set the port
speed to 10Mbps.
43D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 49

Section 3 - Configuration
Routing
This section allows you to define static routes for the WAN types of Static IP, Dynamic IP, Russian PPPoE, and Russian
PPTP with ISPs that require these parameters. Up to 50 Static Routing Rules can be defined.
Interface:
Destination
Address:
Subnet Mask:
Gateway:
Metric:
Select WAN or WAN_Physical from the drop
down menu. Only select WAN_Physical if your
Internet connection type is Russian PPPoE or
Russian PPTP.
Enter the destination address for the static routing
rule.
Enter the subnet mask for the static routing rule.
Enter the gateway for the static routing rule.
Enter the metric for the static routing rule.
44D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 50

Section 3 - Configuration
Certificates
This section is used to configure Certificates that are used with an IPSec based VPN. You can configure local certificates
and the certificates of remote peers. Select one of the three options from the drop-down menu: Local Certificate &
Private key, Certificate of Remote Peers, or Certificate Authorities.
Local Certificate
& Private Key:
Certificate of
Remote Peers:
Certificate
Authorities:
Select this option from the drop-down menu to
configure your local certificates. Enter a name
for the certificate. Click the browse button to look
for the Private Key and the certificate on your
computer.
Select this option from the drop-down menu to
configure the certificates of remote peers. Enter
a name for the certificate. Click the browse button
on your computer to look the Private Key on your
computer.
Select this option from the drop-down menu to
configure Certificate Authority (CA) files to be
used with your router. Enter a name for the CA
file. Click the browse button to look for the CA file
on your computer.
45D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 51

Section 3 - Configuration
User Groups
This section is used to configure Certificates that are used with an IPSec based VPN. You can configure local certificates
and the certificates of remote peers. Select one of the three options from the drop-down menu: Local Certificate &
Private key, Certificate of Remote Peers, or Certificate Authorities.
Authentication
Database:
Group Name:
User Name:
Select a user group from the menu and click the
EDIT button to configure that group.
Enter a name for the user group. Click the Clear
the list below button to erase all of the user
names and passwords for the user group.
Enter the User Name.
Password:
Enter the Password.
46D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 52

Section 3 - Configuration
Administrator Settings
This page will allow you to change the Administrator password. You can also enable Remote Management.
Admin Password:
Enable Remote
Management:
IP Address:
Port:
Enter a new password for the administrator
login. Only the administrator can make changes
to the settings.
Remote management allows the router to be
configured from the Internet by a web browser.
A username and password is still required
to access the Web-Management interface.
In general, only a member of your network
can browse the built-in web pages to perform
Administrator tasks. This feature enables you
to perform Administrator tasks from the remote
(Internet) host.
Enter the IP address of the remote computer.
You may enter * to allow a connection from any
Internet address.
The port number used to access the DIR-330.
Example: http://x.x.x.x:8080 whereas x.x.x.x
is the Internet IP address of the DIR-330 and
8080 is the port used for the Web Management
interface. The schedule may be set to Always,
which will allow the filter to always be enabled. You
can create your own times in the Maintenance
> Schedules section.
47D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 53

Section 3 - Configuration
Time and Date Settings
The Time and Date page allows you to configure, update, and maintain the correct time and date on the internal system
clock. From this section you can set the time zone that you are in and set the Time Server. Daylight Saving can also
be configure to automatically adjust the time when needed.
Time Zone:
Enable Daylight
Saving:
Sync. Your
computer’s time
settings:
Automatic
Time and Date
Configuration:
NTP Server Used:
Manual:
Select the Time Zone from the drop-down
menu.
Check the checkbox to enable daylight savings
time.
Click this button to copy the time settings from
your computer.
Check the box to use NTP (Network Time
Protocol) server. NTP synchronizes computer
clock times in a network of computers. This will
only connect to a server on the Internet, not a
local server.
Select an NTP server from the drop-down
menu.
To manually input the time, enter the values
in these fields for the Year, Month, Day, Hour,
Minute, and Second and then click Save
Settings.
48D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 54

Section 3 - Configuration
System Settings
Save Settings to
Local Hard Drive:
Load Settings
from Local Hard
Drive:
Restore to Factory
Default Settings:
Use this option to save the current router
configuration settings to a file on the hard disk
of the computer you are using. First, click the
Save Configuration button. You will then see a
file dialog, where you can select a location and
file name for the settings.
Use this option to load previously saved
router configuration settings. First, click the
Browse button to find a previously save file of
configuration settings. Then, click the Restore
Configuration from File button to transfer
those settings to the router.
This option will restore all configuration settings
back to the settings that were in effect at the
time the router was shipped from the factory.
Any settings that have not been saved will be
lost, including any rules that you have created. If
you want to save the current router configuration
settings, use the Save Configuration button
above.
Reboot the
DIR-330:
Click to reboot the router.
49D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 55

Section 3 - Configuration
Update Firmware
You can upgrade the firmware of the router here. Make sure the firmware you want to use is on the local hard drive of
the computer. Click on Browse to locate the firmware file to be used for the update. Please check the D-Link support
site for firmware updates at http://support.dlink.com. You can download firmware upgrades to your hard drive from the
D-Link support site.
Browse:
After you have downloaded the new firmware,
click Browse to locate the firmware update on
your hard drive. Click Save Settings to complete
the firmware upgrade.
50D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 56

Section 3 - Configuration
DDNS
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) is a method of keeping a domain name linked to a changing IP Address. The
DDNS feature allows you to host a server (Web, FTP, Game Server, etc.) using a domain name that you have purchased
(www.whateveryournameis.com) with your dynamically assigned IP address. Most broadband Internet Service Providers
assign dynamic IP addresses. Using a DDNS service provider, your friends can enter in your domain name to connect
to your server no matter what your IP address is.
DDNS:
Server Address:
Host Name:
Username or Key:
Password or Key:
Verify Password or
Key:
Timeout:
Check the box to enable DDNS.
Choose your DDNS provider from the drop
down menu.
Enter you Host Name that you registered with
your DDNS service provider.
Enter the Username or Key for your DDNS
account.
Enter the Password or Key for your DDNS
account.
Reenter the password or key for your DDNS
account.
The default value is 240 (hours). Do not change
this value unless otherwise specified by you
DDNS service provider.
51D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 57

Section 3 - Configuration
System Check
The router System Check uses a ping test to send ping packets to test if a computer in on the Internet.
Ping Test:
Ping Results:
Enter the IP address that you wish to ping and
click the Ping button.
The results of your ping attempts will be
displayed here.
52D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 58

Section 3 - Configuration
Schedules
This section is used to manage schedule rules for port forwarding, firewall rules, web filtering, and remote
management.
Name:
Days:
Time:
Save:
Schedule Rules
List:
Enter a name for your new schedule.
Select a day, a range of days, or All Week to
include every day.
Check All Day - 24hrs or enter a start and
end time for your schedule.
Click Save to save your schedule. You must
click Save Settings at the top for your
schedules to go into effect.
The list of schedules will be listed here. Click
the Edit icon to make changes or click the
Delete icon to remove the schedule.
53D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 59

Section 3 - Configuration
Log Settings
SMTP Server/IP
Address:
Email Address:
Save Log File to
Local Hard Drive:
Log Type:
Enter the address of the SMTP server that will
be used to send the logs.
Enter the email address to which the logs will
be sent. Click on Send Mail Now to send the
email.
Click to save the log to your hard drive.
Select the type of log you would like to view.
54D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 60

Section 3 - Configuration
Device Information
This page displays the current information for the router. It will display the LAN, WAN (Internet), and the firmware
version of the router.
If your Internet connection is set up for a Dynamic IP address then a Release button and a Renew button will be
displayed. Use Release to disconnect from your ISP and use Renew to connect to your ISP.
If your Internet connection is set up for PPPoE, a Connect button and a Disconnect button will be displayed. Use
Disconnect to drop the PPPoE connection and use Connect to establish the PPPoE connection.
Displays the MAC address and the private
LAN:
(local) IP settings for the router.
WAN:
Wireless:
Displays the MAC address and the public IP
settings for the router.
Displays the SSID, Channel, and Encryption
information of your wireless network.
55D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 61
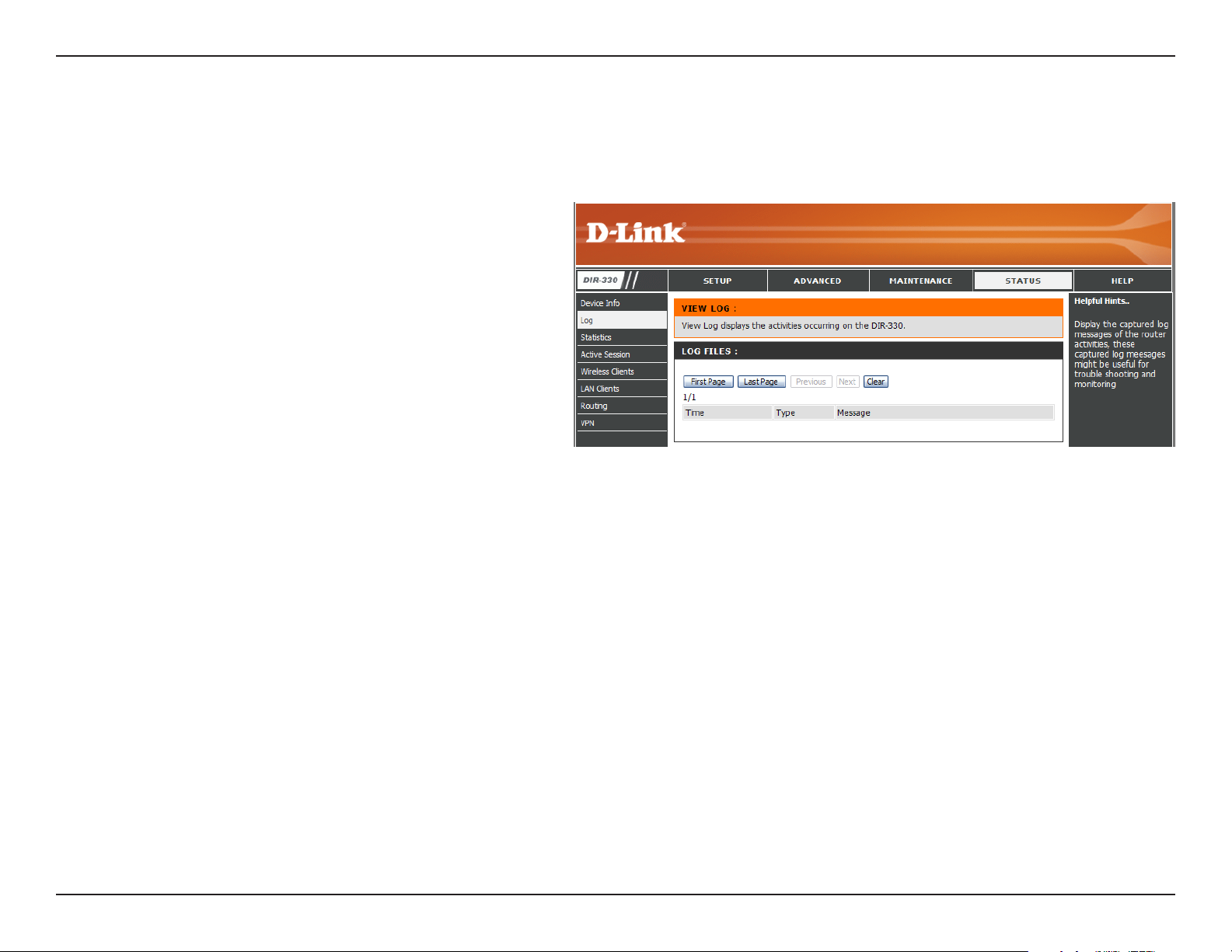
Section 3 - Configuration
Log
This page displays the log events of the router. Here you can view the logs of the router.
First Page:
Last Page:
Previous:
Next:
Clear:
This button will direct you to the current first page
of the log.
This button will direct you to the current last page
of the log.
Click to view the previous page of the log.
Click to view the next page of the log.
Clears all current log content.
56D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 62

Section 3 - Configuration
Statistics
This page displays the current statistics of the router. Here you can view the amount of packets that pass through the
router.
Refresh:
Reset:
WAN:
LAN:
This button will refresh the statistics to display
updated information.
This button will reset the statistics packet
count to zero for all interfaces listed.
Displays the amount of packets transmitted
and received on the WAN interface.
Displays the amount of packets transmitted
and received on the LAN interface.
57D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 63

Section 3 - Configuration
Active Session
The Active Session Status menu shows the active sessions currently running on your router. The list will display the
protocol, the source IP address and the destination IP address for each active session.
First Page:
Last Page:
Previous:
Next:
This button will direct you to the current first
page of the active sessions.
This button will direct you to the current last
page of the active sessions.
This button will direct you to the previous page
of the active sessions.
This button will direct you to the next page of
the active sessions.
58D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 64

Section 3 - Configuration
Wireless Clients
This page displays a list of current connected wireless clients. This page also displays the connection time and MAC
address of the connected wireless clients
LAN Clients
This page displays a list of currently connected wired clients. This table also displays the connection time and MAC
address of the connected wired clients.
59D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 65

Section 3 - Configuration
Routing
This page displays a list of the default and static routes used by the router.
VPN
The VPN table displays a list of current PPTP, L2TP, L2TP over IPsec, and IPsec VPN sessions.
60D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 66

Section 3 - Configuration
Help
61D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 67

Section 4 - Security
Wireless Security
This section will show you the different levels of security you can use to protect your data from intruders. The
DIR-330 offers the following types of security:
• WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) • WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
• WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) • WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
• WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
What is WEP?
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard and uses the RC4 encryption algorithm. WEP
provides security by encrypting data over your wireless network so that it is protected as it is transmitted from one
wireless device to another.
To gain access to a WEP network, you must know the key. The key is a string of characters that you create. When using
WEP, you must determine the level of encryption. The type of encryption determines the key length. 128-bit encryption
requires a longer key than 64-bit encryption. Keys are defined by entering in a string in HEX (hexadecimal - using
characters 0-9, A-F) or ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange – alphanumeric characters) format.
ASCII format is provided so you can enter a string that is easier to remember. The ASCII string is converted to HEX
for use over the network. Four keys can be defined so that you can change keys easily.
62D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 68

Section 4 - Security
What is WPA?
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a Wi-Fi standard that was designed to improve the security features of WEP (Wired
Equivalent Privacy).
The 2 major improvements over WEP:
• Improved data encryption through the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). TKIP scrambles the keys
using a hashing algorithm and, by adding an integrity-checking feature, ensures that the keys haven’t
been tampered with. WPA2 is based on 802.11i and uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) instead
of TKIP.
• User authentication, which is generally missing in WEP, through the extensible authentication protocol
(EAP). WEP regulates access to a wireless network based on a computer’s hardware-specific MAC
address, which is relatively simple to be sniffed out and stolen. EAP is built on a more secure public-key
encryption system to ensure that only authorized network users can access the network.
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses a passphrase or key to authenticate your wireless connection. The key is an alpha-numeric
password between 8 and 63 characters long. The password can include symbols (!?*&_) and spaces. This key must
be the exact same key entered on your wireless router or access point.
WPA/WPA2 incorporates user authentication through the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). EAP is built on a
more secure public key encryption system to ensure that only authorized network users can access the network.
63D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 69

Section 4 - Security
Wireless Security Setup Wizard
To run the security wizard, click on Setup at the top and then
click Launch Wireless Security Setup Wizard.
Click Next to continue.
64D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 70

Section 4 - Security
Enter the SSID (Service Set Identifier). The SSID is the
name of your wireless network. Create a name using up to
32 characters. The SSID is case-sensitive.
Click Next to continue.
Select the level of security for your wireless network:
• Best – WPA2 Authentication
• Better – WPA Authentication
• Good – WEP 128-bit Authentication
• None – No Security
Click Next to continue.
If you selected Best or Better, enter a password between
8-63 characters.
Click Next to continue.
65D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 71

Section 4 - Security
If you selected Good, enter a WEP encryption key (13
characters or 26 Hex (A-F, 0-9) characters).
Click Next to continue.
If you did not enable encryption, the following screen will
appear.
Click Save to finish the Security Wizard.
If you selected Best, the following screen will show you your
Pre-Shared Key to enter on your wireless clients.
Click Save to finish the Security Wizard.
66D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 72

Section 4 - Security
If you selected Better, the following screen will show you your
Pre-Shared Key to enter on your wireless clients.
Click Save to finish the Security Wizard.
If you selected Good, the following screen will show you your
WEP Key to enter on your wireless clients.
Click Save to finish the Security Wizard.
67D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 73

Section 4 - Security
Configure WEP
It is recommended to enable encryption on your wireless router before your wireless network adapters. Please establish
wireless connectivity before enabling encryption. Your wireless signal may degrade when enabling encryption due to
the added overhead.
1. Log into the web-based configuration by opening a
web browser and entering the IP address of the router
(192.168.0.1). Click on Setup and then click Wireless
Settings on the left side.
2. Click the Manual Wireless Connection Setup button.
3. Next to Security Mode, select Enable WEP.
4. Next to Authentication, select Shared Key or Open.
5. Next to WEP Encryption, select the level of ecryption (64
or 128-bit).
6. Next to Default WEP Key, select the key to modify. You
may enter up to 4 different keys.
7. Next to WEP Key, enter a WEP key you create. Make sure
you enter this key exactly on all your wireless devices.
8. Click Save Settings to save your settings. If you are configuring the router with a wireless adapter, you will lose
connectivity until you enable WEP on your adapter and enter the same WEP key as you did on the router.
68D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 74

Section 4 - Security
Configure WPA/WPA2-PSK
It is recommended to enable encryption on your wireless router before your wireless network adapters. Please establish
wireless connectivity before enabling encryption. Your wireless signal may degrade when enabling encryption due to
the added overhead. The configuration of WPA, WPA2, and WPA/WPA2 uses the same options.
1. Log into the web-based configuration by opening a
web browser and entering the IP address of the router
(192.168.0.1). Click on Setup and then click Wireless
Settings on the left side.
2. Click the Manual Wireless Connection Setup button.
3. Next to Security Mode, select Enable WPA, Enable WPA2,
or Enable WPA/WPA2.
4. Next to PSK/EAP, select PSK.
5. Next to Network Key, enter a passphrase.. The passphrase
must be between 8-63 characters. This passphrase must be entered on your wireless clients to connect.
6. Click Save Settings to save your settings. If you are configuring the router with a wireless adapter, you will lose
connectivity until you enable encryption on your adapter and enter the same passphrase as you did on the router.
69D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 75

Section 4 - Security
Configure WPA/WPA2-EAP (RADIUS)
It is recommended to enable encryption on your wireless router before your wireless network adapters. Please establish
wireless connectivity before enabling encryption. Your wireless signal may degrade when enabling encryption due to
the added overhead.
1. Log into the web-based configuration by opening a web browser
and entering the IP address of the router (192.168.0.1). Click on
Setup and then click Wireless Settings on the left side.
2. Click the Manual Wireless Connection Setup button.
3. Next to Security Mode, select Enable WPA, Enable WPA2, or
Enable WPA/WPA2.
4. Next to PSK/EAP, select EAP.
5. Next to RADIUS Server IP Address enter the IP Address of your
RADIUS server.
6. Next to RADIUS Server Port, enter the port you are using with your RADIUS server. 1812 is the default port.
7. Next to RADIUS Server Shared Secret, enter the security key.
8. Click Save Settings to save your settings.
70D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 76

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
Connect to a Wireless Network
Using Windows Vista
™
Windows Vista™ users may use the built-in wireless utility. If you are using another company’s utility or Windows® 2000,
please refer to the user manual of your wireless adapter for help with connecting to a wireless network. Most utilities
will have a “site survey” option similar to the Windows Vista™ utility as seen below.
If you receive the Wireless Networks Detected bubble, click
on the center of the bubble to access the utility.
or
Right-click on the wireless computer icon in your system tray
(lower-right corner next to the time). Select Connect to a
network.
The utility will display any available wireless networks in your
area. Click on a network (displayed using the SSID) and click
the Connect button.
If you get a good signal but cannot access the Internet, check you
TCP/IP settings for your wireless adapter. Refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual for more information.
71D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 77

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
Configure WEP/WPA/WPA2
It is recommended to enable wireless security (WEP/WPA/WPA2) on your wireless router or access point before
configuring your wireless adapter. If you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the security key or
passphrase being used.
1. Open the Windows Vista™ Wireless Utility by right-clicking
on the wireless computer icon in your system tray (lower
right corner of screen). Select Connect to a network.
2. Highlight the wireless network (SSID) you would like to
connect to and click Connect.
72D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 78
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
3. Enter the same security key or passphrase that is on your router
and click Connect.
It may take 20-30 seconds to connect to the wireless network. If the
connection fails, please verify that the security settings are correct.
The key or passphrase must be exactly the same as on the wireless
router.
73D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 79

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
Using Windows® XP
Windows® XP users may use the built-in wireless utility (Zero Configuration Utility). The following instructions are for
Service Pack 2 users. If you are using another company’s utility or Windows® 2000, please refer to the user manual
of your wireless adapter for help with connecting to a wireless network. Most utilities will have a “site survey” option
similar to the Windows® XP utility as seen below.
If you receive the Wireless Networks Detected bubble, click
on the center of the bubble to access the utility.
or
Right-click on the wireless computer icon in your system tray
(lower-right corner next to the time). Select View Available
Wireless Networks.
The utility will display any available wireless networks in your
area. Click on a network (displayed using the SSID) and click
the Connect button.
If you get a good signal but cannot access the Internet, check you
TCP/IP settings for your wireless adapter. Refer to the Networking
Basics section in this manual for more information.
74D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 80

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
Configure WEP
It is recommended to enable WEP on your wireless router or access point before configuring your wireless adapter. If
you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the WEP key being used.
1. Open the Windows® XP Wireless Utility by right-clicking
on the wireless computer icon in your system tray
(lower-right corner of screen). Select View Available
Wireless Networks.
2. Highlight the wireless network (SSID) you would like to
connect to and click Connect.
75D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 81

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
3. The Wireless Network Connection box will appear. Enter the same
WEP key that is on your router and click Connect.
It may take 20-30 seconds to connect to the wireless network. If the
connection fails, please verify that the WEP settings are correct. The
WEP key must be exactly the same as on the wireless router.
76D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 82

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
Configure WPA-PSK
It is recommended to enable WEP on your wireless router or access point before configuring your wireless adapter. If
you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the WEP key being used.
1. Open the Windows® XP Wireless Utility by right-clicking
on the wireless computer icon in your system tray
(lower-right corner of screen). Select View Available
Wireless Networks.
2. Highlight the wireless network (SSID) you would like to
connect to and click Connect.
77D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 83

Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network
3. The Wireless Network Connection box will appear. Enter the
WPA-PSK passphrase and click Connect.
It may take 20-30 seconds to connect to the wireless network. If the
connection fails, please verify that the WPA-PSK settings are correct.
The WPA-PSK passphrase must be exactly the same as on the
wireless router.
78D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 84

Section 6 - Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
This section provides solutions to problems that can occur during the installation and operation of the DIR-330. Read the
following descriptions if you are having problems. (The examples below are illustrated in Windows® XP and Vista™. If you
have a different operating system, the screenshots on your computer may look similar to the following examples.)
1. Why can’t I access the web-based configuration utility?
When entering the IP address of the D-Link router (192.168.0.1 for example), you are not connecting to a website on
the Internet or have to be connected to the Internet. The device has the utility built-in to a ROM chip in the device itself.
Your computer must be on the same IP subnet to connect to the web-based utility.
• Make sure you have an updated Java-enabled web browser. We recommend the following:
• Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher
• Firefox 1.5 or higher
• Netscape 8 or higher
• Mozilla 1.7.12 (5.0) or higher
• Opera 8.5 or higher
• Safari 1.2 or higher (with Java 1.3.1 or higher)
• Camino 0.8.4 or higher
• Verify physical connectivity by checking for solid link lights on the device. If you do not get a solid link light, try using
a different cable or connect to a different port on the device if possible. If the computer is turned off, the link light may
not be on.
• Disable any Internet security software running on the computer. Software firewalls such as Zone Alarm, Black Ice,
Sygate, Norton Personal Firewall, and Windows® XP firewall may block access to the configuration pages. Check the
help files included with your firewall software for more information on disabling or configuring it.
79D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 85

Section 6 - Troubleshooting
• Configure your Internet settings:
• Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel. Double-click the Internet Options Icon. From the Security tab,
click the button to restore the settings to their defaults.
• Click the Connection tab and set the dial-up option to Never Dial a Connection. Click the LAN Settings
button. Make sure nothing is checked. Click OK.
• Go to the Advanced tab and click the button to restore these settings to their defaults. Click OK three
times.
• Close your web browser (if open) and open it.
• Access the web management. Open your web browser and enter the IP address of your D-Link router in the address
bar. This should open the login page for your the web management.
• If you still cannot access the configuration, unplug the power to the router for 10 seconds and plug back in. Wait
about 30 seconds and try accessing the configuration. If you have multiple computers, try connecting using a different
computer.
2. What can I do if I forgot my password?
If you forgot your password, you must reset your router. Unfortunately this process will change all your settings back
to the factory defaults. You will lose all your custom settings.
To reset the router, locate the reset button (hole) on the rear panel of the unit. With the router powered on, use a
paperclip to hold the button down for 10 seconds. Release the button and the router will go through its reboot process.
Wait about 30 seconds to access the router. The default IP address is 192.168.0.1. When logging in, the username is
admin and leave the password box empty.
A list of the default settings can be found on page 91.
80D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 86

Section 6 - Troubleshooting
3. Why can’t I connect to certain sites or send and receive e-mails when connecting through my router?
If you are having a problem sending or receiving e-mail, or connecting to secure sites such as eBay, banking sites, and
Hotmail, we suggest lowering the MTU in increments of ten (Ex. 1492, 1482, 1472, etc).
Note: AOL DSL+ users must use MTU of 1400.
To find the proper MTU Size, you’ll have to do a special ping of the destination you’re trying to go to. A destination could
be another computer, or a URL.
• Windows Vista™ users click on Start and type cmd in the Start Search box. Click OK or press Enter.
• Windows® NT, 2000 and XP users click on Start, click Run, and then type cmd in the box. Click OK or
press Enter.
• Windows® 95, 98, and Me users click on Start, click Run, and then type command. Click OK or press
Enter.
• Once the window opens, you’ll need to do a special ping. Use the following syntax:
ping [url] [-f] [-l] [MTU value]
Example: ping yahoo.com -f -l 1472
81D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 87

Section 6 - Troubleshooting
You should start at 1472 and work your way down by 10 each time. Once you get a reply, go up by 2 until you get a
fragmented packet. Take that value and add 28 to the value to account for the various TCP/IP headers. For example,
lets say that 1452 was the proper value, the actual MTU size would be 1480, which is the optimum for the network
we’re working with (1452+28=1480).
Once you find your MTU, you can now configure your router with the proper MTU size.
To change the MTU rate on your router follow the steps below:
• Open your browser, enter the IP address of your router (192.168.0.1) and click OK.
• Enter your username (admin) and password (blank by default). Click OK to enter the web configuration
page for the device.
• Click on Setup and then click Manual Configure.
• To change the MTU enter the number in the MTU field and click Save Settings to save your settings.
• Test your email. If changing the MTU does not resolve the problem, continue changing the MTU in
increments of ten.
4. Why is the date on the logs incorrect?
The router has not successfully connected to a Network Time (NTP) server. Check that your Internet connection settings
are correct. If you have connected for the first time, allow up to 10 minutes to connect.
If the time is off by 1 hour, make sure you have selected the correct time zone and that Daylight Savings is selected.
Refer to Section 3 - Configuration > Time and Date for more information.
82D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 88

Appendix A - Wireless Basics
Wireless Basics
D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide easy-to-use and compatible high-speed wireless
connectivity within your home, business or public access wireless networks. Strictly adhering to the IEEE standard,
the D-Link wireless family of products will allow you to securely access the data you want, when and where you want
it. You will be able to enjoy the freedom that wireless networking delivers.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a cellular computer network that transmits and receives data with radio signals
instead of wires. Wireless LANs are used increasingly in both home and office environments, and public areas such
as airports, coffee shops and universities. Innovative ways to utilize WLAN technology are helping people to work and
communicate more efficiently. Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other fixed infrastructure have proven
to be beneficial for many users.
Wireless users can use the same applications they use on a wired network. Wireless adapter cards used on laptop
and desktop systems support the same protocols as Ethernet adapter cards.
Under many circumstances, it may be desirable for mobile network devices to link to a conventional Ethernet LAN in
order to use servers, printers or an Internet connection supplied through the wired LAN. A Wireless Router is a device
used to provide this link.
83D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 89

Appendix A - Wireless Basics
What is Wireless?
Wireless or Wi-Fi technology is another way of connecting your computer to the network without using wires. Wi-Fi
uses radio frequency to connect wirelessly, so you have the freedom to connect computers anywhere in your home or
office network.
Why D-Link Wireless?
D-Link is the worldwide leader and award winning designer, developer, and manufacturer of networking products.
D-Link delivers the performance you need at a price you can afford. D-Link has all the products you need to build your
network.
How does wireless work?
Wireless works similar to how cordless phone work, through radio signals to transmit data from one point A to point
B. But wireless technology has restrictions as to how you can access the network. You must be within the wireless
network range area to be able to connect your computer. There are two different types of wireless networks Wireless
Local Area Network (WLAN), and Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN).
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
In a wireless local area network, a device called an Access Point (AP) connects computers to the network. The access
point has a small antenna attached to it, which allows it to transmit data back and forth over radio signals. With an
indoor access point as seen in the picture, the signal can travel up to 300 feet. With an outdoor access point the signal
can reach out up to 30 miles to serve places like manufacturing plants, industrial locations, college and high school
campuses, airports, golf courses, and many other outdoor venues.
84D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 90

Appendix A - Wireless Basics
Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN)
Bluetooth is the industry standard wireless technology used for WPAN. Bluetooth devices in WPAN operate in a range
up to 30 feet away.
Compared to WLAN the speed and wireless operation range are both less than WLAN, but in return it doesn’t use
nearly as much power which makes it ideal for personal devices, such as mobile phones, PDAs, headphones, laptops,
speakers, and other devices that operate on batteries.
Who uses wireless?
Wireless technology as become so popular in recent years that almost everyone is using it, whether it’s for home, office,
business, D-Link has a wireless solution for it.
Home
• Gives everyone at home broadband access
• Surf the web, check email, instant message, and etc
• Gets rid of the cables around the house
• Simple and easy to use
Small Office and Home Office
• Stay on top of everything at home as you would at office
• Remotely access your office network from home
• Share Internet connection and printer with multiple computers
• No need to dedicate office space
85D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 91

Appendix A - Wireless Basics
Where is wireless used?
Wireless technology is expanding everywhere not just at home or office. People like the freedom of mobility and it’s
becoming so popular that more and more public facilities now provide wireless access to attract people. The wireless
connection in public places is usually called “hotspots”.
Using a D-Link Cardbus Adapter with your laptop, you can access the hotspot to connect to Internet from remote
locations like: Airports, Hotels, Coffee Shops, Libraries, Restaurants, and Convention Centers.
Wireless network is easy to setup, but if you’re installing it for the first time it could be quite a task not knowing where to
start. That’s why we’ve put together a few setup steps and tips to help you through the process of setting up a wireless
network.
Tips
Here are a few things to keep in mind, when you install a wireless network.
Centralize your router or Access Point
Make sure you place the router/access point in a centralized location within your network for the best performance. Try
to place the router/access point as high as possible in the room, so the signal gets dispersed throughout your home.
If you have a two-story home, you may need a repeater to boost the signal to extend the range.
Eliminate Interference
Place home appliances such as cordless telephones, microwaves, and televisions as far away as possible from the
router/access point. This would significantly reduce any interference that the appliances might cause since they operate
on same frequency.
86D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 92

Appendix A - Wireless Basics
Security
Don’t let you next-door neighbors or intruders connect to your wireless network. Secure your wireless network by turning
on the WPA or WEP security feature on the router. Refer to product manual for detail information on how to set it up.
There are basically two modes of networking:
• Infrastructure – All wireless clients will connect to an access point or wireless router.
• Ad-Hoc – Directly connecting to another computer, for peer-to-peer communication, using wireless network
adapters on each computer, such as two or more DIR-330 wireless network Cardbus adapters.
An Infrastructure network contains an Access Point or wireless router. All the wireless devices, or clients, will connect
to the wireless router or access point.
An Ad-Hoc network contains only clients, such as laptops with wireless cardbus adapters. All the adapters must be in
Ad-Hoc mode to communicate.
Wireless Modes
87D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 93

Appendix B - Networking Basics
Networking Basics
Check your IP address
After you install your new D-Link adapter or if you already have an Ethernet adapter installed on your computer, by
default, the TCP/IP settings should be set to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server (i.e. router) automatically. To
verify your IP address, please follow the steps below.
Windows Vista™ Users:
• Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt. You may
need administrative access to run this application.
• For all additional prompt windows inquiring of running the command prompt
application, select Yes, OK, or Continue.
• At the prompt, type ipconfig and press Enter.
• This will display the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway of your
adapter.
Windows® 2000/XP Users:
• Click on Start > Run. In the run box type cmd and click OK.
• At the prompt, type ipconfig and press Enter.
• This will display the IP address, subnet mask, and the default gateway of your
adapter.
If the address is 0.0.0.0, check your adapter installation, security settings, and the settings on your router. Some firewall software programs
may block a DHCP request on newly installed adapters.
88D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 94
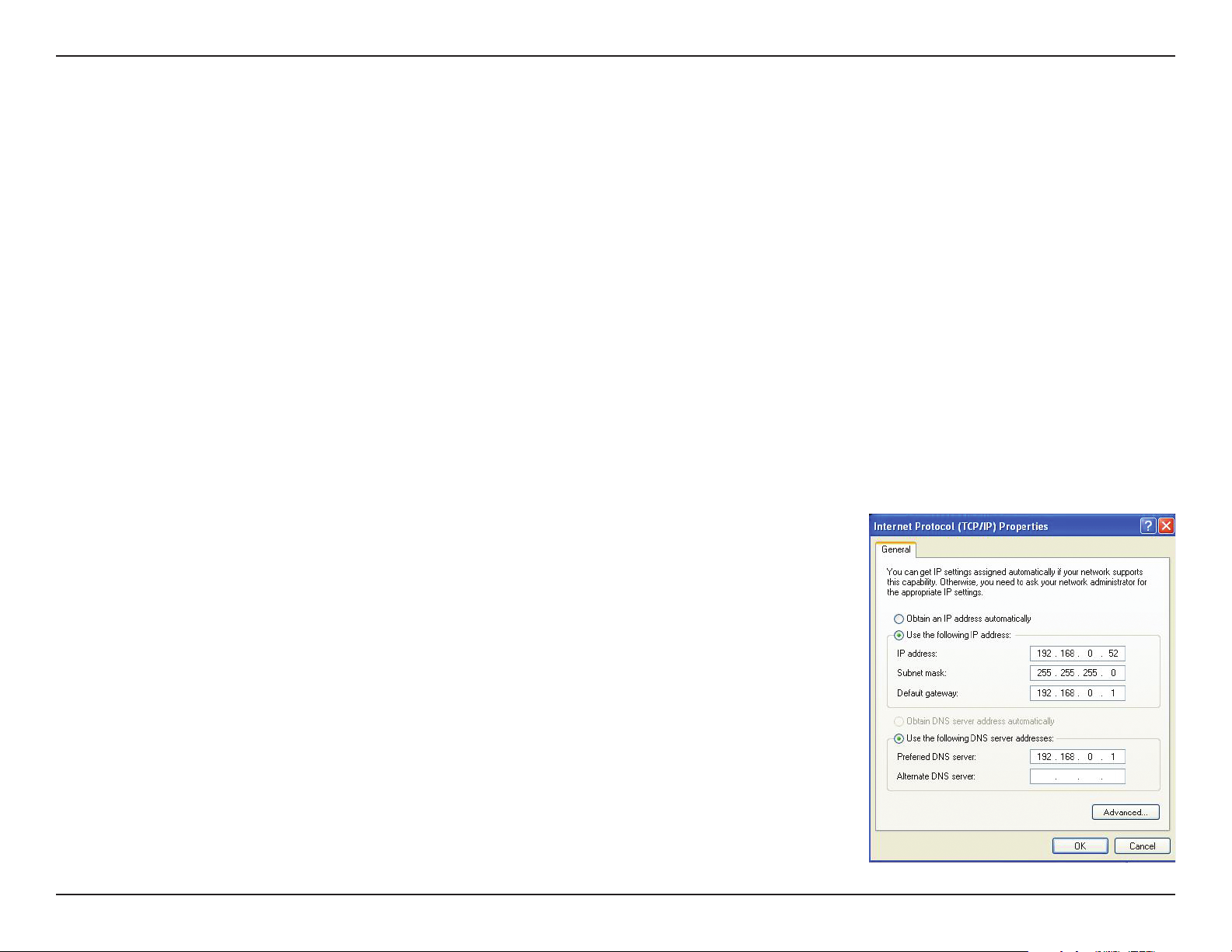
Appendix B - Networking Basics
Statically Assign an IP address
If you are not using a DHCP capable gateway/router, or you need to assign a static IP address, please follow the steps
below:
Windows® XP/2000 Users
• Windows® XP - Click on Start > Control Panel. Make sure you are in Classic View. Double-click on the Network Connections
icon.
Windows® 2000 – From the desktop, right-click My Network Places > Properties.
• Right-click on the Local Area Connection which represents your D-Link network adapter (or other adapter) which will be connected
to your router.
• Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
• Click Use the following IP address and enter an IP address that is on the same subnet as your network or LAN IP address on
your router.
Example: If the router’s LAN IP address is 192.168.0.1, make your IP address 192.168.0.X
where X is a number between 2 and 99. Make sure that the number you choose is not in
use on the network.
• Set Default Gateway the same as the LAN IP address of your router (192.168.0.1).
• Set Primary DNS the same as the LAN IP address of your router (192.168.0.1).
• The Secondary DNS is optional (you may enter a DNS server from your ISP).
• Click OK to save your settings.
89D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 95
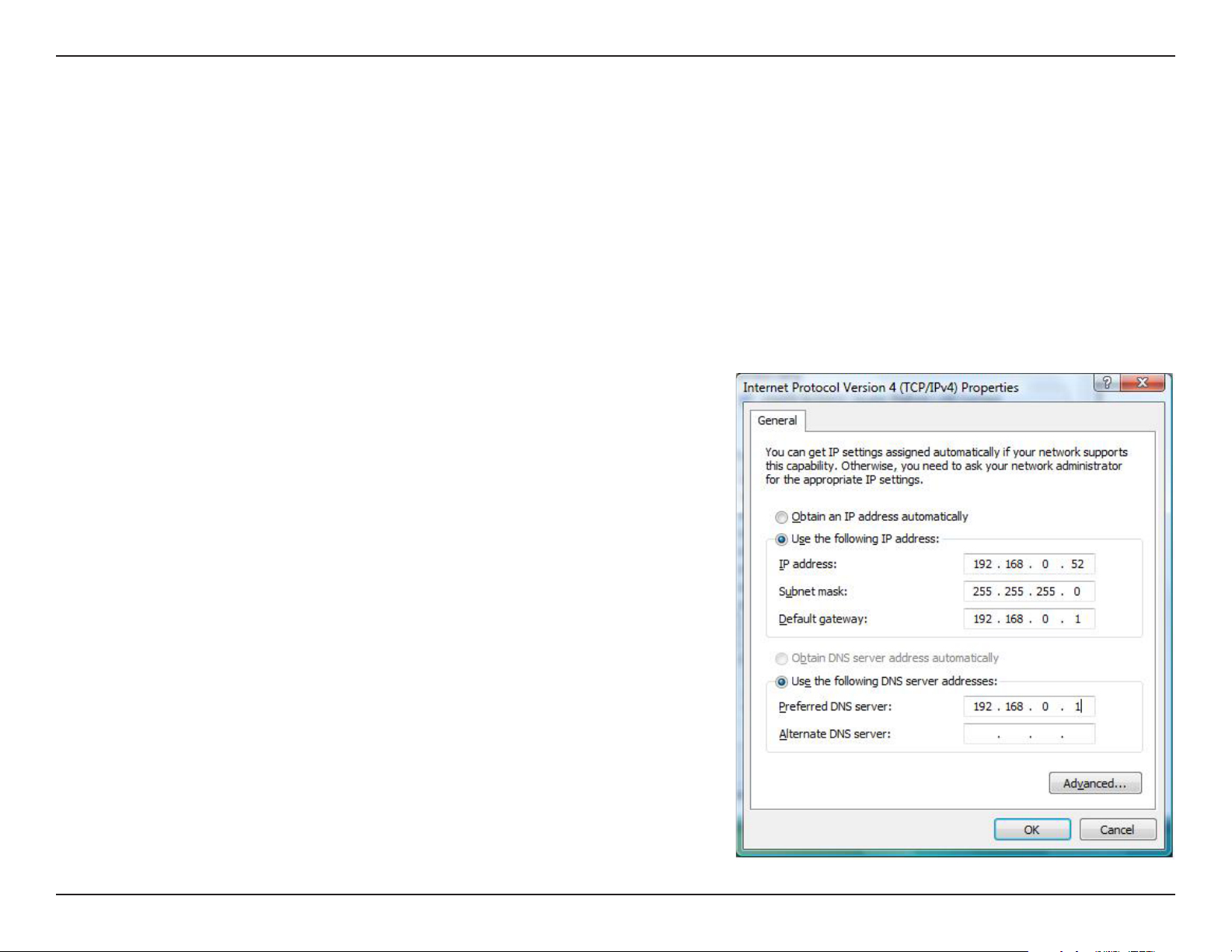
Appendix B - Networking Basics
Windows Vista™ Users
• Click on Start > Control Panel. Make sure you are in Classic View. Double-click on the Network and Sharing Center icon. Along
the left panel in the window, click on Manage network connections.
• Right-click on the Local Area Connection which represents your D-Link network adapter (or other adapter) which will be connected
to your router.
• Highlight Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP /IPv4) and click Properties.
• Click Use the following IP address and enter an IP address that is on the same subnet as your network or LAN IP address on
your router.
Example: If the router’s LAN IP address is 192.168.0.1, make your IP
address 192.168.0.X where X is a number between 2 and 99. Make sure
that the number you choose is not in use on the network.
• Set Default Gateway the same as the LAN IP address of your router
(192.168.0.1).
• Set Primary DNS the same as the LAN IP address of your router
(192.168.0.1).
• The Secondary DNS is optional (you may enter a DNS server from your
ISP).
• Click OK to save your settings.
90D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 96

Appendix C - Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Standards
• IEEE 802.11g
• IEEE 802.11b
• IEEE 802.3
• IEEE 802.3u
Security
• WPA-Personal
• WPA2-Personal
• WPA-Enterprise
• WPA2-Enterprise
• 64/128-bit WEP
Wireless Signal Rates*
• 54Mbps • 48Mbps
• 36Mbps • 24Mbps
• 18Mbps • 12Mbps
• 11Mbps • 9Mbps
• 6Mbps • 5.5Mbps
• 2Mbps • 1Mbps
Frequency Range
• 2.4GHz to 2.483GHz
LEDs
• Power • WAN • Status
• WLAN • LAN (10/100)
Operating Temperature
• 32°F to 104°F ( 0°C to 40°C)
Humidity
• 95% maximum (non-condensing)
Safety & Emissions
• FCC
• CE
• IC
Dimensions
• L = 7.6 inches
• W = 4.6 inches
• H = 1.2inches
Warranty
• 1 Year
Transmitter Output Power
• 16dBm ± 2dB (max.)
External Antenna Type
• Two (2) detachable reverse SMA Antennas
* Maximum wireless signal rate derived from IEEE Standard 802.11g specifications. Actual data throughput will vary. Network conditions and environmental factors,
including volume of network traffic, building materials and construction, and network overhead, lower actual data throughput rate. Environmental factors will adversely
affect wireless signal range.
91D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 97

Appendix C - Technical Specifications
Default Factory Settings
When you receive your router, the default factory settings are in effect as listed in the table below. You may change any
of the network and wireless settings. If you perform a reset (hold the reset button on the back of the unit), the router
will reset with the following settings:
Setting Default Value
Username admin
Password (leave blank)
LAN IP Address 192.168.0.1
DHCP Server Enabled
DHCP IP Range 192.168.0.100 - 192.168.0.150
Filtering / Virtual Server / DMZ / Applications Disabled
Wireless Broadcast Enabled
SSID dlink
WEP / WPA / WPA2 Disabled
Wireless Channel 6
92D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 98

Appendix D - Contacting Technical Support
Contacting Technical Support
U.S. and Canadian customers can contact D-Link technical support through our web site or by phone.
Before you contact technical support, please have the following ready:
• Model number of the product (e.g. DIR-330)
• Hardware Revision (located on the label on the bottom of the router (e.g. rev A1))
• Serial Number (s/n number located on the label on the bottom of the router).
You can find software updates and user documentation on the D-Link website as well as frequently asked questions
and answers to technical issues.
For customers within the United States:
Phone Support:
(877) 354-6555
Internet Support:
http://support.dlink.com
For customers within Canada:
Phone Support:
(877) 354-6560
Internet Support:
http://support.dlink.com
93D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 99

Appendix E - Warranty
Warranty
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth herein, D-Link Systems, Inc. (“D-Link”) provides this Limited Warranty:
• Only to the person or entity that originally purchased the product from D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor, and
• Only for products purchased and delivered within the fifty states of the United States, the District of Columbia, U.S. Possessions
or Protectorates, U.S. Military Installations, or addresses with an APO or FPO.
Limited Warranty:
D-Link warrants that the hardware portion of the D-Link product described below (“Hardware”) will be free from material defects in
workmanship and materials under normal use from the date of original retail purchase of the product, for the period set forth below
(“Warranty Period”), except as otherwise stated herein.
• Hardware (excluding power supplies and fans): One (1) year
• Power supplies and fans: One (1) year
• Spare parts and spare kits: Ninety (90) days
The customer’s sole and exclusive remedy and the entire liability of D-Link and its suppliers under this Limited Warranty will be, at
D-Link’s option, to repair or replace the defective Hardware during the Warranty Period at no charge to the original owner or to refund the
actual purchase price paid. Any repair or replacement will be rendered by D-Link at an Authorized D-Link Service Office. The replacement
hardware need not be new or have an identical make, model or part. D-Link may, at its option, replace the defective Hardware or any part
thereof with any reconditioned product that D-Link reasonably determines is substantially equivalent (or superior) in all material respects
to the defective Hardware. Repaired or replacement hardware will be warranted for the remainder of the original Warranty Period or ninety
(90) days, whichever is longer, and is subject to the same limitations and exclusions. If a material defect is incapable of correction, or if
D-Link determines that it is not practical to repair or replace the defective Hardware, the actual price paid by the original purchaser for the
defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to D-Link of the defective Hardware. All Hardware or part thereof that is replaced
by D-Link, or for which the purchase price is refunded, shall become the property of D-Link upon replacement or refund.
94D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
Page 100

Appendix E - Warranty
Limited Software Warranty:
D-Link warrants that the software portion of the product (“Software”) will substantially conform to D-Link’s then current functional specifications
for the Software, as set forth in the applicable documentation, from the date of original retail purchase of the Software for a period of ninety
(90) days (“Software Warranty Period”), provided that the Software is properly installed on approved hardware and operated as contemplated
in its documentation. D-Link further warrants that, during the Software Warranty Period, the magnetic media on which D-Link delivers the
Software will be free of physical defects. The customer’s sole and exclusive remedy and the entire liability of D-Link and its suppliers under
this Limited Warranty will be, at D-Link’s option, to replace the non-conforming Software (or defective media) with software that substantially
conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software or to refund the portion of the actual purchase price paid that is attributable
to the Software. Except as otherwise agreed by DLink in writing, the replacement Software is provided only to the original licensee, and
is subject to the terms and conditions of the license granted by D-Link for the Software. Replacement Software will be warranted for the
remainder of the original Warranty Period and is subject to the same limitations and exclusions. If a material non-conformance is incapable
of correction, or if D-Link determines in its sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the non-conforming Software, the price paid by
the original licensee for the non-conforming Software will be refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming Software (and all copies
thereof) is first returned to D-Link. The license granted respecting any Software for which a refund is given automatically terminates.
Non-Applicability of Warranty:
The Limited Warranty provided hereunder for Hardware and Software portions of D-Link’s products will not be applied to and does not cover
any refurbished product and any product purchased through the inventory clearance or liquidation sale or other sales in which D-Link, the
sellers, or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the product and in that case, the product is being sold
“As-Is” without any warranty whatsoever including, without limitation, the Limited Warranty as described herein, notwithstanding anything
stated herein to the contrary.
Submitting A Claim:
The customer shall return the product to the original purchase point based on its return policy. In case the return policy period has expired
and the product is within warranty, the customer shall submit a claim to D-Link as outlined below:
• The customer must submit with the product as part of the claim a written description of the Hardware defect or Software
nonconformance in sufficient detail to allow DLink to confirm the same, along with proof of purchase of the product (such
as a copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) if the product is not registered.
• The customer must obtain a Case ID Number from D-Link Technical Support at 1-877-453-5465, who will attempt to assist
the customer in resolving any suspected defects with the product. If the product is considered defective, the customer must
obtain a Return Material Authorization (“RMA”) number by completing the RMA form and entering the assigned Case ID
Number at https://rma.dlink.com/.
95D-Link DIR-330 User Manual
 Loading...
Loading...