Page 1

Page 2

_____________________________________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2011 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permis s ion of D-Link Corporation is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link and the D-LINK logo are trademarks of D-Link Corporation; Microsoft and Windows are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products. D-
Link Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
June 2011 P/N 651GS3200045G
Page 3

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Table of Contents
Intended Readers ........................................................................................................................................................................... xi
Typographical Conventions ........................................................................................................................................................................... xi
Notes, Notices, and Cautions ......................................................................................................................................................................... xi
Safety Cautions .............................................................................................................................................................................................xii
General Precautions for Rack-Mount a b l e Pro duc ts .................................................................................................................................... xiii
Lithium Battery Precaution ..................................................................................................................................................................... xiv
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge .................................................................................................................................................. xiv
Web-based Switch Configuration ................................................................................................................... 1
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Logging onto the Web Manager ...................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Web-based User Int er fa ce ............................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Areas of the User Interface ........................................................................................................................................................................ 2
Web Pages ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Configuration ................................................................................................................................................... 4
Device Information ........................................................................................................................................................................ 5
System Information ........................................................................................................................................................................ 5
Serial Port Settings ......................................................................................................................................................................... 6
IP Address ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Setting the Switch’s IP Address using the Console Interface .................................................................................................................... 7
Port Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Port Auto Negotiation Information ................................................................................................................................................................. 8
Port Detail Information ................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Port Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Port Description Settings............................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Port Error Disabled ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Jumbo Frame Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Static ARP Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Gratuitous ARP ............................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Gratuitous ARP Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Gratuitous ARP Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................... 13
User Accounts .............................................................................................................................................................................. 14
Admin and User Privileges ...................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Command Logging Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 15
System Log Configuration ........................................................................................................................................................... 16
System Log Settings...................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
System Log Host ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
System Severity Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 17
MAC Address Aging Ti me .......................................................................................................................................................... 18
Web Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
Telnet Settings .............................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Password Encryption .................................................................................................................................................................... 19
iii
Page 4

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
CLI Paging Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Firmware Information .................................................................................................................................................................. 20
Dual Configuration Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 21
Power Saving ............................................................................................................................................................................... 23
LED State Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 23
Power Saving Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................. 24
Power Saving LED Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Power Saving Port Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................... 25
MAC Notification Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 26
MAC Notification Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................................ 26
MAC Notification Port Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 26
SNMP Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................. 27
SNMP Global State Settings ......................................................................................................................................................................... 28
SNMP Linkchange Traps Set tings ................................................................................................................................................................ 28
SNMP View Table ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 29
SNMP Group Table ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
SNMP User Table ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 31
SNMP Community Table .............................................................................................................................................................................. 32
SNMP Host Table ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 33
SNMP v6Host Table ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 34
SNMP Engine ID .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 34
SNMP Trap Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................................ 35
RMON .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 35
CPU Filter L3 Control Packet Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 36
Single IP M anagement ................................................................................................................................................................. 36
Single IP Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 38
Topology ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Firmware Upgrade ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 46
Configuration F il e Bac kup/Restore ............................................................................................................................................................... 46
Upload Log File ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 46
SD Card FS Settings (DGS-3200-24 Only) ................................................................................................................................. 47
SD Card Management (DGS-3200-24 Only) ............................................................................................................................... 48
SD Card Backup Settin gs .............................................................................................................................................................................. 48
SD Card Execute Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................. 48
L2 Features ..................................................................................................................................................... 50
VLAN .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
802.1Q VLAN............................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
802.1v Protocol VL AN ................................................................................................................................................................................. 58
802.1v Protocol Group Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 58
802.1v Protocol VL AN Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 59
GVRP Settings .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 60
MAC-based VLAN Settings ......................................................................................................................................................................... 61
Private VLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................. 61
PVID Auto Assign Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Voice VLAN ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 64
iv
Page 5

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Voice VLAN Global Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 64
Voice VLAN Port Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Voice VLAN OUI Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................... 66
Voice VLAN Device ............................................................................................................................................................................... 66
Voice VLAN LLDP-MED Voice Device ................................................................................................................................................ 67
VLAN Trunk Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................... 67
Browse VLAN .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 68
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 68
Egress Filter Settings.................................................................................................................................................................... 69
L2 Multicast Control .................................................................................................................................................................... 69
IGMP Snooping ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 70
IGMP Snooping Settings ......................................................................................................................................................................... 70
IGMP Snooping Rate Limit Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 72
IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 73
IGMP Router Port .................................................................................................................................................................................... 74
IGMP Snooping Group ............................................................................................................................................................................ 74
IGMP Snooping Forwarding Table .......................................................................................................................................................... 75
IGMP Snooping Counter ......................................................................................................................................................................... 75
IGMP Host Table ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 76
MLD Snooping ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 77
MLD Snooping Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................... 77
MLD Snooping Rate Limit Settings ........................................................................................................................................................ 80
MLD Snooping Static Group Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 80
MLD Router Port ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 81
MLD Snooping Group ............................................................................................................................................................................. 82
MLD Snooping Forwarding Table ........................................................................................................................................................... 82
MLD Snooping Counter .......................................................................................................................................................................... 83
MLD Host Table ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 84
Multicast VLAN ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 84
IGMP Multicast Group Profile Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 84
IGMP Snooping Multicast VLAN Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 85
Multicast Filtering ........................................................................................................................................................................ 87
IPv4 Multicast Filtering ................................................................................................................................................................................ 87
IPv4 Multicast Profile Settings ................................................................................................................................................................ 87
IPv4 Limited Multicast Range Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 88
IPv4 Max Multicast Group Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 89
Multicast Filtering Mode............................................................................................................................................................................... 89
Port Mirroring .............................................................................................................................................................................. 90
Spanning Tree .............................................................................................................................................................................. 91
STP Bridge Global Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................... 93
STP Port Settings .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 94
MST Configuration Identification ................................................................................................................................................................. 96
STP Instance Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................... 97
MSTP Port Information ................................................................................................................................................................................ 97
Link Aggregati o n ......................................................................................................................................................................... 98
v
Page 6

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Port Trunking ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 98
LACP Port Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 101
Forwarding & Filtering .............................................................................................................................................................. 101
Unicast Forwarding ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 101
Multicast Forwarding .................................................................................................................................................................................. 102
LLDP .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 103
LLDP .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 103
LLDP Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 103
LLDP Port Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................ 104
LLDP Management Address Lis t .......................................................................................................................................................... 105
LLDP Basic TLVs Settings ................................................................................................................................................................... 105
LLDP Do t1 TLVs Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 106
LLDP Do t3 TLVs Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 107
LLDP Statistics System ......................................................................................................................................................................... 108
LLDP Local Port Information ................................................................................................................................................................ 109
LLDP Remote Port Information ............................................................................................................................................................ 110
LLDP-MED ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 111
LLDP-MED System Settings ................................................................................................................................................................. 111
LLDP-MED Port Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................... 111
LLDP-MED Local Port Information ...................................................................................................................................................... 112
LLDP-MED Remote Port Information .................................................................................................................................................. 113
NLB FDB Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................... 113
L3 Features ................................................................................................................................................... 115
IPv4 Static/Default Route Settings ............................................................................................................................................. 115
IPv4 Route Table ....................................................................................................................................................................... 115
IPv6 Interface Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 116
IPv6 Route S ettings .................................................................................................................................................................... 117
IPv6 Neighbor Settings .............................................................................................................................................................. 117
QoS ................................................................................................................................................................ 119
Bandwidth Control ..................................................................................................................................................................... 121
Queue Bandwidth Control Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 122
Traffic Control ........................................................................................................................................................................... 122
802.1p Default Priority ............................................................................................................................................................... 125
802.1p User Priority ................................................................................................................................................................... 125
QoS Scheduling Mechanism ...................................................................................................................................................... 126
Security ......................................................................................................................................................... 127
RADIUS ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 127
Authentication RADIUS Server Settings .................................................................................................................................................... 127
RADIUS Accounting Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 128
RADIUS Authentication ............................................................................................................................................................................. 129
RADIUS Account Client............................................................................................................................................................................. 130
IP-MAC-Port Binding (IMPB)................................................................................................................................................... 131
IMPB Global Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................. 133
IMPB Port Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 134
vi
Page 7

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
IMPB Entry Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................... 135
MAC Block List .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 136
DHCP Snooping .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 137
DHCP Snoopi ng Maximum Entry Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 137
DHCP Snooping Entry........................................................................................................................................................................... 137
ND Snoop ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 138
ND Snoop Maximum Entry Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 138
ND Snoop Entry .................................................................................................................................................................................... 139
Port Security ............................................................................................................................................................................... 139
Port Security Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................. 139
Port Lock Entries ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 140
DHCP Server Screening ............................................................................................................................................................. 141
DHCP Screening Por t Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 141
DHCP Offer Filtering .................................................................................................................................................................................. 142
802.1X (Port-based and Host-based Access Control) ................................................................................................................ 143
Authentication Server ............................................................................................................................................................................ 144
Authenticator ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 144
Client ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 145
Authentication Process .......................................................................................................................................................................... 145
Understanding 8 02. 1X Port-based and Host-based Network Access Control ........................................................................................ 146
802.1X Global Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................... 148
802.1X Port Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................... 149
802.1X User Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................. 151
Guest VLAN Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................. 151
Authenticator State ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 152
Authenticator Statistics ............................................................................................................................................................................... 152
Authenticator Session Statistics .................................................................................................................................................................. 153
Authenticator Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................................................................... 154
Initialize Port-based Port(s) ......................................................................................................................................................................... 155
Initialize Host-based Port(s ) ........................................................................................................................................................................ 156
Reauthenticate Port-base d P ort ( s ) ............................................................................................................................................................... 156
Reauthenticate Hos t -based Port(s) .............................................................................................................................................................. 156
SSL ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 157
SSL Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 157
SSL Certification Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................... 159
SSH ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 159
SSH Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................................... 160
SSH Authentication Method and Algorithm Settings ................................................................................................................................. 161
SSH User Authentication List ..................................................................................................................................................................... 162
Access Authe nt ic ati o n Co ntr ol ................................................................................................................................................... 163
Enable Admin ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 164
Authentication Policy Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 164
Application Authentication Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 165
Authenticat ion Se r ver Group ...................................................................................................................................................................... 165
Authentication Server Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 167
vii
Page 8

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Login Method Lists Settings ....................................................................................................................................................................... 168
Enable Method Lists Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................... 169
Local Enable Password Settings ................................................................................................................................................................. 170
MAC-based Access Control (MAC) .......................................................................................................................................... 170
MAC-based Access Control Setti ngs .......................................................................................................................................................... 171
MAC-based Access Control Local Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 173
MAC-based Access Control Authentication State ...................................................................................................................................... 173
Web-based Access Control (WAC) ........................................................................................................................................... 174
WAC Global Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................. 176
WAC User Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 177
WAC Port Settings ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 178
WAC Authenticating State .......................................................................................................................................................................... 179
WAC Customize Page ................................................................................................................................................................................ 179
Japanese Web-based Access Control (JWAC) ........................................................................................................................... 180
JWAC Gl obal Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................ 180
JWAC Port Settings .................................................................................................................................................................................... 182
JWAC User Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................... 183
JWAC Authentication State ........................................................................................................................................................................ 184
JWAC Customize Page Language .............................................................................................................................................................. 185
JWAC Customize Page ............................................................................................................................................................................... 185
Compound A uthentication ......................................................................................................................................................... 186
Compound Authent ic a t ion Settings ............................................................................................................................................................ 189
Compound Authentication Guest VLAN Settings ...................................................................................................................................... 191
Compound Authentication MAC Format Settings ...................................................................................................................................... 191
IGMP Access Control Settings .................................................................................................................................................. 192
ARP Spoofing Prevention Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 193
BPDU Attack Protection ............................................................................................................................................................ 194
Loopback Detection Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 195
Traffic Segmentation .................................................................................................................................................................. 196
Safeguard E ngine Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 197
Trusted Host Settings ................................................................................................................................................................. 198
ACL ............................................................................................................................................................... 200
ACL Configuration Wizard ........................................................................................................................................................ 200
Access Profile List ..................................................................................................................................................................... 201
CPU Access Profile List ............................................................................................................................................................. 215
Time Range Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 228
Network Application .................................................................................................................................... 230
DHCP/BOOTP Relay................................................................................................................................................................. 230
DHCP/BOOTP Relay Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................................ 230
DHCP/BOOTP Relay Interface Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 233
DHCPv6 Relay ........................................................................................................................................................................... 233
DHCPv6 Relay Global Settings .................................................................................................................................................................. 233
DHCPv6 Relay Settings .............................................................................................................................................................................. 234
DHCP Server.............................................................................................................................................................................. 234
viii
Page 9

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
DHCP Server Global Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................... 235
DHCP Server Exclude Address Settings ..................................................................................................................................................... 235
DHCP Server Pool Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................ 236
DHCP Server Manual Binding .................................................................................................................................................................... 237
DHCP Server Dynamic Binding ................................................................................................................................................................. 238
DHCP Conflict IP ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 238
DHCP Local Relay Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 238
DHCP Auto Configuration Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 239
DHCP Option 12 Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 240
DNS Resolver ............................................................................................................................................................................ 240
DNS Resolver Global Settings .................................................................................................................................................................... 240
DNS Resolver Static Na me Server Settings ................................................................................................................................................ 241
DNS Resolver Dynamic Name Server T able .............................................................................................................................................. 241
DNS Resolver Static Host Name Settings ................................................................................................................................................... 241
DNS Resolver Dynamic Host Name Table ................................................................................................................................................. 242
PPPoE Circuit ID Insertions Settings ......................................................................................................................................... 242
SMTP Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................... 243
SNTP Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................ 244
Time Settings .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 244
Time Zone Settings ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 244
Ping Test .................................................................................................................................................................................... 246
OAM .............................................................................................................................................................. 248
Ethernet OAM ............................................................................................................................................................................ 248
Ethernet OAM Settings ............................................................................................................................................................................... 248
Ethernet OAM Configuration Settings ........................................................................................................................................................ 249
Ethernet OAM Event Log ........................................................................................................................................................................... 250
Ethernet OAM Statistics ............................................................................................................................................................................. 250
DULD Settings ........................................................................................................................................................................... 251
Cable Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................................................................... 252
Monitoring .................................................................................................................................................... 254
Device Environment................................................................................................................................................................... 254
CPU Utilization .......................................................................................................................................................................... 254
DRAM & Flash Utilization ........................................................................................................................................................ 255
Port Utilization ........................................................................................................................................................................... 256
Packet Size ................................................................................................................................................................................. 256
Packets ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 258
Received (RX) ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 258
UMB_Cast (RX) ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 260
Transmitted (TX) ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 261
Errors .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 263
Received (RX) ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 263
Transmitted (TX) ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 265
Browse ARP Table ..................................................................................................................................................................... 266
Browse Router Port .................................................................................................................................................................... 266
ix
Page 10

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Browse MLD Router Port .......................................................................................................................................................... 267
Browse Session Table ................................................................................................................................................................ 267
IGMP Snooping Group .............................................................................................................................................................. 268
MLD Snooping Group ............................................................................................................................................................... 268
MAC Address Table .................................................................................................................................................................. 269
Syst em Log ................................................................................................................................................................................ 270
Save and Tools .............................................................................................................................................. 271
Save Configuration..................................................................................................................................................................... 272
Save Log .................................................................................................................................................................................... 272
Save All ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 273
Download Configuration File/D ownload Configuration File to NV-RAM ............................................................................... 273
Download Configuration File to SD Card .................................................................................................................................. 274
Download Firmware/Download Firmware to NV-RAM ........................................................................................................... 274
Download Firmware to SD Card ................................................................................................................................................ 274
Upload Configuration File/Upload Configuration File to TFTP ................................................................................................ 275
Upload Log File/Upload Log File to TFTP ................................................................................................................................ 275
Reset ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 276
Reboot System ........................................................................................................................................................................... 276
Appendix A – Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet Content ACL ...................................... 277
Appendix B – Password Recovery Procedure ........................................................................................... 284
Appendix C – System Log Entries .............................................................................................................. 285
Appendix D – Trap Logs ............................................................................................................................. 304
x
Page 11
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Boldface Typewriter
Intended Readers
The DGS-3200 Series Web UI Reference Guide contains information for setup and management of the Switch. T his manual i s
intended for network managers familiar with networ k management concep ts and terminology.
Typographical Con venti ons
Convention Description
[ ]
Bold font
Font
Initial capital letter
Italics
Menu Name > Menu
Option
In a command line, square brackets indicate an optional entry. For example: [copy
filename] means that opti onally you can type cop y followed by the name of the file. Do
not type the brackets.
Indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu, or menu item. For example: Open the File
menu and choose Cancel. Used for emphasis. May also indica te system messages or
prompts appearing on s creen. For example: Y ou have mail. Bold f ont is also used to
represent filenames, program names and commands. For example: use the copy
command.
Indicates comm ands and responses to prompts that m ust be typed exac tly as printed in
the manual.
Indicates a window name. Names of keys on the keyboard have initial capitals. For
example: Click Enter.
Indicates a window nam e or a field. Also can indicate a variables or param eter that is
replaced with an appropr iate word or stri ng. For example: t ype filename means that the
actual filename should be typed instead of the word shown in italic.
Menu Name > Menu Option Indicates the menu structure. Device > Port > Port
Properties means the Port Properties menu option under the Port menu option that is
located under the Device menu.
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
A NOTE indicates important information that helps m ake better use of the
device.
A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hard ware or loss of data
and tells how to avoid the problem.
A CAUTION indic ates a potent ial for propert y damage, personal injury, or
death.
xi
Page 12

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Safety Cautions
Use the following safety guidelines to ensure your own personal safety and to help protect your system from potential damage.
Throughou t this safet y sectio n, the c aution ico n (
) is used to indicate cautions and precautions that need to be reviewed and
followed.
To reduce the risk of bodily injury, electrical shock, fire, and damage to the equipment observe the following precautions.
• Observe and follow service markings.
• Do not service any product except as explained in the system documentation.
• Opening or removing covers that a re marked with the tr iangular s ymbol with a lightning bolt may exp ose the u ser to
electrical shock.
• Only a traine d serv ice technician should service components inside these compartments.
• If any of the fo llowing cond itions occur , unplug the product from the electrical outlet and replace the part or contact your
trained service provider:
• Damage to the power cable, extension cable, or plug.
• An object has fallen into the prod uct.
• The product has been exposed to water.
• The product has been dropped or damaged.
• The product does not operate correctly when the operating instructions are correctly followed.
• Keep your system away from radiators and heat sources. Also, do not block cooling vents.
• Do not spill food or liquids on system components, and never operate t he produc t in a wet e nvironme nt. If the system gets
wet, see the appropriate section in the troubleshooting guide or contact your trained service provider.
• Do not push a ny objects int o the openin gs of the syste m. Doing so ca n cause fire or electri c shock by shor ting out int erior
components.
• Use the product only with approved equipment.
• Allow the product to cool before removing covers or touching internal components.
• Operate the product only from the type of external power source indicated on the electrical ratings label. If unsure of the type
of power source required, consult your service provider or local power company.
• To help avoid damaging the system, be sure the voltage selection switch (if provided) on the power supply is set to match the
power available at the Switch’ s lo c a tion:
• 115 volts (V)/60 hertz (Hz) in most of North and South America and some Far Eastern countries such as South Korea
and Taiwan
• 100 V/50 Hz in eastern Japan and 100 V/60 Hz in western Japan
• 230 V/50 Hz in most of Europe, the Middle East, and the Far East
• Also, be sure that attached devices are electrically rated to operate with the power available in your location.
• Use only approved power cable(s). If you have not been provided with a power cable for your system or for any AC-
powered option intended for your system, purchase a power cable that is approved for use in your country. The power cable
must be rated for the product and for the voltage and current marked on the product's electrical ratings label. The voltage and
current rating of the cable should be greater than the ratings marked on the product.
• To help prevent electric shock, plug the system and peripheral power cables into properly grounded electrical outlets. These
cables are equipped with three-prong plugs to help ensure proper grounding. Do not use adapter plugs or remove the
grounding prong from a cable. If using an extension cable is necessary, use a 3-wire cable with properly grounded plugs.
• Observe extension cable and power strip ratings. Make sure that the total ampere rating of all products plugged into the
extension cable or power strip does not exceed 80 percent of the ampere ratings limit for the extension cable or power strip.
• To help protect the system from sudden, transient increases and decreases in electrical power, use a surge suppressor, line
conditioner, or uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
• Position system cables and power cables carefully; route cables so that they cannot be stepped on or tripped over. Be sure
that nothing rests on any cables.
xii
Page 13
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
ht of more than one extended
• Do not modify power cables or plugs. Consult a licensed electrician or your power company for site modifications. Always
follow your local/national wiring rules.
• When connecting or disconnecting power to hot-pluggable power supplies, if offered with your system, observe the
following guidelines:
• Install the power supply before connecting the power cable to the power supply.
• Unplug the power cable before removing the power supply.
• If the system has multiple sources of power, disconnect power from the system b y unpluggi ng all power cables fro m
the power supplies.
• Move products with care; ensure that all casters and/or stabilizers are firmly connected to the system. Avoid sudden stops
and uneven surfaces.
General Precautions for Rack-Mountable Products
Observe the following precautions for rack stability and safety. Also, refer to the rack installation documentation accompanying
the system and the rack for specific caution statements and procedures.
• Systems are considered to be components in a rack. Thus, "component" refers to any system as well as to various peripherals
or supporting hardware.
CAUTION: Installing s yste ms in a rack without t he f ront and s ide sta bilizers insta lled c ould
cause the rack to t ip o ver , pote nti al l y resul tin g in bo di l y inj ury under certain circums tanc es .
Therefore, always install the stabilizers before installing components in the rack. After
installing system /components in a rack, never pul l more than one component out of th e
rack on its slide assemblies at one time. The weig
component could cause the rack to tip over and may result in serious injury.
• Before working on the rack, make sure that the stabilizers are secured to the rack, extended to the floor, and that the full
weight of the rack rests on the floor. Install front and side stabilizers on a single rack or front stab ilizers for joined multiple
racks befor e working on the rack.
• Always load the rack from the bo ttom up, and load the heaviest item in the ra c k first.
• Make sure that the rack is level and stable before extending a component from the rack.
• Use caution when pressing the component rail release latches and sliding a component into or out of a rack; the slide rails
can pinch your finge r s.
• After a component is inserted into the rack, carefully extend the rail into a locking position, and then slide the component
into the rack.
• Do not overload the AC supply branch circuit that provides power to the rack. The total rack load should not exceed 80
percent of the branch circuit rating.
• Ensure that proper airflow is provided to components in the rack.
• Do not step on or stand on any component when servicing other components in a rack.
NOTE: A qualified electrician must perform all connections to DC power and to safety
grounds. All electrical wiring must comply with applicable local or national codes and
practices.
CAUTION: Ne ver defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipm ent in the absence
of a suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection
authority or an electrician if uncertain that suitable grounding is available.
xiii
Page 14
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
CAUTION: The s ystem chassis m ust be positively grounded to the rack cabine t frame.
Do not attempt to connect power to the system until grounding cables are connected.
Completed power and safety ground wiring must be inspected by a qualified electrical
inspector. An energy hazard will exist if the safety ground cable is omitted or
disconnected.
CAUTION: When mounting the Switch on a cement wall, a proper concrete sleeve
anchor should be used, such as the one that is included in the optional D-Link Wall Mount
kit (DRE-KIT018).
Lithium Batter y Precauti on
CAUTION: Incorrec tl y replac ing the lithi um batter y of the Switch m a y cause the bat tery to
explode. Replace this batter y only with the s ame or equi valent t ype recomm ended by the
manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge
Static electricity can harm delicate components inside the system. To prevent static da mage, dis charge static electricity from your
body before touching any of the electronic components, such as the microprocessor. This can be done by periodically touching an
unpainted metal surface on the chassis.
The following steps can also be taken prevent damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD):
1. When unpacking a static-sensitive component from its shipping carton, do not remove the component from the antistatic
packing material until read y to install the component in the system. Just before un wrappi ng the anti static pac kaging, b e
sure to discharge static electricity from your body.
2. When transporting a sensitive component, first place it in an antistatic container or packaging.
3. Handle all sensitive compone nts in a static-safe area. If possible, use antistatic floor pads, workbench pads and an
antistatic grounding strap.
xiv
Page 15
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Section 1
Web-based Switch Configuration
Introduction
Logging onto the Web Manager
Web-Based User Interface
Introduction
All softwar e func tio ns o f the Swit ch c an be mana ged, configured, and monitored via the embedded web-based (HTML) interface.
Manage the Switch from remote station s anywhere on the network through a standard browser, such as Internet Explorer 5.5 or
later, Netscape 8.0 or later, Firefox 2.0 or later, or Apple Safari 3.0. The browser acts as a universal access tool and can
communicate directly with the Switch using the HTTP protocol.
The Web-based management module and the Console program (and Telnet) are different ways to access the same internal
switching software and configure it. Thus, all settings encountered in web-based management are the same as those found in the
console program.
Logging onto the Web Manager
To begin mana gin g the S wit ch, simpl y ru n the b ro wser i nst alle d o n your c o mputer a nd p oint i t to the IP address you have defined
for the device. The URL in the address bar should read something like: http://123.123.123.123, where the numbers 123 represent
the IP address of the Switch.
NOTE: The factory default IP address is 10.90.90.90.
This opens the management module's user authe ntication window, as seen below.
Figure 1 - 1. Enter Network Password window
Leave both t he User Name field and the Password field blank and click OK. This will open the Web-based user interface. The
Switch management features available in the web-based manager are explained below.
1
Page 16
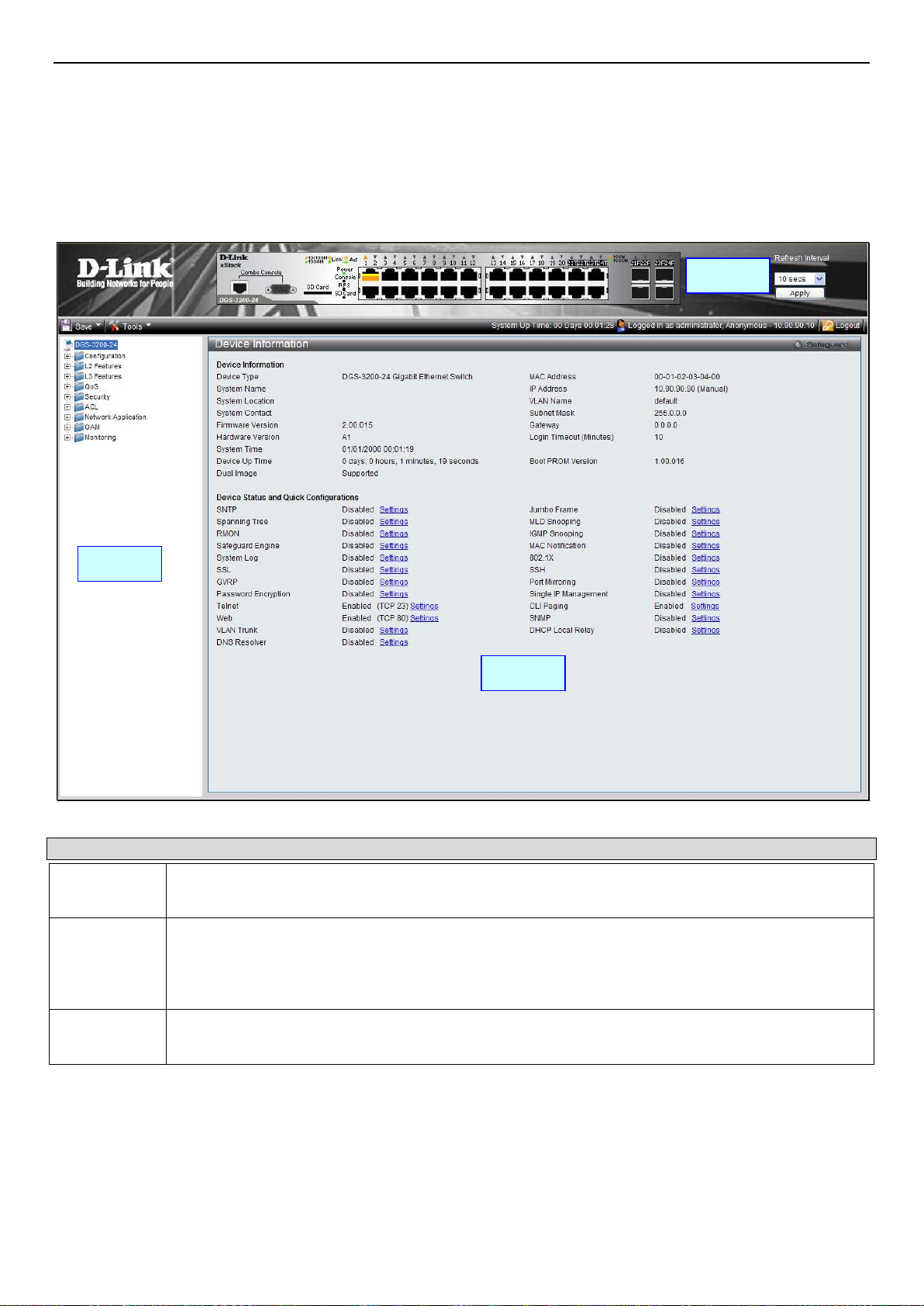
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Area 2
Area 1
Area 3
Web-based User Interface
The user interface provides access to various Switch configuration and management windows, allows the user to view
performance statistics, and permits graphical monitoring of the system status.
Areas of the User Interface
The figure below shows the user interface. Three distinct areas divide the user interface, as described in the table.
Area Function
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
Select the folder or window to display. Open folders and click the hyperlink ed window buttons and
subfolders contained within them to display windows.
Presents a graphica l near real-time image of the fron t panel of the Switch. This area dis plays the
Switch's ports and expansion modules and sho ws port activity, depending on the specified mode.
Some management f unctio ns, incl uding por t m onitorin g are acc ess ible her e. Cl ick the D-Link logo to
go to the D-Link website.
Presents Switch status based on user selection and the entry of configuration data. In addition,
hyperlinks are offered for many Switch features to enable quick configuration.
Figure 1 - 2. Main Web-Manager window
2
Page 17

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Web Pages
When connec ting t o the mana gement mode of the S witch with a web browser, a login screen is displayed. Enter a user name and
password to access the Switch's management mode.
Below is a list of the main folders available in the Web interface:
Configuration - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Switch’s configuration.
L2 Features - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Layer 2 functionality of the Switch.
L3 Features - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Layer 3 functionality of the Switch.
QoS - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Quality of Service functionality of the Switch.
Security - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Switch’s security.
ACL - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Access Control List functionality of the Switch.
Network Application - In this section the user will be able to con figure features regarding network applications handled by the
Switch.
OAM - In this section the user will be able to configure features regarding the Switch’s operations, administration and
maintenance (OAM).
Monitoring - In this section t he user will be able to monitor the Switch’s configuration and statistics.
NOTE: Be sure to configure the user name and password in the User
Accounts window before connecting the Switch to the greater network.
3
Page 18

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Configuration
Device Information
System Information
Serial Port Settings
IP Address
Port Configuration
Static ARP Settings
Gratuitous ARP
User Accounts
System Log Configuration
System Severity Settings
MAC Address Aging Time
Section 2
Web Settings
Telnet Settings
Password Encryption
CLI Paging Settings
Firmware Information
Power Saving
MAC Notification Settings
SNMP Settings
CPU Filter L3 Control Packet Settings
Single IP Management
SD Card FS Settings (DGS-3200-24 only)
SD Card Management (DGS-3200-24 only)
4
Page 19
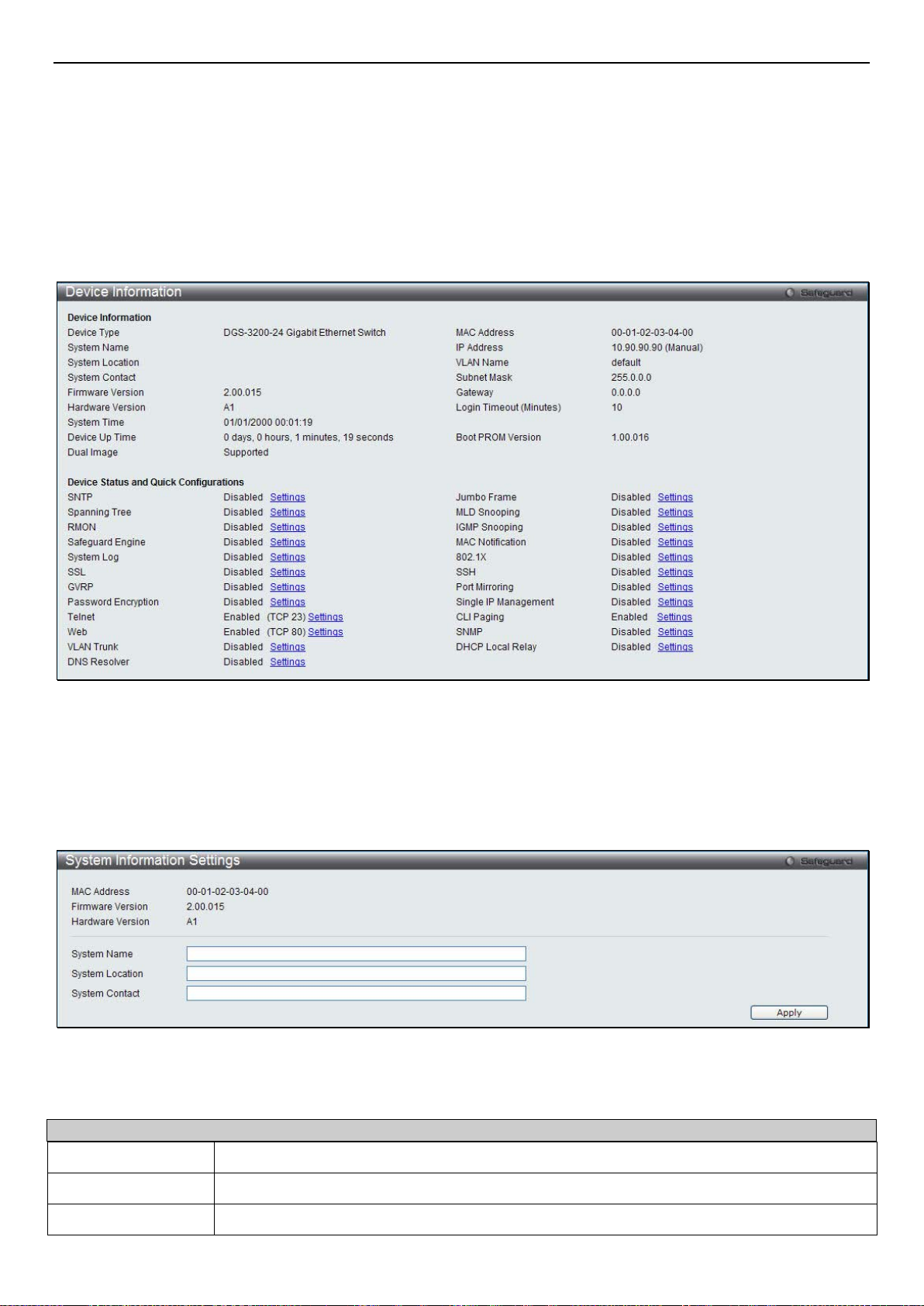
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Device Information
This window co ntains the ma in settings for all major func tions for the Switch. It appears auto matically when you log on to the
Switch. To return to the Device Information window after viewing other windows, click the DGS-3200-10/DGS-3200-16/
DGS-3200-24 folder. The Device Information window shows the Switch’s MAC Address (assigned by the factory and
unchangeable), the Boot PROM Version, Firmware Version, Hardware Version, and many other important types of information.
This is helpful to keep track o f PROM and firmware upda tes and to obtain the Switch’s MAC address fo r entry into another
network de vice’s address table, if necessar y. In addition, this window displays the status of functions on the Switc h to quickly
assess their current global status. Many functions are hyper-linked for easy access to enable quick configuration from this
window.
Figure 2 - 1. Device Information window
System Information
The user can enter a System Name, System Location, and System Contact to aid in defining the Switch.
To view the following window, clic k Configuration > System Information:
Figure 2 - 2. System Information window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
System Name
System Location
System Contact
Enter a system name for the Switch, if desired. This name will identify it in the Switch network.
Enter the location of the Switch, if so desired.
Enter a contact name for the Switch, if so desired.
5
Page 20
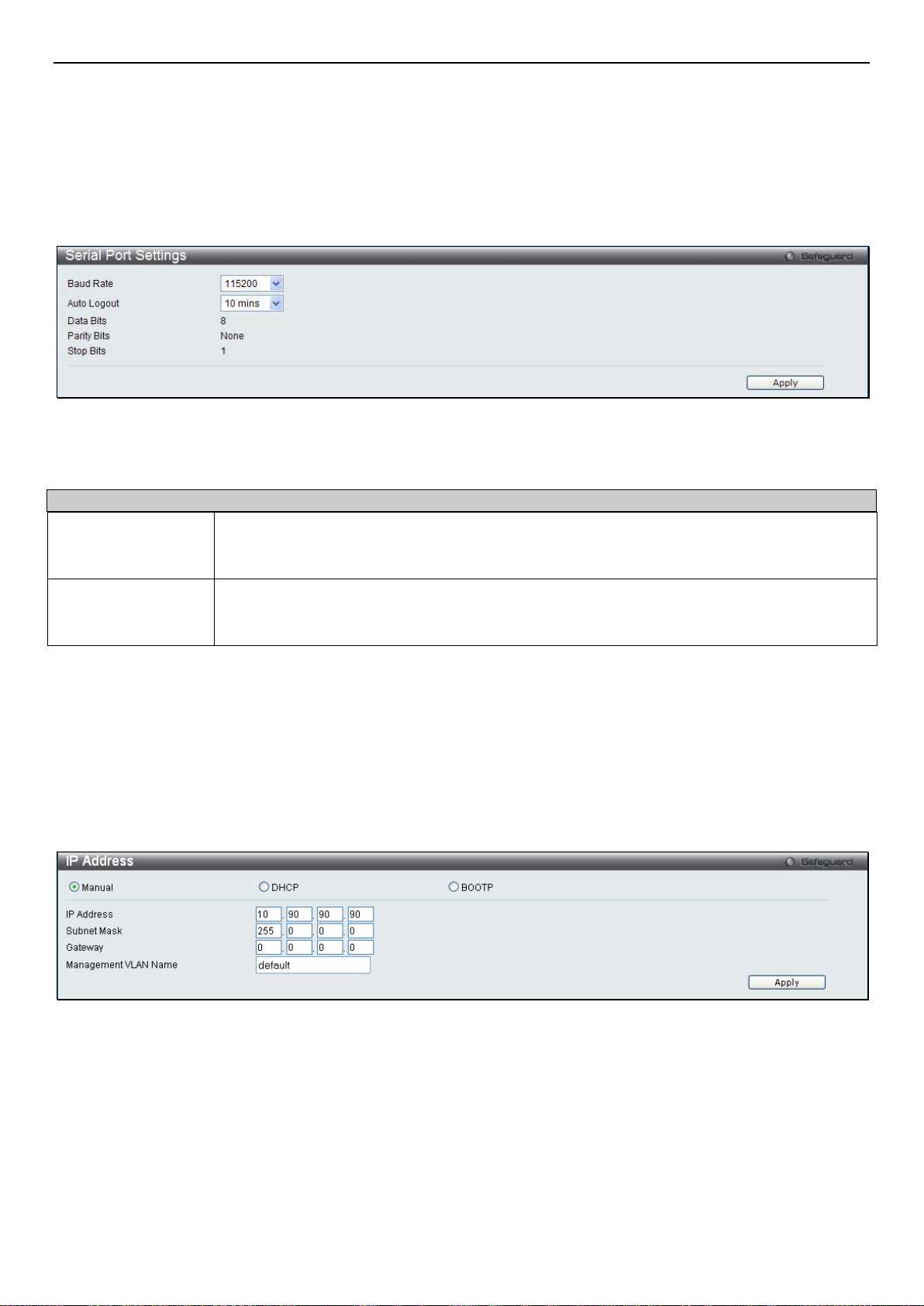
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Click
to implement changes made.
Apply
Serial Port Settings
The user can adjust the Baud Rate and the Auto Logout values.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Serial Port Settings:
Figure 2 - 3. Serial Port Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Baud Rate
This field specifies the baud rate for the serial port on the Switch. There are four possible
baud rates to choose fr om, 9600, 19200, 38400 and 115200. For a connection to the Switch
using the CLI interface, the baud rate must be set to 115200, which is the default setting.
Auto Logout
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Select the logout tim e us ed f or the c ons ole in ter f ac e. This aut omatically logs the user out after
an idle period of time, as defined. Choose from the f ol lo wing options: 2 mins, 5 mins, 10 mins,
15 mins or Never. The default setting is 10 mins.
IP Address
The IP addr ess may initially be se t using the console inter face prior to connec ting to it through the Ethernet. If the Swi tch IP
address has not yet been cha nged, read the intr oduction of the DGS-3200 Series CLI Manual for more information. The Web
manager will display the Switch’s current IP settings.
To view the following window, click Configuration > IP Address:
Figure 2 - 4. IP Address window
To manually assign the Switch’s IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address:
1. Click the Manual radio button a t the top of the window.
2. Enter the appropriate IP Address and Subnet Mask.
3. If accessing the Switch from a different subnet from the one it is installed on, enter the I P address of the default Gateway.
If managing t he Switch fro m the subnet on which it is inst alled, the use r may leave t he default add ress (0.0. 0.0) in this
field.
6
Page 21
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
4. If the Switch has no previously configured VLANs, the user can use the Management VLAN Name entitled “default”.
This defaul t Management VLAN contai ns all of the S witch ports a s members. I f the Switch has previousl y configured
VLANs, the user will need to enter the VLAN ID of the VLAN that conta ins the port connec ted to the manage ment
station that will access the Switch. T he Switch will allow management access from statio ns with the same VID listed
here.
NOTE: The Switch’s factory default IP address is 10.90.90.90 with a subnet
mask of 255.0.0.0 and a default gateway of 0.0.0.0.
To use the DHCP or BOOTP protocols to assign the Switch an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address:
Use the radio button at the top of the window to choose either DHCP or BOOTP. This selects the method the Switch assigns an IP
address on the next reboot.
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Manual
DHCP
BOOTP
Subnet Mask
Gateway
Management
VLAN Name
Allows the entry of an IP address, subnet mask, and a default gateway for the Switch. These fields
should be of the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a number (represented in decimal form)
between 0 and 255. This address should be a unique address on the network assigned for use by
the network admini strator.
The Switch will send out a DHCP broadcast request when it is powered up. The DHCP protocol
allows IP addresses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned by a DHCP server. If
this option is set, the Switch will first look for a DHCP server to provide it with this information
before using the default or previously entered settings.
The Switch will send out a BOOTP broadcast request when it is powered up. The BOOTP protocol
allows IP addresses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned by a central BOOTP
server. If this option is set, the Switch will first look for a BOOTP server to provide it with this
information before using the default or previously entered settings.
A Bitmask that determines the extent of the subnet that the Switch is on. Should be of the form
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a number (represented in decimal) between 0 and 255. The
value should be 255.0.0.0 for a Class A network, 255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, and
255.255.255.0 for a Class C network, but custom subnet masks are allowed.
IP address that determines where packets with a destination address outside the current subnet
should be sent. This is usually the address of a router or a host acting as an IP gateway. If your
network is not part of an intranet, or you do not want the Switch to be accessible outside your local
network, you can leave this field unchanged.
This allows the entry of a VLAN name from which a management station will be allowed to manage
the Switch using TCP/IP (in-band via Web manager or Telnet). Management stations that are on
VLANs other than the one entered here will not be able to manage the Switch in-band unless their
IP addresses are entered in the Trusted Host window (Security > Trusted Host). If VLANs have
not yet been configured for the Switch, the default VLAN contains all of the Switch’s ports. There
are no entries in the Trusted Host table, by default, so any management station that can connect to
the Switch can access the Switch until a management VLAN is specified or Management Station IP
addresses are assigned.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Setting the Switch’s IP Address using the Console Interface
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with an SNMP network mana ger or othe r
TCP/IP application (for example BO OTP, TFTP). The Switch’s default IP address is 10.90.90.90. The default Switch IP address
can be changed to meet the specification of your networking address scheme.
7
Page 22
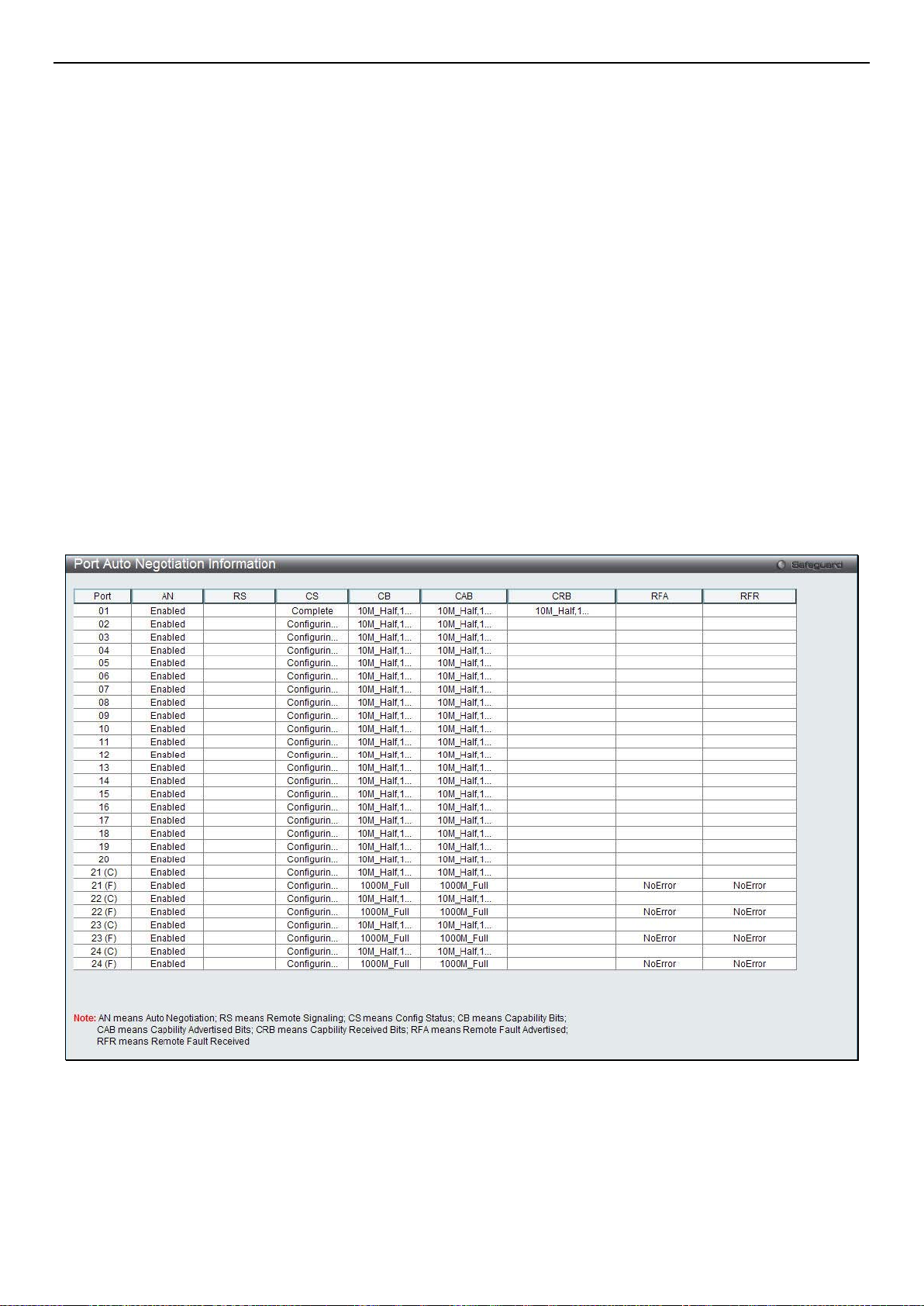
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
The IP address for the Switch must be set be fore the Web-based manager can manage the switch. The Switch IP address can be
automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known. The
IP address may be set using the Command Line Interface (CLI) over the console serial port as follows:
• Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy. Where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the y’s
represent the corresponding subnet mask.
• Alternatively, the user can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z. Where the x’s represent the IP
address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the z represents the corresponding number of subnets in
CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask, which can then be used to connect a
management station to the Switc h’s Telnet or Web-based management agent.
Successful entry of the command will produce a “Success” message, indicating that the command execution was correctly. The
user may now utilize this address to configure or manage the Switch through Telnet, the Command Line Interface (CLI) or the
Web-based management (GUI).
Port Configuration
Port Auto Negotiation Information
The following window displays t he detailed auto negotiation information.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Auto Negotiation Information:
Figure 2 - 5. Port Auto Negotiation Informati o n window
Port Detail Information
This window displays the detail information of ports.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Detail Information:
8
Page 23

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 6. Port Detail Information window
Click the Refresh button to update the information.
Port Settings
This windows is used to configure and display the switch ports settings.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Settings:
9
Page 24
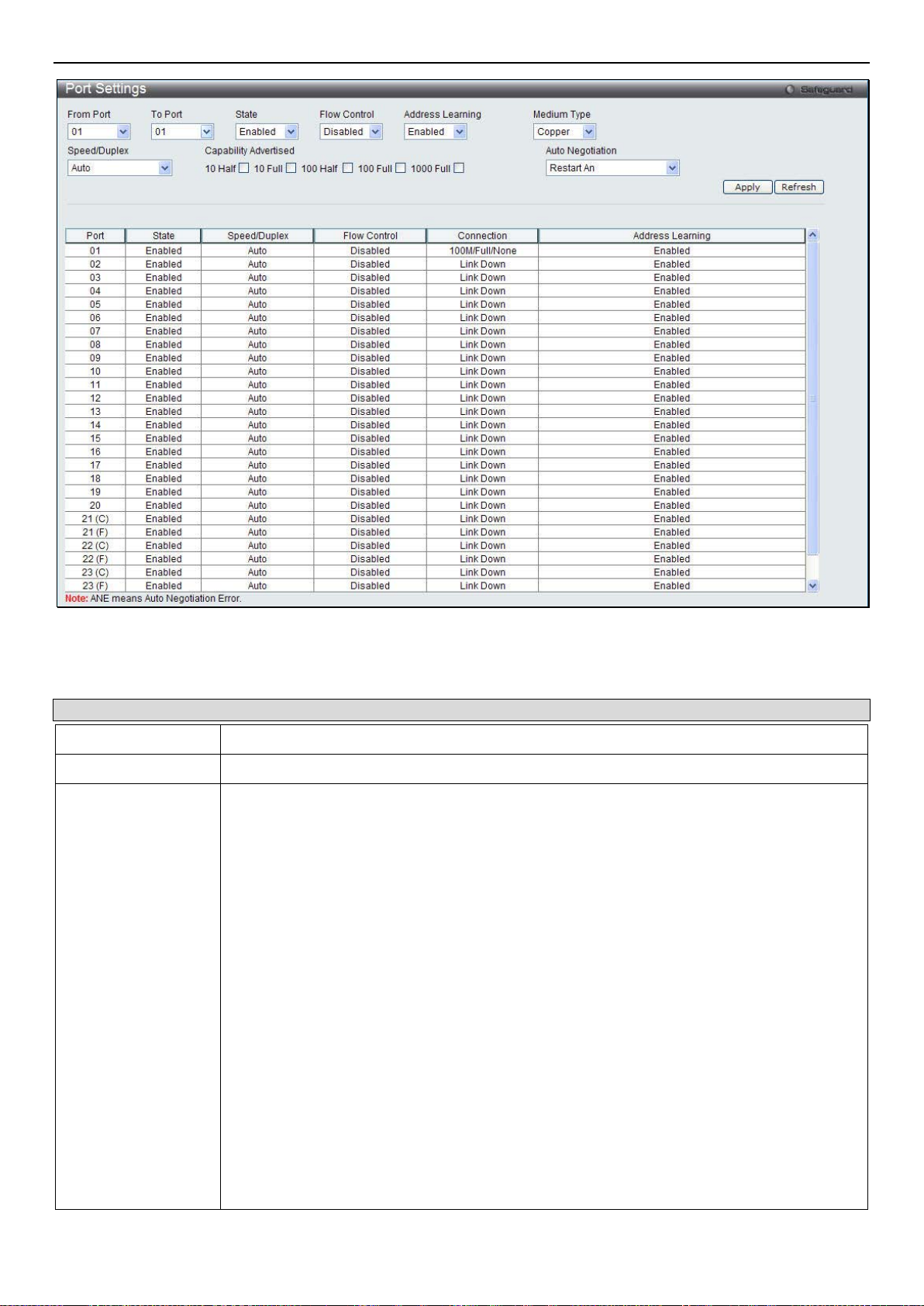
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 7. Port Settings window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Speed/Duplex
Use the drop-down menus to select the ports to be configured.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable a given port or group of ports.
Toggle the Speed/Du plex field to either s elect the speed and duplex/half -duplex s tate of the
port. Auto denotes auto-negotiation between 10 and 100 Mbps devices, in full- or halfduplex. The Auto s etting allows the port t o automatically determ ine the fastest settings the
device the port is connected to can handle, and then to use those settings. The other
options are 10M Half, 10M Full, 100M Half, 100M Full, 1000M Full_Master, 1000M
Full_Slave, and 1000M Full. There is no automatic adjustment of port settings with any
option other than Auto.
The Switch allows the user to configure three types of gigabit connections; 1000M
Full_Master, 1000M Full_Slave, and 1000M Full. Gigabit connections only support full
duplex connections and take on certain characteristics that are different from the other
choices listed.
The 1000M Full_Master and 1000M Full_Slave parameters refer to connections running a
1000BASE-T cable for connection between the Switch port and other device capable of a
gigabit connection. The master setting (1000M Full_Master) will allow the port to advertise
capabilities related to duplex, speed and physical layer type. The master setting will also
determine the master and slave relationship between the two connected physical layers.
This relationship is necessary for establishing the timing control between the two physical
layers. The timing control is set on a master physical layer by a local source. The slave
setting (1000M Full_Slave) uses loop timing, where the timing comes from a data stream
received from the master. If one connection is set for 1000M Full_Master, the other side of
the connection must be set for 1000M Full_Slave. Any other configuration will result in a link
down status for both ports.
10
Page 25
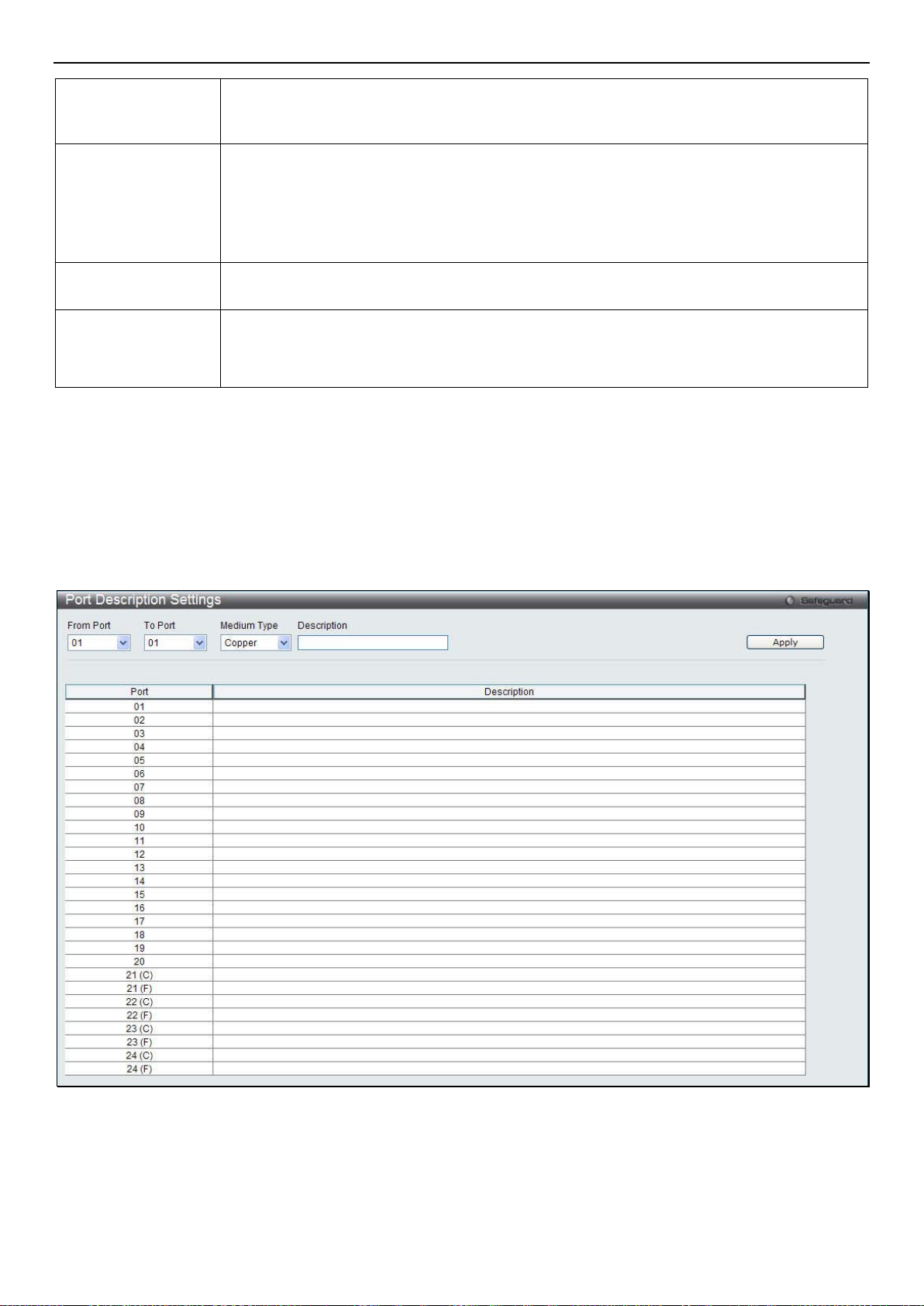
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Flow Control
Address Learning Enable or disable MAC address learning for the selected ports. When Enabled, destination
Medium Type
Auto Negotiation
Click Apply to implement the new setti ngs on the Switch.
Click the Refresh button to refresh the display section of this page.
Displays the flow control scheme used for the various port configurations. Ports configured
for full-duplex use 802.3x flow control, half-duplex ports use backpressure flow config, and
Auto ports use an automatic selection of the two. The default is Disabled.
and source MAC addresses are automatically listed in the forwarding table. When address
learning is Disabled, MAC addresses must be manually entered into the forwarding table.
This is sometimes done for reasons of security or efficiency. See the section on
Forwarding/Filtering for information on entering MAC addresses into the forwarding table.
The default setting is Enabled.
If configuring the Combo ports, this defines the type of transport medium to be used,
whether Copper or Fiber.
Use the drop-down menu to specify the auto-negotiation configuration.
Restart An – Select to restart the auto-negotiation process
Remote Fault Advertisedt - The remote fault advertisement option will be configured.
Port Description Settings
The Switch supports a port description feature where the user may name various ports.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Description:
Figure 2 - 8. Port Description window
Use the Fro m P o r t a nd T o P ort drop-down menu to choose a port or range of ports to describe. Users may then enter a description
for the chosen port(s). If configuring the Combo ports, the Medium Type defines the type of transport medium to be used, whether
Copper or Fiber.
Click Apply to set the descriptions in the Port Description window.
11
Page 26

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Port Error Disabled
The following window will display the information ab out ports that have had their connection status disabled, for reasons such as
storm control or link down status.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Port Error Disabled:
Figure 2 - 9. Port Error Disabled window
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
Port
Port State
Connection Status
Reason
Displays the port that has been error disabled.
Describes the current running state of the port, whether enabled or disabled.
This field will read the uplink status of the individual ports, whether enabled or disabled.
Describes the reason why the port has been error-disabled, such as it has become a
shutdown port for storm control.
Jumbo Frame Settings
The Switch supports jumbo frames. Jumbo frames are Ethernet frames with more than 1,500 bytes of payload. The Switch
supports jumbo frames with a maximum frame size of 10240 bytes.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Port Configuration > Jumbo Frame Settings:
Figure 2 - 10. Jumbo Frame window
The following parameter can be configured:
Parameter Description
Jumbo Frame
To enable or disable Jumbo Frame, use the radio button and click Apply.
This field will enable or disable the Jumbo Frame function on the Switch. The default is
Disabled. The maximum frame size is 10240 bytes.
Static ARP Settings
The Address Resolution Protocol is a TCP/IP protocol that converts IP addresses into physical addresses. This table allows
network managers to view, define, modify, and delete ARP information for specific devices.
Static entries can be defined in the ARP table. When static entries are defined, a permanent entry is entered and is used to translate
IP addresses to MAC addresses.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Static ARP Settings:
12
Page 27
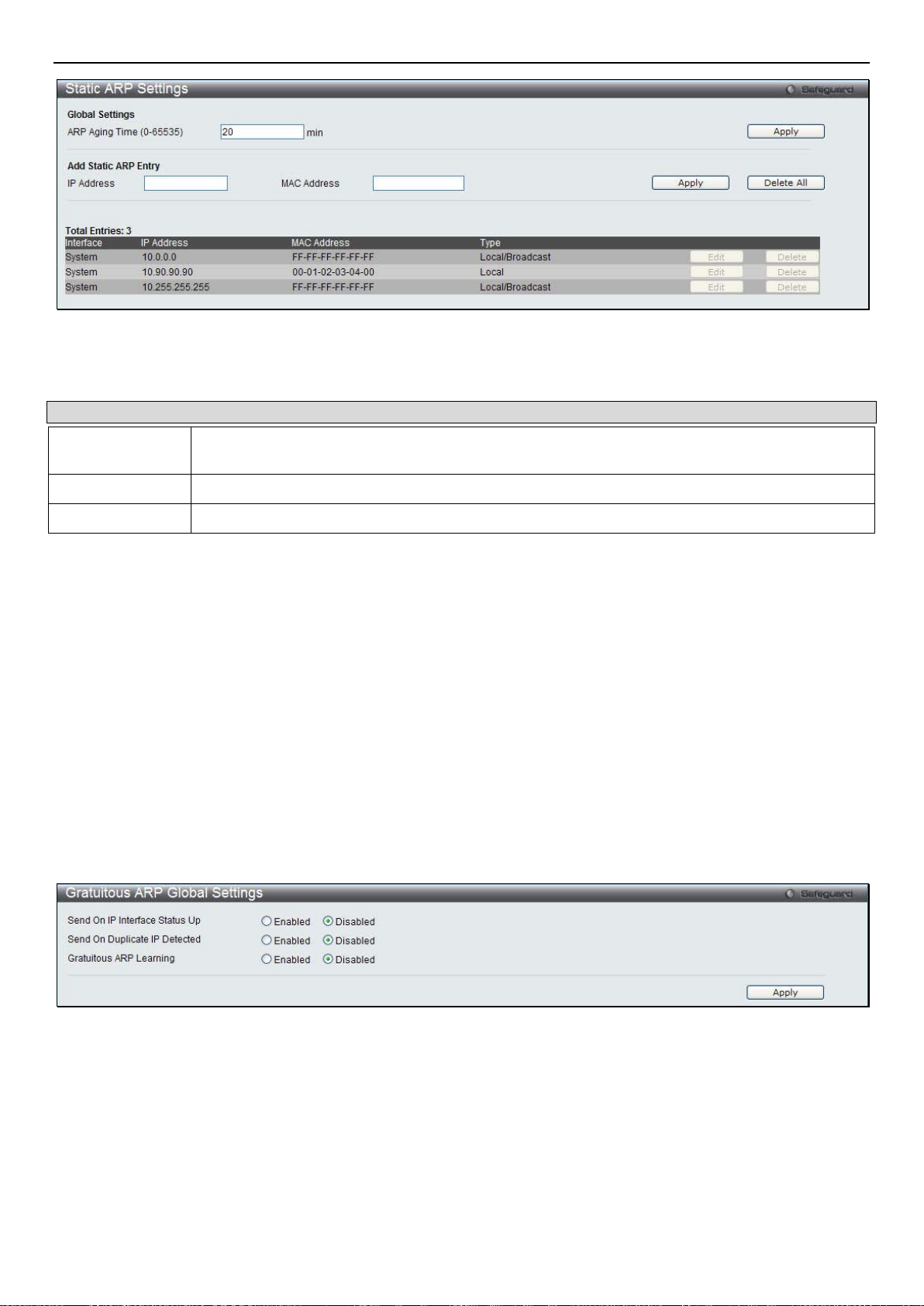
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 11. Static ARP Settings window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
ARP Aging Time
(0-65535)
IP Address
MAC Address
After entering a global ARP Aging Time in seconds, click Apply to allow it to take effect. The default value is 20 seconds.
After entering the IP Address and MAC Address of the Static ARP entry, click Apply to implement the new entry. To completely
clear the static ARP entries, click the Delete All button.
To modify a static ARP entr y, click the Edit button located on the right side of the entry in the ARP table at the bottom of the
window.
To delete a static ARP entry, click the Delete button located on the right side of the entry in the static ARP table at the bottom of
the window.
The ARP entry age-out time, in seconds. The default is 20 minutes.
The IP address of the ARP entry.
The MAC address of the ARP entry.
Gratuitous ARP
Gratuitous ARP Global Settings
The window is used to enable or disable the gratuitous ARP global settings.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Gratuitous ARP > Gratuitous ARP Global Settings:
Figure 2 - 12. Gratuitous ARP Global Settings window
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Gratuitous ARP Settings
The user can configure the IP interface’s gratuitous ARP parameter.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Gratuitous ARP > Gratuitous ARP Settings:
13
Page 28
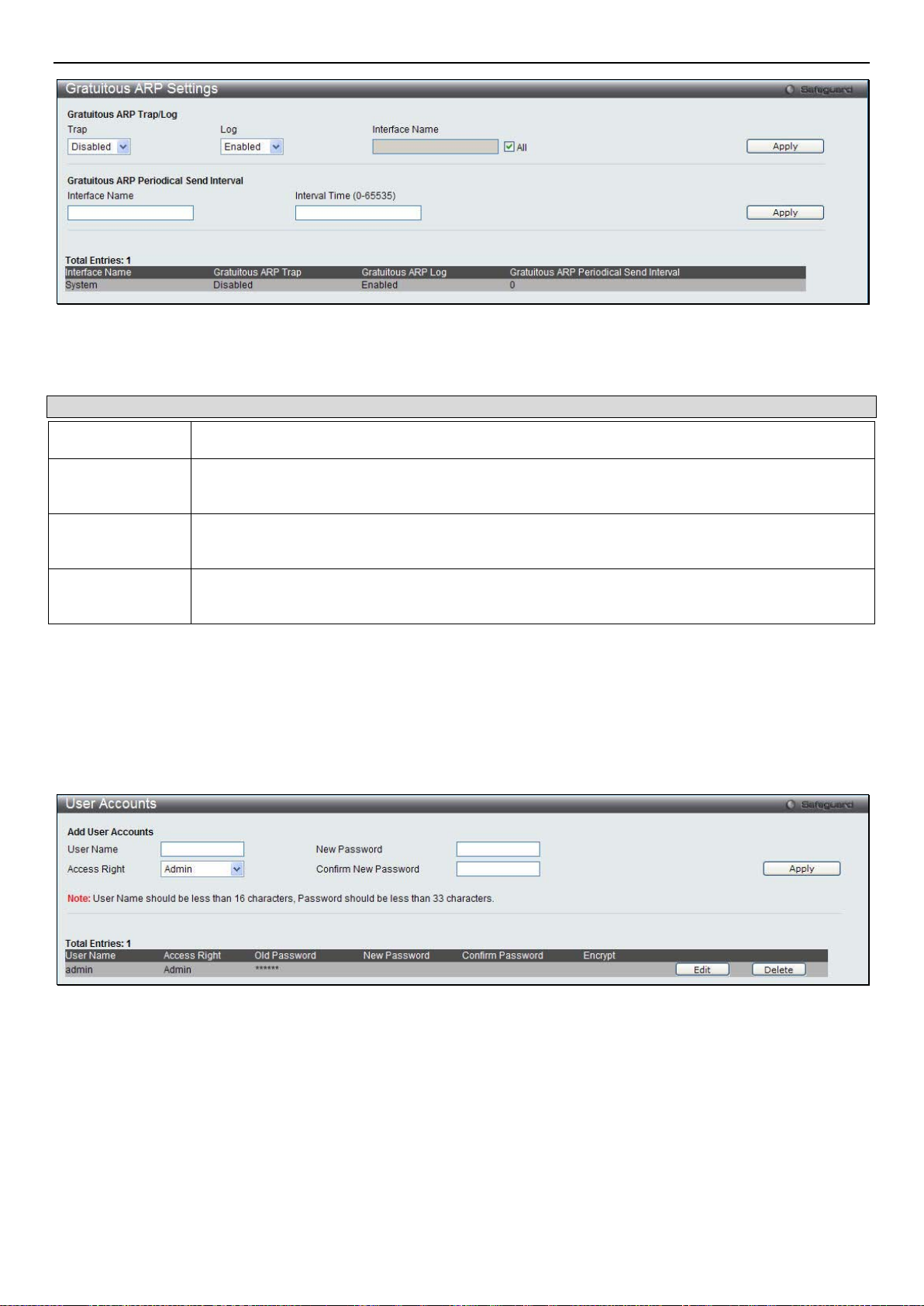
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 13. Gratuitous ARP Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
Trap
Log
Interface Name
Interval Time (0-
65535)
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the trap option. By default the trap is disabled.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the logging option. By default the event log is
enabled.
Enter the interface n ame of the Layer 3 in terface. Sel ect All to enable or d isable gratuit ous ARP
trap or log on all interfaces.
Enter the periodical l y send gr atui tous ARP interval time in seconds. 0 means that gratuitous ARP
request will not be sent periodically. By default the interval time is 0.
User Accounts
The Switch allows the co ntrol of user privile ges.
To view the following window, click Configuration > User Accounts:
Figure 2 - 14. User Accounts window
To add a new user, type in a User Name and N ew P as swo rd and retype the same password in the Confirm New Password field.
Choose the level of privilege (Admin or User) from t he Access Right drop-down menu.
14
Page 29
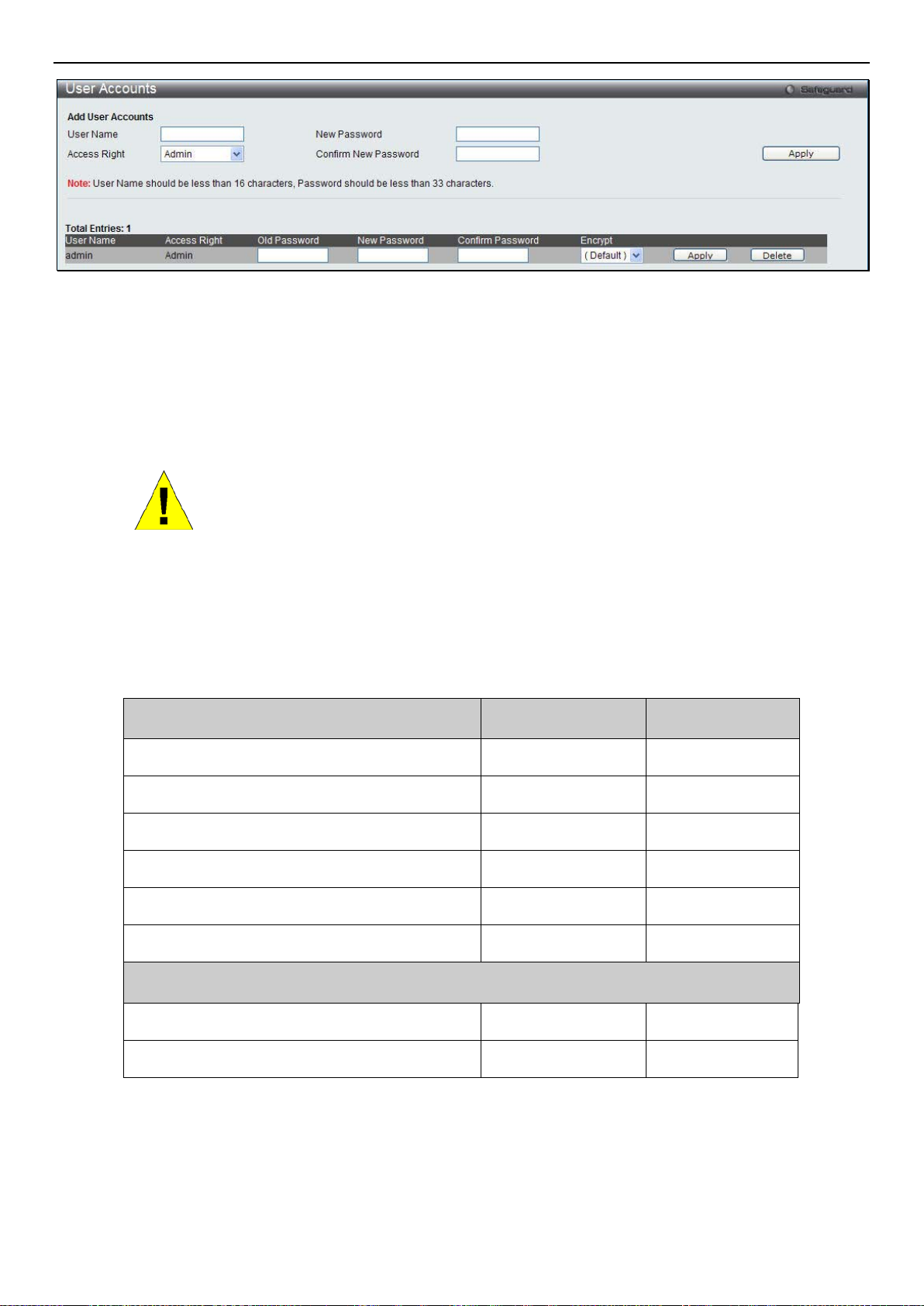
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 15. User Accounts window (Edit)
Modify or delete an existing user account in the table at the bottom of the window. To delete the user account, click the Delete
button. To c hange the passwor d, click the Edit button next to the entry in the table at the bottom of the window. Enter an Ol d
Password, New Password, and retype the new password in the Confirm Password field offered, use the drop-down menu to select
the type of encryption desired (Plain Text or Sha 1), and then click Apply. The level of privilege (Admin or User) can be viewed
in the Access Ri ght column in the table at the bottom of the window.
NOTICE: In case of lost passwords or password corruption, please refer to the
Appendix D, “Password Recovery Procedure,” which will guide you through the
steps necessary to resolve this issue.
Admin and User Privileges
There are two levels of user privileges, Admin and User. Some menu selections available to users with Admin p r ivi le ge s ma y no t
be available to those with User privileges.
The following table summarize s the Admin and User privileges:
Management Admin User
Configuration Yes Read-only
Network Monitoring Yes Read-only
Community Strings and Trap Stations Yes Read-only
Update Firmware and Configuration Files Yes No
System Utilities Yes No
Factory Reset Yes No
User Account Management
Add/Update/Delete User Accounts Yes No
View User Accounts Yes No
Command Logging Settings
This window is used to enable or disable the command logging settings.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Command Logging Settings:
15
Page 30
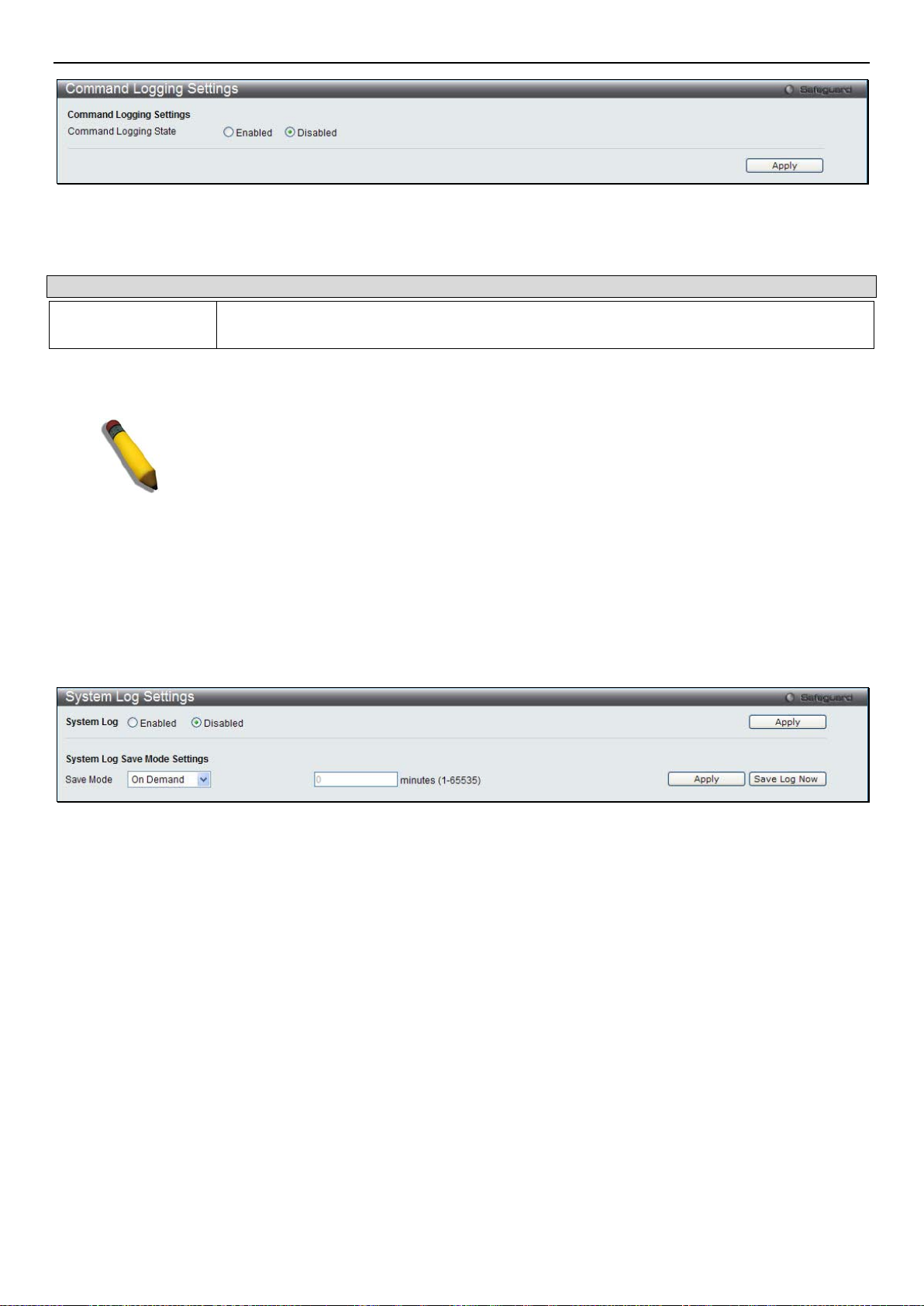
xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 16. Command Logging Settings window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Command Logging
State
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made.
Use the radio buttons to enable or disable the function.
NOTE: When the switch is under the booting or executing downloaded configuration
procedure, all configuration commands will not be logged. When the user uses AAA
authentication to logged in, the user name should not be changed if the user has used the
Enable Admin function to replace its privilege.
System Log Configuration
System Log Settings
The windo w is used to choose a method for which to save the Switch’s log to the flash memory of the Switch.
To view the following window, click Configuration > System Log Configuration > System Log Settings:
Figure 2 - 17. System Log Settings window
Use the drop-down menu to choose the method for saving the switch log to the flash memory. The user has three opt ions:
• Time Interval – Users who choose this method can co nfigur e a t ime i nterval by which t he S witch will sa ve the log files ,
in the box adjacent to this configuration field. The user may set a time between 1 and 65535 minute s.
• On Demand – Users who choose this method will only save log files when they manually tell the Switch to d o so, either
using the Save Log li nk in the Save folder or clicking the Save Log Now button on this window.
• Log Trigger – Users who cho ose this met hod will have log files saved to the Switch every time a log event occurs on the
Switch.
The default setting is On Demand. Click Apply to save changes made. Click Save Log Now to immediately save log files
currently on the switch.
System Log Host
The Switch can send Syslog messages to up to four designated servers using the System Log Server.
To view the following window, click Configuration > System Log Configuration > System Log Host:
16
Page 31

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 18. System Log Host window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Host ID Syslog server settings index (1 to 4).
Host IP Address
UDP Port (514 or
6000-65535)
Severity
Facility Use the drop-down menu to select Local 0, Local 1, Local 2, Local 3, Local 4, Local 5, Local
Status Choose Enabled or Disabled to activate or deactivate.
To set the Sys tem Log Se rver co nfig ura tion, clic k Apply. Click the Edit button to configure the specific entry. To delete an entry
from the Syst em Log Host List table, click the corresponding Delete button next to the entry.
The Ipv4 address of the Syslog server.
Type the UDP port number used for sending Syslog messages. The default is 514.
This drop-down menu allows you to select the level of messages that will be sent. The
options are Warning, Informational, and All.
6, or Local 7.
System Severity Settings
The Switch can be configured to allow alerts be logged or sent as a trap to an SNMP agent or both. The level at which the alert
triggers either a log entry or a trap message can be set as well. Use the System Severity Settings window to set the criteria for
alerts. The current settings are displayed below the System Severity Table.
To view the following window, click Configuration > System Severity Settings:
Figure 2 - 19. System Severity Settings window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
System Severity Choose how the alerts are used from the drop-down menu. Select Log to send the alert of the
Severity Type configured to the Switch’s log for analysis. Choose Trap to send it to an SNMP
agent for analysis, or select All to send the chosen alert type to an SNMP agent and the
Switch’s log for analysis.
Severity Level
Choose what level of alert will trigger sending the lo g entry or trap message as defined by the
17
Page 32

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Severity Name. Select Critical to send only critical events to the Switch’s log or SNMP agent.
Choose Warning to send critical and warning events to the Switch’s log or SNMP agent.
Select Information to send informational, warning, and critical events to the Switch’s log or
SNMP agent.
Click Apply to implement the new System Severity Settings.
MAC Address Aging Time
Users can configure the MAC Address aging time on the Switch.
To view the following window, clic k Configuration > MAC Address Aging Time:
Figure 2 – 20. MAC Address Aging Time window
The following parameter may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
MAC Address
Aging Time (10-
875)
Click Apply to set the MAC Address Aging Time.
Specify the length of time a learned MAC Address will rem ain in the forwarding table withou t
being accessed (tha t is , how lo ng a learned MAC Add ress is allo wed t o rem ain id le). T o chang e
this, type in a diff erent value to represe nt the MAC addres s age-out time in sec onds. The MAC
Address Aging Tim e can be set to an y value between 10 and 875 seconds. The default s etting
is 300 seconds.
Web Settings
Users can configure the Web settings on the Switch.
To view the following window, clic k Configuration > Web Settings:
Figure 2 – 21. Web Settings window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Web Status
Port (1-65535)
Click Apply to set the web set tings.
Web-based management is Enabled by default. If you choose to disable this by clicking
Disabled, you wil l lose the abilit y to configur e the system through the web interface as so on as
these settings are applied.
The TCP port num ber used for W eb-based m anagement of the Switc h. The “well-k nown” TCP
port for the Web protocol is 80.
18
Page 33

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Telnet Settings
Users can configure Telnet Settings on the Switch.
To view the following window, clic k Configuration > Telnet Settings:
Figure 2 – 22. Telnet Settings window
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Telnet Status
Port (1-65535)
Click Apply to set the Telnet setting.
Telnet configuration is Ena bled by default. If you do not want to allow configurati on of the system
through Telnet choose Disabled.
The TCP port num ber used for Telnet m anagement of the Switch. The “well-known” T CP port for
the Telnet protocol is 23.
Password Encrypt ion
Users can configure Password Encryption on the Switch.
To view the following window, clic k Configuration > Password Encryption:
Figure 2 – 23. Password Encryption window
The following parameter may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Password
Encryption Status
Click Apply to set the password encryption.
Password encryption is Disabled by default. To enable password encryption, click the
Enabled radio button.
CLI Paging Settings
Users can stop t he scrolling of multipl e pages beyond the li mi ts of the console when using the Command Line Interface.
To view the following window, clic k Configuration > CLI Paging Settings:
Figure 2 – 24. CLI Paging Settings window
19
Page 34

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
The following parameter may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
CLI Paging
Status
Click Apply to set the CLI Paging setting.
Command Line Interf ace paging stops each page at t he end of the console. Thi s allows you to
stop the scrolling of multiple pages of text beyond the limits of the console. CLI Paging is
Enabled by default. To disable it, click the Disabled radio button.
Firmware Information
Users can view, set the next boot-up status, and delete current firmware images stored on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Firmware Information:
Figure 2 – 25. Firmware Information windo w (DGS-3200-10 and DGS-3200-16 models)
Figure 2 – 26. Firmware Information window (DGS-3200-24 model)
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
ID
States the image ID number of the firmware in the Switch’s memory. The Switch can store 2
firmware images for use. Image ID 1 will be the default boot-up firmware for the Switch unless
otherwise configured by the user.
20
Page 35

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Version
Size
Update Time
From
User
Path Name
(DGS-3200-24
model only)
States the firmware version.
States the size of the corresponding firmware, in bytes.
States the specific time the firmware version was downloaded to the Switch.
States the IP address of the origin of the firmware. There are six ways firmware may be
downloaded to the Switch. Boot-up files are denoted by an asterisk (*) next to the file.
Console – If the IP address has the word Console next to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade
through the Console Serial Port (RS-232).
Telnet – If the IP address has the word Telnet next to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade through
Telnet.
SNMP – If the IP address has the word SNMP next to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade through
the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
WEB – If the IP address has the word WEB next to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade through the
web-based management interface.
SSH – If the IP address has the word SSH next to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade through the
Secure Shell (SSH).
SIM – If the IP address has the word SIM next to it, it denotes a firmware upgrade through the
Single IP Management feature.
States the user who downloaded the firmware. This field may read “Anonymous” or “Unknown”
for users that are not identified.
This parameter is used to boot the Switch up from a firmware image stored on an SD card.
To boot the Switch from a firmware image stored on an SD card carry out the following:
• Input the path of the firmware image on the SD-card (such as "c:\DGS3200.had").
• Click the adjacent Set Boot button to use the firmware image, stored on the SD-card, as
the bootup image.
To set firmware as the boot-up firmware the next time the Switch is restarted, click the Set Boot button. To remove the firmware
from this wi ndow, click the Delete button.
Dual Configuration Settings
Users can display dual configuratio n settings o n the Switch. The S witch allows two con figurations to b e stored in its memor y and
either can be configured as the boot-up confi gurat io n for the Swit ch ( the DG S-3200-24 also allows configurations to be stored on
an SD-card). The user may select a boot-up configurat ion for t he Swit ch b y clic king t he Boot button to select it. This will instruct
the Switch to use this newly selected configuration the next time the Switch is restarted. To delete a configuration, click the
adjacent Delete button. To set a configuration as the active configuration, click the adjacent Active button.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Dual Configuration Settings:
21
Page 36

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 27. Dual Configuration Settings window (DGS-3200-10 and DGS-3200-16 models)
Figure 2 - 28. Dual Configuration Settings window (DGS-3200-24 model)
The following parameters may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
ID
File Name
Version
Size (Bytes)
Update Time
From
States the configuation ID number of the configuaration in the Switch’s memory. The Sw itch can
store 2 configurations for use. Configuration ID 1 will be the default boot-up configuration for the
Switch unless otherwise configured by the user.
States the file name.
States the configuration version.
States the size of the corresponding configuration, in bytes.
States the specific time the configuration version was downloaded to the Switch.
States the IP address of the origin of the configuration. There are five ways a configuration may
be downloaded to the Switch. Boot-up files are denoted by an asterisk (*) next to the file.
22
Page 37

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Console – If the IP address has the word Console next to it, it denotes a configuration upgrade
through the Console Serial Port (RS-232).
Telnet – If the IP address has the word Telnet next to it, it denotes a configuration upgrade
through Telnet.
SNMP – If the IP address has the word SNMP next to it, it denotes a configuration upgrade
through the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
WEB – If the IP address has the word WEB next to it, it denotes a configuration upgrade through
the web-based management interface.
SSH – If the IP address has the word SSH next to it, it denotes a configuration upgrade using
Secure Shell (SSH).
SIM – If the IP address has the word SIM next to it, it denotes a configuration upgrade through
the Single IP Management feature.
User
Boot Up States if the configuration will be used to boot up the Switch or not. Yes indicates that the
Path Name
(DGS-3200-24
model only)
Setting the Boot Up Configuration:
Click the
•
A
Success
•
The Boot Up parameter next to the configuration that will be used to boot up the Switch will read Yes.
•
States the user who downloaded the configuration. This field may read “Anonymous” or
“Unknown” for users that are not identified.
configuration will be used as the boot up configuration. No indicates that the configuration will not
be used as the boot up configuration.
This parameter is used to boot the Switch up from a configuration stored on an SD card.
To boot the Switch from a configuration stored on an SD card carry out the following:
• Input the path of configuration on the SD-card (such as "c:\DGS3200.had").
• Click the adjacent Set Boot button to use the configuration, stored on the SD-card, as
the bootup configuration.
• Click the adjacent Active button to make the configuration, stored on the SD-card, the
active configuration.
button next to the configuration you want to use as the Boot Up configuration.
Boot
message appears to indicate that the configuration that will be used for booting up the Switch has changed.
Setting the Active Configuration:
Click the
•
A
Success
•
An asterisk will appear next to ID of the configuration that is being used as the active configuration.
•
Deleting a Configuration:
Click the
•
A
Success
•
button next to the configuration you want to use as the Active configuration.
Active
message appears to indicate that the configuration that will be used as the active configuration has changed.
button next to the configuration you want to delete.
Delete
message appears to indicate that the configuration has been deleted.
Power Saving
LED State Settings
This window is used to configure the port LED state.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Power Saving > LED State Settings:
23
Page 38

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 – 29. Port LED State Settings window
The following parameter may be configured:
Parameter Description
Port LED State
Click Apply to save the settings.
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable the port LED state.
Power Saving Settings
This windo w al lows the user to imple me nt t he S wi tc h’ s b uil t -i n power saving features and set the schedule to enforce the settings.
When the Po wer Saving Mode Link Detection State is Enabled, a port which has a link down status will be turned off to sa ve
power to the Switch. This will not affect the port’s capab ilities when the port status is link up. When the Power Saving Mode
Length Detection State is Enabled, the Switc h will automatically determine the length of the cable a nd adjust the power flow
accordingly. When Power Saving Mode LED Sta te is Enabled, the LED’s state of ports will be turned off during the confi gured
time range. When Power Saving Mode Port State is Enabled, the por ts will be shut down during the configured ti me ra nge. W he n
Power Saving Mode Hibernation State is Enabled, the Switch will go into a low power state and be id le during the configured
time range. It will shut do wn all the ports, all network funct ion (telnet, pin g, etc.) will not work, and only the co nsole connectio n
will wor k via the RS232 port. If the Switch is an endpoint type PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment), it will not provide power to the
port.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Power Saving > Power Saving Settings:
Figure 2 – 30. Power Saving Settings windo w
The following parameter may be configured or viewed:
Parameter Description
Power Saving Mode
Link Detection State
Power Saving Mode
Length Detection
State
Power Saving Mode
LED State
Power Saving Mode
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable the link detection state.
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable length detection state.
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable LED state.
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable port state.
24
Page 39

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Port State
Power Saving Mode
Hibernation State
Action
Time Range Name
Click Apply to set the password encryption. Click the Clear Time Range to remove all the entries.
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable hibernation state.
Use the drop down menu to add or delete the schedule.
Specify the name of the schedule.
Power Saving LED Settings
This window is used to add or delete the power saving schedule on the LED of all ports.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Power Saving > Power Saving LED Settings:
Figure 2 – 31. Power Saving LED Settings window
The following parameter may be configured:
Parameter Description
Action
Time Range Name
Click the Apply button to save the settings. Click the Clear Time Range to remove all the entries.
Use the drop down menu to add or delete the schedule.
Specify the name of the schedule.
Power Saving Port Settings
This window is used to set the power saving state.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Power Saving > Power Saving Port Settings:
Figure 2 – 32. Power Saving Port Settings window
The following parameter may be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
Action
Time Range Name
Use the drop-down menu to select the ports to be configured.
Use the drop down menu to add or delete the schedule.
Specify the name of the schedule.
25
Page 40

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Click the Apply button to save the settings.
Click the Clear Time Range to remove all the entries.
MAC Notification Settings
MAC Notification is used to monitor MAC addresses learned and entered into the forwarding database.
MAC Notification Global Settings
This window allows you to glob a lly set MAC notification on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Configuration > MAC Notification Settings > MAC Notification Global Sett ings:
Figure 2 - 33. MAC Notification Global Settings window
The following parameters may be viewed and modified:
Parameter Description
State
Interval (1-2147483647)
History Size (1-500)
Click Apply to implement your changes.
Enable or disable MAC notification globally on the Switch
The time in seconds between notifications.
The maximum number of entries listed in the history log used for notification. Up to
500 entries can be specified.
MAC Notification Port Settings
Users can set MAC notification for individual ports on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Configuration > MAC Notification Settings > MAC Notification Port Settings:
26
Page 41

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 34. MAC Notification Port Settings window
To change MAC notification settings for a port or gro up of ports on the Switch, configure the following parameters:
Parameter Description
From Port
To Port
State
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Select a beginning port to enable for MAC notification using the drop-down menu.
Select an ending port to enable for MAC notification using the drop-down menu.
Enable MAC Notification for the ports selected using the drop-down menu.
SNMP Settings
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed specifically for managing and
monitoring network device s. SNMP enab les network mana gement statio ns to read and modi fy the settings of gateways, ro uters,
switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system features for proper operation, monitor performance and
detect potential problems in the Switch, switch group or network.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the device. A defined set of
variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the device. These objects are defined in a
Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard presentation of the information controlled by the on-board
SNMP agent. SNMP defines both the format of the MIB specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the
network.
The Switch supports the SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of security provided between
the management station and the ne twork device.
In SNMP v.1 a nd v.2, us er authe ntica tion is ac compl ished using ‘c ommun ity strin gs’, which func tion like password s. The remote
user SNMP application and the Switch SNMP must use the same community string. SNMP packets from any station that has not
been authenticated are ignored (dropped).
The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2 management access are:
• public – Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects.
• private – Allows authorized management stations to retr ieve and modify MIB objects.
27
Page 42

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
SNMPv3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is separated into two parts. The first part is to maintain a list of
users and their attributes that are allowed to act as SNMP managers. The second part describes what each user on that list can do
as an SNMP manager.
The Switch al lows groups of users to be listed and configured with a shared set of privileges. The SNMP version may also be set
for a listed group of SNMP managers. Thus, you may create a group of SNMP managers that are allowed to view read-only
information or receive traps using SNMPv1 while a ssign ing a higher l evel o f secur ity to anothe r gro up, gra ntin g read/ write privileges usin g S NMPv3.
Using SNMPv3 individual users or groups of SNMP managers can be allowed to perform or be restricted from performing
specific SNMP management functions. The functions allowed or restricted are defined using the Object Identifier (OID)
associated with a specific MIB. An additional layer of security is available for SNMPv3 in that SNMP messages may be
encrypted. To read more about how to configure SNMPv3 settings for the Switch read the next section.
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the Switch. The events can be as serious as a reboot
(someone accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port status c hange. The Switch generates traps and sends
them to the tr ap r ec ip ie nt ( o r net work ma na ge r) . Typical traps include tr ap me ssa ge s fo r A uthe nt ication Failure, To po lo gy C ha nge
and Broadcast\Multicast Storm.
MIBs
The Switch in the Management Information Base (MIB) stores management and counter information. The Switch uses the
standard MIB-II Management Informatio n Ba se mod ule. Co nsequently, values for MIB objects can be retrieved from any SNMPbased network management software. In addition to the standard MIB-II, the Switch also supports its own p roprietary enterprise
MIB as an extended Management Information Base. Specifying the MIB Object Identifier may also retrieve the proprietary MIB.
MIB values can be either read-only or read-write.
The Switch incorp orate s a fle xible SNMP manage ment for the s witchi ng en viron ment. S NMP manage ment can b e cus tomize d to
suit the needs of the networks and the preferences of the network administrator. Use the SNMP V3 menus to select the SNMP
version used for specific tasks.
The Switch supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, 2c, and 3. The administrator can specify the
SNMP version used to monitor and control the Switch. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of security provided
between the management station and the network device.
SNMP settings are configured using the menus located on the SNMP Settings folder of the Web manager. Wor kstations on the
network that are allowed SNMP privileged access to the Switch can be restricted with the Management Station IP Address menu.
SNMP Global State Settings
SNMP global state settings can be enabled or disabled.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Setting s > SNMP Global State Settings:
Figure 2 - 35. SNMP Global State Settings window
Click the
button to let your change take effect.
Apply
SNMP Linkchange Traps Settings
Users can set SNMP linkchange traps.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Setting s > SNMP Linkchange Trap Settings:
28
Page 43

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 36. SNMP Linkchange Trap Settings window
The following parameters may be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Click Apply to implement the changes.
Use the drop-down menu to select the ports to be configured.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the SNMP linkchange traps.
SNMP View Table
Users can assign views to community strings that define which MIB objects can be accessed by a remote SNMP manager. The
SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users (identified in the SNMP User Table) to the views created in the previous
window.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP View Table:
29
Page 44

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Figure 2 - 37. SNMP View Table window
View Name
Subtree OID
View Type Select Included to include this object in the list of objects that an SNMP manager can access.
To delete an existing SNMP View Table entry, click the Delete button corresponding to the entr y to delete . T o crea te a new entry,
enter the information above the table and then click the Apply button.
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the new SNMP
view being created.
Type the Object Identifier (OID) Subtree for the view. The OID identifies an object tree (MIB
tree) that will be included or excluded from access by an SNMP manager.
Select Excluded to exclude this object from the list of objects that an SNMP manager can
access.
SNMP Group Table
An SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users (identified in the SNMP User Table) to the views created in the
previous wind ow.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Group Table:
30
Page 45

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 38. SNMP Group Table window
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Group Name
Read View Name
Write View Name
Notify View Name
Security Model SNMPv1 – Specif ies that S NMP vers i on 1 will be used .
Security Level
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the new SNMP
group of SNMP users.
This name is used to specify the SNMP group created can request SNMP messages.
Specify an SNMP group name for users that are allowed SNMP write privileges to the Switch’s
SNMP agent.
Specify a SNMP group name for users that can receive SNMP trap messages generated by
the Switch’s SNMP agent.
SNMPv2 – Specif ies that S NMP vers i on 2c will be used. The SNMPv2 supports both
centralized and distributed network management strategies. It includes improvements in the
Structure of Management Information (SMI) and adds some security features.
SNMPv3 – Specifies that the SNMP version 3 will be used. SNMPv3 provides secure access
to devices through a combination of authentication and encrypting packets over the network.
The Security Level settings only apply to SNMPv3.
NoAuthNoPriv – Specifies that there will be no authorization and no encryption of packets sent
between the Switch and a remote SNMP manager.
AuthNoPriv – Specifies that authorization will be required, but there will be no encryption of
packets sent between the Switch and a remote SNMP manager.
AuthPriv – Specifies that authorization will be required, and that packets sent between the
Switch and a remote SNMP manger will be encrypted.
To delete an existing SNMP Group Table entry, click the Delete button next to the c orresponding entry.
To add a ne w e ntry to the Switch’s SNM P Group Table, enter the information at the top of the window and then click Apply.
SNMP User Table
This window displays all of the SN MP User’s currently c onfigured on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP User Table:
31
Page 46

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 39. SNMP User Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
User Name
Group Name
SNMP Version V3 – Indicates that SNMP version 3 is in use.
SNMP V3
Encryption
Auth-Protocol MD5 – Specifies that the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level will be used. This field is only
Priv-Protocol None – Specifies that no authorization protocol is in use.
To delete an existing SNMP User Table entry, click the Delete button corresponding to the entry to delete.
To implement changes made, click Apply.
An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the SNMP users.
This name is used to specify the SNMP group created can request SNMP messages.
Use the drop-down menu to enable encryption for SNMP V3. This is only operable in SNMP V3
mode. The choices are None, Password, or Key.
operable when V3 is selected in the SNMP Version field and the Encryption field has been
checked. This field will require the user to enter a password.
SHA – Specifies that the HMAC-SHA authentication protocol will be used. This field is only
operable when V3 is selected in the SNMP Version field and the Encryption field has been
checked. This field will require the user to enter a password.
DES – Specifies that DES 56-bit encryption is in use, based on the CBC-DES (DES-56)
standard. This field is only operable when V3 is selected in the SNMP Version field and the
Encryption field has been checked. This field will require the user to enter a password between 8
and 16 alphanumeric characters.
SNMP Community Table
Users can create an SNMP community string to define the relationship between the SNMP manager and an agent. The community
string acts like a password to permit access to the agent on the Switch. One or more of the following characteristics can be
associated with the community string:
• An Access List of IP addresses of SNMP managers that are permitted to use the community string to gain access to the
Switch’s SNMP agent.
• Any MIB view that defines the subset of all MIB objects will be accessible to the SNMP community.
• Read/write or read-only level permission for the MIB objects accessible to the SNMP community.
To view the following window, click SNMP Settings > Configuration > SNMP Community Table:
32
Page 47

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
V3-NoAuthNoPriv – To specify that the SNMP version 3 will be used, with a NoAuth-NoPriv
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Figure 2 - 40. SNMP Community Table window
Community Name
View Name
Access Right Read Only – Specifies that SNMP community members using the community string created
To implement the new settings, click Apply. To delete an entry from the SNMP Community Table, click the Delete button
corresponding to the entry to d e le te .
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that is used to identify members of an
SNMP community. This string is used like a password to give remote SNMP managers access
to MIB objects in the Switch’s SNMP agent.
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters that is used to identify the group of MIB
objects that a remote SNMP manager is allowed to access on the Switch. The view name must
exist in the SNMP View Table.
can only read the contents of the MIBs on the Switch.
Read Write – Specifies that SNMP community members using the community string created
can read from, and w rite to the contents of the MIBs on the Switch.
SNMP Host Table
Users can set up SNMP trap recipients for IPv4.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Host Table:
Figure 2 - 41. SNMP Host Table window
The following parameters can set:
Parameter Description
Host IP Address
SNMP Version V1 – To specify that SNMP version 1 will be used.
Type the IP address of the remote management station that will serve as the SNMP host for
the Switch.
V2c – To specify that SNMP version 2c will be used.
33
Page 48

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
security leve l.
V3-AuthNoPriv – To spec if y that the SNM P vers ion 3 will be used, with an Auth-NoPriv
security leve l.
V3-AuthPriv – To specify that the SNMP version 3 will be used, with an Auth-Priv sec urit y
level.
Community String /
SNMP V3 User Name
To add a new entry to the Switch’s SNMP Host Table, enter the information at the top of the windo w and then click the Apply
button. To delete an existing SNMP Host Table entry, click the Delete button corresponding to the entry to delete.
Type in the community string or SNMP V3 user name as appropriate.
SNMP v6Host Table
Users can set up SNMP trap recipients for IPv6.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP v6Host Table:
Figure 2 - 42. SNMP v6Host Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Host IPv6 Address
SNMP Version V1 – To specify that SNMP version 1 will be used.
Community String /
SNMPv3 User Name
To add a new entry to the Switch’s SNMP v6Host Table, enter the information at the top of the windo w and the n cl ick the Apply
button. To delete an existing SNMP v6Host Table entry, click the Delete button corresponding to the entry to delete.
Type the IP address of the remote management station that will serve as the SNMP host for
the Switch.
V2c – To specify that SNMP version 2c will be used.
V3-NoAuthNoPriv – To specify that the SNMP version 3 will be used, with a NoAuth-NoPriv
security leve l.
V3-AuthNoPriv – To specify that the SNMP version 3 will be used, with an Auth-NoPriv
security leve l.
V3-AuthPriv – To specify that the SNMP version 3 will be used, with an Auth-Priv security
level.
Type in the community string or SNMP V3 user name as appropriate.
SNMP Engine ID
The Engine ID is a unique identifier used for SNMP V3 implementations on the Switch.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Eng i ne ID :
34
Page 49

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 43. SNMP Engine ID window
The following parameter can be configured:
Parameter Description
Engine ID
Click Apply to implement the changes.
The SNMP engine ID displays the identification of the SNMP engine on the Switch. The
default value is suggested in RFC2271. The very first bit is 1, and the first four octets are set
to the binary equivalent of the agent’s SNMP management private enterprise number as
assigned by IANA (D-Link is 171). The fifth octet is 03 to indicate the rest is the MAC
address of this device. The sixth to eleventh octets is the MAC address.
SNMP Trap Configuration
Users can enable and disable global SNMP trap support, SNMP authentication failure trap support, Linkchange Traps, Coldstart
Traps, and Warmstart Traps. To enable Linkchange Traps for a specific port or range of ports, go to the SNMP Linkcha nge T rap s
Settings window.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > SNMP Trap Configuration:
Figure 2 - 44. SNMP Trap Configuration window
To enable or disable the SNMP Traps, SNMP Authenticate Traps, Linkchange Traps, Coldstart Traps, and Warmstart Traps, use
the corresponding drop-down menu to change and click Apply.
RMON
Users can enable and disable re mote monitor ing (RMON) sta tus for the SNMP func tion on the S witc h. In add ition, RM ON Risi ng
and Falling Alarm Traps can be enabled and disabled.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SNMP Settings > RMON:
Figure 2 - 45. RMON window
To enable or disable RMON for SNMP, use the radio buttons. Click Apply when finished.
35
Page 50

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
CPU Filter L3 Control Packet Settings
Users can discard and display Layer 3 control packets sent to the CPU from specific ports.
To view the following window, click Configuration > CPU Filter L3 Control Packet Settings:
Figure 2 - 46. CPU Filter L3 Control Packet Settings window
To set CPU filter Layer 3 c ontrol packet settings on the Switch, use the From Port and To Port drop-down menus to select the
desired port range, change the State to Enabled, and tick the desired Layer 3 categories (IGMP Query, DVMRP, PIM, OSPF, RIP,
VRRP, or All). Clic k
when finished.
Apply
Single IP Management
Simply put, D -Link Single IP Management is a concept that will stack switches together over Ethernet instead of using stacking
ports or modules. There are some advantages in implement ing the “Single IP Management” feature:
1. SIM can simplify management of small workgroups or wiring closets while scaling the network to handle increased
bandwidth demand.
2. SIM can reduce the number of IP address needed in your network.
3. SIM can eliminate any specialized cables for stacking connectivity and remove the distance barriers that typically limit
your topology options when using other stacking technology.
Switches using D-Link Single IP Management (labeled here as SIM) must conform to the following rules:
• SIM is an optional feature on the Switch and can easily be enabled or disabled through the Command Line Interface or
Web Interface. SIM grouping has no effect on the normal operation of the Switch in the user’s network.
• There are three classifications for switches using SIM. The Commander Switch ( CS), which is the master switch of the
group, Member Switch (MS), which is a switch that is recognized by the CS a member of a SIM group, and a
Candidate Switch (Ca S), which is a Switch that has a physical link to the SIM group but has not been recognized by the
CS as a member of the SIM group.
• A SIM group can only have one Commander Switch (CS).
36
Page 51

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
• All switches in a particular SIM group must be in the same IP subnet (broadcast domain). Members of a SIM group
cannot cross a router.
• A SIM group accepts up to 32 switches (numbered 1-32), not including the Commander Switch (numbered 0).
• There is no l imit to t he number o f SIM group s in the sa me IP subnet (broadcast domain); however a single switch can
only belong to one group.
• If multiple VLANs are configured , the SI M group will only utilize the default VLAN on any switch.
• SIM allows intermediate devices that do not support SIM. This enables the user to manage switches that are more than
one hop awa y from the CS.
The SIM group is a group of switches that are managed as a single entity. The Switch may take on three different roles:
1. Commander Switch (CS) – T his is a switch that has been manually configured as the controlling device for a group, and
takes on the following characteristics:
• It has an IP Addre s s.
• It is not a command switch or member switch of another Single IP group.
• It is connected to the member switches through its management VLAN.
2. Member Switch (MS) – This is a switch that has joined a single IP group and is accessible from the CS, and it takes on
the following characteristics:
• It is not a CS or MS of another IP group.
• It is connected to the CS through the CS management VL AN.
3. Candidate Switch (Ca S) – This is a switch that is ready to join a SIM gro up but i s not yet a member of the SIM group.
The Candid ate Switch may join the SIM group of the S witch by man ually confi guring it to be a MS of a SIM gr oup. A
switch configured as a CaS is not a member of a SIM group and will take on the following characteristics:
• It is not a CS or MS of another Single IP group.
• It is connected to the CS through the CS management VL AN
The following rules also apply to the above roles:
• Each device begins in a Candidate state.
• CS's must change their role to CaS and then to MS, to become a MS of a SIM group. Thus, the CS cannot directly be
converted to a MS.
• The user can manually configure a CS to become a CaS.
• A MS can become a CaS by:
• Being configured as a CaS through the CS.
• If report packets from the CS to the MS time out.
• The user can manually configure a CaS to become a CS
• The CaS can be configured through the CS to become a MS.
After configuring one switch to operate as the CS of a SIM group, additional DGS-3200 Series switches may join the group by
manually configuring the Switch to be a MS. The CS will then serve as the in band entry point for access to the MS. The CS’s IP
address will become the path to all MS’s of the group and the CS’s Administrator’s password , and/or authentication will control
access to all MS’s of the SIM group.
With SIM enabled, the applications in the CS will redirect the packet instead of executing the packets. The applications will
decode the packet from the administrator, modify some data, and then send it to the MS. After execution, the CS may receive a
response packet from the MS, which it will encode and send it back to the administrator.
When a CaS becomes a MS, it automatically becomes a member of the first SNMP community (including read/write and read
only) to which the CS belongs. However, if a MS has its own IP address, it can belong to SNMP communities to which other
switches i n the group, including the CS, do not belong.
Upgrade to v1.61
To better improve SIM manage ment, the DGS-320 0 Series switches have been upgraded to version 1.61 in this release. Many
improvements have been made, including:
37
Page 52

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Commander – Choosing this parameter will make the Switch a Commander Switch (CS). The
4. The Commander Switch (CS) now has the capability to automatically rediscover member switches that have left the SIM
group, either through a reboot or web malfunction. This feature is accomplished through the use of Discover packets and
Maintenance packets that previously set SIM members will emit after a reboot. Once a MS has had its MAC address and
password saved to the CS’s database, if a reboot occurs in the MS, the CS will keep this MS information in its database
and when a MS has been rediscovered, it will add the MS back into the SIM tree automatically. No configuration will be
necessary to rediscover these switches.
There are some instances where pre-saved MS switches cannot be rediscovered. For example, if the Switch is still powered down,
if it has become the member of another group, or if it has been configured to be a Commander Switch, the rediscovery process
cannot occur.
2. The topology map now includes new features for connections that are a
member of a port trunking group. It will display the speed and number of Ethernet
connections creating this por t trunk gro up, as shown in the adjacent picture.
5. This version will support s witch upload and downloads for firmware, configuration files and log files, as follows:
• Firmware – The switch now supports MS firmware downloads from a TFTP server.
• Configuration Files – This switch now supports downloading and uploading of configuration files both to (for
configuration restoration) and from (for configuration backup) MS’s, using a TFTP server.
• Log – The Switch now supports uploading MS log files to a TFTP server.
6. The user may zoom in and zoom out when utilizing the topology window to get a better, more defined view of the
configurations.
Single IP Settings
The Switch is set as a Candidate (CaS) as the factory default configuration and Single IP Management is disabled.
To enable SIM for the Switch using the Web interface, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Single IP Settings:
Figure 2 - 47. Single IP Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
SIM State Use the drop-down menu to either enable or disable the SIM state on the Switch. Disabled will
render all SIM functions on the Switch inoperable.
Trap
Role State
Use the drop-down menu to either enable or disable a trap. This is designed to control the
sending of traps issued from a member switch.
Use the drop-down menu to change the SIM role of the Switch. The two choices are:
Candidate – A Candidate Switch (CaS) is not the member of a SIM group but is connected to
a Commander Switch. This is the default setting for the SIM role of the Switch.
38
Page 53

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
user may join other switches to this Switch, over Ethernet, to be part of its SIM group.
Choosing this option will also enable the Switch to be configured for SIM.
Group Name
Discovery Interval
(30-90)
Hold Time Count
(100-255)
Click Apply to implement the changes. After enabling the Switch to be a Commander Switch (CS), the Single IP Management
folder will t hen contain four ad ded links to aid the u ser in configuring SI M through the web, i ncluding Topology, Firmware
Upgrade, Configura tion Backup/Restore and Upload Log.
Enter a Group Name in this textbox. This is optional.
The user may set the discovery protocol interval, in seconds that the Switch will send out
discovery packets. Returning information to a Commander Switch will include information
about other switches connected to it. (Ex. MS, CaS). The user may set the Discovery Interval
from 30 to 90 seconds. The default value is 30 seconds.
This parameter may be set for the time, in seconds; the Switch will hold information sent to it
from other switches, utilizing the Discovery Interval. The user may set the hold time from 100
to 255 seconds. The default value is 100 seconds.
Topology
This window will be used to c onfigure and manage the Switch within the SIM group and requires Java script to function properly
on your computer.
The Java Runtime Environment on your server should initiate and lead you to the Topology window, as seen below.
Figure 2 - 48. Topology window
The Topology window holds the following information on the Data tab:
Parameter Description
Device Name
This field will display the Device Name of the switches in the SIM group configured by the user.
39
Page 54

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
If no device is configured by the name, it will be given the name default and tagged with the
last six digits of the MAC Address to identify it.
Local Port
Speed
Remote Port
MAC Address
Model Name
To view the Topology View window, op en the View drop-down menu in the toolbar and then click Topology, which will open
the following Topology Map. This window will refresh itself periodically (20 seconds by default).
Displays the number of the physical port on the CS that the MS or CaS is connected to. The
CS will have no entry in this field.
Displays the connection speed between the CS and the MS or CaS.
Displays the number of the physical port on the MS or CaS to which the CS is connected. The
CS will have no entry in this field.
Displays the MAC Address of the corresponding Switch.
Displays the full Model Name of the corresponding Switch.
Figure 2 - 49. Topology View window
This windo w wil l di spla y ho w the dev ice s wi thin t he S in gle I P M anage ment Gr oup conne ct t o o ther gr oup s a nd de vice s. Possible
icons on this window are as follows:
Icon Description
Group
Layer 2 commander switch
Layer 3 commander switch
Commander switch of other group
Layer 2 member switch.
40
Page 55

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Layer 3 member switch
Member switch of other group
Layer 2 candidate switch
Layer 3 candidate switch
Unknown device
Non-SIM devices
Tool Tips
In the Topology view window, the mouse plays an important role in configuration and in viewing device information. Setting the
mouse cursor over a specific device in t he top olog y windo w ( too l tip) will display t he same in for mation abo ut a sp ecific device a s
the Tree view does. See the window below for an example.
Figure 2 - 50. Device Information Utilizing the Tool Tip
Setting the mouse cursor over a line between two devices will display the connection speed between the two devices, as shown
below.
41
Page 56

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 2 - 51. Port Speed Utilizing the Tool Tip
Right-Click
Right-clicking on a device wil l a llo w the user t o pe rfor m va rio us func tio ns, d ep endin g on the r ole of the Swit ch i n the S IM gr oup
and the icon associated with it.
Group Icon
Figure 2 - 52. Right-Clicking a Group Icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
• Collapse – To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
• Expand – To e xpand the SIM group, in detail.
• Property – To pop up a window to display the group information.
42
Page 57

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Parameter Description
Figure 2 - 53. Property window
Device Name
Module Name
MAC Address
Remote Port No.
Local Port No.
Port Speed
This field will display the Device Name of the switches in the SIM group configured by the user.
If no Device Name is configured by the name, it will be given the name default and tagged with
the last six digits of the MAC Address to identify it.
Displays the full module name of the switch that was right-clicked.
Displays the MAC Address of the corresponding Switch.
Displays the number of the physical port on the MS or CaS that the CS is connected to. The CS
will have no entry in this field.
Displays the number of the physical port on the CS that the MS or CaS is connected to. The CS
will have no entry in this field.
Displays the connection speed between the CS and the MS or CaS
Commander Switch Icon
Figure 2 - 54. Right-Clicking a Commander Icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
• Collapse – To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
• Expand – To e xpand the SIM group, in detail.
• Property – To pop up a window to display the group information.
43
Page 58

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Member Switch Icon
Figure 2 - 55. Right-Clicking a Member icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
• Collapse – To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
• Expand – To e xpand the SIM group, in detail.
• Remove from group – Remove a member from a group.
• Configure – Launch t he web management to configure the Switch.
• Property – To pop up a window to display the device information.
Candidate Switch Icon
Figure 2 - 56. Right-Clicking a Candidate icon
The following options may appear for the user to configure:
• Collapse – To collapse the group that will be represented by a single icon.
• Expand – To e xpand the SIM group, in detail.
• Add to group – Add a candidate to a group. Clicking this option will reveal the following dialog box for the user to enter a
password for authentication from the Candidate Switch before being added to the SIM group. Click OK to enter the
password or Cancel to exit the dialog box.
Figure 2 - 57. Input password dialog box
• Property – To pop up a window to display the device information.
44
Page 59

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Menu Bar
The Single IP Ma nagement window contains a menu bar for device configurations, as seen below.
Figure 2 - 58. Menu Bar of the Topology View
The five menus on the menu bar are as follows.
File
• Print Setup – Will view the image to be printed.
• Print Topology – Will print the topology map.
• Preference – Will set display properties, such as polling interval, and the views to open at SIM startup.
Group
• Add to group – Add a candidate to a group. Clicking this optio n will reveal the following dialog b ox for the user to enter a
password for authentication from the Candidate Switch before being added to the SIM group. Click OK to enter the
password or Cancel to exit the dialog box.
Figure 2 - 59. Input password dialog box
• Remove from Group – Remove an MS from the group.
Device
• Configure – Will open the Web manager for the specific device.
View
• Refresh – Update the views with the latest status.
• Topology – Display the Topology view.
Help
• About – Will display the SIM information, including the current SIM version.
45
Page 60

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Firmware Upgrade
The Commander Switch may be used for firmware upgrades of member switches. Member Switches will be listed in the table and
will be specified by Port (port on the CS where the MS resides), MAC Address, Model Name and Version. To specify a certain
Switch for firmware download, click its corresponding check box under the Port heading. To update the firmware, enter the Server
IP Address where the firmware resides and enter the Path/Filename of the firmware. Click Download to initiate the file transfer.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Firmware Upgrade:
Figure 2 - 60. Firmware Upgrade window for Single IP Management
Configuration File Backup/Restore
The Commander Switch can instruct configuration file backup and restore to the Member Switch using a TFTP server. Member
Switches will be listed in the table and will be specified by Port (port on the CS where the MS resides), MAC Address, Model
Name and Version. To specify a certain Switch for upgrading configuration files, click its corresponding radio button under the
Port heading. To update the configuration file, enter the Server IP Address where the file resides and enter the Path/Filename of
the configuration file. Click Restore to initiate the file transfer fro m a TFTP server to the Switch. Click Backup to b ackup the
configuration file to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Configuration File Backup/Restore:
Figure 2 - 61. Configuration File Backup/Restor e window for Single IP Management
Upload Log File
The Commander Switch can order a log file from a member switch sent to a server. Provide the Server IP address for storing the
log and the log file path and filename on the member swit ch. Click Upload to send the log file to a TFTP server.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Single IP Management > Upload Log File:
Figure 2 - 62. Upload Log File window for Single IP Management
46
Page 61

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
SD Card FS Settings (DGS-3200-24 Only)
Users can plug an SD flash card into a front slot on the DGS-3200-24 (DGS-3200-10 and DGS-3200-16 do not support this
feature). The SD flash card allows users to carry out the following:
• Save the Switch log to the SD card
• Save the Switch configuration to the SD card
• Save the Switch Runtime image to the SD card
• Save the Switch Prom image to the SD card
• Copy images from the SD card to the flash memory on the Switch to replace Runtime image 1 or Runtime image 2
• Copy configuration files from the SD card to the flash memory on the Switch to replace configuration 1 or configuration 2
• Replace the Prom image by copying a Prom image from the SD card to the flash memory
• Download Runtime image and save to the SD card
• Download configuration and save to the SD card
• Access the files on the SD card via a PC (e.g. using Microsoft Windows)
• Boot up the Switch using a runtime image stored on the SD card
• Boot up the Switch using a configuration stored on the SD card
• SD card is hot swappable
• Switch automatically creates new directories and files automatically on the SD card. A warning message will display if
there is an existing file or folder with the same name, asking the user to overwrite or keep the existing file or folder
To view the following window, click Configuration > SD Card FS Settings :
Figure 2 - 63. SD Card FS Settings window
To use a firmware image and configuration on an SD card, carry out the following steps:
1. Insert the SD flash card into the SD ca r d slot on the front of the Switch.
2. Type the path of the firmware image in the Current Path field.
3. Click Go.
In addition to using a firmware image and configuration from an SD flash card, the SD Card FS Settings window allows users to
manage the directories and files stored on the SD card. The table below describes the buttons used to manage the files and
directories, stored on the SD flash card.
Parameter Description
Previous
Create Directory
Copy Flash
Format
Click this button to navigate to the previous folder.
Click this button to create a new directory.
Click this button to copy files from/to the SD Flash card or internal Flash memory.
If you have inserted a new SD Flash card this button will appear.
47
Page 62

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Click this button to format the new SD Flash card.
Copy to
Move to
Rename
Delete
Click this button to copy a file to another location.
Click this button to move a file to another location.
Click this button to rename the corresponding file or folder.
Click this button to delete the corresponding file or folder.
SD Card Management (DGS-3200-24 Only)
SD Card Backup Settings
This window is used to create a schedule to back up the configuration or log to file system.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SD Card management > SD Card Backup Settings:
Figure 2 - 64. SD Card Backup Settings window
The following parameter may be configured:
Parameter Description
Type
Time Range Name
File Name
State
Click Add to create a new entry. Click Delete All to remov e all the en tries fro m the table. Click Edit to modify the specific entry.
Click Delete to remove the specific entry.
Use the drop-down menu to back up configuration or log.
Specify the schedule to back up the configuration or log.
Specify the backup file name.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the backup schedule.
SD Card Execute Settings
This window is used to configure a schedule to execute the configuration on file system.
To view the following window, click Configuration > SD Card management > SD Card Execute Settings:
Figure 2 - 65. SD Card Execute Settings window
48
Page 63

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
The following parameter may be configured:
Parameter Description
File Name
Increment
Reset
Time Range Name
State
Click Execute to execute c on figurat ion on file s ystem. Clic k Add to create a new entry. Click Delete All to remove all the entries
from the table. Click Edit to modify the specific entry. Click Delete to remove t he specific entry.
The filename of the configuration on file system.
If this option is specified, the current configuration will not be reset before executing the
configuration.
If this option is specified, the current configuration will be reset before executing the
configuration.
The time range for schedule to execute the configuration.
Enable or disable the executive schedules.
49
Page 64

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
L2 Features
VLAN
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Setti n g s
Egress Filter Settings
L2 Multicast Control
Multicast Filtering
Port Mirroring
Spanning Tree
Link Aggregation
Forwarding & Filtering
LLDP
NLB FDB Settings
Section 3
VLAN
802.1Q VLAN
Understanding IEEE 80 2. 1 p Pri ority
Priority tagging is a function defined by the IEEE 802.1p standard designed to provide a means of managing traffic on a network
where many different types of data may be transmitted simultaneously. It is int ended to alleviate pro blems associated with the
delivery of time critical data over congested networks. The quality of applications that are dependent on such time critical data,
such as video conferencing, can be severely and adversely affected by even very small delays in transmission.
Network devices that are in compliance with the IEEE 802.1p standard have the ability to recognize the priority level of data
packets. These devices can also assign a priority label or tag to packets. Compliant devices can also strip priority tags from
packets. This priority tag determines the packet’s degree of expeditiousness and determines the queue to which it will be assigned.
Priority tags are given values from 0 to 7 with 0 being assigned to the lowest pr iority data and 7 assigned to the hi ghest. The
highest priority tag 7 is generally only used for data associated with video or audio applications, which are sensitive to even slight
delays, or for data from specified end users whose data transmissions warrant special consideration.
The Switch allows you to further tailor how priority tagged data packets are handled on your network. Us ing queues t o manage
priority tagged data allows you to specify its relative priority to suit the needs of your networ k. There may be circumstances where
it would be advantageous to group two or more differently tagged packets into the same queue. Generally, however, it is recommended t hat the highe st prio rity queue , Queue 7 , be reser ved for d ata packet s with a prio rity value o f 7. Pac kets that have not
been given any priority value are placed in Queue 0 and thus given the lowest priority for delivery.
Strict mode and weighted round robin system are employed on the Switch to determine the rate at which the queues are emptied of
packets. The ratio used for clearing the queues is 4:1. This means that the highest priority queue, Queue 7, will clear 4 packets for
every 1 packet cleared from Queue 0.
Remember, the priority queue settings on the Switc h are for all ports, and all devices connected to the Switch will be affected.
This priority queuing system will be especially beneficial if your network employs switches with the capability of assigning
priority tags.
VLAN Description
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical scheme rather than the physical
layout. VLANs can be used to combine any collection of LAN segments into an autonomous user group that appears as a single
LAN. VLANs also logically segment the network into different broadcast domains so that packets are forwarded only between
ports within the VLAN. Typically, a VLAN corresponds to a particular subnet, although not necessarily.
50
Page 65

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
VLANs can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific domains.
A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic instead of physical location. End nodes that frequently communicate with
each other are assigned to the same VLAN, regardless of where they are physically on the network. Logically, a VLAN can be
equated to a broadcast domain, because broadcast packets are forwarded to only members of the VLAN on which the broadcast
was initiated.
Notes about VLANs on the Switch
• No matter what basis is used to uniquely identify end nodes and assign these nodes VLAN membership, packets cannot
cross VLANs without a network device performing a routing function between the VLANs.
• The Switch supports IEEE 802.1Q VLANs. The port untaggi ng function can be used to remove the 802.1Q tag from
packet headers to maintain compatibility with devices that are tag-unaware.
• The Switch’s default is to assign all ports to a single 802.1Q VLAN named “default.”
• The “default” VLAN has a VID = 1.
• The member ports of Port-based VLANs may overlap, if desired.
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
Some relevant terms:
• Tagging – The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
• Untagging – The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
• Ingress port – A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the Switch and VLAN decisions must be made.
• Egress port – A port on a s witch where packets are flowing out of t he Switch, either to another switch or to an end
station, and tagging decisions must be made.
IEEE 802.1Q (tagged) VLANs are implemented on the Switch. 802.1Q VLANs require taggin g, which ena bles the m to span the
entire network (assuming all switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant).
VLANs allow a network to be segmented in order to reduce the size of broadcast domains. All packets entering a VLAN will only
be forwarded to the stations (over IEEE 802.1Q enabled switches) that are members of that VLAN, and this includes broadcast,
multicast and unicast packets from unknown sources.
VLANs can also provide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLANs will only deliver packets b et ween statio ns that
are members of the VLAN.
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs allows VLANs to work
with legacy switches that don’t reco gnize VLAN tags in packet headers. The tagging feature allows VLANs to span multiple
802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical connection and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work
normally.
The IEEE 802.1Q standard restricts the forwarding of untagged packets to the VLAN the receiving port is a member of.
The main characteristics of IEEE 802.1Q are as follows:
• Assigns packets to VLANs by filtering.
• Assumes the presence of a single global spanning tree.
• Uses an expli cit tagging scheme with one-level tagging.
• 802.1Q VLAN Packet Forwarding
• Packet forwarding decisions are made based upon the following three types of rules:
• Ingress rules – rules relevant to the classification of received frames belonging to a VLAN.
• Forwarding rules between ports – decides whether to filter or forward the packet.
• Egress rules – determines if the packet must be sent tagged or untagged.
51
Page 66

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 1. IEEE 802.1Q Packet Forwarding
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure be low shows the 802.1 Q VLAN tag. There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC address. Their
presence is indicated by a value of 0x8100 in the EtherType field. When a packet’s EtherType field is equal to 0x8100, the packet
carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag. The tag is contained in the following two octets and consists of 3 bits of user priority, 1 bit of
Canonical Format Identifier (CFI – used for encap sula tin g T oke n Ring packets so they can be carried across Ethernet backbones),
and 12 bits of VLAN ID (VID). The 3 bits of user priority are used by 802.1p. The VID is the VLAN identifier and is used by the
802.1Q standard. Because the VID is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLANs can be identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets. All of the i nformation origi nally contained
in the packet is retained.
Figure 3 - 2. IEEE 802.1Q Tag
52
Page 67

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
The EtherType and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address, but before the original EtherType/Length or Logical
Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) must be
recalculated.
Figure 3 - 3. Adding an IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q compliant network device
to another with the VLAN information intact. This allows 802.1Q VLANs to span network devices (and indeed, the entire
network, if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
Unfortunately, not all network devices are 802.1Q compliant. These devices are referred to as tag-unaware. 802.1Q devices are
referred to as tag-aware.
Prior to the adoption of 802.1Q VLANs, port-based and MAC-based VLANs were in common use. These VLANs relied upon a
Port VLAN ID (PVID) to forward packets. A packet received on a given port would be assigned that port’s PVID and then be
forwarded to the port that corresponded to the packet’s destination address (found in the Switch’s forwarding table). If the PVID
of the port that received the packet is different from the PVID of the port that is to transmit the packet, the Switch will drop the
packet.
Within the Switch, different PVIDs mean different VLANs (remember that two VLANs cannot communicate without an externa l
router). So, VLAN identification based upon the PVIDs cannot create VLANs that extend outside a given switch (or switch stack).
Every physical port on a switch has a PVID. 802.1Q ports are also assigned a PVID, for use within the Switch. I f no VL ANs ar e
defined on the Switch, all ports are then assigned to a default VLAN with a PVID equal to 1. Untagged packets are assigned the
PVID of the port on which they were received. Forwarding decisions are based upon this PVID, in so far as VLANs are concerned. Tagged packets are forwarded according to the VID contained within the tag. Tagged packets are also assigned a PVID,
but the PVID is not used to make packet-forwarding decisions, the VID is.
Tag-aware switches must kee p a table to relate PVIDs within the Switch to VIDs on the network. T he Switch will compare the
VID of a packet to be transmitted to the VID of the port that is to transmit the packet. If the t wo VIDs are different, the Switch
will drop the packet. Because of the existence of the PVID for untagged packets and the VID for tagged packets, tag-aware and
tag-unaware network devices can coexist on the same network.
A switch port can have only one PVID, but can have as many VIDs as the Switch has memory in its VLAN table to store them.
Because some devices on a network may be tag-unaware, a decision must be made at each port on a tag-aware device before
packets are transmitted – should the packet to be transmitted have a tag or not? If the transmitti ng port is connected to a tagunaware device, the packet should be untagged. If the transmitting port is connected to a tag-aware device, the packet should be
tagged.
Tagging and Untagging
Every port on an 802.1Q compliant switch can be configured as tagging or untagging.
Ports with tagging enabled will put the VID number, pr iority and other VL AN information into the heade r of all packets that flo w
into and out of it. If a packet has previously been tagged, the port will not alter the packet, thus keeping the VLAN information
53
Page 68

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
intact. Other 802.1Q compliant devices on the network to make packet-forwarding d ecis ions ca n then use the VL AN infor matio n
in the tag.
Ports with untagging enabled will strip the 80 2.1Q tag from all packets that flow into and out of those po rts. If the packet doesn’t
have an 802.1Q VLAN tag, the port will not alter the packet. Thus, all packets received by and forwarded by an untagging port
will have no 8 02. 1Q VLAN i nfor mation. (Re membe r that t he PVI D is onl y used i nterna lly wit hin the Swit ch). Untagg ing is u sed
to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant network device to a non-compliant network device.
Ingress Filtering
A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the Switch and VLAN decisions must be made is referred to as an ingress port.
If ingress filtering is enabled for a port, the Switch will examine the VLAN information in the packet header (if present) and
decide whether or not to forward the packet.
If the packet is tagged with V LAN information, the ingress po rt will first determine if the ingress por t itself is a member of the
tagged VLAN. If it is not, the packet will be dropped. If the ingress port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN, the Switch then
determines if the destination port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN. If it is not, the packet is dropped. If the destination port is a
member of the 802.1Q VLAN, the packet is forwarded and the destination port transmits it to its attached network segment.
If the packet is not tagged with V LAN infor mation, the ingre ss port will tag the packet with its o wn PVID as a VI D (if the p ort is
a tagging port). The switch then determines if the destination port is a member of the same VLAN (has the same VID) as the
ingress port. If it does not, the packet is dropped. If it has the same VID, the packet is forwarded and the destination port transmits
it on its attached network segment.
This process is referred to as ingress filtering and is used to conserve bandwidth within the Switch b y dropping packets that are
not on the same VL AN as t he ingres s po rt a t the p oi nt of re ception. This eliminates the subsequent processing of packets that will
just be dropped by the destination port.
Default VLANs
The Switch initially configures one VLAN, VID = 1, called “default.” The factory default setting assigns all ports on the Switch to
the “default.” As new VLANs are configured in Port-based mode, their respective member ports are removed from the “default.”
Packets cannot cross VLANs. If a member of one VLAN wants to connect to another VLAN, the link must be through an external
router.
NOTE: If no VLANs are configured on the Switch, then all pack ets will be forwarded to any
destination port. Packets with unknown source addresses will be flooded to all ports.
Broadcast and multicast packets will also be flooded to all ports.
An example is presented be low:
VLAN Name VID Switch Ports
System (default) 1 5, 6, 7
Engineering 2 9, 10
Sales 5 1, 2, 3, 4
Table 3 - 1. VLAN Example – Assigned Ports
Port-based VLANs
Port-based VLANs limit traffic that flows into a nd out of switch ports. Thus, all de vices connected to a port are members of the
VLAN(s) the port belongs to, whether there is a single computer directly connected to a switch, or an entire department.
On port-based VLANs, NICs do not need to be able to identify 802.1Q tags in packet headers. NICs send and receive normal
Ethernet packets. If the packet’s destination lies on the same segment, communications take place using normal Ethernet
protocols. Even though this is always the case, when the destination for a packet lies on another switch port, VLAN considerations
come into play to decide if the packet gets dropped by the Switch or delivered.
54
Page 69

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
VLAN Segmentation
Take for example a packet that is transmitted by a machine on Port 1 that is a member of VLAN 2. If the destination lies on
another port (found through a normal forwarding table lookup), the Switch then looks to see if the other port (Port 10) is a member
of VLAN 2 (and can therefore receive VLAN 2 packets). If Port 10 is not a member of VLAN 2, then the packet will be dropped
by the Switch and will not reach its destination. If Por t 10 is a member of VLAN 2, the packet will go through. This selective
forwarding feature based on VLAN criteria is how VLANs segment networks. The key point being that Port 1 will only transmit
on VLAN 2.
VLAN and Trunk Groups
The members of a trun k group have the sa me VLAN s etting. Any VLAN se tting o n the membe rs of a t runk group will app ly to
the other member ports.
NOTE: In order to use VLAN segmentation in conjunction with port trunk groups, first set the
port trunk group(s), and then configure the VLAN settings. To change the port trunk grouping
with VLANs already in place it is unnecessary to reconfigure the VLAN settings after changing
the port trunk group settings. VLAN settings will automatically change in conjunction with the
change of the port trunk group settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1Q VLAN:
Figure 3 - 4. VLAN List tab of the 802.1Q VLAN window
The VLAN List tab lists all previously configured VLANs by VLAN ID and VLAN Name. To delete an existing 802.1Q VLAN,
click the corresponding Delete button.
To create a new 802.1Q VLAN or modify an existing 802.1Q VLAN, click the Add/Edit VLAN tab. A new tab will appea r, as
shown belo w, to co nfigure t he po rt setting s and to assig n a unique na me and number to the new VLAN. See the table on the next
page for a description of the parameters in the new window.
55
Page 70

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 5. Add/Edit VLAN tab of the 802.1Q VLAN window
The following fields can then be set in the A dd/Edit VLAN tab:
Parameter Description
VID (VLAN ID) Allows the entry of a VLAN ID or displays the VLAN ID of an existing VLAN in the Add/Edit
VLAN tab. VLANs can be identified by either the VID or the VLAN name.
VLAN Name Allows the entry of a name for the new VLAN or for editing the VLAN name in the Add/Edit
VLAN tab.
Advertisement
Port
Tagged
Untagged
Forbidden
Not Member
Click Apply to implement changes made.
To search for a VLAN, click the
field offered and then click the
description of the parameters in the new window.
Enabling this function will allow the Switch to send out GVRP packets to outside sources,
notifying that they may join the existing VLAN.
Shows all ports of the S witch for the 802.1Q configuration option.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q tagging. Clicking the radio button will designate the port as tagged.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q untagged. Clicking the radio button will designate the port as
untagged.
Click the radio button to specify the port as not being a member of the VLAN and that the port is
forbidden from becoming a member of the VLAN dynamically.
Click the radio button to allow an individual port to be specified as a non-VLAN member.
Find VLAN
button. You will be redirecte d to the
Find
tab. A new tab will appear, as shown below. Enter the VLAN ID number in the
VLAN List
tab. See the table on the next page for a
56
Page 71

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 6. Find VLAN tab of the 802.1Q VLAN window
To create a VLAN Batch entry click the
VLAN Batch Settings
tab, as shown below.
Figure 3 - 7. VLAN Batch Settings tab of the 802.1Q VLAN window
The following fields can be set in the VLAN Batch Settings windows:
Parameter Description
VID List (e.g.: 2-5)
Advertisement
Port List (e.g.: 1-5)
Enter a VLAN ID List that can be added, deleted or configured.
Enabling this function will allow the Switch to send out GVRP packets to outside sources,
notifying that they may join the existing VLAN.
Allows an individual port list to be added or deleted as a member of the VLAN.
Tagged
Specifies the port as 802.1Q tagged. Use the drop-down menu to designate the port as
tagged.
57
Page 72

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Untagged
Forbidden
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Specifies the port as 802.1Q untagged. Use the drop-down menu to designate the port as
untagged.
Specifies the port as not being a member of the VLAN and that the port is forbidden from
becoming a member of the VLAN dynam icall y. Use the drop-down menu to d esig nate the port
as forbidden.
NOTE: The Switch supports up to 4k static VLAN entries.
802.1v Protocol VLAN
The 802.1v Protocol VLAN folder contains two windows: 802.1v Protocol Group Settings and 802.1v Protocol VLAN
Settings.
802.1v Protocol Group Set ti ngs
Users can create Protocol VLAN groups and add protocols to that group. The 802.1v Protocol VLAN Group Settings support
multiple VLANs for each protoc ol and allo ws the user to configure the untagged ports of different protocols on the same physical
port. For example, it allows the user to configure an 802.1Q and 802.1v untagged port on the same physical port. The lower half
of the table displays any previously created groups.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol Group Settings:
Figure 3 - 8. 802.1v Protocol Group Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Group ID Select an ID number for the group, between 1 and 8.
Group Name
This is used to id ent ify the new Protocol VLAN group. Type an alphanumeric strin g of u p to 32
characters.
Protocol
Protocol Value
This function maps packets to protocol-defined VLANs by examining the type octet with in the
packet header to discover the t ype of protoc ol associa ted with it. Use the dro p-down m enu to
toggle between Ethernet II, IEEE802.3 LLC, and IEEE802.3 SN AP.
Enter a value for t he Group . The pr otoc ol va lue is us ed to ide ntif y a protoc ol of th e fr am e type
specified. The form of the input is 0x 0 to 0xffff . Depending on the f rame type, the octet string
will have one of the f ollowing values: For Ethernet II, this is a 16-bit (2-octet) hex value. For
example, IPv4 is 800, IPv6 is 86dd, ARP is 806, etc. For IEEE802.3 SNAP , th is is this is a 16-
58
Page 73

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
bit (2-octet) hex value. For IEEE802.3 LLC, this is the 2-octet IEEE 802 .2 Link Service Acc ess
Point (LSAP) pair. The first octet is for Destination Service Access Point (DSAP) and the
second octet is for Source.
Click
specific entry. Click
to make a new entry. Click
Add
Delte Group
Delete All
to remove the specific entry from the group.
to remove an entry. Click
Delete Settings
to remove the configuration from the
802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings
Users can configure Protocol VLAN settings. The lower half of the table displays any previously created settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN > 802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings:
Figure 3 - 9. 802.1v Protocol VLAN Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Group ID
Group Name
VID (1-4094)
VLAN Name
802.1p Priority
Highlight the corres ponding RADIUS button to select a previously conf igured Group ID from
the drop-down menu.
Highlight the corresponding RADIUS button to select a previously configured Group Name
from the drop-down menu.
Highlight the RADIUS button to enter the VID. This is the VLAN ID that, a long with the VLAN
Name, identifies the VLAN the user wishes to create.
Highlight the RADI US button to enter a V LAN Name. This is th e VLAN Nam e that, along with
the VLAN ID, identifies the VLAN the user wishes to create.
This parameter is specified if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority previously set in
the Switch, which is used to determine the CoS queue to which packets are forwarded to.
Once this field is specified, packets accepted by the Switch that match this priority are
forwarded to the CoS queue specified previously by the user.
Click the corresponding box if you want to set the 802.1p default priori ty of a packet to the
value entered in the Priority (0-7) field, which meets the criteria specified previously in this
command, before for warding it on to the specified CoS queue. Other wise, a packet will have
its incoming 802.1p user priority re-written to its or iginal value before being for warded by the
Switch.
For more information on pr iority queues, CoS queues and m apping for 802.1p, see the QoS
section of this manual.
Port List
Select the specified por ts you wish to configure by entering the por t n umber in this field, or tick
the Select All Ports check box.
59
Page 74

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Search Port List
Click Add to create a new entry. To sear ch for a port list enter the port number you wis h to view and click Find. To displa y all
previously configured port lists on the bottom half of the screen click the Show All button, to clear all previously configured lists
click the Delete All button. Clic k Delete to remove the specific entry.
This function allows the user to search all previously configured port list settings and display
them on the lower half of the table.
GVRP Settings
Users can determine whether the Switch will share its VLAN con figuration information with other GARP V LAN Registration
Protocol (GVRP) enabled switches. In addition, In gress Checking ca n be used to li mit traffic b y filtering inco ming packets whose
PVID does not match the PVID of the port. Results can be seen in the table under the configuration settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > GVRP Settings:
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
GVRP Global Settings
From Port / To Port
PVID
GVRP
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable GVRP settings.
Use the drop-down menus to select a range of ports that will be included in the Port-based
VLAN.
This field is used to manually assign a PVID to a VLAN. The Switch's default is to assign all
ports to the default VLAN with a VID of 1.The PVID is used by the port to tag outgoing,
untagged packets, and to make filtering decisions about incoming packets. If the port is
specified to accept only tagged frames - as tagging, and an untagged packet is forwarded to
the port for transmission, the port will add an 802.1Q tag using the PVID to write the VID in
the tag. When the packet arrives at its destination, the receiving device will use the PVID to
make VLAN forwarding decisions. If the port receives a packet, and Ingress filtering is
Enabled, the port will compare the VID of the incoming packet to its PVID. If the two are
unequal, the port will drop the packet. If the two are equal, the port will receive the packet.
The GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enables the port to dynamically become a
member of a VLAN. GVRP is Disabled by default.
Figure 3 - 10. GVRP Settings window
60
Page 75

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Ingress Checking
Acceptable Frame
Type
Click Apply to implement changes made.
This drop-down menu allows the user to enable the port to compare the VID tag of an
incoming packet with the PVID number assigned to the port. If the two are different, the port
filters (drops) the packet. Disabled disables ingress filtering. Ingress checking is Enabled by
default.
This field denotes the type of frame that will be accepted by the port. The user may choose
between Tagged Only, which means only VLAN tagged frames will be accepted, and All,
which mean both tagged and untagged frames will be accepted. All is enabled by default.
MAC-based VLAN Settings
Users can create new MAC-based VLAN entries and search, edit, and delete existing entries. When an entry is created for a port,
the port will automatically become the untagged member port of the specified VLAN. When a static MAC-based VLAN entry is
created for a user, the traffic from this user will be able to be serviced under the specified VLAN regardless of the authentication
function operating on this port.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > MAC-based VLAN Settings:
Figure 3 - 11. MAC-based VLAN Settings window
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
MAC Address
VID (1-4094)
VLAN Name
Click Find to search for the informatio n entered. Click Add to add the entry. Click View All to see all the entries. Click Delete
All to remove all the entries. Click Delete to remove the specific entry.
Specify the MAC address to be reauthenticated by entering it into the MAC Address field.
Click this button and enter the VLAN ID.
Enter the VLAN name of a previously configured VLAN.
Private VLAN Settings
The Switch allows users to create private VLANs. A private VLAN divides the Layer 2 broadcast domain of a VLAN into
subdomains and are particularly useful for service providers who need to assign a unique VLAN to each of their customers. Each
subdomain is made up of several pairs of private VLANs, with each private VLAN pair consisting of a primary and secondary
VLAN. All of the VLAN pairs in a private VLAN domain are members of the same primary VLAN. Each subdomain is identified
using the secondary VLAN ID.
The diagram below illustrates the structure of a Private VLAN domain:
61
Page 76

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 12. Private VLAN domain
The ports in a private VLAN can be one of the following three types:
Port Type Description
Promiscuous
Isolated
Community
A promiscuous port is a port that is a member of a primary VLAN that can communicate with
all interfaces, including ports that have been configured as community and isolated ports on
secondary VLANs that are associated with the primary VLAN.
An isolated port is used to describe a host port that is a member of an isolated secondary
VLAN. An isolated port is completely isolated at Layer 2 from other ports within the same
private VLAN domain, apart from promiscuous ports. All traffic destined to isolated ports is
blocked, except for tr affic originating from promiscuous ports. An y traffic originating f rom an
isolated port is only forwarded to promiscuous ports.
A community port is used to des cribe a host port th at is a mem ber of a community second ary
VLAN. A community port can communicate with both ports that are members of the same
community VLAN and promiscuous ports. Interfac es that are configured as comm unity ports
are isolated at Layer 2 from all other interfaces that are members of a different community and
from isolated ports that are members of the same private VLAN domain.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Private VLAN Settings:
62
Page 77

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 13. Private VLAN Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name Click the radio button and enter the name of the private VLAN.
VLAN ID (2-4094)
VLAN List
Click Add to create the new Private VLAN entry. Click Find to search for the specific information entered. Click View All to see
all the entries. Click Edit to configure the specific entry. Click Delete to remove the specific entry.
Click Edit to see the following window.
Specify the VLAN ID of the Private VLAN.
Specify a list of VLAN IDs.
Figure 3 - 14. Private VLAN Settings - Edit window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Secondary VLAN Type
Use the drop-down m enu to specif y the Secondar y VLAN Type. The a vailable options are
described below:
Isolated- An Isolated VLAN is a secondar y VLAN whose dis tinctive charact eristic is that all
hosts connected to its ports are isolated at Layer 2. The primar y advantage of a n isolated
VLAN is that it allows a Private VLAN to only use two VLAN identifiers to provide port
isolation and serve any number of end users. A Private VLAN can only support one
isolated VLAN.
63
Page 78

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Community- A Community VL AN is a secondary VLAN that is associated with a group of
ports that connects to a cer tain "com munit y" of end devices with mutual tr ust relat ionships.
There can be multiple distinct community VLANs in a Private VLAN domain.
Secondary VLAN
Name
Secondary VLAN List
Click Add to create a new entry. Click Delete to remove the specific entry.
Click the rad io butt on and e nter the sec on dar y VLAN n ame.
Click the radio button and enter a list of VLAN IDs.
PVID Auto Assign Settings
Users can enable or disable PVID Auto Assign Status. The default setting is enabled.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > PVID Auto Assign Settings:
Figure 3 - 15. PVID Auto Assign Settings window
Click Apply to implement the changes made. Please see the previous section for more information about PVIDs.
Voice VLAN
Voice VLAN Global Settings
This window is used to enable the global vo ice VLAN function on the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Global Settings:
Figure 3 - 16. Voice VLAN Global Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Voice VLAN State
Voice VLAN Name
Voie VID (1-4094)
Click to enable or disable the voice VLAN state.
Specify the name of the voice VLAN.
Specify the VLAN ID of the voice VLAN.
64
Page 79

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
will change its priority. When the voice device sends untagged packets, it will
Priority
Aging Time (1-65535)
Log State
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Specify the priority of the voice VLAN.
Specify the aging time between 1 and 65535 minutes.
Use the drop-down menu to enable the voice VLAN log state.
Voice VLAN Port Settings
This window is used to configure the voice VLAN ports.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Port Settings:
Figure 3 - 17. Voice VLAN Port Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
From Port / To Port
State
Mode
Use the drop-down menus to select a range of ports to be configured.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the voice VLAN function state on ports.
Specify the voice VLAN mode.
Auto - W hen the mode is auto, the port may become the voic e VL AN member port by autolearning. If the MAC addr ess of the received pack et matches the conf igured OUI, the port
will be learned as dynamic member port. The dynam ic membership will be removed via the
aging out mechanism.
Tag - Specify the port to join the voice VLAN as a tagged member.
Untag - Specify the port to join the voice VLAN as an untagged member.
• When the port is working in auto tagged mode, and learns about a voice device
through the device’s OUI, it will join the voice VLAN as a tagged member
automatically. When the voice device sends voice VLAN tagged packets, the switch
65
Page 80

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
forward them to port’s PVID VLAN.
• When the port is working in auto untagged mode, and the port captures a voice
device through the device’s OUI, it will join the voice VLAN as an untagged member
automatically. When the voice device sends voice VLAN, tagged packets, the switch
will change its priority. Should the voice device send untagged packets, the switch
will assign priority to those and add the voice VLAN ID into this packet
• When the switch receives LLDP-MED packets, it checks the VLAN ID, tagged flag
and priority flag.The switch should follow the tagged flag and priority setting.
Manual - When the mode is set to manual, the port needs to be m anually added into or
removed from the voice VLAN by 802.1Q VLAN configuration command.
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Voice VLAN OUI Settings
This window is used to configure the user-defined voice traffic’s OUI.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN OUI Settings:
Figure 3 - 18. Voice VLAN OUI Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
OU I Addre ss
Mask
Description
Click Apply to implement the changes made. Click Delete All to remove all the user-de fined entrie s. Click Edit to confi gure the
specific entry. Click Delete to remove the specific entry.
Specify a user-defined OUI MAC address.
Specify a user-defined OUI MAC address mask.
Specify a description for the user-defined OUI.
Voice VLAN Device
This window is used to show voice devices that are connected to the ports.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN Device:
66
Page 81

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 19. Voice VLAN Device window
Voice VLAN LLDP-MED Voice Device
This window is used to show the voice devices being discovered by the LLDP-MED.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Voice VLAN > Voice VLAN LLDP-MED Voice Device:
Figure 3 - 20. Voice VLAN LLDP-MED Voice Device window
VLAN Trunk Settings
Enable VLAN on a port to allow frames belonging to unknown VLAN groups to pass through that port. This is useful if you want
to set up VLA N groups on end devic es without having to c onfigure the same VLAN groups on intermed i ary devices.
Refer to the following figure for an illustrated example. Suppose you want to create VLAN groups 1 and 2 (V1 and V2) on
devices A and B. Without a VLAN Trunk, you must first configure VLAN groups 1 and 2 o n all intermediary switc hes C, D and
E; otherwise they will drop frames with unkno wn VLAN gr oup tags. Ho wever, wit h VLAN Tr unk enabled on a port(s) in each
intermediary switch, you only need to create VLAN groups in the end devices (A and B). C, D and E automatically allow frames
with VLAN group tags 1 and 2 (VLAN groups that are unknown to those switches) to pass through their VLAN trunking port(s).
Users can combine a number of VLAN ports together to create VLAN trunks. To c reate VLAN T runk P ort setting s on the S witch,
select the ports to be configured, change the VLAN Trunk Global State to Enabled, and click Apply, the new settings will appear
in the VLAN Trunk Settings tabl e in the lower part of the window.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > VLAN Trunk Settings:
Figure 3 - 21. VLAN Trunk Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
67
Page 82

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Parameter Description
VLAN Trunk Global
State
Ports
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Use the radio buttons to Enable or Disable the VLAN trunking global state.
The ports to be configured.
Browse VLAN
This window is used to display the VLA N sta tus.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > VLAN > Browse VLAN:
Figure 3 - 22. Browse VLAN window
Enter a VLAN ID in VID field and click Find to disp lay the VLAN status.
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings
This window is used to configure Layer 2 protocol tunneling settings.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings:
Figure 3 - 23. Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Layer 2 Protocol
Tunneling State
Click to enable or disable the Layer 2 protocol tunneling state.
68
Page 83

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
From Port / To Port
Type
Tunneled Protocol
Threshold (0-65535)
Click Apply to implement the changes made.
Use the drop-down menus to select a range of ports to be configured.
Specify the type of the ports.
UNI - Specify the ports as UNI ports.
NNI - Specify the ports as NNI ports.
None - Disable tunnel on it.
Specify tunneled protocols on the UNI ports.
STP - Specify to use the STP protocol.
GVRP - Specify to use the GVRP protocol.
Protocol MAC - Specify the destination MAC address of the L2 protocol packets that will
tunneled on these UNI ports. The MAC address can be 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC or 01-00-0CCC-CC-CD.
All - All tunnel-abled Layer 2 protocols will be tunneled on the ports.
Specify the drop threshold for packets-per-second accepted on the UNI ports. The ports drop
the PDU if the protocol’s threshold is exceeded.
Egress Filter Settings
Users can configure an egress filter on specific ports for unknown unicast and unregistered multicast packets.
The Switch drops all unknown unicast/multicast pa ckets on egress ports when it detects unk nown unicast/mul ticast packets for
egress ports. Therefore, a user can select which port is permitted or not permitted to receive unknown unicast/multicast packets.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > Egress Filter Settings:
Figure 3 - 24. Egress Filter Settings window
The following fields can then be set:
Parameter Description
Unicast
Select ports to filter unknown unicast packets. These packets will not be forwarded to those
ports. Unselected por ts wil l not f ilt er unknown unicast packets and the pac ket s may be forwar ded
to those ports.
Multicast
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Select ports to filter unregistered multicast packets. These packets will not be forwarded to those
ports. Unselected ports will not filter unregistered multicast packets and the packets may be
forwarded to those ports.
L2 Multicast Control
69
Page 84

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping allows the Switch to recognize IGMP queries and reports sent between
network stations or devices and an IGMP host. When enabled for IGMP snooping, the Switch can open or close a port to a
specific device based on IGMP messages passin g t hrough the Switch.
IGMP Snooping Settings
In order to use IGMP Snooping it must first be enabled for the entire Switch under IGMP Global Settings at the top of the
window. Yo u ma y t he n fi ne -tune the settings for e ach VLAN by clickin g t he co r r esp o nd ing Edit button. When e nab le d for I GM P
snooping, the Switch can open or close a port to a specific multicast group member based on IGMP messages sent from the device
to the IGMP host or vice ver sa. T he Switch monito rs IGM P message s and d isconti nues fo rwardi ng multica st pac kets when there
are no longer hosts requesting that they continue.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Settings:
Figure 3 - 25. IGMP Snooping Settings window
The following parameters may be viewed or configured:
Parameter Description
IGMP Snooping State
Max Learned Entry Value (1-
256)
VID (VLAN ID)
VLAN Name
State Select Enabled to implement IGMP Snooping. This field is Disabled by default.
Parameter Settings Click the Edit button next to the VLAN you want to edit the IGMP Snooping
Click Apply to implement changes made . Click the Edit butto n to configure the IGMP Snooping Parameters Settings.
Click the Modify Router Port link to configure the IGMP Snooping Router Port Settings.
Click the radio button to enable or disable the IGMP snooping state.
Specify the maximum number of groups that can be learned by the data driven
mechanism.
This is the VLAN ID that, along with the VLAN Name, identifies the VLAN the user
wishes to modify the IGMP Snooping Settings for.
This is the VLAN Name that, along with the VLAN ID, identifies the VLAN the user
wishes to modify the IGMP Snooping Settings for.
parameters for.
Click the Edit button to see the following window:
70
Page 85

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 26. IGMP Snooping Parameters Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Query Interval (1-65535)
Max Response Time (1-25)
Robustness Value (1-7)
Last Member Query Interval
(1-25)
Data Driven Group Expiry
Time (1-65535)
Querier State Choose Enabled from the drop-down menu to enable the transmission of IGMP
Fast Leave Choose Enabled from the drop-down menu to enable the Fast Leave function or
State Use the drop-down menu to Enable or Disable the IGMP Snooping feature for the
Report Suppression
This parameter specifies the length of time between sending IGMP Queries.
Default= 125.
This parameter is used to set the maximum amount of time allowed before sending
an IGMP response report. Default= 10.
This parameter is used as a tuning variable that allows for a large number of packets
being lost on subnetworks. Specify a value between 1 and 255. Specify a high value
if you expect your subnetworks to lose a large number of packets. Default= 2.
This parameter is us ed to set the m aximum amount of time betwe en group-specific
query messages, including messages that have been sent in response to leave
group messages. Default= 2.
Specify the data driven group lifetime in seconds.
Query Packets or choose Disabled to disable. Default = Disabled.
choose Disabled to disable. If Fast Leave is Enabled, the membership will
immediately be removed when the system receives an IGMP leave message.
specified VLAN.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable report suppression function. The
Switch uses IGMP report suppression to forward only one IGMP report per multicast
router query to multicast devices.
Data Driven Learning State
Data Driven Learning Aged
Out
Version
After setting the above parameters, click the Apply button in the top section of the window to allow your changes to be
implemented. Click the <<Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Modify Router Port link to see the following window:
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the data driven learning of an IGMP
snooping group.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the aging on the entry.
Use the drop-down menu to specify the version of IGMP packets that will be sent by
the specified ports. If an IGMP packet received by the interface has a version higher
then the specified version, the packet will be dropped.
71
Page 86

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 27. IGMP Snooping Router Port Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Static Router Port
Forbidden Router Port
Dynamic Router Port
Click the Select All button to select all the ports for configuration. Click the Clear All button to unselect all the ports for
configuration. Click the Apply button to accept the changes made. Click the <<Back button to discard the c hanges made and
return to the previous page.
This section is used to designate a range of ports as being connected to multicast-enabled
routers. This will ensure that all packets with such a router as its destination will reach the
multicast-enabled router regardless of the protocol.
This section is used to designate a range of ports as being not connected to multicastenabled routers. This ensures that the forbidden router port will not propagate routing
packets out.
Displays router ports that have been dynamically configured.
IGMP Snooping Rate Limit Set ti ngs
This window is used to configure the IGMP snooping rate limit parameters.
To view the follo wing window, clic k L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Rate Limit
Settings:
Figure 3 - 28. IGMP Snooping Rate Limit Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Port List
VID List
Enter the port list used for this configuration.
Enter the VID list used for this configuration.
72
Page 87

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Rate Limit (1-1000) Enter the IGMP s noo pin g rat e lim it used. By selecting the No Limit check box, the rate
limit for the entered port(s) will be ignored.
Click the Apply button to accept the change s made. Click the Find butto n to locate a specific entry based on the information
entered. Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry. Enter a page number and click the Go button to naviga te to a
specific page when multiple pages exist.
IGMP Snooping Static Gr oup S ett ings
This window is used to view the Switch’s IGMP Snooping Group Table. IGMP Snooping allows the Switch to read the Multicast
Group IP address and the corresponding MAC address from IGMP packets that pass through the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Sno oping Stat ic Group
Settings:
Figure 3 - 29. IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
IPv4 Address
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click the Create butto n to add a new e ntry
based on the information e nter ed. Click the Delete button to remove the specific entr y based on the infor mation e ntered . Clic k the
View All button to display all the existing entries. Click the Edit butto n to re-configure the specific entry. Enter a page number
and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Click the Edit button to see thw following window.
The VLAN name of the multicast group.
The VID list of the multicast group.
Enter the IPv4 address.
Figure 3 - 30. IGMP Snooping Static Group Settings – Edit window
Select the appropriate po r ts individ ually to include them in the IGMP snooping static group settings.
Click the Select All button to select all the ports for configuration. Click the Clear All button to unselect all the ports for
configuration. Click the Apply button to accept the changes made. Click the <<Back button to discard the change s made and
return to the previous page.
73
Page 88

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
IGMP Router Port
This window is used to displa y which of the S witch’s por ts are currently configured as router ports. A router port configured by a
user (using the console or Web-based management interfaces) is displayed as a static router port, designated by S. A router port
that is dynamically configured by the Switch is designated by D, while a Forbidden port is designated by F.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Router Port:
Figure 3 - 31. IGMP Router Port window
Enter a VID (VLAN ID) in the field at the top of the window.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Enter a page number and click the Go button to
navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
IGMP Snooping Group
This window is used to display the Switch’s IGMP Snooping Group Table. IGMP Snooping allows the Switch to read the
Multicast Group IP address and the corresponding MAC address from IGMP packets that pass through the Switch.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Group:
Figure 3 - 32. IGMP Snooping Group window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
Port List
Group IPv4 Address
Data Driven
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click Clear Data Driven to delete the specified
IGMP snooping group learned by the data-driven mechanism. Click View All to see all the e ntries. Clic k Clear All D ata Driven
to delete all the IGMP snooping groups learned by the data-driven mechanism.
The VLAN name of the multicast group.
The VID list of the multicast group.
Specify the port number(s) used to find a multicast group.
Enter the IPv4 address.
Tick to display data-driven IGMP snooping group entries.
74
Page 89

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
IGMP Snooping Forwarding Table
This page displays the switch’s current IGMP snooping forwarding table. It provides an easy way for user to check the list of ports
that the multicast group co mes from and specific sources that it will be forwarded to. The packet comes from the source VLAN.
They will be forwarded to the forwarding VLAN. The IGMP snooping further restricts the forwarding ports.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snoo ping > IGMP Snooping Forwarding
Table:
Figure 3 - 33. IGMP Snooping Forwarding Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click View All to see a ll the entrie s.
The VLAN name of the multicast group.
The VID list of the multicast group.
IGMP Snooping Counter
This window is used to display the Switch’s IGMP Snooping counter table.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Snooping Counter:
Figure 3 - 34. IGMP Snooping Counter window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
The VLAN name of the multicast group.
The VID list of the multicast group.
75
Page 90

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Port List
Click the Find button to locate a speci fic entry based on the information entered. Click View All to see all the entries. Click the
Packet Statistics
Click the Packet Statistics li nk to see the following window.
link to view the IGMP Snooping C ounter Table.
Specify the port number(s) used to find a multicast group.
Figure 3 - 35. Browse IGMP Snooping Counter window
Click the Clear Counter button to clear a ll the infor mation disp la yed in the fields. Click t he Refresh button to refresh the display
table so that new information will a ppear. Click the <<Back button to return to the previous page.
IGMP Host Table
This window is used to display the IGMP hosts that have joined groups on specific ports or specific VLANs.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Host Table:
Figure 3 - 36. IGMP Host Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
Port List
Group Address
Specify the name of the VLAN on which the router port resides.
Specify a list of VIDs on which the router port resides.
Specify the list of ports to display the host information.
Specify the group to display the host information.
76
Page 91

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click View All to see all the entries.
MLD Snooping
MLD Snooping Settings
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) Snooping is an IPv6 function used similarly to IGMP snooping in IPv4. It is used to discover
ports on a VLAN that are requesting multicast data. Instead of flooding all p orts on a selecte d VLAN with multicast traf fic, MLD
snooping will only forward multicast data to ports that wish to receive this data through the use of queries and reports produced by
the requesting ports and the source of the multicast traffic.
MLD snooping is accomplished through the examination of the layer 3 part of an MLD control packet transferred between end
nodes and a MLD router. When the Switch discovers that this route is req uesting multicast traffic, it adds the port directly attached
to it into the correct IPv6 multicast table, and begins the pro cess of forwarding multicast traffic to that port. This entry in the
multicast routing table records the port, the VLAN ID, and the associated multicast IPv6 multicast group address, and then
considers this port to be an active lis te ning port. The active listening ports are the only ones to rece ive multicast group data.
MLD Control Messages
Three types of messages are transferred between devices using MLD snooping. These three messages are all defined by four
ICMPv6 packet headers, labeled 130, 131, 132, and 143.
1. Multicast Listener Query – Similar to the IGMPv2 Host Membership Query for IPv4, and labeled as 130 in the
ICMPv6 packet header, this message is sent by the router to ask if any link is requesting multicast data. There are two
types of MLD query messages emitted by the router. The General Query is used to advertise all multicast addresses that
are ready to send multicast data to all listening ports, and the Multicast Specific query, which advertises a specific
multicast address that is also ready. These two types of messages are distinguished by a multicast destination address
located in the IPv6 header and a multicast address in the Multicast Listener Query Message.
2. Multicast Listener Report, Version 1 – Comparable to the Host Membership Report in IGMPv2, and labeled as 131 in
the ICMP packet header, this message is sent b y the listening port to the Switch stating that it is interested in receivi ng
multicast data from a multicast address in response to the Multicast Listener Query message.
3. Multicast Listener Done – Akin to the Leave Group Message in IGMPv2, and labeled as 132 in the ICMPv6 packet
header, this message is sent by the multicast listening port stating that it is no longer interested in receiving multic a st data
from a specific multicast group address, therefor e stating that it is “done” with the multicast data from this addr ess. Once
this message is received by the Switch, it will no longer forward multicast tra ffic fro m a specific multica st group addr ess
to this listening port.
4. Multicast Listener Report, Version 2 - Comparable to the Host Membership Report in IGMPv3, and labeled as 143 in
the ICMP packet header, this message is sent by the listening por t to the Switch stating t hat it is interested in re ceiving
multicast data from a multicast address in response to the Multicast Listener Query message.
Users can configure the settings for MLD snooping.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Settings:
Figure 3 - 37. MLD Snooping Settings window
The following parameters can be viewed or configured:
77
Page 92

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Parameter Description
MLD Snooping State
Max Learned Entry Value (1-
256)
VID
VLAN Name
State
Click Apply to implement changes made . Click the Edit butto n to configure the MLD Snooping Parameter s Settings.
Click the Modify Router Port link to configure the MLD Snooping Router Port Settings.
Click the Edit button to see the following window:
Click the radio button to enable or disable the MLD snooping state.
Specify the maximum number of groups that can be learned by the data driven
mechanism.
This is the VLAN ID that, along with the VLAN Name, identifies the VLAN for which
to modify the MLD Snooping Settings.
This is the VLAN Name that, along with the VLAN ID, identifies the VLAN for which
to modify the MLD Snooping Settings.
Used to enable or disable MLD snooping for the specified VLAN. This field is
Disabled by default.
Figure 3 - 38. MLD Snooping Parameters Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Query Interval (1-65535 sec)
Max Response Time (1-25
sec)
Robustness Variable (1-7)
This parameter is used to specify the amount of time in seconds between general
query transmissions. Default: 125 seconds.
This parameter is used to specify the maximum amount of time in seconds to wait for
reports from listeners. Default: 10 seconds.
This parameter is used to provide fine-tuning that allows for expected packet losses
on a subnet. The value of the robustness variable is used in calculating the following
MLD message intervals:
• Group listener interval—Amount of time that must pass before a multicast
router decides there are no more listeners of a group on a network. This
interval is calculated as follows: (robustness variable * query interval) + (1 *
query response interval).
• Other querier present interval—Amount of time that must pass before a
multicast router decides that there is no longer another multicast router that
is the querier. This interval is calculated as follows: (robustness variable *
query interval) + (0.5 * query response interval).
• Last listener query count—Number of group-specific queries sent before the
router assumes there are no local listeners of a group. The default number is
the value of the robustness variable.
• By default, the robustness variab le is set to 2. You might want to increase
this value if you expect a subnet to lose a high number of packets.
78
Page 93

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Last Member Query Interval
(1-25)
Data Driven Group Expiry
Time (1-65535)
Querier State Choose Enabled from the drop-down menu to specify that the Switch should act as
Fast Done Choose Enabled from the drop-down menu to enable the Fast Done function or
State Use the drop-down menu to specify if MLD Snooping should be Enabled or Disabled
Report Suppression
Data Driven Learning State
Data Driven Learning Aged
Out
This parameter is us ed to set the m aximum amount of time betwe en group-specific
query messages, including messages that have been sent in response to leave
group messages.
Specify the data driven group lifetime in seconds.
an MLD Querier (sends MLD query packets). Choose Disabled from the drop-down
menu to specify that the Switch should act as a Non-Querier (does not send MLD
query packets).
choose Disabled to disable. If it is enabled, the membership is immediately removed
when the system receive the MLD leave message.
from the specified VLAN.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable report suppression function. The
Switch uses MLD report suppression to forward only one MLD report per multicast
router query to multicast devices.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the data driven learning of a MLD
snooping group.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the aging on the entry.
Version
After setting the above parameters, click the Apply button in the top section of the window to allow your changes to be
implemented. Click the <<Back button to discard the changes made and return to the previous page.
Click the Modify Router Port link to see the following window:
Use the drop-down menu to specify the version of MLD packets that will be sent by
the specified ports. If an MLD packet received by the interface has a version higher
then the specified version, the packet will be dropped.
Figure 3 - 39. MLD Snooping Router Port Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Static Router Port
Forbidden Router Port
This section is used to designate a range of ports as being connected to multicast-enabled
routers. This will ensure that all packets with such a router as its destination will reach the
multicast-enabled router regardless of the protocol.
This section is used to designate a range of ports as being not connected to multicast-
79
Page 94

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
enabled routers. This ensures that the forbidden router port will not propagate routing
packets out.
Dynamic Router Port
Click the Select All button to select all the ports for configuration. Click the Clear All button to unselect all the ports for
configuration. Click the Apply button to accept the changes made. Click the <<Back butto n to discard the change s made and
return to the previous page.
Displays router ports that have been dynamically configured.
MLD Snooping Rate Limit Set ti ngs
This window is used to configure the MLD snooping rate limit parameters.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Rate Limit
Settings:
Figure 3 - 40. MLD Snooping Rate Limit Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Port List
VID List
Rate Limit (1-1000) Enter the MLD snooping rate limit used. By selecting the No Limit check box, the rate limit
Click the Apply b utton to accep t the changes mad e. Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the infor mation
entered. Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry. Enter a page number and click the Go button to naviga te to a
specific page when multiple pages exist.
Enter the port list used for this configuration.
Enter the VID list used for this configuration.
for the entered port(s) will be ignored.
MLD Snooping Static Group Sett ings
This window is used to view the Switch’s MLD Snooping Gro up Table. MLD Snooping allows the Switch to read the Multicast
Group IP address and the corresponding MAC address from MLD packets that pass through the Switch.
To view the follo win g windo w, click L2 Features > L2 M ulticast Co ntrol > MLD Snooping > M LD Snooping Static Group
Settings:
80
Page 95

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 41. MLD Snooping Static Group Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
IPv6 Address
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click the Create button to add a ne w entry
based on the information e nter ed. Click the Delete button to remove the specific entry based on the information entered. Cl ic k t he
View All button to display all the existing entries. Click the Edit button to re-configure the specific entry. Enter a page number
and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
Click Edit to see the following window.
The VLAN name of the multicast group.
The VID list of the multicast group.
Enter the IPv6 address.
Figure 3 - 42. MLD Snooping Static Group Settings – Edit window
Select the appropriate po r ts individ ually to include them in the MLD snooping static group settings.
Click the Select All button to select all the ports for configuration. Click the Clear All button to unselect all the ports for
configuration. Click the Apply button to accept the changes made. Click the <<Back button to discard the change s made and
return to the previous page.
MLD Router Port
This window is used to display which of the Switch’s ports are currently configured as router ports in IPv6. A router port
configured by a user (using the console or Web-based management interfaces) is displayed as a static router port, designated by S.
A router port that is dynamically configured by the Switch is designated by D, while a Forbidden port is designated by F.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Router Port:
Figure 3 - 43. MLD Router Port window
Enter a VID (VLAN ID) in the field at the top of the window.
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Enter a page number and click the Go button to
navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
81
Page 96

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
MLD Snooping Group
This window is used to display MLD Snooping Groups present on the Switch. MLD Snooping is an IPv6 function comparable to
IGMP Snooping for IPv4.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Group:
Figure 3 - 44. MLD Snooping Group window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
Port List
Group IPv6 Address
Data Driven
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click Clear Data Driven to delete the spe cified
IGMP snooping group learned by the data-driven mechanism. Click View All to see all the e ntries. Clic k Clear All D ata Driven
to delete all the IGMP snooping groups learned by the data-driven mechani sm.
The VLAN name of the multicast group.
The VID list of the multicast group.
Specify the port number(s) used to find a multicast group.
Enter the IPv6 address.
Tick to display data-driven IGMP snooping group entries.
MLD Snooping Forwarding Ta ble
This window is used to display the switch’s current MLD snooping forwarding table. It provides an easy way for user to check the
list of ports that the mu lticast group c omes from and specific sources that it will be forwarded to. The packet comes from the
source VLAN. They will be forwarded to the forwarding VLAN. The MLD snooping further restricts the forwarding ports.
To view the fol lowing wi ndow, clic k L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Sno oping Forwarding
Table:
Figure 3 - 45. MLD Snooping Forwaring Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
The name of the VLAN for which you want to view MLD snooping forwarding table information.
82
Page 97

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
VID List
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click View All to see a ll the entrie s.
The ID of the VLAN for which you want to view MLD snooping forwarding table information.
MLD Snooping Counter
This window is used to display the statistics counter for MLD protocol packets that are received by the switch since MLD
Snooping is enabled.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Snooping Counter:
Figure 3 - 46. MLD Snooping Counter window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
Port List
Click the Find button to loc ate a specific entr y based on the infor mation entered. Clic k View All to see all the entries. Click the
Packet Statistics
Click the Packet Statistics li nk to see the following window.
link to view the MLD Snooping Counter Table.
Specify a VLAN name to be displayed.
Specify a list of VLANs to be displayed.
Specify a list of ports to be displayed.
83
Page 98

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
Figure 3 - 47. Browse MLD Snooping Counter window
Click the Clear Counter button to clear a ll the infor mation disp la yed in the field s. Click t he Refresh button to refresh the display
table so that new information will a ppear. Click the <<Back button to return to the previous page.
MLD Host Table
This window is used to display the MLD hosts that have joined groups on specific ports or specific VLANs.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > MLD Snooping > MLD Host Table:
Figure 3 - 48. MLD Host Table window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
VLAN Name
VID List
Port List
Group Address
Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the information entered. Click View All to see a ll the entrie s.
Specify the name of the VLAN on which the router port resides.
Specify a list of VIDs on which the router port resides.
Specify the list of ports to display the host information.
Specify the group to display the host information.
Multicast VLAN
IGMP Multicast Group Profile Settings
Users can add a profile to which multicast address reports are to be received on specified ports on the Switch. This function will
therefore limit the number of reports received and the number of multicast groups configured on the Switch. The user may set an
IP Multicast address or range of IP Multicast addresses to accept reports (Permit) or deny reports (Deny) coming into the specified
switch ports.
To view the following window, click L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > Multicast VLAN > IGMP Multicast Group
Profile Settings:
Figure 3 - 49. IGMP Multicast Group Profile Settings window
84
Page 99

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Profile Name
Click the Add button to add a new entry. Click the Find button to locate a specific entry based on the infor mation entered . Click
the Delete All button to re move all the entrie s lis ted. Click t he View All butto n to d ispla y all the e xisting e ntries. C lick t he Delete
button to re move the co rre spo ndin g entr y. Cl ick t he Group List
the specific entry.
Click the Group List link to see the following window.
Figure 3 - 50. Multicast Group Profile Multicast Address Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
Enter a name for the IP Multicast Profile.
link to configure the Multicast Group Profile Address Settings for
Multicast Address List
Click the Add button to add a new entry based on the information entered. Click the <<Back button to discard the changes made
and return to the previous page. Click the Delete button to remove the corresponding e nt ry.
Enter the multicast address list value .
IGMP Snooping Multicast VLAN Settings
This window is used to configure the IGMP snooping multicast VLAN parameters.
To view the fo llowin g window, c lick L2 Features > L2 Multicast Control > Multicast VLAN > IGMP Snooping M ulticast
VLAN Settings:
Figure 3 - 51. IGMP Snooping Multicast VLAN Settings window
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
IGMP Multicast VLAN State
IGMP Multicast VLAN
Forward Unmatched
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable the IGMP Multicast VLAN state.
Click the radio buttons to enable or disable the IGMP Multicast VLAN Forwarding state.
85
Page 100

xStack® DGS-3200 Series Layer 2 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
VLAN Name
VID (2-4094)
Click the Apply button to accept the changes made for e ach individ ual section. Click the Add button to add a new entry based o n
the information entered. Clic k the Edit button to configure the IGMP Snooping Mult icast VLAN Settings for t he specific entry.
Click the Delete button to remove the specific e ntr y. Clic k the P rofile List
Settings for the specific entry.
Click the Edit button to see the following window.
Figure 3 - 52. IGMP Snooping Multicast VLAN Settings – Edit window
Enter the VLAN Name used.
Enter the VID used.
link to configure the IGMP Snooping Multi ca st V L AN
The following parameters can be configured:
Parameter Description
State
Replace Source IP
Untagged Member Ports
Tagged Member Ports
Tagged Source Ports
Click the Select All button to select all the ports for configuration. Click the Clear All button to unselect all the ports for
configuration. Click the Apply button to accept the changes made. Click the <<Back button to discard the changes made and
return to the previous page.
Click the Profile List link to see the following window.
Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the state.
With the IGMP snooping function, the IGMP report packet sent by the host will be
forwarded to the source port. Before forwarding of the packet, the source IP address in
the join packet needs to be replaced by this IP address. If none is specified, the source
IP address will us e zero IP addres s .
Specify the untagged member port of the multicast VLAN.
Specify the tagged member port of the multicast VLAN.
Specify the source port or range of source ports as tagged members of the multicast
VLAN.
Figure 3 - 53. IGMP Snooping Multicast VLAN Group List Settings window
86
 Loading...
Loading...