Page 1

D-Link
Gigabit CardBus Notebook Adapter
DGE-660TD
Manual
Rev. 3.00 (May 2007)��
Page 2

Contents
Introduction ...................................................................................1
General Description ............................................................................................ 1
About Gigabit Ethernet .................................................................2
About Auto-negotiation ..................................................................3
LED Indicators ...............................................................................5
Summary of Features......................................................................5
Troubleshooting..............................................................................6
Confirming the Connection (LED Indicator) ......................................................... 6
Troubleshooting the Hardware Installation............................................................ 6
Verify Each Computers Identification .................................................................... 7
Verify Network Adapter Installation ..................................................................... 7
Verify Cable Connections ................................................................................... 8
Pinging your DGE-660TD Card ............................................................................ 9
Windows 98SE/Me Network Component Configuration ....................10
Using File And Printer Sharing ............................................................................ 12
Enabling File Sharing ........................................................................................... 12
Enabling Printers Sharing ................................................................................... 14
Windows 2000/XP/Vista Network Component Configuration ............15
Networking Basics..........................................................................18
Computer Identification ....................................................................................... 18
Sharing Files ...................................................................................................... 20
Sharing Printers .................................................................................................. 24
How to Install TCP/IP ............................................................................................. 29
Configuring a Dynamic IP Address....................................................................... 30
Configuring a Static IP Address .......................................................................... 33
Checking the TCP/IP Address ............................................................................ 36
Checking the Connection by Pinging .................................................................. 38
Page 3

Specifications ........................................................................................................ 39
Contacting Technical Support ................................................................................. 41
Warranty ................................................................................................................. 42
Page 4

Introduction
Thank you for choosing the D-Link DGE-660TD, the value leader among Fast
Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet adapters for notebook PCs. This chapter provides a
general description of DGE-660TD features, with a summary of features at the
end of the chapter. Installation instructions are provided in Chapters 2 and 3.
General Description
The D-Link DGE-660TD Gigabit Cardbus PC Card for notebook PCs is a
credit-card sized Gigabit adapter for connecting a notebook PC to an Ethernet,
Fast Ethernet, or Gigabit network. The notebook PC must be equipped with a
Type II Cardbus compliant slot.
NOTE: The terms "PC Card" is used throughout this manual to refer to those
objects as defined in the PCMCIA / PC Card standards published by Personal
Computer Memory Card Industry Association (PCMCIA). The term “slot,” as
used in this manual, is synonymous with “socket” where the standards use the
latter term in reference to the physical receptacles of a host notebook computer,
for insertion/connection of PC Cards. More information on the standards is
available from PCMCIA’s www server at http://www.pc-card.com.
The D-Link DGE-660TD automatically detects the parameters of its Ethernet
environment, and automatically negotiates and determines its own speed and
duplex settings as required for maximum performance within the environment.
(The auto-negotiation function is effective only when the DGE-660TD is
connected to the network by a device (switch or hub) that also has auto-
negotiation functionality.)
Inside its compact case, the D-Link DGE-660TD holds an Ethernet controller,
network processing interface, a 68-pin PC Card Standard front-end plug, which
connects to the notebook PC, and a direct port for connecting a RJ-45 network
-1 -
Page 5

cable. The DGE-660TD requires no pre-installation setup -- simply insert its
front end into the notebook PC's PC-Card slot.
The DGE-660TD is supplied with an RJ-45 receptacle, which receives the
network cable. The direct port features full LED display for linkage and activity
states, speed, transmitting and receiving data, and carrier detection.
About Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a network technology specified by IEEE Standard 802.3ab.
It extends the traditional 100Mbps (100 megabit/sec) Fast Ethernet technology
to achieve 1000Mbps (1000 megabit/sec) transmission and reception. Because
Gigabit Ethernet retains the traditional Ethernet CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense,
Multiple Access, and Collision Detect) protocol, it remains wholly compatible
with 100Mbps Ethernet while providing a tenfold increase in network capacity.
The DGE-660TD provides full-duplex 1000Base-T operation (in Category 5
twisted-pair cable environments utilizing all 4 pair). To provide for traditional
10 or 100Mbps Ethernet operation in twisted-pair cable environments, the
DGE-660TD also offers 10 or 100Mbps Ethernet operation, in full-duplex and
half-duplex modes. The DGE-660TD's auto-negotiation capability provides for
automatic selection of the best operation mode.
- 2 -
Page 6

About Auto-negotiation
The basic idea of auto-negotiation can be understood by reflecting for a
moment on the familiar process of making a dialup connection between two
modems. You have probably heard some exchanges between your local modem
and a modem at the other end of a telephone line. (These exchanges are
ordinarily played out through a speaker in your local modem). As irritating as
those few seconds of noise may be, they do let you know that your modem and
the remote modem are on the job, preparing for your intended communication
with the remote computer.
The preparatory work of the two modems during those few seconds before you
see the “connect” message is to negotiate the best data communication scheme
that is supported by both modems, and to decide which is suitable for the
quality of the telephone-line connection between them. The parameters to be
settled between the two modems include best baud rate, compression method,
and error correction method. When the two modems have tested the phone-line
quality and have switched to the combination of parameters, which will provide
the best data communication, then you are given the “connect” message which
signals the end of the inter-modem negotiation and the beginning of your
intended communication with the remote computer.
Auto-negotiation between devices within an Ethernet LAN is similar in concept,
but much briefer. The two devices involved in the auto-negotiation will be your
DGE-660TD and the switch or hub through which it is connected into the LAN.
(Switches ordinarily provide for auto-negotiation; traditional hubs do not.) The
parameters to be negotiated between the DGE-660TD and its supporting switch
or hub include speed (1000Mbps = Gigabit Ethernet, or 100Mbps = Fast
Ethernet) and duplex mode (half-duplex or full-duplex).
- 3 -
Page 7

Startup communication between the two devices occurs when both devices are
operating, the cable connection between them is good, and the connected
notebook PC's network software is loaded. As soon as those conditions are
satisfied, the preparatory process of auto-negotiation between the DGE-660TD
and its supporting device begins and proceeds automatically.
If the supporting switch or hub has auto-negotiation functionality, then it and the
DGE-660TD exchange a series of messages in which each device signals its
capabilities and listens for corresponding information about the other. The
auto-negotiation process requires only a few milliseconds, and the two devices
select the best communication parameters supported by both devices.
If the supporting device does not have auto-negotiation functionality, then its
monotone (single capability) message will be recognized by the DGE-660TD’s
auto-negotiation facility, and the DGE-660TD will simply switch to the one of
its own capabilities that matches that of the supporting device.
Once the auto-negotiation is completed, the line is ready, and it will provide an
optimal data channel between the DGE-660TD and the supporting device. The
line will remain ready without further auto-negotiation action until the link is
broken. Auto-negotiation then reoccurs at any time that the link is restored,
again making the line ready for optimal data communications.
Minimum System Requirement:
Your computer notebook must support:
Pentium 150MHz or Faster
64MB RAM
32MB Free Hard Drive Space
One Available CardBus Slot
CD-ROM Drive
- 4 -
Page 8

LED Indicators
The DGE-660TD features 2 LED indicators:
1. Link/Activity (Link/ACT)
This indicator lights green when the RJ-45 port is connected to an Ethernet
network, if the indicator is blinking green it is transmitting/receiving data
to/from the Ethernet network.
2. Speed Indicator (100Mbps/Amber; 100Mbps/Green; 10Mbps / Off)
The indicator lights green when the port is connected to a 1000Mbps Gigabit
Ethernet Network and the indicator lights amber when the port is connected to a
100Mbps Fast Ethernet Network. Otherwise, this indicator remains off when the
port is connected to a 10Mbps Ethernet Network.
Summary of Features
Features of Model DGE-660TD Gigabit Cardbus PC Card:
Complies with IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet standard
Complies with IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet standard
Complies with IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet standard
Complies with ANSI / IEEE 802.3 Auto-Negitiation standard
Complies with 32-bit CardBus Standard
Supports Crossover Detection & Auto-Correction
Built-in Transmit/Receive FIFO data buffer (8K/64K)
No manual setup switches -- automatically configured by software
Low power consumption
Supported driver list:
Microsoft Windows Vista
Microsoft Windows XP
Microsoft Windows 2000
Microsoft Windows 98SE/ME
-5-
Page 9

Troubleshooting
Confirming the Connection (LED Indicator)
When the notebook computer is powered “ON,” and the DGE-660TD is inserted
into an open slot connector, please check the following items if your LED light is
not “ON.” When all items are working, your DGE-660TD’s direct port LED light
should light up green (“linkage” state.)
1. Make sure that your Ethernet Cat5 cable is in good working order.
2. Make sure that your hub or switch is powered “ON” and is functioning
properly.
3. If the LED remains dark without any apparent cause, check the “Device
Manager.” If there is an exclamation point next to the DGE-660TD, then
double-click to open. A message indicating the error will appear.
4. After verifying that the DGE-660TD has been installed correctly, check steps
1 and 2 again. If you continue to encounter a problem, please call D-Link
Technical Support for assistance.
Troubleshooting the Hardware Installation
If you experience any problems with the hardware installation, first ascertain
that all network cable connections are firm, that the proper grade of cable is
used for the network connection, and that the cable makeup is correct (straight
without un-needed crossovers in the connector wiring). Check that the
supporting hub is powered-on and operating normally, and that the hub is
properly qualified (under 100Base-TX and/or 1000Base-T standards).
- 6-
Page 10

Verify Each Computers Identification
If more than one computer on your network has the same “Computer name,”
communications may be negatively affected. Also, each computer must have the
same “Workgroup” name to communicate properly.
Verify Network Adapter Installation
If your Network Adapter is not installed, including the Network System
Software or Device drivers, your network will not function properly. Use these
steps to verify that your Network Adapter is properly installed.
1. Double-Click the “System” icon in the Control Panel.
2. Click the “Device Manager” tab on top of the “System Properties” dialog
box.
3. Double-Click “Network Adapters” if you do not see any items
branching out. You should see “D-Link DGE-660TD Cardbus PC
Card” branching out after double-clicking “Network Adapters.”
If you do not see any items branching out after double-clicking “Network
Adapters,” your Network Adapter has not been properly installed. Start at the
beginning of the “Quick Install Guide.”
If you see symbols such as yellow exclamation point or red “X” over the icon
adjacent to “D-Link DGE-660TD Cardbus PC Card,” your card is not installed
properly or may have a problem. Double-click the “D-Link DGE-660TD
Cardbus PC Card” and read the explanation of the problem. This information
will be helpful if you require technical support from D-Link.
-7-
Page 11

Verify Cable Connections
Check to see that the computer you are troubleshooting is properly connected.
Each computer must be connected from its DGE-660TD with Category 5 cables.
Examine the network cables and ensure that none have been walked-on, rolled
over by chairs, caught in doors, or damaged. Additionally, make note of and
alleviate any possible electromagnetic interference that may be affecting your
network.
Your network cables can be plugged into any port on your hub except the
“Uplink” port. The “Uplink” port is only used when connecting your hub to
another hub or switch.
- 8 -
Page 12
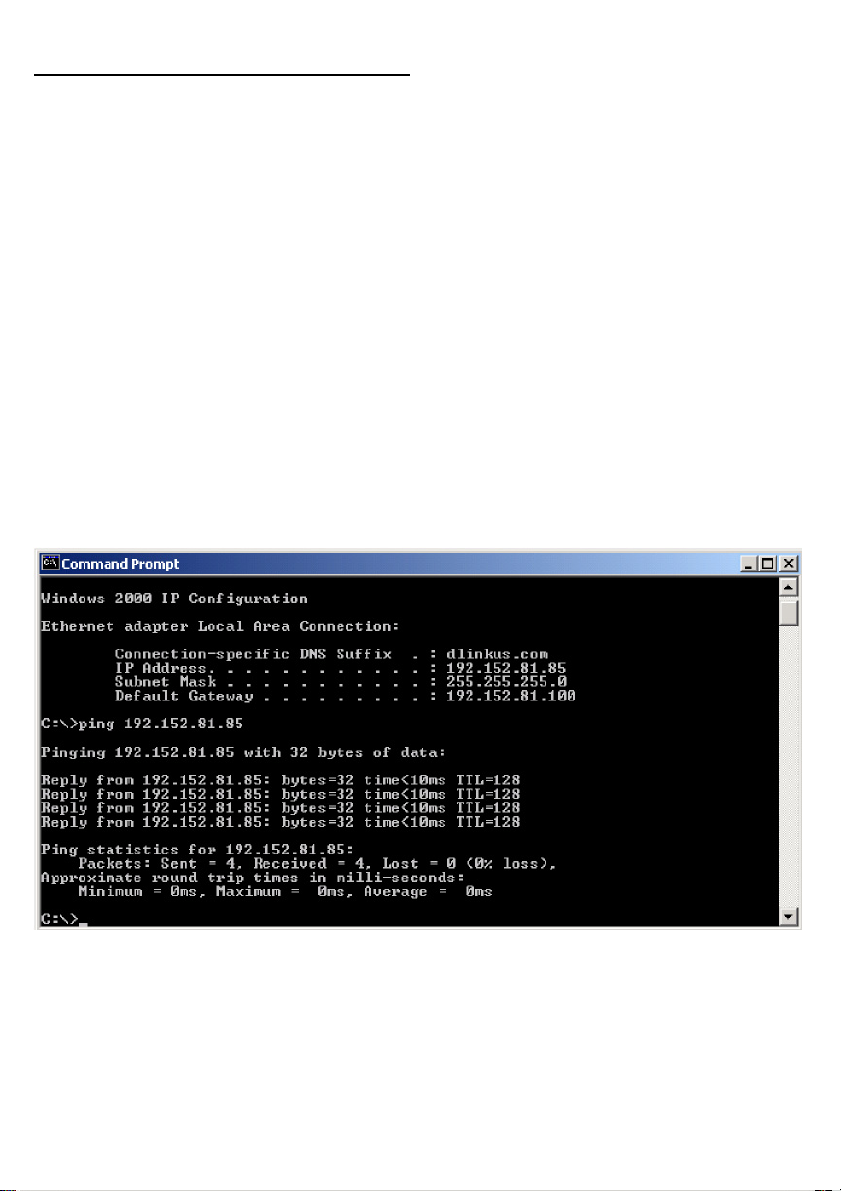
Pinging your DGE-660TD Card
Follow these steps to Ping a device:
Ping is the acronym for Packet Internet Groper (PING), a utility to determine if a
specific IP address is accessible. It works by sending a packet to the specified
address and waiting for a reply. Ping is primarily used to troubleshoot Internet
connections. By sending out a ping, you are verifying that a specific computer
is available. Since all computers on the network must have a unique IP address,
getting a reply means that a computer is on the network and it can communicate.
If you cannot ping another computer, then there is probably a problem with the
hardware. Check the cabling and adapter installation. If you are unable to
network, even when you receive a reply to your ping, it is probably a software
configuration issue. Verify that all the settings are correct.
Start MS-DOS Prompt.
Type in following: ping:xxx.xxx.xx.xx, where xxx.xxx.xx.xx is the IP address to be
pinged (i.e. 192.152.81.85). In this case, computer A is pinging its own IP address.
A successful ping will show four replies.
9 -
-
Page 13

Windows 98SE/Me Network Component
Configuration
Once the driver has been installed, you must make some changes to your
network settings. Click Start > Settings > Control Panel > Network and make
sure that you have all the following components installed.
• Client for Microsoft Networks
• D-Link DGE-660TD
• NetBEUI
• TCP/IP
If any components are missing, click the Add button to add them. Microsoft
includes all of these protocols in Windows. After you click Add, highlight the
component you need, click Add, highlight Microsoft, and then double-click on
the item you want to add.
If you are using Windows 98SE, enable the File and Printer Sharing to make
your computer visible on the network.
Click the Identification tab. Type the name of your computer in the computer
name box. Make up a name that is unique among the computer names on your
network.
Type the name of your workgroup in the workgroup box. The name you type
should be the same workgroup name in use by all of the other PCs on the network.
If one computer on your network has a different workgroup name than the others,
that computer will not be shown in the same workgroup view.
- 10 -
Page 14
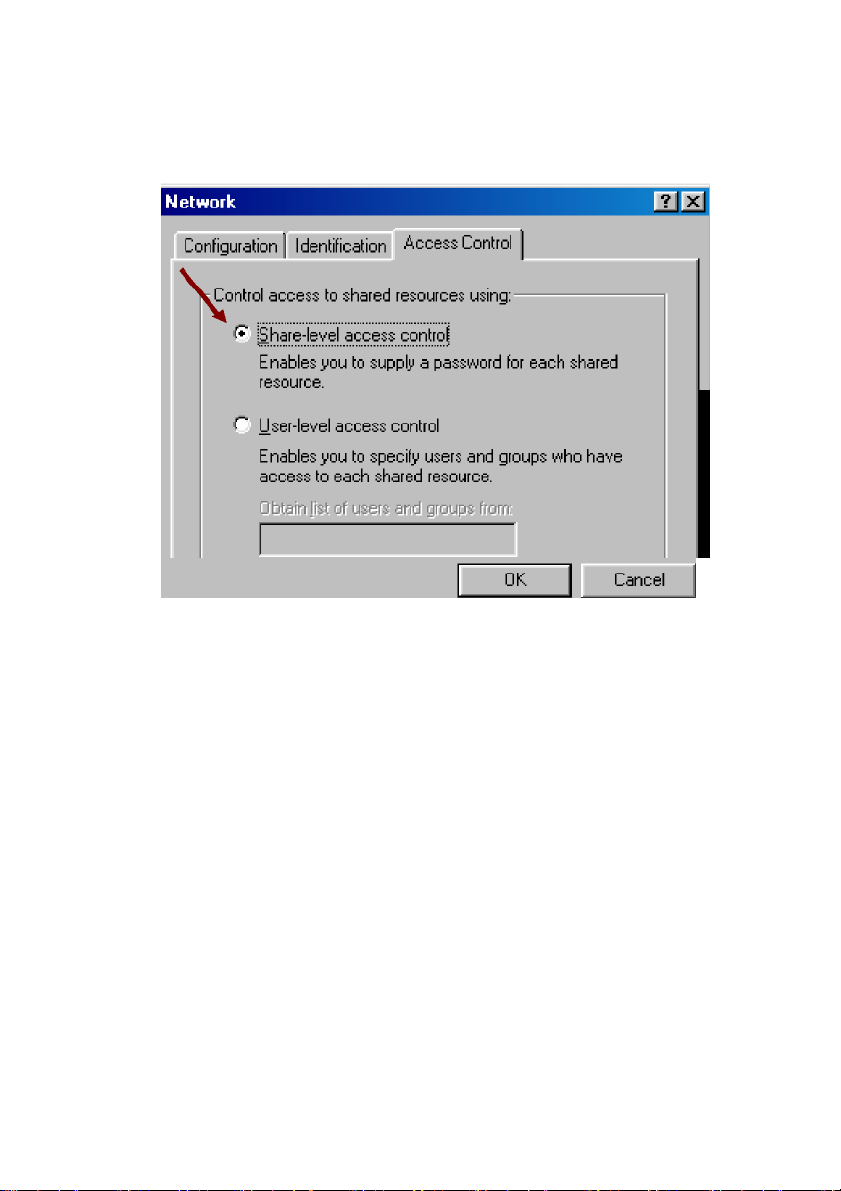
Click the Access Control tab. Make sure that Shared-level access control is
selected. If connecting to a NetWare server, share level can be set to User-level
access control.
When finished, remove all disks from your computer and restart your computer to
activate the new device and new changes to network configuration.
Once the computer has restarted and Windows has booted up, a Logon window
will appear requiring you to enter a username and password. Make up a
username and password, enter them, and click OK. Do not click the Cancel
button, or you will not be able to log onto the network.
- 11 -
Page 15
When you are at the Windows 98SE desktop, double-click the Network
Neighborhood icon. You should see the names of the other PCs on the
network that have enabled file and printer sharing.
Using File And Printer Sharing
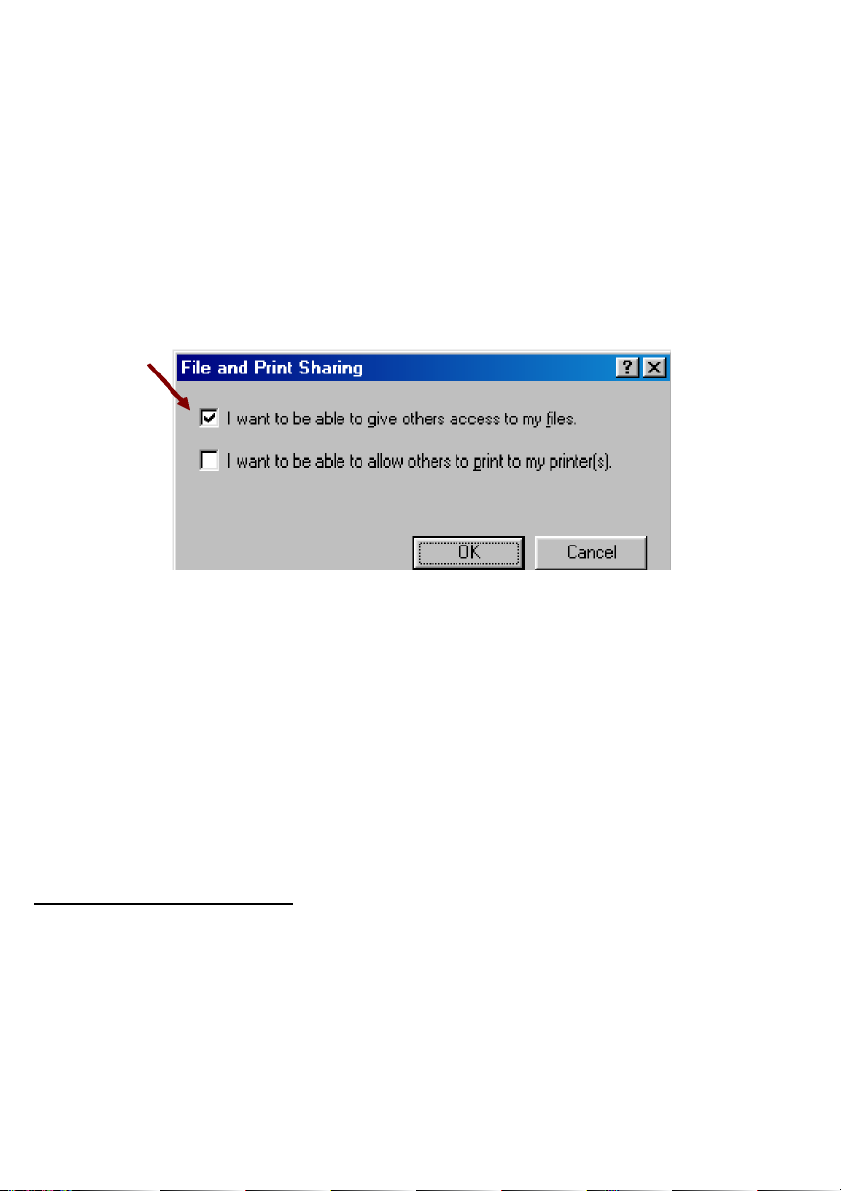
Click Start > Settings> Control Panel. Double-click Network.
Click the Configuration tab, followed by the File and Printer Sharing button.
The File and Printer Sharing window will appear.
If you would like others to be able to access the files on your computer’s hard drive,
select I want to be able to give others access to my files.
If you would like to share your printer with other users on the network, select I
want to be able to allow others to print to my printer.
Click OK. File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks should now appear on
the list of installed components. Click OK. When asked to restart your computer,
choose to do so.
Enabling File Sharing
Double-click My Computer. A window of available disk drives will appear.
Right-click once the drive or folder that you want to make available to other
users.
- 12 -
Page 16

Click Sharing, and then click Share As. In the Share Name box, enter a name for
the drive or folder you are sharing, (eg: C-Drive, CD-ROM, John, etc.).
Next, decide on the access type that you want to give other users. Read-Only
access lets other users view the files on your PC. Full access lets users create,
change, or delete files on your PC. Depends on Password lets users have
Read-Only and/or Full access, depending on the password that you decide to give
them.
Use your mouse to select the access type that you want other users to have. If you
want to assign an access password(s), type them into the Password box(es).
If you are sharing a cable modem or DSL broadband connection that you will be
using to access the Internet, you should protect all of your shared drives and
printers with private passwords. When finished, click Apply, followed by OK.
- 13 -
Page 17

Enabling Printer Sharing
Click Start > Settings> Printers. A window of available printers will
appear.
Right-click the printer that you want to share with other users. Click Sharing,
and then click Share As. In the Share Name box, give a name to the printer you
are about to share (Jack's HP4, for example). If you want to assign a password to
the printer so only certain users can access it, type a password in the Password box.
When you are done, click Apply, followed by OK. Your printer(s) are now
shared.
- 14 -
Page 18

Windows 2000/XP/Vista Network Component
Configuration
This section includes instructions specific to the Windows 2000 operating
system. However, Windows XP and Windows Vista instructions are very
similar. For additional information regarding this section, please consult
your Windows documentation provided my Microsoft.
Go to Start >Settings >Control Panel >Network and Dial-up Connections.
Double-click the Local Area Connection icon; the following figure will
appear.
Click the Properties button. Make sure the following components are installed.
• Client for Microsoft Networks
• File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks
• NetBEUI Protocol
• Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
If any components listed above are missing, click the Install button to add them
manually. Click Close to exit.
- 15 -
Page 19

Go to Start > Settings> Control Panel > System.
Open the Network Identification tab and click the Properties button.
Type the name of your computer in the computer name box. Make up a name
that is unique among the computers names on your network.
- 16 -
Page 20

Type the name of your workgroup in the workgroup box. The name you type
should be the same workgroup name in use by all of the other PCs on the
network.
When finished, remove all disks from your computer and restart your computer to
activate the new device and with new configuration changes.
Once the computer has restarted and Windows 2000 has booted up, a Logon
window will appear requiring you to enter a username and password. Make up a
username and password, enter them, and click OK. Do not click the Cancel
button, or you will not be able to log onto the network.
When you are at the Windows 2000 desktop, double-click My Network Places or
Computers Near Me. You should see the names of the other PCs on the network
that have enabled file and printer sharing. Refer to the Windows 98SE/Me
Network Component Configuration section for instructions on setting up File and
Print sharing.
- 17 -
Page 21

Networking Basics
You may have had some ideas about how to use your new network prior to
installing this product - sharing files, printing from a computer on the network, or
accessing the Internet on multiple computers with one connection. This section
will help you get started on those ideas or even give you some new ones.
However, this section is not intended to be a comprehensive guide to networking,
it is just an outline of a few networking basics.
If you are interested in learning more about networking please visit our website:
http://www.dlink.com
D-Link is one of the largest manufacturers of Ethernet products in the world.
D-Link’s technological expertise and dedication to providing quality products at
a low price makes D-Link a good place to watch for the newest in networking
innovations. Or, you may want to get the newest drivers available for your
Network Adapters.
Computer Identification
If you had previously given your Windows 98SE computers names or if you
are using Windows 98SE, you may need to verify that each computer has a
unique name and common workgroup name.
A. On your Desktop, right-click the icon "Network Places" and select
"Properties" from the context menu.
- 18 -
Page 22

B. Click the "Identification" tab on the top of the dialog box.
C. Type a unique, identifying name for this particular computer
in the "Computer name:" box. This will be the name that other computers on
your network will use to communicate with this computer. Each computer’s
name must be unique on a particular network or confusion will result. (The
computer’s name should be 15 or fewer characters with no spaces.)
D. Type the workgroup name this computer will be a part of in
the "Workgroup:" box. All of the computers on your network should have an
identical Workgroup name.
E. The "Computer Description:" box is optional. You may enter
a description that will help you identify this computer on your network. Then
click "Close."
F. Repeat this process for each computer on your network to
ensure that they all have a unique "Computer Name" and identical
“workgroup."
-19 -
Page 23

Sharing Files
With your computers connected together on a network, you may now open and
save files on another computer. You will be able to specify particular folders or
disk drives to "share" and even password protect them. The steps below will enable
you to share specific files and folders with other computers on your network.
A. On your Desktop, right-click the icon "Network Places" and select
"Properties" from the context menu.
B. This dialog box is what you will use to configure most of your computer
network settings. It is also available through the "Network" icon in the Control
Panel.
- 20 -
Page 24

C. Click the "File and Print Sharing" button.
D. Click to place a check mark next to "I want to be able to give others access
to my files."
E. Click "OK" on the "File and Print Sharing" dialog box.
F. Click "OK" on the "Network" dialog box.
G. Provide the Windows 98SE installation CD or diskette(s) if prompted or
direct Windows to the proper location of the installation files. Reboot if
prompted.
H. You will now be able to identify a particular folder or disk drive to share.
You may want to share a folder that both you and a colleague/family
member need to access occasionally. Or, maybe you want to share a CD-
ROM drive so your other computer that does not have one can read CD’s.
Both processes are the same. Only the disk drives and folders that you
specifically identify as shared will be accessible to other computers on your
network.
I. Find the disk drive or folder you want to share using Windows Explorer or
the "My Computer" icon on your desktop.
- 21 -
Page 25

J. Right-click on the disk drive or folder icon and select "Sharing."
K. Select "Share As:" to set the parameters for sharing this particular disk drive
or folder.
L. The "Share Name:" box is used to identify the disk drive or folder you are
sharing to other computers on the network. You can give it any name you
- 22 -
Page 26

wish. However, a specific identification may help as more resources on your
network are shared.
M. The "Comment:" box is optional. You can use this box to further describe the
disk drive or folder for others on the network.
N. "Access Type:" allows you to designate how much others on the network can
do with this disk drive or folder. "Read-Only" allows others only to look at or
open the files on the disk drive or in the folder. "Full" allows others to read,
write, open, save, copy, move, and delete files on the disk or in the folder.
"Depends on Password" gives other computers access conditional upon the
password they provide.
O. "Passwords:" allow you to apply a level of security to your shared disk
drives and folders. Another computer (user) will be required to enter the
password you designate here before accessing the disk drive or folder. Two
passwords are used to give two levels of security (or access) to others on the
network using the "Depends on Password" setting. Leaving the "Password"
boxes empty gives everyone on the network access to the disk drive or
folder.
P. Click "OK" to continue. You will be prompted to enter the password(s) you
provided for verification. Retype the password(s) just as you entered them
the first time.
Q. You may now access this disk drive or folder from another computer on
your network. Do so by double-clicking the "My Network Places" icon on
your desktop or inside Windows Explorer.
R. Navigate to the computer with the shared disk drive or folder (recognized by
the "Computer Name" you provided), and double-click. You should now see
the disk drive or folder; double-click on the drive or folder. If you specified a
password when sharing this disk drive or folder, you will be prompted for
the password.
S. You can access a disk drive or folder shared over the network from most
Windows applications. To make this process easier, Windows allows you
- 23 -
Page 27

to map these disk drives and folders to a drive letter on another computer. For
example, on a computer where you are accessing a shared folder from another
computer, inside Windows Explorer right-click and select "Map Network
Drive.” You will then be able to assign an available drive letter. Checking
"Reconnect at logon" allows Windows to map this network drive each time
you start your computer.
Sharing Printers
"Sharing" a printer connected to one computer with other computers on your
network can be very convenient, allowing you to print from any computer on the
network. The steps below will enable you to print with other computers on your
network.
A. On your Desktop, right-click the icon "Network Places" and select
"Properties" from the context menu.
B. Click the "File and Print Sharing" button.
- 24 -
Page 28

C. Click to place a check mark next to "I want to be able to allow others to print
to my printer(s)."
D. Click "OK" on the "File and Print Sharing" dialog box.
E. Click "OK" on the "Network" dialog box.
F. You may now share any installed printers connected to this computer with
other computers on your network.
- 25 -
Page 29

Go to START>SETTINGS>PRINTERS
Right click on the printer you want to share with others on the network and
select "Sharing."
G. Click "Share As:" and provide a "Share Name:" to identify the printer to
other computers on the network. "Comment:" and "Password:" are optional.
Then click "OK." For a computer to access a Network Printer, the device
driver or software for that printer must be installed and pointed to the proper
location of the printer. This is done much the same way you installed the
printer on the computer it is connected to.
H. Go to a computer that does not have the printer connected to it. From the
"Start" button on the Task Bar select "Settings" and then "Printers."
I. Double click the "Add Printer" icon.
J. The "Add Printer Wizard" will appear. Click "Next."
K. Choose "Network printer" and click "Next."
L. Now you will identify the location of the Network Printer. If you know the
name of the computer and the share name of the printer, you can type it into
- 26 -
Page 30

the "Network path or queue name:" box. However, it is easier to click the
"Browse" button and navigate to the location of the printer. Click "OK"
when you have selected the desired printer. Finish the installation by
continuing the "Add Printer Wizard" normally.
M. You may now use the Network Printer as if it was connected directly. Note:
the computer that the printer is connected to must be “on” to use the printer.
If you find this inconvenient, devices known as Network Print Servers are
available from D-Link including the DP-301 and DP-101P. A Network Print
Server would allow you to directly connect your printer to your network
without worrying about which computer is “on.”
- 27 -
Page 31

Go to START > SETTINGS > CONTROL PANEL
Double Click on “Network”
- 28 -
Page 32

How to Install TCP/IP
Select “D-Link DGE-660TD Cardbus PC
Card.”
- 29 -
Click on “Add.” Select
“Protocol.”
Click “Add.”
Select “Microsoft.”
Page 33

Click “OK.”
Now the “TCP/IP for D-Link DGE-660TD Cardbus PC Card” is available. The
TCP/IP Installation is complete.
Configuring a Dynamic IP Address
When the drivers are installed, the default setting is set to obtain an IP
dynamically through a DHCP server.
If you need to check or change the settings, then do the following: Go
to START > SETTINGS > CONTROL PANEL
- 30 -
Page 34

Double Click on “Network” Highlight
“TCP/IP.” Click on “Properties.”
- 31 -
Page 35

NOTE: If TCP/IP is not present, see the previous section: “How to Install
TCP/IP.”
When the TCP/IP window opens, choose the “IP Address” tab. Select “Obtain
an IP Address Automatically.”
Click “OK.”
When the network properties window comes back up, click “OK.” Windows
will ask you to reboot. Click “Yes.”
You have completed the configuration of the Dynamic IP Address.
- 32 -
Page 36

Configuring a Static IP Address
Go to START > SETTINGS > CONTROL PANEL
Double Click on “Network”
-
33 -
Page 37

Highlight “TCP/IP.” Scroll down if you cannot see it.
Click on “Properties.”
NOTE: If TCP/IP is not present, please see: “How to Install TCP/IP.”
When the “TCP/IP Properties” window opens, choose the “IP Address” tab.
Select “Specify an IP address.”
- 34 -
Page 38

Enter an IP address into the empty field.
Suggested IP Range is 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.254.
NOTE: IP Addresses must be signed sequentially to each computer. Suggested
Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0.
Click “OK.”
When the “Network Properties” window comes back up click “OK.” Insert
Windows CD if prompted.
Windows will ask you to reboot. Click “Yes.”
- 35 -
Page 39

Checking the TCP/IP Address
Go to Start >
1
Type “winipcfg” in the “OPEN” box.
Click “OK.”
Click "OK." The IP Configuration screen will be displayed. The IP address will
be displayed in the IP Address box.
- 36 -
Page 40

Click on “More Info” to display additional IP information.
- 37 -
Page 41

Checking the Connection by Pinging
Click "OK" to get to a DOS prompt.
Type "ping 192.168.0.1," which is the IP address of the Gateway in this case,
and hit the "Enter" key.
- 38 -
Page 42

A successful ping will show four replies.
Specifications
Standards:
• IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet
• IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet
• IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet
• ANSI/IEEE 802.3 NWay Auto-Negotiation
• PCMCIA 2.x
• 32-bit Cardbus
Network Media:
• Ethernet: UTP Cat3, 4, 5 EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm
• Fast Ethernet: UTP Cat5, EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm
Protocol:
• CSMA/CD
Host Interface:
• 32-bit Cardbus
Diagnostic LEDs:
• Link/Activity
• Speed (Green: 1000M; Amber : 100M; Off : 10M)
- 39 -
Page 43

Network Data Transfer Rate:
• Ethernet: 10Mbps (Half-duplex)
• Ethernet: 20 Mbps (Full-duplex)
• Fast Ethernet: 100Mbps (Half-duplex)
• Fast Ethernet: 200Mbps (Full-duplex)
• Gigabit Ethernet: 2000Mbps (Full-duplex)
Temperature:
• Operating: -10~50 °C (14~122°F)
• Storage: -10~70 °C (14~158°F)
Humidity:
• Operating: 10%~90% RH
• Storage: 5%~90% RG
Driver Support:
• Microsoft Windows Vista
• Microsoft Windows XP
• Microsoft Windows 2000
• Microsoft Windows 98SE/ME
Emission:
• FCC Class B
• CE mark Class B
• VCCI-B
*Check http://www.dlink.com for newest releases of drivers.
Page 44

t
Technical Suppor
You can find software updates and user documentation on the D-Link website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States
and within Canada for the duration of the warranty period on this product.
U.S. and Canadian customers can contact D-Link technical support through our
website, or by phone.
Tech Support for customers within the United States:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(877) 453-5465
24 hours a day,seven days a week
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
email:support@dlink.com
Tech Support for customers within Canada:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(800) 361-5265
Monday to Friday 7:30am to 12:00am EST
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.ca
email:support@dlink.ca
- 40 -
Page 45

Subject to the terms and conditions set forth herein, D-Link Systems, Inc. (“D-Link”) provides this Limited Warranty:
• Only to the person or entity that originally purchased the product from D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor, and
• Only for products purchased and delivered within the fifty states of the United States, the District of Columbia, U.S. Possessions or
Protectorates, U.S. Military Installations, or addresses with an APO or FPO.
Limited Warranty: D-Link warrants that the hardware portion of the D-Link product described below (“Hardware”) will be free from
material defects in workmanship and materials under normal use from the date of original retail purchase of the product, for the period
set forth below (“Warranty Period”), except as otherwise stated herein.
• Hardware (excluding power supplies and fans): One (1) year
• Power supplies and fans: One (1) year
• Spare parts and spare kits: Ninety (90) days
The customer's sole and exclusive remedy and the entire liability of D-Link and its suppliers under this Limited Warranty will be, at DLink’s option, to repair or replace the defective Hardware during the Warranty Period at no charge to the original owner or to refund the
actual purchase price paid. Any repair or replacement will be rendered by D-Link at an Authorized D-Link Service Office. The
replacement hardware need not be new or have an identical make, model or part. D-Link may, at its option, replace the defective
Hardware or any part thereof with any reconditioned product that D-Link reasonably determines is substantially equivalent (or superior)
in all material respects to the defective Hardware. Repaired or replacement hardware will be warranted for the remainder of the original
Warranty Period or ninety (90) days, whichever is longer, and is subject to the same limitations and exclusions. If a material defect is
incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines that it is not practical to repair or replace the defective Hardware, the actual price paid
by the original purchaser for the defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to D-Link of the defective Hardware. All
Hardware or part thereof that is replaced by D-Link, or for which the purchase price is refunded, shall become the property of D-Link
upon replacement or refund.
Limited Software Warranty: D-Link warrants that the software portion of the product (“Software”) will substantially conform to D-Link’s
then current functional specifications for the Software, as set forth in the applicable documentation, from the date of original retail
purchase of the Software for a period of ninety (90) days (“Software Warranty Period”), provided that the Software is properly installed
on approved hardware and operated as contemplated in its documentation. D-Link further warrants that, during the Software Warranty
Period, the magnetic media on which D-Link delivers the Software will be free of physical defects. The customer's sole and exclusive
remedy and the entire liability of D-Link and its suppliers under this Limited Warranty will be, at D-Link’s option, to replace the nonconforming Software (or defective media) with software that substantially conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the Software
or to refund the portion of the actual purchase price paid that is attributable to the Software. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in
writing, the replacement Software is provided only to the original licensee, and is subject to the terms and conditions of the license
granted by D-Link for the Software. Replacement Software will be warranted for the remainder of the original Warranty Period and is
subject to the same limitations and exclusions. If a material non-conformance is incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines in its
sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the non-conforming Software, the price paid by the original licensee for the nonconforming Software will be refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming Software (and all copies thereof) is first returned to
D-Link. The license granted respecting any Software for which a refund is given automatically terminates.
Non-Applicability of Warranty: The Limited Warranty provided hereunder for Hardware and Software portions of D-Link's products
will not be applied to and does not cover any refurbished product and any product purchased through the inventory clearance or
liquidation sale or other sales in which D-Link, the sellers, or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the
product and in that case, the product is being sold "As-Is" without any warranty whatsoever including, without limitation, the Limited
Warranty as described herein, notwithstanding anything stated herein to the contrary.
Submitting A Claim: The customer shall return the product to the original purchase point based on its return policy. In case the return
policy period has expired and the product is within warranty, the customer shall submit a claim to D-Link as outlined below:
• The customer must submit with the product as part of the claim a written description of the Hardware defect or Software
nonconformance in sufficient detail to allow D-Link to confirm the same, along with proof of purchase of the product (such as a
copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) if the product is not registered.
Page 46

• The customer must obtain a Case ID Number from D-Link Technical Support at 1-877-453-5465, who will attempt to assist the
customer in resolving any suspected defects with the product. If the product is considered defective, the customer must obtain a
Return Material Authorization (“RMA”) number by completing the RMA form and entering the assigned Case ID Number at
https://rma.dlink.com/
• After an RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged securely in the original or other suitable shipping package
to ensure that it will not be damaged in transit, and the RMA number must be prominently marked on the outside of the package.
Do not include any manuals or accessories in the shipping package. D-Link will only replace the defective portion of the product
and will not ship back any accessories.
• The customer is responsible for all in-bound shipping charges to D-Link. No Cash on Delivery (“COD”) is allowed. Products sent
COD will either be rejected by D-Link or become the property of D-Link. Products shall be fully insured by the customer and
shipped to D-Link Systems, Inc., 17595 Mt. Herrmann, Fountain Valley, CA 92708. D-Link will not be held responsible for any
packages that are lost in transit to D-Link. The repaired or replaced packages will be shipped to the customer via UPS Ground or
any common carrier selected by D-Link. Return shipping charges shall be prepaid by D-Link if you use an address in the United
States, otherwise we will ship the product to you freight collect. Expedited shipping is available upon request and provided shipping
charges are prepaid by the customer.
D-Link may reject or return any product that is not packaged and shipped in strict compliance with the foregoing requirements, or for
which an RMA number is not visible from the outside of the package. The product owner agrees to pay D-Link’s reasonable handling
and return shipping charges for any product that is not packaged and shipped in accordance with the foregoing requirements, or that is
determined by D-Link not to be defective or non-conforming.
What Is Not Covered: The Limited Warranty provided herein by D-Link does not cover: Products that, in D-Link’s judgment, have been
subjected to abuse, accident, alteration, modification, tampering, negligence, misuse, faulty installation, lack of reasonable care, repair
or service in any way that is not contemplated in the documentation for the product, or if the model or serial number has been altered,
tampered with, defaced or removed; Initial installation, installation and removal of the product for repair, and shipping costs; Operational
adjustments covered in the operating manual for the product, and normal maintenance; Damage that occurs in shipment, due to act of
God, failures due to power surge, and cosmetic damage; Any hardware, software, firmware or other products or services provided by
anyone other than D-Link; and Products that have been purchased from inventory clearance or liquidation sales or other sales in which
D-Link, the sellers, or the liquidators expressly disclaim their warranty obligation pertaining to the product. While necessary
maintenance or repairs on your Product can be performed by any company, we recommend that you use only an Authorized D-Link
Service Office. Improper or incorrectly performed maintenance or repair voids this Limited Warranty.
Disclaimer of Other Warranties: EXCEPT FOR THE LIMITED WARRANTY SPECIFIED HEREIN, THE PRODUCT IS PROVIDED
“AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WHATSOEVER INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. IF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY
CANNOT BE DISCLAIMED IN ANY TERRITORY WHERE A PRODUCT IS SOLD, THE DURATION OF SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTY
SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE APPLICABLE WARRANTY PERIOD SET FORTH ABOVE. EXCEPT AS
EXPRESSLY COVERED UNDER THE LIMITED WARRANTY PROVIDED HEREIN, THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY,
SELECTION AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT IS WITH THE PURCHASER OF THE PRODUCT.
.
Page 47

Limitation of Liability: TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, D-LINK IS NOT LIABLE UNDER ANY CONTRACT,
NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY OR OTHER LEGAL OR EQUITABLE THEORY FOR ANY LOSS OF USE OF THE PRODUCT,
INCONVENIENCE OR DAMAGES OF ANY CHARACTER, WHETHER DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF GOODWILL, LOSS OF REVENUE OR PROFIT, WORK STOPPAGE,
COMPUTER FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION, FAILURE OF OTHER EQUIPMENT OR COMPUTER PROGRAMS TO WHICH D-LINK’S
PRODUCT IS CONNECTED WITH, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA CONTAINED IN, STORED ON, OR INTEGRATED WITH
ANY PRODUCT RETURNED TO D-LINK FOR WARRANTY SERVICE) RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT,
RELATING TO WARRANTY SERVICE, OR ARISING OUT OF ANY BREACH OF THIS LIMITED WARRANTY, EVEN IF D-LINK HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE SOLE REMEDY FOR A BREACH OF THE FOREGOING LIMITED
WARRANTY IS REPAIR, REPLACEMENT OR REFUND OF THE DEFECTIVE OR NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT. THE MAXIMUM
LIABILITY OF D-LINK UNDER THIS WARRANTY IS LIMITED TO THE PURCHASE PRICE OF THE PRODUCT COVERED BY THE
WARRANTY. THE FOREGOING EXPRESS WRITTEN WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ANY
OTHER WARRANTIES OR REMEDIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the State of California. Some states do not allow exclusion or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages, or limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the foregoing limitations and
exclusions may not apply. This Limited Warranty provides specific legal rights and you may also have other rights which vary from state
to state.
Trademarks: D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link Systems, Inc. Other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of
their respective owners.
Copyright Statement: No part of this publication or documentation accompanying this product may be
reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation,
or adaptation without permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc., as stipulated by the United
States Copyright Act of 1976 and any amendments thereto. Contents are subject to change without prior
notice. Copyright 2005 by D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
CE Mark Warning: This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
FCC Statement: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communication. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
For detailed warranty information applicable to products purchased outside the United States, please contact the
corresponding local D-Link office.
Page 48

Product Registration
Register your D-Link product online at http://support.dlink.com/register/
Product registration is entirely voluntary and failure to complete or return this form
will not diminish your warranty rights.
Page 49

Worldwide offices URL
U.S.A
URL: www.dlink.com
Canada
URL: www.dlink.ca
European HQ & UK&I
URL:www.dlink.eu
URL: www.dlink.co.uk
Germany
URL: www.dlink.de
France
URL: www.dlink.fr
Netherlands
URL: www.dlink.nl
Belgium
URL: www.dlink.be
Italy
URL: www.dlink.it
Sweden
URL: www.dlink.se
Denmark
URL: www.dlink.dk
Norway
URL: www.dlink.no
Finland
URL: www.dlink.fi
Spain
URL: www.dlink.es
Portugal
URL: www.dlink.es
Czech Republic
URL: www.dlink.cz
Switzerland
URL: www.dlink.ch
Greece
URL: www.dlink.gr
Luxemburg
URL: www.dlink.be
Poland
URL: www.dlink.pl
Hungary
URL: www.dlink.hu
Singapore
URL: www.dlink-intl.com
Australia
URL: www.dlink.com.au
India
URL: www.dlink.co.in
Middle East (Dubai)
URL: www.dlink-me.com
Turkey
URL: www.dlink.com.tr
Iran
URL: www.dlink-me.com/
Pakistan
URL: www.dlink-me.com/
Egypt
URL: www.dlink-me.com
Israel
URL: www.dlink.co.il
LatinAmerica
URL: www.dlinkla.com
Brazil
URL: www.dlinkbrasil.com.br
South Africa
URL: www.d-link.co.za
Russia
URL: www.dlink.ru
Japan K.K.
URL: www.dlink-jp.com
Korea
URL: www.dlink.co.kr/
China
URL: www.dlink.com.cn
Taiwan
URL: www.dlinktw.com.tw
 Loading...
Loading...