Page 1
2007-01-15
VX.XXXX
MADE IN XXXXXX
2.5 mV or 5 A
0V ~ + 10V or 0m A ~ +20mA
Power input specification
Analog I/O module specification
COM
COM
24+
24-
DC/DC
+15V
-15V
CH1
CH1
voltage output
or less)
parameter
#0
○
#7
#8
#9
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○
○ R
http://www.delta .com.tw/ind ustrialautoma tion/
5011651101-D2E1
Analog Output Module
Instruction Sheet
Warning
9 Please read this instruction carefully before use.
Switch off the power before wiring.
9
DVP04DA-H2 is an OPEN-TYPE device and therefore should be installed in an enclosure free of
9
airborne dust, humidity, electric shock and vibration. The enclosure should prevent non-maintenance
staff from operating the device (e.g. key or specific tools are required to open the enclosure) in case
danger and damage on the device may occur.
DO NOT connect input AC power supply to any of the I/O terminals; otherwise serious damage may
9
occur. Check all the wiring again before switching on the power.
DO NOT tough any terminal when the power is switched on. DO NOT touch any internal circuit in 1
9
minute after the power is switched off.
Make sure the groud terminal is correctly grounded in order to prevent electromagnetic
9
interference.
Introduction
1.1 Model Explanation & Peripherals
Thank you for choosing Delta DVP series. DVP04DA-H2 is able to read and write data of DVP04DA-H2 analog
signal output modules through FROM/TO instructions given by the program of DVP-EH2 series MPU. The
analog signal output module receives 4 groups of 12-bit digital data from PLC MPU and converts the data into 4
points of analog signals for output in either voltage or current.
The user can select voltage or current output by wiring. Range of voltage output: 0V ~ +10VDC (resolution:
2.5mV). Range of current output: 0mA ~ 20mA (resolution: 5μA).
Nameplate Explanation
Delta PLC model name
Barcode, Serial No., Version
Model/Serial No. Explanation
1.2 Product Profile (Indicators, Terminal Block, I/O Terminals)
Unit: mm
1
DIN rail (35mm) 6 Terminals
2 Connection port for extension modules 7 Mounting hole
3 Model name 8 I/O terminals
4 POWER, ERROR, D/A indicator 9 Mounting port for extension modules
5 DIN rail clip
24Vdc 4.5W
04DA-H2 0T6500001
24V 0V
D - V + I + V +
D + COM
CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4RS-485
FG FG FGCOM COM COM
I + V + I + V + I +
8
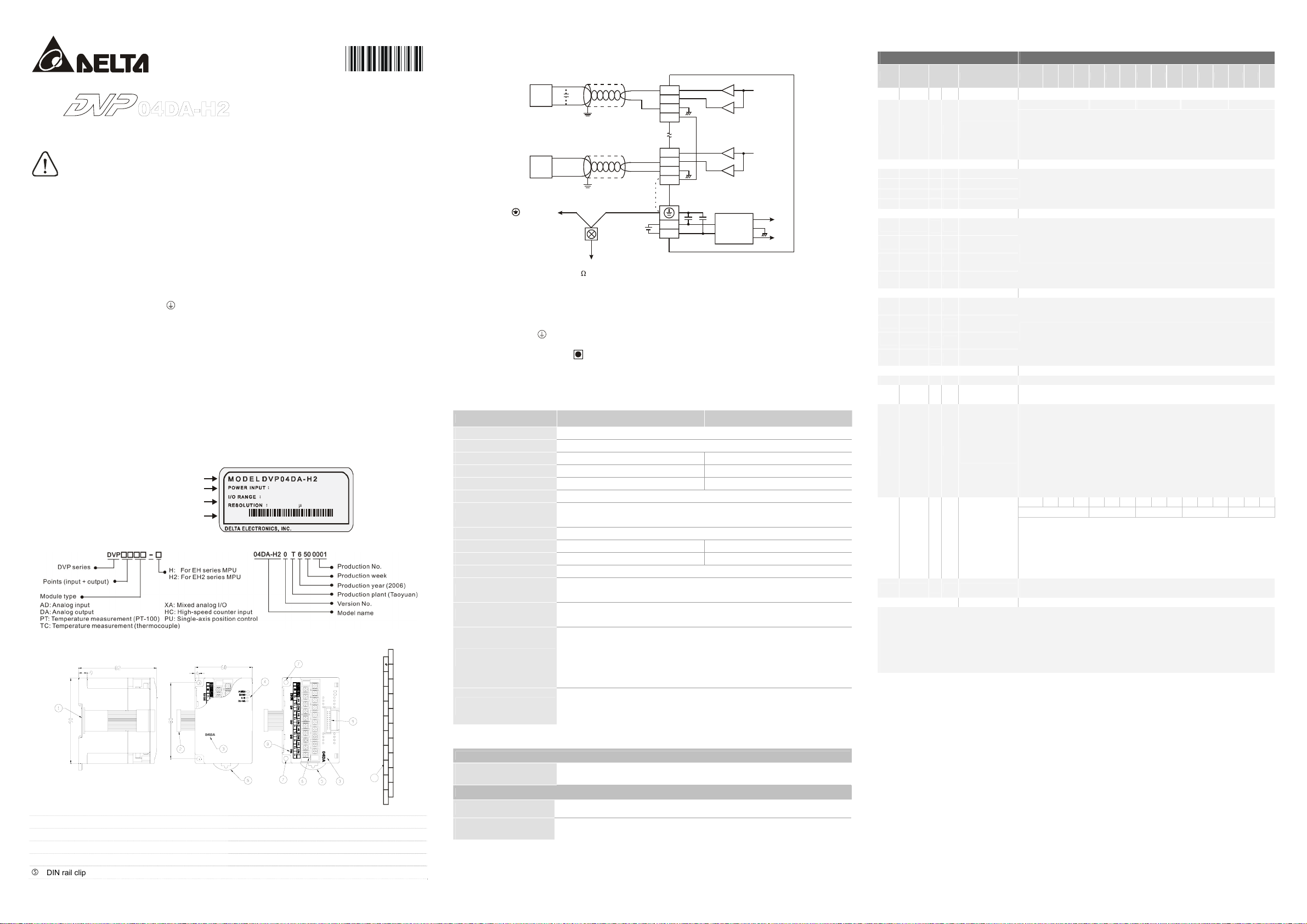
1.3 External Wiring
0V~+10V
*2
AC drive, recorder,
scale valve...
AC drive, recorder,
scale valve...
terminal of
power module
class 3 grounding
(100
shielding cable *1
current outp ut
0mA~20mA
shielding cabl e *1
*3
system grounding
DC24V
CH4
V+
FG
V+
FG
I+
I+
converter
CH4
AG
Note:
1. When performing analog output, please isolate other power wirings.
2. If the ripples at the loaded input terminal are too significant that causes noise interference on the wiring, connect the
wiring to 0.1 ~ 0.47μF 25V capacitor.
3. Please connect the
terminal on both the power modules and DVP04DA-H2 to the system earth point and ground the
system contact or connect it to the cover of power distribution cabinet.
4. DO NOT wire empty terminals
Specifications
2.1. Functions
Digital/Analog (4D/A) Module
Power supply voltage 24 VDC (20.4VDC ~ 28.8VDC) (-15% ~ +20%)
Analog output channel 4 channels/module
Range of analog output 0 ~ 10V 0 ~ 20mA
Range of digital data 0 ~ 4,000 0 ~ 4,000
Resolution 12 bits (1
Output impedance 0.5Ω or lower
Overall accuracy
±0.5% when in full scale (25°C, 77°F)
±1% when in full scale within the range of 0 ~ 55°C, 32 ~ 131°F
Responding time 3ms × the number of channels
Max. output current 10mA (1KΩ ~ 2MΩ) -
Tolerable load impedance - 0 ~ 500Ω
Digital data format 11 significant bits out of 16 bits are available; in 2’s complement
Isolation
Protection
Communication mode
(RS-485)
Internal circuit and analog output terminals are isolated by optical coupler.
No isolation among analog channels.
Voltage output is protected by short circuit. Short circuit lasting for too long may
cause damage on internal circuits. Current output can be open circuit.
ASCII/RTU mode.
Communication speed: 4,800/9,600/19,200/38,400/57,600/115,200 bps
ASCII data format: 7-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (7, E, 1)
RTU data format: 8-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (8, E, 1)
RS-485 cannot be used when connected to PLC MPU.
When connected to
DVP-PLC MPU in series
The modules are numbered from 0 to 7 automatically by their distance from MPU.
No.0 is the closest to MPU and No.7 is the furthest. Maximum 8 modules are allowed
to connect to MPU and will not occupy any digital I/O points.
2.2. Others
Max. rated power
consumption
Operation/storage
Vibration/shock
immunity
24VDC (20.4VDC ~ 28.8VDC) (-15% ~ +20%)., 4.5W supplied by external power
Operation: 0°C ~ 55°C (temperature); 50 ~ 95% (humidity); pollution degree 2
Storage: -40°C ~ 70°C (temperature); 5 ~ 95% (humidity)
International standards: IEC1131-2, IEC 68-2-6 (TEST Fc)/IEC1131-2 & IEC
68-2-27 (TEST Ea)
Voltage Output Current Output
= 2.5mV) 12 bits (1
LSB
= 5 μA)
LSB
Power Supply
Environment
Control Registers
DVP04DA-H2 analog output module
RS-485
CR#
#1 H’4033
#2 ~ #5 Reserved
#6 H’4038 ╳ R/W CH1 output value
#10 ~ #17 Reserved
#18 H’4044
#19 H’4045
#20 H’4046
#21 H’4047
#22 ~ #23 Reserved
#24 H’404A
#25 H’404B
#26 H’404C
#27 H’404D
#28 ~ #29 Reserved
#30 H’4050 ╳ R Error status Register for storing all error status. See the table of error status for more information.
#31 H’4051
#32 H’4052
#33 H’4053
#34 H’4054
#35 ~ #48 For system use.
Symbols
○: latched (when written in through RS-485 communication)
╳: non-latched
R: Able to read data by FROM instruction or RS-485 communication
W: Able to write data by TO instruction or RS-485 communication
LSB (Least Significant Bit): For voltage output 1
Latched Register content b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
address
○
H’4032
H’4039 ╳ R/W CH2 output value
H’403A ╳ R/W CH3 output value
H’403B ╳ R/W CH4 output value
R Model name
Output mode
R/W
setting
Adjusted OFFSET
R/W
value of CH1
Adjusted OFFSET
R/W
value of CH2
Adjusted OFFSET
R/W
value of CH3
Adjusted OFFSET
R/W
value of CH4
Adjusted GAIN
R/W
value of CH1
Adjusted GAIN
R/W
value of CH2
Adjusted GAIN
R/W
value of CH3
Adjusted GAIN
R/W
value of CH4
Communication
R/W
address setting
Communication
speed (baud rate)
R/W
setting
Return to default
setting;
OFFSET/GAIN
R/W
tuning
authorization
Firmware version
For current output 1
Set up by the system. DVP04DA-H2 model code = H’6401
reserved CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Output mode: Default = H’0000
Mode 0: Voltage output (0V ~ 10V)
Mode 1: Voltage output (2V ~ 10V)
Mode 2: Current output (4mA ~ 20mA)
Mode 3: Current output (0mA ~ 20mA)
Range of output value at CH1 ~ CH4: K0 ~ K4,000
Default = K0 (unit: LSB)
Range of OFFSET at CH1 ~ CH4: K-2,000 ~ K2,000
Default = K0 (unit: LSB)
Range of GAIN at CH1 ~ CH4: K-1,600 ~ K8,000
Default = K2,000 (unit: LSB)
For setting up RS-485 communication address. Range: 01 ~ 255
Default = K1
Default = H’0002. For setting up communication speed: 4,800 / 9,600 / 19,200 /
38,400 / 57,600 / 115,200bps
ASCII data format: 7-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (7, E, 1)
RTU data format: 8-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (8, E, 1)
b0: 4,800bps b1: 9,600bps (default)
b2: 19,200bps b3: 38,400bps
b4: 57,600bps b5: 115,200bps
b6 ~ b13: reserved
b14: High/low bit exchange of CRC checksum (only valid in RTU mode)
b15: Switch between ASCII/RTU mode. 0 = ASCII mode (default)
b15 b14 b13 b12 b11 b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
reserved CH4 CH3 CH2 CH1
Default = H’0000. Take the setting of CH1 for example:
1. When b0 = 0, the user is allowed to tune CR#18 (OFFSET) and CR#24 (GAIN)
of CH1. When b0 = 1, the user is not allowed to tune CR#18 (OFFSET) and
CR#24 (GAIN) of CH1.
2. b1 represents whether the OFFSET/GAIN tuning registers are latched. b1 = 0
(default, latched); b1 = 1 (non-latched)
3. When b2 = 1, all settings will return to default values. (except CR#31, CR#32)
Displaying the current firmware version In hex; e.g. version 1.0A is indicated as
H’010A.
= 10V/4,000 = 2.5mV。
LSB
= 20mA/4,000 = 5μA。
LSB
Explanations:
1. CR#0: Model name. The user can read the model name from the program and see if the extension module
exists.
2. CR#1: The working mode of the four channels in the analog input module. There are 4 modes for each channel
which can be set up separately. For example, if the user needs to set up CH1: mode 0 (b2 ~ b0 = 000); CH2:
mode 1 (b5 ~ b3 = 001), CH3: mode 2 (b8 ~ b6 = 010) and CH4: mode 3 (b11 ~ b9 = 011), CR#1 has to be set
as H’000A and the higher bits (b12 ~ b15) have to be reserved. Default value = H’0000.
3. CR#2 ~ CR#5, CR#10 ~ CR#17, CR#22, CR#23, CR#28 and CR#29 are reserved.
4. CR#6 ~ CR#9: The output values of CH1 ~ CH4 (range: K0 ~ K4,000; default = K0; unit: LSB)
5. CR#18 ~ CR#21: The adjusted OFFSET value of CH1 ~ CH4 (default = K0, unit = LSB), representing the analog
output voltage or current when the output digital value = 0 after calculation. The adjustable range: -2,000 ~
+2,000.
The adjustable range of voltage: -5V ~ +5V (-2,000
The adjustable range of current: -10mA ~ +10mA (-2,000
~ +2,000
LSB
LSB
6. CR#24 ~ CR#2: The adjusted GAIN value of CH1 ~ CH4 (default = K2,000, unit = LSB), representing the analog
output voltage or current when the output digital value = 2,000 after calculation.
)
LSB
~ +2,000
Description
)
LSB
Page 2
+4,000
Volta
ge output
Digital inp ut
Mode 0
+4,000
Current o
utput
Digital inp ut
K1000
K1
M1002
K33K1K1
K1
K1
M1002
K33K1K1
K400
No.1 and set CH1 in mode 0 (voltage output 0V
M0K1M1000
D101
D100
D101
K1K1K1
TOM1K1
D100
D
P
CR#25 into D1. Only 2 groups of data is read at
X0
79
D
X0
DTO
D10
Remarks
Lower 16-bit
CR #5
CR #6
CR #7
CR #8
CR #9
CR #10
Designated device
Designated CR
Designated device
16-bit instruction when n=6
32-bit instruction when n=3
The adjustable range of voltage: -4V ~ +20V (-1,600
LSB
The adjustable range of current: -8 mA ~ +40 mA (-1,600
Please note that: GAIN value – OFFSET value = +400
~ +8,000
LSB
~ +6,000
LSB
LSB
~ +8,000
)
)
LSB
(voltage or current). When GAIN –
LSB
OFFSET is small (steep oblique), the resolution of output signal will be finer and variation on the digital value will
be greater. When GAIN – OFFSET is big (gradual oblique), the resolution of output signal will be rougher and
variation on the digital value will be smaller.
7. CR #30: Error status value (See the table below)
Error status Content b15 ~ b8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Abnormal power supply K1(H’1) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Incorrect analog input
value
K2(H’2) 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Incorrect mode setting K4(H’4) 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
OFFSET/GAIN error K8(H’8) 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
Hardware malfunction K16(H’10)
Abnormal digital range K32(H’20)
Incorrect average times
setting
K64(H’40)
Instruction error K128(H’80)
Note: Each error status is determined by the corresponding bit (b0 ~ b7) and there may be more than 2 errors occurring at the same time.
0 = normal; 1 = error
reserved
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8. CR#31: The setting of RS-485 communication address (Range: 01 ~ 255, default = K1).
9. CR#32: The setting of RS-485 communication speed. b0: 4,800bps; b1: 9,600bps (default); b2: 19,200bps; b3:
38,400bps; b4: 57,600bps; b5: 115,200bps; b6 ~ b13: reserved; b14: high/low bit exchange of CRC checksum
(only valid in RTU mode); b15 = 0: ASCII mode; b15 = 1: RTU mode. ASCII data format: 7-bit, Even bit, 1 stop
bit (7, E, 1); RTU data format: 8-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (8, E, 1).
10. CR#33: For authorizations on some internal functions, e.g. OFFSET/GAIN tuning. The latched function will
store the output setting in the internal memory before the power is cut off.
11. CR#34: Firmware version of the model.
12. CR#35 ~ CR#48: Parameters for system use.
13. CR#0 ~ CR#34: The corresponding parameter addresses H’4032 ~ H’4054 are for users to read/write data by
RS-485 communication. When using RS-485, the user has to separate the module with MPU first.
a. Communication baud rate: 4,800/9,600/19,200/38,400/57,600/115,200bps
b. Modbus ASCII/RTU communication protocols: ASCII data format (7-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (7, E, 1)); RTU
data format (8-bit, Even bit, 1 stop bit (8, E, 1)).
c. Function: H’03 (read register data); H’06 (write 1 word datum to register); H’10 (write many word data to
register)
d. Latched CR should be written by RS-485 communication to stay latched. CR will not be latched if written by
MPU through TO/DTO instruction.
Adjusting D/A Conversion Curve
4.1 Explanation
Voltage Output Mode
10V
6V
GAIN
5V
2V
OFFSET
Current Output Mode
20mA
12mA
10mA
4mA
0
OFFSET
GAIN
Mode 1
+2,000
Mode 2
Mode 3
+2,000
CR#1 mode 0
CR#1 mode 1
GAIN
OFFSET
GAIN - OFFSET Range: +1V ~ +15V (+400
GAIN = 5V (2,000
OFFSET = 0V (0
GAIN = 6V (2,400
OFFSET = 2V (800
The voltage output value when the digital
input value = K2,000
Range: -4V ~ +20V (-1,600
The voltage output value when the digital
input value = K0
Range: -5V ~ +5V (-2,000
LSB
LSB
LSB
CR#1 mode 2
CR#1 mode 3
GAIN
OFFSET
GAIN - OFFSET
GAIN = 12mA (2,400
OFFSET = 4mA (800
GAIN = 10mA (2,000
OFFSET = 0mA (0
The current output value when the digital
input value = K2,000
Range: -8mA ~ +40mA (-1,600
+8,000
LSB
The current output value when the digital
input value = K0
Range: -10mA ~ +10mA (-2,000
+2,000
LSB
Range: +2mA ~ +30mA (+400
)
LSB
LSB
)
)
)
)
)
)
LSB
~ +8,000
LSB
~ +2,000
LSB
~ +6,000
LSB
)
LSB
)
LSB
)
LSB
)
LSB
LSB
~
~
LSB
~ +6,000
)
LSB
)
LSB
)
LSB
4.2 Program Example
Example 1: Set the OFFSET value of CH1as 0V (= K0
H10 K1
K1
K1
TO
K18
K24
H0
K0
K1
TO
X0
TO
TO
K1
K1
Example 2: Set the OFFSET value of CH2 as 2mA (= K400
K1
K19
K25
H18
H0
K3600
K1
TO
K1
TO
X0
TO
TO
K1
K1
) and GAIN value as 2.5V (= K1,000
LSB
Write H’10 into CR#1 of analog output module
No.1 and set CH1 in mode 0 (voltage output 0V
~ +10V) and CH2 in mode 2 (current output
4mA ~ +20mA).
Write H’0 into CR#33 and allow OFFSET/GAIN
tuning in CH1 ~ CH4
When X0 goes from Off to On, write the
OFFSET value K0
value K1,000
) and GAIN value as18mA (= K3,600
LSB
into CR#24.
LSB
Write H’18 into CR#1 of analog output module
~ +10V) and CH2 in mode 3 (current output
0mA ~ +20mA).
Write H’0 into CR#33 and allow OFFSET/GAIN
tuning in CH1 ~ CH4
When X0 goes from Off to On, write the
OFFSET value K400
GAIN value K3,600
).
LSB
into CR#18 and the GAIN
LSB
LSB).
into CR#19 and the
LSB
into CR#25.
LSB
Trial Operation & Troubleshooting
LED Display
1. When the module is powered for the first time, POWER LED will be on. After ERROR LED being on for 0.5
second, D/A LED will start to flash.
2. When the power supply is normal, POWER LED will be on and ERROR LED should be off. When the
power supply is less than 19.5V, ERROR LED will keep being on until the power supply is higher than
19.5V.
3. When controlled by RS-485, the RS-485 LED will flash after receiving RS-485 instruction.
4. When the input or output value exceeds the upper bound or falls below the lower bound after conversion,
ERROR LED will flash.
Program Example
FROM
M1013
= K4000 RST
=
M1
K4000
D100
D101
INC D100
ADD D101 K5
RST
TO
END
Read the model name from K1 and see if it is DVP04DA-H2: H’6401.
D100 increases K1 and D101 increases K5 every second.
When D100 and D101 reach K4,000, they will be cleared as 0.
See if the model is DVP04DA-H2 when M1 = On. If so, set up output mode: CH1 in mode 0; CH2 in mode 2.
Write the output settings of D100 and D101 into CR#6 and CR#7. The analog output will change with the
changes in D100 and D101.
D0
K0K1
D0CMP H6401
H10
K2K6
Relevant Instructions
API
78
API
Instruction
Explanation
Instruction
Explanation
Program
Example
Program
Example
FROM
: No. of special module (m1 = 0 ~ 7) : CR# in special module to be read
: Device for storing read data : Number of data to be read at a time
Read CR#24 of special module No.0 into D0 and
a time (n = 2).
FROM K0 K24 D0 K2
TO
P
: No. of special module (m1 = 0 ~ 7) : CR# in special module to be written
: Data to be written into CR : Number of data to be written at a time
Use 32-bit instruction DTO to write the content in D11 and D10 into CR#7 and CR#6 of special
module No.0. Only 1 group of data is written in at a time (n = 1).
Operand rules
1.
: The No. of special modules connected to PLC MPU. No. 0 is the module closest to te
MPU. Maximum 8 modules are allowed to connected to a PLC MPU and they will not occupy
any I/O points.
2.
: CR#. CR (control register) is the 49 16-bit memories built in the special module,
numbered in decimal as #0 ~ #48. All operation status and settings of the special module are
contained in the CR.
3. FROM/TO instruction is for reading/writing 1 CR at a time. DFROM/DTO instruction is for
reading/writing 2 CRs at a time.
Hi gh er 16-b it
CR #10 CR #9
4. Number of groups “n” to be transmitted: n = 2 in 16-bit instructions and n = 1 in 32-bit
instructions mean the same.
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
M1083 for switching instruction modes in EH2 series models
1. When M1083 = Off, during the execution of FROM/TO instruction, all external or internal
interruption subroutines will be forbidden. The interruptions are allowed only after FROM/TO
instruction finishes its execution. FROM/TO instruction can also be used in an interruption
subroutine.
2. When M1083 = On and an interruption signal occurs during the execution of FROM/TO
instruction, the interruption will be processed first (with a 100us delay) and the execution of
FROM/TO will be stopped. After the interruption subroutine finishes its execution, the
program will jump to the next instructio of FROM/TO. FROM/TO cannot be used in an
interruption subroutine.
Read CR data in special modules
Write CR data into special modules
K0 K6
K1
CR #5
CR #6
CR #7
CR #8
CR #9
CR #10
Designated CR number
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
Designated CR
The content of this instruction sheet may be revised without prior notice. Please consult our distributors or
download the most updated version at http://www.delta.com.tw/industrialautomation
 Loading...
Loading...