Dell PowerConnect B-8000 Administrator's Guide

53-1002743-01
14 December 2012
Access Gateway
Administrator’s Guide
®
Supporting Fabric OS v7.1.0

Copyright © 2007-2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Brocade, the B-wing symbol, BigIron, DCX, Fabric OS, FastIron, NetIron, SAN Health, ServerIron, and TurboIron are registered
trademarks, and AnyIO, Brocade Assurance, Brocade NET Health, Brocade One, CloudPlex, MLX, VCS, VDX, and When the Mission
Is Critical, the Network Is Brocade are trademarks of Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., in the United States and/or in other
countries. Other brands, products, or service names mentioned are or may be trademarks or service marks of their respective
owners.
Notice: This document is for informational purposes only and does not set forth any warranty, expressed or implied, concerning
any equipment, equipment feature, or service offered or to be offered by Brocade. Brocade reserves the right to make changes to
this document at any time, without notice, and assumes no responsibility for its use. This informational document describes
features that may not be currently available. Contact a Brocade sales office for information on feature and product availability.
Export of technical data contained in this document may require an export license from the United States government.
The authors and Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. shall have no liability or responsibility to any person or entity with
respect to any loss, cost, liability, or damages arising from the information contained in this book or the computer programs that
accompany it.
The product described by this document may contain “open source” software covered by the GNU General Public License or other
open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing
terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit
http://www.brocade.com/support/oscd.
Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
Corporate and Latin American Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc.
130 Holger Way
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel: 1-408-333-8000
Fax: 1-408-333-8101
E-mail: info@brocade.com
European Headquarters
Brocade Communications Switzerland Sàrl
Centre Swissair
Tour B - 4ème étage
29, Route de l'Aéroport
Case Postale 105
CH-1215 Genève 15
Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 799 5640
Fax: +41 22 799 5641
E-mail: emea-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems China HK, Ltd.
No. 1 Guanghua Road
Chao Yang District
Units 2718 and 2818
Beijing 100020, China
Tel: +8610 6588 8888
Fax: +8610 6588 9999
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen WFOE)
Citic Plaza
No. 233 Tian He Road North
Unit 1308 – 13th Floor
Guangzhou, China
Tel: +8620 3891 2000
Fax: +8620 3891 2111
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Document History
Document title Publication number Summary of changes Publication date
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1000430-01 First version. January 2007
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1000633-01 Added support for the 200E. June 2007
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1000605-01 Added support for new policies
and changes to N_Port
mappings.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1000605-02 Added support for the
300 and 4424 models.
Added support for new features:
- Masterless Trunking
- Direct Target Connectivity
- Advance Device Security policy
- 16- bit routing
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1000605-03 Added support for Cascading
Access Gateway.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1000605-04 Updated to fix the table of
contents.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1001189-01 Updated for Fabric OS v6.2.0. November 2008
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1001345-01 Updated for Fabric OS v6.3.0. July 2009
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1001760-01 Updated for Fabric OS v6.4.0. March 2010
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1002156-01 Updated for Fabric OS v7.0.0. April 2011
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1002475-01 Updated for Fabric OS v7.0.1. December 2011
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 53-1002743-01 Updated for Fabric OS v7.1.0 December 2012
October 2007
March 2008
July 2008
July 2008
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide iii
53-1002743-01

iv Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Contents
About This Document
How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Supported hardware and software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
What’s new in this document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Command syntax conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
Notes, cautions, and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
Key terms for Access Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xvii
Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Brocade resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Other industry resources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Optional Brocade features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
Chapter 1 Access Gateway Basic Concepts
Brocade Access Gateway overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Comparing Native Fabric and Access Gateway modes . . . . . . . . 1
Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Buffer credit recovery support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Forward error correction support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Virtual Fabrics support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Device authentication support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Access Gateway port types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Comparison of Access Gateway ports to standard switch
ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Access Gateway hardware considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Chapter 2 Configuring Ports in Access Gateway Mode
Enabling and disabling Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Port state description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide v
53-1002743-01

Access Gateway mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
F_Port Static Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Device mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Considerations for Access Gateway mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
N_Port configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Displaying N_Port configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Unlocking N_Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Persisting port online state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
D_Port support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Limitations and considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Saving port mappings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Chapter 3 Managing Policies and Features in Access Gateway Mode
Access Gateway policies overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Displaying current policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Access Gateway policy enforcement matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Advanced Device Security policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
How the ADS policy works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Enabling and disabling the ADS policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Allow lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
ADS policy considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for the ADS policy. . .39
Automatic Port Configuration policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
How the APC policy works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Enabling and disabling the APC policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
APC policy considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for the APC policy . . .40
Port Grouping policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
How port groups work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Adding an N_Port to a port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Deleting an N_Port from a port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Removing a port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Renaming a port group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Disabling the Port Grouping policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Port Grouping policy modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Creating a port group and enabling Automatic Login
Balancing mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Enabling MFNM mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Disabling MFNM mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Displaying the current MFNM mode timeout value . . . . . . . . . . 46
Setting the current MFNM mode timeout value . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Port Grouping policy considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for the Port
Grouping policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Device Load Balancing policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Enabling the Device Load Balancing policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Disabling the Device Load Balancing policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Device Load Balancing policy considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
vi Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Persistent ALPA policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Enabling the Persistent ALPA policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Disabling the Persistent ALPA policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Persistent ALPA device data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Clearing ALPA values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Persistent ALPA policy considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Failover policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Failover with port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Failover with device mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Enabling and disabling the Failover policy on an N_Port . . . . .54
Enabling and disabling the Failover policy for a port group . . . 54
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for the Failover
policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Failback policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Failback policy configurations in Access Gateway. . . . . . . . . . .55
Enabling and disabling the Failback policy on an N_Port . . . . 56
Enabling and disabling the Failback policy for a port group. . . 57
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for the Failback
policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Failback policy disabled on unreliable links (N_Port
monitoring) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Trunking in Access Gateway mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
How trunking works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Configuring trunking on the Edge switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Configuration management for trunk areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Enabling trunking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Disabling F_Port trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Monitoring trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
AG trunking considerations for the Edge switch . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Trunking considerations for Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . .65
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for trunking in
Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Adaptive Networking on Access Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
QoS: Ingress rate limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
QoS: SID/DID traffic prioritization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Upgrade and downgrade considerations for Adaptive
Networking in AG mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Adaptive Networking on Access Gateway considerations. . . . . 67
Per-Port NPIV login limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Setting the login limit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Advanced Performance Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
End-to-end monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Frame monitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Limitations for using APM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Considerations for the Brocade 8000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Policy and feature support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Fabric OS command support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Considerations for the Brocade 6505 and 6510 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide vii
53-1002743-01

Chapter 4 SAN Configuration with Access Gateway
Connectivity of multiple devices overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Considerations for connecting multiple devices . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Direct target attachment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Considerations for direct target attachment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Target aggregation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Access Gateway cascading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Access Gateway cascading considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Fabric and Edge switch configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Verifying the switch mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Enabling NPIV on M-EOS switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Connectivity to Cisco fabrics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Enabling NPIV on a Cisco switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Rejoining Fabric OS switches to a fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Reverting to a previous configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Appendix A Troubleshooting
Index
viii Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Figures
Figure 1 Switch function in Native mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Figure 2 Switch function in Access Gateway mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Figure 3 Port usage comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 4 Diagnostic port configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 5 Port mapping example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 6 Example of device mapping to N_Port groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 7 Example device mapping to an N_Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 8 Example of adding an external F_Port (F9) on an embedded switch . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 9 Port grouping behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 10 Port group 1 (PG1) setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 11 Failover behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 12 Failback behavior. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 13 Starting point for QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 14 Direct target attachment to switch operating in AG mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 15 Target aggregation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Figure 16 Access Gateway cascading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide ix
53-1002743-01

x Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Tables
Tab l e 1 Fabric OS components supported on Access Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Tab l e 2 Behavior of sending AG switch and receiving fabric switch with different
policies configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Tab l e 3 Behavior of sending device (HBA) and receiving AG switch with different
policies configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Tab l e 4 Port configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Tab l e 5 Port state description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Tab l e 6 Description of port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Tab l e 7 Access Gateway default port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Tab l e 8 Policy enforcement matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Tab l e 9 Address identifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Tab l e 10 Access Gateway trunking considerations for the Edge switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Tab l e 11 PWWN format for F_Port and N_Port trunk ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Tab l e 1 2 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide xi
53-1002743-01

xii Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

About This Document
•How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
•Supported hardware and software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
•What’s new in this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xv
•Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvi
•Key terms for Access Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xvii
•Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xviii
•Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xix
How this document is organized
This document is a procedural guide to help SAN administrators configure and manage Brocade
Access Gateway (AG).
This preface contains the following components:
• Chapter 1, “Access Gateway Basic Concepts” describes the Brocade Access Gateway and
provides an overview of its key features.
• Chapter 2, “Configuring Ports in Access Gateway Mode” describes how to configure ports in
Access Gateway mode.
• Chapter 3, “Managing Policies and Features in Access Gateway Mode” describes how to
enable policies on a switch in Access Gateway mode. It also provides information on how to set
up failover and failback, and discusses how trunking and Adaptive Networking work in AG.
• Chapter 4, “SAN Configuration with Access Gateway” describes how to connect multiple
devices using Access Gateway.
• Appendix A, “Troubleshooting” provides symptoms and troubleshooting tips to resolve issues.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide xiii
53-1002743-01

Supported hardware and software
In those instances in which procedures or parts of procedures documented here apply to some
switches but not to others, this guide identifies which switches are supported and which are not.
Although many different software and hardware configurations are tested and supported by
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., for Fabric OS v7.1.0, documenting all possible
configurations and scenarios is beyond the scope of this document.
All Fabric OS switches must be running Fabric OS v6.1.0 or later; all M-EOS switches must be
running M-EOSc 9.1 or later, M-EOSn must be running 9.6.2 or later, and Cisco switches with SAN
OS must be running 3.0 (1) and 3.1 (1) or later.
Fabric OS v7.1.0 supports the following Brocade hardware platforms for Access Gateway:
• Brocade 300
• Brocade 5100
• Brocade M5424
• Brocade 5430
• Brocade 5450
• Brocade 5460
• Brocade 5470
• Brocade 5480
• Brocade 6505
• Brocade 6510
• Brocade 8000
• NC-4380
• Brocade VA-40FC
What’s new in this document
The following information has been added since this document was last released:
• Preface
- Brocade 5430 added to list of “Supported hardware and software” on page xiv for Access
Gateway.
• Chapter 1
- Described support for buffer credit recovery, diagnostic port, fabric assigned PWWN
(FA-PWWN), Forward Error Correction (FEC), and device authentication policy features
under “Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode” on page 3.
- Added information about diagnostic port (D_Port) under “Access Gateway port types” on
page 9“.
xiv Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

• Chapter 2
- Added port mapping details for the Brocade 5430 switch to “Access Gateway default port
mapping” on page 17. Table 5,
- Added “D_Port support” on page 32.
• Chapter 3
- Added notes to “Failover policy” on page 50 and “Failback policy” on page 55 that If
failover and failback policy are disabled, an F_Port mapped to an N_Port will go offline
when the N_Port goes offline and it will go online when the N_Port comes online.
- Under“Considerations for the Brocade 6505 and 6510” on page 72, added that all ports
on demand (POD) licenses must be present to support Access Gateway.
For further information, refer to the release notes.
Document conventions
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notices formats.
Text formatting
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used in this document are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords and operands
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
italic text Provides emphasis
Identifies variables
Identifies paths and Internet addresses
Identifies document titles
code text Identifies CLI output
Identifies syntax examples
For readability, command names in the narrative portions of this guide are presented in mixed
lettercase: for example, switchShow. In actual examples, command lettercase is often all
lowercase.
Command syntax conventions
Command syntax in this manual follows these conventions:
command Commands are printed in bold.
--option, option Command options are printed in bold.
-argument, arg Arguments.
[ ] Optional element.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide xv
53-1002743-01
NOTE
ATTENTION
CAUTION
DANGER
variable Variables are printed in italics. In the help pages, values are underlined
enclosed in angled brackets < >.
... Repeat the previous element, for example “member[;member...]”
value Fixed values following arguments are printed in plain font. For example,
--show WWN
or
| Boolean. Elements are exclusive. Example:
--show -mode egress | ingress
Notes, cautions, and warnings
The following notices appear in this document.
A note provides a tip, guidance, or advice, emphasizes important information, or provides a
reference to related information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
A Caution statement alerts you to situations that can be potentially hazardous to you or cause
damage to hardware, firmware, software, or data.
A Danger statement indicates conditions or situations that can be potentially lethal or extremely
hazardous to you. Safety labels are also attached directly to products to warn of these conditions
or situations.
Notice to the reader
This document may contain references to the trademarks of the following corporations. These
trademarks are the properties of their respective companies and corporations.
These references are made for informational purposes only.
Corporation Referenced trademarks and products
Cisco Systems, Inc. Cisco
Oracle Corporation. Sun, Solaris
Netscape Communications Corporation Netscape
Red Hat, Inc. Red Hat, Red Hat Network, Maximum RPM, Linux Undercover
xvi Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Corporation Referenced trademarks and products
Emulex Corporation Emulex
QLogic Corporation QLogic
Key terms for Access Gateway
For definitions of SAN-specific terms, visit the Storage Networking Industry Association online
dictionary at:
http://www.snia.org/education/dictionary
For definitions specific to Brocade and Fibre Channel, see the Brocade Glossary.
The following terms are used in this manual to describe Access Gateway mode and its components.
Access Gateway (AG) Fabric OS mode for switches that reduces storage area network (SAN)
deployment complexity by leveraging N_Port ID Virtualization (NPIV).
Device Any host or target device with a distinct WWN. Devices may be physical or
virtual.
D_Port A port configured as a diagnostic port on an AG switch, connected fabric
switch, or connected cascaded AG switch to run diagnostic tests between the
ports and test the link.
E_Port An interswitch link (ISL) port. A switch port that connects switches together to
form a fabric.
Edge switch A fabric switch that connects host, storage, or other devices, such as Brocade
Access Gateway, to the fabric.
F_Port A fabric port. A switch port that connects a host, host bus adapter (HBA), or
storage device to the SAN. On Brocade Access Gateway, the F_Port connects
to a host or a target.
Mapping In Access Gateway, mapping defines the routes between devices or F_Ports to
the fabric facing ports (N_Ports).
N_Port A node port. A Fibre Channel host or storage port in a fabric or point-to-point
connection. On Brocade Access Gateway, the N_Port connects to the Edge
switch.
NPIV N_Port ID Virtualization. This is a Fibre Channel facility allowing multiple
N_Port IDs to share a single physical N_Port. This allows multiple Fibre
Channel initiators to occupy a single physical port, easing hardware
requirements in storage area network design, especially for virtual SANs.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide xvii
53-1002743-01

Additional information
This section lists additional Brocade and industry-specific documentation that you might find
helpful.
Brocade resources
To get up-to-the-minute information, go to http://my.brocade.com to register at no cost for a user ID
and password.
White papers, online demonstrations, and data sheets are available through the Brocade website
at:
http://www.brocade.com/products-solutions/products/index.page
For additional Brocade documentation, visit the Brocade website:
http://www.brocade.com
Release notes are available on the MyBrocade website and are also bundled with the Fabric OS
firmware.
Other industry resources
• White papers, online demonstrations, and data sheets are available through the Brocade
website athttp://www.brocade.com/products-solutions/products/index.page.
• Best practice guides, white papers, data sheets, and other documentation are available
through the Brocade Partner website.
For additional resource information, visit the Technical Committee T11 website. This website
provides interface standards for high-performance and mass storage applications for Fibre
Channel, storage management, and other applications:
http://www.t11.org
For information about the Fibre Channel industry, visit the Fibre Channel Industry Association
website:
http://www.fibrechannel.org
Optional Brocade features
For a list of optional Brocade features and descriptions, see the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
Getting technical help
Contact your switch support supplier for hardware, firmware, and software support, including
product repairs and part ordering. To expedite your call, have the following information available:
1. General Information
• Technical Support contract number, if applicable
xviii Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01
• Switch model
• Switch operating system version
• Error numbers and messages received
• supportSave command output
• Detailed description of the problem, including the switch or fabric behavior immediately
following the problem, and specific questions
• Description of any troubleshooting steps already performed and the results
• Serial console and Telnet session logs
• Syslog message logs
2. Switch Serial Number
The switch serial number and corresponding bar code are provided on the serial number label,
as shown here:
:
*FT00X0054E9*
FT00X0054E9
The serial number label is located as follows:
• Brocade 300, 5100, 8000, VA-40FC, 6505, and 6510—On the switch ID pull-out tab
located inside the chassis on the port side on the left
• Brocade M5424, 5450, 5460, 5470, 5480—Serial number label attached to the module
3. World Wide Name (WWN)
Use the licenseIdShow command to display the WWN of the chassis.
If you cannot use the licenseIdShow command because the switch is inoperable, you can get
the WWN from the same place as the serial number.
Document feedback
Quality is our first concern at Brocade and we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and
completeness of this document. However, if you find an error or an omission, or you think that a
topic needs further development, we want to hear from you. Forward your feedback to:
documentation@brocade.com
Provide the title and version number of the document and as much detail as possible about your
comment, including the topic heading and page number and your suggestions for improvement.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide xix
53-1002743-01

xx Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Chapter
Access Gateway Basic Concepts
•Brocade Access Gateway overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
•Access Gateway port types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
•Access Gateway hardware considerations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Brocade Access Gateway overview
Brocade Access Gateway (AG) is a Fabric OS feature that you can use to configure your Enterprise
fabric to handle additional devices instead of domains. You do this by configuring F_Ports to
connect to the fabric as N_Ports, which increases the number of device ports you can connect to a
single fabric. Multiple AGs can connect to the DCX enterprise-class platform, directors, and
switches.
Access Gateway is compatible with M-EOS v9.1 or v9.6 or later, and Cisco-based fabrics v3.0 (1) or
later and v3.1 (1) or later. You can use the command line interface (CLI), Web Tools, or Brocade
Network Advisor (BNA) to enable and disable AG mode and configure AG features on a switch. This
document describes configurations using the CLI commands. Refer to the Fabric OS Command
Reference Manual, the Web Tools Administrator’s Guide, or the Brocade Network Advisor User
Guide for more information about AG support in those tools.
1
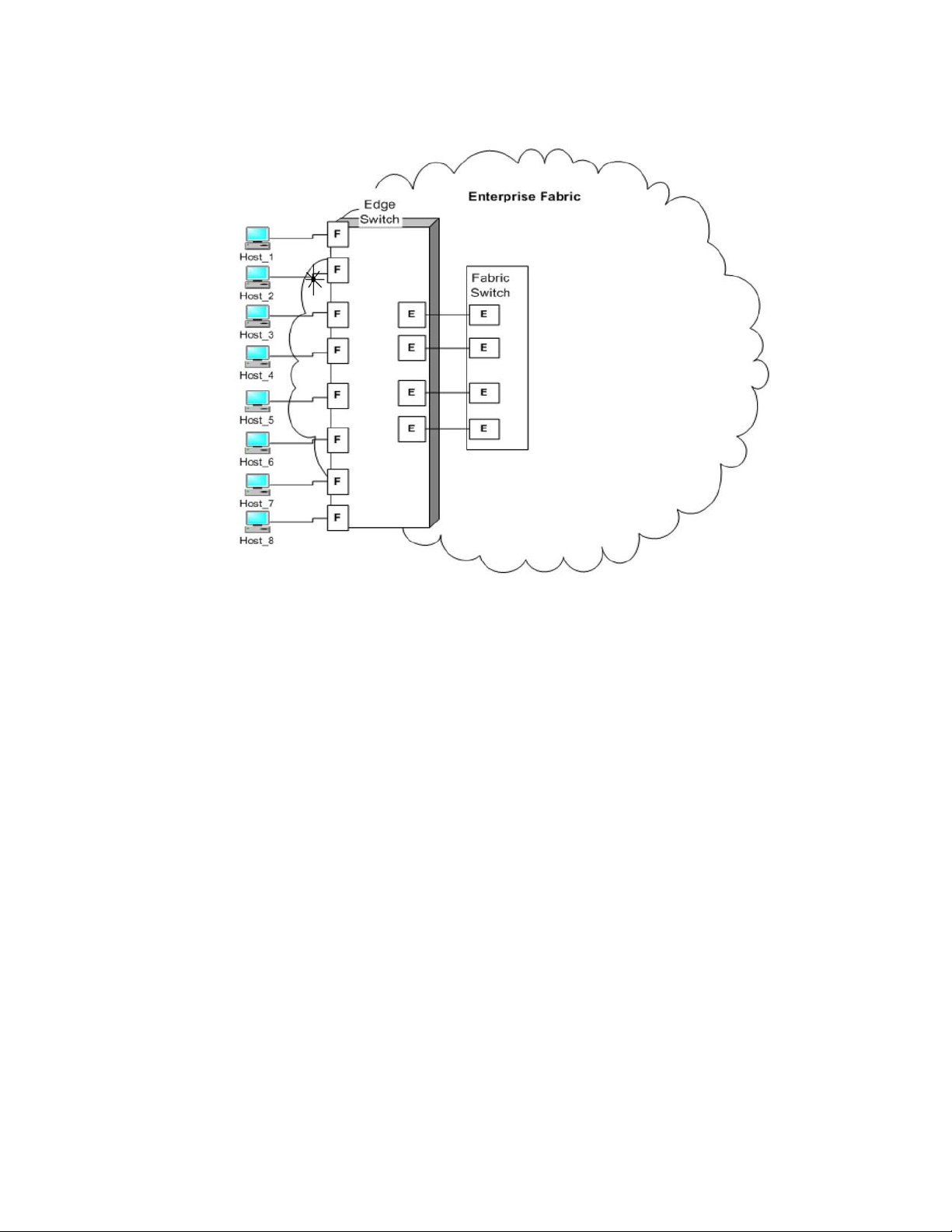
After you set a Fabric OS switch to AG mode, the F_Ports connect to the Enterprise fabric as
N_Ports rather than as E_Ports. Figure 1 shows a comparison of a configuration that connects
eight hosts to a fabric using AG to the same configuration with Fabric OS switches in Native mode.
Switches in AG mode are logically transparent to the host and the fabric. Therefore, you can
increase the number of hosts that have access to the fabric without increasing the number of
switch domains. This simplifies configuration and management in a large fabric by reducing the
number of domain IDs and ports.
Comparing Native Fabric and Access Gateway modes
The following points summarize the differences between a Fabric OS switch functioning in Native
operating mode and a Fabric OS switch functioning in AG operating mode:
• The Fabric OS switch in Native mode is a part of the fabric; it requires two to four times as
many physical ports, consumes fabric resources, and can connect to a Fabric OS fabric only.
• A switch in AG mode is outside of the fabric; it reduces the number of switches in the fabric
and the number of required physical ports. You can connect an AG switch to a Fabric OS,
M-EOS, or Cisco-based fabric.
For comparison, Figure 1 illustrates switch function in Native mode and Figure 2 illustrates switch
function in AG mode.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 1
53-1002743-01
Brocade Access Gateway overview
1
FIGURE 1 Switch function in Native mode
2 Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
1
FIGURE 2 Switch function in Access Gateway mode
Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
Tab le 1 lists Fabric OS components that are supported on a switch when AG mode is enabled.
“Yes” indicates that the feature is supported in Access Gateway mode. “No” indicates that the
feature is not provided in AG mode. “NA” indicates the feature is not applicable in Access Gateway
mode. A single asterisk (*) indicates the feature is transparent to AG; that is, AG forwards the
request to the Enterprise fabric. Two asterisks (**) indicates that the feature may not be available if
the Enterprise fabric is not a Brocade fabric. For more information on these features, refer to the
Fabric OS Administrator's Guide and Fabric OS Command Reference.
TABLE 1 Fabric OS components supported on Access Gateway
Feature Support
Access Control
Adaptive Networking Yes
Admin Domains No
Audit Yes
Beaconing Yes
Bottleneck Detection Yes
1
Yes (limited roles)
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 3
53-1002743-01

Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
1
TABLE 1 Fabric OS components supported on Access Gateway (Continued)
Feature Support
Buffer Credit Recovery (CR) Yes -
Config Download/Upload Yes
Device Authentication Yes
DHCP Yes
Diagnostic Port (D_Port) Yes
Encryption Configuration
and Management
Environmental Monitor Yes
Error Event Management Yes
Extended Fabrics No
Fabric Assigned PWWN
(FA-PWWN)
Fabric Device Management
Interface (FDMI)
Fabric Manager Yes**
Fabric Provisioning No
Fabric Services No
Fabric Watch Yes
Fibre Channel Routing (FCR)
services
FICON (includes CUP) No
Forward Error Correction
(FEC)
High Availability Yes
Hot Code Load Yes
License Yes**
Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol (LDAP)
Log Tracking Yes
Management Server NA
Manufacturing Diagnostics Yes
N_Port ID Virtualization
(NPIV)
Refer to “Buffer credit recovery support” on
page 5.
Refer to “Device authentication support” on
page 6.
Refer to “D_Port support” on page 32.
No
Yes
Yes *
Refer to the Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide
for applicable support details.
No
Yes
Refer to “Forward error correction support” on
page 6.
Yes
Yes
4 Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
TABLE 1 Fabric OS components supported on Access Gateway (Continued)
Feature Support
Name Server NA
Native Interoperability Mode NA
Network Time Protocol (NTP) No (no relevance from fabric perspective)
Open E_Port NA
Performance Monitor Yes
Persistent ALPA Yes
Port Decommission No
Port Mirroring No
QuickLoop, QuickLoop Fabric
Assist
Remote Authentication
Dial-In User Service
(RADIUS)
Resource Monitor Yes
Security Yes (ADS/DCC Policy)
SNMP Yes
Speed Negotiation Yes
Syslog Daemon Yes
Track Changes Yes
Tru nkin g Yes **
User-Defined Roles Yes
ValueLineOptions (Static
POD, DPOD)
Virtual Fabrics No
Web Tools Yes
Zoning NA
No
Yes
Yes
Refer to “Virtual Fabrics support” on page 6.
2
1
1. When a switch is behaving as an AG, RBAC features in Fabric OS are
available, but there are some limitations. For more information on the
limitations, refer to “Access Gateway hardware considerations” on page 11.
2. In embedded switches, time should be updated by the server management
utility.
Buffer credit recovery support
This Fabric OS feature is supported on 8 Gbps and 16 Gbps platforms in following configurations:
• Between AG switch F_Port and Brocade HBA port using Adapter v3.2 or greater firmware or any
device supporting credit recovery, This feature only works at the maximum supported speed of
the HBA port (8 Gbps or 16 Gbps).
• Between AG switch N_Port and Brocade fabric switch or cascaded AG switch F_Port.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 5
53-1002743-01

Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
1
It is highly recommended that you disable this feature on the AG switch before connecting to a
switch running Fabric OS less than 7.1. Enable and disable CR using the portcfgcreditrecovery
command. Refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference for more information on this command.
Specific switch platforms support this feature either in R_RDY or VC_RDY mode. In VC_RDY mode,
the buffer credit recovery is supported with fabric assigned PWWN (FA-PWWN), FEC, QoS, and
trunking Fabric OS features. In R_RDY mode, this feature is supported without FA-PWWN and QoS
Fabric OS features.
Forward error correction support
Forward error correction (FEC) is a Fabric OS feature supported in the following configurations:
• Between the AG switch F_Port and a Brocade 16 Gbps HBA port running version 3.2 or greater
firmware.
• Between the AG switch N_Port and F_Port on Brocade 16 Gbps fabric switch or cascaded AG
switch.
Following are limitations and considerations for FEC:
• Supported on Brocade 16 Gbps platforms only.
• Supported by Fabric OS 7.1.0 and later.
• Enabled by default.
• A Fabric OS downgrade requires FEC to be disabled.
• Specific switch platforms support this feature either in R_RDY or VC_RDY mode.
Virtual Fabrics support
Although you cannot enable AG mode on a switch enabled for Virtual Fabrics or enable Virtual
Fabrics on an AG switch, you can connect ports on an AG switch to Virtual Fabrics.
Device authentication support
Devices use authentication as a mechanism to log in into switches only after exchanging DH_CHAP
authorization keys. This prevents any unauthorized device from logging into switch and fabric by
default.
Authentication policy is supported in the following configurations for Access Gateway switches.
Regardless of the enabled policy, the AG port disables if the DH-CHAP or FCAP fails to authenticate
each other.
• Access Gateway switch N_Port connected to Brocade fabric switch F_Port. The N-port should
enable authentication when authentication is enabled on the connected switch. This can be
done by enabling switch policy on the AG switch and device policy on the fabric switch.
• Access Gateway switch F_Port connected to an HBA. The F-port also should enable
authentication when the connected device is sending login request with authentication
enabled. This is done by enabling device policy on the AG switch.
By default, Brocade switches use DH-CHAP or FCAP authentication protocols. For authentication
between fabric switches and AG switches, FCAP and DH-CHAP are used. If an FCAP certificate is
present on the AG switch and fabric switch, FCAP has precedence over DHCAP. For authentication
between AG switches and HBAs, DH-CHAP is used since the HBA only supports DH-CHAP.
6 Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
For details on installing FCAP certificates and creating DHCAP secrets on the switch in AG or native
mode, refer to the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide or Fabric OS Command Reference.
For general information on authentication, refer to the section on authentication policy for fabric
elements in the Configuring Security Policies chapter of the Fabric OS Administrator’s Guide.
1
Supported policy modes
The following switch and device policy modes are supported by Access Gateway:
• On - Strict authentication will be enforced on all ports. The ports on the AG connected to the
switch or device will disable if the connecting switch or device does not support authentication
or the policy mode is set to off. During AG initialization, authentication initiates on all ports
automatically.
• Off - The AG switch does not support authentication and rejects any authentication negotiation
request from the connected fabric switch or HBA. A fabric switch with the policy mode set to off
should not be connected to an AG switch with policy mode set to on since the on policy is strict.
This will disable the port if any switch rejects the authentication. You must configure DH-CHAP
shared secrets or install FCAP certificates on the AG and connected fabric switch before
switching from a policy off mode to policy on mode. Off is the default mode for both switch and
device policy.
• Passive - The AG does not initiate authentication when connected to a device, but participates
in authentication if the connecting device initiates authentication. The AG will not initiate
authentication on ports, but accepts incoming authentication requests. Authentication will not
disable AG F_Ports if the connecting device does not support authentication or the policy mode
is set to off. Passive mode is the safest mode to use for devices connected to an AG switch if
the devices do not support authentication.
To perform authentication with switch policy, the on and off policy modes are supported on the AG
switch. To perform authentication with device policy, the on, off, and passive modes are supported
on the AG switch.
Tab le 2 on page 8 describes the authentication behavior between a sending AG switch and
receiving fabric switch.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 7
53-1002743-01

Fabric OS features in Access Gateway mode
NOTE
1
TABLE 2 Behavior of sending AG switch and receiving fabric switch with different policies configured
AG switch with switch
policy mode on
Fabric switch with device
policy mode ON
Authorization negotiation accept
Fabric switch with device
policy mode PASSIVE
Authorization negotiation accept
Fabric switch with device
policy mode OFF
Authorization
negotiation - reject
N_Port without
authentication
No negotiation
N_Port without
authentication
AG switch with switch
policy off
DH-CHAP/FCAP:
Success - N_Port
Failure - disable
No negotiation
No light
DH-CHAP/FCAP:
Success - N_Port
Failure - disable
No Negotiation
N_Port without
authenctication.
Tab le 3 describes the authentication behavior between a sending HBA and receiving AG switch.
TABLE 3 Behavior of sending device (HBA) and receiving AG switch with different policies configured
HBA authentication
enabled
HBA authentication
disabled
AG switch with device
policy mode ON
Authorization negotiation accept
DH-CHAP
Success - F_Port
Failure - disable
No negotiation
No light
AG switch with device policy
mode PASSIVE
Authorization negotiation accept
DH-CHAP
Success - F_Port
Failure - disable
No negotiation
F_Port without
authentication
AG switch with device
policy mode OFF
Authorization
negotiation - reject
F_Port without
authentication
No negotiation
F_Port without
authentication
Supported Fabric OS commands
All Fabric OS commands for authentication policy apply to AG switches, including the following:
• authutil -- policy
• authutil --show
• authutil --set
• secauthsecret --set
• secauthsecret --show
Although authutil --authinit is not supported in AG mode, it is supported in native mode.
For more information, refer to the Fabric OS Command Reference.
Limitations and considerations
• Authentication policy is not supported on cascaded AG switch configurations.
8 Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01

• Authentication is not supported between an AG switch running Fabric OS v7.1.0 or later and a
NOTE
fabric running Fabric OS earlier than v7.1.0. If the AG switch is connected to fabric switch
running Fabric OS earlier than v7.1.0, the AG switch N_Ports will disable if authentication is
enabled on both switches. Devices mapped to N_Ports connected to fabrics operating with
Fabric OS before v7.1.0 will also disable.
• If authentication is disabled on the Fabric Switch, the AG switch N_Port will come online
without authentication policy.
• Device and switch policies must be disabled on the AG before converting the switch to Native
mode.
• Device and switch policies must be disabled on the switch in Native mode before converting it
to AG mode.
• Authentication policy is disabled by default on all ports in AG mode.
• High availability (HA) reboots are supported.
Access Gateway port types
Access Gateway differs from a typical fabric switch because it is not a switch; instead, it is a mode
that you enable on a switch using the ag command. After a switch is set in Access Gateway mode, it
can connect to the fabric using node ports (N_Ports). Typically, fabric switches connect to the
Enterprise fabric using interswitch link (ISL) ports, such as E_Ports.
Access Gateway port types
1
AG uses the following Fibre Channel (FC) ports:
• F_Port - Fabric port that connects a host, HBA, or storage device to a switch in AG mode.
• N_Port - Node port that connects a switch in AG mode to the F_Port of the fabric switch.
• D_Port - Port configured in diagnostic mode so that various tests can run between it and
connected D_Port on another switch across a link.
Initiate the portcfgpersisentenable command on all external or outward facing ports to ensure that
these ports come back online after a switch reboot or power failure. For an embedded switch,
execute this command through the chassis management console and not the switch CLI or the
command may not persist. Refer to “Persisting port online state” on page 31 for more information.
Comparison of Access Gateway ports to standard switch ports
Access Gateway multiplexes host connections to the fabric. It presents an F_Port to the host and an
N_Port to an Edge fabric switch. Using N_Port ID Virtualization (NPIV), AG allows multiple FC
initiators to access the SAN on the same physical port. This reduces the hardware requirements
and management overhead of hosts to the SAN connections.
A fabric switch presents F_Ports (or FL_Ports) and storage devices to the host and presents
E_Ports, VE_Ports, or EX_Ports to other switches in the fabric. A fabric switch consumes SAN
resources, such as domain IDs, and participates in fabric management and zoning distribution. A
fabric switch requires more physical ports than AG to connect the same number of hosts.
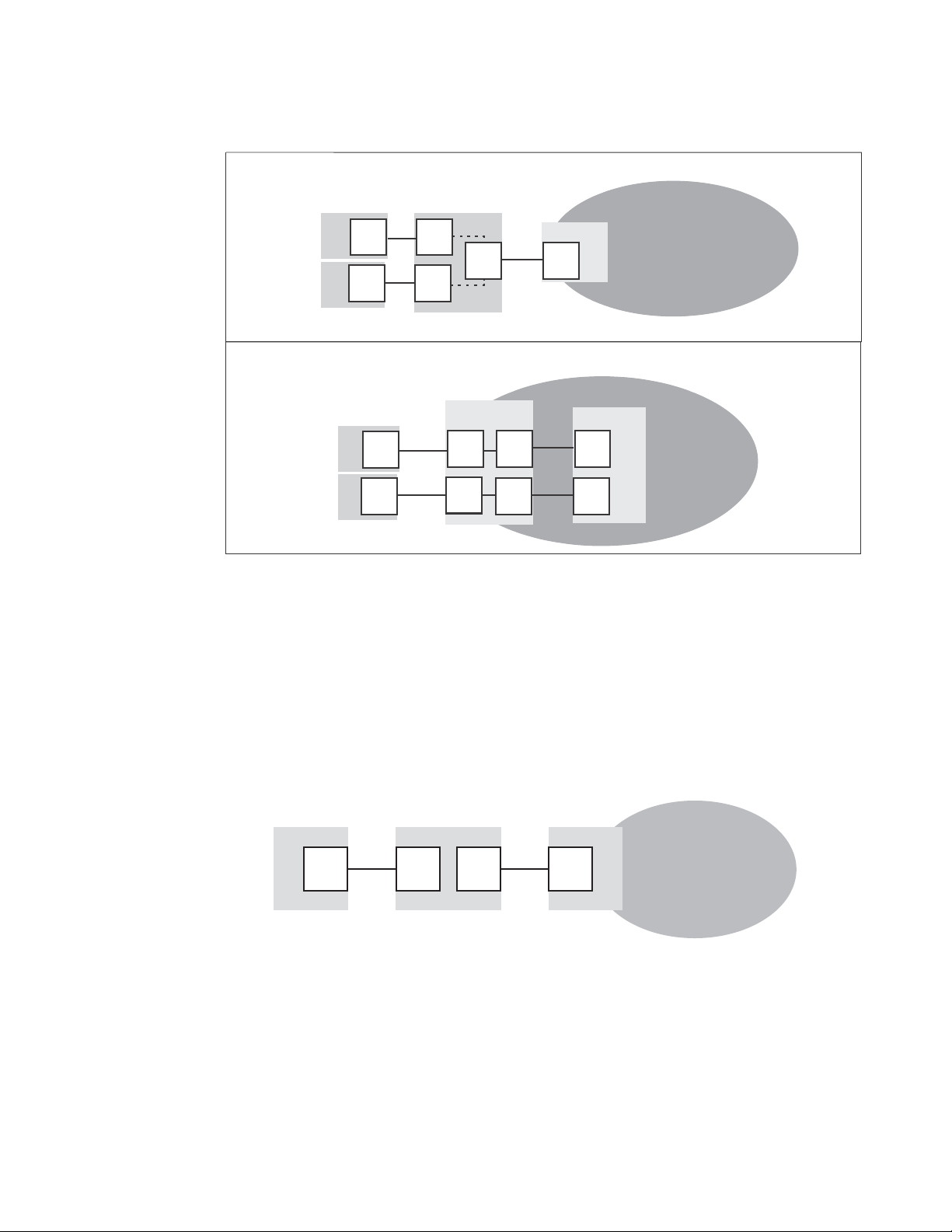
Figure 3 shows a comparison of the types of ports a switch in AG mode uses to the type of ports
that a switch uses in standard mode.
Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide 9
53-1002743-01
Access Gateway port types
N_Port
F_Port
N_Port
F_Port
N_Port
F_Port
Hosts
Switch in AG mode
Edge Switch
Fabric
enabled
NPIV
N_Port
F_Port
E_Port
E_Port
N_Port
F_Port
Hosts
Switch in Native
Fabric Switch
E_Port
E_Port
Fabric
Access Gateway Ports
Fabric Switch Ports
Fabric mode
D-Port D-Port
Edge Switch
Fabric
D-Port
D-Port
Switch in AG modeSwitch in AG mode
Diagnostic Ports
1
FIGURE 3 Port usage comparison
You can convert a Fibre Channel port into a D_Port on AG switch and a connected fabric switch or
another AG switch (cascaded configuration) to test the link between the ports. When you configure
the ports on each end of the link as D_Ports, diagnostic tests automatically initiate on the link
when the D_Ports go online. Results can be viewed using Fabric OS commands during or after
testing. Once in D_Port mode, the port does not participate in fabric operations, login to a remote
device, or run data traffic. Figure 4 on page 10 illustrates the supported D_Port configurations.
FIGURE 4 Diagnostic port configurations
Tab le 4 shows a comparison of port configurations between AG and a standard fabric switch.
10 Access Gateway Administrator’s Guide
53-1002743-01
 Loading...
Loading...