Page 1
FDB035AN06A0
N-Channel PowerTrench® MOSFET
60V, 80A, 3.5mΩ
FDB035AN06A0
July 2002
Features
•r
•Q
• Low Miller Charge
• Low Qrr Body Diode
• UIS Capability (Single Pulse and Repetitive Pulse)
• Qualified to AEC Q101
Formerly developmental type 82584
MOSFET Maximum Ratings T
= 3.2mΩ (Typ.), V
DS(ON)
(tot) = 95nC (Typ.), V
g
GATE
SOURCE
= 10V, ID = 80A
GS
= 10V
GS
TO-263AB
FDB SERIES
DRAIN
(FLANGE)
= 25°C unless otherwise noted
C
Applications
• Motor / Body Load Control
• ABS Systems
• Powertrain Management
• Injection Syste m s
• DC-DC converter s and Off-line UPS
• Distributed P ower Arc hitectures and VRMs
• Primary Switch for 12V and 24V systems
D
G
S
Symbol Parameter Ratings Units
V
DSS
V
GS
Drain to Sou r c e Voltage 60 V
Gate to Source Voltage ±20 V
Drain Curr e nt
I
D
Continuous (T
Continuous (T
< 153oC, VGS = 10V)
C
= 25oC, VGS = 10V, with R
amb
= 43oC/W) 22 A
θJA
80 A
Pulsed Figure 4 A
E
AS
P
D
, T
T
J
STG
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy (Note 1) 625 mJ
Power dissipation 310 W
Derate above 25
o
C2.07W/
Operating and Storage Temperature -55 to 175
o
C
o
C
Thermal Characteristics
R
θJC
R
θJA
R
θJA
This product has been designed to meet the extreme test conditions and environment demanded by the automotive
All Fairchild Semiconductor products are manufactured, assembled and tested under ISO9000 and QS9000 quality
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
ThermalResistance Junctionto Case TO-263 0.48
ThermalResistance Junctionto Ambient TO-263, (Note 2) 62
ThermalResistanceJunctionto AmbientTO-263,1in2copper pad area 43
industry. For a copy of the requirements, see AEC Q101 at: http://www.aecouncil.com/
Reliability data can be found at: http://www.fairchildsemi.com/products/discrete/reliability/index.html.
systems certification.
FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
o
C/W
o
C/W
o
C/W
Page 2
Package Marking and Ordering Information
Device Marking Device Package Reel Size Tape Width Quantity
FDB035AN06A0 FDB035AN06A0 TO-263AB 330mm 24mm 800 units
FDB035AN06A0
Electrical Characteristics
TC = 25°C unless otherwise noted
Symbol Parameter Test Con ditions Min Typ Max Units
Off Characteristics
B
I
DSS
I
GSS
VDSS
Drain to Sou r c e Br ea k down Voltage ID = 250µA, VGS = 0V 60 - - V
V
= 50V - - 1
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current
DS
= 0V TC = 150oC- -250
V
GS
Gate to Source Leakage Current VGS = ±20V - - ±100 nA
On Characteristics
V
GS(TH)
r
DS(ON)
Gate to Source Threshold Voltage VGS = VDS, ID = 250µA2-4V
I
= 80A, VGS = 10V - 0.0032 0.0035
D
I
= 40A, VGS = 6V - 0.0044 0.0066
Drain to S ou r c e On Re si st ance
D
I
= 80A, VGS = 10V,
D
T
= 175oC
J
- 0.0065 0.0071
Dynamic Characteristics
C
C
C
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
ISS
OSS
RSS
g(TOT)
g(TH)
gs
gs2
gd
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance - 1123 - pF
Reverse Transfer Capacitance - 367 - pF
= 25V, VGS = 0V,
V
DS
f = 1MHz
Total Gate Charge at 10V VGS = 0V to 10V
Threshold Gate Charge VGS = 0V to 2V - 12 15 nC
Gate to Source Gate Charg e - 30 - nC
Gate Charge Threshold to Plateau - 18 - nC
V
DD
I
= 80A
D
I
= 1.0m A
g
= 30V
Gate to Drain “Miller” Charge - 24 - nC
- 6400 - pF
95 124 nC
µA
Ω
Switching Characteristics
t
ON
t
d(ON)
t
r
t
d(OFF)
t
f
t
OFF
Turn-On Time
Turn-On Delay Time - 15 - ns
Rise Time - 93 - ns
Turn-Off D elay Time - 38 - ns
Fall Time - 13 - ns
Turn-Off Time - - 75 ns
(VGS = 10V)
= 30V, ID = 80A
V
DD
V
= 10V, RGS = 2.4Ω
GS
--163ns
Drain-Source Diode Characteristics
I
= 80A - - 1.25 V
V
SD
t
rr
Q
RR
Notes:
1: Starting T
2: Pulse Width = 100s
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Source to Drain Diode V oltage
Reverse Recovery Time ISD = 75A, dISD/dt = 100A/µs- -38ns
Reverse Recovered Charge ISD = 75A, dISD/dt = 100A/µs- -39nC
= 25°C, L = 0.255mH, IAS = 70A.
J
SD
= 40A - - 1.0 V
I
SD
Page 3
FDB035AN06A0
Typical Characteristics T
= 25°C unless otherwise noted
C
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
POWER DISSIPATION MULTIPLIER
0
0255075100 175
125
TC, CASE TEMPERATURE (oC)
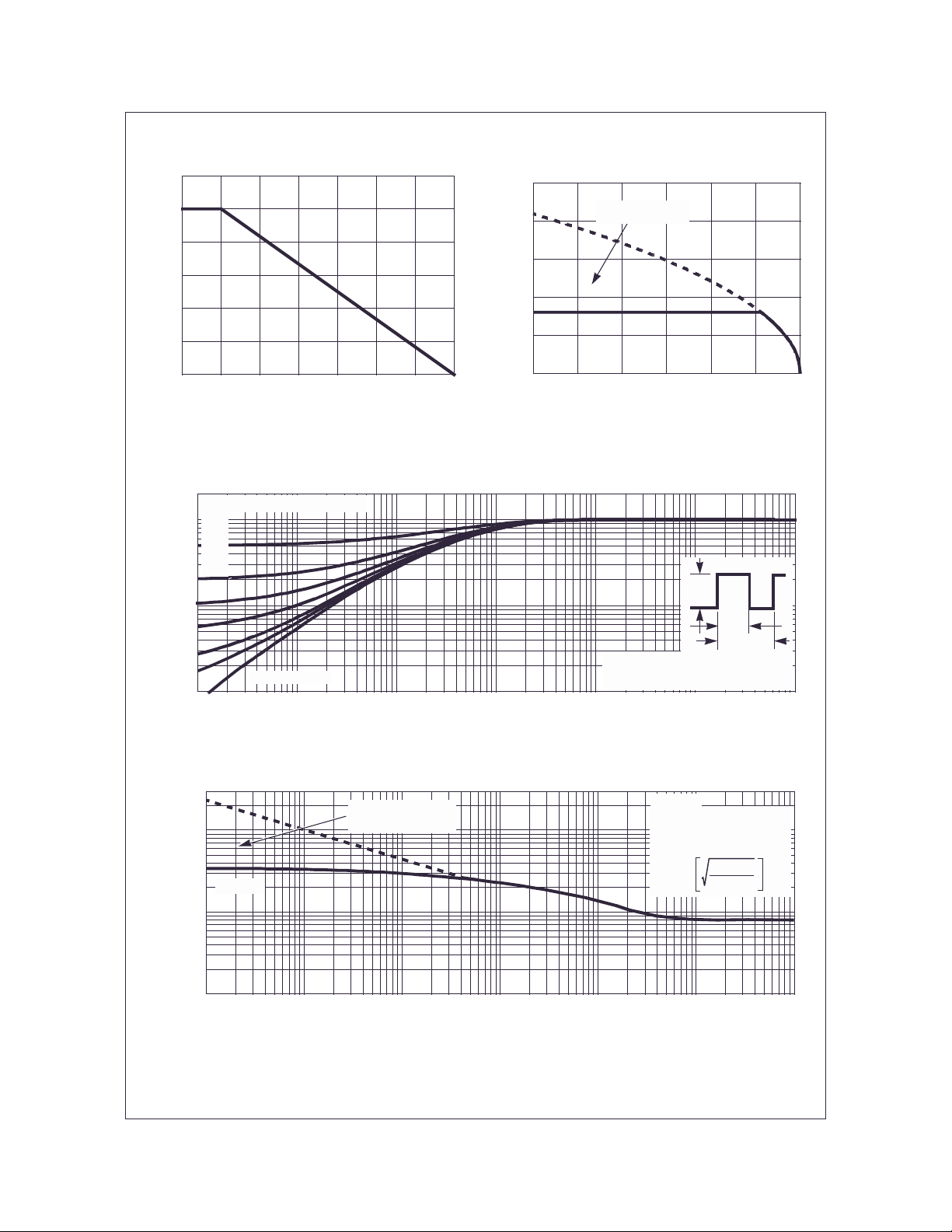
Figure 1. Normalized Power Dissipation vs
Ambient Temperature
2
DUTY CYCLE - DESCENDING ORDER
0.5
1
0.2
0.1
0.05
0.02
0.01
0.1
, NORMALIZED
θJC
Z
THERMAL IMPEDANCE
0.01
-5
10
SINGLE PULSE
-4
10
10
250
200
150
100
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
I
50
0
150
25 50 75 100 125 150 175
Figure 2. Maximum Continuous Drain Curr ent vs
-3
t, RECTANGULAR PULSE DURATION (s)
-2
10
CURRENT LIMITED
BY PACKAGE
TC, CASE TEMPERATURE (oC)
Case Temperature
P
DM
NOTES:
DUTY FACTOR: D = t
PEAK TJ = PDM x Z
-1
10
θJC
10
1/t2
0
x R
θJC
t
+ T
1
t
2
C
1
10
Figure 3. Normalized Maximum Transient Thermal Impedance
3000
TRANSCONDUCTANCE
MAY LIMIT CURRENT
1000
IN THIS REGION
VGS = 10V
100
, PEAK CURRENT (A)
DM
I
10
-5
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
10
t, PULSE WIDTH (s)
TC = 25oC
FOR TEMPERATURES
o
ABOVE 25
C DERATE PEAK
CURRENT AS FOLLOWS:
175 - T
I = I
25
10
C
150
0
1
10
Figure 4. Peak Current Capability
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Page 4
FDB035AN06A0
Typical Characteristics T
2000
1000
100
OPERATION IN THIS
AREA MAY BE
10
LIMITED BY r
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
I
1
SINGLE PULSE
TJ = MAX RATED
T
= 25oC
C
0.1
1 10 100
DS(ON)
V
, DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
DS
= 25°C unless otherwise noted
C
10µs
100µs
1ms
DC
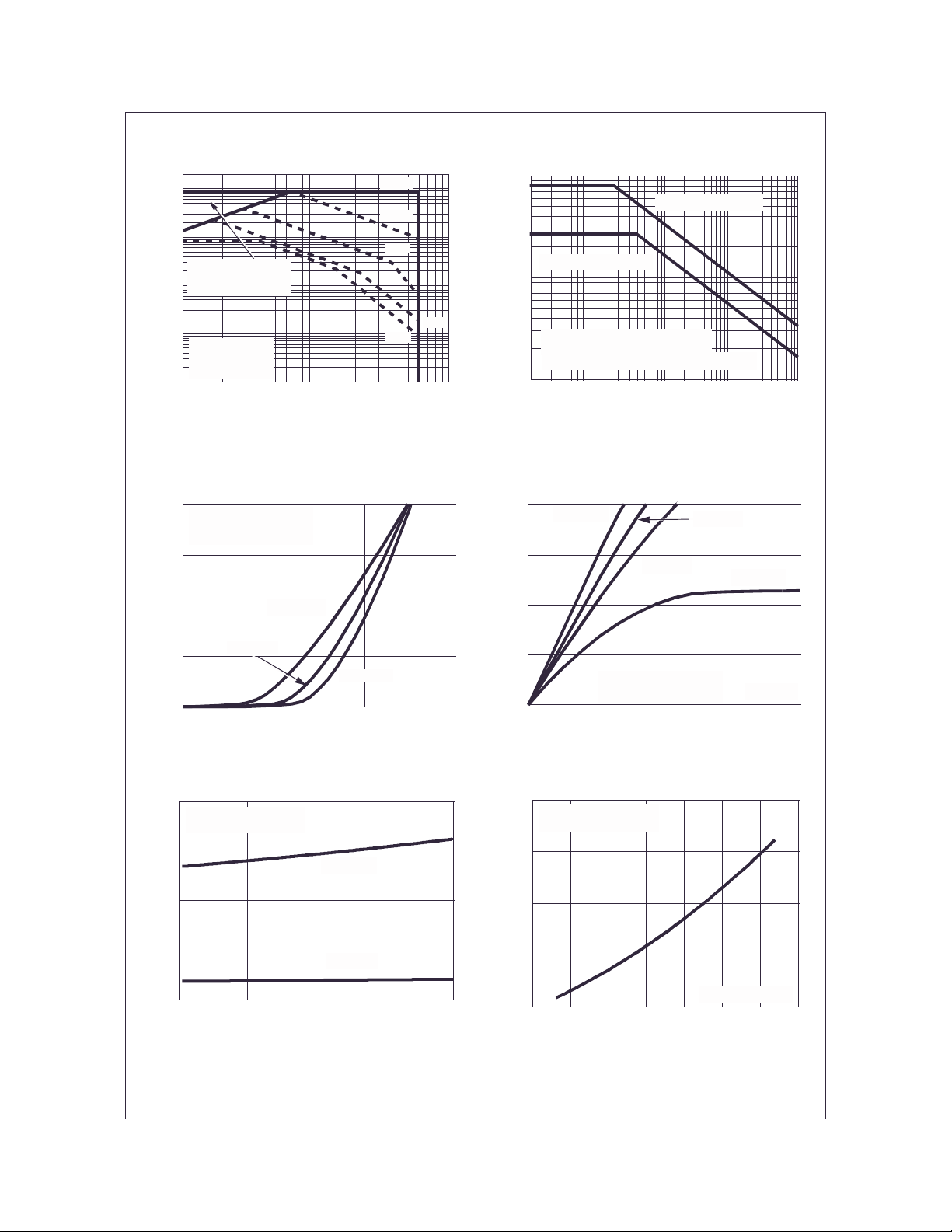
Figure 5. Forward Bias Safe Operating Area
160
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
V
= 15V
DD
120
10ms
100
STARTING TJ = 25oC
STARTING TJ = 150oC
10
, AVALANCHE CURRENT (A)
I
If R = 0
tAV = (L)(IAS)/(1.3*RATED BV
AS
If R ≠ 0
t
= (L/R)ln[(IAS*R)/(1.3*RATED BV
AV
1
0.01 0.1 1 10 100
tAV, TIME IN AVALANCHE (ms)
DSS
- VDD)
DSS
- VDD) +1]
NOTE: Refer to Fairchild Application Notes AN7514 and AN7515
Figure 6. Unclamped Inductive Switching
Capability
160
120
VGS = 20V
VGS = 6V
VGS = 10V
VGS = 5V
80
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
I
40
0
3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6
TJ = 175oC
TJ = 25oC
TJ = -55oC
VGS, GATE TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 7. Transfer Characteristics Figure 8. Saturation Characteristics
5
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
VGS = 6V
4
VGS = 10V
DRAIN TO SOURCE ON RESISTANCE(mΩ)
3
0 20406080
I
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
Figure 9. Drain to So urce On Resistanc e v s Drai n
Current
80
, DRAIN CURRENT (A)
D
I
40
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5
2.5
PULSE DURATION = 80µs
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
2.0
1.5
ON RESISTANCE
1.0
NORMALIZED DRAIN TO SOURCE
0.5
-80 -40 0 40 80 120 160 200
DUTY CYCLE = 0.5% MAX
VDS, DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (oC)
TC = 25oC
VGS = 10V, ID =80A
Figure 10. Normalized Drain to Source On
Resistance vs Junction Temperature
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Page 5

FDB035AN06A0
Typical Characteristics T
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
NORMALIZED GATE
THRESHOLD VOLTAGE
0.4
0.2
-80 -40 0 40 80 120 160 200
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (oC)
= 25°C unless otherwise noted
C
VGS = VDS, ID = 250µA
Figure 11. Normalized G ate Threshol d Voltage vs
Junction Temperatur e
10000
C
= CGS + C
C
≅ C
+ C
OSS
DS
GD
1000
C, CAPACITANCE (pF)
C
= C
RSS
GD
V
= 0V, f = 1MHz
GS
100
0.1 1 10 60
VDS, DRAIN TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
ISS
GD
1.2
ID = 250µA
1.1
1.0
BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE
NORMALIZED DRAIN TO SOURCE
0.9
-80 -40 0 40 80 120 160 200
T
, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (oC)
J
Figure 12. Normalized Drain to Source
Breakdown Voltage vs Junction Temperature
10
VDD = 30V
8
6
4
WAVEFORMS IN
2
, GATE TO SOURCE VOLTAGE (V)
GS
V
0
0 25 50 75 100
Qg, GATE CHARGE (nC)
DESCENDING ORDER:
ID = 80A
= 40A
I
D
Figure 13. Capacitance vs Drain to Sour ce
Voltage
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Figure 14. Gat e Charge Waveforms for Constant
Gate Current
Page 6

Test Circuits and Waveforms
V
DS
L
TO OBTAIN
VARY t
P
REQUIRED PEAK I
V
GS
R
AS
G
+
V
DD
-
I
AS
DUT
t
0V
P
I
AS
0.01Ω
0
Figure 15. Unclamped Energy Test Circuit Figure 16. Unclamped Energy Wavef orm s
V
DS
V
DD
V
Q
I
g(REF)
L
V
GS
DUT
+
V
DD
-
V
GS
0
I
g(REF)
= 2V
Q
gs2
Q
g(TH)
Q
gs
0
Figure 17. Gate Charge Test Circuit Figure 18. Gate Charge Waveforms
BV
DSS
t
P
t
AV
Q
g(TOT)
DS
gd
V
GS
FDB035AN06A0
V
DS
V
DD
V
= 10V
GS
V
DS
R
L
V
GS
R
GS
V
GS
DUT
+
V
DD
-
V
DS
0
V
GS
10%
0
t
d(ON)
90%
t
ON
t
r
t
d(OFF)
t
OFF
t
f
90%
10%
10%
90%
PULSE WIDTH
50%50%
Figure 19. Switching Time Test Circuit Figure 20. Switching Time Waveforms
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Page 7

Thermal Resistance vs. Mounting Pad Area
80
The maximum rated junction temperature, TJM, and the
thermal resistance of the heat dissipating path determines
the maxi mum al lowab le de vice p ower di ssip ation, P
application. Therefore the application’s ambient
temperature, T
must be reviewed to ensure that T
Equation 1 mathematically represents the relationship and
(oC), and th ermal res istance R
A
is never exceeded.
JM
serve s as the basis for establ ishing the rating of the part.
TJMTA–()
P
----------------- ------------=
DM
R
θJA
DM
(oC/W)
θJA
(EQ. 1)
, in an
60
C/W)
o
(
θJA
R
40
R
= 26.51+ 19.84/(0.262+Area) EQ.2
θJA
R
= 26.51+ 128/(1.69+Area) EQ.3
θJA
FDB035AN06A0
In using surface mount devices such as the TO-263
package, the environment in which it is applied will have a
significant influence on the part’s current and maximum
power d issipati on rating s. Precise d etermin ation of P
comple x and influenced by many factors:
DM
is
1. Mou nting pad area ont o which the device is attached and
whet her the re is copp er on one s ide or both side s of the
board.
2. The number of copper layers and the thickness of the
board.
3. The use of external heat sinks.
4. The use of thermal vias.
5. Air flow and board orientation.
6. For no n steady state applic ations, th e pulse widt h, the
duty cycle and the transient thermal response of the part,
the boa rd and the environment they are in.
Fairchild provides thermal information to assist the
designer’s preliminary application evaluation. Figure 21
defines the R
copper (component side) area. This is for a horizontally
for the device as a function of the top
θJA
positi on ed FR-4 board w ith 1oz c o pp er after 1 00 0 se c onds
of stea dy st ate pow er w ith n o air flow . Th is gr aph prov ides
the necessary inf ormation for calculation of the steady state
junction temperature or power dissipation. Pulse
applications can be evaluated using the Fairchild device
Spice t hermal model or manu ally utilizing the no rmalized
maximum transient thermal impedance curve.
20
1100.1
(0.645) (6.45) (64.5)
AREA, TOP COPPER AREA in2 (cm2)
Figure 21. Thermal Resistance vs Mounting
Pad Area
Therma l resi stances correspondi ng to other copper areas
can be obtained from Figure 21 or by calculation using
Equation 2 or 3. Equation 2 is used for copper area defined
in inch es squ are and equ ation 3 is for area in cent imeters
square. The area, in square inches or square centimeters is
the top copper area including the gate and source pads.
19.84
26.51
=
R
θJA
26.51
=
R
θJA
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
-------------------------------------+
0.262 Area+()
Area in Inches Squared
128
----------------------------------+
1.69 Area+()
Area in Centimeters Squared
(EQ. 2)
(EQ. 3)
Page 8

PSPICE Electrical Model
.SUBCKT FDB035AN06A0 2 1 3 ; rev July 04, 2002
Ca 12 8 1.5e-9
Cb 15 14 1.5e-9
Cin 6 8 6.1e-9
Dbod y 7 5 DbodyMOD
Dbreak 5 11 Db reakMOD
Dplcap 10 5 DplcapMOD
Ebreak 11 7 17 18 69.3
Eds 14 8 5 8 1
Egs 13 8 6 8 1
Esg 6 10 6 8 1
Evthres 6 21 19 8 1
Evtemp 20 6 18 22 1
It 8 17 1
Lgat e 1 9 4.81e-9
Ldrain 2 5 1.0e -9
Lsource 3 7 4.63e-9
RLgate 1 9 48.1
RLdr ai n 2 5 10
RLsource 3 7 46.3
Mmed 16 6 8 8 M m edMOD
Mstro 16 6 8 8 MstroMOD
Mweak 16 21 8 8 MweakMOD
Rbreak 17 18 RbreakMOD 1
Rdrain 50 16 RdrainMOD 1e-4
Rgate 9 20 1.36
RSLC1 5 51 RSL CM OD 1e-6
RSLC2 5 50 1e3
Rsource 8 7 RsourceMOD 2.5e-3
Rvthres 22 8 RvthresMO D 1
Rvtemp 18 19 RvtempMOD 1
S1a 6 12 13 8 S1AMOD
S1b 13 12 13 8 S1BM OD
S2a 6 15 14 13 S2AM OD
S2b 13 15 14 13 S2BM OD
Vbat 22 19 DC 1
GATE
1
LGATE
RLGATE
RGATE
9
CA
ESG
+
EVTEMP
+
-
18
22
20
S1A
12
13
8
S1B
EGS EDS
-
13
10
6
8
+
+
RSLC2
6
S2A
14
13
S2B
6
8
-
-
DPLCAP
EVTHRES
+
19
8
CIN
15
CB
-
+
-
5
51
5
51
21
MSTRO
14
5
8
RSLC1
+
ESLC
50
RDRAIN
16
8
MMED
8
DBREAK
11
+
17
EBREAK
18
-
MWEAK
RSOURCE
RBREAK
17 18
IT
RVTHRES
7
RVTEMP
19
-
+
22
LDRAIN
RLDRAIN
DBODY
LSOURCE
RLSOURCE
VBAT
DRAIN
2
SOURCE
3
FDB035AN06A0
ESLC 51 50 VALUE = {(V(5,51)/ ABS(V(5,51)))*(PWR (V (5,51)/(1 e-6*250),10) )}
.MODEL DbodyMOD D (IS=2.4E-11 N=1.04 R S=1.65e-3 TRS1=2.7e-3 TRS2=2e-7
+ CJO=4.35e-9 M=5.4e-1 TT=1e-9 XTI=3.9)
.MODEL DbreakMOD D (RS= 1.5e-1 TRS1=1e-3 TRS2=-8.9e-6)
.MODEL DplcapMOD D (CJO=1.7e-9 IS=1e-30 N=10 M=0.47)
.MODEL MmedMOD NMOS (VTO=3.3 KP=9 IS=1e-30 N=10 TOX=1 L=1u W=1u RG=1.36 T_abs=25)
.MODEL Mstro M OD NMOS (VTO=4.00 KP=275 IS=1e-30 N=10 TOX=1 L=1u W=1u T_abs=25)
.MODEL Mwe akMOD NMOS (VTO=2.72 KP=0. 03 IS=1e-30 N=10 T O X = 1 L=1u W=1u RG=13. 6 RS=0.1 T_ab s=25)
.MODEL Rb reakMOD RES (T C1=9e-4 TC2= -9e-7)
.MODEL Rd rai nMOD RES (TC 1 =4e-2 TC2=1.75 e-4)
.MODEL RSLCMOD RES (TC1=1e-3 TC2=1e-5)
.MODEL RsourceMOD RES (TC1=5e-3 TC2=1 e-6)
.MODEL RvthresMOD RES (T C1=-6.7e-3 TC2=-1.5e-5)
.MODEL RvtempMOD RES (T C1=-2.5e-3 TC 2=1e-6)
.MODEL S1AMOD VSWITC H (RON =1e - 5 ROFF= 0. 1 VON=- 4 VOFF =-1 .5 )
.MODEL S1BMOD VSWITC H (RON= 1e- 5 ROFF = 0.1 VON= - 1.5 VO FF=- 4)
.MODEL S2AMOD VSWITC H (RON= 1e- 5 ROFF = 0.1 VON= - 1 VOFF =0.5)
.MODEL S2BMOD VSWITC H (RON= 1e- 5 ROFF = 0.1 VON= 0 .5 VOFF= -1) .
ENDS
Note: For further discussion of the PSPICE model, consult A New PSPICE Sub-Circuit for the Power MOSFET Featuring Global
Temperature Options; IEEE Power Electronics Specialist Conference Records, 1991, wri t ten by William J. Hepp and C. Frank
Wheatley.
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Page 9

SABER Electrical Model
rev July 4, 2002
template FDB035AN06A0 n2,n1,n3 = m_temp
electrical n2,n1,n3
number m_temp=25
{
var i iscl
dp..model dbodymod = (isl=2.4e-11,nl=1.04,rs=1.65e-3,trs1=2.7e-3,trs2=2e-7,cjo=4.35e-9,m=5.4e-1,tt=1e-9,xti=3.9)
dp..model dbreakmod = (rs=1.5e-1,trs1=1 e-3,trs2=-8.9e-6)
dp..m odel dpl capmod = (cjo=1.7 e-9,isl= 10e-3 0,nl=10 , m = 0.47)
m..model mmedmod = (type=_n,vto=3.3,kp=9,is=1e-30, tox=1)
m..model mstrongmod = (type=_n,vto=4.00,kp=275,is=1e-30, tox=1)
m..model mweakmod = (type=_n,vto=2.72,kp=0.03,is=1e-30, tox=1,rs=0.1)
sw_vcsp.. mo del s1amod = (ron=1e-5,roff=0.1, von=-4,voff=-1.5)
sw_vcsp.. mo del s1bmod = (ron=1e-5,roff=0.1, von=-1.5,voff=-4)
sw_vcsp.. mo del s2amod = (ron=1e-5,roff=0.1, von=-1,voff=0.5)
sw_vcsp.. mo del s2bmod = (ron=1e-5,roff=0.1, von=0.5,voff=-1)
c.ca n12 n8 = 1.5e -9
c.cb n15 n14 = 1.5e-9
c.cin n6 n8 = 6.1e -9
dp.dbody n7 n5 = model=dbodym od
dp.dbreak n5 n11 = model=dbreakmod
dp.dplcap n10 n5 = model=dplca pm od
spe.ebreak n11 n7 n17 n18 = 69.3
GATE
spe.eds n14 n8 n5 n8 = 1
spe.egs n13 n8 n6 n8 = 1
LGATE
1
RLGATE
9
RGATE
ESG
EVTEMP
+
18
22
20
spe.esg n6 n10 n6 n8 = 1
spe.evthres n6 n21 n19 n8 = 1
spe.evtemp n20 n6 n18 n22 = 1
CA
S1A
12
S1B
i.it n8 n17 = 1
l.lgate n1 n9 = 4.81e-9
l.ldrain n2 n5 = 1.0e-9
l.lsource n3 n7 = 4.63e-9
res.rlgate n1 n9 = 48.1
res.rldrai n n2 n5 = 10
res.rlsource n3 n7 = 46.3
m.mmed n16 n6 n8 n8 = m odel=mmedmod, temp=m_temp, l =1u, w=1u
m.mstrong n16 n6 n8 n8 = model=mstrongmod, temp=m_temp, l=1u, w=1u
m.mweak n16 n21 n8 n8 = model=mweakmod, temp=m_temp, l=1u, w=1u
DPLCAP
10
RSLC2
6
8
EVTHRES
+
+
19
8
6
-
S2A
13
14
8
13
S2B
13
+
+
6
EGS EDS
8
-
-
15
CIN
CB
-
+
-
5
MSTRO
14
5
8
RSLC1
51
ISCL
50
RDRAIN
16
21
8
MMED
8
DBREAK
11
MWEAK
EBREAK
+
-
RSOURCE
RBREAK
17 18
IT
RVTHRES
17
18
7
RVTEMP
19
-
+
22
RLSOURCE
LDRAIN
RLDRAIN
DBODY
LSOURCE
VBAT
DRAIN
2
SOURCE
3
FDB035AN06A0
res.rbreak n17 n18 = 1, tc1=9e-4, tc 2=-9e-7
res.rdrain n50 n16 = 1e-4, tc1=4 e-2,tc2=1.75 e-4
res.rgate n9 n20 = 1.36
res.rslc1 n5 n51 = 1e-6, tc1=1e -3, tc2=1e-5
res.rslc2 n5 n50 = 1e3
res.rsour ce n8 n7 = 2.5e-3, tc1=5e-3,tc2=1e-6
res.rvthres n22 n8 = 1, tc1=-6.7e-3,tc2=-1. 5e-5
res.rvtemp n18 n19 = 1, tc1=-2.5e-3,tc2=1e-6
sw_vcsp.s1 a n6 n12 n13 n8 = model= s1amod
sw_vcsp.s1 b n13 n12 n13 n8 = model =s1bmod
sw_vcsp.s2 a n6 n15 n14 n13 = model =s2amod
sw_vcsp.s2 b n13 n15 n14 n13 = model =s2bmod
v.vbat n22 n19 = dc=1
equations {
i (n51->n50) +=iscl
iscl: v(n51,n50) = ((v(n5,n51)/(1e-9+abs(v(n5,n51))))*((abs(v(n5,n51)*1e6/250 ))** 10))
}
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Page 10

PSPICE Thermal Model
REV 23 July 4, 2002
FDB035AN06A0T
CTHERM1 TH 6 6.45e-3
CTHERM2 6 5 3e-2
CTHERM3 5 4 1. 4e-2
CTHERM4 4 3 1. 65e-2
CTHERM5 3 2 4. 85e-2
CTHERM6 2 TL 1e-1
RTHERM1 TH 6 3.24e-3
RTHERM2 6 5 8. 08e-3
RTHERM3 5 4 2. 28e-2
RTHERM4 4 3 1e-1
RTHERM5 3 2 1. 1e-1
RTHERM6 2 TL 1.4e-1
SABER Thermal Model
RTHERM1
RTHERM2
FDB035AN06A0
JUNCTION
th
CTHERM1
6
CTHERM2
5
SABER therm al m odel F DB035AN06A0T
template thermal_model th tl
thermal_ c th , tl
{
ctherm.c t herm1 th 6 =6.45e-3
ctherm.ctherm2 6 5 =3e-2
ctherm.ctherm3 5 4 =1.4e-2
ctherm.ctherm4 4 3 =1.65e-2
ctherm.ctherm5 3 2 =4.85e-2
ctherm.ctherm6 2 tl =1e-1
rtherm.rtherm1 th 6 =3.24e-3
rtherm.rtherm2 6 5 =8.08e-3
rtherm.rtherm3 5 4 =2.28e-2
rtherm.rtherm4 4 3 =1e-1
rtherm.rtherm5 3 2 =1.1e-1
rtherm.rtherm6 2 tl=1.4e-1
RTHERM3
RTHERM4
RTHERM5
RTHERM6
CTHERM3
4
CTHERM4
3
CTHERM5
2
CTHERM6
CASE
tl
©2002 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation FDB035AN06A0 Rev. A
Page 11

TRADEMARKS
The following are registe red and unr egistered trademarks Fairchild Semiconductor owns or is aut horized to use and is not
intended to be an exhaustive list of all such trademarks.
ACEx™
ActiveArray™
Bottomless™
CoolFET™
CROSSVOLT™
DOME™
EcoSPARK™
2
E
CMOS™
EnSigna™
FACT™
FACT Quiet Series™
®
FAST
FASTr™
FRFET™
GlobalOptoisolator™
GTO™
HiSeC™
2
I
C™
Across the board. Around the world.™
The Power Franchise™
ImpliedDisconnect™
ISOPLANAR™
LittleFET™
MicroFET™
MicroPak™
MICROWIRE™
MSX™
MSXPro™
OCX™
OCXPro™
OPTOLOGIC
®
OPTOPLANAR™
PACMAN™
POP™
Power247™
PowerTrench
®
QFET™
QS™
QT Optoelectronics™
Quiet Ser ies™
RapidConfigure™
RapidConnect™
SILENT SWITCHER
SMART START™
SPM™
Stealth™
SuperSOT™-3
SuperSOT™-6
SuperSOT™-8
SyncFET™
TinyLogic™
TruTranslation™
UHC™
UltraFET
®
VCX™
®
DISCLAIMER
FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MAKE CHANGES WITHOUT FURTHER NOTICE TO ANY
PRODUCTS HEREIN TO IMPROVE RELIABILITY, FUNCTION OR DESIGN. FAIRCHILD DOES NOT ASSUME ANY
LIABILITY ARISING OUT OF THE APPLICATION OR USE OF ANY PRODUCT OR CIRCUIT DESCRIBED HEREIN;
NEITHER DOES IT CONVEY ANY LICENSE UNDER ITS PATENT RIGHTS, NOR THE RIGHTS OF OTHERS.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
FAIRCHILD’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR
CORPORATION.
As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems
which, (a) ar e int ende d fo r s urgic al i mpla nt into the bo dy,
or (b) support or sustain life, or (c) whose failure to perform
when properly used in accordance with instructions for use
provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to
result in significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life support
device or system whose failure to perform can be
reasonably expected to cause the failure of the life support
device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
PRODUCT STATUS DEFINITIONS
Definition of Terms
Datasheet Identification Product Status Definition
Adva nce Information Formative or I n
Design
Preliminary First Production This datasheet contains preliminary data, and
No Identification Needed Full Production This datasheet contains final specifications. Fairchild
Obsolete Not In Production This datasheet contains specifications on a product
This datasheet contains the design specifications for
product development. Specifications may change in
any manner without notice.
supple m entary data will be published at a later dat e.
Fairchild Semiconductor reserves the right to make
changes at any time without notice in order to improve
design.
Semiconductor reserves the righ t to make chan ges at
any time without notice in order to improve design.
that has been discontinued b y Fairchild semico nductor.
The datasheet is printed for reference information only.
Rev. I
 Loading...
Loading...