Page 1

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
D10590-01
October 2009
DASCOM Europe GmbH
Heuweg 3
D-89079 Ulm
Germany
www.dascom.com
E-mail: support.de@dascom.com or
support.gb@dascom.com
Page 2

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Introduction
Table of Contents
1 Preface............................................................................................................................................3
1.1.1 FSL Features...................................................................................................... 3
2 Introduction to FSL Feature .........................................................................................................4
2.1 FSL Concept.......................................................................................................................5
2.2 The Escape Character........................................................................................................ 5
2.2.1 Defining temporary escape character ................................................................. 6
2.2.2 Removing temporary escape character ..............................................................6
2.2.3 Defining a permanent escape character .............................................................7
2.2.4 Removing a permanent escape character ..........................................................7
Appendix A. Supported Coax FSL Functions - For Printer Driver = PCL5.....................................8
Appendix B. FSL Coax Quick Reference - For Printer Driver = PCL5........................................... 10
Appendix C. Supported Coax FSL Functions - For Printer Driver = Matrix..................................21
Appendix D. FSL Coax Quick Reference - For Printer Driver = Matrix .........................................23
Appendix E. Supported TN5250e FSL Functions - For Printer Driver = PCL5............................. 30
Appendix F. FSL TN5250e Quick Reference - For Printer Driver = PCL5..................................... 32
Appendix G. Supported TN5250e FSL Functions - For Printer Driver = Matrix ...........................36
Appendix H. FSL TN5250e Quick Reference - For Printer Driver = Matrix ...................................37
Appendix I. Test printout ....................................................................................................................39
Appendix J. Abbreviations.................................................................................................................40
2
Page 3

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Introduction
1 Preface
The FSL features are used with SCS or DCA sessions in the Print Server.
The TN3270e or the TN5250e protocols are used for these sessions and the
input and output parameters are selectable via PrintGuide.
The SCS/DCA datastream transforms are add-on features to the standard Print
Server.
NOTE:
As this manual deals only with functions and operations related to the FSL
features, you are referred to the other manuals supplied with the product for
additional information as to the general and advanced operation of the Print
Server.
1.1.1 FSL Features
There are 4 different levels of FSL features depending on the attached host
system and on the type of the attached printer:
− In the IBM 3270 environment the Print Server supports convertion of
SCS datastream received via TN3270e and TCP/IP. The FSL
features depend on whether the connected printer is a PCL5 Laser
printer or a Matrix/Line printer.
− In the IBM 5250 environment the Print Server supports convertion of
SCS/DCA datastream received via TN5250e and TCP/IP. The FSL
features depend on whether the connected printer is a PCL5 Laser
printer or a Matrix/Line printer.
NOTE: The TCP/IP protocol must be installed and configured for Telnet
sessions.
3
Page 4

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Introduction
2 Introduction to FSL Feature
With your Print Server FSL features, you will be able to emulate legacy data
applications processed in coax or twinax environments that contain FSL
sequences as well as the same applications running in a LAN environment
NOTE:
In the Appendix sections you will find details on the specific subsets of FSL
functions supported in the original Coax and Twinax environments. Moreover,
you are provided with a quick set-up reference to the supported functions,
including syntax and supported parameters.
4
Page 5

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Introduction
2.1 FSL Concept
Function Selection via the Line (FSL) sequences are special commands used for
downloading of settings.
The syntax of an FSL command is shown below.
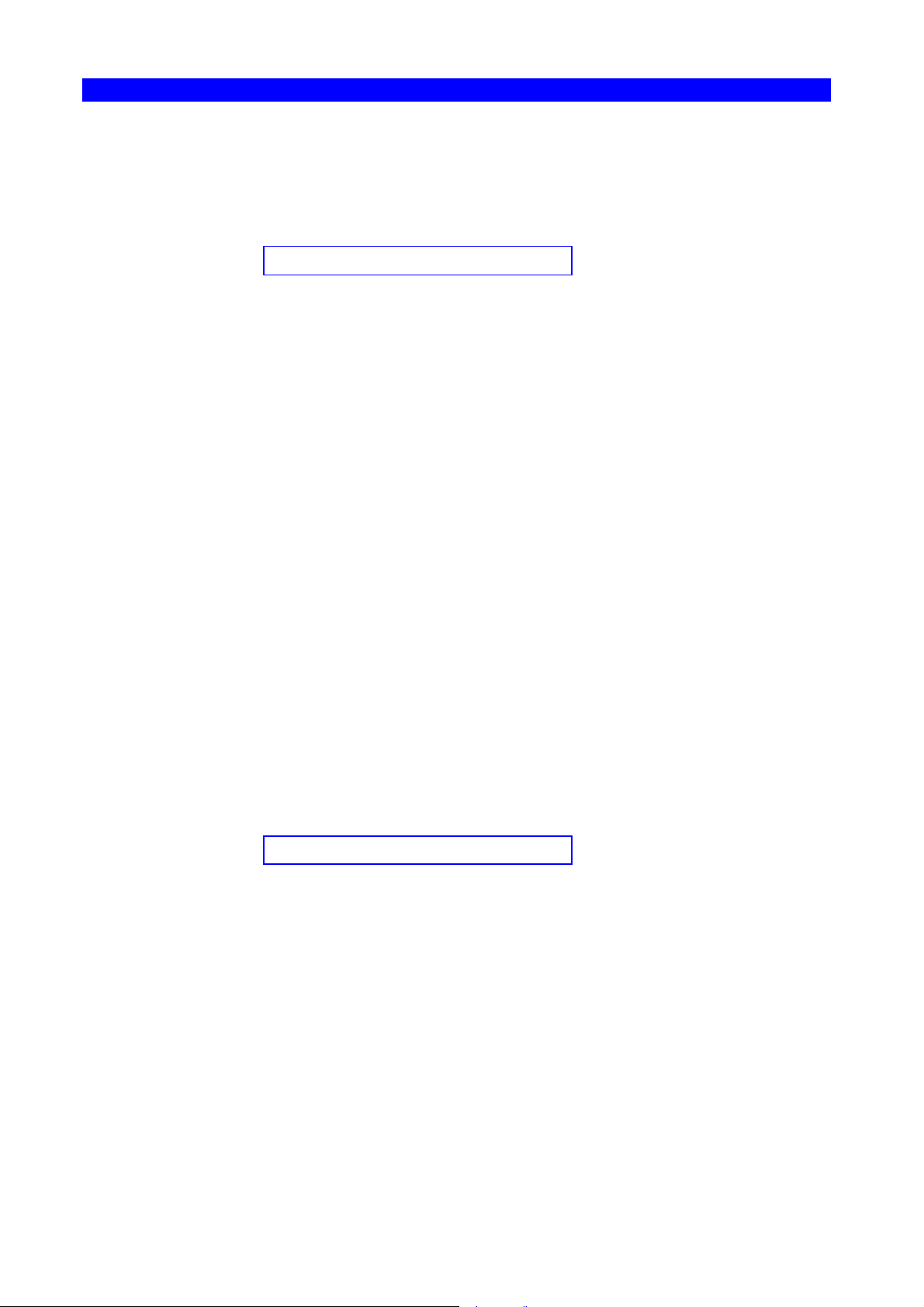
"%" is the defined escape character (i.e. ESC character). See Figure 1 for
definition of an escape character.
%Y<Function number>, <parameter>%
Figure 1, Defining the escape character
When you send the FSL syntax via the line, the "Y" and the following number will
select an FSL Function.
All spaces and IBM control codes between the leading and the trailing ESC
characters will be ignored.
The FSL Functions are used for setting up the printer to special applications, to
carry out a special print job, or to gain access to special facilities in the printer.
NOTE:
Functions not saved using “<ESC>X1” will apply for the actual job only.
2.2 The Escape Character
If you wish to program the FSL top, you must first define an ESC character.
An ESC character is a signal to the interface that the characters following the
ESC character form a command sequence.
Once a character has been defined as the ESC character, it cannot be printed or
used as a normal character. However, it is not necessary to have an ESC
character defined permanently. When the ESC character has served its purpose,
it can be deleted.
5
Page 6
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Introduction
2.2.1 Defining temporary escape character
No ESC character has been defined from the factory.
If you wish to change the settings from the host system, you will have to define
an ESC character. See below how to define "%" as the temporary ESC character.
Figure 2, Defining "%" as a temporary ESC character.
The five characters shown should be sent to the printer from the host system.
The ESC character is not defined permanently. When the power is turned off, it
will be lost. If you wish to save the defined ESC character you must define it as a
permanent escape character. (See section 2.2.3,)
NOTE:
The characters "," ";" and ":" must never be used as ESC character, as they
are used as separators in escape sequences and will give unpredictable
printing results.
The same applies to 0-9, A-F, a-f and K,S,T,X,Y,Z, simple quote ('), & and
?. These must not be used as escape characters.
Avoid using your national characters as escape characters.
The following EBCDIC HEX codes have been defined as national language
characters and must not be used as ESC characters:
4A 4C 4F 5A 5F 6A 79 7B 7C 7F A1 C0 D0 E0
&&??%
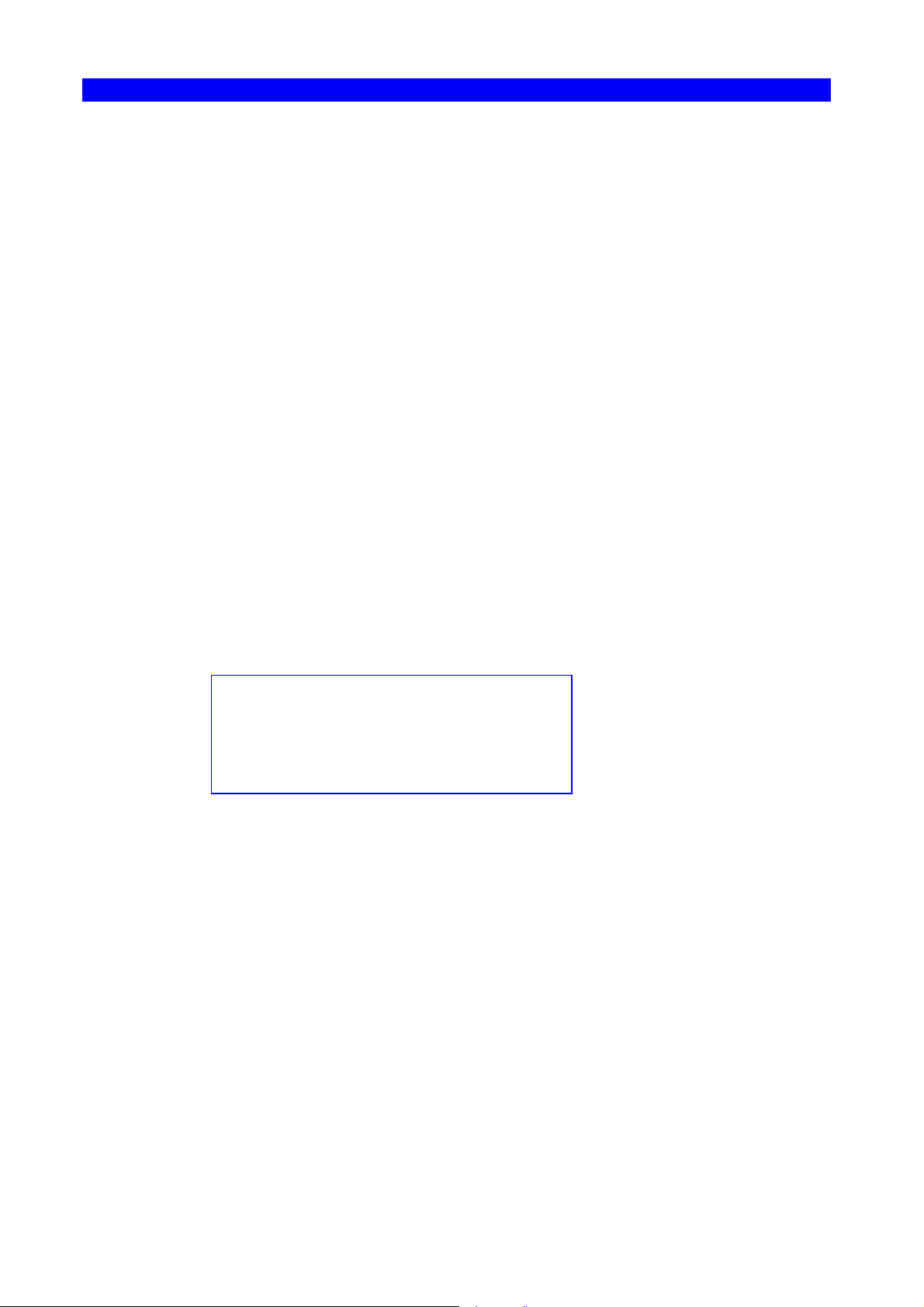
2.2.2 Removing temporary escape character
If you wish to remove the temporary escape character in order to use that
character as a printable character, you can define it as a space.
Figure 3, Removing the temporary ESC character .
&&??<space>
6
Page 7
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Introduction
2.2.3 Defining a permanent escape character
If you wish to define and save a permanent ESC character, you will have to
define a temporary escape character, use Function Y48, (Select Permanent
Escape Character) and save the settings in the permanent memory by the
command (ESC) X1 before powering off.
You can define the permanent ESC character using the apostrophe notation,
e.g.
%Y48,'<'%
NOTE:
If the character used in Function Y48, Select Permanent Escape Character, is
different from the one specified as temporary ESC character, the latest specified
character will take precedence immediately after you have defined Function Y48.
2.2.4 Removing a permanent escape character
The permanent ESC character may be removed again in the following way:
1. Set Function Y48, Select Permanent Escape Character, to ' ' ('space' or
No ESC character).
2. Define a new temporary ESC character as described above.
3. Save the settings using the command "<ESC> X1".
Examples of these commands are shown below (in the example, the permanent
ESC character is ">"):
>Y48, ' ' >
&&??%
%X1
Figure 4 Removing permanent escape character (">").
7
Page 8
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
Appendix A.
Supported Coax FSL Functions -
For Printer Driver = PCL5
(FSL 22 = 4)
The following FSL 3270 functions will be supported when the PCL5 Printer Driver
is selected. These functions will be received and accepted with the values stated.
Other functions will be received and ignored.
Should you need further information on the use of the FSL functions, please
contact your point of purchase.
FSL Number Function
2 LPI
3 CPI
5 Form Length
6 Maximum Print Position
8 LU1 Language
9 Quality
10 Page Format
11 Paper Path
12 Paper Size
19 Duplex printing
22 Printer Driver Selection
34 Last LF on Page Sent as FF
35 Form Feed Usage
36 Suppress IBM Control Codes
37 IBM Printer Emulation Selection
39 Suppress Empty Forms
47 ESC Mode Selection
48 Permanent ESC Character Selection
51 User-Defined String(s) at Begin Job
59 Bar Code Type Definition
60 Font Link
61 Setup for User Strings
62 Setup for IBM-Defined Strings
72 Reset Translate Table
73 Select Translate Table
74 Printer Symbol Set Definition Strings
75 Overwrite Translate Table
77 Reset APL Translate Table
78 Select APL Translate Table
80 Overwrite APL Translate Table
85 Overwrite Translate Table in LU1
88 Physical Margins
89 Physical Margin Compression
90 User ESC String Definition
91 Font Definition
92 Font Point Size Definition String
8
Page 9

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
FSL Number Function
93 Font Attribute Definition string
94 Font Typeface Definition String
96 Font Change Simulation
98 Automatic Page Orientation
T(est)
Functions:
T4 = Print out Settings
T5 = Print out Character Set
Z Function:
Zn = Send user-defined string
W Function:
Wn = Print Barcode
X Functions:
X1 = Store RAM in FLASH
X2 = Factory default
X3 = Factory default to RAM
X4 = Restore default
9
Page 10
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
Appendix B.
FSL Coax Quick Reference -
For Printer Driver = PCL5
(FSL 22 = 4)
No. Name Syntax Parameters
2 LPI %Y2,<n1>% 0 = Ignored
3 CPI %Y3,<n1>% 0 = Prop.spacing
5 Form Length %Y5,<n1>% 0 = Pass FF and NL from system
6 Maximum Print Position %Y6,<n1>% 0 = Do not generate NL at MPP and
3 = 3 LPI
4 = 4 LPI
*6 = 6 LPI
8 = 8 LPI
*10 = 10 CPI
12 = 12 CPI
15 = 15 CPI
16 = 16.7 CPI
20 = 20 CPI
27 = 27 CPI
and ignore MPL in SVF
001
to
255 = Set FL in no. of lines
*66 EU
**62 US
ignore MPP in SVF
001
to
255 = Set MPP in no. of characters
*132
10
Page 11
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
8 LU1 Language %Y8,<n1>% 1 = English US EBCDIC CP 37
9 Quality %Y9,<n1>% *1 = Draft Print Quality
3 = Austrian/German CP 273
5 = Brazilian CP 275
6 = Canadian (French) CP 260
7 = Danish/Norwegian CP 277
8 = Danish/Norwegian Alt CP 287
9 = Finnish/Swedish CP 278
10 = Finnish/Swedish Alt CP 288
13 = Austrian/German Alt CP 286
14 = International CP 500
15 = Italian CP 280
16 = Japanese(English CP 281
19 = Spanish CP 284
20 = Spanish CP 289
22 = English UK CP 285
30 = French 105-characters CP 297
65 = English US EBCDIC CP 1140
67 = Austrian/German CP 1141
71 = Danish/Norwegian CP 1142
73 = Finnish/Swedish CP 1143
78 = International CP 1148
79 = Italian CP 1144
83 = Spanish CP 1145
86 = English UK CP 1146
94 = French 105-chr. CP 1147
101 = Iceland CP 1149
37 = English US EBCDIC
260 = Canadian (French)
273 = Austrian/German
275 = Brazilian
277 = Danish/Norwegian
278 = Finnish/Swedish
280 = Italian
281 = Japanese(English)
284 = Spanish
285 = English UK
286 = Austrian/German Alt
287 = Danish/Norwegian Alt
288 = Finnish/Swedish Alt
289 = Spanish Alt
297 = French 105-characters
500 = International
Code Pages with €-sign:
1140 = English US EBCDIC
1141 = Austrian/German
1142 = Danish/Norwegian
1143 = Finnish/Swedish
1144 = Italian
1145 = Spanish
1146 = English UK
1147 = French 105-characters
1148 = International
1149 = Iceland
2 = Near Letter Quality
3 = Correspondence
11
Page 12
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
10 Page Format %Y10,<n1>[,n2]%
11 Paper Path %Y11,<n1>% 0 = Ignore PPM and do not send
12 Paper Size %Y12,<n1>[,n2]%
19 Duplex printing
%Y19<n1>% *0 = Simplex
n1
*0 = Portrait
1 = Landscape
2 = COR
3 = Reserved
4 = 8" x 11" Portrait
5 = 8" x 12" Portrait
6 = 13.2" x 8.5" Landscape
7 = Landscape Listing
8 = Portrait Listing 11"
9 = Portrait Listing 12"
12 = COR, 65% of LPI
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1
3 = Drawer 2
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3
7 = Auxilary
8 = Drawer 4
9 = Drawer 5
10= = Drawer 6
Tray Select to Printer
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1
3 = Drawer 2
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3
7 = Auxilary
8 = Drawer 4
9 = Drawer 5
10 = Drawer 6
n1
*1 = A4
2 = Legal
**3 = Letter
4 = Executive
5 = Letter (Monarch)
6 = Business (Com 10)
7 = International DL
8 = International C5
10 = A3
11 = US Ledger
12 = A5
19 = Wide A4
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1
3 = Drawer 2
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3
7 = Auxilary
8 = Drawer 4
9 = Drawer 5
10= = Drawer 6
1 = Long-edge duplex
2 = Short-edge duplex
12
Page 13
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
22 Printer Driver Selection %Y22,<n1>% 0 = Non specific driver (must be
34 Last LF on Page Sent as
FF
35 Form Feed Usage %Y35,<n1>% 0 = Pass FF from Host
36 Suppress IBM Control
Codes
37 IBM Printer Emulation
Selection
39 Suppress Empty Forms %Y39,<n1>% 0 = No forms suppressed
47 ESC Mode Selection %Y47,<n1>% *1 = ESC xx sent as "xx" HEX
48 Permanent ESC Character
Selection
51 User-Defined String(s) at
Begin Job
%Y34,<n1>% 0 = No
%Y36,<n1>% *0 = Respect all codes
%Y37,<n1>% 0 = 3287 Emulation
%Y48,<'char.'>%
or
%Y48,<xx>%
%Y48,<n1>[;n2
[;n3]]%
%Y51,<n1>% 0-7 = One or more strings defined
programmed in FSL Y62)
1 = IBM Pro Printer
(preprogrammed)
4 = PCL5 (preprogrammed)
6 = Epson FX (preprogrammed)
7 = Epson LQ (preprogrammed)
9 = IBM Pro XL24 Printer
(preprogrammed)
16 = PCL II (preprogrammed)
*1 = Yes, count lines in FSL 5 and
send FF
*1 = Count the lines in FSL 5 and
send FF
1 = Suppress all codes
2 = Reserved
*1 = 3268/4214 Emulation
2 = HEX 00-3F sent transparently
except valid SCS codes. TRN
sent non-transparently
4 = HEX 00-3F sent as blanks
except valid SCS codes. TRN
sent transparently
6 = HEX 00-3F sent transparantly
except valid SCS codes. TRN
sent transparantly
8 = HEX 00-3F are suppressed
except valid SCS codes.
HEX 00-3F in TRN are
printed as spaces..
*1 = Empty forms suppressed
3 = Double Escape Feature
n1
'char.'
= character selected from the
current IBM char. table in
apostrophe notation
xx
= HEX value of the character
selected
from the LU3 table
n2
a max. of 5 chars. to introduce
transparancy (invalid values: 0-9
and A-F)
Lead-in sequence
n3
a max. of 5 chars. to introduce
transparancy (invalid values: 0-9
and A-F)
Lead-out sequence
*00
in FSL 61
13
Page 14
FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
59 Bar Code Type Definition
(See W Function below for
printing of bar codes)
60 Font Link %Y60,<n1>,<n2>%
61 Setup for User Strings
(See Z function below for
sending user-defined
strings)
%Y59,<n1>,<n2>,<n3>,<n4>
%
%Y61,<n1>,<n2>%
n1
1-8 = Bar code def. no.
n2
22-39 = Bar code type
n3
1-255 = Height
n4
1-32 = Horizontal expansion
*1
n1
0,10,13,15,16,20,27 = CPI
n2
1-65535 = GFID No.
n1
0-7 = User String no.
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX or in
apostrophe notation
14
Page 15

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
62 Setup for IBM Defined
Strings
72 Reset Translate Table %Y72,<n1>% 1-8 = Reset the indicated table
73 Select Translate Table %Y73,<n1>% 1-8 = Select the indicated table
74 Printer Symbol Set
Definition Strings
%Y62,<n1>,<n2>% Paper Feed:
%Y74,<n1>,<n2>%
120 Tractor (Upper)
preprogrammed with &l1H
selected by FSL Y11,1
121 Envelope feeder
preprogrammed with &l1H
selected by FSL Y11,5
122 Auxilary
preprogrammed with &l4H
selected by FSL Y11,7
123 Manual feeder preprogrammed
with &l2H
selected by FSL Y11,4
124 Drawer 6
preprogrammed with &l6H
selected by FSL Y11,10
125 Drawer 1
preprogrammed with &l5H
selected by FSL Y11,2
126 Drawer 2
preprogrammed with &l8H
selected by FSL Y11,3
127 Drawer 3
preprogrammed with &l20H
selected by FSL Y11,6
128 Drawer 4
preprogrammed with &l21H
selected by FSL Y11,8
129 Drawer 5
preprogrammed with &l22H
selected by FSL Y11,9
Attributes:
130 Bold start
131 Bold stop
132 Underscore start
133 Underscore stop
Colour:
160 Default Colour
161 Blue
162 Red
163 Pink
164 Green
165 Turquoise
166 Yellow
168 Black
178 Multicolor
Printing:
270 Simplex
271 Short-edge duplex
272 Long-edge duplex
273 Duplex page shift
280 Line wrap
281 Line cut
n1
1-8 = Symbol set no.
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
15
Page 16

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
75 Overwrite Translate Table %Y75,<n1>[,n2],<n3>%
77 Reset APL Translate
Table
78 Select APL Translate
Table
80 Overwrite APL Translate
Table
%Y77,<n1>% 1-8 = Reset the indicated APL table
%Y78,<n1>% 1-8 = Select the indicated APL table
%Y80,<n1>[,n2],<n3>%
n1
00-FF = LU3 position in HEX of
character to be translated
n2
1-8 = Symbol set defined in FSL 74
n3
00-FF = Data in ASCII HEX required
to print the character
n1
00-FF = The position in HEX of
the APL character to
be translated
n2
1-8 = Symbol set defined in FSL 74
n3
00-FF = Data in ASCII HEX required
to print the character
16
Page 17

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
85 Overwrite Translate Table
in LU1
88 Physical Margins %Y88,<n1>,<n2>
89 Physical Margin
Compression
90 User ESC String Definition %Y90,<n1>,<n2>%
%Y85,<n1>[,n2],
<n3>%
[,n3]%
%Y89,<n1>[,n2]%
n1
40-FF = LU1 position in HEX of
character to be translated
n2
1-8 = Symbol set defined in FSL 74
n3
00-FF = Data in ASCII HEX required
to print the character
n1
-32000 to 32000
= Horizontal margin compensation in
1/1440"
*0
n2
-32000 to 32000
= Vertical margin compensation in
1/1440"
*0
n3
0-9 = Page format as defined in FSL
10
20 = Margins for MPI Mainframe
software
21 = Support for back page in
Duplex
n1
*0 = No compensation
1 = Compensation as defined in
FSL 88
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1
3 = Drawer 2
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3
7 = Auxilary
8 = Drawer 4
9 = Drawer 5
10= = Drawer 6
n1
0 = Erase strings
01-FF = String no. in HEX
n2
'<string>'
= String contents in apostrophe
notation
17
Page 18

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
91 Font Definition %Y91,<n1>,<n2>,<n3>,<n4>,<
92 Font Point Size Definition
String
93 Font Attribute Definition
String
94 Font Typeface Definition
String
96 Font Change
Simulation
n5>[,n6]%
%Y92,<n1>,<n2>%
%Y93,<n1>,<n2>%
%Y93,<n1>,<n2>%
%Y96,<n1>% 1-65535 = GFID no. in decimal
n1 (IBM GFID)
1-65535 = IBM GFID no.
n2 (Typeface)
0-255 = Pre-programmed typeface
value
(or Y94 string no.)
n3 (Attribute)
0 = No attributes
1 = Bold
2 = Italic
3 = Bold and Italic
4 = Proportional
5 = Prop. Bold
6 = Prop. Italic
7 = Prop. Bold and Italic
(or Y93 string no.)
n4 (Symbol Set)
1 = Roman-8
2 = IBM PC-8
3 = ECMA Latin 1
5 = US ASCII
6 = OCR A
7 = OCR B
8 = PC 850
(or Y74 string no)
n5 (Point Size)
1-255 = Point size
(or Y92 string no.)
n6 (Translate Table)
0 = IBM Resident
1 = Roman-8
2 = IBM PC-8
3 = ECMA Latin 1
5 = US ASCII
6 = OCR A
7 = OCR B
8 = PC 850
n1
1-255 = String no. in decimal
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
n1
1-255 = String no. in decimal
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
n1
1-255 = String no. in decimal
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
18
Page 19

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
98 Automatic Page
Orientation
%Y98,<n1>[,n2]%
n1
*0 = Activate Automatic Page
Orientation
1 = Deactivate Automatic Page
Orientation
2 = Activate APO IBM 3812
compatible
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1
3 = Drawer 2
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3
7 = Auxilary
8 = Drawer 4
9 = Drawer 5
10= = Drawer 6
19
Page 20

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
T(est) Functions
Six different tests may be run via the line. Use the following syntax:
%T<test number>
Test Number Test
1 Offline HEX Dump
2 Online HEX Dump
3 ASCII HEX dump
4 Print out settings
5 Print out character sets
6 Cancel Test 3 (On-line ASCII HEX dump)
Test 4 can also be generated via the TEST key on the interface's rear panel. Test 3 is
terminated by pressing the TEST key on the rear panel.
Z Function (Sending user-defined strings)
This function is used for sending user-defined strings (up to 8 strings can be defined see FSL 61). Use the following syntax:
%Z<string number>
W Function (Bar code printing)
This function is used for sending bar codes (up to 8 bar codes can be defined - see FSL
59). Use the following syntax:
%W<no><barcode data>%
X Functions (Storing and restoring settings)
The X commands allow you to store the temporarily defined settings or to overwrite these
settings by reading the power up default settings. You may also restore the settings to
factory default.
%X1 Saves temporarily defined settings as power-up settings.
%X3 Reads and activates factory default settings.
%X4 Reads and activates power-up default settings.
20
Page 21

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
Appendix C.
Supported Coax FSL Functions -
For Printer Driver = Matrix
(FSL 22 = 1, 6, 7 or 9)
The following FSL 3270 functions will be supported when a Matrix Printer Driver
is selected. These functions will be received and accepted with the values stated.
Other functions will be received and ignored.
Should you need further information on the use of the FSL functions, please
contact your point of purchase.
FSL Number Function
2 LPI
3 CPI
5 Form Length
6 Maximum Print Position
8 LU1 Language
9 Quality
10 Page Format
11 Paper Path
22 Printer Driver Selection
34 Last LF on Page Sent as FF
35 Form Feed Usage
36 Suppress IBM Control Codes
37 IBM Printer Emulation Selection
39 Suppress Empty Forms
47 ESC Mode Selection
48 Permanent ESC Character Selection
51 User-Defined String(s) at Begin Job
59 Bar Code Type Definition
61 Setup for User Strings
62 Setup for IBM-Defined Strings
72 Reset Translate Table
73 Select Translate Table
75 Overwrite Translate Table
77 Reset APL Translate Table
78 Select APL Translate Table
80 Overwrite APL Translate Table
85 Overwrite Translate Table in LU1
90 User ESC String Definition
T(est)
Functions:
T4 = Print out Settings
T5 = Print out Character Set
Z Function:
Zn = Send user-defined string
21
Page 22

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
FSL Number Function
W Function:
Wn = Print Barcode
X Functions:
X1 = Store RAM in FLASH
X2 = Restore default
X3 = Factory default to RAM
X4 = Restore default
22
Page 23

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
Appendix D.
FSL Coax Quick Reference -
For Printer Driver = Matrix
(FSL 22 = 1, 6, 7 or 9)
No. Name Syntax Parameters
2 LPI %Y2,<n1>% 0 = No LPI sent to printer
3 CPI %Y3,<n1>% 0 = No LPI sent to printer
5 Form Length %Y5,<n1>% 0 = Convert FF to NL
3 = 3 LPI
4 = 4 LPI
*6 = 6 LPI
8 = 8 LPI
*10 = 10 CPI
12 = 12 CPI
15 = 15 CPI
16 = 16.7 CPI
20 = 20 CPI
27 = 27 CPI
001
to
255 = Set FL in no. of lines
*66 EU
**62 US
23
Page 24

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
6 Maximum Print Position %Y6,<n1>% 0 = Do not generate NL at MPP and
8 LU1 Language %Y8,<n1>% 1 = English US EBCDIC CP 37
9 Quality %Y9,<n1>% 0 = No quality command is sent to
ignore MPP in SVF
001
to
255 = Set MPP in no. of characters
*132
3 = Austrian/German CP 273
5 = Brazilian CP 275
6 = Canadian (French) CP 260
7 = Danish/Norwegian CP 277
8 = Danish/Norwegian Alt CP 287
9 = Finnish/Swedish CP 278
10 = Finnish/Swedish Alt CP 288
13 = Austrian/German Alt CP 286
14 = International CP 500
15 = Italian CP 280
16 = Japanese(English CP 281
19 = Spanish CP 284
20 = Spanish CP 289
22 = English UK CP 285
30 = French 105-characters CP 297
65 = English US EBCDIC CP 1140
67 = Austrian/German CP 1141
71 = Danish/Norwegian CP 1142
73 = Finnish/Swedish CP 1143
78 = International CP 1148
79 = Italian CP 1144
83 = Spanish CP 1145
86 = English UK CP 1146
94 = French 105-chr. CP 1147
101 = Iceland CP 1149
37 = English US EBCDIC
260 = Canadian (French)
273 = Austrian/German
275 = Brazilian
277 = Danish/Norwegian
278 = Finnish/Swedish
280 = Italian
281 = Japanese(English)
284 = Spanish
285 = English UK
286 = Austrian/German Alt
287 = Danish/Norwegian Alt
288 = Finnish/Swedish Alt
289 = Spanish Alt
297 = French 105-characters
500 = International
Code Pages with €-sign:
1140 = English US EBCDIC
1141 = Austrian/German
1142 = Danish/Norwegian
1143 = Finnish/Swedish
1144 = Italian
1145 = Spanish
1146 = English UK
1147 = French 105-characters
1148 = International
1149 = Iceland
the printer
*1 = Draft Print Quality
2 = Near Letter Quality
3 = Correspondence
24
Page 25

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
11 Paper Path %Y11,<n1>% 0 = No tray select sent to the
22 Printer Driver Selection %Y22,<n1>% 0 = Non specific driver (must be
34 Last LF on Page Sent as
FF
35 Form Feed Usage %Y35,<n1>% 0 = Pass FF from Host
36 Suppress IBM Control
Codes
37 IBM Printer Emulation
Selection
39 Suppress Empty Forms %Y39,<n1>% 0 = No forms suppressed
%Y34,<n1>% 0 = No
%Y36,<n1>% *0 = Respect all codes
%Y37,<n1>% 0 = 3287 Emulation
printer, SD in PPM command is
ignored
1 = Sent the string in Y62,120
Tractor - preprogrammed
2 = Sent the string in Y62,125
Drawer 1 - preprogrammed
3 = Sent the string in Y62,126
Drawer 2 - preprogrammed
4 = Sent the string in Y62,123
5 = Sent the string in Y62,121
6 = Sent the string in Y62,127
7 = Sent the string in Y62,122
8 = Sent the string in Y62,128
9 = Sent the string in Y62,129
10 = Sent the string in Y62,124
programmed in FSL Y62)
1 = IBM Pro Printer
(preprogrammed)
4 = PCL5 (preprogrammed)
6 = Epson FX (preprogrammed)
7 = Epson LQ (preprogrammed)
9 = IBM Pro XL24 Printer
(preprogrammed)
16 = PCL II (preprogrammed)
*1 = Yes, count lines in FSL 5 and
send FF
*1 = Count the lines in FSL 5 and
send FF
1 = Suppress all codes
2 = Reserved
*1 = 3268/4214 Emulation
2 = HEX 00-3F sent transparently
except valid SCS codes. TRN
sent non-transparently
4 = HEX 00-3F sent as blanks
except valid SCS codes. TRN
sent transparently
6 = HEX 00-3F sent transparantly
except valid SCS codes. TRN
sent transparantly
8 = HEX 00-3F are suppressed
except valid SCS codes.
HEX 00-3F in TRN are
printed as spaces..
*1 = Empty forms suppressed
25
Page 26

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
47 ESC Mode Selection %Y47,<n1>% *1 = ESC xx sent as "xx" HEX
48 Permanent ESC Character
Selection
51 User-Defined String(s) at
Begin Job
59 Bar Code Type Definition
(See W Function below for
printing of bar codes)
(Barcodes in PCL only for
Y22=0 (Non Specific
Printer) and Y22=16 (PCL
II)
61 Setup for User Strings
(See Z function below for
sending user-defined
strings)
%Y48,<'char.'>%
or
%Y48,<xx>%
%Y48,<n1>[;n2
[;n3]]%
%Y51,<n1>% 0-7 = One or more strings defined
%Y59,<n1>,<n2>,<n3>,<n4>%
%Y61,<n1>,<n2>%
3 = Double Escape Feature
n1
'char.'
= character selected from the
current IBM char. table in
apostrophe notation
xx
= HEX value of the character
selected
from the LU3 table
n2
a max. of 5 chars. to introduce
transparancy (invalid values: 0-9
and A-F)
Lead-in sequence
n3
a max. of 5 chars. to introduce
transparancy (invalid values: 0-9
and A-F)
Lead-out sequence
*00
in FSL 61
n1
1-8 = Bar code def. no.
n2
22-39 = Bar code type
n3
1-255 = Height
n4
1-32 = Horizontal expansion
*1
n1
0-7 = User String no.
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX or in
apostrophe notation
26
Page 27

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
62 Setup for IBM Defined
Strings
72 Reset Translate Table %Y72,<n1>% 1-8 = Reset the indicated table
73 Select Translate Table %Y73,<n1>% 1-8 = Select the indicated table
74 Printer Symbol Set
Definition Strings
%Y62,<n1>,<n2>% LPI:
%Y74,<n1>,<n2>%
101 3 LPI
102 4 LPI
1 or 103 6 LPI
2 or 104 8 LPI
CPI:
111 5 CPI
3 or 112 10 CPI
4 or 113 12 CPI
5 or 114 15 CPI
115 13.3 CPI
6 or 116 16.7 CPI
117 20 CPI
118 27 CPI
Paper Feed:
19 or 120 Tractor (Upper)
selected by FSL Y11,1
121 Envelope feeder
selected by FSL Y11,5
122 Auxilary
selected by FSL Y11,7
123 Manual feeder
selected by FSL Y11,4
124 Drawer 6
selected by FSL Y11,10
20 or 125 Drawer 1
selected by FSL Y11,2
21 or 126 Drawer 2
selected by FSL Y11,3
127 Drawer 3
selected by FSL Y11,6
128 Drawer 4
selected by FSL Y11,8
129 Drawer 5
selected by FSL Y11,9
Attributes:
22 or 130 Bold start
23 or 131 Bold stop
7 or 132 Underscore start
8 or 133 Underscore stop
Quality:
17 or 140 Draft Print Quality
18 or 141 Near Letter Quality
142 Correspondance
Colour:
160 Default Colour
10 or 161 Blue
11 or 162 Red
12 or 163 Pink
13 or 164 Green
14 or 165 Turquoise
15 or 166 Yellow
9 or 168 Black
16 or 178 Multicolor
n1
1-8 = Symbol set no.
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
27
Page 28

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
75 Overwrite Translate Table %Y75,<n1>[,n2],
77 Reset APL Translate
Table
78 Select APL Translate
Table
80 Overwrite APL Translate
Table
85 Overwrite Translate Table
in LU1
90 User ESC String Definition %Y90,<n1>,<n2>%
<n3>%
%Y77,<n1>% 1-8 = Reset the indicated APL table
%Y78,<n1>% 1-8 = Select the indicated APL table
%Y80,<n1>[,n2],
<n3>%
%Y85,<n1>[,n2],
<n3>%
n1
00-FF = LU3 position in HEX of
character to be translated
n2
1-8 = Symbol set defined in FSL 74
n3
00-FF = Data in ASCII HEX required
to print the character
n1
00-FF = The position in HEX of
the APL character to
be translated
n2
1-8 = Symbol set defined in FSL 74
n3
00-FF = Data in ASCII HEX required
to print the character
n1
40-FF = LU1 position in HEX of
character to be translated
n2
1-8 = Symbol set defined in FSL 74
n3
00-FF = Data in ASCII HEX required
to print the character
n1
0 = Erase strings
01-FF = String no. in HEX
n2
'<string>'
= String contents in apostrophe
notation
28
Page 29

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 3270 emulation
T(est) Functions
Six different tests may be run via the line. Use the following syntax:
%T<test number>
Test Number Test
4 Print out settings
5 Print out character sets
Test 4 can also be generated via the TEST key on the interface's rear panel.
Z Function (Sending user-defined strings)
This function is used for sending user-defined strings (up to 8 strings can be defined see FSL 61). Use the following syntax:
%Z<string number>
W Function (Bar code printing)
This function is used for sending bar codes (up to 8 bar codes can be defined - see FSL
59). Use the following syntax:
%W<no><barcode data>%
X Functions (Storing and restoring settings)
The X commands allow you to store the temporarily defined settings or to overwrite these
settings by reading the power up default settings. You may also restore the settings to
factory default.
%X1 Saves temporarily defined settings as power-up settings.
%X3 Reads and activates factory default settings.
%X4 Reads and activates power-up default settings.
29
Page 30

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 5250 emulation
Appendix E.
Supported TN5250e FSL Functions -
For Printer Driver = PCL5
(FSL 22 = 4)
The following 5250 FSL functions will be supported in the SCS/DCA datastream
when the PCL5 Printer Driver is selected. The Print Server will emulate an IBM
3812 printer and accept both DCA and SCS datastreams.
The FSL commands will be received and accepted with the values stated. Other
commands will be received and ignored. See Appendix F,
FSL TN5250e Quick Reference for Language = PCL5
FSL Number (Y) Function
2 LPI
3 CPI
8 Language
10 Page Format
12 Paper Size
22 Printer Driver Selection
40 Absolute Horizontal Positioning
48 Permanent ESC Character Selection
59 Bar Code Type Definition
61 Setup for User Strings
62 Setup for IBM-Defined Strings
88 Physical Margins
89 Physical Margin Compression
90 User ESC String Definition
96 Font Change Simulation
97 User GFID / Font Selection
98 Automatic Page Orientation
30
Page 31

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 5250 emulation
T(est) Functions:
T4 = Print out Settings
Z Function:
Zn = Send user-defined string
S Function:
Sn = Send user-defined string
W Function:
Wn = Print Barcode
X Functions:
X1 = Store RAM in FLASH
X3 = Factory default to RAM
X4 = Restore default
PCL Macro Functions:
On = Activate PCL overlay macro
In = Excecute PCL macro
31
Page 32

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 5250 emulation
Appendix F.
FSL TN5250e Quick Reference -
For Printer Driver = PCL5
(FSL 22 = 4)
No. Name Syntax Parameters
2 LPI %Y2,<n1>% 3 = 3 LPI
3 CPI %Y3,<n1>% 5 = 5 CPI
8 Language %Y8,<n1>% **37 English US EBCDIC
10 Page Format %Y10,<n1>[,n2]%
4 = 4 LPI
*6 = 6 LPI
8 = 8 LPI
*10 = 10 CPI
12 = 12 CPI
15 = 15 CPI
16 = 16.7 CPI
273 Austrian/German
274 Belgium
275 Brazilian
277 Danish/Norwegian
278 Finnish/Swedish
280 Italian
281 Japanese(English)
282 Portuguese
283 Spanish
284 Spanish Speaking
285 English UK
297 French 105-characters
*500 International
871 Iceland
1140 English US EBCDIC with Euro
1141 Austrian/German with Euro
1142 Danish/Norwegian with Euro
1143 Finnish/Swedish with Euro
1144 Italian with Euro
1145 Spanish with Euro
1146 English UK with Euro
1147 French 105-chr with Euro
1148 International with Euro
1149 Iceland with Euro
n1
0 = Portrait
1 = Landscape
*2 = COR
82 = COR (Y10,82)then COR is
independent of print quality
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1 (Upper)
3 = Drawer 2 (Lower)
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3 (Lower)
32
Page 33

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 5250 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
12 Paper Size %Y12,<n1>[,n2,n3]%
22 Printer Driver Selection %Y22,<n1>% 0 = Non specific driver (must be
40 Absolute Horizontal
Positioning
48 Permanent ESC
Character Selection
%40, <n1>%
%Y48,<'char.'>%
or
%Y48,<xx>%
n1 (Physical paper size)
1 = A4 *
2 = Legal
3 = Letter**
4 = Executive
5 = Letter (Monarch)
6 = Business
7 = International DL
8 = International C5
9 = B5
10 = A3
11 = Ledger
15 = Comm 9 Envelope
16 = B5 Envelope
17 = US Legal 13"
18 = 215mm x 315mm
99 = Use system SPPS or SHF /
SVF values
n2 (Tray)
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1 (Upper)
3 = Drawer 2 (Lower)
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3 (Lower)
7-255 = Reserved for optional
feeder
(20)=(Reserved forDOD)
n3 (Validation paper size)
1 = A4 *
2 = Legal
3 = Letter**
4 = Executive
5 = Letter (Monarch)
6 = Business
7 = International DL
8 = International C5
9 = B5
10 = A3
11 = Ledger
15 = Comm 9 Envelope
16 = B5 Envelope
17 = US Legal 13"
18 = 215mm x 315mm
99 = Use system
SPPS or SHF / SVF values
programmed in FSL Y62)
1 = IBM Pro Printer
(preprogrammed)
4 = PCL5 (preprogrammed)
6 = Epson FX (preprogrammed)
7 = Epson LQ (preprogrammed)
9 = IBM Pro XL24 Printer
(preprogrammed)
16 = PCL II (preprogrammed)
n1
10 = AHP is done using spaces
11 = AHP is done using positioning
command
'char.'
= character selected from the
current IBM characte table
xx
= HEX value of the character
selected from the table
*00
33
Page 34

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 5250 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
59 Bar Code Type Definition %Y59,<n1>,<n2>,<n3>,<n4>[,n5]
61 Setup for User Strings %Y61,<n1>,<n2>%
62 Setup for IBM-defined
strings (Tray select
strings)
88 Physical Margins %Y88,<n1>,<n2>[,n3]%
89 Physical Margin
Compensation
90 User ESC String
Definition
%
%62,<n1>,<string>%
%Y89,<n1>[,n2]%
%Y90,<n1>,<n2>%
n1
1-8 = Bar code def. no.
n2
22-39 = Bar code type
n3
1-255 = Height
n4
1-32 = Horizontal expansion
*1
n1
0-7 = User String No.
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
n1
120 = Tractor Tray 1
121 = Envelope feed
123 = Manual Cutsheet Feeder
125 = Tray 1
126 = Tray 2
127 = Tray 3
n1
-32000 to 32000 = Horizontal margin
compensation in 1/1440"
*0
n2
-32000 to 32000 = Vertical margin
compensation in 1/1440"
*0
n3
0-2 = Page format as defined in FSL
Y10
n1
*0 = No compensation
1 = Compensation as defined
in FSL 88
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1 (Upper)
3 = Drawer 2 (Lower)
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3 (Lower)
n1
0 = Erase strings
01-FF = String no. in HEX
n2
'<string>'
= String contents in apostrophe
notation
34
Page 35

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section - FSL Commands for IBM 5250 emulation
No. Name Syntax Parameters
96 Font Change Simulation
97 User GFID/Font Selection %Y97,<n1>,<n2>[:n3]%
98 Automatic Page
Orientation (APO)
%Y96,<n1>% 1-65535 = GFID no.
%Y98,<n1>[,n2]%
n1
1-65535 = GFID No.
n2
<string> = String for 0° rotation
n3
<string> = String for 90° rotation
n1
*0 = Activate APO
1 = Deactivate APO
2 = Validate APO on physical page
n2
1 = Tractor (Upper)
2 = Drawer 1 (Upper)
3 = Drawer 2 (Lower)
4 = Manual feeder
5 = Envelope feeder
6 = Drawer 3 (Lower)
35
Page 36

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section
Appendix G.
Supported TN5250e FSL Functions -
For Printer Driver = Matrix
(FSL 22 = 1, 6, 7 or 9)
The following 5250 FSL functions will be supported in the SCS/DCA datastream
when a Matrix Printer Driver is selected. The Print Server will emulate an IBM
5219 printer and accept both DCA and SCS datastreams.
The FSL commands will be received and accepted with the values stated. Other
commands will be received and ignored. See Appendix F,
FSL TN5250e Quick Reference for Language = Matrix
FSL Number (Y) Function
2 LPI
3 CPI
8 Language
22 Printer Driver Selection
40 Absolute Horizontal Positioning
48 Permanent ESC Character Selection
61 Setup for User Strings
62 Setup for IBM-Defined Strings
90 User ESC String Definition
96 Font Change Simulation
97 User GFID / Font Selection
T(est) Functions:
T4 = Print out Settings
Z Function:
Zn = Send user-defined string
S Function:
Sn = Send user-defined string
X Functions:
X1 = Store RAM in FLASH
X3 = Factory default to RAM
X4 = Restore default
36
Page 37

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section
Appendix H.
FSL TN5250e Quick Reference -
For Printer Driver = Matrix
(FSL 22 = 1, 6, 7 or 9)
No. Name Syntax Parameters
2 LPI %Y2,<n1>% 3 = 3 LPI
3 CPI %Y3,<n1>% 5 = 5 CPI
8 Language %Y8,<n1>% **37 English US EBCDIC
4 = 4 LPI
*6 = 6 LPI
8 = 8 LPI
*10 = 10 CPI
12 = 12 CPI
15 = 15 CPI
16 = 16.7 CPI
273 Austrian/German
274 Belgium
275 Brazilian
277 Danish/Norwegian
278 Finnish/Swedish
280 Italian
281 Japanese(English)
282 Portuguese
283 Spanish
284 Spanish Speaking
285 English UK
297 French 105-characters
*500 International
871 Iceland
1140 English US EBCDIC with Euro
1141 Austrian/German with Euro
1142 Danish/Norwegian with Euro
1143 Finnish/Swedish with Euro
1144 Italian with Euro
1145 Spanish with Euro
1146 English UK with Euro
1147 French 105-chr with Euro
1148 International with Euro
1149 Iceland with Euro
37
Page 38

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section
No. Name Syntax Parameters
22 Printer Driver Selection %Y22,<n1>% 0 = Non specific driver (must be
36 Suppress control codes %Y36,<n1>%
40 Absolute Horizontal
Positioning
48 Permanent ESC
Character Selection
61 Setup for User Strings %Y61,<n1>,<n2>%
62 Setup for IBM-defined
strings (Tray select
strings)
90 User ESC String
Definition
96 Font Change Simulation
97 User GFID/Font Selection %Y97,<n1>,<n2>[:n3]%
%40, <n1>%
%Y48,<'char.'>%
or
%Y48,<xx>%
%62,<n1>,<string>%
%Y90,<n1>,<n2>%
%Y96,<n1>% 1-65535 = GFID no.
programmed in FSL Y62)
1 = IBM Pro Printer
(preprogrammed)
4 = PCL5 (preprogrammed)
6 = Epson FX (preprogrammed)
7 = Epson LQ (preprogrammed)
9 = IBM Pro XL24 Printer
(preprogrammed)
16 = PCL II (preprogrammed)
n1
0 = Respect all IBM control codes
1 = Suppress all IBM control codes
2 = Suppress IBM Multibyte control
3 = Reserved
4 = Suppress IBM Multibyte Control
Codes and Form Feed
5 = Suppress IBM Multibyte Controll
codes
n1
10 = AHP is done using spaces
11 = AHP is done using positioning
command
'char.'
= character selected from the
current IBM characte table
xx
= HEX value of the character
selected from the table
*00
n1
0-7 = User String No.
n2
00-FF = String contents in HEX
n1
120 = Tractor Tray 1
121 = Envelope feed
123 = Manual Cutsheet Feeder
125 = Tray 1
126 = Tray 2
127 = Tray 3
n1
0 = Erase strings
01-FF = String no. in HEX
n2
'<string>'
= String contents in apostrophe
notation
n1
1-65535 = GFID No.
n2
<string> = String for 0° rotation
n3
<string> = String for 90° rotation
38
Page 39

FSL Reference Manual for Print Servers
Appendix Section
Appendix I. Test printout
TEST key
Pressing the TEST key on the rear panel once generates a settings printout. This
test printout consists of two or more pages: The first two pages contain details of
device settings and information related to the protocol used. The following pages
contain detailed information about each session available in the Print Server.
Additional pages will be printed depending whether SCS/DCA is enabled.
39
Page 40

Appendix J Abbreviations
Appendix J. Abbreviations
Abbreviation Full name Explanation
AFP Advanced Function Presentation IBM concept for print data
formatting that defines how
print control files should be
structured. This is the current
standard.
APL A Programming Language
ASCII American Standard Code for
Information Interchange
CPI Characters Per Inch
DCA Document Content Architecture
DIMM Dual Inline Memory Module
DIP Dual Inline Packet
DSC Data-Stream Compatibility Print datastream generated
FLASH (Usually memory) Memory chip able to store
FSL Function Selection via the Line Used to configure default
GFID Global Font ID
HEX Hexadecimal
by IBM mainframes.
Contains almost exclusively
text, i.e. text that could be
produced by a type writer.
information permanently
without power. Depending on
the type, flash memory can
be ‘written’ between 1.000
and 100.000 times.
values in MPI Tech
interfaces for line data
printing. Also used for
printjob specific formatting
like bold and font change.
- 40 -
Page 41

Appendix J Abbreviations
Abbreviation Full name Explanation
IPDS Intelligent Printer Data Stream IPDS is generated and sent
by e.g. PSF and translated to
PCL by e.g. the MPI Tech
PrintServer/Protocol Converter. IPDS supports the
complete print datastream
and communication between
IPDS capable devices
(including software devices).
LAN Local Area Network Usually TokenRing or
Ethernet. Coax and Twinax
are usually regarded as
WAN’s
LED Light-Emitting Diode
LPD Line Printer Demon Part of the standard TCP/IP
stack (programs). Two major
(incompatible) variations of
LPR/LPD are generally used
Works only in conjunction
with LPR. The sender of a
printjob via TCP/IP will be
LPR and the receiver will be
LPD.
LPR Line Printer Requester Part of the standard TCP/IP
stack (programs). Two major
(incompatible) variations of
LPR/LPD are generally used
Works only in conjunction
with LPD. The sender of a
printjob via TCP/IP will be
LPR and the receiver will be
LPD.
- 41 -
Page 42

Appendix J Abbreviations
Abbreviation Full name Explanation
MVS Multiple Virtual Machine IBM operating system for
mainframes. This is the most
commonly used operating
system for large
corporations.
OS/390 New name for MVS IBM operating system for
mainframes. This is the most
commonly used operating
system for large
corporations. The only
operating system that
supports IBM CMOS and
SYSPLEX technology.
PPD Page Printer Demon Enhanced version of
LPR/LPD. The enhancement
enables bidirectional
communication when
printing. Not part of the
standard TCP/IP stack
(programs). Used by ida
Psxx, ida RPPC, IBM
Network printers, PSF/AIX
and others. Works only in
conjunction with PPR. The
sender of a printjob via
TCP/IP will be PPR and the
receiver will be PPD.
PPR Page Printer Requester Enhanced version of
LPR/LPD. The enhancement
enables bidirectional commu-
nication when printing. Not
part of the standard TCP/IP
stack (programs). Used by
ida PSS, ida HPR and PSF.
Works only in conjunction
with PPR. The sender of a
printjob via TCP/IP will be
PPR and the receiver will be
PPD.
- 42 -
Page 43

Appendix J Abbreviations
Abbreviation Full name Explanation
PSF Print Service Facility IBM printer driver for AFP
printing. Converts line data
and AFP data to IPDS only.
PSF/AIX and PSF/2 is
capable of converting the
data to PCL as well.
PSS (ida PSS) Print Subsystem MPI Tech print system for
OS/390 (MVS) and VM
systems. Prints AFP and line
data files on all remote
printers, NOT channel
attached printers.
RAM Random Access Memory Memory chip that is able to
store information while
powered on. RAM can be
‘written’ an indefinite number
of times.
SCS SNA Character String Control information for
simple print formatting like
e.g. set CPI, LPI and Form
Feed.
SIMM Single Inline Memory Module
SNA Systems Network Architecture IBM networking concept
usually for Mainframe and
AS/400. On mainframes the
actual program that
implements SNA is called
VTAM.
TCP/IP Transmission Control
Program/Internet Protocol
VTAM Virtual TeleAccess Method IBM network communcation
Suite of programs for net-
work communication. TCP/IP
can be installed on almost
every existing operating
system, but the supported
functions vary between
operating systems. TCP/IP
consist of a base TCP
program and various other
programs providing support
for e.g. LPD, Telnet or
BootP.
program. VTAM is used to
connect printers and
terminals to OS/390 (MVS)
and VM systems
- 43 -
Page 44

Appendix J Abbreviations
Abbreviation Full name Explanation
VM Virtual Machine IBM operating system for
mainframes. OS/390 (MVS)
and other operating systems
can run under control of VM.
WAN Wide Area Network Usually Coax and Twinax
networks. Today it is also
used for larger TokenRing
and Ethernet networks
and/or Router base
networks.
- 44 -
 Loading...
Loading...