Page 1

Service Manual
DOT MATRIX PRINTER
MODEL
Rev.1.00 Newly issued on Mar, 1989
CBM-710/720
Page 2

CONTENTS
Chapter 1. Printer Disassembly and Assembly ....................................................................................... 1
1 How to Remove Upper Cover and Rear Cover ............................................................................................ 2
2 How to Remove The Printer Mechanism...................................................................................................... 3
3 How to Remove the Control Board .............................................................................................................. 3
4 How to Remove the Power Board and AC power Unit ................................................................................4
5 How to Remove the Auto Cutter (CBM-720 only)....................................................................................... 5
6 How to Remove the Operation Panel and PE Sensor ................................................................................... 5
Chapter 2. Circuit Description ................................................................................................................. 6
1 Outline .......................................................................................................................................................... 7
2 CPU Peripheral Circuit ................................................................................................................................. 8
3 Printer Control Circuit ................................................................................................................................ 10
4 Cutter Control Circuit ..................................................................................................................................11
5 Interface and Operation Panel..................................................................................................................... 12
6 Paper End Sensor Circuit ............................................................................................................................ 13
7 Parallel Interface Circuit ............................................................................................................................. 14
8 Serial Interface Circuit................................................................................................................................ 16
9 RS422A interface Circuit............................................................................................................................ 18
10 Power Supply Circuit.................................................................................................................................. 19
Chapter 3. Auto Cutter ........................................................................................................................... 20
1 Maintenance and Handling ......................................................................................................................... 21
2 Mechanism and Principle of Operation ...................................................................................................... 22
3 Repairing and Troubleshooting................................................................................................................... 24
4 Disassembly and Assembly ........................................................................................................................ 26
Chapter 4. Circuit Diagram.................................................................................................................... 28
1 Power Supply Circuit.................................................................................................................................. 29
2 Noise Filter Circuit ..................................................................................................................................... 30
3 Operation Panel Circuit .............................................................................................................................. 30
4 Paper End Sensor Circuit ............................................................................................................................ 30
5 OP Junction Circuit..................................................................................................................................... 31
6 Parallel ........................................................................................................................................................ 32
7 RS232C ....................................................................................................................................................... 33
8 PS422A ....................................................................................................................................................... 34
Chapter 5. Parts List ............................................................................................................................... 35
1 Exploded View............................................................................................................................................ 36
2 Block Diagram ............................................................................................................................................ 41
3 Power Supply Unit...................................................................................................................................... 43
4 Noise Filter Unit ......................................................................................................................................... 45
5 Control Board Unit: RS232C...................................................................................................................... 47
6 Control Board Unit: Parallel ....................................................................................................................... 51
7 Control Board Unit: RS422A ..................................................................................................................... 55
8 OP Panel/PE Detector/OP Junction Unit .................................................................................................... 59
9 Auto Cutter ................................................................................................................................................. 63
10 Winder......................................................................................................................................................... 67
i
Page 3

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Chapter 1
Printer Disassebly and Assembly
1
Page 4
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
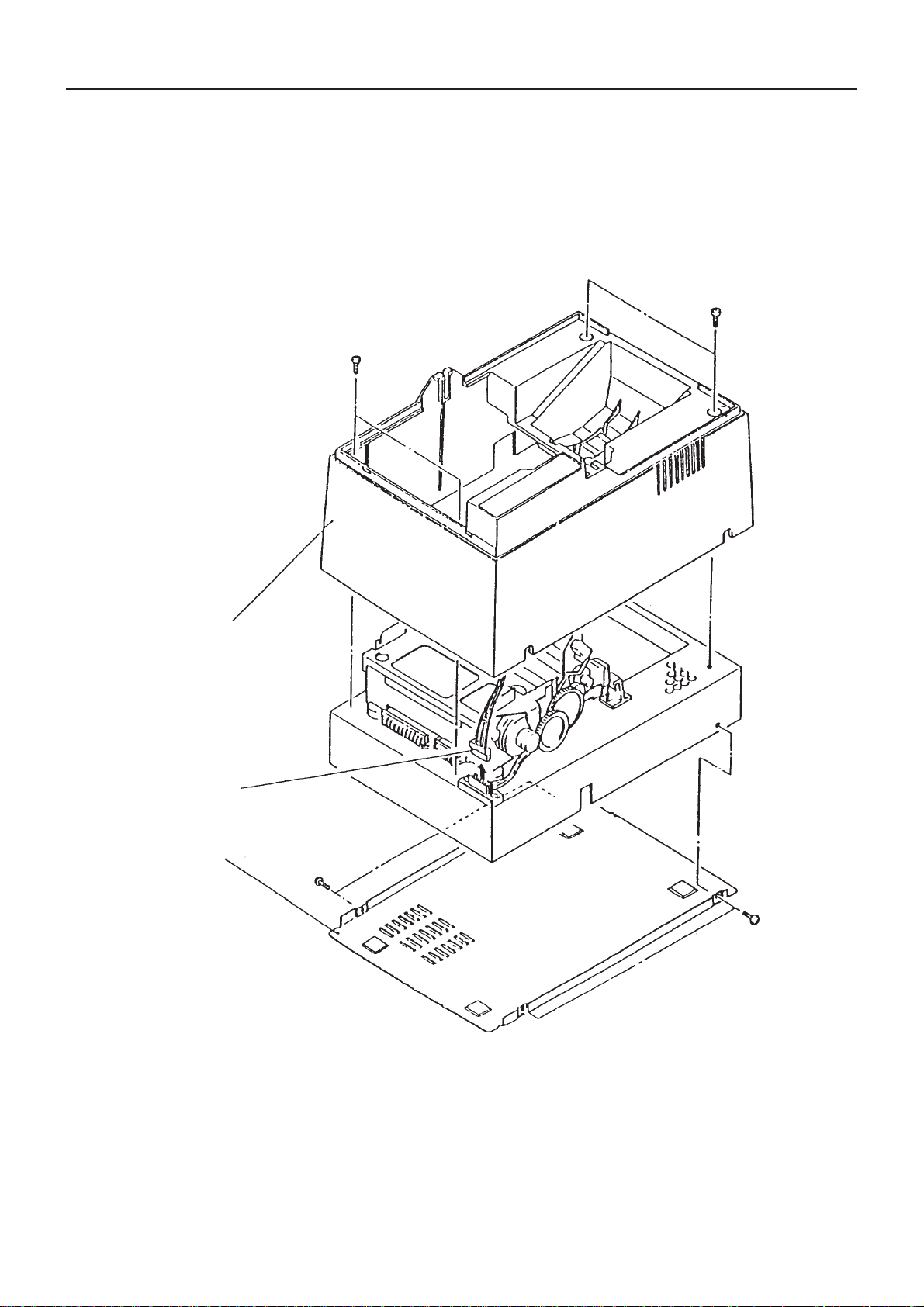
1. How to the Upper Cover and Rear Cover
1) Unfasten 4 screws (M3 x 6) as shown in the figure and lift the upper cover upward, while disconnecting the
connector.
2) Unfasten 4 screws (M3 x 6) at both sides and remove the rear cover.
Upper Cover
Connector
Rear Cover
2
Page 5
2. How to Remove the Printer Mechanism
• Remove the upper cover.
• Unfasten 2 screws (M3 x 14) as shown in
the figure.
• Lift the printer mechanism in the arrow
position for removal.
Printer Mechanism
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
3. How to Remove the Control Board
• Remove the rear cover.
• Disconnect each connector.
• Unfasten 4 pieces of board mounting screws
for removal of the control board.
Control Board
3
Page 6

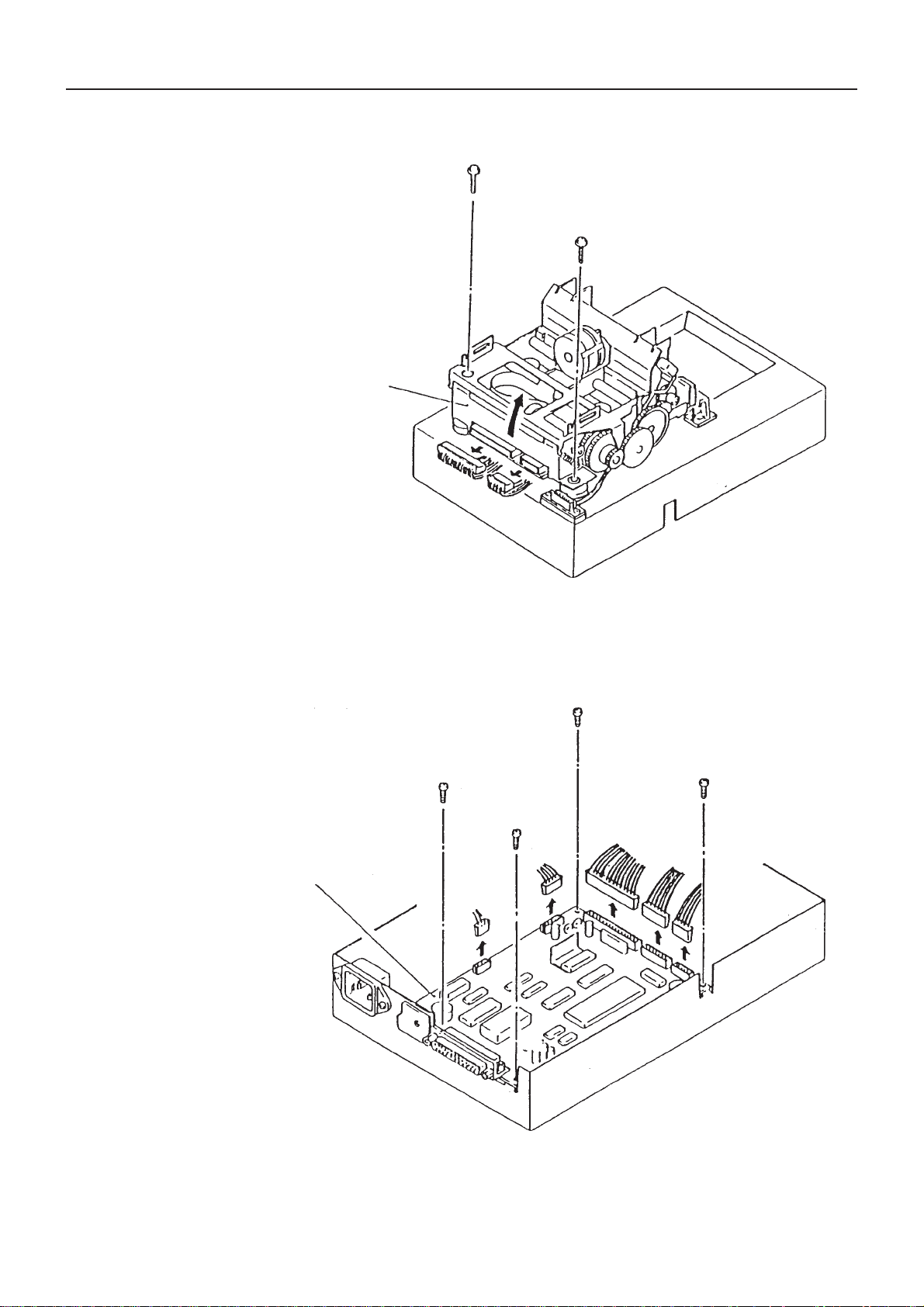
4. How to Remove the Power Board and AC Power Unit
1) How to Remove the Power Board
• Disconnect 2 connectors.
• Unfasten 2 screws (M3 x 8) and 2 tapping screws (M3 x 8).
• Remove the board, paying attention to the lead wire.
2) How to Remove the AC Power Unit
• Unfasten 2 inlet set screws (M3 x 10) and an earth wire mounting screw (M4 x 6).
• Unfasten 2 noise filter plate mounting screws (M3 x 6).
• Unfasten 4 power transformer mounting screws (M4 x 6).
• Disconnect the connector at the secondary side of the power transformer and take away the entire unit.
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Noise Filter Plate
Inlet
Po wer Transformer
Power Board
4
Page 7
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
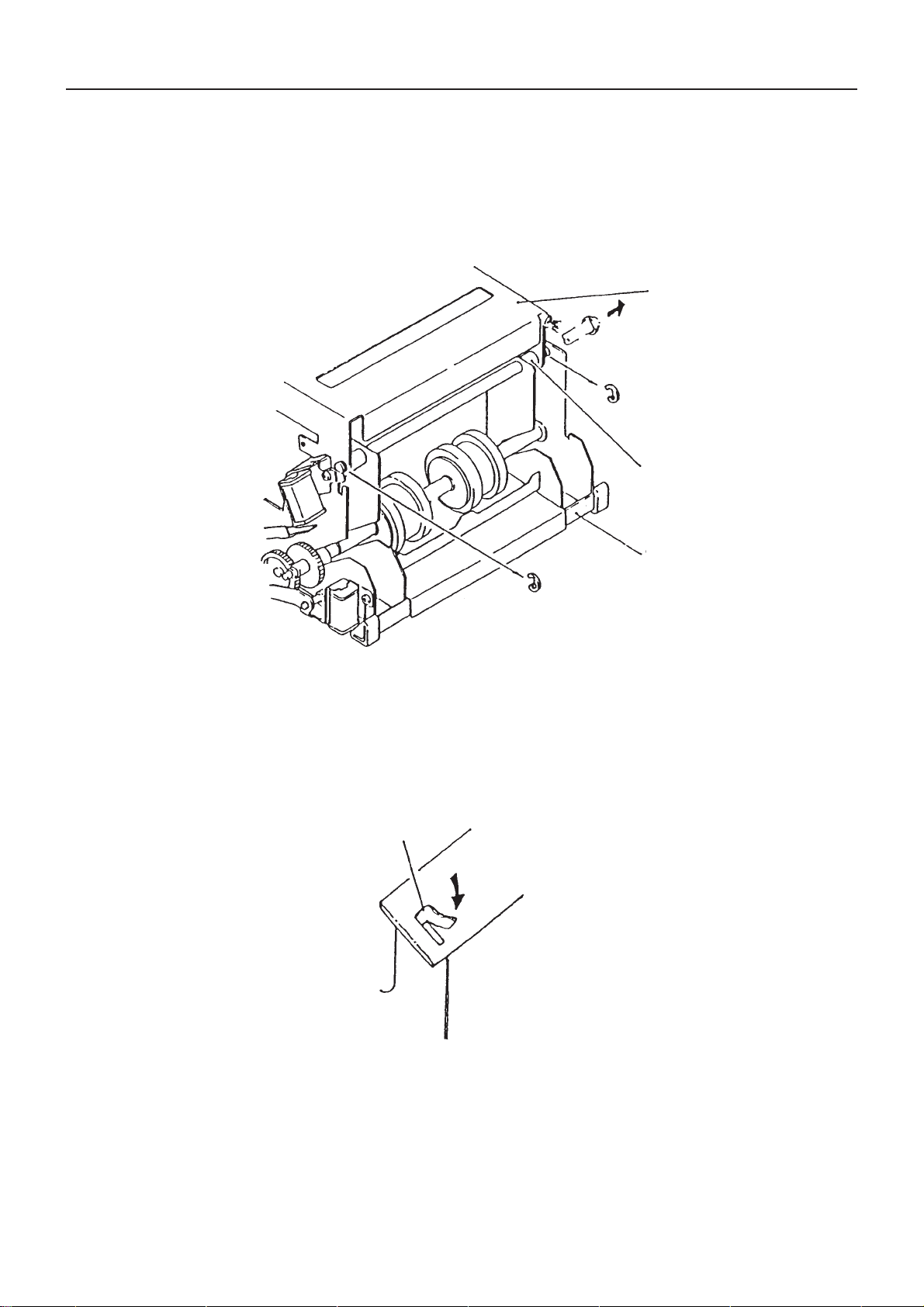
5. How to Remove the Auto Cutter Unit (720)
• Remove the printer mechanism from the main body.
• Remove 2 E3’s as shown in the figure.
• Pull out the shaft in the arrow direction for removal of the auto cutter unit. (Note that 2 spacers come off at the
same time).
Auto Cutter Unit
Spacer
Printer Mechanism
6. How to Remove the Operation Panel Board and PE Sensor Board
• Remove the upper cover and unfasten 2 tapping screws for removal of the operation panel board.
• Remove the printer mechanism and unfasten a screw for removal of the PE sensor board assembled with the PE
sensor holder. To remove the board only, remove the lug of the PE sensor holder.
Lug
5
Page 8

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Chapter 2
Circuit Description
6
Page 9
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
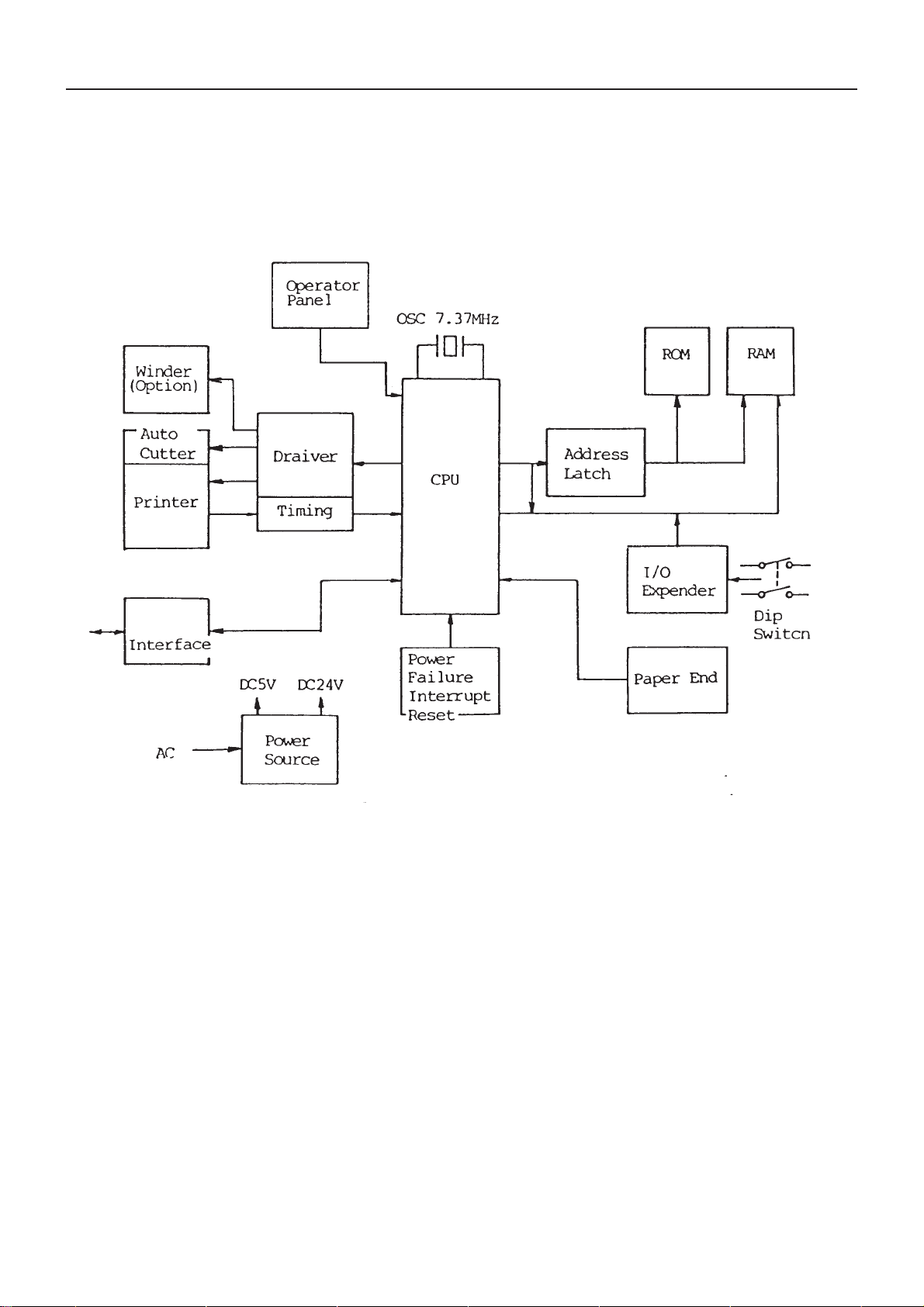
1. Outline
A block diagram of this printer is shown in Fig. 1-1. It consists of the control circuit centered around CPU, ROM,
RAM and peripheral circuits, interface circuit for interfacing with each host computer, operator panel circuit for
operating switch input and LED display, printer mechanism, auto cutter, and power circuit for furnishing power
supply to each part.
Fig. 1-1 Block Diagram
7
Page 10
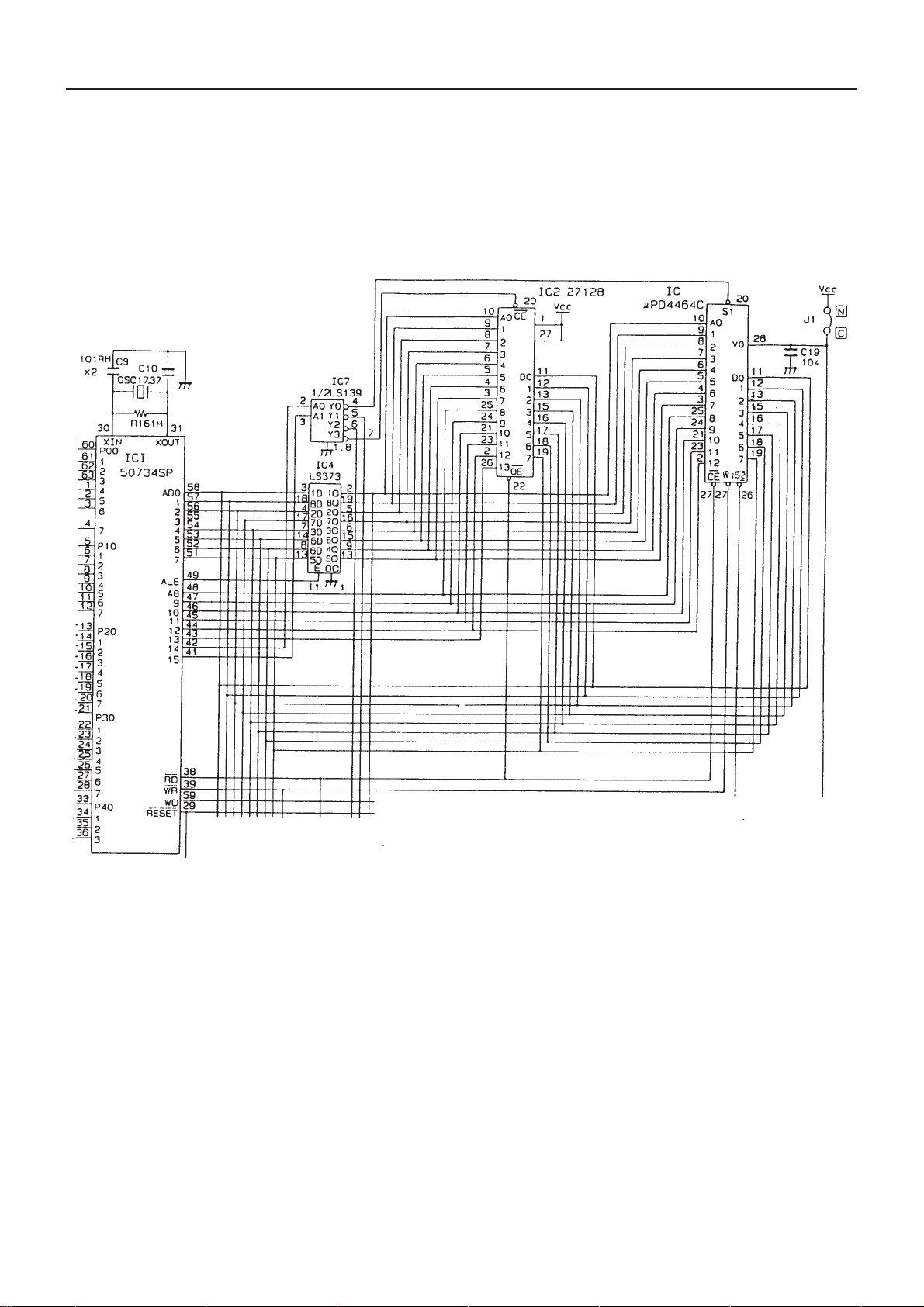
2. CPU Peripheral Circuits
1) CPU and ROM/RAM
The CPU M50734SP has a external memory type. Lower 8-bit address is fetched via the A0/D0 bus line by
the 8-bit latch LS373. The 128-KB ROM and 64-KB RAM are used for performing the backup operation for
power failure by the super capacitor. The ceramic oscillator is used as CPU clock and transmits 7.37 MHz.
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Fig. 2-1 CPU and ROM/RAM Circuit
2) Initial Resetting and Power Failure Interrupt Circuit
The IC12 is an IC for generating the power failure interrupt signal and reset signal. When the power supply
voltage decreased due to power failure, etc. this IC performs the voltage inspection and stores all data in the
CPU buffer into RAM while printing.
8
Page 11
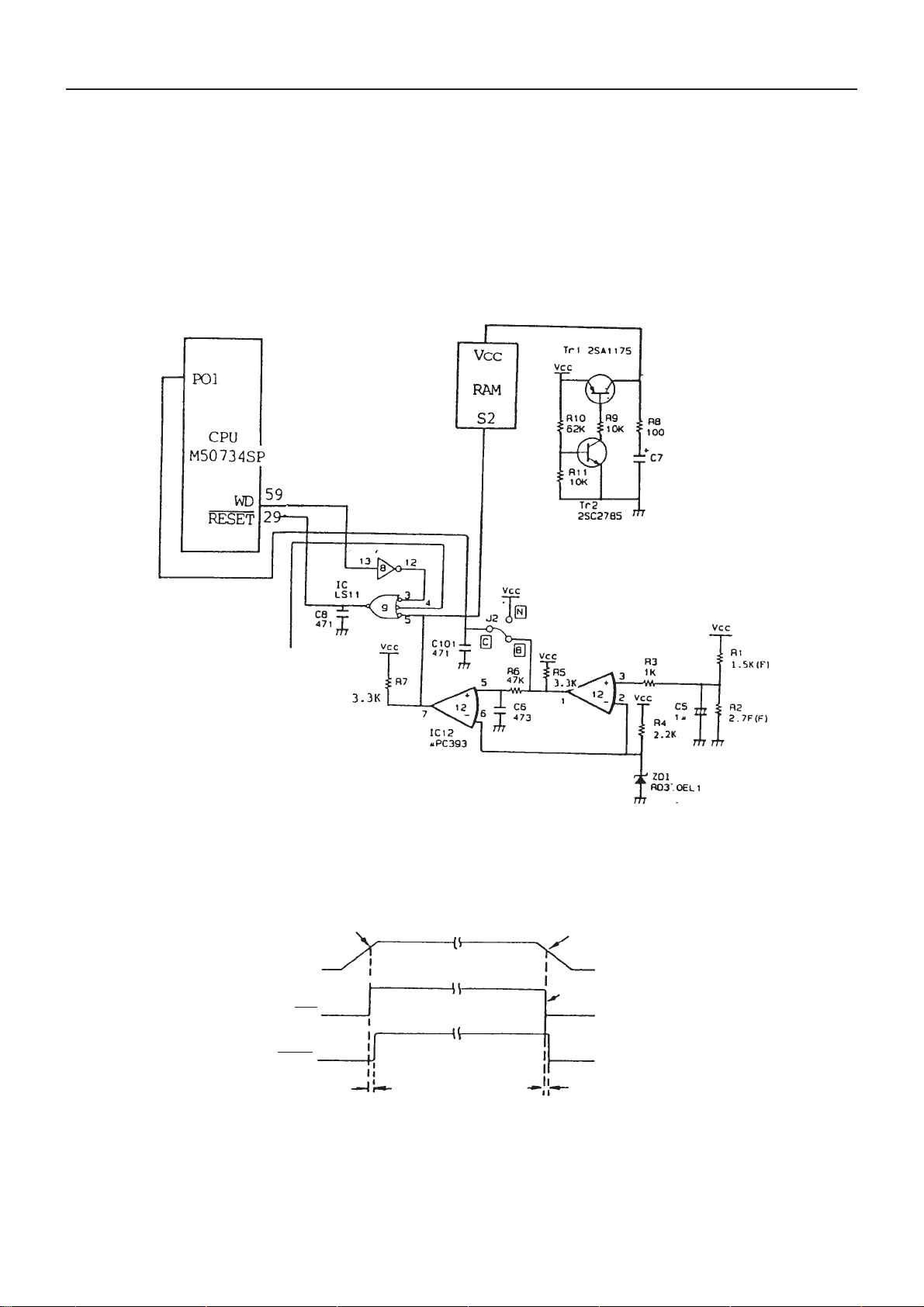
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
As can be seen in the timing chart, it detects that Vcc decreased up to about 4.5 V for power failure and
generates the power failure interrupt signal and sends it to CPU. Upon receipt of the signal, CPU transmits
the data in its buffer to RAM. This processing is done within about 200 µs. After about 1 ms, the reset signal
is generated at IC12 and given to CPU, etc., causing all circuits to reset for prevention of explosive running.
When the power supply is turned on, reset is released after Vcc increases up to 4.5 V or more and then initial
setting is performed. The WD terminal of CPU is called “Watch Dog”, which is the output terminal used for
explosive running.
Super Capacitor 0.047F
External Reset Input
(To interface circuit)
Fig. 2-2 Power Failure Interrupt Circuit and Initial Resetting
4.5V
Vcc (5V)
INT
(Power Failure Interrupt)
Reset
About 1ms
4.5V
Power failure interrupt
signal generated
About 1ms (Data stored)
Fig. 2-3 Timing Chart
9
Page 12
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
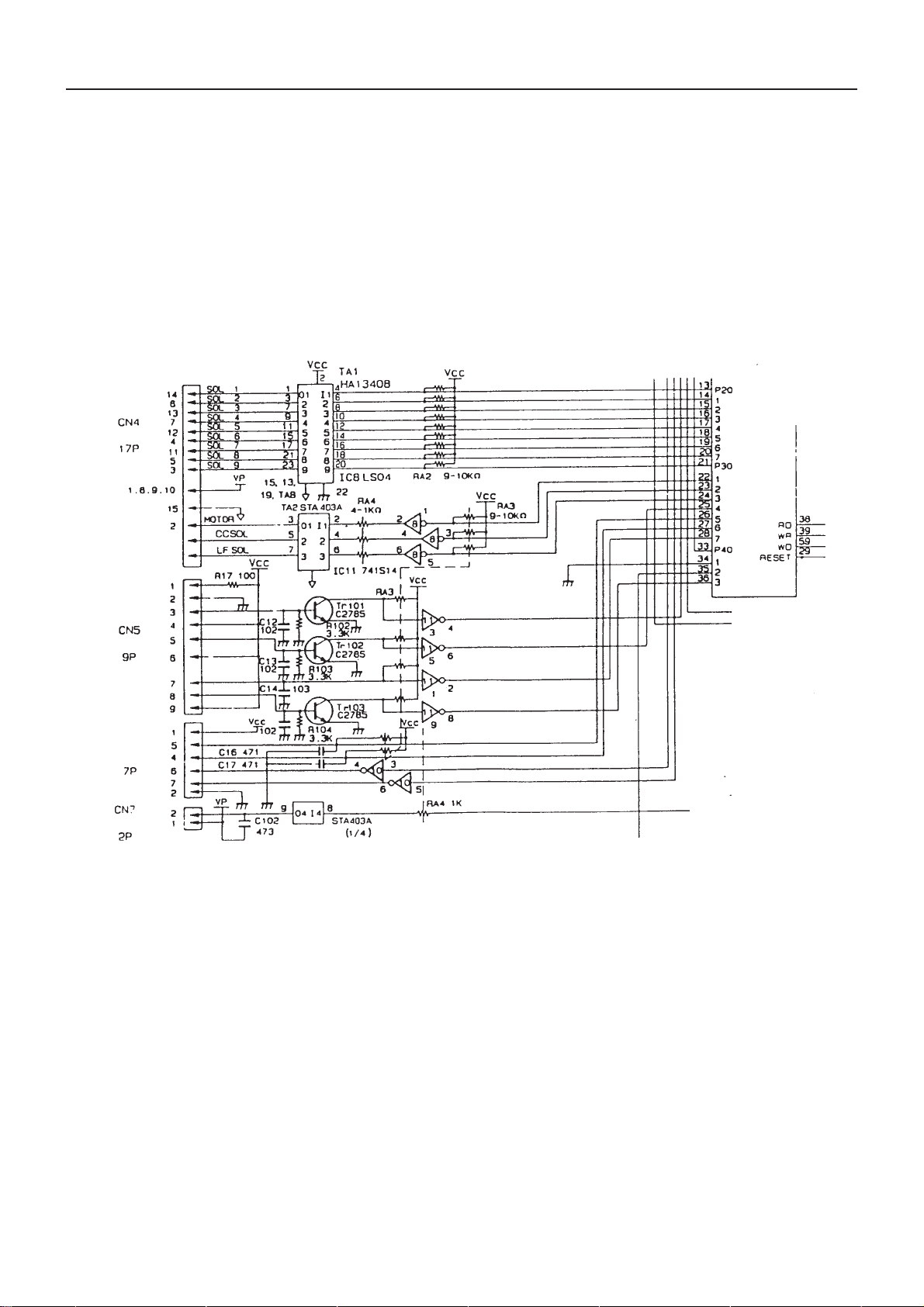
3. Printer Control Circuit
1) When L is output to the CPU port P31, the motor rotates and a timing pulse appears at the DP terminal of
CN5.
2) After rotation of the motor, printing starts in timing at which the port P34 is changed into L from H by the
home pulse of the printer.
3) In 9 ports of CPU output ports P20 to 27 and P30, the L pulse is output to the necessary port. Electricity is
applied once to the DOT solenoid for two timing pulses and characters are printed.
4) The paper is fed when the CPU port P33 becomes L in the specified timing.
5) Color is changed when the CPU port P32 becomes L in the specified timing.
PrinterPrinter
Operation Panel
CN6
Winder
Fig. 3-1. Printer Control Circuit
10
Page 13
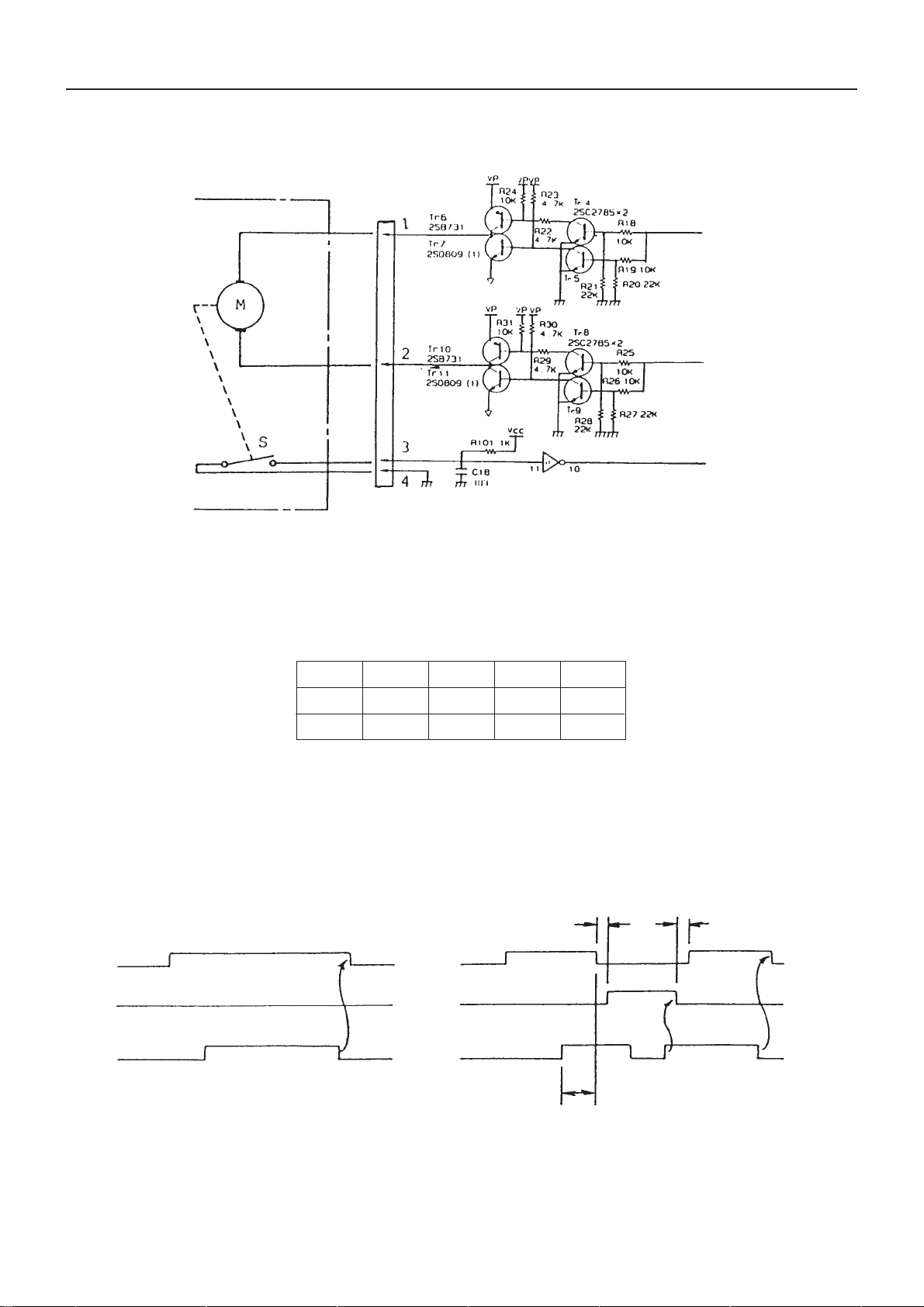
4. Cutter Control Circuit
Cutter Side
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
X
Y
S
Fig. 4-1 Cutter Control Circuit
The cutter control circuit is as shown in Fig. 4-1. In the cutter side, M indicates the motor and S the home switch.
The motor can make forward and reverse rotation by controlling X and Y inputs of the control circuit as shown in
the table below.
Normal
Reverse Stop Stop
HLLHX
LHLHY
The timing chart is provided in Fig. 4-2. The rising of S when the motor makes forward rotation is the home
position, where the motor stops. For full cut, the blade returns to the home position with only forward rotation of
the motor after turn-around. For partial cut, on the way of cut after forward rotation of the motor, make reverse
rotation to return the blade. Then stop the blade at the home position by making forward rotation again.
1) Full Cut 2) Partial Cut
1 mS 1 mS
X
X
Y
S
Fig. 4-2 Timing Chart
Y
S
15 mS
11
Page 14
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
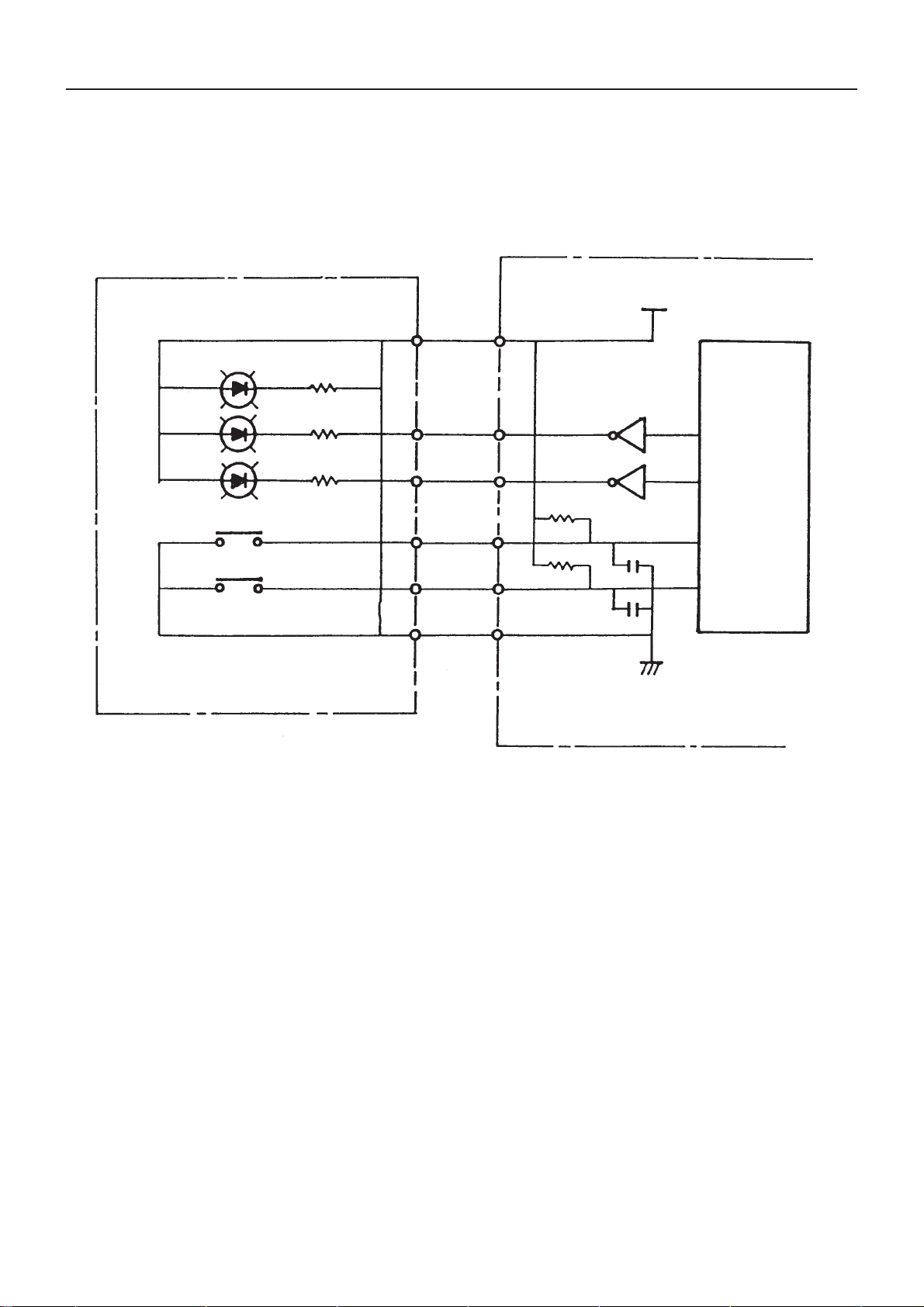
5. Interface with Operation Panel
As shown in Fig. 5-1, the operation panel circuit has the on-line switch and line feed switch. Each switch is
connected to CPU input ports and each LED is connected through the driver to CPU output ports.
Control circuit
Operation Panel Circuit
Vcc
LED1
LED2
LED3
SW1
SW2
POWER
ON-LINE
ALARM
ON-LINE
FEED
R1
R2
R3
Fig. 5-1 Operation Panel Circuit
CPU
P04
P05
P35
P36
12
Page 15
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
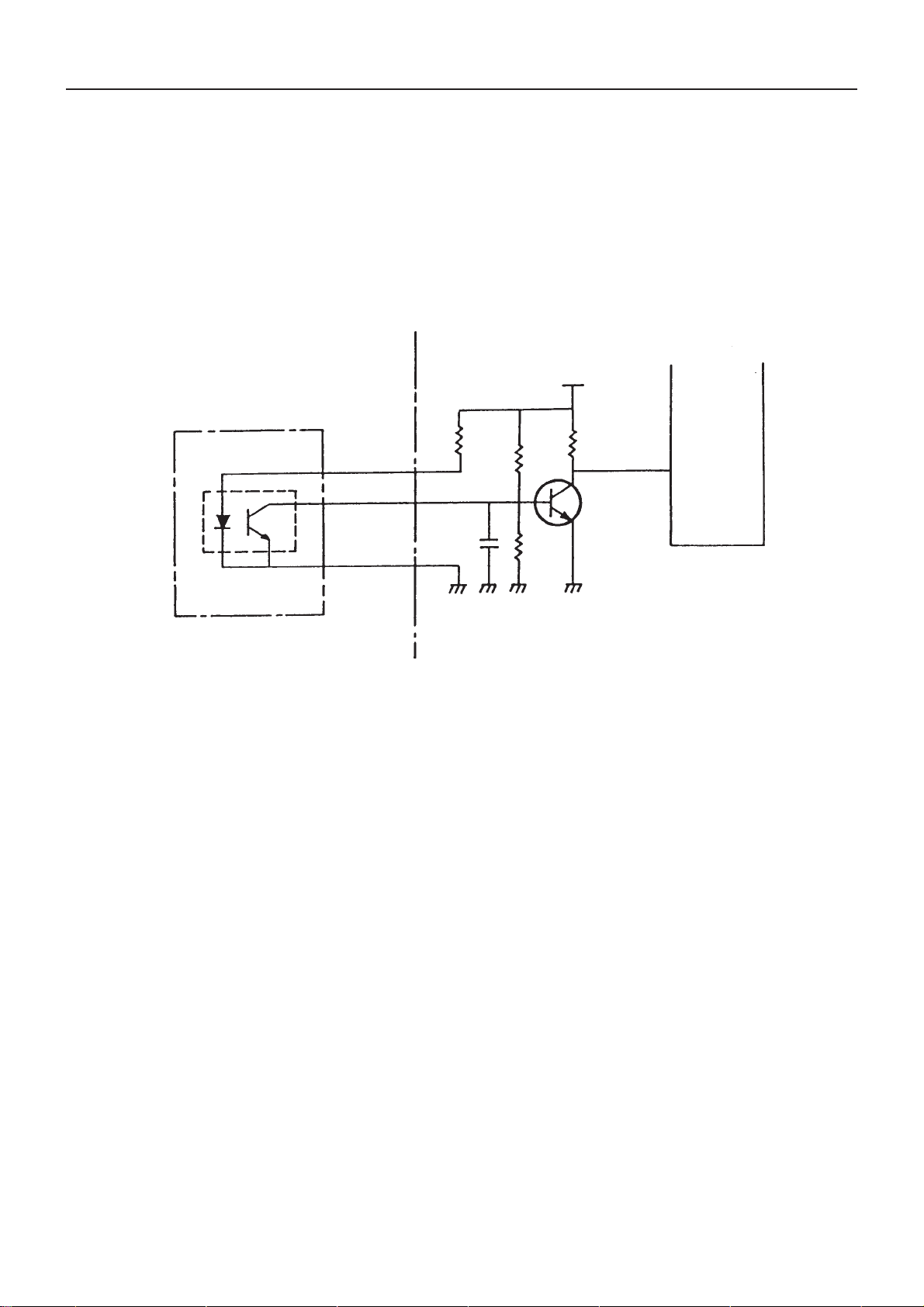
6. Paper End Sensor Circuit
Fig. 6-1 shows the paper end sensor circuit. The reflection type photo-interrupter is used as a sensor. When some
paper is still left, the light reflected by paper strikes upon the photo-transistor; thus, the collector of the phototransistor is L. When paper becomes short, no light is reflected, causing the collector to go H. As a result, the CPU
input port P40 becomes H, going into the paper end state.
Control Circuit
Paper End Sensor
PHI 1
R12
R13
C11
R14
Fig. 6-1 Paper End Sensor Circuit
Vcc
R15
Tr3
CPU
P40
13
Page 16
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
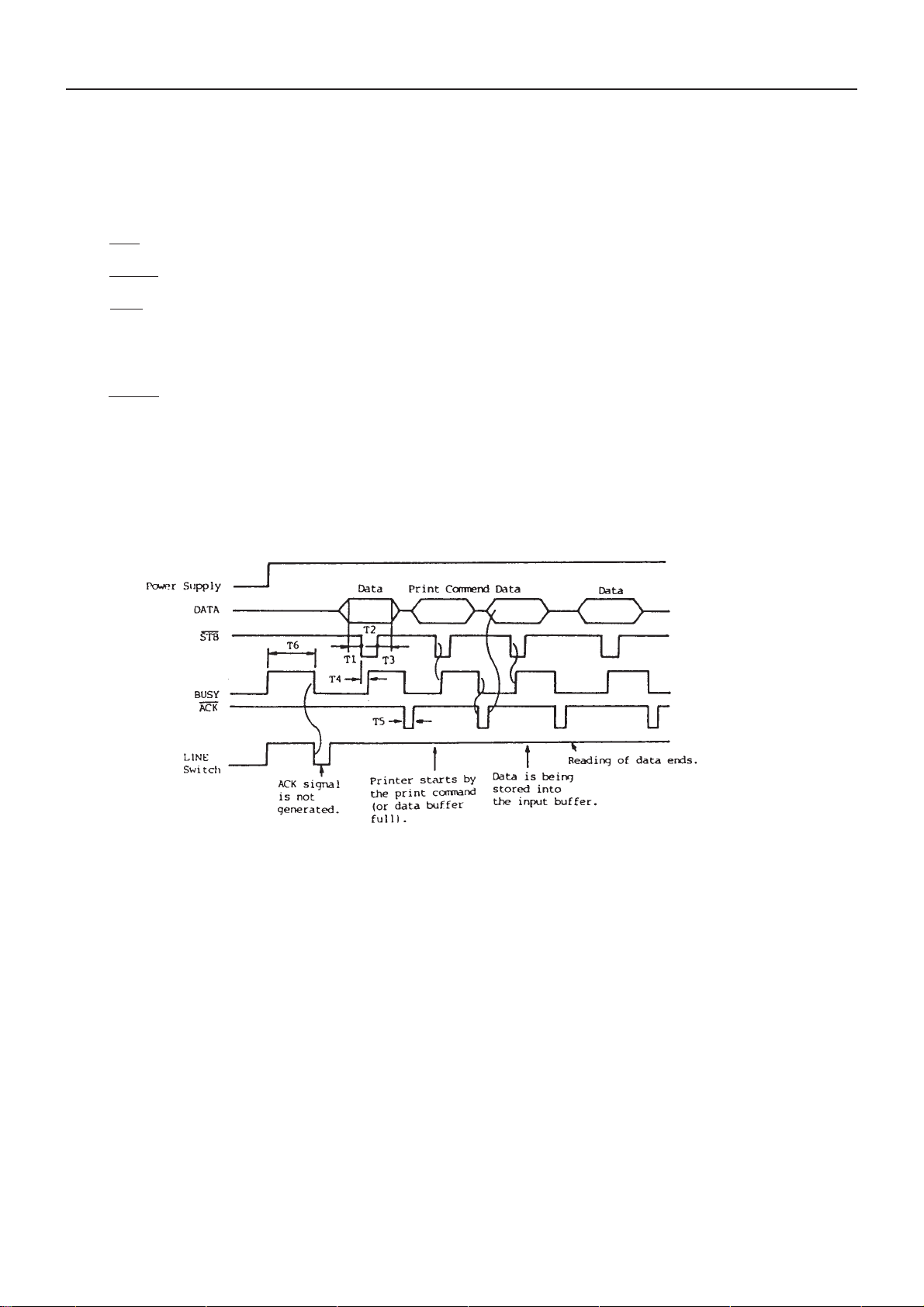
7. Parallel Interface Circuit
This circuit conforms to the standard interface. Description will be made for each signal of interface connector as
follows. Fig. 7-1 shows the data input and print timing chart and Fig. 7-2 the parallel interface circuit diagram.
DATA (D1~D8) : 8-bit parallel signal (Positive logic)
STB : Strobe signal for reading 8-bit data (Negative logic)
RESET : Signal for resetting the printer (Negative logic)
ACK : Data request signal to be output at the end of BUSY signal (Negative logic)
BUSY : Signal for indicating if the printer is in the busy state; it goes into the busy state for H. (Positive
logic)
FAULT : Signal to be output when the printer is in the abnormal state; at this time all control circuits in
the printer stop. (Negative logic)
PE : Signal to be output when the print paper becomes short (Positive logic)
FG : Frame ground
Fig. 7-1 Data Input and Print Timing Chart
14
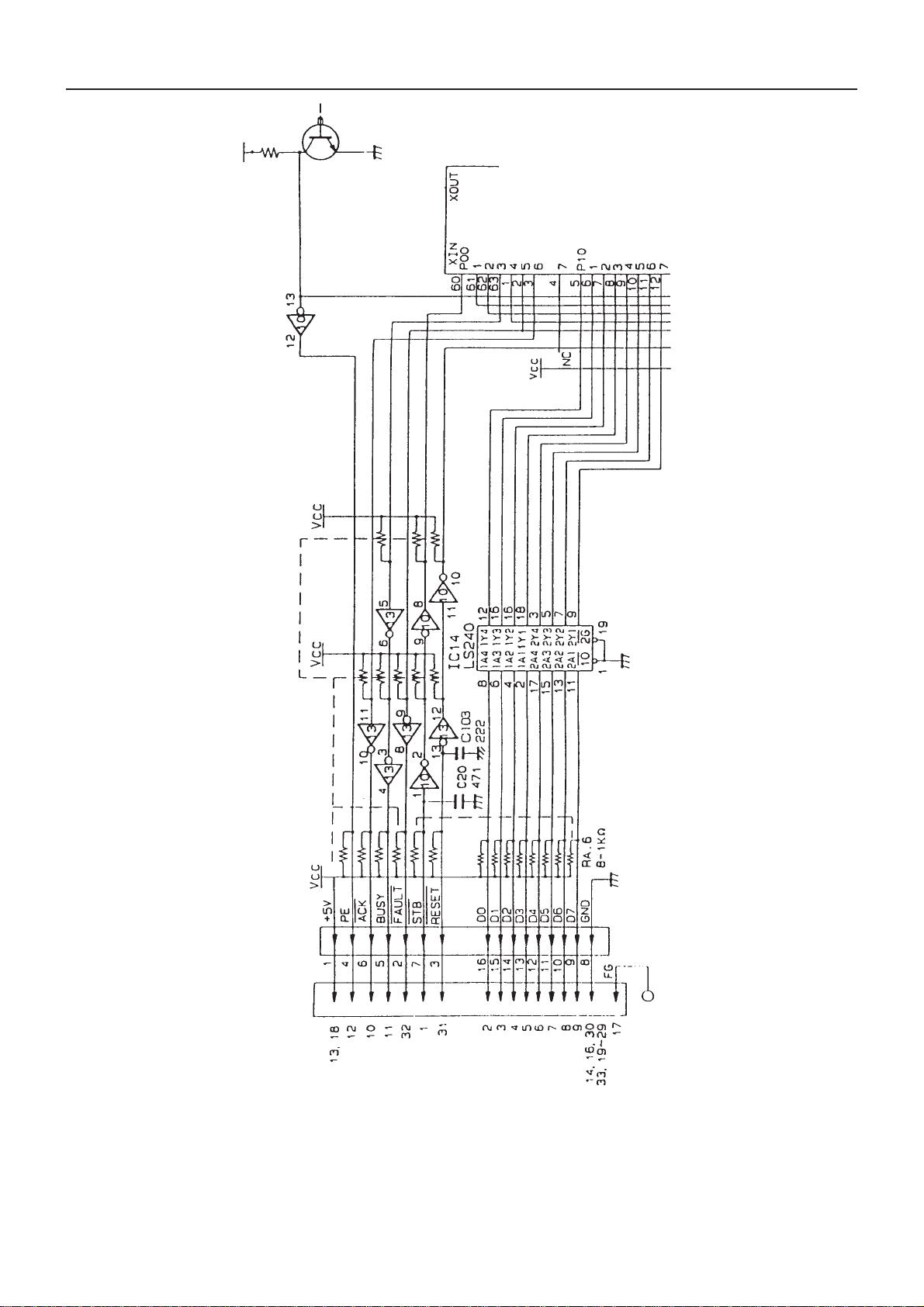
Page 17
Vcc
R15
IC10
7406
33k
IC1
50734SP
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
RA5
16P
CN3
CN2
IC137406
12-33kΩ
Fig. 7-2. Parallel Interface Circuit
15
Page 18

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
8. Serial Interface Circuit
As the serial interface specification, RS-232C and 20 mA current loop can be switched by the slide switch. It can
be switched by the user although fixed by setting at delivery time.
1) RS-232C
By using MAX232C for data receiving (RD), data transmitting and BUSY (DTR), data is transmitted and
received at level of RS-232C. The baud rates of 110 to 9600 bps can be selected by switching the DIP
switch.
2) 20 mA Current Loop
The photo coupler is used for transmitting and receiving. The photo coupler LED is used for receiving data
and the photo transistor for transmitting data.
3) DIP Switch Reading
The baud rate, word length, parity check, parity condition are set by the DTP switch.
4) Positive/Negative Power Supply for RS-232C
±12 V power supply is required for obtaining RS-232C voltage level. In this printer, however, as IC
MAX232C for interface is used, ±12 V is generated at the power circuit built in IC. Thus, no other power
supply is required.
The serial interface circuit diagram is shown in Fig. 8-1.
16
Page 19
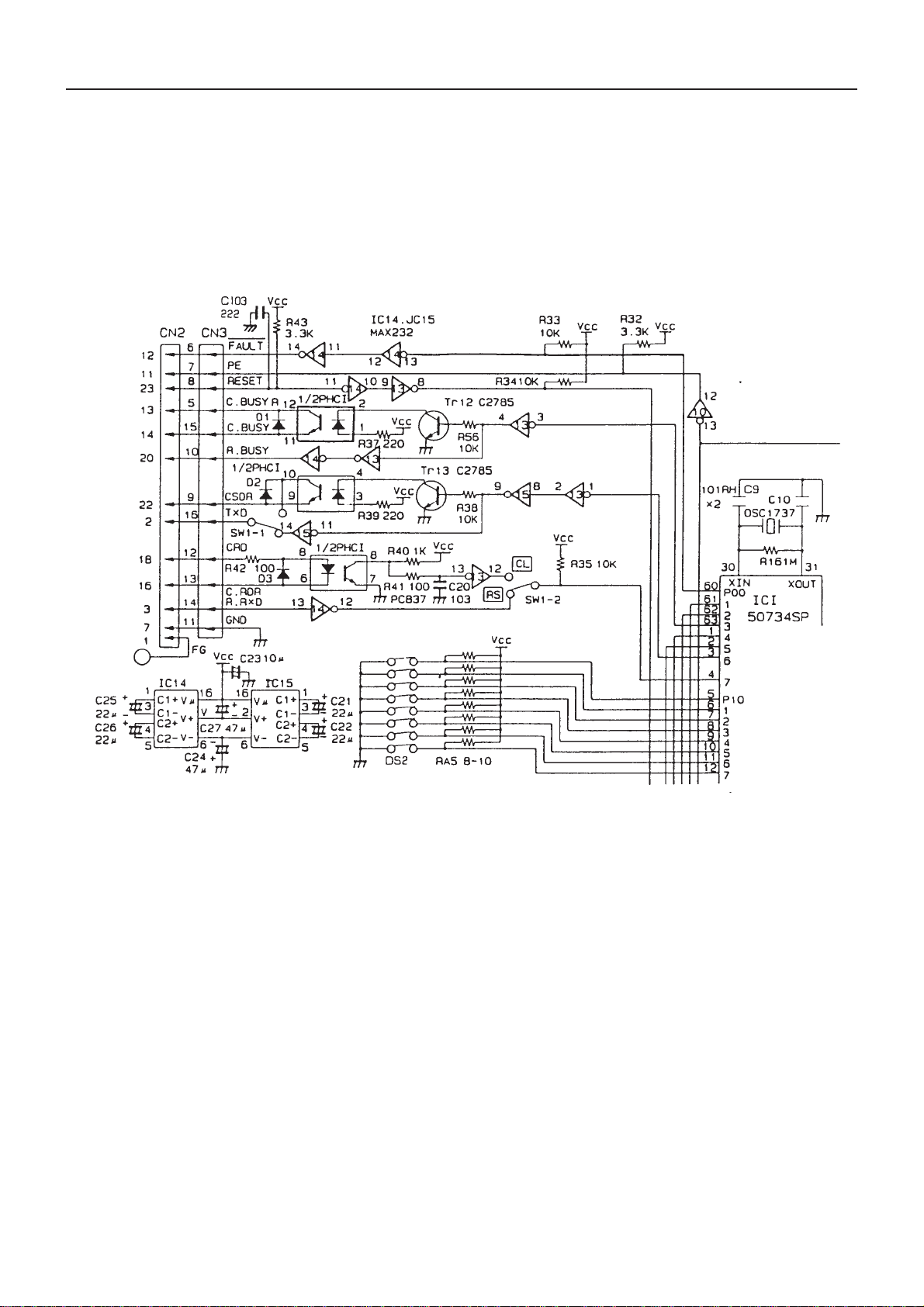
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Fig. 8-1 Serial Interface Circuit Diagram
17
Page 20
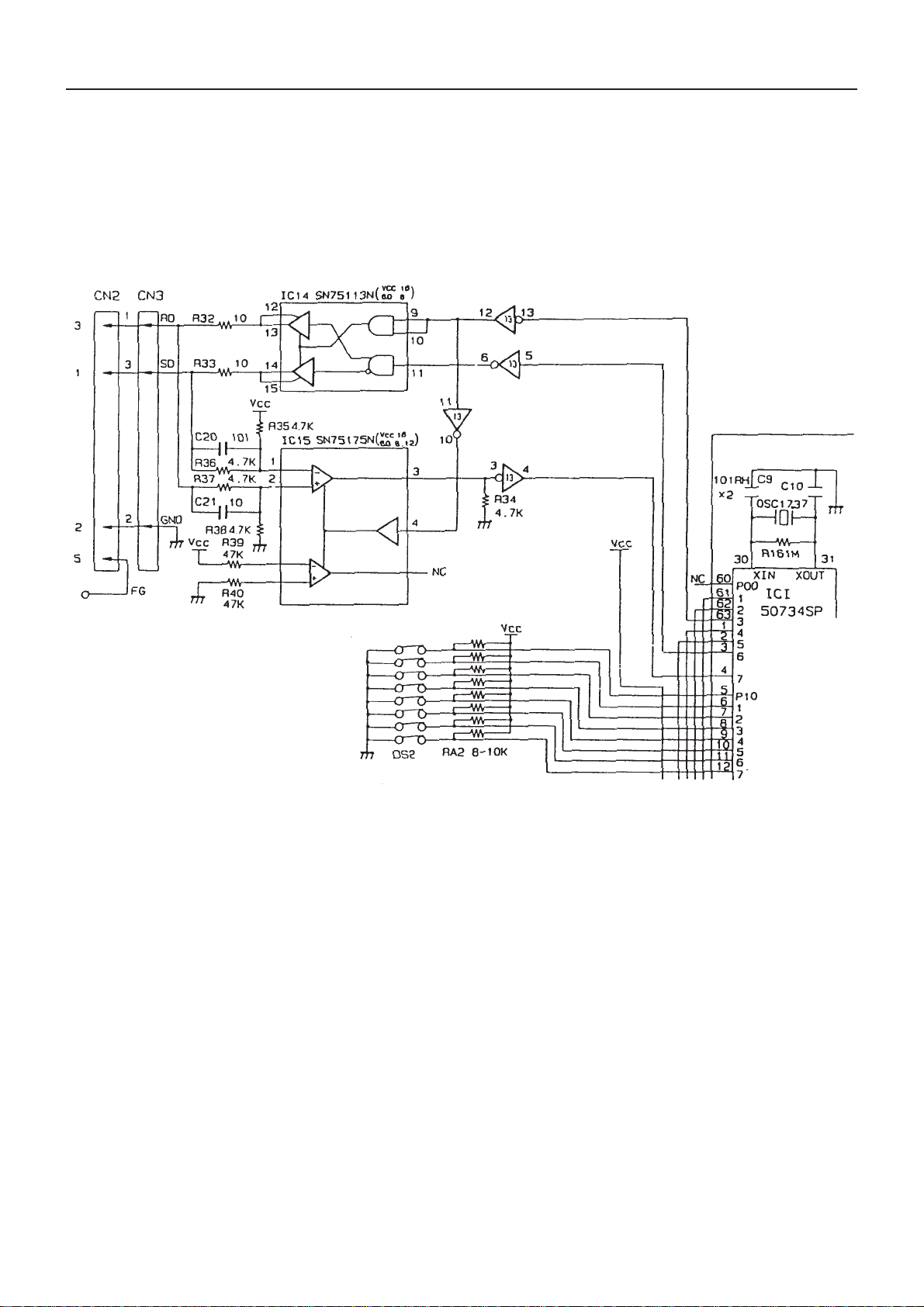
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
9. RS422A Interface Circuit
The RS422A interface circuit diagram is shown in Fig. 9-1. As can be seen in the figure, when TXD CONTROL is
L, the line driver IC14 becomes enable, going into the ready-to-receive state. At this time, the line receiver IC15
becomes disable. When TXD CONTROL is H, IC14 becomes disable, while IC15 becomes enable, going into the
ready-to-receive state. Communication is actually made through 2 lines although usually done through 4 lines
(including GND FG). These 2 lines are used for both transmitting and receiving of data.
TXD CONTROL
TXD
RXD
Fig. 9-1 RS422A Interface Circuit
18
Page 21
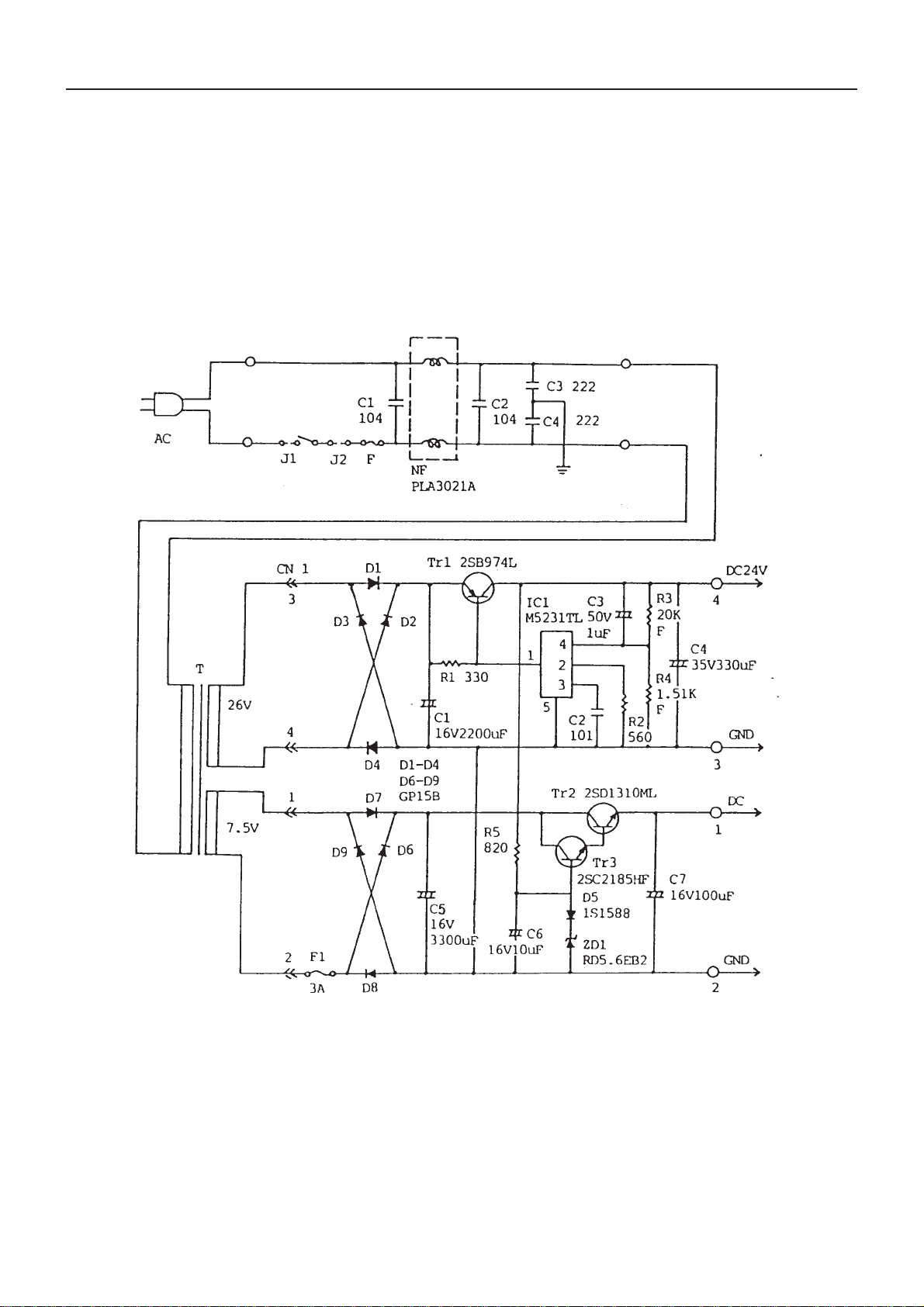
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
10. Power Circuit
This power circuit supplies DC 5 V for the control circuit and DC 24 V for driving the printer mechanism. When
the POWER switch is turned on, the AC voltage is applied to the transformer T after noise is eliminated by the
capacitors C1 to C4 and noise filter NF. For the secondary voltage of transformer, all waveforms are rectified at
both the DC 5 V side and DC 24 V side. IC1 indicates the regulator IC and Tr1 the current boosting transistor
which can generate DC 24 V constantly. The constant voltage can be obtained by the diode connected to the base
side of Tr3 and Zener diode, while DC 5 V can be obtained by the Darlington-connected transistor Tr2 for current
boost. The diode D5 also serves as temperature compensation.
Fig. 10-1. Power Supply Circuit
19
Page 22

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Chapter 3
Auto Cutter
20
Page 23

1. Maintenance and Handling
1) Precautions for Handling
(1) Precautions for use
Do not cut the paper other than the specified recording paper or do not pull the recording paper on the
way of cutting; otherwise, resulting in damage of the blade section and reduction of service life.
(2) Precautions for storage
Store the unit avoiding dust, dirt, high temperature and high humidity.
2) Cleaning
(1) Remove the dust of recording paper properly.
A good cleaning can be given by using the vacuum cleaner, etc.
(2) Use alcohol or benzine as a clearing solvent.
Thinner, trichlene, ketone, etc. may damage the plastic parts.
(3) After cleaning, lubricate as needed.
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
3) Lubrication
Lubrication is not especially required within 150,000 cuts.
However, the blade operates slow, oil is used up for cleaning, and disassembly, assembly and replacement
are made, lubrication should be required.
Gear pivot Maltenp Brushing
Lock level shaft " "
Crank pin Mo grease "
Movable blade sliding section " "
21
Page 24

2. Mechanism and Principle of Operation
1) Outline of Mechanism
The AC-2 and AC-3 are designed as the DP-505 and DP-600 small dot printers and characterized by compact
and lightweight types. The mechanism of this unit consists of 4 blocks; frame, power transmission
mechanism, detector, and movable blade mechanism.
2) Mechanism and Principle of Operation
2)-1 Power transmission mechanism
Cutter Gear
Worm
Motor Gear
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
The reduction gear train of this auto cutter is composed of the motor gear mounted onto the motor shaft,
worn, and two cutter gears. One rotation of the motor gear rotates the cutter gear by 7/520 (
(See. Fig. 1.)
2)-2 Detector
The detector is composed of the mechanism contract switch and cutter gear cam.
This detector detects the home position of the movable blade for partial cut (see Fig. 2), turn-around
position (see Fig. 3) and returned blade. It is turned on when the blade is at the home position and turned
off when the blade returns. The position where the detector is turned off from on after starting of the
movable blade is the turn-around position for partial cut.
Fig. 1
1/74)
22
Page 25

Cam
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Cutter Gear
Fig. 2 Fig. 3
2)-3 Movable blade mechanism
The movable blade is changed into a linear motion by the crank pins and starts cutting the recording
paper.
(1) Full cut
At full cut, the crank pins turn one time and return to the home position. The movable blade moves 12
mm.
(2) Partial cut
Switch
Fig. 4
Blade
Crank Pin
Fig. 5
At partial cut, the crank pins go into reverse at the moment they receive the switch signal and return to
the home position. The movable blade moves 9 mm.
23
Page 26

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
3. Repairing (Troubleshooting)
For troubleshooting, the repairing method will be explained by classifying the items as shown below.
Make sure of the cause according to the items and find out the trouble portions for repairing.
(1) Phenomenon ----------------- Find out the phenomenon of trouble from this column.
(2) Condition --------------------- Even in the same faulty phenomenon, the trouble condition may be different.
Check it, comparing with the content of this column.
(3) Cause-------------------------- The causes are listed on the basis of the trouble condition. Find out which cause is
applied.
(4) Check Point and Method --- The check method to find out the cause if described.
(5) Troubleshooting ------------- Repair the faulty portions according to the method described in this column.
24
Page 27

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
power supply circuit.
• If the voltage is out of rating, correct the
supply is furnished. Check the both
• Make sure that the input power
• Replace the motor if not rotate.
terminals of the motor with the
tester, etc.
• Apply the rated voltage to the both
• Eliminate the foreign matters.
terminals of the motor and check if
the motor rates.
movable section.
• Detach the cutter cover to check the
found.
• Replace the switch if an abnormality is
tester, etc.
• Check the switch output with a
• Use the specified recording paper.
• Measure the thickness of the
• Eliminate the foreign matters.
recording paper.
(0.1 mm or less).
• Check the paper passage.
• Replace the cover if deformed.
• Eliminate the paper dust and lubricate.
warping, etc.
• Detach the cutter cover to check its
• Detach the cutter cover to check the
• Replace the blade if damaged or worn.
paper dust.
check its edge.
• Dismount the movable blade to
supply for motor
1. Abnormality in input power
rotate even if the rotation
• The motor does not
Phenomenon Condition Cause Check Point and Method Troubleshooting
does not
1. The motor
2. Motor failure
command is entered.
rotate.
matters into the rotation section
3. Lock due to entrance of foreign
1. Detecting switch failure
temporarily and stops
when the rotation
• The motor operates
1. Inappropriate recording paper
command is entered.
• The blade returns on the
2. The recording
25
the passage of recording paper
2. Entrance of foreign matters into
way though it attempts
to cut the paper.
paper cannot
be cut.
shortage of the blade sliding
1. Deformation of the cutter cover
2. Clogging of paper wastes or oil
portions or more remain
• Full cut is normal
• In partial cut, four uncut
section
movable blade
1. Damage or abrasion of the
well
• The blade does not cut
Page 28

4. Disassembly/Assembly
1) Disassembling Procedure
Perform the disassembly in a reverse manner of the assembling procedure.
2) Assembling Procedure
Perform the assembly according to the assembling procedure as shown in the separate table. Numbers in
Exploded View at the end of this chapter are used as drawing numbers.
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
26
Page 29

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
27
Page 30

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Chapter 4
Circuit Diagram
28
Page 31

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Fig. 4-1. Power Supply Circuit Diagram CBM710/720-001-00
29
Page 32

Fig. 4-2. Noise Filter Circuit Diagram CBM710/720-002-00
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Fig. 4-3. Operation Panel circuit Diagram CBM710/720-003-00
30
Page 33

Fig. 4-4. Paper End Sensor Circuit Diagram CBM710/720-004-00
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Cord Assy CA5
PC Board PC710-06
Fig. 4-5. OP Junction Circuit Diagram CBM 710/720-005-00
31
Page 34

4-6. Circuit Diagram: Parallel
CBM710/720-006-00
13, 18
14, 16, 30
33, 19-29
Printer
PrinterPanelOpe.WinderCutter
CN2 CN3
12
10
11
32
1
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
17
CN4
17P
1, 8, 9, 10
CN5
9P
CN5
7P
CN7
2P
CN8
4P
FG
14
13
12
11
15
16P
1
4
6
5
2
7
3
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
6
7
4
5
3
2
Vcc Vcc
+5V
PE
ACK→
BUSY
FAULT
STB
RESET
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
GND
SOL 1
SOL 2
SOL 3
SOL 4
SOL 5
SOL 6
SOL 7
SOL 8
SOL 9
VP
MOTOR
CCSOL
LFSOL
R17 100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
5
4
6
7
2
2
1
1
Vcc
C16 471
C17 471
VP
2SB731
2SD809(1)
2
2SB731
2SD809(1)
3
4
RA5
12-33kΩ
A
.6
R
8-1KΩ
15, 13
19, T AB
Vcc
C12
102
C13
102
C14 103
C15
102
C102
473
Tr6
Tr7
Tr10
Tr11
R101 1K
IC137406
10
11
13
3
4 6 5
13
8
9
13
1
2
10
C20
471
Vcc
1
O1
3
2
7
3
9
4
11
5
15
6
17
7
21
8
23
9
TA2STA403A
3
01
I1
5
2
7
3
R103
3.3K
R104
3.3K
04 I4
VP
R24
10K
VP
R31
10K
Vcc
C18
103
13
13
C103
222
TA1
2
HA13408
I1
6
2
9
3
10
4
12
5
14
6
16
7
18
8
20
9
IC8LS04
22
4-1KΩ
2
4
2
6
3
IC11 741S14
Tr101
C2785
R102
3.3K
Tr102
C2785
Tr103
C2785
89
STA403A
VP VP
R23
4.7K
R22
4.7K
VP VP
R30
4.7K
R29
4.7K
12
RA4
RA3
34
10
(1/4)
Tr4
2SC2785 x 2
Tr5
Tr8
2SC2785 x 2
Tr9
11
18
17
15
13
11
6
R21
22K
R28
22K
1011
IC14
LS240
1A4
6
1A3
4
1A2
2
1A1
2A4
2A3
2A2
2Y1
10
1 19
9-10KΩ
2
8
6
Vcc
Vcc
10
13
9
10
1Y4
1Y3
1Y2
1Y1
2Y4
2Y3
2Y2
2Y1
2G
RA2
1
8
8
5
11
11
11
11
5
RA4 1K
R18
10K
R19 10K
R20 22K
R25
10K
R26 10K
R27 22K
11
12
16
16
18
3
5
7
9
Vcc
Vcc
IC10
7406
12
13
10
Vcc
101RH
C9
OSC1737
R161M
30
XIN
P00
1
2
50734SP
3
4
5
6
7
P10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P30
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P40
1
2
3
10 10 11
7
9
C10
ICI
RESET
XOUT
AD0
ALE
RD
WR
WD
8
811 9
31
58
57
1
56
2
55
3
54
4
53
5
52
6
51
7
49
48
A8
47
9
46
10
45
11
44
12
43
13
42
14
41
15
38
39
59
29
8
x 2
8
10
10
Vcc
NC
Vcc
RA3
9-10KΩ
60
61
62
63
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
33
34
35
36
43
65
8
R15
3.3K
Tr3
2SC2758
R14
33K
2
3
3
18
4
17
7
14
8
13
12
21
89
6
13
5
11
LS375
E1
1Q
4Q
2Q
3Q
IC5
E2
1D
4D
2D
3D
124
1
15
7
9
9
2AY
18
1A1
3
2Y4
16
1Y2
5
2Y3
14
1Y3
7
2Y2
12
1Y4
LS240
Vcc
BZ
1
10
2
2 3 1
R13
68K
C11
103
IC7
1/2LS139
A0A1Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
1.8
IC4
LS373
1D
1Q
19
8D
8Q
2D
2Q
16
7D
7Q
3D
3Q
15
6D
6Q
6D
4Q
13
5D
5Q
E
0Q
11 1
15
E
2B
2YA
2A
IC7
1/2LS139
19
1
2Q
1Q
2AY
1A1
2A4
1A2
2A3
1A3
2A2
1A4
IC5
11
2
17
4
15
6
13
8
R12
180
4
5
6
2
5
6
9
13
16
(PE)
CN9
Vcc
7
RA1
8-10K
Vcc
3P
C8
471
DS1
2P
IC
LS11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
25
24
21
23
2
26
13 12
8
9
Vcc
R7
3.3K
A0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
3
5
20
CE
D0
CE
22
4
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
C101
471
IC12
µPC393
IC2 27128
Vcc
1
27
11
12
13
15
16
17
18
19
J2
C
5
+
12
6
–
Vcc
R6
47K
N
B
C5
473
VP
Vcc
IC
µPD4464C
Vcc
R10
62K
R11
10K
Tr2
Vcc
2SC2785
R5
3.3K
1
C3
104
16V 100µ
S1
10
A0
9
1
V0
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
D0
5
4
6
3
7
25
8
24
9
21
10
23
11
2
12
W
S2
CE
27 27 26
Tr1 2SA1175
R9
R8
10K
100
+
3
+
12
Vcc
2
–
C4 35V 47µ
L1
L2
C2
20
28
11
12
1
13
2
15
3
16
4
17
5
18
6
19
7
C7
R3
1K
R4
2.2K
ZD1
RD3.0EL1
C1
104
C19
104
0.047F
C5
1µ
J1
Vcc
Vcc
R1
1.5K(F)
R2
2.7K(F)
5
3.4
1
2
N
C
CN1
5P
Power
32
Page 35

4-7. Circuit Diagram: RS232C
CBM710/720-007-00
CN4
17P
Printer
CN5
PrinterPanelOpe.WinderCutter
9P
CN6
7P
CN7
2P
CN8
4P
1, 8, 9, 10
Vcc
C103
233
CN2 CN3
6
12
7
11
8
23
5
13
15
14
10
20
9
22
16
2
12
18
13
16
14
3
11
7
1
FG
Vcc
IC14
1
16
+
+
C25
C25µ
C26
22µ
14
6
13
7
12
4
11
5
3
15
2
1
2
3
4
C1
3
–
C1
+
C2
4
–
C2
5 6 6
SOL 1
SOL 2
SOL 3
SOL 4
SOL 5
SOL 6
SOL 7
SOL 8
SOL 9
VP
MOTOR
CCSOL
LFSOL
R17 100
Vcc
–
+
–
Vµ
V+
V–
C24
47µ
15, 13
19, T AB
C12
102
V
C27 47µ
1
3
7
9
11
15
17
21
23
TA2STA403A
3
5
7
THC1 C2785
5
6
7
8
9
1
5
4
6
C16 471
C17 471
Vcc
C13
102
C14
C15
103
102
7
2
VP
2
1
1
2SD809(1)
2
3
4
C102
473
Tr6
2SB731
Tr7
Tr10
2SB731
Tr11
2SD809(1)
9
04 I4
VP
VP
R101 1K
C18
103
FAULT
PE
RESET
C. BUSY R
01
C. BUSY
R. BUSY
1/2PHCI
D2
CSOR
T x D
SW1-1
CPD
R42 100
D3
C. RDR
R. RXD
GNC
C2310µ
IC15
16
Vµ
2
V+
V–
Vcc
2
I1
O1
2
2
3
3
10
4
4
12
5
5
14
6
6
16
7
7
18
8
8
20
9
9
2
01
I1
4
2
2
6
3
3
IC11 741S14
R102
3.3K
R103
3.3K
Tr103
C2785
R104
3.3K
8
VP VP
R24
10K
VP VP
R31
10K
Vcc
R43
3.3K
14
2/1PHCI
12
11
10
9
14
15
8
6
131312
1
+
C1
3
–
C1
+
C2
4
–
C2
5
TA1
HA13408
4
6
8
22
RA4
4-1KΩ
Tr102
C2785
4
10
STA403A
(1/4)
R23
4.7K
R22
4.7K
R30
4.7K
R29
4.7K
11
11
10
14
11
14
11
10 9
14
2
1
R37 220
4
3
R39 220
11
2/1PHCI
14
+
C21
–
C22µ
+
C22
–
22µ
RA2 9-10KΩIC8LS04
1
2
8
4
6
8
5
Vcc
RA3
Vcc
3
10
5
6
RA4 1K
Tr4
2SC2785 x 2
Tr5
R21
22K
Tr8
2SC2785 x 2
R26 10K
Tr9
R28
22K
IC14 JC15
MAX232
14
12 13
8
13
Tr12 C2785
Vcc
13
Tr13 C2785
Vcc
Vcc
R40 1K
8
7
R41 100
RC837
DS2 RA5 8-10
Vcc
Vcc
3
8
11
43
11
5
6
11
1
2
11
9
8
R18
10K
R19 10K
R20 22K
R25
10K
R27 22K
R56
10K
R38
10K
C20
103
RA3
9-10KΩ
R3410K
9 2
12
13
RS
Vcc
R33
10K
3
4
13
Vcc
CL
SW1-2
R32
Vcc Vcc
3.3K
18
1315
R35 10K
Vcc
BZ
12
10
13
C9
101RH
60
61
62
63
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
33
34
35
36
8
x 2
8
30
XIN
P00
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P30
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
P40
1
2
3
10
10
9
C10
OSC1737
R161M
XOUT
ICI
50734SP
RESET
10
8
7
811
3
13
5
11
LS375
1
2
AD0
ALE
WR
WD
E1
1Q
4Q
2Q
3Q
IC6
RD
31
58
57
1
56
2
55
3
54
4
53
5
52
6
51
7
49
48
A8
47
9
46
10
45
11
44
12
43
13
42
14
41
15
38
39
59
29
11
8
9
124
E2
1
1D
15
4D
7
2D
9
3D
R15
3.3K
Tr3
2SC2753
Vcc
R14
33K
18
16
14
12
2
3
18
17
14
13
11 1
12
9
3
5
7
2 3 1
R13
68K
C11
103
IC7
1/2LS139
A0A1Y0
IC4
LS373
3
1D
8D
4
2D
7D
7
3D
6D
8
4D
5D
E
E
2Y0
1 19
1Q
2Y1
2A1
1Y1
1A1
2Y4
2A4
1Y2
1A2
2Y3
2A3
1Y3
1A3
2Y2
2A2
1Y4
1A4
IC5
LS240
Y1
Y2
Y3
1.8
1Q
8Q
2Q
7Q
3Q
6Q
4Q
5Q
0Q
15
2B
2A
2Q
(PE)
CN9
Vcc
R12
180
4
5
6
7
2
19
5
16
6
15
9
13
13
16
IC7
1/2LS139
11
2
17
4
15
6
13
8
RA1
8-10K
Vcc
DS1
2P
IC
LS11
J1
C19
104
0.047F
Vcc
R1
1.5K(F)
R2
2.7K(F)
Vcc
5
3.4
1
2
N
C
CN1
5P
Power
N
B
C6
473
Vcc
IC
µPD4464C
Vcc
Tr1 2SA1175
R10
62KR910K
R11
10K
Tr2
2SC2785
R5
3.3K
12
1
VP
Vcc
C3
104
16V 100µ
S1
10
A0
9
1
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
5
4
6
3
7
25
8
24
9
21
10
23
11
2
12
W
CE
27 27 26
3
+
2
–
R4
2.2K
C4 35V 47µ
L1
L2
C2
V0
D0
R8
100
+
Vcc
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
S2
C7
R3
1K
28
11
12
13
15
16
17
18
19
C5
1µ
ZD1
RD3.0EL1
C1
104
IC2 27128
20
12
CE
D0
CE
22
7
1
27
11
12
1
13
2
15
3
16
4
17
5
18
6
19
7
4
C101
471
IC12
µPC393
Vcc
12
Vcc
J2
C
R6
47K
5
+
6
–
10
A0
9
1
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
5
4
6
3
7
25
8
24
9
21
10
23
11
2
12
26
13
13
8
3
9
C8
5
471
Vcc
Vcc
R7
3.3K
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
33
Page 36

4-8. Circuit Diagram: RS422A
CBM710/720-008-00
14
6
13
1, 8, 9, 10
7
12
4
11
5
3
15
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
5
4
6
7
2
2
1
1
2
3
4
CN4
17P
Printer
CN5
PrinterPanelOpe.Winder
9P
CN5
7P
CN7
2P
CN8
4P
Cutter
RA2 9-10KΩ
2
8
4
6
8
Vcc
RA3
Vcc
3
10
6
5
Tr4
2SC2785 x 2
Tr5
R21
22K
Tr8
2SC2785 x 2
R26 10K
Tr9
R28
22K
10
Vcc 18
60.8
9 12 13
10
11
11
Vcc 18
10
60.8.12
3
4
NC
RA2 8-10K
DS2
Vcc
1
3
8
5
11
4
3
11
6
5
11
2
1
11
8
9
RA4 1K
R18
10K
R19 10K
R20 22K
R25
10K
R27 22K
Vcc
13
RA3
9-10K
13
6 5
13
3
13
R34
4.7K
Vcc
Ω
2 3 1
R13
68K
C11
103
IC7
1/2LS139
A0A1Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
IC4
LS373
3
1D
1Q
8D
8Q
4
2D
2Q
7D
7Q
7
3D
3Q
6D
6Q
8
4D
4Q
5D
5Q
E
0Q
11
15
E
2B
2Y0
2A
IC7
1/2LS139
1 19
1Q
2Q
2A1
1A1
2A4
1A2
2A3
1A3
2A2
1A4
IC5
1.8
(PE)
CN9
3P
N
B
IC
µPD4464C
Vcc
Tr1 2SA1175
R10
62KR910K
R11
10K
Vcc
Tr2
2SC2785
R5
3.3K
12
1
VP
Vcc
C3
104
16V 100µ
S1
10
A0
9
1
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
5
4
6
3
7
25
8
24
9
21
10
23
11
2
12
W
CE
27
27 26
3
+
2
–
C4 35V 47µ
L1
L2
C2
V0
D0
R8
100
Vcc
20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
S2
C7
R3
1K
28
11
12
13
15
16
17
18
19
0.047F
R4
2.2K
ZD1
RD3.0EL1
C1
104
IC2 27128
20
12
CE
D0
CE
22
7
1
27
11
12
1
13
2
15
3
16
4
17
5
18
6
19
7
4
C101
471
IC12
µPC393
Vcc
Vcc
J2
C
R6
47K
5
+
12
C5
6
–
473
Vcc
R12
180
4
5
6
7
2
19
5
16
6
15
9
12
1
13
16
Vcc
11
2
17
4
15
6
13
8
RA1
8-10K
DS1
2P
IC
LS11
C8
471
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10
A0
9
1
8
2
7
3
6
4
5
5
4
6
3
7
25
8
24
9
21
10
23
11
2
12
26
13
13
8
3
9
5
Vcc
Vcc
R7
3.3K
Vcc
N
J1
C
C19
104
Vcc
R1
1.5K(F)
C5
R2
1µ
2.7K(F)
5
3.4
CN1
1
2
5P
Power
Vcc
R15
3.3K
Tr3
AD0
ALE
RD
WR
WD
IC6
2SC2758
31
58
57
1
56
2
55
3
54
4
53
5
52
6
51
7
49
48
A8
47
9
46
10
45
11
44
12
43
13
42
14
41
15
38
39
59
29
8
9
124
E2
1
1D
15
4D
7
2D
9
3D
R14
33K
2
3
18
17
14
13
12
9
2Y1
18
1Y1
3
2Y4
16
1Y2
5
2Y3
14
1Y3
7
2Y2
12
1Y4
4
Vcc
101RH
x 2
30
XIN
60NC
P00
61
1
62
2
63
3
1
4
2
5
3
6
4
7
5
P10
6
1
7
2
8
3
9
4
10
5
11
6
12
7
13
P20
14
1
15
2
16
3
17
4
18
5
19
6
20
7
21
P30
22
1
23
2
24
3
25
4
26
5
27
6
28
7
33
P40
34
1
35
2
36
3
8
C9
OSC1737
R161M
ICI
50734SP
10
10 11
9
7
11
13
C10
XOUT
RESET
8
8
3
5
11
E1
1Q
4Q
2Q
3Q
LS375
LS240
Vcc
BZ
1
10
2
101
4.7K
R39
47K
R40
47K
01
103
04 I4
10
10
Vcc
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
01
2
3
R103
3.3K
R104
3.3K
R24
10K
R31
10K
Vcc
I1
Vcc
12
13
14
15
R35 4.7K
1
2
2
4
I1
6
2
8
3
10
4
12
5
14
6
16
7
18
8
20
9
22
2
4
2
6
3
IC11 741S14
Tr101
C2785
R102
3.3K
Tr102
C2785
Tr103
C2785
8
VP VP
VP VP
IC14 SN75113N ( )
IC15 SN75175N ( )
–
+
–
+
TA1
HA13408
IC8LS04
RA4
Ω
4-1K
4
10
STA403A
(1/4)
R23
4.7K
R22
4.7K
R30
4.7K
R29
4.7K
11
11
CN2
CN3
1
RD
FG
VP
Tr6
2SB731
Tr7
2SD809(1)
Tr10
2SB731
Tr11
2SD809(1)
SD
GND
Vcc
Vcc
102
C102
473
R32
R33
C20
R38
R37 4.7K
C21 10
R38 4.7K
Vcc
1
3
7
9
11
15
17
21
23
15, 13
19, T AB
T A2STA403A
3
5
7
C12
102
C13
102
C14
9
VP
VP
R101 1K
C18
103
3
3
1
2
2
5
SOL 1
SOL 2
SOL 3
SOL 4
SOL 5
SOL 6
SOL 7
SOL 8
SOL 9
MOTOR
CCSOL
LFSOL
R17 100
C16 471
C17 471
VP
34
Page 37

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Chapter 5
Parts List
35
Page 38

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
1. Exploded View CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8-1
12
11
13
14
15
16
17
18-1
-2
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 4002-230
E 4002-240
E 4035-620
E 6601-210
E 4000-520
E 4018-140
E 4000-530
E 4004-180
E 4000-510
E 4000-500
E 4000-515
E 4023-040
E 4001-740
E 4001-745
E 4018-160
E 4000-490
E
E 4024-040
E 4800-975
E 4800-980
E 4800-985
Chassis Sub Assy
Cover for PCB
Grounding Plate
Supporter for Printer
PE Detector unit
Spacer for PCB
Operation Panel Junction Unit
Inlet NC-174-C
Noise Filter Unit 120V
Noise Filter Unit 230V EMI Class A
Noise Filter Unit 230V EMI Class B
NF PCB Holder
Power Transformer 25-0091
Power Transformer 25-0092
Supporter for PCB
Power Supply Unit
Control Board Unit
Connector Cover
Cord Assy CA 1
Cord Assy CA 2
Cord Assy CA 3
(1)
(1)
(1)
1
1
1
2
1
1
115V
220-240V
220-240V
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
115V
only
220-240V
only
AW only
Validation
19
20-1
-2
21
22
23
24
E 6601-220
E 6600-780
E 6600-790
E 6600-800
E 6600-810
E 8000-010
E 8000-
E 6202-800
E 6302-190
E 62010160
E 5200-070
Printer Stand
Printer DP610-DFC
Printer DP612-DFC
Printer DP617-DFC
Printer DP614-DFC
Auto Cutter AC-2
Auto Cutter AC-2F
Bottom Plate
Rubber Foot
Top Case
OP. Panel Overlay 1S
2
1
1
4
1
1
CBM720
only
36
Page 39

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
25
26-1
-2
27-1
-2
-3
30
31
32
33
34
35
37
38
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 4000-530
E 6204-590
E 6204-600
E 6204-700
E 6204-710
E 6204-720
S 3 X 6-S
S 3 X 10-S
SW 3 X 6
SBST 3 X 8
S 3 X 6
S 3 X 10
SW 3 X 14
SWT 4 X 6
Operation Panel Unit
Printer Cover
Printer Cover (AC)
Paper Cover
Paper Cover (AC)
Paper Cover (V)
Pan Head Screw M3 x 6
Pan Head Screw M3 x 10
Pan Head Screw/W M3 x 6
Tapping Screw M3 x 8
Pan Head Screw M3 x 6
Pan Head Screw M3 x 10
Pan Head Screw/W M3 x 14
Pan Head Screw/TW M4 x 6
15
1
CBM710
only
1
1
1
1
6
2
3
4
4
2
5
CBM720
only
CBM710
only
CBM720
only
Validation
40
E 6100-530
E 6200-535
AC Cord
AC Cord
(1)
(1)
115V
only
220-240V
only
37
Page 40

CBM-710,720
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
27-2
27-1
26-2
26-1
23
34
24
38
25
33
Page 41

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
CBM-710
18-1
18-2
19
20-1
37
34
4
32
2
32
5
3
8-1
38
34
35
17
31
7
30
11
30
13
30
6
38
35
12
14
15
34
33
16
35
21
39
34
22
Page 42

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
CBM-720
20-1
18-1
37
18-2
19
20-2
32
34
32
5
3
2
8-1
38
34
35
17
1
4
31
7
30
11
30
13
6
38
35
30
12
14
15
33
16
35
34
21
40
34
22
Page 43

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
2. Block Diagram CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
CA 1
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 6100-530
E 6100-535
E 4004-180
E 4001-740
E 4001-745
E 4800-975
2
3
4
5
7
8
E 4800-980
E 4800-985
E 4800-990
E 4800-960
E 48000010
E 4800-970
AC cord 25-0102
AC cord 25-0103
Inlet NC-174C
Power Transformer 25-0091
Power Transformer 25-0093
Cord Assy CA 1
Cord Assy CA 2
Cord Assy CA 3
Cord Assy CA 4
Cord Assy CA 5
Cord Assy CA 7
Cord Assy CA 8
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
115V
only
220-240V
only
115V
only
220-240V
only
CBM720
only
41
Page 44

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
BLOCK DIAGRAM
42
Page 45

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
4. Power Supply Unit CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
IC 1
TR 1
2
3
D 1-4
6-9
5
ZD
R1
2
3
4
5
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 390-110
E 324-010
E 360-040
E 359-278
E 400-130
E 400-010
E 405-130
E 3331-041
E 3561-041
E 3203-100
E 3152-110
E 3821-041
Regulator M5231TL
Transistor 2SB974L
Transistor 2SD1310M1
Transistor 2SC2785HF
Diode GP-15B
Diode 1S1588
Zener Diode RD5. 6EB2
Resistor 1/4W 330 J
Resistor 1/4W 560 J
Resistor 1/4W 20K F
Resistor 1/4W 1.54K F
Resistor 1/4W 820 J
1
1
1
1
8
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
C1
2
3
4
5
6
7
CN 13
F1
E 2022-740
E 2110-170
E 2001-650
E 2033-750
E 2033-740
E 2010-020
E 2010-010
E 4800-965
E 4800-970
E 4010-300
E 4019-100
E 4005-465
E 4006-220
S 3 x 8-S
S 3 x 6-S
El. Capacitor 63PN-G2200A (25X30)
C. Capacitor DD804B101K50
El. Capacitor 50MR-1
El. Capacitor 35MR-330
El. Capacitor 16MR-3300
El. Capacitor 16MR-10
El. Capacitor 16MR-100
Connector 5273-04A
Cord Assy CA 8
Heat Sink 25-0061
Insulation Sheet 2067A-5051
Fuse 5MF-3A
Fuse Holder UF-0033#01
Pan Head Screw M3 x 8
Pan Head Screw M3 x 6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
2
2
2
TR 1,2
TR 1,2
43
Page 46

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Cord assy
CA 8
INSULATOR
Screw M3x8/2
Screw M3x6/2
D1 - D4, D6 - D9 : GP15B
D5 : 1S1588
ZD1: RD5. 6EB2
44
PC BOARD
PC710-07A
PARTS POSITION : POWER SUPPLY UNIT
Page 47

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
4. Noise Filter Unit CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
SW 1
F1
NF
C 1,2
3,4
3,4
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 4003-495
E 4005-470
E 4005-475
E 4006-220
E 4009-270
E 2310-010
E 2122-735
E 2122-725
Power Switch SF-W101A-01BB
Fuse EAWK-500mA
Fuse 5MF-1A
Fuse Holder UF-0033#01
Noise Filter PLA3021A
Film Capacitor CFX22E104M
C. Capacitor DE7100F222MVA1-KC
C. Capacitor DE1410E222MACT4-KD
1
1
1
2
1
2
2
2
220-240V
only
100, 115V
only
100, 115V
only
220-240V
only
45
Page 48

FUSE HOLDER
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
FUSE
EAWK-500mA: 220-240V
5MF-1A : 100/115V
POWER SWITCH
(MOUNTED ON BACK)
PC BOARD
PC710-08
C. CAPACITOR
46
PARTS POSITION : NOISE FILTER UNIT
Page 49

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
5. Control Board Assy : RS232C CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
IC 1
8, 13
10
11
12
14, 15
TA 1
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 104-200
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
2
E 107-130
E 104-220
E 2010170
E 2010220
E 2010230
E 2010240
E 2010250
E 2010260
E 2010200
E 2010270
E 202-610
E 2010040
E 390-100
E 390-120
LSI (CPU) M50734SP
LSI (PROM) M5L27128K
LSI (RAM) uPD4464C-15L
IC (TTL) SN74LS373N
IC (TTL) SN74LS240N
IC (TTL) SN74LS375N
IC (TTL) SN74LS139N
IC (TTL) SN74LS04N
IC (TTL) SN741S11N
IC (TTL) SN7406N
IC (TTL) SN74LS14N
IC uPC393C
IC (CMOS) MAX232CPE
Tr . Array HA13408
Tr . Array STA403A
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
TR 1
2-5
8,9
12,13
101-103
6,10
7,11
ZD 1
D 1-3
PHC 1
RA 1,5
2,3
E 319-117
E 359-278
E 327-030
E 360-020
E 403-060
E 400-010
E 391-080
E 3103-140
E 3103-170
4
E 3013-090
Transistor 2SA1175HF
Transistor 2SC2785HF
Transistor 2SB731L
Transistor 2SD809(1)L
Zener Diode RD3. 0EL1
Diode IS1588
Photocupprer PC837
Re. Array SR-8RA-10K
Re. Array SR-9RA-10K
Re. Array SR-4RB-1K
1
11
2
2
1
3
1
2
2
1
47
Page 50

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
CONTROL BOARD ASSY : RS232C CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
R1
2
3,40,101
4
5,7,15
32,43
102-104
6
8,17,41
42
9,11,18
19,24-26
31,33-36
38
10
12
13
14
16
20,21
27,28
22,23
29,30
37,39
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 3152-100
E 3272-090
E 3102-041
E 3222-041
E 3332-041
E 3473-041
E 3101-041
E 3103-041
E 3623-041
E 3181-041
E 3683-041
E 3333-041
E 3105-041
E 3223-041
E 3472-041
E 3221-041
Resistor 1/4W 1.5K F
Resistor 1/4W 2.7K F
Resistor 1/4W 1K J
Resistor 1/4W 2.2K J
Resistor 1/4W 3.3K J
Resistor 1/4W 47K J
Resistor 1/4W 100 J
Resistor 1/4W 10K J
Resistor 1/4W 62K J
Resistor 1/4W 180 J
Resistor 1/4W 68K J
Resistor 1/4W 33K J
Resistor 1/4W 1M J
Resistor 1/4W 22K J
Resistor 1/4W 4.7K J
Resistor 1/4W 220 J
1
1
3
1
8
1
4
13
1
1
1
1
1
4
4
2
C 1,3,19
6,102
8,16
17,101
9,10
11,14
20
12,13
15
18
21,22
25,26
23
24,27
E 2104-330
2
4
5
7
E 2010-010
E 2047-640
E 2001-650
E 2310-220
E 2000-020
E 2147-060
E 2110-340
E 2110-270
E 2110-380
E 2110-290
E 2022-500
E 2010-650
E 2047-615
C. Capacitor DD306-63F104Z12
El. Capacitor 16MR-100
El. Capacitor 35MR-47
El. Capacitor 50MR-1
My. Capacitor DMY21H473K
El. Capacitor FS0H-473Z
C. Capacitor DD804-63B471K50
C. Capacitor DD107-63R101J50
C. Capacitor DD806-63F103Z50
C. Capacitor DD804-63B102K50
C. Capacitor DD806-63F103K50
El. Capacitor 16MR-22
El. Capacitor 50MR-10
El. Capacitor 16MR-47
3
1
1
1
2
1
4
2
3
3
1
4
1
2
48
Page 51

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
CONTROL BOARD ASSY : RS232C CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
CP 1,5,8
11,13
OSC
L 1,2
BZ
DS 1,2
SW 1
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 2110-300
E 501-150
E 4009-300
E 7151-120
E 5103-350
E 5104-330
E 4010-290
C. Capaciotr DD306-63F104Z12
Crystal CSA7.37MT40
Coil SN-3-200
Buzzer MEB-12-5
Dip Switch KSD-8
Slide Switch MMS A2-2
Heat Sink
5
1
2
1
2
1
1
for T A 1
CN 1
S 3 x 8
N 3-1-N
S 3 x 10-S
E 4800-915
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
E 4800-920
E 4800-925
E 4800-930
E 4800-935
E 4800-940
E 4800-945
E 4800-950
Pan Head Screw M3 x 8
Nut M3
Pan Heat Screw M3 x 10
Connector 5267-05A-X
Connector 25KC0050-120
Connector 5267-17A-X
Connector 5267-09A-X
Connector 5267-07A-X
Connector 5268-02A-X
Connector 5267-04A-X
Connector 5267-03A-X
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
for T A 1
for T A 1
for CN 2
49
Page 52

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Jump Wire Setting : RS232C
with Back Up (B) without Back Up (N)
Jumper 1 Open C-N Short
Jumper 2
C-B Short C-N Short
PARTS POSITION : CONTROL BOARD UNIT RS232C
50
Page 53

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
6. Control Board Assy : Parallel CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
IC 1
5,14
10,13
11
12
TA 1
TR 1
2-5,8
101-103
6,10
7,11
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 104-200
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
2
9
E 107-130
E 104-220
E 2010170
E 2010220
E 2010230
E 2010240
E 2010250
E 2010260
E 2010200
E 2010270
E 202-610
E 390-100
E 390-120
E 319-117
E 359-278
E 327-030
E 360-020
LSI (CUP) M50734SP
LSI (PROM) M5L27128K
LSI (RAM) uPD4464C-15L
IC (TTL) SN74LS373N
IC (TTL) SN74LS240N
IC (TTL) SN74LS375N
IC (TTL) SN74LS139N
IC (TTL) SN74LS04N
IC (TTL) SN74LS11N
IC (TTL) SN7406N
IC (TTL) SN74LS14N
IC uPC393C
Tr . Array HA13408
Tr . Array STA403A
Transistor 2SA1175HF
Transistor 2SC2785HF
Transistor 2SB731L
Transistor 2SD809(1)L
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
9
2
2
ZD 1
RA 1
2,3
4
5
6
R1
2
3,101
4
5,7,15
101-104
6
E 403-060
E 3103-140
E 3103-170
E 3013-090
E 3332-120
E 3102-110
E 3152-100
E 3272-090
E 3102-041
E 3222-041
E 3332-041
E 3473-041
Zener Diode RD3.0EL1
Re. Array SR-8RA-10K
Re. Array SR-9RA-10K
Re. Array SR-4RB-1K
Re. Array SR-12RA-3.3K
Re. Array SR-10RA-1K
Resistor 1/4W 1.5K F
Resistor 1/4W 2.7K F
Resistor 1/4W 1K J
Resistor 1/4W 2.2K J
Resistor 1/4W 3.3K J
Resistor 1/4W 47K J
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
6
1
51
Page 54

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
CONTROL BOARD ASSY : PARALLEL CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
R 8,17
9,11,18
19,24-26
31
10
12
13
14
16
20,21
27,28
22,23
29,30
C 1,3,19
6,102
8,16,17
9,10
11,14
18
12,13
15
20,101
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 3101-041
E 3103-041
E 3623-041
E 3181-041
E 3683-041
E 3333-041
E 3105-041
E 3223-041
E 3472-041
E 2104-330
2
4
5
7
E 2010-010
E 2047-640
E 2001-650
E 2310-220
E 2000-020
E 2147-060
E 2110-340
E 2110-270
E 2110-380
E 2147-060
Resistor 1/4W 100 J
Resistor 1/4W 10K J
Resistor 1/4W 62K J
Resistor 1/4W 180 J
Resistor 1/4W 68K J
Resistor 1/4W 33K J
Resistor 1/4W 1M J
Resistor 1/4W 22K J
Resistor 1/4W 4.7K J
C. Capacitor DD306-63F104Z12
El. Capacitor 16MR-100
El. Capacitor 35MR-47
El. Capacitor 50MR-1
My. Capacitor DMY21H473K
El. Capacitor FSOH-473Z
C. Capacitor DD804-63B471K50
C. Capacitor DD107-63R101J50
C. Capacitor DD806-63F103Z50
C. Capacitor DD804-63B102K50
C. Capacitor DD804-63B471K50
2
8
1
1
1
1
1
4
4
3
1
1
1
2
1
3
2
3
3
2
CP 1,5,8
10,12
OSC
L 1,2
BZ
E 2104-330
E 501-150
E 4009-300
E 7151-120
C. Capacitor DD306-63F104Z12
Crystal CSA7.37MT40
Coil SN-3-200
Buzzer MEB-12-5
52
5
1
2
1
Page 55

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
CONTROL BOARD ASSY : PARALLEL CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
DS 1
CN 1
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 5103-350
E 4010-290
S 3 x 8
N 3-1-N
E 4800-915
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
E 4800-895
E 4800-925
E 4800-930
E 4800-935
E 4800-940
E 4800-945
E 4800-950
Dip Switch KSD-8
Heat Sink 50-0032
Pan Head Screw M3 x 8
Nut M3
Connector 5267-05A-X
Connector MRD-36SB-130
Connector 5267-17A-X
Connector 5267-09A-X
Connector 5267-07A-X
Connector 5268-02A-X
Connector 5267-04A-X
Connector 5267-03A-X
1
1
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
for T A 1
for T A 1
for T A 1
53
Page 56

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Jump Wire Setting : PARALLEL
with Back Up (B) without Back Up (N)
Jumper 1 Open C-N Short
Jumper 2
C-B Short C-N Short
PARTS POSITION : CONTROL BOARD UNIT PARALLEL
54
Page 57

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
7. Control Board Assy : RS422A CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
IC 1
8,13
10
11
12
14
15
TA 1
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 104-200
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
2
E 107-140
E 104-220
E 2010170
E 2010220
E 2010230
E 2010240
E 2010250
E 2010260
E 2010200
E 2010270
E 202-610
E 202-620
E 202-630
E 390-100
E 390-120
LSI (CPU) M50734SP
LSI (PROM) M5L27128K
LSI (RAM) uPD4464C-15L
IC (TTL) SN74LS373N
IC (TTL) SN74LS240N
IC (TTL) SN74LS375N
IC (TTL) SN74LS139N
IC (TTL) SN74LS04N
IC (TTL) SN74LS11N
IC (TTL) SN7406N
IC (TTL) SN74LS14N
IC uPC393C
IC (TTL) SN75113
IC (TTL) SN75175
Tr . Array HA13408
Tr . Array STA403A
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
TR 1
2-5
8,9
101-103
6,10
7,11
ZD
RA 1,5
2,3
4
R1
2
3,101
4
5,7,15
102-104
E 319-117
E 359-278
E 327-030
E 360-020
E 403-060
E 3103-140
E 3103-170
E 3013-090
E 3152-100
E 3272-090
E 3102-041
E 3222-041
E 3332-041
Transistor 2SA1175HF
Transistor 2SC2785HF
Transistor 2SB731L
Transistor 2SD809(1)L
Zener Diode RD3. 0EL1
Re. Array SR-8RA-10K
Re. Array SR-9RA-10K
Re. Array SR-4RB-1K
Resistor 1/4W 1.5K F
Resistor 1/4W 2.7K F
Resistor 1/4W 1K J
Resistor 1/4W 2.2K J
Resistor 1/4W 3.3K J
1
9
2
2
1
2
2
1
1
1
2
1
6
55
Page 58

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
CONTROL BOARD ASSY : RS422A CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
R 6,35
38-40
8,17
9,11
18,19
24-26
31
10
12
13
14
16
20,21
27,28
22,23
29,30
34,36
37
32,33
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 3473-041
E 3101-041
E 3103-041
E 3623-041
E 3181-041
E 3683-041
E 3333-041
E 3105-041
E 3223-041
E 3472-041
E 3100-041
Resistor 1/4W 47K J
Resistor 1/4W 100 J
Resistor 1/4W 10K J
Resistor 1/4W 62K J
Resistor 1/4W 180 J
Resistor 1/4W 68K J
Resistor 1/4W 33K J
Resistor 1/4W 1M J
Resistor 1/4W 22K J
Resistor 1/4W 4.7K J
Resistor 1/4W 10 J
5
2
8
1
1
1
1
1
4
7
2
C 1,3,19
6,102
8,16
17
9,10
11,14
18
12,13
15
20,21
101
CP 1,5,8
11,13
E 2104-330
2
4
5
7
E 2010-010
E 2047-640
E 2001-650
E 2310-220
E 2000-020
E 2147-060
E 2110-340
E 2110-270
E 2110-380
E 2110-330
E 2110-300
C. Capacitor DD306-63F104Z12
El. Capacitor 16MR-100
El. Capacitor 35MR-47
El. Capacitor 50MR-1
My. Capacitor DMY21H473K
El. Capacitor FSOH-473Z
C. Capacitor DD804-63B471K50
C. Capacitor DD107-63R101J50
C. Capacitor DD806-63F103Z50
C. Capacitor DD804-63B102K50
C. Capacitor DD804-63B101K50
C. Capacitor DD306-63F104Z12
3
1
1
1
2
1
3
2
3
3
3
5
56
Page 59

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
Control Board Assy : RS422A CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
OSC 1
L 1,2
BZ
DS 1,2
CN 1
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
E 501-150
E 4009-300
E 7151-120
E 5103-350
E 4010-290
S 3 x 8
N 3-1-N
E 4800-915
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
E 4800-955
E 4800-925
E 4800-930
E 4800-935
E 4800-940
E 4800-945
E 4800-950
Crystal CSA7.37MT40
Coil SN-3-200
Buzzer MEB-12-5
Dip Switch KSD-8
Heat Sink 50-0032
Pan Head Screw M3 x 8
Nut M3
Connector 5267-05A-X
Connector JEY9S-1A1A-90
Connector 5267-17A-X
Connector 5267-09A-X
Connector 5267-07A-X
Connector 5268-02A-X
Connector 5267-04A-X
Connector 5267-03A-X
1
2
1
2
1
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
for T A 1
for T A 1
for T A 1
E 4024-050
M 3 x 10
Connector Cover
Pan Head Screw M3 x 10
1
1
57
Page 60

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
Jump Wire Setting : RS422A
with Back Up (B) without Back Up (N)
Jumper 1
Jumper 2 C-B Short C-N Short
Open C-N Short
PARTS POSITION : CONTROL BOARD UNIT RS422A
58
Page 61

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
8. OPERATION PANEL UNIT/PE DETECTOR UNIT/OPERATION PANEL JUNCTION UNIT
CBM-710/720
Ref. No.
D 1,2
R 1,2
SW 1,2
CA 5
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
** OPERATION PANEL UNIT **
E 480-250
3
3
E 480-260
E 3221-041
E 3471-041
E 5102-410
E 4800-960
LED Lamp GL9NG22
LED Lamp GL9PR22
Resistor 1/4W 220 J
Resistor 1/4W 470 J
Tact Switch SKH-KAA
Cord assy CA 5
** PE DETECTOR UNIT**
2
1
2
1
2
1
PH 1
CA 7
CN 12
CA 5
E 4000-520
E 391-090
E 6650-040
E 48000010
E 4000-530
E 4800-935
E 4800-960
P.E. PCB Assy
Photointerrupter GP2S05
PE Holder
Cord Assy CA 7
** OPERATION PANEL JUNCTION UNIT **
O.P. PCB Assy
Connector 5267-07A-X
Cord assy CA 5
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
59
Page 62

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
LED (GREEN)
LED (RED)
TACT SWITCH
CORD ASSY CA 5
PC BOARD PC710-04
PARTS POSITION : OPERATION PANEL UNIT
60
Page 63

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PHOTOINTERRUPTER
GR2S05
PC BOARD PC710-05
CORD ASSY CA 7
PARTS POSITION : PE DETECTOR UNIT
61
Page 64

5267-07A
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
CORD ASSY CA 5
PC BOARD PC710-06
OP Junction Block
62
Page 65

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
9. Auto Cutter AC-2/AC-3
Q’ty
Ref. No.
Parts No. Description
AC-2
AC-3
Remarks
10
10-1
10-2
10-3
10-4
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
E 8010-010
E 8010-020
E 8011-010
S 2.6 x 8
E 8012-010
E 8013-010
E 3
E 8014-010
E 8015-010
E 2.5
E 8016-010
E 8016-020
E 8017-010
E 8017-020
E 8018-010
E 8019-010
E 48000070
E 8020-010
S 2.6 x 5-s
SW 2 x 8
E 4031-060
E 8021-010
E 8022-010
E 8030-010
E 8023-010
E 8024-010
E 8030-020
E 8025-010
E 8026-010
E 8027-010
E 8026-020
E 8027-020
Frame Assy (2)
Frame Assy (3)
Paper Guid (2)
Pan Head Screw M2.6 x 8
Lock Lever Sssy R
Lock Lever Assy L
E Ring 3
Lock Lever Spring
Cutter Gear Assy
E Ring 2.5
Motor Assy (DC24V, 50mA)
Motor Assy (DC12V, 65mA)
Motor (DH515, DC24v, 50mA)
Motor (DH416, DC12V, 65mA)
Limit Switch D2F-01FL
Motor Gear
Cord Assy (25-0080)
Worm Gear Assy
Pan Head Screw M2.5 x 6
Pan Head Screw/W M2 x 8
Wire Band T18S
Blade Spring
Guide Plate
Blade
Blade Cover
Frame Shift
Blade (Full Cut Type)
Spacer
Hook R
Bracket R
Hook L
Bracket L
1
1
1
4
1
1
7
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
4
2
2
2
DC 24V
1
DC 12V
1
1
1
1
1
4
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
63
Page 66

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
AC-2
12
3
1
7
10-2
5
6
4
13
15
16
20
6
19
2
10
10-1
14
10-3
8
11
9
17
18
21, 22
6
3
64
Page 67

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
AC-3
10-4
10-2
12
3
1
15
16
2
13
10-3
10
10-1
14
11
8
9
17
18
21, 22
6
65
3
12
Page 68

CBM-710/720 Service Manual
PARTS LIST
10. Winder AW-2
Ref. No.
2-1
-2
-3
Parts No. Description Q’ty Remarks
1
2
3
6
7
8
9
E 8500-010
E 8510-010
E 8017-010
E 8512-010
E 8513-010
E 8514-010
E 8515-010
E 8516-010
E 4
E 8520-010
AW Frame Assy
Motor Assy (DC24V, 50mA)
Motor (DH515, DC24V, 50mA)
Motor Gear
Cord Assy (25-0082)
Motor Cover
W Gear
Idle Gear
E Ring
AW Cover
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
E 8521-010
E 8522-010
E 8530-010
E 8531-010
E 8532-010
S 3 X 6-S
E 4031-060
A W Top Cover
Bottom Plate
Rear Shaft
Rear Frange
Paper Guide
Pan Head Screw M3 x 6
Wire Band T18S
1
1
1
1
1
7
1
66
Page 69

AW-2
CBM-710/720 Service Manual
10
13
14
15
3
12
15
9
1
6
2-3
16
2-1
2
2-2
7
11
15
8
67
 Loading...
Loading...