Cisco Systems ATBRTH16 Manual
C H A P T E R 6
Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
The Cisco Wireless Mobile Interface Card (WMIC) is a Cisco 3200 Series router interface card in a standard PC/104-Plus form factor.
It is one component of the Cisco 3200 Series routers and provides a wireless interface:
•2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) – Cisco 3201
•4.9 GHz (public safety) – Cisco 3202
•5.0 GHz (802.11h) – Cisco 3205 (The C3205WMIC-K9 and C3205WMIC-TP-K9 WMICs are available only in the European Telecommunications Standards Institute [ETSI] domain.)
Caution The 4.9 GHz (public safety) radio requires an operators license and can only be operated by US Public Safety operators who meet the requirements specified under FCC Part 90.20.
This chapter provides basic information about the WMIC hardware for the purpose of performing simple troubleshooting, such as reconnecting a loose cable. To solve more difficult problems, please contact your vendor.
WMIC Component Systems
The ISA buses and PCI buses on the Cisco 3200 Series router cards provide power to the components on the cards. The WMIC does not receive or transmit communications signals on either bus, but it will pass signals through the bus to a card above or below the WMIC. Both buses comply with the PC/104-Plus standard.
The PCI bus signals allow the Cisco cards to communicate. Non-Cisco cards cannot communicate with the Cisco 3200 Series Router cards over the PCI bus.
Caution If you add non-Cisco cards that generates signals on the PCI bus, the router might shut down. Please do not add non-Cisco cards that generate signals on the PCI bus.
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
|
OL-5816-09 |
6-1 |
|
|
|
Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
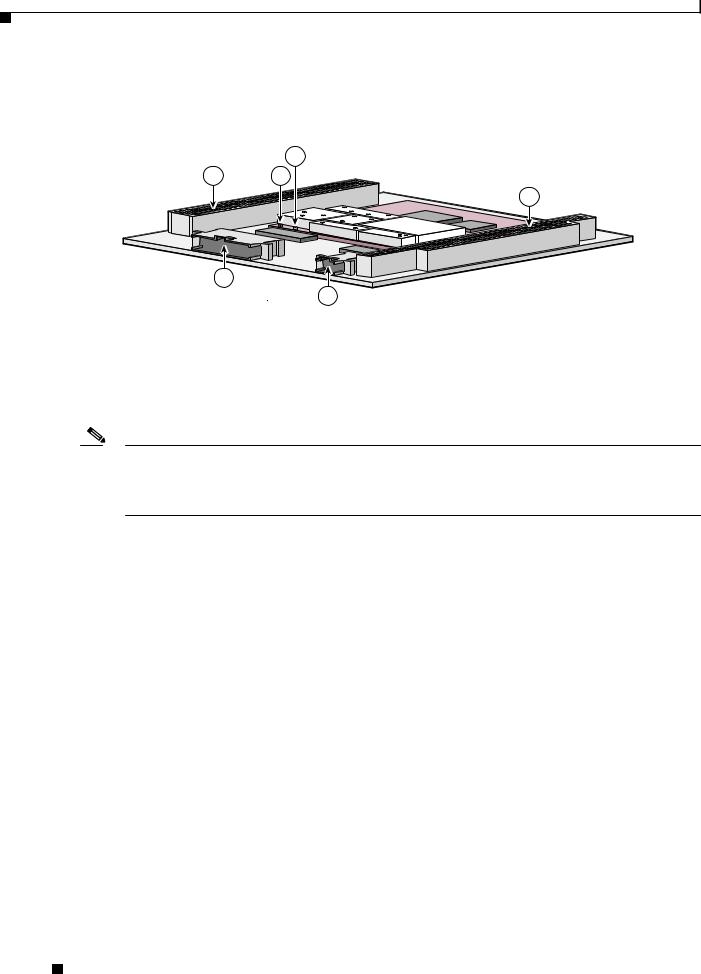
Figure 6-1 shows the WMIC header and bus locations.
Figure 6-1 WMIC Header and Bus Locations
3
1 2
4
6
5
103981
1 |
PCI bus |
2 |
Left antenna connector (J2) |
|
|
|
|
3 |
Right antenna connector (J1) |
4 |
ISA bus |
|
|
|
|
5 |
10-pin Fast Ethernet header |
6 |
24-pin multifunction header |
|
|
|
|
Note The PC/104-Plus standard requires that the PCI bus and the ISA bus utilize keying features in the standard stacking headers to guarantee proper module installation. On the PCI bus, pin D30 is removed and the D30 opening is plugged. On the ISA bus, pin C19 and pin B10 are removed, and the C19 and B10 openings are plugged.
Antenna Connector
On the radio card, there are two ultra-miniature coaxial connectors (U.FL connector) that are used to connect the coax cables between the WMIC and the external antenna connectors. Two connectors are used to support antenna diversity.
The cable should be as short as possible to minimize the loss in strength of the radio frequency (RF) signal. The cable carries the RF signal from the antenna to the low noise amplifier (LNA) on the receiver and transmits the RF signal from power amplifier (PA) to the antenna that radiates the RF signal.
There are many antenna connector families. The Cisco RP-TNC antenna connector can be used to support standard antennas.
WMIC Console and Fast Ethernet Ports
Cisco 3200 Series router cards do not support any ISA bus signals. The PCI bus connector supports communication between Cisco 3200 Series router card and the Fast Ethernet Switch Mobile Interface Card (FESMIC) and Serial Mobile Interface Card (SMIC).
In a Cisco rugged enclosure, the WMIC communicates with the router through the WMIC Fast Ethernet interface. The WMIC Fast Ethernet ports are connected internally to Fast Ethernet ports that provide a communications link with the router.
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-2 |
OL-5816-09 |
|
|

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
The WMIC interfaces are configured through a WMIC console port. In contrast, the Serial Mobile Interface Card (SMIC) and FESMIC communicate with the router through the PC/104-Plus bus. The interfaces are configured through the router console port, and all of the router and FESMIC Fast Ethernet ports are identified by using the slot/port format.
The WMIC runs an independent IOS image and when it is configured, the link between the WMIC and the router forms an internal LAN. In standard configurations, a WMIC Fast Ethernet port is never brought out to the end cap.
The WMIC console port is brought out to the corresponding RJ-45 port on the I/O end cap, replacing a Fast Ethernet port. If the router includes one WMIC, the RS-232 WMIC console port replaces a Fast Ethernet port on the end cap. If the router includes two WMICs, two WMIC RS-232 console ports replace two Fast Ethernet ports on the end cap.
Note Currently, even if the router contains zero WMICs, in standard configurations a maximum of three Fast Ethernet ports are brought out to the end cap. Unused RS-232 ports are sealed.
Fast Ethernet Signals on the WMIC
The Fast Ethernet signals are delivered through a 10-pin header. LED signals and RS-232 console signals are provided through the 24-pin multifunction header.
There is one set of fixed Fast Ethernet signals on the WMIC. The Fast Ethernet port signals are in compliance with IEEE 802.3. They are provided through the Ethernet headers, which support the following:
•Auto-negotiation for 10/100BASE-TX connection
•Full-duplex and half-duplex modes
•Low-power sleep mode
•10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX using a single Ethernet connection
•Robust baseline wander correction performance
•Standard carrier signal multiple access collision detect (CSMA/CD) or full-duplex operation
•Integrated LED drivers
Note If Auto-MDIX is disabled, when connecting to Ethernet switches or repeaters a straight-through cable can be used. When connecting to compatible workstations, servers, and routers, a crossover cable should be used. If Auto-MDIX is enabled, either a straight-through or crossover cable can be used can be used to make the connection, as the router automatically changes the signals on the pins to compensate.
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
|
OL-5816-09 |
6-3 |
|
|
|

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
LED Behavior
During normal operations, the indicator signals on the wireless device have the following meanings.
•The status indicator signals operational status. Steady green indicates that the wireless device is associated with at least one wireless client. Blinking green indicates that the wireless device is operating normally but is not associated with any wireless devices.
•The radio indicator blinks green to indicate radio traffic activity. The light is normally off, but it blinks whenever a packet is received or transmitted over the radio.
•The Ethernet indicator signals traffic on the wired LAN. This indicator is normally green when an Ethernet cable is connected, and blinks green when a packet is received or transmitted over the Ethernet infrastructure. The indicator is off when the Ethernet cable is not connected.
Table 6-1 shows the details of LED behavior.
Table 6-1 |
Indicator Signals |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Message |
|
Ethernet |
Status |
Radio |
Meaning |
type |
|
indicator |
indicator |
indicator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Boot loader |
|
Green |
– |
Green |
DRAM memory test. |
status |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
Amber |
Red |
Board initialization test. |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
Blinking |
Blinking |
Flash memory test. |
|
|
|
green |
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amber |
Green |
– |
Ethernet initialization test. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Green |
Green |
Green |
Starting Cisco IOS software. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Association |
|
– |
Green |
– |
At least one wireless client device is |
status |
|
|
|
|
associated with the unit. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
Blinking |
– |
No client devices are associated; check the |
|
|
|
green |
|
wireless device SSID and WEP settings. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating |
|
– |
Green |
Blinking |
Transmitting/receiving radio packets. |
status |
|
|
|
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Green |
– |
– |
Ethernet link is operational. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blinking |
– |
– |
Transmitting/receiving Ethernet packets. |
|
|
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Boot Loader |
|
Red |
– |
Red |
DRAM memory test failure. |
Errors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
Red |
Red |
File system failure. |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Red |
Red |
– |
Ethernet failure during image recovery. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amber |
Green |
Amber |
Boot environment error. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Red |
Green |
Red |
No Cisco IOS image file. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amber |
Amber |
Amber |
Boot failure. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-4 |
OL-5816-09 |
|
|

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-1 |
Indicator Signals (continued) |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Message |
|
Ethernet |
Status |
|
Radio |
Meaning |
|
type |
|
indicator |
indicator |
|
indicator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operation |
|
– |
Green |
|
Blinking |
Maximum retries or buffer full occurred on |
|
Errors |
|
|
|
|
amber |
the radio. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blinking |
– |
|
– |
Transmit/receive Ethernet errors. |
|
|
|
amber |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
– |
Blinking |
|
– |
General warning. |
|
|
|
|
amber |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration |
|
– |
Amber |
|
– |
Resetting the configuration options to |
|
Reset |
|
|
|
|
|
factory defaults. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Failures |
|
Red |
Red |
|
Red |
Firmware failure; try disconnecting and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
reconnecting unit power. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blinking red |
– |
|
– |
Hardware failure. The wireless device |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
must be replaced. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firmware |
|
– |
Red |
|
– |
Loading new firmware image. |
|
Upgrade |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Features
The key features of the Cisco wireless devices are listed in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2 Key Features
Feature |
Description |
|
|
Wireless Medium |
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) |
|
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) |
|
|
Radio Media Access |
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) |
Protocol |
|
|
|
SNMP Compliance |
MIB I and MIB II |
|
|
Encryption Key Length |
128-bit |
|
|
Quality of Service |
Prioritization of traffic for different requirements, such as voice and video. |
(QoS) Support |
|
|
|
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
|
OL-5816-09 |
6-5 |
|
|
|

Chapter 6 Wireless Mobile Interface Cards (WMICs)
Table 6-2 Key Features (continued)
Feature |
Description |
|
|
Security |
Cisco Wireless Security Suite: |
|
Authentication: |
|
• 802.1X support including LEAP, PEAP, EAP-TLS, and EAP-SIM to |
|
yield mutual authentication and dynamic, per-user, per-session WEP |
|
keys |
|
• MAC address and by standard 802.11 authentication mechanisms |
|
Encryption: |
|
• Static and dynamic IEEE 802.11 WEP keys of 40 bits and 128 bits |
|
• 802.11i/WPAv2 Advanced Encryption Standard-Counter Mode with |
|
Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol |
|
(AES-CCMP); 128-bit key length |
|
• Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) WEP enhancements: key |
|
hashing (per-packet keying), message integrity check (MIC), and |
|
broadcast key rotation by using WPA TKIP |
|
All WMICs in Root Mode: |
|
PEAP, EAP-TTLS, LEAP, EAP-TLS, EAP-FAST, and EAP-SIM. |
|
Cisco 3201 WMICs in Client Mode: |
|
LEAP, EAP-TLS & EAP-FAST |
|
Cisco 3202 and Cisco 3205 WMICs in Client Mode: |
|
LEAP |
|
|
Status Indicators |
LEDs provide information concerning association status, operation, |
|
error/warning, firmware upgrade, and configuration, network/modem, and |
|
radio status |
|
|
Memory |
8 MB Flash |
|
32 MB DRAM |
|
|
Automatic Configuration |
BOOTP and DHCP |
Support |
|
|
|
Remote Configuration |
Telnet, HTTP, FTP, TFTP, and SNMP |
Support |
|
|
|
Uplink |
Auto-sensing 10/100BaseT Ethernet |
|
|
Local Configuration |
Console port |
|
|
Cisco 3200 Series Router Hardware Reference
6-6 |
OL-5816-09 |
|
|
 Loading...
Loading...