Carrier 19XRT User Manual

19XRT Hermetic Centrifugal Liquid Chillers
50/60 Hz with PIC II Controls and HFC-134a
Start-Up, Operation, and Maintenance Instructions
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Centrifugal liquid chillers are designed to provide safe and reliable service when operated within design speci- ®cations. When operating this equipment, use good judgment and safety precautions to avoid damage to equipment and property or injury to personnel.
Be sure you understand and follow the procedures and safety precautions contained in the chiller instructions as well as those listed in this guide.
DO NOT VENT refrigerant relief valves within a building. Outlet from rupture disc or relief valve must be vented outdoors in accordance with the latest edition of ANSI/ASHRAE 15 (American National Standards Institute/American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air Conditioning Engineers). The accumulation of refrigerant in an enclosed space can displace oxygen and cause asphyxiation.
PROVIDE adequate ventilation in accordance with ANSI/ASHRAE 15, especially for enclosed and low overhead spaces. Inhalation of high concentrations of vapor is harmful and may cause heart irregularities, unconsciousness, or death. Misuse can be fatal. Vapor is heavier than air and reduces the amount of oxygen available for breathing. Product causes eye and skin irritation. Decomposition products are hazardous.
DO NOT USE OXYGEN to purge lines or to pressurize a chiller for any purpose. Oxygen gas reacts violently with oil, grease, and other common substances.
NEVER EXCEED speci®ed test pressures, VERIFY the allowable test pressure by checking the instruction literature and the design pressures on the equipment nameplate.
DO NOT USE air for leak testing. Use only refrigerant or dry nitrogen.
DO NOT VALVE OFF any safety device.
BE SURE that all pressure relief devices are properly installed and functioning before operating any chiller.
DO NOT WELD OR FLAMECUT any refrigerant line or vessel until all refrigerant (liquid and vapor) has been removed from chiller. Traces of vapor should be displaced with dry air or nitrogen and the work area should be well ventilated. Refrigerant in contact with an open ¯ame produces toxic gases.
DO NOT USE eyebolts or eyebolt holes to rig chiller sections or the entire assembly.
DO NOT work on high-voltage equipment unless you are a quali- ®ed electrician.
DO NOT WORK ON electrical components, including control panels, switches, starters, or oil heater until you are sure ALL POWER IS OFF and no residual voltage can leak from capacitors or solidstate components.
LOCK OPEN AND TAG electrical circuits during servicing. IF WORK IS INTERRUPTED, con®rm that all circuits are deenergized before resuming work.
AVOID SPILLING liquid refrigerant on skin or getting it into the eyes. USE SAFETY GOGGLES. Wash any spills from the skin with soap and water. If liquid refrigerant enters the eyes, IMMEDIATELY FLUSH EYES with water and consult a physician.
NEVER APPLY an open ¯ame or live steam to a refrigerant
cylinder. Dangerous over pressure can result. When it is necessary to heat refrigerant, use only warm (110 F [43 C]) water.
DO NOT REUSE disposable (nonreturnable) cylinders or attempt to re®ll them. It is DANGEROUS AND ILLEGAL. When cylinder is emptied, evacuate remaining gas pressure, loosen the collar and unscrew and discard the valve stem. DO NOT INCINERATE.
CHECK THE REFRIGERANT TYPE before adding refrigerant to the chiller. The introduction of the wrong refrigerant can cause damage or malfunction to this chiller.
Operation of this equipment with refrigerants other than those cited herein should comply with ANSI/ASHRAE 15 (latest edition). Contact Carrier for further information on use of this chiller with other refrigerants.
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO REMOVE ®ttings, covers, etc., while chiller is under pressure or while chiller is running. Be sure pressure is at 0 psig (0 kPa) before breaking any refrigerant connection.
CAREFULLY INSPECT all relief devices, rupture discs, and other relief devices AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR. If chiller operates in a corrosive atmosphere, inspect the devices at more frequent intervals.
DO NOT ATTEMPT TO REPAIR OR RECONDITION any relief device when corrosion or build-up of foreign material (rust, dirt, scale, etc.) is found within the valve body or mechanism. Replace the device.
DO NOT install relief devices in series or backwards.
USE CARE when working near or in line with a compressed spring. Sudden release of the spring can cause it and objects in its path to act as projectiles.
DO NOT STEP on refrigerant lines. Broken lines can whip about and release refrigerant, causing personal injury.
DO NOT climb over a chiller. Use platform, catwalk, or staging. Follow safe practices when using ladders.
USE MECHANICAL EQUIPMENT (crane, hoist, etc.) to lift or move inspection covers or other heavy components. Even if components are light, use mechanical equipment when there is a risk of slipping or losing your balance.
BE AWARE that certain automatic start arrangements CAN ENGAGE THE STARTER, TOWER FAN, OR PUMPS. Open the disconnect ahead of the starter, tower fans, or pumps.
USE only repair or replacement parts that meet the code requirements of the original equipment.
DO NOT VENT OR DRAIN waterboxes containing industrial brines, liquid, gases, or semisolids without the permission of your process control group.
DO NOT LOOSEN waterbox cover bolts until the waterbox has been completely drained.
DOUBLE-CHECK that coupling nut wrenches, dial indicators, or other items have been removed before rotating any shafts.
DO NOT LOOSEN a packing gland nut before checking that the nut has a positive thread engagement.
PERIODICALLY INSPECT all valves, ®ttings, and piping for corrosion, rust, leaks, or damage.
PROVIDE A DRAIN connection in the vent line near each pressure relief device to prevent a build-up of condensate or rain water.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, speci®cations or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book |
2 |
|
PC 211 |
Catalog No. 531-977 |
Printed in U.S.A. |
Form 19XRT-2SS |
Pg 1 |
11-98 |
Replaces: New |
Tab |
5a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
ABBREVIATIONS AND EXPLANATIONS . . . . . . . 4
CHILLER FAMILIARIZATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Chiller Information Plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Cooler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Condenser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Motor-Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Turbine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Factory-Mounted Starter (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Storage Vessel (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
REFRIGERATION CYCLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
MOTOR AND LUBRICATING OIL
COOLING CYCLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
LUBRICATION CYCLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Oil Reclaim System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
·PRIMARY OIL RECOVERY MODE
·SECONDARY OIL RECOVERY MODE
STARTING EQUIPMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10,11
Unit-Mounted Solid-State Starter (Optional) . . . 10
Unit-Mounted Wye-Delta Starter (Optional) . . . . 11
CONTROLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-44
De®nitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
·ANALOG SIGNAL
·DISCRETE SIGNAL
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
PIC II System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
·CHILLER VISUAL CONTROLLER (CVC)
·INTEGRATED STARTER MODULE (ISM)
·CHILLER CONTROL MODULE (CCM)
·OIL HEATER CONTACTOR (1C)
·OIL PUMP CONTACTOR (2C)
·HOT GAS BYPASS CONTACTOR RELAY (3C) (Optional)
·CONTROL TRANSFORMERS (T1, T2)
CVC Operation and Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
·GENERAL
·ALARMS AND ALERTS
·CVC MENU ITEMS
·BASIC CVC OPERATIONS (Using the Softkeys)
·TO VIEW STATUS
·OVERRIDE OPERATIONS
·TIME SCHEDULE OPERATION
·TO VIEW AND CHANGE SET POINTS
·SERVICE OPERATION
PIC II System Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
·CAPACITY CONTROL
·ECW CONTROL OPTION
·CONTROL POINT DEADBAND
·PROPORTIONAL BANDS AND GAIN
·CHILLER TIMERS
·OCCUPANCY SCHEDULE
Safety Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Shunt Trip (Option) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Default Screen Freeze . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Ramp Loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Page
Capacity Override . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
High Discharge Temperature Control . . . . . . . . . 36
Oil Sump Temperature Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Oil Cooler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Remote Start/Stop Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Spare Safety Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Spare Safety Alarm Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Refrigerant Leak Detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Condenser Pump Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Condenser Freeze Prevention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Tower-Fan Relay Low and High . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Auto. Restart After Power Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Water/Brine Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
·RESET TYPE 1
·RESET TYPE 2
·RESET TYPE 3
Demand Limit Control Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Surge Prevention Algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Surge Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Lead/Lag Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
·COMMON POINT SENSOR INSTALLATION
·CHILLER COMMUNICATION WIRING
·LEAD/LAG OPERATION
·FAULTED CHILLER OPERATION
·LOAD BALANCING
·AUTO. RESTART AFTER POWER FAILURE
Ice Build Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
·ICE BUILD INITIATION
·START-UP/RECYCLE OPERATION
·TEMPERATURE CONTROL DURING ICE BUILD
·TERMINATION OF ICE BUILD
·RETURN TO NON-ICE BUILD OPERATIONS
Attach to Network Device Control . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 · ATTACHING TO OTHER CCN MODULES
Service Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
·TO ACCESS THE SERVICE SCREENS
·TO LOG OUT OF NETWORK DEVICE
·HOLIDAY SCHEDULING
START-UP/SHUTDOWN/RECYCLE
SEQUENCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45,46
Local Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Shutdown Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Automatic Soft Stop Amps Threshold . . . . . . . . 46
Chilled Water Recycle Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Safety Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
BEFORE INITIAL START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47-59
Job Data Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Equipment Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Using the Optional Storage Tank
and Pumpout System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Remove Shipping Packaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Open Oil Circuit Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Tighten All Gasketed Joints and
Guide Vane Shaft Packing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Check Chiller Tightness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Refrigerant Tracer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Leak Test Chiller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Standing Vacuum Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Chiller Dehydration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Inspect Water Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Check Optional Pumpout Compressor
Water Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Check Relief Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Inspect Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
2
CONTENTS (cont)
Page
Carrier Comfort Network Interface . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Check Starter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
·MECHANICAL STARTER
·BENSHAW, INC. REDISTART MICRO SOLID-STATE STARTER
Oil Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
Power Up the Controls and |
|
Check the Oil Heater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
· SOFTWARE VERSION |
|
Software Con®guration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
Input the Design Set Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
Input the Local Occupied Schedule |
|
(OCCPC01S) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
Input Service Con®gurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
54 |
·PASSWORD
·INPUT TIME AND DATE
·CHANGE CVC CONFIGURATION IF NECESSARY
·TO CHANGE THE PASSWORD
·TO CHANGE THE CVC DISPLAY FROM ENGLISH TO METRIC UNITS
·MODIFY CONTROLLER IDENTIFICATION IF NECESSARY
·INPUT EQUIPMENT SERVICE PARAMETERS IF NECESSARY
·MODIFY EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION IF NECESSARY
Perform A Control Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
·COOLER AND CONDENSER PRESSURE TRANSDUCER AND WATERSIDE FLOW DEVICE CALIBRATION
Check Optional Pumpout System
Controls and Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
High Altitude Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Charge Refrigerant Into Chiller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
·CHILLER EQUALIZATION WITHOUT PUMPOUT UNIT
·CHILLER EQUALIZATION WITH PUMPOUT UNIT
·TRIMMING REFRIGERANT CHARGE
INITIAL START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59,60 Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Dry Run to Test Start-Up Sequence . . . . . . . . . . 59
Check Motor Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
·IF THE MOTOR ROTATION IS CLOCKWISE
·IF THE MOTOR ROTATION IS NOT CLOCKWISE
Check Oil Pressure and Compressor Stop . . . . 60 To Prevent Accidental Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 Check Chiller Operating Condition . . . . . . . . . . . 60 Instruct the Customer Operator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
·COOLER-CONDENSER
·OPTIONAL STORAGE TANK AND PUMPOUT SYSTEM
·MOTOR COMPRESSOR ASSEMBLY
·MOTOR COMPRESSOR LUBRICATION SYSTEM
·CONTROL SYSTEM
·AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
·DESCRIBE CHILLER CYCLES
·REVIEW MAINTENANCE
·SAFETY DEVICES AND PROCEDURES
·CHECK OPERATOR KNOWLEDGE
·REVIEW THE START-UP, OPERATION, AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60-62
Operator Duties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Prepare the Chiller for Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
To Start the Chiller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Check the Running System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
To Stop the Chiller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61 After Limited Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Page
Preparation for Extended Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . 61 After Extended Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Cold Weather Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Manual Guide Vane Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Refrigeration Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
PUMPOUT AND REFRIGERANT TRANSFER PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63-65
Preparation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Operating the Optional Pumpout
Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63 · TO READ REFRIGERANT PRESSURES
Chillers with Storage Tanks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
·TRANSFER REFRIGERANT FROM PUMPOUT STORAGE TANK TO CHILLER
·TRANSFER THE REFRIGERANT FROM CHILLER TO PUMPOUT STORAGE TANK
Chillers with Isolation Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
·TRANSFER ALL REFRIGERANT TO CHILLER CONDENSER VESSEL
·TRANSFER ALL REFRIGERANT TO CHILLER COOLER VESSEL
·RETURN REFRIGERANT TO NORMAL OPERATING CONDITIONS
GENERAL MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66,67 Refrigerant Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 Adding Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 Removing Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Adjusting the Refrigerant Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 Refrigerant Leak Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Leak Rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Test After Service, Repair, or Major Leak . . . . . 66
·REFRIGERANT TRACER
·TO PRESSURIZE WITH DRY NITROGEN
Repair the Leak, Retest, and Apply
Standing Vacuum Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Checking Guide Vane Linkage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Trim Refrigerant Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
WEEKLY MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Check the Lubrication System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
67-71 |
Service Ontime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. . 67 |
Inspect the Control Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 67 |
Check Safety and Operating Controls |
|
Monthly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 67 |
Changing Oil Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 67 |
Oil Speci®cation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Oil Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
· TO CHANGE THE OIL |
|
Refrigerant Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Oil Reclaim Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Inspect Refrigerant Float System . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Inspect Relief Valves and Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Turbine Strainer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Turbine Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 68 |
Compressor Bearing and Gear Maintenance . |
. 68 |
Inspect the Heat Exchanger Tubes and Flow |
|
Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 70 |
· COOLER AND FLOW DEVICES |
|
· CONDENSER AND FLOW DEVICES |
|
Water Leaks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Water Treatment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Inspect the Starting Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Check Pressure Transducers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Optional Pumpout System Maintenance . . . . . . 70
·OPTIONAL PUMPOUT COMPRESSOR OIL CHARGE
·OPTIONAL PUMPOUT SAFETY CONTROL SETTINGS
3

CONTENTS (cont)
Page
Ordering Replacement Chiller Parts . . . . . . . . . . 71
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71-97
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Checking the Display Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Checking Temperature Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
·RESISTANCE CHECK
·VOLTAGE DROP
·CHECK SENSOR ACCURACY
·DUAL TEMPERATURE SENSORS
Checking Pressure Transducers . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
· TRANSDUCER REPLACEMENT
Control Algorithms Checkout Procedure . . . . . 72
Control Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Control Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
·RED LED (Labeled as STAT)
·GREEN LED (Labeled as COM)
Notes on Module Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Page
Chiller Control Module (CCM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
·INPUTS
·OUTPUTS
Integrated Starter Module (ISM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
·INPUTS
·OUTPUTS
Replacing Defective Processor Modules . . . . . . 83
· INSTALLATION
Solid-State Starters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
·TESTING SILICON CONTROL RECTIFIERS IN BENSHAW, INC., SOLID-STATE STARTERS
·SCR REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
Physical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 INDEX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
INITIAL START-UP CHECKLIST FOR 19XRT HERMETIC CENTRIFUGAL
LIQUID CHILLER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . CL-1 to CL-12
INTRODUCTION |
ABBREVIATIONS AND EXPLANATIONS |
Prior to initial start-up of the 19XRT chiller, those involved in the start-up, operation, and maintenance should be thoroughly familiar with these instructions and other necessary job data. This book is outlined to familiarize those involved in the start-up, operation and maintenance of the unit with the control system before performing start-up procedures. Procedures in this manual are arranged in the sequence required for proper chiller start-up and operation.
This unit uses a microprocessor control system. Do not short or jumper between terminations on circuit boards or modules. Control or board failure may result.
Be aware of electrostatic discharge (static electricity) when handling or making contact with circuit boards or module connections. Always touch a chassis (grounded) part to dissipate body electrostatic charge before working inside control center.
Use extreme care when handling tools near circuit boards and when connecting or disconnecting terminal plugs. Circuit boards can be damaged easily. Always hold boards by the edges, and avoid touching components and connections.
This equipment uses, and can radiate, radio frequency energy. If not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, it may interfere with radio communications. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A computing device pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take whatever measures may be required to correct the interference.
Always store and transport replacement or defective boards in an anti-static shipping bag.
Frequently used abbreviations in this manual include:
CCM |
Ð |
Chiller Control Module |
CCN |
Ð |
Carrier Comfort Network |
CVC |
Ð |
Chiller Visual Control |
CCW |
Ð |
Counterclockwise |
CW |
Ð Clockwise |
|
ECDW |
Ð |
Entering Condenser Water |
ECW |
Ð |
Entering Chilled Water |
EMS |
Ð |
Energy Management System |
HGBP |
Ð Hot Gas Bypass |
|
I/O |
Ð |
Input/Output |
ISM |
Ð |
Integrated Starter Module |
LCD |
Ð |
Liquid Crystal Display |
LCDW |
Ð |
Leaving Condenser Water |
LCW |
Ð |
Leaving Chilled Water |
LED |
Ð |
Light-Emitting Diode |
OLTA |
Ð |
Overload Trip Amps |
PIC II |
Ð |
Product Integrated Control II |
RLA |
Ð Rated Load Amps |
|
SCR |
Ð |
Silicon Controlled Recti®er |
SI |
Ð |
International System of Units |
TXV |
Ð |
Thermostatic Expansion Valve |
Words printed in all capital letters or in italics may be viewed on the Chiller Visual Control (CVC) (e.g., LOCAL, CCN, ALARM, etc.).
Words printed in both all capital letters and italics can also be viewed on the CVC and are parameters (e.g., CONTROL MODE, COMPRESSOR START RELAY, ICE BUILD OPTION, etc.) with associated values (e.g., modes, temperatures, percentages, pressures, on, off, etc.).
Words printed in all capital letters and in a box represent
softkeys |
on the CVC |
control panel (e.g., |
ENTER |
, |
|||
|
, |
|
, |
|
, etc.). |
||
EXIT |
INCREASE |
QUIT |
|||||
Factory-installed additional components are referred to as options in this manual; factory-supplied but ®eld-installed additional components are referred to as accessories.
The chiller software part number of the 19XRT unit is located on the back of the CVC.
4

CHILLER FAMILIARIZATION (Fig. 1 and 2)
Chiller Information Plate Ð The information plate is located on the right side of the chiller control panel.
System Components Ð The components include the cooler and condenser heat exchangers in separate vessels, motor-compressor, turbine, lubrication package, control panel, and motor starter. All connections from pressure vessels have external threads to enable each component to be pressure tested with a threaded pipe cap during factory assembly.
Cooler Ð This vessel (also known as the evaporator) is located underneath the compressor. The cooler is maintained at lower temperature/pressure so evaporating refrigerant can remove heat from water ¯owing through its internal tubes.
Condenser Ð The condenser operates at a higher temperature/pressure than the cooler and has water ¯owing through its internal tubes in order to remove heat from the refrigerant.
Motor-Compressor Ð This component maintains system temperature and pressure differences and moves the heatcarrying refrigerant from the cooler to the condenser.
Turbine Ð The turbine serves 2 purposes. First, it acts as the expansion device to separate condenser pressure from cooler pressure. Second, using the pressure differential between the cooler and condenser, the turbine converts the pressure drop to energy and uses this energy to supplement the compressor motor, thereby reducing the required horsepower.
Control Panel Ð The control panel is the user interface for controlling the chiller. It regulates the chiller's capacity as required to maintain proper leaving chilled water temperature. The control panel:
·registers cooler, condenser, and lubricating system pressures
·shows chiller operating condition and alarm shutdown conditions
·records the total chiller operating hours
·sequences chiller start, stop, and recycle under microprocessor control
·displays status of motor starter
·provides access to other CCN (Carrier Comfort Network) devices
Fig. 1 Ð 19XRT Identi®cation
5

1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 11 12 13 |
14 |
15 |
|
|
LEGEND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Ð Turbine Housing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
Ð Power Panel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Ð Motor Housing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Ð Oil Level Sight Glasses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Ð Guide Vane Actuator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Ð Demistor Vent Line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Ð Suction Elbow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Ð Chiller Visual Control (CVC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
9 |
Ð Condenser Pumpout Connection (Hidden) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
Ð Condenser Relief Valves |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
11 |
Ð Relief Transfer Valve |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
Ð Condenser Pressure Transducer (Hidden) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
Ð Cooler Relief Valve |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
Ð Cooler Pressure Transducer (Hidden) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
Ð Cooler Pumpout Connection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
Ð Cooler/Condenser Water¯ow Device |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
Ð Condenser In/Out Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thermistors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
Ð Cooler In/Out Temperature Thermistors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
Ð Chiller Identi®cation Nameplate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Location |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
Ð Float Chamber |
|
|
22 |
|
21 |
|
20 |
|
|
19 |
|
18 17 |
|
21 |
Ð Refrigerant Charging Valve |
|
|
|
RIGHT END VIEW |
|
|
|
|
|
22 |
Ð Oil Drain Charging Valve |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
23 |
24 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 27 |
|
|
|
|
LEGEND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
Ð Take-Apart, Connector (Upper) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
Ð Waterbox Vent Connection (Typical) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
Ð Cooler Liquid Return Line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
Ð Oil Filter Access Cover |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
Ð Refrigerant Oil Cooler |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
Ð Take-Apart, Rabbet-Fit Connector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Lower) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29 |
Ð Cooler Return-End Waterbox Cover |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
Ð Waterbox Drain Port (Typical) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
Ð Condenser Return-End Waterbox Cover |
31 |
|
30 |
29 |
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
LEFT END VIEW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
LEGEND |
|
3 |
Ð Turbine Suction |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
1 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
Ð Nozzle (Typical, 1 of 6 Shown) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Ð Nozzle Block |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Ð High Efficiency Motor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Ð Transmission |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Ð Compressor Base |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Ð Guide Vane Actuator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Ð Oil Filter Housing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
Ð Turbine Wheel |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
Ð Turbine Housing |
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
Ð Turbine Discharge |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
Ð Turbine Sight Glass |
11 |
10 |
9 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
TURBINE COMPONENTS
Fig. 2 Ð Typical 19XRT Components
6
Factory-Mounted Starter (Optional) Ð The starter allows for the proper start and disconnect of electrical energy for the compressor-motor, oil pump, oil heater, and control panel.
Storage Vessel (Optional) Ð There are 2 sizes of storage vessels available. The vessels have double relief valves, a magnetically-coupled dial-type refrigerant level gage, a one-inch FPT drain valve, and a 1¤2-in. male ¯are vapor connection for the pumpout unit.
NOTE: If a storage vessel is not used at the jobsite, factoryinstalled isolation valves on the chiller may be used to isolate the chiller charge in either the cooler or condenser. An optional pumpout system is used to transfer refrigerant from vessel to vessel.
REFRIGERATION CYCLE
The compressor continuously draws refrigerant vapor from the cooler, at a rate set by the amount of guide vane opening (Fig. 3). As the compressor suction reduces the pressure in the cooler, the remaining refrigerant boils at a fairly low temperature (typically 38 to 42 F [3 to 6 C]). The energy required for boiling is obtained from the water ¯owing through the cooler tubes. With heat energy removed, the water becomes cold enough for use in an air conditioning circuit or process liquid cooling.
After taking heat from the water, the refrigerant vapor is compressed. Compression adds still more heat energy and the refrigerant is quite warm (typically 98 to 102 F [37 to 40 C]) when it is discharged from the compressor into the condenser.
Relatively cool (typically 65 to 90 F [18 to 32 C]) water ¯owing through the condenser tubes removes heat from the refrigerant, and the vapor condenses to a liquid. Further removal of heat from the refrigerant occurs in the lower chamber of the condenser, which is called the sensible subcooler. At this point, the liquid refrigerant is subcooled by contact with the coolest (entering water) condenser tubes.
After leaving the sensible subcooler section of the condenser, the liquid refrigerant enters the ¯oat valve chamber. The main ¯oat valve maintains a liquid level in the subcooler to prevent hot gas bypass from the condenser to the cooler at part load conditions. A second valve in the ¯oat valve chamber opens at part load conditions when the liquid level increases in the condenser to bypass liquid from the ¯oat chamber directly to the cooler inlet. The liquid refrigerant from the main ¯oat valve then ¯ows into the turbine housing chamber on the compressor. The liquid refrigerant passes through the turbine nozzles and impacts the turbine blades where energy is reclaimed as the refrigerant expands through the turbine to the lower cooler pressure. The turbine wheel is attached to the motor shaft which allows the turbine to supplement and reduce motor power requirements. At this point the refrigerant ¯ashes to a mixture of gas and liquid which removes heat from the remaining liquid. This mixture ¯ows back to the cooler where it is now at the same temperature and pressure at which the cycle began.
MOTOR AND LUBRICATING OIL
COOLING CYCLE
The motor and the lubricating oil are cooled by liquid refrigerant taken from the bottom of the condenser vessel (Fig. 3). Refrigerant ¯ow is maintained by the pressure
differential that exists due to compressor operation. After the refrigerant ¯ows past an isolation valve, an in-line ®lter, and a sight glass/moisture indicator, the ¯ow is split between the motor cooling and oil cooling systems.
Flow to the motor cooling system passes through an ori- ®ce and into the motor. Once past the ori®ce, the refrigerant is directed over the motor by a spray nozzle. The refrigerant collects in the bottom of the motor casing and is then drained back into the cooler through the motor refrigerant drain line. The refrigerant outlet from the motor casing is sized to act as an ori®ce to maintain a higher pressure in the motor shell than in the cooler/oil sump. The motor is protected by a temperature sensor imbedded in the stator windings. An increase in motor winding temperature past the motor override set point overrides the temperature capacity control to hold, and if the motor temperature rises 10° F (5.5° C) above this set point, closes the inlet guide vanes. If the temperature rises above the safety limit, the compressor shuts down.
Refrigerant that ¯ows to the oil cooling system is regulated by thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs). The TXVs regulate ¯ow into the oil/refrigerant plate and frame-type heat exchanger (the oil cooler in Fig. 3). The expansion valve bulbs control oil temperature to the bearings. The refrigerant leaving the oil cooler heat exchanger then returns to the chiller cooler.
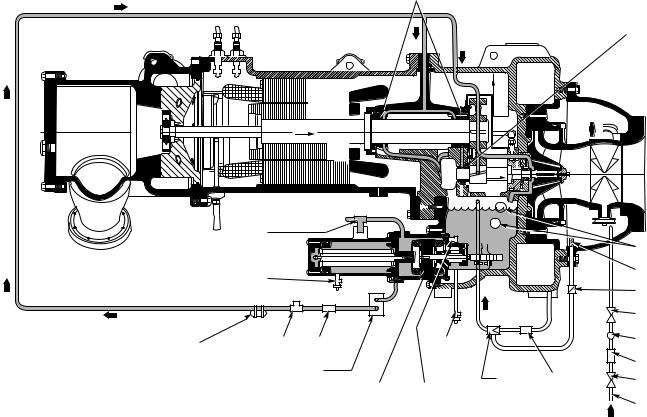
LUBRICATION CYCLE
Summary Ð The oil pump, oil ®lter, and oil cooler make up a package located partially in the transmission casting of the compressor-motor-turbine assembly. The oil is pumped into a ®lter assembly to remove foreign particles and is then forced into an oil cooler heat exchanger where the oil is cooled to proper operational temperatures. After the oil cooler, part of the ¯ow is directed to the gears and the high speed shaft bearings; the remaining ¯ow is directed to the motor shaft bearings. Oil drains into the transmission oil sump to complete the cycle (Fig. 4).
Details Ð Oil is charged into the lubrication system through a hand valve. Two sight glasses in the oil reservoir permit oil level observation. Normal oil level is between the middle of the upper sight glass and the top of the lower sight glass when the compressor is shut down. The oil level should be visible in at least one of the 2 sight glasses during operation. Oil sump temperature is displayed on the CVC (Chiller Visual Control) default screen. During compressor operation, the oil sump temperature ranges between 125 to 150 F (52 to 66 C).
The oil pump suction is fed from the oil reservoir. An oil pressure relief valve maintains 18 to 25 psid (124 to 172 kPad) differential pressure in the system at the pump discharge. This differential pressure can be read directly from the CVC default screen. The oil pump discharges oil to the oil ®lter assembly. This ®lter can be closed to permit removal of the ®lter without draining the entire oil system (see Maintenance sections, pages 66-71, for details). The oil is then piped to the oil cooler heat exchanger. The oil cooler uses refrigerant from the condenser as the coolant. The refrigerant cools the oil to a temperature between 120 and 140 F (49 to 60 C).
7
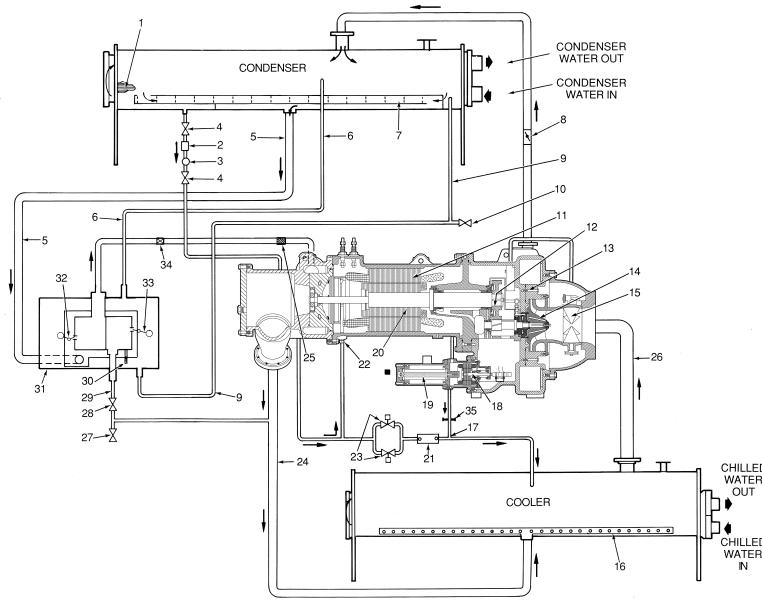
8
LEGEND
1Ð Condenser Tubes
2Ð Filter/Drier
3Ð Moisture Indicator
4Ð Refrigerant Cooling Isolation Valves
5Ð Main Condenser Liquid Drain Line
6Ð Float Chamber Vent
7Ð Subcooler
8Ð Discharge Isolation Valve (Optional)
9Ð High Condenser Level Drain
10Ð Condenser Side Refrigerant Charging Valve
11Ð Stator
12Ð Transmission
13Ð Diffuser
14Ð Impeller
15Ð Inlet Guide Vanes
16Ð Cooler Distribution Pipe
17Ð Refrigerant Cooling Drain Lines
18Ð Oil Pump
19Ð Oil Filter
20Ð Rotor
21Ð Oil Cooler
22Ð Ori®ced Fitting
23Ð Thermal Expansion Valve for
Oil Cooling
24Ð Cooler Refrigerant Supply Line
25Ð Turbine Suction Line Strainer
26Ð Cooler Suction Line
27Ð Cooler Refrigerant Charging Valve
28Ð Turbine Bypass Line Isolation Valve
29Ð Turbine Bypass Line
30Ð Pilot Drain Line From Turbine Bypass
31Ð Float Chamber
32Ð Turbine Float Valve
33Ð Turbine Bypass Float Valve
34Ð Turbine Suction Isolation Valve (Optional)
35Ð Motor Back Pressure Ori®ce
Fig. 3 Ð Refrigerant, Motor Cooling, and Oil Cooling Cycles
JOURNAL
BEARINGS
REAR PINION
BEARING
|
|
THRUST |
|
|
|
THRUST |
|
|
FILTER |
|
|
|
ISOLATION |
SIGHT |
|
|
VALVE |
||
OIL |
GLASSES |
||
|
|||
|
|
||
SUPPLY |
FILTER |
STRAINER |
|
LINE |
|
||
|
OIL DRAIN |
CHECK |
|
|
|
VALVE |
|
|
|
ISOLATION |
|
|
|
VALVE |
THERMAL |
OIL SUPPLY |
ISOLATION |
OIL |
SIGHT |
CHARGE |
GLASS |
|||
EXPANSION |
PRESSURE |
VALVE |
VALVE |
FILTER |
VALVE BULB |
TRANSDUCER |
OIL |
|
|
|
|
EDUCTOR STRAINER |
|
|
|
|
COOLER |
ISOLATION |
|
|
|
OIL PUMP |
OIL PRESSURE |
VALVE |
|
|
AND MOTOR |
RELIEF VALVE |
COOLER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OIL |
|
|
|
|
RECLAIM |
|
|
|
|
LINE |
Fig. 4 Ð Lubrication System
As the oil leaves the oil cooler, it passes the oil pressure transducer and the thermal bulb for the refrigerant expansion valve on the oil cooler. The oil is then divided. Part of the oil ¯ows to the thrust bearing, forward pinion bearing, and gear spray. The rest of the oil lubricates the motor shaft bearings and the rear pinion bearing. The oil temperature is measured in the bearing housing as it leaves the thrust and forward journal bearings. The oil then drains into the oil reservoir at the base of the compressor. The PIC II (Product Integrated Control II) measures the temperature of the oil in the sump and maintains the temperature during shutdown (see Oil Sump Temperature Control section, page 36). This temperature is read on the CVC default screen.
During the chiller start-up, the PIC II energizes the oil pump and provides 45 seconds of prelubrication to the bearings after pressure is veri®ed before starting the compressor. During shutdown, the oil pump will run for 60 seconds to post-lubricate after the compressor shuts down. The oil pump can also be energized for testing purposes during a Control Test.
Ramp loading can slow the rate of guide vane opening to minimize oil foaming at start-up. If the guide vanes open quickly, the sudden drop in suction pressure can cause any refrigerant in the oil to ¯ash. The resulting oil foam cannot be pumped efficiently; therefore, oil pressure falls off and lubrication is poor. If oil pressure falls below 15 psid (103 kPad) differential, the PIC II will shut down the compressor.
If the controls are subject to a power failure that lasts more than 3 hours, the oil pump will be energized periodically when the power is restored. This helps to eliminate refrigerant that has migrated to the oil sump during the power failure. The controls energize the pump for 60 seconds every 30 minutes until the chiller is started.
Oil Reclaim System Ð The oil reclaim system returns oil lost from the compressor housing back to the oil reservoir by recovering the oil from 2 areas on the chiller. The guide vane housing is the primary area of recovery. Oil is also recovered by skimming it from the operating refrigerant level in the cooler vessel.
PRIMARY OIL RECOVERY MODE Ð Oil is normally recovered through the guide vane housing on the chiller. This is possible because oil is normally entrained with refrigerant in the chiller. As the compressor pulls the refrigerant up from the cooler into the guide vane housing to be compressed, the oil normally drops out at this point and falls to the bottom of the guide vane housing where it accumulates. Using discharge gas pressure to power an eductor, the oil is drawn from the housing and is discharged into the oil reservoir.
SECONDARY OIL RECOVERY MODE Ð The secondary method of oil recovery is signi®cant under light load conditions, when the refrigerant going up to the compressor suction does not have enough velocity in which to bring oil along. Under these conditions, oil collects in a greater concentration at the top level of the refrigerant in the cooler. This oil and refrigerant mixture is skimmed from the side of the cooler and is then drawn up to the guide vane housing. There is a ®lter in this line. Because the guide vane housing pressure is much lower than the cooler pressure, the refrigerant boils off, leaving the oil behind to be collected by the primary oil recovery method.
9
STARTING EQUIPMENT
The 19XRT requires a motor starter to operate the centrifugal hermetic compressor motor, the oil pump, and various auxiliary equipment. The starter is the main ®eld wiring interface for the contractor.
See Carrier Speci®cation Z-415 for speci®c starter requirements. All starters must meet these speci®cations in order to properly start and satisfy mechanical safety requirements. Starters may be supplied as separate, free-standing units or may be mounted directly on the chiller (unit mounted) for low-voltage units only.
Three separate circuit breakers are inside the starter. Circuit breaker CB1 is the compressor motor circuit breaker. The disconnect switch on the starter front cover is connected to this breaker. Circuit breaker CB1 supplies power to the compressor motor.
The main circuit breaker (CB1) on the front of the starter disconnects the main motor current only. Power is still energized for the other circuits. Two more circuit breakers inside the starter must be turned off to disconnect power to the oil pump, PIC II controls, and oil heater.
Circuit breaker CB2 supplies power to the control panel, oil heater, and portions of the starter controls.
Circuit breaker CB3 supplies power to the oil pump. Both CB2 and CB3 are wired in parallel with CB1 so that power is supplied to them if the CB1 disconnect is open.
All starters must include a Carrier control module called the Integrated Starter Module (ISM), excluding the Benshaw solid-state starters. This module controls and monitors all aspects of the starter. See the Controls section on page 11 for additional ISM information. All starter replacement parts are supplied by the starter manufacturer excluding the ISM (contact Carrier's Replacement Component Division [RCD]).
Unit-Mounted Solid-State Starter (Optional) Ð The 19XRT chiller may be equipped with a solid-state, reduced-voltage starter (Fig. 5 and 6). This starter's primary function is to provide on-off control of the compressor motor. This type of starter reduces the peak starting torque, reduces the motor inrush current, and decreases mechanical shock. This capability is summed up by the phrase ``soft starting.'' The solid-state starter is available as a 19XRT option (factory supplied and installed). The solid-state starters manufacturer name is located inside the starter access door.
A solid-state, reduced-voltage starter operates by reducing the starting voltage. The starting torque of a motor at full voltage is typically 125% to 175% of the running torque. When the voltage and the current are reduced at start-up, the starting torque is reduced as well. The object is to reduce the starting voltage to just the voltage necessary to develop the torque required to get the motor moving. The voltage is reduced by silicon controlled recti®ers (SCRs). The voltage and current are then ramped up in a desired period of time. Once full voltage is reached, a bypass contactor is energized to bypass the SCRs.
When voltage is supplied to the solid-state circuitry, the heat sinks in the starter as well as the wires leading to the motor and the motor terminal are at line voltage. Do not touch the heat sinks, power wiring, or motor terminals while voltage is present or serious injury will result.
There is a display on the front of the Benshaw, Inc., solidstate starters that is useful for troubleshooting and starter checkout. The display indicates:
·voltage to the SCRs
·SCR control voltage
·power indication
·proper phasing for rotation
·start circuit energized
·over-temperature
·ground fault
·current unbalance
·run state
·software con®guration
The starter is further explained in the Check Starter and Troubleshooting Guide sections, pages 53 and 71.
6
1
2
3
5 
4 
LEGEND
1Ð Ready-Start Micro Input/Output Card
2Ð Circuit Breaker 2 (CB2):
Machine Control and Heater Power
3Ð Circuit Breaker 3 (CB3): Oil Pump Power
4Ð Ready-Start Micro Central Processing Unit Card (CPU)
5Ð Restart Micro Power Card (hidden, not depicted)
6Ð Restart Micro Bypass Card (hidden, not depicted)
Fig. 5 Ð Solid-State Starter Box,
Internal View
10
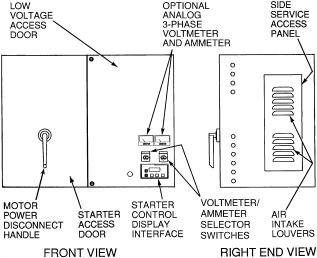
Fig. 6 Ð Typical Starter External View
(Solid-State Starter Shown)
Unit-Mounted Wye-Delta Starter (Optional)
Ð The 19XRT chiller may be equipped with a wye-delta starter mounted on the unit. This starter is intended for use with low-voltage motors (under 600 v). It reduces the starting current inrush by connecting each phase of the motor windings into a wye con®guration. This occurs during the starting period when the motor is accelerating up to speed. Once the motor is up to speed, the starter automatically connects the phase windings into a delta con®guration. Starter control, monitoring, and motor protection is provided by Carrier's Integrated Starter Module (ISM).
CONTROLS
De®nitions
ANALOG SIGNAL Ð An analog signal varies in proportion to the monitored source. It quanti®es values between operating limits. (Example: A temperature sensor is an analog device because its resistance changes in proportion to the temperature, generating many values.)
DISCRETE SIGNAL Ð A discrete signal is a 2-position representation of the value of a monitored source. (Example: A switch produces a discrete signal indicating whether a value is above or below a set point or boundary by generating an on/off, high/low, or open/closed signal.)
General Ð The 19XRT hermetic centrifugal liquid chiller contains a microprocessor-based control center that monitors and controls all operations of the chiller (see Fig. 7). The microprocessor control system matches the cooling capacity of the chiller to the cooling load while providing state-of-the-art chiller protection. The system controls cooling load within the set point plus the deadband by sensing the leaving chilled water or brine temperature and regulating the inlet guide vane via a mechanically-linked actuator motor. The guide vane is a variable ¯ow pre-whirl assembly that controls the refrigeration effect in the cooler by regulating the amount of refrigerant vapor ¯ow into the compressor. An increase in guide vane opening increases capacity. A decrease in guide vane opening decreases capacity. The microprocessor-based control center protects the chiller by monitoring the digital and analog inputs and executing capacity overrides or safety shutdowns, if required.
PIC II System Components Ð The chiller control system is called PIC II (Product Integrated Control II). See Table 1. The PIC II controls the operation of the chiller by monitoring all operating conditions. The PIC II can diagnose a problem and let the operator know what the problem is and what to check. It promptly positions the guide vanes to maintain leaving chilled water temperature. It can interface with auxiliary equipment such as pumps and cooling tower fans to turn them on when required. It continually checks all safeties to prevent any unsafe operating condition. It also regulates the oil heater while the compressor is off and regulates the hot gas bypass valve, if installed. The PIC II controls provide critical protection for the compressor motor and controls the motor starter.
The PIC II can interface with the Carrier Comfort Network (CCN) if desired. It can communicate with other PIC I or PIC II equipped chillers and other CCN devices.
The PIC II consists of 3 modules housed inside 3 major components. The component names and corresponding control voltages are listed below (also see Table 1):
·control panel
Ðall extra low-voltage wiring (24 v or less)
·power panel
Ð230 or 115 v control voltage (per job requirement)
Ðup to 600 v for oil pump power
·starter cabinet
Ðchiller power wiring (per job requirement)
Table 1 Ð Major PIC II Components and
Panel Locations*
PIC II COMPONENT |
PANEL |
|
LOCATION |
||
|
||
Chiller Visual Controller (CVC) and Display |
Control Panel |
|
Integrated Starter Module (ISM) |
Starter Cabinet |
|
Chiller Control Module (CCM) |
Control Panel |
|
Oil Heater Contactor (1C) |
Power Panel |
|
Oil Pump Contactor (2C) |
Power Panel |
|
Hot Gas Bypass Relay (3C) (Optional) |
Power Panel |
|
Control Transformers (T1, T2) |
Power Panel |
|
Temperature Sensors |
See Fig. 7. |
|
Pressure Transducers |
See Fig. 7. |
|
|
|
|
*See Fig. 5 and Fig. 7-11. |
|
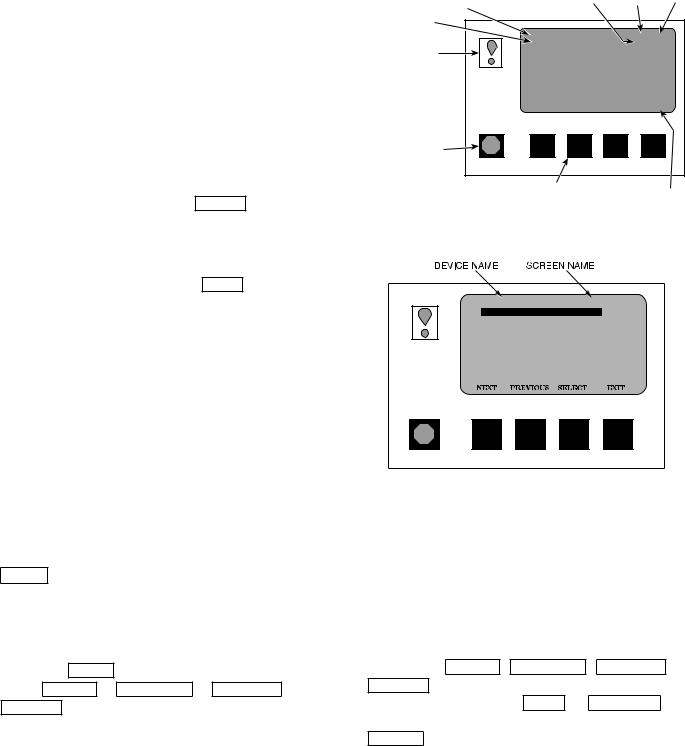
CHILLER VISUAL CONTROLLER (CVC) Ð The CVC is the ``brain'' of the PIC II. This module contains all the operating software needed to control the chiller. The CVC is mounted to the control panel (Fig. 10) and is the input center for all local chiller set points, schedules, con®gurable functions, and options. The CVC has a stop button, an alarm light, four buttons for logic inputs, and a backlight display. The backlight will automatically turn off after 15 minutes of non-use. The functions of the four buttons or ``softkeys'' are menu driven and are shown on the display directly above the softkeys.
The viewing angle of the CVC can be adjusted for optimum viewing. Remove the 2 bolts connecting the control panel to the brackets attached to the cooler. Place them in one of the holes to pivot the control panel forward to backward to change the viewing angle. See Fig. 10. To change the contrast of the display, access the adjustment on the back of the CVC. See Fig. 10.
11

LEGEND
1Ð Condenser Temperature Sensor Connection
2Ð Condenser Pressure Transducer Connection
TOP VIEW
COMPRESSOR AREA
Fig. 7 Ð 19XRT Control and Sensor Locations
12
INTEGRATED STARTER MODULE (ISM) Ð This module is located in the starter cabinet. This module initiates commands from the CVC for starter functions such as starting and stopping the compressor, condenser, chilled water pumps, tower fan, spare alarm contacts, and the shunt trip. The ISM monitors starter inputs such as line voltage, motor current, ground fault, remote start contact, spare safety, condenser high pressure, oil pump interlock, starter 1M, and run contacts. The ISM contains logic capable of safety shutdown. It shuts down the chiller if communications with the CVC are lost.
CHILLER CONTROL MODULE (CCM) Ð This module is located in the control panel. The CCM provides the input and outputs necessary to control the chiller. This module monitors refrigerant pressure, entering and leaving water temperatures, and outputs control for the guide vane actuator, oil heaters, and oil pump. The CCM is the connection point for optional demand limit, chilled water reset, remote temperature reset, and refrigerant leak sensor.
OIL HEATER CONTACTOR (1C) Ð This contactor is located in the power panel (Fig. 11) and operates the heater at either 115 or 230 v. It is controlled by the PIC II to maintain oil temperature during chiller shutdown.
OIL PUMP CONTACTOR (2C) Ð This contactor is located in the power panel. It operates all 200 to 575-v oil pumps. The PIC II energizes the contactor to turn on the oil pump as necessary.
HOT GAS BYPASS CONTACTOR RELAY (3C) (Optional) Ð This relay, located in the power panel, controls the opening of the hot gas bypass valve. The PIC II energizes the relay during low load, high lift conditions.
CONTROL TRANSFORMERS (T1, T2) Ð These transformers convert incoming control voltage to 24 vac power for the 3 power panel contactor relays, CCM, and CVC.
Fig. 8 Ð Control Sensors (Temperature)
Fig. 9 Ð Control Sensors
(Pressure Transducers, Typical)
13
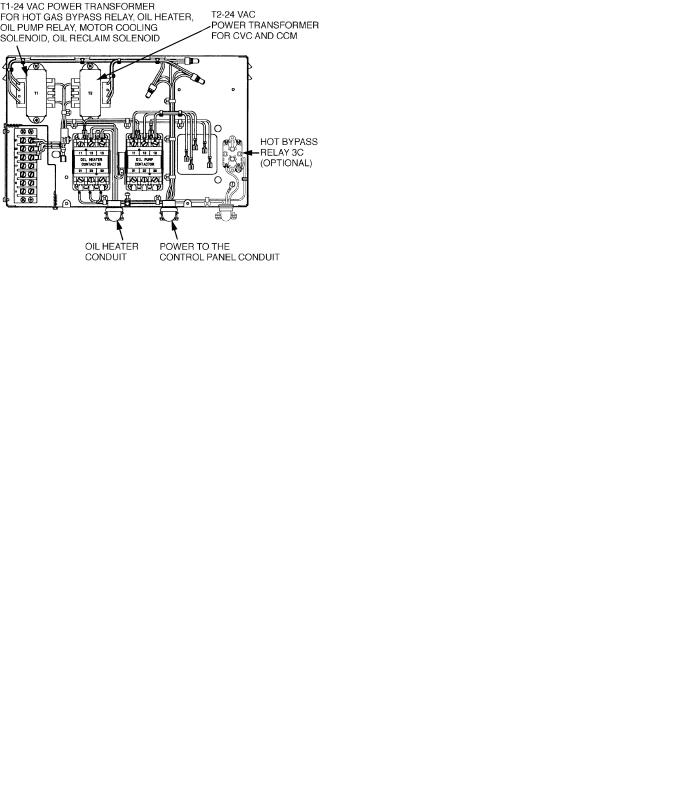
Fig. 10 Ð Control Panel
Fig. 11 Ð Power Panel
14
CVC Operation and Menus (Fig. 12-18)
GENERAL
·The CVC display automatically reverts to the default screen after 15 minutes if no softkey activity takes place and if the chiller is not in the pumpdown mode (Fig. 12).
·If a screen other than the default screen is displayed on the CVC, the name of that screen is in the upper right corner (Fig. 13).
·The CVC may be set to display either English or SI units. Use the CVC con®guration screen (accessed from the Service menu) to change the units. See the Service Operation section, page 44.
·Local Operation Ð The PIC II can be placed in local operating mode by pressing the LOCAL softkey. The PIC II then accepts commands from the CVC only and
uses the Local Time Schedule to determine chiller start and stop times.
·CCN Operation Ð The PIC II can be placed in the CCN
operating mode by pressing the CCN softkey. The
PIC II then accepts modi®cations from any CCN interface or module (with the proper authority), as well as from the CVC. The PIC II uses the CCN time schedule to determine start and stop times.
ALARMS AND ALERTS Ð An alarm shuts down the compressor. An alert does not shut down the compressor, but it noti®es the operator that an unusual condition has occurred. An alarm (*) or alert (!) is indicated on the STATUS screens on the far right ®eld of the CVC display screen.
Alarms are indicated when the control center alarm light
(!) ¯ashes. The primary alarm message is displayed on the default screen. An additional, secondary message and troubleshooting information are sent to the ALARM HISTORY table.
When an alarm is detected, the CVC default screen will freeze (stop updating) at the time of alarm. The freeze enables the operator to view the chiller conditions at the time of alarm. The STATUS tables will show the updated information. Once all alarms have been cleared (by pressing the
RESET softkey), the default CVC screen will return to nor-
mal operation.
CVC MENU ITEMS Ð To perform any of the operations described below, the PIC II must be powered up and have successfully completed its self test. The self test takes place automatically, after power-up.
Press the MENU softkey to view the list of menu struc-
tures: STATUS , SCHEDULE , SETPOINT , and
SERVICE .
·The STATUS menu allows viewing and limited calibration or modi®cation of control points and sensors, relays and contacts, and the options board.
·The SCHEDULE menu allows viewing and modi®cation of the local and CCN time schedules and Ice Build time schedules.
·The SETPOINT menu allows set point adjustments, such as the entering chilled water and leaving chilled water set points.
PRIMARY STATUS |
COMPRESSOR |
DATE |
TIME |
|||
MESSAGE |
ONTIME |
|
|
|
|
|
SECONDARY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
STATUS |
RUNNING TEMP CONTROL |
01-01-95 11:48 |
||||
MESSAGE |
||||||
LEAVING CHILLED WATER |
28.8 HOURS |
|||||
ALARM LIGHT |
CHW IN |
CHW OUT |
EVAP REF |
|||
55.1 |
|
44.1 |
40.7 |
|||
(ILLUMINATED |
|
|||||
CDW IN |
CDW OUT |
COND REF |
||||
WHEN POWER ON) |
||||||
85.0 |
|
95.0 |
98.1 |
|||
BLINKS CONTINUOUSLY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
•ON FOR AN ALARM |
OIL PRESS |
OIL TEMP |
AMPS % |
|||
•BLINKS ONCE TO |
21.8 |
132.9 |
|
93 |
||
CCN |
LOCAL |
RESET |
MENU |
|||
CONFIRM A STOP |
||||||
STOP BUTTON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
•HOLD FOR ONE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECOND TO STOP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SOFT KEYS |
MENU |
|
EACH KEY'S FUNCTION IS |
||
LINE |
||
DEFINED BY THE MENU DESCRIPTION |
||
ON MENU LINE ABOVE |
|
Fig. 12 Ð CVC Default Screen
19XRT_II |
SERVICE |
ALARM HISTORY
CONTROL TEST
CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS
EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION
ISM (STARTER) CONFIGURATION DATA
EQUIPMENT SERVICE
TIME AND DATE
ATTACH TO NETWORK DEVICE
LOG OUT OF DEVICE
CVC CONFIGURATION
Fig. 13 Ð CVC Service Screen
·The SERVICE menu can be used to view or modify information on the Alarm History, Control Test, Control Algorithm Status, Equipment Con®guration, ISM Starter Con®guration data, Equipment Service, Time and Date, Attach to Network Device, Log Out of Network Device, and CVC Con®guration screens.
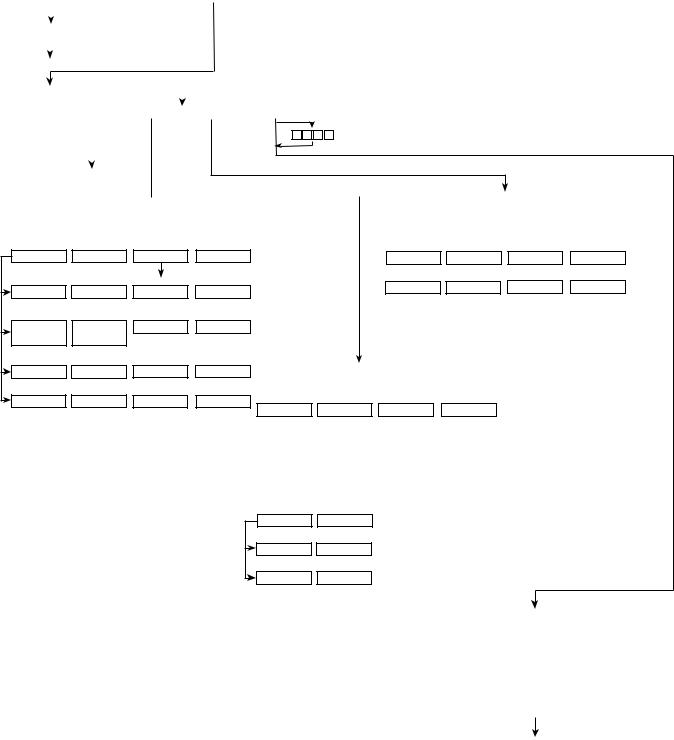
For more information on the menu structures, refer to Fig. 15.
Press the softkey that corresponds to the menu structure
to be viewed : STATUS , SCHEDULE , SETPOINT , or
SERVICE . To view or change parameters within any of
these menu structures, use the NEXT and PREVIOUS soft-
keys to scroll down to the desired item or table. Use the
SELECT softkey to select that item. The softkey choices
that then appear depend on the selected table or menu. The softkey choices and their functions are described below.
BASIC CVC OPERATIONS (Using the Softkeys) Ð To perform any of the operations described below, the PIC II must be powered up and have successfully completed its self test.
15

·Press QUIT to leave the selected decision or ®eld without
·Press ENTER to leave the selected decision or ®eld and save
·Press NEXT to scroll the cursor bar down in order to
highlight a point or to view more points below the current screen
· Press PREVIOUS to scroll the cursor bar up in order to
·Press SELECT to view the next screen level (high-
lighted with the cursor bar), or to override (if allowable) the
· Press
·Press INCREASE or DECREASE to change the highlighted
TO VIEW STATUS (Fig. 14) Ð The status table shows the actual value of overall chiller status such as CONTROL MODE, RUN STATUS, AUTO CHILLED WATER, RESET, and REMOTE RESET SENSOR.
1.On the menu screen, press STATUS to view the list of point status tables.
2.Press NEXT or PREVIOUS to highlight the desired status table. The list of tables is:
·MAINSTAT Ð Overall chiller status
·STARTUP Ð Status required to perform startup of chiller
·COMPRESS Ð Status of sensors related to the compressor
·HEAT_EX Ð Status of sensors related to the heat exchangers
·POWER Ð Status of motor input power
·ISM_STAT Ð Status of motor starter
·CVC_PSWD Ð Service menu password forcing access screen
3.Press SELECT to view the desired point status table.
4. On the point status table, press NEXT or
PREVIOUS until the desired point is displayed on the screen.
|
|
|
19XRT_II MAINSTAT |
POINT STATUS |
|||||
|
|
|
Control Mode |
|
OFF |
||||
|
|
|
Run Status |
|
Ready |
||||
|
|
|
Start Inhibit Timer |
|
0.0 Min |
||||
|
|
|
Occupied? |
|
|
NO |
|||
|
|
|
System Alert/Alarm |
NORMAL |
|||||
|
|
|
Chiller Start/Stop |
|
STOP |
||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Remote Start Contact |
|
Open |
||||
|
|
|
Temperature Reset |
|
0.0 F |
||||
|
|
|
Control Point |
|
44.0 F |
||||
|
|
|
Chilled Water Temp |
|
44.6 F |
||||
|
|
|
Active Demand Limit |
100% |
|||||
|
|
|
Average Line Current |
0.0% |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 14 Ð Example of Status Screen
OVERRIDE OPERATIONS
To Override a Value or Status
1. From any point status screen, press NEXT or
16
|
|
|
|
|
|
DEFAULT SCREEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
CCN |
|
LOCAL |
|
RESET |
|
MENU |
|
(SOFTKEYS) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Start Chiller In CCN Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Start Chiller in Local Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Clear Alarms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Access Main Menu |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
STATUS |
|
|
SCHEDULE |
|
SETPOINT |
|
SERVICE |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 1 1 1 |
(ENTER A 4-DIGIT PASSWORD) |
|
|
|
List the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Status Tables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
List the Service Tables |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Display The Setpoint Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•MAINSTAT
•STARTUP
• COMPRESS |
List the Schedules |
|
• HEAT_EX |
|
• Base Demand Limit |
|
• LCW Setpoint |
|
• POWER |
|
|
|
• ECW Setpoint |
|
• ISM_STAT |
|
|
|
• Ice Build Setpoint |
|
• CVC_PSWD |
|
|
|
• Tower Fan High Setpoint |
|
Select a Status Table |
|
|
|
Select the Setpoint |
|
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
EXIT |
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
EXIT |
|
Select a Modification Point |
|
|
Modify the Setpoint |
|
|
|||
|
|
INCREASE |
DECREASE |
QUIT |
ENTER |
|||
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
EXIT |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
Modify a Discrete Point |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
START |
STOP |
RELEASE |
ENTER |
|
|
|
|
|
ON |
OFF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modify an Analog Point |
|
|
• OCCPC01S – LOCAL TIME SCHEDULE |
|
|
|||
INCREASE |
DECREASE |
RELEASE |
ENTER |
|
|
|||
• OCCPC02S – ICE BUILD TIME SCHEDULE |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Modify Control Options |
|
|
• OCCPC03S – CCN TIME SCHEDULE |
|
|
|
||
ENABLE |
DISABLE |
QUIT |
ENTER |
Select a Schedule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
EXIT |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 Override
Select a Time Period/Override
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
Modify a Schedule Time |
|
INCREASE |
DECREASE |
Add/Eliminate a Day |
|
ENABLE |
DISABLE |
SELECT |
|
EXIT |
|
|
|
(ANALOG VALUES) |
|
ENTER |
|
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
(DISCRETE VALUES) |
ENTER |
|
EXIT |
|
ALARM HISTORY
CONTROL TEST
CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS
EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION
ISM (STARTER) CONFIG DATA
EQUIPMENT SERVICE
TIME AND DATE
ATTACH TO NETWORK DEVICE
LOG OUT OF DEVICE
CVC CONFIGURATION
NEXT |
|
PREVIOUS |
|
SELECT |
|
EXIT |
SEE FIGURE 16
Fig. 15 Ð 19XRT CVC Menu Structure
17

SERVICE TABLE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
NEXT |
|
|
PREVIOUS |
|
|
SELECT |
|
|
|
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
ALARM HISTORY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Display Alarm History |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(The table holds up to 25 alarms and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
alerts with the most recent alarm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
at the top of the screen.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
CONTROL TEST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
List the Control Tests |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•CCM Thermistors |
|
||||||||||
|
CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•CCM Pressure Transducers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Pumps |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Discrete Outputs |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
List the Control Algorithm Status Tables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Guide Vane Actuator |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
•CAPACITY (Capacity Control) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Diffuser Actuator |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
•OVERRIDE (Override Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Pumpdown/Lockout |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
•LL_MAINT (Lead Lag Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•Terminate Lockout |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
• ISM_HIST (ISM Alarm History) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Test |
•Guide Vane Calibration |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
• LOADSHED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
•WSMDEFME (Water System Manager Control Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEXT |
|
|
PREVIOUS |
|
|
SELECT |
|
EXIT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
•OCCDEFCM (Time Schedule Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEXT |
|
PREVIOUS |
|
|
SELECT |
|
|
|
|
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCCDEFM (Time |
|
|
Schedule Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•CAPACITY (Capacity Control Algorithm) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Data Select Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•OVERRIDE (Override Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
NEXT |
|
|
PREVIOUS |
|
|
|
SELECT |
|
|
EXIT |
|
|
•LL_MAINT (LEADLAG Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•WSMDEFM2 (Water System Manager Control Status) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCCPC01S (Local Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCCPC02S (CCN, ICE BUILD Status) |
|
Maintenance Table Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCCPC03S (CCN Status) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION |
|
List the Equipment Configuration Tables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•NET_OPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•BRODEF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•OCCEFCS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•HOLIDAYS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•CONSUME |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•RUNTIME |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEXT |
|
PREVIOUS |
|
|
SELECT |
|
|
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Parameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEXT |
|
|
PREVIOUS |
|
|
SELECT |
|
|
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Modify a Parameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INCREASE |
|
DECREASE |
|
|
QUIT |
|
|
|
ENTER |
|
(ANALOG VALUES) |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENABLE |
|
|
DISABLE |
|
|
QUIT |
|
|
|
ENTER |
|
(DISCRETE VALUES) |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONTINUED
ON NEXT PAGE
Fig. 16 Ð 19XRT Service Menu Structure
18
SERVICE MENU CONTINUED
FROM PREVIOUS PAGE
|
|
ISM (STARTER CONFIG DATA) |
|
|
|
|
||
EQUIPMENT SERVICE |
|
|
|
|
4 4 4 4 (ENTER A 4-DIGIT PASSWORD) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Service Tables: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
•OPTIONS |
|
|
|
Service Tables: |
|
|
|
|
•SETUP1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
•ISM (STARTER) CONFIG PASSWORD |
|
|||
|
•SETUP2 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
• ISM_CONF |
|
|
||
|
• LEADLAG |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• RAMP_DEM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• TEMP_CTL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Service Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Service Table Parameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|
Modify a Service Table Parameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
INCREASE |
DECREASE |
QUIT |
ENTER |
(ANALOG VALUES) |
|
|
|
|
ENABLE |
DISABLE |
QUIT |
ENTER |
(DISCRETE VALUES) |
|
|
|
|
TIME AND DATE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Display Time and Date Table: |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
•To Modify — Current Time |
— Day of Week |
|||
ATTACH TO NETWORK DEVICE |
|
|
— Current Date |
— Holiday Today |
||||
|
|
|
|
INCREASE |
DECREASE |
ENTER |
EXIT |
(ANALOG VALUES) |
|
List Network Devices |
|
YES |
NO |
ENTER |
EXIT |
(DISCRETE VALUES) |
|
|
•Local |
• Device 6 |
|
|||||
|
• Device 1 • Device 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Device 2 • Device 8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Device 3 • Device 9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
• Device 4 • Attach To Any Device |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
• Device 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Select a Device |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NEXT |
PREVIOUS |
SELECT |
ATTACH |
|
|
|
|
|
Modify Device Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INCREASE |
DECREASE |
ENTER |
EXIT |
|
|
|
|
|
•Use to attach CVC to another CCN network or device |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
•Attach to "LOCAL" to enter this machine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
•To upload new tables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOG OUT OF DEVICE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Default Screen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CCN |
LOCAL |
RESET |
MENU |
|
|
CVC CONFIGURATION
CVC Configuration Table |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
INCREASE |
|
DECREASE |
|
ENTER |
|
|
EXIT |
|
|
•To Modify — CVC CCN Address |
•To View — CVC Software Version |
|||||||
|
— English (US IMP) or S.I. Metric Units |
|
(last 2 digits of part number |
||||||
|
— Password |
|
|
|
|
|
indicate software version) |
||
|
LEGEND |
CCN |
Ð Carrier Comfort Network |
CVC |
Ð Chiller Visual Control |
IMP |
Ð Imperial |
ISM |
Ð Integrated Starter Module |
PIC II |
Ð Product Integrated Control II |
Fig. 16 Ð 19XRT Service Menu Structure (cont)
19

3. Press
For Discrete Points Ð Press YES or NO to select the desired state.
For Analog Points Ð Press INCREASE or
4. Press
NOTE: When overriding or changing metric values, it is necessary to hold down the softkey for a few seconds in order to see a value change, especially on kilopascal values.
To Remove an Override
1. On the point status table press NEXT or
PREVIOUS
2. Press
3.Press RELEASE to remove the override and return the point
Override Indication Ð An override value is indicated by
``SUPVSR,'' ``SERVC,'' or ``BEST'' ¯ashing next to the point value on the STATUS table.
TIME SCHEDULE OPERATION (Fig. 17)
1. On
20
2.Press NEXT or PREVIOUS to highlight the desired schedule.
OCCPC01S Ð LOCAL Time Schedule OCCPC02S Ð ICE BUILD Time Schedule
3. Press
4. Press NEXT or PREVIOUS to highlight the de-
5.Press SELECT to access the highlighted period or override
6.a. Press INCREASE or DECREASE to change the time values. Override values are in one-hour incre-
Fig. 17 Ð Example of Time Schedule
Operation Screen
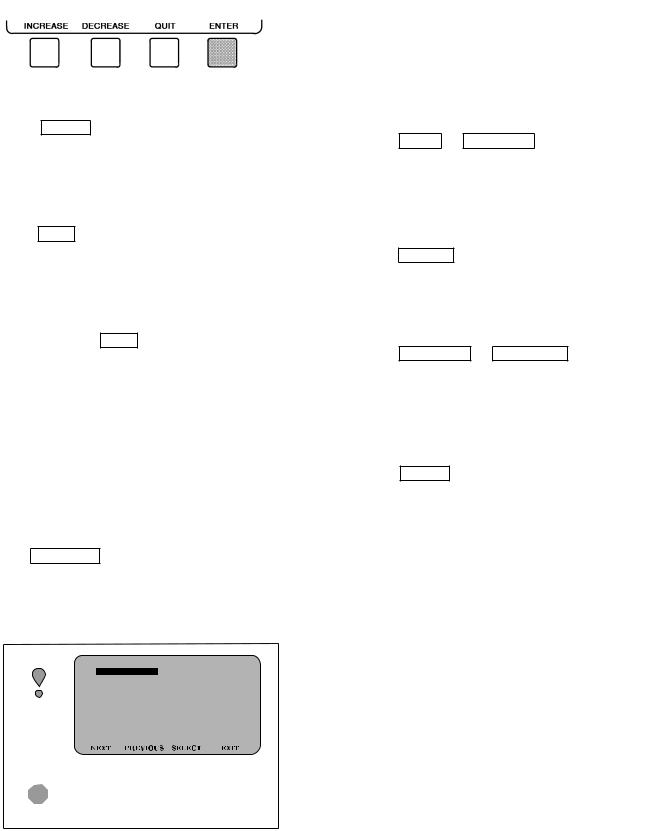
b.Press ENABLE to select days in the day-of-week ®elds. Press DISABLE to eliminate days from the
7. Press ENTER to register the values and to move
8. Press
9.Either return to Step 4 to select another period or override, or press EXIT again to leave the current time schedule
10.The Holiday Designation (HOLIDEF table) may be found in the Service Operation section, page 44. The month, day, and duration for the holiday must be assigned. The Broadcast function in the BRODEF table also must be enabled for holiday periods to function.
TO VIEW AND CHANGE SET POINTS (Fig. 18)
1. To view the SETPOINT table, from the MENU screen
press
|
|
|
19XR_II |
SETPOINT |
SETPOINT SELECT |
|||||
|
|
|
Base Demand Limit |
100% |
||||||
|
|
|
Control Point |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
LCW Setpoint |
|
|
50.0 F |
||||
|
|
|
ECW Setpoint |
|
|
60.0 F |
||||
|
|
|
ICE BUILD Setpoint |
|
|
40.0 F |
||||
|
|
|
Tower Fan High Setpoint |
|
|
85.0 F |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.There are 5 set points on this screen: BASE DEMAND LIMIT, LCW SETPOINT (leaving chilled water set point), ECW SETPOINT (entering chilled water set point), ICE BUILD SETPOINT, and TOWER FAN HIGH SETPOINT. Only one of the chilled water set points can be active at one time. The set point that is active is determined from the SERVICE menu. See the Service Operation section, page 44. The ice build (ICE BUILD) function is also activated and con®gured from the SERVICE menu.
3.Press NEXT or PREVIOUS to highlight the desired set
4.Press SELECT to modify the highlighted set point.
5.Press INCREASE or DECREASE to change the selected set point value.
6.Press ENTER to save the changes and return to the previous
SERVICE OPERATION Ð To view the menu-driven programs available for Service Operation, see Service Operation section, page 44. For examples of CVC display screens, see Table 2.
Fig. 18 Ð Example of Set Point Screen
21
Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data
IMPORTANT: The following notes apply to all Table 2 examples.
1.Only 12 lines of information appear on the CVC screen at any one time. Press the NEXT or PREVIOUS softkey to highlight a point or to view items below or above the current screen. Press the NEXT softkey twice to page forward; press the
PREVIOUS softkey twice to page back.
2.To access the information shown in Examples 9 through 21, enter your 4-digit password after pressing the SERVICE softkey. If
no softkeys are pressed for 15 minutes, the CVC automatically logs off (to prevent unrestricted access to PIC II controls) and reverts to the default screen. If this happens, you must reenter your password to access the tables shown in Examples 9 through 21.
3.Terms in the Description column of these tables are listed as they appear on the CVC screen.
4.The CVC may be con®gured in English or Metric (SI) units using the CVC CONFIGURATION screen. See the Service Operation section, page 44, for instructions on making this change.
5.The items in the Reference Point Name column do not appear on the CVC screen. They are data or variable names used in CCN or Building Supervisor (BS) software. They are listed in these tables as a convenience to the operator if it is necessary to cross reference CCN/BS documentation or use CCN/BS programs. For more information, see the 19XRT CCN literature.
6.Reference Point Names shown in these tables in all capital letters can be read by CCN and BS software. Of these capitalized names, those preceded by a dagger can also be changed (that is, written to) by the CCN, BS, and the CVC. Capitalized Reference Point Names preceded by two asterisks can be changed only from the CVC. Reference Point Names in lower case type can be viewed by CCN or BS only by viewing the whole table.
7.Alarms and Alerts: An asterisk in the far right ®eld of a CVC status screen indicates that the chiller is in an alarm state; an exclamation point in the far right ®eld of the CVC screen indicates an alert state. The asterisk (or exclamation point) indicates that the value on that line has exceeded (or is approaching) a limit. For more information on alarms and alerts, see the Alarms and Alerts section, page 15.
|
LEGEND |
12T |
Ð Motor Overload |
CCN |
Ð Carrier Comfort Network |
CHW |
Ð Chilled Water |
CR |
Ð Control Relay |
CT |
Ð Current Transformer |
CVC |
Ð Chiller Visual Control |
ECW |
Ð Entering Chilled Water |
HGBP Ð Hot Gas Bypass |
|
ISM |
Ð Integrated Starter Module |
LCW |
Ð Leaving Chilled Water |
LRA |
Ð Locked Rotor Amps |
mA |
Ð Milliamps |
P |
Ð Pressure |
SS |
Ð Solid State |
T |
Ð Temperature |
VFD |
Ð Variable Frequency Drive |
WSM |
Ð Water System Manager |
EXAMPLE 1 Ð CVC DEFAULT SCREEN
The following data is displayed in the CVC Default screen.
DESCRIPTION |
RANGE |
UNITS |
REFERENCE POINT NAME |
DISPLAY |
|||||
(ALARM HISTORY) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
(PRIMARY MESSAGE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(SECONDARY MESSAGE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(DATE AND TIME) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compressor Ontime |
0-500000.0 |
HOURS |
C |
|
HRS |
|
|||
Entering Chilled Water |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
ECW |
|
|
|
CHW IN |
||
Leaving Chilled Water |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
LCW |
CHW OUT |
|||||
Evaporator Temperature |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
ERT |
EVAP REF |
|||||
Entering Condenser Water |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
ECDW |
CDW IN |
|||||
Leaving Condenser Water |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
LCDW |
CDW OUT |
|||||
Condenser Temperature |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
CRT |
COND REF |
|||||
Oil Pressure |
0-420 |
PSI |
OILPD |
OILPRESS |
|||||
Oil Sump Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
OILT |
OIL TEMP |
|||||
Average Line Current |
0-999 |
% |
AMPS % |
AMPS % |
|||||
|
0-1 |
|
CCN |
|
|
|
|||
|
0-1 |
|
LOCAL |
|
|||||
|
0-1 |
|
RESET |
|
|||||
NOTE: The last three entries are used to indicate operating mode to the PIC II. These values may be forced by the CVC only.
22
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXAMPLE 2 Ð MAINTSTAT DISPLAY SCREEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To access this display from the CVC default screen: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
1. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MENU |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
will be highlighted). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
STATUS |
( |
MAINSTAT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
3. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
SELECT |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
|
|
|
|
POINT |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Control Mode |
NOTE 1 |
NOTE 1 |
CMODE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Run Status |
NOTE 2 |
NOTE 2 |
RUNSTAT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Start Inhibit Timer |
0-15 |
min |
T |
|
|
START |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Occupied ? |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
OCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
System Alert/Alarm |
0-2 |
NOTE 3 |
SYS |
|
|
|
|
|
ALM |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
*Chiller Start/Stop |
0/1 |
STOP/START |
CHIL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
S S |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
*Remote Start Contact |
0/1 |
OFF/ON |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
REMCON |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Temperature Reset |
−30-30 |
DEG F |
T |
|
|
RESET |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
*Control Point |
10-120 |
DEG F |
LCW |
|
|
|
STPT |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Chilled Water Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
CHW |
|
|
|
|
|
TMP |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
*Active Demand Limit |
40-100 |
% |
DEM |
|
|
|
|
LIM |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Average Line Current |
0-999 |
% |
AMPS |
|
|
|
|
|
% |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Motor Percent Kilowatts |
0-999 |
% |
KW |
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Auto Demand Limit Input |
4-20 |
mA |
AUTODEM |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Auto Chilled Water Reset |
4-20 |
mA |
AUTORES |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Remote Reset Sensor |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
R |
|
|
|
|
|
RESET |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Total Compressor Starts |
0-99999 |
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
STARTS |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Starts in 12 Hours |
0-8 |
|
|
|
STARTS |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Compressor Ontime |
0-500000.0 |
HOURS |
C |
|
|
|
|
HRS |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
*Service Ontime |
0-32767 |
HOURS |
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HRS |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Ice Build Contact |
0-1 |
OPEN/CLOSE |
ICE |
|
|
|
|
CON |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Refrigerant Leak Sensor |
0-20 |
mA |
REF |
|
|
|
|
|
LEAK |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES:
1.Reset, Off, Local, CCN
2.Timeout, Ready, Recycle, Prestart, Start-up, Ramping, Running, Demand, Override, Shutdown, Trippout, Pumpdown, Lockout
3.Normal, Alert, Alarm
4.All variables with capital letter point names are available for CCN read operation. Those shown with (*) support write operations for all CCN devices.
EXAMPLE 3 Ð STARTUP DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press STATUS .
3.Scroll down to highlight STARTUP .
4.Press SELECT .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
|
POINT |
|||||||
Actual Guide Vane Pos |
0-100 |
% |
GV |
|
|
|
|
|
POS |
||
**Chilled Water Pump |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
CHWP |
|
|
|
|||||
Chilled Water Flow |
0-1 |
NO/YES |
CHW |
|
|
FLOW |
|||||
**Condenser Water Pump |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
CDP |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Condenser Water Flow |
0-1 |
NO/YES |
CDW |
|
|
FLOW |
|||||
Oil Pump Relay |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
OILR |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
**Oil Pump Delta P |
−6.7-200 |
^PSI |
OILPD |
||||||||
Compressor Start Relay |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
CMPR |
||||||||
Compressor Start Contact |
0-1 |
OPEN/CLOSED |
1M |
|
|
|
AUX |
||||
Starter Trans Relay |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
TRANS |
||||||||
Compressor Run Contact |
0-1 |
OPEN/CLOSED |
2M |
|
AUX |
||||||
**Tower Fan Relay Low |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
TFR |
|
|
|
LOW |
||||
**Tower Fan Relay High |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
TFR |
|
|
|
HIGH |
||||
Starter Fault |
0-1 |
ALARM/NORMAL |
|
|
|
||||||
STARTFLT |
|||||||||||
Spare Safety Input |
0-1 |
ALARM/NORMAL |
SAFETY |
||||||||
Shunt Trip Relay |
0-1 |
OFF/ON |
TRIPR |
||||||||
Starter Fault Status |
0-255 |
|
ISMFLT |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation. Those shown with (**) shall support write operations for the CVC only.
23

Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 4 Ð COMPRESS DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press STATUS .
3.Scroll down to highlight COMPRESS .
4.Press SELECT .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
|
|||||||
Actual Guide Vane Pos |
0-100 |
% |
GV |
POS |
|||||||
Guide Vane Delta |
0-100 |
% |
GV |
|
|
|
DELTA |
||||
**Target Guide Vane Pos |
0-100 |
% |
GV |
|
|
|
TRG |
||||
Oil Sump Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
OILT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**Oil Pump Delta P |
−6.7-200 |
PSI |
OILPD |
|
|||||||
Comp Discharge Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
CMPD |
|
|||||||
Comp Thrust Brg Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
MTRB |
|
|||||||
Comp Motor Winding Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
MTRW |
|
|||||||
Spare Temperature 1 |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
SPARE |
|
T1 |
||||||
Spare Temperature 2 |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
SPARE |
|
T2 |
||||||
Oil Heater Relay |
0/1 |
OFF/ON |
OILHEAT |
|
|
||||||
Diffuser Actuator |
0-100 |
% |
DIFF |
|
|
ACT |
|||||
**Target VFD Speed |
0-110 |
% |
VFD |
|
|
|
OUT |
||||
**Actual VFD Speed |
0-100 |
% |
VFD |
|
|
ACT |
|||||
Surge Protection Counts |
0-5 |
|
SPC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation. Those shown with (**) shall support write operations for the CVC only.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXAMPLE 5 Ð HEAT |
EX DISPLAY SCREEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
To access this display from the CVC default screen: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
1. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MENU |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STATUS |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3. |
Scroll down to highlight |
HEAT |
|
EX |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
4. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
SELECT |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
STATUS |
|
UNITS |
|
|
POINT |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
**Chilled Water Delta P |
|
−6.7-420 |
|
PSI |
CHWPD |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Entering Chilled Water |
|
−40-245 |
|
DEG F |
ECW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Leaving Chilled Water |
|
−40-245 |
|
DEG F |
LCW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Chilled Water Delta T |
|
−6.7-420 |
|
^ F |
CHW |
|
|
|
|
|
DT |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Chill Water Pulldown/Min |
|
−20-20 |
|
^ F |
CHW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PULL |
||||||||||||
|
|
Evaporator Refrig Temp |
|
−40-245 |
|
DEG F |
ERT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
**Evaporator Pressure |
|
−6.7-420 |
|
PSI |
ERP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Evaporator Approach |
|
0-99 |
|
|
^ F |
EVAP |
|
|
|
|
APP |
|||||||||||||
|
|
**Condenser Water Delta P |
|
−6.7-420 |
|
PSI |
CDWPD |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Entering Condenser Water |
|
−40-245 |
|
DEG F |
ECDW |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Leaving Condenser Water |
|
−40-245 |
|
DEG F |
LCDW |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Condenser Refrig Temp |
|
−40-245 |
|
DEG F |
CRT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
**Condenser Pressure |
|
−6.7-420 |
|
PSI |
CRP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Condenser Approach |
|
0-99 |
|
|
^ F |
COND |
|
|
|
|
APP |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Hot Gas Bypass Relay |
|
0/1 |
|
|
OFF/ON |
HGBYPASS |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Surge/HGBP Active ? |
|
0/1 |
|
|
NO/YES |
SHG |
|
|
|
|
|
ACT |
||||||||||||
|
|
Active Delta P |
|
0-200 |
|
|
PSI |
DP |
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Active Delta T |
|
0-200 |
|
|
DEG F |
DT |
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Surge/HGBP Delta T |
|
0-200 |
|
|
DEG F |
DT |
|
C |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation. Those shown with (**) shall support write operations for the CVC only.
24

Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 6 Ð POWER DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press STATUS .
3.Scroll down to highlight POWER .
4.Press SELECT .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
|
POINT |
|||||||||||
Average Line Current |
0-999 |
% |
AMPS |
% |
|||||||||||
Actual Line Current |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMP |
|
|
|
|
A |
|
||||||
Average Line Voltage |
0-999 |
% |
VOLT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
||||
Actual Line Voltage |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLT |
|
|
|
|
A |
|||||||
Power Factor |
0.0-1.0 |
|
POW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FACT |
||||
Motor Kilowatts |
0-99999 |
kW |
KW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Motor Kilowatt-Hours |
0-99999 |
kWH |
KWH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Demand Kilowatts |
0-99999 |
kWH |
DEM |
|
|
|
|
|
KW |
||||||
Line Current Phase 1 |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMPS |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|||||||
Line Current Phase 2 |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMPS |
|
|
|
2 |
||||||||
Line Current Phase 3 |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMPS |
|
|
|
3 |
||||||||
Line Voltage Phase 1 |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLT |
|
1 |
||||||||||
Line Voltage Phase 2 |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLT |
|
|
2 |
|||||||||
Line Voltage Phase 3 |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLT |
|
|
3 |
|||||||||
Ground Fault Phase 1 |
0-999 |
AMPS |
GF |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Ground Fault Phase 2 |
0-999 |
AMPS |
GF |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Ground Fault Phase 3 |
0-999 |
AMPS |
GF |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Frequency |
0-99 |
Hz |
FREQ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
12T Sum Heat-Phase 1 |
0-200 |
% |
SUM1HEAT |
||||||||||||
12T Sum Heat-Phase 2 |
0-200 |
% |
SUM2HEAT |
||||||||||||
12T Sum Heat-Phase 3 |
0-200 |
% |
SUM3HEAT |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EXAMPLE 7 Ð ISM |
STAT SCREEN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To access this display from the CVC default screen: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
1. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MENU |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STATUS |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
3. |
Scroll down to highlight |
ISM |
|
STAT |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
4. |
Press |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
SELECT |
. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
DESCRIPTION |
|
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
ISM Fault Status |
|
0-223 |
|
|
ISMFLT |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Single Cycle Dropout |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
CYCLE |
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Phase Loss |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
PH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
LOSS |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Overvoltage |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
OV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLT |
||||||||||
|
|
Undervoltage |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
UN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOLT |
|||||||||||
|
|
Current Imbalance |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
AMP |
|
|
|
|
UNB |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Voltage Imbalance |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
VOLT |
|
|
UNB |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Overload Trip |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
OVERLOAD |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Locked Rotor Trip |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
LRATRIP |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Starter LRA Trip |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
SLRATRIP |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Ground Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
GRND |
|
FLT |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Phase Reversal |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
PH |
REV |
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Frequency Out of Range |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
FREQFLT |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
ISM Power on Reset |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
ISM |
|
|
|
|
POR |
|||||||||||||
|
|
Phase 1 Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
PHASE |
|
1 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Phase 2 Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
PHASE |
|
2 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Phase 3 Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
PHASE |
|
3 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
ICR Start Complete |
|
0-1 |
|
FALSE/TRUE |
START |
|
OK |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
1M Start/Run Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
1M |
FLT |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
2M Start/Run Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
2M |
|
|
|
FLT |
||||||||||||||
|
|
Pressure Trip Contact |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
PRS |
|
|
TRIP |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Starter Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
STRT |
|
|
FLT |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
Motor Amps Not Sensed |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
NO |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
AMPS |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Starter Acceleration Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
ACCELFLT |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
High Motor Amps |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
HIGHAMPS |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
1CR Stop Complete |
|
0-1 |
|
FALSET/TRUE |
STOP |
|
OK |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
1M/2M Stop Fault |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
1M2MSTOP |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Motor Amps When Stopped |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
AMPSTOP |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Hardware Failure |
|
0-1 |
|
NORMAL/ALARM |
HARDWARE |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation.
25
Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 8 Ð SETPOINT DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SETPOINT (Base Demand Limit will be highlighted).
3.Press SELECT .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
DEFAULT |
||||||||
Base Demand Limit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control Point |
40-100 |
% |
DLM |
|
|
|
|
100 |
||||
LCW Set Point |
10-120 |
DEG F |
lcw |
|
sp |
50.0 |
||||||
ECW Set Point |
15-120 |
DEG F |
ecw |
|
|
|
|
|
sp |
60.0 |
||
Ice Build Set Point |
15-60 |
DEG F |
ice |
|
|
|
sp |
40.0 |
||||
Tower Fan High Set Point |
55-105 |
DEG F |
TFH |
|
|
SP |
75 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on set point screens.
EXAMPLE 9 Ð CAPACITY DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight CAPACITY .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
||||||||
Entering Chilled Water |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
ECW |
|
|
|
|
||||
Leaving Chilled Water |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
LCW |
|
|
|
|
||||
Capacity Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control Point |
10-120 |
DEG F |
ctrlpt |
|
|
|
|
||||
Control Point Error |
−99-99 |
DEG F |
cperr |
|
|
|
|
||||
ECW Delta T |
−99-99 |
DEG F |
ecwdt |
|
|
|
|
||||
ECW Reset |
−99-99 |
DEG F |
ecwres |
||||||||
LCW Reset |
−99-99 |
DEG F |
lcwres |
||||||||
Total Error + Resets |
−99-99 |
DEG F |
error |
|
|
|
|
||||
Guide Vane Delta |
−2-2 |
% |
gvd |
|
|
|
|
||||
Target Guide Vane Pos |
0-100 |
% |
GV |
|
|
|
|
TRG |
|||
Actual Guide Vane Pos |
0-100 |
% |
GV |
|
|
|
|
POS |
|||
Target VFD Speed |
0-100 |
% |
VFD |
|
|
|
OUT |
||||
Actual VFD Speed |
0-100 |
% |
VFD |
|
|
|
ACT |
||||
VFD Gain |
0.1-1.5 |
|
VFD |
|
|
|
|
CTRL |
|||
Demand Inhibit Active |
0-1 |
NO/YES |
DEM |
|
|
|
|
|
INH |
||
Amps/kW Ramp |
0-100 |
% |
DMDLIM |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on maintenance screen.
26

Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 10 Ð OVERRIDE DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight OVERRIDE .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
|
|
|
POINT |
|||||||
Comp Motor Winding Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
MTRW |
||||||||||
Comp Motor Temp Override |
150-200 |
DEG F |
MT |
|
|
|
|
|
OVER |
||||
Condenser Pressure |
0-420 |
PSI |
CRP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cond Press Override |
90-180 |
PSI |
CP |
OVER |
|||||||||
Evaporator Refrig Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
ERT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Evap Ref Override Temp |
2-45 |
DEG F |
ERT |
|
|
|
|
OVER |
|||||
Comp Discharge Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
CMPD |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Comp Discharge Alert |
125-200 |
DEG F |
CD |
|
|
ALEERT |
|||||||
Comp Thrust Brg Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
MTRB |
|
|
|
|||||||
Comp Thrust Brg Alert |
165-185 |
DEG F |
TB |
|
ALERT |
||||||||
Actual Superheat |
−20-99 |
^ F |
SUPRHEAT |
||||||||||
Superheat Required |
6-99 |
^ F |
SUPR REQ |
||||||||||
Condenser Refrig Temp |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
CRT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on maintenance screens.
EXAMPLE 11 Ð LL MAINT DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS .
4.Press SELECT .
5. Scroll down to highlight LL MAINT. .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
||||||||||||||
Lead Lag Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LEAD/LAG: |
NOTE 1 |
|
leadlag |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Con®guration Current Mode |
NOTE 2 |
|
llmode |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Load Balance Option |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
loadbal |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
LAG START TIME |
2-60 |
MIN |
lagstart |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
LAG STOP TIME |
2-60 |
MIN |
lagstop |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
PRESTART FAULT Time |
2-30 |
MIN |
pre¯t |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Pulldown: Delta T/Min |
x.xx |
^ DEG |
pull |
|
|
dt |
|
|
|
||||||||
Satis®ed? |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
pull |
|
|
|
sat |
||||||||||
LEAD CHILLER in Control |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
leadctrl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
LAG CHILLER: Mode |
NOTE 3 |
|
lagmode |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Run Status |
NOTE 4 |
|
lagstat |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Start/Stop |
NOTE 5 |
|
lag |
|
s |
|
s |
||||||||||
Recovery Start Request |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
lag |
|
|
|
|
rec |
|
|
|
||||||
STANDBY CHILLER: Mode |
NOTE 3 |
|
stdmode |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Run Status |
NOTE 4 |
|
stdstat |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Start/Stop |
NOTE 5 |
|
Std |
|
|
s |
|
|
|
s |
|||||||
Recovery Start Request |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
std |
|
|
|
rec |
|
|
|
|||||||
Spare Temperature 1 |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
SPARE |
|
|
|
|
T1 |
|||||||||
Spare Temperature 2 |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
SPARE |
|
|
|
T2 |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTES:
1.DISABLE, LEAD, LAG, STANDBY, INVALID
2.DISABLE, LEAD, LAG, STANDBY, RECOVERY, CONFIG
3.Reset, Off, Local, CCN
4.Timeout, Ready, Recycle, Prestart, Startup Ramping, Running, Demand, Override, Shutdown, Trippout, Pumpdown, Lockout
5.Stop, Start, Retain
6.All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on maintenance screens.
27

Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 12 Ð ISM HIST DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight ISM HIST .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
|||||||||||||||
ISM FAULT HISTORY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Values At Last Fault: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Line Current Phase 1 |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMPS |
|
|
H1 |
||||||||||||
Line Current Phase 2 |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMPS |
|
|
|
|
|
H2 |
|||||||||
Line Current Phase 3 |
0-99999 |
AMPS |
AMPS |
|
|
|
|
|
H3 |
|||||||||
Line Voltage Phase 1 |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H1 |
||||||
Line Voltage Phase 2 |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H2 |
|||||||
Line Voltage Phase 3 |
0-99999 |
VOLTS |
VOLTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H3 |
|||||||
Ground Fault Phase 1 |
0-999 |
AMPS |
GRFT |
|
|
H31 |
||||||||||||
Ground Fault Phase 2 |
0-999 |
AMPS |
GRFT |
|
|
|
|
H23 |
||||||||||
Ground Fault Phase 3 |
0-999 |
AMPS |
GRFT |
|
|
|
|
H12 |
||||||||||
I2T Sum Heat-Phase 1 |
0-200 |
% |
SUM1HT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
||||||||
I2T Sum Heat-Phase 2 |
0-200 |
% |
SUM2HT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
||||||||
I2T Sum Heat-Phase 3 |
0-200 |
% |
SUM3HT |
|
|
|
|
|
H |
|||||||||
Phase 1 Faulted? |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
PHASE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
H1 |
||||||||
Phase 2 Faulted? |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
PHASE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H2 |
|||||||
Phase 3 Faulted? |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
PHASE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H3 |
||||||
Line Frequency |
0-99 |
Hz |
FREQ |
|
|
|
H |
|
|
|||||||||
ISM Fault Status |
0-9999 |
|
ISMFLT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on maintenance screens.
EXAMPLE 13 Ð WSMDEFME DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight CONTROL ALGORITHM STATUS .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight WSMDEFME .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
WSM Active? |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
WSMSTAT |
Chilled Water Temp |
0.0-99.9 |
DEG F |
CHWTEMP |
Equipment Status |
0/1 |
OFF/ON |
CHLRST |
Commanded State |
XXXXXXXX |
TEXT |
CHLRENA |
CHW setpt Reset Value |
0.0-25.0 |
DEG F |
CHWRVAL |
Current CHW Set Point |
0.0-99.9 |
DEG F |
CHWSTPT |
|
|
|
|
NOTE: All variables with CAPITAL LETTER point names are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on maintenance screens.
28

Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 14 Ð NET OPT DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight EQUIPMENT CONFIGURATION .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight NET OPT .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
DEFAULT |
||
Loadshed Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group Number |
0-99 |
|
LDSGRPN |
0 |
||
Demand Limit Decrease |
0-60 |
% |
LDSDLTA |
20 |
||
Maximum Loadshed Time |
0-120 |
MIN |
MAXSHED |
60 |
||
CCN Occupancy Con®g: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Schedule Number |
3-99 |
|
OCC |
|
NUM |
3 |
Broadcast Option |
0-1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
OCCBRST |
DSABLE |
||
Alarm Con®guration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Re-alarm Time |
0-1440 |
MIN |
RETIME |
30 |
||
Alarm Routing |
0-1 |
|
ROUTING |
10000000 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: No variables are available for CCN read or write operation.
EXAMPLE 15 Ð ISM CONF DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight ISM (STARTER) CONFIG DATA .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight ISM CONF .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
|
|
POINT |
DEFAULT |
|||||||||||||
Starter Type |
0-2 |
|
starter |
1 |
|||||||||||||||
(0 = Full, 1 = Red, 2 = SS/VFD) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Motor Rated Line Voltage |
200-13200 |
VOLTS |
v |
|
fs |
|
|
|
|
460 |
|||||||||
Volt Transformer Ratio:1 |
1-33 |
|
vt |
|
|
|
|
|
rat |
1 |
|||||||||
Overvoltage Threshold |
105-115 |
% |
|
|
|
overvolt |
115 |
||||||||||||
Undervoltage Threshold |
85-95 |
% |
undvolt |
85 |
|||||||||||||||
Over/Under Volt Time |
1-10 |
SEC |
uvuntime |
5 |
|||||||||||||||
Voltage % Imbalance |
1-10 |
% |
v |
unbal |
10 |
||||||||||||||
Voltage Imbalance Time |
1-10 |
SEC |
v |
|
|
|
|
|
time |
5 |
|||||||||
Motor Rated Load Amps |
10-5000 |
AMPS |
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
fs |
|
|
|
|
200 |
||||
Motor Locked Rotor Trip |
100-60000 |
AMPS |
|
motor |
|
|
|
lr |
1000 |
||||||||||
Locked Rotor Start Delay |
1-10 |
cycles |
lrdelay |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|||||||||||
Starter LRA Rating |
100-60000 |
AMPS |
start |
|
|
|
lr |
2000 |
|||||||||||
Motor Current CT Ratio:1 |
3-1000 |
|
ct |
|
|
|
|
turns |
100 |
||||||||||
Current % Imbalance |
5-40 |
% |
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
unbal |
15 |
||||||||
Current Imbalance Time |
1-10 |
SEC |
c |
|
|
|
time |
5 |
|||||||||||
3 Grnd Fault CT's? (1 = No) |
0-1 |
NO/YES |
gf |
|
|
|
phase |
YES |
|||||||||||
Ground Fault CT Ratio:1 |
150 |
|
gf |
|
|
|
|
|
ctr |
150 |
|||||||||
Ground Fault Current |
1-25 |
AMPS |
gf |
|
|
|
|
amps |
15 |
||||||||||
Ground Fault Start Delay |
1-20 |
cycles |
gf |
|
|
|
|
delay |
10 |
||||||||||
Ground Fault Persistence |
1-10 |
cycles |
gf |
|
|
|
|
pers |
5 |
||||||||||
Single Cycle Dropout |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
|
cycdrop |
DSABLE |
||||||||||||||
Frequency = 60 Hz? (No = 50) |
0/1 |
NO/YES |
freq |
|
|
|
|
YES |
|||||||||||
Line Frequency Faulting |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
freq |
en |
DSABLE |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: No variables are available for CCN read or write operation.
29

Table 2 Ð CVC Display Data (cont)
EXAMPLE 16 Ð OPTIONS DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight EQUIPMENT SERVICE .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight OPTIONS .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
POINT |
DEFAULT |
||||||||
Auto Restart Option |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
ASTART |
DSABLE |
||||||||
Remote Contacts Option |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
MODES |
DSABLE |
||||||||
Soft Stop Amps Threshold |
40-100 |
% |
STRTSTOP |
100 |
||||||||
Surge/Hot Gas Bypass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surge Limit/HGBP Option |
0/1 |
|
srg hgbp |
0 |
||||||||
Select: Surge = 0, HGBP = 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Min. Load Point (T1/P1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surge/HGBP Delta T1 |
0.5-20 |
^ F |
hgb |
dt1 |
1.5 |
|||||||
Surge/HGBP Delta P1 |
30-170 |
PSI |
hgb |
|
|
|
|
dp1 |
50 |
|||
Full Load Point (T2/P2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surge/HGBP Delta T2 |
0.5-20 |
^ F |
hgb |
dt2 |
10 |
|||||||
Surge/HGBP Delta P2 |
50-170 |
PSI |
hgb |
|
|
|
dp2 |
85 |
||||
Surge/HGBP Deadband |
0.5-3 |
^ F |
hgb |
|
|
|
db |
1 |
||||
Surge Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Surge Delta % Amps |
5-20 |
% |
surge |
|
a |
10 |
||||||
Surge Time Period |
7-10 |
MIN |
surge |
|
|
|
t |
8 |
||||
Ice Build Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ice Build Option |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
ibopt |
|
|
|
DSABLE |
|||||
Ice Build Termination |
0-2 |
|
ibterm |
0 |
||||||||
0 = Temp, 1 = Contacts, 2 = Both |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ice Build Recycle |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
ibrecyc |
DSABLE |
||||||||
Refrigerant Leak Option |
0/1 |
DSABLE/ENABLE |
LEAK |
|
|
|
EN |
DSABLE |
||||
Refrigerant Leak Alarm mA |
4-20 |
mA |
LEAK |
|
|
|
MA |
20 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: No variables are available for CCN read or write operation.
EXAMPLE 17 Ð SETUP1 DISPLAY SCREEN
To access this display from the CVC default screen: 1. Press MENU .
2.Press SERVICE .
3.Scroll down to highlight EQUIPMENT SERVICE .
4.Press SELECT .
5.Scroll down to highlight SETUP1 .
DESCRIPTION |
STATUS |
UNITS |
|
|
|
|
|
POINT |
DEFAULT |
|||||||||||||||||
Comp Motor Temp Override |
150-200 |
DEG F |
MT |
|
|
OVER |
200 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Cond Press Override |
90-165 |
PSI |
CP |
|
|
|
|
|
OVER |
125 |
||||||||||||||||
Comp Discharge Alert |
125-200 |
DEG F |
C |
|
|
|
|
|
ALERT |
200 |
||||||||||||||||
Comp Thrust Brg Alert |
165-185 |
DEG F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALERT |
175 |
||||||||||||||||
TB |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chilled Medium |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
0/1 |
WATER/BRINE |
MEDIUM |
WATER |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Chilled Water Deadband |
.5-2.0 |
^F |
CS |
|
|
DB |
|
|
|
|
|
1.0 |
||||||||||||||
Evap Refrig Trippoint |
0.0-40.0 |
DEG F |
ERT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TRIP |
33 |
||||||||||||||
Refrig Override Delta T |
2.0-5.0 |
^F |
REF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OVER |
3 |
||||||||||||||
Condenser Freeze Point |
−20 - 35 |
DEG F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
||||||||
CDFREEZE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Evap Flow Delta P Cutout |
0.5 - 50.0 |
PSI |
EVAP CUT |
5.0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Cond Flow Delta P Cutout |
0.5 - 50.0 |
PSI |
COND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CUT |
5.0 |
||||||||||||||
Water Flow Verify Time |
0.5-5 |
MIN |
WFLOW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T |
5 |
||||||||||||||
Oil Press Verify Time |
15-300 |
SEC |
OILPR |
|
T |
|
40 |
|||||||||||||||||||
Recycle Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recycle Restart Delta T |
2.0-10.0 |
DEG F |
RCYCR |
|
|
|
DT |
5 |
||||||||||||||||||
Recycle Shutdown Delta |
0.5-4.0 |
DEG F |
RCYCS |
|
|
|
|
DT |
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
SPARE ALERT/ALARM ENABLE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disable=0, Lo=1/3,Hi=2/4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spare Temp #1 Enable |
0.4 |
|
sp1 |
|
|
|
|
en |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
||||||||||||
Spare Temp #1 Limit |
−40-245 |
DEG F |
sp1 |
|
|
|
|
|
lim |
|
|
|
|
|
245 |
|||||||||||
Spare Temp #2 Enable |
0-4 |
|
sp2 |
|
|
|
|
|
en |
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
|||||||||||
Spare Temp #2 Limit |
-40-245 |
DEG F |
sp2 |
|
|
|
|
|
lim |
|
|
|
|
|
245 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NOTE: No variables are available for CCN read operation; forcing shall not be supported on service screens.
30
 Loading...
Loading...