Page 1
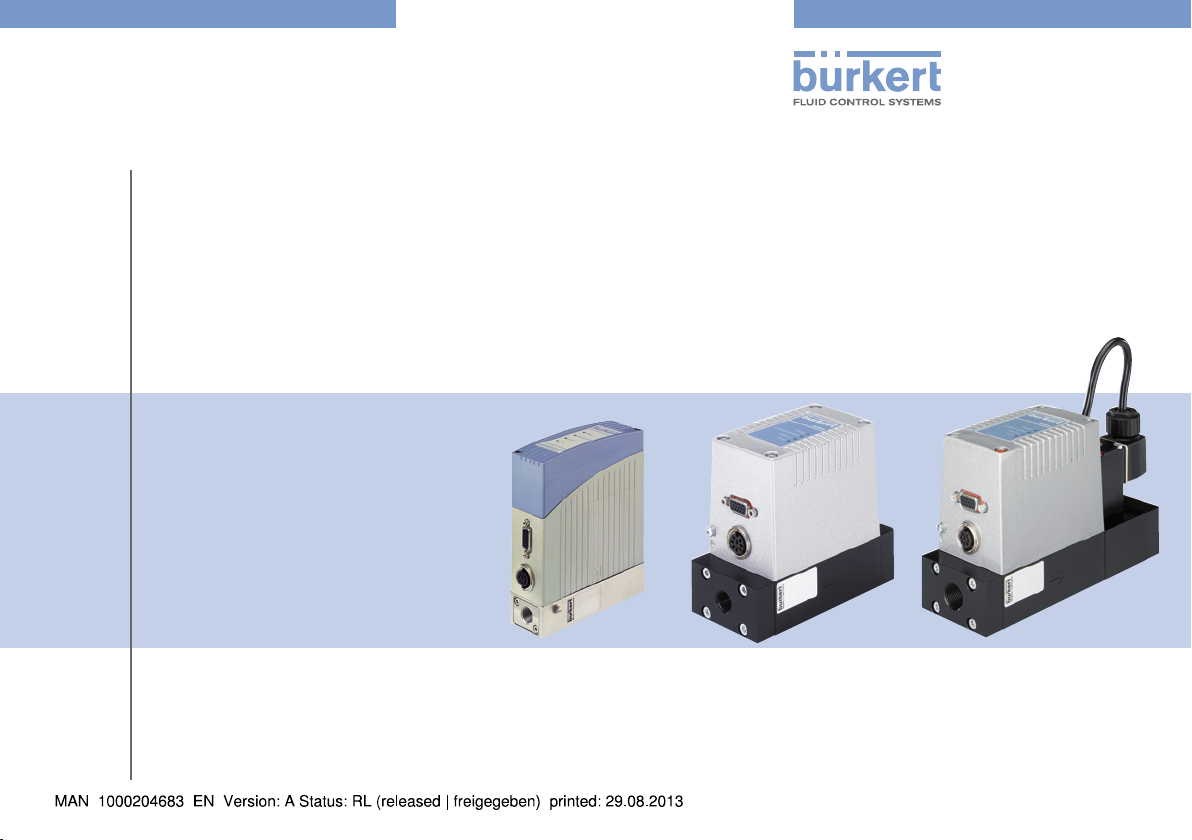
Type 8006 / 8702
MFM, Mass Flow Meter IP65
Type 8626 / 8712
MFC, Mass Flow Controller IP65
Operating Instructions
Bedienungsanleitung
Manuel d‘utilisation
Page 2

We reserve the right to make technical changes without notice.
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten.
Sous réserve de modifications techniques.
© 2013 Bürkert SAS
Operating Instructions 1307/1_EU-ML 00563581
Page 3

Type 8006, 8702 / 8626, 8712
1. ABOUT THIS MANUAL .................................................................................4
1.1. Symbols used ..........................................................................................4
1.2. Definition of the word "device" .......................................................4
2. INTENDED USE ................................................................................................5
3. BASIC SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS .............................................................5
4. GENERAL INFORMATION ...........................................................................7
4.1. Manufacturer's address and international contacts ............7
4.2. Warranty conditions ..............................................................................7
4.3. Information on the Internet ...............................................................7
5. DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM ............................................................7
5.1. General description ..............................................................................7
5.2. Operation of an MFM or MFC sensor ..........................................8
5.3. Detailed operation of an MFC .........................................................8
6. TECHNICAL DATA ........................................................................................11
6.1. Markings on the device.................................................................... 11
6.2. Conditions of use ................................................................................ 12
6.3. Compliance to standards and directives ................................ 13
6.4. Mechanical data ................................................................................... 13
6.5. Dimensions ............................................................................................13
6.6. Fluidic data .............................................................................................20
6.7. Electrical data .......................................................................................22
7. INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING ...........................................23
7.1. Safety instructions .............................................................................. 23
7.2. Prior to installation .............................................................................23
7.3. Description of the MFM / MFC ....................................................24
7.4. Sequence of the steps to be performed ................................ 24
7.5. Setting the parameters .................................................................... 24
7.6. Mechanical installation ..................................................................... 27
7.7. Fluid installation ................................................................................... 27
7.8. Electrical installation .........................................................................28
8. OPERATION AND FUNCTION ................................................................30
8.1. Safety instructions .............................................................................. 30
8.2. Operation of the MFM / MFC ........................................................30
8.3. MFC operating modes ...................................................................... 35
9. MAINTENANCE, TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................ 39
9.1. Safety instructions .............................................................................. 39
9.2. Maintenance ........................................................................................... 40
9.3. Troubleshooting ................................................................................... 42
10. ACCESSORIES / SPARE PARTS ......................................................45
10.1. Accessories ......................................................................................... 45
10.2. Spare part .............................................................................................48
11. SHUTDOWN .................................................................................................. 48
11.1. Safety instructions ........................................................................... 48
11.2. Dismounting of the MFM / MFC ............................................... 49
12. PACKAGING, STORAGE, TRANSPORT ..........................................49
12.1. Packaging, Transport ...................................................................... 49
12.2. Storage ................................................................................................... 49
13. RETURNING THE DEVICE ..................................................................... 50
14. DISPOSAL OF THE PRODUCT ........................................................... 50
English
3
Page 4
Type 8006, 8702 / 8626, 8712
About this manual
1. ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual describes the entire life cycle of the device. Please keep
this manual in a safe place, accessible to all users and any new owners.
This manual contains important safety information.
Failure to comply with these instructions can lead to hazardous
situations.
• This manual must be read and understood.
1.1. Symbols used
danger
Warns against an imminent danger.
• Failure to observe this warning can result in death or in
serious injury.
Warning
Warns against a potentially dangerous situation.
• Failure to observe this warning can result in serious injury
or even death.
attention
Warns against a possible risk.
• Failure to observe this warning can result in substantial
or minor injuries.
note
Warns against material damage.
• Failure to observe this warning may result in damage to the
device or system.
Indicates additional information, advice or important
recommendations.
Refers to information contained in this manual or in
other documents.
→ Indicates a procedure to be carried out.
1.2. Definition of the word "device"
The word "device" used within this manual refers to a Mass Flow
Meter (MFM) type 8006 or 8702, or a Mass Flow Controller (MFC)
type 8626 or 8712.
English
4
Page 5
Type 8626, 8712
Intended use
2. INTENDED USE
Nonconforming use of the MFM / MFC types 8006,
8702 / 8626, 8712 may pose a danger to people, nearby
equipment and the environment.
• Mass flow meter types 8006, 8702 are designed exclusively for
measuring the mass flow-rate of clean, dry gases.
• Mass flow controller types 8626, 8712 are designed for
controlling the mass flow-rate of clean, dry gases.
• Only use the fluids stated on the name plate and the calibration
protocol.
• Protect this device against electromagnetic interference,
ultraviolet rays and, when installed outdoors, the effects of the
climatic conditions.
• This device must be used in compliance with the specifications
and commissioning and use conditions specified in the
contractual documents and in the user manual.
• Requirements for the safe and proper operation of the device
are proper transport, storage and installation, as well as careful
operation and maintenance.
• Only use the device as intended.
• Observe any existing restrictions when the device is exported.
3. BASIC SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
These safety instructions do not take into account:
• any contingencies or occurrences that may arise during
installation, use and maintenance of the devices.
• the local safety regulations, which the operating company is
responsible for ensuring the staff in charge of installation and
maintenance adhere to.
Danger from the heated surfaces when used for prolonged
periods.
• The device must be kept away from any highly flammable
materials or fluids.
• Wear protective gloves to handle the device.
Danger due to high pressure in the installation.
• Shut off the gas flow, relief the pressure and drain the pipe
before loosening the process connections.
Danger due to electrical voltage.
• Shut down and isolate the electrical power supply before
carrying out work on the system.
• Observe all applicable accident protection and safety
regulations for electrical equipment.
English
5
Page 6
Type 8006, 8702
Basic safety instructions
Danger from the outflow of operating fluid
Respect the prevailing regulations on accident prevention and
safety relating to the operating fluids used.
Various dangerous situations
To avoid injury take care:
• to prevent unintentionally switching on the power supply.
• to ensure that installation and maintenance work is carried out
by qualified, authorized personnel in possession of the
appropriate tools,
• to keep the device away from any highly flammable materials or
fluids and avoid any contact with bare hands,
• to guarantee a defined or controlled restarting of the process,
after an interruption to the power supply or medium supply,
• to use the device only if in perfect working order and in compliance
with the instructions provided in the instruction manual,
• to observe best industry practice for the installation and use of
these devices,
• not to use MFM / MFC types 8006, 8702 / 8626, 8712 for
controlling and/or measuring the flow-rate of fluids which contain
particles (particle size > 25 µm),
• not to operate the device without the stainless steel mesh filter
disc installed at the factory,
• not to operate the device in a mounting position which deviates
from the calibration conditions,
• not to operate the device with higher pressures than the
specified tightness pressure (MFC) respectively calibration
pressure (MFM),
• not to subject the device to mechanical loads (e.g. by placing
objects on top of it or by using it as a step).
• not to make any external modifications to the device. Do not
paint or varnish any part of the device. Do not feed any other
fluids into the system other than the designated operating
fluid indicated on the device name plate. Exception: agent for
cleaning and decontaminating the device (see also section
„9.2.1“). In doing so, observe the compatibility of the materials
used for the device. You will find a chemical compatibility chart
on our website, under:
www.burkert.com
Resistance Chart
If in doubt, contact the manufacturer.
note
Elements / Components sensitive to electrostatic discharges
• This device contains electronic components sensitive to
electrostatic discharges. They may be damaged if they are
touched by an electrostatically charged person or object. During
electrostatic discharge, they will become defective immediately
or will fail when energized.
• To minimize or even avoid all damage due to an electrostatic
discharge, take all the precautions described in the standards
EN 61340-5-1 and 5-2.
• Also ensure that you do not touch any of the live electrical
components.
Documentation
Brochures
Chemical
6
English
Page 7
Type 8626, 8712
General information
4. GENERAL INFORMATION
4.1. Manufacturer's address and international contacts
To contact the device manufacturer, use the following address:
Bürkert SAS
Rue du Giessen
F-67220 TRIEMBACH-AU VAL
The addresses of the international subsidiaries are available on the
web page at: www.burkert.com
4.2. Warranty conditions
The condition governing the legal warranty is the conforming use of
the MFM / MFC in observance of the operating conditions specified
in this manual.
4.3. Information on the Internet
You can find the user manuals and technical data sheets regarding the
MFM / MFC at: www.burkert.com
5. DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM
5.1. General description
• Mass flow meter MFM types 8006, 8702 are devices designed for
measuring the mass flow-rate of clean, dry gases.
• Mass flow controller MFC types 8626, 8712 are devices designed
for controlling the mass flow-rate of clean, dry gases.
Type of device Type of sensor
MFM 8006 Inline
8702 MEMS
MFC 8626 Inline
8712 MEMS
5.1.1. General operation of the Mass Flow
Meter (MFM)
The MFM integrates a sensor for measuring the flow-rate. The measured
value for the mass flow-rate is transmitted to a remote device via an
analogue or a digital output (field bus).
English
7
Page 8
Type 8006, 8702
Description of the system
5.1.2. General operation of the Mass Flow
Controller (MFC)
The MFC comprises:
• a sensor for measuring the mass flow rate,
• a control electronics,
• a control valve with low-friction and high sensitivity.
5.2. Operation of an MFM or MFC sensor
• The integrated flow-rate sensors use the thermal measurement
principle (anemometric and calorimetric) to measure the mass
flow-rate. The main components are a heating resistor and a
temperature probe. The gas which passes through the device
modifies the temperature difference measured between
both resistors.
• The thermal measurement principle allows the MFC to control the
required mass flow-rate completely independently of the pressure
and temperature fluctuations in the application concerned.
To obtain an output signal for the effective, dynamic
or uniform value, the damping of the output signal can
be changed with the "Mass Flow Communicator" software
(see section „10.1.3“).
On the MFMs and MFCs types 8712 and 8702, the
integrated sensor technology requires filters to be fitted
upstream of the product when highly soiled fluids are present.
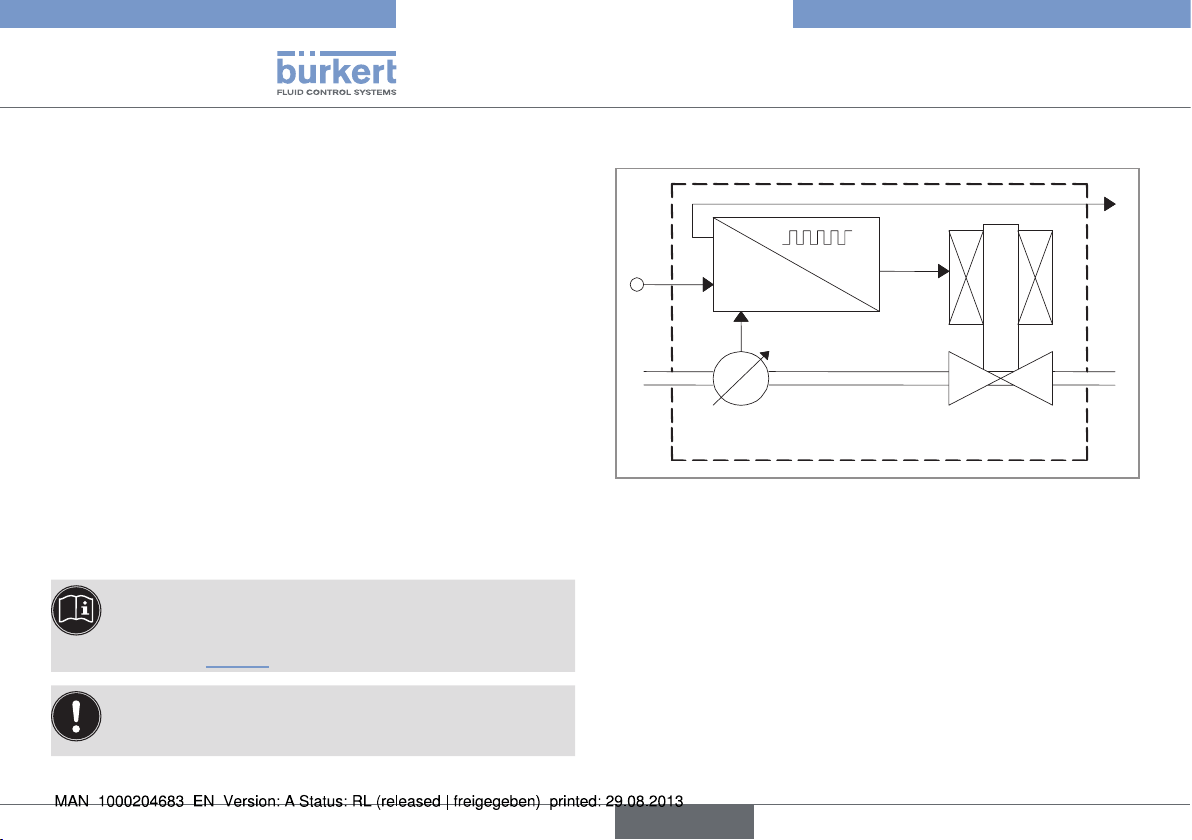
5.3. Detailed operation of an MFC
x
out
w
= w-x
x
d
Gas
inlet
Fig. 1: Operating principle for the Mass Flow Controller
The control electronics compare the mass flow-rate (x) measured by
the integrated flow sensor with the mass flow-rate set-point value
(w) supplied to the MFC. The control electronics then calculate the
actuating variable (y) to be supplied to the solenoid valve to control
its opening. The flow-rate is either maintained at a constant value,
or modified to a predefined profile.
The control operates independently of fluctuations in pressure or
increases in the flow resistance which may be caused by soiling of the
filter. The rapidly responding solenoid valve and the sensor dynamics
define the overall response time.
The measured value for the mass flow-rate is also transmitted (xout) to
a remote device via an analogue output or a digital output (field bus).
x
Sensor
Control
electronics
y
Gas
outlet
Actuating element
(solenoid valve)
8
English
Page 9
Type 8626, 8712
Description of the system
5.3.1. Control electronics
The control electronics:
• process the mass flow-rate set-point values and measured values,
• control the solenoid valve.
Set-point value
The set-point value (w) is transmitted either by an analogue input signal
or digitally via the serial or the field bus interface. If the set-point value
is supplied by analogue transmission, the following assignments are
applied:
Signal
range
4...20 mA 4 mA, w = 0 % 20 mA, w = 100 %
0...20 mA 0 mA, w = 0 % 20 mA, w = 100 %
0...5 V 0 V, w = 0 % 5 V, w = 100 %
0...10 V 0 V, w = 0 % 10 V, w = 100 %
For the control of a system where quick flow-rate changes are not
permitted, a ramp function can be activated. The settings for a raising
and a falling set-point value can be set separately.
More detailed information on the ramp function and on all
other functions can be found in the software documentation
for the MFM / MFC.
Control settings
The initial control settings are set at the factory.
Set-point associated
with the range min.
Set-point associated
with the range max.
• Amplification factors:
After start-up, the controller operates with amplification factors
dependent on the loop properties. When the autotune function runs,
these are determined automatically. This function enables the control
settings to be optimized for the system's actual conditions.
• Control dynamics setting:
The device has a setting which can change the control dynamics
with the aid of the "Mass Flow Communicator" software
(see section „10.1.3“). Its extreme effects are:
1. a very quick adjustment in which overshoots are possible.
This enables the controller to respond immediately to very low
control deviations; which causes the control to be very turbulent,
2. a slower adjustment to the required flow-rate. If the system is less
dynamic, the behaviour of the controller may be damped so that
minor fluctuations in the measured value or set-point value are only
adjusted slowly.
Zero point shut-off
A zero point shut-off is integrated to ensure the sealing function of the
valve. This is activated if the following conditions occur at the same time:
Set-point value < 2 % of
nominal flow-rate Q
(with control range 1:50)
If the zero point shut-off is active, the PWM signal is set to
0 % so that the valve is completely closed.
nom
Measured value < 2 % of
and
nominal flow-rate Q
(with control range 1:50)
nom
English
9
Page 10
5.3.2. MFC solenoid control valve
The solenoid valve used for an MFC is a direct-acting, normally closed
solenoid control valve.
The orifice size of the solenoid valve is determined by the required
nominal flow-rate Q
the process and the density of the operating fluid.
If the device is operated within the specified pressure range,
the solenoid valve also takes over the sealing function
together with the control function. Limitation: in the case
of special hard seal materials, the sealing function cannot
be ensured. In this case an additional shut-off valve may
be required.
, the pressure and temperature conditions in
nom
Type 8006, 8702
Description of the system
10
English
Page 11
Type 8626, 8712
Technical data
6. TECHNICAL DATA
attention
Risk of injury from pressure and outflow of fluid.
Important device-specific technical data is indicated on the name plate and the calibration plate (see section „6.1“).
• Observe the permitted fluid according to the name plate (depending on seal material).
• Observe the permitted pressure range on the calibration plate of the device.
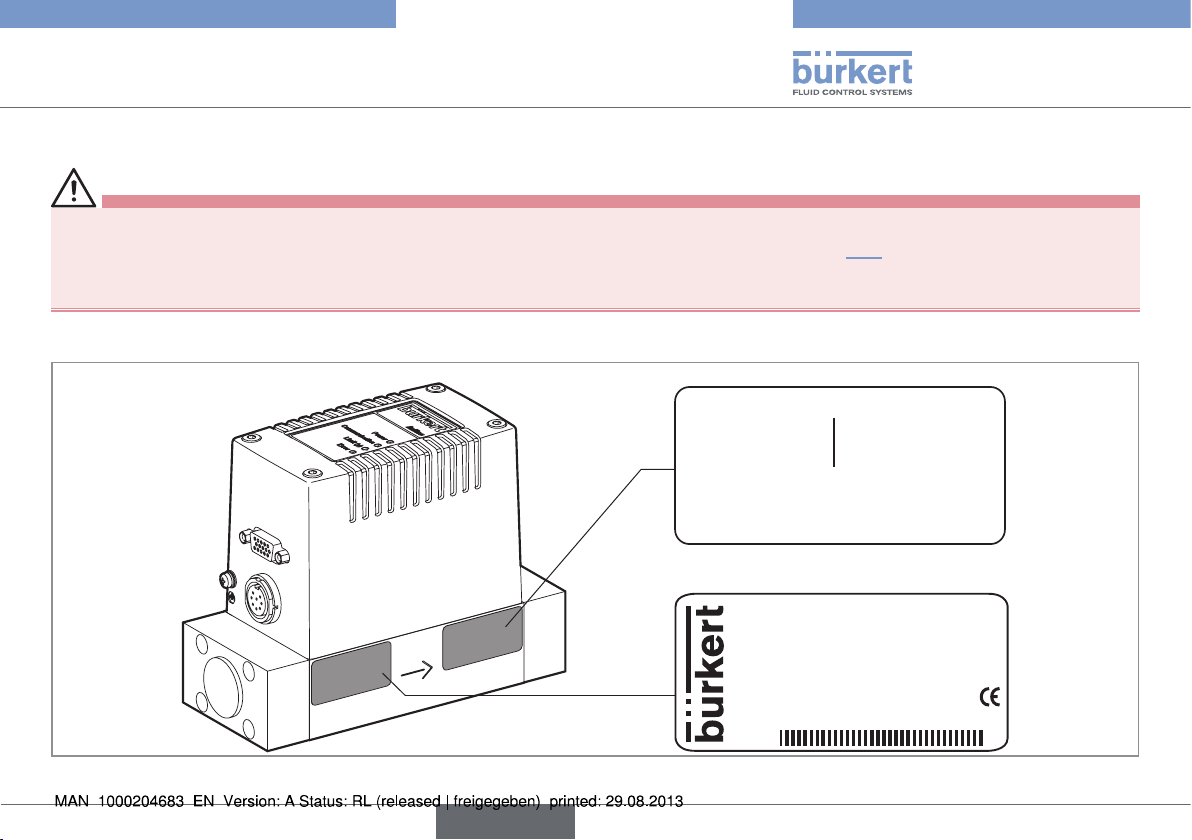
6.1. Markings on the device
Fig. 2: Name plate, calibration plate
Examples:
English
Calibration plate
Calibration data 00182381
Medium 1
P1 : 0,800 barg
Mounting: horizontal upright
QC passed: 25.11.2011
Name plate
8006 35.0 Nm3/h
CH4
24V DC 13W DP
S/N 1004
00182381
Made in France
FKM
W49MM
11
Page 12
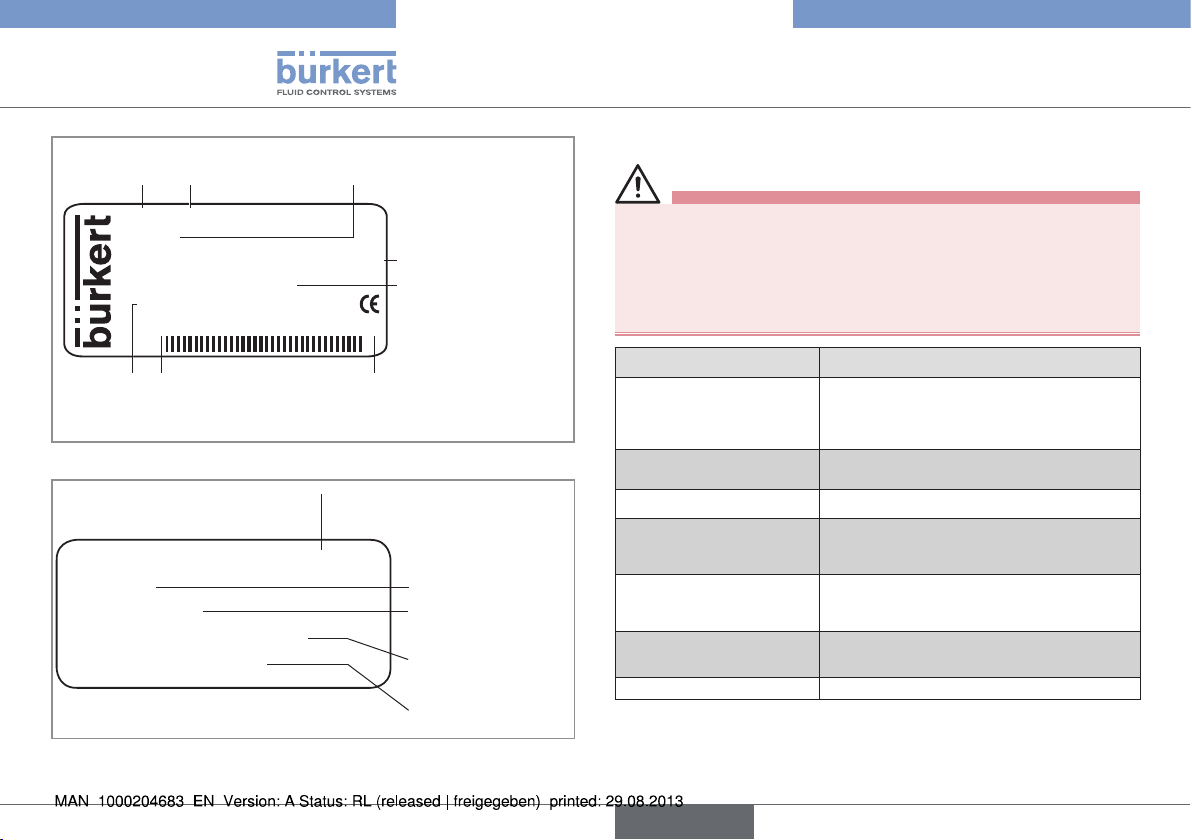
Type 8006, 8702
Technical data
Type of the
device
Nominal flow rate
(Q
) and unit
nom
8006 35.0 Nm3/h
CH4
24V DC 13W DP
S/N 1004
00182381
Made in France
Item no. of the
Serial
number
Fig. 3: Details of a name plate
device
Item no. of the
Calibration data 00202378
Medium 1
P1: 0.700 barg
Mounting: Horizontal mounting
QC passed: 25.11.2011
W49MM
device
Operating medium
FKM
Material of the seal
Supply voltage
Max. power consumed
Output signal
Construction
code
Calibration fluid
Calibration
pressure
Mounting
position
Calibration date
6.2. Conditions of use
Warning
Risk of injury from malfunction due to effects of the weather!
The MFM / MFC is not designed for unrestricted use outdoors.
• Protect the device from direct sunlight.
• Observe the ambient temperature range of the device.
• Protect the device from humidity.
Setting Value
Ambient temperature Types 8702 / 8712: -10 °C to +50 °C
Types 8006 / 8626: -10 °C to +45 °C
For UL devices: 0 °C to 40 °C
Medium temperature for oxygen: -10 °C to +60 °C
Air humidity < 95%, without condensation
Relative humidity for UL
devices
Protection class
according to EN 60529
Absolute height above
sea level for UL devices
Operating environment Indoors, with pollution degree 2
for other fluids: -10 °C to +70 °C
80% up to a temperature of 31°C,
with a linear decrease to a relative
humidity of 50% at 40°C
Only if devices are cabled and the
connectors are plugged in and
tightened: IP65
2000 m max.
Fig. 4: Details of a calibration plate
12
English
Page 13
Type 8626, 8712
Technical data
6.3. Compliance to standards and directives
MFM/MFC conformity with the EC directives comes through the
following standards:
• EMC: EN 61000-6-2, EN 61000-6-3.
The MFMs/MFCs compliant with ATEX Directive 94/9/EEC adhere to
the standards below:
• EN 60079-15
• EN 61241-1.
The MFM / MFC UL devices conform to the following standards:
• UL 61010-1
• CAN/CSA-C22.2 no. 61010-1.
6.4. Mechanical data
The device may be mounted in a horizontal or vertical position: see the
calibration plate and/or the calibration protocol.
Type Base block
material
8006,
8626
1.4305 stainless
steel, 1.4404
stainless steel or
anodized aluminium
8702,
8712
Stainless steel
1.4404
Sealing material: FKM or EPDM (see name plate)
Material of the
housing
Painted
pressure cast
aluminium
Polycarbonate
(PC)
Port connections
G 1/4, G 3/8, G
1/2, G 3/4
NPT 1/4, NPT 3/8,
NPT 1/2, NPT 3/4
G 1/4, NPT 1/4,
flange
Other parts of the solenoid control valve in contact with the medium:
1.4310, 1.4113 and 1.4305
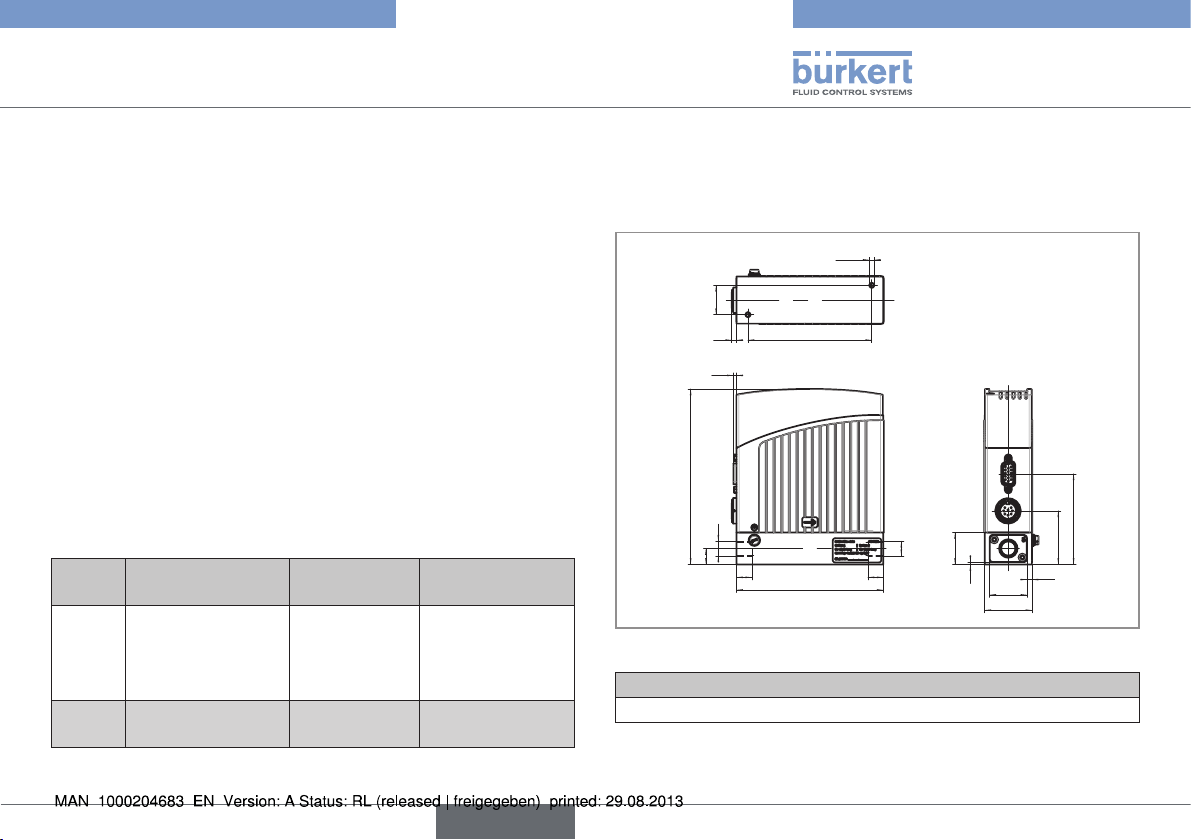
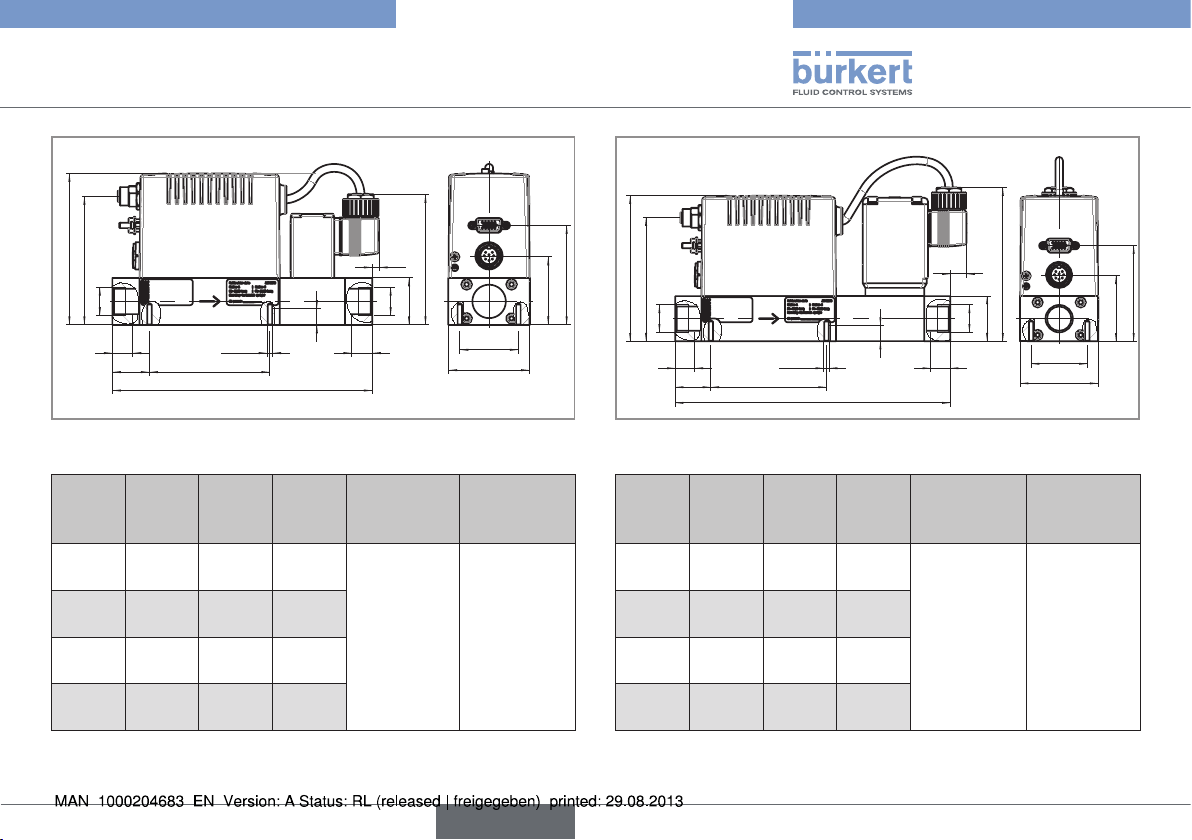
6.5. Dimensions
2x M4
23
4
2,5
138
A
12,5
12
Fig. 5: Dimensions of MFMs type 8702 and MFCs type 8712
Weight stainless steel (kg)
ca. 1.4
97
115
71
29,2
37
42
3,9
A
25
12
1,9
English
13
Page 14
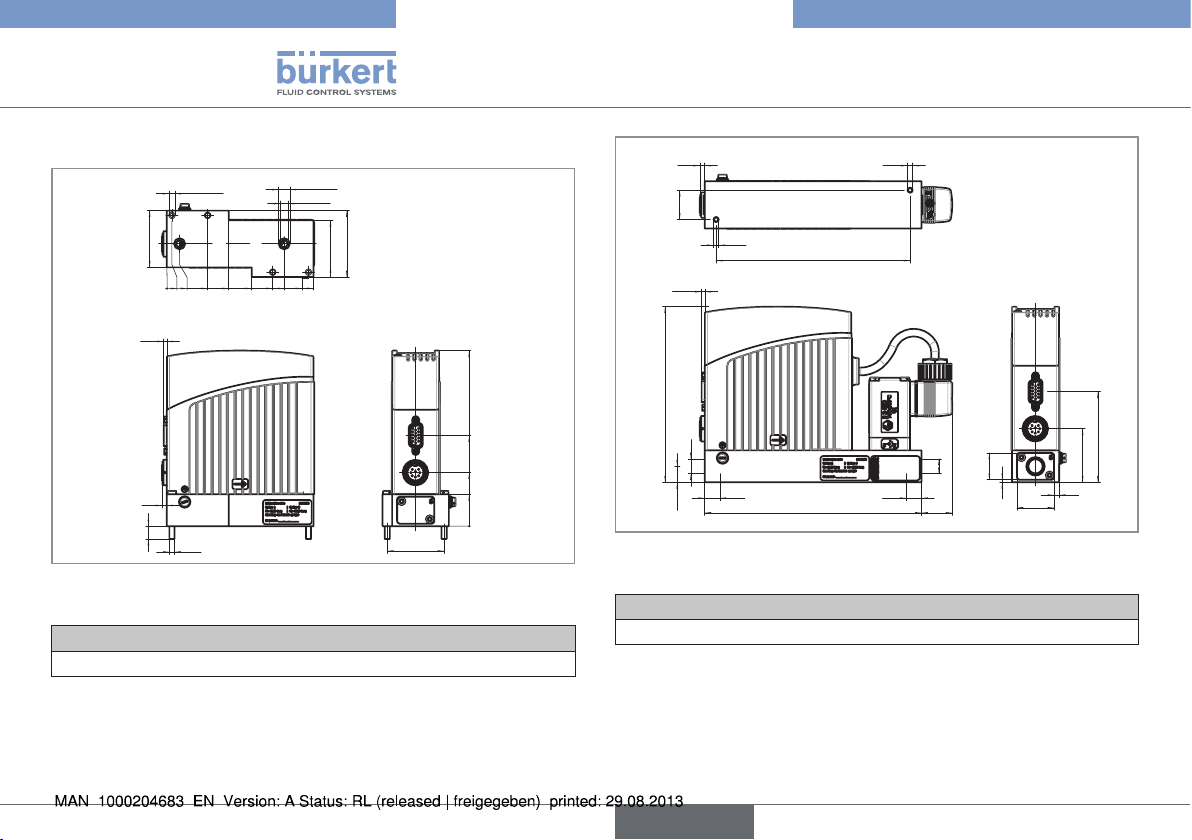
Type 8006, 8702
Technical data
2x
66,5
Ø8,8
2x
Ø6
52
44,5
83
92
111
115
137
71
42
25
44,5
0
44,5
2,5
4
10
Ø
4x
4,5
4
0
10
32
48,5
M
4
Fig. 6: Dimensions of flanged MFMs type 8702, and of flanged
MFCs type 8712
Weight stainless steel (kg)
ca. 1.4
M4
1212
A
21
2
24
29
138
4
23
2,55
12,5
M4
A
152
170
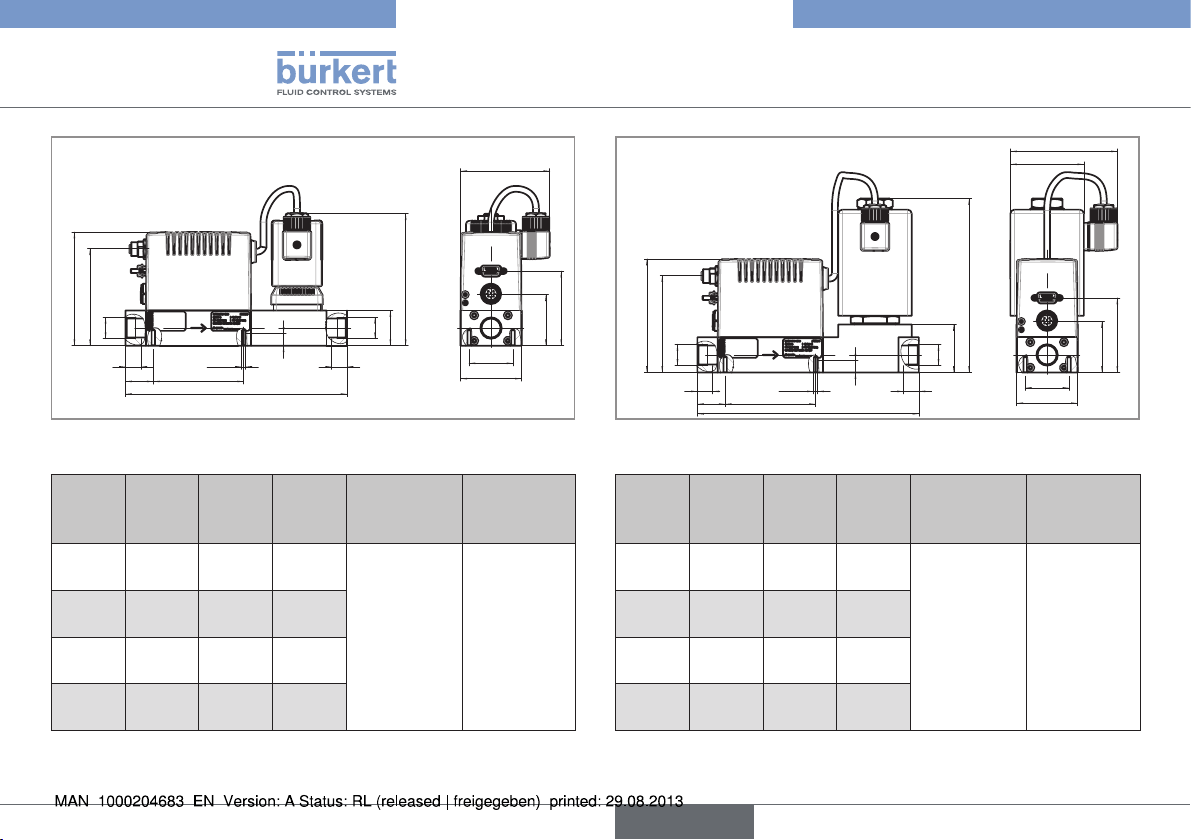
Fig. 7: Dimensions of MFCs type 8712 with external
solenoid valve
Weight stainless steel (kg)
ca. 2.0
71
42
4
14
English
Page 15
Type 8626, 8712
111,5
Technical data
5
95
A
B
C
88,5
4x M
4
D
12
B
96
A
34,5
43
59,5
73
50
111,5
95
A
B
C
88,5
4x M
4
D
12
12,5
117,5
73
A
34,5
B
43
59,5
50
Fig. 8: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with solenoid valve
type 2873
A B
(mm)
C
(mm)
D
(mm)
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
G3/4;
14 27.25 191 ca. 2.0 ca. 4.0
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 191
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 22.25 181
NPT3/8
G1/4;
NPT1/4
10 22.25 181
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
English
Fig. 9: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with solenoid valve
type 2875
A B
(mm)C (mm)D (mm)
G3/4;
14 27.25 210.5 ca. 2.5 ca. 4.6
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 210.5
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 22.25 200.5
NPT3/8
G1/4;
10 22.25 200.5
NPT1/4
15
Page 16
87,25
Type 8006, 8702
Technical data
105
72
111,5
95
A
B
C
88,5
4x M
12
4
D
B
129,5
A
34,5
43
59,5
Fig. 10: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with solenoid valve
type 6024
A B
(mm)C (mm)D (mm)
G3/4;
14 27.25 210.5 ca. 2.5 ca. 4.6
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 210.5
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 22.25 200.5
NPT3/8
G1/4;
10 22.25 200.5
NPT1/4
16
73
50
111,5
95
A
B
C
88,5
4x M
12
4
D
170,5
73
47
A
B
59,5
50
43
Fig. 11: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with solenoid valve
type 2836
A B
(mm)C (mm)D (mm)
G3/4;
14 27.25 191 ca. 3.0 ca. 5.0
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 191
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 22.25 181
NPT3/8
G1/4;
10 22.25 181
NPT1/4
English
Page 17

Type 8626, 8712
Technical data
137
120,5
A
B B
C 88,5
4x M
4
D
5
121,5
A
60
12
43
60
75,5
Fig. 12: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with high fluid flow-rate
base and solenoid valve type 2873
A B
(mm)
G3/4;
15 27.25 191 ca. 2.4 ca. 4.5
C
(mm)
D
(mm)
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 191
NPT1/2
G3/8;
12 27.25 191
NPT3/8
English
98,5
137
120,5
A
B B
C 88,5
4x M
12
4
D
12,5
A
60
136,5
43
60
Fig. 13: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with high fluid flow-rate
base and solenoid valve type 2875
A B
(mm)C (mm)D (mm)
G3/4;
15 27.25 210.5 ca. 3.0 ca. 5.6
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 210.5
NPT1/2
G3/8;
12 27.25 210.5
NPT3/8
75,5
17
98,5
Page 18

Type 8006, 8702
Technical data
87,5
137
120,5
A
B B
C 88,5
4x M
12
4
D
155
A
60
43
60
75,5
Fig. 14: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with high fluid flow-rate
base and solenoid valve type 6024
A B
(mm)
G3/4;
14 27.25 217 ca. 3.0 ca. 5.6
C
(mm)
D
(mm)
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 217
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 27.25 217
NPT3/8
98,5
105
72
183,5
137
120,5
A
B
4x M
88,5C
12
4
D
A
60
B
75,5
43
60
72
Fig. 15: Dimensions of MFC type 8626 with high fluid flow-rate
base and solenoid valve type 2836
A B
(mm)C (mm)D (mm)
G3/4;
14 27.25 217 ca. 4.0 ca. 7.6
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 217
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 27.25 217
NPT3/8
98,5
18
English
Page 19

Type 8626, 8712
Technical data
136,8
120,6
A
12
4x M
27,25
88,5
143
4
A
60
BB
43
60
98,6
75,5
Fig. 16: Dimensions of MFM type 8006
A B
(mm)
C
(mm)
D
(mm)
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
G3/4;
14 27.25 143 ca. 1.2 ca. 3.0
NPT3/4
G1/2;
13 27.25 143
NPT1/2
G3/8;
10 22.25 133
NPT3/8
G1/4;
10 22.25 133
NPT1/4
Weight
stainless
steel (kg)
English
Fig. 17: Dimensions of MFM type 8006 with high fluid flow-rate
base
A B
(mm)
G3/4;
15 ca. 2.2 ca. 4.3
Weight
aluminium
(kg)
Weight stainless
steel
(kg)
NPT3/4
G1/2;
14
NPT1/2
G3/8;
12
NPT3/8
19
Page 20

Type 8006, 8702
Technical data
6.6. Fluidic data
6.6.1. Overview of measurement
specifications
Type 8006, 8626 8702, 8712
Full scale range ref. to
2 (lN/min)
N
Measuring accuracy
(after heating time)
Span/control range
Settling time (MFC) or
response time (MFM)
(ms)
*) 1:20 in case of vertical mounting, with downward flow.
**) Higher span (e.g. 1:100) possible on request.
Repeatability: ± 0.1% of the full scale.
16 … 1500 0.01 … 80
± 1.5 % of the
measured value
± 0.3 % of the full
scale
± 0.8 % of the
measured value
± 0.3 % of the full
scale
1 : 50 *) 1 : 50 **)
< 500 < 150
6.6.2. Operating fluids
• Operating fluids: clean, dry gas.
• Operating fluid for UL devices: neutral, uncontaminated gas.
Other hazardous gases are possible on request; the devices
do not release any hazardous gases under normal operating
conditions. However, to use an MFC with natural gas, only
the solenoid valve Bürkert type 2875 can be used : in this
case, the order key must include the letter "-D" (for example
8626-0100L-CH4-E-A-GM82-ALFF-D-08,0).
• Calibration fluid: operating fluid or air.
• Max. operating pressure: 10 bar (depending on valve nominal
diameter).
To obtain the required measuring accuracy or control quality,
but also to respect the safety requirements, the gas or
gaseous mixture must conform to the following safety criteria,
compliant with ISO standard 8573-1 (Compressed air -
Part 1: Contaminants and purity classes):
• Maximum particle size and density: class 2:
Maximum particle size: 1 µm
Maximum particle density: 1 mg/m³
• Maximum dew point under pressure: class 4: 3 °C
• Maximum oil concentration: class 1: 0.01 mg/m³
1)
1)
1)
20
1)
For more information refer to ISO 8573-1
English
Page 21

Type 8626, 8712
∆
∆p [mbar]
Technical data
6.6.3. Pressure loss specifications
p [mbar]
200
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
0100
200
300
400
1/4''
500
600
700
Fig. 18: Pressure loss diagram (ref. air, with 250 µm inlet filter),
type 8006
The characteristic diagram shows the air pressure loss in the device
for 3 different bases (up to 100 Nl/min, from 100 to 500 Nl/min,
from 500 to 1500 Nl/min) and 4 different connections (1/4'', 1/2'',
3/4'' and 3/8'').
For determining the pressure loss with another gas first calculate the
equivalent air flow-rate of the other gas.
800
900
3/8''
1000
1100
3/4''
1200
1/2''
1300
1500
1400
Q [lN/min]
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0510 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80
flanges
1/4''
Q [l
/min]
N
Fig. 19: Pressure loss diagram (ref. air, with 250 µm inlet filter),
type 8702
The characteristic diagram shows the air pressure loss in the
device for versions with flange connections and versions with 1/4''
connections.
For determining the pressure loss with another gas first calculate
the equivalent air flow-rate of the other gas and respect the fluidics
needed with the other gas.
English
21
Page 22

Type 8006, 8702
Technical data
6.7. Electrical data
Power supply 24 V DC ± 10%; residual ripple < 2% (5% for UL devices)
Power supply (not provided) for UL devices Power supply limited to class 2
Power required (max. in Watt) depending on the type of the
device
MFC only:
Analogue input (configurable)
Binary inputs (configurable) 3 binary inputs
Analogue output (configurable) • 0/4 - 20 mA
On certain versions: Field bus communication
(alternative to "analogue input + outputs")
Relay outputs (configurable) 2 relay outputs
LEDs (configurable) 4 LEDs
Electrical connections M16 female fixed connector, 8-pin and Sub-HD, 15-pin
Additional connections for version with field bus M12 male or female fixed connector, 5-pin, or Sub-D female fixed connector,
8006 8702 8626 8712
12.5 5 36.5 14
• 0/4 - 20 mA
Max. input impedance: 300 Ω, resolution: 5 µA
• 0 - 5/10 V
Min. input impedance: 20 kΩ, resolution: 2.5 mV
Low active
Connect to DGND for activation
Max. load: 600 Ω, resolution: 20 µA
• 0 - 5/10 V
Max. current: 10 mA, resolution: 10 mV
PROFIBUS DP V1, DeviceNet or CANopen
Potential-free changer 60 V, 1 A, 60 VA
Status display for Power, Communication, Limit, Error
9-pin
22
English
Page 23

Type 8626, 8712
Installation and commissioning
7. INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING
7.1. Safety instructions
danger
Risk of injury due to high pressure in the installation.
• Shut off the gas flow, relief the pressure and drain the pipe
before loosening the process connections.
Danger due to electrical voltage.
• Shut down and isolate the electrical power supply before
carrying out work on the system.
• Observe all applicable accident protection and safety
regulations for electrical equipment.
Risk of injury from the outflow of operating fluid
• Respect the prevailing regulations on accident prevention and
safety relating to the operating fluids used.
Warning
Danger due to nonconforming installation or commissioning
• Installation and commissioning can only be carried out by
qualified and skilled staff with the appropriate tools.
Risk of injury due to the installation being accidentally
energized or an uncontrolled restart.
• Take appropriate measures to avoid the installation being
accidentally energized.
• Ensure the installation is subject to a controlled restart after any
intervention on the device.
7.2. Prior to installation
→ Before installing the MFM / MFC, remove dirt from the pipes and
fluid system components.
→ Connect a suitable filter (≤ 25 µm mesh size) upstream to ensure
that the operating fluid is kept clean.
note
• Use a power supply unit with adequate power.
• Observe the maximum permitted residual ripple of the
operating voltage.
English
23
Page 24

Type 8006, 8702
Installation and commissioning
7.3. Description of the MFM / MFC
M12 5-pin fixed connector or
Sub-D 9-pin fixed connector
Fieldbus
Sub HD 15-pin fixed
connector Set-point input /
Measured flow-rate output /
Binary inputs / RS232
Screw for earth
connection
8-pin round fixed connector
24 V supply /
Relay outputs
Connection
to the line
Fig. 20: Description of the MFM / MFC
LEDs
7.4. Sequence of the steps to be performed
1. Mechanical installation
2. Fluid installation
3. Electrical installation
4. Set the device parameters
5. Pressurize the lines with operating fluid
6. Flush the lines with operating fluid at the calibration pressure
and deaerate completely
7.5. Setting the parameters
7.5.1. Setting the bus address
To ensure trouble-free adjustment, reset the device by
switching off the power supply to the device.
The bus address of the device can be set either via the Bürkert
"Mass Flow Communicator" software tool in the "Views" window →
PROFIBUS / DeviceNet / CANopen or directly via the master bus.
The address must be reinitialized after a change on the slave and on
the master. Depending on the bus, it may be necessary to send a
corresponding telegram.
24
English
Page 25

Type 8626, 8712
Installation and commissioning
7.5.2. Pin assignment
8-pin round fixed connector Pin Assignment
7
3
5
8
2
6
1
4
Sub-HD 15-pin fixed connector Pin Assignment of MFCs type 8626, 8712 Assignment of MFMs type 8006, 8002
15
14
13
12
11
1)
On the field bus version of MFC types 8626 / 8712, these pins are not assigned.
2)
On the field bus version of MFC types 8626 / 8712 and MFM types 8702 / 8706, these pins are not assigned.
5
10
4
9
3
8
2
7
1
6
1 24 V - Supply +
2 Relay 1 - centre contact
3 Relay 2 - centre contact
4 Relay 1 - break contact
5 Relay 1 - make contact
6 24 V - GND supply
7 Relay 2 - make contact
8 Relay 2 - break contact
1)
1
1)
2
2)
3
Set-point value input + Not used
Set-point value input GND Not used
Measured value output +
4 Binary input 2
5 12 V - output (for internal use only)
6 RS232 T x D (direct connection to PC)
7 Binary input 1
8 DGND (for binary inputs)
9 Internal use only (do not assign!)
10 12 V - output (for internal use only)
11 12 V - output (for internal use only)
12 Binary input 3
2)
13
Measured value output GND
14 RS232 R x D (direct connection to PC)
15 DGND (for RS232 interface)
English
25
Page 26

Pin assignment for field bus version
PROFIBUS DP socket, B encoded
M12 (DP V1 max. 12 MBaud)
5
4
3
1
2
Type 8006, 8702
Installation and commissioning
Pin Assignment
1 VDD
2 R x D / T x D - N (line A)
3 DGND
4 R x D / T x D - N (line B)
5 Not used
DeviceNet or CANopen
Pin Assignment
M12 connector
5
3
4
2
1
1 Shield
2 Unused / 24V
3 DGND
4
5
CAN_H
CAN_L
Sub-D 9-pin fixed connector Pin Profibus assignment DeviceNet assignment
1 Shield (FE), functional earth Shield (FE), functional earth
2 N.C. (not connected) CAN-L data line
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
3 RxD/TxD-P line B GND
4 RTS control signal for repeater N. C.
5 GND data transmission potential N. C.
6 VDD supply voltage + (P5V) N. C.
7 N. C.
CAN-H data line
8 RxD/TxD-N line A N. C.
9 N. C. N. C.
26
English
Page 27

Type 8626, 8712
Installation and commissioning
7.6. Mechanical installation
Observe the mounting position shown on the calibration plate or the
calibration protocol.
7.7. Fluid installation
danger
Risk of injury due to high pressure in the installation.
• Shut off the gas flow, relief the pressure and drain the pipe
before loosening the process connections.
Select the fluid connections suitable for the maximum flow-rate and
with the optimum pressure loss. There is no minimum upstream piping
length to be observed.
On request, the device may be supplied with the fluid connections fitted.
Warning
Danger from leaks
If flow-rates are low and pressures high, ensure that the system
is sealed to prevent incorrect metering or the operating fluid
from leaking.
• To ensure that the seal is secure, observe the operations
described below.
Install the fittings without subjecting them to any stresses. To seal the
system properly, use fittings with olives.
Use a line with a suitable diameter and a smooth surface.
→ Cut the line squarely [1] and deburr [2].
1 2
→ In order, fit the nut [A] and the olive onto the line.
C
B
Olive
A
English
27
Page 28

Type 8006, 8702
Installation and commissioning
→ Fit the washer [C] and screw the fitting [B] to the device.
C
B
→ Insert the line and manually tighten the nut [A].
A
→ Finish tightening the nut with a suitable wrench to ensure the
mounting is sealed.
7.8. Electrical installation
danger
Risk of injury due to electrical shock
• Shut down and isolate the power supply before carrying out any
work on the system.
• Observe all applicable accident protection and safety
regulations for electrical equipment.
28
English
Page 29

Type 8626, 8712
Installation and commissioning
Warning
Risk of fire and ignition due to electrostatic discharge
If the device is electrostatically charged, highly flammable fluid
vapours may ignite if electrostatic discharge occurs.
• To avoid electrostatic charges, connect the device to the
functional earth (FE) using the shortest possible cable with the
largest possible cross section.
Danger from electromagnetic fields
If the FE connection is not connected, electromagnetic
compatibility is not assured.
• Connect the device to the functional earth (FE) via the shortest
possible cable (largest possible cross section).
note
Important information to ensure trouble-free operation
of the device
The GND or earth connections of the MFM / MFC must always be
connected individually.
If all the GND connections are connected together and only a
single common connection is set up with a view to activation,
the analogue signals risk being subjected to fluctuations
and interference.
be as short as possible and its cross section must be as large
as possible.
→ Connect the functional earth (FE) to the screw indicated,
for example using an earth terminal. The connection cable must
English
29
Page 30

Type 8006, 8702
Operation and function
8. OPERATION AND FUNCTION
8.1. Safety instructions
Warning
Risk of injury due to nonconforming operation.
Nonconforming operation could lead to injuries and damage the
device and its surroundings.
• Operating personnel must familiarize themselves with the
contents of the operating instructions.
• Observe the safety instructions and use the devices as
indicated in this manual.
• Only adequately trained personnel may operate the device.
8.2. Operation of the MFM / MFC
The MFM / MFC is operated by means of analogue standard signals
or field bus communication as well as binary inputs. Four LEDs and
two relay output signals indicate the operating state.
There is a serial interface (RS232) which can be used to connect to a
computer, using the "Mass Flow Communicator" software.
Field bus
Binary
inputs
LEDs
Relay
outputs
30
English
Page 31

Type 8626, 8712
Operation and function
• Selecting the standard signals / Assigning the
binary input ports
The standard signal type as well as the assignment of the
binary input ports can be specified on order placement or
configured via the "Mass Flow Communicator" PC software
(see also section „10.1.3“).
• LED assignment / Binary output ports assignment
The "Communication" and "Limit(y)" LED assignment, and the
binary output ports assignment can be configured via the
software (see also section „10.1.3“).
8.2.1. LED default assignment
Indicator light status Possible cause
Power LED (green) on
Power LED (green) flashes
The device is energized.
The Autotune function
is in progress.
Indicator light status Possible cause
Communication LED (yellow) on
Limit (y) LED (blue) on
Limit (y) LED (blue) flashes
The device is communicating
via the field bus or the serial
interface (RS232).
MFM: indicates that the
measured value has almost
reached the nominal flow-rate.
MFC: indicates that the actuating
variable of the proportional valve
has almost reached 100%. In
practice this usually means that
the pressure on the controller
is not adequate to reach the
required flow-rate.
The device is in an operating
state other than the control mode
or Autotune function.
English
31
Page 32

Type 8006, 8702
Operation and function
Indicator light status Possible cause
Error LED (red) on
Error LED (red) flashes
Minor fault, for example the
Autotune function has failed.
Major fault, sensor damaged,
internal power supply voltage
incorrect or operating pressure
too high.
8.2.2. Inputs
Analogue input/output
The analogue input (MFC only) allows the set-point value, i.e. the
required flow-rate value in the line, to be received.
The analogue output enables the measured flow-rate value to be
supplied to the device to which it is connected.
Bus connection (field bus version only)
The set-point value received and the measured value are sent digitally
via the field bus. It is possible to choose between PROFIBUS DP,
DeviceNet and CANopen (see also the additional operating instructions
for field bus devices).
Binary input ports
If the binary inputs are activated, different operations can be run on the
MFC and the latter can be switched to a specific operating mode. This
is achieved by connecting the binary input to DGND for at least 0.5 s.
Activation
binary input 1
Input Default assignment
Binary input 1 Autotune actuation
Binary input 2 Not used
Binary input 3 Not used
Tab. 1 : Default assignment of binary input signals.
Activation
binary input 2
32
English
Page 33

Type 8626, 8712
Operation and function
Function Description
Actuate Autotune
Switch to
specification 2
Totalizer Reset The integrated totalizer (quantity integrator)
Start set-point
value profile
Control mode
Correct safety
value*
Close the valve
completely*
Open the valve
completely*
Tab. 2 : Possible binary input functions.
* The operating principle of the binary input (active / inactive) can
be selected for these functions
Start of Autotune function for optimization of
the control settings to the conditions available
in the system (see section „8.3“).
The calibration curve saved under Gas 2 as
well as all settings entered there are used.
is reset.
Start of the saved set-point value profile
(see section „8.3“).
Enables the solenoid valve to be opened at a
given value (see section „8.3“).
The safety value stored in the device is used
as a flow-rate set-point value.
In this case, the flow-rate set-point value
received by the analogue input or field bus
is ignored.
Valve completely closed.
In this case, the flow-rate set-point value
is ignored.
Valve completely opened.
In this case, the flow-rate set-point value
is ignored.
8.2.3. Relay output signals
MFMs / MFCs are equipped with 2 relay outputs to indicate the
operating state, limit values outside the maximum / minimum or a fault.
Output Assignment
Relay output 1 y2 Limit
Relay output 2 Fault (in case of a major fault, such as
defective sensor or defective internal voltage)
Tab. 3 : Relay output default assignment
Function Description
Not used No function is assigned to the relay output
Power ON The device is energized.
Autotune activated The Autotune function is in progress.
Gas 1 or 2 active Calibration curve 1 or 2 is used.
User-defined
calibration active
Binary input
1 or 2 active
Activate relay
output by field bus
Correct safety
value active
Set-point value
profile active
Control mode
active
The device operates at the calibration
adjusted by customer.
Binary input 1 or 2 has been activated.
The status of the relay outputs is specified via
the field bus or the serial interface.
The safety value is used as the set-point
value.
The set-point value profile stored in the device
is used as the set-point value.
The control mode is active, i.e. the solenoid
valve is opened at a given value.
English
33
Page 34

Type 8006, 8702
Operation and function
Function Description
Close valve
completely active
Open valve
completely active
Defective power
requirement
Defective internal
power supply
Defective power
supply to the
sensor
Defective data
storage
Sensor fault The device is able to detect a defective
MFI fault The field bus module (MFI) is defective
x Limit The measured value has exceeded or dropped
The close valve completely function is
activated.
The open valve completely function is
activated.
The power requirement of the device is
monitored. If this value is outside defined
limits, this function is actuated. An excessively
high or low power requirement may indicate a
defective device.
The operating voltage of the device is
monitored. If the defined limits exceed the
maximum or drop below the minimum, this
function is actuated.
The power supply voltage to the sensor is
monitored. If the defined limits exceed the
maximum or drop below the minimum, this
function is actuated.
If data storage is in the non-volatile memory of
the device, a fault has occurred.
sensor via a self-test.
If this is the case, this function is activated.
or incorrectly equipped. Field bus
communication is not possible.
below a limit value which can be configured.
Function Description
w Limit The set-point value has exceeded or dropped
below a limit value which can be configured.
y2 Limit The actuating variable has exceeded or
dropped below a limit value which can be
configured.
Totalizer Limit The totalizer has exceeded or dropped below
a limit value which can be configured.
Tab. 4 : Relay output signals possible functions
34
English
Page 35

Type 8626, 8712
Operation and function
8.3. MFC operating modes
The MFC can adopt different operating modes:
Operating mode Status of the LEDs
(default setting)
Standard control mode
(see section „8.3.1“)
Autotune function
(see section „8.3.2“)
Safety function
(see section „8.3.3“)
Power LED (green) on - • Autotune function
Power LED (green)
flashes
Limit LED (blue) flashes As long as the input is active -
Binary input activation mode This operating mode may be interrupted
or ended by
• Safety function
• Set-point value profile
• Control mode
Input active for at least 0.5 s (permanent
input activation leads to a function restart)
• Safety function
• Device reset
English
35
Page 36

Type 8006, 8702
Operation and function
Operating mode Status of the LEDs
(default setting)
Set-point value profile
(see section „8.3.4“)
Control mode
(see section „8.3.5“)
Tab. 5 : Overview of the operating modes.
Limit LED (blue) flashes Input active for at least 0.5 s (permanent
Limit LED (blue) flashes As long as the input is active • Autotune function
Binary input activation mode This operating mode may be interrupted
or ended by
• Autotune function
input activation leads to a function restart)
• Safety function
• Device reset
• Safety function
• Device reset
36
English
Page 37

Type 8626, 8712
Operation and function
8.3.1. Standard control mode
In this operating mode, the flow-rate is controlled to the specified
set-point value with a high dynamic.
The MFC is in this operating mode once energized, after a brief
initialization phase. The green power indicator is on.
The set-point value is specified via the analogue input or the field bus,
depending on the device version.
The controller settings are set in such a way that set-point value
changes or actuating variables are corrected as quickly as possible
without appreciable overshoot occurring.
The measured flow-rate value is available on the analogue output or
the field bus, depending on the device version.
For the MFC:
If the blue Limit (y) LED is on, this means that the control
signal of the solenoid control valve is approaching the
100% limit (see section „9.3“).
The cause may be:
• either an insufficient pressure difference over the MFC,
for example an insufficient inlet pressure,
• or a dirty inlet filter
This means that the set point cannot be achieved and a
difference between the set point and the measured value
(w-x) exists.
For the MFM:
If the blue Limit (y) LED is on, the measured mass flow is
approaching the nominal flow-rate or has even exceeded it
(see section „9.3“).
If a high exceeding of the nominal flow rate occurs, a
difference between the measured and the real flow rates
may appear.
To permit an external reaction to this gap, a binary output
is activated.
English
37
Page 38

Type 8006, 8702
Operation and function
8.3.2. Autotune function
The Autotune function is run through during the final
inspection in the factory, at the operating pressure and with
the calibration fluid indicated in the calibration protocol.
Therefore, the re-actuation of this function is not essential.
However, the Autotune function should be activated if:
• the pressure conditions in the system have changed
significantly,
• the calibration fluid does not correspond to the
operating fluid.
In this operating mode, the device calculates and optimizes the control
settings to the conditions present in the system.
The solenoid control valve is activated according to a predefined profile
resulting in flow-rate changes. Thereby several control settings are
adjusted to the conditions on-site. These settings are stored in the
non-volatile memory of the device at the end of a successful Autotune.
This function of the MFC is obtained by activating a binary input
(configured on this function) for at least 0.5 s. The Power LED (green)
flashes to signal that the function is in progress.
Warning
Various flow-rate changes occur when the Autotune is active.
• Do not switch off the power supply to the MFC.
• Keep the supply pressure constant.
→ Before activating the Autotune function, bring the medium
pressure to a pressure close to the calibration pressure.
While the Autotune function is running, the MFC is not in control mode.
When the Autotune function ends, the MFC returns to the operating
mode it was in prior to activation.
8.3.3. Safety function
In this operating mode, the device behaves as in control mode, except
that the set-point value is ignored and replaced by a predefined safety
set-point value. The default safety set-point value is 0%. This can be
modified with the "Mass Flow Communicator" software.
This function of the MFC is obtained by activating a binary input or via
the field bus, depending on the configuration of the device. The Limit
LED (blue) flashes to signal that the function is in progress.
38
English
Page 39

Type 8626, 8712
Maintenance, Troubleshooting
8.3.4. Set-point value profile
In this operating mode, the device behaves as in standard control mode,
except that the external set-point value is ignored and replaced by a
predefined chronology of up to 30 flow-rate values (configurable with
the "Mass Flow Communicator" software).
This function of the MFC is obtained by activating a binary input
(configured on this function) for at least 0.5 s. The Limit LED (blue)
flashes to signal that the function is in progress.
If the set-point value profile has been activated by binary input and
the input has been reset, once the set-point value profile has been
executed, the device returns to the operating mode it was prior to
activation.
8.3.5. Control mode
In this operating mode, the set-point value enables a duty cycle to be
directly supplied to the proportional valve, for example set-point value
10% → duty cycle of the valve = 10%.
This function of the MFC is obtained by activating a binary input or via
the field bus, depending on the configuration of the device (configurable
with the "Mass Flow Communicator" software). The Limit LED (blue)
flashes to signal that the function is in progress.
9. MAINTENANCE,
TROUBLESHOOTING
9.1. Safety instructions
danger
Risk of injury due to high pressure in the installation.
• Shut off the gas flow, relief the pressure and drain the pipe
before loosening the process connections.
Risk of injury due to electrical voltage.
• Shut down and isolate the electrical power supply before
carrying out work on the system.
• Observe all applicable accident protection and safety
regulations for electrical equipment.
Warning
Risk of injury due to nonconforming maintenance.
• This work may only be carried out by qualified, authorized
technicians trained for working in environments where there is a
risk of explosion and using the appropriate tools.
• Ensure that the installation is subject to a controlled restart after
the power supply is switched off.
English
39
Page 40

9.2. Maintenance
The MFM / MFC does not require any maintenance if used as indicated
in this manual. Routine recalibration is not required.
attention
Risk of injury from operating faults and device failure if the
device is opened.
Inside the device are elements to condition the flow and measure
the flow-rate. Work may only be carried out inside the device,
for example for cleaning, as described in section „9.2.1“.
Any other work carried out inside the device causes a change to
the sensor signal, requiring recalibration at the factory.
• Do not open the device.
• Cleaning other than that described in section „9.2.1“ and
calibration may only be performed by the manufacturer.
Type 8006, 8702
Maintenance, Troubleshooting
7
5
4
3
2
1
6
9.2.1. Maintenance if used with highly
soiled fluids
If highly soiled fluids are used:
→ Regularly check that the stainless steel mesh filter disc [5]
is not soiled.
→ Clean or replace it if necessary.
40
1 - Screws
2 - Inlet flange plate
3 - O-ring
4 - O-ring
5 - Stainless steel mesh filter
6 - Orifice tube
7 - O-ring
Fig. 21: Maintenance, Cleaning
English
Page 41

Type 8626, 8712
Maintenance, Troubleshooting
Procedure:
→ To gain access to the stainless steel mesh filter disc, detach the
input flange plate [2] (see „Fig. 21“).
→ Take out the stainless steel mesh filter disc.
→ Clean the stainless steel mesh filter disc [5] using distilled water
(not tap water), acetone, isopropanol or compressed air.
→ Dry the parts after cleaning.
→ Re-insert parts in the correct sequence and position
(see „Fig. 21“). The fine mesh of the filter disc [5] must face
the input flange plate [2].
9.2.2. Cleaning and recalibration at the
factory
If the sensor is excessively soiled or damaged by the operating gas,
the device may deviate significantly in terms of the mass flow-rate
measurement. Cleaning or replacement followed by recalibration at
the factory will then be required.
note
• Recalibration must be carried out at the factory as it requires
the use of very precise references and a specific digital
communication system.
English
41
Page 42

Type 8006, 8702
Maintenance, Troubleshooting
9.3. Troubleshooting
Problem Possible cause Recommended action
The Power LED is off No power supply. Check the electrical connections.
The Power LED flashes
The Autotune function is in progress. See section „8.3“.
The Power LED goes off
periodically
The Limit (y) LED comes
on
42
The Power supply cuts out periodically; the device
implements a reset.
The voltage drop in the connection cable is too high. Increase the cable cross section.
MFC: the solenoid valve adjustment has almost reached
100%. The set-point value has not been obtained.
MFM: the measured flow-rate has almost reached or
exceeded the nominal flow-rate.
Use a power supply with adequate power.
Reduce the cable length.
Increase the operating pressure (observe the maximum
permitted supply pressure).
Check the cable resistance and reduce if required.
Check the system dimensions.
Check the filters installed in the line and clean
if required.
Reduce the flow-rate.
English
Page 43

Type 8626, 8712
Maintenance, Troubleshooting
Problem Possible cause Recommended action
The limit (y) LED is
flashing
The device is in an operating state other than standard
control mode or the Autotune function.
See section „8.3“.
The Error LED is on
The Error LED flashes
No flow-rate available The set-point value is below the limit for the zero point
Minor fault; for example the Autotune function has failed. Repeat the Autotune
The residual ripple of the supply voltage is too high. Use a power supply with a smooth output voltage at
A major fault has occurred, for example: defective
sensor or internal voltage fault.
The sensor was operated above the permitted maximum
operating pressure.
shut-off.
The device is in an operating state other than standard
control mode.
The lines have been sized too large or may not yet have
been completely deaerated.
English
function or reset the device to acknowledge the fault.
the required power.
Return the device to the manufacturer to have the fault
repaired.
Reduce the operating pressure.
Return the device to the manufacturer to have the fault
repaired.
Increase the set-point value to > 2% of the nominal
flow-rate.
Check the operating state; see also section „8.3“.
Deaerate the lines.
Change the line diameter.
43
Page 44

Type 8006, 8702
Maintenance, Troubleshooting
Problem Possible cause Recommended action
The measured value
fluctuates
Set-point value at 0%,
but the fluid is circulating
Set-point value = 0%,
valve is closed, no
flow-rate in the line;
but the measured
flow-rate is not zero
Set-point value is
not reached
The earth connection (FE) is not correct. Connect the FE to the earthing point (cable as short as
possible, wire at least 2.5 mm²).
The controller must continuously correct fluctuations in
an unstable pressure supply, e.g. by pumping.
The residual ripple of the supply voltage is too high. Use a power supply with a smooth output voltage at
The operating pressure is above the operating pressure
maintained by the proportional valve.
The mounting position of the device is incorrect. Install the MFC in the mounting position shown in the
A fluid other than that designated by the calibration
is used.
The filter is blocked. Clean or replace the filter.
The primary pressure is too low. Increase primary pressure to calibration pressure.
The back pressure is too high. Check components for soiling downstream of the
Connect a suitable pressure controller upstream.
Install a buffer tank to absorb pressure fluctuations.
the required power.
Reduce the operating pressure.
Return the device to the manufacturer to have the fault
repaired.
calibration protocol or the calibration plate and run an
Autotune function to adjust to the operating conditions.
Return device to the manufacturer for recalibration for
the operating fluid.
device and if required clean.
44
English
Page 45

Type 8626, 8712
Accessories / Spare parts
10. ACCESSORIES / SPARE PARTS
attention
Risk of injury and/or damage caused by the use of
unsuitable parts.
Incorrect accessories and unsuitable replacement parts may
cause injuries and damage the device and the surrounding area.
• Use only original accessories from Bürkert.
10.1. Accessories
The Bürkert accessories indicated below are recommended to ensure
problem-free operation, maintenance and repair of the device.
10.1.1. Electrical accessories
Types Item Item no.
8006,
8702,
8626,
8712
M16 connector, 8-pin
(to be soldered)
M16 connector, 8-pin, with 5 m
cable, with stripped end
M16 connector, 8-pin, with 10 m
cable, with stripped end
Sub-HD 15-pin connector with 5 m
cable, with stripped end
Sub-HD 15-pin connector with 10 m
cable, with stripped end
RS232 adapter for PC connection
with an extension cable (item no.
917039)
Extension cable for Sub-D 9-pin
connector, RS232 2 m
RS422 adapter 666 370
USB adapter 670 696
Software "Mass Flow
Communicator"
918 299
787 733
787 734
787 735
787 736
654 757
917 039
Can be
downloaded
at www.
burkert.com
English
45
Page 46

Type 8006, 8702
Accessories / Spare parts
Types Item Item no.
Profibus
version
DeviceNet
/ CANopen
version
* The two previous M12 connectors cannot be used together on the same
side of the Y-junction. At least one of the two M12 connectors must be a
prefabricated cable with a thinner connector.
Straight M12 plug (code B) 918 198
Straight M12 socket (coupling)
(code B)
PROFIBUS* Y-piece 902 098
PROFIBUS T-piece 918 531
PROFIBUS terminal resistor
(code B)
GSD sheet Can be
Straight M12 plug (code A) 917 115
Straight M12 socket (coupling)
(code A)
DVN/CAN* Y-piece
DVN/CAN T-piece Not used
DVN/CAN terminal resistor
(code A)
EDS sheet for DeviceNet Can be
918 447
902 553
downloaded at
www.burkert.
com
917 116
788 643
No bush used
downloaded
at www.
burkert.com
10.1.2. Fluid accessories
The MFM / MFC are equipped with a connection plate which uses a
DIN ISO 228/1 thread process connection.
A threaded fitting available as an accessory is used to connect the
device to a line:
• the connection to the device side has a DIN ISO 228/1 thread,
• the connection to the line side is available in a range of
dimensions.
A sealing ring must be ordered for each screw fitting!
46
English
Page 47

Type 8626, 8712
Accessories / Spare parts
Connection
to the
device, with
DIN ISO 228/1
thread
G 1/4 6 mm
G 1/4 8 mm 901 540 901 575
G 1/4 1/4 " 901 551 901 579
G 1/4 3/8 " 901 553 901 579
G 3/8 8 mm 901 542 901 576
G 3/8 10 mm 901 544 901 576
G 3/8 1/4" 901 555 901 580
G 3/8 3/8" 901 556 901 580
G 1/2 10 mm 901 546 901 577
G 1/2 12 mm 901 548 901 577
G 1/2 1/2" 901 557 901 581
G 1/2 3/4" 901 558 901 581
G 3/4 12 mm 901 549 901 578
G 3/4 3/4" 901 559 901 582
Other accessories for the fluid connection of an
MFM / MFC can be found under Type 1013 in the
Bürkert accessories catalogue.
Diameter of
the line
Material Order code
of the olive
connection
901 538 901 575
Stainless
steel
Order code
of the seal
10.1.3. Mass Flow Communicator
(Software)
The "Mass Flow Communicator" software is made for the communication
with the Mass Flow Controllers and Liquid Flow Controllers supplied
by Bürkert.
The software runs on the Windows platform and
communicates with the MFM / MFC via a serial interface
(RS 232).
This software enables:
• information specific to the device to be read,
• the assignment of binary inputs and outputs to be changed,
• the assignment of LEDs to be changed,
• various functions to be activated,
• certain dynamic properties to be modified,
• a user specific calibration to be performed,
• the firmware to be updated,
• the bus address to be set,
• ...
English
47
Page 48

Type 8006, 8702
Shutdown
10.1.4. Additional documentation
Designation Item no.
Supplement to the operating instructions for field
bus devices
Contamination Declaration 806 075
"Configuration via PROFIBUS with GDS file"
addendum
804 553
805 923
10.2. Spare part
Designation Item no.
Stainless steel mesh filter, mesh size 250 µm,
for 8626 / 8006 (standard fluid base)
Stainless steel mesh filter, mesh size 250 µm,
for 8626 / 8006 (high fluid flow-rate base)
Stainless steel mesh filter, mesh size 250 µm,
for 8702
Stainless steel mesh filter, mesh size 25 µm,
for 8712
646 808
651 694
654 733
676 329
11. SHUTDOWN
11.1. Safety instructions
danger
Danger due to high pressure in the installation.
• Shut off the gas flow, relief the pressure and drain the pipe
before loosening the process connections.
Danger from the outflow of operating fluid.
• Respect the prevailing regulations on accident prevention and
safety relating to the operating fluids used.
Danger due to electrical voltage.
• Shut down and isolate the electrical power supply before
carrying out work on the system.
• Observe all applicable accident protection and safety
regulations for electrical equipment.
Warning
Risk of injury from nonconforming dismounting.
• Maintenance must only be carried out by qualified and skilled
staff with the appropriate tools.
48
English
Page 49

Type 8626, 8712
Packaging, Storage, Transport
11.2. Dismounting of the MFM / MFC
Procedure:
B
A
C
→ Relieve the operating medium pressure in the system.
→ Control the solenoid valve to open.
→ Clean the device using a neutral fluid (nitrogen, for example).
→ Relieve the rinsing medium pressure in the system.
→ Switch off the power supply [A].
→ Disconnect the electrical connections [B].
→ Disconnect the fluid connections [C].
→ Remove the MFM / MFC.
12. PACKAGING, STORAGE, TRANSPORT
12.1. Packaging, Transport
note
Damage due to transport
Inadequately protected equipment may be damaged during transport.
• Remove all cables, connections, separate filters and installation material.
• Clean and air contaminated devices.
• Protect fluid connections from damage and leaks by fitting
protective caps and seal.
• Pack the device in two suitable bags, sealed with protective film.
• During transportation protect the device against humidity and
dirt in shock-resistant packaging.
• Do not expose the device to temperatures outside the storage
temperature range.
12.2. Storage
note
Poor storage can damage the device.
• Store the device in a dry place away from dust.
• Storage temperature: -10 °C to +70 °C.
English
49
Page 50

Type 8006, 8702
Returning the device
13. RETURNING THE DEVICE
No work or tests will be carried out on the device until
there is a valid contamination declaration.
The Contamination Declaration can be downloaded from our
homepage or requested from your local after-sales service.
www.buerkert.fr
Commissioning
To return a device already in use, a returns number
is required.
If you would like to return a device already in use to Bürkert, proceed
as follows:
Service
Contamination Declaration
Servicing/Maintenance/
→ Complete the Contamination Declaration.
→ Send the declaration to the address indicated on the form:
Bürkert will fax or e-mail you a service number for confirmation.
→ Pack the device in consideration of the information in section
„12.1“.
→ Return the device to Bürkert with the contamination declaration,
and mention the service number given before.
Address:
Bürkert Fluid Control Systems
Corporate Quality / Complaint Management
Chr.-Bürkert-Str. 13-17
D-74653 Ingelfingen
Tel. + 49 (0) 7940 - 10 91 599
Fax + 49 (0) 7940 - 10 91 490
E-mail: service.international@burkert.com
14. DISPOSAL OF THE PRODUCT
→
Sort out used products according to their type.
→ Dispose of the device and its packaging in an environmentally-
friendly way.
note
Damage to the environment caused by products
contaminated by fluids.
• Keep to the existing provisions on the subject of waste disposal
and environmental protection.
Comply with the national and/or local regulations which
concern the area of waste disposal.
50
English
Page 51

Page 52

www.burkert.com
 Loading...
Loading...