Page 1
Multi-Protocol On-board Ethernet Multi-function Print Server
NETWORK
USER’S GUIDE
MFC-9440CN
MFC-9450CDN
DCP-9040CN
DCP-9042CDN
DCP-9045CDN
Please read this manual thoroughly before using this machine on
your network. You can view this manual in HTML format from the
CD-ROM at any time, please keep the CD-ROM in a convenient
place for quick and easy reference at all times. You can also
download the manual in PDF format from the Brother Solutions
Center (http://solutions.brother.com/
The Brother Solutions Center (http://solutions.brother.com/
your one stop resource for all your printing needs. Download the
latest drivers and utilities for your machine, read FAQs and
troubleshooting tips or learn about special printing solutions.
Not all models are available in all countries.
).
) is
Version A
ENG
Page 2

Definitions of notes
We use the following icon throughout this User’s Guide:
Notes tell you how you should respond to a situation that may arise or give tips about how the
operation works with other features.
Trademarks
Brother and the Brother logo are registered trademarks and BRAdmin Light and BRAdmin Professional are
trademarks of Brother Industries, Ltd.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Apple, Macintosh and Safari are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Apple Inc.
HP, Hewlett-Packard, Jetdirect and PCL are registered trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
PostScript and PostScript 3 are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Microsoft, Windows and Windows Server are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States and/or other countries.
Windows Vista is either a registered trademark or a trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and other countries.
®
Linux
Java and all Java-based trademarks and logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Firefox is a registered trademark of the Mozilla Foundation.
All other terms, brand and product names mentioned in this User’s Guide are registered trademarks or
trademarks of their respective companies.
Compilation and publication notice
Under the supervision of Brother Industries Ltd., this manual has been compiled and published, covering the
latest product’s descriptions and specifications.
The contents of this manual and the specifications of this product are subject to change without notice.
Brother reserves the right to make changes without notice in the specifications and materials contained
herein and shall not be responsible for any damages (including consequential) caused by reliance on the
materials presented, including but not limited to typographical and other errors relating to the publication.
©2007 Brother Industries Ltd.
i
Page 3

IMPORTANT NOTE
Windows® XP in this document represents Windows® XP Professional, Windows® XP Professional x64
®
Edition and Windows
®
Windows
Server 2003 in this document represents Windows® Server 2003 and Windows® Server 2003
x64 Edition. Go to the Brother Solutions Center (http://solutions.brother.com/) for more information on
®
Windows
Windows Vista
Server 2003 x64 Edition support.
®
in this document represents all edition of Windows Vista®.
XP Home Edition.
ii
Page 4

Brother numbers
IMPORTANT
For technical and operational assistance, you must call the country where you purchased the machine.
Calls must be made from within that country.
For Customer Service
In USA 1-877-BROTHER (1-877-276-8437)
In Canada 1-877-BROTHER
In Brazil helpline@brother.com.br
In Europe Visit http://www.brother.com/
for contact information on your local Brother office.
Service center locator (USA)
For the location of a Brother authorized service center, call 1-877-BROTHER (1-877-276-8437).
Service center locations (Canada)
For the location of a Brother authorized service center, call 1-877-BROTHER.
If you have any comments or suggestions, please write to us at:
In USA Customer Support
Brother International Corporation
100 Somerset Corporate Boulevard
Bridgewater NJ 08807-0911
In Canada Brother International Corporation (Canada), Ltd.
- Marketing Dept.
1 Hôtel de Ville
Dollard des Ormeaux, QC
H9B 3H6
Canada
In Brazil Brother International Corporation do Brasil Ltda.
Av. Paulista, 854 - 15 and. - Ed. Top Center
CEP: 01310-100 - São Paulo - SP - Brasil
In Europe European Product & Service Support
1 Tame Street
Audenshaw
Manchester, M34 5JE, UK
iii
Page 5

Internet address
Brother Global Web Site: http://www.brother.com/
For Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), Product Support, Driver Updates and Utilities:
http://solutions.brother.com/
Ordering accessories and supplies
In USA: 1-877-552-MALL (1-877-552-6255)
1-800-947-1445 (fax)
http://www.brothermall.com/
In Canada: 1-877-BROTHER
http://www.brother.ca/
iv
Page 6

Table of Contents
1 Introduction 1
Overview....................................................................................................................................................1
Network features........................................................................................................................................2
Network printing...................................................................................................................................2
Network scanning ................................................................................................................................2
Network PC Fax (MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only) ................................................................2
Management utilities............................................................................................................................2
Types of network connections ...................................................................................................................4
Network connection example ..............................................................................................................4
Protocols....................................................................................................................................................6
TCP/IP protocols and functions...........................................................................................................6
2 Configuring your network printer 8
Overview....................................................................................................................................................8
IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways ..............................................................................................8
IP address ...........................................................................................................................................8
Subnet mask........................................................................................................................................9
Gateway (and router)...........................................................................................................................9
Setting the IP address and subnet mask .................................................................................................10
Using the BRAdmin Light utility to configure your machine for the network printer...........................10
Using the control panel to configure your machine for a network......................................................12
Using other methods to configure your machine for a network .........................................................12
Changing the print server settings...........................................................................................................13
Using the BRAdmin Light utility to change the print server settings..................................................13
Using the control panel to change the print server settings...............................................................13
Using Web Based Management (web browser) to change the print/scan settings ...........................14
Using the Remote Setup to change the print server settings
(for Windows
®
and Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater) (MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only) ......15
3 Control panel setup 16
LAN menu................................................................................................................................................16
TCP/IP...............................................................................................................................................16
Ethernet.............................................................................................................................................24
Scan to FTP.......................................................................................................................................24
Printing the Network Configuration List ...................................................................................................25
Restoring the network settings to factory default.....................................................................................26
4 Driver Deployment Wizard (Windows® only) 27
Overview..................................................................................................................................................27
Connection methods................................................................................................................................27
Peer-to-peer ......................................................................................................................................27
Network Shared.................................................................................................................................28
How to install the Driver Deployment Wizard software............................................................................29
Using the Driver Deployment Wizard software........................................................................................30
v
Page 7

5 Network printing from Windows®: basic TCP/IP Peer-to-Peer printing 32
Overview..................................................................................................................................................32
For Windows
Configuring the standard TCP/IP port ...............................................................................................32
Other sources of information ...................................................................................................................33
6 Internet printing for Windows
Overview..................................................................................................................................................34
IPP printing for Windows
For Windows Vista
For Windows
Specifying a different URL.................................................................................................................38
Other sources of information ...................................................................................................................38
7 Network printing from Macintosh
Overview..................................................................................................................................................39
How to select the BR-Script 3 printer driver (TCP/IP)..............................................................................39
For Mac OS
For Mac OS
Other sources of information ...................................................................................................................43
®
users (Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003)....................32
®
®
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 ...............................34
®
®
®
X 10.5..........................................................................................................................39
®
X 10.2.4 to 10.4.x........................................................................................................41
..........................................................................................................................34
2000/XP and Windows Server® 2003 .......................................................................36
®
34
39
8 Web Based Management 44
Overview..................................................................................................................................................44
How to connect to your machine using a Browser...................................................................................45
Password information..............................................................................................................................45
Changing the Scan to FTP configuration using a Browser......................................................................45
9 Security features 46
Overview..................................................................................................................................................46
Security terms....................................................................................................................................46
Security protocols..............................................................................................................................47
Security methods for E-mail notification ............................................................................................47
Configuring the protocol settings .......................................................................................................48
Managing your network printer securely..................................................................................................49
Secure Management using Web Based Management (web browser) ..............................................49
Secure Management using BRAdmin Professional (for Windows
Printing documents securely using IPPS.................................................................................................51
Specifying a different URL.................................................................................................................51
Using E-mail notification with user authentication ...................................................................................52
Creating and installing a certificate..........................................................................................................54
Creating and installing a self-signed certificate .................................................................................56
Creating CSR and installing a certificate...........................................................................................68
Import and export the certificate and private key...............................................................................70
®
) .................................................50
vi
Page 8

10 Troubleshooting 72
Overview..................................................................................................................................................72
General problems ....................................................................................................................................72
Network print software installation problems...........................................................................................73
Printing problems.....................................................................................................................................75
Scanning and PC Fax problems ..............................................................................................................76
Protocol-specific troubleshooting.............................................................................................................78
Windows
Web browser troubleshooting (TCP/IP).............................................................................................78
®
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server 2003 IPP troubleshooting....................78
A Appendix A 79
Using services .........................................................................................................................................79
Other ways to set the IP address (for advanced users and administrators)............................................79
Using DHCP to configure the IP address ..........................................................................................79
Using BOOTP to configure the IP address........................................................................................80
Using RARP to configure the IP address ..........................................................................................81
Using APIPA to configure the IP address..........................................................................................81
Using ARP to configure the IP address .............................................................................................82
Using the TELNET console to configure the IP address ...................................................................83
Installation when using a Network Print Queue or Share (printer driver only).........................................84
B Appendix B 85
Print server specifications........................................................................................................................85
Ethernet wired network......................................................................................................................85
Function table and default factory settings..............................................................................................88
Entering Text ...........................................................................................................................................90
C Appendix C 92
Open Source Licensing Remarks ............................................................................................................92
OpenSSL statements ........................................................................................................................92
DIndex 94
vii
Page 9
1
Introduction 1
Overview 1
The Brother machine can be shared on a 10/100 Mb wired Ethernet network using the internal network print
server. The print server supports various functions and methods of connection depending on the operating
system you are running on a network supporting TCP/IP. These functions include printing, scanning, PC Fax
send, PC Fax receive, Remote Setup and Status Monitor. The following chart shows what network features
and connections are supported by each operating system.
1
Operating Systems
10/100BASE-TX Wired Ethernet
(TCP/IP)
Printing rrr
BRAdmin Light rrr
BRAdmin Professional
Web BRAdmin rr
Web Based Management
(web browser)
Internet Printing (IPP) rr
Scanning rr
PC Fax Send
PC Pax Receive
Remote Setup rr
Status Monitor rr
Driver Deployment Wizard rr
2
2
1
Windows® 2000
®
Windows
Windows
Professional x64 Edition
Windows Vista
XP
®
XP
®
rrr
r
rrr
rr
r
Windows Server® 2003
®
Windows Server
x64 Edition
2003
r
Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or
greater
1
BRAdmin Professional and Web BRAdmin are available as a download from http://solutions.brother.com/.
2
Available for MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN.
To use the Brother machine through a network, you need to configure the print server, and set up the
computers you use.
1
Page 10

Introduction
Network features 1
Your Brother machine has the following basic network features.
Network printing 1
The print server provides printing services for Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server®
®
2003 supporting the TCP/IP protocols and Macintosh
protocols.
Network scanning 1
You can scan documents over the network to your computer (See Network Scanning in the Software User’s
Guide).
Network PC Fax (MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only) 1
(Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater) supporting the TCP/IP
1
You can directly send a PC file as a PC Fax over your network (See Brother PC-FAX Software for Windows®
®
and Sending a Fax for Macintosh
can also PC Fax receive (See PC-FAX receiving in the Software User’s Guide).
in the Software User’s Guide for a complete description). Windows® users
Management utilities 1
BRAdmin Light 1
BRAdmin Light is a utility for initial setup of Brother network connected devices. This utility can search for
Brother products on your network, view the status and configure basic network settings, such as IP address
®
from a computer running Windows
®
on Windows
BRAdmin Light will be installed automatically when you install the printer driver. If you have already installed
the printer driver, you don’t have to install it again.
For more information on BRAdmin Light, visit us at http://solutions.brother.com/
BRAdmin Professional (for Windows
BRAdmin Professional is a utility for more advanced management of network connected Brother devices.
This utility can search for Brother products on your network, view the status and configure the network
settings from a computer running Windows
BRAdmin Light.
, please see the Quick Setup Guide provided with the machine. For Macintosh® users,
systems and Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater. For installing BRAdmin Light
.
®
) 1
®
system. BRAdmin Professional has additional features from
For more information and downloading, visit us at http://solutions.brother.com/
.
2
Page 11

Introduction
Web BRAdmin (for Windows®) 1
Web BRAdmin is a utility for managing network connected Brother devices on your LAN and WAN. This utility
can search for Brother product on your network, view its status and configure the network settings. Unlike
®
BRAdmin Professional, which is designed for Windows
only, the Web BRAdmin server utility can be
accessed from any client PC with a web browser that supports JRE (Java Runtime Environment). By installing
1
the Web BRAdmin server utility on a PC running IIS
, administrators with a web browser can connect to the
Web BRAdmin server, which then communicates with the device itself.
1
For more information and downloading, visit us at http://solutions.brother.com/
1
Internet Information Server 4.0 or Internet Information Service 5.0/5.1/6.0/7.0
.
Remote Setup (for MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only) 1
The Remote Setup software allows you to configure network settings from a Windows® or Macintosh® (Mac
®
X 10.2.4 or greater). (See Remote Setup for Windows® in the Software User’s Guide).
OS
Web Based Management (web browser) 1
The Web Based Management allows you to monitor Brother printer’s status or change some of its
configuration settings.
Note
®
We recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
®
Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh
. Please also make sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and
whichever browser you use. We recommend you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript.
If a different web browser is used, make sure it is compatible with HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1.
3
Page 12
Introduction
Types of network connections 1
Network connection example 1
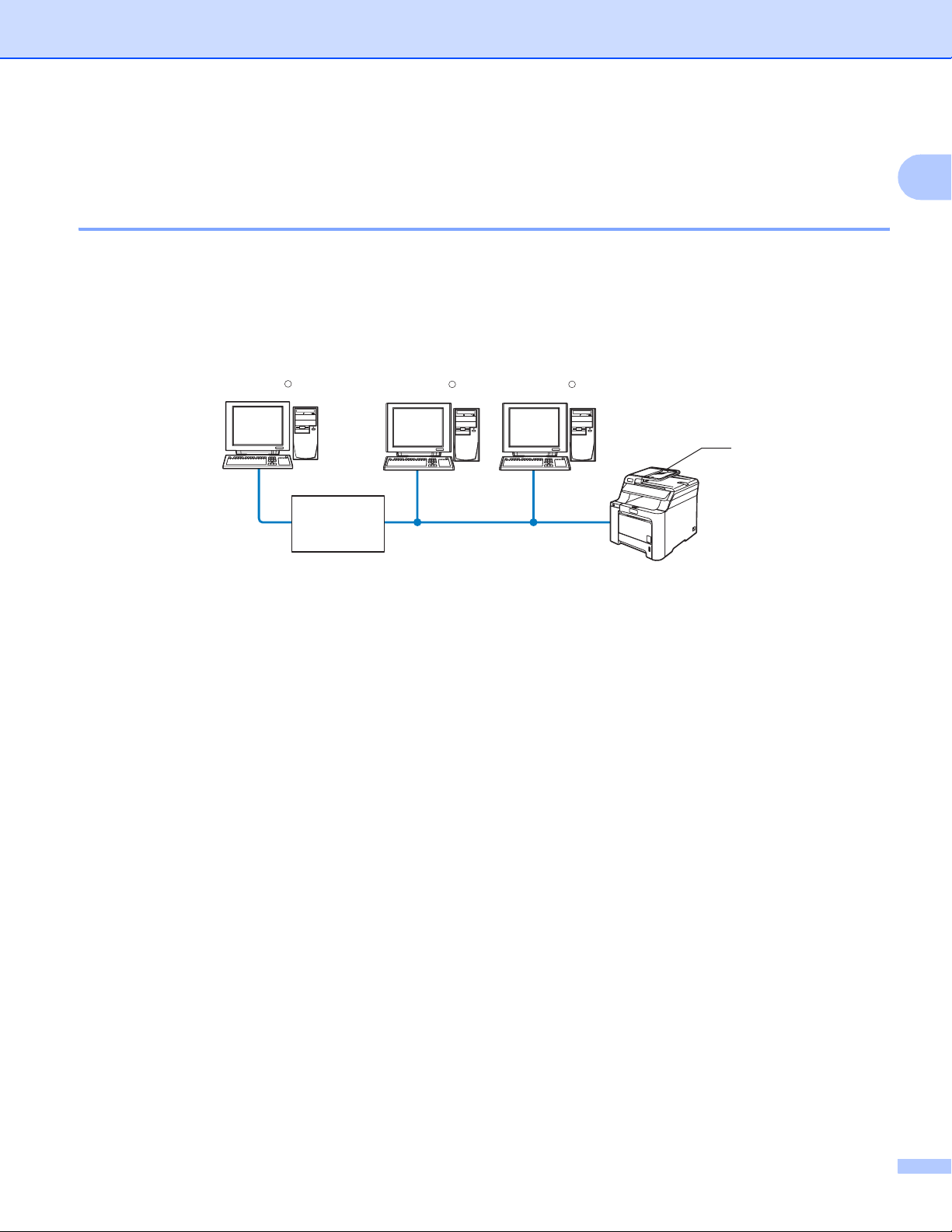
Generally there are two types of network connections. Peer-to-Peer and Network Shared environment.
Peer-to-Peer printing using TCP/IP 1
In a Peer-to-Peer environment, each computer directly sends and receives data to each device. There is no
central server controlling file access or printer sharing.
Windows
R
1
Windows
R
Windows
R
2
TCP/IPTCP/IP
1
1 Router
2 Network printer (your machine)
In a smaller network of 2 or 3 computers, we recommend the Peer-to-Peer printing method as it is easier
to configure than the Network Shared printing method described on the following page. See Network
Shared printing on page 5.
Each computer must use the TCP/IP Protocol.
The Brother machine needs to have an appropriate IP address configuration.
If you are using routers, the Gateway address must be configured on the computers and the Brother
machine.
®
The Brother machine can also communicate with Macintosh
(TCP/IP compatible operating systems).
4
Page 13
Introduction
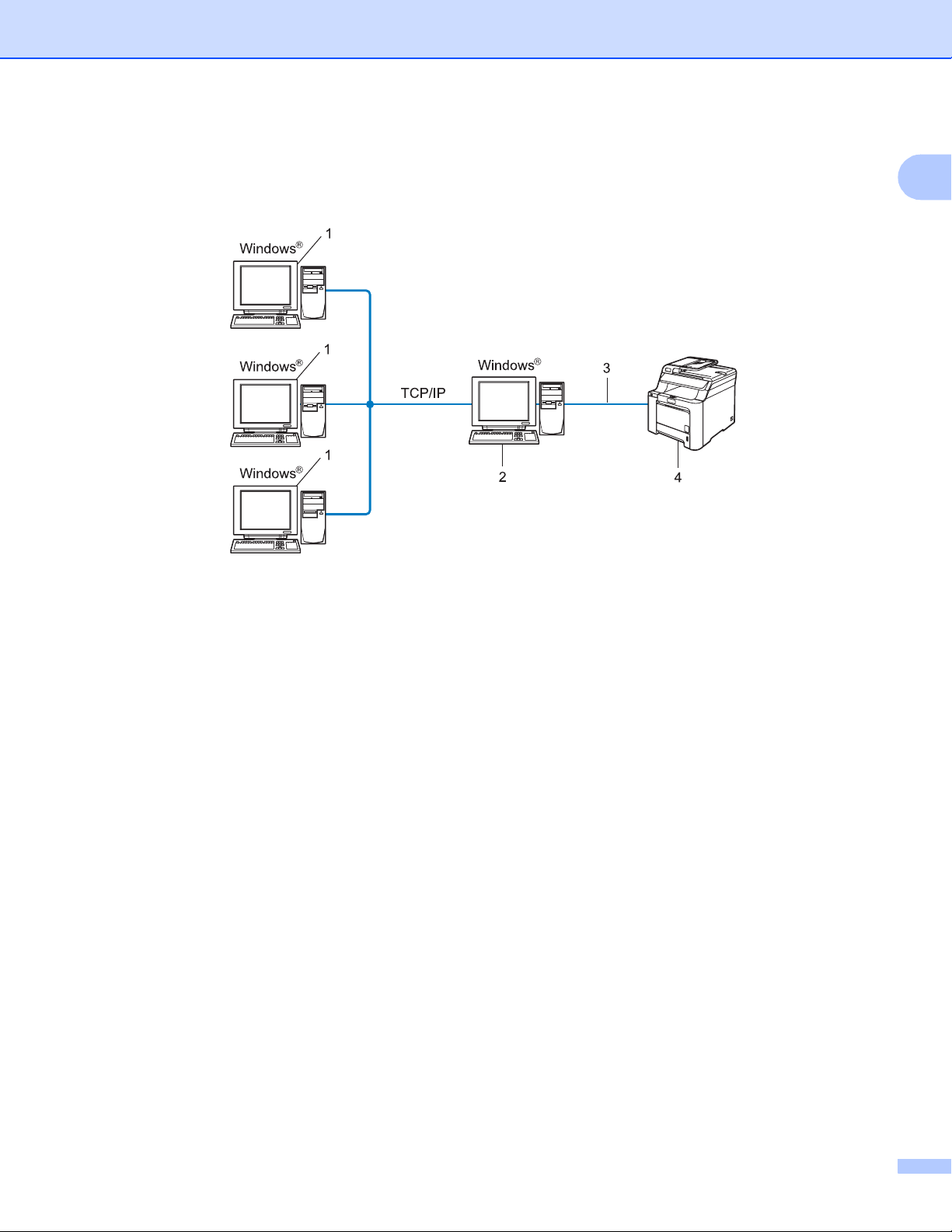
Network Shared printing 1
In a Network Shared environment, each computer sends data via a centrally controlled computer. This type
of computer is often called a “Server” or a “Print Server”. Its job is to control the printing of all print jobs.
1 Client computer
2 Also known as “Server” or “Print server”
1
3 TCP/IP or USB (where available)
4 Printer (your machine)
In a larger network, we recommend a Network Shared printing environment.
The “server” or the “print server” must use the TCP/IP print protocol.
The Brother machine needs to have an appropriate IP address configuration unless the machine is
connected via the USB interface at the server.
5
Page 14

Introduction
Protocols 1
TCP/IP protocols and functions 1
Protocols are the standardized sets of rules for transmitting data on a network. Protocols allow users to gain
access to network connected resources.
The print server used on this Brother product supports the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol) protocol.
TCP/IP is the most popular set of protocols used for communication such as Internet and E-mail. This protocol
®
can be used in almost all operating systems such as Windows
The following TCP/IP protocols are available on this Brother product.
Note
• You can configure the protocol settings by using the HTTP (web browser). See Using Web Based
Management (web browser) to change the print/scan settings on page 14.
• For the protocols of security features, see Security protocols on page 47.
, Macintosh® and Linux.
1
DHCP/BOOTP/RARP 1
By using the DHCP/BOOTP/RARP protocols, the IP address can be automatically configured.
Note
To use the DHCP/BOOTP/RARP protocols, please contact your network administrator.
APIPA 1
If you do not assign an IP address manually (using the control panel of the machine or the BRAdmin software)
or automatically (using a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server), the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)
protocol will automatically assign an IP address from the range 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255.
DNS client 1
The Brother print server supports the Domain Name System (DNS) client function. This function allows the
print server to communicate with other devices by using its DNS name.
LPR/LPD 1
Commonly used printing protocols on a TCP/IP network.
SMTP client 1
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) client is used to send E-mails via Internet or Intranet.
Port9100 1
Another commonly used printing protocol on a TCP/IP network.
6
Page 15

Introduction
IPP 1
The Internet Printing Protocol (IPP Version 1.0) allows you to print documents directly to any accessible
printer via the internet.
mDNS 1
mDNS allows the Brother print server to automatically configure itself to work in a Mac OS® X Simple Network
®
Configured system. (Mac OS
X 10.2.4 or greater).
TELNET 1
The Brother print server supports TELNET server for command line configuration.
SNMP 1
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used to manage network devices including computers,
routers and Brother network ready machines in a TCP/IP network.
Web server (HTTP) 1
The Brother print server is equipped with a built in web server that allows you to monitor its status or change
some of its configuration settings.
Note
We recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
®
Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh
. Please also make sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in
whichever browser you use. We recommend you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript.
If a different web browser is used, make sure it is compatible with HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1.
®
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and
1
FTP 1
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) allows the Brother machine to scan black and white or color documents
directly to an FTP server located locally on your network or on the internet.
IPv6 1
This machine is compatible with IPv6, the next generation internet protocol. For more information on the IPv6
protocol, visit http://solutions.brother com/
.
7
Page 16

2
Configuring your network printer 2
Overview 2
Before you can use your Brother machine on your network, you need to install the Brother software and also
configure the appropriate TCP/IP network settings on the machine itself. To do this, we recommend that you
use the automatic installer on the Brother CD-ROM as this will guide you through the software and network
installation.
If you do not wish to use the automatic installer, or you do not understand some of the terms used by the
automatic installer, refer to the remainder of this chapter for more information.
Note
If you do not wish to, or are unable to use the automatic installer or any of Brother’s software tools, you
can also use the machine’s control panel to change network settings. For more information, see Control
panel setup on page 16.
IP addresses, subnet masks and gateways 2
2
To use the machine in a networked TCP/IP environment, you need to configure its IP address and subnet
mask. The IP address you assign to the print server must be on the same logical network as your host
computers. If it is not, you must properly configure the subnet mask and the gateway address.
IP address 2
An IP address is a series of numbers that identifies each device connected to a network. An IP address
consists of four numbers separated by dots. Each number is between 0 and 255.
Example: In a small network, you would normally change the final number.
192.168.1.1
How the IP address is assigned to your print server: 2
If you have a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server in your network (typically a UNIX®/Linux or Windows® 2000/XP,
Windows Vista
from the DHCP server and register its name with any RFC 1001 and 1002-compliant dynamic name services.
Note
On smaller networks, the DHCP server may be the router.
For more information on DHCP, BOOTP and RARP, see Using DHCP to configure the IP
address on page 79, Using BOOTP to configure the IP address on page 80 and Using RARP to configure the
IP address on page 81.
, 192.168.1.2, 192.168.1.3
®
, Windows Server® 2003 network) the print server will automatically obtain its IP address
8
Page 17

Configuring your network printer
If you do not have a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server, the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) protocol will
automatically assign an IP address from the range 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255. For more information on
APIPA, see Using APIPA to configure the IP address on page 81.
If the APIPA protocol is disabled, the IP address of a Brother print server is 192.0.0.192. However, you can
easily change this IP address number to match with the IP address details of your network. For information
on how to change the IP address, see Setting the IP address and subnet mask on page 10.
Subnet mask 2
Subnet masks restrict network communication.
Example: Computer1 can talk to Computer 2
•Computer 1
IP Address: 192.168.1.2
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
•Computer 2
IP Address: 192.168.1.3
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Note
0 denotes that there is no limit to communication at this part of the address.
In the above example, we can communicate with anything that has an IP address that begins with
192.168.1.x.
2
Gateway (and router) 2
A gateway is a network point that acts as an entrance to another network and sends data transmitted via the
network to an exact destination. The router knows where to direct data that arrives at the gateway. If a
destination is located at an external network, the router transmits data to the external network. If your network
communicates with other networks, you may need to configure the Gateway IP address. If you do not know
the Gateway IP address then contact your Network Administrator.
9
Page 18
Configuring your network printer
Setting the IP address and subnet mask 2
Using the BRAdmin Light utility to configure your machine for the network printer 2
BRAdmin Light 2
The BRAdmin Light utility is designed for initial setup of the Brother network connected devices. It also can
search for Brother products in a TCP/IP environment, view the status and configure basic network settings,
®
such as IP address. The BRAdmin Light utility is available for Windows
®
Server
2003 and Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater.
How to configure your machine using the BRAdmin Light utility 2
Note
• Please use the BRAdmin Light utility version that was supplied on the CD-ROM of your Brother product.
You can also download the latest Brother BRAdmin Light utility version from http://solutions.brother.com/.
2000/XP, Windows Vista®, Windows
2
• If you require more advanced printer management, use the latest Brother BRAdmin Professional utility that
is available as a download from http://solutions.brother.com/
users.
• If you are using personal Firewall software (e.g. Windows Firewall), disable it. Once you are sure that you
can print, re-start your personal Firewall software.
• Node name: Node name appears in current BRAdmin Light. The default Node name of the network card
in the printer is “BRNxxxxxx” (“xxxxxx” is the last six digits of Ethernet address.).
• The default password for Brother print server is “access”.
. This utility is only available for Windows®
a Start the BRAdmin Light utility.
For Windows
Click Start / All Programs
1
Programs for Windows® 2000 users
For Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater users
Double-click Macintosh HD (Startup Disk) / Library / Printers / Brother / Utilities /
BRAdmin Light.jar file.
®
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 users
1
/ Brother / BRAdmin Light / BRAdmin Light.
b BRAdmin Light will search for new devices automatically.
10
Page 19
c Double-click the unconfigured device.
Configuring your network printer
Windows
®
Macintosh
®
Note
• If the print server is set to its factory default settings without using a DHCP/BOOTP/RARP server, the
device will appear as Unconfigured in the BRAdmin Light utility screen.
• You can find the node name and Ethernet address by printing the Network Configuration List. See Printing
the Network Configuration List on page 25 for information on how to print the Network Configuration List
on your print server.
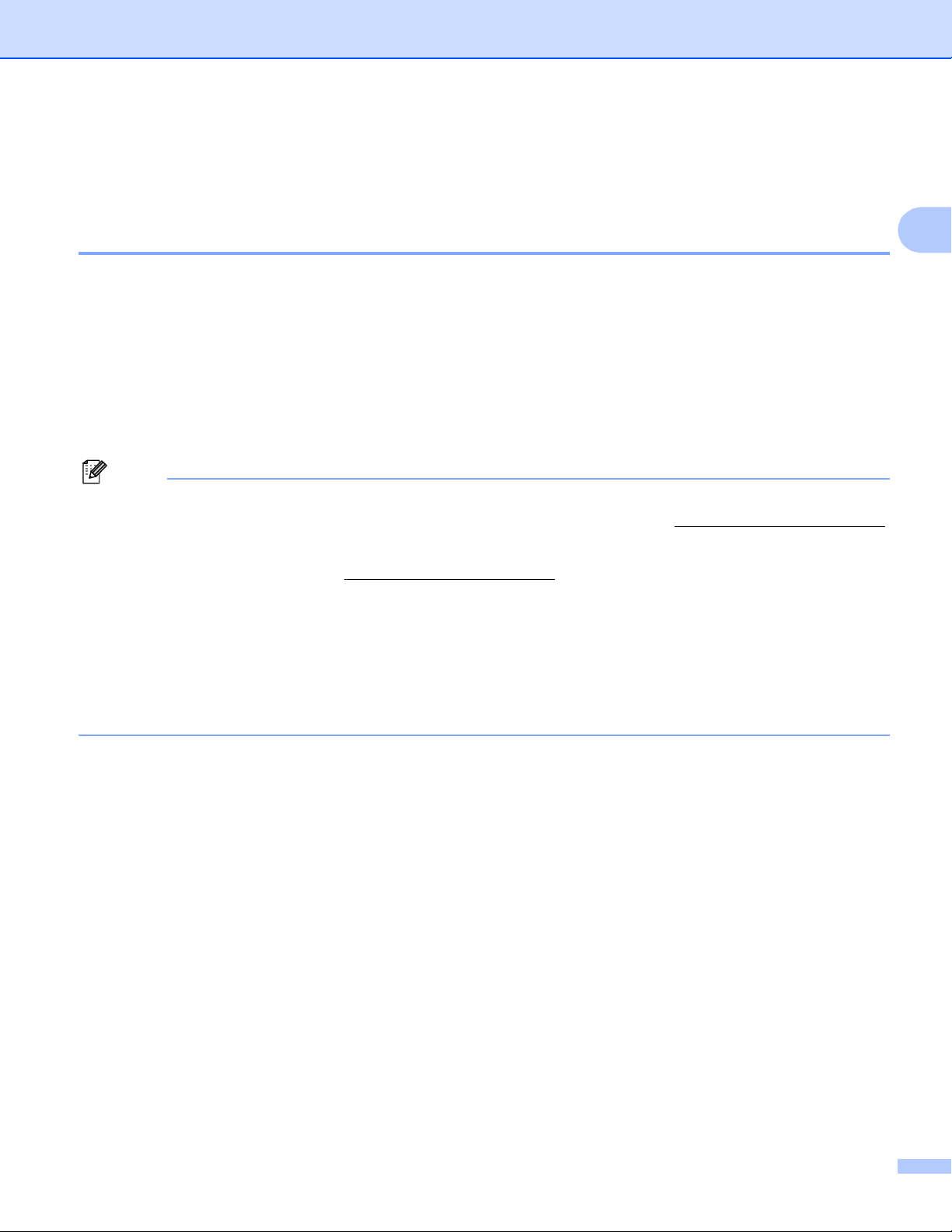
d Choose STATIC from Boot Method. Enter the IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway (if needed) of
your print server.
2
Windows
®
Macintosh
®
e Click OK.
f With the correctly programmed IP address, you will see the Brother print server in the device list.
11
Page 20
Configuring your network printer
Using the control panel to configure your machine for a network 2
You can configure your machine for a network using the control panel LAN menu. See Control panel
setup on page 16.
Using other methods to configure your machine for a network 2
You can configure your machine for a network using other methods. See Other ways to set the IP address
(for advanced users and administrators) on page 79.
2
12
Page 21
Configuring your network printer
Changing the print server settings 2
Using the BRAdmin Light utility to change the print server settings 2
a Start the BRAdmin Light utility.
For Windows
Click Start / All Programs
1
Programs for Windows® 2000 users
For Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater users
Double-click Macintosh HD (Startup Disk) / Library / Printers / Brother / Utilities /
BRAdmin-Light.jar file.
b Select the print server which you want to change the settings.
c Select Network Configuration from the Control menu.
®
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 users
1
/ Brother / BRAdmin Light / BRAdmin Light.
2
d Enter a password. The default password is “access”.
e You can now change the print server settings.
Note
If you want to change more advanced settings, use the BRAdmin Professional utility that is available as a
download from http://solutions.brother.com/
Using the control panel to change the print server settings 2
You can configure and change the print server settings using the control panel LAN menu. See Control panel
setup on page 16.
.
13
Page 22

Configuring your network printer
Using Web Based Management (web browser) to change the print/scan settings2
A standard web browser can be used to change your print server settings using the HTTP (Hyper Text
Transfer Protocol).
Note
• We recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
®
Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh
. Please also make sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in
®
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and
whichever browser you use. We recommend you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript.
If a different web browser is used, make sure it is compatible with HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1.
• To use a web browser, you will need to know the IP address of the print server.
a Type “http://printer’s IP address/” into your browser. (where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP
address or the node name)
For example:
http://192.168.1.2/ (if the printer’s IP address is 192.168.1.2.)
http://BRN123456/ (if the printer’s node name is BRN123456.)
2
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using Domain Name System (DNS), you can
also enter the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names,
you can also enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the
Network Configuration List. To learn how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the
Network Configuration List on page 25. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the
node name and by default it will appear as “BRNxxxxxx” where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the
Ethernet address.
b Click Network Configuration.
c Enter a user name and a password. The default User Name is “admin” and the default password is
“access”.
d Click OK.
e You can now change the printer server settings. If you want to configure the protocol settings, click
Configure Protocol.
Note
If you change the protocol settings, restart the printer after clicking Submit to activate the configuration.
14
Page 23

Configuring your network printer
®
Using the Remote Setup to change the print server settings (for Windows
and
Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater) (MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only) 2
Remote Setup for Windows
The Remote Setup application allows you to configure network settings from a Windows® application. When
you access this application, the settings on your machine will be downloaded automatically to your PC and
displayed on your PC screen. If you change the settings, you can upload them directly to the machine.
a Click the Start button, All Programs
1
Programs for Windows® 2000 users
®
1
, Brother, MFC-XXXX LAN, then Remote Setup.
b Enter a password. The default Password is “access”.
c Click TCP/IP.
d You can now change the print server settings.
Remote Setup for Macintosh
The Remote Setup application allows you to configure many MFC settings from a Macintosh® application.
When you access this application, the settings on your machine will be downloaded automatically to your
®
Macintosh
directly to the machine.
and displayed on your Macintosh® screen. If you change the settings, you can upload them
®
a Double click the Macintosh HD icon on your desktop, Library, Printers, Brother, then Utilities.
2
2
2
b Double click the Remote Setup icon.
c Enter a password. The default password is “access”.
d Click TCP/IP.
e You can now change the print server settings.
15
Page 24

3
Control panel setup 3
LAN menu 3
Before using your Brother product in a network environment, you need to configure the correct TCP/IP
settings. For more information, see Configuring your network printer on page 8.
In this chapter, you will learn how to configure the network settings using the control panel, located on the
front of the machine.
The LAN menu selections of the control panel allow you to set up the Brother machine for your network
configuration. Press Menu, then press a or b to choose LAN. Proceed to the menu selection you wish to
configure. See Function table and default factory settings on page 88.
Please note that the machine is supplied with the BRAdmin Light utility and Remote Setup applications for
®
Windows
the print server settings on page 13.
TCP/IP 3
This menu has ten sections: BOOT Method, IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Node Name,
WINS Config, WINS Server, DNS Server, APIPA and IPv6.
and Macintosh®, which also can be used to configure many aspects of the network. See Changing
3
BOOT Method 3
This selection controls how the machine obtains the IP address for itself. The default setting is Auto.
Note
• If you do not want your print server configured via DHCP, BOOTP or RARP, you must set the BOOT
Method to Static so that the print server has a static IP address. This will prevent the print server from
trying to obtain an IP address from any of these systems. To change the BOOT Method, use the machine’s
control panel, BRAdmin Professional utility, Remote Setup or Web Based Management (web browser).
• You cannot change the BOOT method using the BRAdmin Light utility that was supplied on the CD-ROM
with your Brother product. Please use the latest BRAdmin Professional utility that is available as a
download from http://solutions.brother.com/
. This utility is only available for Windows® users.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose BOOT Method.
Press OK.
16
Page 25

Control panel setup
e Press a or b to choose Auto, Static, RARP, BOOTP or DHCP.
Press OK.
If you chose Auto, RARP, BOOTP or DHCP, go to f.
If you chose Static, go to g.
f Enter how many times the machine tries to obtain the IP address. We recommend you to enter 3 or more.
Press OK.
g Press Stop/Exit.
Auto mode 3
In this mode, the machine will scan the network for a DHCP server, if it can find one, and if the DHCP server
is configured to allocate an IP address to the machine, then the IP address supplied by the DHCP server will
be used. If no DHCP server is available, then the machine will scan for a BOOTP server. If a BOOTP server
is available, and it is configured correctly, the machine will take its IP address from the BOOTP server. If a
BOOTP server is not available, the machine will scan for a RARP server. If a RARP server also does not
answer, the IP Address is scanned through APIPA facility, see Using APIPA to configure the IP
address on page 81. After it is initially powered ON, it may take a few minutes for the machine to scan the
network for a server.
3
Static mode 3
In this mode the machine’s IP address must be manually assigned. Once entered the IP address is locked to
the assigned address.
RARP mode 3
The Brother print server IP address can be configured using the Reverse ARP (RARP) service on your host
computer. For more information on RARP, see Using RARP to configure the IP address on page 81. This is
done by editing the /etc/ethers file (if this file does not exist, you can create it) with an entry similar to the
following:
00:80:77:31:01:07 BRN310107
Where the first entry is the Ethernet address of the print server and the second entry is the name of the print
server (the name must be the same as the one you put in the /etc/hosts file).
If the RARP daemon is not already running, start it (depending on the system the command can be rarpd,
rarpd -a, in.rarpd -a or something else; type man rarpd or refer to your system documentation for additional
®
information). To verify that the RARP daemon is running on a Berkeley UNIX
following command:
ps -ax | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
For AT&T UNIX® based systems, type:
ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
The Brother print server will get the IP address from the RARP daemon when it is powered on.
based system, type the
17
Page 26

Control panel setup
BOOTP mode 3
BOOTP is an alternative to RARP that has the advantage of allowing configuration of the subnet mask and
gateway. For more information on BOOTP, see Using BOOTP to configure the IP address on page 80. In
order to use BOOTP to configure the IP address make sure that BOOTP is installed and running on your host
computer (it should appear in the /etc/services file on your host as a real service; type man bootpd or refer to
your system documentation for information). BOOTP is usually started up via the /etc/inetd.conf file, so you
may need to enable it by removing the “#” in front of the bootp entry in that file. For example, a typical bootp
entry in the /etc/inetd.conf file would be:
#bootp dgram udp wait /usr/etc/bootpd bootpd -i
Note
Depending on the system, this entry might be called “bootps” instead of “bootp”.
In order to enable BOOTP, simply use an editor to delete the “#” (if there is no “#”, then BOOTP is already
enabled). Then edit the BOOTP configuration file (usually /etc/bootptab) and enter the name, network type
(1 for Ethernet), Ethernet address and the IP address, subnet mask and gateway of the print server.
Unfortunately, the exact format for doing this is not standardized, so you will need to refer to your system
®
documentation to determine how to enter this information (many UNIX
systems also have template
examples in the bootptab file that you can use for reference). Some examples of typical /etc/bootptab entries
include:
3
BRN310107 1 00:80:77:31:01:07 192.189.207.3
and:
BRN310107:ht=ethernet:ha=008077310107:\
ip=192.189.207.3:
Certain BOOTP host software implementations will not respond to BOOTP requests if you have not included
a download filename in the configuration file; if this is the case, simply create a null file on the host and specify
the name of this file and its path in the configuration file.
As with RARP, the print server will load its IP address from the BOOTP server when the printer is powered on.
DHCP mode
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is one of several automated mechanisms for IP address
®
allocation. If you have a DHCP server in your network (typically a UNIX
®
Vista
network) the print server will automatically obtain its IP address from a DHCP server and register its
, Windows® 2000/XP, Windows
name with any RFC 1001 and 1002 compliant dynamic name services.
3
18
Page 27

Control panel setup
IP Address 3
This field displays the current IP address of the machine. If you have selected a BOOT Method of Static, enter
the IP address that you wish to assign to the machine (check with your network administrator for the IP
address to use). If you have selected a method other than Static, the machine will attempt to determine its IP
address using the DHCP or BOOTP protocols. The default IP address of your machine will probably be
incompatible with the IP address numbering scheme of your network. We recommend that you contact your
network administrator for an IP address for the network the unit will be connected on.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose IP Address.
Press OK.
e Press 1 to choose Change.
3
f Enter the IP address.
Press OK.
g Press Stop/Exit.
Subnet Mask 3
This field displays the current subnet mask used by the machine. If you are not using DHCP or BOOTP to
obtain the subnet mask, enter the desired subnet mask. Check with your network administrator for the subnet
mask to use.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose Subnet Mask.
Press OK.
e Press 1 to choose Change.
f Enter the Subnet Mask address.
Press OK.
g Press Stop/Exit.
19
Page 28

Control panel setup
Gateway 3
This field displays the current gateway or router address used by the machine. If you are not using DHCP or
BOOTP to obtain the gateway or router address, enter the address you wish to assign. If you do not have a
gateway or router, leave this field blank. Check with your network administrator if you are unsure.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose Gateway.
Press OK.
e Press 1 to choose Change.
f Enter the Gateway address.
Press OK.
g Press Stop/Exit.
Node Name 3
You can register the machine name on the Network. This name is often referred to as a NetBIOS name; it will
be the name that is registered by the WINS server on your network. Brother recommends the name
BRNxxxxxx (where xxxxxx is the last six digits of the Ethernet address) (up to 15 characters).
a Press Menu.
3
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a orb to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose Node Name.
Press OK.
e Press 1 to choose Change.
f Enter the Node Name.
Press OK.
g Press Stop/Exit.
20
Page 29

Control panel setup
WINS Config 3
This selection controls how the machine obtains the IP address of the WINS server.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose WINS Config.
Press OK.
e Press a or b to choose Auto or Static.
Press OK.
f Press Stop/Exit.
3
Auto
Automatically uses a DHCP request to determine the IP addresses for the primary and secondary WINS
servers. You must set the BOOT Method to Auto for this feature to work.
Static 3
Uses a specified IP address for the primary and secondary WINS servers.
WINS Server 3
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose WINS Server.
Press OK.
e Press a or b to choose Primary or Secondary.
Press OK.
3
f Press 1 to choose Change.
g Enter the WINS Server address.
Press OK.
h Press Stop/Exit.
21
Page 30

Control panel setup
Primary WINS Server IP Address 3
This field specifies the IP address of the primary WINS (Windows® Internet Name Service) server. If set to a
®
non-zero value, the machine will contact this server to register its name with the Windows
Service.
Internet Name
Secondary WINS Server IP Address 3
This field specifies the IP address of the secondary WINS server. It is used as a backup to the Primary WINS
server address. If the Primary server is unavailable, the machine still can register itself with a secondary
server. If set to a non-zero value, the machine will contact this server to register its name with the Windows
Internet Name Service. If you have a primary WINS server, but no secondary WINS server, simply leave this
field blank.
®
DNS Server 3
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose DNS Server.
Press OK.
e Press a or b to choose Primary or Secondary.
Press OK.
3
f Press 1 to choose Change.
g Enter the DNS Server address.
Press OK.
h Press Stop/Exit.
Primary DNS Server IP Address
This field specifies the IP address of the primary DNS (Domain Name System) server.
Secondary DNS Server IP Address 3
This field specifies the IP address of the secondary DNS server. It is used as a backup to the Primary DNS
server address. If the Primary server is unavailable, the machine will contact the Secondary DNS server. If
you have a primary DNS server, but no secondary DNS server, simply leave this field blank.
22
3
Page 31

Control panel setup
APIPA 3
The setting of On will cause the print server to automatically allocate a Link-Local IP address in the range
(169.254.1.0 - 169.254.254.255) when the print server cannot obtain an IP address through the BOOT
Method you have set (see BOOT Method on page 16). Selecting Off means the IP address doesn’t change,
when the print server cannot obtain an IP address through the BOOT Method you have set.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose APIPA.
Press OK.
e Press a or b to choose On or Off.
Press OK.
f Press Stop/Exit.
IPv6 3
This machine is compatible with IPv6, the next generation internet protocol. If you want to use the IPv6
protocol, choose On. The default setting for IPv6 is Off. For more information on the IPv6 protocol, visit
http://solutions.brother.com/.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
3
c Press a or b to choose TCP/IP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose IPv6.
Press OK.
e Press a or b to choose On or Off.
Press OK.
f Press Stop/Exit.
23
Page 32

Control panel setup
Ethernet 3
Ethernet link mode. Auto allows the print server to operate in 100BASE-TX full or half duplex, or in 10BASE-T
full or half duplex mode by auto negotiation.
100BASE-TX Full Duplex (100B-FD) or Half Duplex (100B-HD) and 10BASE-T Full Duplex (10B-FD) or Half
Duplex (10B-HD) fix the print server link mode. This change is valid after the print server has been reset
(default is Auto).
Note
If you incorrectly set this value, you may not be able to communicate with your print server.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose Ethernet.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose Auto, 100B-FD, 100B-HD, 10B-FD or 10B-HD.
Press OK.
3
e Press Stop/Exit.
Scan to FTP 3
You can choose the default color file type for the Scan to FTP function.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose Scan to FTP.
Press OK.
d Press a or b to choose Color 150 dpi, Color 300 dpi, Color 600 dpi, B&W 200 dpi or
B&W 200x100 dpi.
Press OK.
e If you chose Color 150 dpi, Color 300 dpi or Color 600 dpi in d, press a or b to choose PDF
or JPEG.
If you chose B&W 200 dpi or B&W 200x100 dpi in d, press a or b to choose PDF or TIFF.
Press OK.
f Press Stop/Exit.
Note
For how to operate Scan to FTP, see Network Scanning of the Software User’s Guide on the CD-ROM.
24
Page 33

Control panel setup
Printing the Network Configuration List 3
Note
Node name: Node name appears in the Network Configuration List. The default Node name is
“BRNxxxxxx” (“xxxxxx” is the last six digits of Ethernet address).
The Network Configuration List prints a report listing all the current network configuration including the
network print server settings.
3
For MFC models:
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose Print Reports.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose Network Config.
Press OK.
d (For US) Press Black Start or Color Start.
(For UK) Press Mono Start or Colour Start.
For DCP models: 3
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose Machine Info.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose User Settings.
Press OK.
d (For US) Press Black Start or Color Start.
(For UK) Press Mono Start or Colour Start.
3
25
Page 34

Control panel setup
Restoring the network settings to factory default 3
If you wish to reset the print server back to its default factory settings (resetting all information such as the
password and IP address information), please follow these steps:
Note
This function restores all network settings to the factory default.
a Press Menu.
b Press a or b to choose LAN.
Press OK.
c Press a or b to choose Factory Reset.
Press OK.
d Press 1 to choose Reset.
e Press 1 to choose Yes for reboot.
f The machine will re-start. You can now reconnect the network cable and configure the network settings
to work with your network.
3
26
Page 35

Driver Deployment Wizard
4
(Windows
Overview 4
The Driver Deployment Wizard software can be used to ease the installation or even automate the installation
of a locally connected or network connected printer. The Driver Deployment Wizard can also be used to
create self running executable files which when run on a remote PC, completely automates the installation of
a printer driver. The remote PC does not have to be connected to a network.
Connection methods 4
The Driver Deployment Wizard supports the two connection methods.
Peer-to-peer 4
The device is connected to the network but each user prints directly to the printer WITHOUT printing through
a central queue.
®
only) 4
4
1 Client computer
2 Network printer (your machine)
27
Page 36

Driver Deployment Wizard (Windows® only)
Network Shared 4
The device is connected to a network and a central print queue is used to manage all print jobs.
4
1 Client computer
2 Also known as “Server” or “Print Server”
3 TCP/IP or USB
4 Printer (your machine)
28
Page 37

Driver Deployment Wizard (Windows® only)
How to install the Driver Deployment Wizard software 4
a Put the supplied CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive. The opening screen will appear automatically.
b Select your language. Then click Install Other Drivers or Utilities.
c Select the Driver Deployment Wizard installation program.
Note
For Windows Vista
d Click Next in response to the Welcome message.
e Read the license agreement carefully. Then follow the on-screen instructions.
f Click Finish. Now the Driver Deployment Wizard software has been installed.
®
, when the User Account Control screen appears, click Continue.
4
29
Page 38

Driver Deployment Wizard (Windows® only)
Using the Driver Deployment Wizard software 4
a When you run the Wizard for the first time you will see a welcome screen. Click Next.
b Choose MFC, and then click Next.
c Choose your connection type to the printer that you want to print to.
d Choose the option you require, and follow the on-screen instructions.
If you choose Brother Peer-to-Peer Network Printer, the following screen is displayed.
4
Setting the IP Address
If the printer does not have an IP address, the Wizard will allow you to change the IP address by
selecting the printer from the list and by selecting the Configure IP option. A dialog box then appears
which allows you to specify information such as the IP address, subnet mask and also the gateway
address.
e Choose the printer you wish to install, and then click Next. If the driver you wish to use is not installed
on your computer, click Have Disk and then specify the path of the printer driver.
30
Page 39

f Click Next after you choose the correct driver.
g A summary screen will appear. Confirm the settings of the driver.
Creating an executable file
The Driver Deployment Wizard software can also be used to create self running .EXE files. These
self-running .EXE files can be saved to the network, copied to a CD-ROM, USB flash memory drive
or even E-mailed to another user. Once run, the driver and its settings are automatically installed
without any user intervention.
Driver Deployment Wizard (Windows® only)
4
• Copy the Driver files to this PC and create an installation program for other users.
Select this option if you wish to install the driver onto your computer and also create a self-running
executable file for use with another computer using the same operating system as your own.
• Only Create an Installation Program for other users.
Select this option if the driver is already installed on your computer and you wish to create a
self-running executable file without again installing the driver on your own computer.
Note
If you work in a "queue" based network and you create an executable file for another user who does not
have access to the same printer queue that you define into the executable file, the driver when installed
on the remote computer will default to LPT1 printing.
h Click Finish. The driver is automatically installed to your computer.
31
Page 40

Network printing from Windows®:
5
basic TCP/IP Peer-to-Peer printing
Overview 5
If you are a Windows® user and want to print using the TCP/IP protocol in a Peer-to-Peer environment, please
follow the instructions in this chapter. This chapter explains how to install the network software and the printer
driver which you will need to be able to print using your network printer.
Note
• You must configure the IP address on your machine before you proceed with this chapter. If you need to
configured the IP address, see Setting the IP address and subnet mask on page 10 first.
• Verify the host computer and print server are either on the same subnet, or that the router is properly
configured to pass data between the two devices.
• If you are connecting to a Network Print Queue or Share (printing only), see Installation when using a
Network Print Queue or Share (printer driver only) on page 84 for installation details.
• The default password for Brother print server is “access”.
5
5
For Windows® users (Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista®
®
and Windows Server
By default, Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 systems install the necessary
print software to enable you to print. This section describes the most commonly used configuration, Standard
TCP/IP Port printing. These Windows
more information, see Internet printing for Windows
If you have already installed the printer driver, jump to Printer driver already installed on page 33.
Configuring the standard TCP/IP port 5
Printer driver not yet installed 5
a Start the CD-ROM installation menu program according to the Quick Setup Guide.
b Select your language (if necessary), and then click Install Other Drivers or Utilities.
c Click Printer Driver (Only, for Network).
d Click Next in response to the Welcome message. Follow the on-screen instructions.
2003) 5
®
systems can also print via the Internet using the IPP protocol. For
®
on page 34.
e Select Standard Installation and click Next.
f Select Brother Peer-to-Peer Network Printer, and then click Next.
32
Page 41

Network printing from Windows®: basic TCP/IP Peer-to-Peer printing
g Follow the on-screen instruction, and then click OK.
Note
Contact your administrator if you are not sure about the location and name of the printer in the network.
h Continue through the wizard clicking Finish when complete.
Printer driver already installed 5
If you have already installed the printer driver and wish to configure it for network printing, follow these steps:
a For Windows Vista
Click button, Control Panel, Hardware and Sound, and then Printers.
For Windows
Click the Start button and select Printers and Faxes windows.
For Windows
Click the Start button and select Settings and then Printers.
®
:
®
XP and Windows Server® 2003:
®
2000.
b Right click on the printer driver you wish to configure, and then select Properties.
c Click the Ports tab and click Add Port.
d Select the port that you wish to use. Typically this would be Standard TCP/IP Port. Then click the
New Port... button.
e The Standard TCP/IP Port Wizard will start.
f Enter the IP address of your network printer. Click Next.
g Click Finish.
h Close Printer Ports and Properties dialog box.
5
Other sources of information 5
See Configuring your network printer on page 8 to learn how to configure the IP address of the printer.
33
Page 42

6
Internet printing for Windows
Overview 6
Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Sever® 2003 users can print using TCP/IP and the
®
®
standard Network Printing IPP protocol software built into any Windows
®
Windows Sever
Note
• You must configure the IP address on your printer before you proceed with this chapter. If you need to
configure the IP address, see Chapter 2 first.
• Verify the host computer and print server are either on the same subnet, or that the router is properly
configured to pass data between the two devices.
• The default password for Brother print servers is “access”.
• This print sever also supports the IPPS printing, see Printing documents securely using IPPS on page 51.
2003 installation.
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and
6
6
IPP printing for Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 6
Use the following instructions if you wish to use the IPP printing capabilities of Windows®2000/XP, Windows
®
Vista
For Windows Vista
a Click button, Control Panel, Hardware and Sound, and then Printers.
b Click Add a printer.
c Select Add a network, wireless or Bluetooth printer.
d Click The printer that I want isn’t listed.
e Select Select a shared printer by name and then enter the following in the URL field:
and Windows Server®2003.
®
http://printer’s IP address:631/ipp (where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP address or the node
name.)
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using Domain Name System (DNS), you can
also enter the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names,
you can also enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the Network
Configuration List. To learn how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the Network
Configuration List on page 25. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name
and by default it will appear as “BRNxxxxxx” where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the Ethernet address.
6
34
Page 43

Internet printing for Windows
®
f When you click Next, Windows Vista
If the printer driver has already been installed:
®
will make a connection with the URL that you specified.
1 You will see the printer selection screen in the Add Printer Wizard. Click OK.
®
If the appropriate printer driver is already installed on your computer, Windows Vista
automatically use that driver for use. In this case, you will simply be asked if you wish to make
the driver the default printer, after which the Add Printer Wizard will complete. You are now
ready to print.
will
2 Go to k.
If the printer driver has NOT been installed:
One of the benefits of the IPP printing protocol is that it establishes the model name of the printer
when you communicate with it. After successful communication you will see the model name of the
®
printer automatically. This means that you do not need to inform Windows Vista
printer driver to be used.
Go to g.
about the type of
g If your printer is not in the list of supported printers, click Have Disk. You will then be asked to insert the
driver disk.
h Click Browse and select the appropriate Brother printer driver that is contained in the CD-ROM or in the
network share. Click Open.
6
i Click OK.
j Specify the model name of the printer. Click OK.
Note
• When the User Account Control screen appears, click Continue.
• If the printer driver that you are installing does not have a Digital Certificate you will see a warning
message. Click Install this driver software anyway to continue with the installation. The Add Printer
Wizard will then complete.
k You will see the Type a printer name screen in the Add Printer Wizard. Check the Set as the default
printer check box if you want to use this printer as the default printer, and then click Next.
l To test the printer connection, click Print a test page, and then click Finish and the printer is now
configured and ready to print.
35
Page 44

Internet printing for Windows
For Windows® 2000/XP and Windows Server® 2003 6
®
a For Windows
Click the Start button and select Printers and Faxes.
For Windows
Click the Start button and select Settings and then Printers.
b For Windows
Click Add a printer to start the Add Printer Wizard.
For Windows
Double click the Add Printer icon to start the Add Printer Wizard.
®
XP and Windows Sever® 2003:
®
2000:
®
XP and Windows Sever® 2003:
®
2000:
c Click Next when you see the Welcome to the Add Printer Wizard screen.
d For Windows
Select A network printer, or a printer attached to another computer.
For Windows
Select Network Printer.
®
XP and Windows Sever® 2003:
®
2000:
e Click Next.
f For Windows
Select Connect to a printer on the Internet or on a home or office network and then enter the
following in the URL field:
http://printer’s IP address:631/ipp
(where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP address or the node name.)
For Windows
Select Connect to a printer on the Internet or on your intranet and then enter the following in the
URL field:
http://printer’s IP address:631/ipp
(Where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP address or the node name).
®
XP and Windows Server® 2003:
®
2000:
6
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using Domain Name System (DNS), you can
also enter the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names,
you can also enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the Network
Configuration List. To learn how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the Network
Configuration List on page 25. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name
and by default it will appear as “BRNxxxxxx” where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the Ethernet address.
36
Page 45

Internet printing for Windows
®
g When you click Next, Windows
URL that you specified.
If the printer driver has already been installed:
®
2000/XP and Windows Sever® 2003 will make a connection with the
1 You will see the printer selection screen in the Add Printer Wizard.
®
If the appropriate printer driver is already installed on your computer, Windows
®
Windows Server
you wish to make the driver the default printer, after which the Add Printer Wizard will complete.
You are now ready to print.
2003 will automatically use that driver. In this case, you will simply be asked if
2000/XP and
2 Go to l.
If the printer driver has NOT been installed:
One of the benefits of the IPP printing protocol is that it establishes the model name of the printer
when you communicate with it. After successful communication you will see the model name of the
®
printer automatically. This means that you do not need to inform Windows
®
Sever
Go to h.
2003 about the type of printer driver to be used.
2000/XP and Windows
h The driver installation starts automatically.
Note
If the printer driver that you are installing does not have a Digital Certificate you will see a warning
message. Click Continue Anyway to continue with the installation.
i For Windows
Click Have Disk. You will then be asked to insert the driver disk.
For Windows
Click OK when you see the Insert Disk screen.
®
XP and Windows Server® 2003:
®
2000:
6
j Click Browse and select the appropriate Brother printer driver that is contained on the CD-ROM or in the
network share. Click Open.
k Click OK.
l Check Yes if you want to use this printer as the default printer. Click Next.
m Click Finish and the printer is now configured and ready to print. To test the printer connection, print a
test page.
37
Page 46

Internet printing for Windows
Specifying a different URL 6
Please note that there are several possible entries that you can enter for the URL field.
http://printer’s IP address:631/ipp
This is the default URL and we recommend that you use this URL. Please note the Get More Info option will
not display any printer data.
http://printer’s IP address:631/ipp/port1
®
This is for HP
http://printer’s IP address:631/
If you forget the URL details, you can simply enter the above text (http://printer’s IP address/) and the printer
will still receive and process data.
Jetdirect® compatibility. Please note the Get More Info option will not display any printer data.
®
Where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP address or the node name.
Other sources of information 6
See Chapter 2 of this User’s Guide to learn how to configure the IP address of the printer.
6
38
Page 47

7
Network printing from Macintosh
Overview 7
®
This chapter explains how to configure the BR-Script 3 (PostScript® 3™ language emulation) printer driver
on a Network. For more information on how to install the Brother standard printer driver on a Network, see
the Quick Setup Guide included with the printer.
How to select the BR-Script 3 printer driver (TCP/IP) 7
For Mac OS® X 10.5 7
a Turn the power of the machine ON.
7
b From the Apple menu, choose System Preferences.
c Click Print & Fax.
d Click + button to add your machine.
e Choose IP.
7
39
Page 48

Network printing from Macintosh
f Enter the IP address of the printer into the Address box.
Note
• The Network Configuration List will allow you to confirm the IP address. For more information on how to
print the configuration page, see Printing the Network Configuration List on page 25.
®
• When specifying the Queue name, use the value “brnxxxxxx_p1_at“ where xxxxxx are the last 6 digits of
the Ethernet address (MAC address).
g From the Print Using pull-down list choose Select a driver to use, and then from the printer model
pull-down list choose your model. For example, choose Brother MFC-XXXX or DCP-XXXX BR-Script3,
and then click Add.
7
40
Page 49

Network printing from Macintosh
h From the Default Printer pull-down list choose your model to set as the default printer. The printer is
now ready.
For Mac OS® X 10.2.4 to 10.4.x 7
a Turn the power of the machine ON.
®
7
b From the Go menu, select Applications.
c Open the Utilities folder.
d Double click the Printer Setup Utility icon. (Mac OS
e Click Add.
f (Mac OS
(Mac OS
(Mac OS
®
X 10.2.4 to 10.3.x) Select IP Printing.
®
X 10.4) Select IP Printer.
®
X 10.2.4 to 10.3.x) (Mac OS® X 10.4)
®
X 10.2.x users, click the Print Center icon.)
41
Page 50

Network printing from Macintosh
®
g (Mac OS
(Mac OS
(Mac OS® X 10.2.4 to 10.3.x) (Mac OS
®
X 10.2.4 to 10.3.x) Enter the IP address of the printer into the Printer Address box.
®
X 10.4) Enter the IP address of the printer into the Address box.
®
X 10.4)
Note
• The Network Configuration List will allow you to confirm the IP address. For more information on how to
print the configuration page, see Printing the Network Configuration List on page 25.
7
• When specifying the Queue Name, use the value “brnxxxxxx_p1_at” where xxxxxx are the last 6 digits of
the Ethernet address.
42
Page 51

Network printing from Macintosh
h From the Printer Model pull-down list select your model. For example, select Brother MFC-XXXX or
DCP-XXXX BR-Script3.
®
®
(Mac OS
X 10.2.4 to 10.3.x) (Mac OS
i Click Add and the printer will be available from the Printer List.
®
X 10.4)
7
Other sources of information 7
See Chapter 2 of this User’s Guide to learn how to configure the IP address of the printer.
43
Page 52

8
Web Based Management 8
Overview 8
A standard Web Browser can be used to manage your machine using the HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer
Protocol). You can get the following information from a machine on your network using a web browser.
Printer status information
Change Fax configuration items, such as General Setup, Quick-Dial settings and Remote Fax
(MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only)
Change network settings such as TCP/IP information.
Configure Scan to FTP search function (MFC-9440CN and MFC-9450CDN only)
Software version information of the machine and print server
Change network and machine configuration details
Note
We recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
®
Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh
whichever browser you use. We recommend you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript.
If a different web browser is used, make sure it is compatible with HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1.
You must use the TCP/IP protocol on your network and have a valid IP address programmed into the print
server and your computer.
. Please also make sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in
®
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and
8
To learn how to configure the IP address on your machine, see Configuring your network
printer on page 8.
®
You can use a web browser on most computing platforms, for example, Macintosh
also able to connect to the machine and manage it.
You can also use the BRAdmin Light and the BRAdmin Professional utilities to manage the printer and its
network configuration.
and UNIX® users are
44
Page 53

Web Based Management
How to connect to your machine using a Browser 8
Type “http://printer’s IP address/” into your browser (where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP address
or the node name.)(You can also use the NetBIOS name of the printer server, if you are in a Microsoft
domain/Workgroup environment). Enter the DNS name of the machine if connecting to a network that uses
the DNS protocol.
®
For Macintosh
machine icon on Status Monitor screen. For more information, see Chapter 7 Status Monitor of the Software
User’s Guide on the CD-ROM.
users, you can have easy access to Web Based Management System by clicking the
Password information 8
Web Based Management offers two levels of password access. Users are able to access to the General
Setup, Fax settings and Lists and Reports. The default user name for User is “user” (case sensitive) and the
default password is “access”.
Administrators are able to access all settings. The login name for the Administrator is “admin” (case
sensitive) and the default password is “access”.
Changing the Scan to FTP configuration using a Browser 8
You can configure and change the following Scan to FTP settings using a web browser. Click Administrator
Settings on your machine’s web page, and then click Scan to FTP. See Chapter 4 of the Software User’s
Guide for more details on Scan to FTP.
Profile Name (Up to 15 characters)
Host Address (FTP server address)
Username
Password
Store Directory
Quality (Color 150, Color 300, Color 600, B&W 200 and B&W 200x100)
File Type (PDF, JPEG or TIFF)
Passive Mode (On or Off)
Port Number
8
45
Page 54

9
Security features 9
Overview 9
In today’s world there are many security threats to your network and the data that travels over it. Your Brother
machine employs some of the latest network security and encryption protocols available today. These
network features can be integrated into your overall network security plan to help protect your data and
prevent unauthorized access to the machine. This chapter explains the various security protocols supported
and how to configure them.
Security terms 9
CA (Certificate Authority)
A CA is an entity that issues digital certificates (especially X.509 certificates) and vouches for the binding
between the data items in a certificate.
CSR (Certificate Signing Request)
A CSR is a message sent from an applicant to a CA in order to apply for issue of a certificate. The CSR
contains information identifying the applicant, the public key generated by the applicant and the digital
signature of the applicant.
Certificate
A Certificate is the information that binds together a public key with an identity. The certificate can be used
to verify that a public key belongs to an individual. The format is defined by the x.509 standard.
Digital signature
A Digital signature is a value computed with a cryptographic algorithm and appended to a data object in
such a way that any recipient of the data can use the signature to verify the data's origin and integrity.
Public key cryptosystem
A Public key cryptosystem is a modern branch of cryptography in which the algorithms employ a pair of
keys (a public key and a private key) and use a different component of the pair for different steps of the
algorithm.
Shared key cryptosystem
A Shared key cryptosystem is a branch of cryptography involving algorithms that use the same key for two
different steps of the algorithm (such as encryption and decryption).
9
46
Page 55

Security features
Security protocols 9
The Brother print server supports the following security protocols.
Note
How to configure the protocol settings, see Using Web Based Management (web browser) to change the
print/scan settings on page 14.
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) / TLS (Transport Layer Security) 9
These security communication protocols encrypt data to prevent security threats.
Web server (HTTPS) 9
The internet protocol that the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) uses SSL.
IPPS 9
The printing protocol that the Internet Printing Protocol (IPP Version 1.0) uses SSL.
Security methods for E-mail notification 9
The Brother print server supports the following security methods for E-mail notification.
Note
How to configure the settings of security methods, see Using Web Based Management (web browser) to
change the print/scan settings on page 14.
POP before SMTP (PbS) 9
The user authentication method for sending E-mail from a client. The client is given permission to use the
SMTP server by accessing the POP3 server before sending the E-mail.
SMTP-AUTH (SMTP Authentication) 9
SMTP-AUTH expands SMTP (the Internet E-mail sending protocol) to include an authentication method that
ensures the true identity of the sender is known.
APOP (Authenticated Post Office Protocol) 9
APOP expands POP3 (the Internet receiving protocol) to include an authentication method that encrypts the
password when the client receives E-mail.
9
47
Page 56

Security features
Configuring the protocol settings 9
You can enable or disable the each protocol and security method using Web Based Management (web
browser).
Note
We recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
®
Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh
whichever browser you use. We recommend you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript.
To use a web browser, you will need to know the IP address of the print server.
. Please also make sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in
®
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and
a Start your web browser.
b Type http://Common Name/ into your browser (where Common Name is the printer’s IP address or
the node name).
For example:
http://192.168.1.2/ (If the Common Name is the printer’s IP address)
http://BRN123456/ (If the Common Name is the printer’s node name)
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using a Domain Name System, you can also enter
the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names, you can also
enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen on the printer settings page.
The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name and by default it will appear as
“BRNxxxxxx” for a wired network (where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the Ethernet address).
c Click Network Configuration.
d Enter a user name and a password. The default User Name is admin and the default password is
access.
e Click OK.
f Click Configure Protocol.
Now you can configure the protocol settings.
Note
If you change the protocol settings, restart the printer after clicking Submit to activate the configuration.
9
48
Page 57

Security features
Managing your network printer securely 9
To manage your network printer securely, you need to use the management utilities with security protocols.
Secure Management using Web Based Management (web browser) 9
To use the HTTPS protocol, the following printer settings are required.
A certificate and private key must be installed in the printer. For how to install a certificate and private key,
see Creating and installing a certificate on page 54.
The HTTPS protocol must be enabled. To enable the HTTPS protocol, see Configuring the protocol
settings on page 48.
Note
®
We recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
®
Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh
. Please also make sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in
whichever browser you use. We recommend you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript.
To use a web browser, you will need to know the IP address of the print server.
a Start the web browser.
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and
b Type “https://Common Name/” into your browser. (Where “Common Name” is the Common Name that
you assigned for the certificate, such as an IP address, node name or domain name. For how to assign
a Common Name for the certificate, see Creating and installing a certificate on page 54.)
For example:
https://192.168.1.2/ (If the Common Name is the printer’s IP address)
https://BRNxxxxxx/ (If the Common Name is the printer’s node name)
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using a Domain Name System, you can also enter
the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names, you can also
enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the Network Configuration
List. To learn how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the Network Configuration
List on page 25. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name and by default
it will appear as “BRNxxxxxx” where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the Ethernet address.
c You can now access the printer using HTTPS.
Note
Disable the TELNET, FTP and TFTP protocols. Accessing the machine using these protocols is not
secure. For how to configure the protocol settings, see Using Web Based Management (web browser) to
change the print/scan settings on page 14.
9
49
Page 58

Security features
Secure Management using BRAdmin Professional (for Windows®) 9
To use the BRAdmin Professional utility securely, you need to follow the points below.
We strongly recommend to use the latest version of the BRAdmin Professional utility or Web BRAdmin
that are available as a download from http://solutions.brother.com/
1
BRAdmin
to manage your brother devices the user authentication will not be secure.
If you want to avoid access to your printer from older version of BRAdmin, you need to disable the older
versions of BRAdmin from Advanced Setting of SNMP on Configure Protocol page by using Web Based
Management (web browser). See Using Web Based Management (web browser) to change the print/scan
settings on page 14.
Disable the TELNET, FTP and TFTP protocols. Accessing the machine using these protocols is not
secure. For how to configure the protocol settings, see Using Web Based Management (web browser) to
change the print/scan settings on page 14.
If you use Web Based Management (web browser), use it with HTTPS protocol. See Secure Management
using Web Based Management (web browser) on page 49.
2
If you are managing a mixed group of older print servers
and the new NC-6500h print server with
BRAdmin Professional, we recommend using a different password in each group. This will ensure security
is maintained on the new NC-6500h print server.
1
BRAdmin Professional older than Ver. 2.80, Web BRAdmin older than Ver. 1.40, BRAdmin Light for Macintosh® older than Ver. 1.10
2
NC-2000 series, NC-2100p, NC-3100h, NC-3100s, NC-4100h, NC-5100h, NC-5200h, NC-6100h, NC-6200h, NC-6300h, NC-6400h, NC-8000,
NC-100h, NC-110h, NC-120w, NC-130h, NC-140w, NC-8100h, NC-9100h, NC-7100w, NC-7200w, NC-2200w
. If you use an older version of
9
50
Page 59

Security features
Printing documents securely using IPPS 9
To print documents securely over the internet, you can use the IPPS protocol.
Note
• Communication using IPPS cannot prevent unauthorized access to the printer server.
®
• IPPS is available for Windows
To use the IPPS protocol, the following printer settings are required.
A certificate and private key must be installed in the printer. For how to install certificate and private key,
see Creating and installing a certificate on page 54.
The HTTPS protocol must be enabled. To enable the HTTPS protocol, see Using Web Based
Management (web browser) to change the print/scan settings on page 14.
The basic steps for IPPS printing are the same as IPP printing. For detailed information, see Internet printing
®
for Windows
in Chapter 6.
Specifying a different URL 9
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003.
Please note that there are several possible entries that you can enter for the URL field.
https://Common Name/ipp
This is the default URL and we recommend that you use this URL. Please note the Get More Info option will
not display any printer data.
https://Common Name/ipp/port1
®
This is for HP
Jetdirect® compatibility. Please note the Get More Info option will not display any printer data.
https://Common Name/
If you forget the URL details, you can simply enter the above text (https://printer’s IP address/) and the printer
will still receive and process data.
Note
If you forget the URL details, you can simply enter the above text (https://Common Name/)and the
printer will still receive and process data.
Where Common Name is that you assigned for the certificate, such as an IP address, node name or
domain name. For how to assign a Common Name for the certificate, see Creating and installing a
certificate on page 54.
• For example:
https://192.168.1.2/ (If the Common Name is the printer’s IP address)
https://BRNxxxxxx/ (If the Common Name is the printer’s node name)
9
51
Page 60

Security features
Using E-mail notification with user authentication 9
To use the E-mail notification function via secure SMTP server that requires user authentication, you need to
use POP before SMTP or SMTP-AUTH method. These methods prevent an unauthorized user from
accessing the mail server. You can use Web Based Management (web browser), BRAdmin professional or
Web BRAdmin to configure these settings.
Note
You need to match the settings of POP3/SMTP authentication with one of the E-mail servers. Contact your
network administrator or your internet service provider about the configuration before using.
How to configure the POP3/SMTP settings using Web Based Management (web browser).
a Start your web browser.
b Type “http://printer’s IP address/” into your browser (where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP
address or the node name.).
For example:
http://192.168.1.2/ (if the printer’s IP address is 192.168.1.2.)
http://BRN123456/ (if the printer’s node name is BRN123456.)
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using Domain Name System, you can also enter
the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names, you can also
enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the Network Configuration
List. To learn how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the Network Configuration
List on page 25. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name and by default
it will appear as “BRNxxxxxx” where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the Ethernet address.
c Click Network Configuration.
d Enter a user name and password.
Note
The login name for the Administrator is "admin" (case sensitive) and the default password is "access".
e Click Configure Protocol.
f Make sure that the POP3/SMTP setting is Enable, and then click Advanced Setting of POP3/SMTP.
9
52
Page 61

g You can configure the POP3/SMTP settings on this page.
Security features
Note
• You can also change the SMTP port number using Web Based Management. This is useful if your ISP
(Internet Service Provider) implements the “Outbound Port 25 Blocking (OP25B)” service. By changing the
SMTP port number to a specific number which your SMTP server decide (for example, port 587), you will
be able to send E-mail via the SMTP server. You will also need to check SMTP-AUTH of SMTP Server
Authentication Method to enable the SMTP server authentication.
• If you can use both POP before SMTP and SMTP-AUTH, we recommend choosing SMTP-AUTH.
• If you choose POP before SMTP for the SMTP Server Authentication Method, you need to configure the
POP3 settings. You can also use the APOP method.
• For more information, see the Help text in the Web Based Management.
• You can also confirm whether the E-mail settings are correct after configuration by sending a test E-mail.
h After configuring, click Submit. The Test E-mail Send Configuration dialog appears.
i Follow the instructions on-screen, if you want to test with the current settings.
9
53
Page 62

Security features
Creating and installing a certificate 9
The Brother print server allows you to use SSL/TLS communication by configuring a certificate and
corresponding private key. This print server supports two certification methods. A self-signed certificate and
a certificate that is issued by a CA (Certificate Authority).
Using self-signed certificate
This print server issues its own certificate. Using this certificate, you can easily use the SSL/TLS
communication without having a certificate from a CA. See Creating and installing a self-signed
certificate on page 56.
Using a certificate from a CA
There are two methods for installing a certificate from a CA. If you already have a CA or if you want to use
a certificate from an outside trusted CA:
• When using a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) from this print server. See Creating CSR and installing
a certificate on page 68.
• When importing a certificate and a private key. See Import and export the certificate and private
key on page 70.
Note
• If you are going to use SSL/TLS communication, we recommend that you contact your system
administrator before using.
• This print server stores only one pair of a certificate and a private key that you installed or previously
imported. This printer overwrites the certificate and the private key if you install a new one.
• When you reset the print server back to its default factory settings, the certificate and the private key that
are installed will be deleted. If you want to keep the same certificate and the private key after resetting the
print server, export them before resetting and re-install them. See How to export the certificate and private
key on page 71.
This feature can be configured using Web Based Management (web browser) only. Follow these steps to
access the configure certificate page using Web Based Management.
a Start your web browser.
b Type “http://printer’s IP address/” into your browser. (where “printer’s IP address” is the printer’s IP
address or the node name.)
For example:
http://192.168.1.2/ (if the printer’s IP address is 192.168.1.2.)
http://BRN123456/ (if the printer’s node name is BRN123456.)
Note
If you have edited the hosts file on your computer or are using Domain Name System, you can also enter
the DNS name of the print server. As the print server supports TCP/IP and NetBIOS names, you can also
enter the NetBIOS name of the print server. The NetBIOS name can be seen in the Network Configuration
List. To learn how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the Network Configuration
List on page 25. The NetBIOS name assigned is the first 15 characters of the node name and by default
it will appear as “BRNxxxxxx” where “xxxxxx” is the last six digits of the Ethernet address.
9
54
Page 63

Security features
c Click Network Configuration.
d Enter a user name and a password. The default User Name is “admin” and the default password is
“access”.
e Click OK.
f Click Configure Certificate.
g You can configure the certificate settings from the screen below.
Note
• The functions that are grayed and unlinked indicate they are not available.
• For more information on configuration, see the Help text in the Web Based Management.
9
55
Page 64

Security features
Creating and installing a self-signed certificate 9
How to create and install a self-signed certificate 9
a Click Create Self-Signed Certificate on the Configure Certificate page.
b Enter a Common Name and a Valid Date, then click Submit.
Note
• The length of the Common Name is less than 64 bytes. Enter an identifier such as an IP address, node
name or domain name to use when accessing this printer through SSL/TLS communication. The node
name is displayed by default.
• A warning will pop-up if you enter a different name in the URL than the Common Name that was used for
the self-signed certificate.
c Now the self-signed certificate is created successfully. Check the box on the left of each function you
want to disable, and then click OK.
Note
• We recommend disabling the TELNET, FTP, TFTP protocols and the network management with older
1
versions of BRAdmin
for secure communication. If you enable them, the user authentication is not
secure.
• A check box only appears for an individual protocol or the older BRAdmin utility if they are already enabled.
1
BRAdmin Professional older than Ver. 2.80, Web BRAdmin older than Ver. 1.40, BRAdmin Light for Macintosh® older than Ver. 1.10.
d Restart the printer to activate the configuration.
e Now the self-signed certificate is saved in your printer memory. To use SSL/TLS communication, the
self-signed certificate also needs to be installed on your computer. Proceed to the next section.
9
56
Page 65

Security features
How to install the certificate to your printer 9
Note
The following steps are for Microsoft Internet Explorer. If you use another web browser, follow the help text
of the web browser itself.
For Windows Vista® users that have administrator rights 9
a Log on your computer with Administrator rights. Click and All Programs.
b Right click Internet Explorer, and then click Run as administrator.
c Click Allow.
9
57
Page 66

Security features
d Type “https://printer’s IP address/” into your browser to access your printer (where “printer’s IP address”
is the printer’s IP address or the node name).
Then, click Continue to this website (not recommended).
e Click Certificate Error, and then click View certificates. For the rest of the instructions, follow the steps
from d on page 65.
9
58
Page 67

Security features
For Windows Vista® users that do not have administrator rights 9
a Click and All Programs.
b Right click Internet Explorer, and then click Run as administrator.
c Choose the Administrator that you want to install with and enter the administrator password, and then
click OK.
9
59
Page 68

Security features
d Type “https://printer’s IP address/” into your browser to access your printer (where “printer’s IP address”
is the printer’s IP address or the node name).
Then, click Continue to this website (not recommended).
e Click Certificate Error, and then click View certificates.
f Choose the Details tab, and then click Copy to File....
9
60
Page 69

g Click Next.
h Make sure that DER encoded binary X.509 (.CER) is chosen, and then click Next.
Security features
i Click Browse....
9
61
Page 70

Security features
j Click Browse Folders.
k Choose a folder you want to save the certificate file in and enter a file name, and then click Save.
Note
If you choose Desktop, the certificate file is saved to the Desktop of the Administrator that you chose.
l Click Next.
9
62
Page 71

m Click Finish.
n Click OK.
Security features
o Click OK.
9
63
Page 72

Security features
p Open the folder that you saved the certificate file in k and double-click the certificate file. For the rest of
the instructions, follow the steps from d on page 65.
For Windows® 2000/XP and Windows Server® 2003 users 9
a Start the web browser.
b Type “https://printer’s IP address/” into your browser to access your printer (where “printer’s IP address”
is the IP address or the print Common Name that you assigned for the certificate).
c When the following dialog appears, click View Certificate.
9
64
Page 73

d Click Install Certificate… from the General tab.
e When the Certificate Import Wizard appears, click Next.
Security features
f Choose Place all certificates in the following store and then, click Browse....
9
65
Page 74

g Choose Trusted Root Certification Authorities and then, click OK.
h Click Next.
Security features
i Click Finish.
9
66
Page 75

Security features
j Click Yes, if the fingerprint (thumbprint) is correct.
Note
The fingerprint (thumbprint) is printed on the Network Configuration List. To learn how to print the Network
Configuration List, see Printing the Network Configuration List on page 25.
k Click OK.
l Now the self-signed certificate is installed on your computer, and the SSL/TLS communication is
available.
9
67
Page 76

Security features
Creating CSR and installing a certificate 9
How to create the CSR 9
a Click Create CSR on the Configure Certificate page.
b Enter a Common Name and your information, such as Organization. Then click Submit.
Note
• We recommend that the Root Certificate from the CA be installed on your computer before creating the
CSR.
• The length of the Common Name is less than 64 bytes. Enter an identifier such as an IP address, node
name or domain name to use when accessing this printer through SSL/TLS communication. The node
name is displayed by default. The Common Name is required.
• A warning will pop-up if you enter a different name in the URL than the Common Name that was used for
the certificate.
• The length of the Organization, the Organization Unit, the City/Locality and the State/Province is less
than 64 bytes.
•The Country/Region should be an ISO 3166 country code composed of two characters.
c When the contents of the CSR appear, click Save to save the CSR file to your computer.
d Now the CSR is created.
Note
• Follow your CA policy regarding the method to send a CSR to your CA.
®
• If you are using Enterprise root CA of Windows Server
Certificate Template when creating the certificate. For more information, visit us at
http://solutions.brother.com/.
2003, we recommend using the Web Server
9
68
Page 77

Security features
How to install the certificate to your printer 9
When you receive the certificate from a CA, follow the steps below to install it into the print server.
Note
Only a certificate issued with this printer’s CSR can be installed.
a Click Install Certificate on the Configure Certificate page.
b Specify the file of the certificate that has been issued by a CA, and then click Submit.
c Now the certificate is created successfully. Check the box on the left of each function you want to disable,
and then click OK.
Note
• We recommend disabling the TELNET, FTP, TFTP protocols and the network management with older
1
versions of BRAdmin
for secure communication. If you enable them, the user authentication is not
secure.
• A check box only appears for an individual protocol or the older BRAdmin utility if they are already enabled.
1
BRAdmin Professional older than Ver. 2.80, Web BRAdmin older than Ver. 1.40, BRAdmin Light for Macintosh® older than Ver. 1.10.
d Restart the printer to activate the configuration.
e Now the certificate is saved in your printer. To use SSL/TLS communication, the Root Certificate from
the CA needs to be installed on your computer. Contact your network administrator about installation.
9
69
Page 78

Security features
Import and export the certificate and private key 9
How to import the certificate and private key 9
a Click Import Certificate and Private Key on the Configure Certificate page.
b Specify the file that you want to import.
c Enter the password if the file is encrypted, and then click Submit.
d Now the certificate and private key are imported successfully. Check the box on the left of each function
you want to disable, and then click OK.
Note
• We recommend disabling the TELNET, FTP, TFTP protocols and the network management with older
1
versions of BRAdmin
secure.
• A check box only appears for an individual protocol or the older BRAdmin utility if they are already enabled.
1
BRAdmin Professional older than Ver. 2.80, Web BRAdmin older than Ver. 1.40, BRAdmin Light for Macintosh® older than Ver. 1.10.
for secure communication. If you enable them, the user authentication is not
e Restart the printer to activate the configuration.
f Now the certificate and private key are imported to your printer. To use SSL/TLS communication, the
Root Certificate from the CA needs to also be installed on your computer. Contact your network
administrator about the installation.
9
70
Page 79

Security features
How to export the certificate and private key 9
a Click Export Certificate and Private Key on the Configure Certificate page.
b Enter the password if you want to encrypt the file.
Note
If a blank password is used, the output is not encrypted.
c Enter the password again for confirmation, and then click Submit.
d Specify the location where you want to save the file.
e Now the certificate and private key are exported to your computer.
Note
You can import the file that you exported.
9
71
Page 80

10
Troubleshooting 10
Overview 10
This chapter explains how to resolve typical network problems you may encounter when using the machine.
If, after reading this chapter, you are unable to resolve your problem, please visit the Brother Solutions Center
at: http://solutions.brother.com/
This chapter is divided into the following sections:
General problems
Network print software installation problems
Printing problems
Scanning and PC Fax problems
Protocol-specific troubleshooting
General problems 10
CD-ROM is inserted, but does not start automatically 10
If your computer does not support Autorun, the menu will not start automatically after inserting the CD-ROM.
In this case, execute setup.exe in the root directory of the CD-ROM.
My computer cannot find the machine/print server
My machine/print server does not appear in the window of Remote Setup, BRAdmin Light or
BRAdmin Professional 10
For Windows
Firewall on your computer may be blocking the necessary network connection to the machine. In this case,
you will need to disable the Firewall on your computer and re-install the drivers.
Windows
®
®
XP SP2 users: 10
a Click the Start button, Control Panel, Network and Internet Connections.
b Click Windows Firewall.
c Click the General tab. Make sure that Off (not recommended) is selected.
d Click OK.
Note
After the Brother software package is installed, re-enable your Firewall.
10
72
Page 81

Troubleshooting
Windows Vista® users: 10
a Click button, Control Panel, Network and Internet, Windows Firewall and click Change
settings.
b When the User Account Control screen appears, do the following.
Users who have administrator rights: Click Continue.
For users who do not have administrator rights: Enter the administrator password and click OK.
c Click the General tab. Make sure that Off (not recommended) is selected.
d Click OK.
Note
After the Brother software package is installed, re-enable your Firewall.
For Macintosh
Re-select your machine in the DeviceSelector application located in
Macintosh HD/Library/Printers/Brother/Utilities or from the model pull-down list of ControlCenter3.
®
Network print software installation problems 10
The Brother print server is not found during setup of the network print software installation or from
®
the printer driver of the Brother machine in Windows
The Brother print server is not found using the Simple Network Configuration capabilities of
®
Mac OS
Make sure you have completed the IP address setting of the Brother print server according to Chapter 2 of
this User’s Guide before installing the network print software or printer driver.
Check the following:
X. 10
a Make sure that the machine is powered on, is on-line and ready to print.
b Check to see if there is any LED activity. Brother print servers have two LEDs on the back panel of the
machine. The upper green LED shows Link/Activity (Received/Transmit) status. The lower orange LED
shows Speed status.
.
10
No light: If the upper LED is off, then the print server is not connected to the network.
The upper LED is green: The Link/Activity LED will be green if the print server is connected to a
Ethernet network.
The lower LED is orange: The Speed LED will be orange if the print server is connected to a
100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet network.
The lower LED is off: The Speed LED will be off if the print server is connected to a 10BASE-T
Ethernet network.
73
Page 82

Troubleshooting
c Print the Network Configuration List and check if the settings such as IP address settings are correct for
your network. The problem may be the result of mismatched or duplicate IP address. Verify that the IP
address is correctly loaded into the print server. And make sure that no other nodes on the network have
this IP address. For information on how to print the Network Configuration List, see Printing the Network
Configuration List on page 25.
d Verify that the print server is on your network as follows:
For Windows
Try pinging the print server from the host operating system command prompt with the command:
ping ipaddress
Where ipaddress is the print server IP address (note that in some instances it can take up to two
minutes for the print server to load its IP address after setting the IP address).
For Mac OS
1 From the Go menu, select Applications.
2 Open the Utilities folder.
®
®
X 10.2.4 or greater
3 Double click the Terminal icon.
4 Try pinging the print server from the Terminal window:
ping ipaddress
Where ipaddress is the print server IP address (note that in some instances it can take up to
two minutes for the print server to load its IP address after setting the IP address).
e If you have tried a to d above and it does not work, then reset the print server back to the default factory
settings and try from the initial setup again. For information how to reset to the default factory settings,
see Restoring the network settings to factory default on page 26.
f (For Windows
If the installation failed, the Firewall on your computer may be blocking the necessary network
connection to the machine. In this case, you will need to disable the Firewall on your computer and reinstall the drivers. For more information, see General problems on page 72. If you are using personal
Firewall software, see the User’s Guide for your software or contact the software manufacturer.
®
)
10
74
Page 83

Troubleshooting
Printing problems 10
Print job is not printed 10
Make sure the status and configuration of the print server. Check following:
a Make sure that the machine is powered on, is on-line and ready to print.
b Print the Network Configuration List of the machine and check if the settings such as IP address settings
are correct for your network. The problem may be the result of mismatched or duplicate IP address.
Verify that the IP address is correctly loaded into the print server. And make sure that no other nodes on
the network have this IP address. For information on how to print the Network Configuration List, see
Printing the Network Configuration List on page 25.
c Verify that the print server is on your network as follows:
For Windows
1 Try pinging the print server from the host operating system command prompt with the command:
ping ipaddress
®
Where ipaddress is the print server IP address (note that in some instances it can take up to
two minutes for the print server to load its IP address after setting the IP address).
2 If a successful response is received, then proceed to Windows
Windows Server 2003 IPP troubleshooting on page 78. Otherwise, proceed to d.
For Mac OS
®
X 10.2.4 or greater
®
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and
1 From the Go menu, select Applications.
2 Open the Utilities folder.
3 Double click the Terminal icon.
4 Try pinging the print server from the Terminal window:
ping ipaddress
Where ipaddress is the print server IP address (note that in some instances it can take up to
two minutes for the print server to load its IP address after setting the IP address).
d If you have tried a to c above and it does not work, then reset the print server back to the default factory
settings and try from the initial setup again. For information how to reset to the default factory settings,
see Restoring the network settings to factory default on page 26.
10
Error during printing
If you try to print while other users are printing large amounts of data (e.g. many pages or color pages with
high resolution), the printer is unable to accept your print job until the ongoing printing is finished. If the waiting
time of your print job exceeds a certain limit, a time out situation occurs, which causes the error message. In
such situations, execute the print job again after the other jobs are completed.
75
10
Page 84

Troubleshooting
Scanning and PC Fax problems 10
The network scanning feature does not work in Windows
The network PC Fax feature does not work in Windows
Firewall settings on your PC may be rejecting the necessary network connection. Follow the instructions
below to disable the Firewall. if you are using personal Firewall software, see the User’s Guide for your
software or contact the software manufacturer.
®
Windows
XP SP2 users: 10
®
®
a Click the Start button, Control Panel, Network and Internet Connections and then Windows
Firewall. Make sure that Windows Firewall on the General tab is set to On.
b Click the Advanced tab and Settings... button.
c Click the Add button.
d To add port 54925 for network scanning, enter the information below:
1. In Description of service: Enter any description, for example, “Brother Scanner”.
2. In Name or IP address (for example 192.168.0.12) or the computer hosting this service on your
network: Enter “Localhost”.
3. In External Port number for this service: Enter “54925”.
4. In Internal Port number for this service: Enter “54925”.
5. Make sure UDP is selected.
6. Click OK.
10
10
e Click the Add button.
f To add port 54926 for network PC Fax, enter the information below:
1. In Description of service: Enter any description, for example, “Brother PC Fax”.
2. In Name or IP address (for example 192.168.0.12) or the computer hosting this service on your
network: Enter “Localhost”.
3. In External Port number for this service: Enter “54926”.
4. In Internal Port number for this service: Enter “54926”.
5. Make sure UDP is selected.
6. Click OK.
g If you still have trouble with your network connection, click the Add button.
h To add port 137 for network scanning, network printing and network PC Fax receiving, enter the
information below:
1. In Description of service: Enter any description, for example, “Brother PC Fax receiving”.
2. In Name or IP address (for example 192.168.0.12) or the computer hosting this service on your
network: Enter “Localhost”.
3. In External Port number for this service: Enter “137”.
4. In Internal Port number for this service: Enter “137”.
5. Make sure UDP is selected.
6. Click OK.
76
Page 85

Troubleshooting
i Make sure if the new setting is added and is checked, and then click OK.
Note
After the Brother software package is installed, enable again your Firewall.
Windows Vista® users: 10
a Click button, Control Panel, Network and Internet, Windows Firewall and click Change
settings.
b When the User Account Control screen appears, do the following.
Users who have administrator rights: Click Continue.
For users who do not have administrator rights: Enter the administrator password and click OK.
c Make sure that Windows Firewall is selected on the General tab.
d Click the Exceptions tab.
e Click the Add port... button.
f To add port 54925 for network scanning, enter the information below:
1. In Name: Enter any description, for example, “Brother Scanner”.
2. In Port number: Enter “54925”.
3. Make sure UDP is selected.
4. Click OK.
g Click the Add port... button.
h To add port 54926 for network PC Fax, enter the information below:
1. In Name: Enter any description, for example, “Brother PC Fax”.
2. In Port number: - Enter “54926”.
3. Make sure UDP is selected.
4. Click OK.
i Make sure that the new setting is added and is checked, and then click OK.
j If you still have trouble with your network connection such as network scanning or printing, check File
and Printer Sharing box in the Exceptions tab and then click OK.
Note
After the Brother software package is installed, enable again your Firewall.
10
77
Page 86

Troubleshooting
Protocol-specific troubleshooting 10
Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server 2003 IPP troubleshooting 10
I want to use a different Port number other than 631. 10
If you are using Port 631 for IPP printing, you may find that your firewall may not let the print data through. If
this is the case, use a different port number (port 80), or configure your Firewall to allow Port 631 data
through.
To send a print job using IPP to a printer using Port 80 (the standard HTTP port) enter the following when
®
configuring your Windows
http://ipaddress/ipp
The “Go to printer’s Web site” option in Windows
The “Get More Info” option in Windows
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 system.
®
XP and Windows Vista® is not working
®
2000 and Windows Server® 2003 is not working 10
If you are using a URL of:
http://ipaddress:631 or http://ipaddress:631/ipp,
the Get More Info option in Windows® 2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 will not
function. if you wish to use the Get More Info option, use the following URL:
http://ipaddress
This will then force Windows
communicate with the Brother print server.
®
2000/XP, Windows Vista® and Windows Server® 2003 to use Port 80 to
Web browser troubleshooting (TCP/IP) 10
a If you cannot connect to the print server using your web browser it may be worth checking the Proxy
Settings of your browser. Looking in the Exceptions setting and if necessary, type in the IP address of
the print server. This will stop your PC from trying to connect to your ISP or proxy server every time you
wish to look at the print server.
b Make sure that you are using the proper web browser, we recommend Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0
(or greater) or Firefox® 1.0 (or greater) for Windows® and Safari™ 1.0 for Macintosh®. Please also make
sure that JavaScript and Cookies are always enabled in whichever browser you use. We recommend
you upgrade to Safari™ 1.2 or greater to enable JavaScript. If a different web browser is used, make
sure it is compatible with HTTP 1.0 and HTTP 1.1.
®
10
78
Page 87

A
Appendix A A
Using services A
A service is a resource that can be accessed by computers that wish to print to the Brother print server. The
Brother print server provides the following predefined services (do a SHOW SERVICE command in the
Brother print server remote console to see a list of available services): Enter HELP at the command prompt
for a list of supported commands.
Service (Example) Definition
BINARY_P1 TCP/IP binary, NetBIOS service
TEXT_P1 TCP/IP text service (adds carriage return after each line feed)
PCL_P1
BRNxxxxxx_P1 TCP/IP binary
BRNxxxxxx_P1_AT
POSTSCRIPT_P1
Where xxxxxx is the last six digits of the Ethernet address (for example, BRN310107_P1).
®
PCL
service (switches PJL-compatible printer to PCL® mode)
PostScript
PostScript
®
service for Macintosh
®
service (switches PJL-compatible printer to PostScript® mode)
®
Other ways to set the IP address (for advanced users and administrators) A
For information on how to configure your machine for a network using the BRAdmin Light utility, see Setting
the IP address and subnet mask on page 10.
Using DHCP to configure the IP address A
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is one of several automated mechanisms for IP address
allocation. If you have a DHCP server in your network, the print server will automatically obtain its IP address
from DHCP server and register its name with any RFC 1001 and 1002-compliant dynamic name services.
Note
If you do not want your print server configured via DHCP, BOOTP or RARP, you must set the BOOT
Method to static so that the print server has a static IP address. This will prevent the print server from trying
to obtain an IP address from any of these systems. To change the BOOT Method, use the machine’s
control panel, BRAdmin Professional utility, Remote Setup or Web Based Management (web browser).
A
79
Page 88

Appendix A
Using BOOTP to configure the IP address A
BOOTP is an alternative to rarp that has the advantage of allowing configuration of the subnet mask and
gateway. In order to use BOOTP to configure the IP address make sure that BOOTP is installed and running
on your host computer (it should appear in the /etc/services file on your host as a real service; type man
bootpd or refer to your system documentation for information). BOOTP is usually started up via the
/etc/inetd.conf file, so you may need to enable it by removing the “#” in front of the bootp entry in that
file. For example, a typical bootp entry in the /etc/inetd.conf file would be:
#bootp dgram udp wait /usr/etc/bootpd bootpd -i
Depending on the system, this entry might be called “bootps” instead of “bootp”.
Note
In order to enable BOOTP, simply use an editor to delete the “#” (if there is no “#”, then BOOTP is already
enabled). Then edit the BOOTP configuration file (usually /etc/bootptab) and enter the name, network type
(1 for Ethernet), Ethernet address and the IP address, subnet mask and gateway of the print server.
Unfortunately, the exact format for doing this is not standardized, so you will need to refer to your system
®
documentation to determine how to enter this information (many UNIX
examples in the bootptab file that you can use for reference). Some examples of typical /etc/bootptab
entries include: (“BRN” below is “BRW” for a wireless network.)
systems also have template
BRN310107 1 00:80:77:31:01:07 192.168.1.2
and:
BRN310107:ht=ethernet:ha=008077310107:\
ip=192.168.1.2:
Certain BOOTP host software implementations will not respond to BOOTP requests if you have not included
a download filename in the configuration file. If this is the case, simply create a null file on the host and specify
the name of this file and its path in the configuration file.
As with RARP, the print server will load its IP address from the BOOTP server when the printer is powered on.
A
80
Page 89

Appendix A
Using RARP to configure the IP address A
The Brother print server’s IP address can be configured using the Reverse ARP (RARP) facility on your host
computer. This is done by editing the /etc/ethers file (if this file does not exist, you can create it) with an
entry similar to the following: (“BRN” below is “BRW” for a wireless network.)
00:80:77:31:01:07 BRN310107
Where the first entry is the Ethernet address of the print server and the second entry is the name of the print
server (the name must be the same as the one you put in the /etc/hosts file).
If the RARP daemon is not already running, start it (depending on the system the command can be rarpd,
rarpd -a, in.rarpd -a or something else; type man rarpd or refer to your system documentation for
®
additional information). To verify that the RARP daemon is running on a Berkeley UNIX
the following command:
ps -ax | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
®
For AT&T UNIX
ps -ef | grep -v grep | grep rarpd
The Brother print server will get the IP address from the RARP daemon when the printer is powered on.
-based systems, type:
based system, type
Using APIPA to configure the IP address A
The Brother print server supports the Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) protocol. With APIPA, DHCP
clients automatically configure an IP address and subnet mask when a DHCP server is not available. The
device chooses it's own IP address in the range 169.254.1.0 through to 169.254.254.255. The subnet mask
is automatically set to 255.255.0.0 and the gateway address is set to 0.0.0.0.
By default, the APIPA protocol is enabled. If you want to disable the APIPA protocol, you can disable it using
control panel of the machine. For more information, see APIPA on page 23.
If the APIPA protocol is disabled, the default IP address of a Brother print server is 192.0.0.192. However,
you can easily change this IP address number to match with the IP address details of your network.
A
81
Page 90

Appendix A
Using ARP to configure the IP address A
If you are unable to use the BRAdmin application and your network does not use a DHCP server, you can
®
also use the ARP command. The ARP command is available on Windows
®
installed as well as UNIX
systems. To use ARP enter the following command at the command prompt:
arp -s ipaddress ethernetaddress
ping ipaddress
Where ethernetaddress is the Ethernet address (MAC address) of the print server and ipaddress is the
IP address of the print server. For example:
®
Windows
Windows
systems
®
systems require the dash “-” character between each digit of the Ethernet address.
arp -s 192.168.1.2 00-80-77-31-01-07
ping 192.168.1.2
®
UNIX
Typically, UNIX
/Linux systems
®
and Linux systems require the colon “:” character between each digit of the Ethernet
address.
systems that have TCP/IP
arp -s 192.168.1.2 00:80:77:31:01:07
ping 192.168.1.2
Note
You must be on the same Ethernet segment (that is, there cannot be a router between the print server and
operating system) to use the arp -s command.
If there is a router, you may use BOOTP or other methods described in this chapter to enter the IP
address.If your administrator has configured the system to deliver IP addresses using BOOTP, DHCP or
RARP your Brother print server can receive an IP address from any one of these IP address allocation
systems. In which case, you will not need to use the ARP command. The ARP command only works once.
For security reasons, once you have successfully configured the IP address of a Brother print server using
the ARP command, you cannot use the ARP command again to change the address. The print server will
ignore any attempts to do this. If you wish to change the IP address again, use a web browser, TELNET
(using the SET IP ADDRESS command) or factory reset the print server (which will then allow you to use
the ARP command again).
A
82
Page 91

Appendix A
Using the TELNET console to configure the IP address A
You can also use the TELNET command to change the IP address.
TELNET is an effective method to change the machine’s IP address. But a valid IP address must already be
programmed into print server.
Type TELNET ipaddress at the command prompt of the system prompt, where ipaddress is the IP address of
the print server. When you are connected, push the Return or Enter key to get the “#” prompt. Enter the
password “access”.
You will be prompted for a user name. Enter anything in response to this prompt.
You will then get the Local> prompt. Type SET IP ADDRESS ipaddress, where ipaddress is the
desired IP address you wish to assign to the print server (check with your network administrator for the IP
address to use). For example:
Local> SET IP ADDRESS 192.168.1.3
You will now need to set the subnet mask by typing SET IP SUBNET subnet mask, where subnet mask
is the desired subnet mask you wish to assign to the print server (check with your network administrator for
the subnet mask to use). For example:
Local> SET IP SUBNET 255.255.255.0
If you do not have any subnets, use one of the following default subnet masks:
255.0.0.0 for class A networks
255.255.0.0 for class B networks
255.255.255.0 for class C networks
The leftmost group of digits in your IP address can identify the type of network you have. The value of this
group ranges from 1 through 127 for Class A networks (e.g., 13.27.7.1), 128 through 191 for Class B networks
(e.g.,128.10.1.30), and 192 through 255 for Class C networks (e.g., 192.168.1.4).
If you have a gateway (router), enter its address with the command SET IP ROUTER routeraddress,
where routeraddress is the desired IP address of the gateway you wish to assign to the print server. For
example:
Local> SET IP ROUTER 192.168.1.4
Type SET IP METHOD STATIC to set the method of IP access configuration to static.
To verify that you have entered the IP information correctly, type SHOW IP.
Type EXIT or Ctrl-D (i.e., hold down the control key and type “D”) to end the remote console session.
A
83
Page 92

Appendix A
Installation when using a Network Print Queue or Share (printer driver only) A
Note
• You must configure the IP address on your machine before you proceed with this section. If you have not
configured the IP address, see Configuring your network printer on page 8 first.
• Verify the host computer and print server are either on the same subnet, or that the router is properly
configured to pass data between the two devices.
• Before installation, if you are using personal Firewall software (e.g. Windows Firewall), disable it. Once
you are sure that you can print, re-start your personal Firewall software.
a Start the CD-ROM installation menu program according to the Quick Setup Guide.
b Select the model name and your language (if necessary), and then click
Install Other Drivers or Utilities.
c Click Printer Driver (Only, for Network).
d Click Next in response to the Welcome message. Follow the on-screen instructions.
e Select Standard Installation and click Next.
f Select Network Shared Printer, and then click Next.
g Select your printer’s queue, and then click OK.
Note
Contact your administrator if you are not sure about the location and name of the printer in the network.
h Click Finish.
A
84
Page 93

B
Appendix B B
Print server specifications B
Ethernet wired network B
Model name NC-6500h
Operating system
support
Protocol support TCP/IP: IPv4 ARP, RARP, BOOTP, DHCP, APIPA (Auto IP),WINS,
Windows
Vista
2003 x64 Edition (print only via network)
Mac OS
TCP/IP: IPv6 (Turned off as default) NDP, RA, DNS, mDNS, LPR/LPD,
®
2000, Windows® XP, Windows® XP Professional x64 Edition, Windows
®
, Windows Server® 2003 (print only via network) and Windows Server®
®
X 10.2.4 or greater
NetBIOS name resolution, DNS resolver, mDNS, LPR/LPD,
Custom Raw Port/Port9100, IPP, IPPS, FTP server, SSL/TLS,
POP before SMTP, SMTP-AUTH, TELNET, SNMPv1,
HTTP/HTTPS server, TFTP client and server, SMTP client,
APOP, LLTD responder, Raw Port (PC scanner), FTP client
Custom Raw Port/Port9100, IPP, IPPS, FTP server, SSL/TLS,
POP before SMTP, SMTP-AUTH, TELNET, SNMPv1,
HTTP/HTTPS server, TFTP client and server, SMTP client,
APOP, LLTD responder, Raw Port (PC scanner)
Network type 10/100BASE-TX Ethernet network
Network printing
Network PC Fax
Network scanning
Windows
Server
Macintosh
Windows
Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater (Send only)
Windows
Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater
®
2000/XP/XP Professional x64 Edition, Windows Vista® and Windows
®
2003 TCP/IP printing
®
printing (Mac OS® X 10.2.4 or greater supporting TCP/IP)
®
2000/XP/XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Vista
®
2000/XP/XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Vista
B
®
®
85
Page 94

Appendix B
Windows® Computer
requirements
(for drivers, BRAdmin
Light and Peer-to-Peer
software)
Processor
Minimum Speed
Minimum RAM
Recommended
RAM
Intel® Pentium® or equivalent for Windows®2000/XP
®
Intel
Pentium® 4 or equivalent 64-bit supported CPU for
Windows Vista
®
Intel® Pentium® III or equivalent for Windows Server® 2003
AMD Opteron™, AMD Athlon™64, Intel
®
EM64T, Intel
Windows
Pentium® 4 with Intel® EM64T or equivalent for
®
XP Professional x64 Edition and Windows Server®
®
Xeon® with Intel®
2003 x64 Edition
®
64 MB for Windows
128 MB for Windows
256 MB for Windows
®
Server
2003 and Windows Server® 2003 x64 Edition
512 MB for Windows Vista
256 MB for Windows
512 MB for Windows
®
Server
2003 and Windows Server® 2003 x64 Edition
1 GB for Windows Vista
2000
®
XP
®
XP Professional x64 Edition, Windows
®
®
2000/XP
®
XP Professional x64 Edition, Windows
®
86
B
Page 95

Appendix B
Macintosh® Computer
Computer
requirements
Processor
Minimum Speed
Minimum RAM
Recommended
RAM
Management utilities BRAdmin
1
Light
BRAdmin
Professional
Web BRAdmin
Ethernet ready Power Macintosh
®
PowerPC G4/G5, Intel
Core™ Solo/Duo
®
Processor PowerPC G3 350MHz
®
128MB for Mac OS
160MB for Mac OS
X 10.2.4 or greater
®
X 10.2.4 or greater
Windows® 2000, Windows® XP, Windows® XP Professional
®
x64 Edition, Windows Vista
®
Windows Server
Mac OS
®
X 10.2.4 or greater
2003 x64Edition
, Windows Server® 2003 and
Windows® 2000, Windows® XP, Windows® XP Professional
1
x64 Edition, Windows Vista
Windows Server
1
Windows® 2000 Professional
Windows Server
Windows
®
®
®
XP Professional (IIS)
2003 x64Edition
2003 Advanced Server
®
, Windows Server® 2003 and
1
BRAdmin Professional and Web BRAdmin are available as a download from http://solutions.brother.com/.
B
87
Page 96

Appendix B
Function table and default factory settings B
Main Menu Submenu Menu Selections Options Page
4.LAN
(DCP-9040CN
and
DCP-9042CDN)
5.LAN
(DCP-9045CDN)
7.LAN
(MFC-9440CN
and
MFC-9450CDN)
1.TCP/IP 1.BOOT Method Auto*
Static
RARP
BOOTP
DHCP
(If you choose Auto, RARP, BOOTP or DHCP, you
will be asked to enter how many times the machine
tries to obtain the IP address.)
2.IP Address [000-255].[000-255].[000-255].
[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
3.Subnet Mask [000-255].[000-255].[000-255].
[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
4.Gateway [000-255].[000-255].[000-255].
[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
5.Node Name BRNXXXXXX
1
1
1
16
19
19
20
20
(up to 15 characters)
6.WINS Config Auto*
Static
7.WINS Server Primary [000-255].[000-255].
[000-255].[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
Secondary [000-255].[000-255].
[000-255].[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
8.DNS Server Primary [000-255].[000-255].
[000-255].[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
Secondary [000-255].[000-255].
[000-255].[000-255]
[000].[000].[000].[000]*
9.APIPA On*
Off
21
B
21
1
1
22
1
1
23
88
Page 97

Appendix B
Main Menu Submenu Menu Selections Options Page
4.LAN
1.TCP/IP
0.IPv6 On
23
(DCP-9040CN
and
DCP-9042CDN)
5.LAN
(DCP-9045CDN)
(continued)
2.Ethernet Auto*
Off*
100B-FD
100B-HD
10B-FD
7.LAN
10B-HD
(MFC-9440CN
and
MFC-9450CDN)
(continued)
3.Scan to FTP Color 150 dpi*
Color 300 dpi
Color 600 dpi
B&W 200 dpi
B&W 200x100 dpi
0.Factory
Reset
1.Reset 1.Yes
2.No
2.Exit —
The factory settings are shown in Bold with an asterisk.
1
On connection to the network, the machine will automatically set the IP address and Subnet Mask to value appropriate for your network.
24
24
26
89
B
Page 98

Appendix B
Entering Text B
When setting certain menu selections, such as the Station ID, you will need to type text characters. The dial
pad keys have letters printed on them. The keys: 0, # and l do not have printed letters because they are used
for special characters.
Press the appropriate dial pad key the required number of times to access the characters below:
Press Key one time two times three times four times
2ABC2
3DEF3
4GH I 4
5JKL5
6MNO6
7PQRS
8TUV8
9WXYZ
Inserting spaces
To enter a space in a fax number, press c once between numbers. To enter a space in a name, press c twice
between characters.
Making corrections B
If you entered a letter incorrectly and want to change it, press d to move the cursor under the incorrect
character, and then press Clear/Back.
Repeating letters B
To enter a character on the same key as the previous character, press c to move the cursor right before
pressing the key again.
B
B
90
Page 99

Appendix B
Special characters and symbols B
Press l, # or 0, and then press d or c to move the cursor to the symbol or character you want.
Press OK to choose it. The symbols and characters below will appear depending on your menu selection.
Press l for
Press # for : ; < = > ? @ [ ] ^ _ ¥ ˜ ‘ | { }
Press 0 for (For MFC-9440CN, MFC-9450CDN, DCP-9040CN and DCP-9042CDN)
(space) ! “ # $ % & ’ ( )
É À È Ê Î Ç Ë Ö 0 (For US and Canada)
Ä Ë Ö Ü À Ç È É 0 (For UK)
(For DCP-9045CDN)
Á À Ã Â Ç É È Ê Ë Í Î Ï Ó Õ Ô Ö Œ Ú Ù Û 0 (For US)
À Â Ç É È Ê Ë Î Ï Ô Œ Ú Ù Û 0 (For Canada)
Ä Ë Ö Ü À Ç È É 0 (For UK)
l + , - . / m
91
B
Page 100

C
Appendix C C
Open Source Licensing Remarks C
OpenSSL statements C
OpenSSL License C
Copyright © 1998-2007 The OpenSSL Project. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that
the following conditions are met:
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the
following disclaimer.
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the
following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
3. All advertising materials mentioning features or use of this software must display the following
acknowledgment: "This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the
OpenSSL Toolkit. (http://www.openssl.org/)"
4. The names "OpenSSL Toolkit" and "OpenSSL Project" must not be used to endorse or promote products
derived from this software without prior written permission. For written permission, please contact opensslcore@openssl.org.
5. Products derived from this software may not be called "OpenSSL" nor may "OpenSSL" appear in their
names without prior written permission of the OpenSSL Project.
6. Redistributions of any form whatsoever must retain the following acknowledgment: "This product includes
software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit. (http://www.openssl.org/)"
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE OpenSSL PROJECT “AS IS” AND ANY EXPRESSED OR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE OpenSSL PROJECT OR ITS CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR
PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGE.
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com). This product
includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
C
92
 Loading...
Loading...