Page 1

LIGHTBUS
Bus Terminal Controller
BC2000
Technical Documentation
Version 1.1
2006-11-06
Page 2

Please note the following
Target group
This description is only intended for the use of trained specialists in control
and automation engineering who are familiar with the applicable national
standards.
Safety requirements
The responsible staff must ensure that the application or use of the
products described satisfy all the requirements for safety, including all the
relevant laws, regulations, guidelines and standards.
The documentation has been prepared with care. The products described
are, however, constantly under development. For that reason the
documentation is not in every case checked for consistency with
performance data, standards or other characteristics, and does not
represent an assurance of characteristics in the sense of § 459, Para. 2 of
the German Civil Code. In the event that it contains technical or editorial
errors, we retain the right to make alterations at any time and without
warning. No claims for the modification of products that have already been
supplied may be made on the basis of the data, diagrams and descriptions
in this documentation.
©
This manual is copyrighted. Any reproduction or third party use of this
protected publication, whether in whole or in part, without the written
permission of Elektro Beckhoff GmbH, is forbidden.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1. Foreword 3
Notes on the documentation 3
Liability Conditions 3
Delivery conditions 3
Copyright 3
Safety Instructions 4
State at Delivery 4
Description of safety symbols 4
2. Basic Principles 5
Description of the BC2000 5
The Beckhoff Bus Terminal System 5
The interfaces 7
Electrical power supply 7
Power contacts feeding points 7
Power contacts 8
Fieldbus connection 8
Configuration and Programming Interface 8
Terminal Bus Contacts 8
Galvanic isolation 8
Operating Modes of the Bus Terminal Controller 9
Mechanical structure 10
Preparing for Operation and Diagnostics 12
3. The Beckhoff BC2000 Lightbus Coupler 15
Introduction to the Beckhoff Lightbus System 15
4. Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager 17
Basic Settings 17
PLC Cycle Time 18
PLC Variables 18
Remanent Variables 19
Terminal Bus Update 19
Program Download via the Fibre Optic Ring 19
Program Download via the RS232 Interface 20
ADS Functions 20
PLC Runtime System 21
Registers of the Bus Terminal Controller 22
Diagnostics in the BC2000 22
5. Settings in TwinCAT PLC 23
Terminal Bus Reset 23
Coupler Reset 23
Manufacturer’s Configuration 23
Cycle Time Measurement 23
Boot Project 23
Coupler Options 24
6. Appendix 25
Absolute Addressing in the BC2000 25
7. Index 26
8. Support and Service 27
Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives 27
Beckhoff Headquarters 27
BC2000 2
Page 4

Foreword
Foreword
Notes on the documentation
This description is only intended for the use of trained specialists in control and automation engineering
who are familiar with the applicable national standards. It is essential that the following notes and
explanations are followed when installing and commissioning these components.
Liability Conditions
The responsible staff must ensure that the application or use of the products described satisfy all the
requirements for safety, including all the relevant laws, regulations, guidelines and standards.
The documentation has been prepared with care. The products described are, however, constantly under
development. For that reason the documentation is not in every case checked for consistency with
performance data, standards or other characteristics. None of the statements of this manual represents a
guarantee (Garantie) in the meaning of § 443 BGB of the German Civil Code or a statement about the
contractually expected fitness for a particular purpose in the meaning of § 434 par. 1 sentence 1 BGB. In
the event that it contains technical or editorial errors, we retain the right to make alterations at any time
and without warning. No claims for the modification of products that have already been supplied may be
made on the basis of the data, diagrams and descriptions in this documentation.
Delivery conditions
In addition, the general delivery conditions of the company Beckhoff Automation GmbH apply.
Copyright
©
This documentation is copyrighted. Any reproduction or third party use of this publication, whether in
whole or in part, without the written permission of Beckhoff Automation GmbH, is forbidden.
3 BC2000
Page 5

Foreword
i
Safety Instructions
State at Delivery
All the components are supplied in particular hardware and software configurations appropriate for the
application. Modifications to hardware or software configurations other than those described in the
documentation are not permitted, and nullify the liability of Beckhoff Automation GmbH.
Description of safety symbols
The following safety symbols are used in this documentation. They are intended to alert the reader to the
associated safety instructions..
This symbol is intended to highlight risks for the life or health of personnel.
Danger
This symbol is intended to highlight risks for equipment, materials or the
Attention
environment.
This symbol indicates information that contributes to better understanding.
Note
BC2000 4
Page 6

Basic Principles
Up to 64 bus terminals
each having 2 I/O channels
for each signal form
De-centralised wiring of
each I/O level
IPC as controller
Standard C - rail assembly
Modularity
Description of the BC2000
The BC2000 is a slave with PLC functionality. It has a fieldbus interface,
the Lightbus. The bus terminal controller is programmable, and is
programmed using the TwinCAT software in the IEC61131-3 programming
languages. Applied in combination with the C1220 or FC200x Lightbus PC
card and the TwinCAT PLC software, the BC2000 permits decentralisation
of the control tasks. This is a way of removing parts of the application out
of the central control system to relieve the CPU and the field bus.
Distributed counters, controllers and switches are typical applications for
the bus terminal controller. The reaction times are dependent upon the bus
communication and the overall control system, and maintenance of
function is possible even when the bus or control system fails (e.g. an
orderly transfer of the processes into a secure condition).
The Beckhoff Bus Terminal System
The bus terminal system is the universal interface between a fieldbus
system and the sensor / actuator level. A unit consists of a bus terminal
controller as the head station, and up to 64 electronic series terminals, the
last one being an end terminal. For each technical signal form, terminals
are available each having two I/O channels, and these can be mixed in any
order. All the terminal types have the same mechanical construction, so
that difficulties of planning and design are minimised. The height and depth
match the dimensions of compact terminal boxes.
Fieldbus technology allows more compact forms of controller to be used.
The I/O level does not have to be brought to the controller. The sensors
and actuators can be wired de-centrally, using minimum cable lengths. The
controller can be installed at any location within the plant. The use of an
industry PC as the controller means that the operating and observing
element can be implemented in the controller’s hardware. The controller
can therefore be located at an operating panel, in a control room, or at
some similar place. The bus terminals form the de-centralised input/output
level of the controller in the switching cabinet and the subsidiary terminal
boxes. The power sector of the plant is also controlled over the bus system
in addition to the sensor/actuator level. The bus terminal replaces the
conventional series terminal as the wiring level in the switching cabinet.
The switching cabinet can have smaller dimensions.
The Beckhoff bus terminal system unites the advantages of a bus system
with the possibilities of the compact series terminal. Bus terminals can be
driven within all the usual bus systems, thus reducing the controller parts
count. The bus terminals then behave like conventional connections for
that bus system. All the performance features of the particular bus system
are supported.
The easy, space-saving assembly on a standard C-rail, and the direct
wiring of actuators and sensors without cross-connections between the
terminals standardises the installation. The consistent labelling scheme
also contributes.
The small physical size and the great flexibility of the bus terminal system
allows it to be used wherever a series terminal is also used. Every type of
connection, such as analogue, digital, serial or the direct connection of
sensors can be implemented.
The modular assembly of the terminal strip with bus terminals of various
Basic Principles
5 BC2000
Page 7
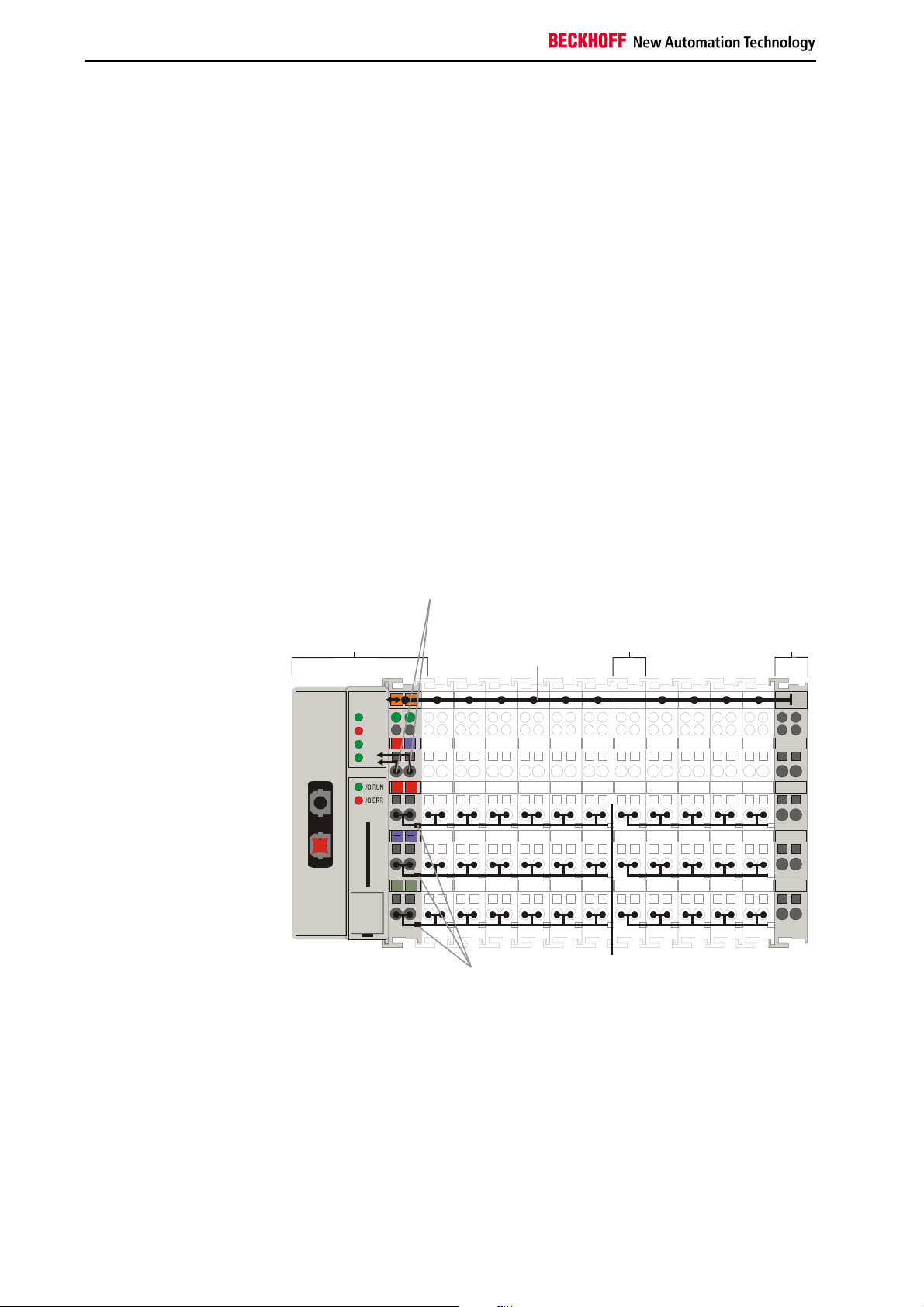
Basic Principles
End terminal
isolation
Potential
contacts
Supply voltage
II/O-Lightbus
Beckhoff Lightbus
Display of the channel state
K bus
End terminal
Potential feed terminals for
galvanically isolated groups
The principle of the
bus terminal
functions limits the number of unused channels to a maximum of one per
function. The presence of two channels in one terminal is the optimum
compromise of unused channels and the cost of each channel. The
possibility of galvanic isolation through potential feed terminals also helps
to keep the number of unused channels low.
The integrated LEDs show the state of the channel at a location close to
the sensors and actuators.
The terminal bus (known as the K bus) is the data path within a terminal
strip. The terminal bus is led through from the bus terminal controller
through all the terminals via six contacts on the terminals‘ side walls. The
end terminal terminates the terminal bus. The user does not have to learn
anything about the function of the terminal bus or about the internal
workings of the terminals and the bus terminal controller. Many software
tools that can be supplied make project planning, configuration and
operation easy.
The operating voltage is passed on to following terminals via three power
contacts. You can divide the terminal strip into arbitrary galvanically
isolated groups by means of potential feed terminals. The feed terminals
play no part in the control of the terminals, and can be inserted at any
points within the terminal strip.
Up to 64 terminals can be used within one terminal strip;
Potential feed terminals and end terminals are included in this count.
bus coupler
BC2000
for the
bus coupler
feed
terminal
Terminal bus
Additional characteristics of
the bus terminal controllers
0201
CYC
ERR
24V
0V
WD
PLC
+ +
BECKHOFF
BC2000
PE PE
Power
Galvanic
The bus terminal controller (BC) differs from the bus coupler (BK) in that in
addition to operating the terminal bus, a PLC task runs in the BC2000.
Unlike bus couplers, the signals from the terminals are processed by the
PLC task, while the fieldbus carries the in- and outputs of the PLC task.
It is also possible to partition the terminals in such a way that some of the
terminals are processed by the PLC task while others are passed over the
fieldbus to a master.
BC2000 6
Page 8
02
01
+
+
PE
PE
B
C
K
H
O
24V
0V
00
X0
CYC
ERR
WD
II/O-Lightbus
Power LEDs
Bus coupler / power contacts
Terminal bus (K bus)
II/O-Lightbus
IN
OUT
Configuration
and programming
interface
Bus coupler power supply
24 V DC / GND
Power contacts
feeding points
Power contacts
WD
PLC
Bus terminal controllers for
various fieldbus systems
The Beckhoff BC2000
Lightbus coupler
Various bus terminal controllers can be used to couple the electronic
terminal strip quickly and easily to different fieldbus systems. It is also
possible to convert to another fieldbus system at a later time. The bus
terminal controller performs all the monitoring and control tasks that are
necessary for operation of the connected bus terminals. The operation and
configuration of the bus terminals is carried out exclusively by the bus
terminal controller. Nevertheless, the parameters that have been set are
stored in each bus terminal, and are retained in the event of voltage dropout. Fieldbus, terminal bus and I/O level are galvanically isolated.
The interfaces
A bus terminal controller has six different methods of connection. These
interfaces are designed as plug connectors and as spring-loaded terminals.
Basic Principles
24 V DC to the topmost
terminals “24 V” and “0 V”
Bottom 3 terminal pairs for
feed
Maximum 24 V
Maximum 10 A
Electrical power supply
The bus terminal controllers require a 24 V DC supply for their operation.
The connection is made by means of the upper spring-loaded terminals
labelled “24 V” and “0 V”. The supply voltage feeds the bus terminal
controller electronics and, over the terminal bus, the bus terminals. The
power supply for the bus terminal controller electronics and that of the
terminal bus are electrically separated from the potential of the field level.
Power contacts feeding points
The bottom six connections with spring-loaded terminals can be used to
feed the supply for the peripherals. The spring-loaded terminals are joined
in pairs to a power contact. The feed for the power contacts has no
connection to the voltage supply for the bus terminal controller. The design
of the feed permits voltages of up to 24 V. The assignment in pairs and the
electrical connection between feed terminal contacts allows the connection
wires to be looped through to various terminal points. The current drawn
from the power contacts must not exceed 10 A for long periods. The
current rating between two spring-loaded terminals is identical to that of the
connecting wires.
7 BC2000
Page 9

Basic Principles
Spring contacts on the side
Beckhoff Lightbus
Fibre optic ring
Beckhoff Z1000 connector
Serial interface under the
front cover
6 contacts on the side
3 potential groups:
Field bus
Terminal bus (K bus)
Peripheral level
Power contacts
On the right hand face of the bus terminal controller there are three spring
contacts for the power contact connections. The spring contacts are hidden
in slots so that they can not be accidentally touched. By attaching a bus
terminal the blade contacts on the left hand side of the bus terminal are
connected to the spring contacts. The tongue and groove guides on the top
and bottom of the bus terminal controllers and of the bus terminals
guarantees that the power contacts mate securely.
Fieldbus connection
There is a recessed front face on the left hand side. The typical Beckhoff
Lightbus connector can be inserted here. The Beckhoff Lightbus consists
of an optical fibre ring into which the bus terminal controller is inserted.
Here the plug out of which red light shines when the Beckhoff Lightbus is
switched on is inserted into the upper socket. On the figure this is labelled
with „IN“. Optical fibre connectors of type Beckhoff Z1000 are required for
the connection.
Configuration and Programming Interface
The bus terminal controllers have an RS232 interface at the bottom of the
front face. The miniature connector can be joined to a PC with the aid of a
connecting cable and the KS2000 configuration software. The interface
permits the bus terminals to be configured, for example adjusting the
amplification factors of the analogue channels. The interface can also be
used to change the assignments of the bus terminal data to the process
image in the bus terminal controller. The functionality of the configuration
interface can also be reached via the fieldbus using string communication
facility.
This interface is also used for programming the BC2000. The cable for the
interface is supplied along with TwinCAT BC.
Terminal Bus Contacts
In order to connect the bus terminal controller to the bus terminals, the bus
terminal controller has gold contacts on the right hand side. When the bus
terminals are pushed together the gold contacts automatically make the
connection between the bus terminals. The voltage supply to the terminal
bus electronics in the bus terminals and the data exchange between the
bus terminal controller and the bus terminals is carried out by the terminal
bus. A part of the data exchange takes place via a ring structure within the
terminal bus. Opening the terminal bus, e.g. by pulling out one of the bus
terminals, opens the ring. Data exchange is no longer possible. Special
mechanisms nevertheless allow the bus terminal controller to identify the
location of the interruption and to report it.
Galvanic isolation
The bus terminal controllers operate by means of three independent
potential groups. The supply voltage feeds the terminal bus electronics in
the bus terminal controller and the terminal bus itself, which is electrically
separate. The supply voltage is also used to generate the operating
voltage for the fieldbus.
Remark: All the bus terminals are galvanically isolated from the terminal
bus. The terminal bus is thus galvanically isolated from everything else.
BC2000 8
Page 10

24VDC
Bus coupler
Bus terminals
Operating Modes of the Bus Terminal
Power On self test
Bus terminal test
Structure list
OK
Structure of the potential
levels in the bus terminal
system
Field bus
Controller
Start-up behaviour of the
bus terminal controller
Immediately after being switched on, the bus terminal controller checks, in
the course of a “self test”, all the functions of its components and the
communication of the terminal bus. The red I/O LED blinks while this is
happening. After completion of the self-test, the bus terminal controller
starts to test the attached bus terminals (in a „bus terminal test“), and reads
in the configuration. The bus terminal configuration is used to generate an
internal structure list, which is not accessible from outside. In case of an
error, the bus terminal controller enters the „STOP“ state. Once the start-up
has completed without error, the bus terminal controller enters the "fieldbus
start" state.
PLC Start /
Communication start
Basic Principles
Terminal bus (K bus)
Peripheral level
Stop
9 BC2000
Page 11

Basic Principles
1
0
0
49
12
02
01
+
+
PE
PE
00
X0
00
.1
PE
PE
PLC
The bus terminal controller can be made to enter the normal operating
state by switching it on again once the fault has been rectified.
Mechanical structure
The system of the Beckhoff bus terminals is characterised by low physical
volume and high modularity. When planning a project it must be assumed
that at least one bus terminal controller and a number of bus terminals will
be used. The mechanical dimensions of the bus terminal controllers are
independent of the fieldbus system. If optical fibre cable with Z1000 plugs
is used, the clearances of the bus terminal controller are not exceeded.
Bus terminal controller
dimensions
II/O-Lightbus
CYC
ERR
WD
24V
E0
0V
.0
Assembly and connection
+ +
94
BECKHOFF
BC2000
The total width of the unit is composed of the width of the bus terminal
controller with the KL9010 bus end terminal plus the width of the bus
terminals being used. Depending on function, the bus terminals are 12 or
24 mm wide. The front wiring increases the total height of 68 mm by about
5 to 10 mm, depending on the wire thickness.
The bus terminal controller and all the bus terminals can be clipped by light
pressure onto a 35 mm C-mounting rail. A locking mechanism prevents the
individual housings from being pulled off again. For removal from the
mounting rail the orange coloured tension strap releases the latching
mechanism, allowing the housing to be pulled off the rail without any force.
Up to 64 bus terminals can be attached to the bus terminal controller on
the right hand side. When plugging the components together, be sure to
assemble the housings with groove and tongue against each other. A
properly working connection can not be made by pushing the housings
together on the mounting rail. When correctly assembled, no significant
gap can be seen between the attached housings.
The right hand part of the bus terminal controller can be compared to a bus
terminal. Eight connections on the top permit connection with solid or fine
wires. The connection is implemented with the aid of a spring device. The
spring-loaded terminal is opened with a screwdriver or rod, by exerting
gentle pressure in the opening above the terminal. The wire can be
BC2000 10
Page 12

Basic Principles
Insulation testing
PE power contacts
inserted into the terminal without any force. The terminal closes
automatically when the pressure is released, holding the wire securely and
permanently.
The connection between the bus terminal controller and the bus terminals
is automatically realised by pushing the components together. The transfer
of the data and the supply voltage for the intelligent electronics in the bus
terminals is performed by the terminal bus. The supply of the field
electronics is performed through the power contacts. Plugging together the
power contacts creates a supply rail. Since some bus terminals (e.g.
analogue bus terminals or 4-channel digital bus terminals) are not looped
through these power contacts (or not completely) the bus terminal contact
assignments must be considered. The potential feed terminals interrupt the
power contacts, and represent the start of a new supply rail. The bus
terminal controller can also be made use of to feed the power contacts.
The power contact labelled “PE” can be used as a protective earth. For
safety reasons this contact mates first when plugging together, and can
ground short-circuit currents of up to 125 A. It should be noted that, for
reasons of electromagnetic compatibility, the PE contacts are
capacitatively coupled to the mounting rail. This can both lead to
misleading results and to damaging the terminal during insulation testing
(e.g. breakdown of the insulation from a 230 V power consuming device to
the PE conductor). The PE conductor to the bus terminal controller must be
disconnected for the insulation testing. In order to uncouple further feed
locations for the purposes of testing, the feed terminals can be pulled at
least 10 mm out from the connected group of other terminals. In that case,
the PE conductors do not have to be disconnected.
The “PE” power contact must not be used for other potentials.
Technical data BC 2000
Number of bus terminals
Digital peripheral signals
Analogue peripheral signals
Peripheral bytes
Fieldbus medium
Plug connector
Baud rate
Electrical power supply
Input current
Power-on surge
Terminal bus output current
Voltage of the power
contact
Power contacts current
drawn
Voltage stability
Typical weight
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Relative humidity
Vibration/shock stability
EMC immunity, burst / ESD
Installation location
Protection class
64
256 inputs and outputs
128 inputs and outputs
512 inputs and 512 outputs
Z1100 optical fibre
Z1000 for Z1100
2.5 Mbaud
24 V (- 15% / +20%) EN 61131
70 mA + (total terminal bus current)/4
500 mA max.
2.5 x steady operating current
1750 mA max.
24 V DC / AC
10 A
500 Veff (power contact / supply voltage)
170 g
0°C ... +55°C
-25°C ... +85°C
95% without dew formation
according to IEC 68-2-6 / IEC 68-2-27
according to EN 61000-4-4 / EN 61000-4-2, limit values in accordance with
EN 50082-2
arbitrary
IP20
11 BC2000
Page 13

Basic Principles
PLC data
Programmability
Program memory
Data memory
Remanent flags
Runtime system
PLC cycle time
Programming languages
BC 2000
via the programming interface (TwinCAT BC/TwinCAT)
or via optical fibre ring (TwinCAT)
32 kbytes / 96 kbytes
32 kbytes / 64 kbytes
512 bytes
1 PLC task
approx. 3 ms for 1000 instructions (including terminal bus I/O cycle)
IL, LD, FBD, SFC, ST
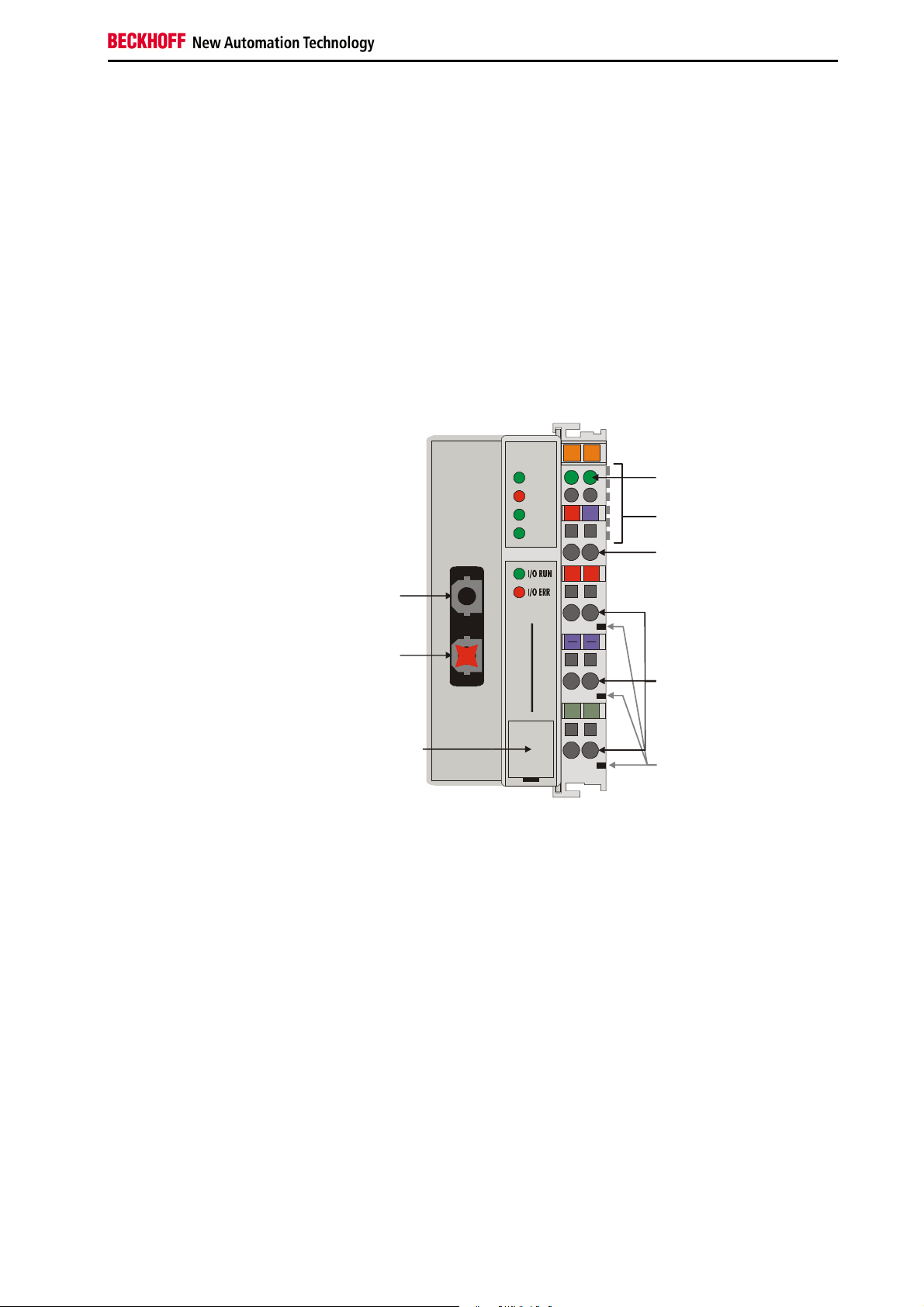
The diagnostic LEDs
Local errors
Blink code
Preparing for Operation and Diagnostics
After switching on, the bus terminal controller immediately checks the
connected configuration. Error-free start-up is signalled by extinction of the
red LED “I/O ERR“. If the “I/O ERR” LED blinks, an error in the area of the
terminals is indicated. The error code can be determined from the
frequency and number of blinks. This permits rapid rectification of the error.
There is a detailed description in the chapter on „The Diagnostic LEDs“.
The bus terminal controller has two groups of LEDs for the display of
status. The upper group with four LEDs indicates the status of the
respective field bus. The significance of the “field bus status LEDs“ is
explained in the next sections of this manual - it conforms to conventional
field bus displays.
On the upper right hand side of the bus terminal controllers are two more
green LEDs that indicate the supply voltage. The left hand LED indicates
the 24 V supply of the bus terminal controller. The right hand LED signals
the supply to the power contacts.
Two LEDs, the “I/O” LEDs, in the area below the field bus status LEDs
referred to above, serve to indicate the operating status of the bus
terminals and the connections to these terminals. The green LED lights up
in order to indicate fault-free operation. „Fault-free“ means that the
communication with the fieldbus system is also running. The red LED
flashes to indicate an error. The red LED blinks with two different
frequencies. The error is encoded in the blinks as follows:
Fast blinking
First slow sequence
Second slow sequence
Start of the error code
Error type
Error location
Start of the error code Error type Error location
BC2000 12
Page 14

Error code Error
argument
Persistent,
continuous
blinking
1 pulse
2 pulses
3 pulses
4 pulses
5 pulses
9 pulses
14 pulses
15 pulses
16 pulses
EMC problems - Check power supply for overvoltage or
0
1
2
0
n (n > 0)
0 Terminal bus command error - No terminal connected; attach terminals.
0
n
n Terminal bus error with register
0
n
n Terminal n has the wrong format - Start the coupler again, and if the error
n Number of terminals is no longer
n Length of the terminal bus data is no
Description Remedy
EEPROM checksum error
Inline code buffer overflow
Unknown data type
Programmed configuration
Incorrect table entry / bus coupler
Incorrect table comparison
(terminal n)
Terminal bus data error
Break behind terminal n
communication with terminal n
Checksum error in program flash
memory
Terminal n is not consistent with the
configuration that existed at boot
image entry
correct
longer correct
Error location
The number of pulses indicates the position of the last bus terminal before
the fault. Passive bus terminals, such as a power feed terminal, are not
included in the count.
When the error is rectified, the bus terminal controller does not stop
flashing. Operating state of the bus terminal controller: „Stop“. The bus
terminal controller can only be re-started by switching off the supply
voltage.
Fieldbus errors
The fieldbus status LEDs indicate the operational state of the fieldbus. The
functions of the Beckhoff Lightbus are indicated by the „CYC“, „ERR“ and
„WD“ LEDs.
The meaning of the first three LEDs is:
CYC the LED lights up for the duration of each telegram
ERR is switched on by a faulty telegram, and switched off again by
three correct telegrams
WD watchdog, lights for 100 ms after the bus terminal controller has
been addressed
Basic Principles
undervoltage peaks
- Implement EMC measures
- If a terminal bus error is present, it can be
localised by a restart of the coupler (by
switching it off and then on again)
- Set manufacturer’s setting with the KS2000
- Connect fewer terminals; too many entries in
the table for the programmed configuration
- Software update required for the coupler
- Check programmed configuration for
correctness
- Incorrect table entry / bus coupler
- One of the terminals is defective; halve the
number of terminals attached and check
whether the error is still present with the
remaining terminals. Repeat until the
defective terminal is located.
- Check whether the n+1 terminal is correctly
connected; replace if necessary.
– Check whether the end terminal 9010 is
connected.
Replace terminal n.
- Set manufacturer’s setting with the KS2000
- Set manufacturer's setting with the KS2000,
which will delete the boot project
occurs again then exchange the terminal
- Start the coupler again, and if the error
occurs again after this, use the KS2000
software to set manufacturer’s settings
- Start the coupler again, and if the error
occurs again after this, use the KS2000
software to set manufacturer’s settings
13 BC2000
Page 15

Basic Principles
PLC
PLC LED
If the PLC LED lights, the program has started on the BC2000. The LED
flashes while a boot project is being created.
Diagnostic LEDs on the
BC2000
CYC
ERR
WD
CYC ERR WD Meaning Remedy
lit
lit
lit
blinking
off
off
off
off lit Telegrams are passing cyclically along
off lit I/O-RUN flashes The PLC cycle time that has been
off off The ring is functioning, but the bus
off off The controller only occasionally
lit off (Physical) bus fault, faulty telegrams are
blinking off Occasional CRC error (green I/O LED
off off No operating voltage, serious fault, no
The bus terminal controller interrogates the configuration of the bus
terminals after it has been switched on, then performs exchange of data
with the terminals. This means that the red I/O LED goes out after a faultfree start-up, and the green I/O LED lights. The green I/O-LED lights with
the PLC timing on the bus terminal controller. If no program is running on
the BC2000, the pre-set cycle time for triggering the terminal bus is used.
Everything is satisfactory
the ring
Inputs are read and outputs are set.
set is too long > 100 ms
Re-examine the control software
terminal controller is not being
addressed
accesses the bus. The outputs drop
away.
circulating in the ring, e.g. optical fibre
damaged, previous module faulty, plug
not properly inserted
lights)
Inputs are read; outputs are not
updated;
function
or the assignment list
Re-examine the control software
Check:
- whether the optical fibre cable is
inserted
- whether the optical fibre cable is
broken
- whether previous module is
ready for operation
Optical fibre connection damaged
- Electrical power supply
BC2000 14
Page 16

The Beckhoff BC2000 Lightbus Coupler
The Beckhoff BC2000 Lightbus Coupler
System configurations and
device types
Introduction to the Beckhoff Lightbus
System
The Beckhoff Lightbus has achieved wide acceptance in the world of
automation engineering through its speed and its compatibility across
manufacturers. The Beckhoff Lightbus was developed within a control
concept for the implementation of NC axes on the industry PC. The goal of
the project was to develop a fast, secure I/O level for the PC suitable for
industrial application. Nowadays a large number of various products are
available from independent manufacturers. The operation of different
Beckhoff Lightbus devices in one bus system is ensured by the
implementation support and the protocol ASICs from BECKHOFF.
The Beckhoff Lightbus is designed for fast data exchange on the sensor /
actuator level. Central control devices (such as, for example,
programmable logic controllers) communicate here over a fast serial
connection with distributed input and output devices. Data is exchanged
with these distributed devices cyclically, and, if necessary, with different
priorities. The central controller (master) reads the input information from
the slaves, and sends the output information to the slaves. The bus cycle
time must here be shorter than the central controller’s program cycle time,
which in many applications is less than 1 ms.
A high data throughput is not in itself sufficient for successful use of a bus
system. Ease of handling, good diagnostic facilities and secure
transmission technology are also of the utmost importance if the user’s
demands are to be satisfied. These properties are ideally combined in the
Beckhoff Lightbus.
For the transmission of 512 bits of input data and 512 bits of output data
distributed over 32 bus devices, the Beckhoff Lightbus needs approx.
0.8 ms at a transmission rate of 2.5 Mbit/s. The demand for a short system
reaction time is thus ideally satisfied.
A single master system can be implemented with the Beckhoff Lightbus. A
maximum of 254 slaves can be connected to one bus. In the BC2000 bus
terminal controller, a station address between 1 and 254 is automatically
selected during the start-up phase. The specifications for the system
configuration contain the number of stations, the assignment of the station
addresses to the I/O addresses, data consistency of the I/O data and the
format of the diagnostics messages. Every Beckhoff Lightbus system
consists of different device types
A Beckhoff Lightbus slave is a peripheral device (sensor/actuator) that
reads input information and passes output information on to the
peripherals. It is also possible to have devices that only handle either input
or output information. Typical Beckhoff Lightbus slaves are devices with
binary inputs/outputs for 24 V or 230 V, analogue inputs, analogue outputs,
counters, incremental encoders etc.. The quantity of input and output
information is device-dependent, and is limited to 32 bits of input data and
32 bits of output data for each protocol ASIC. For slaves that handle more
than 32 bits of data, such as, for instance, the BC2000, an extended
procedure is utilised. Using an addressed access procedure, reading and
writing up to 256 x 16 bits is possible. This means that a system can
handle up to 254 stations x 508 bytes (not all of the 512 bytes are available
for user data) with only one Beckhoff Lightbus system. For reasons of
expense, and for technical reasons associated with implementation, the
masters that are available nowadays work with a max. user data length of
3 kbyte (24000 inputs and outputs).
15 BC2000
Page 17

The Beckhoff BC2000 Lightbus Coupler
Master interfaces supporting the bus terminal controller are the PC cards
C1220 as from Version 4.01, and the FC200x. These cards are supported
by TwinCAT software as from version 2.6 (build 315).
Fundamental properties of
optical fibre transmission
technology
The Medium
Network topology
Medium
Number of
stations
Transmission rate
Max. bus length
Min. bending
radius
Plug connector
Ring system, active devices between the cable sections
Z1100 plastic optical fibre
Z1101 plastic optical fibre with PU cladding
Z1110 HCS – optical fibre
Z1111 HCS – optical fibre
254 stations in the ring
2.5 Mbit/s
with plastic optical fibre with HCS optical fibre
0.3 m to 45 m up to 300 m
3 cm 4 cm
Z1000 standard plug for
plastic optical fibres
Z1010 standard plug for HCS
optical fibres
BC2000 16
Page 18

Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
Basic Settings
The basic properties of the bus terminal controller are handled in the
system manager.
The terminals of the bus terminal controller can be assigned directly to the
Lightbus master or to the BC2000. Terminals that are assigned directly to
the BC2000 are displayed in the system manger with „PLC“, and are not
visible to the master. A further distinction between „Complex“ and
„Compact“ is also made in the analogue terminals.
Complex: complete representation of the analogue terminals with
control/status, 4 bytes input/output per channel
Compact: user data only, 2 bytes per channel
The terminals that are assigned to the master are invisible to the bus
terminal controller. If it is desired to make a terminal visible to both systems,
the terminal must first be assigned to the BC2000, and then the data from
the terminal are transmitted to the master via the PLC variables.
17 BC2000
The settings for the PLC in the bus terminal controller are found under the
„PLC“ tab. All the basic settings that control the properties of the PLC in the
BC2000 are handled there.
Page 19

Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
Back
-
PLC Cycle Time
Example of cycle time
optimisation
Mean cycle time
PLC Cycle Time
The PLC cycle time determines the program’s repetition frequency. This
time is not deterministic. This means that when the program in the bus
terminal controller needs more time, the PLC cycle time rises. If the
program needs less than the cycle time, it is repeated at intervals of the set
cycle time.
The processing of the Lightbus and the serial interfaces is executed in the
background time. This should be set to approx. 20 % of the PLC cycle time.
The „mean cycle time“ is measured in order to optimise the system. You will
find this item in PLC Control under Online\Coupler. About 20% – 30% is
added to this, and the result entered as the PLC cycle time. The
background time is then set to 20% of the PLC cycle time.
PLC cycle time
Mean cycle time
10 ms
ground
time
PLC cycle time = mean cycle time + 20% = 10 ms + 20% = 12 ms
Background time = PLC cycle time * 0,2 = 12 ms * 0,2 = 2,4 ms ≈ 2 ms
The measured cycle time also includes that required for the terminal bus
update. This results in a connection between the number of terminals that
are inserted and the cycle time. Before initiating the program, the bus
terminal controller executes a terminal bus update, in order to interrogate
the inputs. After the program has been executed, the BC2000 carries out
another terminal bus update, in order to write the current outputs. The
background time follows this. The cycle time can also be shortened, if the
terminal bus update is carried out simultaneously for inputs and outputs
(see Terminal Bus Update).
PLC Variables
PLC variables are variables that are situated in the BC2000 from addresses
%IB128 and %QB128. This offset can be shifted. These addresses are not
assigned to any terminal, so that signals or data can be transmitted to or
received from the master via the PLC variables.
BC2000 18
Page 20

Remanent Variables
Retained or remanent variables are data that retain their value when
voltage is not present. In PLC Control this data is placed in the allocated
flags area. Following the default setting, this means that all the variables
from %MB0 - %MB63 are RETAIN data. The maximum setting is 512 bytes.
Terminal Bus Update
Double Cycle Terminal bus inputs before the PLC cycle
Before PLC Terminal bus inputs and outputs before the PLC cycle
After PLC Terminal bus inputs and outputs after the PLC cycle
Program Download via the Fibre Optic Ring
TwinCAT offers a facility for transferring the program to the BC2000 over
the optical fibre ring. To do this, string communication and the Ams/Ads
must be activated in the system manager under the ADS/AMS tab. The
TwinCAT system is started after the configuration has been saved. Now the
BC2000 target system can be selected in PLC Control.
Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
Terminal bus outputs after the PLC cycle
Selection of the target
platform
(Only for TwinCAT)
Selection of the target
system
When TwinCAT PLC Control is restarted, the program asks for the target
platform, i.e. the device on which the user will want his program to run.
TwinCAT offers two target platforms, the PC as a controller and the BC2000
coupler. For the program transfer with the bus terminal controller there are
again two possibilities. „AMS“ is for communication over the fieldbus, while
the „serial“ communication takes place via the PC’s serial interface and the
BC2000 programming interface.
Once the program has been written, the target system is selected under the
„Online“ symbol bar. In this example, the C1220 with the Box1 and the RunTime1 of the bus terminal controller.
19 BC2000
Page 21

Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
Communication parameters
Program Download via the RS232 Interface
Every bus terminal controller offers the possibility of being programmed via
the PC’s RS232 interface. This can be implemented with the aid of a special
cable (included when TwinCAT BC is supplied).
For this purpose, the serial interface is selected in PLC Control.
The settings for the serial interface, port number, baud rate etc. are found
under Online/Communication parameters in PLC Control.
The bus terminal controller requires the following setting:
Baud rate 19200
Stop bits: 1
Parity: even
General
BC2000 20
ADS Functions
The ADS functions provide a method for accessing the bus terminal
controller information directly. ADS function blocks can be used in TwinCAT
PLC Control for this. The function blocks are contained in the
„PLCSystem.lib“ library. It is also equally possible to call the ADS functions
from AdsOCX. The properties of the PLC runtime system can be retrieved
through port number 800, while port number 100 give access to the
Page 22

registers of the bus terminal controller and the terminals.
Port 800
Index Group / Index Offset
Example
PLC Runtime System
The port number in the BC2000 for the PLC is fixed at 800.
Index Group Meaning
16#4020
16#4021
16#4080
16#F020
16#F021
16#F030
16#F031
The variable in the flags area %MB10 is read directly by the PLC
programme in TwinCAT. The NetId of the target system is given for this
purpose. This number is found in the system manager, and is entered as a
string. The variable „Var1“ is declared as a 2 byte variable (INT or WORD).
As soon as Go_ADSREAD is switched to TRUE, the function block is
active, and the value contained in the BC2000 at %MB10 and %MB11 is
returned in „Var1“.
Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
Index Offset
Allocated flags area
%MB
Allocated bit flags area
%MX
Cycle time and basic settings 0: minimum cycle time in 1/125
Input
%IB
Input bit
%IX
Output
%QB
Output bit
%QX
0 .. 511
0 .. 4095
ms WORD
1: maximum cycle time in 1/125
ms WORD
2: current cycle time in 1/125 ms
WORD
3: mean cycle time in 1/125 ms
WORD
4: Number of PLC cycles after the
start DWORD
5: Nominal cycle time in ms
WORD
6: Background time in ms WORD
7: Length of the remanent flags
from %MB0 WORD
8: Start(1)/Stop(0) of the cycle
time measurement WORD
9: Time of the terminal bus cycle
WORD
0: Double Cycle
1: Before Cycle
2: After Cycle
0 .. 511
0 .. 4095
0 .. 511
0 .. 4095
21 BC2000
Page 23

Settings in the TwinCAT System Manager
i
Port 100
Index Group / Index Offset
Note
Registers of the Bus Terminal Controller
The port number in the BC2000 for register communication is fixed at 100.
Index Group
0
1-64
Index Offset
High WORD Low WORD
0-127 0-255 Controller registers
0-3 1-64 Terminal registers
Meaning
High WORD table number of the
controller
Low WORD register number of
the table
High WORD channel number
Low WORD register number of
the terminal
When reading registers it should be noted that the time out for the ADS
block is set to a time longer than 1 sec.
Diagnostics in the BC2000
It is possible to read the diagnostic data in the bus terminal controller. This
information is located in the flags area.
Flag byte
%MW508
%MW510
Meaning
Bit 0: Fieldbus error
Bits 1-15: reserved
Bit 0: Terminal bus error
Bit 1: Configuration error
Bits 2-15: reserved
BC2000 22
Page 24

Settings in TwinCAT PLC
Some of the settings for the BC2000 are only possible in PLC Control.
These are primarily a matter of properties that have a direct effect on the
program.
The points that follow here are found in PLC Control under „ONLINE“
„Coupler“.
Settings in TwinCAT PLC
Terminal Bus Reset
The terminal bus reset has its effect on the coupler’s internal bus. If there is
an error, which can be seen by the flashing of the „I/O ERR“ LED, the
terminal bus can be re-started. At the same time the number of connected
terminals is shown to the user in a message box.
Coupler Reset
The coupler will go through the same initialisation sequence as occurs
when the coupler is switched on.
Manufacturer’s Configuration
The coupler’s default values are written into the tables, and any boot project
that may be present is de-activated. The manufacturer’s configuration is
only activated after the coupler is reset.
Cycle Time Measurement
This measurement is related to the running time needed for the program to
execute and the terminal bus update. (See the chapter on „PLC Cycle
Time“)
Boot Project
In order to save the program, „Create a boot project“ is found under the
„Online“ menu item. This permits the program to be started automatically
after switching on. If the boot project is saved in the bus terminal controller
the „PLC“ LED on the BC2000 flashes.
23 BC2000
Page 25

Settings in TwinCAT PLC
Coupler Options
The maximum size of the program memory and of the data memory can be
set in PLC Control under „Projects“, „Options“, „Coupler“. In the „small
memory model“, a variable size for the data and program memories is
possible. The maximum memory size is 64 kbyte. In the „large memory
model“ a maximum of 96 kbyte program memory and 64 kbyte data
memory are the upper limits.
It should be noted that in the „large memory model“ the EEPROM is also
used.
BC2000 24
Page 26

Appendix
Appendix
Absolute Addressing in the BC2000
Input Output
KL3002 %IB0 Status KL3002 %QB0 Control
KL3002 %IB1 Empty KL3002 %QB1 Empty
KL3002 %IB2 D0 KL3002 %QB2 D0
KL3002 %IB3 D1 KL3002 %QB3 D1
KL3002 %IB4 Status KL3002 %QB4 Control
KL3002 %IB5 Empty KL3002 %QB5 Empty
KL3002 %IB6 D0 KL3002 %QB6 D0
KL3002 %IB7 D1 KL3002 %QB7 D1
2 x KL1002 %IX8.0..
%IX8.3
KL4002 %QB9 D1
KL4002 %QB10 D0
KL4002 %QB11 D1
2 x KL2012 %QX12.0..
... ... ... ...
PLC variable
INT Offset0_1
Inputs
PLC variable
INT Offset0_2
Inputs
%IB128..129 PLC variable
%IB130..131 PLC variable
KL4002 %QB8 D0
%QX12.3
%QB128..129
INT Offset0_1
Outputs
%QB130..131
INT Offset0_2
Outputs
Terminals 2, 3, 6, 7 and 10 are directly assigned to the Lightbus master,
and are therefore neither visible to the BC2000, nor do they appear in the
PLC’s input and output process image.
25 BC2000
Page 27

Index
Index
A
ADS Functions 18
Assembly 8
B
Background time 16
BC2000 dimensions 8
Blink code 10
Boot project 21
C
Configuration Interface 6
Connection 8
Coupler options 22
Coupler reset 21
Cycle time 16
Cycle time measurement 21
D
Data memory 22
Device description 3
Diagnostic LEDs 10
Diagnostics 10, 20
E
Electrical power supply 5
End terminal 4
F
Fieldbus connection 6
Fieldbus errors 11
K
K bus 4
L
Lightbus 13
Lightbus connector 6
M
Manufacturer’s configuration 21
Master interface 13
Mechanical structure 8
N
Number of terminals 3
O
Optical fibre 14
P
PLC Cycle Time 16
PLC data 10
PLC Variables 16
Port 100 20
Port 800 19
Power contacts 5
Program download 17
Program memory 22
R
Remanent Variables 17
G
Galvanic isolation 6
S
Setting up for operation 10
System Manager 15
I
Insulation testing 8
Interfaces 5
T
Terminal bus reset 21
Terminal Bus Update 17
BC2000 26
Page 28

Support and Service
Support and Service
Beckhoff and their partners around the world offer comprehensive support and service, making available
fast and competent assistance with all questions related to Beckhoff products and system solutions.
Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives
Please contact your Beckhoff branch office or representative for local support and service on Beckhoff
products!
The addresses of Beckhoff's branch offices and representatives round the world can be found on her
internet pages: http://www.beckhoff.com
You will also find further documentation for Beckhoff components there.
Beckhoff Headquarters
Beckhoff Automation GmbH
Eiserstr. 5
33415 Verl
Germany
phone: + 49 (0) 5246/963-0
fax: + 49 (0) 5246/963-198
e-mail: info@beckhoff.com
web: www.beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Support
Support offers you comprehensive technical assistance, helping you no only with the application of
individual Beckhoff products, but also with other, wide-ranging services:
• support
• design, programming and commissioning of complex automation systems
• and extensive training program for Beckhoff system components
hotline: + 49 (0) 5246/963-157
fax: + 49 (0) 5246/963-9157
e-mail: support@beckhoff.com
Beckhoff Service
The Beckhoff Service Center supports you in all matters of after-sales service:
• on-site service
• repair service
•
spare parts servive
• hotline service
hotline: + 49 (0) 5246/963-460
fax: + 49 (0) 5246/963-479
e-mail: service@beckhoff.com
27 BC2000
 Loading...
Loading...