Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR
TRANSFORMER DIFFERENTIAL RELAY
BE1-87T
BE1-87T
TRANSFORMER DIFFERENTIAL
Style No. D2E A1J D1S0F
R
Serial No. XXXXXXXXXXXX
PUSH TO
ENERGIZE
OUTPUT
R
U
P0052-22
Publication: 9171300990
Revision: V 03/12
Page 2

Page 3

INTRODUCTION
This instruction manual provides information about the operation and installation of the BE1-87T
Transformer Differential relay. To accomplish this, the following information is provided:
General Information and Specifications
Controls and Indicators
Functional Description
Installation
Test Procedures
WARNING!
To avoid personal injury or equipment damage, only qualified personnel should
perform the procedures in this manual.
NOTE
Be sure that the BE1-87T is hard-wired to earth ground with no smaller than 12
AWG copper wire attached to the ground terminal on the rear of the unit case.
When the BE1-87T is configured in a system with other devices, it is
recommended to use a separate lead to the ground bus from each unit.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Introduction i
Page 4

First Printing: June 1990
Printed in USA
Copyright © 1990-2012 Basler Electric, Highland Illinois 62249 USA
All Rights Reserved
March 2012
CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION
of Basler Electric, Highland Illinois, USA. It is loaned for confidential use,
subject to return on request, and with the mutual understanding that it will not
be used in any manner detrimental to the interest of Basler Electric.
It is not the intention of this manual to cover all details and variations in equipment, nor does this manual
provide data for every possible contingency regarding installation or operation. The availability and design
of all features and options are subject to modification without notice. Should further information be
required, contact Basler Electric.
For terms of service relating to this product and software, see the Commercial Terms of Products and
Services document available at www.basler.com/terms
.
BASLER ELECTRIC
12570 STATE ROUTE 143
HIGHLAND IL 62249-1074 USA
http://www.basler.com, info@basler.com
PHONE +1 618.654.2341 FAX +1 618.654.2351
ii BE1-87T Introduction 9171300990 Rev V
Page 5

REVISION HISTORY
The following information provides a historical summary of the changes made to the BE1-87T instruction
manual (9171300990). Revisions are listed in reverse chronological order.
Manual
Revision and Date
V, 03/12
U, 08/11
T, 03/11
S, 09/10
R, 09/07
Q, 10/05
P, 05/03
N, 09/00
Change
Updated format of Table 1-3, Power Supply Ratings, to be consistent
with other manuals.
Standardized case and cover drawings in Section 4.
nd
Updated 2
harmonic restraint specs for 5 A & 1 A CTs in Section 5.
Updated formatting to current style used.
nd
Updated 2
& 5th harmonic restraint specs in Section 1.
Updated “K” type power supply burden in Table 1-3.
Updated GOST-R statement in Section 1.
Updated rear case drawings in Section 4.
Removed references to extender card in Sections 4 and 5.
Updated Storage statement in Section 4.
Replaced magnetic type targets with electronic type targets.
Updated power supply burden data and output contact ratings.
Updated front panel illustrations to show laser graphics.
Moved content of Section 6, Maintenance to Section 4, Installation.
Added GOST-R certification to Section 1, General Information.
In Section 1, General Information, Specifications, corrected values for
Maximum Current per Input for 1 Ampere CT Units.
In Section 5, Test Procedures, corrected values inside CAUTION box
for 1 AMP CT on page 5-14.
Added a thumbscrew to the figure on the manual front cover.
Added “not all styles” to the Power Supply Output heading on page 3-
4 as well as added “NOTE” and a text box around the second last
paragraph on page 3-4.
Added the new thumbscrew to Figure 4-1 and changed the height
dimensions in Figure 4-2.
Clarified the terminal numbers on Figure 4-6b.
Added a shorting bar between terminals 6 & 7 in Figure 4-11.
Added a shorting bar and normally open contact and normally closed
contact effecting terminals 1, 2, & 5 in Figure 4-12.
Step 13 was corrected on pages 4-31 and 4-39 to include R
in the
w
formulas.
Values were changed to Table 5-4 under Option 1-0 for Unrestrained
Trip.
Corrected Table 1-3 to show power supply ranges.
Changed instruction manual front cover, Figures 4-1, 4-3, and 4-5 to
show new unit case covers.
Changed Figure 4-32 per markup.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Introduction iii
Page 6

Manual
Revision and Date
M, 04/99
L, 05/97
K, 03/97
J, 01/96
Change
Table 3-1 changed mid range nominal volt 125 Vac to 120 Vac.
Corrected Figures 4-24, 4-31a, and A-3
Corrected page 4-38, Step 10; added note to page 4-39, Step 13, and
corrected Steps 14 and 16.
Page A-2, changed 3-Phase fault ratio current to 3-phase fault
current.
Page A-3, corrected formulas for Figure A-3.
Under Section 4, Procedure One, Verify CT Performance, changed
the procedure to the ANSI accuracy class method. This forced
changes in the following steps: 12, 13, 14, 16, 18, 20, and 21.
Under Section 4, Procedure Two, Verify CT Performance, changed
the procedure to the ANSI accuracy class method. This forced
changes in the following steps: 12, 13, 14, and 16.
Added ECO revision information to Table 8-1.
Added Setting Note 7 (ANSI Accuracy Class Method) to Appendix A.
To delete the part number from the front cover of the manual.
Deleted all references to Service Manual 9171300620.
Changed the Title of Section 2 from “Controls and Indicators” to
“Human-Machine Interface”.
Replaced the Power Supply Options paragraphs with a new Power
Supply paragraph explaining the new power supply design.
Deleted Figure 3-2 and added Table 3-1, Wide Range Power Supply
Voltage Ranges.
Changed Power Supply Status Output for Type G power supply on
the formerly page 3-6 (now page 3-4) from terminals 9 and 20 to
terminals 9 and 19.
Added information to Section 4 to help the user understand the
procedures better.
Deleted all NOTES FOR USERS OF SENSING INPUT TYPE F
RELAYS and added Section 7, Difference Data.
Changed previous Section 7, Manual Change Information, to Section
8.
Added an Appendix A to clarify the setting procedures.
Added an index to help the user find information easier.
Changed the format of the manual.
Deleted “Difference Data” (formerly Section 7) and included notes for
users of Type F relays.
Moved all information regarding relay settings and checking relay
setting from Section 5, Testing and Setting, to Section 4, Installation.
Section 5 now contains information on test procedures.
Combined 50 and 60 Hz Verification Tests.
Various editorial changes.
Reformatted instruction manual as Windows Help file for electronic
documentation.
iv BE1-87T Introduction 9171300990 Rev V
Page 7

Manual
Revision and Date
I, 01/95
Added outline (box) to Figure 5-8 to highlight the figure.
Change
Page 5-42, Step 5, changed, “should be less than 4.45” to, “must be
less than 4.45”.
Added note to page 5-43, Step 10 and corrected the formula in Step
10.
Page 5-45, Step 18, corrected formula and high side results; and
Step 19, changed last sentence from H (13 x tap) to S (21 x tap).
Page 5-46, Steps 20 and 21, corrected figure references.
H, 12/94
Page 1-6, changed Specification for Restrained Output, Pickup
Accuracy.
Changed Section 5, Testing and Setting, Verification Tests (all
models): Steps 1, 4, 5, and 8; and Table 5-4.
Page 5-50, Jumper Positions Wye-Delta 1, Step 3: Corrected Input 2
terminal identifications.
Page 5-51, Jumper Positions Delta2-Delta2, Step 2: Corrected
verification statement.
G, 09/94
Changed all sections to reflect new Option 1-1.
Added to Section 5 four examples for testing relays to clarify test
procedures.
Added to Section 5 one procedure for setting relays.
Corrected typographical and illustration errors.
F, 03/93
Changed formula pages 5-4, 5-10, 5-16, and 5-22 from I = the square
root of K over t, to I = K over the square root of t.
E, 01/93
Manual was revised to incorporate a revision in the relay that made
sensing input type F obsolete and included the 1 A, 60 hertz and 5 A,
50 hertz model relays.
Section 5, Test Setup, diagrams were changed to clarify relay
connections.
Added three relay Internal Connection diagrams.
Changed unrestrained maximum time to trip, reference old Tables 5-4
and 5-8 (new Tables 5-4, 5-8, 5-12, and 5-16).
Renamed Section 7, Manual Change Information to Section 8,
Manual Change Information and added new Section 7, Difference
Data to support BE1-87T relays with Sensing Input Type F.
D, 06/92
Manual was revised to include the 1 A, 50 Hz model relay and
reformatted to a new Instruction Manual style.
Additional connection diagrams were included in Section 4 and test
plug information was added to Section 6.
Minor typographical errors were also corrected.
C, 03/91
Table 5-1 was expanded and Figure 5-4 Test Setup illustration was
added.
Miscellaneous editing.
B, 03/91
Manual (with the exception of Section 2) was rewritten for ease of
use.
A, 06/90
Figure 3-1 (Functional Block Diagram) corrected.
Formula in caution note (formerly on p. 4-17, now on p. 5-2)
corrected.
Miscellaneous editing.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Introduction v
Page 8

vi BE1-87T Introduction 9171300990 Rev V
Page 9

CONTENTS
SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION ................................................................................................ 1-1
SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS ........................................................................................ 2-1
SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................... 3-1
SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................. 4-1
SECTION 5 • TEST PROCEDURES ........................................................................................................ 5-1
SECTION 6 • DIFFERENCE DATA .......................................................................................................... 6-1
APPENDIX A • SETTING NOTES ............................................................................................................ A-1
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Introduction vii
Page 10

viii BE1-87T Introduction 9171300990 Rev V
Page 11

SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION ................................................................................................ 1-1
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................ 1-1
Description ............................................................................................................................................. 1-1
Application.............................................................................................................................................. 1-2
Single-Phase ...................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Three-Phase ....................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Percentage Restraint .......................................................................................................................... 1-2
Second-Harmonic Restraint ............................................................................................................... 1-2
Fifth-Harmonic Restraint .................................................................................................................... 1-3
Unrestrained Trip ................................................................................................................................ 1-3
Options ................................................................................................................................................... 1-3
Push-To-Energize Output Pushbuttons ............................................................................................. 1-3
Auxiliary Output Contacts ................................................................................................................... 1-3
Power Supply ..................................................................................................................................... 1-3
Model and Style Number ....................................................................................................................... 1-4
Style Number Example ....................................................................................................................... 1-4
Specifications ......................................................................................................................................... 1-5
Figures
Figure 1-1. Style Number Identification Chart ........................................................................................... 1-4
Figure 1-2. Percentage Restraint Characteristic ....................................................................................... 1-6
Figure 1-3. Unrestrained Response Times and Restrained Response Times .......................................... 1-8
Tables
Table 1-1. Multiples of Tap ........................................................................................................................ 1-6
Table 1-2. Harmonic Attenuation
Table 1-3. Power Supply Specifications
............................................................................................................... 1-7
.................................................................................................... 1-9
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T General Information i
Page 12

ii BE1-87T General Information 9171300990 Rev V
Page 13

SECTION 1 • GENERAL INFORMATION
Introduction
These instructions provide information concerning the operation and installation of BE1-87T Transformer
Differential Relays. To accomplish this, the following is provided:
• Specifications
• Functional characteristics
• Mounting information
• Setting procedures and examples
WARNING!
To avoid personal injury or equipment damage, only qualified personnel should
perform the procedures presented in these instructions.
These instructions may be used in place of all earlier editions. For change information, see Section 8.
Description
BE1-87T Transformer Differential Relays provide primary protection for power transformers and are
available in either Single-Phase or Three-Phase configurations. The solid-state BE1-87T compares the
currents entering and leaving the protected transformer. If a fault is detected, the relay initiates a trip
signal to isolate the power transformer. This limits damage to the transformer and minimizes the impact on
the power system.
BE1-87T relays use three types of restraint:
NOTE FOR USERS OF SENSING INPUT TYPE F RELAYS
Users of BE1-87T relays with Sensing Input Type F (three-phases three inputs
per phase) will find Difference Data in Section 6 of this manual that describes
features specific to these relays. The three-phase, three inputs per phase
design, previously available as Sensing Input Type F, has been modified and
is now available as Sensing Input Type G. Due to differences in components
and output terminal connections, Type G relays are not compatible with earlier
versions of the BE1-87T with Sensing Input Type F. There are also differences
in the output connections as described in Section 6, Difference Data.
• Percentage of through-current
• Second harmonic
• Fifth harmonic
Selectivity in differential relaying is based on the ability to distinguish between internal and external faults.
This is achieved by comparing the currents into and out of a power transformer. Comparing these currents
often requires more than two inputs. For example:
• Power transformers may have a significant portion (greater than 10%) of the current flowing in a
third or tertiary winding.
• Power transformers can have multiple breakers for a given winding (e.g., ring bus or breaker-and-
a-half bus).
BE1-87T relays are available with up to five restraint inputs for the single-phase unit and up to three
restraint inputs per phase for the three-phase unit.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T General Information 1-1
Page 14

Application
In general, power transformers have different values of current flowing through their primary, secondary,
and tertiary windings. These currents have specific phase relationships depending upon the connections
of the individual windings (e.g., wye/delta). As inputs to a differential relay, these currents must be
compensated or scaled so that the relay can compare the inputs and determine when an unbalance
exists. Under ideal operating conditions, the scaled vector sum of these currents is zero.
Because it is practically impossible to match the magnitudes of these detected currents from the various
power windings using standard CT ratios, the currents are matched within the relay by scaling each of the
applied currents by an appropriate factor called a Tap Setting. This is set by means of the front panel
INPUT dials. By selecting suitable tap ratios, the applied currents are scaled within the relay to achieve
the desired balance for normal operating conditions. BE1-87T relays offer a range of available tap settings
for inputs between 0.4 A to 1.78 A (Sensing Input Range Options 2 and 4 for a 1 A CT) or 2.0 to 8.9 A
(Sensing Input Range Options 1 and 3 for a 5 A CT). These settings are independently adjustable in
increments of 0.02 A for Sensing Input Range Options 2 and 4, or 0.1 A for Sensing Input Range Options
1 and 3. These small increments allow more precise scaling of the applied currents and usually eliminate
the need for installing auxiliary ratio-matching CTs.
Single-Phase
BE1-87T Single-Phase relays require phase angle compensation to be accomplished externally by proper
connection of the system CT secondaries. A wye/delta transformer requires that the CT secondaries be
connected in delta for the wye winding and in wye for the delta winding. This type of connection also
eliminates the zero-sequence component of current which could cause a false trip (operation) during
external ground fault conditions on the wye system.
Three-Phase
BE1-87T Three-Phase relays can provide zero-sequence filtering and compensation for phase shifts
introduced by the connections of the power transformer. This 30° Phase Shift compensation (either ±30°
or no compensation) is field selectable. Additionally, this feature allows sharing the transformer differential
relay CTs with other relays or instrumentation.
BE1-87T relays use the highest input current (in per unit values) to operate on maximum restraint. The
relay does not have a conventional operate winding in the internal magnetics. Operating current is
developed within the electronics of the relay.
Percentage Restraint
A primary concern in differential relay applications is security against high current levels caused by faults
outside the protected zone. Inevitable differences in the saturation characteristics between current
transformers require a compensating decrease in relay sensitivity. It is also necessary to be able to adjust
the sensitivity to compensate for transformer voltage taps or CT mismatches. This is accomplished by
providing a restraint factor proportional to the current flowing through the protected zone (throughcurrent).
BE1-87T relays maintain sensitivity at a specified ratio of trip current to through current. This ratio,
generally referred to as slope, is front-panel adjustable in 5% increments from 15 to 60%.
Second-Harmonic Restraint
Magnetizing inrush current presents another problem unique to transformer differential relays. Relays
must be capable of detecting the small differences in current caused by the shor ting of a limited number
of turns, yet remain secure against the occurrence of magnetizing currents many times the transformer
rating (as seen at one set of terminals).
Although magnetizing inrush is usually associated with the energizing of the transformer, any abrupt
change in the energizing voltage may produce this phenomenon. Common causes are the transients
generated during the onset, evolution, and removal of external faults. Desensitizing the relay only during
energization is therefore insufficient.
Magnetizing inrush produces an offset sine wave rich in all harmonics. BE1-87T relays use the second
harmonic to restrain operation because it predominates and because it does not occur in significant
magnitude or duration at other times.
1-2 BE1-87T General Information 9171300990 Rev V
Page 15

Three-phase BE1-87T relays use second-harmonic sharing. The second-harmonic content of all three
phases is summed together to derive the restraint for each phase. As a result, the second-harmonic
inhibit range and the associated factory setting, is higher than on single-phase relays.
Fifth-Harmonic Restraint
Power transformer overexcitation causes additional exciting current to flow into one set of terminals. This
presents an apparent differential (or operating) current not attributable to an internal fault. Although
potentially damaging, overexcitation is not an internal fault and, therefore, is not an appropriate condition
for transformer differential relay operation. One of the principal components in the complex waveform
produced during overexcitation is the fifth harmonic. BE1-87T relays use fifth-harmonic restraint to inhibit
the differential relay operation.
Unrestrained Trip
Severe internal transformer faults may cause CT saturation. Under such circumstances, harmonicrestraint transformer differential relays may fail to trip because of the extremely high harmonic content in
the waveform. Lack of operation can result in severe transformer damage.
BE1-87T relays provide an independent unrestrained tripping function. When set above the possible
inrush current magnitude, this function provides high-speed protection for the most severe internal faults.
Options
Push-To-Energize Output Pushbuttons
Two PUSH-TO-ENERGIZE OUTPUT switches are available as a means to verify external output wiring
without the inconvenience of having to test the entire relay. Option 2-S provides a small pushbutton switch
for each isolated output function (Restrained and Unrestrained) and may be actuated by inserting a thin,
non-conducting rod through access holes in the front panel. Refer to Figures 2-1 through 2-4 for location.
Appropriate power must be applied to Power Supply terminals 3 and 4 (shown in Figures 4-7 through 4-
10) for these pushbuttons to operate the output relays. However, it is not necessary to apply currents to
the sensing inputs of the relay for these switches to function.
Auxiliary Output Contacts
Three types of auxiliary output contacts are available: Normally open, normally closed and SPDT. The
contacts can be made to respond to a restrained trip, an unrestrained trip, or both. Refer to the Functional
Description: Auxiliary Relay Option for further information.
Power Supply
Various power supply options are available to allow the BE1-87T to be used with standard supply
voltages. See the Style Number Identification Chart, Figure 1-1, for details.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T General Information 1-3
Page 16

Model and Style Number
The electrical characteristics and operational features of the BE1-87T Transformer Differential Relay are
defined by a combination of letters and numbers that make up its Style Number. The Model Number
together with the Style Number, describe the options included in a specific device and appear on the front
panel, drawout cradle and inside the case assembly.
Upon receipt of a relay, be sure to check the Style Number against the requisition and the packing list to
ensure that they agree.
Style Number Example
The Style Number Identification Chart (Figure 1-1) defines the electrical characteristics and operational
features included in BE1-87T relays. For example, if the Style Number were G1E-A1Y-D1S0F, the device
would have the following:
BE1-87T
G
1
E
A1
Y
D
1
S
0
F
Model Number (designates the relay as a Basler Electric, Class 100, Transformer Differential
Relay)
Three-phase sensing with three inputs per phase
2.0 to 8.9 A Sensing Range at 60 Hz
One unrestrained output contact and one restrained output contact
No intentional delay in the outputs
48/125 Vdc switchable
Current operated targets
Percent I
Push-to-Energize outputs
No auxiliary output
Semi-flush mounting
display and high-speed trip
OP
Figure 1-1. Style Number Identification Chart
1-4 BE1-87T General Information 9171300990 Rev V
Page 17

Specifications
I
K
t
=
Maximum
I
Minimum Pi
ckup
Percent of
Slope
Restraint
=
Minimum Pi
ckup
Percent of
Slope
=
=
0.35
20
1.75
%
The BE1-87T relay is available in either single-phase or three-phase configurations and with the following
features and capabilities.
Current Sensing Inputs
Maximum Current Per Input
1 Ampere CT Units 4 A continuous; 50 A or 50 X tap (whichever is less) for 1 second.
5 Ampere CT Units 20 A continuous; 250 A or 50 X tap (whichever is less) for 1
For ratings other than one second, the rating may be calculated as:
Where:
Current Sensing Burden
Tap Setting Control (Scaling)
1 Ampere CT Units 0.4 to 1.78 in 0.02 A increments.
5 Ampere CT Units 2.0 to 8.9 A, in 0.1 A increments.
The unit is designed to operate from the secondary of current
transformers rated at either 1 A or 5 A. Frequency range is ±5 Hz of
nominal.
second.
t is the time (in seconds) that the current flows
K = 50 A or 50 X tap, whichever is less (1 Amp CT Units), or
K = 250 A or 50 X tap, whichever is less (5 Amp CT Models)
Less than 0.02 ohm per phase.
Front panel rotary switches, labeled INPUT, permit scaling the
sensed input current (or tap setting) over the range of:
Restrained Output
Pickup Range Front panel thumbwheel switches adjust pickup of the restrained
Pickup Accuracy
Minimum Pickup
For example:
output as a percentage of the through current. The range is 15 to
60% of the operating current in 5% increments.
±6% of pickup ±100 mA (5 Ampere Units) or ±20 mA (1 Ampere
units).
0.35 ±6% of tap setting. Refer to Tabl e 1-1 and Figure 1-2. Table 1-1
provides calculated intersection points of the slope characteristic
and the minimum pickup (in multiples of tap) as shown in Figure
1-2. The calculation was derived from the formula:
The relay operates when the per unit difference current (operating
current) is above the 0.35 pu or the slope line in Figure 1-2.
Calculation examples are found in Section 5.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T General Information 1-5
Page 18

Table 1-1. Multiples of Tap
Front Panel Setting % 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60
Maximum Restraint
Current At Minimum
Pickup In Multiples of
Tap
2.33 1.75 1.40 1.17 1.00 0.875 0.778 0.700 0.636 0.583
Figure 1-2. Percentage Restraint Characteristic
Second-Harmonic Restraint Inhibit of the restrained output occurs when the second-
harmonic component exceeds a pickup setting which is 12%
of the operating current for single-phase units or 18% for
three-phase units.
Fifth-Harmonic Restraint Inhibit of the restrained output occurs when the fifth-harmonic
component exceeds a pickup setting which is 35% of the
operating current.
Unrestrained Output
Pickup Range Front panel thumbwheel switches adjust the pickup point of
Pickup Accuracy
the unrestrained output over a range of 6 to 21 times the tap
setting in increments of 1 x Tap.
±3% of the front panel setting.
1-6 BE1-87T General Information 9171300990 Rev V
Page 19

Outputs
Resistive
120/240 Vac Make 30 A for 0.2 seconds, carry 7 A continuously and break
250 Vdc Make and carry 30 A for 0.2 seconds, carry 7 A continuously
500 Vdc Make and carry 15 A for 0.2 seconds, carry 7 A continuously
Inductive
120/240 Vac, 125/250 Vdc Make and carry 30 A for 0.2 seconds, carry 7 A continuously
Output contacts are rated as follows.
7 A.
and break 0.3 A.
and break 0.1 A.
and break 0.3 A, (L/R = 0.04).
Target Indicators
Single-Phase Units Either an internally-operated or a current-operated target is
Three-Phase Units Either internally operated or current operated targets (as
Harmonic Attenuation
Parameter
(50 Or 60 Hz Models)
Through Current 0 0 0 0 12 dB
Operating Current 0 0 0 0 12 dB
2nd Harmonic Restraint 12 dB 0 12 dB 12 dB 12 dB
5th Harmonic Restraint 12 dB 12 dB 12 dB 0 12 dB
Target indicators may be either internally-operated or currentoperated (operated by a minimum of 0.2 A through the output
trip circuit). When the target is current-operated, the
associated output circuit must be limited to 30 A for 0.2
seconds, 7 A for 2 minutes and 3 A continuously.
supplied (as selected by the Style Number) for each trip
output (i.e., the restrained and the unrestrained functions).
selected) indicate the function (restrained or unrestrained)
that caused the trip, and the tripped phase (A, B, C).
Refer to Tabl e 1-2.
Table 1-2. Harmonic Attenuation
Minimum Attenuation at Indicated Fundamental
50/60 Hz 100/120 Hz 150/180 Hz 250/300 Hz 500 Hz
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T General Information 1-7
Page 20

Timing
(For 60 Hz units only)
Refer to Figure 1-3 for Unrestrained Response Times and
Restrained Response Times.
Figure 1-3. Unrestrained Response Times and Restrained Response Times
1-8 BE1-87T General Information 9171300990 Rev V
Page 21

Isolation
In accordance with IEC 255-5 and ANSI/IEEE C37.90-1989,
one minute dielectric (high potential) tests, as follows:
All circuits to ground: 2,121 Vdc
Input to output circuits: 1,500 Vac or 2,121 Vdc
Power Supply
Type
K (midrange) 48 Vdc 24 to 150 Vdc 9.0 W
J (midrange)
L (low range) 24 Vdc 12 to 32 Vdc * 9.0 W
Y (midrange)
Z (high range)
* Type L power supply initially requires 14 Vdc to begin operating. Once operating, the input voltage may
be reduced to 12 Vdc and operation will continue.
Surge Withstand Capability
Refer to Tabl e 1-3.
Table 1-3. Power Supply Ratings
Nominal
Input Voltage
125 Vdc 24 to 150 Vdc 9.0 W
120 Vac 90 to 132 Vac 21.0 VA
48 Vdc 24 to 150 Vdc 8.5 W
125 Vdc 24 to 150 Vdc 9.0 W
250 Vdc 68 to 280 Vdc 9.5 W
240 Vac 90 to 270 Vac 28.0 VA
Qualified to ANSI/IEEE C37.90.1-1989, Standard Surge
Withstand Capability (SWC) Tests for Protective Relays and
Relay Systems, and IEC 255-5 Impulse Test and Dielectric
Tes t.
Input Voltage Range
Burden at
Nominal
Radio Frequency Interference
(RFI)
UL Recognition
GOST-R Certification
Patent
Shock
Vibration
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature
Maintains proper operation when tested in accordance with
IEEE C37.90.2-1987, Trial-Use Standard Withstand
Capability of Relay Systems to Radiated Electromagnetic
Interference from Transceivers.
UL Recognized per Standard 508, UL File No. E97033. Note:
Output contacts are not UL Recognized for voltages greater
than 250 V.
GOST-R certified per the relevant standards of Gosstandart
of Russia.
Patented in U.S., 1991, U.S. Patent No. 5014153.
Patented in Canada, 1993.
In standard tests, the relay has withstood 15 g in each of
three mutually perpendicular axes without structural damage
or degradation of performance.
In standard tests, the relay has withstood 2 g in each of three
mutually perpendicular axes swept over the range of 10 to
500 Hz for a total of six sweeps, 15 minutes each sweep,
without structural damage or degradation of performance.
–40°C (–40°F) to 70°C (158°F)
–65°C (–85°F) to 100°C (212°F)
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T General Information 1-9
Page 22

Weight
22.3 lbs (10.1 kg) maximum (three-phase unit)
Case Size
19.5 lbs (8.85 kg) maximum (single-phase unit)
All units are supplied in an M1 case size. See Section 4,
Installation for case dimensions.
1-10 BE1-87T General Information 9171300990 Rev V
Page 23

SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS ........................................................................................ 2-1
Location of Controls and Indicators ....................................................................................................... 2-1
Figures
Figure 2-1. Sensing Input Range 1 or 3 Three-Phase, Three Inputs ........................................................ 2-4
Figure 2-2. Sensing Input Range 1 or 3, Single-Phase, Five Inputs ......................................................... 2-5
Figure 2-3. Sensing Input Range 2 or 4, Three-Phase, Two Inputs .......................................................... 2-6
Figure 2-4. Controls Mounted Inside the Relay ......................................................................................... 2-7
Figure 2-5. Sensing Input Range 2 or 4, Option 1-1, Single-Phase, Five Inputs, % OF TRIP Option ...... 2-8
Tables
Table 2-1. Controls and Indicators ............................................................................................................ 2-1
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Controls and Indicators i
Page 24

ii BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 9171300990 Rev V
Page 25

SECTION 2 • CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
Location of Controls and Indicators
Table 2-1 lists and briefly describes the operator controls and indicators of the BE1-87T Transformer
Differential Relay. Reference the call-out letters A through M to Figures 2-1 to 2-3; N through Q to Figure
2-5. Exploded views of controls that are mounted inside the relay (call-out letters B, D and I) are shown in
Figure 2-4.
Table 2-1. Controls and Indicators
Letter Control or Indicator Function
A INPUT (or TAP) Switches Front panel INPUT switches are used to scale the
transformer currents. There are two of these rotary
switches for each input.
1 Ampere CT Units
5 Ampere CT Units
B 30° Phase Shift Jumpers
(three-phase units ONLY)
C
D CALIBRATE Switch
E POWER Indicator
UNRESTRAINED PICKUP
LEVEL Switches
(three-phase units ONLY)
Each of the upper switches is calibrated to represent
the tenths and units digits (0.4 through 1.6) of tap
value. Each of the lower switches is calibrated to
represent two-hundredths of tap value for each
increment. Always add the setting of the lower switch to
that of the upper switch. For example, if a setting of
1.02 is desired, the upper switch must be at 1.0 and the
lower switch must be at 0.02. The total setting range for
each input is 0.4 to 1.78.
Each of the upper switches is calibrated to represent
the units digit (2 through 8) of tap value. Each of the
lower switches is calibrated to represent tenths of tap
value. Always add the setting of the lower switch to that
of the upper switch. For example, if a setting of 5.0 is
desired, the upper switch is set to 5.0, the lower switch
must be at 0.0. The total setting range for each input is
2.0 to 8.9.
These jumpers control the internal phase shift of the
relay, either +30°, -30°, or 0°, depending upon the
position of the jumpers provided for each input on the
Analog #2 Board, shown in Figure 2-4. Additional
information is in Section 4.
This thumbwheel switch establishes the desired pickup
setting for all phases of the unrestrained output. The
adjustment range is from 6 to 21 times the phase tap
setting, in increments of 1.
A two-position switch is located on each Analog #1
Board and is easily accessible on the right side of the
relay when it is withdrawn from the case. In the
CALIBRATE position, these switches inhibit the
harmonic share feature when calibrating the 2nd
Harmonic Restraint. In the NORMAL position, the relay
will operate normally.
This LED will illuminate when operating power is
supplied to the internal circuitry of the relay.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 2-1
Page 26

Letter Control or Indicator Function
F
G FUNCTION Targets Option
H Target Reset Switch
I Auxiliary Relay Control
J ELEMENT Targets Option
K
L UNREST. TRIP Indicator
M REST. TRIP Indicator
N M Indicator Red LED lights when the % OF TRIP pushbutton P is
O S Indicator Red LED lights when the % OF TRIP pushbutton P is
P Percent of Trip Pushbutton Pushbutton that is used to activate the % of TRIP
PUSH-TO-ENERGIZE
OUTPUT Switches Option
Switches Option
(three-phase units ONLY)
RESTRAINED PICKUP
LEVEL Switches
Two momentary pushbutton switches are accessible by
inserting a 1/8 inch diameter non-conducting rod
through access holes in the front panel. Switch R,
when actuated, closes the Restrained Output Relay
contacts. Switch U, when actuated, closes the
Unrestrained Output Relay contact(s).
NOTE
The optional Auxiliary Relay contacts (Option 3-1, 3-2
or 3-5) will also be operated by the PUSH-TO-
ENERGIZE switches if enabled by the two internal
Auxiliary Relay Control Switches. (Refer to LETTER I.)
Electronically-latched LED targets that indicate an
unrestrained or restrained output has occurred.
Resets the electronically-latched targets.
Two internal slide switches, S1 and S2, enable the
optional Auxiliary Output Relay to close only when a
restrained output occurs (S1 ON), only when an
unrestrained output occurs (S2 ON), or to close when
either output occurs (S1 and S2 ON).
When shipped from the factory, the Auxiliary Relay will
be configured with S1 and S2 ON.
NOTE
The switches are located on the mother board and are
only accessible by withdrawing the relay case.
Electronically-latching LED targets indicate the phase
that caused a trip operation.
Thumb-wheel switches (one per phase element) are
used to adjust the desired percent of allowable
through-current restraint from 15 to 60 % in 5 %
increments. (Through-current is the greatest relative
individual input current.)
The through-current restraint characteristic is
individually adjustable for phases A, B, and C.
In a three-phase unit, all three switches are typically
kept at identical settings.
Red LED lights when there is an unrestrained pickup.
Red LED lights when there is a restrained pickup.
pressed and the restraint current is below the slope
characteristic kneepoint as defined in Table 1-1. That
is, the relay will operate at minimum pickup (0.35 times
tap).
pressed and the restraint current is above the slope
characteristic kneepoint as defined in Table 1-1. That
is, the relay will operate based on the restraint
characteristic.
LEDs.
2-2 BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 9171300990 Rev V
Page 27

Letter Control or Indicator Function
Q % OF TRIP Indicators Option When the % OF TRIP pushbutton P is pushed, eight
LEDs, shown in Figure 2-5, are used to indicate the
approximate percentage of operating current to:
Minimum pickup (LED M also lights); or
Slope characteristic pickup (LED S also lights).
The eight LEDs represent the following approximate
percentages.
1 LED: 3% (Yellow LED)
2 LEDs: 7% (Yellow LED)
3 LEDs: 11% (Yellow LED)
4 LEDs: 20% (Red LED)
5 LEDs: 40% (Red LED)
6 LEDs: 60% (Red LED)
7 LEDs: 80% (Red LED)
8 LEDs: 100% (Red LED)
A bar chart above the LEDs shows the relative
percentage of trip.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 2-3
Page 28

Figure 2-1. Sensing Input Range 1 or 3 Three-Phase, Three Inputs
2-4 BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 9171300990 Rev V
Page 29

Figure 2-2. Sensing Input Range 1 or 3, Single-Phase, Five Inputs
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 2-5
Page 30

Figure 2-3. Sensing Input Range 2 or 4, Three-Phase, Two Inputs
2-6 BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 9171300990 Rev V
Page 31

SECTION OF THE (VERTICAL)
MOTHER BOARD AT LEFT
REAR OF RELAY
I
S2
2
AUX
UNRES
P6
J2
D
B
AUX RES
ON
S1
CR19
CR7
42
LH EDGE OF ANALOG #2
BOARD (THE 4TH BOARD
DOWN, COUNTING THE
MAGNETIC BOARD.)
AR
J11
J2
VR2
TP+12V
C1
J1
0A
0B
0C
J9
J10
IN
1
IN
2
IN
3
∆
1
∆
2
WYE
∆
1
∆
2
WYE
∆
1
∆
2
WYE
P0052-26
BE1-87T
Figure 2-4. Controls Mounted Inside the Relay
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 2-7
Page 32
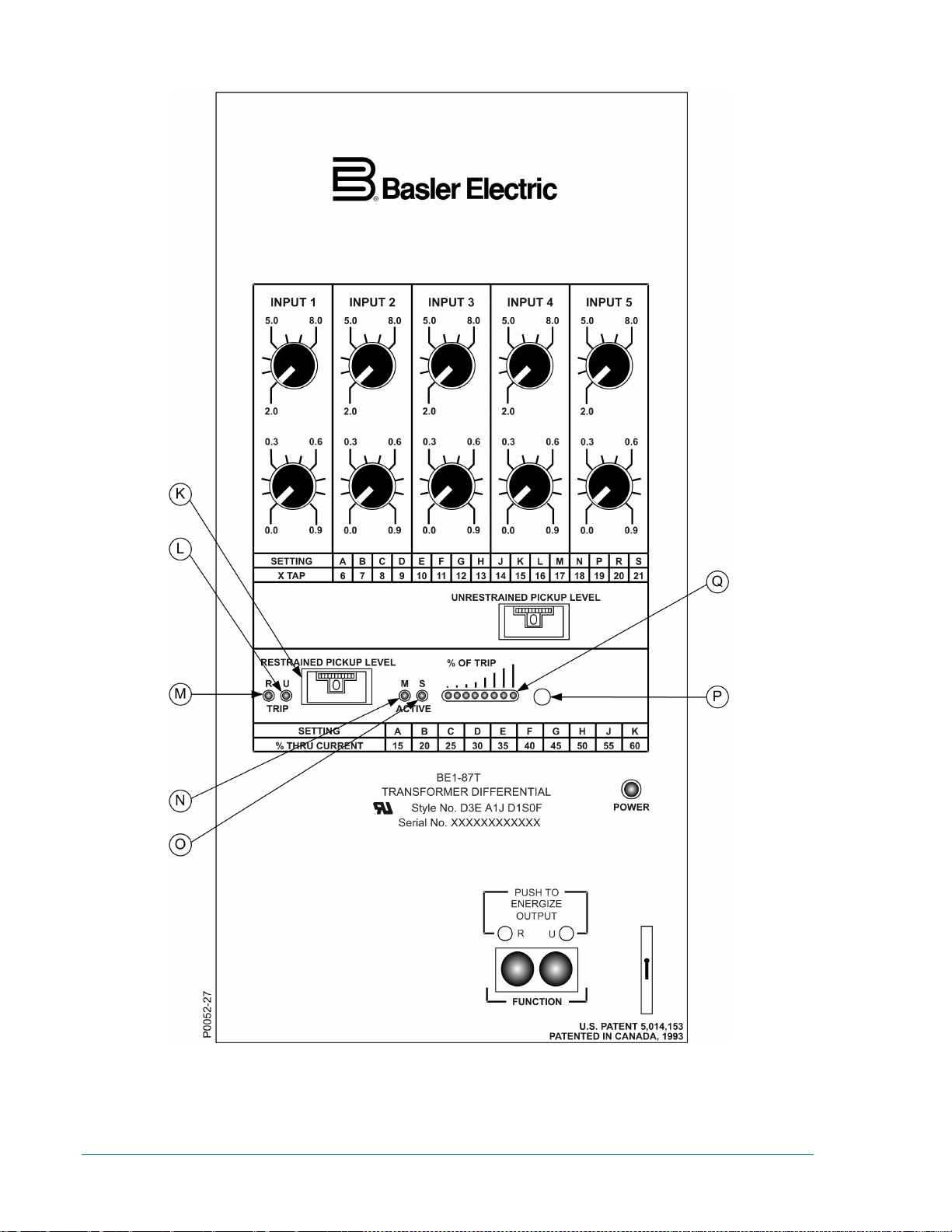
Figure 2-5. Sensing Input Range 2 or 4, Option 1-1, Single-Phase, Five Inputs, % OF TRIP Option
2-8 BE1-87T Controls and Indicators 9171300990 Rev V
Page 33

SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ........................................................................................... 3-1
General .................................................................................................................................................. 3-1
Description ............................................................................................................................................. 3-1
Current Transformers ......................................................................................................................... 3-1
Scaling ................................................................................................................................................ 3-1
Summing ............................................................................................................................................ 3-1
30° Internal Phase Shift (Three-Phase Relays ONLY) ...................................................................... 3-1
Restrained Trip Output ....................................................................................................................... 3-3
Unrestrained Trip Output .................................................................................................................... 3-3
Auxiliary Relay Option ........................................................................................................................ 3-4
Power Supply ..................................................................................................................................... 3-4
Power Supply Status Output (Optional) ............................................................................................. 3-4
Target Indicators (Optional)................................................................................................................ 3-4
% of Trip ............................................................................................................................................. 3-5
Figures
Figure 3-1. Functional Block Diagram ....................................................................................................... 3-2
Figure 3-2. Functional Block Diagram, Phase B and Phase C ................................................................. 3-2
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Functional Description i
Page 34

ii BE1-87T Functional Description 9171300990 Rev V
Page 35

SECTION 3 • FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3
General
BE1-87T relays are solid-state devices that protect transformers by providing output contact closure when
the scaled current into the protected transformer does not equal the scaled current out, within defined
limits. These relays are harmonically restrained to prevent tripping during initial energization and external
fault conditions. A through-current restraint also provides security against tripping for external faults. An
unrestrained tripping element is included to provide a high-speed trip in the event of a particularly severe
fault within the transformer.
Description
The functional block diagrams of Figures 3-1 and 3-2 illustrate the overall operation of the BE1-87T
Transformer Differential Relay. (Figure 3-1 shows Phase A or single-phase functions; Figure 3-2 shows
the additional functions for phases B and C.) Since the three phases are functionally similar, only phase A
is shown in detail in Figure 3-1. Note that in a three-phase unit, there may be one restrained output for
each phase (Output Type Option E in the third position of the Style Number), or one restrained output that
serves for all three phases (Option F in the third position). When Target Option C or D is specified for a
three-phase Unit (in the seventh position), an individual target is supplied for each phase.
Current Transformers
In the protected zone of the power system, CTs with a 1 ampere or 5 ampere secondary winding supply
not
the sensing current for each input. This is
connected ahead of the BE1-87T. Sensing currents are, in turn, applied to relay internal input
transformers. These transformers provide system isolation.
shown in Figure 3-1 or Figure 3-2. Other relays may be
Scaling
Input currents are scaled by the front panel INPUT rotary switches that introduce resistances to the
internal CT secondaries. The switches are calibrated in 0.02 ampere increments from 0.4 to 1.78 ampere
for 1 ampere CT units (Options 2 or 4 in the second position of the Style Number), and in 0.1 ampere
increments from 2.0 to 8.9 amperes for 5 ampere CT models (Options 1 or 3 in the second). The many
graduations of adjustment are provided to allow each input to approach an ideal representation of the
actual operating per unit value.
Summing
Analog signals representing each input contribution are vector summed (shown as Summing in Figure 3-
1). This summing process produces the operating current (I
currents.
Ideally, and with perfectly matched CTs, a transformer without an internal fault should cause I
exactly zero on a continuous basis. When not zero, a fault would be indicated. However, saturation effects
caused by heavy through-current or magnetic inrush can cause a temporary imbalance even though no
internal fault has occurred. To prevent a false trip under such conditions, various types of restraint are
used. Each restraint is specific to a potential cause of misoperation. These are individually discussed in
the topic Restrained Trip Output.
) that is the phasor sum of the input
OP
to be
OP
30° Internal Phase Shift (Three-Phase Relays ONLY)
For three-phase units, the inputs to the Summing function are first routed through the 30° Phase Shift
circuit. There the signals may be advanced or retarded by 30° or passed through unchanged.
Compensating phase shift direction (shown as the Phase Shift Setting circuit in Figure 3-1) is determined
by the position of three jumpers on the internal Analog #2 Board. (The location of these jumpers is shown
in Figure 2-4.) The internal phase shift will accomplish the corresponding zero sequence blocking. The
current magnitude will be increased by
later in detail in Section 4).
and must be taken into account in the tap setting (explained
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Functional Description 3-1
Page 36

Figure 3-1. Functional Block Diagram
B
C
4
RESTRAINED
UNRESTRAINED
RESTRAINED
UNRESTRAINED
TARGET
TARGET
B SAME AS A
0
0
OR
OR
B
0
C0C SAME AS A
0
0
0
0
OPTIONAL
RESTRAINED
CONTACTS
FOR EACH OF
3 PHASES
(SEE NOTE
5
BE1-87T
D741-001b
7-11-94
COM.
IN. 1
IN. 2
IN. 3
COM.
IN. 1
IN. 2
IN. 3
0
B
0
C
S2
S1
IN. 3, B SCALE
IN. 3, C SCALE
0
0
IN. 1, B SCALE
IN. 1, C SCALE
0
0
OPERATING
POWER
POWER
SUPPLY
POWER
SUPPLY
STATUS
5
REST.
TRIP
AUX.
OPTION
UNREST
TRIP
TARGET
UNRESTRAINED
B
RESTRAINED
6
POWER
TO INTERNAL
CIRCUITRY
Iop1
SHIFT SETTING:
+30
°
, -30
°
, 0
°
8
LEDs
CALCULATE
MAXIMUM
INDIVIDUAL
CURRENT
THEN TRIP
op
I
IF
>
%
max
I
% OF
TRIP
UNREST. SETTING
COM.
IN. 1
IN. 2
IN. 3
IN. 4
IN. 5
TO OTHER PHASES
(THREE-PHASE ONLY)
UNREST
TRIP
(6 TO 21
TIMES TAP)
2
0
30
°
SHIFT
(ONLY ON
3 UNITS)
0
0
SCALING
( TAP)
SCALING
( TAP)
SCALING
( TAP)
IN. 2, B SCALE
IN. 2, C SCALE
0
0
SCALING
( TAP)
0
C05TH >
SETTING
=INHIBIT
3
2ND >
SETTING
=INHIBIT
3
OR
B
C00
4
TARGET
TARGET
SCALING
( TAP)
POWER
SUPPLY
SENSOR
FIFTH
HARMONIC
RESTRAINT
FILTERS
SECOND
HARMONIC
RESTRAINT
FILTERS
SUMMING:
ALGEBRAIC
SUM OF
INPUTS =
OPERATING
CURRENT
( )
I
op
OR
30
°
SHIFT
(ONLY ON
3 UNITS)
0
0
30
°
SHIFT
(ONLY ON
3 UNITS)
0
0
2
max
I
% I
max
REST.
T
PICKUP
CONTROL
% I
max
op
I
UNREST.
SETTING
THEN TRIP
IF I >
op
A
OR
1
0
0
BE1-87T
D741-001a
7-11-94
NOTES
1 Present in three-phase units ONLY.
2 Inputs 4 and 5 are available in single-phase units ONLY.
3 The settings are calibrated to a specified percentage of the harmonic to the fundamental. See Harmonic
Restraints for factory settings.
4 Phase Targets are supplied on three-phase units ONLY.
5 Restrained Trip Contact:
• One contact for single-phase units.
• One contact or one contact per phase available on three-phase units.
6 Three-phase units use the sum of the second harmonic from each phase to restrain each phase.
7 Phase Targets are supplied on three-phase units ONLY.
8 Restrained Trip Contact:
• One contact for single-phase units.
• One contact or one contact per phase available on three-phase units.
3-2 BE1-87T Functional Description 9171300990 Rev V
Figure 3-2. Functional Block Diagram, Phase B and Phase C
Page 37

Restrained Trip Output
Restrained trip output contacts are subject to three types of restraint (i.e., inhibit) signals:
• Percentage restraint
• Second-harmonic restraint
• Fifth-harmonic restraint
These signals are developed within the relay in response to external conditions and block the restrained
output contacts from closing.
Percentage Restraint
Percentage restraint developed from the maximum through current and the slope setting determines the
minimum operating current I
produce a Restraint Trip output. The I
(Figure 3-1) in a comparator where I
OP
desired trip level is adjustable on the front panel RESTRAINED
OP
PICKUP LEVEL switches shown in Figures 2-1 through 2-3.
Comparators in the Calculate Max. Individual Current circuit determine which input (of a particular phase)
is receiving the greatest current. That input is chosen and then called the I
then scaled by the front panel RESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL switches (shown as the Restrained Pickup
Control in Figure 3-1). The resulting signal (%I
extended to the Then Trip comparator and the I
The Then Trip circuitry compares the operating current (I
than %I
(and there is no 5th or 2nd harmonic restraint to cause an inhibit as described below), a
MAX
), that represents the percentage of through-current is
MAX
Divided By %I
OP
OP
MAX
) to %I
function.
Restrained Trip output is produced.
Divided By %I
I
OP
. If IOP is greater than the preset percent of %I
%I
MAX
contains eight comparators and compares IOP to the preset percentage levels of
MAX
for a specific comparator, the LED associated with
MAX
that comparator lights. The eight LEDs represent the following approximate percentages:
First LED: 3%
Second LED: 7%
Third LED: 11%
Fourth LED: 20%
Fifth LED: 40%
Sixth LED: 60%
Seventh LED: 80%
Eighth LED: 100%
must be greater than %I
OP
signal. The I
MAX
. If the operating current is greater
MAX
output is
MAX
MAX
to
NOTE
As each successive LED lights, all previous or lesser percentage value LEDs
will also light.
Harmonic Restraints
Development of a restrained trip output may be inhibited by either of two harmonic restraints. These are
generated by bandpass filters tuned to the second and fifth harmonics of the operating current.
Comparators monitor these signals. When the fifth-harmonic content exceeds 35% of the operate current
(indicating overexcitation of the transformer) or when the second-harmonic content exceeds 12% (singlephase) or 18% (three-phase) of the operate current (indicating a magnetic inrush condition), an inhibit
signal is developed that blocks operation of the Restrained Trip output contact. (Stated percentages
represent the factory setting.)
Unrestrained Trip Output
IOP is also compared against a reference established by the front panel UNRESTRAINED PICKUP
LEVEL switch is shown in Figures 2-1 through 2-5. When this reference is exceeded, the Unrestrained
Tr i p output relay is energized. An unrestrained trip is not affected by through-current or harmonic inhibits.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Functional Description 3-3
Page 38

Auxiliary Relay Option
Auxiliary relays (Option 3-1, 3-2 or 3-5 in the tenth position of the Style Number) are accompanied by two
switches, S1 and S2, which allow the relays to respond to a restrained trip (S1 ON) or to an unrestrained
trip (S2 ON), or both (S1 and S2 ON). These switches (letter I of Figure 2-4 and described in Table 2-1)
are located on the mother board and are shipped in the ON position. Auxiliary relays may be disabled by
opening both switches (S1 and S2 OFF).
Power Supply
Relay operating power is developed by a wide-range, isolated, low-burden, switching power supply that
delivers ±12 Vdc to the relay’s internal circuitry. The power supply is not sensitive to the input power
polarity. A front panel LED power indicator lights to indicate that the power supply is functioning properly.
Style number designations and input voltage ranges for the available power supply models are provided
in Section 1, General Information.
Power Supply Status Output (Optional)
The Power Supply Status output relay has normally closed (NC) contacts. The relay is energized by the
presence of nominal voltage at the output of the power supply. Normal operating voltage then keeps the
relay continuously energized and its contacts open. However, if the power supply voltage falls below
requirements, the Power Supply Status output relay will de-energize and close the contacts.
The Power Supply Status output is not associated with any magnetically latched target. The POWER LED
on the front panel provides a visual indication of the normal operating status of the power supply.
NOTE
Sensing Input Types A through E (first position of the Style Number) have
paddle-operated shorting bars included in the relay case (terminals 19 and 20)
so that the Power Supply Status output terminals can provide a remote
indication that the BE1-87T has been withdrawn from its case or that it has
been taken out of service by removing the connection plugs. Sensing Input
Type G relays do NOT have shorting bars on the Power Supply Status output.
Sensing Input Type G units use terminal 9 (lower terminal block) and terminal
19 (upper terminal block) for the Power Supply Status output.
Target Indicators (Optional)
When the Target option is specified as either C or D, shown in the seventh position of the Style Number,
electronically latched indicators, labeled FUNCTION, are incorporated in the front panel. The
electronically latched and reset targets consist of red LED indicators. The appropriate target is tripped
when either a restrained (R) or unrestrained (U) output occurs. Latched targets are reset by operating the
target reset switch on the front panel. If relay operating power is lost, any illuminated (latched) targets are
extinguished. When relay operating power is restored, the previously latched targets are restored to their
latched state.
When targets are specified for three-phase relays, three additional ELEMENT targets are incorporated to
indicate the phase involved. Only the FUNCTION targets, restrained (R) or unrestrained (U) are available
for single-phase units.
Relays can be equipped with either internally operated targets (Type C) or current operated targets (Type
D). Both target types are reset by operating the target reset switch.
• Type C target (referred to as internally operated) is actuated by an integral driver circuit that
responds directly to the relay internal logic. This type of target is tripped regardless of the amount
of current flowing through the associated output contact.
• Type D target (referred to as current operated) is actuated when a minimum of 0.2 A flows
through the associated output contacts. To accomplish this, a special reed relay is placed in
series with the contact to signal the target indicator. (The series impedance of the reed relay is
less than 0.1 ohm.) Current in the output circuit must be limited to 30 amperes for 0.2 seconds, 7
amperes for 2 minutes and 3 amperes continuously.
3-4 BE1-87T Functional Description 9171300990 Rev V
Page 39

NOTE
87T target indicators consisted of
Prior to September 2007, the BE1magnetically latched, disc indicators. These mechanically latched target
indicators have been replaced by the electronically latched LED targets in use
today.
% of Trip
When the % of trip pushbutton Q is pushed, eight LEDs, shown in Figure 2-5, are used to indicate the
percentage of operating current to: Minimum pickup (LED M also lights); or Slope characteristic pickup
(LED S also lights). The eight LEDs represent the following percentages:
1 LED: 3% (Yellow LED)
2 LEDs: 7% (Yellow LED)
3 LEDs: 11% (Yellow LED)
4 LEDs: 20% (Red LED)
5 LEDs: 40% (Red LED)
6 LEDs: 60% (Red LED)
7 LEDs: 80% (Red LED)
8 LEDs: 100% (Red LED)
A bar chart above the LEDs shows the relative percentage of trip.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Functional Description 3-5
Page 40

3-6 BE1-87T Functional Description 9171300990 Rev V
Page 41

SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION .................................................................................................................. 4-1
General .................................................................................................................................................. 4-1
Relay Operating Precautions ................................................................................................................. 4-1
Mounting ................................................................................................................................................ 4-2
Dielectric Test ........................................................................................................................................ 4-9
Connections ........................................................................................................................................... 4-9
Relay Disassembly .............................................................................................................................. 4-17
Precautions ...................................................................................................................................... 4-17
Circuit Board Removal Procedure .................................................................................................... 4-17
Disabling Unused Inputs ...................................................................................................................... 4-18
Single-Phase Units ........................................................................................................................... 4-20
Three-Phase Units ........................................................................................................................... 4-20
Sensing Connection Diagrams ............................................................................................................ 4-20
Single-Phase Input Sensing Connections ........................................................................................ 4-20
Three-Phase Input Sensing Connections ........................................................................................ 4-24
Setting the BE1-87T ............................................................................................................................. 4-33
Method.............................................................................................................................................. 4-33
Procedure One ................................................................................................................................. 4-33
Procedure Two ................................................................................................................................. 4-42
Checking the Relay Settings and System Inputs ................................................................................. 4-49
Maintenance......................................................................................................................................... 4-50
Storage ................................................................................................................................................. 4-50
Test Plug .............................................................................................................................................. 4-51
Figures
Figure 4-1. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Semi-Flush, M1 Case .......................................................................... 4-2
Figure 4-2. M1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount ................................... 4-3
Figure 4-3. M1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount
Figure 4-4. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Double Ended, Projection Mount, M1 Case
Figure 4-5. M1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Projection Mount
Figure 4-6. M1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Projection Mount
Figure 4-7. M1 Case Cover Dimensions, Front View
Figure 4-8. Case Terminals: Single-Phase
Figure 4-9. Case Terminals: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option E
Figure 4-10. Case Terminals: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option F
Figure 4-11. Case Terminals: Three-Phase, Three Input (Sensing Input Type G), Output Option E
Figure 4-12. Internal Connections: Single-Phase, Five Input (Sensing Input Type D), Output Option E
Figure 4-13. Internal Connections: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option E
Figure 4-14. Internal Connections: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option F
Figure 4-15. Internal Connections: Three-Phase, Three Input (Sensing Input Type G), Output Option E
15
Figure 4-16. Control Circuits: Single-Phase, Output Option E
Figure 4-17. Control Circuits: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input E), Output Option E
Figure 4-18. Control Circuits: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input E), Output Option F
Figure 4-19. Control Circuits: Three-Phase, Three Input (Sensing Input G), Output E
Figure 4-20. Side View of Cradle Assembly
Figure 4-21. Unused Input-Disabling Jumpers, Analog #1 Board: Option 1-0
Figure 4-22. Unused Input-Disabling Jumpers, Analog #1 Board: Option 1-1
Figure 4-23. Typical Single-Phase Sensing Connections
Figure 4-24. Single-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration ........................................................ 4-21
Figure 4-25. Single-Phase Connections, Wye-Wye Configuration
Figure 4-26. Single-Phase Connections, Delta-Delta-Wye Configuration
Figure 4-27. Single-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration With Two Load Busses
Figure 4-28. 30° Phase Shift Compensation Jumpers
. 4-
................................... 4-4
........................................ 4-5
..................................... 4-6
...................................... 4-7
................................................................................ 4-8
............................................................................................... 4-9
.......... 4-10
........ 4-10
..... 4-11
4-12
4-13
4-14
................................................................ 4-15
.................. 4-16
.................. 4-16
.......................... 4-17
............................................................................................ 4-18
........................................ 4-19
........................................ 4-19
....................................................................... 4-21
......................................................... 4-22
............................................... 4-23
.................. 4-24
............................................................................ 4-26
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation i
Page 42

Figure 4-29. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration, CT Compensation .......................... 4-27
Figure 4-30. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration, Internal Phase Compensation
Figure 4-31. Three-Phase Connections, Wye-Delta Configuration, Internal Phase Compensation
Figure 4-32. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Delta Configuration
Figure 4-33. Three-Phase Connections, Wye-Wye or Autotransformer Configuration, CT Compensation
30
Figure 4-34. Three-Phase Connections, Wye-Wye or Autotransformer Configuration, Internal Phase
Compensation
Figure 4-35. Three-Phase Connections, Autotransformer With Loaded Delta Tertiary
Figure 4-36. Application Example: Autotransformer With Tertiary Winding
Figure 4-37. Slope Needed to Accommodate Total Mismatch with Adequate Margin
Figure 4-38. Two Winding Transformer Relay Setting Calculation Example
4-
Tables
Table 4-1. List of Variables ...................................................................................................................... 4-34
Table 4-2. Examples of Suitable Slope Settings
Table 4-3. Single-Phase Input Terminals
Table 4-4. Input Conditions For Non-Trip Three-Phase Sensing
....... 4-27
....... 4-28
........................................................ 4-29
.......................................................................................................................................... 4-31
.......................... 4-32
............................................ 4-35
............................ 4-40
.......................................... 4-42
..................................................................................... 4-41
................................................................................................ 4-49
............................................................ 4-50
ii BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 43

SECTION 4 • INSTALLATION
General
When not shipped as part of a control or a switchgear panel, the relay is shipped in a sturdy carton to
prevent damage during transit. Immediately upon receipt of a relay, check the model and Style Number
against the requisition and packing list to see that they agree. Visually inspect the relay for damage that
may have occurred during shipment. If there is evidence of damage, immediately file a claim with the
carrier and notify the Regional Sales Office, or contact a sales representative at Basler Electric, Highland,
Illinois.
In the event the relay is not to be installed immediately, store the relay in its original shipping carton in a
moisture- and dust-free environment. For more information, see Storage in Section 4. When the relay is to
be placed in service, it is recommended that the Verification Tests, shown in Section 5, be performed
prior to installation.
Relay Operating Precautions
Before installation or operation of the relay, note the following precautions.
1. A minimum of 0.2 A in the output circuit is required to ensure operation of current-operated
targets.
2. The relay is a solid-state device and has been type tested in accordance with the requirements
defined under Dielectric Test. If a wiring insulation test is required on the panel assembly in
which the relay is to be installed, it is suggested that the connection plugs (or paddles) of the
relay be removed and the cradle withdrawn from the case so as not to produce false readings
during the wiring insulation test.
3. When the connection plugs are removed, the relay is disconnected from the operating circuit
and will not provide system protection. Always be sure that external operating (monitored)
conditions are stable before removing a relay for inspection, testing, or servicing. Be sure that
connection plugs are in place before replacing the front cover.
CAUTION
To prevent possible false tripping, the upper connection plug should be in
place prior to removing or installing the lower connection plug.
4. Thumbwheel switches should not be changed while the relay is in service. Momentary
undesired indications and outputs may occur.
WARNING!
The TEST PROCEDURES require familiarity with solid-state relay circuits. To
avoid personal injury or equipment damage, do not proceed unless qualified in
this area.
NOTE
Several procedures in this manual require the removal of printed circuit
boards. Refer to the topic Relay Disassembly before installing the BE1-87T.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-1
Page 44
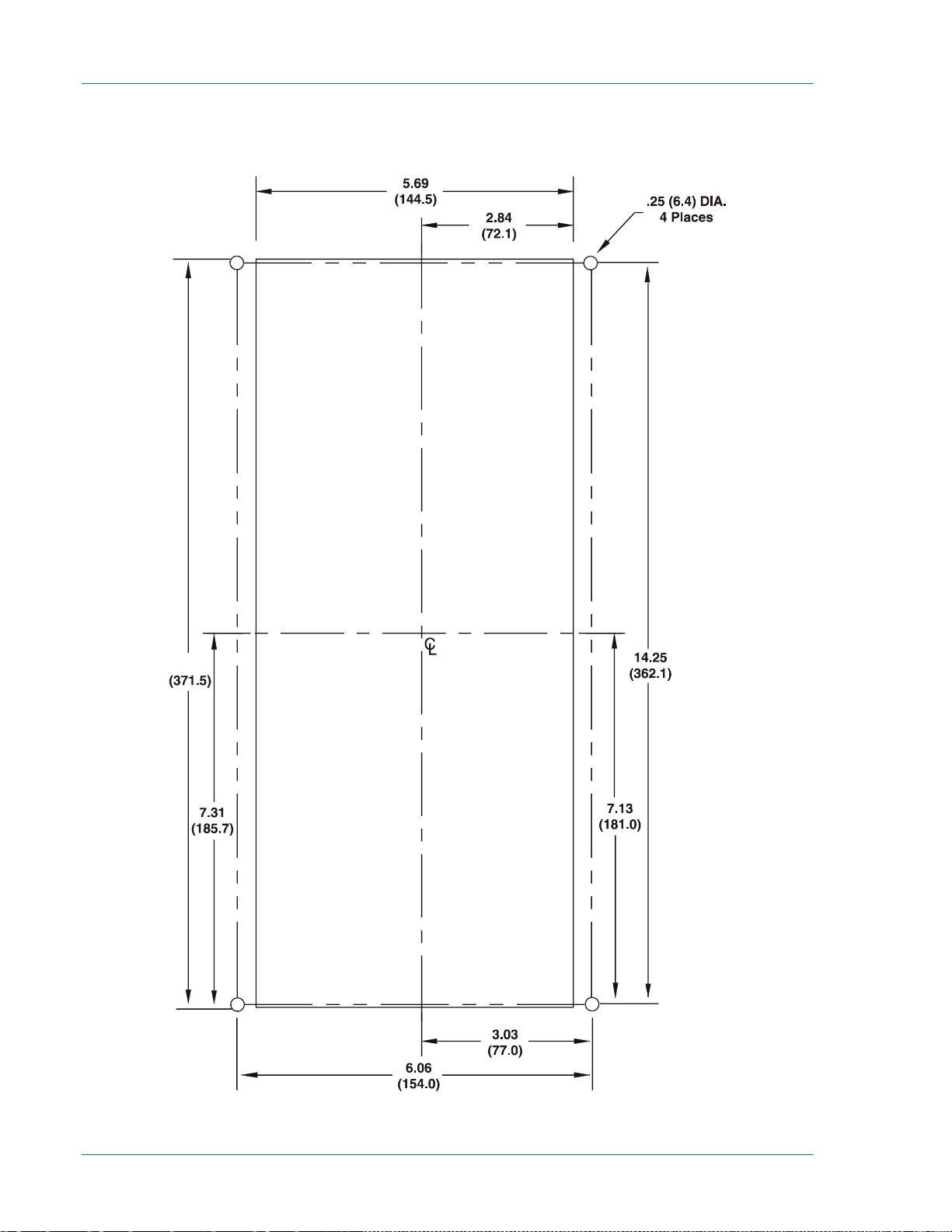
Mounting
14.63
P0066-74
Because the BE1-87T, Transformer Differential Relay, is of solid-state design. It does not have to be
mounted vertically. Any convenient mounting angle may be chosen. The BE1-87T relay is supplied in a
standard M1 size drawout case and can be either semi-flush or projection mounted (Option 4). Refer to
Figures 4-1 through 4-7 for outline dimensions and panel drilling diagrams.
Figure 4-1. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Semi-Flush, M1 Case
4-2 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 45

Figure 4-2. M1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-3
Page 46

P0066-76
10-32 SCREWS
10-32 SCREWS
MOUNTING PANEL
2.195
(55.75)
.31
(7.9)
.31
(7.9)
.75
(19.1)
6.19
(157.2)
1.95
(49.53)
7.03
(178.56)
7.03
(178.56)
Figure 4-3. M1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Semi-Flush Mount
4-4 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 47

Figure 4-4. Panel Cutting/Drilling, Double Ended, Projection Mount, M1 Case
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-5
Page 48

Figure 4-5. M1 Case Dimensions, Rear View, Double Ended, Projection Mount
4-6 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 49

P0066-78
10-32 SCREWS
10-32 SCREWS
2.195
(55.75)
.31
(7.9)
.31
(7.9)
.75
(19.1)
6.19
(157.2)
1.95
(49.53)
7.03
(178.56)
7.03
(178.56)
TERMINAL EXTENTION (TYP.)
FOR DETAILED INSTRUCTIONS,
SEE THE TERMINAL PROJECTION
MOUNTING KIT SUPPLIED.
.25
(6.4)
5/16-18 STUD
2 PLACES
MOUNTING PANEL
Figure 4-6. M1 Case Dimensions, Side View, Double Ended, Projection Mount
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-7
Page 50

P0066-79
Figure 4-7. M1 Case Cover Dimensions, Front View
4-8 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 51

Dielectric Test
In accordance with IEC 255-5 and ANSI/IEEE C37.90-1989, one minute dielectric (high potential) tests
may be performed as follows.
• All circuits to ground: 2,121 Vdc
• Input to output circuits 1,500 Vac or 2,121 Vdc
Note that this device employs decoupling capacitors to ground at all the output terminals, and at the
power supply terminals (3, 4). Accordingly, a leakage current of approximately 15 milliamperes per 1000
Vac is to be expected.
Connections
Incorrect wiring may result in damage to the relay. Be sure to check the model and Style Number against
the options listed in the Style Number Identification Chart (Figure 1-1) before connecting and energizing a
particular relay.
NOTE
Be sure the relay case is hard-wired to earth ground with no smaller than 12
AWG copper wire attached to the ground terminal on the rear of the relay
case. When the relay is configured in a system with other protective devices, it
is recommended to use a separate lead to the ground bus from each relay.
Except as noted above, connections should be made with a minimum wire size of 14 AWG. Figures 4-7
through 4-10 show case terminals designations for four typical relay configurations. Figures 4-11 through
4-14 show the internal connections of the BE1-87T. Control circuit connections are shown in Figures 4-15
through 4-18.
CAUTION
To prevent possible false tripping, the upper connection plug should be in
place prior to removing or installing the lower connection plug.
Figure 4-8. Case Terminals: Single-Phase
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-9
Page 52

Figure 4-9. Case Terminals: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option E
Figure 4-10. Case Terminals: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option F
4-10 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 53
Figure 4-11. Case Terminals: Three-Phase, Three Input (Sensing Input Type G), Output Option E
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-11
Page 54

Figure 4-12. Internal Connections: Single-Phase, Five Input (Sensing Input Type D), Output Option E
4-12 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 55

Figure 4-13. Internal Connections: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option E
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-13
Page 56
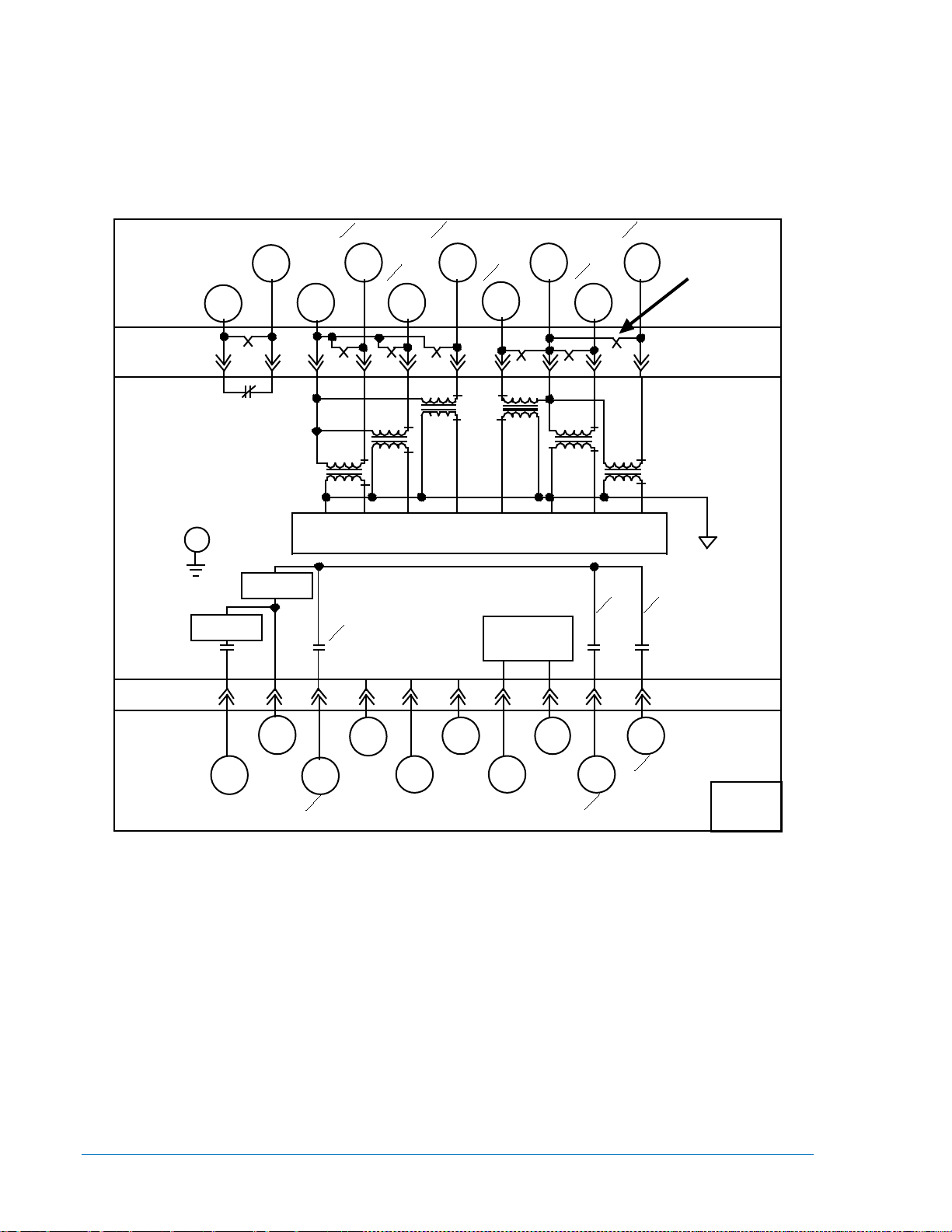
EXTERNAL
CASE
GROUND
TERMINAL
PADDLE
OPERATED
SHORTING
BARS
POWER
SUPPLY
STATUS
INTERNAL CIRCUITRY
TARGET
11
13
12
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1 3
2 4
5
6
7
8
9
10
UNREST
COM
REST REST
REST
D983-025
2-18-93
BE1-87T
POWER
SUPPL Y
UNREST
.
TRIP
C2 A2 COM 1
COM2
B2 C1
0
0
0
0
B1
0
A1
0
TARGET
REST
TRIP
C
0
REST
TRIP
B
0
REST
TRIP
A
0
B
0
A
0
C
0
Figure 4-14. Internal Connections: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input Type E), Output Option F
4-14 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 57

D983-023
2-18-93
BE1-87T
POWER
SUPPLY
STATUS
TRIP
UNREST
POWER
SUPPLY
EXTERNAL
CASE
GROUND
TERMINAL
INTERNAL CIRCUITRY
11
12
13
14
15
16
18
17
PSS
19
20
COM
REST
TRIP
TARGET
UNREST
10
PSS
1
3
COM3
2
5
4
6
7
REST
8
9
PADDLE
OPERATED
SHORTING
BARS
C2 A2 COM 1
COM2
B2 C1
0
0
0
0
B1
0
A1
0
C3
0
B3
0
A3
0
TARGET
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
86
86
9
8
10
RESTRAINED
UNREST
3
4
5
6
7
19
20
POWER
SUPPLY
STATUS
1
D240-008
4-21-94
BE1-87T
87T
POWER
TARGET
(OPTIONAL)
TARGET
(OPTIONAL)
LEGEND:
SINGLE-PHASE: NO, NC, OR SPDT
.
OPTIONAL CURRENT-OPERATED
87T
TRANSFORMER DIFFERENTIAL
86 LOCKOUT RELAY
1
2
RELAY
TARGETS
AUXILIARY OUTPUT OPTION FOR
2
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-15
Figure 4-15. Internal Connections: Three-Phase, Three Input (Sensing Input Type G), Output Option E
Figure 4-16. Control Circuits: Single-Phase, Output Option E
Page 58

87T
87T
87T 87T 87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
87T
86
86
9
8
10
RESTRAINED
UNREST
3
4
1 5
2
19
20
D240-015
4-21-94
BE1-87T
87T
POWER
1
TARGET
(OPTIONAL)
TARGET
(OPTIONAL)
POWER
SUPPLY
STATUS
LEGEND:
SINGLE-PHASE: NO, NC, OR SPDT
.
OPTIONAL CURRENT-OPERATED
87T
TRANSFORMER DIFFERENTIAL
86 LOCKOUT RELAY
1
2
RELAY
TARGETS
AUXILIARY OUTPUT OPTION FOR
2
87T
UNRESTRAINED
87T
RESTRAINED
PHASE A
87T
RESTRAINED
PHASE B
87T
RESTRAINED
PHASE C
86
87T
20
87T
19
87T
3
87T
4
87T
10
87T
8
87T
9
87T
2
87T
1
D329-004
3-7-91
BE1-87T
1
TARGET
(OPTIONAL)
TARGET
(OPTIONAL)
POWER
SUPPLY
STATUS
LEGEND:
.
1
86
87T
POWER
OPTIONAL CURRENT-
87T
TRANSFORMER
86 LOCKOUT RELAY
1
DIFFERENTIAL RELAY
OPERATED
TARGETS
Figure 4-17. Control Circuits: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input E), Output Option E
4-16 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Figure 4-18. Control Circuits: Three-Phase, Two Input (Sensing Input E), Output Option F
Page 59
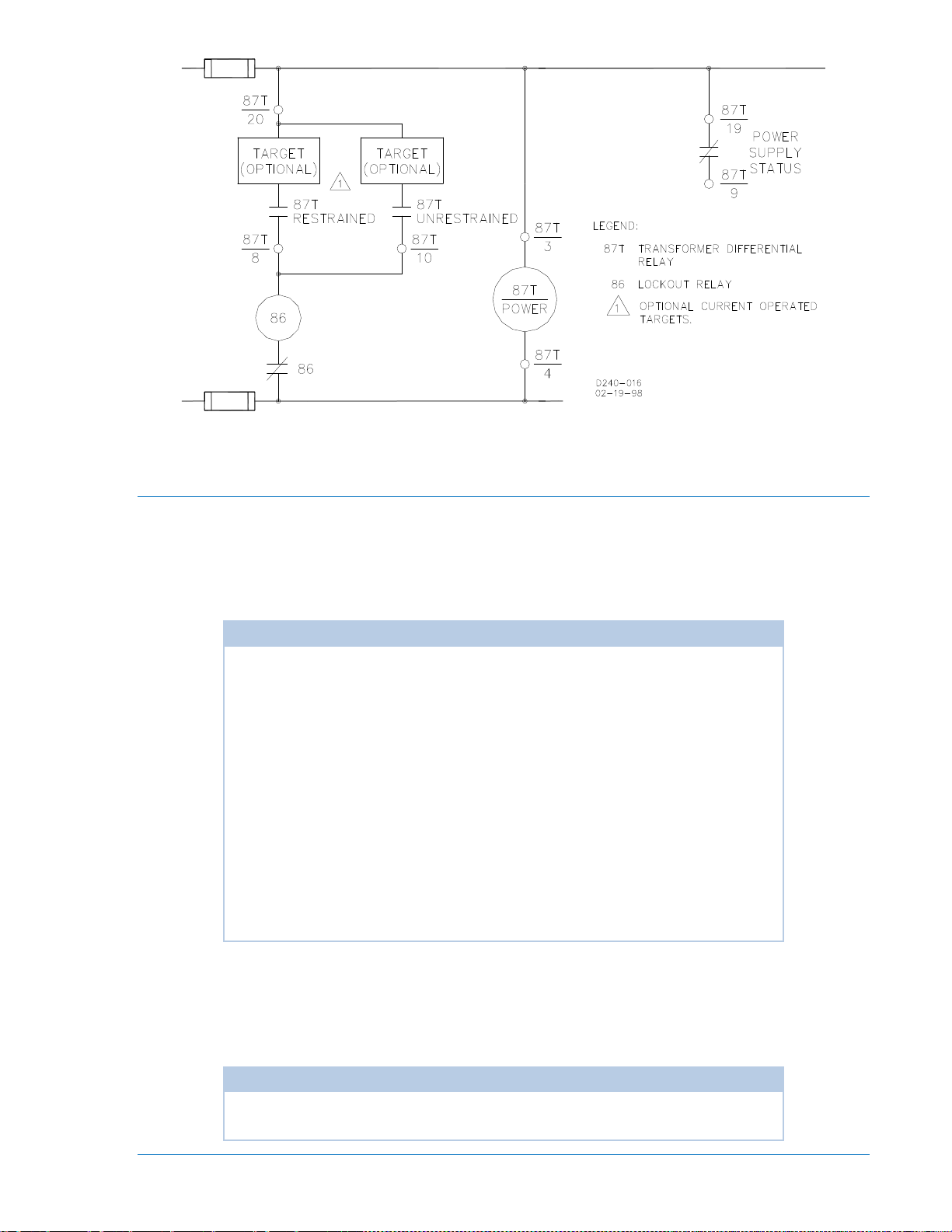
Figure 4-19. Control Circuits: Three-Phase, Three Input (Sensing Input G), Output E
Relay Disassembly
Precautions
The following procedures require the removal and handling of the internal printed circuit boards. Figure 419 shows the location of major components and assemblies. Because some of the components are
vulnerable to electrostatic charge, the following precautions should be observed.
CAUTION
1. Always remove power from the BE1-87T by removing the connection
plugs before removing or installing a printed circuit board.
2. Always neutralize static body charge before placing a printed circuit board
on—or removing one from—metal surfaces. This can be accomplished by
placing your hand on the metal surface before handling the boards.
3. Never pass a printed circuit board to another person whose static body
charge has not been neutralized.
4. Testing or troubleshooting should always be done on a conductive and
grounded (static-controlled) surface.
5. Never test printed circuit boards with an ohmmeter. The test current from
the ohmmeter may exceed component ratings.
6. Printed circuit boards or integrated circuits should be transported only in
electrically conductive containers. The use of ordinary plastic bags may
result in damage from static charge buildup.
Circuit Board Removal Procedure
Step 1. Remove the front cover and connection plugs.
CAUTION
To prevent possible false tripping, the upper connection plug should be in
place prior to removing or installing the lower connection plug.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-17
Page 60

Step 2. Withdraw the cradle assembly (see Figure 4-19).
proceed unless
Relay Operating
MOTHERBOARD
FRONT
PANEL
FRONT
PANEL
MOTHERBOARD
SINGLE-PHASE THREE-PHASE
ANALOG BOARD #1
POWER SUPPLY
POWER SUPPLY
ANALOG BOARD #2
ANALOG BOARD #1
ANALOG BOARD #1
ANALOG BOARD #1
ANALOG BOARD #2
UPPER SWITCH BOARD
LOWER SWITCH BOARD
UPPER SWITCH BOARD
LOWER SWITCH BOARD
D638-003
2-23-93
BE1-87T
0 A
0 B
0 C
Step 3. Remove the four screws that attach the front panel to the cradle assembly, and remove the
front panel.
Step 4. With a slight side-to-side rocking motion, withdraw Analog Board #1.
Disabling Unused Inputs
To eliminate the possibility of a spurious input from induced currents within the relay, special internal
jumpers have been provided to disable any inputs that are not connected to CT wires.
Disabling unused inputs requires disassembly of the relay and must be done
when the relay has been taken out of service. Access to the input-disabling
jumpers requires the removal of the Analog #1 Board, shown in Figure 4-19.
To avoid personal injury or equipment damage, do NOT
thoroughly familiar with the instructions in sections
Precautions and Relay Disassembly: Precautions.
Figure 4-20. Side View of Cradle Assembly
CAUTION
4-18 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 61

R59
R60
OBJECTIVE JUMPER POSITION
DISABLE INPUT 3
ENABLE INPUT 3
DISABLE INPUT 5
ENABLE INPUT 5
DISABLE INPUT 4
ENABLE INPUT 4
J3
J2
J1
J1
J2
J3
RIGHT-HAND EDGE OF ANALOG BOARD #1
(LOOKING FROM FRONT OF RELAY.)
FOR ALL 2-INPUT RELAYS (BOTH SINGLE- AND
THREE-PHASE), ALL JUMPERS MUST BE IN
THE DISABLE POSITION AT ALL TIMES.
FOR OTHER RELAYS, SEE CHART BELOW .
.
C33
C44
AR22
AR19
AR18
AR21
CR14
CR15
C45
R48
R29
R21
R28
R54
R3
R49
C21
C34
C18
R58
U10
22
3
J3
J2
J1
EN
OIS
NOTE:
D641-001
9-21-94
BE1-87T
DISABLE INPUT 3
ENABLE INPUT 3
DISABLE INPUT 5
ENABLE INPUT 5
DISABLE INPUT 4
ENABLE INPUT 4
FACTORY
ADJUSTMENT
J9
NOT FIELD
ADJUSTABLE
OBJECTIVE
JUMPER
POSITION
J2 & J5
J3 & J6
J1 & J4
J1 & J4
J3 & J6
J2 & J5
TP1
TP2
TP3
TP4
TP7
TP8
TP9
TP10
TP11
J1
J2
J3
J4
J5
J6
J9
AGND
AR5
U17
R177
C2
TP6
-12V
R163
+
D1924-12
9-21-94
BE1-87T
Figure 4-21. Unused Input-Disabling Jumpers, Analog #1 Board: Option 1-0
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-19
Figure 4-22. Unused Input-Disabling Jumpers, Analog #1 Board: Option 1-1
Page 62

Single-Phase Units
Single-Phase Units with Option 1-0
Three Input-Disabling Jumpers are located on each Analog Board #1 as shown in Figure 4-20.
Single-Phase Units with Option 1-1
Three additional Input-Disabling Jumpers are also located on each Analog Board #1 as shown in Figure
4-21. J9 is a factory adjustment and is not intended to be changed in the field.
BE1-87T single-phase units are shipped with all inputs enabled.
Three-Phase Units
Three-Phase Units with Option 1-0
Three Input-Disabling jumpers are located on each Analog Board #1 as shown in Figure 4-20.
Three-Phase Units with Option 1-1
Three additional Input-Disabling jumpers are also located on each Analog Board #1 as shown in Figure 4-
21. J9 is a factory adjustment and is not intended to be changed in the field.
For Three-Phase Units with Input Sensing Type E (two inputs per phase)
The jumpers shown in Figures 4-20 and 4-21 are shipped in the disabled position and no further
adjustment should ever be necessary.
For Three-Phase Units with Input Sensing Type G (three inputs per phase)
The jumpers shown in Figures 4-20 and 4-21 are shipped with Input 3 enabled, and Inputs 4 and 5
disabled. If only two inputs are actually used (which must be Inputs 1 and 2), it is important to disable the
unused input of each phase by means of the internal Input-Disabling jumpers provided on each of the
three Analog Boards #1 as shown in either Figure 4-20 or Figure 4-21. J9 in Figure 4-21 is a factory
adjustment and is not intended to be changed in the field.
Sensing Connection Diagrams
Each connection diagram provides, as an example, typical transformer terminal markings, and voltage
diagrams that might be found on a transformer nameplate with the winding interconnections shown. The
designations for high side and low side windings are for illustrative purposes only. For example, a
diagram for a delta-wye transformer is applicable to a wye-delta transformer if the winding
interconnections are the same. The phase shifts shown in the voltage diagrams assume A-B-C Phase
sequence (rotation).
Each connection diagram shows the CT circuit safety ground located at the switch board panel terminal
block as recommended in ANSI Standard C57.13.3.
Single-Phase Input Sensing Connections
Typical single-phase input sensing connections are illustrated in Figure 4-22.
Single-phase units may also be used in three-phase configurations, one on each phase. Figure 4-23
through Figure 4-26 show several typical three-phase sensing examples using three BE1-87T singlephase relays. Many other configurations are possible.
4-20 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 63

Figure 4-23. Typical Single-Phase Sensing Connections
COM
INPUT 5
OPTIONAL
INPUTS
87T
1
1
1
1
1
1
INPUT 4
INPUT 3
INPUT 2
INPUT
D240-003
7-1-92
BE1-87T
BREAKER
BREAKER
BREAKER
BREAKER
BREAKER
13
11
C12
12
12
11
13
13
11
12
03-12-98
D1186-02
C
B
A
C
B
A
X
3
X
2
X
1
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
0
SWITCH BOARD
TERMINAL BLOCKS
BE1-87T-1
BE1-87T-2
BE1-87T-3
C12
C12
B
CA
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
1
X
2
X
3
Figure 4-24. Single-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-21
Page 64

13
11
C12
12
12
11
13
13
11
12
04-16-99
D1186-20.vsd
C
B
A
C
B
A
X
3
X
2
X
1
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
0
SWITCH BOARD
TERMINAL BLOCKS
BE1-87T-1
BE1-87T-2
BE1-87T-3
C12
C12
H
0
B
CA H
3
H
2
H
1
X
1
X
2
X
3
H
0
X
0
4-22 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Figure 4-25. Single-Phase Connections, Wye-Wye Configuration
Page 65

03-12-98
D1186-03
C
B
A
C
B
A
Y
1
Y
2
Y
3
H
1
H
2
H
3
X
1
X
2
X
3
C
B
A
X
0
BE1-87T-1
13
12
14
C
(2)
(3)
(1)
11
BE1-87T-2
13
12
14
C
(2)
(3)
(1)
11
BE1-87T-3
13
12
14
C
(2)
(3)
(1)
11
SWICH BOARD
TERMINAL BLOCKS
B
C
A
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
1
X
2
X
3
Y
3
Y
2
Y
1
Figure 4-26. Single-Phase Connections, Delta-Delta-Wye Configuration
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-23
Page 66

Figure 4-27. Single-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration With Two Load Busses
03-12-98
D1186-04
C
B
A
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
3
X
2
X
1
X
0
C
B
A
C
B
A
BE1-87T-1
13
11
12
(2)
(1)
(3)
14
C
BE1-87T-1
13
11
12
(2)
(1)
(3)
14
C
BE1-87T-1
13
11
12
(2)
(1)
(3)
14
C
BE1-87T B TYPE SENSING
SWITCH BOARD
TERMINAL BOARDS
B
CA
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
1
X
2
X
3
Three-Phase Input Sensing Connections
Phase Shift Compensation
Three-phase units must be connected in a way that will negate any phase shift introduced by the
protected power transformer. This is accomplished by one of two methods:
1. By connecting the system CTs to complement the power transformer connections (i.e., a
wye/delta CT may negate the phase shift of a delta/wye power transformer, and vice versa).
2. By utilizing the internal 30° Phase Shift Compensation that is a feature of three-phase BE1-87T
relays.
Advantages of Internal Phase Compensation
Three-phase units provide for internal phase angle compensation. Among the advantages of this method
is the ability to connect all the CTs in wye. This not only simplifies the connections but also facilitates
sharing the CTs with other devices. Furthermore, the wye connection reduces the burden on the CTs.
A set of movable jumpers (Figure 4-27) determines the direction of the compensating internal phase shift
for each input. Because each jumper can be shifted +30°, –30°, or 0°; a total of 60° is achievable between
two inputs for special applications. In this way, the appropriate direction of phase shift can be matched to
the shift in the protected transformer. This alleviates the need for an extra set of external CTs in most
applications.
Figures 4-28 through 4-34 illustrate the use of internal phase shift in lieu of matching by external CT
connections. These are typical of the many combinations that can occur.
4-24 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 67

CAUTION
Assigning 30° Phase Shift Compensation requires disassembly of the relay,
and must be done when the relay has been taken out of service. Access to the
30° Phase Shift jumpers requires the removal of the Analog #2 Board, shown
in Figure 4-27. To avoid personal injury or equipment damage, do NOT
proceed unless thoroughly familiar with the instructions in the sections on
Relay Operating Precautions and Relay Disassembly: Precautions.
30° Phase Shift Compensation Adjustment Procedure
The position of a set of movable jumpers on Analog Board #2 determines the state of the internal
compensation. To gain access to these jumpers, it is necessary to remove Analog Board #2. Refer to the
topic RELAY DISASSEMBLY for instructions on gaining access to the circuit board then adjust the
jumpers shown in Figure 4-27 as follows:
• In cases where no phase shift is wanted, all three jumpers (φA, φB, and φC) shown in Figure 4-
27 are in the WYE-WYE position. (Relays are shipped with all jumpers in this position.)
• If one of the inputs requires a shift in phase, the jumpers for all three phases are moved as
follows:
1. The
2. The
The internal phase shift compensation is performed electronically as shown in the chart of Figure 4-27.
The internal compensation can apply to any power transformer with any combination of wye, delta, or
autotransformer winding connections.
A procedure to check the differential balance is described later in this section, Checking the Relay
Settings and System Inputs.
∆2 position develops A-B, B-C, C-A.
∆1 position develops A-C, B-A, C-B.
NOTE
The result of each of these vector differences has a magnitude of the square
root of three times each component.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-25
Page 68

Figure 4-28. 30° Phase Shift Compensation Jumpers
The transformer in the example shown in Figure 4-28 and 4-29 has a delta connection on the primary
winding. The currents in each winding of the delta are A, B and C respectively as reflected from the wye
connected secondary winding. The delta connection of the transformer windings causes the current
flowing in the phase leads connected to the delta winding to be A-B, B-C and C-A respectively. The CT
currents on the wye side must be combined similarly to provide A-B, B-C and C-A to compensate. This is
done in Figure 4-28 by connecting the wye side CTs in delta such that the currents sent to the relay are
A-B, B-C and C-A. This is shown in Figure 4-29 by selecting phase compensation jumper position ∆2 for
the wye side input.
4-26 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 69

H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
X
2
X
1
X
0
X
3
C
B
A
17
18
15
16
14
13
11
12
WYE
WYE
*
BE1-87T
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
Phase shift jumper
position on analog
board #2.
X
0
*An alternative to grounding one corner of the delta
connected CTs is to connect the ground to a lead
connected to terminal 18.
D2751-21
03-12-98
B
CA
H
3
H
2
H
1
X
1
X
2
X
3
H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
X
2
X
1
X
0
X
3
C
B
A
17
18
15
16
14
13
11
12
∆
2
WYE
BE1-87T
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
Phase shift jumper
position on analog
board #2.
D2751-22
02-05-98
Figure 4-29. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration, CT Compensation
Figure 4-30. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Wye Configuration, Internal Phase Compensation
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-27
Page 70

Figure 4-31. Three-Phase Connections, Wye-Delta Configuration, Internal Phase Compensation
H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
X
2
X
1
X
3
C
B
A
17
18
15
16
14
13
11
12
WYE
BE1-87T
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
Phase shift jumper
position on analog
board #2.
D2751-23
03-12-98
∆
1
H
0
X
2
X
3
X
1
H
2
H
3
H
1
H
0
B
CA
The transformer in the example shown in Figure 4-30 has a delta connection on the secondary winding.
The currents in each winding of the delta are A, B and C respectively as reflected from the wye connected
primary winding. The delta connection of the transformer windings causes the current flowing in the phase
leads connected to the delta winding to be A-C, B-A and C-B respectively. The CT currents on the wye
side must be combined similarly to provide A-C, B-A and C-B to compensate. This is shown in Figure 427 by selecting phase compensation jumper position ∆1 for the wye side input.
4-28 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 71

H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
X
2
X
1
X
3
C
B
A
17
18
15
16
14
13
11
12
WYE
BE1-87T
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
D2751-24
03-12-98
X
2
X
3
X
1
WYE
B
CA
H
3
H
2
H
1
Phase shift jumper
position on analog
board #2.
Figure 4-32. Three-Phase Connections, Delta-Delta Configuration
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-29
Page 72
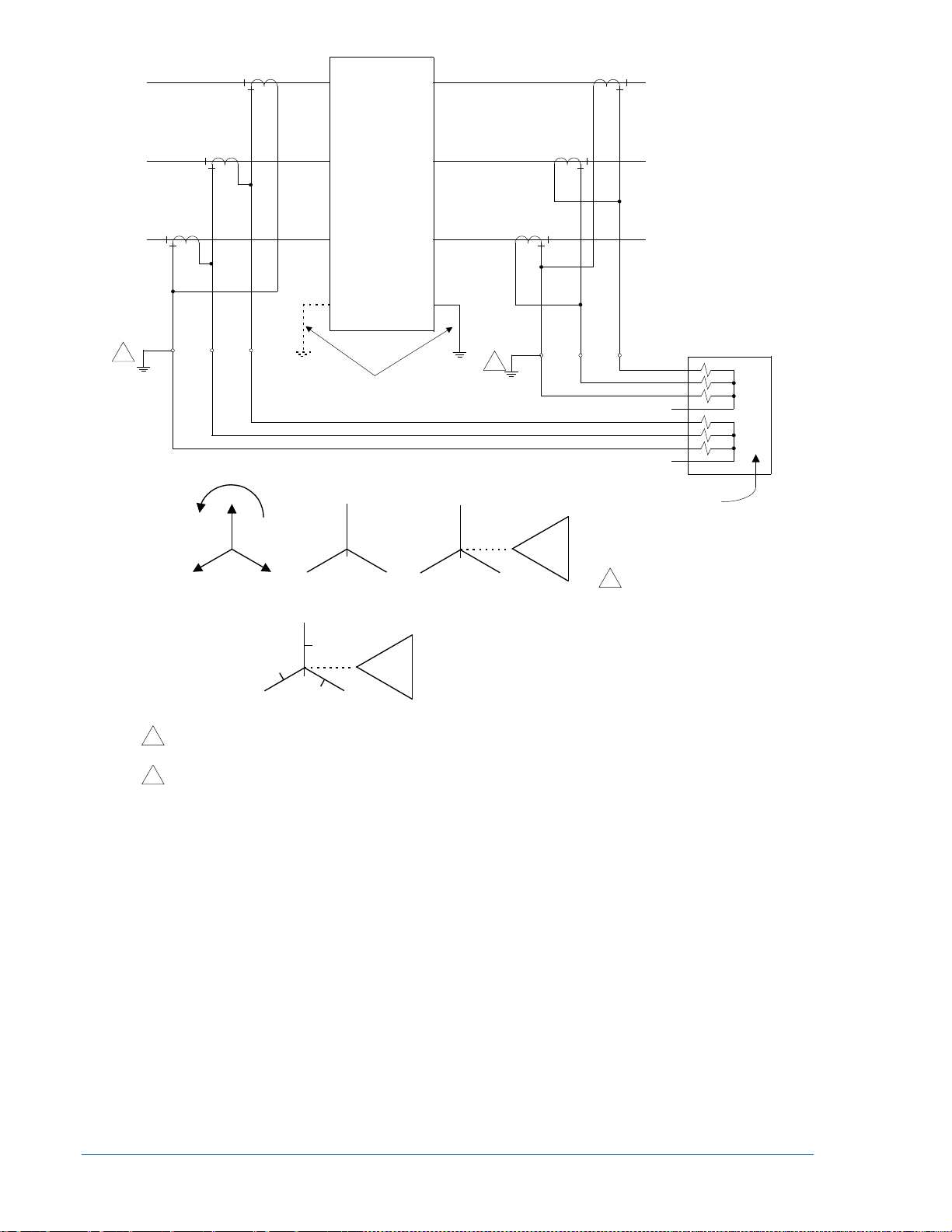
H
C
3
X
3
C
B
A
1
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
D2751-25
04-16-99
H
2
H
1
H0, X0, OR H0 X0 BUSHING, AS
APPROPRIATE
B
H
2
X
2
X
1
1
X
2
Phase shift jumper
position on analog
B
A
17
16
15
18
14
12
11
13
C
B
A
N
C
B
A
N
BE1-87T
WYE
WYE
board #2.
H
H
CA
0
1
X
H
1
3
X
3
(WITH UNLOADED TERTIARY)
2
H
2
X
2
X
1
X
3
H0 X
0
1
H
3
NOTES:
OR
H
1
AN ALERNATIVE TO GROUNDING THE CORNER OF THE THE DELTA CONNECTED CTs
IS TO CONNECT THE GROUND TO LEADS CONNECTED TO TERMINALS 13 AND18.
2
IF THERE IS NOT A DELTA TERTIARY, OR IF THE WYE WINDING IS UNGROUNDED, IT IS
UNNECESSARY TO DELTA SHIFT THE CURRENTS FOR ZERO SEQUENCE BLOCKING.
Figure 4-33. Three-Phase Connections, Wye-Wye or Autotransformer Configuration, CT Compensation
The Wye-Wye or Autotransformer does not require phase shift compensation. However, it is necessary to
Delta compensate the currents to block zero sequence currents being supplied by the transformer bank.
This is shown in Figure 4-32 by connecting the CTs in Delta. In Figure 33, compensation is shown by
internal phase compensation jumper setting.
4-30 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 73

H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
D2751-26
03-12-98
H0, X
0
, OR H
0
X0 BUSHING,
AS APPROPRIATE
X
2
X
1
X
3
C
B
A
16
17
18
15
12
14
13
11
∆
1 OR
∆
2*
BE1-87T
C
B
A
N
B
C
N
A
*THE BE1-87T MUST USE THE SAME PHASE COMPENSATION JUMPER
POSITION ON ALL INPUTS.
NOTES:
∆
1 OR
∆
2*
Phase shift jumper
position on analog
board #2.
Figure 4-34. Three-Phase Connections, Wye-Wye or Autotransformer Configuration,
Internal Phase Compensation
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-31
Page 74

H
2
H
1
H
3
C
B
A
Switch
board
terminal
blocks
D2751-27.vsd
09-07-00
Y
2
Y
1
Y
3
C
B
A
16 17
18
15
12
14
13
11
∆2
X
3
X
2
X
1
C
B
A
6
7
2
5
BE1-87T
WYE
∆
2
PHASE COMPENSATION JUMPER POSITION ON ANALOG BOARD #2.
Y
1
X
2
Y
3
H
2
H
1
X
1
H
3
X
3
H
0
X
0
Y
2
H
0 X0
B
C
A
Figure 4-35. Three-Phase Connections, Autotransformer With Loaded Delta Tertiary
The transformer in the example shown in Figure 4-34 has a delta connection on the tertiary winding. The
currents in each winding of the delta are A, B, and C respectively as reflected from the wye or auto
connected winding. The delta connection of the transformer windings causes the current flowing in the
phase leads connected to the delta winding to be A-B, B-C and C-A respectively. The CT currents on the
wye or auto windings must be combined similarly to provide A-B, B-C and C-A to compensate. This is
shown in Figure 4-34 by selecting phase compensation jumper position ∆2 for these inputs. This also
provides zero sequence blocking for these inputs since this transformer configuration is a source of zero
sequence currents.
4-32 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 75
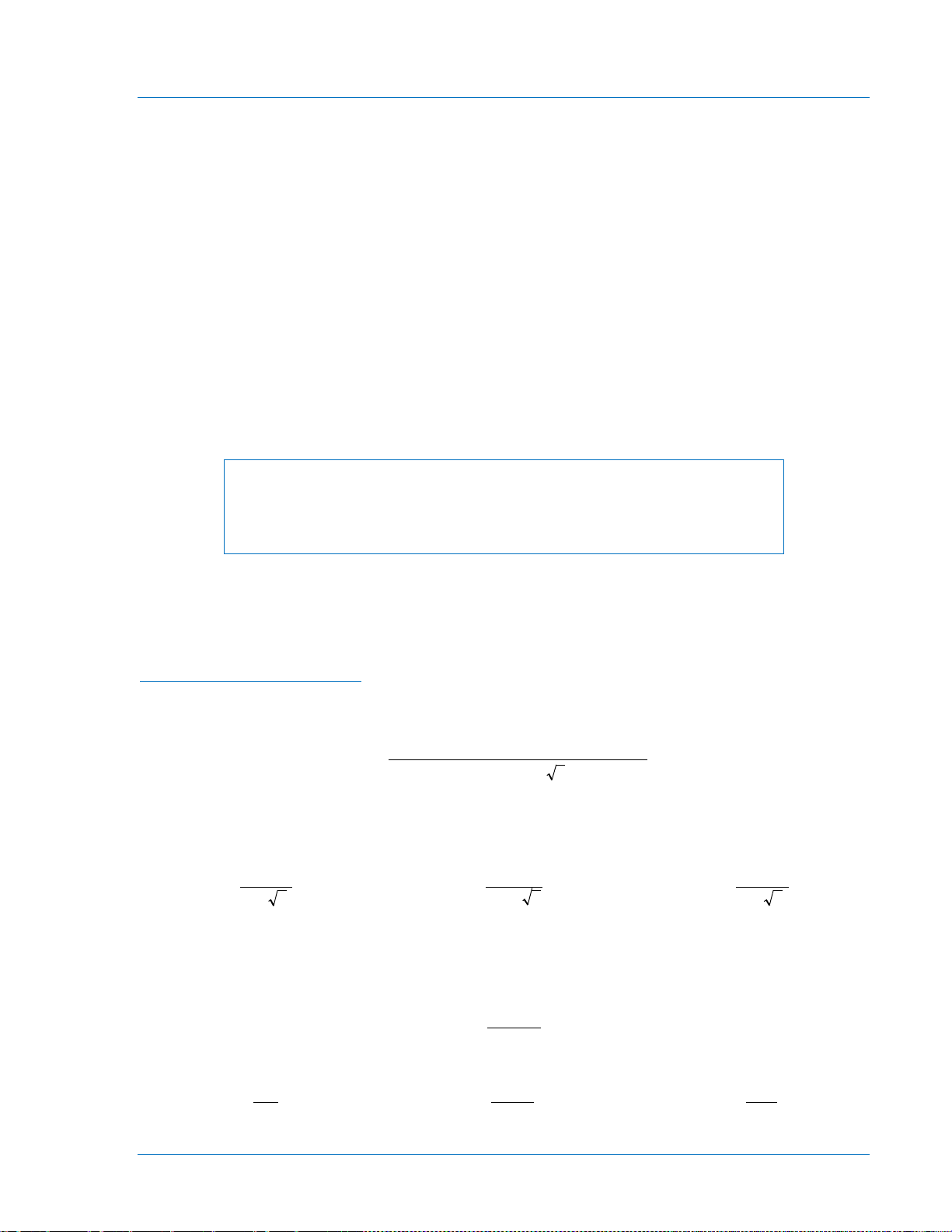
Setting the BE1-87T
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
I
I
P
P
=
=
250,000
13.2
3
10,935
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
I
P
=
(MVA rating of transformer) (X 1,000)
V
3
LINE- LINE
(
)
(
)
I
P
I
P
=
=
250,000
345
418
3
I
I
P
P
=
=
250,000
138
3
1,046
I
I
S
P
=
CT ratio
I
I
S
S
=
=
418
120
349.
I
I
S
S
=
=
10
935
600
18
22,.II
S
S
=
=
1046
240
436.
The following setting procedures include two examples:
1. Using the MVA rating of the highest-rated winding for all the other windings when making the
calculations.
2. Using the top kVA rating of the transformer.
Each procedure can be used as a means to understand the principles involved, and by replacing the
variables of the example, can become a procedure of general application. Variable abbreviations and
definitions are provided in Table 4-1, List of Variables.
Method
Both procedures determine:
1. The matching tap and slope settings required to implement the restrained function, and
2. The unrestrained pickup setting as a multiple of the BE1-87T tap setting (i.e., the INPUT
switches).
The matching tap procedure is conventional, providing tap values proportional to the normal currents as
seen by the relay. An exception occurs with multiple-winding banks where zero-balance current is
assumed in each pair of windings, successively.
NOTE
The dc component of the input current is effectively blocked by the gapped
cores of the input CTs. Therefore, for offset fault currents or magnetic inrush,
the dc component of the waveform can be ignored in fault current calculations.
Procedure One
Refer to Figure 4-35 for a one-line drawing of this example. Refer to Figure 4-34 for the three-line
representation of this transformer.
Tap and Phase Shift Settings
Step 1. Determine the primary current (I
Use the MVA rating of the highest-rated winding for all the other windings when making the
calculations. (This procedure assures that the taps follow the voltage ratios. Refer to Appendix
A, Setting Note 1.)
Step 2. Determine the CT secondary current (I
) of each winding:
P
)of each winding:
S
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-33
Page 76

D
IE
Table 4-1. List of Variables
P
The driving input number, a procedural term designating the current input
terminal whose tap is the first selected. (The setting procedure is simplified if
the driving input is the input of least current, I
)
M
Maximum external fault current in multiples of tap (the larger of three-phase or
line-ground values)
ID
IF
IF3
IFG
IM
IP
IR
IS
IT
MN
MR
MT
N
NA
RL
Driving input relay current used for matching in amperes
The larger of I
and IFG
F3
Relay input current at the maximum external three-phase fault level in
secondary amperes
Relay input current at the maximum external line-ground fault level in
secondary amperes
The input with the least minimum current
CT primary current in amperes
Relay input current in amperes
CT secondary current in amperes
Rated self-cooled current of the power transformer in multiples of tap
Current mismatch, with power transformer on its neutral tap
Multiple rating CT, i.e., a tapped CT
Total mismatch, including the maximum transformer tap excursion
Total number of CT turns available
Number of CT turns in use
One-way lead resistance in ohms
RW
RR
S
SF
T
TD
VB
VB3
VBG
VC
VCE
x TA P
CT winding resistance in ohms
Relay resistance in ohms
Restrained slope setting (from 15 to 60%)
Saturation factor, which equals V
B/VCE
Relay current tap (0.4 to 1.78 for 1 A CT, 2 to 8.9 for 5 A CT)
Desired tap, based on the current ratio
The larger of V
The CT burden voltage with I
The CT burden voltage with I
or VBG
B3
flowing
F3
flowing
FG
Base accuracy class CT voltage rating
Accuracy class CT effective voltage where not all turns are used, which equals
/N)
V
C(NA
Unrestrained pickup setting, in multiples of tap (6 to 21)
4-34 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 77

Figure 4-36. Application Example: Autotransformer With Tertiary Winding
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
Position:
X
X
600/5MR
600/5T
3360 A (3 ∅)
3375 A (1 ∅)
13,280 A (3 ∅)
3000/5
2000/5MR
1200/5T
138 kV
8400 A (3 ∅)
9000 A (1 ∅)
345 kV
02-12-98
D240-004
BE1-87T
WYE (3)
WYE (3)
(12)
(12)
13.2
kV
WYE (3)
A
1
(12)
+
10% LTC (11)
HIGH
SIDE
TERTIARY
LOW SIDE
I
I
R
S
=
×
Conversion
Factor
(See Figure 4-34 for 3-phase connections.)
Specifications High side Tertiary Low side
kV 345 13.2 138
MVA 200/250 40/50 200/250
CT Ratio 600/5 (MR)
600/5 (T)
3000/5 2000/5 (MR)
1200/5 (T)
CT Accuracy Class C400 C800 C400
CT Resistance (ohms) 0.3 1.5 0.6
One-Way Lead Burden (ohms) 0.7 0.7 0.7
CT Connection (Three-Phase) WYE WYE WYE
NOTE
Three-phase is the most common application of the BE1-87T. Using singlephase relays requires a Delta connection for the High side and Low side CTs
(IA-IB to match the tertiary connection in the example detailed in Figure 4-34).
Step 3. Three-Phase Units Only: Adjust the phase compensation jumpers on Analog Board #2, shown
in Figure 2-4 and Figure 4-27, (or use the procedure listed in Testing Three-Phase Units without
Changing Jumpers, in Section 5).
Because of the grounded winding in this example, as shown in Figure 4-35 and 4-34, the high-
side, and low-side zero-sequence currents must be canceled.
∆2 position is selected to align
the High side and Low side secondary current phasors with the tertiary phasors which lead by
30° in this example:
Jumper
Step 4. Determine the relay current (I
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-35
):
R
∆2
WYE
∆2
Page 78

Three-Phase Units only: When using either ∆2 or ∆1 jumper positions, shown in Figure 2-4,
(INPUT 1)
(INPUT 2)
(INPUT 3)
TERTIARY
LOW
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
T = 2.0
T = 6.0
T = 2.5
I
I
R
R
=
=
3.49
6.04
3
I
I
R
R
=
=
(18.22)
18.22
(1)
I
I
R
R
=
=
4.3637.55
DP
I
DP
M
=
=
HIGH (INPU
T 1)
HIGH
T12
0
=
.
T
T
I
I
D
R
R
2
1
2
1
2.0
18.22
6.04
6.03
=
)
(
=
)
(
=
T
T
I
I
D
R
R
3
1
3
2.0
7.55
6.04
2.50
=
=
=
1
)
(()
multiply the secondary current I
CTs were connected in delta. Remember that, if system CTs are connected in delta, the same
square-root-of-three conversion factor must be applied.
by the conversion factor (square-root of three) just as if the
S
HIGH
Step 5. Determine the spread ratio of the relay currents (largest/smallest):
Spread = 18.22/6.04 = 3.0
Step 6. Determine the Driving Input (DP), which we define as the input assigned to the smallest current
in Step 4:
Step 7. Determine the Driving Input Tap (T
87T:
Choosing the 2.0 setting for the minimum inputs will yield maximum sensitivity.
Step 8. Determine the Desired Tap (T
D
TERTIARY
), which must be less than the 4.45 capability of the BE1-
1
):
LOW
Step 9. Select taps by rounding TD to the nearest tenth:
4-36 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 79

Step 10. Determine the CT mismatch (MN):
LOW
TERTIARY
−
=
)((−)
=
(
)−(
)
=
=
M
N
I
ITT
100
3
232
100
18
22
7
55
6
0
2
5
100
2
0
(the smaller of the above)
(the smaller of the above)
2.41-2.40
...
.
.40
.4%
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
)R3R3R(IV
RL3F3B
++=
W
HI
GH
LOW
−
=
(
−
)
)
=
−
=
=
M
IIT
T
N
100
100604
7
55
2
0
2
5
100
0
80
0%
131
3
(the smaller of the above)
0.80-0.80
...
.
.
(
(the smaller of the above)
())
(
HI
GH
TERTIARY
−
=
−
=
−
=
=
M
IIT
T
N
100
100
18
22
6
04
6
0
2
0
100
3
0
0
6%
2
1
2
1
(the smaller of the above)
3.02-3.0
...
.
.
.
())
(
())
(
(the smaller of the above)
M
M
T
N
=
+
LTC
M
T
=+=
0610106 %..
I
F
3
3360
120
=
=
28 A
I
F
3
13
600
=
=
,280
22 A
IF3
8400
240
=
=
35 A
I
FG
=
=
3375
120
28 A
I
FG
=
=
9000
240
38 A
Step 11. Determine the total mismatch (M
Add the maximum CT mismatch M
position) to the total permissible tap excursion from neutral. In this example, a
change (LTC) must be accommodated. Therefore:
This procedure uses the ANSI accuracy class method. See Appendix A,
Setting Note 7 for more information.
):
T
(based on the power transformer in the neutral tap
N
NOTE
Verify CT Performance
Step 12. Determine the maximum CT secondary fault current for external faults (I
for line-to-ground). Refer again to Figure 4-35 for this example. The maximum fault current is
I
FG
recorded for each set of terminals for all combinations of external faults.
±10% load tap
for three-phase, and
F3
Step 13. Determine the worst case burden voltage for a three-phase fault (VB3).
Where:
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-37
• For wye-connected CTs:
)(
RRIV +=
33 RLFB
• For delta-connected CTs, based on a three-phase fault (refer to Appendix A, Setting Note 2):
R
Neglecting R
= determined in Step 12
I
F3
= winding burden
W
, use RL from Figure 4-35:
R
R
= relay resistance in ohms (< 0.05 ohm)
R
= one-way lead resistance in ohms
R
L
Page 80

HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
6.19=
)7.0(22
3
=
B
V
4.15=
)7.0(353=
B
V
5.24=
( )
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
( )
)7.0(228=
BG
V
2.39=
NONE
( )
2.53=
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
400
2.39
=
F
S
1.0=
800
4.15
=
F
S
02.0=
240
2.53
=
F
S
22.0=
V
V
N
N
CE
C
A
=
=
(
)
(Base Accuracy)
(Number of CT Turns in Use)
Maximum Ratio
V
CE
=
=
400
600
600
(
)
400
V
CE
=
=
800
3000
3000
(
)
800
V
CE
=
=
400
1200
2000
240
(
)
S
F
V
B
V
CE
=
V
B
)7.0(283=
Step 14. Determine the burden voltage for a line-to-ground fault (VBG).
• For wye-connected CTs:
RLFGBG RRIV += 2
Where:
= determined in Step 12
I
FG
= one-way lead resistance in ohms
R
L
= relay resistance in ohms (< 0.05 ohm)
R
R
• For delta-connected CTs: V
is a function of the proportion of positive-sequence to zero-
BG
sequence currents but may be approximated by the same equation.
Neglecting R
, use RW and RL from Figure 4-35:
R
)7.0(238=BGV
Step 15. Determine the effective CT accuracy class (V
Step 16. Determine the saturation factor (SF):
Note: V
is the largest burden voltage from steps 13 and 14.
B
):
CE
4-38 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 81

Maximum recommended SF=0.5.
I
I
T
E
F
= =
Maximum Relay Fault Current
Corresponding Tap
I
I
T
E
F
=
3
3( )
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
I
E
=
=
22
6
0
3
7..
I
E
=
=
35
3
2
524.
(
)
()=
0.7
X
TAP
×
I
MaxE(.)
HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
IE not maximum
IE not maximum
X TAP = (0.7)24
= 16.8
I
E
=
=
28
3
2
024.
(
)
I
I
T
T
R
=
MVA
MVA
SELF
-
COOLED
FORCED
-
COOLED
(
)
(
)
Instantaneous (Unrestraint) Unit Setting
NOTE
Step 17. Determine the maximum external fault multiple (I
).
E
• For wye-connected CTs and with WYE jumpers on Analog Board #2, shown in Figure 2-
4:
• For delta-connected CTs, or with ∆1 or ∆2 jumpers on Analog Board #2, shown in Figure
2-4, (and based on a phase-to-phase fault): (Refer to Appendix A, Setting Note 3.)
Step 18. Determine the unrestrained pickup level in multiples of tap (X TAP): Refer to Appendix A,
Setting Note 4.
NOTE
The restrained element will not operate due to the large 2nd harmonic
component present in the highly distorted current.
Step 19. Using the results of Step 18, set the UNRESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL control. Referring to
the table on the BE1-87T front panel, select the tap position (X TAP) that is higher than the
result obtained in Step 18. Therefore, for this example, select SET position P (=19 X TAP)
which is higher than the above result of 18.2 A.
Slope Setting
Step 20. Determine the multiples of self-cooled current (I
Where:
I
T = the input tap (from Step 9)
= relay current (from Step 4)
R
): Refer to Appendix A, Setting Note 5.
T
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-39
MVA
SELF COOLED
and MVA
FORCED COOLED
are given in Figure 4-35.
Page 82

HIGH
TERTIARY
LOW
)50)(0.6(
)40)(8.16(
=
T
I
)250)(5.2(
)200)(55.7(
=
T
I
S
M
I
T
T
=
+
+
−
3
35
3
23
4
(
)
I
T
=
=
604200
20250
2
.
.
.42
(
)()
(
)
(
)
60%
15%
MARGIN
MARGIN
XMFR EXCITING CURRENT
D610-010
3-2-91
BE1-87T
MAXIMUM I IN MULTIPLES OF TAP
R
TOTAL MISMATCH
M
U
LTI
P
L
E
S
O
F
T
A
P
IopI
N
=2.24
=2.42
Step 21. Select the restrained slope setting.
The recommended restrained slope setting (S) is a function of the total mismatch and the
power transformer exciting current. This provides an ample security margin with respect to the
characteristic kneepoint of the BE1-87T. Refer to Figure 4-36.
Figure 4-37. Slope Needed to Accommodate Total Mismatch with Adequate Margin
Specifically, if the maximum saturation factor S
(from Step 16) exceeds 0.5, set the
F
RESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL to setting K which is equal to 60 as shown in the table on the
front panel.
For all other cases including this example, use the following equation:
Where:
S = restrained slope setting
M
I
= total mismatch in percent
T
= rated self-cooled current of the power transformer in multiples of tap
T
For a three-winding transformer application, such as this example, the maximum of the three
and of IT is used.
T
M
values of M
is 10.6 (from Step 11) and IT is 2.42 (Step 20):
T
4-40 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 83

)42.2(423
)36.10(35
3
−
+
+=S
= 38.8
Because the maximum saturation factor S
for this example is less than 0.5 (from Step 16), use
F
the next highest slope. Select position F which = 40%.
For examples of suitable slope settings, see Table 4-2.
Table 4-2. Examples of Suitable Slope Settings
Maximum
Mismatch in %
(MT)
Current Rating of Power
Transformer in
Multiples of TAP (IT)
Recommended Minimum
2.5 1.5 15
2.5 2 20
5 2 25
10 1.5 30
12.5 1.5 35
15 1.5 40
15 2 45
15 2.5 50
20 1.5 55
RESTRAINED PICKUP
LEVEL Setting* (Slope)
20 2 60
* SF=VB/VCE
>0.5, set the RESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL setting (slope) to S=60%.
If S
F
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-41
Page 84

Procedure Two
HIGH
LOW
I
P
=
×
MVA rating
of transf
ormer
1,000
V
3
LINE- LINE
()(
)
()(
)
I
P
I
P
=
=
20,000
69
167.35
3
I
I
P
P
=
=
20,000
12
3
925
.47
.
98
Refer to Figure 4-37 for a one-line drawing of this example.
Data
Figure 4-38. Two Winding Transformer Relay Setting Calculation Example
Specifications High side Low side
kV 69 12.47
MVA 12/20 12/20
CT Ratio 600 1200
C T Tap 300 800
CT Accuracy Class 400 800
CT Resistance (ohms) 0.18 0.48
One-Way Lead Burden
(ohms)
XFMR Connection*
CT Connection WYE WYE
Input # 1 2
Fault Current (ThreePhase)
Fault Current (SinglePhase)
* Standard connection: High voltage leads low voltage by 30°.
Tap and Phase Shift Settings
Step 1. Determine the full load primary current (I
0.7 0.7
D E LTA WYE
1,916 10,603
1,171 11,231
) of each winding:
P
Use the top kVA rating of the transformer when making the calculations:
4-42 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 85

Step 2. Determine the CT secondary current (IS):
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
LOW
Jumper Position:
WYE
2
HIGH
LOW
I
I
S
P
=
CT ratio
I
I
S
S
=
=
167.35
60
2.79II
S
S
=
=
925.98
160
5.79
I
I
R
R
=
=
(2.279)
(1)
79
.II
R
R
=
=
5
310..79
02
Step 3. Three-Phase Units Only: Adjust the phase compensation jumpers on Analog Board #2, shown
in Figure 2-4 (or use the procedure listed in TESTING THREE-PHASE UNITS WITHOUT
CHANGING JUMPERS, in Section 5). Because of the grounded winding in this example, as
shown in Figure 4-37, the high-side and low-side zero-sequence currents must be canceled.
Because the CTs are connected in wye and the high-side currents lead the low-side currents by
30°, select the ∆2 position. This connection advances the low side phasors by 30° to match the
phasors from the high-side.
∆
On single-phase units, the zero-sequence currents must be canceled by connecting the low
side CTs in delta.
Step 4. Determine the relay current (I
Three-Phase Units Only: When using either
multiply the secondary current I
):
R
I
x Conversion Factor
R=IS
∆1 or ∆2 jumper positions, shown in Figure 2-4,
by the conversion factor (square root of three) just as if the
S
CTs were connected in delta. If the system CTs are connected in delta (either three-phase or
single-phase units), the same square root-of-three conversion factor must be applied.
Step 5. Determine the spread ratio of the relay currents (largest/smallest) which must be less than the
4.45 capability of the BE1-87T:
Spread = 10.02/2.79 = 3.59
If the spread exceeds 4.45, consider changing CT ratios or use auxiliary CTs.
Step 6. Determine the Driving Input (DP) which we define as the input assigned to the smallest current
in Step 4.
DP=I
M
DP=HIGH (INPUT 1)
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-43
Page 86

Step 7. Determine the Driving Input Tap (TI).
M
N
=
100
Current Ratio - Tap Ratio
the smaller of the above
IIT
T
Smaller
R2
=
-
R1
1
2
100
=
0
216
0
22 %
=
-
2.79
2.0
Smaller
100
or
.
.
=
-
0.2784
0.2778
0.2778
100
10.02
7.2
TTI
I
D
R
R
2
1
2
1
2.0
10.02
2.79
7
=
(
)
=
=
.
18
(
)
If both relay currents are between 2.0 and 8.9 amperes, the tap settings can be set equal to the
relay currents (to the nearest 0.1 ampere). However, choosing the 2.0 tap setting for the
minimum input will yield maximum sensitivity.
T
= 2.00
1
Step 8. Determine the desired Tap (T
Step 9. Select taps by rounding T
T
T
= 2.0
1
= 7.2
2
to the nearest tenth:
D
Step 10. Determine the CT mismatch (M
) for Input 2:
D
):
N
Step 11. Determine the total mismatch (M
Add the maximum CT mismatch M
position) to the total permissible tap excursion from neutral. In this example, a
):
T
M
= MN + LTC
T
(based on the power transformer in the neutral tap
N
±10 % load-tap
change (LTC) must be accommodated. Therefore:
M
=0.22 + 10 = 10.22%
T
4-44 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 87
Verify CT Performance
HIGH
LOW
I
F
3
1916
60==32 A
I
F
3
10603
160==66 A
I
FG
=
=
1171
60
19.5 A
I
FG
=
=
11231
160
70 A
HIGH
LOW
V
B
3
(32)(0.7)
=
=
22.4 V
V
B
3
(66)(0.7)
46.2 V
=
=
This procedure uses the ANSI accuracy class method. See Appendix A,
Setting Note 7 for more information.
NOTE
Step 12. Determine the maximum CT secondary fault current for external faults at F (I
for single-phase). Refer again to Figure 4-37 for this example:
and I
FG
Step 13. Determine the worst case CT burden voltage for a three-phase fault (VB3).
• For wye-connected CTs:
= IF3(RL + RR)
V
B3
• For delta-connected CTs, for three-phase fault:
= IF3(RW + 3RL + 3RR)
V
B3
Note that the wye connection produces a lower burden on the CTs (see Appendix A, Note 2).
Where:
I
R
= determined in Step 12 R
F3
= winding burden R
W
= one-way lead resistance in ohms
L
= relay resistance in ohms (< 0.05 ohm)
R
for three-phase,
F3
Neglecting R
, use RW and RL from Figure 4-37:
R
Step 14. Determine the worst case burden voltage for a line-to-ground fault (VBG).
• For wye-connected CTs:
= IFG(2RL + RR)
V
BG
Where:
I
R
R
= determined in Step 12
FG
= one-way lead resistance in ohms
L
= relay resistance in ohms
R
• For delta-connected CTs:
V
is a function of the proportion of positive-sequence to zero-sequence currents but may be
BG
approximated by the same equation (for worst case).
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-45
Page 88
Neglecting RR, use RW and RL from Figure 4-37:
HIGH*
LOW
V
BG
=
=
19.5(0.7)
13.6 V
V
BG
== 70
(2(0.7))
98.0 V
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
LOW
11.0
4.22
18.0
3.533
0.98
=
=
F
S
I
I
T
E
F
= =
Maximum Relay Fault Current
Corresponding Tap
V
V
N
N
CE
C
A
=
=
(Base Accuracy)
(Number of CT Turns in Use)
Maximum Ratio
(
)
V
CE
=
=
(400)
300
600
200
V
CE
=
=
800
800
2000
533
3
(
)
.
S
F
V
B
V
CE
=
NOTE
Since a phase-to-ground fault looks like a phase-to-phase fault on the delta
side of a delta/wye transformer, each CT only has to carry one times the one
way lead burden.
Step 15. Determine the effective CT accuracy class (VCE):
Step 16. Determine the saturation factor (SF):
VB is the largest of the burden voltages calculated in steps 13 and 14.
=FS
200
=
NOTE
Maximum Recommended SF = 0.5.
Larger saturation factors will make the relay insecure for external faults. The only solution is to increase
the CT quality.
Instantaneous (Unrestraint) Unit Setting
Step 17. Determine the maximum external fault multiple (I
).
E
• For wye-connected CTs and with WYE jumpers on Analog Board #2, shown in Figure 2-
4:
4-46 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 89

• For delta-connected CTs, or with ∆1 or ∆2 jumpers on Analog Board #2, shown in Figure
I
I
F3
T
E
=
3
(
)
HIGH
LOW
I
E
=
=
32
2
0
15.96
.
I
E
=
=
66
3
7
2
15.9
(
)
.
HIGH
LOW
X TAP
== (0.7)15.96
11.17
IE not maximum
()=
0.7XTAPxI
MaxE(.)
I
I
T
T
R
=
MVA
MVA
SELF-COOLED
FORCED
-
COOLED
(
)
(
)
2-4, (and based on phase-to-phase fault): (See Setting Note 3.)
Step 18. Determine the unrestrained pickup level in multiples of tap (X TAP): (See Setting Note 4.)
This calculation assumes that the CTs carrying the maximum fault saturate severely, yielding only 30% of
the expected ratio current. This leaves 70% of the fault current as a false differential current.
NOTE
The restrained element will not operate due to the large 2nd harmonic
component present in the highly distorted current.
Step 19. Using the results of Step 18, set the UNRESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL control.
Referring to the table on the BE1-87T front panel, select the tap position (X TAP) that is higher
than the result obtained in Step 18. Therefore, for this example, select SET position G (=12 X
TAP) which is higher than the above result of 11.17 X TAP.
If this value exceeds 21 (max setting), raise the tap settings toward the upper end of the tap
range. If after the highest tap has been reached the unrestrained trip settings still exceeds 21,
security is affected. The user should remember that the 70% saturation is conservative. A close
look at the system L/R and CT performance is recommended. Chances are that the risk will be
tolerable.
Slope Setting
The slope equation determines the slope setting required to maintain a margin of about 12% of I
breakpoint of the slope characteristic. This margin varies slightly with the actual taps but remains secure
over the tap range.
Step 20. Determine the multiples of self-cooled current (IT): Refer to Appendix A, Setting Note 5.
Where:
at the
OP
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-47
T = the input tap (from Step 9)
MVA
= relay current (from Step 4)
I
R
SELF COOLED
and MVA
FORCE COOLED
are given in Figure 4-35.
Page 90

HIGH
LOW
Step 21. Select the restrained slope setting.
S
=
=
26.5%
35(10.2 + 3)
23 - 4(0.84)
3 +
I
T
=
=
27912
2
0
20084
.
.
.
()()()(
)
I
T
=
=
100212
7220084..
.
()(
)())(
SMI
T
T
=
+
+
-
3
35
3
23
4
(
)
The recommended restrained slope setting (S) is a function of the total mismatch and the
power transformer exciting current. This provides an ample security margin with respect to the
characteristic kneepoint of the BE1-87T. Refer to Figure 4-36.
Specifically, if the maximum saturation factor
SF (from Step 16) exceeds 0.5, set the
RESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL to setting K, which is equal to 60 as shown in the table on the
front panel.
For all other cases, including this example, use the following equation:
Where:
S = restrained slope setting
= total mismatch in percent
T
= rated self-cooled current of the power transformer in multiples of tap
T
M
M
I
is 10.2 (from Step 11) and IT is 0.84 (Step 20):
T
Because the maximum saturation factor S
for this example is less than 0.5 (from Step 16), use
F
the next highest slope. Select position D, which = 30%.
For examples of suitable slope settings, see Table 4-2.
4-48 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 91

Checking the Relay Settings and System Inputs
Steps 1 and 2 check that the current inputs from the power transformer are correct and consistent with
the BE1-87T settings. The remaining steps check that the relay settings are within acceptable
parameters.
CAUTION
DO NOT install connection plugs, apply power, remove circuit boards, or carry
out any of the other instructions given unless you are thoroughly familiar with
the instructions in the sections on Relay Operating Precautions on page 4-1
and Relay Disassembly: Precautions on page 4-11.
Step 1. Insert the cradle assembly into the relay case, then:
Three-Phase Units with Sensing Input Type G: Remove the lower connection plug first. Then
remove the upper connection plug. Insert two Test Plugs (P/N 10095 or equivalent) in place of
the top and bottom connection plugs. For further information, refer to TEST PLUG in Section 6,
MAINTENANCE. Terminal 20 (trip output common) shown in Figure 4-10, must be isolated for
this test.
All other styles: Replace the top connection plug with a Test Plug (P/N 10095 or equivalent).
For further information, refer to TEST PLUG in Section 6, MAINTENANCE. Terminal 9 (trip
output common) shown in Figures 4-7 through 4-9 must be isolated for this test.
Step 2. Using an ammeter and phase angle meter, measure the magnitude and phase angle of each
current input, testing two inputs at a time. Begin with Inputs 1 and 2.
CAUTION
When more than two inputs are present, all inputs not being tested must be
shorted to ground.
Single-Phase Units: Relay must not trip when the current to each input (of the pair being
tested) is equal to the other in magnitude and the two currents are 180° out of phase (e.g.,
Inputs 1 and 2 measured, with Inputs 3, 4 and 5 shorted). For input terminal numbers, see
Table 4-3.
Three-Phase Units: Relay must not trip when the current to Input 1 is equal to that of Input 2 in
magnitude and the phase angle is as shown in Table 4-4. If there are three inputs per phase,
interchange Inputs 2 and 3 and repeat the procedure, this time with magnitudes and phase
angles as shown in Table 4-4. (Testing may require six synchronized current sources.)
Step 3. Using the Test Plug, reestablish all input connections and verify that the front panel REST.
TRIP and UNREST. TRIP LEDs are extinguished.
This assures that the X TAP settings and jumper settings (refer to Figures 4-20, 4-21 and 4-27)
are within acceptable parameters and that the differential current is below pickup.
If the REST. TRIP or UNREST. TRIP LEDs light, recheck the system current inputs and relay
settings.
Table 4-3. Single-Phase Input Terminals
Input 1 Input 2 Input 3 Input 4 Input 5
Terminals:
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-49
11 & 13 12 & 13 14 & 13 15 & 13 16 & 13
Page 92

Table 4-4. Input Conditions For Non-Trip Three-Phase Sensing
I
θ
I
θ
+
240
I
θ
+
120
I
θ
+
180
I
θ
+
60
I
θ
+
300
I
θ
I
θ
+
240
I
θ
+
120
I
3
(
)
θ
+
150
I
3
(
)
θ
+
30
I
3
(
)
θ
+
270
I
θ
I
θ
+
240
I
θ
+
120
÷
I
3
(
)
θ
+
210
÷
I
3
(
)
θ
+
90
÷
I
3
(
)
θ
+
330
I
θ
I
θ
+
240
I
θ
+
120
I
3
(
)
θ
+
210
I
3
(
)
θ
+
90
I
3
(
)
θ
+
330
I
θ
I
θ
+
240
I
θ
+
120
÷
I
3
(
)
θ
+
150
÷
I
3
(
)
θ
+
30
÷
I
3
(
)
θ
+
270
30° Phase Shift
Compensation Jumper
Settings
(Ref. Figure 4-27)
WYE-WYE, ∆1-∆1, or ∆2-
∆2.
(In these cases, input
currents are equal and
° out-of-phase.)
180
Input 1 is ∆1, Input 2 is
WYE.
Input 1 is WYE, Input 2 is
∆1.
Input 1 is ∆2, Input 2 is
WYE.
Input 1 is WYE, Input 2 is
∆2.
NOTES:
1. Table 4-4 is for reference only and applies to three-phase units with Input 3 at zero amperes.
* For A-B-C rotation.
2.
Input 1 *
Phase Terminals Phase Angle Terminals Phase Angle
A
B
C
A
B
C
A
B
C
A
B
C
A
B
C
11 & 13
12 & 13
14 & 13
11 & 13
12 & 13
14 & 13
11 & 13
12 & 13
14 & 13
11 & 13
12 & 13
14 & 13
11 & 13
12 & 13
14 & 13
15 & 18
16 & 18
17 & 18
15 & 18
16 & 18
17 & 18
15 & 18
16 & 18
17 & 18
15 & 18
16 & 18
17 & 18
15 & 18
16 & 18
17 & 18
Input 2 *
Maintenance
BE1-87T relays require no preventative maintenance other than a periodic operational check. If the relay
fails to function properly, contact Technical Sales Support at Basler Electric to coordinate repairs.
Storage
This device contains long-life electrolytic capacitors. For devices that are not in service (spares in
storage), the life of these capacitors can be maximized by energizing the device for 30 minutes once per
year.
4-50 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 93

Test Plug
Test plugs (Basler p/n 10095) provide a quick, easy method of testing relays without removing them from
their case. Test plugs are simply substituted for the connection plugs. This provides access to the
external stud connections as well as to the internal circuitry.
Test plugs consist of a black and red phenolic molding with 20 electrically separated contact fingers
connected to 10 coaxial binding posts. The 10 fingers on the black side are connected to the inner
binding posts (black thumbnuts) and tap into the relay internal circuitry. The 10 fingers on the red side of
the test plug are connected to the outer binding posts (red thumbnuts) and also connect to the relay case
terminals.
When testing circuits connected to the bottom set of case terminals, the test plug is inserted with the
numbers 1 through 10 facing up. When using the test plug in the upper part of the relay, the numbers 11
through 20 are face up. It is impossible, due to the construction of the test plug, to insert it with the wrong
orientation.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Installation 4-51
Page 94

4-52 BE1-87T Installation 9171300990 Rev V
Page 95

SECTION 5 • TEST PROCEDURES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5 • TEST PROCEDURES ........................................................................................................ 5-1
Overview ................................................................................................................................................ 5-1
Equipment Required .............................................................................................................................. 5-1
Restrained Pickup Testing Examples .................................................................................................... 5-2
Increasing One Input from Balance .................................................................................................... 5-2
Decreasing One Input from Balance .................................................................................................. 5-4
Test Setup Diagrams ............................................................................................................................. 5-7
Verification Tests: 5 Amp CT, 50 or 60 Hz Units ................................................................................... 5-9
Restrained Pickup Verification ........................................................................................................... 5-9
Input (or Tap) Switch Verification ..................................................................................................... 5-10
Unrestrained Pickup Verification ...................................................................................................... 5-11
Second-Harmonic Restraint Verification .......................................................................................... 5-11
Fifth-Harmonic Restraint Verification ............................................................................................... 5-12
Response Time Verification ............................................................................................................. 5-13
Verification Tests: 1 Amp CT, 50 or 60 Hz Units ................................................................................. 5-14
Restrained Pickup Verification ......................................................................................................... 5-14
Input (or Tap) Switch Verification ..................................................................................................... 5-15
Unrestrained Pickup Verification ...................................................................................................... 5-16
Second-Harmonic Restraint Verification .......................................................................................... 5-17
Fifth-Harmonic Restraint Verification ............................................................................................... 5-17
Response Time Verification ............................................................................................................. 5-18
Operational Test Procedures ............................................................................................................... 5-19
Restrained Pickup ............................................................................................................................ 5-19
Unrestrained Pickup ......................................................................................................................... 5-19
Second-Harmonic Inhibit .................................................................................................................. 5-19
Fifth-Harmonic Inhibit ....................................................................................................................... 5-20
Testing Three-Phase Units without Changing Jumpers ...................................................................... 5-20
Jumper Positions WYE-WYE ........................................................................................................... 5-21
Jumper Positions WYE-∆1 ............................................................................................................... 5-21
Jumper Positions WYE-∆2 ............................................................................................................... 5-22
Jumper Positions ∆1-∆1 ................................................................................................................... 5-22
Jumper Positions ∆2-∆2 ................................................................................................................... 5-23
Jumper Positions ∆1-∆2 ................................................................................................................... 5-23
Figures
Figure 5-1. Test Setup: Single-Phase ....................................................................................................... 5-7
Figure 5-2. Test Setup: Three-Phase, Sensing Input Type E, Output Option E ....................................... 5-7
Figure 5-3. Test Setup: Three-Phase, Sensing Input Type E, Output Option F ....................................... 5-8
Figure 5-4. Test Setup: Three-Phase, Sensing Input Type G, Output Option E ....................................... 5-8
Tables
Table 5-1. Restrained Pickup Test: 5 A, 50 or 60 Hz .............................................................................. 5-10
Table 5-2. Input Verification*: 5 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-3. Unrestrained Pickup Verification: 5 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-4. Timing: 5 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-5. Restraint Pickup Test: 1 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-6. Input Verification*: 1 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-7. Unrestrained Pickup Verification, 1 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-8. Timing, 1 A, 50 or 60 Hz
Table 5-9. Input Signals to Comparison Circuits Based On Jumper Positions
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Test Procedures i
....................................................................................... 5-11
................................................................ 5-11
......................................................................................................... 5-13
................................................................................. 5-15
....................................................................................... 5-16
................................................................ 5-16
......................................................................................................... 5-18
....................................... 5-21
Page 96

ii BE1-87T Test Procedures 9171300990 Rev V
Page 97

SECTION 5 • TEST PROCEDURES
Overview
BE1-87T Transformer Differential Relays are calibrated and tested for correct operation at the factory and
all calibration pots are sealed.
Immediately upon receipt of the relay, or after extended service, it is recommended that the Verification
Tests provided in this section be performed. These comprehensive tests verify all operating parameters
including calibration.
BE1-87T relay Verification Tests are divided into two groups based on the current CT ampere rating and
the nominal operating frequency: (See the first position of the Style Number and the Sensing Input Range
Option as shown in Figure 1-1.)
Five Amperes CT, 60 Hz Units (Range 1) and Five Amperes CT, 50 Hz Units (Range 3)
One Ampere CT, 60 Hz Units (Range 4) and One Ampere CT, 50 Hz Units (Range 2)
Within each group are separate tests that can be performed individually to make it easier to focus on a
particular problem. However, all of these tests should be performed prior to putting the relay into service.
To help field users understand the verification procedures, four examples for restrained pickup testing are
provided before the actual Verification Tests begin. Two examples are for increasing one input from
balance and two examples are for decreasing one input from balance. These examples are not a
necessary part of verification testing, but are provided for clarification.
For routine assurance that the BE1-87T is operating correctly, the simplified OPERATIONAL TESTS may
be performed.
Before starting a test program, check the Style Number of the relay against the Style Number
Identification Chart, Figure 1-1, to identify the specific features and options to be tested. For location of
the switches and controls, refer to Figures 2-1 and 2-2 for Input Range 1 or 3, and Figures 2-3 and 2-4 for
Input Range 2 or 4.
NOTE
LEDs and targets (if provided) should be checked for proper operation and
targets reset after they have been tripped. Current-operated (Type D) targets
will only operate when a minimum of 0.2 A is present in the trip circuit.
Similarly, the auxiliary contacts (if present) should be checked for proper
operation. Switches S1 and S2, located on the mother board and shown in
Figure 2-4 allow the auxiliary output to operate in conjunction with a restrained
trip, an unrestrained trip, or both.
Equipment Required
The following test equipment (or equivalent) is required for either the Operational Tests or the
Verification Tests:
1. Two current sources with independently regulated current outputs. Must be able to produce
outputs 180° out of phase. If harmonic testing is desired, harmonic capability is also required.
2. Counter, 0 to 0.5 second range.
3. Two Test Plugs, Basler p/n 10095 (see Test Plug in Section 4, Installation).
4. Phase angle meter or oscilloscope with an ungrounded plug or ground isolation transformer.
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Test Procedures 5-1
Page 98

Restrained Pickup Testing Examples
ITI
T
112
2
−
I
T
or
I
T
1
1
2
2
I I
T
T
Amps
1 2
1
2
=
×
0 35
.
I
T
slope
slope
2
2
0 35
100
1
100
>
−
.
I
I
sTT
trip1
2 1
2
1
min
=
−
×
I T
I
T
trip1 1
2
2
0 35
min
.= +
unbalance >
(maximum restraint)
or 0.35 pu, whichever is greater
slope
100
I
I
slope
trip min
balance
1
1
1
(100)
=
-
(in pu)
I
balance
slope
slope
1
0
35
100
1
100
<
-
(
)
.
(in pu)
(
)
I
I
trip min
balance
1
1
=
+
0.35 (
in pu)
Increasing One Input from Balance
The formula to determine the unbalance value at which the restrained trip occurs is:
Where:
unbalance = absolute value of (I
slope = the RESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL setting (15 to 60)
maximum restraint = larger of I
By increasing the I
1) When:
input current from balance: (The balance current is
1
I
>
balance1
1
This means the pu restraint current is to the right of the intersection of the slope characteristic with the
0.35 MPU horizontal line (see Figure 1-2).
the minimum trip point is established as:
- I2) in per unit (pu) i.e.
1
or I2 in pu i.e.
1
OR
slope
−
100
slope
100
(in pu)
OR
2) When:
the minimum trip point is established as:
OR
5-2 BE1-87T Test Procedures 9171300990 Rev V
(in Amps)
(in Amps)
(Equation 1)
(Equation 1a)
(Equation 2)
(Equation 2a)
Page 99

Example One:
tap tap slope
1 2
2 3 8 15%= = =, . ,
I
trip1
2
3 8
3 8
0 35
2 7
= +
=
.
.
.
. A
tap tap slope
1 2
2 3 8 15%= = =, . ,
Inputs I A pu
I
T
pu
I A pu
I
T
pu
: ( )
. ( )
.
.
1
1
1
2
2
2
6 3
6
2
3
11 4 3
11 4
3 8
3
= = =
= = =
I
balance
slope
slope
1
0.35
100
1
100
<
>
−
(in pu)
<
1
1.983
(
)
(
)
1<>
0.35
0.15
1 - 0.15
(
)
I
trip
1
=
1 pu+0.35
=
1.35 pu
I
tap
trip
1
(2
0)
2
70
=
x
=
±
±
1.35 pu
=
(1.35)
A
6%
100 mA
.
.
Assume:
1
I
Inputs I A pu
: ( )
1
2 1
= = =
2
I A pu
. ( )
38 1
= = =
Check:
Therefore: Use Equation 2 or 2a.
From Figure 1-2 (the percentage restraint characteristic of the BE1-87T at 15% slope), the minimum
current where trip occurs is:
2
1
T
2
2
I
38
2
T
38
pu
1
.
.
pu
1
In terms of current, the trip current is:
Using Equation 2a:
Example Two:
Assume:
9171300990 Rev V BE1-87T Test Procedures 5-3
Page 100

Check:
I
trip1
11 4
1 0 1523 8
7 06
min
.
. .
.
=
−
×
= A
I I
T
T
2 1
2
1
= ×
I
slope
balance2
0 35
100
>
.
(in pu)
I
T
slope
1
1
0 35
100
>
.
I
balance
slope
slope
1
0.35
100
1
100
<
>
-
(in pu)
>
3
1.983
(
)
(
)
3<>
0.35
0.15
1 - (0.15)
)
(
I
trip
1
1
15
3 pu
0
3.53 pu
=
-
=
.
I
trip
1
3.53 pu
tap
=
(3.53) (2
.0)
=
7.06 A
6%
100 mA
=
x
±
±
unbalance
(maximum restraint)
or 0.35 pu, whichever is greater
>
slope
100
I
I
slope
trip
balance
2
2
1
100
=
-
)
(in pu)
(
Therefore: Use Equation 1 or 1a.
From Figure 1-2 (the percentage restraint characteristic of the BE1-87T at 15% slope), the minimum
current where trip occurs is:
In terms of current, the trip current is:
Using Equation 1a:
Decreasing One Input from Balance
The formula to determine the unbalance value at which the restrained trip occurs is:
Where:
unbalance - absolute value of I
slope = the RESTRAINED PICKUP LEVEL setting (15 to 60)
maximum restraint = larger of I
By decreasing the I
input current from balance:
2
- I2 in per unit (pu)
1
or I2 in pu =I
1
r
The balance current is
1) When:
the value of I
5-4 BE1-87T Test Procedures 9171300990 Rev V
is defined as:
2 trip max.
OR
(Equation 3)
 Loading...
Loading...