Page 1

Switches | Product Information
CentreCOM® GS970M Series
Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switches
The Allied Telesis CentreCOM GS970M Series of Layer 3 Gigabit
switches offer an impressive set of features in a compact design,
making them ideal for applications at the network edge.
Overview
Allied Telesis CentreCOM GS970M
Series switches provide an excellent
access solution for today’s networks,
supporting Gigabit to the desktop for
maximum performance. The Power
over Ethernet Plus (PoE+) models
provide an ideal solution for connecting
and remotely powering wireless access
points, IP video surveillance cameras,
and IP phones. The GS970M models
feature 8, 16 or 24 Gigabit ports,
and 2 or 4 SFP uplinks, for secure
connectivity at the network edge.
Specifications
Performance
ۼۼ Supports 10K jumbo frames
ۼۼ Wirespeed multicasting
ۼۼ Up to 16K MAC addresses
ۼۼ 512MB DDR SDRAM (GS970M non PoE)
ۼۼ 256MB DDR SDR AM (GS970M PS)
ۼۼ 4094 configurable VLANs (GS970M non PoE)
ۼۼ 2048 configurable VLANs (GS970M PS)
ۼۼ 64MB flash memory
ۼۼ Packet Buffer memory: 1.5MB
Diagnostic tools
ۼۼ Active Fiber Monitoring detects tampering on
optical links
ۼۼ Built-In Self Test (BIST)
ۼۼ Find-me device locator
ۼۼ Cable fault locator (TDR)
ۼۼ Optical Digital Diagnostics Monitoring ( DDM)
ۼۼ Automatic link flap detection and port shutdown
ۼۼ Ping polling for IPv4 and IPv6
ۼۼ Port and VLAN mirroring (RSPAN)
ۼۼ TraceRoute for IPv4 and IPv6
IP Features
ۼۼ IPv4 static routing and RIP
ۼۼ Device management over IPv6 networks with
SNMPv6, Telnetv6, SSHv6
ۼۼ NTPv6 client
Management
ۼۼ Allied Telesis Autonomous Management
Framework™ (AMF) enables powerful centralized
management and zerotouch device installation and
recovery
ۼۼ Console management port on the front panel for
ease of access
ۼۼ Eco-friendly mode allows por ts and LEDs to be
disabled to save power
ۼۼ Industry-standard CLI with context-sensitive help
ۼۼ Powerful CLI scripting engine
ۼۼ Comprehensive SNMP MIB support for standards-
based device management
ۼۼ Built-in text editor
ۼۼ Event-based triggers allow user-defined scripts to
be executed upon selected system events
ۼۼ SD/SDHC memory card socket allows software
release files, configurations and other files to be
stored for backup and distribution to other devices
ۼۼ Configurable logs and triggers provide an audit trail
of SD card insertion and removal
Quality of Service (QoS)
ۼۼ Eight priority queues with a hierarchy of high-
priority queues for real-time traffic, and mixed
scheduling, for each switch port
ۼۼ Limit bandwidth per port or per traffic class down
to 64kbps
ۼۼ Wirespeed traffic classification with low latency
essential for VoIP and real-time streaming media
applications
ۼۼ Policy-based QoS based on V LAN, port, M AC and
general packet classifiers
ۼۼ Policy-based storm protection
ۼۼ Extensive remarking capabilities
ۼۼ Taildrop for queue congestion control
ۼۼ Strict priority, weighted round robin or mixed
scheduling
ۼۼ IP precedence and DiffServ marking based on
Layer 2, 3 and 4 headers
Resiliency Features
ۼۼ Control Plane Prioritization (CPP) ensures the CPU
always has sufficient bandwidth to process network
control traffic
ۼۼ Dynamic link failover (host attach)
ۼۼ EPSRing™ (Ethernet Protection Switched Rings)
with enhanced recovery
ۼۼ Loop protection: loop detection and thrash limiting
ۼۼ PVST+ compatibility mode
ۼۼ STP root guard
ۼۼ UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD)
Security Features
ۼۼ Access Control Lists (ACLs) based on Layer 2, 3
and 4 headers
ۼۼ Configurable auth-fail and guest VLA Ns
ۼۼ Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
(AAA)
ۼۼ Bootloader can be password protected for device
security
ۼۼ BPDU protection
ۼۼ DHCP snooping, IP source guard and Dynamic ARP
Inspection (DAI)
ۼۼ Dynamic VLAN assignment
ۼۼ MAC address filtering and MAC address lock-down
ۼۼ Network Access and Control (NAC) features
manage endpoint security
ۼۼ Port-based learn limits (intrusion detection)
ۼۼ Private VLANs provide security and port isolation
for multiple customers using the same VLAN
ۼۼ Secure Copy (SCP)
ۼۼ Strong password security and encryption
ۼۼ Tri-authentication: MAC-based, Web-based and
IEEE 802.1x
Key Features
ۼۼ Modular AlliedWare Plus operating
system
ۼۼ Allied Telesis Autonomous
Management Framework (AMF)
edge node
ۼۼ Eco-friendly
ۼۼ IPv6 features
ۼۼ IEEE 802.1x/MAC/Web
authentication support
ۼۼ Graphical User Interface (GUI) for
easy management
ۼۼ L3 features supported
ۼۼ Static routing
ۼۼ RIP
alliedtelesis.com
NETWORK SMARTER
Page 2
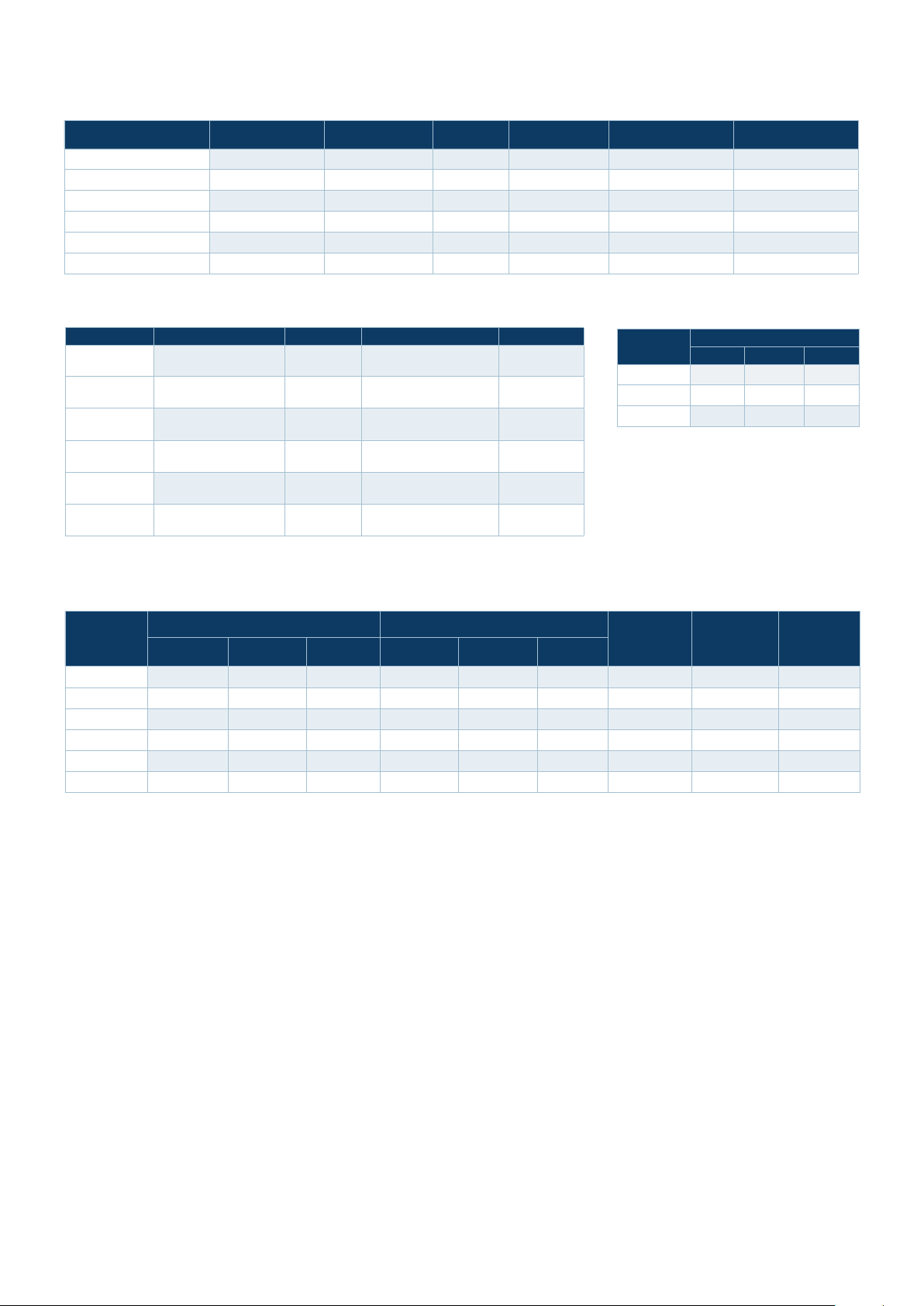
CentreCOM GS970M Series | Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switches
Product Specifications
PRODUCT
GS970M/10PS
GS970M/10
GS970M/18PS
GS970M/18
GS970M/28PS
GS970M/28
10/10 0/10 00T (RJ -45 )
COPPER PORTS
8 2 10 8 20Gbps 14.9Mpps
8 2 10 - 20Gbps 14.9Mpps
16 2 18 16 36Gbps 26.8Mpps
16 2 18 - 36Gbps 26.8Mpps
24 4 28 24 56Gbps 41.7 Mpps
24 4 28 - 56Gbps 41.7Mpps
100/1000X SFP PORTS TOTAL PORTS
POE+ ENABLE
Physical specifications
PRODUCT WIDTH X DEPTH X HEIGHT WEIGHT PACKAGED DIMENSIONS WEIGHT
GS970M/10PS
GS970M/10
GS970M/18PS
GS970M/18
GS970M/28PS
GS970M/28
210 x 275 x 42.5 mm
(8.27 x 10.8 3 x 1.67 in)
265 x 180 x 42.5 mm
(10.43 x 7.08 x 1.67 in)
341 x 231 x 44 mm
(13.42 x 9.09 x 1.73 in)
341 x 231 x 44 mm
(13.42 x 9.09 x 1.73 in)
440 x 290 x 44 mm
(17.32 x 11.42 x 1.73 in)
341 x 231 x 44 mm
(13.42 x 9.09 x 1.73 in)
2.1 kg (4.6 lb) 43 x 36 x 15 cm
1.5 kg (3.3 lb) 43 x 36 x 15 cm
3.0 kg (6.6 lb) 43 x 36 x 15 cm
2.4 kg (5.3 lb) 43 x 36 x 15 cm
4.7 kg (10.4 lb) 53 x 43 x 15 cm
2.4 kg (5.3 lb) 43 x 36 x 15 cm
(16.93 x 14.17 x 5.90 in)
(16.93 x 14.17 x 5.90 in)
(16.93 x 14.17 x 5.90 in)
(16.93 x 14.17 x 5.90 in)
(20.86 x 16.93 x 5.90 in)
(16.93 x 14.17 x 5.90 in)
3.45 kg (7.6 lb)
2.85 kg (6.3 lb)
4.35 kg (9.6 lb)
4.0 kg (8.8 lb)
6.35 kg (14.0 lb)
4.0 kg (8.8 lb)
Power characteristics
100-240 VAC, 50-60Hz, 2.4A maximum
PORTS
SWITCHING FABRIC FORWARDING RATE
Latency (microseconds)
PRODUCT
GS970M/10
GS970M/18
GS970M/28
PORT SPEED
10MBPS 100MBPS 1GBP S
55µs 7.8 µs 3.4µs
56µs 7.9 µs 3.4µs
59µs 8.6µs 4.3µs
PRODUCT
GS970M/10PS
GS970M/10
GS970M/18PS
GS970M/18
GS970M/28PS
GS970M/28
MAX POWER
CONSUMPTION
16W 55 BTU/hr 33 dBA 180W 126 BTU/hr 41 d BA 124 W 8 4
16W 55 BTU/hr Fanless - - - - - -
21W 72 BTU/hr 3 4 dBA 330W 169 B TU/ hr 42 dBA 247W 16 8
18W 61 BTU/hr 29 dBA - - - - - -
37W 127 B TU/hr 33 dBA 520W 303 BTU/hr 42 dBA 370W 24 12
26W 89 BTU/ hr 3 4 dBA - - - - - -
NO POE LOAD FULL POE+ LOAD
MAX HEAT
DISSIPATION
Cryptographic Algorithms
FIPS Approved Algorithms
Encryption (Block Ciphers):
ۼۼ AES (ECB, CBC, CFB and OFB Modes)
ۼۼ 3DES (ECB, CBC, CFB and OFB Modes)
Block Cipher Modes:
ۼۼ CCM
ۼۼ CMAC
ۼۼ GCM
ۼۼ XTS
Digital Signatures & Asymmetric Key Generation:
ۼۼ DSA
ۼۼ ECDSA
ۼۼ RSA
Secure Hashing:
ۼۼ SHA -1
ۼۼ SHA-2 (SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384. SHA-512)
Message Authentication:
ۼۼ HMAC (SHA-1, SHA-2(224, 256, 384, 512)
Random Number Generation:
ۼۼ DRBG (Hash, HMAC and Counter)
NOISE
Non FIPS Approved Algorithms
RNG (AES128/192/256)
DES
MD5
MAX POWER
CONSUMPTION
MAX HEAT
DISSIPATION
Ethernet
IEEE 802.2 Logical L ink Control (LLC)
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T
IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE )
IEEE 802.3at Power over Ethernet plus (PoE+)
IEEE 802.3az Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE)
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-X
IEEE 802.3x Flow control - full-duplex operation
IEEE 802.3z 1000BASE-X
IPv4 Features
RFC 768 User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
RFC 791 Internet Protocol (IP)
RFC 792 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
RFC 793 Transmission C ontrol Protocol (TCP)
RFC 826 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
RFC 89 4 Standard for the transmission of IP datagrams
over Ethernet networks
RFC 919 Broadcasting Internet datagrams
NOISE
MAX POE
POWER
RFC 92 2 Broadcasting Internet datagrams in the
presence of subnets
RFC 932 Subnetwork addressing scheme
RFC 950 Internet standard subnetting procedure
RFC 1042 Standard for the transmission of IP datagrams
over IEEE 802 networks
RFC 1071 Computing the Internet checksum
RFC 1122 Internet host requirements
RFC 1191 Path MT U discover y
RFC 1518 An architecture for IP address allocation with
CIDR
RFC 1519 Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
RFC 1812 Requirements for IPv4 routers
RFC 1918 IP addressing
RFC 25 81 TCP congestion control
MAX POE
PORTS AT 15W
PER PORT
MAX POE+
PORTS AT 30W
PER PORT
IPv6 Features
RFC 1981 Path MT U discover y for IPv 6
RFC 246 0 IPv6 specification
RFC 246 4 Transmission of I Pv6 packets over Ethernet
networks
RFC 3484 Default address selection for IPv6
RFC 3587 IPv6 global unicast address format
RFC 3596 DNS extensions to support IP v6
RFC 4007 IPv6 scoped address architecture
alliedtelesis.com
NETWORK SMARTER
Page 3

CentreCOM GS970M Series | Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switches
RFC 4193 Unique local IPv6 unicast addresses
RFC 4213 Transition mechanisms for IP v6 hosts and
routers
RFC 4291 IPv6 addressing architecture
RFC 4443 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMPv6)
RFC 4861 Neighbor discovery for IPv6
RFC 4862 IPv6 Stateless Address Auto-Configuration
(SLA AC)
RFC 5014 IPv6 socket API for source address selection
RFC 5095 Deprecation of type 0 routing headers in IPv6
Management
AMF edge node
AT Enterprise MIB including AMF MIB and SNM P traps
SNMPv1, v2c and v3
IEEE 802.1AB Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
RFC 1155 Structure and identification of management
information for TCP/IP-based Internets
RFC 1157 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
RFC 1212 Concise MIB definitions
RFC 1213 MIB for network management of TC P/IP-based
Internets: MIB-II
RFC 1215 Convention for defining traps for use with the
SNMP
RFC 1227 SNMP MUX protocol and MIB
RFC 1239 Standard MIB
RFC 1724 RIPv2 MIB extension
RFC 2578 Structure of Management Information v2
(SMIv2)
RFC 2579 Textual conventions for SM Iv2
RFC 25 80 Conformance statements for SMIv2
RFC 2674 Definitions of managed objects for bridges
with traffic classes, multicast filtering and
VLAN extensions
RFC 2741 Agent extensibility (AgentX) protocol
RFC 2819 RMON M IB (groups 1,2,3 and 9)
RFC 28 63 Interfaces group MIB
RFC 3411 An architecture for describing SNMP
management frameworks
RFC 3412 Message processing and dispatching for the
SNMP
RFC 3413 SNMP applications
RFC 3414 User-based Security Model (U SM) for SNMPv3
RFC 3415 View-based Access Control Model (VAC M) for
SNMP
RFC 3416 Version 2 of the protocol operations for the
SNMP
RFC 3417 Transport mappings for the SNMP
RFC 3418 MIB for S NMP
RFC 3621 Power over Ethernet (Po E) MIB
RFC 3635 Definitions of managed objects for the
Ethernet-like interface types
RFC 3636 IEEE 802.3 MA U MIB
RFC 4022 MIB for the Transmission Control Protocol
(TCP)
RFC 4113 MIB for the User Datagram Protocol (UDP )
RFC 4188 Definitions of managed objects for bridges
RFC 4292 IP forwarding table M IB
RFC 4293 MIB for the Internet Protocol (IP)
RFC 4318 Definitions of managed objects for bridges
with RSTP
RFC 4 560 Definitions of managed objects for remote ping,
traceroute and lookup operations
RFC 5424 The Syslog protocol
1
Multicast Support
IGMP query solicitation
IGMP snooping (IGMPv1, v2 and v3)
IGMP snooping fast-leave
MLD snooping (MLDv1 and v 2)
RFC 2715 Interoperability rules for multicast routing
protocols
RFC 3306 Unicast-prefix-based IPv6 multicast addresses
RFC 4541 IGMP and MLD snooping switches
Quality of Service (QoS)
IEEE 802.1p Priority tagging
RFC 2211 Specification of the controlled-load network
element service
RFC 2474 DiffServ precedence for eight queues/port
RFC 2475 DiffServ architecture
RFC 2597 DiffServ Assured Forwarding (A F)
RFC 26 97 A single-rate three-color marker
RFC 26 98 A two-rate three-color marker
RFC 3246 DiffServ Expedited Forwarding ( EF)
Resiliency Features
IEEE 802.1AX Link aggregation (static and LACP)
IEEE 802.1D MAC bridges
IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MST P)
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Proto col (RS TP)
IEEE 802.3ad Static and dynamic link aggregation
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
RFC 1058 Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
RFC 20 82 RIP-2 MD5 authentication
RFC 2453 RIPv2
Security Features
SSH remote login
SSLv2 and S SLv3
TACACS + Accounting, Authentication and Authorisation
(AAA)
IEEE 802.1X authentication protocols (TL S, TTLS, PE AP
and MD5)
IEEE 802.1X multi-supplicant authentication
IEEE 802.1X port-based network access control
RFC 25 60 X.509 Online Certificate Status Protocol
(OCSP)
RFC 2818 HTTP over TL S (“HT TPS”)
RFC 28 65 RADIUS authentication
RFC 28 66 RADIUS accounting
RFC 2986 PKCS #10: certification request syntax specifi
cation v1.7
RFC 3546 Transport L ayer Security (T LS) extensions
RFC 3580 IEEE 802.1x RADIUS usage guidelines
RFC 3748 PPP Extensible Authentication Protocol (EA P)
RFC 4251 Secure Shell (SSH v2) proto col architecture
RFC 4252 Secure Shell (SSH v2) authentication protocol
RFC 425 3 Secure Shell (SSH v2) transport layer protocol
RFC 425 4 Secure Shell (SSH v2) connection protocol
RFC 5246 Transport L ayer Security (T LS) v1.2
RFC 5280 X.509 certificate and Certificate Revocation
List (CRL) profile
RFC 5425 Transport L ayer Security (T LS) transport
mapping for Syslog
RFC 5656 Elliptic cur ve algorithm integration for SSH
RFC 6125 Domain-based application service identity
within PKI using X.509 certificates with TLS
RFC 6614 Transport L ayer Security (T LS) encryption for
RADIUS
RFC 6668 SHA-2 data integrit y verification for SS H
Services
Services
RFC 854 Telnet protocol specification
RFC 855 Telnet option specifications
RFC 857 Telnet echo option
RFC 858 Telnet suppress go ahead option
RFC 1091 Telnet terminal-type option
RFC 1350 Trivial File Transfer Protocol ( TFTP)
RFC 1985 SMTP service ex tension
RFC 20 49 MIME
RFC 2131 DHCP v4 client
RFC 2616 Hyper text Transfer Protocol - HT TP/1.1
RFC 2821 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
RFC 2822 Internet message format
RFC 4330 Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) version 4
RFC 59 05 Network Time Protocol (NT P) version 4
VLAN support
IEEE 802.1Q Virtual L AN (VLA N) bridges
IEEE 802.1v VLAN classification by protocol and por t
IEEE 802.3ac VLAN tagging
Voice over IP (VoIP)
LLDP-MED ANSI/TIA-1057
Voice VLAN
Environmental Specifications
Operating ambient temp. 0°C to 50°C (32°F to 113°F)
Storage temp. -25°C to 70°C (-13°F to 158°F )
Operating humidity 5% to 90% non-condensing
Storage humidity 5% to 95% non-condensing
Maximum operating Altitude 3,000 m (9,842 f t)
Maximum Non operating Altitude 4,000 m (13,100 ft)
Safety and Electromagnetic Emissions
EMI (Emissions) : FCC Class A, EN55022 Class A,
EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3,
VCCI Class A, CI SPR Class A
EMC (Immunity) : EN55024
Electrical and Laser Safety : E N60950-1 (TUV), UL 6095 0-
1(cULus), EN60825-1
Compliance Marks UL, cU L, UL-EU, CE
Restrictions on Hazardous Substances
(RoHS) Compliance
ۼۼ EU RoHS compliant
ۼۼ China RoHS compliant
Country of origin
ۼۼ China
1
AMF ed ge is for produ cts used at the edge of the ne twork, and only
suppor t a single AMF link . They canno t use cross link s or virtual links .
alliedtelesis.com
NETWORK SMARTER
Page 4

CentreCOM GS970M Series | Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switches
Ordering Information
AT-GS970M/10PS-R
L3 switch with 8 x 10/100/1000T PoE ports and
2 x 100/1000X SFP ports with rack mount kit
AT-GS 970M /10
L3 switch with 8 x 10/100/1000T ports and
2 x 100/1000X SFP ports
AT-GS970M/18PS-R
L3 switch with 16 x 10/100/1000T PoE ports and
2 x 100/1000X SFP ports with rack mount kit
AT-GS 970M /18
L3 switch with 16 x 10/100/1000T ports and
2 x 100/1000X SFP ports
AT-GS970M/28PS
L3 switch with 24 x 10/100/1000T PoE ports and
4 x 100/1000X SFP ports
AT-GS970M/28
L3 switch with 24 x 10/100/1000T ports and
4 x 100/1000X SFP ports
AT-R KMT- J0 5
Rack mount kit for GS970M/10
AT-R KMT- J13
Rack mount kit for GS970M/18 and 18PS
AT-R KMT- J14
Rack mount kit for GS970M/10PS
AT-R KMT- J15
Rack mount shelf kit for two GS970M/10 units
AT-B RKT- J23
Wall mount kit for GS970M /10
AT-B RKT- J24
Wall mount kit for GS970M /18, 28, 10PS, 18PS
and 28PS
SFP modules
AT-SPFX /2
100FX multi-mode 1310 nm fiber up to 2 km
AT-SPFXBD-LC-13
100BX Bi-Di (1310 nm Tx, 1550 nm Rx) fiber up to
10 km
AT-SPFXBD-LC-15
100BX Bi-Di (1550 nm Tx, 1310 nm Rx) fiber up to
10 km
AT-SP TX
1000T 100 m copper
AT-SPSX
1000SX GbE multi-mode 850 nm fiber up to 550 m
AT-SPSX / I
1000SX GbE multi-mode 850 nm fiber up to 550 m
industrial temperature
AT-SPEX
1000X GbE multi-mode 1310 nm fiber up to 2 km
AT-SPLX10
1000L X GbE single-mode 1310 nm fiber up to
10 km
AT-SPLXI0/I
1000L X GbE single-mode 1310 nm fiber up to
10 km industrial temperature
AT-SPBDI0-13
1000L X GbE Bi-Di (1310 nm Tx, 1490 nm Rx) fiber
up to 10 km
AT-SPBDI0-14
1000L X GbE Bi-Di (1490 nm Tx, 1310 nm Rx) fiber
up to 10 km
AT-SPLX40
1000L X GbE single-mode 1310 nm fiber up to 40 km
AT-SPZX 80
1000ZX GbE single-mode 1550 nm fiber up to 80 km
AT-SPBD20-13/I
1000BX GbE Bi-Di (1310 nm Tx, 1550 nm Rx) fiber
up to 20 km, industrial temperature
AT-SPBD20-14/I
1000BX GbE Bi-Di (1490 nm Tx, 1310 nm Rx) fiber
up to 20 km, industrial temperature
AT-SPFX / 15
100FX single-mode 1310 nm fiber up to 15 km
Feature Licenses
NAME DESCRIPTION INCLUDES
AT-FL-GS97-UDLD
UniDirectional Link Detection
ۼۼ UDLD
NETWORK SMARTER
North America Headquarters | 19800 Nor th Creek Parkway | Suite 100 | Bothell | WA 98011 | USA | T: +1 800 424 4284 | F: +1 425 481 3895
Asia-Pacific Headquarters | 11 Tai Seng Link | Singapore | 53418 2 | T: +65 6383 3832 | F: +65 6383 3830
EMEA & CSA Operations | Incheonweg 7 | 1437 EK Rozenburg | The Netherlands | T: +31 20 7950020 | F: +31 20 7950021
alliedtelesis.com
© 2017 Allied Teles is, Inc. All rights r eserved. Infor mation in this docum ent is subject to chang e without notice. A ll company names, lo gos, and product d esigns that are trade marks or register ed trademarks are t he property of t heir respective ow ners.
617-000622 RevE
 Loading...
Loading...