Page 1
… g o i n g o n e s t e p f u r t h e r
B60
(1000213)
Page 2

2
Page 3

®
Latin
1 Myofibrilla
2 Mitochondrium
3 Membrana postsynaptica
4 Synaptic gap with basal lamina
5 Membrana praesynaptica
6 Vesicula praesynaptica
7 Schwann cell
8 Nucleus
9 Myosin and actin filament
10 Sarkomer
11 Actin filament
12 Stratum myelini
13 Neurofibra
14 Sarkolemma
15 Transversal-Tubulus (T-Tubulus)
16 Trias
17 Reticulum sarkoplasmaticum
18 Lamina basalis
19 Fibrae reticularis
3
Page 4

®
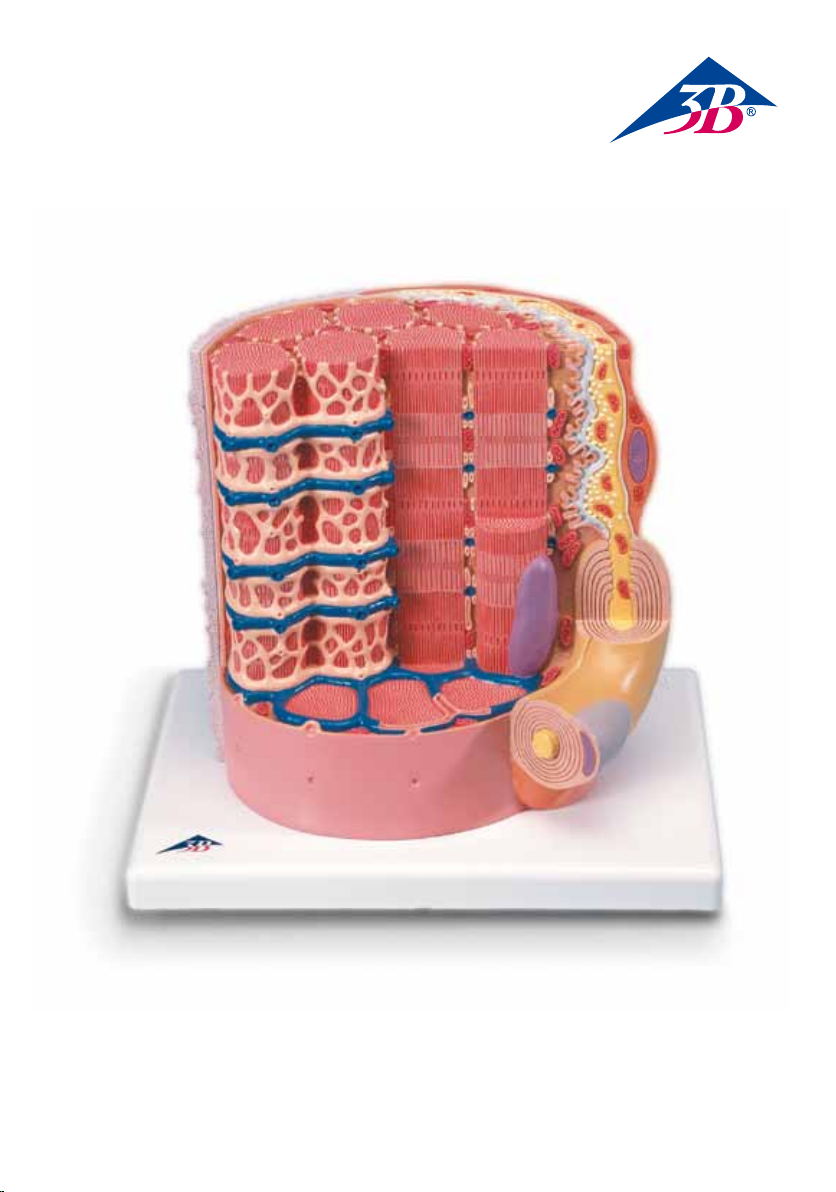
3B MICROanatomy™ Muscle Fiber
The model illustrates a section of a skeletal muscle fiber and its neuromuscular end plate magnified
approx. 10,000 times.
The muscle fiber is the basic element of the diagonally striped skeletal muscle. It is a giant cell (1 – 10 cm
long and up to 0.1 mm thick) with many nuclei. Its chief functional element is formed by myofibrils. The
myofibrils are made of the myofilaments myosin and actin and are surrounded by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The characteristic longitudinal striping of the skeletal muscle is caused by the specific arrangement of
the myofilaments. The thick myosin filaments, which are optically bi-refracted, form the A (transverse)
band. The thin actin filaments, by contrast, are uni-refracted and form the I (isotropic) band. The Z line
(intermediate stripe) runs through its center. The section between two Z lines is called the sarcomere.
Starting from the cell membrane, the cytoplasm is run through by membranous tubes, called the transversal tubuli, which together with the terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum form a triad. The nuclei
are situated in the cell periphery. Mitochondria, the “power plants of the cells” run parallel to the myofibrils.
The neuromuscular end plate is the name of the area in which a motor nerve ending is in contact with the
skeletal muscle cell. The nerve ending is covered by a Schwann cell. The synaptic gap, which is filled by a
common basal lamina of the muscle and Schwann cell, lies between the muscle cell and the nerve ending.
The nerve ending contains mitochondria as well as presynaptic vesicles that are filled with transmitter substances (usually acetylcholine).
1 Myofibrils
2 Mitochondrium
3 Postsynaptic membrane
4 Synaptic gap with basal lamina
5 Presynaptic membrane
6 Presynaptic vesicle
7 Schwann cell
8 Nucleus
9 Myosin and actin filament
10 Sarcomere
11 Actin filament
12 Myelin sheath
13 Neurofibers
14 Cell membrane (sarcolemma)
15 Transverse membrane tube
16 Triad
17 Sarcoplasmic reticulum
18 Basal lamina
19 Reticular fibers
English
4
Page 5

®
Deutsch
Das Modell zeigt einen Abschnitt einer Skelettmuskelfaser mit motorischer Endplatte in ca. 10 000facher
Vergrößerung.
Die Muskelfaser stellt das Grundelement des quergestreiften Skelettmuskels dar. Sie ist eine Riesenzelle (1 –
10 cm lang und bis 0,1 mm dick) mit zahlreichen Zellkernen. Ihr funktioneller Hauptbestandteil wird durch
Myofibrillen gebildet. Die Myofibrillen bestehen aus den Myofilamenten Myosin sowie Aktin und werden
von sarkoplasmatischem Retikulum umgeben. Durch die bestimmte Anordnung der Myofilamente kommt
die charakteristische Querstreifung des Skelettmuskels zustande. Die dicken Myosinfilamente, die optisch
doppelbrechend sind, bilden die A-Bande. Im Gegensatz dazu stehen die dünnen Aktinfilamente, die einfach lichtbrechend sind und die I-Bande bilden, in dessen Mitte ein Zwischenstreifen (Z-Streifen) verläuft.
Der Abschnitt zwischen zwei Z-Streifen wird Sarkomer genannt. Ausgehend von der Zellmembran durchqueren Membranschläuche, die so genannten Transversal-Tubuli, das Zytoplasma, die unter anderem
zusammen mit den terminalen Zisternen des sarkoplasmatischen Retikulums eine Triade bilden. In der
Zellperipherie liegen die Zellkerne. Parallel zu den Myofibrillen befinden sich Mitochondrien, die
„Kraftwerke der Zellen“.
Die motorische Endplatte kennzeichnet den Bereich, in dem eine motorische Nervenendigung mit der
Skelettmuskelzelle in Kontakt steht. Die Nervenendigung wird von einer Schwann-Zelle bedeckt. Zwischen
der Muskelzelle und der Nervenendigung liegt der synaptische Spalt, der mit einer gemeinsamen
Basallamina der Muskel- und Schwann-Zelle ausgefüllt ist. Die Nervenendigung enthält neben Mitochondrien präsynaptische Bläschen (Vesikel), die mit Transmitterstoffen (meist Azetylcholin) gefüllt sind.
1 Myofibrille
2 Mitochondrium
3 postsynaptische Membran
4 synaptischer Spalt mit Basallamina
5 präsynaptische Membran
6 präsynaptische Vesikel
7 Schwann-Zelle
8 Zellkern
9 Myosin- und Aktinfilamente
10 Sarkomer
11 Aktinfilamente
12 Markscheide (Myelinscheide)
13 Nervenfaser
14 Zellmembran (Sarkolemm)
15 transversaler Membranschlauch
16 Triade
17 Sarkoplasmatisches Retikulum
18 Basallamina
19 retikuläre Fasern
3B MICROanatomy™ Muskelfaser
5
Page 6

®
3B MICROanatomy™ Fibra muscular
El modelo representa una porción de una fibra muscular esquelética con una placa motora terminal, a
10 000 aumentos aproximadamente.
La fibra muscular es el elemento básico del músculo esquelético estriado. Es una célula gigante ( de 1 - 10
cms. de longitud y de hasta 0,1 mm de espesor) con numerosos núcleos. Su principal componente funcional son las miofibrillas. Las miofibrillas aparecen constituidas por los miofilamentos miosina y actina y
están rodeadas por el retículo sarcoplásmico. Debido a la disposición determinada de los miofilamentos, el
músculo esquelético tiene su diseño característico de estrías transversales. Los filamentos gruesos de miosina, los cuales son ópticamente de refracción doble, constituyen la banda A. En cambio, los filamentos delgados de actina, los cuales son ópticamente de refracción simple, constituyen la banda I, en cuyo centro se
encuentra una banda intermedia (banda Z). El segmento entre dos bandas Z se denomina sarcómera. A
partir de la membrana celular, unos túbulos membranosos, los así llamados túbulos transversos, traviesan
el citoplasma y, entre otras cosas, forman junto con las cisternas terminales del retículo sarcoplásmico una
tríada. En la periferia celular se encuentran los núcleos. Paralelamente a las miofibrillas, se encuentran
mitocondrias, las „centrales energéticas de las células“.
La placa motora terminal designa la zona, en la cual una terminación nerviosa está en contacto con la
célula muscular esquelética. La terminación nerviosa está cubierta de una célula de Schwann. Entre la
célula muscular y la terminación nerviosa se encuentra la hendidura sináptica que está llena de una lámina basal conjunta de la célula muscular y la de Schwann. Además de las mitocondrias, la terminación nerviosa contiene vesículas presinápticas que están llenas de sustancias neurotransmisoras (en la mayoría de
los casos acetilcolina).
1 Miofibrilla
2 Mitocondria
3 Membrana postsináptica
4 Hendidura sináptica con lámina basal
5 Membrana presináptica
6 Vesícula presináptica
7 Célula de Schwann
8 Núcleo
9 Filamentos de actina y myosina
10 Sarcómera
11 Filamentos de actina
12 Vaina medular (vaina de mielina)
13 Fibra nerviosa
14 Membrana celular (sarcolema)
15 Túbulo transverso (túbulo T)
16 Tríada
17 Retículo sarcoplásmico
18 Lámina basal
19 Fibras reticulares
Español
6
Page 7

®
Français
Le modèle montre une partie de la fibre d’un muscle strié squelettique avec plaque terminale motrice ;
agrandissement environ 10.000 fois. La fibre musculaire représente l’élément de base du muscle strié squelettique. Il s’agit d’une cellule géante (1 à 10 cm de longueur et pouvant atteindre une épaisseur jusqu’à
0,1 mm) possédant de nombreux noyaux cellulaires. Son composant fonctionnel principal est constitué de
myofibrilles. Les myofibrilles se composent des myofilaments myosine et actine et sont entourées par le
réticulum sarcoplasmatique. La disposition définie des myofilaments détermine la striation caractéristique
du muscle squelettique. Les myofilaments épais, biréfringents, forment la bande A. Les myofilaments minces, uniréfringents et formant la bande I, sont traversés par une fine bande intermédiaire (bande Z). Le segment compris entre deux bandes Z est le sarcomère. Les tubules transversaux, tubes membranaires provenant de la membrane cellulaire, traversent le cytoplasme, formant entre autres une triade avec les
citernes terminales du réticulum sarcoplasmatique. Les noyaux cellulaires se trouvent à la périphérie de la
cellule. Les mitochondries, les „centrales de la cellule“, sont situées parallèlement aux myofibrilles. La plaque motrice terminale caractérise le domaine où une terminaison nerveuse motrice est en contact avec la
cellule du muscle squelettique. La terminaison nerveuse est recouverte par une cellule de Schwann. Entre
la cellule musculaire et la terminaison nerveuse se trouve la fente synaptique, remplie de lame basale
commune de la cellule musculaire et de la cellule de Schwann. La terminaison nerveuse comprend en plus
des mitochondries des vésicules présynapti ques, remplie s de médiate urs (la plupart du tem ps,
d’acétylcholine).
1 Myofibrille
2 Mitochondrie
3 Membrane postsynaptique
4 Fente synaptique avec lame basale
5 Membrane présynaptique
6 Vésicule présynaptique
7 Cellule de Schwann
8 Noyau
9 Filaments d’actine et myosine
10 Sarcomère
11 Filaments d’actine
12 Gaine de myéline
13 Fibre nerveuse
14 Membrane cellulaire (sarcolemme)
15 Tube membranaire transversal
16 Triade
17 Réticulum sarcoplasmatique
18 Lame basale
19 Fibres réticulaires
Fibre musculaire 3B MICROanatomy™
7
Page 8

18
17
15
16
15
14
1
2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
8
8
Page 9

1
18
19
7
9
Page 10

®
Português3B MICROanatomy™ Fibras musculares
O modelo mostra um trecho de da fibra de um músculo esquelético com placa motora final numa ampliação de aprox. 10 000 vezes. A fibra muscular representa o elemento básico do músculo estriado esquelético. Ela é uma célula gigante (1 a 10 cm de comprimento e até 0,1 m de espessura) com numerosos núcleos.
A sua parte constitutiva funcional principal é formada por miofibrilas. As miofibrilas são constituídas pelos
miofilamentos miosina e actina e estão rodeadas pelo retículo sarcoplasmático. Através do padrão regular
específico que os miofilamentos originam, surge o aspecto estriado característico dos músculos esqueléticos. Os miofilamentos grossos, que à vista aparecem duplos, formam a banda A. Contrariamente a isto,
estão os finos filamentos de actina, que são simples e formam a banda I, no meio da qual transcorre uma
faixa intermediária (as linhas Z). O trecho entre duas linhas Z chama-se sarcômero. Saindo da membrana
celular, tubos membranosos, os chamados túbulos transversais, atravessam o citoplasma e formam entre
outros a tríade muscular junto com a cisterna terminal do retículo sarcoplasmático. Os núcleos celulares se
encontram na periferia da célula. Paralelamente às miofibrilas também encontram-se as mitocôndrias, „as
centrais energéticas das células“.
A placa motora consiste na área onde uma terminação nervosa motora entra em contato com a célula do
músculo esquelético. A terminação nervosa é coberta por uma célula de Schwann. Entre a célula muscular
e a terminação nervosa encontra-se a fissura sináptica, a qual está preenchida com uma lâmina basal
comum às células musculares e às células de Schwann. A terminação nervosa contém, além de mitocôndrias, as vesículas pré-sinápticas, as quais estão cheias de neurotransmissores (na maioria dos casos acetilcolina).
1 Miofibrila
2 Mitocôndrio
3 Membrana pós-sináptica
4 Fissura sináptica com lâmina basal
5 Membrana pré-sináptica
6 Vesícula pré-sináptica
7 Célula de Schwann
8 Núcleo
9 Filamentos de actina e miosina
10 Sarcômero
11 Filamentos de actina
12 Estrato mielínico
13 Neurofibras
14 Sarcolema
15 Túbulo transversal
16 Tríade
17 Retículo sarcoplasmático
18 Lâmina basal
19 Fibras reticulares
10
10
Page 11

®
EnglishItaliano 3B MICROanatomy™ Fibra muscolare
Questo modello presenta la sezione di una fibra del muscolo striato con placca motrice ingrandita ca.
10 000 volte.
La fibra muscolare rappresenta l’elemento basilare del muscolo striato trasversalmente. Si tratta di una cellula di grandi dimensioni (lunga 1 – 10 cm e con spessore fino a 0,1 mm) con numerosi nuclei cellulari. Il
principale componente funzionale è formato da miofibrille. Le miofibrille sono costituite da miofilamenti,
miosina e actina e sono circondate da un reticolo sarcoplasmatico. La caratteristica striatura trasversale del
muscolo striato deriva dalla disposizione dei miofilamenti. I miofilamenti, più grossi e di aspetto birifrangente, formano la banda A, mentre i sottili actofilamenti sono semplicemente rifrangenti e formano la
banda I, con al centro una stria intermedia (stria Z). Il tratto tra due strie Z viene chiamato sarcomero. I
tubi della membrana, i cosiddetti tubuli trasversali, partono dalla membrana cellulare e attraversano il
citoplasma, che forma una triade assieme alle cisterne terminali del retiloco sarcoplasmatico. Alla periferia
cellulare ci sono i nuclei cellulari. Parallelamente alle miofibrille si trovano i mitocondri, le „centrali energetiche delle cellule“.
La placca motrice contraddistingue l’area nella quale una terminazione nervosa motoria sta a contatto con
la cellula muscolare striata. La terminazione nervosa viene coperta da una cellula di Schwann. Tra la cellula del muscolo e la terminazione nervosa c’è la fessura sinaptica, riempita dalla lamina basale comune
della cellula muscolare e della cellula di Schwann. La terminazione nervosa contiene, oltre ai mitocondri,
le vescicole presinaptiche, che sono piene di trasmettitori (per lo più acetilcolina).
1 Miofibrilla
2 Mitocondrio
3 Membrana postsinaptica
4 Fessura sinaptica con lamina basale
5 Membrana presinaptica
6 Vescicola presinaptica
7 Cellula di Schwann
8 Nucleo
9 Filamenti di actina e miosina
10 Sarcomero
11 Filamenti di actina
12 Guaina di mielina
13 Fibre nervose
14 Membrana cellulare (sarcolemma)
15 Tubulo trasversale della membrana
16 Triade
17 Reticolo sarcoplasmatico
18 Lamina basale
19 Fibre reticolari
11
Page 12

3B MICROanatomy™ 筋繊維モデル
このモデルは骨格筋繊維とその運動終板の断面を約10,000倍に拡大表示したものです。骨格筋(横紋筋)は
著しく長く(長さ1〜10cm,厚さ最大0.1mm),主な機能的要素は多核の細胞である筋繊維から構成されてい
ます。この筋繊維はミオシンフィラメントとアクチンフィラメントという大小のフィラメントの束が筋小胞体
に包まれた筋源繊維から形成されています。
骨格筋の特長である縦方向のすじはこのフィラメントの独特な配列方法より生じます。太いミオシンフィラメ
ントは暗く見えるA帯を形成します。反対に,細いアクチンフィラメントは明るく見えるI帯を形成します。A
帯とI帯の中央には暗く見えるZ線があります。2つの隣接するZ線の間にある部分を筋節といい,横紋筋の機
能的単位となります。横行小管は細胞膜が嵌入した管で細胞質内を通り,筋小胞体の終末槽と結合して三連構
造を形成します。核は細胞の周辺部に位置し,「細胞のエネルギー工場」としての役割を担うミトコンドリア
は筋源繊維と平行に位置します。
運動終板は運動神経の末端が骨格筋繊維に達する場所です。シュワン細胞はこの運動神経の末端を包んでいま
す。筋細胞と神経末端の間にはシナプス間隙があり,その筋細胞とシュワン細 胞の基底膜で満たされていま
す。神経の末端にはミトコンドリアと神経伝達物質(アセチルコリンなど)が含まれています。
1 筋原繊維
2 ミトコンドリア
3 シナプス後膜
4 シナプス間隙と基底膜
5 シナプス前膜
6 前シナプス小胞
7 シュワン細胞
8 核
9 ミオシンフィラメント,アクチンフィラメント
10 サルコメア
11 アクチンフィラメント
12 ミエリン鞘(髄鞘)
13 神経線維
14 細胞膜(筋線維鞘,筋鞘)
15 横行小管(T管)
16 三連構造(トライアッド−筋小胞体と横行小管の結合)
17 筋小胞体
18 基底膜
19 細網繊維
日本語
12
12
12
Page 13

®
DeutschРусский
3B MICROanatomy™
Мышечное волокно
Модель иллюстрирует срез волокна скелетной мышцы и его нейромышечную концевую пластинку
с увеличением приблизительно в 10000 раз. Мышечное волокно является основным элементом
диагональной поперечнополосатой скелетной мышцы. Это гигантская клетка (длиной 1 - 10
см и толщиной до 0,1 мм) с большим количеством ядер. Ее главный функциональный элемент
сформирован из миофибрилл. Миофибриллы состоят из миофиламентов миозина и актина и
окружены саркоплазматическим ретикулумом. Характерная продольная исчерченность скелетной
мышцы связана с определенным расположением миофиламентов. Толстые миозиновые филаменты,
которые обладают оптически двойным лучепреломлением, формируют диск А (поперечный).
Тонкие актиновые филаменты, напротив, обладают одинарным лучепреломлением и формируют
диск I (изотропный). Z-линия (промежуточная пластинка) проходит через его центр. Участок между
двумя Z-линиями называют саркомером. Начиная от мембраны клетки, цитоплазма протекает по
мембранозным трубочкам, называемым поперечными трубочками, которые вместе с терминальными
цистернами саркоплазматического ретикулума формируют триаду. Ядра расположены на периферии
клетки. Митохондрии, «энергетические станции клеток», располагаются параллельно миофибриллам.
Нейромышечная концевая пластинка – это название области, в которой окончание двигательного
нерва соприкасается с клеткой скелетной мышцы. Нервное окончание покрыто Шванновской клеткой.
Синаптическая щель, заполненная общей базальной пластинкой мышцы и Шванновской клеткой,
располагается между мышечной клеткой и нервным окончанием. Нервное окончание содержит
митохондрии, а также пресинаптические пузырьки, заполненные передающими веществами (обычно
ацетилхолином).
1 Миофибрилла
2 Митохондрия
3 Постсинаптическая мембрана
4 Синаптическая щель с базальной пластинкой
5 Пресинаптическая мембрана
6 Пресинаптический пузырек
7 Шванновская клетка
8 Ядро
9 Филамент миозина и актина
10 Саркомер
11 Филамент актина
12 Миелиновая оболочка
13 Нервные волокна
14 Клеточная мембрана (сарколемма)
15 Поперечная мембранная трубочка
16 Триада
17 Саркоплазматический ретикулум
18 Базальная пластинка
19 Ретикулярные волокна
13
Page 14

®
3B肌纤维显微解剖模型
中文
MICRO
该模型清晰地展示了骨骼肌纤维的横断面结构,以及神经肌肉接头的局部细节,放大率大约为1000
倍。 肌纤维为骨骼肌的基本组成单位。一个肌纤维为一个巨型细胞,具有很多细胞核(细胞的长
度大约为1-10 cm,厚度可以达到0.1 mm)。同样肌纤维也是形成肌原纤维的主要功能元件。肌原
纤维由肌球蛋白以及肌动蛋白,及其周围的肌浆网组成。骨骼肌的纵型纤维束是由肌纤维细胞按照
一种特殊的方式组合而成。粗肌丝由肌球蛋白组成,具有较强的双折光性,形成结构上的横带(A
带)。相反,细肌丝,由肌动蛋白组成,具有较弱的单折光性,形成结构上的I带,具有各向同性的
特征。z线,又叫中间带,位于肌单元的中间部。两条z线之间的部分又称肌小节。肌横管起源于肌
细胞膜,贯穿胞浆。肌横管与两端肌浆网的终池形成一个三联结构。肌细胞核位于肌细胞的周边。
线粒体为肌肉的供能结构,与肌纤维长轴相平行。神经肌肉接头位于运动神经纤维的末端与骨骼肌
细胞形成紧密的接触连接。神经末端由施万氏细胞包裹。突触间隙位于肌细胞与神经末端之间,其
内由肌肉的末端的膜性结构以及神经的施万氏细胞组成。神经末端有线粒体以及突触前小泡,突触
前小泡内存在神经递质组成(通常为乙酰胆碱)。
1 肌纤维
2 线粒体
3 突触后膜
4 突触间隙,前方的肌膜层
5 突触前膜
6 突触前小泡
7 施万氏细胞
8 细胞核
9 肌球蛋白丝以及肌动蛋白丝
10 肌小节
11 肌动蛋白丝
12 肌纤维鞘
13 神经纤维
14 细胞膜,浆膜
15 肌横管
16 肌三联结构
17 肌浆网
18 肌纤维末端
19 网状纤维
anatomy
™
Page 15

®
Türkçe
Model ortalama 10.000 kez büyütülmüş iskelet kas lifini ve nöromüsküler son katmanı örneklendirmektedir.
Kas lifi iskelet kasının çaprazlama çizgili halidir. Birçok nükleisi olan oldukça büyük bir hücredir (1-10 cm
uzunluğunda ve 0.1 mm kalınlığında) ana fonksiyonel elementi miyo fibrillerdir. Miyo fibriller miyo filament
miyosin ve aktinden yapılmış olup, skarkoplazmik retikulum ile çevrilmiştir. iskelet kasının boylamsal özelliği miyo
filamentlerin belli düzenlemelerinden meydana gelmektedir. Optik olarak kırılan kalın miyosin filamentler A (ters)
bandını oluşturur. Z hattı (orta çizgi) merkezden geçer. İki Z hattı arasındaki bölüm sarkomer olarak adlandırılır.
hücre zarından başlayarak, sitoplazma zarımsı tüplerden geçer. Ters tubuli olarak adlandırılır ve sarkoplazmik
retikulumun terminal keseleri ile birlikte triad oluşturur. Çekirdekler hücre periferinde bulunur. „Hücrenin güç santrali“ olan mitokondri miyo fibrillerle paralel hareket ederler. Nöromüsküler uç plakası motor sinir ucunun iskelet
kas hücresi ile temasta olduğu yerin adıdır. Sinir ucu schwann hücresi ile kaplıdır. Kasın ortak bazal laminası ve
schwann hücresi ile dolu olan sinaptik aralık, kas hücresi ve sinir ucu arasında yatmaktadır. Sinir ucu mitokondri
ve aktarıcı madde ile dolu olan presinaptik kesecikler içermektedir.
1 Miyo fibril
2 Mitokondrium
3 Postsinapitk membran
4 Bazal lamina ile sinaptik aralık
5 Presinaptik membran
6 Presinaptik kese
7 Shcwann hücresi
8 Çekirdek
9 Miyosin ve aktin filament
10 sarkomer
11 Aktin filament
12 Miyelin kılıfı
13 Nöro fiber
14 Hücre zarı (sarkolemma)
15 Ters membran tübü
16 Tirad
17 Sarkoplasmik retikulum
18 Bazal lamina
19 Retiküler tel
3B MICROanatomy™ Kas Lifi
15
Page 16

B60 (1000213)-11/13-250001969
3B Scientific
A wo r l d w i d e g ro u p o f c o mp a n i e s
3B Sci entific GmbH
Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany
Tel.: + 49-40-73966-0 • Fax: + 49-40-73966-100
www.3bscientific.com • 3b@3bscientific.com
© Copyright 2002 / 2013 for instruction manual and design of product:
3B Scientific GmbH, Germany
 Loading...
Loading...