Page 1

Default Login Details
User’s Guide
LTE3316-M604
4G LTE-A Indoor IAD
LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.1
User Name admin
Password 1234
Version 1.00 Edition 3, 06/2020
Copyright © 2020 Zyxel Communications Corporation
Page 2

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from what you see due to differences in release
versions or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure that the information
in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the managed device.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the LTE3316-M604
.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
2
Page 3
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
Note: Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may need to
configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The LTE3316-M604 in this user’s guide may be referred to as the “LTE” in this guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example, Configuration >
Network > WAN > Management WAN means you first click Configuration in the navigation panel, then
Network, then the WAN sub menu and finally the Management WAN tab to get to that screen.
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this user guide may use the following generic icons. The LTE icon is not an exact representation
of your device.
LTE Generic Router Switch
Server Firewall Printer
Antenna Tower
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
User’s Guide ......................................................................................................................................12
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... 13
Web Configurator ................................................................................................................................. 20
Setup Wizard ......................................................................................................................................... 27
Tutorials .................................................................................................................................................. 32
Technical Reference ........................................................................................................................39
Status ...................................................................................................................................................... 40
Monitor ................................................................................................................................................... 43
WAN ....................................................................................................................................................... 51
Wireless LAN .......................................................................................................................................... 64
LAN ......................................................................................................................................................... 86
DHCP Server .......................................................................................................................................... 88
NAT ......................................................................................................................................................... 93
DDNS .................................................................................................................................................... 102
Routing ................................................................................................................................................. 104
Interface Group .................................................................................................................................. 107
Firewall ................................................................................................................................................. 109
Content Filtering ................................................................................................................................. 114
IPv6 Firewall ......................................................................................................................................... 117
VPN ....................................................................................................................................................... 119
SMS ....................................................................................................................................................... 129
Voice Call ............................................................................................................................................ 132
MGMT Interface .................................................................................................................................. 135
Bandwidth Management .................................................................................................................. 138
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP) ......................................................................................................... 143
TR-069 ................................................................................................................................................... 158
Maintenance ...................................................................................................................................... 160
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................. 168
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Document Conventions ... .... .... ............................................... ............................................................3
Contents Overview .............................................................................................................................4
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................................5
Part I: User’s Guide.......................................................................................... 12
Chapter 1
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................13
1.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 13
1.2 Applications .................................................................................................................................... 13
1.2.1 Wireless WAN (3G/4G/LTE) Connection ............................................................................. 14
1.2.2 WAN Priority ........................................................................................................................... 14
1.2.3 Wireless LAN (WiFi) Connection ...........................................................................................14
1.3 Ways to Manage the LTE ............................................................................................................... 14
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the LTE .............................................................................................. 14
1.5 Hardware Connections ................................................................................................................. 15
1.5.1 LEDs ......................................................................................................................................... 15
1.5.2 Rear Panel .............................................................................................................................. 16
1.6 Wall Mounting ................................................................................................................................. 18
Chapter 2
Web Configurator...............................................................................................................................20
2.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 20
2.2 Login Accounts ............................................................................................................................... 20
2.3 Accessing the Web Configurator ................................................................................................. 20
2.4 Navigating the Web Configurator ............................................................................................... 22
2.4.1 Title Bar ................................................................................................................................... 23
2.4.2 Navigation Panel .................................................................................................................. 23
2.4.3 Dashboard ............................................................................................................................. 24
Chapter 3
Setup Wizard.......................................................................................................................................27
3.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 27
3.2 Accessing the Wizard ..................................................................................................................... 27
3.3 Wizard Setup ................................................................................................................................... 28
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Chapter 4
Tutorials...............................................................................................................................................32
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 32
4.2 Connecting to the LTE Using WPS ................................................................................................. 32
4.2.1 Push Button Configuration (PBC) ........................................................................................ 32
4.2.2 PIN Configuration .................................................................................................................. 33
4.3 Connect to LTE Wireless Network Without WPS ........................................................................... 34
4.4 Using Multiple SSIDs on the LTE ...................................................................................................... 36
4.4.1 Configuring Security Settings of Multiple SSIDs .................................................................. 36
Part II: Technical Reference........................................................................... 39
Chapter 5
Status...................................................................................................................................................40
5.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 40
5.2 Status ................................................................................................................................................ 40
Chapter 6
Monitor................................................................................................................................................43
6.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 43
6.2 What You Can Do .......................................................................................................................... 43
6.3 Log .................................................................................................................................................... 43
6.3.1 View Log ................................................................................................................................ 43
6.4 DHCP Table ..................................................................................................................................... 45
6.5 ARP Table ........................................................................................................................................ 45
6.6 Packet Statistics .............................................................................................................................. 46
6.7 WLAN Station Status ....................................................................................................................... 47
6.8 LTE Modem Status ........................................................................................................................... 48
Chapter 7
WAN ....................................................................................................................................................51
7.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 51
7.2 What You Can Do .......................................................................................................................... 51
7.3 What You Need To Know .............................................................................................................. 52
7.4 WAN Management ........................................................................................................................ 54
7.4.1 WAN Management Edit 3G/4G .......................................................................................... 54
7.4.2 WAN Management Edit Ethernet ....................................................................................... 57
7.5 Network Scan .................................................................................................................................. 60
7.6 IPv6 ................................................................................................................................................... 61
7.7 PIN Management ........................................................................................................................... 63
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
6
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 8
Wireless LAN .......................................................................................................................................64
8.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 64
8.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................. 64
8.1.2 What You Should Know ........................................................................................................ 65
8.2 General Wireless LAN Settings ....................................................................................................... 67
8.3 Wireless Security .............................................................................................................................. 70
8.3.1 No Security ............................................................................................................................. 70
8.3.2 WPA2-PSK ............................................................................................................................... 71
8.3.3 WPA/WPA2 ............................................................................................................................ 73
8.4 More AP ........................................................................................................................................... 75
8.4.1 More AP Edit .......................................................................................................................... 76
8.5 MAC Filter ........................................................................................................................................ 77
8.6 Wireless LAN Advanced Settings .................................................................................................. 79
8.7 Quality of Service (QoS) ................................................................................................................ 80
8.8 WPS ................................................................................................................................................... 81
8.9 WPS Station ...................................................................................................................................... 82
8.10 Scheduling ..................................................................................................................................... 83
8.11 WDS ................................................................................................................................................ 84
Chapter 9
LAN......................................................................................................................................................86
9.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 86
9.2 What You Can Do .......................................................................................................................... 86
9.3 What You Need To Know .............................................................................................................. 86
9.4 LAN IP ............................................................................................................................................... 87
Chapter 10
DHCP Server........................................................................................................................................88
10.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 88
10.1.1 What You Can Do ............................................................................................................... 88
10.1.2 What You Need To Know ...................................................................................................88
10.2 DHCP Server General Settings .................................................................................................... 88
10.3 Advanced DHCP Server Setting ................................................................................................. 90
10.4 DHCP Client List ............................................................................................................................. 92
Chapter 11
NAT......................................................................................................................................................93
11.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 93
11.1.1 What You Can Do ............................................................................................................... 93
11.2 General Settings ........................................................................................................................... 94
11.3 Port Forwarding ............................................................................................................................. 94
11.3.1 Edit Port Forwarding ............................................................................................................ 96
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Table of Contents
11.4 Port Trigger ..................................................................................................................................... 98
11.5 ALG ................................................................................................................................................. 99
11.6 Technical Reference .................................................................................................................... 99
11.6.1 NAT Port Forwarding: Services and Port Numbers ........................................................... 99
11.6.2 NAT Port Forwarding Example ......................................................................................... 100
11.6.3 Trigger Port Forwarding .................................................................................................... 100
11.6.4 Trigger Port Forwarding Example .................................................................................... 101
11.6.5 Two Points To Remember About Trigger Ports ............................................................... 101
Chapter 12
DDNS .................................................................................................................................................102
12.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 102
12.2 General Settings ......................................................................................................................... 102
Chapter 13
Routing..............................................................................................................................................104
13.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 104
13.2 Static Route ................................................................................................................................. 104
13.2.1 Add/Edit Static Route ....................................................................................................... 105
13.3 Dynamic Routing ........................................................................................................................ 106
Chapter 14
Interface Group ...............................................................................................................................107
14.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 107
14.2 Interface Group .......................................................................................................................... 107
14.2.1 Add Interface Group ........................................................................................................ 108
Chapter 15
Firewall..............................................................................................................................................109
15.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 109
15.1.1 What You Can Do ............................................................................................................. 109
15.1.2 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 109
15.2 General Settings ......................................................................................................................... 110
15.3 Firewall Services .......................................................................................................................... 111
Chapter 16
Content Filtering...............................................................................................................................114
16.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 114
16.2 Content Filter ............................................................................................................................... 114
Chapter 17
IPv6 Firewall......................................................................................................................................117
17.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 117
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
8
Page 9

Table of Contents
17.2 IPv6 Firewall ................................................................................................................................. 117
Chapter 18
VPN....................................................................................................................................................119
18.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 119
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 119
18.2 What You Need to Know ........................................................................................................... 119
18.3 L2TP Server ................................................................................................................................... 120
18.4 L2TP Client ................................................................................................................................... 121
18.4.1 Add L2TP Client ................................................................................................................. 122
18.5 GRE ............................................................................................................................................... 124
18.5.1 Add GRE ............................................................................................................................. 126
18.6 VPN Passthrough ......................................................................................................................... 127
Chapter 19
SMS....................................................................................................................................................129
19.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 129
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 129
19.2 SMS Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 129
Chapter 20
Voice Call........... .... .... ... ................................................ ...................................................................132
20.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 132
20.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 132
20.2 General Settings ......................................................................................................................... 132
20.3 Call Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 133
Chapter 21
MGMT Interface ...............................................................................................................................135
21.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 135
21.2 What You Can Do ...................................................................................................................... 135
21.3 What You Need To Know .......................................................................................................... 135
21.3.1 System Timeout .................................................................................................................. 135
21.4 Local MGMT ................................................................................................................................ 135
21.5 Remote MGMT ............................................................................................................................ 137
Chapter 22
Bandwidth Management................................................................................................................138
22.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 138
22.2 What You Can Do ...................................................................................................................... 138
22.3 What You Need To Know .......................................................................................................... 139
22.4 General Settings ......................................................................................................................... 139
22.4.1 Add Bandwidth Management Rule ............................................................................... 140
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Table of Contents
Chapter 23
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)............................................................................ .... ......................143
23.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 143
23.2 What You Need to Know ........................................................................................................... 143
23.2.1 NAT Traversal ..................................................................................................................... 143
23.2.2 Cautions With UPnP ........................................................................................................... 143
23.3 UPnP Settings ............................................................................................................................... 144
23.4 Turn on UPnP in Windows 7 Example ........................................................................................ 144
23.4.1 Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device .................................................... 146
23.5 Turn on UPnP in Windows 10 Example ...................................................................................... 148
23.5.1 Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device .................................................... 150
23.6 Web Configurator Easy Access in Windows 7 ......................................................................... 153
23.7 Web Configurator Easy Access in Windows 10 ....................................................................... 155
Chapter 24
TR-069................................................................................................................................................158
24.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 158
24.2 TR-069 Settings ............................................................................................................................. 158
Chapter 25
Maintenance....................................................................................................................................160
25.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 160
25.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 160
25.2 General Settings ......................................................................................................................... 160
25.3 User Account .............................................................................................................................. 161
25.3.1 Modify a User Account ..................................................................................................... 162
25.4 Time Settings ................................................................................................................................ 162
25.5 Firmware Upgrade ...................................................................................................................... 164
25.6 Module Upgrade ........................................................................................................................ 165
25.7 Configuration Backup/Restore ................................................................................................. 166
25.8 System Reboot ............................................................................................................................ 167
Chapter 26
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................168
26.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 168
26.2 Power, and Hardware Installation ............................................................................................ 168
26.3 LTE Access and Login ................................................................................................................. 168
26.4 Internet Access ........................................................................................................................... 169
26.5 Wireless Connections ................................................................................................................. 170
26.6 Getting More Troubleshooting Help .........................................................................................171
Appendix A Customer Support ..................................................................................................... 172
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
10
Page 11

Table of Contents
Appendix B Common Services...................................................................................................... 178
Appendix C Legal Information ...................................................................................................... 181
Index.................................................................................................................................................188
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
11
Page 12

PART I
User’s Guide
12
Page 13
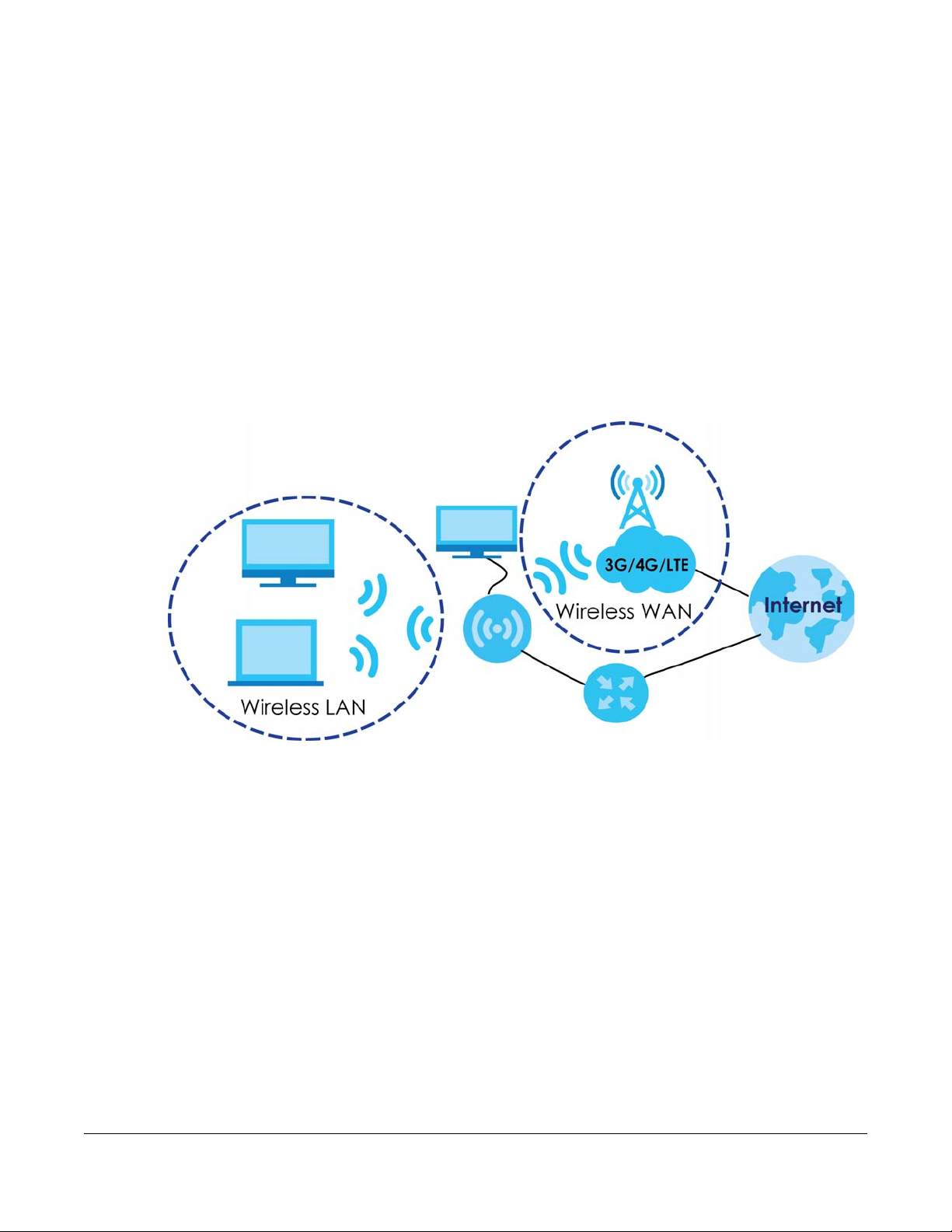
1.1 Overview
Ethernet WAN
LTE
This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the LTE.
The LTE is a wireless router, which can connect to a mobile network and the Internet through a wireless
WAN connection and provide easy network access to users without additional wiring.You can set up a
2.4G of IEEE 802.11b/g/n and 5G of 201.11a/n/ac wireless network.
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
A range of services such as a firewall are also available for secure Internet computing.
Your LTE is easy to install, configure and use. The embedded Web-based configurator enables simple,
straightforward management and maintenance. See the Quick Start Guide for how to make hardware
connections.
The LTE has two internal antennas for WAN connection. Additionally, you can install two external
antennas to improve your wireless WAN signal strength. Note that external antennas are not provided.
They are the default antennas for signal transmission when the LTE is starting up.
1.2 Applications
Your can have the following networks with the LTE:
• Wired LAN. You can connect network devices via the Ethernet ports of the LTE so that they can
communicate with each other and access the Internet.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Chapter 1 Introduction
• Wireless LAN. Wireless clients can wirelessly connect to the LTE to access network resources. You can
use WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) to create an instant network connection with another WPS
compatible device.
1.2.1 Wireless WAN (3G/4G/LTE) Connection
The LTE comes with a built-in 3G/4G module for 3G/4G connections. To set up a 3G/4G connection
using the built-in 3G/4G module, just insert a 3G/4G SIM card into the SIM card slot at the back of the
LTE.
Note: You must insert the 3G/4G SIM card into the card slot before turning on the LTE.
1.2.2 WAN Priority
The WAN connection priority is as follows:
• 3G/4G/Ethernet WAN
If you have a 3G/4G connection and Ethernet WAN connection at the same time, go to the Status
screen to see which connection is up. Please see Section 7.4 on page 54 for more information about
WAN management.
1.2.3 Wireless LAN (WiFi) Connection
The LTE is a wireless Access Point (AP) for wireless clients, such as notebook computers or tablets and
iPads. It allows them to connect to the Internet without having to rely on inconvenient Ethernet cables.
By default, the wireless LAN (WLAN) is enabled on the LTE.
1.3 Ways to Manage the LTE
Use any of the following methods to manage the LTE.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the LTE using a (supported)
web browser.
• WPS (WiFi Protected Setup). You can use the WPS section of the Web Configurator to set up a wireless
network with your LTE Device.
• TR-069. This is an auto-configuration server used to remotely configure your device.
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the LTE
Do the following things regularly to make the LTE more secure and to manage it more effectively.
• Change the password often. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different
types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
14
Page 15
Chapter 1 Introduction
Ethernet
Signal
Strength
WPS
Voice
Power Internet
WiFi/
LTE/3G
LTE/3G/
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier working
configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you forget your
password, you will have to reset the LTE to its factory default settings. If you backed up an earlier
configuration file, you won’t have to totally re-configure the LTE; you can simply restore your last
configuration.
1.5 Hardware Connections
See your Quick Start Guide for information on making hardware connections. You need to insert a SIM
card to the SIM card slot at the side of the LTE before you can use it.
1.5.1 LEDs
The following graphics display the front panel of the LTE. You can check the LED lights to see the 3G/4G/
LTE connection status, signal strength, and the wireless connection status.
Figure 1 LTE Front Panel
Figure 2 LEDs
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
15
Page 16
Chapter 1 Introduction
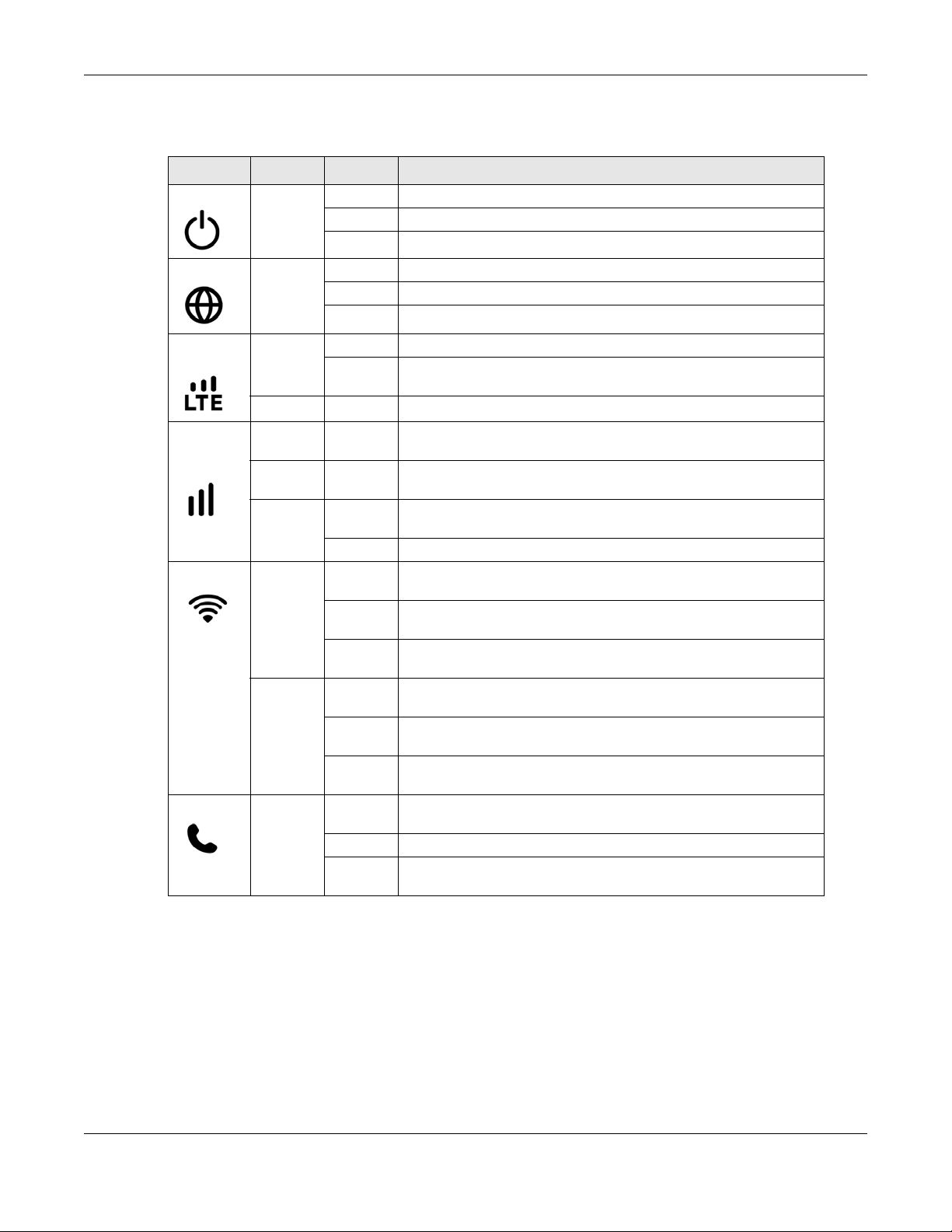
The following table describes the LED lights.
Table 1 Front Panel LEDs
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Power White On The LTE is receiving power and functioning properly.
Blinking The LTE is in the process of starting up or default restoring.
Off The LTE is not receiving power.
Internet White On The LTE’s WAN connection is ready, but there is no traffic.
Blinking The LTE is transmitting and receiving data through the WAN.
Off The WAN connection is not ready, or has failed.
LTE/3G/
Ethernet
LTE/3G
Signal
Strength
WiFi/WPS White On The LTE is ready and the 5G wireless LAN is on, but is not sending/
Voice White On A telephone connected to the PHONE port has its receiver on the
White On The LTE is successfully connected to a 4G or LTE network.
Blinking
(slow)
Green On The LTE is successfully connected to an Ethernet WAN network.
Green On A valid SIM card is inserted and the wireless WAN interface is
Amber On A valid SIM card is inserted and the wireless WAN interface is
Red On A valid SIM card is inserted and the wireless WAN interface is
Blinking A valid SIM card is inserted, but no signal is detected.
Blinking
(fast)
Blinking
(slow)
Green On The LTE is ready and the 2.4G wireless LAN is on, but is not sending/
Blinking
(fast)
Blinking
(slow)
Blinking The LTE is receiving an incoming call.
Off A telephone connected to the PHONE port has its receiver off the
The LTE is successfully connected to a 3G network.
enabled, this indicates the signal strength is good.
enabled, this indicates the signal strength is fair.
enabled, this indicates the signal strength is poor.
receiving data through the wireless LAN.
The LTE is sending/receiving data through the 5G wireless LAN.
The LTE is connecting to a 5G WiFi-Connection via WPS.
receiving data through the wireless LAN.
The LTE is sending/receiving data through the 2.4G wireless LAN.
The LTE is connecting to a 2.4G WiFi-Connection via WPS.
hook.
hook.
1.5.2 Rear Panel
To turn on the device, press the power button.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
16
Page 17
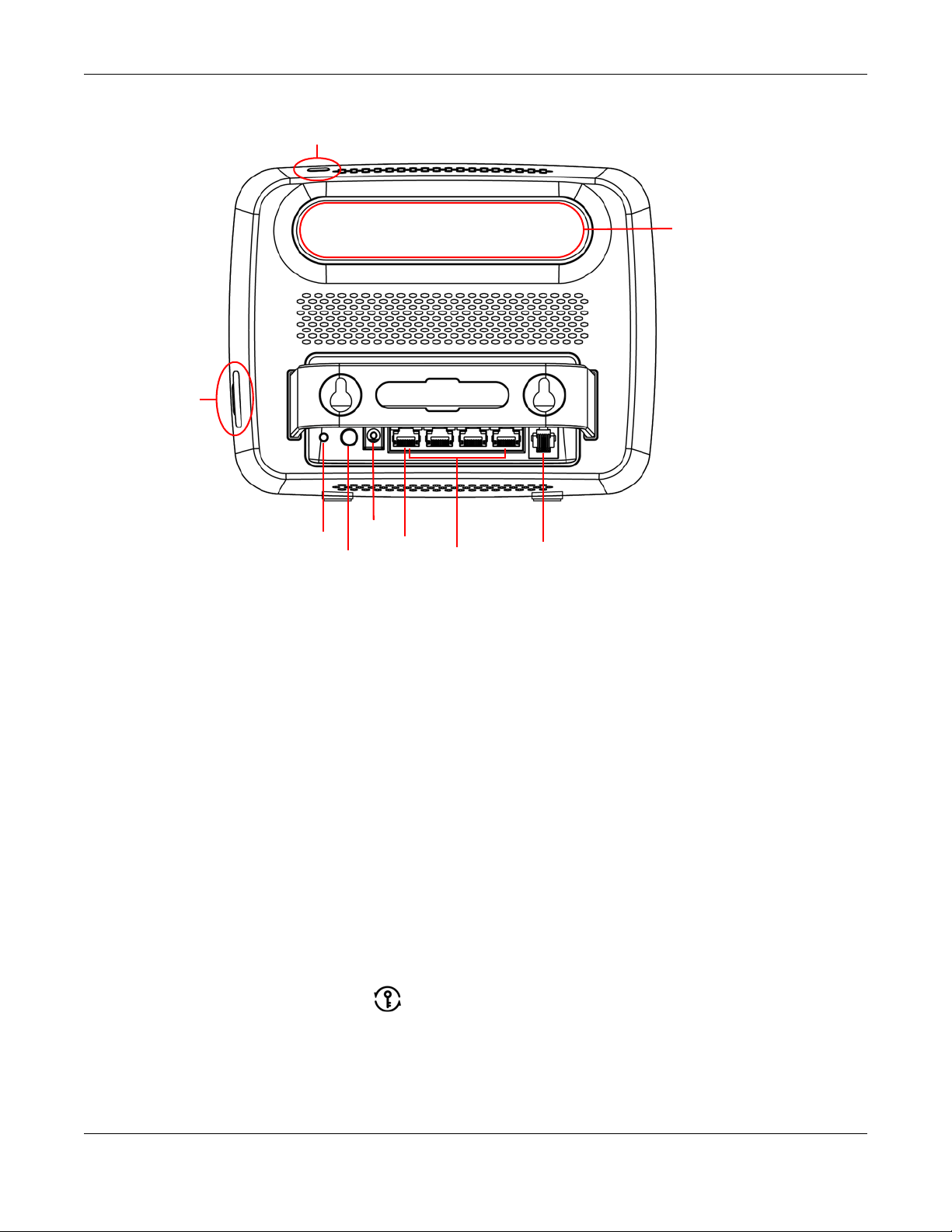
Figure 3 LTE Power Button
WPS Button
SIM
Card
Slot
Reset
On/
Power
Input
WAN/
LAN
LAN
Phone
Off
External
Antenna Ports
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.5.2.1 SIM Card Slot
The LTE comes with a built-in 3G/4G/LTE module for mobile connections. To set up a mobile connection
using the built-in 3G/4G/LTE module, just insert a SIM card into the SIM card slot at the back of the LTE.
Note: You must insert the SIM card into the card slot before turning on the LTE.
1.5.2.2 The WPS Button
Your LTE supports WiFi Protected Setup (WPS), which is an easy way to set up a secure wireless network.
WPS is an industry standard specification, defined by the WiFi Alliance.
WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to configure
security settings manually. Each WPS connection works between two devices. Both devices must
support WPS (check each device’s documentation to make sure).
Depending on the devices you have, you can either press a button (on the device itself, or in its
configuration utility) or enter a PIN (a unique Personal Identification Number that allows one device to
authenticate the other) in each of the two devices. When WPS is activated on a device, it has two
minutes to find another device that also has WPS activated. Then, the two devices connect and set up
a secure network by themselves.
You can use the WPS button ( ) on the side panel of the LTE to activate WPS in order to quickly set
up a wireless network with strong security.
1 Make sure the power LED is on (not blinking).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
17
Page 18

2 Press the WPS button for more than five seconds and release it. Press the WPS button on another WPS
enabled device within range of the LTE.
Note: You must activate WPS in the LTE and in another wireless device within two minutes of
each other.
Note: The LTE’s WPS is disabled by default for security reasons. To use this feature you will need
to enable WPS, for more information see Section 4.2 on page 32.
1.5.2.3 The Reset Button
If you forget your password or IP address, or you cannot access the Web Configurator, you will need to
use the physical Reset button to reload the factory-default configuration file. This means that you will
lose all configurations that you had previously saved, the password will be reset to 1234 and the IP
address will be reset to 192.168.1.1.
Reseting the LTE to Factory-Default Settings
1 Press the Reset button on the rear panel for more than five seconds to set the LTE back to its factory
default configurations.
Chapter 1 Introduction
2 Wait until the Power LED turns on steady white. his means the LTE is ready for use.
Restarting or Rebooting the LTE
1 Press the Reset button on the rear panel for two seconds to restart/reboot the LTE.
2 Wait until the Power LED turns on steady white. This means the LTE is ready for use.
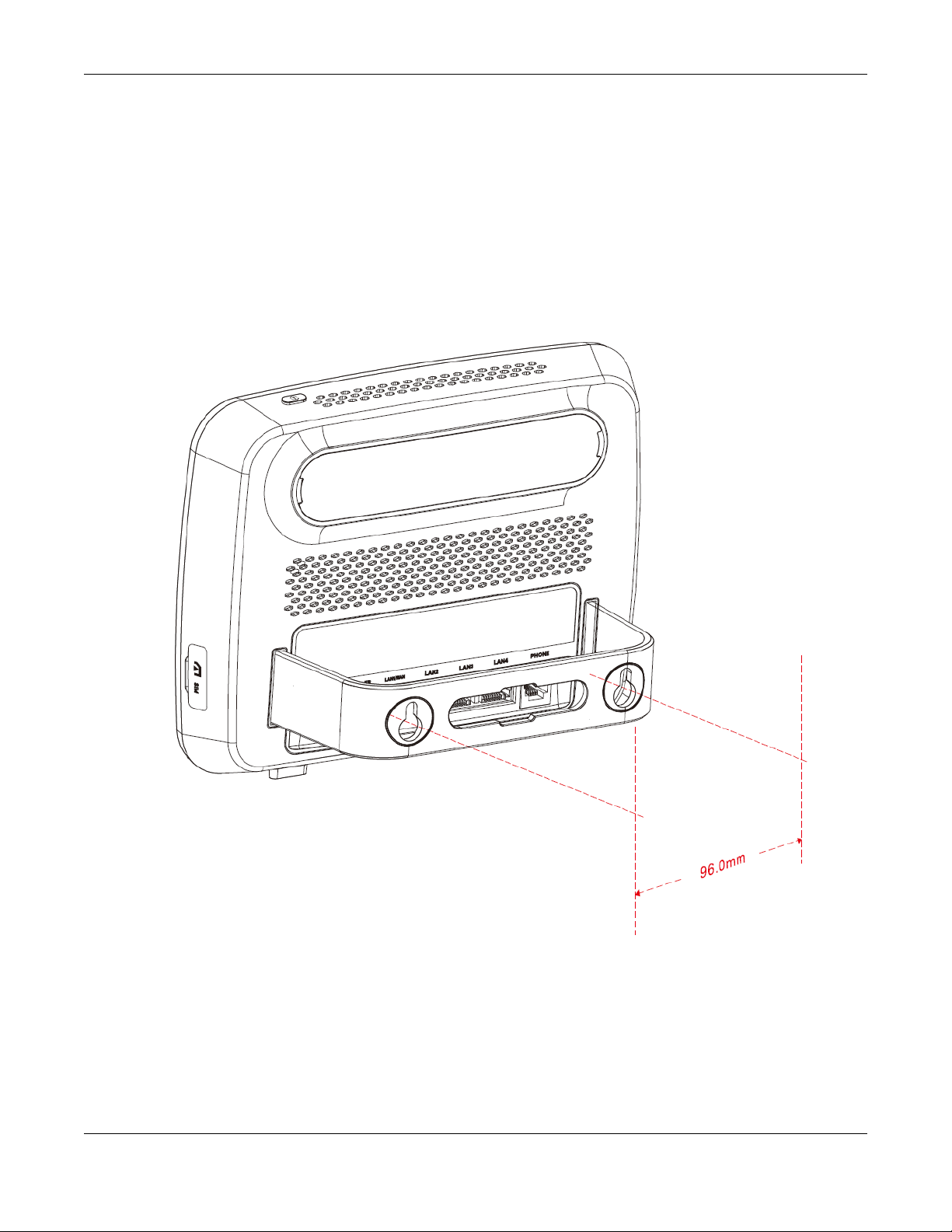
1.6 Wall Mounting
You may need screw anchors if mounting on a concrete or brick wall.
Table 2 Wall Mounting Information
Distance between holes 100 mm
M4 Screws Two
Screw anchors (optional) Two
1 Select a position free of obstructions on a wall strong enough to hold the weight of the device.
2 Mark two holes on the wall at the appropriate distance apart for the screws.
Be careful to avoid damaging pipes or cables located inside the wall
when drilling holes for the screws.
Do not wall mount the LTE over a height of 2 m.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
18
Page 19
Chapter 1 Introduction
3 If using screw anchors, drill two holes for the screw anchors into the wall. Push the anchors into the full
depth of the holes, then insert the screws into the anchors. Do not insert the screws all the way in - leave
a small gap of about 0.5 cm.
If not using screw anchors, use a screwdriver to insert the screws into the wall. Do not insert the screws all
the way in - leave a gap of about 0.5 cm.
4 Make sure the screws are fastened well enough to hold the weight of the LTE with the connection
cables.
5 Align the holes on the back of the LTE with the screws on the wall. Hang the LTE on the screws.
Figure 4 Wall Mounting Example
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
19
Page 20

2.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to access the LTE Web Configurator and provides an overview of its screens.
The Web Configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy system setup and
management via Internet browser. Use a browser that supports HTML5, such Internet Explorer 11, Mozilla
Firefox, or Google Chrome. The recommended screen resolution is 1024 by 768 pixels.
In order to use the Web Configurator, you must:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device.
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
CHAPTER 2
Web Configurator
Refer to the Troubleshooting chapter (Chapter 26 on page 168) to see how to make sure these functions
are allowed in Internet Explorer.
2.2 Login Accounts
There is one system account that you can use to log in to the LTE: “admin”. The admin account allows
you full access to all system configurations. The default admin user name is “admin” and password is
“1234”.
2.3 Accessing the Web Configurator
1 Make sure your LTE hardware is properly connected and prepare your computer or computer network
to connect to the LTE (refer to the Quick Start Guide).
2 Launch your web browser.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
20
Page 21
Chapter 2 Web Configurator
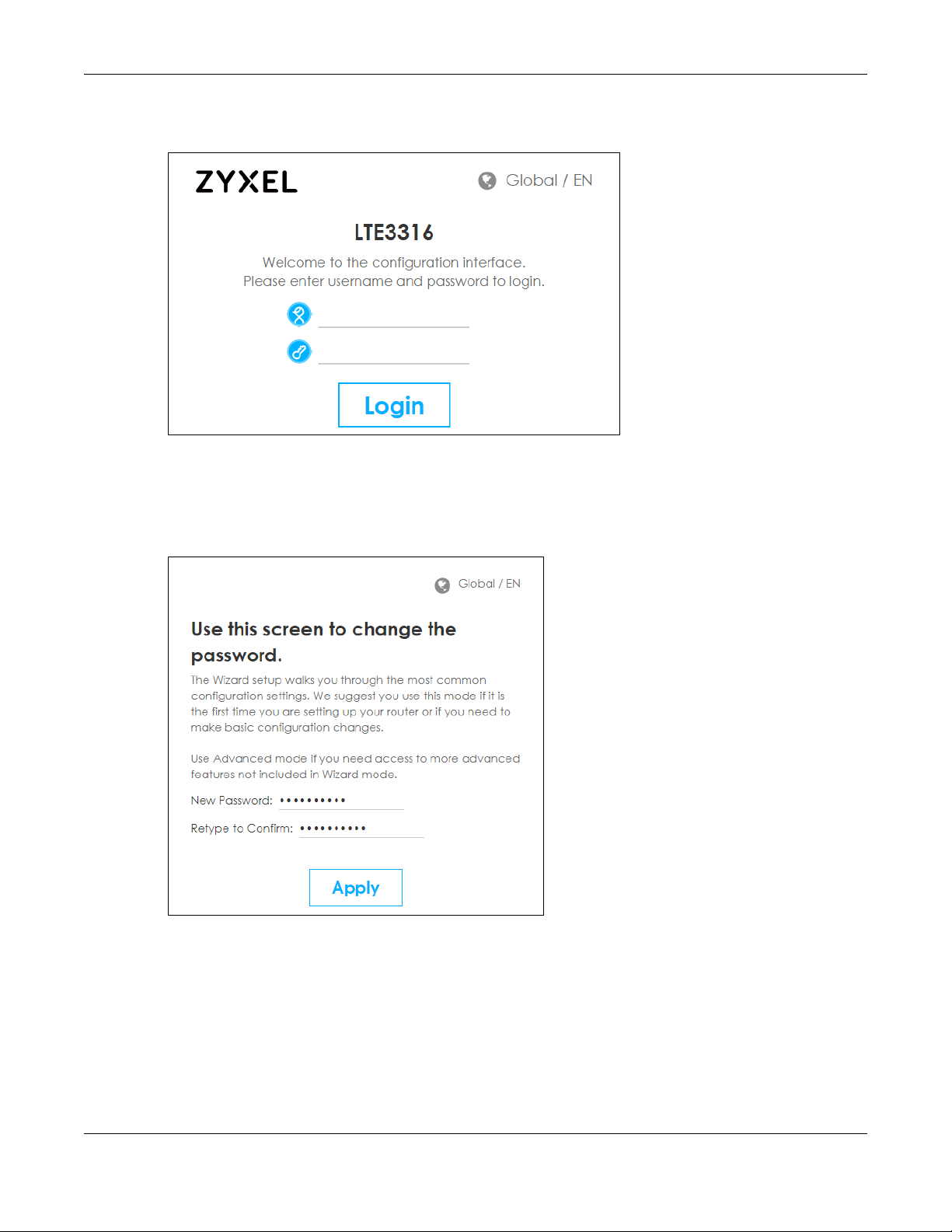
3 Enter "http://192.168.1.1" as the website address. The Login screen appears.
Your computer must be in the same subnet in order to access this website address.
4 Enter the User Name (default: “admin”) and Password (default: “1234”). See Section 2.2 on page 20 for
more information about login accounts. Click Login.
5 The following screen displays if you have not yet changed your password. Enter a new password, retype
it to confirm and click OK.
6 The Home screen appears.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
21
Page 22
Chapter 2 Web Configurator
A
B
C
D
2.4 Navigating the Web Configurator
The following summarizes how to navigate the Web Configurator from the Home screen.
Figure 5 The Web Configurator’s Main Screen
The Web Configurator’s main screen is divided into these parts:
• A - Title Bar
• B - Navigation Panel: Main Menus
• C - Navigation Panel: Sub-Menus
• D - Main Window
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
22
Page 23
2.4.1 Title Bar
The title bar provides some useful links that always appear over the screens below, regardless of how
deep into the Web Configurator you navigate.
Figure 6 Title Bar
The icons provide the following functions.
Table 3 Title Bar: Web Configurator Icons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SIM This shows whether a SIM card is inserted in the LTE.
WiFi This shows whether the LTE’s WiFi LAN network is enabled.
Chapter 2 Web Configurator
The icon shows if there is no SIM card inserted.
The following icon displays when the WiFi LAN network is disabled.
WAN Connection This displays the type of mobile data connection (4G+, 4G, 3G) the LTE has to the ISP.
Signal Strength This shows the current signal strength to the mobile network.
The icon shows no bars if the mobile data connection is not up.
Setup Wizard Click this icon to open the Setup Wizard for the LTE.
Help Click this to open a screen where you can click a link to visit the Zyxel website to see
detailed product information.
Logout Click this icon to log out of the Web Configurator.
Language Choose your language from the drop-down list on the upper right corner of the title bar.
2.4.2 Navigation Panel
Use the menu items on the navigation panel to open screens to configure LTE features. The following
sections introduce the LTE’s navigation panel menus and their screens.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
23
Page 24
Figure 7 Navigation Panel
2.4.3 Dashboard
Use the menu items in the navigation panel on the right to open screens to configure the Zyxel Device’s
features.
Figure 8 Navigation Panel
Chapter 2 Web Configurator
The following table describes the navigation panel menus and sub-menus.
Table 4 Navigation Panel
MENU SUB-MENU DESCRIPTION
Status
This screen shows the LTE’s general device, system and interface status information. Use this screen to access the
summary statistics tables.
Monitor
Log View Log Use this screen to see the logs for the categories that you selected in the
Log Settings screen.
Log Setting Use this screen to configure to where and when the LTE is to send the
logs and which logs and/or immediate alerts it is to send.
DHCP Table Use this screen to view current DHCP client information.
ARP Table Use this screen to view the ARP table. It displays the IP and MAC address
Packet Statistics Use this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
WLAN Station
Status
LTE Modem Status Use this screen to view the detailed information about the LTE module,
Configuration
Network
of each DHCP connection
Use this screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated
to the LTE’s 2.4G and 5G wireless LAN.
cellular interface, and SIM card. You can also view the LTE connection
status.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
24
Page 25
Chapter 2 Web Configurator
Table 4 Navigation Panel (continued)
MENU SUB-MENU DESCRIPTION
WAN WAN Management This screen allows you to configure ISP parameters, WAN IP address
assignment, and DNS servers.
Network Scan Use this screen to specify the type of the mobile network to which the LTE
connected and how you want the LTE to connect to an available
mobile network.
IPv6 Use this screen to configure the LTE’s IPv6 settings.
PIN Management Use this screen to enable PIN code authentication and enter the PIN
code.
Wireless LAN General Use this screen to enable the wireless LAN and configure wireless LAN
and wireless security settings.
More AP Use this screen to configure multiple BSSs on the LTE.
MAC Filter Use the MAC filter screen to allow or deny wireless stations based on their
Advanced This screen allows you to configure advanced wireless LAN settings.
QoS Use this screen to configure Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service (WMM
WPS Use this screen to configure the WPS settings.
WPS Station Use this screen to add a wireless station using WPS.
Scheduling Use this screen to schedule the times the Wireless LAN is enabled.
WDS Use this screen to enable and configure the WDS settings.
LAN IP Use this screen to configure LAN IP address and subnet mask.
DHCP Server General Use this screen to enable the LTE’s DHCP server.
Advanced Use this screen to assign IP addresses to specific individual computers
Client List Use this screen to view information related to your DHCP status.
NAT General Use this screen to enable NAT.
Port Forwarding Use this screen to configure servers behind the LTE and forward incoming
Port Trigger Use this screen to change your LTE’s port triggering settings.
ALG Use this screen to enable or disable SIP (VoIP) ALG (Application Layer
DMZ Use this screen to set the IP address of your network DMZ (if you have
Dynamic DNS Dynamic DNS Use this screen to set up dynamic DNS.
Routing Static Route Use this screen to configure IP static routes.
Dynamic Routing Use this screen to enable and configure RIP on the LTE.
Interface Group Interface Group Use this screen to create a new interface group.
Security
Firewall General Use this screen to activate/deactivate the firewall.
Services This screen shows a summary of the firewall rules, and allows you to edit/
Content Filter Content Filter Use this screen to restrict web features and designate a trusted
MAC addresses from connecting to the LTE.
QoS). WMM QoS allows you to prioritize wireless traffic according to the
delivery requirements of individual services.
based on their MAC addresses and to have DNS servers assigned by the
DHCP server.
service requests to the servers on your local network.
Gateway) in the LTE.
one) for the LTE.
add a firewall rule.
computer. You can also block certain web sites containing certain
keywords in the URL.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 2 Web Configurator
Table 4 Navigation Panel (continued)
MENU SUB-MENU DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Firewall Services Use this screen to configure IPv6 firewall rules.
Application
VPN L2TP Server Use this screen to configure the LTE L2TP server settings.
L2TP Client Use this screen to configure the L2TP VPN client settings.
GRE Use this screen to configure the GRE VPN client mode tunnel settings.
VPN Passthrough Use this screen to allow VPN traffic to pass through the LTE.
SMS SMS Use this screen to view the SIM card’s SMS inbox and send short
messages.
Voice Call General Use this screen to enable voice service in the LTE.
Call Conf. Use this screen to configure enable call forwarding and configure call
forwarding rules in the LTE.
Management
MGMT Interface Local MGMT Use this screen to specify from which zones you can access the LTE using
Remote MGMT Use this screen to enable specific traffic directions for network services.
Bandwidth MGMT General Use this screen to enable bandwidth management, set the upstream
UPnP UPnP Use this screen to enable UPnP on the LTE.
TR069 TR069 Use this screen to configure your LTE to be managed by an ACS.
Maintenance
General General Use this screen to view and change administrative settings such as
Account User Account Use this screen to change the user name and password of your LTE.
Time Time Setting
Firmware
Upgrade
Module Upgrade Module Upgrade
Backup / Restore Backup / Restore Use this screen to backup and restore the configuration or reset the
Reboot System Reboot
Firmware Upgrade Use this screen to upload firmware to your LTE.
HTTP, HTTPS, SSH or Telnet.
bandwidth and edit a bandwidth management rule.
system and domain names.
Use this screen to change your LTE’s time and date.
Use this screen to upload firmware for the built-in LTE module.
factory defaults to your LTE.
This screen allows you to reboot the LTE without turning the power off.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
26
Page 27
3.1 Overview
This chapter provides information on the Wizard setup screens in the Web Configurator.
The Web Configurator’s Wizard helps you configure your device to access the Internet and change the
wireless LAN settings. Refer to your ISP for your Internet account information. Leave a field blank if you
don’t have that information.
3.2 Accessing the Wizard
1 Launch your web browser and enter "http://192.168.1.1" as the website address. Type "admin" (default)
as the user name, "1234" (default) as the password and click Login.
CHAPTER 3
Setup Wizard
2 Click the Wizard icon in the right corner of the Web Configurator’s title bar to open the Wizard screen.
Figure 9 Wizard Icon
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
27
Page 28
3.3 Wizard Setup
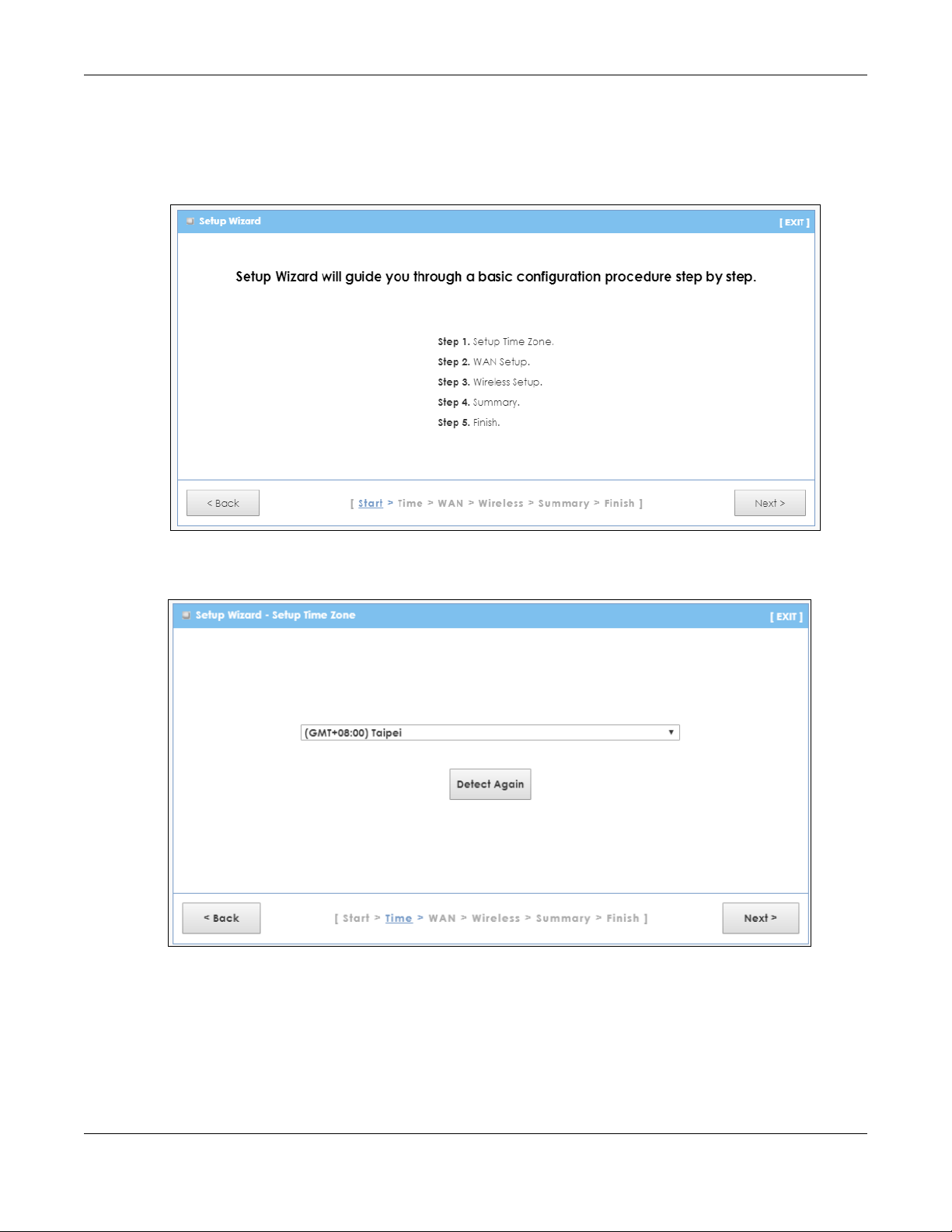
1 The first Wizard screen displays showing the main steps in the Wizard setup. Click Next to proceed with
the time zone setup screen.
Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
2 The LTE automatically detects your location and displays the correct time zone. If the result is not
correct, click Detect Again or manually select the time zone of the LTE and click Next.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
28
Page 29
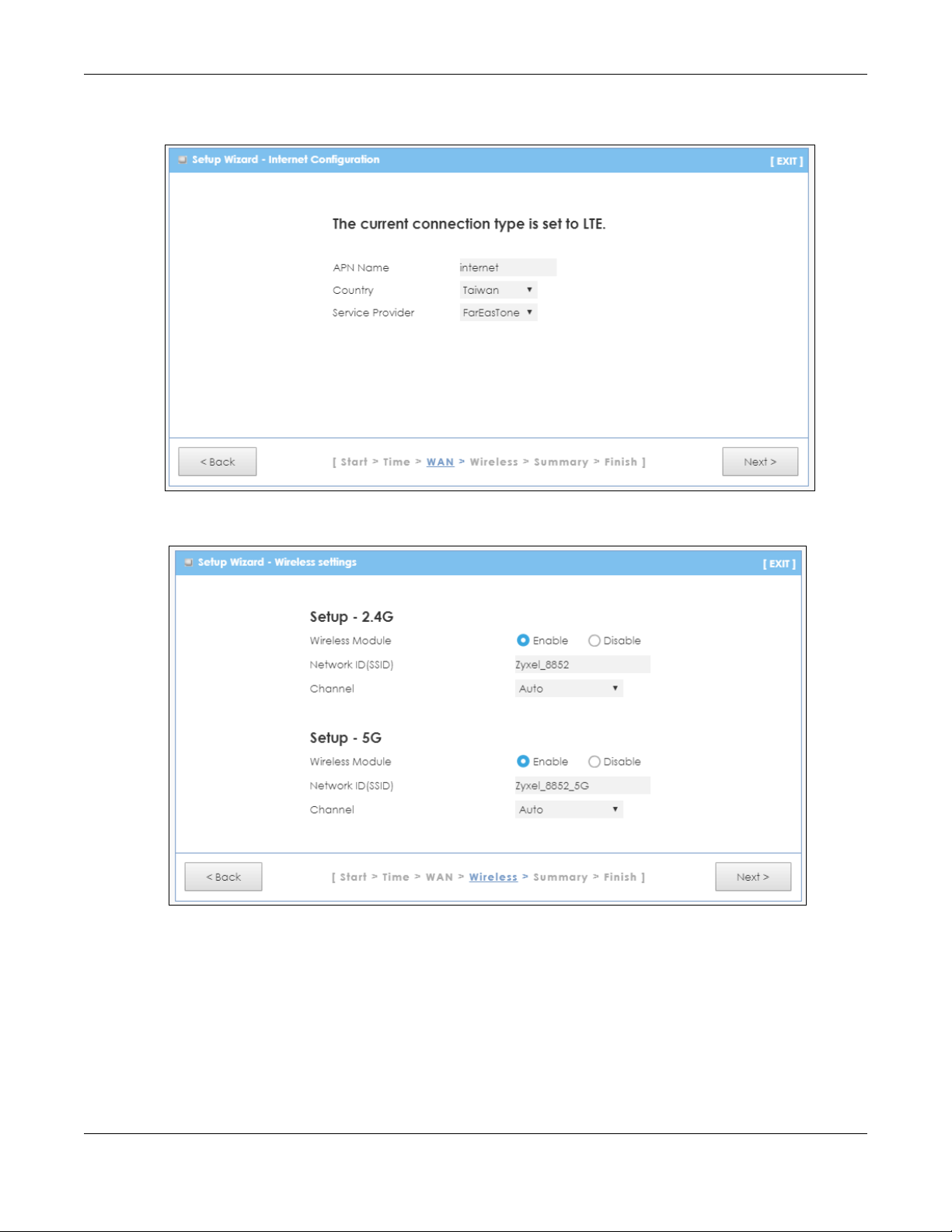
Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
3 Enter your APN (Access Point Name) provided by your service provider. Select the country where the LTE
is located and your service provider name. Click Next.
4 Use this screen to enable or disable the LTE’s wireless LAN, and enter the wireless network name (SSID).
Select a channel or use Auto to have the LTE automatically determine a channel to use. Click Next.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
29
Page 30
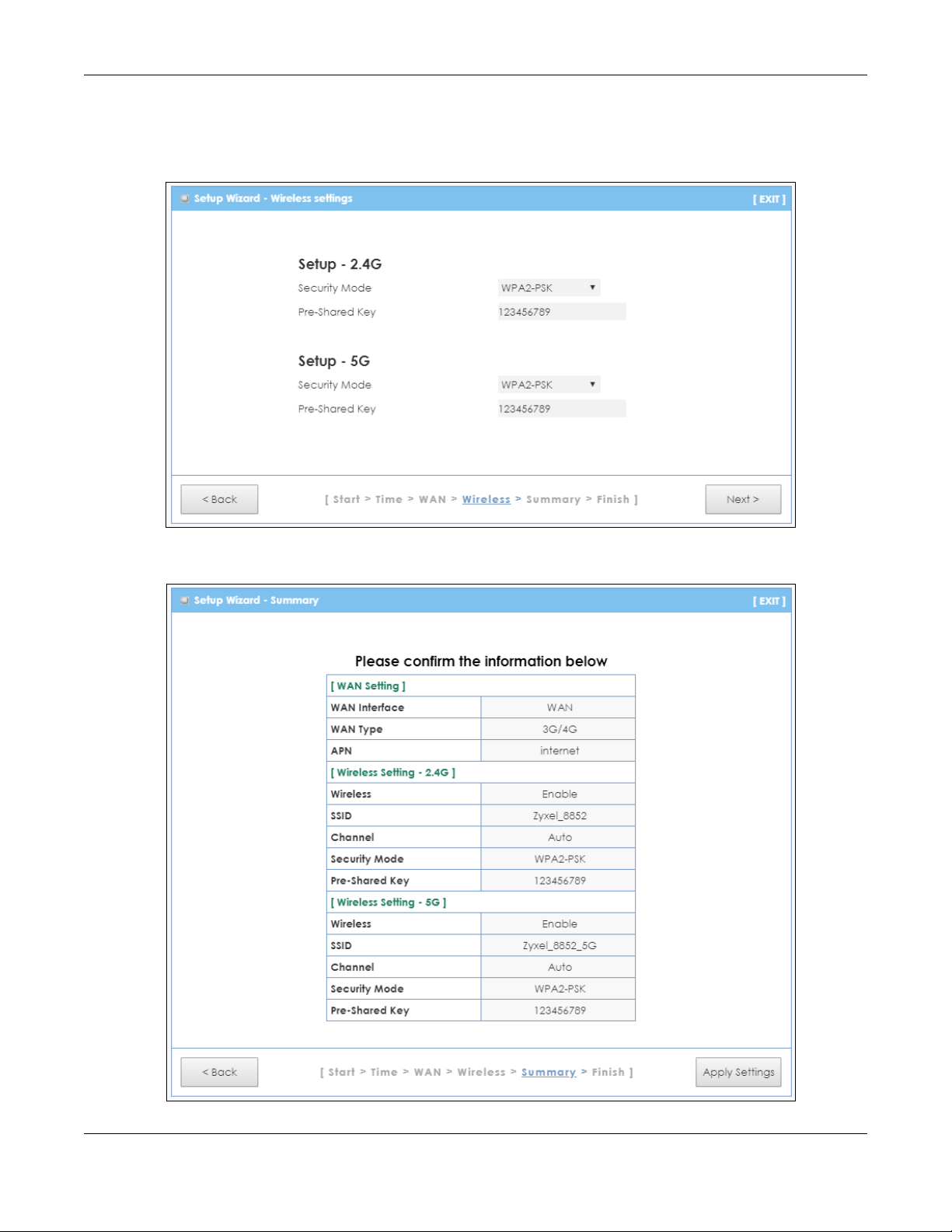
Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
5 Select WPA2-PSK and enter a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive characters for data
encryption.The wireless clients which want to associate with this wireless network must have the same
wireless security settings. Otherwise, select No Security to allow any client to associate with this network
without any data encryption or authentication. Click Next.
6 Use the read-only summary table to check whether what you have configured is correct. Click Apply
Settings to save your settings. Otherwise, click Back to go back to the previous screens.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
30
Page 31

Chapter 3 Setup Wizard
7 The system takes about 120 seconds to apply settings.
8 Click Finish to complete the wizard setup.
You are now ready to connect wirelessly to your LTE and access the Internet.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
31
Page 32

4.1 Overview
This chapter provides tutorials for setting up your LTE.
• Connecting to the LTE Using WPS
• Connect to LTE Wireless Network Without WPS
• Using Multiple SSIDs on the LTE
4.2 Connecting to the LTE Using WPS
This section gives you an example of how to set up a wireless network using WPS. This example uses the
LTE as the AP and a WPS-enabled Android 4.4.2 smartphone as the wireless client.
CHAPTER 4
Tutorials
There are two WPS methods for creating a secure connection via the Web Configurator or utility. This
tutorial shows you how to do both.
• Push Button Configuration (PBC) - create a secure wireless network simply by pressing a button. See
Section 4.2.1 on page 32. This is the easier method.
• PIN Configuration - create a secure wireless network simply by entering a wireless client's PIN (Personal
Identification Number) in the LTE’s interface. See Section 4.2.2 on page 33. This is the more secure
method, since one device can authenticate the other.
4.2.1 Push Button Configuration (PBC)
1 Make sure that your LTE is turned on and that it’s within range of your computer.
2 WPS is disabled by default on the LTE. log into LTE’s Web Configurator and turn it on in the Configuration
> Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station screen. You can either press the WPS button on the LTE’s panel or
press the Push Button in the Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station screen.
Note: It doesn’t matter which button is pressed first. You must press the second button within
two minutes of pressing the first one.
The LTE sends the proper configuration settings to the wireless client. This may take up to two minutes.
Then the wireless client is able to communicate with the LTE securely.
The following figure shows you an example of how to set up a wireless network and its security by
pressing a button on both LTE and wireless client (the Android 4.4.2 phone in this example).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
32
Page 33

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Wireless Client
SECURITY INFO
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
AP
Press and hold
for more than
2 seconds
COMMUNICATION
Figure 10 Example WPS Process: PBC Method
4.2.2 PIN Configuration
1 Go to your phone settings and turn on WiFi. Open the WiFi networks list and tap WPS PIN Entry to get a
2 Enter the client’s PIN number to the PIN field in the Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
3 Click the Start button (or button next to the PIN field) on the LTE’s WPS Station screen within two minutes.
When you use the PIN configuration method, you need to check the client’s PIN number and use the
LTE’s configuration interface.
PIN number.
screen on the LTE.
The LTE authenticates the wireless client and sends the proper configuration settings to the wireless
client. This may take up to two minutes. Then the wireless client is able to communicate with the LTE
securely.
The following figure shows you how to set up a wireless network and its security on a LTE and a wireless
client (android 4.4.2 smartphone) by using PIN method.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 4 Tutorials
SECURITY INFO
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
Enter WPS PIN
WPS
from other device:
WPS
START
Wireless Client
AP
Authentication by PIN
COMMUNICATION
Figure 11 Example WPS Process: PIN Method
4.3 Connect to LTE Wireless Network Without WPS
This example shows you how to configure wireless security settings with the following parameters on your
LTE and connect your computer to the LTE wireless network.
SSID SSID_Example3
Channel 6
Security WPA-PSK
(Pre-Shared Key: 1234567890)
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
34
Page 35

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Follow the steps below to configure the wireless settings on your LTE.
The instructions require that your hardware is connected (see the Quick Start Guide) and you are
logged into the Web Configurator through your LAN connection (see Section 2.3 on page 20).
1 Make sure the WIFI switch (at the back panel of the LTE) is set to ON.
2 Open the Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General screen in the AP’s Web Configurator.
3 Confirm that the wireless LAN is enabled on the LTE.
4 Enter SSID_Example3 as the SSID and select Channel-06 as the channel. Set security mode to WPA2-PSK
and enter 1234567890 in the Pre-Shared Key field. Click Apply.
5 Open the Status screen. Verify your wireless and wireless security settings under Device Information and
check if the WLAN connection is up under Interface Status.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 4 Tutorials
LTE
4.4 Using Multiple SSIDs on the LTE
You can configure more than one SSID on a LTE. See Section 8.4 on page 75.
This allows you to configure multiple independent wireless networks on the LTE as if there were multiple
APs (virtual APs). Each virtual AP has its own SSID, and wireless security type. That is, each SSID on the LTE
represents a different access point/wireless network to wireless clients in the network.
Clients can associate only with the SSIDs for which they have the correct security settings. Clients using
different SSIDs can access the Internet and the wired network behind the LTE (such as a printer).
For example, you may set up three wireless networks (A, B and C) in your office. A is for workers, B is for
guests and C is specific to a VoIP device in the meeting room.
4.4.1 Configuring Security Settings of Multiple SSIDs
The LTE is in router mode by default.
This example shows you how to configure the SSIDs with the following parameters on your LTE.
SSID SECURITY TYPE KEY
Zyxel_Worker WPA2-PSK
WPA Compatible
Zyxel_VWorker2 WPA-PSK 12345678
Zyxel_Guest WPA-PSK keyexample123
1 Connect your computer to the LAN port of the LTE using an Ethernet cable.
2 The default IP address of the LTEis “192.168.1.1”. In this case, your computer must have an IP address in
the range between “192.168.1.2” and “192.168.1.254”.
DoNotStealMyWirelessNetwork
3 Click Start > Run on your computer in Windows. Type “cmd” in the dialog box. Enter “ipconfig” to show
your computer’s IP address.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
36
Page 37

Chapter 4 Tutorials
4 After you’ve set your computer’s IP address, open a web browser such as Internet Explorer and enter
“http://192.168.1.1” as the web address in your web browser.
5 Enter “admin” as the user name and “1234” (default) as the password and click Login.
6 Type a new password and retype it to confirm, then click Apply. Otherwise, click Ignore.
7 Go to Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP. Click the Edit icon of the first entry to configure
wireless and security settings for SSID_Worker.
8 Configure the screen as follows. In this example, you enable Intra-BSS Traffic for SSID_Worker to allow
wireless clients in the same wireless network to communicate with each other. Click Apply.
9 Click the Edit icon of the second entry to configure wireless and security settings for SSID_Worker2.
10 Configure the screen as follows. You do not enable Intra-BSS Traffic for SSID_Worker2. Click Apply.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 4 Tutorials
11 Click the Edit icon of the third entry to configure wireless and security settings for SSID_Guest.
12 Configure the screen as follows. In this example, you enable Intra-BSS Traffic for SSID_Guest to allow
wireless clients in the same wireless network to communicate with each other. Click Apply.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
38
Page 39

PART II
Technical Reference
39
Page 40

5.1 Overview
Use the Status screen to check status information about the LTE.
5.2 Status
This screen is the first thing you see when you log into the LTE. It also appears every time you click the
Status icon in the navigation panel. The Status screen displays the LTE’s connection mode, wireless LAN
information and traffic statistics.
Figure 12 Status
CHAPTER 5
Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Information
Item This column shows the type of data the LTE is recording.
Data This column shows the actual data recorded by the LTE.
Host Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > General screen. It is for
Model Number This is the model name of your device.
Firmware Version This is the firmware version and the date created.
WAN Information
identification purposes.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
40
Page 41

Chapter 5 Status
Table 5 Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Address This shows the WAN Ethernet adapter MAC address of your device.
IP Address This shows the WAN port’s IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This shows the WAN port’s subnet mask.
Default Gateway This shows the WAN port’s gateway IP address.
IPv6 Address This shows the IPv6 address of the LTE on the WAN.
Operation Band This shows the network type and the frequency band used by the mobile network to which
the LTE is connecting.
Network Type This shows the type of network to which the LTE is connected.
Network Status This shows cellular WAN connection and Ethernet WAN connection status.
Firewall This shows Enable when the firewall is activated, and Disable when it is deactivated.
LAN Information
MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC address of your device.
IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Server or Disable.
IPv6 Address This shows the IPv6 address of the LTE on the LAN.
WLAN Information
WLAN Mode This is the device mode to which the LTE’s wireless LAN is set.
MAC Address This shows the 2.4G wireless adapter MAC address of your device.
WLAN 2.4G
SSID This shows a descriptive name used to identify the LTE in the 2.4G wireless LAN.
Channel This shows the channel number for the current operation channel.
802.11 Mode This shows the wireless standards the LTE supports.
Security This shows the level of wireless security the LTE is using.
WLAN 5G
SSID This shows a descriptive name used to identify the LTE in the 5G wireless LAN.
Channel This shows the channel number for the current operation channel.
802.11 Mode This shows the wireless standards the LTE supports.
Security This shows the level of wireless security the LTE is using.
Caller Status
Voice Service This displays the service type of call made through the LTE.
System Status
Call State This shows the status of call/voice mode status.
System Up time This is the total time the LTE has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your LTE’s present date and time.
System Resource
CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the LTE’s processing ability is currently used. When this
percentage is close to 100%, the LTE is running at full load, and the throughput is not going
to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have more throughput, you should
turn off other applications (for example, using bandwidth management.)
Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the LTE is using.
Interface Status
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 5 Status
Table 5 Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Item This displays the LTE port types. The port types are: Cellular WAN, Ethernet WAN, LAN 1~LAN
4, WLAN 2.4G and WLAN 5G.
Rate/Status For the LAN and WAN ports, this field displays Off (line is down) or On (line is up or
connected). For the LAN ports it displays the port speed or is left blank when the line is
disconnected. For the WAN port, it always displays the maximum transmission rate.
For the WLAN 2.4G, it displays On when the 2.4G WLAN is enabled or Off when the 2.4G
WLAN is disabled. For the WLAN 5G, it displays On when the 5G WLAN is enabled or Off
when the 2.4G WLAN is disabled. It displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN
is enabled and is left blank when the WLAN is disabled.
Summary
Packet Statistics Click Details... to go to the Monitor > Packet statistics screen (Section 6.6 on page 46). Use
WLAN Station Status Click Details... to go to the Monitor > WLAN station status screen (Section 6.7 on page 47).
LTE Modem Status Click Details... to go to the Monitor > LTE modem status screen (Section 6.8 on page 48). Use
this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
Use this screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated to the LTE’s 2.4G
wireless LAN.
this screen to view the detailed information about the LTE module, cellular interface, and
SIM card. You can also view the LTE connection status.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
42
Page 43

6.1 Overview
This chapter discusses read-only information related to the device state of the LTE.
To access the Monitor screens, click after login.
You can also click the links in the Summary table of the Status screen to view the packets sent/received
as well as the status of wireless clients connected to the LTE.
6.2 What You Can Do
• Use the Log screen to see the logs for the activity on the LTE (Section 6.3 on page 43).
• Use the DHCP Table screen to view information related to your DHCP status (Section 6.4 on page 45).
• Use the ARP Table screen to view the mapping of IP and MAC addresses (Section 6.5 on page 45).
• Use the Packet Statistics screen to view port status, packet statistics, the system up time (Section 6.6
on page 46).
• Use the WLAN station status screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated to the LTE
(Section 6.7 on page 47).
• Use the LTE modem status screen to view the detailed information about the LTE module, cellular
interface, and SIM card. You can also check the LTE connection status (Section 6.8 on page 48).
CHAPTER 6
Monitor
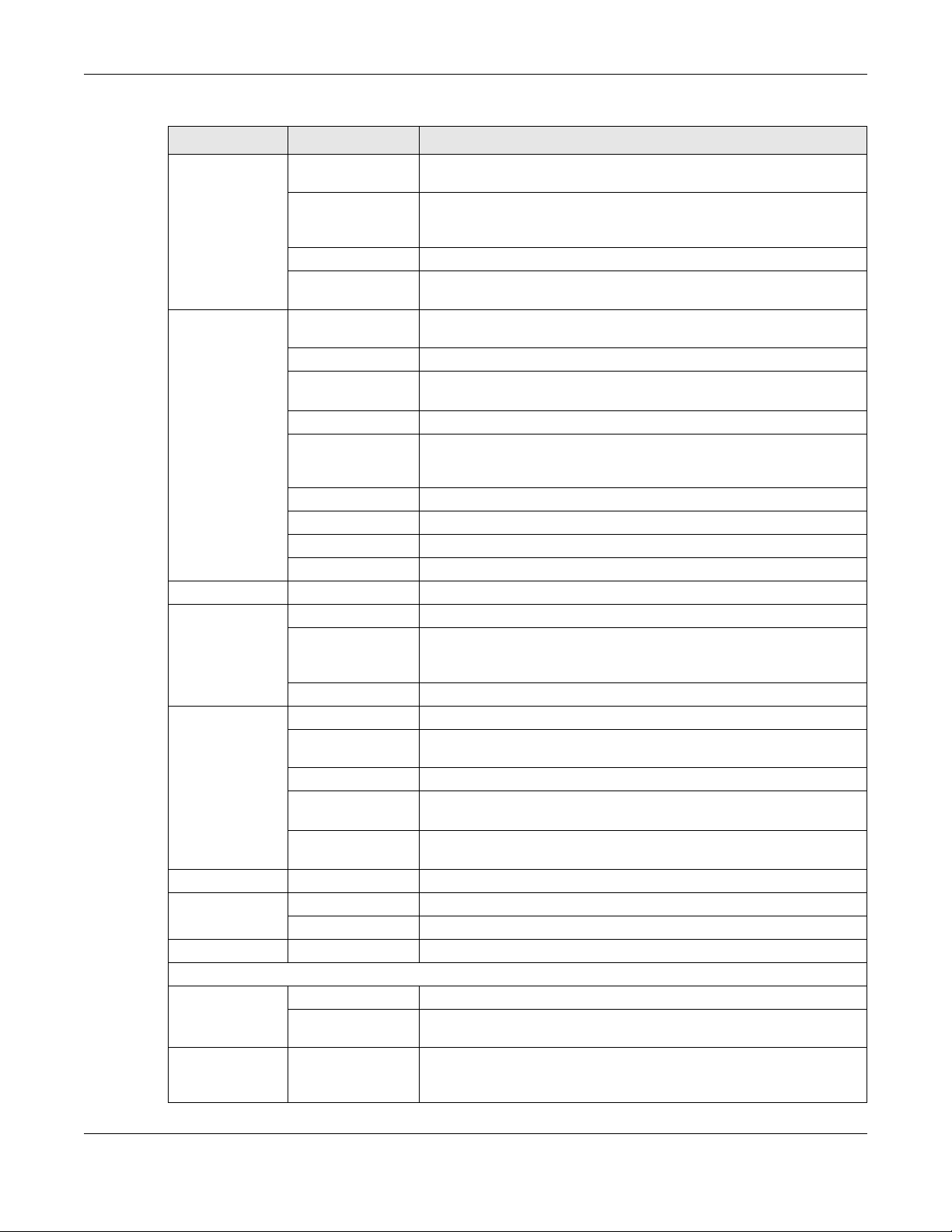
6.3 Log
The Web Configurator allows you to look at all of the LTE’s logs in one location.
6.3.1 View Log
Use the View Log screen to see the logged messages for the LTE. The log wraps around and deletes the
old entries after it fills. Select what logs you want to see in the Log Setting screen. Click Refresh to renew
the log screen. Click Clear Log to delete all the logs.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Figure 13 Monitor > Log > View Log
Chapter 6 Monitor
You can configure which logs to display in the View Log screen. Go to the Log Setting screen and select
the types of logs you wish to display. You can enable the log server, to send detailed events to this
server. Enter it’s IP address or a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), and port. Then select the types of
logs you wish to send to this server.
Click Apply to save your settings. Click Cancel to start the screen afresh.
Figure 14 Monitor > Log > Log Setting
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
44
Page 45

6.4 DHCP Table
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual clients to obtain
TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can configure the LTE’s LAN as a DHCP server or
disable it. When configured as a server, the LTE provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If DHCP
service is disabled, you must have another DHCP server on that network, or else the computer must be
manually configured.
Click Monitor > DHCP Table to open this screen. Read-only information here relates to your DHCP status.
The DHCP table shows current DHCP client information (including MAC address, and IP address) of all
network clients using the LTE’s DHCP server.
Figure 15 Monitor > DHCP Table
Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Table 6 Monitor > DHCP Table
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of the entry.
Status This field displays whether the connection to the host computer is up (a lit bulb) or
Host Name This field displays the computer host name.
IP Address This field displays the IP address relative to the # field listed above.
MAC Address This field shows the MAC address of the computer with the name in the Host Name
Reserve Select this if you want to reserve the IP address for this specific MAC address.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
6.5 ARP Table
down (a gray bulb).
field.
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address which
uniquely identifies a device. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists
of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to
a physical machine address, also known as a Media Access Control or MAC address, on the local area
network. Use the ARP table to view IP-to-MAC address mappings.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 6 Monitor
Click Monitor > ARP Table to open the following screen.
Figure 16 Monitor > ARP Table
The following screen describes the labels on this screen.
Table 7 Monitor > ARP Table
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of the entry.
IP Address This is the learned IPv4 or IPv6 IP address of a device connected to a port.
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the device with the listed IP address.
State This column shows the current status of the connection.
6.6 Packet Statistics
Click Monitor > Packet Statistics or the Packet Statistics (Details...) hyperlink in the Status screen. Read
only information here includes port status, packet specific statistics and the “system up time”. The Poll
Interval(s) field is configurable and is used for refreshing the screen.
Figure 17 Monitor > Packet Statistics
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
46
Page 47

Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Table 8 Monitor > Packet Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This is the LTE’s interface type.
Status For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or Down when the
TxPkts This is the number of transmitted packets on this port.
RxPkts This is the number of received packets on this port.
Collisions This is the number of collisions on this port.
Tx B/s This displays the transmission speed in bytes per second on this port.
Rx B/x This displays the reception speed in bytes per second on this port.
Up Time This is the total time the LTE has been for each session.
System Up Time This is the total time the LTE has been on.
Poll Interval(s) Enter the time interval in seconds for refreshing statistics in this field.
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Poll Interval(s) field.
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
line is disconnected.
For the WAN port, it displays Up when the mobile data connection is up, Connecting
when the LTE is trying to bring the mobile data connection up, and displays Down
when the 3G/4G connection is down or not activated.
For the WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN is enabled
and Down when the WLAN is disabled.
6.7 WLAN Station Status
Click Monitor > WLAN station status or the WLAN Station Status (Details...) hyperlink in the Status screen.
View the wireless stations that are currently associated to the LTE’s 2.4G and 5G wireless network in the
Association List. Association means that a wireless client (for example, your network or computer with a
wireless network card) has connected successfully to the AP (or wireless router) using the same SSID,
channel and security settings.
Click Monitor > WLAN Station Status to open the following screen.
Figure 18 Monitor > WLAN Station Status
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
47
Page 48

The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Table 9 Monitor > WLAN Station Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of an associated wireless station.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of an associated wireless station.
Association Time This field displays the time a wireless station first associated with the LTE’s WLAN.
6.8 LTE Modem Status
Click Monitor > LTE Modem Status to open the following screen.
Figure 19 Monitor > LTE Modem Status
Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Table 10 Monitor > LTE Modem Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Modem Information
Module Name This displays the name of the built-in LTE module.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
48
Page 49

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 10 Monitor > LTE Modem Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IMEI/MEID This displays the International Mobile Equipment Number (IMEI) or Mobile Equipment
Identifier (MEID), which is the serial number of the built-in LTE module. It is a unique
15-digit number used to identify a mobile device.
HW Version This displays the hardware version of the built-in LTE module.
FW Version This displays the firmware version of the built-in LTE module.
SIM Status
PIN Code Status This displays the status of PIN code authentication.
PIN Code Remaining Times This displays how many times you can enter the PIN code.
PUK Code Remaining Times This displays how many times you can enter the PUK code.
Service Information
Operator This displays the name of the service provider.
Cell Broadcast This displays whether the one-to-many messaging service is available.
MCC This displays the Mobile Country Code (MCC), which is used to identify the country
MNC This displays the Mobile Network Code (MNC), which is used in combination with
LAC This displays the 2-octet Location Area Code (LAC), which is used to identify a
TAC This displays the Tracking Area Code (TAC), which is to identify a tracking area within
Cell ID This displays the ID of a cell at the physical layer.
Service Type This displays the type of the mobile network to which the LTE is connecting.
Operation Band This displays the network type and the frequency band used by the mobile network
RSSI This displays the received signal strength indicator (RSSI), that is, the received signal
CS Register Status This displays the Circuit Switched (CS) network registration status.
Eclo This displays the ratio (in dB) of the received energy per chip and the interference
PS Register Status This displays the Packet Switched (PS) network registration status.
PS Attached Status This displays the Packet switched Domain Attachment status.
Roaming Status This displays whether the LTE is connected to another service provider’s mobile
IMSI This displays the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) stored in the SIM
SMSC This displays the number for Short Message Service Center (SMSC), which stores,
MSISDN This displays the MSISDN (Mobile Subscriber ISDN) number, a phone number assigned
RSRP This displays the Reference Signal Receive Power (RSRP), which is the average
RSRQ This displays the Reference Signal Received Quality (RSRQ), which is the ratio of RSRP
of a mobile subscriber.
MCC to identify the public land mobile network (PLMN) of a mobile subscriber.
location area within a PLMN.
a PLMN.
to which the LTE is connecting.
strength in dBm.
level.
network using roaming.
(Subscriber Identity Module) card. The SIM card is installed in a mobile device and
used for authenticating a customer to the carrier network. IMSI is a unique 15-digit
number used to identify a user on a network.
forwards and delivers SMS text message.
to a mobile subscriber to call a mobile device.
received power of all Resource Elements (RE) that carry cell-specific Reference
Signals (RS) within the specified bandwidth.
to the E-UTRA carrier RSSI and indicates the quality of the received reference signal.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 10 Monitor > LTE Modem Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SINR This displays the Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR). A negative value
means more noise than signal.
PLMN This displays the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) code of the mobile network.
MIMO This displays the MIMO (Multi-input Multi-output) technology supported by the LTE,
such as 1T2R (1 Transmit and 2 Receive paths/antennas) or TM1-TM4 (Transmission
Mode 4).
Support Band List This displays the frequency bands that are supported by the LTE.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
50
Page 51

7.1 Overview
LTE
Ethernet WAN
This chapter discusses the LTE’s WAN screens. Use these screens to configure your LTE for Internet access.
A WAN (Wide Area Network) connection is an outside connection to another network or the Internet. It
connects your private networks such as a LAN (Local Area Network) and other networks, so that a
computer in one location can communicate with computers in other locations.
3G and 4G standards for the sending and receiving of voice, video, and data in a mobile environment.
You can insert a 4G SIM card and set the LTE to use this 3G/4G connection as your WAN.
Figure 20 LAN/Wireless LAN and Wireless WAN
CHAPTER 7
WAN
7.2 What You Can Do
• Use the WAN Management screen to configure 3G/4G WAN connection settings (Section 7.4 on
page 54).
• Use the Network Scan screen to specify the type of the mobile network to which the LTE is connected
and how you want the LTE to connect to an available mobile network (Section 7.5 on page 60).
• Use the IPv6 screen to configure the LTE’s IPv6 settings (Section 7.6 on page 61).
• Use the PIN Management screen to enable or disable PIN code authentication (Section 7.7 on page
63).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 7 WAN
7.3 What You Need To Know
The information in this section can help you configure the screens for your WAN connection, as well as
enable/disable some advanced features of your LTE.
3G
3G (Third Generation) is a digital, packet-switched wireless technology. Bandwidth usage is optimized as
multiple users share the same channel and bandwidth is only allocated to users when they send data. It
allows fast transfer of voice and non-voice data and provides broadband Internet access to mobile
devices.
4G
4G is the fourth generation of the mobile telecommunications technology and a successor of 3G. Both
the WiMAX and Long Term Evolution (LTE) standards are the 4G candidate systems. 4G only supports allIP-based packet-switched telephony services and is required to offer gigabit speed access.
DNS Server Address Assignment
Use Domain Name System (DNS) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice versa,
for instance, the IP address of www.zyxel.com is 204.217.0.2. The DNS server is extremely important
because without it, you must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it.
The LTE can get the DNS server addresses in the following ways.
1 The ISP tells you the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of an information sheet, when you sign up.
If your ISP gives you DNS server addresses, manually enter them in the DNS server fields.
2 If your ISP dynamically assigns the DNS server IP addresses (along with the LTE’s WAN IP address), set the
DNS server fields to get the DNS server address from the ISP.
Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1 recipient) or
Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of hosts on
the network - not everybody and not just 1.
Figure 21 Multicast Example
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
52
Page 53

Chapter 7 WAN
In the multicast example above, systems A and D comprise one multicast group. In multicasting, the
server only needs to send one data stream and this is delivered to systems A and D.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership in a
multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. The LTE supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP v1), IGMP
version 2 (IGMP v2) and IGMP version 3 (IGMP v3).
At start up, the LTE queries all directly connected networks to gather group membership. After that, the
LTE periodically updates this information. IP multicasting can be enabled/disabled on the LTE WAN
interface in the Web Configurator.
IPv6 Introduction
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), is designed to enhance IP address size and features. The increase in
IPv6 address size to 128 bits (from the 32-bit IPv4 address) allows up to 3.4 x 10
use IPv4/IPv6 dual stack to connect to IPv4 and IPv6 networks, and supports IPv6 stateless
autoconfiguration (SLAAC).
38
IP addresses. The LTE can
IPv6 Addressing
The 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons (:). This is an
example IPv6 address 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
IPv6 addresses can be abbreviated in two ways:
• Leading zeros in a block can be omitted. So 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000 can be
written as 2001:db8:1a2b:15:0:0:1a2f:0.
• Any number of consecutive blocks of zeros can be replaced by a double colon. A double colon can
only appear once in an IPv6 address. So 2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f:0000:0000:0015 can be
written as 2001:0db8::1a2f:0000:0000:0015, 2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f::0015,
2001:db8::1a2f:0:0:15 or 2001:db8:0:0:1a2f::15.
IPv6 Prefix and Prefix Length
Similar to an IPv4 subnet mask, IPv6 uses an address prefix to represent the network address. An IPv6
prefix length specifies how many most significant bits (start from the left) in the address compose the
network address. The prefix length is written as “/x” where x is a number. For example,
2001:db8:1a2b:15::1a2f:0/32
means that the first 32 bits (2001:db8) is the subnet prefix.
IPv6 Subnet Masking
Both an IPv6 address and IPv6 subnet mask compose of 128-bit binary digits, which are divided into
eight 16-bit blocks and written in hexadecimal notation. Hexadecimal uses four bits for each character
(1 ~ 10, A ~ F). Each block’s 16 bits are then represented by four hexadecimal characters. For example,
FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FC00:0000:0000:0000.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
53
Page 54

7.4 WAN Management
The summary table shows you the WAN connections configured on the LTE. Click Configuration >
Network > WAN > WAN Management from the Configuration menu.
Figure 22 Configuration > Network > WAN > WAN Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 Configuration > Network > WAN > WAN Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface Name This field displays the name of the WAN interface for this connection.
Physical Interface This field displays the LTE’s WAN physical connections.
IP Address This field displays the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses of the WAN connection.
Operation Mode This field indicates whether the IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity is available.
WAN Type This field displays the type of the WAN connection.
Action Click the Edit icon to configure the WAN connection settings.
Chapter 7 WAN
7.4.1 WAN Management Edit 3G/4G
Use this screen to change your LTE’s 3G/4G WAN connection settings. Click the Edit icon in the Physical
Interface: 3G/4G row in the Configuration > Network > WAN > WAN Management screen.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
54
Page 55

Chapter 7 WAN
Figure 23 WAN Management Edit 3G/4G
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 Management WAN Edit: 3G/4G
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Cellular WAN
Antenna Select Select Internal for the LTE to use its internal antennas for WAN connection. If you
attached external antennas (not included) to the LTE, select External. Select Auto for the
LTE to automatically select the antennas for WAN connection.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 7 WAN
Table 12 Management WAN Edit: 3G/4G (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network Type Select the type of the network (4G or 3G) to which you want the LTE to connect.
Otherwise, select Auto to have the LTE connect to an available network using the default
settings on the SIM card. If the currently registered mobile network is not available or the
mobile network’s signal strength is too low, the LTE switches to another available mobile
network.
Band Selection Select Manual to select the frequency bands the LTE uses to connect to the mobile
network. Otherwise, select Auto to have the LTE connect to any available frequency
band using the default settings
Band List Select the frequency bands you want the LTE to use to connect to the mobile network.
You can only select the frequency bands from this list if you selected Manual in the Band
Selection field.
Roaming 3G/4G roaming is to use your mobile device in an area which is not covered by your
service provider. Enable roaming to ensure that your LTE is kept connected to the
Internet when you are traveling outside the geographical coverage area of the network
to which you are registered.
Dial-Up Profile Select Auto-Detection to have the LTE use the inserted SIM card’s default settings to
connect to any available mobile network.
Select Manual and enter the information provided by your service provider to connect to
the service provider’s mobile network.
APN Connections with different APNs (Access Point Names) may provide different services
(such as Internet access or MMS (Multi-Media Messaging Service)) and charge method.
The corresponding APN automatically displays when you select a pre-defined service
provider.
If you select Manual in the Dial-Up Profile field, manually enter the APN provided by your
service provider. You can enter up to 32 ASCII printable characters. Spaces are allowed.
Dial Number This is the phone number (dial string) used to dial up a connection to your service
provider’s base station. Your service provider should provide the phone number. For
example, *99# is the dial string to establish a GPRS or 3G/4G connection in Taiwan.
The corresponding phone number automatically displays when you select a pre-defined
service provider.
If you select Others in the Service Provider field, manually enter the phone number
provided by your service provider.
Account Type the user name (of up to 64 ASCII printable characters) given to you by your service
provider.
Password Type the password (of up to 64 ASCII printable characters) associated with the user
name above.
Authentication The LTE supports PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) and CHAP (Challenge
IP Type Select IPv4 if you want the LTE3202-M430 to run IPv4 only.
IP Mode Select Dynamic IP if you have a dynamic IP address.
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Static IP in the IP Mode field.
IP Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask in this field if you selected Static IP in the IP Mode field.
Handshake Authentication Protocol). CHAP is more secure than PAP; however, PAP is
readily available on more platforms
Select an authentication protocol (PAP, or CHAP) used by the service provider.
Otherwise, select Auto to have the LTE accept either CHAP or PAP.
Select IPv6 if you want the LTE3202-M430 to run IPv6 only.
Select IPv4/IPv6 to allow the LTE3202-M430 to run IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time.
Select Static IP if you have a fixed IP address assigned by your service provider.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
56
Page 57

Chapter 7 WAN
Table 12 Management WAN Edit: 3G/4G (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Gateway Enter the gateway IP address in this field if you selected Static IP in the IP Mode field.
Primary DNS Enter the first DNS server address assigned by the service provider.
Secondary DNS Enter the second DNS server address assigned by the service provider.
MTU Enter the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) of each data packet, in bytes, that can move
through the WAN connection.
IGMP Select this to enable multicasting. This applies to traffic routed from the WAN to the LAN.
Disable it to turn off this feature. This may cause incoming traffic to be dropped or sent to
all connected network devices.
IGMP Proxy Select this option to have the LTE act as an IGMP proxy on this connection. This allows the
LTE to get subscribing information and maintain a joined member list for each multicast
group. It can reduce multicast traffic significantly.
Bridge Mode Select this option to allow the computer connected to the first Ethernet LAN port to get
Bridge Mode Fixed
MAC
Network Monitoring Select this option to have the LTE test the WAN connection.
Checking By Select DNS Query to periodically send a DNS query to a DNS server. Select ICMP
Loading Check Select this option to check how many packets have been transmitted or received
Check Interval Type a number of seconds (0 to 99999) to set the time interval between checks. Allow
Check Timeout Type the number of seconds (0 to 99999) for your LTE to wait for a response to the ping or
Latency Threshold Type a number of milliseconds (0 to 99999) for the latency threshold.
an individual IP address from the ISP’s DHCP server directly. In Bridge mode, the Multy
Device broadcasts traffic to the local network from the Internet. Choose Bridge mode if
you have an existing router in your network and you do not want to reconfigure routing
settings.
Specify the MAC address to which the WAN IP address is destined.
Checking to send a ping to either the default gateway or the addresses you specify in
the Target1 and Target2 fields.
through the WAN connection within a time period specified in the Check Interval field.
more time if your destination IP address handles lots of traffic.
DNS query before considering the check to have failed. This setting must be less than the
Check Interval. Use a higher value in this field if your network is busy or congested.
If the specified latency threshold is exceeded, the LTE considers the check to have failed
and makes a new connection after (Latency Threshold * Fail Threshold) seconds.
Fail Threshold Type how many WAN connection checks can fail (0 to 99999) before the connection is
considered "down" (not connected). The LTE still checks a "down" connection to detect if
it reconnects.
Target1 / Target 2 Select DNS1 to have the LTE send a DNS query to the first DNS server address assigned by
the service provider.
Select DNS2 to have the LTE send a DNS query to the second DNS server address
assigned by the service provider.
Select Gateway to have the LTE ping the WAN interface's default gateway IP address.
Select Other Host and enter a domain name or IP address of a reliable nearby computer
to have the LTE ping that address.
7.4.2 WAN Management Edit Ethernet
The LTE has 4 LAN Ethernet ports, you can configure LAN 1 port to work as a WAN port if needed. This
WAN port will work as a fail-over port, which means that if the 3G/4G WAN connection fails, the LTE will
use the WAN Ethernet connection for backup.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 7 WAN
Use this screen to enable the LAN 1 port as a WAN port, and configure its settings. Click the Edit icon in
the Physical Interface: Ethernet row in the Configuration > Network > WAN > Management WAN screen.
Figure 24 WAN Management Edit Ethernet
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 WAN Management Edit Ethernet
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ethernet WAN
Port 1 config as WAN port Select this so the LAN 1 Ethernet port works a WAN port.
WAN Type Select the routing method used by your ISP from the drop-down list box.
Select Static IP if you have a fixed IP address assigned by your ISP.
Select Dynamic IP if you want to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server.
Select PPPoE if your ISP requires your to use a PPPoE connection to the Internet. This
method of connection typically requires you to enter a Username and Password
(provided by your ISP) to gain access to the Internet. You need to ensure that any
PPPoE client software on your computer is removed or disabled.
Dynamic IP WAN Type Configuration
These fields appears when you select Dynamic IP in the WAN Type field.
Host Name Type a host name for the Ethernet WAN interface.
ISP Registered MAC Address Click the Clone button and the LTE will enter the MAC address of the computer on
the LAN automatically.
Click the Clear button to remove the MAC address from this field.
Static IP WAN Type Configuration
These fields appears when you select Static IP in the WAN Type field.
WAN IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field.
WAN Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask in this field.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
58
Page 59

Chapter 7 WAN
Table 13 WAN Management Edit Ethernet (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WAN Gateway Enter the gateway IP address.
Primary DNS Enter the first DNS server address assigned by the service provider.
Secondary DNS Enter the second DNS server address assigned by the service provider.
PPoE WAN Type Configuration
These fields appears when you select PPPoE in the WAN Type field.
PPPoE Account Type the user name or account given by your ISP.
PPPoE Password Type the password associated to this account.
Primary DNS Enter the first DNS server address assigned by the service provider.
Secondary DNS Enter the second DNS server address assigned by the service provider.
Service Name Type the PPPoE Service Name from your ISP provider. PPPoE uses a service name to
Assigned IP Address Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP.
MTU Enter the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) of each data packet, in bytes, that can
Network Monitoring Select this option to have the LTE test the WAN connection by periodically sending
Loading Check Select this option to check how many packets have been transmitted or received
Check Interval Type a number of seconds (0 to 99999) to set the time interval between checks.
Check Timeout Type the number of seconds (0 to 99999) for your LTE to wait for a response to the
Latency Threshold Type a number of milliseconds (0 to 99999) for the latency threshold.
Fail Threshold Type how many WAN connection checks can fail (0 to 99999) before the
Target1 / Target 2 Select DNS1 to have the LTE send a DNS query to the first DNS server address
identify and reach the PPPoE server.
move through the WAN connection.
DNS Query to a DNS server or sending a ping (ICMP Checking) to either the default
gateway or the addresses you specify in the Target1 and Target2 fields.
through the WAN connection within a time period specified in the Check Interval
field.
Allow more time if your destination IP address handles lots of traffic.
ping or DNS query before considering the check to have failed. This setting must be
less than the Check Interval. Use a higher value in this field if your network is busy or
congested.
If the specified latency threshold is exceeded, the LTE considers the check to have
failed and makes a new connection after (Latency Threshold * Fail Threshold)
seconds.
connection is considered "down" (not connected). The LTE still checks a "down"
connection to detect if it reconnects.
assigned by the service provider.
Select DNS2 to have the LTE send a DNS query to the second DNS server address
assigned by the service provider.
Select Gateway to have the LTE ping the WAN interface's default gateway IP
address.
Select Other Host and enter a domain name or IP address of a reliable nearby
computer to have the LTE ping that address.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
59
Page 60

7.5 Network Scan
Use this screen to set how you want the LTE to connect to an available mobile network. Click
Configuration > Network > WAN > Network Scan from the Configuration menu.
Figure 25 Configuration > Network > WAN > Network Scan
Chapter 7 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Configuration > Network > WAN > Network Scan
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Physical Interface This shows the type of the interface used by the WAN connection.
Network Type Select the type of the network (4G only, 3G only, or Auto) to which you want the LTE to
connect when there is a SIM card inserted.
Scan Approach Select Auto to have the LTE connect to an available network using the default settings on
Network Provider List This table is available only when you set Scan Approach to Manual.
Provider Name This shows the name of the service provider.
Mobile System This shows the mobile telecommunications standard supported by the mobile network.
Network Status This shows whether the mobile network is available.
Action Click Select to have the LTE establish a connection to the selected mobile network.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Refresh Click Refresh to update this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
the SIM card. If the currently registered mobile network is not available or the mobile
network’s signal strength is too low, the LTE switches to another available mobile network.
Select Manual to search for and select the mobile networks to which you want the LTE to
connect.
Click Scan to search for available mobile networks based on the network type you
selected.
Click Apply to save your changes in the Action field.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
60
Page 61

7.6 IPv6
Use this screen to configure the LTE’s IPv6 settings. Click Configuration > Network > WAN > IPv6 from the
Configuration menu.
Figure 26 Configuration > Network > WAN > IPv6
Chapter 7 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15 Configuration > Network >WAN > IPv6
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Select Enable to allow the LTE to run IPv6. Otherwise, select Disable.
IPv6 Connection This displays Static IPv6 if you have a fixed IPv6 address assigned by your ISP.
This displays DHCPv6 if you want to obtain an IPv6 address from a DHCPv6 server.
(These fields appear when the IPv6 Connection is set to Static IPv6.)
IPv6 Address Enter the IPv6 address on the WAN side in this field.
Subnet Prefix Length Enter the address prefix length to specify how many most significant bits in an IPv6
address compose the network address.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the next-hop gateway. The gateway is a router or switch on the
same segment as your LTE's interfaces. The gateway helps forward packets to their
destinations.
Primary DNS Address
Secondary DNS
Address
(These fields appear when the IPv6 Connection is set to DHCPv6.)
DNS Setting Select Obtain DNS Server address Automatically to have the LTE get the IPv6 DNS server
Enter the first IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Enter the second IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
addresses from the ISP automatically.
Select Use the following DNS address to have the LTE use the IPv6 DNS server addresses
you configure manually.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 7 WAN
Table 15 Configuration > Network >WAN > IPv6 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Primary DNS Address Enter the first IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Secondary DNS
Address
(These fields appear when the IPv6 Connection is set to PPPoE.)
Address Mode Select Dynamic IP if you have a dynamic IP address.
IP Address Enter the static IP address provided by your ISP.
Username Enter a user name (of up to 31 printable characters) for login using PPPoE connection.
Password Enter the password associated with the user name above.
Service Name Enter the name of your PPPoE service here.
Reconnect Mode Select Auto Reconnect (always-on) if you do not want the connection to time out.
Maximum Idle Time Specify the time in minutes that elapses before the LTE automatically disconnects from
(These fields appear when the IPv6 Connection is set to 6RD.)
Remote IPv4 Address Enter the IPv4 address of the relay server,
IPv4 Mask Length Enter the IPv4 subnet mask number (1 to 32).
Remote Prefix Enter an IPv6 prefix for tunneling IPv6 traffic to the ISP’s Border Relay router and
Prefix Length Enter the address prefix length to specify how many most significant bits in an IPv6
Primary DNS Address
Secondary DNS
Address
LAN IPv6 Address Enter the IPv6 address for the LTE LAN interface in this field.
LAN IPv6 Link-Local
Address
Auto configuration Click Enable if you want the devices on your local area network to obtain network
Auto configuration
Type
IPv6 Address Range
(Start)
IPv6 Address Range
(End)
IPv6 Address Lifetime If you select Stateful (DHCPv6), specify how long (in minutes) the IPv6 addresses remain
Enter the second IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Select Static IP if the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Select Connection-on-Demand if you want to connect for a certain amount of time
before the router automatically disconnects from the PPPoE server. If you select this you
will need to enter the number of minutes in the Maximum Idle Time field.
Select Manually if want to make the connection manually.
the PPPoE server.
connecting to the native IPv6 Internet.
address compose the network address.
Enter the first IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Enter the second IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
This shows the IPv6 Link-local address in the LAN side. This is used by LTE when
communicating with neighboring devices on the same link. It allows IPv6-capable
devices to communicate with each other in the LAN side.i
address that are not managed by a DHCPv6 server. Otherwise, select Disable.
Select Stateless if you want the LTE interface to automatically generate a link-local
address via stateless auto configuration.
Select Stateful (DHCPv6) when the devices connected to your LAN needs to have their
TCP/IP configuration set to DHCPv6 or obtain an IPv6 address automatically.
If you select Stateful (DHCPv6), specify the range of IPv6 addresses from which the
DHCPv6 server assigns to the clients. Enter the smallest value of the last block of the IPv6
addresses which are to be allocated.
If you select Stateful (DHCPv6), specify the range of IPv6 addresses from which the
DHCPv6 server assigns to the clients. Enter the largest value of the last block of the IPv6
addresses which are to be allocated.
valid.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
62
Page 63

7.7 PIN Management
Use this screen to enable PIN authentication and configure the PIN code. Click Configuration > Network
> WAN > PIN Management from the Configuration menu.
Figure 27 Configuration > Network > WAN > PIN Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 Configuration > Network > WAN > PIN Management
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PIN Code Request function
SIM PIN Code
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select Enable to turn on PIN code authentication. A PIN (Personal Identification
Number) code is a key to a SIM card. Without the PIN code, you cannot use the SIM
card.
Select Disable to turn off PIN code authentication.
If you select Enable, enter the 4-digit PIN code (0000 for example) provided by your
ISP for the inserted SIM card.
Chapter 7 WAN
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
63
Page 64

8.1 Overview
LTE
This chapter discusses how to configure the wireless network settings in your LTE.
See the appendices for more detailed information about wireless networks.
The following figure provides an example of a wireless network.
Figure 28 Example of a Wireless Network
CHAPTER 8
Wireless LAN
The wireless network is the part in the blue circle. In this wireless network, devices A and B are called
wireless clients. The wireless clients use the access point (AP) to interact with other devices (such as the
printer) or with the Internet. Your LTE is the AP.
8.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the General screen to turn the wireless connection on or off, set up wireless security between the
LTE and the wireless clients, and make other basic configuration changes (Section 8.2 on page 67).
• Use the More AP screen to set up multiple wireless networks on your LTE (Section 8.4 on page 75).
• Use the MAC Filter screen to allow or deny wireless stations based on their MAC addresses from
connecting to the LTE (Section 8.5 on page 77).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
64
Page 65

• Use the Advanced screen to allow intra-BSS networking and set the RTS/CTS Threshold (Section 8.6 on
page 79).
• Use the QoS screen to ensure Quality of Service (QoS) in your wireless network (Section 8.7 on page
80).
• Use the WPS screen to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to
configure security settings manually (Section 8.8 on page 81).
• Use the WPS Station screen to add a wireless station using WPS (Section 8.9 on page 82).
• Use the Scheduling screen to set the times your wireless LAN is turned on and off (Section 8.10 on
page 83).
• Use the WDS screen to configure the LTE’s WDS settings (Section 8.11 on page 84).
8.1.2 What You Should Know
Every wireless network must follow these basic guidelines.
• Every wireless client in the same wireless network must use the same SSID.
The SSID is the name of the wireless network. It stands for Service Set IDentity.
• If two wireless networks overlap, they should use different channels.
Like radio stations or television channels, each wireless network uses a specific channel, or frequency,
to send and receive information.
• Every wireless client in the same wireless network must use security compatible with the AP.
Security stops unauthorized devices from using the wireless network. It can also protect the
information that is sent in the wireless network.
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Wireless Security Overview
The following sections introduce different types of wireless security you can set up in the wireless
network.
SSID
Normally, the AP acts like a beacon and regularly broadcasts the SSID in the area. You can hide the
SSID instead, in which case the AP does not broadcast the SSID. In addition, you should change the
default SSID to something that is difficult to guess.
This type of security is fairly weak, however, because there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the
SSID. In addition, unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network.
MAC Address Filter
Every wireless client has a unique identification number, called a MAC address.1 A MAC address is
usually written using twelve hexadecimal characters
To get the MAC address for each wireless client, see the appropriate User’s Guide or other
documentation.
1. Some wireless devices, such as scanners, can detect wireless networks but cannot use wireless networks. These
kinds of wireless devices might not have MAC addresses.
2. Hexadecimal characters are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
2
; for example, 00A0C5000002 or 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
You can use the MAC address filter to tell the AP which wireless clients are allowed or not allowed to use
the wireless network. If a wireless client is allowed to use the wireless network, it still has to have the
correct settings (SSID, channel, and security). If a wireless client is not allowed to use the wireless
network, it does not matter if it has the correct settings.
This type of security does not protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Furthermore,
there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the MAC address of an authorized wireless client. Then,
they can use that MAC address to use the wireless network.
User Authentication
You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use it. This is called user
authentication. However, every wireless client in the wireless network has to support IEEE 802.1x to do
this.
For wireless networks, there are two typical places to store the user names and passwords for each user.
• In the AP: this feature is called a local user database or a local database.
• In a RADIUS server: this is a server used in businesses more than in homes.
If your AP does not provide a local user database and if you do not have a RADIUS server, you cannot
set up user names and passwords for your users.
Unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network, even if they cannot
use the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless users to get a valid user
name and password. Then, they can use that user name and password to use the wireless network.
Local user databases also have an additional limitation that is explained in the next section.
Encryption
Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless network.
Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot understand the
message.
The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of user authentication. (See page 66 for
information about this.)
Table 17 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication
NO AUTHENTICATION RADIUS SERVER
Weakest No Security WPA
WPA-PSK
Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA2
For example, if the wireless network has a RADIUS server, you can choose WPA/WPA2 or WPA2. If users do
not log in to the wireless network, you can choose None, WPA-PSK, or WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK.
Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every wireless client in the wireless network
supports. For example, suppose the AP does not have a local user database, and you do not have a
RADIUS server. Therefore, there is no user authentication. Suppose the wireless network has two wireless
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
66
Page 67

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
clients. Device A only supports WEP, and device B supports WEP and WPA. Therefore, you should set up
Static WEP in the wireless network.
Note: It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK, WPA, or stronger encryption.
IEEE 802.1x and WEP encryption are better than none at all, but it is still possible for
unauthorized devices to figure out the original information pretty quickly.
Note: It is not possible to use WPA-PSK, WPA or stronger encryption with a local user database.
In this case, it is better to set up stronger encryption with no authentication than to set
up weaker encryption with the local user database.
When you select WPA2 or WPA2-PSK in your LTE, you can also select an option (WPA/WPA-PSK
Compatible) to support WPA/WPA-PSK as well. In this case, if some wireless clients support WPA and
some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK or WPA2 (depending on the type of wireless network
login) and select the WPA/WPA-PSK Compatible option in the LTE.
Many types of encryption use a key to protect the information in the wireless network. The longer the
key, the stronger the encryption. Every wireless client in the wireless network must have the same key.
WPS
WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) is an industry standard specification, defined by the WiFi Alliance. WPS
allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to configure security
settings manually. Depending on the devices in your network, you can either press a button (on the
device itself, or in its configuration utility) or enter a PIN (Personal Identification Number) in the devices.
Then, they connect and set up a secure network by themselves. See how to set up a secure wireless
network using WPS in the Section 4.2 on page 32.
8.2 General Wireless LAN Settings
Use this screen to configure the SSID and wireless security of the wireless LAN.
Note: If you are configuring the LTE from a computer connected to the wireless LAN and you
change the LTE’s SSID, channel or security settings, you will lose your wireless connection
when you press Apply to confirm. You must then change the wireless settings of your
computer to match the LTE’s new settings.
Click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN to open the General screen.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Figure 29 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General
The following table describes the general wireless LAN labels in this screen.
Table 18 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Setup - 2.4G / Wireless Setup - 5G
Wireless LAN Status Select Enable to activate the 2.4G/5G wireless LAN. Select Disable to turn it off.
You can also enable or disable the 2.4G/5G wireless LANs by using the WLAN/WPS button
located on the side panel of the LTE.
Name (SSID) The SSID (Service Set IDentity) identifies the Service Set with which a wireless client is
associated. Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable characters found on a typical English
language keyboard) for the wireless LAN.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
68
Page 69

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Table 18 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Hide SSID Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a station cannot
obtain the SSID through scanning using a site survey tool.
Channel Selection Set the operating frequency/channel depending on your particular region.
Select a channel from the drop-down list box. The options vary depending on the frequency
band and the country you are in.
Refer to the Connection Wizard chapter for more information on channels. This option is only
available if Auto Channel Selection is disabled.
Auto Channel
Selection
Operating
Channel
Channel Width Select the wireless channel width used by LTE.
802.11 Mode In Wireless Setup for 2.4G network you can select from the following:
Select this check box for the LTE to automatically choose the channel with the least
interference. De-select this check box if you wish to manually select the channel using the
Channel Selection field.
This displays the operating frequency/channel depending on your particular region.
A standard 20 MHz channel(HT20) offers transfer speeds of up to 144 Mbps (2.4G) or 217 Mbps
(5G) whereas a 40 MHz channel(HT40) uses two standard channels and offers speeds of up to
300 Mbps (2.4G) or 450 Mbps (5G). An IEEE 802.11ac-specific 80 MHz channel (HT80) offers
speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps.
Because not all devices support 40 MHz and/or 80 MHz channels, select Auto to allow the LTE
to adjust the channel bandwidth automatically.
HT40 (channel bonding or dual channel) bonds two adjacent radio channels to increase
throughput. A HT80 channel consists of two adjacent 40 MHz channels. The wireless clients
must also support HT40 or HT80. It is often better to use the 20 MHz setting in a location where
the environment hinders the wireless signal.
Select HT20 if you want to lessen radio interference with other wireless devices in your
neighborhood or the wireless clients do not support channel bonding.
• 802.11b Only: allows either IEEE 802.11b compliant WLAN devices to associate with the LTE.
In this mode, all wireless devices can only transmit at the data rates supported by IEEE
802.11b.
• 802.11g Only: allows IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN devices to associate with the Device.
IEEE 802.11b compliant WLAN devices can associate with the LTE only when they use the
short preamble type.
• 802.11n Only: allows IEEE 802.11n compliant WLAN devices to associate with the LTE. This
can increase transmission rates, although IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g clients will not be
able to connect to the LTE.
• 802.11b/g Mixed: allows either IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN devices to
associate with the LTE. The LTE adjusts the transmission rate automatically according to the
wireless standard supported by the wireless devices.
• 802.11g/n Mixed: allows either IEEE 802.11g or IEEE 802.11n compliant WLAN devices to
associate with the LTE. The transmission rate of your LTE might be reduced.
• 802.11b/g/n Mixed: allows IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11g and IEEE802.11n compliant WLAN
devices to associate with the LTE. The transmission rate of your LTE might be reduced.
In Wireless Setup for 5G network you can select from the following:
• 802.11a Only: allows only IEEE 802.11a compliant WLAN devices to associate with the LTE.
• 802.11n Only: allows IEEE 802.11n compliant WLAN devices to associate with the LTE. This
can increase transmission rates, although IEEE 802.11a clients will not be able to connect
to the LTE.
• 802.11a/n Mixed: allows both IEEE802.11n and IEEE802.11a compliant WLAN devices to
associate with the LTE. The transmission rate of your LTE might be reduced.
• 802.11a/n/ac Mixed: allows both IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.11n and IEEE802.11ac compliant
WLAN devices to associate with the LTE. The transmission rate of your LTE might be
reduced.
Security - 2.4G / Security - 5G
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Table 18 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Select WPA2-PSK, WPA2, WPA/WPA2, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK to add security on this wireless
network. The wireless clients which want to associate to this network must have same wireless
security settings as this device. After you select to use a security, additional options appears in
this screen. See Section 8.3 on page 70 for detailed information on different security modes.
Or you can select Open to allow any client to associate this network without authentication.
Note: If the WPS function is enabled (default), only Open and WPA2-PSK are
available in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
See the rest of this chapter for information on the other labels in this screen.
8.3 Wireless Security
The screen varies depending on what you select in the Security Mode field.
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
8.3.1 No Security
Select Open to allow wireless clients to communicate with the access points without any data
encryption.
Note: If you do not enable any wireless security on your LTE, your network is accessible to any
wireless networking device that is within range.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
70
Page 71

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Figure 30 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General: No Security
8.3.2 WPA2-PSK
Select WPA2-PSK from the Security Mode list.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Figure 31 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA2-PSK
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Select WPA2-PSK to enable data encryption.
Encryption Select the encryption type of data encryption.
Select AES if your wireless clients can all use AES.
Select TKIP / AES to allow the wireless clients to use either TKIP or AES.
Pre-Shared Key WPA2-PSK uses a simple common password for authentication.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive keyboard characters.
Group Key Update
Timer
The Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP sends a new group key out to all
clients.
The default is 3600 seconds (60 minutes).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
72
Page 73

Table 19 Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA2-PSK (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
8.3.3 WPA/WPA2
Select WPA or WPA2 from the Security Mode list.
Note: WPA or WPA2 is not available if you enable WPS before you configure WPA or WPA2 in
the Wireless LAN > General screen.
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Figure 32 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA / WPA2
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA / WPA2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Select WPA or WPA2 to enable data encryption.
RADIUS Server
RADIUS Server IP
RADIUS Server Port
RADIUS Shared Key
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server to be used for authentication.
Enter the port number of the RADIUS server to be used for authentication.
Enter the shared secret password of the RADIUS server to be used for authentication.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
74
Page 75

Table 20 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > General: WPA / WPA2 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Encryption Select the encryption type of data encryption.
Group Key Update
Time
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
8.4 More AP
This screen allows you to enable and configure multiple wireless networks and guest wireless network
settings on the LTE.
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Select AES if your wireless clients can all use AES.
Select TKIP / AES to allow the wireless clients to use either TKIP or AES.
The WPA Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP (if using WPA-PSK key
management) or RADIUS server (if using WPA key management) sends a new group key
out to all clients. The re-keying process is the WPA equivalent of automatically changing
the WEP key for an AP and all stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis. Setting of the WPA
Group Key Update Timer is also supported in WPA-PSK mode. The default setting is 3600
seconds (60 minutes).
You can configure up to four SSIDs to enable multiple BSSs (Basic Service Sets) on the LTE. This allows you
to use one access point to provide several BSSs simultaneously. You can then assign varying security
types to different SSIDs. Wireless clients can use different SSIDs to associate with the same access point.
Click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP. The following screen displays.
Figure 33 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of each SSID profile.
Status This shows whether the SSID profile is active (a yellow bulb) or not (a gray bulb).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Table 21 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SSID An SSID profile is the set of parameters relating to one of the LTE’s BSSs. The SSID (Service Set
Security This field indicates the security mode of the SSID profile.
Edit Click the Edit icon to configure the SSID profile.
8.4.1 More AP Edit
Use this screen to edit an SSID profile. Click the Edit icon next to an SSID in the More AP screen. The
following screen displays.
Figure 34 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP: Edit
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
IDentifier) identifies the Service Set with which a wireless device is associated.
This field displays the name of the wireless profile on the network. When a wireless client scans
for an AP to associate with, this is the name that is broadcast and seen in the wireless client
utility.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select this to activate the SSID profile.
Name (SSID) The SSID (Service Set IDentity) identifies the Service Set with which a wireless client is associated.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable characters found on a typical English language
keyboard) for the wireless LAN.
Hide SSID Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a station cannot obtain
the SSID through scanning using a site survey tool.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
76
Page 77

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Table 22 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > More AP: Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Intra-BSS Traffic A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients or between a
wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point (AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When Intra-BSS is enabled, wireless
clients can access the wired network and communicate with each other. When Intra-BSS is
disabled, wireless clients can still access the wired network but cannot communicate with each
other.
WMM QoS Check this to have the LTE automatically give a service a priority level according to the ToS
value in the IP header of packets it sends.
WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of Service) gives high priority to voice and video, which
makes them run more smoothly.
Security Mode Select WPA2-PSK, WPA/WPA2 to add security on this wireless network. The wireless clients which
want to associate to this network must have same wireless security settings as this device. After
you select to use a security, additional options appears in this screen. See Section 8.3 on page
70 for detailed information on different security modes. Or you can select Open to allow any
client to associate this network without authentication.
Note: If the WPS function is enabled (default), only Open and WPA2-PSK are
available in this field.
Encryption Select the encryption type of data encryption.
Select AES if your wireless clients can all use AES.
Pre-Shared Key Type a password the wireless stations need to enter to connect to the wireless network.
Group Key
Update Timer
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
8.5 MAC Filter
The MAC filter screen allows you to configure the LTE to give exclusive access to devices (Allow) or
exclude devices from accessing the LTE (Deny). Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media
Access Control) address. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of
hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC address of the
devices to configure this screen.
To change your LTE’s MAC filter settings, click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter. The
screen appears as shown.
Select TKIP / AES to allow the wireless clients to use either TKIP or AES.
The WPA Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP (if using WPA-PSK key
management) or RADIUS server (if using WPA key management) sends a new group key out to
all clients. The re-keying process is the WPA equivalent of automatically changing the WEP key
for an AP and all stations in a WLAN on a periodic basis. Setting of the WPA Group Key Update
Timer is also supported in WPA-PSK mode. The default setting is 3600 seconds (60 minutes).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Figure 35 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
The following table describes the labels in this menu.
Table 23 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Address
Filter
Filter Action Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the MAC Filter Summary table.
MAC Filter Summary
Set This is the index number of the MAC address.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the wireless station that are allowed or denied access to the LTE.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select to turn on (Enable) or off (Disable) MAC address filtering.
Select Allow to permit access to the LTE, MAC addresses not listed will be denied access to the
LTE.
Select Deny to block access to the LTE, MAC addresses not listed will be allowed to access the
LTE.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
78
Page 79

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
8.6 Wireless LAN Advanced Settings
Use this screen to allow wireless advanced features, such as the output power, RTS/CTS Threshold
settings.
Click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 36 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Advanced Setup - 2.4G / Wireless Advanced Setup - 5G
RTS/CTS Threshold Data with its frame size larger than this value will perform the RTS (Request To Send)/ CTS
Fragmentation
Threshold
Intra-BSS Traffic A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients or between
(Clear To Send) handshake.
This field is not configurable and the LTE automatically changes to use the maximum value if
you select 802.11n, 802.11gn or 802.11bgn in the Wireless LAN > General screen.
The threshold (number of bytes) for the fragmentation boundary for directed messages. It is
the maximum data fragment size that can be sent.
This field is not configurable and the LTE automatically changes to use the maximum value if
you select 802.11n, 802.11gn or 802.11bgn in the Wireless LAN > General screen.
a wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point (AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When Intra-BSS is enabled, wireless
clients can access the wired network and communicate with each other. When Intra-BSS is
disabled, wireless clients can still access the wired network but cannot communicate with
each other.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Table 24 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Green AP Select Enable to reduce the power consumption by adjusting the output power. The LTE
reduces the output power of the transmitter from about 260mA to 188mA when there is no
IEEE 802.11 wireless clients associated with the LTE wireless network.
Tx Power Set the output power of the LTE in this field. If there is a high density of APs in an area,
Beacon Interval When a wirelessly networked device sends a beacon, it includes with it a beacon interval. This
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
decrease the output power of the LTE to reduce interference with other APs. Select one of
the following 100%, 90%, 75%, 50%, 25% or 10%.
specifies the time period before the device sends the beacon again. The interval tells
receiving devices on the network how long they can wait in low-power mode before waking
up to handle the beacon. A high value helps save current consumption of the access point.
8.7 Quality of Service (QoS)
The QoS screen allows you to automatically give a service (such as VoIP and video) a priority level.
Click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > QoS. The following screen appears.
Figure 37 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > QoS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WMM QoS (2.4G) Select Enable to have the LTE automatically give a service a priority level according to
the ToS value in the IP header of packets it sends. WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of
Service) gives high priority to voice and video, which makes them run more smoothly.
This field is not configurable and the LTE automatically enables WMM QoS if you select
802.11n, 802.11g/n Mixed, or 802.11b/g/n Mixed in the Wireless LAN > General screen.
WMM QoS (5G) Select Enable to have the LTE automatically give a service a priority level according to
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
the ToS value in the IP header of packets it sends. WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of
Service) gives high priority to voice and video, which makes them run more smoothly.
This field is not configurable and the LTE automatically enables WMM QoS if you select
802.11n, 802.11a/n Mixed, or 802.11a/n/ac Mixed in the Wireless LAN > General screen.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
80
Page 81

8.8 WPS
Use this screen to enable/disable WPS, view or generate a new PIN number and check current WPS
status. To open this screen, click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS.
Note: With WPS, wireless clients can only connect to the wireless network using the first SSID on
Figure 38 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
the LTE.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPS Setup 2.4G / 5G
WPS Select Enable to turn on the WPS feature. Otherwise, select Disable.
PIN Code Select Enable so the LTE can connect by WPS using the PIN Configuration Method. Select
Disable so it can only connect by WPS using the Push Button Method.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Table 26 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PIN Number This is the WPS PIN (Personal Identification Number) of the LTE. Enter this PIN in the
configuration utility of the device you want to connect to the LTE using WPS.
The PIN is not necessary when you use WPS push-button method.
Click Generate to generate a new PIN number.
WPS Status - 2.4G / WPS Status - 5G
Status This displays Configured when the LTE has configured wireless security settings.
802.11 Mode This is the 802.11 mode used. Only compliant WLAN devices can associate with the LTE.
SSID This is the name of the wireless network (the LTE’s first SSID).
Security This is the type of wireless security employed by the network.
Release
Configuration
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Click this button to remove all configured wireless and wireless security settings for WPS
connections on the LTE.
8.9 WPS Station
Use this screen when you want to add a wireless station using WPS. To open this screen, click
Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station tab.
Note: After you click Push Button on this screen, you have to press a similar button in the
wireless station utility within 2 minutes. To add the second wireless station, you have to
press these buttons on both device and the wireless station again after the first 2
minutes.
Figure 39 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
82
Page 83

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPS Station Setup - 2.4G / WPS Station Setup - 5G
Push Button Use this button when you use the PBC (Push Button Configuration) method to configure
Or input station’s PIN
number
8.10 Scheduling
Use this screen to set the times your wireless LAN is turned on and off. Wireless LAN scheduling is disabled
by default. The wireless LAN can be scheduled to turn on or off on certain days and at certain times. To
open this screen, click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Scheduling tab.
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
wireless station’s wireless settings.
Click this to start WPS-aware wireless station scanning and the wireless security information
synchronization.
Use this button when you use the PIN Configuration method to configure wireless station’s
wireless settings.
Type the same PIN number generated in the wireless station’s utility. Then click Start to
associate to each other and perform the wireless security information synchronization.
Figure 40 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Scheduling
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Scheduling
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless LAN
Scheduling
Policy Select On or Off to specify whether the wireless LAN is turned on or off. This field works in
Select Enable to activate the wireless LAN scheduling feature. Select Disable to turn it off.
conjunction with the Day and For the following times fields.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Table 28 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > Scheduling (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Scheduling
Day Select Everyday or the specific days to turn the wireless LAN on or off. If you select Everyday
For the following
times (24-Hour
Format)
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
8.11 WDS
A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a wireless connection between two or more APs. Use this screen to
configure the LTE’s WDS settings. To open this screen, click Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WDS
tab.
Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
you cannot select any specific days. This field works in conjunction with the For the following
times field.
Select a begin time using the first set of hour and minute (min) drop down boxes and select
an end time using the second set of hour and minute (min) drop down boxes. If you have
chosen On earlier for the WLAN Status the wireless LAN will turn on between the two times
you enter in these fields. If you have chosen Off earlier for the WLAN Status the wireless LAN
will turn off between the two times you enter in these fields.
Figure 41 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WDS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WDS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WDS Setup - 2.4G / WDS Setup - 5G
Basic Setting Select Disable to turn off the WDS function on the LTE.
Select AP+Bridge to have the LTE function as a bridge and access point simultaneously.
Select Bridge Only to have the LTE act as a wireless bridge only.
Local MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the LTE.
Remote MAC
Address
Type the MAC address of the peer device in a valid MAC address format, that is, six
hexadecimal character pairs, for example, 12:34:56:78:9a:bc.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
84
Page 85

Chapter 8 Wireless LAN
Table 29 Configuration > Network > Wireless LAN > WDS (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
85
Page 86

9.1 Overview
LTE
This chapter describes how to configure LAN settings.
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a shared communication system to which many computers are
attached. A LAN is a computer network limited to the immediate area, usually the same building or floor
of a building.
Figure 42 LAN Example
CHAPTER 9
LAN
The LAN screens can help you configure a manage IP address, and partition your physical network into
logical networks.
9.2 What You Can Do
Use the IP screen to change the IP address for your LTE (Section 9.4 on page 87).
9.3 What You Need To Know
The actual physical connection determines whether the LTE ports are LAN or WAN ports. There are two
separate IP networks, one inside the LAN network and the other outside the WAN network as shown
next.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
86
Page 87

Chapter 9 LAN
Figure 43 LAN and WAN IP Addresses
The LAN parameters of the LTE are preset in the factory with the following values:
• IP address of 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (24 bits).
• DHCP server enabled with 32 client IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.33.
These parameters should work for the majority of installations. If your ISP gives you explicit DNS server
address(es), read the embedded Web Configurator help regarding what fields need to be configured.
9.4 LAN IP
Use this screen to change the IP address for your LTE. Click Configuration > Network > LAN > IP.
Figure 44 Configuration > Network > LAN > IP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 Configuration > Network > LAN > IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address Type the IP address of your LTE in dotted decimal notation.
IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your LTE will
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP address that you assign. Unless
you are implementing subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the LTE.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
87
Page 88

10.1 Overview
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual clients to obtain
TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can configure the LTE’s LAN as a DHCP server or
disable it. When configured as a server, the LTE provides the TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If DHCP
service is disabled, you must have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the computer must be
manually configured.
10.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the General screen to enable the DHCP server (Section 10.2 on page 88).
• Use the Advanced screen to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual computers based
on their MAC addresses (Section 10.3 on page 90).
• Use the Client List screen to view the current DHCP client information (Section 10.4 on page 92).
CHAPTER 10
DHCP Server
10.1.2 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
MAC Addresses
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address. The MAC address is assigned
at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. Find
out the MAC addresses of your network devices if you intend to add them to the DHCP Client List screen.
IP Pool Setup
The LTE is pre-configured with a pool of 32 IP addresses starting from 192.168.1.33 to 192.168.1.64. This
configuration leaves 31 IP addresses (excluding the LTE itself) in the lower range (192.168.1.2 to
192.168.1.32) for other server computers, for instance, servers for mail, FTP, TFTP, web, etc., that you may
have.
10.2 DHCP Server General Settings
The LTE has built-in DHCP server capability that assigns IP addresses to systems that support DHCP client
capability. Use this screen to enable the DHCP server. Click Configuration > Network > DHCP Server. The
following screen displays.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
88
Page 89

Chapter 10 DHCP Server
Figure 45 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 31 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DHCP Server Select Enable to activate DHCP for LAN.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual
clients (computers) to obtain TCP/IP configuration at startup from a server. Enable the
DHCP server unless your ISP instructs you to do otherwise. Select Disable to stop the LTE
acting as a DHCP server. When configured as a server, the LTE provides TCP/IP
configuration for the clients. If not, DHCP service is disabled and you must have another
DHCP server on your LAN, or else the computers must be manually configured. When set
as a server, fill in the following four fields.
IP Pool Starting Address This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool for LAN.
Pool Size This field specifies the size, or count of the IP address pool for LAN.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 10 DHCP Server
Table 31 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DHCP Relay Select this option to have the LTE forward DHCP requests to the DHCP server.
DHCP Server IP This field is configurable only when you select DHCP Relay.
Enter the IP address of the actual remote DHCP server in this field.
Lease Time This is the period of time DHCP-assigned addresses is used. DHCP automatically assigns IP
VLAN DHCP x Server
This section is configurable only when you create a corresponding VLAN group in the Interface Group screen.
DHCP Server Select Enable to activate DHCP for the VLAN group.
DHCP Server IP Address Enter the LAN IP address you want to assign to your LTE in this VLAN group.
IP Pool Starting Address Specify the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool for LAN.
Pool Size Specify the size, or count of the IP address pool for LAN.
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
addresses to clients when they log in. DHCP centralizes IP address management on
central computers that run the DHCP server program. DHCP leases addresses, for a
period of time, which means that past addresses are “recycled” and made available for
future reassignment to other systems.
Specify the IP addresses up to two DNS servers for the DHCP clients to use.
Select Obtained From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the
LTE's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP address
that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server's IP
address in the field to the right.
Select DNS Relay to have the LTE act as a DNS proxy. The LTE's LAN IP address displays in
the field to the right (read-only). The LTE tells the DHCP clients on the LAN that the LTE itself
is the DNS server. When a computer on the LAN sends a DNS query to the LTE, the LTE
forwards the query to the LTE's system DNS server (configured in the WAN screen) and
relays the response back to the computer.
10.3 Advanced DHCP Server Setting
This screen allows you to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual computers based on their
MAC addresses. You can also use this screen to configure the DNS server information that the LTE sends
to the DHCP clients.
To change your LTE’s static DHCP settings, click Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > Advanced. The
following screen displays.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
90
Page 91

Chapter 10 DHCP Server
Figure 46 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > Advanced
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 32 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static DHCP Table
# This is the index number of the static IP table entry (row).
MAC Address Type the MAC address (with colons) of a computer on your LAN.
IP Address Type the LAN IP address of a computer on your LAN.
DNS Server
DNS Servers
Assigned by DHCP
Server
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
The LTE passes a DNS (Domain Name System) server IP address (in the order you specify
here) to the DHCP clients. The LTE only passes this information to the LAN DHCP clients when
you enable DHCP Server in the General screen. When you disable DHCP Server, DHCP
service is disabled and you must have another DHCP sever on your LAN, or else the
computers must have their DNS server addresses manually configured.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server's IP
address in the field to the right.
Select DNS Relay to have the LTE act as a DNS proxy. The LTE's LAN IP address displays in the
field to the right (read-only). The LTE tells the DHCP clients on the LAN that the LTE itself is the
DNS server. When a computer on the LAN sends a DNS query to the LTE, the LTE forwards the
query to the LTE's system DNS server (configured in the WAN screen) and relays the response
back to the computer.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
91
Page 92

10.4 DHCP Client List
The DHCP table shows current DHCP client information (including IP address, Host Name and MAC
address) of network clients using the LTE’s DHCP servers.
Configure this screen to always assign an IP address to a MAC address (and host name). Click
Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > Client List.
Note: You can also view a read-only client list by clicking Monitor > DHCP Server.
Figure 47 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > Client List
Chapter 10 DHCP Server
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 33 Configuration > Network > DHCP Server > Client List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of the host computer.
Status This field displays whether the connection to the host computer is up (a yellow bulb) or down (a
gray bulb).
Host Name This field displays the computer host name.
IP Address This field displays the IP address relative to the # field listed above.
MAC Address This field shows the MAC address of the computer with the name in the Host Name field.
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address which uniquely
identifies a device. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of
hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
Reserve Select this if you want to reserve the IP address for this specific MAC address.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
92
Page 93

11.1 Overview
LTE
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP address of a host in a
packet. For example, the source address of an outgoing packet, used within one network is changed to
a different IP address known within another network.
The figure below is a simple illustration of a NAT network. You want to assign ports 21-25 to one FTP, Telnet
and SMTP server (A in the example), port 80 to another (B in the example) and assign a default server IP
address of 192.168.1.35 to a third (C in the example).
You assign the LAN IP addresses to the devices (A to D) connected to your LTE. The ISP assigns the WAN
IP address. The NAT network appears as a single host on the Internet. All traffic coming from A to D going
out to the Internet use the IP address of the LTE, which is 192.168.1.1.
Figure 48 NAT Example
CHAPTER 11
NAT
Note: You must create a firewall rule in addition to setting up NAT, to allow traffic from the
WAN to be forwarded through the LTE.
11.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the General screen to enable NAT (Section 11.2 on page 94).
• Use the Port Forwarding screen to set a default server and change your LTE’s port forwarding settings
to forward incoming service requests to the servers on your local network (Section 11.3 on page 94).
• Use the Port Trigger screen to change your LTE’s trigger port settings (Section 11.4 on page 98).
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
93
Page 94

• Use the ALG screen to enable or disable SIP (VoIP) ALG (Application Layer Gateway) in the LTE
(Section 11.5 on page 99).
11.2 General Settings
Use this screen to enable NAT and set a default server. Click Configuration > Network > NAT to open the
General screen.
Figure 49 Configuration > Network > NAT > General
Chapter 11 NAT
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 34 Configuration > Network > NAT > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network Address
Translation (NAT)
NAT Loopback NAT loopback allows local users to use a domain name to access a server on the local
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows the translation of an Internet protocol address
used within one network (for example a private IP address used in a local network) to a
different IP address known within another network (for example a public IP address used on
the Internet).
Select Enable to activate NAT. Select Disable to turn it off.
network. A packet sent to the public (WAN) IP address is always forwarded to the default
gateway (the LTE). With NAT loopback enabled, the LTE uses the WAN interface’s IP address
as the packet’s source address and treats the packet as if it came from the WAN interface.
The packet then can be forwarded to the local server according to the port forwarding rule.
Select Enable to activate NAT loopback. Select Disable to turn it off.
11.3 Port Forwarding
Use this screen to forward incoming service requests to the servers on your local network and set a
default server. You may enter a single port number or a range of port numbers to be forwarded, and the
local IP address of the desired server. The port number identifies a service; for example, web service is on
port 80 and FTP on port 21. In some cases, such as for unknown services or where one server can support
more than one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might be better to specify a range of
port numbers.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
94
Page 95

Chapter 11 NAT
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A service request that does
not have a server explicitly designated for it is forwarded to the default server. If the default is not
defined, the service request is simply discarded.
Note: Many residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server processes
(such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may periodically check for
servers and may suspend your account if it discovers any active services at your
location. If you are unsure, refer to your ISP.
Port forwarding allows you to define the local servers to which the incoming services will be forwarded.
To change your LTE’s port forwarding settings, click Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Forwarding. The
screen appears as shown.
Note: If you do not assign a Default Server, the LTE discards all packets received for ports that
are not specified in this screen or remote management.
Refer to Appendix B on page 178 for port numbers commonly used for particular services.
Figure 50 Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Forwarding
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 11 NAT
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 35 Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Forwarding
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Service Name Select a pre-defined service from the drop-down list box. The pre-defined service port
Service Protocol Select the transport layer protocol supported by this virtual server. Choices are TCP, UDP, or
WAN Interface Select the WAN interface on which the matched packets are received.
Port Range Specify the first and last external port numbers that identify the service.
Translation Port
Range
Server IP Address Enter the inside IP address of the virtual server here and click Add to add it in the port
# This is the number of an individual port forwarding server entry.
Status This icon is turned on when the rule is enabled.
Name This field displays a name to identify this rule.
Protocol This is the transport layer protocol used for the service.
WAN Interface This field displays the WAN interface on which the matched packets are received.
Port This field displays the port numbers.
Translation Port This field displays the internal port numbers that identifies the service.
Server IP Address This field displays the inside IP address of the server.
Modify Click the Edit icon to open the edit screen where you can modify an existing rule.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
numbers and protocol will be displayed in the port forwarding summary table.
Otherwise, select User define to manually enter the service name and port numbers and
select the IP protocol.
TCP_UDP.
If you have chosen a pre-defined service in the Service Name field, the protocol will be
configured automatically.
If you have chosen a pre-defined service in the Service Name field, the port numbers will be
configured automatically.
Specify the first and last internal port numbers that identify the service.
If you have chosen a pre-defined service in the Service Name field, the port numbers will be
configured automatically.
forwarding summary table.
Click the Delete icon to remove a rule.
11.3.1 Edit Port Forwarding
This screen lets you edit a port forwarding rule. Click a rule’s Edit icon in the Port Forwarding screen to
open the following screen.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
96
Page 97

Chapter 11 NAT
Figure 51 Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Forwarding Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 36 Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Forwarding Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Forwarding Select Enable to turn on this rule and the requested service can be forwarded to the host with
a specified internal IP address.
Select Disable to disallow forwarding of these ports to an inside server without having to delete
the entry.
Service Name Select User define and type a name (of up to 31 printable characters) to identify this rule in the
first field next to Service Name. Otherwise, select a predefined service in the second field next
to Service Name. The predefined service name and port numbers will display in the Service
Name and Port Range fields.
Service Protocol Select the transport layer protocol supported by this virtual server. Choices are TCP, UDP, or
TCP_UDP.
If you have chosen a pre-defined service in the Service Name field, the protocol will be
configured automatically.
WAN Interface Select the WAN interface on which the matched packets are received.
Port Range Type a port numbers to define the service to be forwarded to the specified server.
To specify a range of ports, enter the first number and the last number of the range.
Translation Port
Range
Server IP Address Type the IP address of the server on your LAN that receives packets from the ports specified in
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Enter a port number to which you want the incoming ports translated.
For a range of ports, enter the first number and the last number of the range.
the Port Range field.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
97
Page 98

11.4 Port Trigger
To change your LTE’s trigger port settings, click Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Trigger. The screen
appears as shown.
Note: Only one LAN computer can use a trigger port (range) at a time.
Figure 52 Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Trigger
Chapter 11 NAT
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 37 Configuration > Network > NAT > Port Trigger
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the rule index number (read-only).
Name Type a unique name (up to 15 characters) for identification purposes. All characters are
WAN Interface Select the WAN interface through which the matched packets are transmitted.
Incoming Port Incoming Port is a port (or a range of ports) that a server on the WAN uses when it sends out a
Start Port Type a port number or the starting port number in a range of port numbers.
End Port Type a port number or the ending port number in a range of port numbers.
Trigger Port The trigger port is a port that causes (or triggers) the LTE to record the IP address of the LAN
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
permitted - including spaces.
particular service. The LTE forwards the traffic with this port (or range of ports) to the client
computer on the LAN that requested the service.
computer that sent the traffic to a server on the WAN.
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
98
Page 99

11.5 ALG
Some NAT routers may include a SIP Application Layer Gateway (ALG). A SIP ALG allows SIP calls to pass
through NAT by examining and translating IP addresses embedded in the data stream. When the LTE
registers with the SIP register server, the SIP ALG translates the LTE’s private IP address inside the SIP data
stream to a public IP address. You do not need to use STUN or an outbound proxy if your LTE is behind a
SIP ALG.
To enable and disable the SIP ALG in the LTE, click Configuration > Network > NAT > ALG. The screen
appears as shown.
Figure 53 Configuration > Network > NAT > ALG
Chapter 11 NAT
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 38 Configuration > Network > NAT > ALG
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ALG-SIP Select Enable to make sure SIP (VoIP) works correctly with port-forwarding and address-
mapping rules. Otherwise, select Disable to turn off the SIP ALG.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the LTE.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
11.6 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the LTE features described in this
chapter.
11.6.1 NAT Port Forwarding: Services and Port Numbers
A port forwarding set is a list of inside (behind NAT on the LAN) servers, for example, web or FTP, that you
can make accessible to the outside world even though NAT makes your whole inside network appear
as a single machine to the outside world.
Use the Port Forwarding screen to forward incoming service requests to the servers on your local
network. You may enter a single port number or a range of port numbers to be forwarded, and the local
IP address of the desired server. The port number identifies a service; for example, web service is on port
80 and FTP on port 21. In some cases, such as for unknown services or where one server can support
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 11 NAT
more than one service (for example both FTP and web service), it might be better to specify a range of
port numbers.
In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A service request that does
not have a server explicitly designated for it is forwarded to the default server. If the default is not
defined, the service request is simply discarded.
Note: Many residential broadband ISP accounts do not allow you to run any server processes
(such as a Web or FTP server) from your location. Your ISP may periodically check for
servers and may suspend your account if it discovers any active services at your
location. If you are unsure, refer to your ISP.
11.6.2 NAT Port Forwarding Example
Let's say you want to assign ports 21-25 to one FTP, Telnet and SMTP server (A in the example), port 80 to
another (B in the example) and assign a default server IP address of 192.168.1.35 to a third (C in the
example). You assign the LAN IP addresses and the ISP assigns the WAN IP address. The NAT network
appears as a single host on the Internet.
Figure 54 Multiple Servers Behind NAT Example
11.6.3 Trigger Port Forwarding
Some services use a dedicated range of ports on the client side and a dedicated range of ports on the
server side. With regular port forwarding you set a forwarding port in NAT to forward a service (coming in
from the server on the WAN) to the IP address of a computer on the client side (LAN). The problem is that
port forwarding only forwards a service to a single LAN IP address. In order to use the same service on a
different LAN computer, you have to manually replace the LAN computer's IP address in the forwarding
port with another LAN computer's IP address.
Trigger port forwarding solves this problem by allowing computers on the LAN to dynamically take turns
using the service. The LTE records the IP address of a LAN computer that sends traffic to the WAN to
request a service with a specific port number and protocol (a "trigger" port). When the LTE's WAN port
receives a response with a specific port number and protocol ("incoming" port), the LTE forwards the
traffic to the LAN IP address of the computer that sent the request. After that computer’s connection for
that service closes, another computer on the LAN can use the service in the same manner. This way you
LTE3316-M604 User’s Guide
100
 Loading...
Loading...