Page 1

1
0 °
查询Z86319供应商
FEATURES
ROM
Device
Z86319 2 125 13 4.5V to 5.5V
Note: *General-Purpose (144K Total RAM)
C to + 40 ° C Operating Temperature Range
■
■
Low-Power Consumption: 25 mW (Typical)
(KB)
RAM*
(Bytes)
I/O
Lines
Voltage
Range
P
RELIMINARY
P
RODUCT
S
PECIFICATION
Z86319
PS/2 M
■
■
■
■
■
OUSE
P24-P27 Can Be Configured with a Voltage Divider
During Input Mode
On-Chip Oscillator (Tolerance = ± 10%)
Fast Instruction Pointer: 1.5 µ s @ 4 MHz
ESD Protection Circuitry
Hardwired Watch-Dog Timer (WDT)
ONTROLLER
C
1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Z86319 is a member of the Z8 family of CMOS microcontrollers architecture to be used in mouse applications.
These devices offer on-board pull-up and pull-down resistors, a trip-point buffer to accommodate opto-transistor
outputs, and high drive ports capable of up to 10 mA current sinking per pin (3 pins maximum).
A permanently enabled Watch-Dog Timer ensures operational reliability across a broad range of mouse application
environments. The precision RC oscillator filters out highfrequency noise from the oscillator input pin. When configured as inputs, P24-P27 have built in voltage dividers (25K
pull-up /7.5K pull-down). The input levels are designed for
connection to the emitters of the opto-transistors and
switch at a voltage level of 0.4 V
DD
.
■
Excellent System Level EMI/EFT/ESD
For applications requiring powerful I/O capabilities, the
Z86319 provides dedicated input and output lines that are
grouped into three ports. There are two basic address
spaces available to support this configuration: Program
Memory, and 125 bytes of general-purpose registers.
The Z86319 device provides two on-chip 8-bit programmable counter/timers with a large number of user-selectable
modes. Each counter/timer is driven by its own 6-bit programmable prescaler. The Z86319 counter/timers off-load
system real-time tasks such as counting/timing and input/output data communications for increased system efficiency.
DS97KEY1605
P R E L I M I N A R Y
1
Page 2
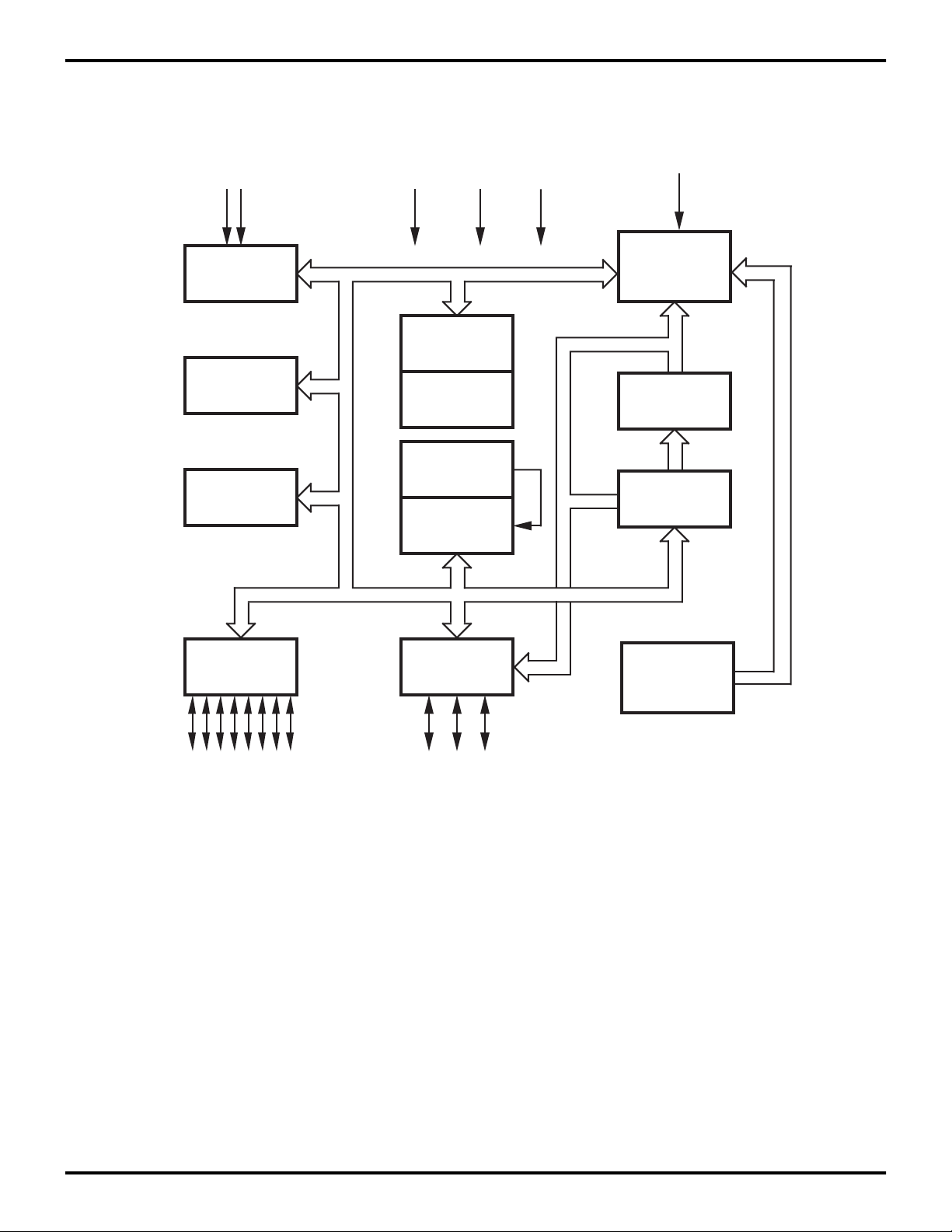
2
Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
GENERAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Input
Port 3
Counter/
Timers (2)
Interrupt
Control
VDD
ALU
FLAG
Register
Pointer
Register File
144 x 8-Bit
GND
AGND
RCIN
Machine
Timing & Inst.
Control
Prg. Memory
2048 x 8-Bit
Program
Counter
Port 2
I/O
(Bit Programmable)
Port 0
I/O
Figure 1. Z86319 Functional Block Diagram
WDT
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS97KEY1605
Page 3

1
Z86319
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
P24
P25
P26
P27
VDD
RCIN
AGND
P31
GND
Figure 2. 18-Pin DIP/SOIC Pin Configuration
Table 1. 18-Pin DIP/SOIC Pin Identification
Pin # Symbol Function Direction
1-4 P24-P27 Port 2, Pins 4,5,6,7 In/Output
5V
6 RCIN RC Oscillator Input
7 AGND Analog Ground Ground
8 P31 Port 3, Pin 1 Input
9 GND Ground Input
10 P33 Port 3, Pin 3, Input
11-13 P00-P02 Port 0, Pins 0,1,2 In/Output
14 GND Ground Ground
15-18 P20-P23 Port 2, Pins 0,1,2,3 In/Output
DD
1
18 - Pin
DIP/SOIC
910
Power Supply Power
18
P23
P22
P21
P20
GND
P02
P01
P00
P33
DS97KEY1605
P R E L I M I N A R Y
3
Page 4
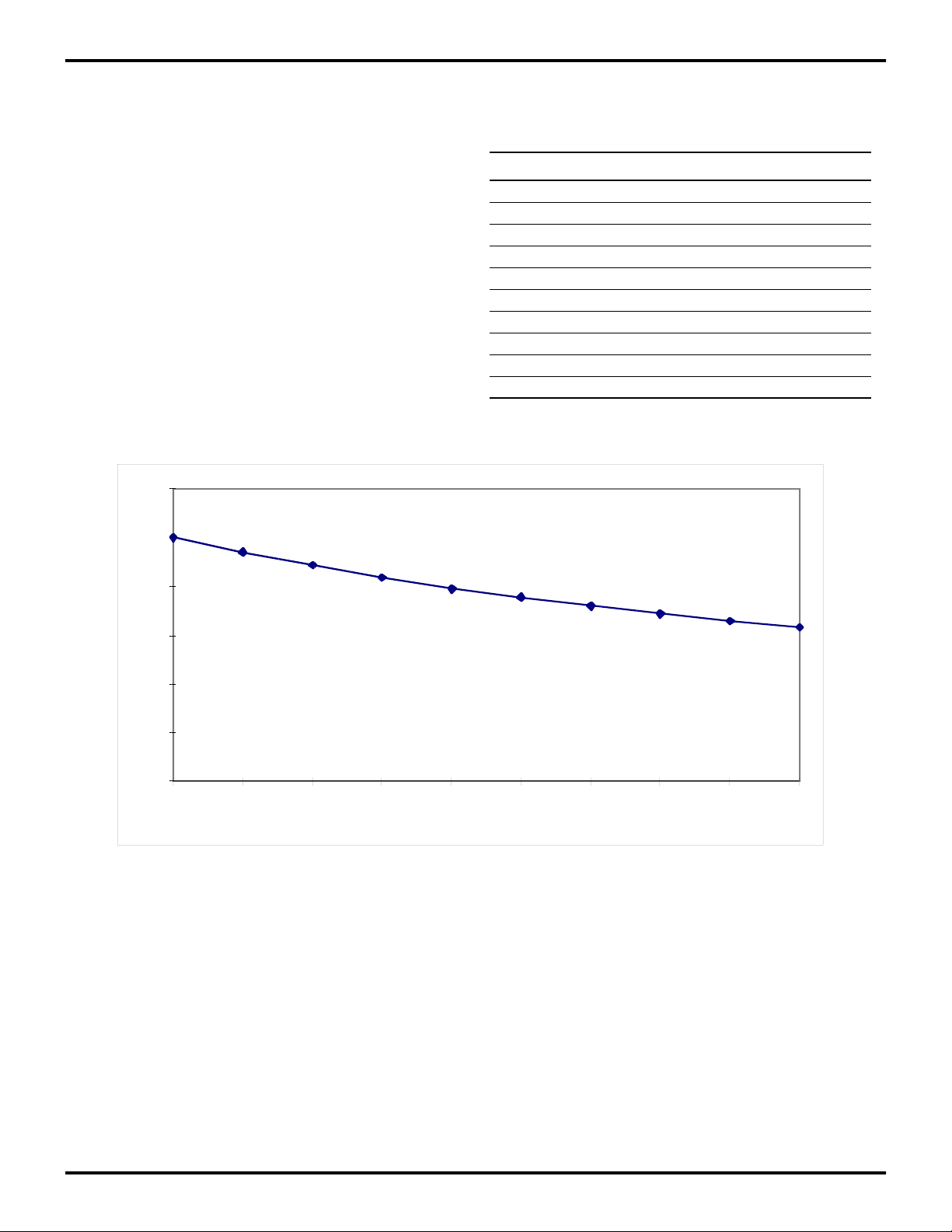
4
Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
PIN FUNCTIONS
RCIN. A precision 1% resistor is connected to RCIN,
generating oscillation with an internal capacitor.
Resistor values and corresponding typical frequencies are
shown in Table 2 and graph chart (Figure 3).
6
5
Table 2. Resistor Values and Corresponding
Typical Frequencies
External Resistor Average Frequency
14.0K 5.01 MHz
15.0K 4.70 MHz
16.0K 4.43 MHz
17.0K 4.19 MHz
18.0K 3.97 MHz
19.0K 3.78 MHz
20.0K 3.60 MHz
21.0K 3.44 MHz
22.0K 3.30 MHz
23.0K 3.16 MHz
4
3
2
FREQUENCY (MHz)
1
0
14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
RESISTOR VALUE (K OHMS)
Figure 3. Z86319 RC Frequency in Function of the External Resistance
(typical numbers)
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS97KEY1605
Page 5
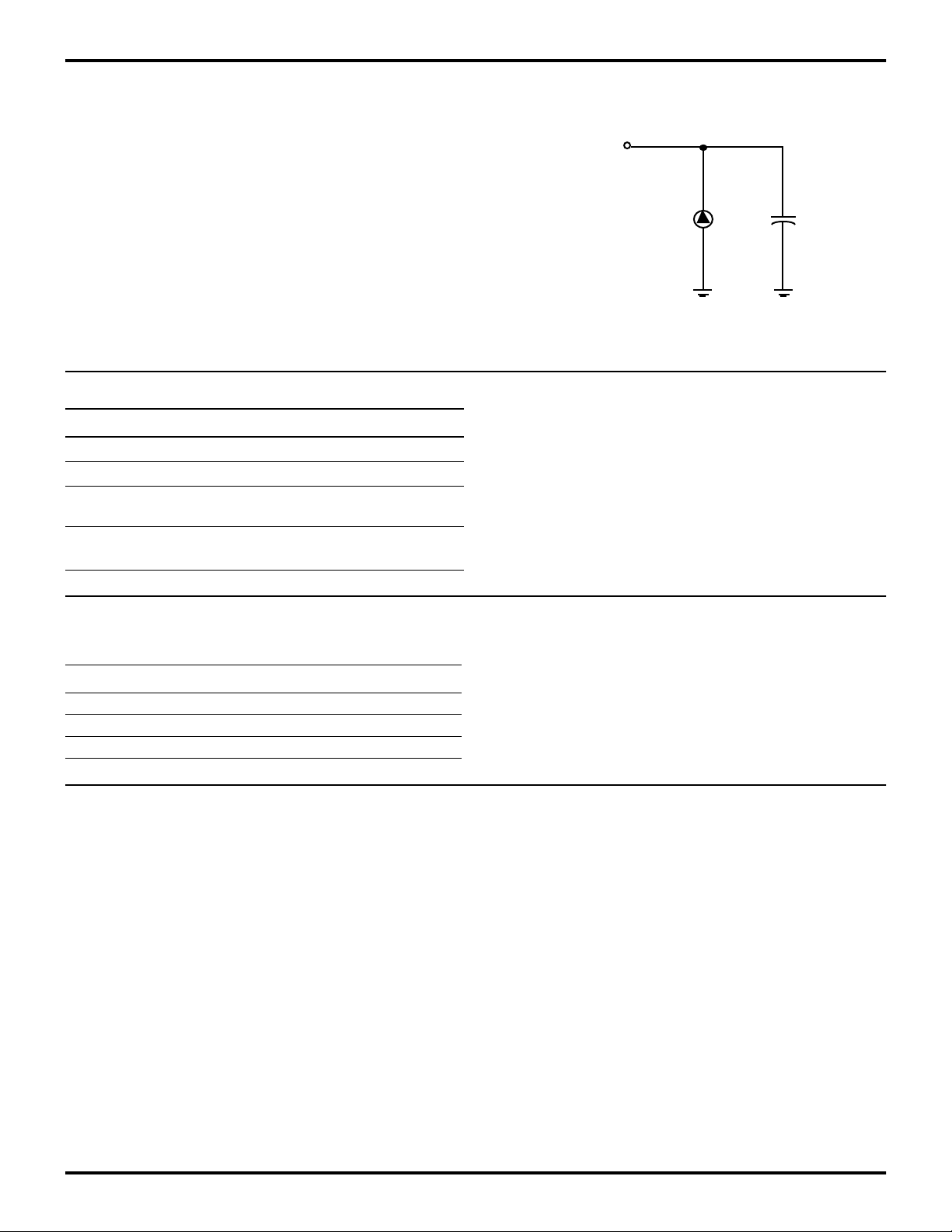
1
t
t
40 °
Z86319
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
STANDARD TEST CONDITIONS
The characteristics listed below apply for standard test
conditions as noted. All voltages are referenced to
Ground. Positive current flows into the referenced pin
(Figure 4).
From Outpu
Under Tes
150 pFI
Figure 4. Test Load Diagram
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Sym Parameter Min Max Units
V
T
STG
T
A
Notes:
*Voltages on all pins with respect to Ground.
Supply V oltage* –0.3 +7 V
DD
Storage Temp –65 °
Oper Ambient
Temp
0 °
+150 °
C
C
Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device.
This rating is a stress rating only; operation of the device
at any condition above those indicated in the operational
sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
CAPACITANCE
T
= GND = 0V, f = 1.0 MHz, unmeasured pins returned to Ground.
A
Parameter Min Max
Input Capacitance 0 10 pF
Output Capacitance 0 20 pF
I/O Capacitance 0 25 pF
V
SPECIFICATION
CC
V
= 4.5V to 5.5V
CC
Using the precision RC oscillator feature, f = 4.0 MHz ± 10% under the following conditions:
■
V
= 5.0V ± 10%
CC
Temp 0 to 40 ° C
■
■
Application board capacitance:
– 2.0 pF max.
– 0.5 pF min.
DS97KEY1605
P R E L I M I N A R Y
5
Page 6

6
≤
Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
4.5V ≥ V
Sym Parameter Min Max Units Conditions
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL1
V
OL2
V
LV
V
TP
I
IL
I
OL
I
DD
I
DD1
I
PU
I
PD
I
PU
5.5V
DD
T
= 0 ° C to +40 ° C
A
Rising Input
2.3 3.2 V Note 1
Schmitt-Triggered
Falling Input
1.3 2.2 V Note 1
Schmitt-Triggered
Input Low Voltage CMOS Input V
Output High Voltage V
Output Low Voltage 0.4 V I
Output Low Voltage 0.8 V I
V
Low Voltage Protection 2.25 2.95 V @ 4 MHz Max, Note 2
CC
Trip Point Voltage
(P24-P27)
Input Leakage –1.0 1.0
– 0.4 V I
DD
= –2.0 mA;
OH
V
=4.5V
DD
= +4.0 mA;
OL
V
=5.5V
DD
= 10.0 mA,
OL
3 Pin Max; V
1.9 2.5 V P24-P27; V
1.5 2.1 V V
AV
=4.5V
DD
= 0V, or V
IN
DD
DD
=5.5V
CC
Note 4
Output Leakage –1.0 1.0 µAVIN = 0V, or V
CC
Note 4
Supply Current 4.5 mA @ 4 MHz, Note 3;
VDD=5.5V
Standby Current 2.2 mA @ 4 MHz, Note 3;
VDD=5.5V
Pull-Up Current (100K) –20 µAVIH @ 1V
P00-02, P31, P33 –95 µAVIH @ 1V
Pull-Down Current (100K) +20 µAVIL @ 3V
P00-02, P31, P33 +85 µAVIL @ 4V
Pull-Up Current (10K) –370 µAVIL = 0V
P20, P22 –670 µAVIL = 0V
=5.5V
µ
Notes:
1. The min. and max. values of the Schmitt-Trigger input voltages track each other over temperature, V
process variations.
2. The device is functional from V
voltage at ambient temperature. The VLV voltage increases as the temperature decreases.
3. All input pins are tied to GND and all output pins are floating.
down to VLV voltage. The minimum operational VDD is determined by the value of the V
DD
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DD
, and
LV
DS97KEY1605
Page 7
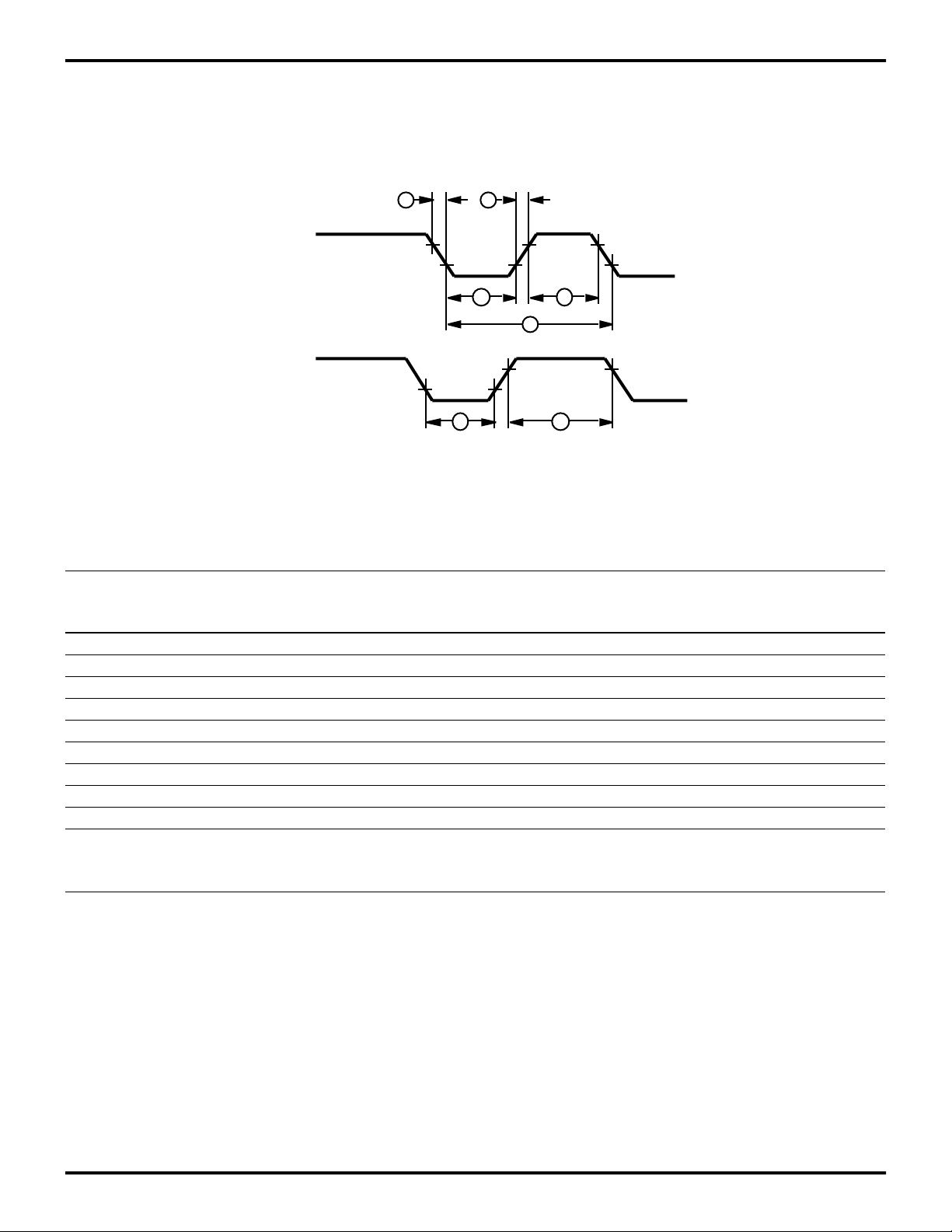
Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Timing Diagrams
1 1
T
IN
IRQ
2
N
5
3
4
6
Figure 5. Electrical Timing Diagram
TA = 0°C to +40°C
No Symbol Parameter
V
DD
Min Max Units Notes
1 TrTin, TtTin Timer Input Rise and Fall Time 5.5V 100 ns 1
2 TwTinL Timer Input Low Width 5.5V 70 ns 1
3 TwTinH Timer Input High Width 5.5V 2.5TpC 1
4 TpTin Timer Input Period 5.5V 4TpC 1
5 TwIL Int. Request Input Low Time 5.5V 70 ns 1,2
6 TwIH Int. Request Input High Time 5.5V 2.5TpC 1,2
Twdt Watch-Dog Timer Time Out 5.5V 10 ms
TPOR Power-On Reset Time 5.5V 2 10 ms
TpC RC Oscillator Clock Period 5.5V 220 5000 ns
Notes:
1. Timing Reference uses 0.9 V
2. Interrupt request through Port 3 (P33-P31)
for a logic 1 and 0.1 VDD for a logic 0.
DD
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 7
Page 8

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
PIN FUNCTIONS
Port 0 (P02-P00). Port 0 is a 3-bit, I/O programmable, bi-
directional, CMOS-compatible I/O port. These three I/O
lines can be configured under software control to be input
or output (Figure6). When Port 0 is configured as an input
port, all lines have the capability to either sink or source
(ROM mask selectable) current emulating a 100K pull-
OE
down or pull-up resistor. Port 00-02 can be accessed
through the P0 register (register address 00). The upper 5
bits of this 8-bit register always reads “11111.” Writing to
the upper 5 bits has no effect (see Figure 34). The lower 3
bits of the P0 register are read/write. Current versus pin
voltage graphs are shown in Figures 7 and 8.
Pull-Up Enable
(Mask Option)
Pad
Out
In
Pull-Down / Enable
(Mask Option)
Figure 6. Port 0 Configuration
8 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 9

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
vdrain
Figure 7. Current vs Pin Voltage Values
Figure 8. Current vs Pin Voltage Values
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 9
Page 10

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
Port 2 (P27-P20). Port 2 is an 8-bit, bit programmable, bi-
directional, CMOS-compatible I/O port. These eight I/O
lines can be configured under software control to be input
or output, independently. Bits programmed as outputs
may be globally programmed as either push-pull or opendrain. When configured as inputs, P20 and P22 have 10
kOhm (typical) pull-up resistors (Figure 9). However, P21
and P23 do not have resistors (Figure 10).
Open-Drain
OE
When configured as inputs, P24-P27 are configured with a
voltage divider. The voltage divider consists of an internal
25K pull-up resistor (Figure 11), and a 7.5K pull-down resistor. The input levels on P24-P27 are adjusted for connection to the emitters of the opto-transistors and switch at
a voltage level of 0.4 V
(± 300 mV). For input voltages
DD
on P24-P27, refer to Table 3.
Table 3. P24-P27 Input Open Circuit Voltage
(No off-chip resistance)
V
DD
Min Max
4.5V 0.95V 1.15V
5.0V 1.05V 1.25V
5.5V 1.15V 1.39V
V
DD
10 Kohm, ±20%
Out
In
Pad
Figure 9. Port 2 P20, P22 Configuration
10 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 11

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
VDD
Open-Drain
OE
Pad
Out
In
Figure 10. Port 2 P21, P23 Configuration
Open-Drain
OE
Out
In
Resistance T olerance (0-40°C)
Min. Max.
Pull-Down
Pull-Up
5.2K 8.9K
18K 30K
25K
7.5K
Pad
0.4 VDD ± 300 mV
Trip Point Buffer
Figure 11. Port 2 P27-P24 Configuration
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 11
Page 12

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
Port 3 (P33, P31). Port 3 is a 2-bit, CMOS-compatible
port with two fixed input lines (P33, P31). These two lines
can also be used as the interrupt sources IRQ2 and IRQ1.
P31 can also be configured as a timer input. Both lines can
be configured through ROM mask selection to sink or
source current emulating a 100K pull-up or pull-down re-
Pad
P31
Pull-Down/Enable
(Mask Option)
sistor (Figure 12). Port 33-31 can be accessed through
the P3 register. The upper 4 bits of this 8-bit register always reads “1111.” Bit D2 reads 0 and Bit D0 reads 1. Bits
D3 and D1 represent P33 and P31 respectively (see Figure 36).
Pull-Up Enable
(Mask Option)
Data Latch
IRQ2, TIN
Pad
Pull-Up Enable
(Mask Option)
Data Latch
IRQ1
P33
Pull-Down/Enable
(Mask Option)
Figure 12. Port 3 P33, P31 Configuration
12 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 13

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The Z86319 MCU incorporates the following special features to enhance the Z8 architectural core for use in mice,
trackballs, and other consumer applications.
POR
(Cold Start)
Figure 13. Internal Reset Configuration
Addr. Reg. D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 Comments
F1 TMR 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
F2 T1 U U U U U U U U
F3 PRE1 U U U U U U 0 0
F4 T0 U U U U U U U U
F5 PRE0 U U U U U U U 0
F6 P2M 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Inputs after reset
F7 P3M U U U U U U 1 0
F8 P01M U U U 0 U U 0 1
F9 IPR U U U U U U U U
FA IRQ U U 0 0 0 0 0 0
FB IMR 0 U U U U U U U
FC FLAGS U U U U U U U U
FD RP U U U U U U U U
FF SPL U U U U U U U U
Delay
TPOR
Table 4. Z86319 Control Registers
Reset Values
Reset. Upon power-up, the Power-On Reset circuit waits
for TPOR, plus 18 clock cycles, then starts program execution at address 000CH (Figure 13). The Z86319 control
registers' reset values are shown in Table 4.
RC OSC
18 CLK
Reset Filter
Chip
Reset
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 13
Page 14

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Program Memory. The Z86319 can address up to 2 KB
of internal program memory (Figure 14). The first 12 bytes
of program memory are reserved for the interrupt vectors.
These locations contain four 16-bit vectors that correspond to the four available interrupts. Bytes 0-2047 are
on-chip mask-programmed ROM.
2047
Location of
First Byte of
Instruction
Executed
After RESET
Interrupt
Vector
(Lower Byte)
Interrupt
Vector
(Upper Byte)
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
On-Chip
ROM
IRQ5
IRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ4
Reserved
Reserved
IRQ2
IRQ2
IRQ1
IRQ1
Reserved
Reserved
Register File. The Register File consists of three I/O
port registers, 125 general-purpose registers, and 14 control and status registers, R0-R3, R4-R127 and R241R255, respectively (Figure 15). The Z86319 instructions
can access registers directly or indirectly via an 8-bit address field. This field allows short, 4-bit register addressing
using the Register Pointer. In the 4-bit mode, the register
file is divided into eight working register groups, each occupying 16 continuous locations. The Register Pointer addresses the starting location of the active working-register
group.
LOCATION IDENTIFIERS
R255
R254
R253
R252
R251
R250
R249
R248
R247
R246
R245
R244
R243
R242
R241
R240
Stack Pointer (Bits 7-0)
General-Purpose
Register Pointer
Program Control Flags
Interrupt Mask Register
Interrupt Request Register
Interrupt Priority Register
Ports 0-1 Mode
Port 3 Mode
Port 2 Mode
T0 Prescaler
Timer/Counter0
T1 Prescaler
Timer/Counter1
Timer Mode
SPL
GPR
RP
FLAGS
IMR
IRQ
IPR
P01M
P3M
P2M
PRE0
T0
PRE1
T1
TMR
Not Implemented
Figure 14. Program Memory Map
R128
R127
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
General-Purpose
Registers
Port 3
Port 2
Reserved
Port 0
P3
P2
P0
Figure 15. Register File
14 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 15

Z86319
1
e
e
k
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
Stack Pointer. The Z86319 features an 8-bit Stack
Pointer (R255) used for the internal stack that resides within the general-purpose registers.
Counter/Timer. There are two 8-bit programmable
counter/timers (T0 and T1), each driven by its own 6-bit
programmable prescaler. The T1 prescaler can be driven
by internal or external clock sources, however, the T0 can
be driven by the internal clock source only (Figure 16).
The 6-bit prescalers can divide the input frequency of the
clock source by any integer number from 1 to 64. Each
prescaler drives its counter, which decrements the value
(1 to 256) that has been loaded into the counter. When
both counter and prescaler reach the end of count, a timer
interrupt request IRQ4 (T0) or IRQ5 (T1) is generated.
Write Write Read
PRE0
Initial Value
Register
OSC
The counter can be programmed to start, stop, continue,
or restart from the initial value. The counters can also be
programmed to stop upon reaching zero (single pass
mode) or to automatically reload the initial value and continue counting (modulo-n continuous mode).
The counters, but not the prescalers, are read at any time
without disturbing their value or count mode. The clock
source for T1 is user-definable and can be either the internal microprocessor clock divided by four, or an external
signal input via Port 3. The Timer Mode register configures
the external timer input (P31) as an external clock, a trigger
input that is retriggerable or not retriggerable, or as a gate
input for the internal clock.
Internal Data Bus
T0
Initial Value
Register
T0
Current Valu
Register
Clock
Logic
T P31
IN
Internal
Clock
External Clock
÷4
Internal Clock
Gated Clock
Triggered Cloc
÷4
Write
6-Bit
Down
Counter
6-Bit
Down
Counter
PRE1
Initial Value
Register
Write
8-Bit
Down
Counter
8-Bit
Down
Counter
T1
Initial Value
Register
Internal Data Bus
Figure 16. Counter/Timers Block Diagram
IRQ4
IRQ5
T1
Current Valu
Register
Read
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 15
Page 16

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Interrupts. The Z86319 features four interrupts from
four different sources. These interrupts are maskable and
prioritized (Figure 17). The four sources are divided as follows: the falling edge of P31, P33, and the two
counter/timers. The Interrupt Mask Register globally or individually enables or disables the four interrupt requests
(Table 5).
When more than one interrupt is pending, priorities are resolved by a programmable priority encoder that is controlled by the Interrupt Priority register. All Z86319 interrupts are vectored through locations in program memory.
When an interrupt machine cycle is activated, an interrupt
request is granted, thereby disabling all subsequent interrupts, saving the Program Counter and Status Flags, and
branching to the program memory vector location reserved
for that interrupt. This memory location and the next byte
contain the 16-bit starting address of the Interrupt Service
Routine for that particular interrupt request.
To accommodate polled interrupt systems, interrupt inputs
are masked and the Interrupt Request Register is polled to
determine which of the interrupt requests requires service.
Table 5. Interrupt Types, Sources, and Vectors
Source Name Vector Location Comments
P33 IRQ1 2,3 External Falling Edge
P31 IRQ2 4,5 External Falling Edge
T0 IRQ4 8,9 Internal
T1 IRQ5 10,11 Internal
IRQ1 - IRQ5
IRQ
Interrupt
Request
IMR
Global
Interrupt
Enable
IPR
Priority
Logic
Vector Select
Figure 17. Interrupt Block Diagram
6
16 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 17

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
RC Oscillator. The Z86319 features an on-chip RC pre-
cision oscillator that requires a 1% precision resistor externally connected between VDD and pin 6 (Figure 18). The
tolerance of the RC oscillator is less than ±10% over the
voltage range of 4.5V to 5.5V and over a temperature
range of 0-40°C. Pin 7 is the Analog Ground for the oscillator.
Increased parasitic board capacitance will slow down the
RC oscillator and deteriorate the RC frequency tolerance.
The minimum and maximum parasitic board capacitances
are 0.5 pF and 2 pF, respectively.
VDD
1%
6
RCIN
7
AGND
Precision
RC Oscillator
Figure 18. Oscillator Configuration
HALT Mode. This instruction turns off the internal CPU
clock but not the precision RC oscillator. The counter/timers, their interrupts, and external interrupts IRQ1 and IRQ2
remain active. The device can be recovered by interrupts,
either externally or internally generated. An interrupt must
be enabled prior to the HALT Mode, and executed to exit
the HALT Mode. After the interrupt service routine, the
program continues from the instruction after the HALT.
In HALT Mode, the value of each output line prior to the
HALT instruction is retained.
Watch-Dog Timer (WDT). The Watch-Dog Timer is enabled upon power-up of the MCU and is clocked by its own
internal RC oscillator. The WDT instruction does not affect
the Zero (Z), Sign (S), and Overflow (V) flags.
Opcode WDT (5FH). Execution of WDT clears the WDT
counter. The time interval between any 2 consecutive
WDT instructions has to be smaller than T
WDT
min.
Low Voltage Protection (VLV). The device will function normally between 5.5V and 4.5V under all specified
conditions. Below 4.5V, the device is still internally functional until the Low Voltage trip point (V
) is reached,
LV
however, it is not guaranteed to meet all AC and DC Characteristics. When the supply voltage drops below VLV, an
automatic hardware reset occurs as VDD returns above
VLV. Essentially, this action helps in reinitializing the
Z86319.
The actual VLV is a function of temperature, operating frequency and process parameters. The typical VLV is a
function of the ambient temperature for a frequency of 4
MHz. The device is functional down to VLV voltage. The
min. operational VDD is determined by the value of the V
LV
voltage at ambient temperatures. The VLV voltage increases as the temperature decreases (Figure 19).
In order to enter HALT Mode, it is necessary to first flush
the instruction pipeline to avoid suspending execution in
mid-instruction. To flush the pipeline, the user must execute a NOP (Opcode=FFH) immediately before the HALT
instruction. i.e.:
FF NOP ; clear the pipeline
7F HALT ; enter the HALT Mode
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 17
Page 18

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
2.85
2.80
2.75
2.70
2.65
Volts
2.60
VLV (Typical)
2.55
2.50
2.45
2.40
2.35
–5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Temperature (°C)
Figure 19. Typical Z86319 VLV vs Temperature
18 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 19

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
Z8 CONTROL REGISTERS
R241 TMR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 20. Timer Mode Register
(F1H: Read/Write)
R242 T1
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
0 No Function
1 Load T0
0 Disable T0 Count
1 Enable T0 Count
0 No Function
1 Load T1
0 Disable T1 Count
1 Enable T1 Count
TIN Modes
00 External Clock Input
01 Gate Input
10 Trigger Input
(Non-retriggerable)
11 Trigger Input
(Retriggerable)
Reserved (Must be 0)
T1 Initial Value
(When Written)
(Range 1-256 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
T1 Current Value
(When READ)
R244 T0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 23. Counter/Timer 0 Register
(F4H: Read/Write)
R245 PRE0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 24. Prescaler 0 Register
(F5H: Write Only)
R246 P2M
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
T0 Initial Value
(When Written)
(Range: 1-256 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
T0 Current Value
(When READ)
Count Mode
0 T0 Single Pass
1 T0 Modulo N
Reserved (Must be 0)
Prescaler Modulo
(Range: 1-64 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
Figure 21. Counter Timer 1 Register
(F2H: Read/Write)
243 PRE1
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 22. Prescaler 1 Register
(F3H: Write Only)
Count Mode
0 T1 Single Pass
1 T1 Modulo
Clock Source
1 T1 Internal
0 T1 External Timing Input
(TIN) Mode
Prescaler Modulo
(Range: 1-64 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
Figure 25. Port 2 Mode Register
(F6H: Write Only)
R247 P3M
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 26. Port 3 Mode Register
(F7H: Write Only)
P27- P20 I/O Definition
0 Defines Bit as OUTPUT
1 Defines Bit as INPUT
0 Port 2 Open-Drain
1 Port 2 Push-Pull
Reserved (Must be 0)
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 19
Page 20

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
Z8 CONTROL REGISTERS (Continued)
R248 P01M
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 27. Port 0 and 1 Mode Register
(F8H: Write Only)
R249 IPR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reserved
(Must be 0.)
Figure 28. Interrupt Priority Register
(F9H: Write Only)
R250 IRQ
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
P00-P03 Mode
0 Output
1 Input
Reserved (Must be 0)
Don’t care
Reserved (Must be 0)
0000
Reserved
0001
IRQ1>4>5>2
0010
Reserved
0011
IRQ4>1>5>2
0100
IRQ5>2>1>4
0101
IRQ5>1>4>2
0110
IRQ5>2>4>1
0111
IRQ5>4>1>2
1000
IRQ2>1>4>5
1001
IRQ1>4>2>5
1010
IRQ2>4>1>5
1011
IRQ4>1>2>5
1100
IRQ2>5>1>4
1101
Reserved
1110
IRQ2>5>4>1
1111
Reserved
R251 IMR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 Enables IRQ
(DX = IRQX)
Reserved (Must be 0)
1 Enable Interrupts
Figure 30. Interrupt Mask Register
(FBH: Read/Write)
R252 Flags
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
User Flag F1
User Flag F2
Half Carry Flag
Decimal Adjust Flag
Overflow Flag
Sign Flag
Zero Flag
Carry Flag
Figure 31. Flag Register
(FCH: Read/Write)
R253 RP
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reserved (Must be 0)
Don't Care
Register Pointer
IRQ1 = P33 Input
IRQ2 = P31 Input
Reserved (Must be 0)
IRQ4 = T0
IRQ5 = T1
Reserved (Must be 0)
R255 SPL
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 32. Register Pointer
(FDH: Read/Write)
Figure 29. Interrupt Request Register
(FAH: Read/Write)
Stack Pointer Lower
Byte (SP0-SP7)
Figure 33. Stack Pointer
(FFH: Read/Write)
20 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 21

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
Z8 PORT REGISTERS
R0 Port 0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
P00
P01
P02
Reads as “11111”
Writing has NO
EFFECT
Figure 34. Port 0 Register (Read/Write)
R0 Port 2
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
P27
P26 P25
P24 P23 P22 P21 P20
Figure 35. Port 2 Register (Read/Write)
R3 Port 3
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reads 1
P31
Reads 0
P33
Reads 1111
Figure 36. Port 3 Register (Read Only)
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 21
Page 22

Z86319
PS/2 Mouse Controller Zilog
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Figure 37. 18-Pin DIP Package Diagram
Figure 38. 18-Pin SOIC Package Diagram
22 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS97KEY1605
Page 23

Z86319
1
Zilog PS/2 Mouse Controller
ORDERING INFORMATION
Z86319
Z8631904PSC Z8631904SSC
For fast results, contact your local Zilog sales offices for assistance in ordering the part required.
CODES
Package
P = DIP
S = SOIC
Temperature
S = 0°C to +40°C
Example:
Z 86319 0 4 P S C is a Z86319, 4 MHz, DIP, 0° to +40°C, Plastic Standard Flow
Environmental Flow
Temperature
Package
Speed
Product Number
Zilog Prefix
© 1998 by Zilog, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by
any means without the prior written consent of Zilog, Inc.
The information in this document is subject to change
without notice. Devices sold by Zilog, Inc. are covered by
warranty and patent indemnification provisions appearing
in Zilog, Inc. Terms and Conditions of Sale only.
ZILOG, INC. MAKES NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS,
STATUTORY, IMPLIED OR BY DESCRIPTION,
REGARDING THE INFORMATION SET FORTH HEREIN
OR REGARDING THE FREEDOM OF THE DESCRIBED
DEVICES FROM INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
INFRINGEMENT. ZILOG, INC. MAKES NO WARRANTY
OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY
PURPOSE.
Speed
04 = 4 MHz
Environmental
C = Plastic Standard
Zilog, Inc. shall not be responsible for any errors that may
appear in this document. Zilog, Inc. makes no commitment
to update or keep current the information contained in this
document.
Zilog’s products are not authorized for use as critical
components in life support devices or systems unless a
specific written agreement pertaining to such intended use
is executed between the customer and Zilog prior to use.
Life support devices or systems are those which are
intended for surgical implantation into the body, or which
sustains life whose failure to perform, when properly used
in accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in
significant injury to the user.
Zilog, Inc. 210 East Hacienda Ave.
Campbell, CA 95008-6600
Telephone (408) 370-8000
FAX 408 370-8056
Internet: http://www.zilog.com
DS97KEY1605 P R E L I M I N A R Y 23
 Loading...
Loading...