Page 1

Page 2

Copyright
Copyright © 2020 YEALINK(XIAMEN) NETWORK TECHNOLOGY
Copyright © 2020 Yealink (Xiamen) Network Technology CO., LTD. All rights reserved. No parts of this publication may
be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, for any purpose, without the express written permission of Yealink (Xiamen) Network Technology CO., LTD.
Under the law, reproducing includes translating into another language or format.
When this publication is made available on media, Yealink (Xiamen) Network Technology CO., LTD. gives its consent to
downloading and printing copies of the content provided in this file only for private use but not for redistribution. No
parts of this publication may be subject to alteration, modification or commercial use. Yealink (Xiamen) Network Technology CO., LTD. will not be liable for any damages arising from use of an illegally modified or altered publication.
Trademarks
Yealink®, the logo and the name and marks is trademark of Yealink (Xiamen) Network Technology CO., LTD, which are
registered legally in China, the United States, EU (European Union) and other countries.
All other trademarks belong to their respective owners. Without Yealink’s express written permission, recipient shall not
reproduce or transmit any portion hereof in any form or by any means, with any purpose other than personal use.
End User License Agreement
This End User License Agreement ("EULA") is a legal agreement between you and Yealink. By installing, copying or otherwise using the Products, you: (1) agree to be bounded by the terms of this EULA, (2) you are the owner or an authorized user of the device, and (3) you represent and warrant that you have the right, authority and capacity to enter into
this agreement and to abide by all its terms and conditions, just as if you had signed it. The EULA for this product is
available on the Yealink Support page for the product.
Patent Information
China, the United States, EU (European Union) and other countries are protecting one or more patents of accompanying products and/or patents being applied by Yealink.
Customer Feedback
We are striving to improve our documentation quality and we appreciate your feedback. Email your opinions and comments to DocsFeedback@yealink.com.
Technical Support
Visit Yealink WIKI (http://support.yealink.com/) for the latest firmware, guides, FAQ, Product documents, and more.
For better service, we sincerely recommend that you use Yealink Ticketing system (https://ticket.yealink.com) to submit
all your technical issues.
Page 3

GNU GPL INFORMATION
Yealink device firmware contains third-party software under the GNU General Public License (GPL). Yealink uses software under the specific terms of the GPL. Please refer to the GPL for the exact terms and conditions of the license.
The original GPL license, source code of components licensed under GPL and used in Yealink products can be downloaded online: http://www.yealink.com/onepage_83.html.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System Introduction
Components of the DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Deployments of the DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Related Documentations
First Steps
Preparing to Use the Multi-Cell System
Defining the Device Role
LED Indicators on the W80DM/W80B
Configuring the System via Web User Interface
Accessing Web User Interface
Navigating the Web User Interface
Logging out of the Web User Interface
Initialization Instructions
Initialization Process Overview
Loading the ROM File
Configuring the VLAN
Querying the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server
Contacting the Provisioning Server
Updating Firmware
Downloading the Resource Files
Verifying Startup
1
12
12
13
13
15
15
15
16
17
17
18
18
19
19
19
19
19
19
20
20
20
Setting up the Base Stations
Base Station Pre-registration
Base Station Pre-registration Configuration
Manually Registering Base Stations to the DM
DM IP
DM IP Configuration
Base Station Settings
Base Station Settings Configuration
Managing the Connected Base Stations
Base Station Synchronization
Synchronization Planning
Managing the Handsets
Registering Handsets via Web User Interface
IPUI Registration
Obtaining the IPUI Code of the Handset
Notes on Configuring IPUI
IPUI Code Configuration
21
21
21
22
22
22
23
23
24
25
26
27
27
27
27
28
28
1
Page 5

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Handset Registration Center
Registering Handsets Time-Controlled
Registering Handsets at Once
Manually Closing the Registration
De-registering a Handset
Account Settings
Account Registration
Supported Accounts
SIP Server Template Configuration
Accounts Registration Configuration
Registration Settings Configuration
Outbound Proxy in Dialog
Outbound Proxy in Dialog Configuration
Server Redundancy
Behaviors When Working Server Connection Fails
Registration Method of the Failover/Fallback Mode
Fallback Server Redundancy Configuration
Failover Server Redundancy Configuration
SIP Server Name Resolution
SIP Server Name Resolution Configuration
Static DNS Cache
Behave with a Configured DNS Server
Static DNS Cache Configuration
Number of Simultaneous Outgoing Calls
Number of Simultaneous Outgoing Calls Configuration
Number of Active Handsets Per Base
Number of Active Handsets Per Base Configuration
28
29
29
29
30
31
31
31
31
33
35
37
37
38
39
40
40
40
42
42
43
44
44
47
47
48
48
Network Configurations
IPv4 Network Settings
IPv4 Configuration
DHCP Option for IPv4
Supported DHCP Option for IPv4
DHCP Option 66, Option 43 and Custom Option
DHCP Option 42 Option 2
DHCP Option 12
DHCP Option 12 Hostname Configuration
DHCP Option 60
DHCP Option 60 Configuration
VLAN
LLDP Configuration
CDP Configuration
Manual VLAN Configuration
DHCP VLAN Configuration
VLAN Change Configuration
49
49
49
51
51
51
52
52
52
52
53
53
53
54
54
55
56
2
Page 6

Table of Contents
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) Ports
RTP Ports Configuration
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT Traversal Configuration
Keep Alive Configuration
Rport Configuration
SIP Port and TLS Port Configuration
VPN
OpenVPN Related Files
VPN Configuration
Quality of Service (QoS)
Voice and SIP QoS Configuration
TR-069 Device Management
Supported RPC Methods
TR-069 Configuration
802.1x Authentication
802.1x Authentication Configuration
Web Statistics
Base Station Group
Base Station Statistics
Cluster Graph Statistics
Viewing Base Station Group Statistics
All Calls
All Calls Statistics
Viewing All Calls Statistics
Base Stations Calls
Base Stations Calls Statistics
Viewing Base Stations Calls Statistics
Handsets Calls
Handsets Calls Statistics
Viewing Handsets Calls Statistics
Abnormal Calls
Abnormal Calls Statistics
Viewing Abnormal Calls Statistics
Upgrade Information
Upgrade Information Statistics
Viewing Upgrade Information Statistics
DECT Signal
DECT Signal Statistics
Viewing DECT Signal Statistics
56
56
57
57
60
61
61
62
62
62
63
63
64
64
65
66
66
69
69
69
70
71
72
73
73
74
74
75
75
75
76
77
77
77
78
78
79
80
80
80
Phone Provisioning
Boot Files, Configuration Files, and Resource Files
Boot Files
Common Boot File
82
82
82
82
3
Page 7

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
MAC-Oriented Boot File
Boot File Attributes
Customizing a Boot File
Configuration Files
Common CFG File
MAC-Oriented CFG File
MAC-local CFG File
Configuration File Customization
Customizing a Configuration File
Configuration File Attributes
Resource Files
Supported Resource Files
Files Download Process
Provisioning Methods
Provisioning Methods Priority
Web User Interface
Quick Login Configuration
Web Server Type Configuration
Central Provisioning
Auto Provisioning Settings Configuration
Setting Up a Provisioning Server
Supported Provisioning Protocols
Provisioning Protocols Configuration
Supported Provisioning Server Discovery Methods
PnP Provision Configuration
DHCP Provision Configuration
Static Provision Configuration
Configuring a Provisioning Server
Keeping User’s Personalized Settings after Auto Provisioning
Keeping User’s Personalized Settings Configuration
Auto Provisioning Flowchart for Keep User’s Personalized Configuration Settings
Example: Keeping User’s Personalized Settings
Clearing User's Personalized Configuration Settings
Custom Handset Related Configurations
83
83
83
84
84
84
84
85
85
85
85
86
86
87
87
88
88
89
90
91
96
96
96
97
97
97
98
99
99
99
101
101
102
102
Security Features
User and Administrator Identification
User and Administrator Identification Configuration
User Access Level Configuration
Auto Logout Time
Auto Logout Time Configuration
Base PIN
Base PIN Configuration
Emergency Number
Emergency Number Configuration
4
104
104
104
105
106
106
106
106
107
107
Page 8

Table of Contents
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Supported Cipher Suites
Supported Trusted and Server Certificates
Supported Trusted Certificates
TLS Configuration
Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP)
SRTP Configuration
Encrypting and Decrypting Files
Configuration Files Encryption Tools
Configuration Files Encryption and Decryption
Encryption and Decryption Configuration
Example: Encrypting Configuration Files
Incoming Network Signaling Validation
Incoming Network Signaling Validation Configuration
Firmware Upgrade
Firmware for Each Phone Model
Firmware Upgrade Configuration
Upgrading Multiple Handsets via Web User Interface
Audio Features
Alert Tone
Alert Tone Configuration
Ringer Device
Ringer Device Configuration
Tones
Supported Tones
Tones Configuration
Audio Codecs
Supported Audio Codecs
Audio Codecs Configuration
Packetization Time (PTime)
Supported PTime of Audio Codec
PTime Configuration
Early Media
Early Media Configuration
Acoustic Clarity Technology
Background Noise Suppression (BNS)
Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
VAD Configuration
Comfort Noise Generation (CNG)
CNG Configuration
Jitter Buffer
Jitter Buffer Configuration
DTMF
107
108
109
109
111
113
115
115
115
115
116
117
119
119
121
121
121
123
125
125
125
125
126
126
126
127
129
129
130
131
132
132
133
133
133
133
133
134
134
134
134
134
135
135
5
Page 9

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
DTMF Keypad
Transmitting DTMF Digit
Transmitting DTMF Digit Configuration
Suppress DTMF Display
Suppress DTMF Display Configuration
Handset Customization
Power LED Indicator of Handset
Power LED Indicator of Handset Configuration
Handset Keypad Light
Handset Keypad Light Configuration
Handset Backlight
Handset Backlight Configuration
Handset Wallpaper
Handset Wallpaper Configuration
Handset Screen Saver
Handset Screen Saver Configuration
Language
Supported Languages
Language Display Configuration
Language for Web Display Customization
Customizing a Language Pack for Web Display
Custom Language for Web Display Configuration
Time and Date
Time Zone
NTP Settings
NTP Configuration
DST Settings
Auto DST File Attributes
Customizing Auto DST File
DST Configuration
Time and Date Manually Configuration
Time and Date Format Configuration
Date Customization Rule
Input Method
Input Method Configuration
Search Source List in Dialing
Search Source File Customization
Search Source File Attributes
Customizing Search Source File
Search Source List Configuration
Call Display
Call Display Configuration
Display Method on Dialing
Display Method on Dialing Configuration
136
136
136
138
138
139
139
139
140
140
140
141
141
142
142
142
143
143
143
144
144
145
146
146
149
149
151
151
152
152
154
154
156
157
157
158
158
158
159
159
161
161
162
162
6
Page 10

Table of Contents
Key As Send
Key As Send Configuration
Recent Call Display in Dialing
Recent Call in Dialing Configuration
Warnings Display
Warnings Display Configuration
Advisory Tones
Advisory Tones Configuration
Shortcut Customization
Shortcut Customization Configuration
Directory
Local Directory
Local Contact File Customization
Local Contact File Elements and Attributes
Customizing Local Contact File
Local Contact Files and Resource Upload
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
LDAP Attributes
LDAP Configuration
Remote Phone Book
Remote Phone Book File Customization
Remote Phone Book File Elements
Customizing Remote Phone Book File
Remote Phone Book Configuration
Example: Configuring a Remote Phone Book
Shared Directory
Shared Directory Configuration
Shared Contact File Customization
Shared Contact File Elements and Attributes
Customizing Shared Contact File
XML Phonebook
XML Phonebook Configuration
Directory Search Settings
Directory Search Settings Configuration
162
162
163
163
163
163
164
164
165
165
167
167
167
167
168
168
168
168
169
174
174
174
175
175
176
176
177
177
177
178
178
178
179
179
Call Log
Call Log Display
Call Log Configuration
Call Features
Dial Plan
Basic Regular Expression Syntax for Four Patterns
Replace Rule File Customization
Replace Rule File Attributes
Customizing the Replace Rule File
180
180
180
181
181
182
182
182
183
7
Page 11

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Dial Now File Customization
Dial Now File Attributes
Customizing the Dial Now File
Replace Rule Configuration
Dial Now Configuration
Area Code Configuration
Block Out Configuration
Example: Adding Replace Rules Using a Replace Rule File
Emergency Dialplan
Emergency Dialplan Configuration
Off Hook Hot Line Dialing
Off Hook Hot Line Dialing Configuration
Call Timeout
Call Timeout Configuration
Anonymous Call
Anonymous Call Configuration
Call Number Filter
Call Number Filter Configuration
Auto Answer
Auto Answer Configuration
Anonymous Call Rejection
Anonymous Call Rejection Configuration
Call Waiting
Call Waiting Configuration
Do Not Disturb (DND)
DND Settings Configuration
DND Feature Configuration
DND Configuration
DND Synchronization for Server-side Configuration
Call Hold
Call Hold Configuration
Call Forward
Call Forward Settings Configuration
Call Forward Feature Configuration
Call Forward Configuration
Call Forward Synchronization for Server-side Configuration
Call Transfer
Call Transfer Configuration
Conference
Conference Type Configuration
Network Conference Configuration
End Call on Hook
End Call on Hook Configuration
183
183
183
183
184
185
186
187
187
187
189
190
190
190
191
191
192
192
192
193
193
193
194
194
195
195
196
196
197
197
197
198
198
199
199
202
203
203
204
204
204
205
205
Advanced Features
8
206
Page 12

Table of Contents
Call Park and Retrieve
Call Park and Retrieve Configuration
Shared Line
Shared Call Appearance (SCA) Configuration
SCA Configuration
Voice Mail
MWI for Voice Mail Configuration
General Features
Line Identification Presentation
CLIP and COLP Configuration
Return Code for Refused Call
Return Code for Refused Call Configuration
Accept SIP Trust Server Only
Accept SIP Trust Server Only Configuration
100 Reliable Retransmission
100 Reliable Retransmission Configuration
SIP Session Timer
SIP Session Timer Configuration
Session Timer
Session Timer Configuration
Reboot in Talking
Reboot in Talking Configuration
Reserve # in User Name
Reserve # in User Name Configuration
Busy Tone Delay
Busy Tone Delay Configuration
206
206
207
207
207
208
208
211
211
211
213
213
213
213
214
214
215
215
216
216
217
217
217
218
218
218
Configuration Parameters
BroadSoft Parameters
BroadSoft Settings
Broadsoft XSI
Broadsoft Network Directory
Broadsoft Call Park
BroadSoft Call Waiting Sync
BroadSoft DND and Forward Sync
Ethernet Interface MTU Parameter
SIP Settings Parameters
Call Settings Parameters
Troubleshooting Methods
All Base Diagnostics
Diagnostics File Type and Naming Rules
All Base Diagnostics Configuration
Log Files
Local Logging
220
220
220
220
222
225
226
226
227
227
228
230
230
230
230
232
232
9
Page 13

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Local Logging Configuration
Exporting the Log Files to a Local PC
Viewing the Log Files
Syslog Logging
Syslog Logging Configuration
Viewing the Syslog Messages on Your Syslog Server
Resetting Phone and Configuration
Resetting the IP phone to Default Factory Settings
Resetting the IP phone to Custom Factory Settings
Custom Factory Configuration
Deleting the Custom Factory Settings Files
Packets Capture
Capturing the Packets via Web User Interface
Capturing the Packets in Enhanced Way
Capturing the Packets in Normal Way
Watch Dog
Watch Dog Configuration
Analyzing Configuration Files
Exporting CFG Configuration Files from Phone
Importing CFG Configuration Files to Phone
Configuration Files Import URL Configuration
Exporting BIN Files from the Phone
Importing BIN Files from the Phone
BIN Files Import URL Configuration
Exporting All the Diagnostic Files
Device Status
Viewing Device Status
Phone Reboot
Rebooting the IP Phone Remotely
Notify Reboot Configuration
Rebooting the Device via Web User Interface
232
235
235
236
236
239
239
240
240
240
241
241
241
241
242
242
242
243
243
243
244
244
244
244
244
245
245
245
245
246
246
Troubleshooting Solutions
IP Address Issues
The device does not get an IP address
Time and Date Issues
Display time and date incorrectly
Phone Book Issues
Difference between a remote phone book and a local phone book
Audio Issues
Increasing or decreasing the volume
Get poor sound quality during a call
There is no sound when the other party picks up the call
Play the local ringback tone instead of media when placing a long-distance number without plus 0
Firmware and Upgrading Issues
10
247
247
247
247
247
247
247
248
248
248
248
248
248
Page 14

Table of Contents
Fail to upgrade the phone firmware
Verifying the firmware version
The IP phone does not update the configurations
System Log Issues
Fail to export the system log to a provisioning server (FTP/TFTP server)
Fail to export the system log to a syslog server
Password Issues
Restore the administrator password
The web screen displays "Default password is in use. Please change!"
Power and Startup Issues
Both PoE cable and power adapter is connected to the phone
The power LED indicator has no lights
Other Issues
The difference among user name, register name, and display name
On code and off code
The difference between RFC 2543Hold enabled and disabled
How does the DM configuration changes take effect when the handset is in the call?
Base Issue
Why doesn’t the power indicator on the base station light up?
Why doesn’t the network indicator on the base station slowly flash?
Handset Issues
How to check which area the handset is used for?
Register Issue
Why cannot the handset be registered to the base station?
Display Issue
Why does the handset prompt the message “Not Subscribed”?
Why does the handset prompt the message “Not in Range” or “Out Of Range”?
Why does the handset prompt the message “Network unavailable”?
Why does the handset display “No Service”?
Upgrade Issue
Why doesn’t the DECT IP phone upgrade firmware successfully?
248
249
249
249
249
249
250
250
250
250
250
250
250
250
250
250
251
252
252
252
252
252
252
252
252
252
253
253
253
253
253
Appendix
RFC and Internet Draft Support
W80DM Menu Structure Overview
W80B Menu Structure Overview
254
254
257
258
11
Page 15
W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System Introduction
W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System Introduction
The DECT IP multi-cell system is used for connecting multiple DECT base stations to a VoIP PBX. It supports the roaming
& handover feature, and provides a wider DECT signal coverage, and more handsets and simultaneous calls than the
single-cell.
Topics
Components of the DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Deployments of the DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Related Documentations
Components of the DECT IP Multi-Cell System
The following illustration shows the components of the DECT IP multi-cell system and the way the system is embedded
in the IP phone environment:
Components Description
Management unit for a group of base stations. At least one DECT manager must be used for
W80DM DECT Manager
(sometimes just referred
to as DM)
W80B Base Stations
each installation.
• Manages base stations synchronization within the clusters.
• Enables the account registration and centrally stores the account configuration.
• Enables centralized configuration and deployment.
Up to 30 base stations can be supported by one DECT manager.
• Provide cell site DECT features.
• Provide media processing from handsets directly towards PBX.
• Provide connection channels for the handsets, the number depends on various factors such
as the approved bandwidth.
12
Page 16
Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Components Description
Up to 100 handsets can be supported by one DECT manager. Up to 100 DECT calls can be
Handsets
(Mobile Devices)
PBX
made simultaneously for VoIP call.
Subscribers can accept or initiate calls in all base stations with their handsets (Roaming), and
can also switch handsets DECT connection between the base stations during a call
(Handover). A handover is only possible if base stations are synchronized.
IP PBX or Provider with VoIP (SIP) connections.
• Establishes the connection to a public phone network.
• Enables the centralized management of phone connections, remote phone book, and voice
mail.
Deployments of the DECT IP Multi-Cell System
The DECT IP multi-cell system can be deployed in the multi-story office building, supermarket, store, warehouse, hotel,
and so on.
Device Description
W80DM DECT Manager At least one
W80B Base Stations Up to 30 per DECT manager
Handsets
(Mobile Devices)
Up to 100 per DECT manager
Related Documentations
The following related documents are available:
13
Page 17

W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System Introduction
l Quick Start Guide, describes how to install the W80DM/W80B and obtain the device's IP address.
l User Guide, describes how to configure and use the basic and advanced features available in the DECT IP multi-cell
system.
l Deployment Guide, explains the necessary preparatory work for the installation and describes how to carry out meas-
urements in order to find the best positions for your base stations.
For support or service, please contact your Yealink reseller or go to Yealink Technical Support online: http://sup-
port.yealink.com/.
Read the Yealink Products Regulatory Notices guide for all regulatory and safety guidance.
14
Page 18
First Steps
First Steps
This chapter provides the information you need to prepare to configure your multi-cell system at the DECT manager.
Topics
Preparing to Use the Multi-Cell System
Defining the Device Role
Configuring the System via Web User Interface
Preparing to Use the Multi-Cell System
Defining the Device Role
The W80DM is shipped as a DECT Manager (DM) and the W80B is shipped as a base station.
The W80DM/W80B device supports the following roles:
l Base: The device works as a base station. You can configure the IP address of the DM via the web user interface or
RPS.
15
Page 19
Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
l DM: The device works as a DECT manager.
If you want to change the device role of the W80DM/W80B, you can upgrade the firmware.
Related Topics
Firmware Upgrade
LED Indicators on the W80DM/W80B
LAN LED: indicates the LAN connection status.
LAN LED Description
Green Successful connection to LAN
Slowly flashing green (1s) No connection to LAN or no IP address available/ assigned
Off Power off
ROLE LED: indicates the device role.
ROLE LED Description
Orange Device role: DM.
Green Device role: Base.
Slowly flashing orange (1s) Active calls in the system
DECT LED: indicates the connection status to the DM.
DECT LED Description
Green Successful connection to DM, status: Active and synced
Off Successful connection to DM, status: Active, Deactive, or Offline
Slowly flashing green (1s) Active calls on the base station
LED indicators (some common status)
LAN LED ROLE LED DECT LED Description
Slowly flashing
green (1s)
Slowly flashing
green (1s)
Green Off Device role: Base, no connection to LAN
Orange Off Device role: DM, no connection to LAN
Green Green Green Synchronized, status: Active and synced
Green Green Off Not synchronized, status: Active, Deactive, or Offline
Green Green
16
Slowly flashing Successful connection to DM, active calls on the base
Page 20
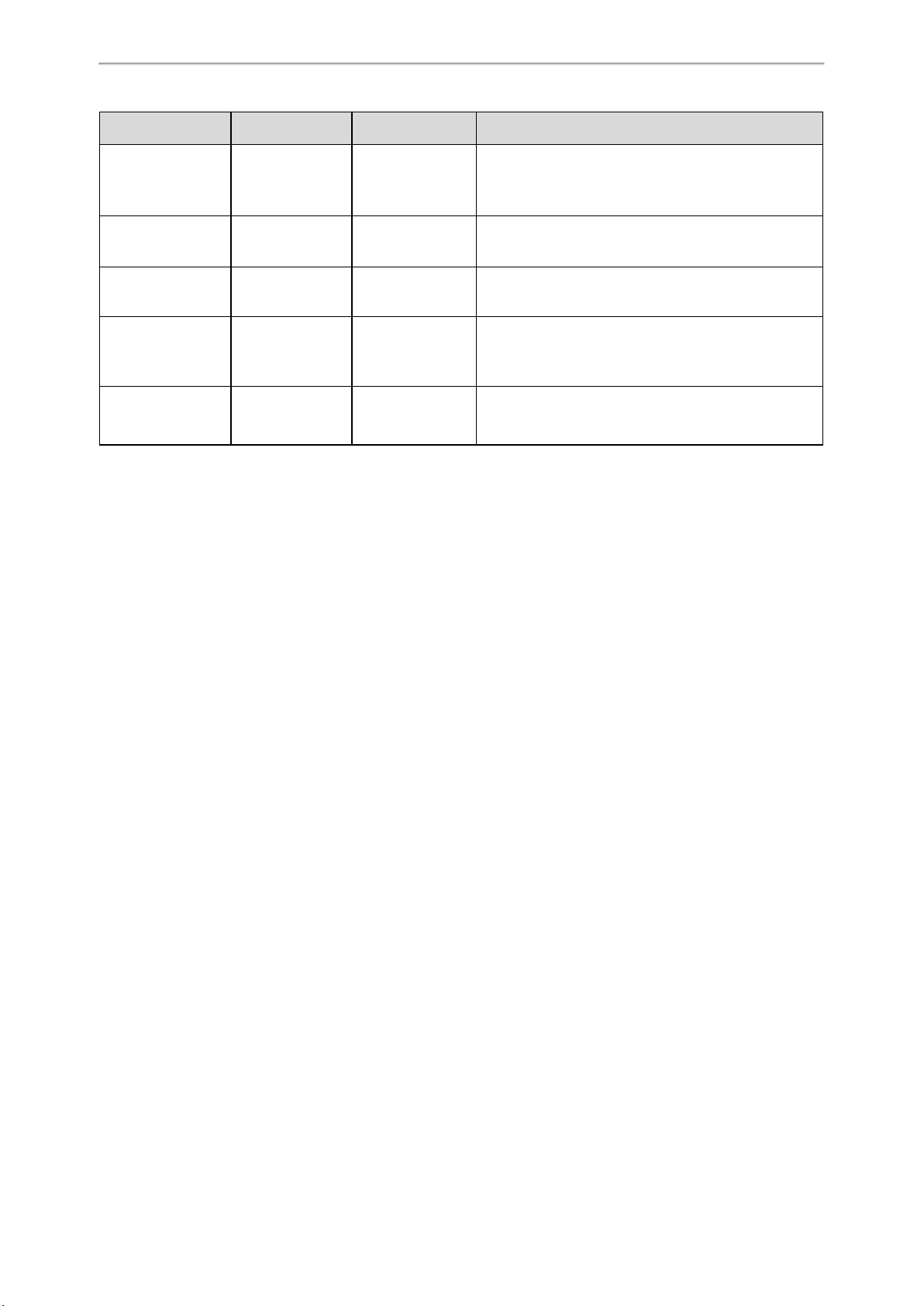
LAN LED ROLE LED DECT LED Description
green(1s) station
Green Orange Green First-level base station connected
Green Orange Off No connected base on the DM
First Steps
Green
Fast flashing green
(0.5s)
Slowly flashing
orange (1s)
Fast flashing green
(0.5s)
Green Active calls in the system
Fast flashing green
(0.5s)
Firmware update in progress
Configuring the System via Web User Interface
System settings are made via the web user interface of the W80DM and cannot be changed using the handsets.
This applies in particular for:
l De-registering the handset at the phone system.
l Renaming the handset.
l All settings for the VoIP account used by a handset for calls.
l Rebooting or restarting the base station.
l Configuration of the remote phone book.
Handset-specific settings are changed on your handset individually. For example, language, wallpaper, ring tones, and
volume.
Topics
Accessing Web User Interface
Navigating the Web User Interface
Logging out of the Web User Interface
Accessing Web User Interface
You can configure and manage features of the multi-cell system via the web user interface.
When configuring via the web user interface, you require a user name and password for access. For a user - who has
only limited access to some settings, the default user name and password are “user” (case-sensitive). For an administrator - who has unlimited access to call features of the web user interface, the default user name and password are
“admin” (case-sensitive).
Procedure
1. Find the current IP address of the device on the DHCP server in the list of registered DHCP clients.
2. Open a web browser on your computer, enter the IP address into the address bar (for example,
"https://192.168.0.10" or "192.168.0.10"), and then press the Enter.
3. Enter the user name and password on the login page and click Login.
17
Page 21
Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
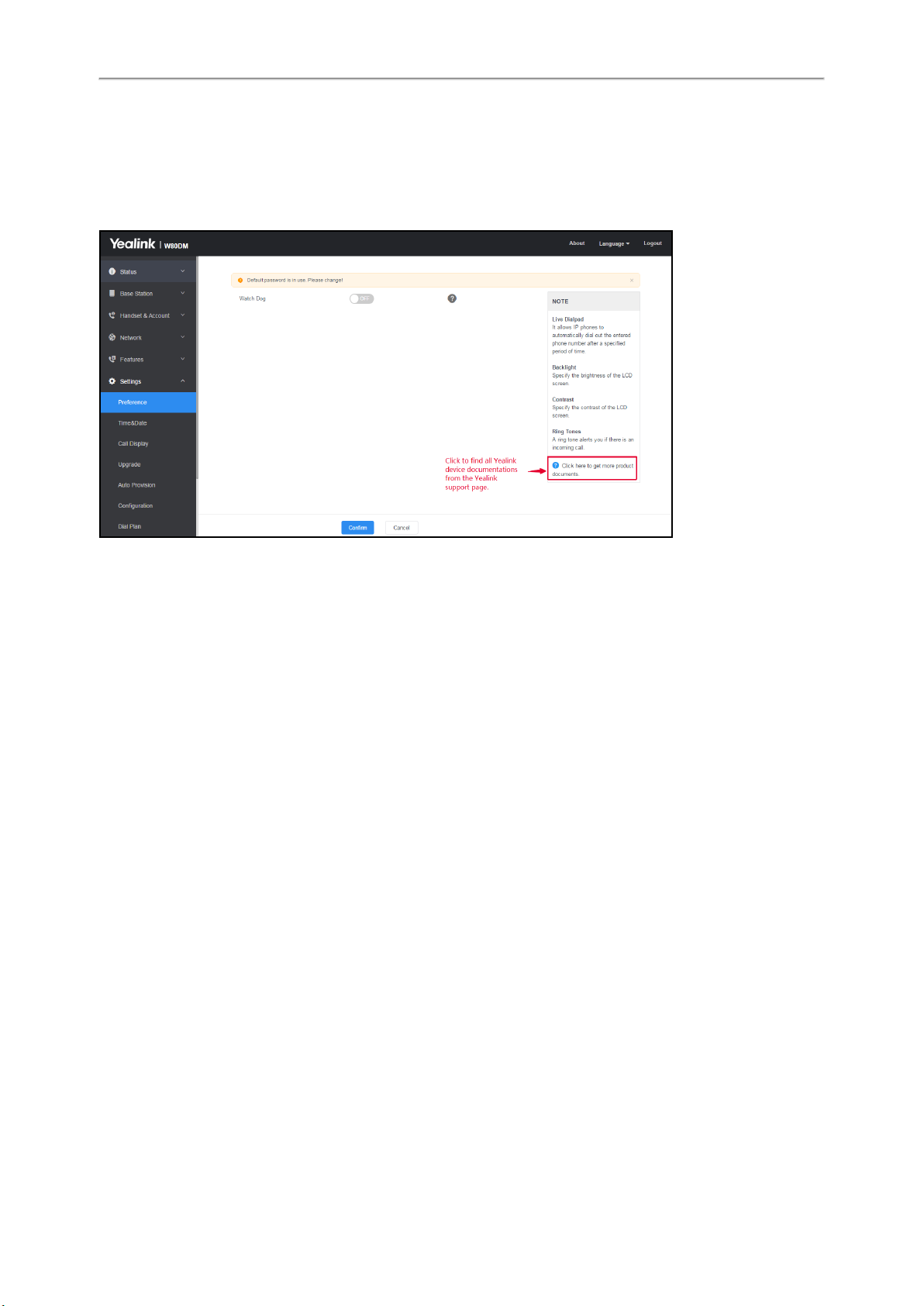
Navigating the Web User Interface
When you log into the web user interface successfully, the device status is displayed on the first page of the web user
interface.
The following figure is an example when you navigate to Settings > Preference:
Logging out of the Web User Interface
By default, the device will automatically log out of the web user interface after five minutes of inactivity. You can also
manually log out of the web user interface.
Procedure
1. Click Logout at the top right of each web page.
18
Page 22

Initialization Instructions
Initialization Instructions
This chapter provides basic initialization instructions of devices.
Topics
Initialization Process Overview
Verifying Startup
Initialization Process Overview
The initialization process of the device is responsible for network connectivity and operation of the device in your local
network. Once you connect your device to the network and to an electrical supply, the device begins its initialization
process.
Topics
Loading the ROM File
Configuring the VLAN
Querying the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server
Contacting the Provisioning Server
Updating Firmware
Downloading the Resource Files
Loading the ROM File
The ROM file resides in the flash memory of the device. The device comes from the factory with a ROM file preloaded.
During initialization, the device runs a bootstrap loader that loads and executes the ROM file.
Configuring the VLAN
If you connect the device to a switch, the switch notifies the device of the VLAN information defined on the switch (if
using LLDP or CDP). The device can then proceed with the DHCP request for its network settings (if using DHCP).
Querying the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server
The device is capable of querying a DHCP server.
After establishing network connectivity, the device can obtain the following network parameters from the DHCP server
during initialization:
l IP Address
l Subnet Mask
l Default Gateway
l Primary DNS (Domain Name Server)
l Secondary DNS
By default, the devices obtain these parameters from a DHCPv4. You can configure network parameters of the device
manually if any of them are not supplied by the DHCP server.
Contacting the Provisioning Server
If you configure the device to obtain configurations from the provisioning server, it will be connected to the provisioning server, and then download the boot file and configuration file(s) during startup. The device will be able to
resolve and update configurations written in the configuration file(s). If the device does not obtain configurations from
the provisioning server, it will use the configurations stored in the flash memory.
19
Page 23

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Updating Firmware
If you define the access URL of firmware in the configuration file, the device will download the firmware from the provisioning server. If the MD5 value of the downloaded firmware file differs from that stored in the flash memory, the
device will perform a firmware update.
You can manually upgrade the firmware if the device does not download the firmware from the provisioning server.
Downloading the Resource Files
In addition to the configuration file(s), the device may require resource files before it provides service. These resource
files are optional, but if you deploy some particular features, these files are required.
Verifying Startup
After connected to the power and available network, the LAN LED indicator glows green. As a base station, the ROLE
LED indicator glows green; as a DECT manager, the ROLE LED indicator glows orange.
20
Page 24
Setting up the Base Stations
Setting up the Base Stations
The W80B device must be registered to the DM for normal use.
In the multicast network, the DM automatically recognizes the base stations within the network. In the non-multicast
network, the DM recognizes the base stations only when the IP address of DM is configured to the base stations via the
web user interface or RPS.
After recognized, the base stations need to be registered, activated, and synchronized.
Topics
Base Station Pre-registration
DM IP
Base Station Settings
Base Station Synchronization
Base Station Pre-registration
In the multicast network, you can pre-register all base stations at the DM. After that, the base stations will be automatically registered at the DM once being detected in the network.
If the detected base station has not been pre-registered at the DM, you need to manually register the base stations via
the web user interface.
Topics
Base Station Pre-registration Configuration
Manually Registering Base Stations to the DM
Base Station Pre-registration Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to pre-register the base station.
Parameter station.allowed.X.mac
Description It sets the MAC address of the pre-registration base station.
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
Parameter station.allowed.X.name
Description It sets the name of the pre-registration base station.
Permitted
Values
String within 32 characters
String within 32 characters
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default Blank
Parameter station.allowed.X.sync.cluster
Description It sets the sync cluster of the pre-registration base station.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
21
Page 25
Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
Parameter station.allowed.X.sync.level
Description It sets the sync level of the pre-registration base station.
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
[1]
X is the pre-registration ID. X=1-30.
Integer from 1 to 10
Integer from 1 to 10
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Manually Registering Base Stations to the DM
You are allowed to manually register the base stations to the DM in the base station standby list.
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the device.
2. Navigate to Base Station > Base Station Registration.
3. Click next to the base station.
4. Complete the corresponding information of the base station, and click OK.
The base station is successfully registered to the DM.
Related Topic
Accessing Web User Interface
DM IP
In the non-multicast network, the DM can detect and connect the base station only when you have configured the IP
address of the DM on the W80B base station.
Note: You can configure the IP address of the DM for all base stations using RPS.
Topic
DM IP Configuration
DM IP Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure the DM IP.
Parameter features.dect_management.ip_address <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the IP address of the DM.
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Status > Base Mode > DM IP
22
Page 26
Base Station Settings
You can modify all settings of the registered base stations at the DECT manager.
Topics
Base Station Settings Configuration
Managing the Connected Base Stations
Base Station Settings Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to modify the base station settings.
Setting up the Base Stations
Parameter station.X.name
Description It sets the name of the base station.
Permitted
Values
Default Base station X
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > Name / Location
Parameter station.X.sync.cluster
Description It sets the sync cluster to which the base station belongs.
Permitted
Values
Default 1
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > Cluster
Parameter station.X.sync.level
Description It sets the sync level of the base station.
Permitted
Values
String within 32 characters
Integer from 1 to 10
Integer from 1 to 10
[1]
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 1
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > Sync Level
Parameter station.X.sync.type
Description It sets the sync type of the base station.
Permitted
Values
Default 2
Parameter station.X.active
0-Disabled
2-Over the air synchronization
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
23
Page 27
Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Description It triggers the active base station feature to on or off.
Permitted
Values
0-OFF
1-ON
Default 1
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > Active Base Station
Parameter
static.station.X.network.type
[1]
Description It configures the type of network.
Permitted
Values
0-DHCP
2-Static IP
Default 0
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > IP Address Type
Parameter
static.station.X.network.ip
[1]
It configures the IPv4 address.
Description
Note: It works only if "static.station.X.network.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > IP Address
Parameter
static.station.X.network.mask
[1]
It configures the IPv4 subnet mask.
Description
Note: It works only if "static.station.X.network.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > Subnet Mask
Parameter
static.station.X.network.gateway
[1]
It configures the IPv4 default gateway.
Description
Note: It works only if "static.station.X.network.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Base Station > Base Station Settings > Edit > Default Gateway
[1]
X is the registration location ID. X=1-30.
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Managing the Connected Base Stations
You can edit the data for a base station or manage a base station that is already registered to the DM.
24
Page 28

You can customize the following information of the connected base stations:
Item Description
Setting up the Base Stations
Base Station
Name of the base station. When added to the list, Base Station X (X ranges from 1to 30) is used as
the name.
Radio Fixed Part Number. The base station identity allocated by the DECT system.
RPN
Note: This cannot be edited.
Cluster Number of the cluster to which the base station belongs.
Sync Level Sync level within the sync hierarchy.
Synchronization status of the base station.
• Offline: not available.
Status
• Deactive: available but not activated.
• Active: activated but not synchronized.
• Active and synced: activated and synchronized.
Activates or deactivates the base station.
Active
Note: A base station must be active to manage calls of the connected handsets. If it is deactivated,
it will no longer connect handsets but it still stays in the list of connected base stations.
Procedure
1. You can do the following:
l Select ON or OFF to activate or deactivate the base station.
Note: Please ensure that the base station you want to deactivate is not with sync level 1. Check your sync settings
before deactivating the base station. Otherwise, your system may no longer work properly.
l Click , and enter a descriptive name, assign the cluster, and set the sync level for the base station.
l Click and select OK to reboot the base station.
All existing connections managed by the base station are terminated.
l Click and select OK to delete the base station.
l Click Reboot All to reboot all connected base stations.
Base Station Synchronization
Base station synchronization is the prerequisite for the functioning of the multi-cell system, inter-cell handover, and
overload balancing. Overload balancing means that a handset can roam to another available base when the current
base is fully loaded and cannot accept further handset connections.
Base stations can be synchronized "over the air", meaning that they are synchronized via DECT.
Note: Synchronization always refers to a cluster. In case you set up several clusters that are not synchronized with one
another, these will be no possibility of a handover or overload balancing between them.
Topic
Synchronization Planning
25
Page 29
Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
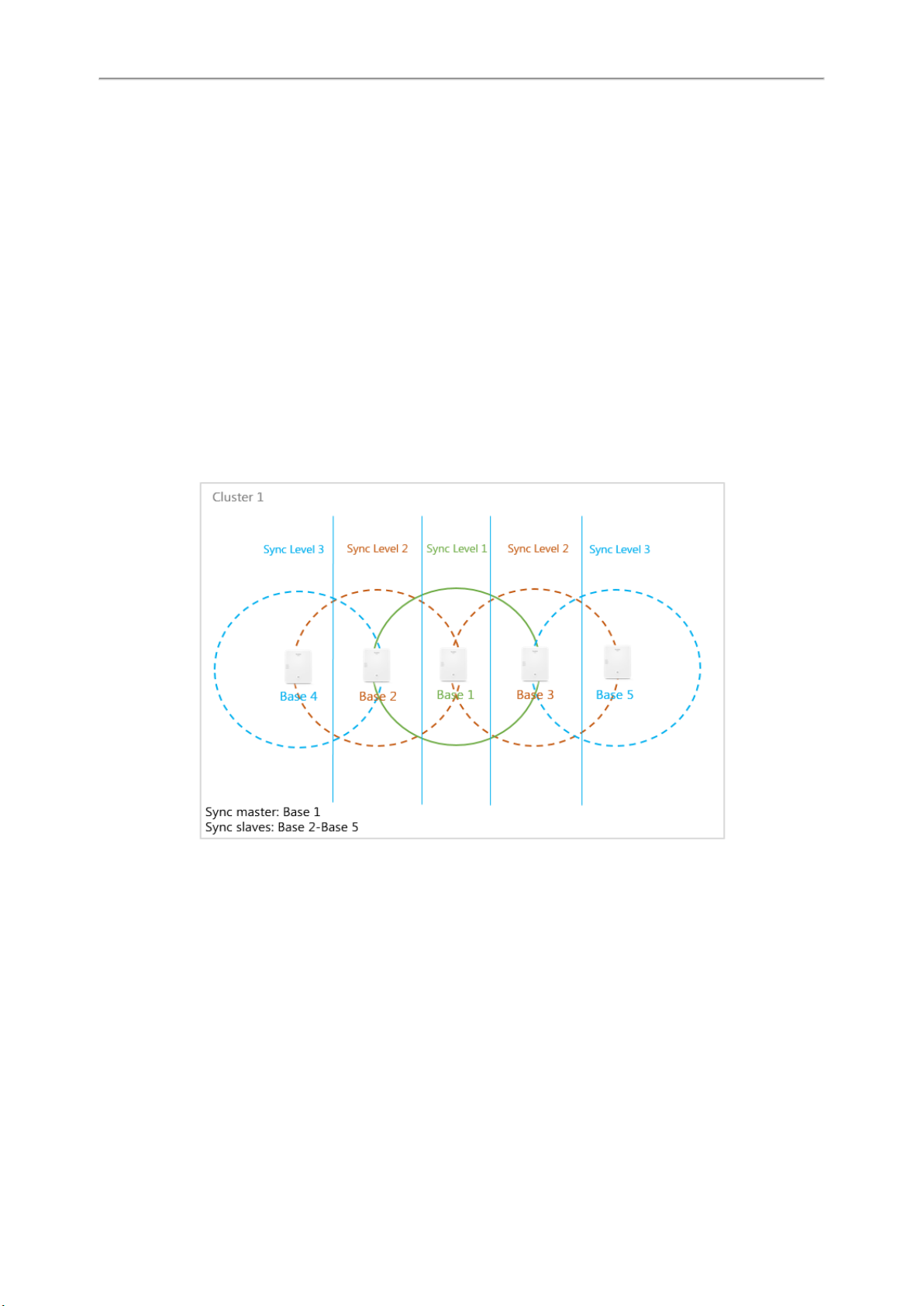
Synchronization Planning
Base stations in the multi-cell system must synchronize with one another to ensure a smooth transition of the handsets
from cell to cell (handover). No handover and no overload balancing are possible between cells that are not synchronized.
The synchronization within a cluster takes place in a master/slave procedure. It means that one base station (sync master) defines the synchronization cycle for one or more additional base stations (sync slaves). A base station can synchronize with each base station on a higher sync level. The sync level concept allows base stations to automatically
select the best suitable base station (having a lower sync level number) to receive synchronization signal from.
During configuration, assign one sync level to each base. Sync level 1 is the highest level, which is the level of the sync
master and appears only once in each cluster. A base station always synchronizes itself with a base station that has a
better sync level. If it sees several base stations with a better sync level, it synchronizes itself with the base station that
provides the best signal quality. If it does not see any base station with a higher sync level, it cannot synchronize.
To ensure the synchronization, you should plan the level 1 base station in the center as much as possible, and place the
next sync level's base stations around the center.
The following is an example of a synchronization scenario:
26
Page 30

Managing the Handsets
Managing the Handsets
You can use the web user interface to register all handsets or delete them from the multi-cell system.
Topics
Registering Handsets via Web User Interface
De-registering a Handset
Registering Handsets via Web User Interface
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Handset & Account > Handset Registration.
3. Click Add Handset.
4. Click Start Register Handset to set the DM to the registration mode.
5. On the handset, do one of the following:
l Press the Reg soft key on the handset to register quickly.
l Press OK > Register Handset and then select the desired base to register the handset.
l Press OK > Settings > Registration > Register Handset and then select the desired base to register the handset.
On the DDphone, navigate to Menu > Settings >Registration > Register Handset.
After registration, the handset prompts “Handset Subscribed”.
Note: The default base PIN is 0000.
Related Topic
Accessing Web User Interface
IPUI Registration
You can register handsets in batches by the IPUI code.
Topics
Obtaining the IPUI Code of the Handset
Notes on Configuring IPUI
IPUI Code Configuration
Obtaining the IPUI Code of the Handset
IPUI is a random code that includes 10 characters mixed with numbers and letters.
There are three ways to obtain the IPUI code:
l Handset UI: on the W56H/W53H handset, navigate to OK > Status > Handset > IPUI Code; on the CP930W, nav-
igate to Menu > Status > Phone Status > IPUI Code; on the DDphone, navigate to Menu > Status > Dongle
Status > IPUI Code.
l Giftbox: Obtain it from the sticker label on the handset's giftbox.
l Shipping system: Check it in the shipping system.
27
Page 31

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Notes on Configuring IPUI
A few notes you should know when registering handsets using IPUI code:
l The registration status will not be disabled automatically if you enable it by "handset.X.reg.enable".
l If you duplicate the IPUI code during the configuration, only the IPUI with the smaller handset number takes effect.
l If you configure another IPUI code for another handset but the handset number is the same as an existing one, the
existing IPUI will be overwritten.
l If you configure the IPUI code for the registered handset, the handset will be unregistered.
l When the handset is deleted, the handset and its IPUI code will be deleted at the same time.
l You cannot directly modify the IPUI code via the web user interface. The IPUI code can only be modified via auto
provisioning, or re-entered after deleted via the web user interface.
IPUI Code Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to import the IPUI code.
Parameter handset.X.reg.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It enables or disables the registration status for handset X.
Description
Note: The value of X corresponds to that of "account.X.user_name". When the IPUI code is invalid or not
configured, the registration status cannot be enabled by this parameter.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset > Start Register Handset
Parameter handset.X.ipui
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IPUI code of handset X.
Description
Note: The IPUI code is not case sensitive.
Permitted
Values
String within 10 characters (only contain numbers and letters)
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset > IPUI
[1]
X is the handset ID. X=1-100.
Related Topics
Obtaining the IPUI Code of the Handset
Handset Registration Center
The registration center allows you to register groups of handsets in one registration process. During this time, the system will automatically register the handset and assign the corresponding account according to the IPUI code.
You can find the following information from the registration center:
l Total Handsets: Shows how many handsets are registered in the current system.
l Registered Handsets: Shows how many handsets are registered through the registration center this time
l Current Time: Shows the current system time. It is updated in real time.
28
Page 32

Managing the Handsets
Topics
Registering Handsets Time-Controlled
Registering Handsets at Once
Manually Closing the Registration
Registering Handsets Time-Controlled
A registration process is started automatically according to the time you set.
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Handset & Account > Registration Center.
3. In the Registration Start Time field, enter the time when the next registration process should be started.
Valid value: at least 1 minute later than the current time but no more than 24 days.
3. In the Registration Duration field, enter the duration that the DM should stay in registration mode.
Default: 3 minutes.
4. Click Confirm.
Related Topic
Manually Closing the Registration
Registering Handsets at Once
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Handset & Account > Registration Center.
3. In the Registration Duration field, enter the duration that the DM should stay in registration mode.
Default: 3 minutes.
4. Click Start Now.
The DM starts registration at once.
Related Topic
Manually Closing the Registration
Manually Closing the Registration
When the time is up, the system will automatically disable the registration status. You can also manually close the registration.
Procedure
29
Page 33

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
1. Click Close.
The screen prompts you whether to close the registration.
2. Click OK.
Related Topic
Registering Handsets Time-Controlled
De-registering a Handset
You can only delete a handset from the multi-cell system via the web user interface.
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Handset & Account > Handset Registration.
3. Click .
4. Click OK to delete a handset.
All registration information for the handset is deleted.
30
Page 34

Account Settings
Account Settings
This chapter shows you how to register accounts and configure account settings on Yealink devices.
Topics
Account Registration
Outbound Proxy in Dialog
Server Redundancy
SIP Server Name Resolution
Static DNS Cache
Number of Active Handsets Per Base
Account Registration
Any handset must get assigned an individual SIP account. After registering the handset to the system, the handset can
be assigned an account for receiving and sending VoIP connection.
Topics
Supported Accounts
SIP Server Template Configuration
Accounts Registration Configuration
Registration Settings Configuration
Supported Accounts
The number of registered accounts must meet the following:
Registered Accounts on W80DM Assigned Account per Handset
100 Only one
SIP Server Template Configuration
You can use up to ten different SIP servers in the system. You can pre-configure up to 10 SIP server templates for
choose when registering SIP accounts.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the SIP server template.
Parameter template.X.name
Description It sets the name of the SIP server template.
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > Template Name
Parameter template.X.sip_server.Y.address
[1][2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
31
Page 35

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Description It configures the IP address or domain name of the SIP server Y in which the account is registered.
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Web UI
Parameter template.X.sip_server.Y.port
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > SIP Server Y
[1][2]
Description It configures the port of SIP server Y.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 5060
Web UI
Parameter template.X.sip_server.Y.transport_type
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > SIP Server Y
[1][2]
Description It configures the type of transport protocol.
0-UDP
1-TCP
Permitted
Values
2-TLS
3-DNS-NAPTR, if no server port is given, the device performs the DNS NAPTR and SRV queries for the ser-
vice type and port.
[2]
> Server Host
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
[2]
> Port
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 0
Web UI
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > SIP Server Y
Parameter template.X.sip_server.Y.expires
[1][2]
[2]
> Transport
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the registration expiration time (in seconds) of SIP server Y.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 30 to 2147483647
Default 3600
Web UI
Parameter
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > SIP Server Y
template.X.sip_server.Y.retry_counts
[1][2]
[2]
> Server Expires
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the retry times for the device to resend requests when the SIP server Y is unavailable or there
Description
is no response from the SIP server Y.
The handset moves to the next available server after three failed attempts.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 20
Default 3
Web UI
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > SIP Server Y
[2]
> Server Retry Counts
32
Page 36

Account Settings
Parameter
template.X.outbound.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the device to send requests to the outbound proxy server.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > Enable Outbound Proxy Server
Parameter
template.X.outbound.Y.address
[1][2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IP address or domain name of the outbound proxy server Y.
Description
Note: It works only if “template.X.outbound.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Web UI
Parameter
Base Station > SIP Server Settings > Edit > Outbound Proxy Server Y
template.X.outbound.Y.port
[1][2]
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the port of the outbound proxy server Y.
Description
Note: It works only if “template.X.outbound.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 5060
Web UI
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > Outbound Proxy Server Y
template.X.outbound.fallback_interval
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the time interval (in seconds) for the device to detect whether the working outbound proxy
server is available by sending the registration request after the fallback server takes over call control.
Integer from 30 to 2147483647
Default 3600
Web UI Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > Proxy Fallback Interval
[1]
X is the template ID. X=1-10.
[2]
Y is the server ID. Y=1-2.
Accounts Registration Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to register accounts.
Parameter
account.X.enable
Description It defines the activation status of the account.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
[2]
> Port
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
33
Page 37

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Line Active
Parameter
account.X.label
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the display label of the account.
Permitted
Values
String within 99 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Label
Parameter
account.X.display_name
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the display name of the account.
Permitted
Values
String within 99 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Display Name
Parameter
account.X.auth_name
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the user name for authentication registration.
Permitted
Values
String within 99 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Register Name
Parameter
account.X.user_name
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the user name of the account.
Permitted
Values
String within 99 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Username
Parameter
account.X.password
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures password of the account.
Permitted
Values
String within 99 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Password
Parameter
account.X.sip_server.template
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures which SIP server template to use for registering an account.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1 to 10
34
Page 38

Account Settings
Default 1
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > SIP Server
Parameter
account.X.reg_fail_retry_interval
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
It configures the re-registration period (in seconds) after the account registration fails.
Description
Note: It works only if "account.X.reg_failed_retry_min_time" and "account.X.reg_failed_retry_max_time"
are set to 0.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 1800
Default 30
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > SIP Registration Retry Timer (0~1800s)
Parameter
account.X.reg_failed_retry_min_time
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
It configures the base time to wait (in seconds) for the phone to retry to re-register after the account registration fails.
Description
how long to wait. The algorithm is defined in RFC 5626. We recommend that you set this value to an
integer between 10 to 120 if needed. If the values of this parameter and the parameter "account.X.reg_
failed_retry_max_time" are set to 0, the interval configured by "account.X.reg_fail_retry_interval" will be
used.
Note: It is used in conjunction with the parameter "account.X.reg_failed_retry_max_time" to determine
Permitted
Values
Integer greater than or equal to 0
Default 0
Parameter
account.X.reg_failed_retry_max_time
It configures the maximum time to wait (in seconds) for the phone to retry to re-register after the account
registration fails.
Note: It is used in conjunction with the parameter "account.X.reg_failed_retry_min_time" to determine
Description
how long to wait. The algorithm is defined in RFC 5626. We recommend that you set this value to an
integer between 60 to 1800 if needed. If the values of this parameter and the parameter "account.X.reg_
failed_retry_min_time" are set to 0, the interval configured by "account.X.reg_fail_retry_interval" will be
used.
Permitted
Values
Integer greater than or equal to 0
Default 60
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
[2]
Y is the server ID. Y=1-2.
Registration Settings Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to change the registration settings.
Parameter
account.X.enable_user_equal_phone
Description It enables or disables the phone to add “user=phone” to the SIP header of the INVITE message.
Permitted
0-Disabled
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
35
Page 39

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Values 1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Send user=phone
Parameter
account.X.register_mac
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the phone to add MAC address to the SIP header of the REGISTER message.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > SIP Send MAC
Parameter
account.X.register_line
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
It enables or disables the phone to add a line number to the SIP header of the REGISTER message.
Description
0-99 stand for line1-line100.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > SIP Send Line
Parameter
account.X.unregister_on_reboot
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the phone to unregister first before re-registering account X after a reboot.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Unregister When Reboot
Parameter
account.X.sip_server_type
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Description It configures the type of SIP server.
0-Default
Permitted
Values
2-BroadSoft (It works only if “bw.enable" is set to 1(Enabled))
8-Genesys
10-Genesys Advanced
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > SIP Server Type
Parameter
sip.reg_surge_prevention
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the waiting time (in seconds) for account register after startup.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 60
Default 0
36
Page 40

Account Settings
Web UI Network > Advanced > Registration Random > Registration Random (0~60s)
Parameter
Description It enables or disables the phone to subscribe to the registration state change notifications.
account.X.subscribe_register
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Subscribe Register
Parameter phone_setting.disable_account_without_username.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the phone to disable the account whose username is empty.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Parameter
Description It configures the renewal time (in seconds) away from the registration lease.
Permitted
Values
Default -1
Parameter
Description It configures the renewal time (in seconds) away from the subscription lease.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
account.X.register_expires_overlap
Positive integer and -1
account.X.subscribe_expires_overlap
Positive integer and -1
[1]
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
<MAC>.cfg
Default -1
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
[2]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
Outbound Proxy in Dialog
An outbound proxy server can receive all initiating request messages and route them to the designated destination. If
the device is configured to use an outbound proxy server within a dialog, all SIP request messages from the device will
be sent to the outbound proxy server as a mandatory requirement.
Note: To use this feature, make sure the outbound server has been correctly configured on the device. For more inform-
ation on how to configure the outbound server, refer to Server Redundancy.
Topic
Outbound Proxy in Dialog Configuration
Outbound Proxy in Dialog Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure the outbound proxy in dialog.
37
Page 41

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Parameter sip.use_out_bound_in_dialog <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It enables or disables the phone to send all SIP requests to the outbound proxy server mandatorily in a dia-
Description
log.
Note: It works only if "template.X.outbound.enable" is set to 1 (Enabled).
0-Disabled, only the new SIP request messages from the phone will be sent to the outbound proxy server
Permitted
Values
in a dialog.
1-Enabled, all the SIP request messages from the phone will be sent to the outbound proxy server in a dialog.
Default 0
Web UI Features > General Information > Use Outbound Proxy In Dialog
Server Redundancy
Server redundancy is often required in VoIP deployments to ensure continuity of phone service, for example, take the
call server offline for maintenance, the server fails, or the connection between the device and the server fails.
Two types of redundancy are possible. In some cases, a combination of the two may be deployed:
l Failover: In this mode, the full phone system functionality is preserved by having a second equivalent capability call
server take over from the one that has gone down/off-line. This mode of operation should be done using the DNS
mechanism from the primary to the secondary server. Therefore, if you want to use this mode, the server must be
configured with a domain name.
l Fallback: In this mode, a second less featured call server with SIP capability takes over call control to provide the
basic calling capability, but without some advanced features (for example, shared line and MWI) offered by the
working server. The phones support configuration of two servers per SIP registration for the fallback purpose.
Note: For concurrent registration mode, it has a certain limitation when using some advanced features, and for successive
registration mode, the phone service may have a brief interrupt while the server fails. So we recommend that you use the
failover mode for server redundancy because this mode can ensure the continuity of the phone service and you can use all
the call features while the server fails.
Phone Configuration for Redundancy Implementation
To assist in explaining the redundancy behavior, an illustrative example of how an IP phone may be configured is
shown below. In the example, server redundancy for fallback and failover purposes is deployed. Two separate servers (a
working server and a fallback server) are configured for per line registration.
38
Page 42

Account Settings
l Working Server: Server 1 is configured with the domain name of the working server. For example yealink.pbx.com.
DNS mechanism is used such that the working server is resolved to multiple servers with different IP addresses for
failover purpose. The working server is deployed in redundant pairs, designated as primary and secondary servers.
The primary server (for example, 192.168.1.13) has the highest priority server in a cluster of servers resolved by the
DNS server. The secondary server (for example, 192.168.1.14) backs up a primary server when the primary server fails
and offers the same functionality as the primary server.
l Fallback Server: Server 2 is configured with the IP address of the fallback server. For example 192.168.1.15. A fall-
back server offers less functionality than the working server.
Yealink devices support Failover and Fallback server redundancy types. In some cases, you can deploy a combination
of the two server redundancy types.
Topics
Behaviors When Working Server Connection Fails
Registration Method of the Failover/Fallback Mode
Fallback Server Redundancy Configuration
Failover Server Redundancy Configuration
Behaviors When Working Server Connection Fails
For Outgoing Call
When you initiate a call, the phone will go through the following steps to connect the call:
1. Sends the INVITE request to the primary server.
2. If the primary server does not respond correctly to the INVITE (that is, the primary server responds to the INVITE
with 503 message or the request for responding with 100 Trying message times out (64*T1 seconds, defined in RFC
3261)), then tries to make the call using the secondary server.
3. If the secondary server is also unavailable, the phone will try the fallback server until it either succeeds in making a
call or exhausts all servers at which point the call will fail.
39
Page 43

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
At the start of a call, server availability is determined by SIP signaling failure. SIP signaling failure depends on the
SIP protocol being used as described below:
l If TCP is used, then the signaling fails if the connection or the send fails.
l If UDP is used, then the signaling fails if ICMP is detected or if the signal times out. If the signaling has been
attempted through all servers in the list (this list contains all the server addresses resolved by the DNS server) and
this is the last server, then the signaling fails after the complete UDP timeout defined in RFC 3261. If it is not the
last server in the list, the maximum number of retries depends on the configured retry counts (configured by
"template.X.sip_server.Y.retry_counts").
Registration Method of the Failover/Fallback Mode
Registration method of the failover mode:
The IP phone must always register to the primary server first except in failover conditions. If this is unsuccessful, the
phone will re-register as many times as configured until the registration is successful. When the primary server registration is unavailable, the secondary server will serve as the working server. As soon as the primary server registration
succeeds, it returns to be the working server.
Registration methods of the fallback mode include (not applicable to outbound proxy servers):
l Concurrent registration (default): The IP phone registers to SIP server 1 and SIP server 2 (working server and fall-
back server) at the same time. Note that although the IP phone registers to two SIP servers, only one server works at
the same time. If it fails, a fallback server can take over the basic calling capability, but without some advanced features (for example, shared lines and MWI) offered by the working server.
l Successive registration: The IP phone only registers to one server at a time. The IP phone first registers to the work-
ing server. In a failure situation, the phone registers to the fallback server, and the fallback server can take over all
calling capabilities.
Fallback Server Redundancy Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure fallback server redundancy.
Parameter
account.X.fallback.redundancy_type
It configures the registration mode in fallback mode.
Description
Note: It is not applicable to outbound proxy servers.
Permitted
Values
0-Concurrent registration
1-Successive registration
Default 0
Parameter
account.X.fallback.timeout
It configures the time interval (in seconds) for the phone to detect whether the working server is available
Description
by sending the registration request after the fallback server takes over call control.
Note: It is not applicable to outbound proxy servers.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 10 to 2147483647
Default 120
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
[1]
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
<MAC>.cfg
Failover Server Redundancy Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure failover server redundancy.
40
Page 44

Account Settings
Parameter
Description
account.X.sip_server.Y.register_on_enable
It enables or disables the phone to send registration requests to the secondary server when encountering
a failover.
[1][2]
<MAC>.cfg
0-Disabled, the phone will not attempt to register to the secondary server, since the phone assumes that
Permitted
Values
the primary and secondary servers share registration information. So the phone will directly send the
requests to the secondary server.
1-Enabled, the phone will register to the secondary server first, and then send the requests to it.
Default 0
Parameter sip.skip_redundant_failover_addr <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It enables or disables the phone only to send requests to the servers with different IP addresses when
encountering a failover.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
Parameter
account.X.sip_server.Y.only_signal_with_registered
[1][2]
<MAC>.cfg
It enables or disables the phone to only send requests to the registered server when encountering a failover.
Description
Note: It works only if “account.X.sip_server.Y.register_on_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled) and “account.X.sip_
server.Y.failback_mode” is set to 1, 2 or 3.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 3
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
account.X.sip_server.Y.invite_retry_counts
[1][2]
<MAC>.cfg
It configures the number of retries attempted before sending requests to the next available server when
encountering a failover.
Integer from 1 to 10
account.X.sip_server.Y.failback_mode
[1][2]
<MAC>.cfg
It configures the mode for the phone to retry the primary server in failover.
Note: It works only if "template.X.sip_server.Y.address" is set to the domain name of the SIP server.
0-newRequests: all requests are sent to the primary server first, regardless of the last server that was used.
1-DNSTTL: the phone will send requests to the last registered server first. If the time defined by DNSTTL
on the registered server expires, the phone will retry to send requests to the primary server.
2-Registration: the phone will send requests to the last registered server first. If the registration expires,
the phone will retry to send requests to the primary server.
3-duration: the phone will send requests to the last registered server first. If the time defined by the
“account.X.sip_server.Y.failback_timeout” parameter expires, the phone will retry to send requests to the
primary server.
Default 0
Parameter
account.X.sip_server.Y.failback_timeout
[1][2]
<MAC>.cfg
41
Page 45

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
It configures the timeout (in seconds) for the phone to retry to send requests to the primary server after
failing over to the current working server.
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 3600
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 0
[2]
Y is the server ID. Y=1-2.
If you set the parameter to 0, the phone will not send requests to the primary server until a failover event
occurs with the current working server.
If you set the parameter between 1 and 59, the timeout will be 60 seconds.
Note: It works only if “account.X.sip_server.Y.failback_mode” is set to 3 (duration).
0, Integer from 60 to 65535
account.X.sip_server.Y.failback_subscribe.enable
It enables or disables the phone to retry to re-subscribe after registering to the secondary server with different IP addresses when encountering a failover.
Note: It works only if "account.X.sip_server.Y.failback_mode" is set to 1, 2 or 3.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the phone will immediately re-subscribe to the secondary server, for ensuring the normal use
of the features associated with the subscription (for example, BLF, SCA).
SIP Server Name Resolution
[1][2]
<MAC>.cfg
If a domain name is configured for a server, the IP address(es) associated with that domain name will be resolved
through DNS as specified by RFC 3263. The DNS query involves NAPTR, SRV and A queries, which allows the IP phone
to adapt to various deployment environments. The IP phone performs NAPTR query for the NAPTR pointer and transport protocol (UDP, TCP, and TLS), the SRV query on the record returned from the NAPTR for the target domain name
and the port number, and the A query for the IP addresses.
If an explicit port (except 0) is specified, A query will be performed only. If a server port is set to 0 and the transport
type is set to DNS-NAPTR, NAPTR and SRV queries will be tried before falling to A query. If no port is found through
the DNS query, 5060 will be used.
Topic
SIP Server Name Resolution Configuration
SIP Server Name Resolution Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the SIP server name resolution.
Parameter
Description It configures the type of transport protocol.
Permitted
Values
template.X.sip_server.Y.transport_type
0-UDP
1-TCP
2-TLS
[1][2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
42
3-DNS-NAPTR, if no server port is given, the device performs the DNS NAPTR and SRV queries for the ser-
Page 46

Default 0
Web UI
Parameter
vice type and port.
Handset & Account > SIP Server Settings > Edit > SIP Server Y
account.X.naptr_build
[4]
<MAC>.cfg
[2]
> Transport
Account Settings
Description
It configures the way of SRV query for the phone to be performed when no result is returned from the
NAPTR query.
Permitted
Values
0-SRV query using UDP only
1-SRV query using UDP, TCP, and TLS.
Default 0
Parameter sip.dns_transport_type <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the transport protocol the phone uses to perform a DNS query.
Permitted
Values
0-UDP
1-TCP
Default 0
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
static.network.dns.query_timeout
It configures the interval (in seconds) at which the phone retries to resolve a domain name when the DNS
server does not respond.
Integer from 0 to 65535
[3]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 3
Parameter
static.network.dns.retry_times
[3]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the retry times when the DNS server does not respond.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 2
[1]
X is the template ID. X=1-10.
[2]
Y is the server ID. Y=1-2.
[3]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
[4]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
Static DNS Cache
Failover redundancy can only be utilized when the configured domain name of the server is resolved to multiple IP
addresses. If the IP phone is not configured with a DNS server, or the DNS query returns no result from a DNS server,
you can statically configure a set of DNS NAPTR/SRV/A records into the IP phone. The phone will attempt to resolve
the domain name of the SIP server with static DNS cache.
43
Page 47

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Support for negative caching of DNS queries as described in RFC 2308 is also provided to allow faster failover when
prior DNS queries have returned no results from the DNS server.
Topics
Behave with a Configured DNS Server
Static DNS Cache Configuration
Behave with a Configured DNS Server
When the phone is configured with a DNS server, it will behave as follows to resolve the domain name of the server:
l The phone performs a DNS query to resolve the domain name from the DNS server.
l If the DNS query returns no results for the domain name, or the returned record cannot be contacted, the values in
the static DNS cache (if configured) are used when their configured time intervals are not elapsed.
l If the configured time interval is elapsed, the phone will attempt to perform a DNS query again.
l If the DNS query returns a result, the phone will use the returned record from the DNS server and ignore the stat-
ically configured cache values.
When the phone is not configured with a DNS server, it will behave as follows:
l The phone attempts to resolve the domain name within the static DNS cache.
l The phone will always use the results returned from the static DNS cache.
Static DNS Cache Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure static DNS cache.
[2]
[1]
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
<MAC>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Parameter
Description
account.X.dns_cache_type
It configures whether the phone uses the DNS cache for domain name resolution of the SIP server and
caches the additional DNS records.
0-Perform real-time DNS query rather than using DNS cache.
Permitted
Values
1-Use DNS cache, but do not record the additional records.
2-Use DNS cache and cache the additional DNS records.
Default 1
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
account.X.static_cache_pri
It configures whether preferentially to use the static DNS cache for domain name resolution of the SIP
server.
0-Use domain name resolution from server preferentially
1-Use static DNS cache preferentially
Default 0
Parameter
dns_cache_naptr.X.name
Description It configures the domain name to which NAPTR record X refers.
Permitted
Values
Domain name
Default Blank
Parameter
dns_cache_naptr.X.order
[2]
Description It configures the order of NAPTR record X.
44
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Page 48

NAPTR record with the lower order is more preferred.
Account Settings
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 0
Parameter
dns_cache_naptr.X.preference
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the preference of NAPTR record X.
Description
NAPTR record with lower preference is more preferred.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 0
Parameter
dns_cache_naptr.X.replace
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures a domain name to be used for the next SRV query in NAPTR record X.
Permitted
Values
Domain name
Default Blank
Parameter
dns_cache_naptr.X.service
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the transport protocol available for the SIP server in NAPTR record X.
SIP+D2U-SIP over UDP
Permitted
Values
SIP+D2T-SIP over TCP
SIPS+D2T-SIPS over TLS
Default Blank
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
dns_cache_naptr.X.ttl
It configures the time interval (in seconds) that NAPTR record X may be cached before the record should
be consulted again.
Integer from 30 to 2147483647
[2]
Default 300
Parameter
dns_cache_srv.X.name
[2]
Description It configures the domain name in SRVrecord X.
Permitted
Values
Domain name
Default Blank
Parameter
dns_cache_srv.X.port
[2]
Description It configures the port to be used in SRV record X.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 0
Parameter
dns_cache_srv.X.priority
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
45
Page 49

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Description
It configures the priority for the target host in SRV record X.
Lower priority is more preferred.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 0
Parameter
dns_cache_srv.X.target
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the domain name of the target host for an A query in SRV record X.
Permitted
Values
Domain name
Default Blank
Parameter
dns_cache_srv.X.weight
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the weight of the target host in SRVrecord X.
Description
When priorities are equal, weight is used to differentiate the preference. Higher weight is more preferred.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 65535
Default 0
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
dns_cache_srv.X.ttl
It configures the time interval (in seconds) that SRV record X may be cached before the record should be
consulted again.
Integer from 30 to 2147483647
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 300
Parameter
dns_cache_a.X.name
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the domain name in A record X.
Permitted
Values
Domain name
Default Blank
Parameter
dns_cache_a.X.ip
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the IP address that the domain name in A record X maps to.
Permitted
Values
IP address
Default Blank
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
dns_cache_a.X.ttl
It configures the time interval (in seconds) that A record X may be cached before the record should be
consulted again.
Integer from 30 to 2147483647
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 300
Parameter
static.network.dns.ttl_enable
[3]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
46
Page 50

Description It enables or disables the phone to use TTL (Time To Live) in the A record.
Account Settings
Permitted
Values
Default 1
Parameter static.network.dns.last_cache_expired <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 3600
Parameter static.network.dns.last_cache_expired.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 0
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
It configures the validity period of the expired DNS cache.
Note: It works only if "static.network.dns.last_cache_expired.enable" is set to 1(Enabled).
Integer from 0 to 65535
0-the expired DNS cache can only be used once. After using, the phone will perform a DNS query again.
1 to 65535-the phone will use the expired DNS cache during the specified period. After that, the phone
will perform a DNS query again.
It enables or disables the phone to use the DNS cache (even if the cache has expired) when the DNS
server fails to resolve the domain name.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
[2]
X is the record ID. X=1-12.
[3]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
Number of Simultaneous Outgoing Calls
Number of simultaneous outgoing calls allows you to configure the max number of simultaneous outgoing calls for a
specific account on a base.
The number of active handsets affects this feature.
Related Topics
Number of Active Handsets Per Base
Number of Simultaneous Outgoing Calls Configuration
Number of Simultaneous Outgoing Calls Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure the number of simultaneous outgoing calls.
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
account.X.simultaneous_outgoing.num
It configures the max number of simultaneous outgoing calls for a specific account on a base station.
Note: You should set the value of this parameter lower than or equal to “base.active_handset.number”.
Integer from 1 to 8
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Default 8
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
47
Page 51

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Number of Active Handsets Per Base
You can limit the max number of active handsets per W80B base station. The active handsets are free to communicate,
access menu, configure features and so on. Operation is restricted on the inactive handsets, and the idle screen of the
handset prompts "Path Busy".
The number of active handsets will also affect the number of simultaneous active calls on the base station.
Call Supported
Wide-band Calls 4 4 8
Narrow-band Calls 8 8 8
Related Topics
Number of Active Handsets Per Base Configuration
Number of Active
Handsets Per Base
Maximum Number of Sim-
ultaneous Active Calls
Maximum Number of Sim-
ultaneous Calls
Number of Active Handsets Per Base Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure the number of active handsets per base.
Parameter
Description It configures the maximum number of active handsets per base in the DECT multi-cell system.
Permitted
Values
Default 8
Web UI Features > General Information > Number Of Active Handset Per Base
base.active_handset.number
4, 8
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
48
Page 52

Network Configurations
You can make custom network configurations.
Topics
IPv4 Network Settings
DHCP Option for IPv4
VLAN
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) Ports
Network Address Translation (NAT)
VPN
Quality of Service (QoS)
802.1x Authentication
TR-069 Device Management
IPv4 Network Settings
You can configure the devices to operate in IPv4 mode.
Network Configurations
After establishing network connectivity, the devices obtain the IPv4 network settings from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCPv4) server.
You can also configure IPv4 network settings manually.
Note: Yealink devices comply with the DHCPv4 specifications documented in RFC 2131, and ICMPv6 specifications doc-
umented in RFC 4443.
Topics
IPv4 Configuration
IPv4 Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure IPv4.
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Parameter
Description It configures the Internet port type for IPv4.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type
Parameter
static.network.internet_port.type
0-DHCP
2-Static IP
static.network.internet_port.ip
Description
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
It configures the IPv4 address.
Note: It works only if "static.network.internet_port.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
IPv4 Address
49
Page 53

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type (Static IP) > IP Address
Parameter
static.network.internet_port.mask
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IPv4 subnet mask.
Description
Note: It works only if "static.network.internet_port.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted
Values
Subnet Mask
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type (Static IP) > Subnet Mask
Parameter
static.network.internet_port.gateway
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IPv4 default gateway.
Description
Note: It works only if "static.network.internet_port.type" is set to 2 (Static IP).
Permitted
Values
IPv4 Address
Default Blank
Phone UI
Parameter
Settings > Advanced Settings (default password: admin) > Network > WAN Port > IPv4 > Type (Static IP)
> Gateway
static.network.static_dns_enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It triggers the static DNS feature to on or off.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.network.internet_port.type” is set to 0 (DHCP).
Permitted
Values
0-Off, the phone will use the IPv4 DNS obtained from DHCP.
1-On, the phone will use manually configured static IPv4 DNS.
Default 0
Web UI Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Static DNS
Parameter
static.network.primary_dns
[1]
It configures the primary IPv4 DNS server.
Description
Note: In the DHCP environment, you need to make sure “static.network.static_dns_enable" is set to 1
(On).
Permitted
Values
IPv4 Address
Default Blank
Web UI
Parameter
Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type (Static IP)/Configuration Type (DHCP) > Primary
DNS
static.network.secondary_dns
[1]
It configures the secondary IPv4 DNS server.
Description
Note: In the DHCP environment, you need to make sure “static.network.static_dns_enable" is set to 1
(On).
Permitted
Values
IPv4 Address
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
50
Page 54

Default Blank
Network Configurations
Web UI
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
Network > Basic > IPv4 Config > Configuration Type (Static IP)/Configuration Type (DHCP) > Secondary
DNS
DHCP Option for IPv4
The phone can obtain IPv4-related parameters in an IPv4 network via the DHCP option.
Note: For more information on DHCP options, refer to RFC 2131 or RFC 2132.
Topics
Supported DHCP Option for IPv4
DHCP Option 66, Option 43 and Custom Option
DHCP Option 42 Option 2
DHCP Option 12
DHCP Option 60
Supported DHCP Option for IPv4
The following table lists common DHCP options for IPv4 supported by Yealink phones.
Parameters
DHCP
Option
Description
Subnet Mask 1 Specify the client’s subnet mask.
Time Offset 2
Router 3 Specify a list of IP addresses for routers on the client’s subnet.
Time Server 4 Specify a list of time servers available to the client.
Domain Name Server 6 Specify a list of domain name servers available to the client.
Host Name 12 Specify the name of the client.
Domain Server 15
Network Time Protocol
Servers
Vendor-Specific Information
Vendor Class Identifier 60 Identify the vendor type.
TFTP Server Name 66
Specify the offset of the client's subnet in seconds from Coordinated Universal
Time (UTC).
Specify the domain name that the client should use when resolving hostnames
via DNS.
42 Specify a list of NTP servers available to the client by IP address.
43 Identify the vendor-specific information.
Identify a TFTP server when the 'sname' field in the DHCP header has been used
for DHCP options.
DHCP Option 66, Option 43 and Custom Option
During the startup, the phone automatically detects the DHCP option for obtaining the provisioning server address.
The priority is as follows: custom option > option 66 (identify the TFTP server) > option 43.
The phone can obtain the Auto Configuration Server (ACS) address by detecting option 43 during startup.
51
Page 55

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Note: If you fail to configure the DHCP options for discovering the provisioning server on the DHCP server, enable the
phone to automatically discover the provisioning server address. One possibility is that connecting to the secondary DHCP
server that responds to DHCP INFORM queries with a requested provisioning server address. For more information, refer to
RFC 3925.
Related Topic
DHCP Provision Configuration
DHCP Option 42 Option 2
Yealink phones support using the NTP server address offered by DHCP.
DHCP option 42 is used to specify a list of NTP servers available to the client by IP address. NTP servers should be listed
in order of preference.
DHCP option 2 is used to specify the offset of the client’s subnet in seconds from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
Related Topic
NTP Settings
DHCP Option 12
You can specify a hostname for the phone when using DHCP. The DHCP client uses option 12 to send a predefined
hostname to the DHCP registration server.
See RFC 1035 for character set restrictions.
Topic
DHCP Option 12 Hostname Configuration
DHCP Option 12 Hostname Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure DHCP option 12 hostname.
Parameter
Description It specifies a hostname for the phone when using DHCP.
Permitted
Values
Default SIP-W80B
Web UI Features > General Information > DHCP Hostname
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
static.network.dhcp_host_name
String within 99 characters
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
DHCP Option 60
DHCP option 60 is used to indicate the vendor type. Servers can use option 43 to return the vendor-specific information to the client.
You can set the DHCP option 60 type.
Topic
DHCP Option 60 Configuration
52
Page 56

DHCP Option 60 Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure DHCP option 60.
Parameter static.network.dhcp.option60type <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the DHCP option 60 type.
Network Configurations
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Parameter static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.option60_value <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the vendor class identifier string to use in the DHCP interaction.
Permitted
Values
Default yealink
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > IPv4 DHCP Option Value
0-ASCII, vendor-identifying information is in ASCII format.
1-Binary, vendor-identifying information is in the format defined in RFC 3925.
String within 99 characters
VLAN
The purpose of VLAN configurations on the phone is to insert a tag with VLAN information to the packets generated
by the phone. When VLAN is properly configured for the ports (Internet port and PC port) on the phone, the phone will
tag all packets from these ports with the VLAN ID. The switch receives and forwards the tagged packets to the corresponding VLAN according to the VLAN ID in the tag as described in IEEE Std 802.3.
In addition to manual configuration, the phone also supports the automatic discovery of VLAN via LLDP, CDP or DHCP.
The assignment takes effect in this order: assignment via LLDP/CDP, manual configuration, then assignment via DHCP.
Topics
LLDP Configuration
CDP Configuration
Manual VLAN Configuration
DHCP VLAN Configuration
VLAN Change Configuration
LLDP Configuration
LLDP (Linker Layer Discovery Protocol) is a vendor-neutral Link Layer protocol, which allows the phones to advertise its
identity and capabilities on the local network.
When LLDP feature is enabled on the phones, the phones periodically advertise their own information to the directly
connected LLDP-enabled switch. The phones can also receive LLDP packets from the connected switch and obtain
their VLAN IDs.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure LLDP.
Parameter
Description It enables or disables the LLDP feature.
Permitted
Values
static.network.lldp.enable
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the phone attempts to determine its VLAN ID through LLDP.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
53
Page 57

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > LLDP > Active
Parameter
static.network.lldp.packet_interval
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 60
Web UI Network > Advanced > LLDP > Packet Interval (1~3600s)
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
It configures the interval (in seconds) that how often the phone sends the LLDP request.
Note: It works only if “static.network.lldp.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Integer from 1 to 3600
CDP Configuration
CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) allows the phones to receive and/or transmit device-related information from/to directly connected devices on the local network.
When CDP feature is enabled on the phones, the phones periodically advertise their own information to the directly
connected CDP-enabled switch. The phones can also receive LLDP packets from the connected switch and obtain their
VLAN IDs.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure CDP.
Parameter
Description It enables or disables the CDP feature.
Permitted
Values
static.network.cdp.enable
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the phone attempts to determine its VLAN ID through CDP.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > CDP > Active
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 60
Web UI Network > Advanced > CDP > Packet Interval (1~3600s)
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
static.network.cdp.packet_interval
It configures the interval (in seconds) that how often the phone sends the CDP request.
Note: It works only if “static.network.cdp.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Integer from 1 to 3600
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Manual VLAN Configuration
You can configure VLAN for the Internet port manually. Before configuring VLAN on the phones, you need to obtain
the VLAN ID from your network administrator.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure VLAN manually.
54
Page 58

Network Configurations
Parameter
static.network.vlan.internet_port_enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the VLAN for the Internet port.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > WAN Port > Active
Parameter
static.network.vlan.internet_port_vid
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the VLAN ID for the Internet port.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.network.vlan.internet_port_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1 to 4094
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > WAN Port > VID (1-4094)
Parameter
static.network.vlan.internet_port_priority
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the VLAN priority for the Internet port.
Description
7 is the highest priority, 0 is the lowest priority.
Note: It works only if “static.network.vlan.internet_port_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 0 to 7
Default 0
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > WAN Port > Priority
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
DHCP VLAN Configuration
When the VLAN discovery method is set to DHCP, the phone examines the DHCP option for a valid VLAN ID. You can
customize the DHCP option used to request the VLAN ID.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure DHCP VLAN discovery.
Parameter
static.network.vlan.dhcp_enable
Description It enables or disables the DHCP VLAN discovery feature.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > DHCP VLAN > Active
Parameter
static.network.vlan.dhcp_option
It configures the DHCP option from which the phone will obtain the VLAN settings.
Description
Multiple DHCP options (at most five) are separated by commas.
Permitted
Integer from 1 to 255
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
55
Page 59

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Values
Default 132
Web UI Network > Advanced > VLAN > DHCP VLAN > Option (1-255)
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
VLAN Change Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure the VLAN change.
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 0
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
static.network.vlan.vlan_change.enable
It enables or disables the phone to obtain VLAN ID using lower preference of VLAN assignment method,
or to close the VLAN feature when the phone cannot obtain VLAN ID.
The priority of each method is LLDP/CDP > Manual > DHCP VLAN.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the phone attempts to use the lower priority method when failing to obtain the VLAN ID using
higher priority method. If all the methods are attempted, the phone will disable VLAN feature.
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) Ports
Since the phone supports conferencing and multiple RTP streams, it can use several ports concurrently. You can specify the phone’s RTP port range.
The UDP port used for RTP streams is traditionally an even-numbered port. If the port 11780 is used to send and receive
RTP for the first voice session, additional calls would then use ports 11782, 11784, 11786, and so on. The phone is compatible with RFC 1889 - RTP: A Transport Protocol for Real-Time Applications - and the updated RFC 3550.
Topic
RTP Ports Configuration
RTP Ports Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure RTP ports.
Parameter
Description It configures the minimum local RTP port.
Permitted
Values
Default 11780
Web UI Network > Advanced > Local RTP Port > Min RTP Port (1024~65535)
Parameter
Description It configures the maximum local RTP port.
Permitted
Values
56
static.network.port.min_rtpport
Integer from 1024to 65535
static.network.port.max_rtpport
Integer from 1024to 65535
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Page 60

Network Configurations
Default 12780
Web UI Network > Advanced > Local RTP Port > Max RTP Port (1024~65535)
Parameter features.rtp_symmetric.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the symmetrical RTP feature.
0-Disabled
Permitted
Values
Default 0
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
1-reject RTP packets arriving from a non-negotiated IP address
2-reject RTP packets arriving from a non-negotiated port
3-reject RTP packets arriving from a non-negotiated IP address or a non-negotiated port
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT enables phones with private unregistered addresses to communicate with devices with globally unique registered
addresses.
Topics
NAT Traversal Configuration
Keep Alive Configuration
Rport Configuration
SIP Port and TLS Port Configuration
NAT Traversal Configuration
The phones can traverse NAT gateways to establish and maintain connections with external devices.
Yealink phones support three NAT traversal techniques: manual NAT, STUN and ICE. If you enable manual NAT and
STUN, the phone will use the manually-configured external IP address for NAT traversal. The TURN protocol is used as
part of the ICE approach to NAT traversal.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure NAT traversal.
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > NAT
Parameter
Description It enables or disables the manual NAT feature.
account.X.nat.nat_traversal
It enables or disables the NAT traversal for a specific account.
Note: If it is set to 1 (STUN), it works only if “static.sip.nat_stun.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled); if it is set to 2
(Manual NAT), it works only if “static.network.static_nat.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
0-Disabled
1-STUN
2-Manual NAT
static.network.static_nat.enable
[1]
[2]
<MAC>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
57
Page 61

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Network > NAT > Manual NAT > Active
Parameter static.network.static_nat.addr <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IP address to be advertised in SIP signaling.
Description
It should match the external IP address used by the NAT device.
Note: It works only if “static.network.static_nat.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
IP Address
Default Blank
Web UI Network > NAT > Manual NAT > IP Address
Parameter static.sip.nat_stun.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs) feature.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Network > NAT > STUN > Active
Parameter static.sip.nat_stun.server <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IP address or domain name of the STUN server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.sip.nat_stun.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
String
Default Blank
Web UI Network > NAT > STUN > STUN Server
Parameter static.sip.nat_stun.port <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the port of the STUN server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.sip.nat_stun.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1024to 65535
Default 3478
Web UI Network > NAT > STUN > STUN Port (1024~65535)
Parameter
static.ice.enable
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment) feature.
Permitted
Values
58
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Page 62

Default 0
Web UI Network > NAT > ICE > Active
Network Configurations
Parameter
static.sip.nat_turn.enable
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the TURN (Traversal Using Relays around NAT) feature.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
Web UI Network > NAT > TURN > Active
Parameter
static.sip.nat_turn.server
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the IP address or the domain name of the TURN server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.sip.nat_turn.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
IP Address or Domain Name
Default Blank
Web UI Network > NAT > TURN > TURN Server
Parameter
static.sip.nat_turn.port
[2]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the port of the TURN server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.sip.nat_turn.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1024to 65535
Default 3478
Web UI Network > NAT > TURN > TURN Port (1024~65535)
Parameter
static.sip.nat_turn.username
[2]
It configures the user name to authenticate to the TURN server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.sip.nat_turn.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
String
Default Blank
Web UI Network > NAT > TURN > User Name (Username)
Parameter
static.sip.nat_turn.password
[2]
It configures the password to authenticate to the TURN server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.sip.nat_turn.enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
String
Default Blank
Web UI Network > NAT > TURN > Password
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
59
Page 63

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Parameter features.media_transmit.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It enables or disables the media stream to be forward forcibly on the DECT manager (DM) during a
STUN/ICE call.
Description
Note: The value configured by the parameter “account.X.media_transmit.enable” takes precedence over
that configured by this parameter.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 0
You need to enable this feature when there are some network differences between the DM and base station. For example:
1. You assigned a static NAT address to the DM only and did NAT mapping on the firewall or gateway.
Case Scenario
2. LLDP/VLAN is enabled on the DM but not on the base station, and the router only limits LLDP/VLAN
access to the external network.
3. The base stations are connected to the DM, but the DM and the far-site device establish a connection
through a VPN.
4. For security, the DM's IP address is added in the whitelist but the base's IP address is not added in the
whitelist.
Parameter
account.X.media_transmit.enable
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
It enables or disables the media stream to be forward forcibly on the DECT manager (DM) during a
STUN/ICE call.
Description
Note: The value configured by this parameter takes precedence over that configured by the parameter
“features.media_transmit.enable”.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default Blank
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
[2]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
Keep Alive Configuration
Yealink phones can send keep-alive packets to the NAT device for keeping the communication port open.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure keep alive.
Parameter
account.X.nat.udp_update_enable
Description It sets the type of keep-alive packets sent by phone.
0-Disabled
Permitted
Values
1-Default (the phone sends the corresponding packets according to the transport protocol)
2-Options (the phone sends SIP OPTIONS packets to the server)
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Default 1
60
3-Notify (the phone sends SIP NOTIFY packets to the server)
Page 64

Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Keep Alive Type
Parameter
account.X.nat.udp_update_time
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Network Configurations
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 30
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > Keep Alive Interval (Seconds)
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
It configures the interval (in seconds) at which the phone sends a keep-alive package.
Note: It works only if “account.X.nat.udp_update_enable” is set to 1, 2 or 3.
Integer from 15 to 2147483647
Rport Configuration
Rport allows a client to request that the server sends the response back to the source IP address and port from which
the request originated. It helps the phone traverse symmetric NATs.
Rport feature depends on support from a SIP server. For more information, refer to RFC 3581.
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure rport.
Parameter
Description It enables or disables the phone to add the "rport" parameter in the Via header.
Permitted
Values
account.X.nat.rport
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, the INVITE Contact header uses the port in the "rport" parameter but does not use the source
IP address in the "received" parameter in the Via header of server's response.
2-Enable Direct Process, the INVITE Contact header uses the port in the "rport" parameter and uses the
source IP address in the "received" parameter in the Via header of server's response.
[1]
<MAC>.cfg
Default 0
Web UI Handset & Account > Handset Registration > Add Handset/Edit > RPort
[1]
X is the account ID. X=1-100.
SIP Port and TLS Port Configuration
You can configure the SIP and TLS source ports on the phone. Otherwise, the phone uses default values (5060 for
UDP/TCP and 5061 for TLS).
If NAT is disabled, the port number shows in the Via and Contact SIP headers of SIP messages. If NAT is enabled, the
phone uses the NAT port number (and NAT IP address) in the Via and Contact SIP headers of SIP messages, but still
using the configured source port.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure SIP port and TLS port.
Parameter sip.listen_port <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It specifies the local SIP port.
If it is set to 0, the phone will automatically listen to the local SIP port.
0, Integer from 1024to 65535
61
Page 65

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Default 5060
Parameter sip.tls_listen_port <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 5061
It specifies the local TLS listen port.
If it is set to 0, the phone will not listen to the TLS service.
0, Integer from 1024to 65535
VPN
Yealink phones use OpenVPN to achieve VPN feature. To prevent disclosure of private information, tunnel endpoints
must authenticate each other before a secure VPN tunnel is established. After you configure VPN feature on the IP
phone, the phone will act as a VPN client and use the certificates to authenticate with the VPN server.
Topics
OpenVPN Related Files
VPN Configuration
OpenVPN Related Files
To use OpenVPN, you should collect the VPN-related files into one archive file in .tar format and then upload this tar
file. The VPN-related files include certificates (ca.crt and client.crt), key (client.key) and the configuration file (vpn.cnf)
of the VPN client.
The following table lists the unified directories of the OpenVPN certificates and key in the configuration file (vpn.cnf)
for Yealink phones:
VPN Files Description Unified Directories
ca.crt CA certificate /config/openvpn/keys/ca.crt
client.crt Client certificate /config/openvpn/keys/client.crt
client.key Private key of the client /config/openvpn/keys/client.key
VPN Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the VPN.
Parameter
Description It enables or disables the VPN feature.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Network > Advanced > VPN > Active
Parameter static.openvpn.url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the access URL of the *.tar file for OpenVPN.
Permitted
static.network.vpn_enable
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
URL within 511 characters
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
62
Page 66

Network Configurations
Values
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Advanced > VPN > Upload VPN Config
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
Quality of Service (QoS)
VoIP is extremely bandwidth and delay-sensitive. QoS is a major issue in VoIP implementations, regarding how to guarantee that packet traffic is not delayed or dropped due to interference from other lower priority traffic. VoIP can guarantee high-quality QoS only if the voice and the SIP packets are given priority over other kinds of network traffic. The
phones support the DiffServ model of QoS.
Voice QoS
In order to make VoIP transmissions intelligible to receivers, voice packets should not be dropped, excessively delayed,
or made to suffer varying delay. DiffServ model can guarantee high-quality voice transmission when the voice packets
are configured to a higher DSCP value.
SIP QoS
The SIP protocol is used for creating, modifying, and terminating two-party or multi-party sessions. To ensure good
voice quality, SIP packets emanated from the phones should be configured with a high transmission priority.
DSCPs for voice and SIP packets can be specified respectively.
Note: For voice and SIP packets, the phone obtains DSCP info from the network policy if LLDP feature is enabled, which
takes precedence over manual settings. For more information on LLDP, refer to LLDP Configuration.
Topic
Voice and SIP QoS Configuration
Voice and SIP QoS Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure voice QoS and SIP QoS.
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 46
static.network.qos.audiotos
It configures the DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) for voice packets.
The default DSCP value for RTP packets is 46 (Expedited Forwarding).
Integer from 0 to 63
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Web UI Network > Advanced > QoS > Voice QoS (0~63)
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
static.network.qos.signaltos
It configures the DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) for SIP packets.
The default DSCP value for SIP packets is 26(Assured Forwarding).
Integer from 0 to 63
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
63
Page 67

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Default 26
Web UI Network > Advanced > QoS > SIP QoS (0~63)
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
TR-069 Device Management
TR-069 is a technical specification defined by the Broadband Forum, which defines a mechanism that encompasses
secure auto-configuration of a CPE (Customer-Premises Equipment), and incorporates other CPE management functions into a common framework. TR-069 uses common transport mechanisms (HTTP and HTTPS) for communication
between CPE and ACS (Auto Configuration Servers). The HTTP(S) messages contain XML-RPC methods defined in the
standard for configuration and management of the CPE.
Topics
Supported RPC Methods
TR-069 Configuration
Supported RPC Methods
The following table provides a description of RPC methods supported by the phones.
RPC Method Description
GetRPCMethods This method is used to discover the set of methods supported by the CPE.
SetParameterValues This method is used to modify the value of one or more CPE parameters.
GetParameterValues This method is used to obtain the value of one or more CPE parameters.
GetParameterNames This method is used to discover the parameters accessible on a particular CPE.
GetParameterAttributes This method is used to read the attributes associated with one or more CPE parameters.
SetParameterAttributes This method is used to modify attributes associated with one or more CPE parameters.
Reboot This method causes the CPE to reboot.
This method is used to cause the CPE to download a specified file from the designated location.
Download
File types supported by the phones are:
l Firmware Image
l Configuration File
This method is used to cause the CPE to upload a specified file to the designated location.
Upload
ScheduleInform
File types supported by the phones are:
l Configuration File
l Log File
This method is used to request the CPE to schedule a one-time Inform method call (separate
from its periodic Inform method calls) sometime in the future.
FactoryReset This method resets the CPE to its factory default state.
TransferComplete
This method informs the ACS of the completion (either successful or unsuccessful) of a file
transfer initiated by an earlier Download or Upload method call.
64
Page 68

Network Configurations
RPC Method Description
AddObject This method is used to add a new instance of an object defined on the CPE.
DeleteObject This method is used to remove a particular instance of an object.
TR-069 Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure TR-069.
Parameter static.managementserver.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the TR-069 feature.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Settings > TR069 > Enable TR069
Parameter static.managementserver.username <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
Web UI Settings > TR069 > ACS Username
Parameter static.managementserver.password <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
It configures the TR-069 ACS server user name used to authenticate the phone.
Leave it blank if no authentication is required.
String within 128 characters
It configures the TR-069 ACS server password used to authenticate the phone.
Leave it blank if no authentication is required.
String within 64 characters
Web UI Settings > TR069 > ACS Password
Parameter static.managementserver.url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the access URL of the TR-069 ACS server.
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
Web UI Settings > TR069 > ACS URL
Parameter static.managementserver.connection_request_username <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the user name used to authenticate the connection requests from the ACS server.
Permitted
Values
URL within 511 characters
String within 128 characters
65
Page 69

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Default Blank
Web UI Settings > TR069 > Connection Request Username
Parameter static.managementserver.connection_request_password <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the password used to authenticate the connection requests from the ACS server.
Permitted
Values
String within 64 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Settings > TR069 > Connection Request Password
Parameter static.managementserver.periodic_inform_enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables the phone to periodically report its configuration information to the ACSserver.
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
Web UI Settings > TR069 > Enable Periodic Inform
Parameter static.managementserver.periodic_inform_interval <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the interval (in seconds) at which the phone reports its configuration to the ACS server.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.managementserver.periodic_inform_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 5 to 4294967295
Default 60
Web UI Settings > TR069 > Periodic Inform Interval (seconds)
802.1x Authentication
Yealink phones support the following protocols for 802.1x authentication:
l EAP-MD5
l EAP-TLS (requires Device and CA certificates, requires no password)
l EAP-PEAP/MSCHAPv2 (requires CA certificates)
l EAP-TTLS/EAP-MSCHAPv2 (requires CA certificates)
l EAP-PEAP/GTC (requires CA certificates)
l EAP-TTLS/EAP-GTC (requires CA certificates)
l EAP-FAST (supports EAP In-Band provisioning, requires CA certificates if the provisioning method is Authenticated
Provisioning)
Topic
802.1x Authentication Configuration
802.1x Authentication Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure 802.1x authentication.
Parameter
static.network.802_1x.mode
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
66
Page 70

Description It configures the 802.1x authentication method.
0-EAP-None, no authentication
1-EAP-MD5
2-EAP-TLS
Network Configurations
Permitted
Values
3-EAP-MSCHAPv2
4-EAP-TTLS/EAP-MSCHAPv2
5-EAP-PEAP/GTC
6-EAP-TTLS/EAP-GTC
7-EAP-FAST
Default 0
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > 802.1x Mode
Parameter
static.network.802_1x.eap_fast_provision_mode
[1]
It configures the EAP In-Band provisioning method for EAP-FAST.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.network.802_1x.mode” is set to 7 (EAP-FAST).
0-Unauthenticated Provisioning, EAP In-Band provisioning is enabled by server unauthenticated PAC
Permitted
Values
(Protected Access Credential) provisioning using the anonymous Diffie-Hellman key exchange.
1-Authenticated Provisioning, EAP In-Band provisioning is enabled by server authenticated PAC provisioning using certificate-based server authentication.
Default 0
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > Provisioning Mode
Parameter
static.network.802_1x.anonymous_identity
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the anonymous identity (user name) for 802.1X authentication.
Description
It is used for constructing a secure tunnel for 802.1X authentication.
Note: It works only if “static.network.802_1x.mode” is set to 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7.
Permitted
Values
String within 512 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > Anonymous Identity
Parameter
static.network.802_1x.identity
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the identity (user name) for 802.1x authentication.
Permitted
Values
String within 32 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > Identity
Parameter
static.network.802_1x.md5_password
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It configures the password for 802.1x authentication.
67
Page 71

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Note: It is required for all methods except EAP-TLS.
Permitted
Values
String within 32 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > MD5 Password
Parameter static.network.802_1x.root_cert_url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the URL for uploading the 802.1x CA certificate.
The format of the certificate must be *.pem, *.crt, *.cer or *.der.
Description
Note: It works only if “static.network.802_1x.mode” is set to 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7. If the authentication method
is EAP-FAST, you also need to set “static.network.802_1x.eap_fast_provision_mode” to 1 (Authenticated
Provisioning).
Permitted
Values
URL within 511 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > CA Certificates
Parameter static.network.802_1x.client_cert_url <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the URL for uploading the 802.1x client certificate.
Description
The format of the certificate must be *.pem.
Note: It works only if “static.network.802_1x.mode” is set to 2 (EAP-TLS).
Permitted
Values
URL within 511 characters
Default Blank
Web UI Network > Advanced > 802.1x > Device Certificates
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
68
Page 72

Web Statistics
Web Statistics
Web statistics is the measurement, collection, analysis and reporting of system data for purposes of understanding and
optimizing the multi-cell system. When an abnormality occurs in the system, you can preliminarily check and locate
the problem through the Statistics page.
Topics
Base Station Group
All Calls
Base Stations Calls
Handsets Calls
Abnormal Calls
Upgrade Information
DECT Signal
Base Station Group
The module of base station group shows the synchronization information among base stations. It can display the
information of up to 30 base stations.
Topics
Base Station Statistics
Cluster Graph Statistics
Viewing Base Station Group Statistics
Base Station Statistics
The properties are shown below:
Item Description
Base Station Name of the base station.
RPN Radio Fixed Part Number. The base station identity allocated by the DECT system.
IP IP address of the base station.
MAC MAC address of the base station.
Sync Level Sync level within the sync hierarchy.
Synchronization status of the base station.
Base Status
• Offline: not available.
• Deactive: available but not activated.
• Active: activated but not synchronized.
• Active and synced: activated and synchronized.
• Upgrading: firmware upgrading.
69
Page 73

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Item Description
RPN and signal value of the synchronous base.
RSSI
For example, "RPN3 (-76dBm)" indicates that the current base is synchronized with the base that
is numbered RPN3 and the signal value is -76dBm.
Note: RSSI refreshes automatically every 20 seconds.
Interference Number of interferences detected by base.
Fre: frequency band where the base on a higher sync level is located.
Slot: slot where the base on a higher sync level is located.
For example, "8/6 (Good)" indicates that the frequency band of the base on a higher sync level is
Fre/Slot
8, the slot is 6, and the synchronization with the base is Good.
Note: The synchronization with the base on a higher sync level includes Good, Normal, Weak,
Unknown, and "-", where Unknown is displayed when the information is not updated, and "-"
is displayed when the base is offline.
Signal Num The number of signals that is greater or equal to -88dbm (RSSI > =-0x48) detected by base.
Network Drop The number of network disconnections.
The latest startup time of the base.
Start Time
Note: It will not be reset even if you manually clear the statistical data.
Due to the different base statuses, the following items are specially explained:
l Async、Network Drop: Corresponding values are displayed for any base status.
l Signal Num、Start Time: A value is displayed only when the base status is Active or Active and synced, and "—" is
displayed for other base statuses.
l RSSI、Fre/Slot: A value is displayed only when the base status is Active and synced, and "—" is displayed for other
base statuses.
l For the base with sync level 1, the following items always display "-": RSSI, Async, and Fre/Slot.
Cluster Graph Statistics
The tree map is described as follows:
(1) Cables
Different cables are used between the bases to indicate the synchronized base signal.
l
Solid blue line ( ): -85dBm <= RSSI <= -28dBm
l
Red dotted line ( ): -99dBm < RSSI <= -86dBm
l
Gray dotted line ( ): No data available
Note
When the base status is not Active and synced, the base does not display the synchronized RSSI value. Both are connected
with a gray dotted line.
If the previous base on a higher sync level cannot be found (such as the base was deleted), there is no connection line, it is
displayed individually and placed under the base with sync level 1.
70
Page 74

Web Statistics
(2) Circles
Different circles are used to indicate different base status.
l
White hollow circle ( ): Active and synced
l
Red solid circle ( ): Offline, Active, Upgrading
l
Gray solid circle ( ): Deactive
Hovering the mouse over the corresponding base will display the base details in the floating window, as shown below:
Viewing Base Station Group Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Status > Base Station Group.
3. You can do the following:
l Select the desired cluster from the Base Station Cluster drop-down menu, and click Show Cluster Graph to
view the synchronization information of the base.
71
Page 75

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
To save the tree map, click Save Image.
The picture is stored in PNG format by default.
l Select the desired cluster from the Base Station Cluster drop-down menu, select the search type and enter the
search criteria to perform a search.
l Click Reset to clear and restart the statistics.
l Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
Related Topics
Base Station Statistics
Cluster Graph Statistics
All Calls
The module of all calls shows the call information of all handsets in the system. Up to 100 call records can be displayed,
and the oldest one will be automatically deleted if the max limit has been reached.
Topics
All Calls Statistics
Viewing All Calls Statistics
72
Page 76

All Calls Statistics
The properties are shown below:
Item Description
Call Time Time when the call was established.
Duration Call duration.
Call Type Call type, including Placed Calls, Received Calls, and Missed Calls.
Local identity of the call. Local User is the local account, and Handset is the local handset
number.
Local User (Handset)
For example, 5707 (H7) indicates that the local account is 5707 and the handset number is
H7.
Remote User Far-site information of the call.
Web Statistics
Call performance during a call, including Transfer, Conference, and Forward.
Operation
Note: Only when a network conference is performed during a call will it be recorded as Con-
ference.
Viewing All Calls Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Statistics > All Calls.
3. Select the desired call type from the Call Type drop-down menu.
4. You can do the following:
l
Click to customize the properties displayed in the statistics table.
l Click Reset to clear and restart the statistics.
l Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
73
Page 77

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Related Topics
All Calls Statistics
Base Stations Calls
The module of base station calls shows the call information on each base station in the system. Up to 100 call records
can be displayed, and the oldest one will be automatically deleted if the max limit has been reached.
Topics
Base Stations Calls Statistics
Viewing Base Stations Calls Statistics
Base Stations Calls Statistics
The following shows base stations calls information:
Item Description
Base Station Name of the base station.
IP IP address of the base station.
MAC MAC address of the base station.
Active Number of active handsets on the base station.
Max Active
Busy
Handover In Number of incoming handovers
Handover Out
Call Drops
Maximum number of active handsets that have appeared on the base station.
Note: The maximum number of active handsets in narrowband is 8and in wideband is 4.
Number of busy-state the base station has entered. The busy-state indicates that the number of
active handsets under the base station reaches the limit (narrowband: 8; wideband: 4).
Number of outgoing handovers
Note: If a call is established on a base, the outgoing handovers are all recorded by this base. For
example, if H1 establishes a call on Base1, roams to Base2 during the call, and then roams to
Base3, the number of outgoing handovers on Base1 is 2, and the number of incoming handovers
on Base1, Base2, and Base3 is 1.
Number of lost connections, for example, interrupted calls
Format: number of lost connections / total number of calls
For example, "1/4 (25%)" indicates that the total number of calls is 4, and the call is interrupted
once.
Number of silent calls on the base.
No Audio
74
Format: number of silent calls / total number of calls
For example, "1/4 (25%)" indicates that the total number of calls is 4, and the silent call occurs
once.
Page 78

Item Description
Note: The number of silent times during a call is counted as one, and only the silent that occurs
when the handset is not roaming during the call can be counted.
Note
The last line is the sum of all base call statistics.
Viewing Base Stations Calls Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Statistics > Base Stations Calls.
3. Select the desired call type from the Call Type drop-down menu.
Web Statistics
4. You can do the following:
l
Click to customize the properties displayed in the statistics table.
l Click Reset to clear and restart the statistics.
l Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
Related Topics
Base Stations Calls Statistics
Handsets Calls
The module of handsets calls shows the call information on each handset in the system. It can display the information
of up to 100 handsets.
Topics
Handsets Calls Statistics
Viewing Handsets Calls Statistics
Handsets Calls Statistics
The following shows all handsets call information:
75
Page 79

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Field Description
Handset
Handset name
The registered handsets are displayed in ascending order.
Account Account number of the handset.
Abnormal Calls /
Total
All abnormal calls / total calls of the handset.
Average Call Average call duration of all calls on the handset.
Max Call Maximum call duration for all calls on the handset.
Min Call
Minimum call duration for all calls on the handset, including the number of calls with a duration
of 0, such as Missed Call, Outgoing Rejection, and Incoming Call Rejection.
Note
The last line is the sum of all handset call statistics. Handsets that have not yet established a call are not counted.
Viewing Handsets Calls Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Statistics > Handsets Calls.
3. You can do the following:
l Select the search type and enter the search criteria to perform a search.
l
Click to customize the properties displayed in the statistics table.
l Click Reset to clear and restart the statistics.
l Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
Related Topics
Handsets Calls Statistics
76
Page 80

Web Statistics
Abnormal Calls
The module of abnormal calls shows the abnormal call information in the system. Up to 30 call records can be displayed, and the oldest one will be automatically deleted if the max limit has been reached.
Topics
Abnormal Calls Statistics
Viewing Abnormal Calls Statistics
Abnormal Calls Statistics
The following shows all abnormal calls information:
Item Description
Call Time Time when the call was established.
Handset Handset which has an abnormal call.
Account Account number for the current handset.
Call Type Call type, including Placed Calls, Received Calls, and Missed Calls.
Duration Call duration.
Base Handover Base received a handover during the call.
Codec SIP codec used for the call negotiation.
Remote User Far-site information of the call.
Status Final state of the call.
Reason Reason why the abnormality occurs during the call.
Packet Loss Rate
Packet loss rate of the call.
Note: This function is not supported for the time being, it is displayed as "—".
Viewing Abnormal Calls Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Statistics > Abnormal Calls.
3. Select the desired call type from the Call Type drop-down menu.
77
Page 81

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
4. You can do the following:
l Select the search type and enter the search criteria to perform a search.
l
Click to customize the properties displayed in the statistics table.
l Click Reset to clear and restart the statistics.
l Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
Related Topics
Abnormal Calls Statistics
Upgrade Information
The module of upgrade information shows the information about handset upgrade, including upgrading via web user
interface, auto provisioning, or the handset. Up to 6 records will be displayed and the oldest will be automatically
deleted.
Topics
Upgrade Information Statistics
Viewing Upgrade Information Statistics
Upgrade Information Statistics
The following shows all the upgrade information:
Field Description
Upgrade Time Start time of the upgrade.
Upgrade mode, including Normal and Grayscale Upgrade.
Upgrade Method
Note: When upgrading via the web user interface, you can choose to upgrade in normal or gray-
scale mode, and the default upgrade mode for the handset upgrade is the grayscale mode.
Duration How long the upgrade process lasts.
Devices
Type of the device that is upgraded at this time, including W53H, W56H, T41S + DD10K, and
CP930W.
78
Page 82

Field Description
Total Total number of handsets to be upgraded this time.
Successed Number of handsets successfully upgraded this time.
Failed Number of handsets that failed to upgrade this time.
No Upgrade Number of handsets that are not upgraded this time.
Handset that failed to upgrade.
If there are more than 3, the first 3 will be displayed, and the following will be displayed as an
ellipsis. Such as "H1, H2, H3 ...", when you hover your mouse to this place, all the information of
Description
the handsets that failed to upgrade will be displayed.
If all handsets are successfully upgraded, it displays nothing.
Note: It will not be recorded if the handset is not upgraded due to the same firmware version.
Web Statistics
You may need to know the following statistical rules for the same version upgrade:
l If all handsets involved in this upgrade are the same as the upgraded version, there is no upgrade record.
l If some of the handsets involved in this upgrade are the same as the upgraded version, records of no upgrade
caused by the same version will be recorded in the No Upgrade field.
Viewing Upgrade Information Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Statistics > Upgrade Information.
3. You can do the following:
l Select the search type and enter the search criteria to perform a search.
l
Click to customize the properties displayed in the statistics table.
l Click Reset to clear and restart the statistics.
l Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
Related Topics
79
Page 83

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Upgrade Information Statistics
DECT Signal
The module of DECT signal shows signal interference around each base station in the system.
Topics
DECT Signal Statistics
Viewing DECT Signal Statistics
DECT Signal Statistics
The following shows some special values:
dBm RSSI Description
0 FF The position of the base or the position of the handset under the base.
The meaning of each color in the statistical table is as follows.
RSSI dBm RSSI
[-73,-27] [70,D8]
[-88,-73) [48,70)
[-97,-88) [30,48)
[-99,-97)&0 [0,30)&FF
Note
The data presented in the statistics table includes the signal data transmitted by the base of the same system and the calls
under the base.
The frequency bands in different regions of different versions are different. The frequency bands here start from 0. The
actual number of frequency bands is based on actual conditions. For example, the frequency band used by Korea is Freq6Freq8, but Freq0- Freq2 are displayed instead.
Viewing DECT Signal Statistics
Procedure
1. Access the web user interface of the DM.
2. Navigate to Statistics > DECT Signal.
3. Select the desired base station.
4. Select the desired unit.
80
Page 84

5. Click Refresh to refresh the current statistics.
Related Topics
DECT Signal Statistics
Web Statistics
81
Page 85

Phone Provisioning
Phone Provisioning
You can provision multiple phones with the same settings for large-scale deployments.
For more information, refer to Yealink SIP IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide.
Topics
Boot Files, Configuration Files, and Resource Files
Provisioning Methods
Setting Up a Provisioning Server
Keeping User’s Personalized Settings after Auto Provisioning
Boot Files, Configuration Files, and Resource Files
You can use boot files, configuration files, and resource files to configure phone features and apply feature settings to
phones. You can create or edit these files using a text editor such as Notepad++.
You can ask the distributor or Yealink FAE for template files. You can also obtain the template files online: http://sup-
port.yealink.com/documentFront/forwardToDocumentFrontDisplayPage.
Topics
Boot Files
Configuration Files
Resource Files
Files Download Process
Boot Files
Yealink phones support boot files. The boot files maximize the flexibility to allow you to customize features and settings for multiple phones.
With the boot file, you can specify which configuration files should be downloaded. It is effective for you to provision
the phones in different deployment scenarios:
l For all phones
l For a group of phones
l For a single phone
Yealink phones support two types of boot files: common boot file and MAC-Oriented boot file. You can use the default
boot template file “y000000000000.boot” to create MAC-Oriented boot file by making a copy and renaming it.
Note: You can select whether to use the boot file or not according to your deployment scenario. If you do not want to use
the boot file, please go to Configuration Files.
Topics
Common Boot File
MAC-Oriented Boot File
Boot File Attributes
Customizing a Boot File
Common Boot File
Common boot file, named y000000000000.boot, is effective for all phones. You can use a common boot file to apply
common feature settings to all of the phones rather than a single phone.
82
Page 86

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
MAC-Oriented Boot File
MAC-Oriented boot file, named <MAC>.boot. It will only be effective for a specific IP phone. In this way, you have
high permission to control each phone by making changes on a per-phone basis.
You can create a MAC-Oriented boot file for each phone by making a copy and renaming the boot template file
(y000000000000.boot). For example, if your phone MAC address is 00156574B150, rename the template file as
00156574b150.boot (lowercase).
Tip: MAC address, a unique 12-digit serial number is assigned to each phone. You can obtain it from the bar code on the
back of the base.
Boot File Attributes
The following table lists the attributes you need to know in the boot template file.
Attributes Description
#!version:1.0.0.1 It must be placed in the first line. Do not edit and delete.
Each “include” statement can specify a location of a configuration file. The configuration file format must be *.cfg.
The locations in the angle brackets or double quotation marks support two forms:
include:config <xxx.cfg>
include:config "xxx.cfg"
l Relative path (relative to the boot file):
For example, sip.cfg, HTTP Directory/sip.cfg
l Absolute path (or URL):
For example, http://10.2.5.258/HTTP Directory/sip.cfg
The location must point to a specific CFG file.
Enable or disable the overwrite mode.
1-(Enabled) - If the value of a parameter in configuration files is left blank, or if a
non-static parameter in configuration files is deleted or commented out, the factory default value takes effect.
overwrite_mode
0-(Disabled) - If the value of a parameter in configuration files is left blank, deleted
or commented out, the pre-configured value is kept.
Note: Overwrite mode can only be used in boot files. If a boot file is used but “overwrite_mode” is not configured, the overwrite mode is enabled by default.
Tip: The line beginning with “#” is considered to be a comment. You can use “#” to make any comment on the boot file.
Customizing a Boot File
Procedure
1. Open a boot template file.
2. To add a configuration file, add include:config < > or include:config “” to the file. Each starts on a separate line.
3. Specify a configuration file for downloading.
For example:
include:config <configure/sip.cfg >
include:config “http://10.2.5.206/configure/account.cfg”
include:config “http://10.2.5.206/configure/dialplan.cfg”
83
Page 87

Phone Provisioning
4. Specify the overwrite mode.
For example:
overwrite_mode = 1
5. Save the boot file and place it on the provisioning server.
Related Topic
Boot File Attributes
Configuration Files
Yealink supports two configuration template files: Common CFG file and MAC-Oriented CFG file.
These configuration files contain two kinds of parameters:
l Static: The parameters start with a prefix “static.”, for example, static.auto_provision.custom.protect.
l Non-static: The parameters do not start with a prefix “static.”, for example, local_time.date_format.
You can deploy and maintain a mass of Yealink phones automatically through configuration files stored in a provisioning server.
Note: For protecting against unauthorized access, you can encrypt configuration files. For more information on encrypting
configuration files, refer to Encrypting and Decrypting Files.
Topics
Common CFG File
MAC-Oriented CFG File
MAC-local CFG File
Configuration File Customization
Configuration File Attributes
Common CFG File
Common CFG file, named <y0000000000xx>.cfg, contains parameters that affect the basic operation of the IP phone,
such as language and volume. It will be effective for all phones in the same model. The common CFG file has a fixed
name for each phone model.
The name of the common CFG file for W80DM device is y000000000103.cfg.
MAC-Oriented CFG File
MAC-Oriented CFG file, which is named after the MAC address of the IP phone. For example, if the MAC address of an
IP phone is 00156574B150, the name of MAC-Oriented CFG file is 00156574b150.cfg (lowercase). It contains parameters
unique to a particular phone, such as account registration. It will only be effective for a MAC-specific IP phone.
MAC-local CFG File
MAC-local CFG file, which is named after the MAC address of the IP phone. For example, if the MAC address of an IP
phone is 00156574B150, the name of the MAC-local CFG file is 00156574b150-local.cfg (lowercase). It contains changes
associated with a non-static parameter that you make via the web user interface or handset user interface (for example,
changes for time and date formats).
This file generates only if you enable the provisioning priority mechanism. It is stored locally on the IP phone and you
can upload it to the provisioning server each time the file updates. This file enables the users to keep their personalized
configuration settings, even though the IP phone performs auto provisioning.
Note: The non-static changes that you made before enabling the provisioning priority mechanism are not saved in the gen-
erated MAC-local file, but the previous settings still take effect on the phone. The static changes are never be saved to the
84
Page 88

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
<MAC>-local.cfg file.
The provisioning priority mechanism is enabled by the parameter “static.auto_provision.custom.protect”.
Configuration File Customization
You can create some new CFG files by making a copy and renaming the configuration template file (for example,
sip.cfg, account.cfg). You can rearrange the parameters in the configuration template file and create your own configuration files with parameters you want. This flexibility is especially useful when you want to apply specific settings to
a group of phones.
Topic
Customizing a Configuration File
Customizing a Configuration File
1. Copy and rename a configuration template file. For example, sip.cfg.
2. Rearrange the parameters in the sip.cfg, and set the valid values for them.
For example:
account.1.anonymous_call = 1
3. Save the configuration file and place it on the provisioning server.
Related Topic
Configuration File Attributes
Configuration File Attributes
The following table lists the attributes you need to know in the configuration template file.
Attributes Description
#!version:1.0.0.1 It must be placed in the first line. Do not edit and delete.
Specify the parameters and values to apply specific settings to the phones.
Configuration Parameter=Valid
Value
(for example, account.1.dnd.enable = 1)
l Separate each configuration parameter and value with an equal sign
l Set only one configuration parameter per line
l Put the configuration parameter and value on the same line and do not break
the line
Tip: The line beginning with “#” is considered to be a comment. You can use “#” to make any comment on the boot file.
Resource Files
Resource files are optional, but if the particular feature is being employed, these files are required. You need to place
resource files on the provisioning server. The phones request the resource files in addition to the configuration files during auto provisioning.
Tip: If you want to specify the desired phone to use the resource file, the access URL of the resource file should be spe-
cified in the MAC-Oriented CFG file. During auto provisioning, the phones will request the resource files in addition to the
configuration files.
Topic
Supported Resource Files
85
Page 89

Phone Provisioning
Supported Resource Files
Yealink supplies some template of resource files for you, so you can directly edit the files as required.
The following table lists the resource files Yealink supplies:
Template File File Name Description Reference in Section
AutoDST Template AutoDST.xml Add or modify time zone and DST settings. DST Settings
Language Packs
Replace Rule Template
Dial Now Template DialNow.xml Customize dial now rules for the dial plan.
Super Search Template
Local Contact File contact.xml Add or modify multiple local contacts.
Remote Phone Book
Template
For example,
1.English.js
DialPlan.xml Customize replace rules for the dial plan.
super_
search.xml
Department.xml
Menu.xml
Customize the translation of the existing language
on the web user interface.
Customize the search source list.
Add or modify multiple remote contacts.
Language for Web Display
Customization
Replace Rule File Customization
Dial Now File Customization
Search Source File Customization
Local Contact File Customization
Remote Phone Book File
Customization
Files Download Process
When you provision the phones, the phones will request to download the boot files, configuration files and resource
files from the provisioning server according to the following flowchart:
86
Page 90

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
The parameters in the newly downloaded configuration files will override the same parameters in files downloaded
earlier.
Provisioning Methods
Yealink provides two ways to provision your phones:
l Manual Provisioning: provisioning via the handset user interface or web user interface.
l Central Provisioning: provisioning through configuration files stored in a central provisioning server.
The method you use depends on how many phones need to be deployed and what features and settings to be configured. Manual provisioning on the web or handset user interface does not contain all of the phone settings available
with the centralized method. You can use the web user interface method in conjunction with a central provisioning
method and handset user interface method. We recommend using centralized provisioning as your primary provisioning method when provisioning multiple phones.
Topics
Provisioning Methods Priority
Web User Interface
Phone User Interface
Central Provisioning
Provisioning Methods Priority
There is a priority for configuration among the provisioning methods - settings you make using a higher priority provisioning method override settings made using a lower priority provisioning method.
The precedence order for configuration parameter changes is as follows (highest to lowest):
87
Page 91

Phone Provisioning
Note: The provisioning priority mechanism takes effect only if “static.auto_provision.custom.protect” is set to 1. For more
information on this parameter, refer to Keeping User’s Personalized Settings Configuration.
Static parameters have no priority. They take effect no matter what method (web user interface or phone user interface
or configuration files) you are using for provisioning.
Static parameters are the parameters that start with a prefix “static.”, for example, the parameters associated with auto
provisioning/network/syslog, TR069 settings and internal settings (the temporary configurations to be used for program running).
Web User Interface
You can configure the phones via the web user interface, a web-based interface that is especially useful for remote configuration.
Because features and configurations vary by phone models and firmware versions, options available on each page of
the web user interface can vary as well. Note that the features configured via the web user interface are limited. Therefore, you can use the web user interface in conjunction with a central provisioning method and phone user interface.
Note: When you manually configure a phone via the web user interface or handset user interface, the changes associated
with non-static parameters you make will be stored in the MAC-local CFG file. For more information on the MAC-local CFG
file, refer to MAC-local CFG File.
Topics
Quick Login Configuration
Web Server Type Configuration
Quick Login Configuration
You can access the web user interface quickly using the request URI. It will locate you in the Status web page after
accessing the web user interface. It is helpful to quickly log into the web user interface without entering the username
and password on the login page.
Note: Accessing the web user interface by request URI may be restricted by the web explorer (for example, Internet
Explorer).
For security purposes, we recommend that you use this feature in a secure network environment.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure quick login.
Parameter wui.quick_login <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It enables or disables the quick login feature.
Note: It works only if “static.wui.https_enable” is set to 1 (Enabled).
0-Disabled
1-Enabled, you can quickly log into the web user interface using a request URI (for example, https://IP/ap-
88
Page 92

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
i/auth/login?@admin:admin).
Default 0
Parameter wui.secure_domain_list <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the valid domain name to access the web user interface of the phone.
Multiple domain names are separated by semicolons.
Example:
Description
wui.secure_domain_list = test.abc.com
You are only allowed to use test.abc.com or IP address to access the web user interface of the phone.
Note: To use a domain name to access the web user interface of the phone, make sure your DNS server
can resolve the domain name to the IP address of the phone.
String
Permitted
Values
If it is left blank, you are only allowed to use the IP address to access the web user interface of the phone.
If it is set to “any”, you can use IP address or any domain name to access the web user interface of the
phone.
Default any
Web Server Type Configuration
Yealink phones support both HTTP and HTTPS protocols for accessing the web user interface. You can configure the
web server type. Web server type determines the access protocol of the web user interface. If you disable to access the
web user interface using the HTTP/HTTPS protocol, both you and the user cannot access the web user interface.
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the web server type.
Parameter
static.wui.http_enable
Description It enables or disables to access the web user interface of the phone over a non-secure tunnel (HTTP).
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > Web Server > HTTP
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
static.network.port.http
It configures the port used to access the web user interface of the phone over a non-secure tunnel
(HTTP).
Integer from 1 to 65535
[1]
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Default 80
Web UI Network > Advanced > Web Server > HTTP Port (1~65535)
Parameter
static.wui.https_enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It enables or disables to access the web user interface of the phone over a secure tunnel (HTTPS).
Permitted
Values
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
89
Page 93

Phone Provisioning
Default 1
Web UI Network > Advanced > Web Server > HTTPS
Parameter
Description It configures the port used to access the web user interface of the phone over a secure tunnel (HTTPS).
static.network.port.https
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Permitted
Values
Default 443
Web UI Network > Advanced > Web Server > HTTPS Port (1~65535)
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
Integer from 1 to 65535
Central Provisioning
Central provisioning enables you to provision multiple phones from a provisioning server that you set up, and maintain
a set of boot files, configuration files and resource files for all phones in the central provisioning server.
The following figure shows how the phone interoperates with provisioning server when you use the centralized provisioning method:
Yealink phones can obtain the provisioning server address during startup. Then the phones first download boot files
and configuration files from the provisioning server and then resolve and update the configurations written in configuration files. This entire process is called auto provisioning. For more information on auto provisioning, refer to
Yealink SIP IP Phones Auto Provisioning Guide.
90
Page 94

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
The phones can be configured to upload log files (log files provide a history of phone events), call log files and contact
files to the provisioning server. You can also configure a directory for each of these three files respectively.
Topics
Auto Provisioning Settings Configuration
Auto Provisioning Settings Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure settings for auto provisioning.
Parameter static.auto_provision.attempt_expired_time <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the timeout (in seconds) to transfer a file via auto provisioning.
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 5
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Attempt Expired Time(s)
Parameter
Note: It has a higher priority than the value defined by the parameter “static.network.attempt_expired_
time”.
Integer from 1 to 300
static.network.attempt_expired_time
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the timeout (in seconds) to transfer a file for HTTP/HTTPS connection.
Description
Note: It has a lower priority than the value defined by the parameter “static.auto_provision.attempt_
expired_time”.
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1 to 20
Default 10
Parameter static.auto_provision.attempt_before_failed <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It configures the maximum number of attempts to transfer a file before the transfer fails during auto provisioning.
Integer from 1 to 10
Default 3
Parameter static.auto_provision.retry_delay_after_file_transfer_failed <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It configures the time (in seconds) to wait after a file transfer fails before retrying the transfer via auto provisioning.
Integer from 0 to 300
Default 5
Parameter
static.auto_provision.reboot_force.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
91
It enables or disables the phone to reboot after auto provisioning, even if there is no specific configuration requiring a reboot.
Note: It works only for the current auto provisioning process. If you want the phone to reboot after every
auto provisioning process, the parameter must be always contained in the configuration file and set to 1.
If the phone reboots repeatedly after it is set to 1, you can try to set “static.auto_provision.power_on" to 0
Page 95

(Off).
Phone Provisioning
Permitted
Values
Default Blank
Parameter static.auto_provision.power_on <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It triggers the power on feature to on or off.
Permitted
Values
Default 1
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Power On
Parameter static.auto_provision.repeat.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It triggers the repeatedly feature to on or off.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Repeatedly
Parameter static.auto_provision.repeat.minutes <y0000000000xx>.cfg
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
0-Off
1-On, the phone performs auto provisioning when powered on.
0-Off
1-On
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 1440
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Interval(Minutes)
Parameter static.auto_provision.weekly.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It triggers the weekly feature to on or off.
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Weekly
Parameter static.auto_provision.weekly_upgrade_interval <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
It configures the interval (in minutes) for the phone to perform auto provisioning repeatedly.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.repeat.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Integer from 1 to 43200
0-Off
1-On, the phone performs an auto provisioning process weekly.
It configures the time interval (in weeks) for the phone to perform auto provisioning.
If it is set to 0, the phone performs auto provisioning at the specific day(s) configured by the parameter
“static.auto_provision.weekly.dayofweek” every week.
If it is set to other values (for example, 3), the phone performs auto provisioning at a random day between
the specific day(s) configured by the parameter “static.auto_provision.weekly.dayofweek” every three
weeks.
92
Page 96

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.weekly.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Weekly Upgrade Interval(0~12week)
Parameter static.auto_provision.inactivity_time_expire <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 0
Integer from 0 to 12
It configures the delay time (in minutes) to perform auto provisioning when the phone is inactive at regular week.
If it is set to 0, the phone performs auto provisioning at random between a starting time configured by
the parameter “static.auto_provision.weekly.begin_time” and an ending time configured by the parameter
“static.auto_provision.weekly.end_time”.
If it is set to other values (for example, 60), the phone performs auto provisioning only when it has been
inactivated for 60 minutes (1 hour) between the starting time and ending time.
Note: The phone may perform auto provisioning when you are using the phone during office hour. It
works only if “static.auto_provision.weekly.enable” is set to 1(On). The operations on the handset will not
change the inactive status; only the functional operations related base station, such as calling, will
change the inactive status.
Integer from 0 to 120
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Inactivity Time Expire(0~120min)
Parameter static.auto_provision.weekly.dayofweek <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the days of the week for the phone to perform auto provisioning weekly.
Example:
static.auto_provision.weekly.dayofweek = 01
Description
Permitted
Values
If “static.auto_provision.weekly_upgrade_interval” is set to 0, it means the phone performs auto provisioning every Sunday and Monday.
If “static.auto_provision.weekly_upgrade_interval” is set to other value (for example, 3), it means the
phone performs auto provisioning by randomly selecting a day from Sunday and Monday every three
weeks.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.weekly.enable” is set to 1 (On).
0,1,2,3,4,5,6 or a combination of these digits
0-Sunday
1-Monday
2-Tuesday
3-Wednesday
4-Thursday
93
5-Friday
Page 97

6-Saturday
Default 0123456
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Day of Week
Phone Provisioning
Parameter
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 00:00
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Time
Parameter static.auto_provision.flexible.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 0
static.auto_provision.weekly.begin_time
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
static.auto_provision.weekly.end_time
It configures the starting/ending time of the day for the phone to perform auto provisioning weekly.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.weekly.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Time from 00:00 to 23:59
It triggers the flexible feature to on or off.
Note: The day within the period is based upon the phone's MAC address and does not change with a
reboot, whereas the time within the start and end is calculated again with every reboot. The timer starts
again after each auto provisioning.
0-Off
1-On, the phone performs auto provisioning at random between a starting time configured by the para-
meter "static.auto_provision.flexible.begin_time" and an ending time configured by the parameter "static.auto_provision.flexible.end_time" on a random day within the period configured by the parameter
"static.auto_provision.flexible.interval".
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Flexible Auto Provision
Parameter static.auto_provision.flexible.interval <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the interval (in days) for the phone to perform auto provisioning.
The auto provisioning occurs on a random day within this period based on the phone's MAC address.
Description
Permitted
Values
Default 30
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Flexible Interval Days
Parameter static.auto_provision.flexible.begin_time <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
The phone performs auto provisioning on a random day (for example, 18) based on the phone's MAC
address.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.flexible.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Integer from 1 to 1000
It configures the starting time of the day for the phone to perform auto provisioning at random.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.flexible.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Time from 00:00 to 23:59
94
Page 98

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Default 02:00
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Flexible Time
Parameter static.auto_provision.flexible.end_time <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the ending time of the day for the phone to perform auto provisioning at random.
If it is left blank or set to a specific value equal to starting time configured by the parameter “static.auto_
provision.weekly.begin_time”, the phone performs auto provisioning at the starting time.
If it is set to a specific value greater than starting time configured by the parameter “static.auto_pro-
Description
vision.weekly.begin_time”, the phone performs auto provisioning at random between the starting time
and ending time.
If it is set to a specific value less than starting time configured by the parameter “static.auto_provision.weekly.begin_time”, the phone performs auto provisioning at random between the starting time on
that day and ending time in the next day.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.flexible.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Permitted
Values
Time from 00:00 to 23:59
Default Blank
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > Flexible Time
Parameter static.auto_provision.dns_resolv_nosys <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It enables or disables the phone to resolve the access URL of the provisioning server using download libraries mechanism.
0-Disabled, the phone resolves the access URL of the provisioning server using the system mechanism.
1-Enabled
Default 1
Parameter static.auto_provision.dns_resolv_nretry <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the retry times when the phone fails to resolve the access URL of the provisioning server.
Description
Note: For each different DNS server, it works only if “static.auto_provision.dns_resolv_nosys" is set to 1
(Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1 to 10
Default 2
Parameter static.auto_provision.dns_resolv_timeout <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the timeout (in seconds) for the phone to retry to resolve the access URL of the provisioning
server.
Description
Note: For each different DNS server, it works only if “static.auto_provision.dns_resolv_nosys" is set to 1
(Enabled).
Permitted
Values
Integer from 1 to 60
Default 5
[1]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
95
Page 99

Phone Provisioning
Setting Up a Provisioning Server
You can use a provisioning server to configure your phones. A provisioning server allows for flexibility in upgrading,
maintaining and configuring the phone. Boot files, configuration files, and resource files are normally located on this
server.
Topics
Supported Provisioning Protocols
Supported Provisioning Server Discovery Methods
Configuring a Provisioning Server
Supported Provisioning Protocols
Yealink phones support several transport protocols for provisioning:
l Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
l File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
l Hyper Text Transfer Protocol – Secure (HTTPS)
l File Transfer Protocol – Secure (FTPS)
Note: There are two types of FTP methods—active and passive. The phones are not compatible with active FTP.
You can specify the transport protocol in the provisioning server address, for example, http://xxxxxxx. If not specified,
the TFTP protocol is used.
Topic
Provisioning Protocols Configuration
Provisioning Protocols Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure provisioning protocols.
Parameter static.auto_provision.server.type <y0000000000xx>.cfg
It configures the protocol the phone uses to connect to the provisioning server.
Description
Permitted
Values
Default tftp
Parameter
Note: It works only if the protocol type is not defined in the access URL of the provisioning server con-
figured by the parameter "static.auto_provision.server.url".
1-http
2-https
3-ftp
Other values-tftp
static.auto_provision.user_agent_mac.enable
[1]
<y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description
Permitted
Values
It enables or disables the phone's MAC address to be included in the User-Agent header of HTTP/HTTPS
request via auto provisioning.
0-Disabled
1-Enabled
Default 1
[2]
If you change this parameter, the phone will reboot to make the change take effect.
96
Page 100

Administrator’s Guide for W80 DECT IP Multi-Cell System
Supported Provisioning Server Discovery Methods
After the phone has established network settings, it must discover a provisioning server to obtain software updates and
configuration settings.
The IP phone supports the following methods to discover the provisioning server address:
l PnP: PnP feature allows the phones to discover the provisioning server address by broadcasting the PnP SUBSCRIBE
message during startup.
l DHCP: DHCP option can be used to provide the address or URL of the provisioning server to phones. When the IP
phone requests an IP address using the DHCP protocol, the resulting response may contain option 66 (for IPv4) or
the custom option (if configured) that contains the provisioning server address.
l Static: You can manually configure the server address via the handset user interface or web user interface.
Topics
PnP Provision Configuration
DHCP Provision Configuration
Static Provision Configuration
PnP Provision Configuration
The following table lists the parameter you can use to configure PnP provision.
Parameter static.auto_provision.pnp_enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It triggers the Plug and Play (PnP) feature to on or off.
0-Off
Permitted
Values
1-On, the phone broadcasts SIP SUBSCRIBE messages to obtain a provisioning server URL where the
phone can request the configuration from during startup.
Default 1
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > PNP Active
DHCP Provision Configuration
The following table lists the parameters you can use to configure the DHCP provision.
Parameter static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.enable <y0000000000xx>.cfg
Description It triggers the DHCP Active feature to on or off.
Permitted
Values
Default 1
Web UI Settings > Auto Provision > DHCP Active
Parameter static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.list_user_options <y0000000000xx>.cfg
0-Off
1-On, the phone obtains the provisioning server address by detecting DHCP options.
Description
Permitted
Values
97
It configures the IPv4 custom DHCP option for requesting provisioning server address.
Multiple options are separated by commas.
Note: It works only if “static.auto_provision.dhcp_option.enable” is set to 1 (On).
Integer from 128 to 254
 Loading...
Loading...