
Service Training
Self-study programme 464
The Amarok Powertrain and drive concept
Design and function
Commercial
Ve h i c le s

S464_002
With the Amarok, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles is deliberately and self-assuredly taking part in the global
trend towards multifunctional vehicle s.
As such, the company is making consistent use of its extensive experience in manufacturing vehicles with both rear
and front-wheel drive. The newly developed drive concept offers outstanding driving properties.
Comfortable handling and operation similar to a passenger car are features of the Amarok. Magnificent assistance
is given for everyday use through a range of support systems in order to provide road safety and handling benefits
when offroad.
In all cases and in all variants, the Amarok can be used both onroad and for heavy-duty offroad use. Depending
on use, the four-wheel drive version of the Amarok is available either with permanently or non-permanently
engaged four-wheel drive. The Amarok is also available in a standard version with rear-wheel drive. The entire
driveline of the Amarok is a new development and has been specifically adapted for use as a commercial vehicle.
Please also refer to self-study programme no. 463
"The Amarok".
The self-study programme presents the
design and function of
new developments!
The content will not be updated.
Current testing , setting an d repair instructions
can be found in the provided
service literature.
Important
note
2

At a glance
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Four-wheel drive development at Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles . . . . . . . 4
The drive concept of the Amarok . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
The driveline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
The operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
The offroad drive programme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6-speed manual gearbox 0C6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
The 6-speed manual gearbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
The gearbox structure and function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
The gearbox sectional view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
The powerflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
The external selector mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
The internal selector mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Transfer box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
The non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive with transfer box 0C7 . . . 32
The transfer box with limited-slip interaxle differential 0BU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Rear final drive 0CC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
The rear final drive 0CC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Front final drive 0C1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
The front final drive 0C1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Test your knowledge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
3

Introduction
Four-wheel drive development at
Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles
Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles began to manufacture four-wheel drive vehicles in-house in 1983
in the form of the LT1 4x4.
This was an early response to the desire for as wide a range of vehicle applications as possible – from driving on
smooth roads through to use on very difficult ground.
The four-wheel drive is better able to overcome traction problems when used in sports applications and, in
particular, as a commercial vehicle.
LT1 4x 4
from 1983
T3 syncro
from 1985
T4 syncro
from 1993
4

Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles markets vehicles all over the world, therefore the company is used to taking
account of special conditions, such as in remote areas and difficult open ground – four-wheel drive represents an
ideal solution for this.
Amarok 4MOTION
from 2010
Caddy 4MOTION
from 2009
T5 4MOTION
from 2004
S464_051
5

Introduction
The drive concept of the Amarok
The drive concept of the Amarok offers 3 different drive variants.
The Amarok's powertrain is efficiently supported by intelligent vehicle dynamics programmes.
S464_058
Vehicle dynamics programmes
The Amarok is equipped with the following vehicle dynamics programmes:
● ABS (as standard)
● TCS (as standard)
MSR (as standard)
EDL (as standard)
● ESP
6
● Offroad drive programme (as standard)
● Hill-descent assist
● Hill-hold assist

Rear final drive
In the Amarok with rear-wheel drive, the power is
transmitted via a propshaft to the rear axle only.
Even with only rear-wheel drive, the Amarok can be
used on both consolidated and non-consolidated
roads as well as offroad.
Permanent four-wheel drive
with limited-slip interaxle
differential 0BU
In the Amarok with permanently engaged four-wheel
drive, the powerflow to both driven axles is distributed
by means of a transfer box with permanent
engagement using a limited-slip interaxle differential.
This offers improved traction compared to rear-wheel
drive, above all when offroad.
S464_006
Non-permanently engaged
four-wheel drive with part-time
transfer box 0C7
In the Amarok with non-permanently engaged fourwheel drive, the powerflow to the driven axle is
distributed using a transfer box with electrically
engaged front final drive. It is also possible to engage
a reduction stage (offroad ratio) in this transfer box.
In this version, the Amarok is even better suited for
use on difficult ground.
S464_074
S464_005
7

Introduction
The driveline
The Amarok has a modular driveline in which the individual
components such as manual gearbox, front final drive, transfer
box and rear final drive are independent subassemblies.
Gearbox
At present, the 6-speed manual gearbox 0C6 is used
for transmitting power from the engine
Rear axle
Transfer box
Power is distributed to the final drives either by means
of the transfer box 0C7 (non-permanently engaged
four-wheel drive) or 0BU (permanently engaged
four-wheel drive).
Rear final drive
Lad der f ram e
Propshafts
Three different two-part propshafts are used for driving the rear axle.
The front part of the propshaft has a length that is adapted to the particular drive version.
A one-piece propshaft is fitted for driving the front axle. This is identical in both versions of the four-wheel drive.
8
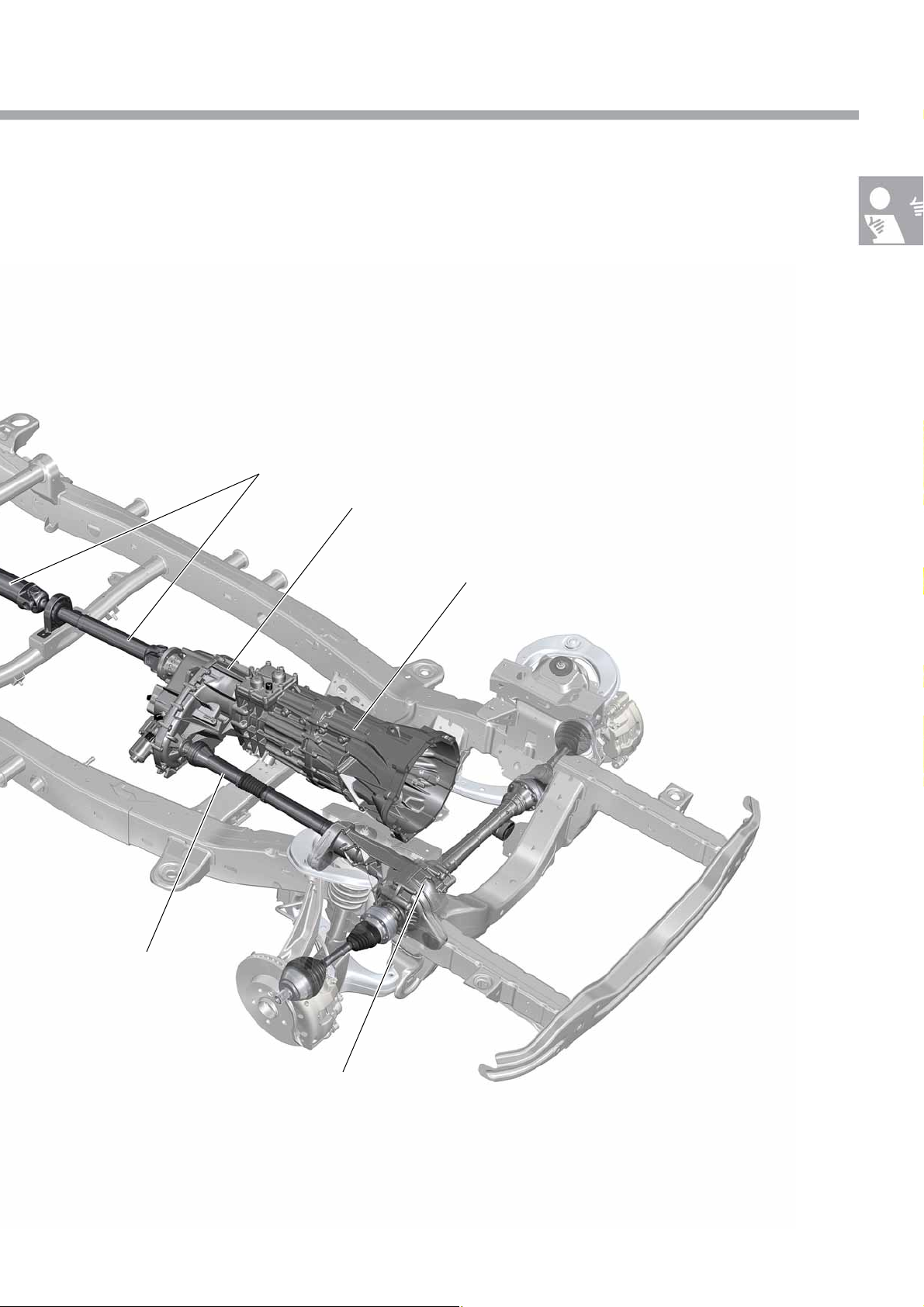
Rear final drive, front final drive
The rear final drive 0CC arranged in a symmetrical installation position is used for driving the rear axle. The rear
axle differential can be locked up.
The front final drive 0C1 is used for driving the front axle, and is available in two different designs. The front final
drive is asymmetrically arranged.
Rear propshaft
Transfer box
6-speed manual gearbox
Front propshaft
Front final drive
The illustration shows the drivetrain with non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive.
S464_007
9
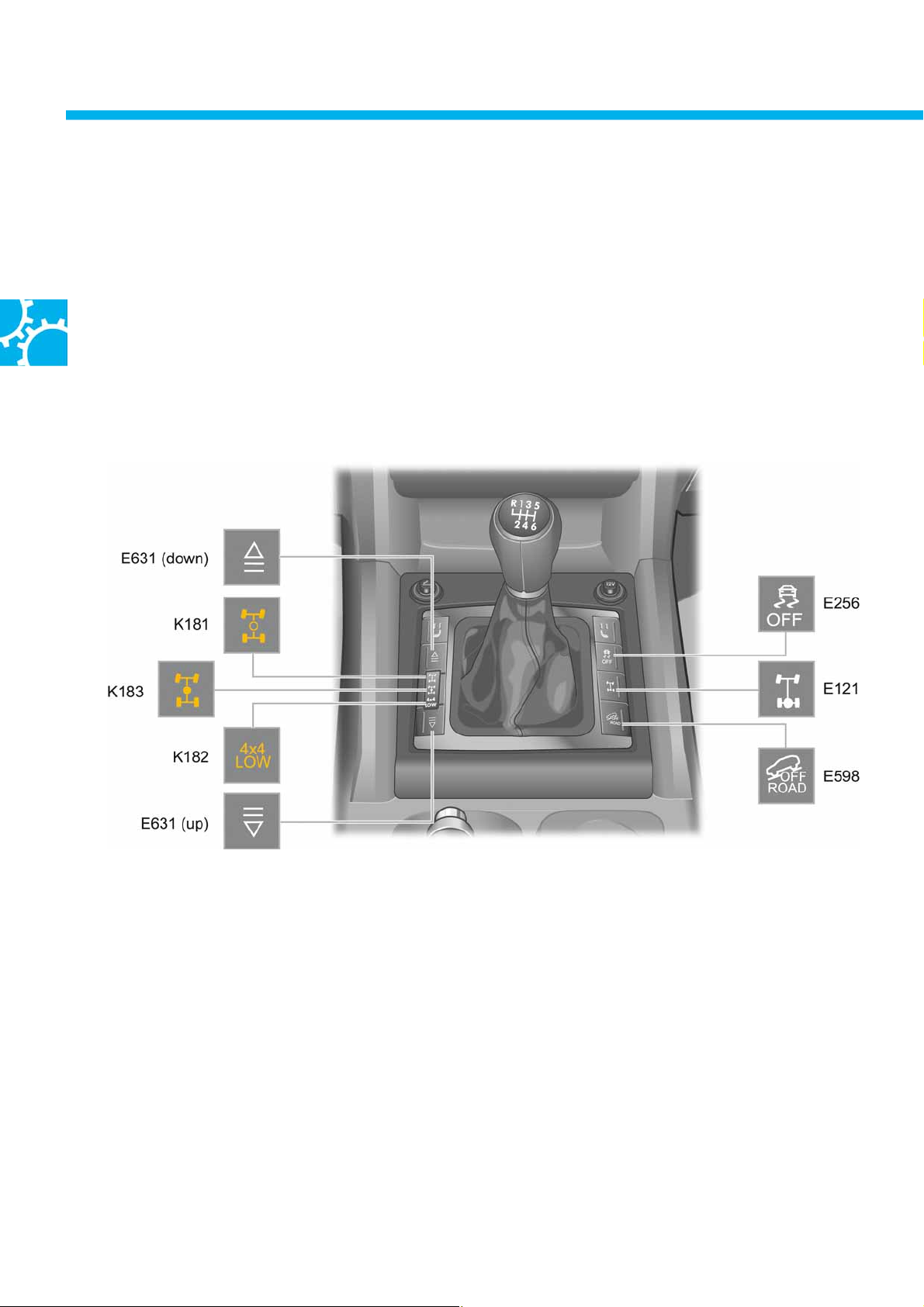
Operation
The operation
Four-wheel drive, the reduction ratio (offroad ratio), the differential lock and the offroad drive programme are
engaged and disengaged using a button panel in the centre console. The status is displayed by warning lamps
K181, K182 and K183.
The four-wheel drive components are each electrically connected to the gearbox.
This means no additional selector levers are required for operating the four-wheel drive ranges.
Centre console button assignments
10
Key
E631 (down) = Running gear programme switch
(switching on)
K181 Normal operation warning lamp in transfer box
operating unit (4x2)
K183 Longitudinal lock-up warning lamp in transfer
box operating unit (4x4 HIGH)
K182 Reduction gearing warning lamp in transfer box
operating unit
(4x4 LOW)
E631 (up) = Running gear programme switch
(switching off)
S464_049
E256 TCS and ESP button (TCS deactivation)
E121 Rear differential lock switch
E598 Driving programme button (offroad driving
programme)
E256, E121 and E598 do not have function
lighting
In right-hand drive vehicles, button panel E631 is fitted
on the other side of the selector lever.
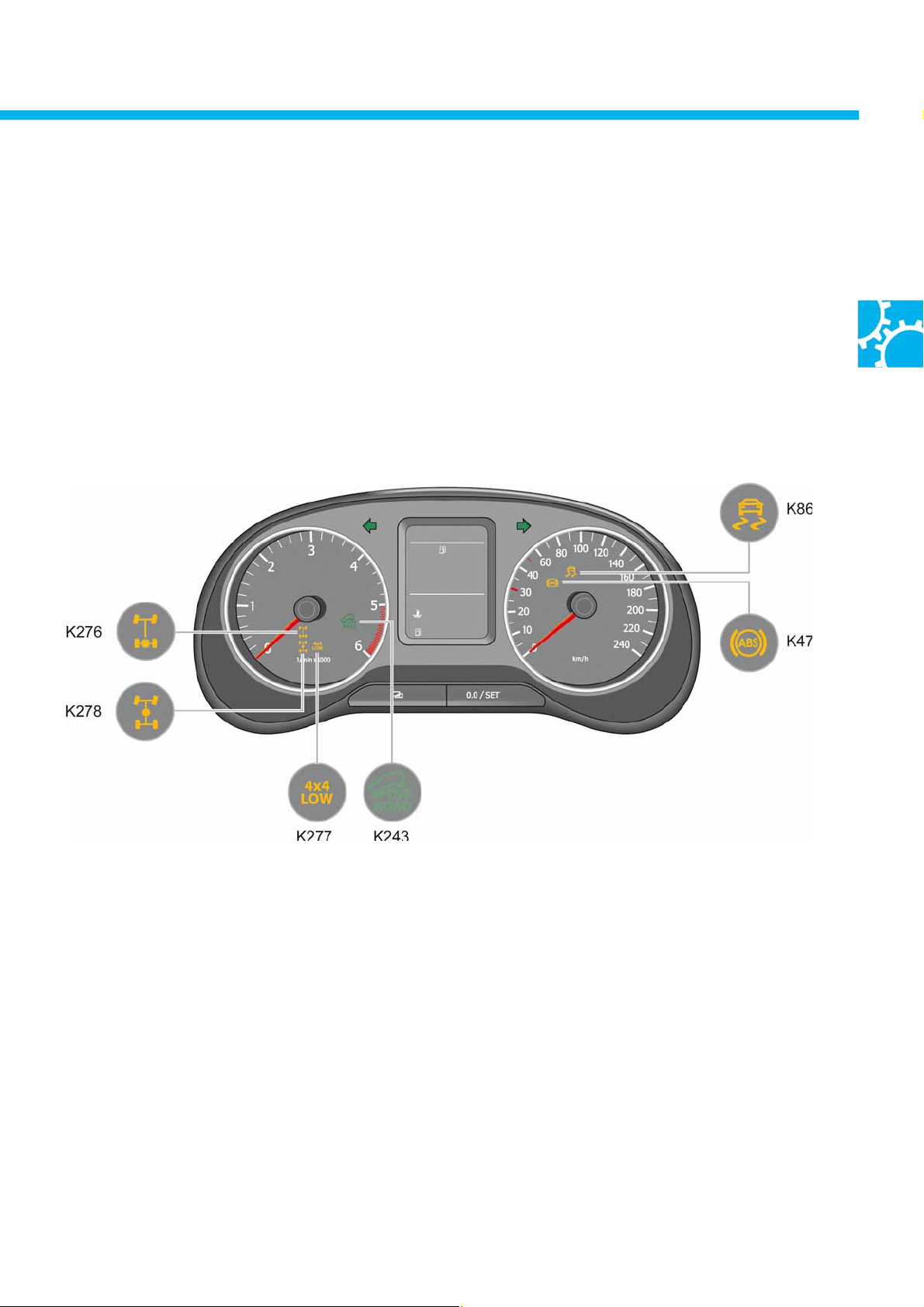
Displays on the dash panel insert
Each of the four-wheel drive statuses that are activated during operation is backlit in the button panel and also
shown in the dash panel insert as a status display.
The status of 4x2 rear-axle mode is only displayed in the centre console.
Key
K278 Longitudinal lock-up warning lamp (4x4 HIGH)
K277 Warning lamp for gearbox low range
K276 Warning lamp for rear transverse lock
K47 ABS warning lamp (ABS fault or ABS deactivated)
K86 Traction control system warning lamp (fault, control or deactivated)
K243 Driving programme warning light (offroad driving programme)
S464_050
11
Operation
Four-wheel drive 4x4 HIGH
Display in the dash panel insert
… four-wheel drive is engaged
(interaxle lock engaged)
S464_077
Switch-on conditions
● Ter m in al 1 5 " ON "
● E631 (up) pressed > 0.5 s
● Can be engaged at any vehicle speed
● No undervoltage
● No relevant error memory entry
Offroad range 4x4 LOW
Display in the dash panel insert
Switch-off conditions
● Ter m i n al 15 " O N"
● E631 (down) pressed > 0.5 s
● Can be switched off at any vehicle speed
● No undervoltage
● No relevant error memory entry
… four-wheel drive is engaged and LOW
reduction ratio engaged
12
S464_079
Switch-on conditions
● Engine speed < 1500 rpm
● E631 (up) pressed > 0.5 s
● Vehicle speed v < 1 km/h
● 4x4 HIGH engaged
● No undervoltage
● No relevant error memory entry
Switch-off conditions
● Engine speed < 1500 rpm
● E631 (down) pressed > 0.5 s
● Vehicle speed v < 1 km/h
● No undervoltage
● No relevant error memory entry

Differential lock
Display in the dash panel insert
… differential lock engaged
S464_081
Switch-on conditions
● Engine running
● E121 pressed > 0.5 s
● Can be engaged at any vehicle speed
● No undervoltage
● No relevant error memory entry
● With non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive:
Four-wheel drive range 4x4 LOW engaged
Switch-off conditions
● Button pressed > 0.5 s (E121)
● Can be switched off at any vehicle speed
● 30 s follow-on operation after tl. 15 "OFF".
If the engine stalls whilst driving with the
differential lock engaged, the lock remains
engaged for a period of 30 seconds after tl. 15
"OFF". This means restarting and moving off are
possible with the lock engaged. As a result , driving
comfort is increased when driving offroad.
The following applies to all variants 4x4 HIGH, 4x4 LOW and for the differential lock with regard to operation
The driver's request for engaging the required four-wheel drive range is stored for 10 s. If the required activation
conditions are met within this period then the four-wheel drive ranges 4x4 HIGH, 4x4 LOW and the differential lock
are engaged. Operating comfort is therefore improved.
ABS/ESP system statuses
ABS/ESP control is retained during four-wheel drive operation (4x4 HIGH and 4x4 LOW) in all equipment variants of
the Amarok. In vehicles with non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive, ABS/ESP control is deactivated when the
differential lock is engaged. The mechanical link-up between the two axles (4x4 HIGH /4x4 LOW) and the additional
link-up between the two rear wheels means that individual ABS/ESP control for individual wheels is no longer
possible. Deactivation is displayed by warning lamps K86 and K47 in the dash panel insert. In vehicles with
permanently engaged four-wheel drive, the ABS/ESP function is also retained when the differential lock is engaged.
13

Operation
The offroad drive programme
The offroad drive programme is used as standard in all vehicle variants of the Amarok.
It is intended to assist the driver in special driving situations when offroad. The possible extended functions of the
ABS/ESP control unit are used in this case.
● Offroad ABS (adaptations in the ABS control behaviour)
● Offroad ESP (adaptations in the ABS and ESP control behaviour)
● Hill-descent assist
Activation of the offroad programme and indication
The offroad programme is activated
● Manually – by pressing the driving programme button E598
(in the centre console, on the right of the selector lever) or
● Automatically – when 4x4 LOW drive range is activated
Display showing activation of the offroad drive programme
Activation of the offroad drive programme is indicated by the driving
programme warning light K243 in the dash panel insert.
Configurations
● Vehicles with ABS (MK25 E) have offroad ABS
● Vehicles with ESP (MK25 XT) have offroad ABS/ESP
and hill descent control
Activation conditions for the offroad
programme
The offroad drive programme remains active
● Ter m i na l 15 " O N "
● E598 pressed > 0.5 s
Special case in vehicles with non-permanently
engaged four-wheel drive
When 4x4 LOW drive range is engaged, the offroad
programme is activated automatically.
following activation until the next change of ignition
status, without interruption.
For example, if the engine is stalled when driving
offroad, the offroad drive programme also remains
activated after restarting, with a follow-on operation
of 30 s after a change of status on tl. 15.
This increases driving comfort.
E598
S464_073
S464_072
14

Features of the offroad drive programme
Offroad ABS
Vehicles with offroad ABS can brake better on
unconsolidated ground such as sand and gravel.
In ABS control, the pressure buildup and pressure
holding phases are extended. The depressurisation is
shorter and takes place later. This means wheel slip
can occur in each control phase, thereby building up
a skid wedge of loose material in front of the wheels.
The skid wedge brakes the vehicle additionally and
shortens the braking distance depending on the
composition of the ground.
Offroad ESP
Skid wedge
S464_076
Special information about using offroad ABS can be
found in the owner's manual .
Vehicles with ESP have adapted ESP control behaviour
as well as offroad ABS in order to improve traction:
● ESP intervenes somewhat later at speeds below
50 km/h when the vehicle is understeering.
● ESP intervenes somewhat later at speeds below
70 km/h when the vehicle is oversteering.
● ASR intervenes somewhat later at speeds below
70 km/h.
Hill-descent assist
The hill-descent assist makes descending steep hills more straightforward and more controllable. It limits the speed
by active brake intervention at all 4 wheel brakes using the ESP hydraulics. It keeps the speed constant after the
vehicle has started its descent. The driver can increase or reduce the speed at any time using the accelerator and
brakes. The hill-descent assist adjusts speed within its control range between 2 and max. 30 km/h. The system
functions when driving forwards and in reverse.
Switch-on conditions for hill-descent assist
● E598 pressed > 0.5 s
● Special feature with non-permanently engaged
four-wheel drive: automatic activation in 4x4 LOW
● Engine running
● Slope forwards > 10 %, reverse > 8 %
● Vehicle speed v < 30 km/h (> 30 km/h change to
standby mode)
● Driver brakes less than the downslope force
● Accelerator pedal is not pressed
For more information about the basic
function of the hill-descent assist, refer
to self-study programme 374
"Slip control and assistance systems".
15

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
The 6-speed manual gearbox
A modern, fully synchronised 2-shaft gearbox of conventional design is used for transmitting power. It has a robust
structure and is designed for the specific requirements of commercial vehicles. The developer and manufacturer of
the 0C6 gearbox is ZF-Getriebe GmbH
● The 6-speed manual gearbox has a uniform housing for all drive variants.
● The same gear ratios are used for all engines.
● The newly-developed 6-speed manual gearbox is exclusively used in the Amarok at present.
S464_052
Gearbox – output adapter
There are two different gearbox variants for the two drive variants of rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive. These
only differ in the area of the connection to the propshaft in vehicles with rear-wheel drive or the transfer box in
four-wheel drive vehicles.
Four-wheel drive – The torque is transferred from the manual gearbox to the transfer box via an adapter shaft.
The adapter shaft is connected to the gearbox output shaft by means of splines with a light press-fit seat , and is
additionally bolted.
Rear-wheel drive – The torque is transmitted onto the propshaft to the rear axle by means of an output flange. The
output flange is mounted on the splines of the output shaft by means of a light press-fit seat, and is additionally
secured by a bolted connection.
Adapter shaft for
four-wheel drive
Output flange for
rear-wheel drive
Picture corresponds
to adapter shaft for
four-wheel drive
16
S464_062

Techn ic al d ata
Gearbox designation 0C6
Gearbox type 6-speed manual gearbox
Gearbox code e.g. MQU (4x2) NFG, NCR
MQV, MJE (4x4) NFF, NCQ, MJE
max. transmissible torque 400 Nm
Shafts Input shaft and coaxial output shaft, layshaft, R-gear reverse shaft
Installation location Longitudinal installation
Use with the engines … 90/120kW TDI engines
118kW TSI engine
Shaft clearance 85 mm
Structural length 690 mm
Weigh t 61 kg
Gear oil specification Synthetic gear oil (SAE 75W-80)
Fill quantity of lifetime fill First fill: 1.5 l, change volume: 1.4 l
Change interval Lifetime fill
Clutch mechanism Hydraulic
Ratios
Gear ratio
1st gear 4.82
2nd gear 2.54
3rd gear 1.49
4th gear 1.0
5th gear 0.76
6th g ear 0.64
Reverse gear 4.37
Spread 7.5 3
The gear ratios in all gearbox variants are the same. 5th and 6th gears are configured as overdrive.
The vehicle's maximum speed is reached in 5th gear and also in 6th gear. 6th gear is an override used for saving
fuel, since the engine rpm is significantly lower.
This reduces CO2 emissions and reduces wear in the engine.
Example: 120kW TDI engine (calculated values)
– Vmax 5th gear = 179.5 km/h at 4135 rpm
– Vmax 6th gear = 178.9 km/h at 3457 rpm
1st gear has a relatively high mechanical advantage, specifically for a commercial vehicle. This is used for moving
off without overloading the clutch when the vehicles are heavily loaded and/or towing a trailer.
17
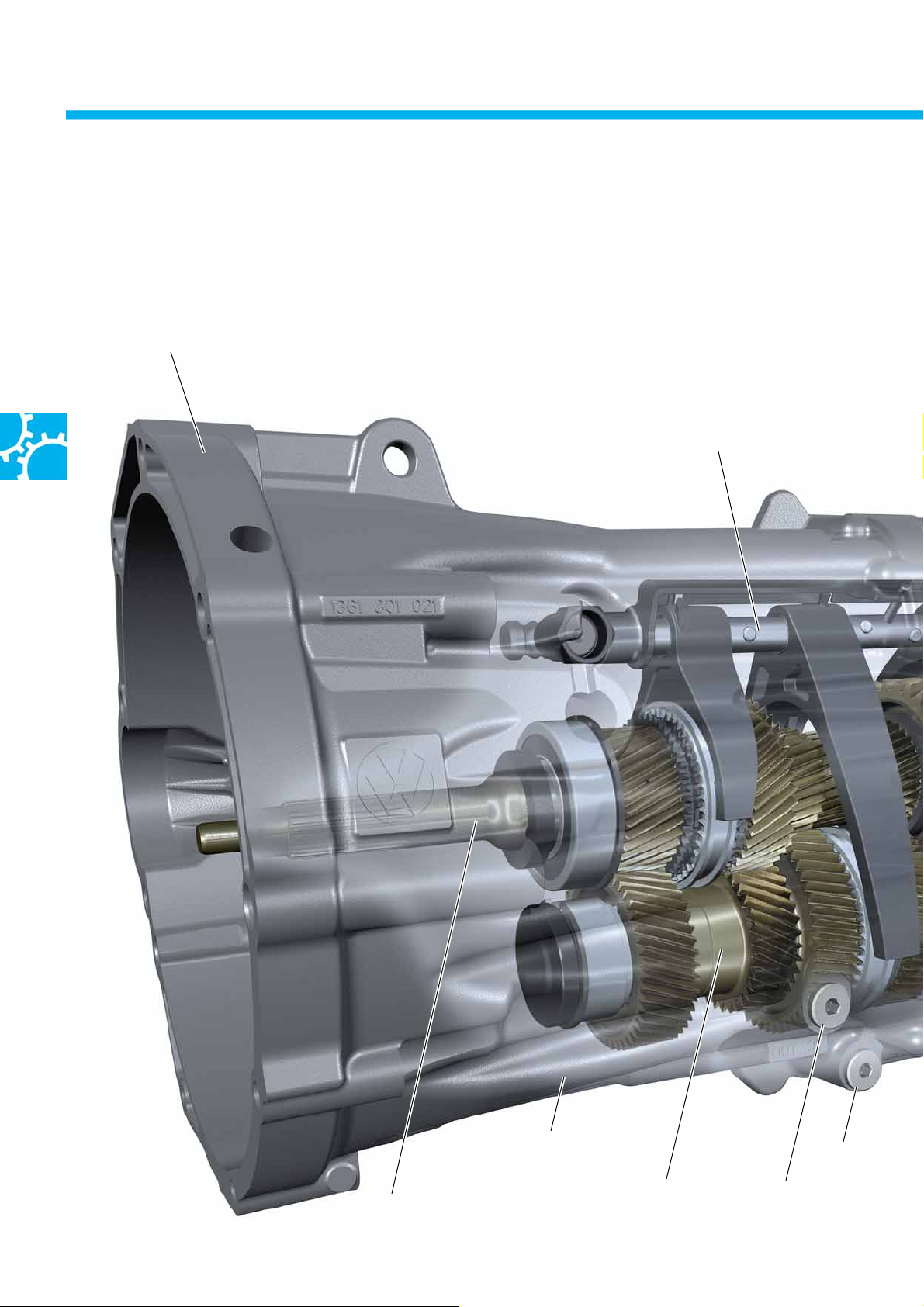
6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
The gearbox structure and function
The two-part gearbox housing is made from aluminium diecastings.
Housing flange
for connection to the engine
Centre selector shaft
18
Input shaft
Front gearbox housing
Laysha ft
Oil drain plug
Oil filler plug

Reversing light switch F4
Reversing light switch F4 is activated by means of
a ramp. The ramp is attached to the reverse gear
selector fork. The reversing lights are activated
directly by F4.
The signal from reversing light switch F4 is also
supplied to the onboard supply control unit J519.
Ventilation
Selector module
Selector fork
for R gear
Ramp for F4
Reversing light
switch F4
Rear gearbox housing
S464_018
Housing flange for
transfer box
Output shaft
R gear reverse shaft
The oil level with a correct oil fill is below the
bottom edge of the thread for the oil filler plug.
Follow the information in E LSA regarding the oil
fill and checking.
19

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
The gearbox sectional view
The manual gearbox in the Amarok is a two-stage
fully synchronised locking collar speed-changing
gearbox.
It has an input shaft, an output shaft, a layshaft and
the R-gear reverse shaft.
All synchromeshed gears are all on needle bearings
and are distributed over the output shaft and layshaft.
The input shaft and the output shaft are mounted in
ball bearings.
The layshaft is mounted in ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings.
Synchromeshed gear
4th gear/
input gear for
constant
Synchromeshed gear
3rd gear
20
Input shaft
Constant
Syn chrom eshe d gea r
6th gear

The gears are shifted using a gear selector and a gate
selector turning shaft which are mounted in a rotating
arrangement in the selector module.
All selector forks are activated by the centre selector
shaft.
The oil drain plug is not magnetic. A magne t is
installed in the front gearbox housing in order to
collect metallic fragments from the synchronisers or
metallic particles in case of mechanical gearbox
damage.
2nd gear
synchromeshed gear
1st gear
synchromeshed gear
R gear
synchromeshed gear
Gate selection
turning shaft
Selector turning
shaft
Selector module
Centre selector shaft
Oil guide hole
Lay sh af t Outpu t s h aft
5th gear
synchromeshed gear
R gear reverse
shaft
The shafts of the 0C6 gearbox
are solid.
The oil supply to the lubrication
points is provided by centrifugalforce lubrication and via oil
guide holes in the gear
mechanism.
Adapter shaft
S464_004
21

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
Input shaft
The input shaft is mounted in the front gearbox
housing in a deep-groove ball bearing as a fixed
bearing.
The cylindrical roller bearing is used as a moving
bearing between the input shaft and the output shaft.
It is located in the hole in the input shaft.
The input shaft gear of the constant stage is a
component of the input shaft.
Cylindrical roller bearing
S464_015
Locking collar
3rd/4th gear
Synchro-hub
3rd/4th gear
Hole
S464_008
22
Input shaft
Deep-groove ball
bearing
Input shaft gear
(constant stage)
Output shaft

Output shaft
The output shaft has a deep-groove ball bearing as its
fixed bearing, which is mounted in the rear gearbox
housing. The cylindrical roller bearing is used as a
moving bearing between the input shaft and the
output shaft.
The fixed gears of the 5th and 6th gear are
components of the output shaft. The synchromeshed
gears of 1st, 2nd, 3rd and reverse gears are mounted
on needle bearings, allowing them to rotate freely.
These synchromeshed gears are also referred to as
idler gears – they rotate constantly with the
corresponding fixed gears.
The synchro-hubs of 1st/2nd and 3rd/4th gears are
firmly connected to the output shaft by means of
splines. It is a special feature that the synchromeshed
gear and synchro-hub of the reverse g ear form one
structural unit. The clutch splines of reverse gear are
connected to the output shaft in a non-rotating
arrangement via splines.
S464_016
It is only when a gear is engaged that the
synchromeshed gears are firmly connected to the
output shaft by means of the locking collar and
corresponding synchro-hub, thereby allowing them
to transmit torque.
3rd gear
synchromeshed gear
Locking collar
3rd/4th gear
Synchro-hub
3rd/4th gear
Synchromeshed gear
4th gear/
constant input gear
Input shaft 6th gear fixed gear 5th gear fixed gear
2nd gear
synchromeshed gear
1st/2nd gear
synchro-hub
Locking collar
1st/2nd gear
R-gear synchromeshed
gear with synchro-hub
1st gear
synchromeshed
gear
R gear locking collar
R gear clutch splines
Output shaft
S464_009
Deep-groove ball bearingCylindrical roller bearing
23

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
Layshaft
A fixed and a moving bearing are also used for
mounting the layshaft. The double deep-groove ball
bearing is fitted as a fixed bearing in the front
gearbox housing, and the cylindrical roller bearing
as a moving bearing in the rear gearbox housing.
The fixed gears of 1st and 2nd gear are milled out of
the layshaft, making them components of the layshaft.
The fixed gear of 1st gear is also used as a drive gear
for the reverse shaft.
The synchromeshed gears for 5th and 6th gears are
idler gears – they are mounted on needle bearings.
S464_017
The fixed gear for 3rd gear and the constant are
firmly connected to the layshaft by means of a press
fit.
The synchro-hubs of 5th/6th gear are also firmly
connected to the layshaft by splines.
Constant
Synchromeshe d gear
6th gear
Locking collar
5th/6th gear
Synchro-hub
5th/6th gear
Synchromeshed gear
5th gear
Fixed gear
1st gear
Layshaft
S464_010
24
Double deep-groove ball
bearing
Fixed gear
3rd gear
Cylindrical roller ball
bearing
Fixed gear
2nd gear

Synchronisation
Due to the design conditions and different dimensions of the gears which need to be synchronised with one
another, different synchronisation variants are used in the manual gearbox.
Both bonded and brazed sintered powder linings are used.
Single synchronisation with bonded sintered powder lining
This synchronisation is used in the 3rd/4th gear – 5th/6th gear and R gear.
Locking collar
Synchro-hub
Synchro-ring
Clutch splines
Thrust piece
Illustration shows example of 4th gear
1st/2nd gear – double synchronisation with brazed sintered powder linings
This synchronisation is used with 1st/2nd gear.
Locking collar
Synchro-hub
Synchro-ring with locking splines
Thrust piece
S464_066
Intermediate ring
Inner ring
Clutch spli nes
Illustration shows example of 1st gear
S464_065
25

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
The powerflow
The engine torque is transmitted into the gearbox via
the input shaft. The powerflow is transmitted to the
layshaft by means of the constant stage gear pair
which is constantly in mesh.
Except for 4th gear, the powerflow in all other gears
runs from the layshaft through the corresponding
gear pairing of the engaged gear onto the output
shaft.
Reverse gear (R gear)
The 4th gear is directly engaged. In this case, the
powerflow runs directly from the input to the output
shaft.
When reverse gear is engaged, the powerflow runs
from the layshaft to the output shaft by means of the
additional R-gear shaft, thereby reversing the
direction of rotation of the output shaft.
1st gear
26
2nd gea r

3rd gear 5th gear
4th gear 6th gear
S464_019
27

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
The external selector
mechanism
The design of the selector mechanism with coupling
rod represents a new development for Volkswagen.
Selector lever
Coupling rod
The gearshift positions are transmitted to the selector
unit of the gearbox by means of two separate selector
rods …
… through the
● selector rod for gear selection and the
● selector rod for gate selection
Selector housing
Selector housing
bottom part
Relay lever with damping weight
Relay lever
top part
S464_046
Coupling rod
28
Selector rod for gate
selection
Selector rod for
gear selection

Decoupling of selector lever
The coupling rod is used for decoupling the selector lever from the gearbox. It presents vibrations from being
transmitted to the selector lever. This design measures increases operating comfort when driving.
Structure and function
The coupling rod is rigidly connected to the gearbox
at the front end by means of a holding pin. At the rear
end, it is connected to the gearshift kinematics in the
selector housing by means of a rocker. The rocker is
mounte d on both sides in the selector housing upp er
part.
Selector lever
Selector lever guide
Gate selector
axis of rotation
The coupling rod keeps the shaft of the gearshift
kinematics at a constant distance from the gearbox
at all times. During the gearshift procedure, all
movements of the gearshift kinematics take place
via this shaft.
Vibrations and load change-dependent relative
movements of the drivetrain are compensated for by
relative movement of the gearshift kinematics shaft –
due to the connection via the coupling rod.
The selector mechanism always remains free from
vibration and feedback of engine/gearbox
movements
Rear view – in driving d irection
S464_087
Axis of rotation
Rocker
Gearshift kinematics
shaft
Rocker
Rocker mounting in the
selector housing top part
Selector housing
top part
Rocker
Selector lever guide
Axis of rotation
Rocker
Gearshift kinematics
shaft
S464_103
29

6-speed manual gearbox 0C6
The internal selector mechanism
Structure and function
The gear selector and gate selector turning shafts are mounted in the gearshift module in a rotating arrangement.
Both turning shafts engage in the centre selector shaft via the central driver by means of a lever mechanism.
The centre selector shaft is mounted in Teflon plain bearings and is connected to all selector forks whilst still being
able to rotate. The selector turning shaft pushes the centre selector shaft axially in both directions, thereby
engaging both the gears in one gate. A selector fork is allocated to each selector finger.
The gate selection turning shaft rotates the centre selector shaft radially in both directions, thereby selecting the
gate. The centre selector shaft as well as the selector turning shaft and gate selection turning shaft are mounted in
Teflon-coated plain bearings.
Selector turning shaft
Gate selection turning shaft
Selector module
Locking – radial centre
selector shaf t position
(neutral position in
relation to 3rd/4th gear)
Loc kin g bar
Gearshift finger
Selector fork
3rd/4th gear
30
Centre selector shaft
Central driver
Selector fork
R gear
Selector fork
1st/2nd gear
S464_054
Selector fork
5th/6th gear

The locking bar is mounted on the centre selector shaft in a rotating arrangement – it cannot be moved axially. The
locking bar is moved as well when the gate is selected, by means of the driver pin that is firmly connected to the
centre selector shaft. The locking bar has mechanical coding and there is also coding on the selector forks in order
to ensure sequential engagement of the individual gears. A guide plate on the central driver provides additional
mechanical coding for the gearshift procedure.
Selector turning shaft
Selector fork lock
R gear
selecto r fo rk
Gate selection turning shaft
Guide plate
Reversing light switch F4
Driver pin
Gearshift finger
Locking bar
1st/2nd gear
selector fork
5th/6th gear
selector fork
3rd/4th gear
selector fork
Centre selector shaft
S464_055
Locking –
axial position of the
centre selector shaft
31

Transfer box
The non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive with
transfer box 0C7
The transfer box that is flange-mounted on the manual gearbox distributes the input torque to the front and rear
axles. It makes it possible to engage the front final drive (4x4 HIGH) and the additional reduction stage (offroad
range, 4x4 LOW).
The gear engagement procedures are performed by a control motor that engages the gear ratios by means of two
separate locking collars.
Output flange
Non-permanently engaged fourwheel drive
Mechanical structure
to rear final drive
● Newly developed transfer box
● Robust structure
● Specifically designed for offroad use
● Offroad range (reduction stage) for all gear
stages
● Integration of the system into vehicle dynamics
programme
● Input torque distribution:
Even force distribution by rigid connection
between front and rear axles
● Weig ht = 34 k g
● Oil fill volume 1.25 l
● The developer and manufacturer of the transfer
box 0C7 is Magna powertrain
Selector shaft drive gear
Hall sender for transfer box G759
Gearbox switch for
transfer box interaxle
lock F438
32
Transfer box control motor V455
Tra ns fer ch ai n
Sprocket

Output to rear fina l
drive
Input from main
gearbox
Oil pump
Gearshift sprocket
Main shaft
S464_039
Output to front final
drive
Output shaft to front final driv e
Input from main gearbox
Reduction stage (offroad range)
Ventilation
Selector shaft
S464_012
33

Transfer box
Rear final drive 4x2
Mode of function
Selector fork 4x4 HIGH
Selector shaft input gear
Output flange to
rear final drive
Main shaft
Tra ns fer c h ai n
Roll pin
4x4 LOW
Sprocket
Output shaft
to front fina l driv e
Selector fork 4x4 LOW
Selector shaft
Sun gear output spli nes
Dog teeth
Locking collar
4x4 LOW
Powerflow
34
Input splines for oil pump Gearshift sprocket
Locking collar
4x4 HIGH
The main shaft is a shaft that has been drilled through
hollow. The main shaft is used for accommodating the
gearshift sprocket, both locking collars for 4x4 HIGH
and 4x4 LOW and the propshaft flange.
In addition, the drive splines for the oil pump are on
the main shaft.
Input splines
Sun gear
Planetary gearbox
Locking collar
4x4 LOW
Ring gear
S464_014
The gearshift sprocket is mounted on the main shaft
and can rotate freely.
The 4x4 LOW locking collar is firmly connected to the
main shaft by means of its internal splines, and forms
a unit with the dog teeth.

Norm ally, the vehicle is in 4x2 mode – in which case only the rear axle is driven.
Both selector forks for 4x4 HIGH and 4x4 LOW are in their rest position.
The input torque is transmitted from the main gearbox directly via the sun gear of the planetary gearbox onto the
main shaft of the transfer box.
Powerfl ow
Sun gear input splines –> sun gear output splines –>
4x4 LOW locking collar dog teeth –> main shaft –>
output flange to rear final drive.
The torque distribution is 100 % to the rear axle.
Planetary gearbox
The transmitted torque is always input into transfer
box 0C7 via a planetary gearbox on the input end.
It has two functions:
– Force input into the transfer box
– Implementation of offroad range
The planetary gearbox consists of a single planetary
gear set. The ring gear of the planetary gearbox is
firmly pressed into the gearbox housing. The planet
carrier with 3 planet gears runs in this ring gear.
The sun gear is inserted into the planet carrier to drive
the planet gears. The planet gears simultaneously
engage in the driving sun gear and the ring gear and
the planet carrier.
(The planet carrier is only half inserted into
the ring gear in order to clarify the view)
Planet carrier
output splines
Planet carrier
Sun gear
output splines
S464_091
Ring gear
S464_090
Sun gear
Planet gear
The ratio means that the planet carrier rotates with a
lower speed than the driving sun gear – this is the
reduction. The output splines of the planet carrier
(4x4 LOW) and the output splines of the sun gear
(4x2, 4x4 HIGH) transmit the input torque on to the
4x4 LOW locking collar and the main shaft.
Single planetary gear set (schematic view)
Sun gear
Planet gear
Planet carrier
Ring gear
S464_092
35

Transfer box
Four-wheel drive 4x4 HIGH
Engaging
Roll pin 4x4 LOW
Return spring
Roll pin 4x4 HIGH
Selector shaft input gear
Output flange to
rear final drive
Main shaft
Selector fork
4x4 HIGH
Transfer chain
Input shaft
to front final drive
Sprocket
Selector shaft
Sun gear output splines
Dog teeth
Locking collar
4x4 LOW
Powerflow
Tooth spacing – small
Tooth spacing – large
In order to engage 4x4 mode, the transfer box control
motor V455 is energised by the transfer box control
unit J646 with a pulse-width modulated signal. The
motor rotates the selector shaft via the input gear
through 90° clockwise. When this happens, the
4x4 HIGH roll pin firmly connected to the selector
shaft pushes the 4x4 HIGH selector fork towards the
gearshift sprocket by means of a control ramp.
4x4 mode is activated by the 4x4 HIGH locking collar
being moved along the straight-splined dog teeth of
the gearshift sprocket. The gearshift sprocket is now in
a fixed rotating connection with the main shaft.
Locking collar
4x4 HIGH
Input splines
Sun gear
Gearshift sprocket
Planetary gearbox
Locking collar
4x4 LOW
Ring gear
S464_068
Powerflow
Sun gear input splines –> sun gear output splines –>
4x4 LOW locking collar dog teeth –> main shaft –>
output flange to rear final drive/gearshift sprocket –>
transfer chain –> sprocket –> Output shaft to front
final drive.
4x4 mode represents a 100% interaxle lock between
the front axle and rear axle.
As a result, the input torque is evenly distributed
between the front and rear axles.
36

The gearshift procedure is not synchronised.
4x4 mode can be engaged at any driving speed. During driving, there can in some cases be very small rotation
speed difference s between the front and rear axles (due to slip, the road surf ace, different tyre wear, etc.).
To facilitate engaging 4x4 mode whilst driving, the tooth pitch on the dog teeth of the gearshift sprocket is twice as
large as that of the main shaft. When 4x4 mode is engaged, this system means there is an idle travel in the
powerflow to the front final drive amounting to a few degrees of angle. This idle travel is not a fault, nor does it
lead to any restrictions in driving comfort or impairments in the durability of the transfer box.
Disengaging
The shift back to 4x2 mode is performed by the
control motor for the interaxle lock turning the selector
shaft through about 90° anticlockwise. The selector
fork is pushed back into the 4x2 position solely by the
effect of the return spring in this case.
Due to the driving situation, torque wind-up can occur
in the driveline in 4x4 mode under certain
circumstances. This tension cannot be dissipated when
driving on ground that does not permit wheel slip. The
tension leads to increased static friction between the
locking collar and the dog teeth of the gearshift
sprocket.
Static friction means that the locking collar remains in
its position when 4x4 mode is deactivated. As soon as
the tension has been dissipated by a load change or
change of steering direction during driving, the
selector fork is moved back to the 4x2 position
subsequently by the return spring.
37

Transfer box
Offroad range 4x4 LOW
Engaging
Roll pin 4x4 LOW:
the position indicated
corresponds to the 4x4 HIGH
position
Selector shaft input gear
Guide plate
Output shaft
to front final drive
Adjusting spring
Selector fork 4x4 LOW
Planet carrier output splines
Dog teeth
Locking collar
4x4 LOW
Powerf low
Main shaft
Output flange
to rear final drive
Gearshift sprocket
To engage 4x4 LOW offroad range, the transfer box
control motor V455 is energised by the transfer box
control unit J646 with a pulse-width modulated signal.
The motor turns the selector shaft starting from 4x4
HIGH position via the input gear through about 120 –
130° clockwise. When this happens, the 4x4 LOW roll
pin that is firmly connected to the selector shaft
pushes the 4x4 LOW selector fork into 4x4 LOW
position via the guide plate. (The roll pin can no
longer be seen in this engagement position – it is
now covered, on the rear of the guide plate.)
The system design means that the reduction can only
be engaged after 4x4 HIGH has been engaged.
Input splines
Locking collar
4x4 LOW
Ring gear
Sun gear
Planetary gearbox
S464_069
The gearshift procedure is not synchronised, and is
only possible when the vehicle is stationary.
Powerflow
Sun gear input splines –> planetary gearbox –>
planet carrier output splines –> 4x4 LOW locking
collar dog teeth –> main shaft –> output flange to
rear final drive/gearshift sprocket –> transfer chain
–> sprocket –> output shaft to front final drive.
The ratio of the reduction stage (offroad range) is i =
2.72 in all vehicles.
38

Disengaging
To switch back to 4x4 HIGH, the control motor for the interaxle lock rotates the selector shaft anticlockwise back to
the 4x4 HIGH position. The selector fork is moved back along the gate guide into its initial position in this case. The
powerflow is now direct from the sun gear to the main shaft without a reduction.
Adjusting spring
The adjusting spring acts in both directions of movement of the 4x4 LOW selector fork. It operates the 4x4 LOW
selector fork. In the normal gearshift procedure, the spring is located in its position without tension. The inclined
profiles of the dog teeth on the 4x4 LOW locking collar and the planetary gear set means that the engagement
generally takes place without resistance.
In case of "tooth-on-tooth" positions, the adjusting spring is preloaded by the rotation of the selector shaft. As soon
as the angle position of the sun gear changes by a minimum amount, the engagement procedure can take place
with the pre-imposed spring force of the adjusting spring. If the aforementioned situation occurs ("tooth-on-tooth"
positions) then the design of the system means there may be grating noises. For this reason, it is advantageous for
the gearbox to be shifted to neutral when engaging and disengaging 4x4 LOW, so as to minimise the probability of
gearshift grating.
The dog teeth on the locking collar and in the
planetary gearbox have symmetrically angled
tooth flanks for shifting from HIGH to LOW and
asymmetrically angled tooth flanks for shifting
from LOW to HIGH. The angled tooth flanks that
operate in both movement directions of the dog
teeth support the gearshift procedure when
engaging and disengaging 4x4 LOW. The dog
teeth from LOW to HIGH are optimised for
forwards driving because of the asymmetrical
tooth flank position.
Sun gear output splines
Planet carrier output splines
4x4 LOW locking collar
dog teeth
S464_094
Engagement of locking collar spines in planet carrier splines Engagement of locking collar spines in sun gear splines
Gearshift tooth
planet carrier
Before
engagement
Engagement
completed
Gearshift tooth
locking collar
Engagement starts
Before
engagement
Gearshift tooth
sun gear
S464_095
Engagement
completed
39

Transfer box
Oil supply
Lubricating oil is supplied by means of force-feed circulating lubrication. The oil pump driven by the main shaft
splines supplies the lubricating points by means of oil ducts in the drilled-out main shaft.
The oil pump is configured as a rotor pump.
The oil is drawn in through a suction pipe with oil
strainer from the lowest point in the housing.
Under the strainer, there is a magnet for collecting
ferromagnetic abrasion.
Oil pump
Oil pump
S464_071
Intake connecting pipe with strainer
Main shaft
Oil outlet hole – to the
lubricating points in the planetary gearbox
Intake connecting pipe with strainer
S464_096
40

Selector shaft drive
The transfer box control motor V455 bolted onto the
gearbox housing is connected to the input worm. The
input worm rotates the input gear of the selector shaft
via spur gearing.
Input gear with spur gearing
Transfer box control motor V455
Trans fe r box control motor V45 5
Task
S464_086
Transfer box control motor V455
S464_070
Input worm
Transfer box control motor V455
Output to input worm
The control motor rotates the selector shaft
mechanically in order to engage the required drive
mode , 4x2, 4x4 or 4x4 LOW.
Mode of function
The control motor operates as a permanent magnet
electric motor, in which case the motor is controlled
via a PWM signal from the transfer box control unit
J646.
S464_097
Effects in case of failure
● Fault entry in error memory
● Flashing warning lamp in dash panel insert
● No gearshift procedure possible any longer
● The transfer box remains in the position that was
last engaged.
41

Transfer box
Control of the transfer box
Two sensors are required for registering the system statuses and for controlling the gearshift procedures in the
transfer box. They supply the transfer box control unit J646 with all the information required.
Gearbox switch for
transfer b ox interaxle lock F438
Hall sender for
transfer box G759
Hall sender for transfer box G759
Task
● Position detection of the selector shaft.
● Control of the gearshift procedures in the transfer
box.
The Hall sender outputs a voltage level according to
the position of the selector shaft.
● 4x2 = 4.0 V
● 4x4 HIGH = 2.0 V
● 4x4 LOW = 1.0 V
S464_098
Hall sender for
transfer box G759
S464_085
Effects in case of failure
● Fault entry in error memory
● Flashing warning lamp in dash panel inser t
● No gearshift procedure possible any longer
● The transfer box remains in the position that was
last engaged.
42

Mode of function
The sensor operates using the Hall principle.
The input link of the rotation sensor is connected to the
selector shaft by means of an opening. A permanent
magnet acts on the sensor shaft, and produces
fluctuations in the magnetic field in the sensor during
rot ation.
The sensor electronics evaluate the signal changes
and provides the control unit with an analogue
voltage that is dependent on the turn angle.
Sensor electronics
Hall sender for
transfer box G759
S464_102
The Hall sender for transfer box G759 is bolted on in
the rear housing of the transfer box. 3 asymmetrically
arranged securing bolts, a coding lug and the
asymmetrical position of the input link mean that the
Hall sender cannot be installed in a twisted position.
Sensor electronics
Coding lug
Sensor shaft
Input link
Selector shaft
Opening
S464_099
43

Transfer box
Gearbox switch for transfer box interaxle lock F438
Mode of function
The gearbox switch F438 operates as a simple
mechanical button. It is controlled by a ramp on the
4x4 HIGH selector fork.
The switch is open in 4x2 mode.
Task
● Sensing the actual position of the 4x4 selector fork,
i.e. whether four-wheel drive really is disengaged
and the selector fork is in the 4x2 position.
● In addition, the control logic of the longitudinal
lock-up warning lamp K278 is controlled by means
of the gearbox switch for transfer box interaxle
lock F438. Warning lamp K278 is no longer
activated when the transfer box has completed the
gearshift procedure into 4x2 more.
Gearbox switch for transfer
box interaxle lock F438
S464_084
F438
44
Effects in case of failure
● Fault entry in error memory
● Flashing warning lamp in dash panel insert
● No functional restrictions for four-wheel drive.
S464_101
Selector fork 4x4 HIGH

System overview
E631 (down) = Running gear programme switch
E631 (up) = Running gear programme switch
F438 Gearbox switch for transfer box interaxle lock
G759 Hall sender for transfer box
J285 Control unit in dash panel insert
J646 Control unit for transfer box
(installed centrally under dash panel)
Powertra in CAN
S464_035
K181 Normal operation warning lamp in transfer
box ope rating unit
K182 Reduction gearing warning lamp in transfer
box ope rating unit
K183 Longitudinal lock-up warning lamp in transfer
box ope rating unit
K277 Warning lamp for gearbox low range
K278 Longitudinal lock-up warning lamp
V455 Servomotor for transfer box
45

Transfer box
The transfer box with limited-slip interaxle differential 0BU
The design of the transfer box with limited-slip interaxle differential is based on the transfer box of the Audi Q7 and
the Touareg 2011. It has been adapted for use in the Amarok.
Technical features
● Modern "four-wheel drive" technology in the
Amarok
● Sturdy system operating purely mechanically
● Suitable for onroad and offroad use
● Permanent four-wheel drive
● Differential compensation between the front and
rear axles
● Limited-slip interaxle differential with
basic distribution of the input torque (when driving
without slip on the front and rear axles): front axle
= 40 %, rear axle = 60 %
Variable torque distribution: front axle =
20 – 60 %, rear axle = 40 – 80 %
● Integration in vehicle dynamics programmes
● Full ESP suitability in four-wheel drive and locked-
up rear axle differential
● Weig ht 23 k g
Output to
rear final drive
Drive from
main gea rbox
S464_038
Output to
front final drive
Output flange to rear final drive
Limited-slip interaxle differential
Oil collector with oil guide
Ven ti l at io n
46
Transfer cha in
Output shaf t to
front final drive
Input shaft
S464_013

Limited-slip interaxle differential type C
The limited-slip interaxle differential, firstly, compensates for rotation speed differentials between the front and rear
axles and, secondly, dynamically adjusts the input torque distribution between the front and rear axles depending
on the wheel slip.
The basis structure of the limited-slip interaxle differential corresponds to a single planetary gear set with planet
carrier, planet gears, ring gear and sun gear.
In addition, friction discs made from nickel steel are fitted in the interaxle differential. These friction discs and the
ATF oil significantly influence the friction torque and therefore the slip value of the differential. The friction torque
comes about through the self-locking effect of the helical gearing and by the contact pressure of the sun gear and
ring gear on the friction discs.
Ring gear
Planet gears
Sun gear
Planet carrie r
Friction discs
Limited-slip interaxle differential
Oil collector with oil guide
Input shaft/hollow shaft
S464_023
Housing
Oil collector with oil guide
For more information about the design and
function of the limited-slip interaxle differential,
refer to self-study programme 363 "Audi Q7
powertrain/transfer box 0AQ" and self-study
programme 469 "The Touareg 2011 – running
gear and four-wheel drive concept".
Oil level/oil volume
S464_045
47

Rear final drive 0CC
The rear final drive 0CC
The rear final drive in the Amarok drives via a newly
developed rigid axle with leaf suspension and drum
brakes.
This axle represents a basic design feature for all
variants of the Amarok.
Manufacturer and developer:
American Axle & Manufacturing
Ventilation
S464_040
Propshaft flange
Rear final drive
48
Advantages of the r igid axle:
– Wheel guidance with constant toe and camber over the entire suspension travel
– No reduction in ground clearance in compression travel
– Large load volume
– Robust design

Rear final drive
The rear final drive is currently produced with 2 different ratios
i = 4.1 for 120kW TDI engine and
i = 4.3 for 90 kW TDI engine and 118kW FSI engine
Right axle tube
Differential lock
Lef t a xle t ube
Differential
Crown wheel
Pinion
Propshaft flange
Optionally, the rear final drive is available with an electrically engaged differential lock for
all vehicle variants
S464_020
49

Rear final drive 0CC
Component overview
The final drive housing is positioned in the centre of
the axle and is made from grey cast iron. The axle
tubes are made of a steel tube and are welded onto
the final drive housing. The stub shafts are solid
shafts.
The position of the pinion in relation to the crown
wheel is set using a shim behind the inner bearing of
the pinion. The bearing preload for the pinion is set
using a ram sleeve.
The oil filler plug is located in the housing cover. Only
vehicles with a differential lock have an oil drain plug
fitted.
Venting is provided by a hose into the ladder frame.
1 Pinion collar nut
2 Propshaft flange
3Shaft oil seal
4 External tapered roller bearing
5Ram sleeve
6 Oil drain plug
7Thrust washer
8 Inner tapered roller bearing
9Shim
10 Pinion
11 Crown wheel
12 Housing cover seal
13 Housing cover
14 Oil filler plug
15 Bolt
17
16
16 Bolt
17 Bearing support
18 Differential with housing
19 Shim
20 Differential lock
21 Wheel hub
22 Wheel bearing
20
15
14
12
13
50

22
21
3
23
25
24
18
9
8
7
10
6
11
29
4
5
26
1
2
27
23 Wheel bearing collar nut
24 Wheel speed sensor
25 Oil drain
26 Stub shaft
27 Handbrake cable
28 Drum brake
29 Axle tube
19
28
S464_021
51

Rear final drive 0CC
Differential lock
The differential lock is activated by means of the rear
differential lock switch E121 in the centre console. The
status display is located in the dash panel insert. ESP
and ABS are deactivated (depending on equipment
and variants) when the differential lock is activated.
Differential lock Differential
Function
The differential lock is controlled by a differential lock
control unit J187 incorporated in the p owertrain CAN,
which is fitted on the centre console close to the
handbrake lever.
● G460 = Axle differential lock Hall sender 1
(sensor for detecting position of
differential lock)
● N5 = Control solenoid (actuator)
The actuator is connected to the axle housing in a
rotationally fixed arrangement via the retaining tabs.
The pressure plate and shift dog are connected to the
differential housing in a rotationally fixed
arrangement.
When the differential lock is activated, the magnetic
coil of the differential lock control unit J187 integrated
in the actuator is energised. The control solenoid
moves out and presses against the shift dog via a
metal ring and the thrust plate. The shift dog engages
in the lock gearing of the axle bevel gear and blocks
it.
The axle bevel gear is now connected to the differential housing in a rotationally fixed arrangement. This
means the differential is locked. The magnetic coil is
energised with pulse width modulation in order to
avoid impermissible heating of the control solenoid.
The control unit processes the sig na ls from the a xle
differential lock Hall sender 1 G460 for activation
purposes.
Component overview
Axle differential lock
Hall sender 1 G460
Retaining tab
S464_053
Thru s t pl at e
Permanent magnet
Metal ring
Retaining ring
Control solenoid N5
(actuator)
52

The axle differential lock Hall sender 1 G460 is fitted on control solenoid N5 (actuator).
This position sensor operates according to the Hall principle – it detects the actual position of the control solenoid
or pressure plate. This means the differential lock control unit J187 is informed of the actual position of the
differential lock (opened, actuated, "tooth-on-tooth" position). The control solenoid must remain energised for the
entire duration of the activation.
Thrust washer
Guide ring
Shift dog
Return spring
Axle bevel gear with
lock gearing
Differential bevel
gear
Differential housing
S464_022
For more information about repair work,
see ELSA.
When the lock has been deactivated, the shift dog is
returned to its rest position by means of a return
spring.
Following repair work, the differential lock control unit
J187 must be adapted to the axle differential lock Hall
sender 1 G460 using the VAS diagnostic tester.
The final drive must be removed in order for some
repair work to be performed on the differential lock.
Measuring and setting work is required for this.
53

Rear final drive 0CC
System overview – differential lock
E121 Rear differential lock switch
G460 Axle differential lock Hall sender 1
J187 Differential lock control unit
J285 Control unit in dash panel insert
K276 Warning lamp for rear transverse lock
N5 Control solenoid
Powertrain CAN
S464_067
54

The front final drive 0C1
Front-wheel drive 0C1
The design of the front final drive is based on the
technology of the VW Touareg and the Audi Q7.
Two different versions of it are installed in the Amarok,
depending on the drive type.
Both variants are based on the same design principle.
The manufacturer and developer is
ZF Getriebe GmbH.
Configuratio n for vehicles with
permanent four-wheel drive
Ven ti l at io n
S464_037
Reinforcing ribs
In vehicles with non-permanently engaged four-wheel
drive (part time transfer box), relatively high stresses
can build up in the driv etrain when d riving in fourwheel drive without wheel slip.
Therefore, these vehicles have a reinforced housing
with adapted bearings and a larger crown wheel is
used .
Ventilation takes place via a hose in the engine
compartment in the area of the right inner wing.
Configuration for vehicles w it h part-time transfer box
Ven ti l at io n
S464_083
Reinforcing ribs
55

Front final drive 0C1
Structure of the front final drive 0C1
The front final drive 0C1 consists of a bevel gear/crown wheel gearset with hypoid gearing.
The differential effect is achieved using axle bevel gears.
The position of the pinion in relation to the crown wheel is set using a shim in front of the inner bearing of the
pinion. The bearing preload is set using a ram sleeve.
The backlash between the bevel gear and crown wheel is adjusted using two shims on the differential housing.
To compensate for the asymmetrical installation position of the front axle box, the left drive flange shaft has been
extended accordingly. This means the support torques resulting from the input torques are symmetrically carried by
the front axle. Negative effects on the steering properties are thus eliminated.
Needle bearing for left drive shaft
Drive left front wheel
Ratios
The front final drive is offered with two different ratios and two different crown wheel diameters.
Rat io i = 4.1 for 120 kW engine;
Rat io i = 4.3 for 90kW and 118 kW engines;
Crown wheel diameter: 175 mm in all vehicles with permanently engaged four-wheel drive
Crown wheel diameter: 195 mm in all vehicles with non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive
(part-time transfer box)
56

Differential
Shim (for backlash)
Crown wheel
Pinion
Right front wheel drive
Oil duct
Drive from transfer box
S464_025
Shim for setting the position of the
pinion in relation to the crown wheel
57

Test your knowledge
Which answer is correct?
One or more of the model answers could be correct.
1. Under what conditions can the 4x4 LOW offroad range be engaged?
The following engagement conditions must be met:
a) Engine speed < 1500 rpm, can be engaged at any driving speed, 4x4 HIGH four-wheel drive engaged
b) Engine speed < 1500 rpm, driving speed < 1 km/h, 4x4 HIGH four-wheel drive engaged
c) Engine speed < 1500 rpm, 4x4 HIGH four-wheel drive engaged, differential lock engaged
2. What features apply to the offroad drive programme?
a) The control behaviour of the ABS is adapted. The pressure buildup and pressure holding phases are
extended. The depressurisation is shorter and takes place later.
b) The control behaviour of the ABS is adapted. The pressure buildup and pressure holding phases are
shortened. The depressurisation is longer and takes place earlier.
c) The control behaviour of the ABS is unchanged. The ASR and EDL control is adapted.
3. What is the task of the adapter shaft in the manual gearbox 0C6?
a) The rear axle in vehicles without four-wheel drive function is driven via the adapter shaft.
b) The drive torque is transferred from the engine to the manual gearbox via the adapter shaft.
c) The drive torque is transferred from the manual gearbox to the transfer box via the adapter shaft.
4. What is the special feature of R gear in the manual gearbox 0C6?
a) There is no reverse shaft in the manual gearbox 0C6. 2nd gear is used for the reversal of the direction of
rotation.
58
b) The synchromeshed gear and synchro-hub of the R gear form one structural unit.
c) The R gear is not synchronised.

5. Which statement regarding the selector mechanism of the manual gearbox 0C6 is correct?
a) The coupling rod always keeps the axis of rotation of the gearshift kinematics at the same distance from the
gearbox.
b) The coupling rod engages reverse gear.
c) The coupling rod prevents several gears from being engaged at the same time.
6. What is the gearshift procedure in the non-permanently engaged four-wheel drive 0C1?
a) The return spring holds the 4x4 LOW selector fork firmly in its rest position.
b) In the gearshift procedure from 4x4 HIGH to 4x2 mode, the 4x4 HIGH selector fork is exclusively moved by
the force of the return spring.
c) In the gearshift procedure from 4x4 LOW to 4x2 HIGH, the 4x4 LOW selector fork is exclusively moved by
the force of the return spring.
7. The Hall sender for transfer box G759 ...
a) … senses the position of the selector shaft and controls the gearshift procedures in the transfer box.
b) … registers the output speed of the transfer box and prevents four-wheel drive from being engaged if there
are speed differences between the front and rear axles.
c) … only registers the position of the selector shaft in 4x2 mod e.
8. How does the differential lock function in the rear final drive 0CC?
a) The control solenoid N5 operates the multi-disc clutch for blocking the differential.
b) The control solenoid N5 keeps the axle bevel gear fixed in position inductively due to its magnetic field.
c) The control solenoid N5 operates the shift dog via the thrust plate in order to block the axle bevel gear
1. b); 2. a); 3. c); 4. b); 5. a); 6. b); 7. a); 8. c
Answers
59

464
© VOLKSWAGEN AG, Wolfsburg
All rights re ser ved . Subject to t echnical modifications .
000.2812.37.20 Technical status 07.2010
Vo l ks wag en AG
After Sales Qualifizierung
Service Training VSQ-1
Brieffach 1995
D-38436 Wolfsburg
❀ This paper was manufactured using pulp bleached without the use of chlorine.
 Loading...
Loading...