Viking Pump TSM350 H User Manual
SECTION TSM 350
TECHNICAL SERVICE
MANUAL
INSTALLATION, START UP, TROUBLESHOOTING,
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE, DO’S & DON’TS
SERIES
HG-08 & HG-10 HELICAL GEAR PUMPS
PAGE 1 OF 10
ISSUE A
CONTENTS
Installation ...................................................... 1
Mounting ......................................................... 2
Start Up .......................................................... 3
Troubleshooting .............................................. 6
Miscellaneous ................................................. 8
Do’s and Don’ts ............................................. 9
Warranty ....................................................... 10
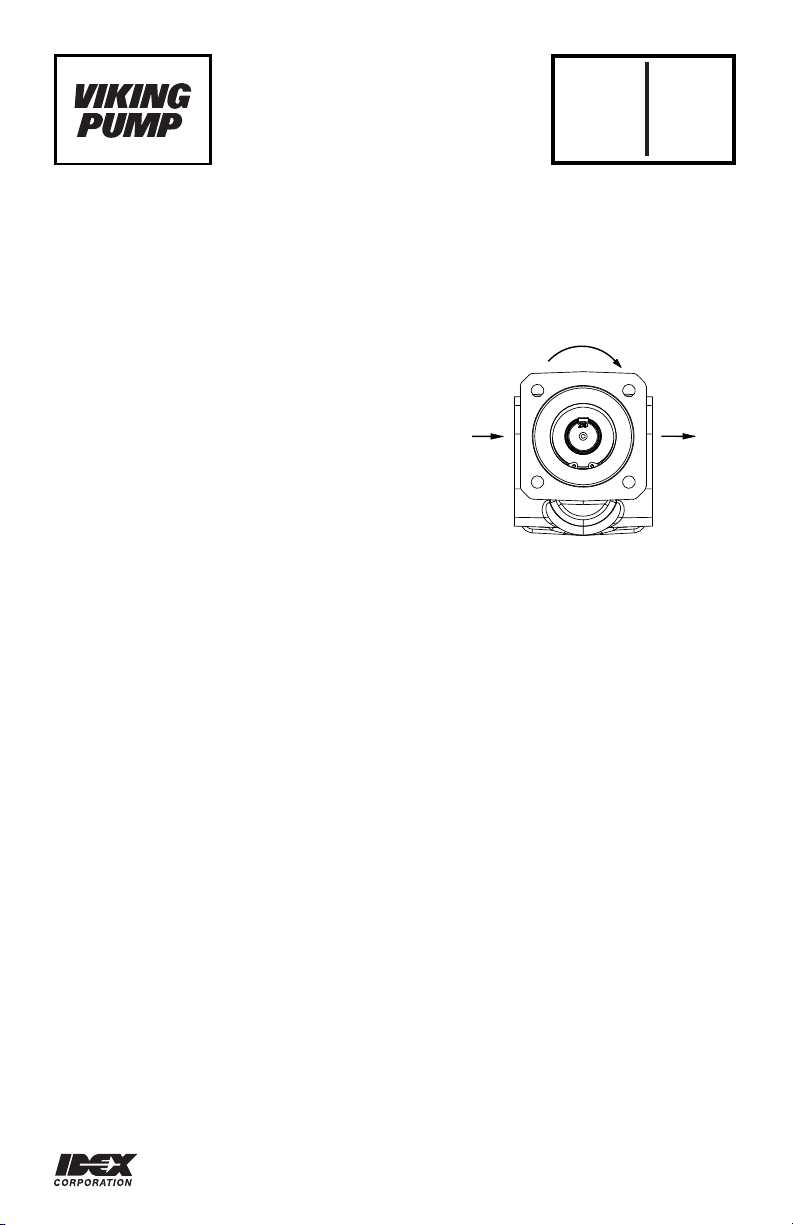
ROTATION
DS
FIGURE 1
INSTALLATION
General
The following items must be considered prior to pump installation:
1. Location - locate the pump as close as possible to the liquid supply. If possible locate the
pump below the liquid supply. Viking pumps are self-priming; but the better the suction
conditions, the better the pump will perform.
2. Accessibility – the pump must be accessible for inspection, maintenance and repair.
3. Suction/Discharge - HG Series pumps are designed for clockwise rotation as standard
(viewed from end of shaft). Refer to Figure 1.
4. Pressure Relief Valve - the HG Series is a positive displacement pump and requires
some form of over pressure protection. Without pressure protection, if the discharge
line is blocked or becomes closed, pressure will build up until the motor stalls, drive
equipment fails, a pump part breaks, or the piping and/or other equipment in the system
bursts. To prevent the possibility of any one or more of the above from occurring, the use
of a pressure relief valve is recommended.
5. Storage - drain the pump and apply a light coat of non-detergent SAE 30 weight oil to all
internal pump parts. Apply grease to the pump shaft extension. Viking suggests rotating
the pump shaft by hand one complete revolution every 30 days to circulate the oil.
VIKING PUMP, INC. • A Unit of IDEX Corporation • www.vikingpump.com
MOUNTING
1. Surfaces to which the pump mounts must be clean, flat and free of dings and burrs.
2. Use ISO Class 8.8 or better capscrews to mount pump.
3. The 4 mounting capscrews for the HG-08 pumps must have a minimum of 12 millimeters
thread engagement, and must be evenly torqued to 22-24 Nm (16-18 ft lbs).
4. The 4 mounting capscrews for the HG-10 pumps must have a minimum of 18
millimeters thread engagement, and be evenly torqued to 79-83 Nm (56-62 ft lbs).
5. Standard HG Series pumps are designed to be used with jaw type couplings that do not
induce axial thrust on the pump shaft. If an improper type of coupling is used, internal
damage may result.
6. Do not strike or press the pump drive coupling to install. Internal pump damage will
result. If the coupling does not slide onto the shaft, inspect the coupling, shaft and
key for nicks or burrs and remove.
7. Once the pump has been mounted and the coupling installed, it is recommended to put
lube oil into the suction port and turn the pump by hand to make sure it turns freely.
Alignment
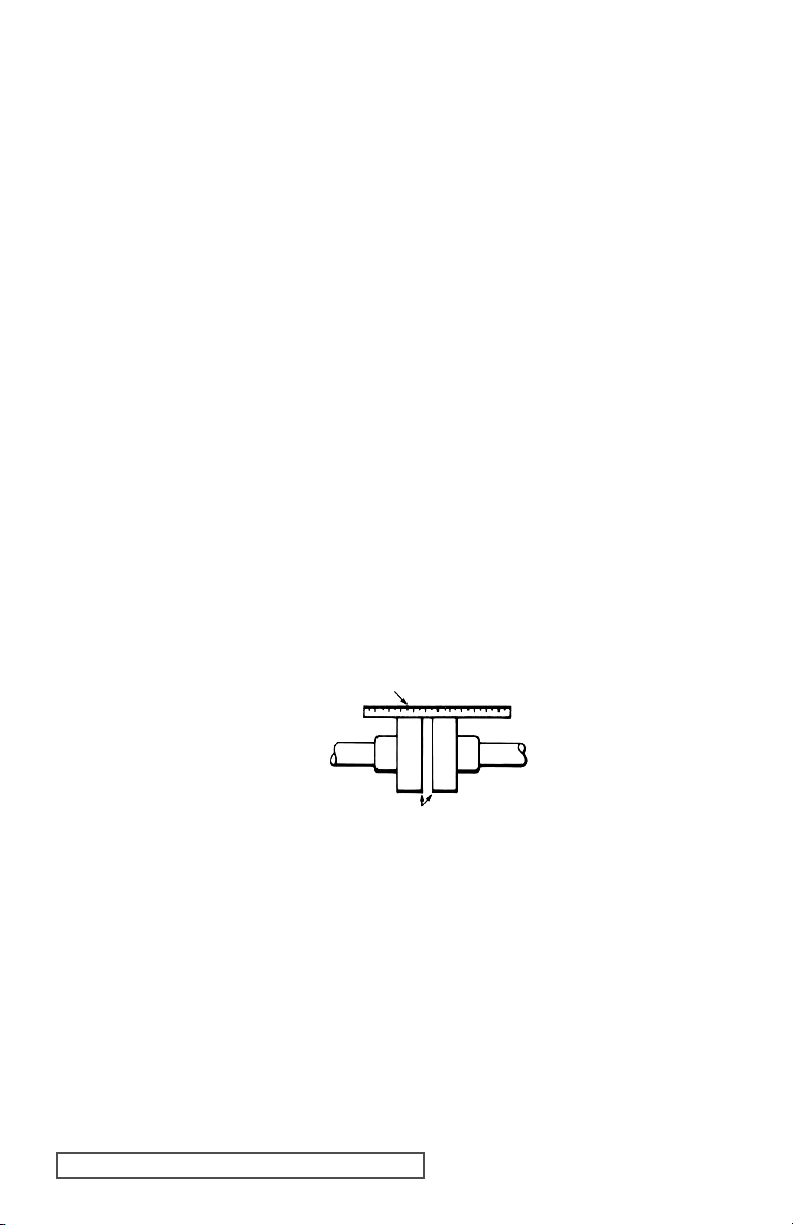
Check alignment after mounting.
1. Make sure that the driver has been “locked out” so that it cannot be inadvertently
started while checking alignment.
2. If the unit has a flexible coupling, remove any coupling guards or covers and check
alignment of coupling halves. A straight edge (piece of key stock will work) across the
coupling must rest evenly on both rims at the top, bottom and sides. See Figure 3.
3. Make a final check on alignment after the piping is hooked up.
USE STRAIGHT EDGE. THESE
SURFACES MUST
BE PARALLEL
CHECK WIDTH BETWEEN THESE SURFACES WITH INSIDE CALIPERS OR FEELER
GAUGE TO BE CERTAIN THE FACES ARE EQUAL DISTANCE APART AND PARALLEL.
FIGURE 3
Piping/Hose
The cause of many pumping problems can be traced to the suction piping. It should always be
as large in diameter and as short in length as possible.
Before starting the layout and installation of your piping system, consider the following points:
1. Never use piping smaller than the pump port connections. Piping larger in diameter than
the port connection is sometimes required to reduce friction losses.
SECTION TSM 350 ISSUE A PAGE 2 OF 10
2. Be sure the inside of the pipe is clean before installing.
3. When approaching an obstacle to the suction line, go around instead of over it. Going
over an obstacle can create an air pocket. Where practical, slope the piping so no air or
liquid pockets will be formed. Air pockets in the suction line make it hard for the pump to
prime.
4. A strainer on the suction side of the pump should always be considered in any pumping
system. The strainer will keep foreign matter from entering the pump. The strainer mesh
or perforation size should be large enough so that it does not cause excessive pressure
drop, but fine enough to protect the pump. Use of a strainer is particularly important at
start up to help clean the system of weld beads, pipe scale and other foreign objects.
5. A pressure relief valve is required in the discharge line. See Pressure Relief Valves,
General page 1 item 4.
6. The pump must not be used to support the piping. Hangers, supports, stands, etc. must
carry the weight of the pipes.
7. When fastening piping to the pump do not impose any strain on the pump casing.
“Springing” or “drawing” the piping up to the pump will cause distortion, possible
misalignment and probable rapid wear of the pump. Do not use the pump to correct errors
in piping layout or assembly.
8. All joints of piping system must be tight; liquid thread sealant will help assure leak free
threaded joints. Loose joints result in liquid leaks or suction side leaks. Air leaks make
the pump noisy and reduce flow. CAUTION: Be careful not to over tighten fittings as this
can cause cracked joints. Do not use PTFE tape. Reduced friction makes over tightening
very easy and will result in cracked ports. Leaks in the suction line can permit air to be
drawn in, and will cause a noisy pump and reduction in capacity.
9. Drive alignment must be checked after piping is hooked up.
10. Provide a pressure relief device in any part of a pump and piping system that can be
valved off and, thus, completely isolated. A rise in temperature will cause a liquid to
expand. If there is no provision for pressure relief in the closed off section, there is a
chance that the pump or piping will rupture.
Danger !
Before starting pump, be sure all drive equipment guards are in place.
Failure to properly mount guards may result in serious injury or death.
START UP
Before pushing “start” button, check the following:
1. Are vacuum and pressure gauges (liquid filled) mounted near the pump? Gauges are the
quickest and most accurate way of finding out what is happening in the pump.
2. Is the pump correctly aligned with the drive equipment?
3. Make sure there is no pipe strain on the pump ports.
4. Rotate the pump shaft by hand to be sure it turns freely.
SECTION TSM 350 ISSUE A PAGE 3 OF 10
 Loading...
Loading...