Page 1

Operation Manual
Benutzerhandbuch
Mode d’Emploi
オペレーションマニュアル
Page 2

English
Page 3

Matthias Klag, Michael Ruf
Revision and quality control: Cristina Bachmann, Heiko Bischoff, Marion Bröer, Sabine Pfeifer, Heike Schilling, Benjamin
Schütte
This PDF provides improved access for vision-impaired users. Please note that due to the complexity and number of im-
ages in this document, it is not possible to include text descriptions of images.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part
of Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH. The software described by this document is subject to a License Agreement
and may not be copied to other media except as specifically allowed in the License Agreement. No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced, or otherwise transmitted or recorded, for any purpose, without prior written permission
by Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH. Registered licensees of the product described herein may print one copy of
this document for their personal use.
Steinberg, HALion, VST, and ASIO are registered trademarks of Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH. Windows 7,
Windows Vista and DirectX are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Macintosh, Mac, Mac OS, and Logic are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. Pentium
and Intel Core are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. All other
product and company names are ™ or ® trademarks of their respective holders.
Release Date: May 31, 2011
© Steinberg Media Technologies GmbH, 2011.
All rights reserved.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Page 5

7 Installation and Setup
8 Welcome
8 Key Command Conventions
8 How You Can Reach Us
9 Installation
10 Setting Up
12 The HALion Control Panel
13 Introduction
13 Configuring the Control Panel
14 Setting the Focus
15 Working with Multiple Windows
15 Screen Sets
16 Overview of the Available Editors
17 Macro Pages
18 Managing Your Sounds
19 The Slot Rack
21 Managing Multis
22 Managing Files via the MediaBay
25 Content Files and Folder Structure
25 Loading HALion 3 Programs
26 Working with General MIDI Files
27 Loading and Managing Programs
28 Introduction
28 The Columns of the Program Table
28 Loading Programs into the Program Table
29 Loading Programs from the Program Table to the
Slot Rack
29 Editing the Program Table
30 Using the Program Tree
31 Introduction
31 The Program Tree Structure
32 Editing Zones, Programs, and Layers
33 Making Selections
34 Navigating in the Program Tree
34 Muting, Soloing, and Hiding
36 Adding MIDI Modules
36 Adding Insert Effects
36 Changing the Order of MIDI Modules and Insert
Effects
36 Adding Audio Busses
36 Customizing the Program Tree
38 Global Functions and Settings
39 Introduction
39 The Plug-in Functions Section
40 The Toolbar
41 The Keyboard Editor
42 The Options Editor
45 Quick Controls
48 AI-Knob Support
49 Common Editing Methods
50 Introduction
50 Using Controls in HALion
51 Using Key Commands
51 Working with Presets
52 Using Automation
53 Using Effects
54 Using MIDI Modules
55 Importing and Exporting Samples
56 Importing Samples
58 Finding Missing Samples
59 Exporting Samples
61 Replacing Samples
62 Importing Third-Party Sampler Programs
63 Importing Sliced Loops
66 Editing Programs and Layers in the
Sound Editor
67 Introduction
67 The Main Section
67 The Trigger Section
69 The Voice Management Section
71 The Variation Groups Section
72 The Quick Control Assignments Section
72 The Note Expression Section
5
Table of Contents
Page 6

74 Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
75 Introduction
75 Global Zone Settings
75 Editing Selected Zones or All Zones
75 Absolute and Relative Editing
75 HALion 3 compatibility
76 The Voice Control Section
78 The Pitch Section
78 The Oscillator Section
80 The Sample Oscillator Section
81 The Filter Section
84 The Amplifier Section
85 The Envelope Section
89 The LFO Section
91 The Step Modulator Section
92 The Modulation Matrix Section
97 Mapping Zones
98 Introduction
98 The Mapping Editor
101 Mapping Zones
102 Filling Gaps between Zones
102 Setting the Root Key
102 Selecting Zones with the Mapping Editor
Keyboard
122 Effects Reference
123 Introduction
123 Reverb and Delay Effects
126 EQ Effects
127 Distortion Effects
128 Modulation Effects
131 Dynamics Effects
134 Panner and Routing Effects
135 HALion 3 Legacy Effects
140 MIDI Modules Reference
141 Introduction
141 The FlexPhraser
144 The Trigger Pads
145 Mono Envelope
147 Mono LFO
148 MegaTrig
150 Layer Alternate
151 Key Switch Alternate
152 Key Switch Remote
153 MIDI Randomizer
154 True Pedaling
154 CC Mapper
155 Velocity Curve
156 Tuning Scale
103 Editing Samples in the Sample Editor
104 Introduction
104 Overview
105 The Parameter Section
105 General Operations
108 Creating Loops
112 MIDI Editing and Controllers
113 The MIDI Editor
114 Using MIDI Controllers
114 Assigning MIDI Controllers
114 Assigning MIDI Controllers to AUX FX
114 Saving a MIDI Controller Mapping as Default
115 Automation and Factory MIDI Controller
Assignments
115 CC 121 Support
116 Mixing and Routing
117 The Audio Bus Architecture
119 The HALion Mixer
Table of Contents
157 Key Commands Reference
158 The Default Key Commands
159 Using the HALion Standalone Version
160 Introduction
160 Making Preferences Settings
161 Selecting the MIDI Input and the Audio Output
161 The Scratch Pad
164 Index
6
Page 7

1
Installation and Setup
Page 8

Welcome
Key Command Conventions
Congratulations and thank you for purchasing Steinberg’s
HALion 4.
Ten years after the release of the first version of HALion,
Steinberg is very proud to present the fourth incarnation of
its acclaimed VST sampler. When the idea of HALion was
first formed over a decade ago, the approach was to de
velop a highly user-friendly, yet powerful software sampler
with an unparalleled feature set and a seamless integra
tion into modern DAWs.
Today, HALion 4 embodies the original philosophy better
than ever before. When comparing HALion 4 with its pre
decessors, you find many similarities, but the immense advancements throughout the application stand out a mile.
HALion 4 has undergone a massive overhaul and a shift to
an entirely new virtual instrument, Steinberg’s VST sam
pler and sound creation system.
For the first time in its history, HALion combines a premium sample engine with a virtual analog synthesizer and
in this way opens the door to new sonic spheres. The integrated mixing console, the studio-grade effects and the
flexible user interface are just some of the features that will
truly inspire your creativity. One of the key objectives dur
ing the development process was to further optimize the
workflow concept. When you get started with HALion 4,
you will soon discover the many useful details that help to
turn your vision into reality.
HALion 4 was designed according to the requirements of
professional sound designers and was relentlessly refined
during the engineering process, resulting in the ultimate
tool for discerning sound designers as well as finding the
appreciation of musicians, producers, and composers.
First of all, check out the massive sound library. With more
than 1,600 instruments and patches, HALion 4 includes the
complete sound collection of the appraised HALion Sonic
workstation alongside many fresh new sounds.
After you have registered HALion 4 online, take some time
to explore the community section at www.steinberg.net/
forum. You will find lots of useful information and get to
know other users in our discussion forums. Registering at
www.steinberg.net/mysteinberg also gives you access to
special offers from Steinberg in the future.
Have fun creating your sound. Your way.
The Steinberg HALion Team
-
-
Many of the default key commands in HALion use modifier
keys, some of which are different depending on the operating system. For example, the default key command for
Undo is [Ctrl]-[Z] under Windows and [Command]-[Z] un
der Mac OS X.
-
When key commands with modifier keys are described in
this manual, they are shown with the Windows modifier
key first:
[Win modifier key]/[Mac modifier key]-[key]
For example, [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Z] means “press [Ctrl]
under Windows or [Command] under Mac OS X, then
press [Z]”.
Similarly, [Alt]/[Option]-[X] means “press [Alt] under Win-
dows or [Option] under Mac OS X, then press [X]”.
Please note that this manual often refers to right-clicking,
for example, to open context menus. If you are using a Mac
with a single-button mouse, hold down [Ctrl] and click.
How You Can Reach Us
Clicking the Steinberg logo in the top right corner of
HALion opens a pop-up menu containing items for getting
additional information and help:
• This menu contains links to various Steinberg web
pages. Selecting a link automatically launches your
browser application and opens the page.
On the web pages, you can find support and compatibility information,
answers to frequently asked questions, links for downloading new driv
ers, etc. This requires that you have a browser application installed on
your computer and a working internet connection.
• When you choose the Help item, an online version of
the documentation opens.
• You also find a menu item for the registration of your
product.
For further information, see “Register Your Software!” on page 10.
-
-
Installation and Setup
8
Page 9

Installation
!
!
!
Please read the following section before installing
HALion.
The USB-eLicenser
Many Steinberg products, including HALion, use the
USB-eLicenser, a hardware copy protection device.
HALion will not run without an eLicenser containing an activated license.
The USB-eLicenser is a separate product and is not
included in the product package of HALion.
System Requirements
To use HALion, your computer must meet the following
requirements:
Windows
• Windows Vista or Windows 7
• Pentium/Athlon 2.0 GHz dual core CPU
•2 GB RAM
• Approx. 15 GB of free hard disk space
• Display resolution 1280 x 800 pixels recommended
• DirectX compatible audio hardware (ASIO compatible audio
hardware recommended for low-latency performance)
• DVD-ROM drive with dual-layer support
• USB port for USB-eLicenser (license management)
• USB-eLicenser (not included)
• Internet connection for license activation
• For using HALion as a plug-in, a VST2 or VST3 compatible
host is required.
The USB-eLicenser
The USB-eLicenser is a USB device on which your Steinberg software licenses are stored. All hardware-protected
Steinberg products use the same type of device, and you
can store more than one license on one device. Also, li
censes can (within certain limits) be transferred between
USB-eLicensers. This is helpful if you want to sell a piece
of software, for example.
The product package of HALion contains an activation
code, which is found on the Essential Product License In
formation card within the product package. To make unlimited use of your version of HALion, you must manually
download a license to an USB-eLicenser connected to
your computer, and activate your permanent license using
the activation code.
In the eLicenser Control Center you can activate new
licenses and check which licenses are installed on your
USB-eLicenser.
Control Center
After installation of HALion, the eLicenser
can be opened via the Start menu on Win-
dows systems or the Applications folder on a Mac.
Ö If you are using other copy-protected Steinberg products, you may want to transfer all licenses for your applications to one USB-eLicenser, thus using up only one USB
port of your computer. Please refer to the eLicenser Control Center Help for information on how to transfer licenses
between USB-eLicensers.
Macintosh
•Mac OS X 10.6
•Intel Core Duo 2.0 GHz processor
•2 GB RAM
• Approx. 15 GB of free hard disk space
• Display resolution 1280 x 800 pixels recommended
• CoreAudio compatible audio hardware
• DVD-ROM drive with dual-layer support
• USB port for USB-eLicenser (license management)
• USB-eLicenser (not included)
• Internet connection for license activation
-
• For using HALion as a plug-in, a VST3 or AU compatible host
is required.
Installing HALion
HALion provides a large amount of content and is distributed on a set of two DVDs. Please have all DVDs ready
for the installation
The HALion installer allows you to save the content
files on a different hard drive than the program files.
.
Installation and Setup
9
Page 10

Proceed as follows:
1. Insert the first DVD into your DVD drive.
An interactive Start Center appears. If it is does not open automatically
or if you have a Macintosh computer, you can manually open it by dou
ble-clicking the file “HALion_Start_Center.exe” (Windows) or “HALion
”
Start Center.app
(Mac).
-
2. Follow the instructions on screen to start the installation of HALion and browse through the additional options
and information presented.
If you do not want to install HALion via the interactive Start
Center, follow the instructions below:
Windows
1. Double-click the file called “Setup.exe”.
2. Follow the instructions on screen.
Macintosh
1. Double-click the file called “HALion.mpkg”.
2. Follow the instructions on screen.
Register Your Software!
We encourage you to register your software! By doing so
you are entitled to technical support and kept aware of up
dates and other news regarding HALion.
• To register HALion, click the Steinberg logo in the top
right corner of the control panel and select “Register
HALion now!” from the pop-up menu.
This option opens the registration page of the Steinberg web site in your
web browser. To register, follow the instructions on screen.
Setting Up
The following sections describe how to use HALion as a
plug-in in different host applications. HALion can also be
used as a standalone application. This is described in de
tail in the chapter “Using the HALion Standalone Version”
on page 159.
Setting Up HALion as a VST Instrument in
Cubase
We assume that you have correctly set up Cubase as well
as your MIDI and audio hardware, and that Cubase receives MIDI data from your external MIDI keyboard. If you
want to use HALion in another VST host application,
please refer to the documentation of the corresponding
application.
Cubase provides two ways of working with VST instruments: the VST Instruments window and instrument
tracks.
Accessing HALion via the VST Instruments Window
Proceed as follows:
1. Open the Devices menu in Cubase and select the
VST Instruments option.
The VST Instruments window opens.
2. Click one of the empty slots to open the instrument
pop-up menu, and select HALion.
You are asked whether you want to create an associated MIDI track connected to the VST instrument.
3. Click Create.
HALion is loaded and activated, and its control panel
opens. A MIDI track called HALion is added to the track
list. The output of this track is routed to HALion.
Accessing HALion via an Instrument Track
Proceed as follows:
1. On the Project menu, open the Add Track submenu,
and select “Instrument”.
The Add Instrument Track dialog opens.
2. On the instrument pop-up menu, select HALion.
3. Click OK to create the instrument track.
-
4. Click the Edit Instrument button in the Cubase Inspector to open the HALion control panel.
HALion is now set up as a VST instrument in Cubase. For
more details about the handling of VST instruments, see
the Cubase Operation Manual.
10
Installation and Setup
Page 11

Selecting Outputs
HALion loads with a stereo output configuration by de-
fault. However, you can use up to 32 stereo outputs plus
one 5.1 output in Cubase. This allows you to route all 64
program slots to a dedicated Cubase Mixer channel.
To make these outputs available, proceed as follows:
1. Open the VST Instruments window.
2. Click the output button for the HALion instrument.
3. Activate the required outputs.
Cubase automatically creates a MIDI track for each additional output and adds a channel to its Mixer. You can now
route HALion programs or layers to these outputs for fur
ther signal processing within Cubase.
Using HALion in an AU Compatible
Application
You can use HALion in an AU host application (e. g.
Logic). The AU version of HALion is installed in your AU
plug-ins folder and lets HALion work in an AU environment without any performance loss or incompatibilities.
For Logic Pro, proceed as follows:
1. Open the Track Mixer and select the instrument channel that you want to use.
2. Click in the I/O field, and select the AU Instruments
submenu.
3. On the Steinberg submenu, select HALion.
4. Select Multi Output or Stereo from the submenu.
HALion is now loaded as an AU instrument.
-
11
Installation and Setup
Page 12

2
The HALion Control Panel
Page 13

Introduction
A view with a
single editor.
A view with
multiple editors
on different tabs.
HALion provides flexible and highly customizable window management. You can arrange the available editors in the window, structure the window sections using tabs, and even configure several separate windows for your work. The size of
each window, and window section, is freely adjustable. This allows you to make the most of the available screen space.
Configuring the Control Panel
You can set up the control panel exactly the way you want
it, by determining the number of different sections (which
are referred to as “views” in this document) that you want
the window to contain, and by further configuring these
sections, for example by adding tabs. For each of these el
ements (views or tabs), you can specify the editor that is
displayed.
All these functions can be performed via the setup options. For views, these can be accessed via the View popup menu. For tabs, they are available on the context menu.
The following setup options are available:
Select… (Editor)
To select the editor to be displayed, open the Editor submenu, and select the editor or choose “Select…” to display a pane showing icons for the available editors and
click on an icon.
“Split |” and “Split --”
You can add a view or tab to the window by splitting an
existing view or tab.
• To perform a vertical split, select “Split |”. This adds a
new editor to the right of the current editor.
• To perform a horizontal split, select “Split --”. This adds
an editor below the current editor.
The HALion Control Panel
13
Page 14

• You can also create a split view or tab by clicking its upper left corner and dragging it to another position in the
window.
This creates a copy of the view or tab at the drop position. A colored
frame indicates where it will be inserted when you drop it.
Adjusting the Size of a Split View
• To adjust the size of two split views, point the mouse at
the divider between these two, click, and drag.
If a view is split into three or more parts, these parts are resized proportionally. To resize an individual part, hold down [Ctrl]/[Command] and drag.
Ö Some editors have fixed default sizes for height or
width. For example, the Slot Rack can only be resized ver
tically but not horizontally.
Create Tab
• Select “Create Tab” to create a tab.
You can also create tabs within tabs.
You can also create tabs the following way:
• Click in the upper left corner of an existing view or tab
and drag it onto another one.
• Click the plus icon to the right of the rightmost tab and
click the icon for the editor you want to display.
Ö If a view contains more tabs than can be displayed, arrow buttons are displayed to navigate between the tabs.
Renaming Tabs
When you create a tab, it gets the name of the editor it
displays. You can rename tabs via the context menu.
Close
• To remove a view or a tab, select Close.
Further Setup Options
Moving Views and Tabs
• To move a view or tab, hold down [Shift], click in its upper left corner, and drag it to another position.
Depending on the drop position, it is added as a tab or as part of a split
view.
Expanding and Resizing Editor Sections
Some editors, such as the Options editor, contain expandable sections. These sections can be resized or collapsed so that they only show their title bar. This helps you
save space and focus on the edited parameters.
-
• To expand or collapse a section, click the “+” or “-” icon
on the left of the title bar, or click the title bar.
• To open several sections at the same time, hold down
[Ctrl]/[Command] and click the “+” icon or the title bar.
• To resize a section, click in the middle of its lower border (the position is indicated by a dotted line) and drag up
or down.
Undock
• To create a duplicate of the view or tab in a new window, select Undock.
The HALion Control Panel
Setting the Focus
It is useful to know which view, window, or tab has the focus, because this is where your key commands are applied, for example. The view that has the focus is indicated
by a blue frame.
• To set the focus on a specific view, use one of its controls or edit a parameter.
You can also click on the frame of a view or in an empty background of a
section.
14
Page 15

Working with Multiple Windows
Screen Sets
Creating Additional Windows
You can create new windows from existing views using
the following methods:
• Click in the upper left corner of an existing view or tab
and drag it out of the current window.
• Use the Undock command, see “Undock” on page 14.
The window menu bar contains a pop-up menu from
which you can select the program that you want to edit.
Using Window Presets
HALion comes with several preconfigured window presets. You can open these by clicking the “Open New Window” button in the top bar and selecting a preset from the
pop-up menu. You can also create your own window pre
sets using the corresponding commands on the pop-up
menu.
Locking Windows
When you open an additional window, HALion shows the
settings belonging to the focused object (program, layer,
zone etc.). This way, all editors and separate windows relate to the same material.
However, in some cases it might be necessary to show
different objects in different windows, for example, to
compare the parameter sets of two zones or layers. This
can be achieved by locking a window.
• To lock a window, click the lock button in the upper
right corner. If this is activated, the window no longer fol
lows selection and focus changes in the main plug-in window. Instead, it displays the settings of the program that
was selected when you clicked the lock button.
When you have set up the HALion control panel to your
liking, you can save this configuration as a “screen set”.
This way, you can preconfigure HALion for different workflows and editing situations.
When you start HALion for the first time, the default
screen set is used, which is optimized for wide-screen
monitors and contains all editors.
The following factory screen sets are available:
Screen Set Recommended
Default 1440 x 900 Full editor screen set.
Basic 1024x768 A minimized single slot player view.
Extended1 1280x800 Optimized for laptops.
Extended2 1440 x 900 As Extended 1, but slightly more
-
Advanced 1440 x 900 Full editor screen set.
Resolution
Description
complex.
Managing Screen Sets
You can load, save, and delete screen sets by clicking the
screen set button on the toolbar in the plug-in functions
section and selecting the corresponding command from
the pop-up menu.
Ö Factory screen sets cannot be deleted.
-
The HALion Control Panel
15
Page 16

Overview of the Available Editors
HALion provides a large amount of different editors that
give you access to the parameters of the plug-in and its
programs and modules.
The following editors are available:
Slot Rack
Allows you to load and manage the loaded programs, see
“The Slot Rack” on page 19.
MIDI
Allows you to configure the ranges and MIDI parameters
of the slots, see
Program Table
Shows all programs that are loaded. This includes the
programs that are used in the Slot Rack as well as those
that can be loaded via MIDI program change, see “Load-
ing and Managing Programs” on page 27.
Program Tree
Allows you to create programs by combining samples, layers, busses, as well as MIDI and audio effects, see “Using
the Program Tree” on page 30.
“The MIDI Editor” on page 113.
Sound Editor
Gives you access to the parameters of the various program components. It can display the parameters of programs, layers, zones, MIDI modules, busses, and effects.
Which parameters are displayed depends on the object
that is selected in the Program Tree.
Zone Editor
The Zone editor allows you to edit the parameters of all
zones of the focused layer simultaneously (including any
sublayers).
In case any specific zones are selected in the Program
Tree or Mapping editor, only these zones can be modified.
MIDI Modules Editor
The MIDI Modules editor allows you to edit the parameters
of all MIDI modules of the currently focused layer.
In case any specific MIDI modules are selected in the Program Tree or Mapping editor, only these modules are displayed and available for modification.
Optionally, you can show any MIDI modules found higher
up in the signal flow by clicking the corresponding button.
Macro
This is a content-specific editor that provides a set of the
most important program parameters. Whether such an
editor is available for a program, depends on the content
set, see
“Macro Pages” on page 17.
Mapping Editor
Allows you to specify and visualize how samples are distributed over the keyboard and velocity range, see “The
Mapping Editor” on page 98.
Sample Editor
Allows you to define all sample and loop parameters, see
“Editing Samples in the Sample Editor” on page 103.
Mixer
Allows you to mix the program slots, access the output
and AUX busses, and manage effects, see “Mixing and
Routing” on page 116.
The HALion Control Panel
16
Page 17

Import
Allows you to import external sampler formats like Apple
EXS, GigaSampler, Kontakt, and others, see “Importing
and Exporting Samples” on page 55.
MediaBay
Allows you to load programs and layers, see “Managing
Files via the MediaBay” on page 22.
Options
Contains global plug-in settings regarding the overall performance, global edit functions, and MIDI controllers, see
“The Options Editor” on page 42.
Undo History
The Undo History lists all of your actions and allows you to
undo changes, see
“Undo/Redo” on page 41.
Keyboard
Combines a keyboard, two wheels, and the HALion
Sphere. You can use these controls to simulate external
hardware, see
“The Keyboard Editor” on page 41.
Quick Controls
Allows you to remote-control any parameter inside the
program, see “Quick Controls” on page 45.
Macro Pages
VST Sound Instrument Sets provide dedicated editors,
so-called Macro pages. These Macro pages are preconfigured to show the most important parameters for the
specific programs.
Whether it is possible to edit a program only via its Macro
page or whether you have access to all underlying zone
and layer parameters depends on the instrument set.
If a program comes with a Macro page, it is displayed
when you open the Macro editor.
When loading a program that contains one or multiple layers with Macro pages, all Macro pages are shown together in the Macro editor. For each existing Macro page,
HALion inserts a navigation button on the toolbar that al
lows you to switch between the different Macro pages.
-
Trigger Pads
Allow you to assign and trigger notes and chords. Furthermore it is possible to use the trigger pads to switch the
states of FlexPhraser modules, see
page 144.
“The Trigger Pads” on
The HALion Control Panel
17
Page 18

3
Managing Your Sounds
Page 19
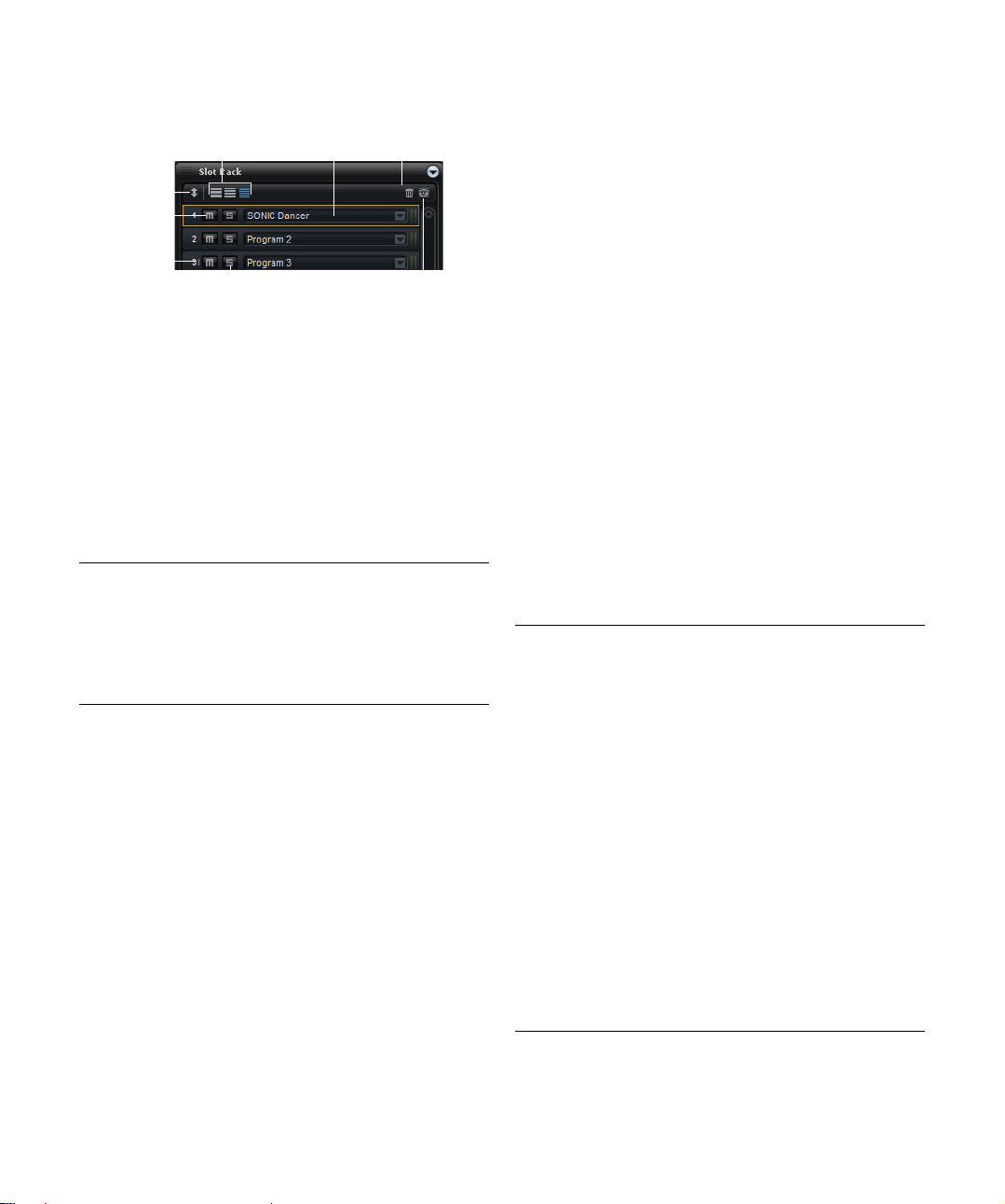
The Slot Rack
Program Loader
Mute Slot
Solo Slot
MIDI Activity
Indicator
Sort Slots
Remove All Programs
Show Empty Slots
Slot Sizes
The Slot Rack allows you to load up to 64 programs into
so-called slots. Slots are created dynamically for each
loaded program. Their order can be arranged freely,
sorted by MIDI channel, or slot index.
Use the scrollbar to the right of the slots to navigate to the
slot that you want to make settings for.
Changing the Slot Size
You can change the size of the slots that are displayed using the sizing buttons above the slots. The following options are available:
Size Features
Small Shows MIDI Indicator, Mute, Solo, Program Loader
Medium Shows MIDI Indicator, Mute, Solo, Program Loader, MIDI
Large Shows Instrument Icon, Mute, Solo, Program Loader, MIDI
Showing Empty Slots
By default the Slot Rack only shows slots that are currently filled with programs.
• To show all empty slots, activate the “Show Empty
Slots” option on the toolbar.
Loading Programs
Programs and layers can be dragged from the following
locations into the Slot Rack:
• HALion or Cubase MediaBay
• Program Table or Program Tree
•Import View
• Explorer (Win) or Finder (Mac)
Port/Channel, Level, Pan, Level Meter
Indicator, MIDI Port/Channel, Polyphony, Level, Pan, Output,
Level Meter
Replacing Programs
You can replace the program in a slot by dragging another
program or layer onto this slot.
Alternatively you can use the “Load Program” button at the
right of the slot to load a new program.
Loading Programs in between Slots
• If you want to add a program or layer in a new slot between two existing slots, you can drag it between these
slots.
A red line indicates that a slot will be inserted at this position.
Ö The slot number is taken from the first available slot
and does not necessarily reflect the order in which the
slots are listed.
Loading Layers into Slots
If you load a layer into a slot, HALion creates a new program.
Managing Programs via the Slot Context
Menu
The slot context menu provides additional functions for
managing programs. The following options are available:
Option Description
Load Programs This option opens the “Load Program” dialog. Select
Save Program This option saves the program. Please note that fac-
Save Program
As…
Remove Program Select this option to remove the program from the
Revert to Last
Saved Program
Cut Program Select this option to copy and remove the program
Copy Program Select this option to copy the program without re-
Paste Program Select this option to paste the copied program into
Rename Program Select this option to enter a new name.
a program or layer and click OK to load it into the slot.
tory content cannot be overwritten. Instead, the “Save
Program” dialog is opened and you can save the ed
ited program under a new name.
This option opens the “Save Program” dialog where
you can save the edited program under a new name.
slot.
Select this option to discard any changes made to
the program in the slot.
from the slot.
moving it.
the slot. If the slot already contains a program, it is re
placed.
-
-
Managing Your Sounds
19
Page 20

Option Description
Reset Selected
Slot
Reset All Slots Select this option to reset all slots to the default
Select this option to reset the selected slot to the default values.
values.
Loading Samples and Third-Party Programs
Samples and third-party programs can be loaded into the
Slot Rack from a file browser or the Import editor using
drag and drop.
Renaming Programs
You can rename a program via the context menu.
Ö To make the program with its new name available in
the MediaBay, you must save it.
Sorting Modes
By default, slots are arranged freely. New slots are set to
the next available index number.
• To change the sorting mode, click the Sort Slots button
on the left side of the Slot Rack toolbar, and choose a
mode:
Mode Description
Custom Sorting Default mode.
Sort Slots by MIDI
Port and Channel
Sort Slots by Index Slots are sorted by their index-number. No reor-
Slots are sorted by their MIDI channels. No reordering is possible. New slots are set to MIDI channel A1.
dering is possible. New slots are set to the next
available index-number.
Slot Controls
Depending on the selected slot display size you get access to additional slot controls.
Level
The level fader controls the output level of a program. The
parameter has an influence on all outputs used by layers
and zones inside the program.
Pan
Pan controls the stereo position of a program. The parameter has an influence on all outputs used by layers and
zones inside the program.
Ö The Pan control is disabled if the slot bus has a surround configuration.
Solo
Activate the Solo button of a slot in order to hear only the
corresponding program. Several slots can be soloed at
the same time.
Mute
Activate the Mute button to turn off playback of the program.
MIDI Port and Channel
Here you can specify on which MIDI port and channel the
slot receives MIDI messages.
MIDI Activity Indicator
A green bar next to the slot number and symbol indicates
incoming MIDI data.
Polyphony
Here, you can specify how many notes can be triggered
simultaneously.
Ö The number of resulting voices can be much higher if
one note triggers several zones at the same time.
Output
The output selector lets you define to which output bus
the slot sends its signal.
Ö This setting does not affect any output routing that has
been set up for individual layers or zones inside the pro
-
gram.
Level Meter
The level meter indicates the signal level of the slot output
bus.
Ö Layers and zones inside the program that are routed to
individual outputs do not show any meter activity.
The Relationship between Slot and Program
Table
The Program Table provides a list of all programs that are
loaded into slots as well as programs that are not yet
loaded but can be addressed by a program change.
Managing Your Sounds
20
Page 21

Save MultiProgram
Remove Multi-Program
Load Multi-
Program
Save VST Sound
Content
Save Multi-Progr am
with Sample
When a program is loaded into a slot, it is also inserted in
a free place in the Program Table.
When replacing a program in a slot, the table updates accordingly. If multiple slots have used the same program, all
slots are updated with the new program.
Managing Multis
Multis can load multiple sounds or programs and combine
them. You can use multis, for example, to layer several
programs or to create split sounds by setting several pro
grams to the same MIDI input channel. However, the most
common usage is to create sound sets with different in
struments set to individual MIDI channels.
A multi-program contains all plug-in parameters. When
using HALion as a plug-in in Cubase or Nuendo, these
multis are listed in the Preset Management pop-up menu
of the host application. You can drag multis and programs
from the Cubase or Nuendo MediaBay to a slot in HALion.
When using HALion as a plug-in in a different host application, you can use either the preset functionality from the
host application, or the multi management features provided by HALion.
Loading Multis
• Open the MediaBay and double-click a multi, or drag
and drop a multi onto the multi slot.
• Alternatively, click the “Load Multi-Program” button in
the multi slot to open the “Load Multi-Program” dialog, se
lect a multi and click on OK.
Removing Multis
• To remove all programs of the current multi, click the
“Remove All Programs” button on the toolbar of the Slot
Rack.
This also resets all slot parameters and removes effects from the slot
busses. However, AUX and Master effects are not removed.
-
Managing Your Sounds
Ö Removing the programs from the slots does not remove them from the Program Table.
Saving Multis
-
To save multis, proceed as follows:
1. Click the “Save Multi-Program” button.
2. Enter the name of the multi.
3. Assign any attributes you require and click OK.
If the entered name already exists, the “Make Unique Name” option adds
a number suffix to the name of the new multi.
Creating Subfolders for User-Defined Multis
You can create subfolders inside the user preset folder to
organize presets.
• To create a new folder, click the “Create New Folder”
icon at the top left of the “Save Multi-Program” dialog.
Navigating Through the Folder Hierarchy
You can move through the folder hierarchy using the three
-
navigation buttons at the top left of the dialog.
They allow you to navigate to the previous or next browse
location, or browse the containing folder.
Editing Attributes
In the “New Preset Tags” section on the right of the “Save
Multi-Program” dialog you can edit the attribute values
that are assigned to the preset.
21
Page 22

1. To edit an attribute, click on a value field, and enter the
new name or value.
2. Click OK to save the preset.
Ö For further information about attributes, see “Editing
Preset Attributes” on page 24.
Exporting Multis with Samples
Multis with samples can be exported, to transfer a complete multi to another computer. Programs that use samples from VST Sound containers cannot be exported.
To export a multi with samples, proceed as follows:
1. Click the “Export Multi as VST3 Preset with Samples”
button next to the multi slot.
2. Enter the name of the multi, and click OK.
The multi is written to the specified location. Additionally a folder named
after the preset that contains all samples is created.
Managing Files via the MediaBay
The MediaBay gives access to the HALion presets, such
as multis, programs, and layers.
Exporting VST Sound Files
You can produce your own HALion VST Sound files, containing all plug-in settings, programs, and samples.
1. Click the “Export Multi as VST Sound” button next to
the multi slot.
2. Enter the required information (marked with an asterisk) and provide additional data (optional).
3. Enter the path or click the browse button to specify a
file name and folder.
4. Click OK.
Ö You cannot include samples that originate from pro-
tected VST Sound files.
The MediaBay is divided into two sections. In the top section you can define which kind of sounds you want to look
for. The lower section presents the corresponding results
list. You can drag the divider at the top of the results list to
adjust the size of the two sections.
Loading Programs into Slots
To load a program into one of the slots of the Slot Rack,
you have the following possibilities:
• Select the slot into which you want to load the program
and double-click the program in the results list.
• Drag a program from the results list to an empty space
in the Slot Rack to create a new slot. If you drag it to an
existing slot, the current program is replaced.
• Right-click the program and select “Load Program into
selected Slot” from the context menu.
Importing Presets
You can import existing program presets from any file location using the Explorer (Win) or Finder (Mac). To import
presets, proceed as follows:
1. Select the preset in the Explorer/Finder.
2. Drag it to the MediaBay.
The imported presets are copied to your user folder.
Managing Your Sounds
22
Page 23

Deleting Presets
Multi Program
Layer
• To delete a user preset, right-click it to open the context
menu, and select Delete.
Ö Factory presets cannot be deleted.
Applying Filters
Category Filter
You can filter the results list based on up to four filter criteria using the configurable attribute columns.
Standard attributes are Category, Sub Category, Style,
and Character. By clicking on specific values in the col
umns, you define the filter. Only the files that match the
selected values are displayed in the results list. Select
more values from other columns to refine the filter.
• To select different filter criteria, click the column header,
and select a different attribute from the submenu.
Instrument Set Filter
Use the “Instrument Set Filter” pop-up menu to search a
certain content set only. By default, the search is performed in any of the installed content sets.
-
Columns
The columns of the results list show all the attribute values
for the presets that match the filters that you set up in the
top section.
You can reorder the columns in the results list by dragging
the table headers to another position. Furthermore, you
can use the column headers to change the sorting of the
list entries. The triangle in the column header shows the
sorting direction.
Setting Up the Result Columns
You can select which attribute columns are displayed, by
clicking the “Set up Result Columns” button on the tool
bar of the results list. The attributes that you choose are
added at the right of the list.
Rating Filter
You can limit the results list to presets that have a certain
rating. The rating slider allows you to define the minimum
rating.
Text Search
Using the Results List
The results list shows all files that have been found according to the category filter.
View Filters
The toolbar of the results list has three filter buttons to define which preset types are displayed. Presets can be multis, programs, and layers. To show a preset, activate the
corresponding icon. In the results list, the corresponding
icon is shown to the left of the preset name.
In the text search field on the results list toolbar you can
enter text contained in the name or any of the attributes of
a preset that you are looking for. The results list updates
immediately and the Category search section above
shows all categories that contain presets matching the
text search.
Resetting the Result Filter
• To reset the text-based result filter, click the Reset button to the left of the search field.
23
Managing Your Sounds
Page 24

Content Filter
!
The content filter buttons allow you to define whether you
want to see all presets, only the factory presets, or only
your user presets.
The Results Counter
The number of presets that match the filter criteria is displayed at the far right of the results list toolbar.
Using the Context Menu of the Results List
The context menu of the results list offers additional options for managing the selected presets. The following options are available for factory and user presets:
Options Description
Load Program into
selected Slots/
Load Multi-Program
Select All This selects all presets in the results list.
Select None This cancels any selection.
This loads the highlighted preset.
The following options are available for user presets only:
Options Description
Copy This copies the selected presets to the clipboard.
Rename This opens a dialog for renaming the highlighted
Delete This moves the selected presets to the trash bin of
Show in Explorer/
Reveal in Finder
Set or remove Write
Protection
This way, you can paste them at a different loca
tion using the file browser of your OS.
preset.
your operating system.
This shows the preset in the file browser of your
operating system.
This sets or removes the write protection for the
selected presets.
Programs from the HALion factory content are writeprotected and cannot be deleted or renamed.
Editing Preset Attributes
Each preset can be described using a predefined set of
attributes. These attributes can be set directly in the results list or in the section “New Preset Attributes” of the
Save dialog.
1. Click in the field of the attribute value that you want to
set.
Depending on the attribute, a menu or a dialog opens.
2. Select a value.
Ö Attribute values are written directly into the corre-
sponding preset files. However, this is not possible for
write protected factory content. In this case, the data is
saved within HALion’s MediaBay database.
Attributes
Attribute values can be set directly in the results list or the
Save dialog. The following table shows how to edit the
various attribute values:
-
Attribute
type
Media
Musical
Attribute Editing method
Name Display only.
Rating Drag to set the rating.
Comment Click to select, double-click to
edit.
Content Summary Click to select, double-click to
edit.
Write Protection Display only, use context menu to
set protection.
Library Name Click to select, double-click to
edit.
Library Manufacturer Click to select, double-click to
edit.
Author Click to select, double-click to
edit.
Category Click to select.
Sub Category Click to select.
Style Click to select.
Sub Style Click to select.
Character Click to open an editor dialog.
Tempo Click to select, double-click to
edit.
Managing Your Sounds
24
Page 25

Bars & Beats Click to select, double-click to
Signature Click to select, double-click to
Key Click to select.
GM Sound Click to select.
edit.
edit.
Loading HALion 3 Programs
HALion 4 allows to load HALion 3 presets either from
HSB container files or from FXP/FXB files. To be able to
load presets from HALion 3 HSB files, they have to be
registered in the HALion 4 MediaBay.
Setting the Character Values
Character attribute values can be set via a dedicated editor. This editor provides a list of values that describe the
character of a sound.
Content Files and Folder Structure
HALion has a large amount of ready-to-use sound content, made up of hundreds of multis, programs, and layers.
This content is write-protected. You can edit files while
they are loaded in HALion, but you cannot overwrite the
factory content files themselves.
To save edits to the factory content, save the files under a
new name. These files have the name extension “.vstpreset” and are referred to as “user content”. They can be
searched and categorized in the same way as factory
content.
User content is saved in a predefined folder structure on
your hard disk. You can create subfolders within this struc
ture, to facilitate moving or exchanging content (see “Cre-
ating Subfolders for User-Defined Multis” on page 21).
Registering HSB Files
1. Click the Import button on the right of the Category
Filter toolbar, and select “Register HSB/VST Sound
Files”.
2. Navigate to the HSB/VST files, select them, and click
OK.
The MediaBay now has access to the presets.
• Alternatively, HSB/VST files can be registered by dragging them from the Windows Explorer or Mac OS Finder
into the HALion MediaBay.
Registering VST Sound Files
Programs that are contained in VST Sound files can only
be seen and accessed by the MediaBay if the corresponding VST Sound file has been registered. HALion’s
factory content is located in a directory that is automatically scanned when HALion is loaded. However, it is possible to add further VST Sound files that are not located in
that directory.
To register a VST Sound File, proceed as follows:
1. Click the Import button on the right of the Category filter toolbar.
2. Select “Register HSB/VST Sound Files“.
3. Navigate to the VST Sound file, select it, and click OK.
The MediaBay now has access to the presets.
-
Loading FXP/FXB Files
To load FXP/FXB files there are two possibilities:
• Drag and drop the FXP/FXB files from the Windows Explorer or the Mac OS Finder onto the Slot Rack.
• Drag and drop the FXP/FXB files to the Slot Rack/Multi
Loader.
HALion converts the FXP/FXB files into HALion programs/multi-programs.
Managing Your Sounds
25
Page 26

Importing FXP/FXB Files
To import multiple FXP/FXB files without loading them in
HALion, proceed as follows:
1. Click the Import button to the right of the Category Filter and select “Import HALion FXP/FXB Files”.
2. Navigate to the folder that contains the FXP/FXB file.
3. Select the file you want to import and click OK.
The presets are converted into the HALion 4 format and saved as VST
presets in the user preset folder.
Ö Alternatively, import multiple FXP/FXB files by dragging them from the Windows Explorer or Mac OS Finder
into the MediaBay.
Working with General MIDI Files
HALion can play back files in the General MIDI format. For
this, the following preparations must be made:
1. Load a GM multi from the MediaBay.
The first 16 slots are prepared with send effects for Chorus and Reverb.
2. Open the Options editor, navigate to MIDI Controller,
and activate “Receive Program Changes” and “Receive
RPNs 0/1/2”.
3. Load the GM file that you want to use.
HALion loads the necessary programs and adjusts chorus and reverb
levels.
Managing Your Sounds
26
Page 27

4
Loading and Managing Programs
Page 28

Introduction
HALion allows you to load a virtually unlimited number of
programs per instance. All loaded programs, i. e. programs
that can be used in the current project, are shown in the
Program Table. You can load these programs into any of
the 64 slots in the Slot Rack.
The first 128 entries of the Program Table correspond to
the 128 MIDI program change numbers. You can load
these programs into a slot by sending MIDI program
change messages on the slot’s MIDI channel.
Ö You can set the focus on any of the programs, for example to verify settings or to copy zones from there, without having it assigned to any slot. In that case you cannot
play and hear the program.
The Columns of the Program Table
The Program Table contains the following columns:
Column Description
Program Number Displays the program number, which corre-
Program Name Shows the program name. The name can be ed-
Used Displays the number of slots in which the pro-
Preload Shows if a program is preloaded, even if it is not
File Size Displays the size of the program with all samples
sponds to the MIDI program change number.
ited in place.
gram is loaded.
being used in a slot.
as it is stored on the hard disk.
Changing the Width of a Column
• Drag the right border of the column header left or right
to change its width.
Ö All modifications are stored with the project.
Loading Programs into the Program Table
There are several ways to load a program into the Program
Table:
• Drag it from the MediaBay to the Program Table.
• In the MediaBay, right-click a program to open the con-
text menu, and select “Load Program into selected Slot”.
• Click the “Load Program” button in the Program Table
toolbar, select a program, and click OK.
If the selected entry in the Program Table already contains
a program, the current program is replaced. All slots that
are making use of that program then refer to the new pro
gram.
When multiple programs are dropped on a list entry, not
only the target program is replaced but also the following
programs. The number of programs that are replaced corresponds to the number of programs that you have
dragged to the Program Table.
Ö You can also drag and drop programs from third-party
sampler formats using the Import Tree, see “Importing
Third-Party Sampler Programs” on page 62.
-
Configuring Columns
Inserting Columns
• Right-click the column header at the position where you
want to insert the new column, and select the parameter
or column that you want to insert.
Removing Columns
• Right-click the header of the column you want to remove, and select “Remove…”.
Reordering Columns
• Drag and drop the header of the column left or right to
the new position.
Loading and Managing Programs
28
Page 29

Loading Programs from the Program Table to the Slot Rack
When dropping a program onto a free Program Table entry, it is added to the table without being actually loaded to
any of the slots. This way you can create a program table
without having to load all programs immediately.
If you want to use the program in a slot, you can create a
new slot or replace the program in an existing slot.
In case a program is loaded multiple times to different
slots the slot rack focus jumps to the first slot.
Creating New Slots
• Make sure that no slot is selected and double-click the
program.
• Drag a program to an empty space in the Slot Rack.
Replacing Programs in Slots
• Double-click a program to replace the program in the
selected slot.
• Drag a program from the table into an existing slot.
To quickly see which programs are assigned to slots their
program numbers are displayed in yellow.
Preloading Programs
When a program was loaded to the Program Table but is
not used by one of the slots, its samples are not preloaded. However, you can preload unassigned programs
to allow for a faster MIDI program change. You can activate the Preload option individually for each program. This
setting is saved with the project and plug-in preset. Pro
ceed as follows:
• Open the context menu for a program and select “Always Preload”.
• Activate the Preload icon of the program in the Preload
column.
• To deactivate preloading, select “Preload Program On
Demand” on the context menu, or deactivate the icon in
the Preload column.
-
Editing the Program Table
Deleting Programs
You can delete the selected program by clicking the trash
icon on the toolbar. Alternatively, you can press the [De
lete]-key on your computer keyboard or use the Delete
command on the context menu.
Exchanging the List Positions of Two
Programs
Once a program has been loaded to a specific table entry,
it is also associated with the corresponding MIDI program
change number.
For example, loading a program at position 3 of the list
means that this program can be loaded into a slot when it
receives MIDI program change number 3 on its MIDI
channel.
If you want to quickly assign the program to another MIDI
program change number, you can drag it to the corresponding list position. In case another program already
occupies this position, the two programs change places.
Cut, Copy, and Paste
Cut, copy, and paste programs by clicking the corresponding icons on the Program Table toolbar, using the
commands on the context menu, or using key commands.
Renaming Programs
• Select the program you want to rename and click the
program name a second time, or press [F2] (Win)/[Return]
(Mac).
• Right-click the program and select Rename on the context menu.
-
Loading and Managing Programs
29
Page 30

5
Using the Program Tree
Page 31

Introduction
The main area for navigating and making selections in
HALion is the Program Tree. It shows the selected program with all its layers, zones, and modules. Furthermore,
it allows you to load programs and layers, to add, import,
or delete zones, etc.
Zones
A zone is the element on the lowest level in the tree structure. The zones are the elements creating the sounds in
HALion.
You can choose between synth and sample zones. These
zone types differ in their basic sound source. While a
synth zone provides an oscillator section with three main
oscillators, a sub oscillator, a noise generator, and a ring
modulation stage, the sample zone loads a specific sam
ple instead.
Busses
Busses allow you to set up the audio routing in HALion
and add audio effects.
MIDI Modules
MIDI Modules can be added for programs and layers, see
“Adding MIDI Modules” on page 36.
-
The first three columns in the Program Tree give you access to the Visibility, Mute, and Solo functions inside the
program. In the section to the right, the selected program
and its elements are displayed. They are organized in a hierarchical structure, with the program at the topmost level.
Each element in the Program Tree is displayed with an
icon in front of its name, indicating the type of the element.
Programs and Layers
Programs are the top-level elements in the Program Tree.
Only one program is displayed at a time.
A HALion program is a complex instrument or sound that
combines layers, sample zones, synth zones, busses, MIDI
modules, and FX modules. Often, a program contains a
single layer that already comes with all necessary compo
nents such as the synthesis part or insert effects. This is
because a layer already is a complete sound structure on
its own. Layers can be used to organize programs, for example by grouping a number of zones. This is useful if you
want to apply the same settings to a number of zones in
one go. The program adds the possibility of combining different layers to build up more complex sounds or to create
combinations of sounds you want to load as a unit. A typical example is a bass/piano split sound or a piano/string
layer sound.
Audio Effects
Audio effects can be added for busses. For a detailed description of the available audio effects, see the chapter
“Effects Reference” on page 122.
The Program Tree Structure
The Program Tree represents the signal flow inside the
program from top to bottom:
The MIDI comes in at the top and goes down through the
layers and MIDI modules. The processing order of the MIDI
modules inside the program or layers is from top to bottom.
The audio is output via busses that can have any number
of FX modules. The processing order of the FX modules
-
inside the busses is also from top to bottom.
Number of Selected Zones
Below the Program Tree, there are three numbers that indicate the following:
• The first number indicates the number of selected
zones.
• The second number indicates the number of zones contained in the focused layer.
Using the Program Tree
31
Page 32

• The third number indicates the total number of zones in
the program.
The three numbers are particularly useful while editing or
deleting zones. For example, if you have a piano that was
recorded with several velocity layers per note, you will know
that each velocity layer has 88 sample zones. Let’s say, you
want to edit or delete a whole velocity layer. With a look at
the three numbers you will know if you selected the right
amount of sample zones before you edit or delete them.
The Color Scheme
To indicate additional information, the icons of the program, layers, and zones change their color.
Icon Color Description
Light blue This is the standard color for zones. For sample zones
Red The icon turns red if a sample zone cannot find its sam-
Yellow When you create a new sample zone, it is not linked to a
Magenta To free memory on your computer, you can remove the
Dark blue To reduce hard-disk load, HALion can playback sam-
this color means all samples were found and loaded
without problems.
ple, for example, because a removable hard drive is not
connected.
sample, yet. To indicate this, the icons of the corre
sponding sample zones turn yellow.
samples completely from RAM. The samples are played
back from the hard disk only. To indicate this, the icons
of the corresponding sample zones turn magenta.
ples from RAM only. To indicate this, the icons of the
corresponding sample zones turn dark blue.
-
Editing Zones, Programs, and Layers
Creating Zones
To create a new zone, you have the following possibilities:
• Drag and drop samples from the Cubase MediaBay,
Windows Explorer, or Mac OS Finder to a program or layer.
• Right-click a layer in the Program Tree, open the New
submenu, and select Zone.
• Click the Zone icon on the toolbar of the Program Tree.
Ö When creating new zones, HALion uses the default
zone preset to set the zone parameters to their default val
ues. This preset contains all zone parameters, but no sample-related parameters (sample start/end, loop start/end,
etc.).
To use specific zone settings, modify the default preset,
and save it as default in your “user presets” directory.
Creating Layers
To create new layers you have the following possibilities:
• Click the “Create New Layer” icon on the toolbar. When
a layer is selected, the new layer is added within this layer.
When a zone is selected, the new layer is added on the
same hierarchy level as the zone.
• Too add multiple layers on the same level, [Shift]-click
the “Create New Layer” icon on the toolbar.
• Right-click a layer, open the New submenu, and select
Layer.
Saving Programs and Layers
You can save programs and layers from the Program Tree
as VST presets.
• To save a program, click the Save icon on the toolbar, or
use the “Save Program” command on the Load/Save submenu of the context menu.
• To save a certain layer, open the context menu, select
the “Load/Save” submenu, and select “Save Layer”.
Deleting Programs, Layers, and Zones
• Select the program or any number of layers and zones,
and click the trash icon on the toolbar, or press [Backspace], or open the context menu and select Delete.
Ö Deleting zones does not delete any samples on your
hard drive.
Renaming Entries
When you create a new element in the Program Tree, it
automatically gets a generic name. You can change this
name in the following ways:
• Select an entry, click it a second time, and enter the
new name.
• Select an entry, press [F2] (Win) or [Return] (Mac), and
enter the new name.
-
Using the Program Tree
32
Page 33

Drag and Drop
Select the program or any number of layers and zones and
drag the selection to a layer to move the selection inside
this layer.
Using Cut, Copy, and Paste
• To cut the selected elements, use the Cut icon on the
toolbar, the Cut command on the context menu, or the key
command [Ctrl]/[Command]-[X].
• To copy the selected elements, use the Copy icon on
the toolbar, the Copy command on the context menu, or
the key command [Ctrl]/[Command]-[C].
• To insert the copied data, use the Paste icon on the
toolbar, the Paste command on the context menu, or the
key command [Ctrl]/[Command]-[V].
Ö You can also copy or move the selection from one program to another. Furthermore, it is possible to move a
complete program into another one. In this case the moved
program becomes a layer inside the target program.
Paste to New Layer
To paste zones to a new layer, open the context menu for
a zone, layer or program (depending on where you want to
insert the new layer), and select “Paste to new Layer”.
Copying and Pasting Zone Settings
1. Right-click the zone that contains the settings that you
want to copy, and select “Copy Zone Settings” from the
context menu.
2. Right-click one of the selected zones, and select
“Paste Zone Settings” from the context menu.
Transfer Settings to Mapping
Zones often have varying Fine Tune and Level settings,
while other settings stay the same across all zones. To
avoid varying Fine Tune and Level settings in the zones,
you can transfer these settings to the Tune and Gain pa
rameter of the mapping.
1. Right-click the program or the layers and zones.
2. Open the “Transfer Settings to Mapping” submenu
and specify which settings to transfer: “Select All” to
transfer Fine Tune and Level at the same time or select
“Fine Tune” or “Level” to transfer them individually.
• The corresponding zone settings are transferred to the
mapping and reset to their default afterwards.
Applying Layer Settings to Zones
In some cases it can be helpful to apply the layer settings
to the zones they contain.
1. Open the context menu in the Program Tree and select “Apply Layer Settings to Zones”.
2. Select which settings to apply. You can either apply all
settings at once or one of the following settings individu
ally: Key Range, Velocity Range, Fine Tune, and Level Pan.
All layer offsets are now calculated into the correspondent zone settings
and then reset to a neutral position.
Example:
A program contains layers that are limited to a specific key
range. The contained zones, however, use the full key
range. In this case, all these zones fill the whole key range
in the mapping editor and it is impossible to see their real
limitations. To solve this, use the “Apply Layer Settings to
Zones – Key Range” option so that the zones inherit the
limits of the layers. The layers themselves are reset to the
complete key range. Now, you can see the key range in
the mapping.
Making Selections
The selection you make in the Program Tree defines which
part of the program can be edited in HALion. The editors
automatically follow the selection and display the available
parameters. The name of the selected entry is marked in
blue. If several elements are selected, the one with the fo
cus is available for editing. It is indicated by an orange
frame around its name. Any editing you perform always
applies to the selection.
Selecting Elements
• To select an element, click on it.
-
• Use [Shift] and [Ctrl]/[Command] to select a range of
elements.
• To select all zones within the same layer, double-click
one of its zones.
• To select all elements of a layer, double-click the layer.
-
-
Using the Program Tree
33
Page 34

• To select the entire content of a program, open the context menu, select the Selection submenu, and choose
“Select All”.
• To select all subentries of an element, open the context
menu, select the Selection submenu, and choose “Select
Tree”.
Using the Selection Filter
The Selection Filter lets you select a group of elements by
double-clicking on a program, layer, or zone. By default, a
double-click selects all elements of the Program Tree.
The Selection Filter can be set to select only zones, layers,
effects, MIDI modules, or busses. Different icons indicate
which Selection Filter is active.
• To select a Selection Filter, click on the Selection Filter
icon, and choose an option.
Expanding and Collapsing the Tree
• To show or hide the content of a layer, click the plus or
minus sign in front of the icon.
• To expand or collapse an entire layer, including any sublayers, open the context menus for the layer, and select
“Expand Tree” or “Collapse Tree”.
Navigating in the Program Tree
When the Program Tree has the window focus, you can
use the arrow keys for navigating in the Program Tree.
• When a single entry is selected, use the up and down
arrow keys to select the previous or next entry, respectively.
• To open or close a selected layer, use the right or left
arrow key, respectively.
• To expand the selection, use the up/down arrow keys
while holding [Shift].
• With multiple entries selected, use the up and down arrow keys to set the focus to the previous or next selected
entry.
If the Program Tree does not have the window focus, you
can use the hotkeys [W], [A], [D], and [X] to navigate in it.
• To select the previous or next element in the Program
Tree, press [W] or [D], respectively.
• To open or close the focused layer, press [D] or [A],
respectively.
• If you are working with undocked views that have a Program Tree of their own, the hotkeys are applied to the view
that has the window focus, provided the lock icon is activated.
Editing the Focused Entry
The Sound editor automatically shows the parameters of
the focused entry, such as a zone or layer. By using the
Sound editor together with the Program Tree you can easily access and edit all parts of the program.
Muting, Soloing, and Hiding
By muting, soloing, or hiding layers and zones, you can focus on editing certain parts of the program.
In addition, the Program Tree allows you to list a customizable set of zone parameters. This way, you can compare
values between different zones directly in the Program Tree.
Using the Program Tree
34
Page 35

Muting Layers, Zones, and the Program
Layers and zones that are muted are not output when you
hit a key. For muted zones or layers the Mute icon turns
yellow. When a muted program or layer contains zones,
these zones are muted as well. This is indicated by an or
ange Mute icon in front of the zones.
• To mute an element in the Program Tree, click the Mute
icon in front of it. The corresponding icon turns yellow.
• To reset the muting settings, click the Mute icon on the
toolbar.
• To mute the selected zones, open the context menu of
the Program Tree, open the Mute/Solo submenu, and se
lect “Mute Selected Zones”.
• To mute all zones, open the context menu of the Program Tree, open the Mute/Solo submenu, and select
“Mute All Zones”. The program itself and any of its layers
are not muted by this.
Soloing Layers, Zones, and the Program
When a layer or zone is soloed, only that layer or zone can
be heard. For soloed zones or layers the Solo icon turns
red. When a program or layer contains zones that are so
loed, its icon turns pink.
• To solo an element in the Program Tree, click the Solo
icon in front of it. The corresponding icon turns red.
• To reset the soloing settings, click the Solo icon on the
toolbar.
• To solo the selected zones, open the context menu of
the Program Tree, open the Mute/Solo submenu, and se
lect “Solo Selected Zones”. Alternatively, press [S] on
your computer keyboard.
• To solo all zones, open the context menu of the Program
Tree, open the Mute/Solo submenu, and select “Solo All
Zones”. The program itself and any of its layers are not so
loed by this.
Making all Zones Audible Again
• On the context menu, open the Mute/Solo submenu,
and select “Make All Zones Audible”.
This resets all mute and solo states for the program.
• Alternatively click the header of the Mute or Solo column to reset all mute or solo states.
Using “Solo Follows Selection”
The “Solo Follows Selection” function on the Mute/Solo
submenu automatically solos the layers and zones you select. Other parts of the program are muted. This is useful if
-
you want to switch between layers and zones and only
have the current selection played back.
Using the Visibility Settings
Hidden layers and zones are not displayed in the Mapping
editor.
Visible zones have an eye icon in the first column of the
Program Tree. For invisible zones or layers the eye icon is
dimmed. When a program or layer contains hidden zones,
its icon changes to a half dimmed eye.
To hide or show layers and zones, you have the following
possibilities:
• Click in the Visibility column for the layer or zone you
want to hide or show.
• Use the options on the Visibility submenu of the context
menu.
• To show a single layer or zone, [Alt]/[Option]-click its
eye icon.
All other layers and zones are hidden.
• To show only the selected layers and zones, press
[Ctrl]-[U] (Win) or [Alt]-[U] (Mac).
• To show all layers and zones, press [Shift]-[Ctrl]-[U]
(Win) or [Shift]-[Alt]-[U] (Mac).
Using “Auto Visibility”
The “Auto Visibility” automatically shows the selected
zones and any of their direct siblings that are part of the
same layer. Other zones are hidden.
• To activate Auto Visibility, open the context menu, se-
-
lect the Visibility submenu, and choose Auto Visibility.
Ö With this option active, you can still toggle the visibility
of zones inside the visible layers.
Using the Program Tree
35
Page 36

Adding MIDI Modules
Customizing the Program Tree
MIDI modules process the stream of MIDI events inside a
program. They can produce monophonic modulation signals, which can be used as sources in the modulation matrix. The MIDI modules can be assigned to the whole
program or a single layer.
To add a module, proceed as follows:
1. With the program or a layer selected, click the “Create
New MIDI Module” icon on the toolbar of the Program
Tree.
2. On the menu, select the MIDI module you want to add.
• Alternatively, open the context menu, select New and
MIDI Module, and select the module from the submenu.
Adding Insert Effects
To add insert effects to an audio bus, proceed as follows:
• Select the audio bus, click the FX icon on the toolbar,
and select the effect you want to add from the menu.
• Alternatively, open the context menu for the audio bus,
select New and FX, and select an effect from the submenu.
Changing the Order of MIDI Modules and Insert Effects
The order of MIDI modules and insert effects in the Program Tree also determines the order of the processing.
The topmost element is processed first, the lowest last.
You can change the order of the elements using drag and
drop.
Adding Audio Busses
If you want to add an insert effect to a program or layer, it
has to contain an audio bus.
• To create an audio bus, select the program or a layer,
and click the “Create New Bus” icon on the toolbar.
• Alternatively, open the context menu for the program or
layer, open the New submenu, and select Bus.
By default, the Program Tree has the columns Visibility,
Mute, Solo, and Name. You can add further columns that
show more information.
The following columns can be added to the Program Tree:
Column Description
Velocity Range This shows the velocity range of the zones.
Key Range This shows the key range of the zones.
Root Key This shows the root key of the zones.
Tune This shows the tune offset of sample zones.
Gain This shows the gain offset of sample zones.
File Size This shows the size of the samples as stored on
Preload This shows the amount of preload per sample.
Mute This shows the Mute column.
Solo This shows the Solo column.
Visibility This shows the Visibility column.
Learn Zone
Parameter
Normally, Tune is set in the Mapping editor.
Normally, Gain is set in the Mapping editor.
the hard disk. Programs and layers show the
sum of the samples they contain.
To display a zone parameter in a column, use
this option.
Configuring Columns
• To add a column, right-click the column header and select the element you want to show.
• To remove a column, right click the column header and
select Remove.
You can also add a zone parameter as a column using the
Learn function. Proceed as follows:
1. Right-click the column header, and choose “Learn
Zone Parameter”.
The mouse pointer changes to a question mark to indicate that HALion is
in Learn mode.
2. In the editor for the zone, click the parameter that you
want to add as a column in the Program Tree.
Using the Program Tree
36
Page 37

Sorting Layers and Zones
You can change the sorting order of layers and zones using the Sorting Options submenu on the context menu for
the column or manually via drag and drop.
Sorting by Columns
The layers and zones in the Program Tree can be sorted
according to columns in ascending or descending order.
The triangle in the header of a column indicates that the
sorting via this column is active. The tip of the triangle
points up for ascending and down for descending order.
• To activate the sorting via a column, click the header of
the corresponding column.
• To switch between ascending and descending order,
click the header of the column again.
• To deactivate the sorting via the column, click a third
time.
Sorting the Name Column
By default, the Name column is sorted in alphabetical order. However, you can change the sorting according to
pitch, velocity, or root key.
• To change the sorting, open the context menu, select
Sorting Options and choose an option.
Changing the Sorting Order Manually
Samples are imported and shown in a certain order. When
the column sorting is not activated for a column, you can
change the order manually using drag and drop.
Using the Program Tree
37
Page 38

6
Global Functions and Settings
Page 39

Introduction
This chapter describes global functions and settings in
HALion.
The Master Section
The Plug-in Functions Section
The top section of the HALion window contains the plugin functions section. This section gives you access to
functions that affect both the loaded programs, and the
plug-in in general.
The Plug-in Name
If you click the program name on the left, the About box
opens. It contains information regarding the version and
build number of the plug-in. Use this information to verify if
your software is up-to-date. To close the about box, click
on it or press [Esc] on your computer keyboard.
The Program Slot Section
The program slot shows the program that is selected in
the Slot Rack. The slot parameters are the same as in the
Slot Rack, see
In addition, the following parameters are available:
Program Icon
The program icon on the left shows to which sound category a program belongs, if a category is set.
Slot Number
• Click the slot number and select a slot.
“The Slot Rack” on page 19.
The master section can be used to set up volume and tuning for the plug-in.
Master Volume
Use the Master Volume slider to adjust the overall volume.
Master Tune
You can set the Master Tune slider within a range from
Hz to 466.2 Hz (-100 cents to +100 cents). The de-
415.3
fault value is 440 Hz.
The Performance Displays
The performance displays to the right of the master section provide information about the current system load.
CPU
This meter shows the processor load during playback. The
more voices you play, the higher the processor load. If the
red overload indicator lights up, reduce the Max Voices set
ting in the Options editor (see “Max Voices” on page 42).
Disk
This meter shows the hard disk transfer load during the
streaming of samples or when loading presets. If the red
overload indicator lights up, the hard disk is not supplying
data fast enough. In such a case, adjust the Disk vs. RAM
slider in the Options editor towards RAM or decrease the
Max Voices setting in the Options editor.
# – Polyphony
The first number indicates the number of voices currently
played back, to help you trace performance problems. If
you have to reduce the Max Voices setting in the Options
editor, you can verify your settings by monitoring the num
ber of voices currently playing. The second number indicates the number of audio channels. For example, one
stereo voice displays two audio channels.
-
-
Global Functions and Settings
39
Page 40

MEM (Memory)
Missing
Busses
Find Missing Samples…
Insert Effects/
AUX Effects/
FlexPhrasers
RAM
Save
Enable MIDI Mapping
Selection Options
MIDI
Reset
Undo/
Redo
This display indicates the overall amount of RAM currently
used by the plug-in, to help you trace performance problems. The number refers to the streaming buffer and the
preloaded samples. For example, if you need to free up
memory for other applications, you can do so by adjusting
the Balance slider in the Options editor towards Disk and
verify your settings by monitoring the MEM display.
The Toolbar
The toolbar is situated below the plug-in functions section. On the left, controls for loading multi-programs are
located, see
these, two buttons for managing screen sets are located,
see “Screen Sets” on page 15.
The right section of the toolbar contains various buttons
with useful global functions.
Missing Busses
If one or more bus connections could not be established,
this button allows you to open the Pending Busses dialog.
Here you can select alternative busses to be used instead,
“Automatic Output Connection” on page 119.
see
Find Missing Samples
If you load a program that cannot find all samples that it
uses, the “Find Missing Samples” dialog opens, see
“Finding Missing Samples” on page 58. If you close this
dialog without resolving all missing samples, this button
becomes available. It allows you to open the “Find Missing
Samples” dialog after you have loaded a program.
“Managing Multis” on page 21. To the right of
Global Functions and Settings
Global Insert Effects/AUX Effects/
FlexPhrasers
Use these buttons to switch off all insert effects, all AUX
effects, or all FlexPhrasers for the plug-in at once. You can
use this feature to compare sounds with and without ef
fects, for example.
RAM Save Mode
The RAM Save function can be helpful for optimizing the
performance of your system. It scans the playback of your
project and unloads unused samples. Proceed as follows:
1. Click the RAM Save button.
2. In the dialog, click Yes to start collecting the neces-
sary samples.
The RAM Save button starts blinking.
3. Play back the project in your host application from the
beginning to the end or to the point where no new notes
are played.
4. Click the RAM Save button again.
A dialog opens asking if you want to unload all unused samples.
5. Click Yes to unload the unused samples.
If you click Yes, the button lights up, to indicate that RAM Save mode is
active.
• To deactivate RAM Save and reload the unused samples, click the RAM Save button again.
Ö RAM Save mode always keeps samples that are within
the range of the highest and lowest note of the played
programs. This also applies for unused expression layers
that can be controlled via key switches. This allows you to
switch between expressions within the valid note range af
ter applying RAM Save mode.
Ö If a program randomly triggers notes (for example different guitar slide noises), it is possible that these notes
are not triggered during the RAM Save analysis process,
and the samples are therefore removed. To prevent this,
make sure that the highest required note is manually trig
gered during the RAM Save analysis.
40
-
-
-
Page 41

MIDI Select
Pitchbend
wheel
Modulation
wheel
When this option is activated, played MIDI notes can be
used to select zones. This also influences zone parameters displayed in the editors.
This parameter is linked to the corresponding option in the
Mapping editor so that you can remote-control the option
even if the Mapping editor is not visible, see
“Selecting
Zones with the Mapping Editor Keyboard” on page 102.
MIDI Reset
Sometimes notes can “hang”, due to the plug-in losing the
MIDI connection, or the plug-in receiving wrong MIDI con
troller data. In such a case, you can “emergency reset” the
plug-in.
• Click the MIDI Reset button (the lightning icon) to send
an “All Sound Off” and “Reset All Controllers” message to
the plug-in.
The plug-in stops playback immediately and resets the controllers to
their default values.
Undo/Redo
You can click the Undo/Redo buttons to undo or redo a
single step, or you can click the small triangles to open a
list of the performed steps, and go back (or forward) to
that particular step.
Ö The Undo History can also be opened as a separate
editor. This allows for a better overview over the undo/
redo steps.
The Keyboard Editor
The Keyboard editor contains the wheel controls, the
sphere control and the internal keyboard.
The modulation wheel is hardwired to MIDI controller #1
which is normally used as a source in the modulation matrix, but can be used as a quick control as well. Typically,
you assign the modulation wheel to a parameter of an insert effect, such as the speed of the Rotary effect.
Internal Keyboard
The internal keyboard in HALion spans the entire MIDI
note range from C-2 to G8. You can use it for several pur
poses. The simplest one is to trigger notes just as playing
them on a MIDI keyboard, but you can also drop samples
onto it to import and map samples.
Display Options
You can resize the internal keyboard horizontally and vertically. A vertical resize changes the size of the individual
keys and a horizontal resize defines how many octaves are
visible. When the horizontal size is not sufficient to display
all octaves you can use the left/right arrow buttons to both
sides of the keys to shift the visible range by octaves.
For each key, the keyboard indicates whether a sample is
mapped to it. Empty keys are displayed in light gray.
The following color scheme is used for the keys:
Color Description
Yellow A key switch is assigned to that key.
Beige A remapped key switch is assigned to that key.
Red The key is assigned to an expression in the Layer
Blue The key is assigned to a trigger pad.
Green A loop trigger note is assigned to that key.
Alternate MIDI module.
-
Wheel Controls
To the left of the internal keyboard, the pitchbend wheel
and the modulation wheel are located.
41
Global Functions and Settings
Page 42

Triggering Notes
The vertical position where you click the key defines the
velocity that is used to trigger a note. Click on the lower
end of a key to use the highest velocity, and click on the
upper end of a key to use the lowest velocity.
• Right-click a key to open a context menu that contains
information about the key. The “Assigned Zones” sub
menu displays the names of all zones that are mapped to
this key, allowing you to select a zone. The Info submenu
shows pitch and velocity information. Select “Clear key” to
remove all assignments.
You can import samples to a specific key (or key range) by
dragging them onto the keyboard, see
porting Samples” on page 55.
“Importing and Ex-
-
Sphere Control
The Options Editor
The Options editor contains global settings regarding performance issues, global functions, and MIDI controllers.
The Sphere is a two-dimensional control. It allows you to
adjust two parameters simultaneously, by dragging the
mouse horizontally (Sphere H) and vertically (Sphere V).
Typically, two parameters that belong together are as
signed to the Sphere, such as cutoff and resonance.
Ö The small triangles for indicating the horizontal and
vertical axis are only available if parameters are assigned
to Sphere H and V.
You can reset the sphere to the center position using the
corresponding options on the context menu.
-
Global Functions and Settings
Performance Section
This section contains settings to optimize the overall CPU
performance of HALion.
Max Voices
This specifies a maximum number of voices that a plug-in
instance of HALion can play back simultaneously. As soon
as the limit is reached, HALion starts “stealing” voices.
Max CPU
To avoid clicks caused by CPU overload, you can specify
a maximum limit for the CPU load of the plug-in instance in
percent. When the limit is reached, HALion automatically
starts stealing voices. At a setting of 100
stolen.
Ö Because HALion needs some time to react, you can
get CPU peaks that exceed the limit you specified, which
can lead to artifacts such as audio drop-outs. Therefore, it
is advisable to set the Max CPU value a bit lower than ac
tually needed.
42
%, no voices are
-
Page 43

Voice Fade Out
This adjusts the fade out time for voices that need to be
stolen because the Max Voices or the Max CPU setting of
the plug-in instance is reached.
Osc ECO Mode
When this is activated, the oscillators of synth layers run in
ECO mode, and use less CPU. This allows you to play
more voices, but also produces more aliasing at higher
pitches.
Streaming Section
Some of the programs include up to 1 GB of samples,
such as the acoustic piano. This is a large amount of data
and your computer cannot load all samples into the RAM,
especially if you are using all slots. Instead, HALion only
loads the first milliseconds of each sample into the RAM
and constantly loads more manageable portions from the
hard disk while you play. With every additional note you
play, the hard disk load increases, therefore, it is a good
idea to load as much material as possible into the RAM
beforehand. This, of course, leaves less RAM for other ap
plications. For an optimum performance of your system,
you can balance the hard disk versus RAM usage.
Balance
With this slider, you can balance the hard disk versus
RAM usage.
• If you need more RAM for other applications, drag the
slider to the left towards the Disk setting.
• If your hard disk is not supplying data fast enough, drag
the slider to the right towards the RAM setting.
The memory displays are updated accordingly.
Ö The Balance setting always applies to all plug-in in-
stances. It is not saved with the project. You have to set it
up only once for your computer system.
Used Memory and Available Memory
These displays provide information of the memory load in
MB according to the current Balance slider setting.
Performance Meter Section
The Performance Meter section provides a variety of performance relevant information. Each meter displays the
current value, the peak value, and a curve showing the
changes over time. To reset all peaks, click the reset but
ton (the lightning icon) in the title bar of the section. The
following values are displayed:
Option Description
Voices The number of played voices.
Streamed MB/s The quantity of sample data that is streamed from
CPU Avg Load The average CPU load.
CPU Peak Load The CPU peak load.
Dropout/s The number of dropouts per second. (This can be
Preload Memory The quantity of samples loaded into the RAM of
the hard disk.
an indicator for hard disks that are too slow.)
your computer.
Edit Section
This section contains some common settings of HALion
and you can specify an external wave editor that you want
to use for editing your samples.
Ö The settings in the Edit section are not saved with a
particular project, but affect HALion as a whole.
Show Tooltips
Activates and deactivates the tooltips.
Show Value Tooltips
When this is activated, parameters without a value field indicate their value in a tooltip when you use the control.
Auto Collapse Sections
By default, all collapsable sections can be freely collapsed
and expanded. Activate “Auto Collapse Sections” to automatically collapse all other sections when expanding a
specific section.
Ö You can also right-click on the title bar of a section
and select the “Auto Collapse Sections” option.
-
Global Functions and Settings
43
Page 44

Key Commands
This opens the Key Commands dialog. For detailed information, see “Using Key Commands” on page 51.
External Wave Editor
HALion allows you to specify an external sample editor application that can be used to perform destructive offline
editing on a sample, for example applying EQs, filtering, or
denoising.
Here, you can specify which application to use. You can
either type in the path manually or click the Browse button
to navigate to the corresponding application folder. For
more information, see
“Editing Samples in an External Ed-
itor” on page 108.
Temp Folder
Here, you can specify a temp folder for exchanging samples between HALion and the external editor.
Update Sample
Here, you can specify the behavior of HALion when a
sample is saved in the external editor. The following op
-
tions are available:
Option Description
Ask When switching back to HALion, you are asked whether
Always HALion accepts the modified sample.
With Backup HALion accepts the modified sample and automatically
Never Modified samples are never accepted automatically. You
the changed sample should replace the current sample.
creates a backup of the old sample file.
have to import the modified sample manually from the
temp folder.
Option Description
Ignore Error Always removes temporary files without further notice. If a
Never Temporary files are never deleted. You have to delete
file cannot be deleted, no error message is shown.
them manually.
MIDI Controller Section
Here, you can make MIDI controller settings.
Controller Assignment
• To restore the factory MIDI controller assignments, click
the “Reset to Factory” button.
• To save the current MIDI controller assignments as default, click the “Save as Default” button.
Ö “Save as Default” does not include any of the MIDI
controller assignments of the AUX effects.
Ö The MIDI controller mapping is also saved with each
project. This allows you to transfer your settings to other
systems. The project includes the MIDI controller assign
ments of the AUX effects as well.
Receive Program Changes
Activate this option if you want HALion to respond to program change messages. These are generally used by
General MIDI (GM) files, for example.
Receive RPNs 0/1/2
GM files can contain information about pitchbend range,
coarse tuning, and fine tuning. This information is transmit
ted as RPNs (Registered Parameter Numbers). Activate
this option if you want HALion to respond to RPNs.
-
-
Temp Cleanup
After a certain period of time, HALion removes temporary
sample files from the temp folder. The Temp Cleanup op
tion allows you to specify how HALion handles these samples. The following options are available:
Option Description
Ask You are prompted to confirm the cleanup of the temp
folder.
Always Always removes temporary files without further notice. If a
file cannot be deleted, an error message is shown.
Global Functions and Settings
Smoothing
MIDI controllers have a maximum resolution of 128 steps.
This is rather low. When you use a MIDI controller as a
modulation source in the modulation matrix or to remote-
control a quick control, the parameter does not change
smoothly, which can produce an effect often referred to as
“zipper noise”. To avoid this, HALion offers MIDI controller
smoothing.
• Turn the control to the left to increase controller
smoothing.
Parameter changes triggered by MIDI controllers are less immediate.
44
Page 45

• Turn the control to the right to decrease controller
smoothing.
This way, parameters respond faster to MIDI controllers.
Velocity Note-On to Note-Off
Some keyboards do not transmit note-off velocity messages. If this option is activated, the played note-on velocity value is also used as note-off velocity for the notes.
FlexPhraser Hold Reset
Sends a global Hold Reset message to all FlexPhraser
modules that are used in HALion.
The Reset Controller pop-up menu allows you to assign a
dedicated MIDI controller to the FlexPhraser Hold Reset
button for remote-controlling it.
Quick Controls
Quick controls allow you to remote-control any parameter
inside the program. For each program and layer, eight
quick controls are available. Furthermore, “Sphere H”,
“Sphere V”, and the modulation wheel can also serve as
quick controls.
The quick controls can be accessed via the Quick Controls editor for a program or layer.
Assigning Quick Controls
You can assign quick controls to a parameter of the program or one of its layers, to zones inside a program or
layer, or to parameters of a MIDI module or an effect.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Program Tree, select the element that you want
to remote-control via a quick control.
2. Open the Sound editor.
3. Right-click the control to which you want to assign a
quick control and open the Assign Quick Control submenu.
4. On the submenu for the program or layer, select the
quick control that you want to assign.
Ö You can assign the same quick control to different parameters. This allows you to make complex sound settings
with a single control. However, you cannot assign different
quick controls to the same parameter.
• To remove a quick control assignment, right-click the
quick control, and select “Forget Quick Control”.
• To unassign a quick control in the Quick Control Assignments section, select the quick control that you want
to edit in the list on the left, right-click its assignment in the
list to the right, and select “Remove Assignment”.
Single Assignment vs. Multi Assignment
You can assign a quick control to a single parameter of a
zone or module (single assignment) or to the same parameter of all zones inside a layer (multi assignment).
• Single assignments override multi assignments. For example, if a quick control remote-controls the cutoff of all
zones inside a layer and you assign the cutoff of one of
these zones to another quick control, the multi assignment
is overridden by this single assignment.
• If you remove a single assignment from a parameter of a
zone that is part of a layer that has a multi assignment on
the same parameter of all other zones, the zone becomes
part of the multi assignment again.
• If you add another zone to a layer that has a multi assignment, the added zone gets the same quick control assignments as the other zones of that layer.
Managing Quick Controls
A dedicated section of the Sound editor for programs and
layers, the Quick Control Assignments section, allows you
to manage and edit assigned quick controls. The eight
quick controls are listed on the left. The assignments of
the selected quick control are listed on the right. Each as
signment is displayed in a separate row with parameters
to adjust the behavior of the quick control assignment.
Ö If the selected quick control has no assignments, the
list on the right is empty.
-
Global Functions and Settings
45
Page 46

Naming Quick Controls
1. Open the Quick Control Assignments section of the
program or layer that holds the quick control.
2. In the Name column in the section on the left, click the
quick control you want to rename, and enter a new name.
Ö You can also enter the name for a quick control in the
Quick Controls editor.
Duplicating Quick Controls
You can duplicate a quick control assignment using the
“Duplicate Assignment” command on the context menu
for the quick control.
Changing the Order of Quick Control Assignments
Drag an assignment between two other quick controls.
When a line is shown, release the mouse button to insert
the quick control assignment.
Replacing Quick Control Assignments
Drag an assignment onto another quick control. When a
rectangle is shown, release the mouse button to replace
the quick control assignment.
Assigning Quick Controls to Another Parameter
In the Quick Control Assignments section, you can reassign a quick control to another parameter.
Proceed as follows:
1. Select the quick control that you want to edit.
2. In the list on the right, click the parameter name to
open the pop-up menu, and select a parameter from the
menu.
Ö You can only select parameters within the same layer,
zone or module. In other words, if the quick control is as
signed to a layer parameter, you cannot reassign it to a
zone parameter.
Setting the Scope of Quick Control
Assignments
By default, all zones inside the layer that the quick control
belongs to respond to the quick control. To prevent zones
inside a program from responding to the quick control, you
can change the scope of the quick control for a single
layer or zone.
The pop-up menu in the middle of each assignment row
displays which part of the program is affected by this
quick control assignment. If the name of a zone or module
is displayed here, only that zone or module is affected by
the quick control assignment. If the name of the program
or one of its layers is displayed, all zones inside the pro
gram or layer are affected. You can change which part of
the program is affected by selecting the corresponding
option from the pop-up menu.
Ö When a quick control is assigned to a parameter of
the program or one of its layers, the scope of that assign
ment is always that program or layer only. Any layers from
deeper hierarchy levels are not affected by the quick control. This behavior is different to assignments that apply to
zone parameters: Assignments for all zones inside a program or layer always affect the zones that are on a deeper
hierarchy level, too.
Ö You can also deactivate the “Receive Quick Controls”
button for certain layers, see
on page 47.
“Receiving Quick Controls”
Setting the Minimum/Maximum Range
You can set the minimum and maximum range for each assignment separately. This gives you better control over the
parameter change.
You can set the range for a control either by specifying a
minimum and maximum value on the context menu of the
control itself, or by using the corresponding value fields in
the Quick Control Assignments section. To edit the range
graphically, click and drag the blue handles in the curve
display.
-
-
Global Functions and Settings
46
Page 47

Trimming the Range
The Trim Range function allows you to optimize the quick
control range depending on the current parameter value.
Proceed as follows:
1. Right-click the assignment in the list on the right.
2. To trim the range of a single assignment, select “Trim
Range”. To trim the range of all quick controls, select
“Trim Range of all Quick Controls”.
3. The minimum and maximum values are set automatically.
Whenever you change the original parameter, you have to
apply the Trim Range function again to guarantee the best
control range.
Setting the Default Range
This function sets the quick control to the maximum possible range.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Quick Control Assignments section, right-click
the assignment on the right.
2. To set the default range of a single assignment, select
“Set Default Range”. To set the default range of all quick
controls, select “Set Default Range of all Quick Controls”.
As soon as you change the original parameter in the editor
section again, the Set Default Range function has to be
reapplied to guarantee the best control range.
Adjusting the Curvature
You can adjust the curvature of each assignment separately.
Proceed as follows:
1. On the left of the Quick Controls Assignment section,
select the quick control you want to edit.
2. On the right, specify the curvature in the value field between the minimum and maximum value field.
Positive values change the curvature towards logarithmic and negative
values towards exponential behavior.
• You can also edit the curvature graphically in the display
on the right by dragging it up and down.
Setting the Behavior of Quick Control
Assignments
A quick control behaves either as continuous control or as
a switch. In addition, it remote-controls a parameter either
in relative or absolute mode. Relative mode changes the
values of the assigned parameters without loosing their
relative settings. Absolute mode changes the assigned
parameters by overwriting them with the current quick
control value. You can specify a mode for each assign
ment. You can set the behavior in the context menu for the
control itself or via the pop-up menu in the Quick Control
Assignments section.
The following options are available:
Option Description
Relative Remote-controls the parameter values continu-
Absolute Remote-controls the parameter values continu-
Switch Relative Switches between the minimum and maximum
Switch Absolute Switches between the minimum and maximum
ously. Parameter changes can still be heard.
ously. Parameter changes are overwritten.
value. Parameter changes can still be heard.
value. Parameter changes are overwritten.
Receiving Quick Controls
In the upper right corner of the Quick Control Assignments section the Receive Quick Controls button is located. Use this button to determine whether zones inside
a layer respond to quick controls. This includes any single
and multi assignment to zones. Quick control assignments
belonging to the layer itself are not affected.
This is useful if you assigned quick controls to the whole
program and you want to exclude parts of it, such as the
layer containing the instrument noises.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Program Tree, select the program or layer that
you want to respond to the quick controls.
2. In the Quick Control Assignments section, click the
“Receive Quick Controls” button (the antenna icon).
When the Antenna button is activated, zones inside a layer respond to
quick controls from outside.
Global Functions and Settings
47
Page 48

Bypassing Quick Controls
To hear a sound without quick control assignments, bypass them temporarily by clicking the corresponding Mute
button in the Quick Control Assignments section.
Assigning Quick Controls in the Modulation
Matrix
In addition to assigning the quick controls directly to parameter controls, you can also assign them as source or
modifier in the modulation matrix. This way, you can com
bine the quick control with other modulation sources.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Program Tree, select the zones you want to edit.
Make sure that the zones are part of the program or layer
with the quick controls you want to use.
2. In the Sound editor, scroll down to the Modulation Matrix section.
3. On the pop-up menu in the Source/Modifier column,
open the Assign Quick Control submenu, and select the
quick control.
The submenu lists only the quick controls that belong to the same layer
or that are on a higher hierarchy level.
AI-Knob Support
-
HALion can be controlled with the ai-knob of Steinberg’s
CC121, CI 2, and CI2+ controller units.
To change a parameter value, move the mouse pointer
over the control you want to change and turn the ai-knob
to set the value.
Ö Certain parameters cannot be controlled by the aiknob due to internal differences in parameter resolution.
For example, sample marker positions cannot be changed
with the ai-knob because their ranges vary too much.
Global Functions and Settings
48
Page 49

7
Common Editing Methods
Page 50

Introduction
This chapter describes common editing methods in
HALion.
Using Controls in HALion
Knobs and Sliders
Most of the editing methods are the same for knobs and
sliders. The following applies:
• You can adjust the value by clicking on a knob or fader,
and dragging up and down, or by using the mouse wheel.
• When you press [Alt]/[Option] and click on a knob, a
small fader appears, allowing you to set the parameter.
• Press [Shift] and move the knob or use the mouse
wheel to make fine adjustments.
• Press [Ctrl]/[Command] and click on a control to restore the default value.
• Knobs and sliders can be unidirectional or bidirectional.
Unidirectional values, for example level values, start at a
minimum value and go up to the maximum. Bidirectional
controls start from the middle position and go to the left
for negative and to the right for positive values.
• To navigate to the next parameter, press [Tab]. To jump
backwards to the previous parameter, press [Shift]-[Tab].
Ö When no parameter is selected inside a focused view,
pressing [Tab] always jumps to the very first parameter.
Multi Selection and Parameter Controls
When several zones are selected and they do not share
the exact same values, most of the controls indicate this
by turning entirely or partially red. This is true for knobs,
On/Off buttons, combo boxes, value fields and text faders.
For example, if you have selected 3 zones with cutoff frequency values of 1200, 1400, and 2500 Hz, the corona of
the frequency knob shows a range from 1200 to 2500.
The corresponding field shows the value of the focused
zone in red.
Ö More complex controls (for example the envelope editors) only show the values of the focused zone.
You can adjust the value range of a parameter using the
corona of the knob. The values for the zones are distributed
within the new range, keeping their relative distances.
• Drag the corona to compress or expand the value range.
• [Ctrl]/[Command]-drag the corona to adjust the upper
limit of the range.
• [Alt]/[Option]-drag the corona to adjust the lower limit of
the range.
On/Off Buttons
These controls normally know two states, Off and On.
When you move the mouse over an On/Off button, it
changes its appearance to show that you can click it.
Push Buttons
In contrast to an On/Off button, a push button only triggers an action and then goes back to its inactive state.
Such buttons can be found in several places for opening
menus or file dialogs.
Value Fields
You have the following options:
• To type in a value, click in the value field, start typing,
and press [Enter].
If the entered value exceeds the parameter range, it is automatically set
to the maximum value.
• Click in the value field and drag up or down to change
the value.
• Position the mouse over the value field and use the
mouse wheel to adjust the value.
• [Ctrl]/[Command]-click a value field to set it to the default value.
• [Alt]/[Option]-click a value field to bring up a fader.
• Click the up/down triangles next to the field to adjust
the value.
You can adjust musical values, such as key ranges or the
root key, using your MIDI keyboard.
• To enter a value with your MIDI keyboard, double-click
the value field, press a key on your MIDI keyboard, and
press [Return].
Common Editing Methods
50
Page 51

Using Key Commands
Load Preset Save
Delete
Key commands can be assigned to most operations that
can be performed via the standalone panel of HALion. The
Key Commands dialog contains a list of all available commands, arranged in a hierarchical way. When you open a
category folder by clicking the “+” sign beside it, the items
and functions it contains are displayed with the assigned
key commands.
• To open the Key Commands dialog, open the Options
editor, and click the corresponding button in the Edit section.
Ö You can set up several key commands for the same
function.
Searching for Functions
• To search for a specific function, enter its name in the
search field at the top of the dialog, and click the search
button.
Removing Key Command Assignments
• To remove a key command assignment, select the corresponding command in the Commands list, select the
key command in the Keys list, and click the Delete button
(trash icon).
Working with Presets
HALion offers two types of presets: Firstly, there are section and module presets that allow you to store and recall
the setup of a specific user interface component. Sec
ondly, there are VST presets that allow you to store and
recall the settings relating to a program. During the setup,
HALion installs its factory presets in a dedicated folder
and creates a user folder for your own presets. The han
dling of presets is the same throughout HALion.
-
-
Setting Up Key Commands
1. In the Commands list on the left, select a category.
2. Click the “+” sign to open the category folder.
You can also click the global “+” and “-” signs in the top left corner to
open and close all category folders simultaneously.
3. Select the item to which you want to assign a key
command.
Assigned key commands are shown in the Keys column and in the Keys
section in the top right corner.
4. Click in the “Type in Key” field, and enter a new key
command.
You can choose any single key or a combination of one or several modifier keys plus any key.
5. Click the Assign button above the field to assign the
key command to the function.
The new key command is displayed in the Keys list.
6. Click OK to close the dialog.
Ö Factory presets are write-protected, but may be overwritten when a software update is executed. Presets in
your user folder are never changed by the software.
Section and Module Presets
MIDI and effect modules as well as many sections in the
Sound editor, such as the LFO and the Step Modulator
sections, come with their own preset controls.
Loading Presets
The available presets can be selected from the presets
pop-up menu at the top right of the section module.
51
Common Editing Methods
Page 52

Saving Presets
1. Click the Save button (disk icon) to open a file dialog.
2. Name the preset and click Save to save the parameter
set as a preset.
Ö You can modify a factory preset and save it under the
same name in your user folder.
Deleting Presets
You can only delete user presets.
1. Click the Delete button (trash icon).
2. Click Yes to confirm.
Reverting to the Last Saved Program
• To revert to the last saved version of a program, open
the context menu for the program, choose the Load/Save
submenu, and select “Revert to last Saved Program”.
Using Automation
You can automate any program that is loaded into a slot.
Each slot has its own set of automation parameters, i.e.,
Mute, Solo, Level, and Pan. In addition, you can automate
the Quick Controls of the program. You can access the
automation parameters from the automation track of your
sequencer software.
VST Presets
Loading VST Presets
When you load a VST preset, the current program is replaced. Proceed as follows:
1. On the Program Tree toolbar, click the Load icon.
2. Select a VST preset and click OK.
Inserting VST Presets as Layers
1. Right-click the program or layer for which you want to
insert the VST preset, open the “Load/Save” submenu,
and select “Load to new Layer”.
2. Select a VST preset and click OK.
The program is inserted as an additional layer.
Alternatively, drag the VST preset from the MediaBay or
file browser into the Program Tree, and drop it on a layer.
Replacing Programs and Layers with VST Presets
1. Right-click the program or layer you want to replace.
2. Open the “Load/Save” submenu, and select “Replace
Program” or “Replace Layer”.
3. Select a VST preset and click OK.
Alternatively, drag the VST preset from the MediaBay or
file browser into the Program Tree, and drop it on a pro
gram or layer.
-
Automation Parameters
Each slot offers the following pre-assigned automation
parameters:
Parameter Description
Mute This automates the Mute button of the corre-
Solo This automates the Solo button of the correspond-
Level This automates the loudness of the corresponding
Pan This automates the panorama position of the cor-
Quick Controls 1-8 This automates the Quick Controls 1 to 8 of the
sponding slot.
ing slot.
slot.
responding slot.
program that is loaded into the slot.
Common Editing Methods
52
Page 53

Using Effects
HALion features AUX busses that can be used to realize
classical send effects. All slot, program, and layer busses
as well as zones can send signal portions to these busses.
Each bus hosts up to eight insert effects, which allows
you to set up complex effects. The busses are then routed
to either the main plug-in output or to one of the individual
outputs. Furthermore, the Mixer provides access to the
master output bus. These can be used to add a global EQ
or compressor to the signal chain, for example.
In the Mixer, you can set up insert effects for AUX busses.
Using the Insert Effect Slots
Changing the Output Assignments
• To change the output assignment of an AUX bus, open
the Output pop-up menu, and select a different output.
Adjusting the Output Levels
• Move the fader of the AUX bus.
• Alternatively, double-click the value in the field below
the fader, and enter a new value.
Muting AUX Busses
• To mute an AUX bus, click the Mute icon.
The icon turns yellow.
The Master Effect Bus
The master bus works similar to the AUX busses. The only
difference you will find is that the master bus has no bus
output selector since it is “hard-wired” to the main plug-in
output (1/2).
Multi-Channel Effects
HALion comes with a large number of effects that are
mainly intended for use on stereo busses. However, most
of them can also be used on surround busses. In this case
the effect is processed on all channels. When a bus
changes from stereo to surround, the effect follows. For
effects with level meters, the number of meters is adapted
accordingly.
All busses, including the master bus, have eight slots for
insert effects. The handling is the same for all slots:
• To assign an insert effect, click the effect slot, and select an effect from the pop-up menu.
• To remove an insert effect, click the effect slot, and select None from the pop-up menu.
The effect is removed, including its settings.
• To bypass an insert effect, click the bypass button in
front of the effect name.
The bypass is active when the button lights up yellow.
• To edit an insert effect, click the “e” button of the corresponding slot.
You can edit only one effect at a time. The parameters of the corresponding insert effect are displayed in the bottom section.
Common Editing Methods
53
Page 54

Using MIDI Modules
The MIDI modules available in HALion range from standard modules like an Arpeggiator (the so-called FlexPhraser) to more dedicated modules that trigger specific
events or deliver special modulation signals, e.g., to con
trol articulations of sampled instruments. In general, MIDI
modules process the stream of MIDI events inside a program. In addition, they are able to produce monophonic
modulation signals, which can be used as sources in the
modulation matrix. MIDI modules can be assigned to the
whole program or just a single layer. This way, you can
process the MIDI stream of the whole program or just
parts of it. To cover more complex tasks, multiple MIDI
modules can be assigned in series.
Inserting a MIDI Module
1. In the Program Tree, select the program or layer where
you want to insert the MIDI module.
2. Right-click to open the context menu, open the New
submenu, and select “MIDI Modules”.
3. Select the MIDI module that you want to insert.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 to insert multiple modules in
series.
Changing the Order of MIDI Modules
The order of the MIDI modules in the Program Tree has
great influence on the processing of the MIDI events.
• To change the order, drag the MIDI modules to new positions in the Program Tree. The routing between the MIDI
modules changes accordingly.
Bypassing a MIDI Module
Any MIDI module can be bypassed. This way, you can play
the layer without the FlexPhraser or the conditions that
have been set with the MegaTrig module.
• To bypass a MIDI module, click the crossed out speaker
icon in the upper right corner of the caption of the MIDI
module.
Assigning MIDI Modules in the Modulation
Matrix
Some MIDI modules, like the FlexPhraser, directly process
the MIDI events. Other MIDI modules like True Pedaling,
produce modulation signals, which you must assign in the
modulation matrix before you can use them.
To assign a MIDI module as source or modifier in the modulation matrix:
1. In the Program Tree, select the zones you want to edit.
Make sure that the zones are part of a program or layer
with a MIDI module that produces modulation signals, e.g.
True Pedaling.
2. Open the Sound editor and scroll to the Modulation
Matrix section.
3. On the pop-up menu of the Source/Modifier column,
open the Modulation Module submenu.
The submenu lists only the MIDI modules that belong to the same layer or
that are higher up in the hierarchy.
4. On the submenu, select a MIDI module.
Deleting a MIDI Module
1. In the Program Tree, select the MIDI modules that you
want to delete.
2. Open the context menu and select Delete. Alternatively, press Delete on your computer keyboard.
Common Editing Methods
54
Page 55

8
Importing and Exporting Samples
Page 56

Importing Samples
HALion offers convenient functions to import samples and
map them automatically on import. You can specify how
the samples are mapped and also extract mapping information from sample file and folder names.
You can import samples into HALion using the Import
submenu of the Program Tree context menu. In the Import
Samples dialog, you can select the samples to import and
make mapping settings for them.
The lower section of the Import Samples dialog contains
the Mapping Options.
Setting the Key Range
On the Key Range pop-up menu, the following options are
available:
Option Description
From Sample File The samples are mapped to the key range that is
Text from Sample
Name
Number from Sample
Name
From Sample Name
Pattern
Root Key Only Each sample is mapped to its root key only.
Root Key Fill
Centered
Root Key Fill Up The samples are mapped to their root key. The
Root Key Fill Down The samples are mapped to their root key. The
Chromatic The samples are mapped chromatically to the
White Keys The samples are mapped to white keys in ascend-
Black Keys The samples are mapped to black keys in ascend-
Fixed The samples are mapped to the key range that you
saved in the file header of the sample. If this does
not contain any key range information, the settings
for Start and End Key are used instead.
The samples are mapped to the key range that is
extracted from the name of the sample. This func
tion searches for a key range that is defined in text
form, for example “Sample_Name_B2-C#3”.
As above, but instead of searching for text information, this function searches for MIDI note numbers, for example “Sample_Name_59-61”.
The samples are mapped to the key range that is
extracted from the name of the sample according
to the name pattern you set.
The samples are mapped to their root key. The
zones expand to the left and right from the root key
to fill empty spaces.
zones expand from the root key upwards to fill
empty spaces.
zones expand from the root key downwards to fill
empty spaces.
white and black keys in ascending order, starting
at the key specified with the Start value. The root
key is set accordingly.
ing order, starting at the key you set with the Start
Key parameter. The root keys are set accordingly.
ing order, starting at the key you specify with the
Start Key parameter. The root keys are set accord
ingly.
specify with the Start and End Key parameters.
-
-
Ö Only values between 0 and 127 can be extracted as
MIDI note numbers for any of the parameters described in
the following sections (e.
g. “Number from Sample”). The
smaller value is used as the lower limit and the higher
number as the upper limit (e.
g. “Sample_Name_76-121”).
Importing and Exporting Samples
Ö The Chromatic, White Keys and Black Keys options
alter the root key. All other options map the root key according to the settings you make on the Root Key menu.
56
Page 57

Setting the Root Key
The Root Key menu and settings allow you to specify how
the root key for the samples is obtained. The following options are available:
Option Description
From Sample File The root key is read from the file header.
Text from Sample
Name
Number from
Sample Name
From Sample
Name Pattern
Fixed The root key is set to a fixed key, specified in the field
The root key is extracted from the file name. This
function searches for root key information in text form,
for example “Sample_Name_C#3”.
The root key is extracted from the file name, as above,
but instead of searching for text information, this func
tion searches for MIDI note numbers, for example
“Sample_Name_61”.
The root key is extracted from the sample file name
according to the name pattern you set.
to the right.
Ö If no root key information is found, the fixed root key is
used.
Specifying the Velocity Range
You can specify the velocity range for the imported samples using the Vel Range parameters in the Import dialog.
The following options are available:
Option Description
From Sample
File
From Sample
Name
From Sample
Name Pattern
From Folder
Name
Velocity Layers The samples are layered, that is, distributed evenly over
Fixed Velocity
Range
The samples are mapped to the velocity range saved in
the file header.
The samples are mapped to the velocity range that is
extracted from the file name.
The samples are mapped to the velocity range that is
extracted from the file name according to the defined
name pattern.
The samples are mapped to the velocity range that is
extracted from the sample’s folder name.
the velocity range.
The samples are mapped to the velocity range speci-
fied with the Start and End key values.
Obtaining Information from File and Folder
Names
Depending on the mapping settings, the information for
root key, key range, and velocity range is retrieved differently for file and folder names.
Using Name Patterns
Usually, names of sample files follow a certain naming
scheme, for example, “Sample_C3_Key_59-61_Vel_80100”. You can extract all this information from the sample
-
file name by selecting the “From Sample Name Pattern”
option on the Key Range, Root Key, or Vel Range pop-up
menus and defining a pattern in the lower part of the Map
ping Options section.
You can use the Pattern field to manually edit your pattern
and select variables from the pop-up menu to the right.
For the Name Pattern to work, your files and folders must
be named exactly as defined in the pattern, including un
derscores, hyphens, etc.
The following variables are available for building name
patterns:
Option Description
Key Low Number
$(KeyLow)
Key High Number
$(KeyHigh)
Key Low Text
$(KeyLowText)
Key High Text
$(KeyHighText)
Velocity Low
$(VelLow)
Velocity High
$(VelHigh)
Root Key Number
$(RootKey)
Root Key Text
$(RootKeyText)
The MIDI note number is extracted and is used as
the lower limit of the key range.
The MIDI note number is extracted and is used as
the upper limit of the key range.
The name of the note is extracted and is used as the
lower limit of the key range.
The name of the note is extracted and is used as the
upper limit of the key range.
The number for the velocity value is extracted and is
used as the lower limit of the velocity range.
The number for the velocity value is extracted and is
used as upper limit of the velocity range.
The MIDI note number is extracted and is used as
the root key.
The name of the note is extracted and is used as the
root key.
-
-
Ö If no information on the velocity range is found, the
samples are mapped to the Start and End Velocity settings instead.
Importing and Exporting Samples
Ö Samples can only be mapped correctly on import if all
samples follow the same name pattern. If no matching pattern is found, the samples use the settings for Root Key,
Start and End Key and Start and End Velocity instead.
57
Page 58

Using the Position Setting
The Position setting determines the position in the file
name at which the program searches for the information.
• When this is set to “0”, the entire file name is searched.
• When you select a number from the pop-up menu, the
program starts searching after this number of characters.
Every character is taken into account, including spaces.
The Tune and Gain Settings
The file header of the sample can contain information on
the tuning and the gain of the sample. On import, this in
-
formation is retrieved as well.
To switch off reading the Tune and Gain information dur-
ing import, deactivate the corresponding options below
the Pattern field.
Listening to Samples before Import
You can listen to the samples before importing them. The
corresponding controls can be found above the Mapping
Options section in the Import dialog.
The following controls are available:
Option Description
Play Click the Play button to play back the focused sample.
Stop Click the Stop button to stop playback of the sample. The play
Pause Click the Pause button to stop playback of the sample, click
Loop Activate the Loop button to play back the sample repeatedly.
Auto Play Activate Auto Play to automatically start playback of the se-
Level This fader adjusts the playback level.
Position The position slider displays the playback position within the
locator jumps back to the sample start.
again to continue playback.
lected sample.
sample. To select another position for playback, click on the
slider or drag the handle to the new position.
Sample Zone Presets
When importing samples, HALion uses a “Default” zone
preset. This sets all zone parameters to default values, but
excludes sample-specific parameters (Sample Start,
Sample End, Loop Start, Loop End, etc.). You can modify
this preset in the Sound editor for a zone and save it as
“Default” to your user preset directory. HALion then uses
this preset instead.
Importing Folders
Usually, sample collections are organized in folder structures, where each velocity layer or each key group is
saved in a separate folder. In HALion, you can import
complete folders, including their subfolders.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Program Tree, right-click the selected program
or layer.
2. On the context menu, open the Import/Export submenu, and select “Import Folder…”.
3. In the Import Folder dialog, click the button to the right
of the Folder field, navigate to the folder that you want to
import, and click OK.
4. Activate “Include Subfolders” to import samples from
deeper hierarchy levels too.
5. To create layers that correspond to the hierarchy of
the subfolders on disk, activate “Create Layers from Sub
folders”.
6. Set up the Mapping Options as needed.
They are identical to the options in the Import Samples dialog.
7. Click OK.
Finding Missing Samples
There might be situations where loaded programs cannot
find the samples they use. This can happen if the refer
enced samples are located on a different drive and the
drive name has changed, or because the program was
created on a different computer system.
When this happens, the “Find Missing Sample” dialog
opens, showing a list of all samples that are missing, with
additional information about the format, size, and creation
date. The list groups all samples that are located in the
same subfolder.
Entering a Search Path
Below the list you can enter the search path to find the
missing samples.
Ö All the subdirectories are searched before the results
are displayed, therefore the search takes longer if you
specify entire drives.
-
-
Importing and Exporting Samples
58
Page 59

Start the Search
• Once you have specified the search path, click the Start
Search button to start the search process.
If the search only finds a single result for each missing
sample, the sample path is automatically corrected in the
program and the sample disappears from the “Missing
Files” list. If all samples are found, the dialog is closed.
Using Favorite Paths
If a path might be helpful for future searches, you can add
it to the search path list. The next time the dialog opens, it
allows you to select one or multiple predefined paths to
specify which places to include in the search.
• To add a path, click the “+” sign.
Multiple Results
It can happen that samples are found in several places. If
this is the case, an additional “Found File” list appears below the “Missing File” list. This shows the available samples and their file locations.
• To select a sample or a complete folder that is to be
used to resolve the missing samples, double-click on it in
the “Found Files” list.
Each sample or folder that is resolved this way disappears from the
“Missing Files” list.
Once all samples are resolved the dialog closes.
Exporting Samples
Samples can be exported together with the corresponding program or layer as VST presets, or on their own. In
both cases, you use the “Export Samples…” option on the
Program Tree context menu. For VST presets, the corre
sponding dialog has additional preset options.
• To export a VST preset, select the program or layer in
the Program Tree. On the context menu, open the Import/
Export submenu, and select “Export Samples…”.
This opens the Export Preset with Samples dialog.
• To export samples without a preset, select the samples
in the Program Tree. On the context menu, open the Im
port/Export submenu, and select “Export Samples…”.
This opens the Export Samples dialog.
Ö Samples loaded from HSB files or protected VST
sound files cannot be exported.
-
-
Search Options
By default, HALion searches for samples that do not only
have the same file name, but also correspond in terms of
time, size and format information. Only if all of the informa
tion are identical, a sample is considered “found”. However, you can exclude this information by activating the
“Ignore File Time and Size” and “Ignore Audio Format” op
tions.
Importing and Exporting Samples
-
-
Creating Folders using Variables
You can automatically create folders when exporting samples using variables for the Sample Path.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Sample Path field, set the cursor at the position
where you want to insert the variable.
2. On the pop-up menu next to the field, select a variable.
59
Page 60

3. Where necessary, complete the file path by typing in a
back-slash (Win) or a slash (Mac).
You can combine several variables, separating them with hyphens,
spaces, etc.
The resulting sample path is displayed in the Example
Name field.
The following variables are available:
Option Description
Sample Folder
$(SampleFolder)
Layer Structure
$(Structure)
Layer Name
$(Layer)
Program Name
$(Program)
Sample Rate
$(SampleRate)
Bit Depth
$(BitDepth)
Date
$(Date)
Time
$(Time)
Creates a folder with the name of the folder of the
original samples.
Creates folders following the structure of the selected program or layer.
Creates a folder with the name of the layer.
Creates a folder with the name of the program.
Creates folders that are named according to the sample rate of the samples.
Creates folders that are named according to the bit
depth of the samples.
Creates a folder with the name of the current system
date (in the format yymmdd).
Creates a folder with the name of the current system
time (in the format hhmm).
Renaming Samples
You can also rename the samples automatically on export
using sample name variables. You can combine several
variables.
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Sample Name field, set the cursor at the position where you want to insert the variable.
2. On the pop-up menu next to the field, select a variable.
3. If needed, add further variables. You can combine sev-
eral variables, separating them with hyphens, spaces, etc.
The resulting sample name is displayed in the Example
Name field.
The following variables are available:
Option Description
Sample Name
$(Sample)
This variable uses the file name of the original sample. Use it if you do not want to modify the sample
file names.
Option Description
Sample Folder
$(SampleFolder)
Zone Name
$(Zone)
Layer Name
$(Layer)
Program Name
$(Program)
Key Low Number
$(KeyLow)
Key High Number
$(KeyHigh)
Key Low Text
$(KeyLowText)
Key High Text
$(KeyHighText)
Velocity Low
$(VelLow)
Velocity High
$(VelHigh)
Root Key Number
$(RootKey)
Root Key Text
$(RootKeyText)
Sample Rate
$(SampleRate)
Bit Depth
$(BitDepth)
Date
$(Date)
Time
$(Time)
The name of the folder of the original samples is
used in the file name.
The name of the zone is used in the file name.
The name of the layer is used in the file name.
The name of the program is used in the file name.
The MIDI note number of the lower limit of the key
range is used in the file name.
The MIDI note number of the upper limit of the key
range is used in the file name.
The name of the note of the lower limit of the key
range is used in the file name.
The name of the note of the upper limit of the key
range is used in the file name.
The number of the lower limit of the velocity range is
used in the file name.
The number of the upper limit of the velocity range is
used in the file name.
The MIDI note number of the root key is used in the
file name.
The name of the root key is used in the file name.
For example, $(Sample)_$(RootKeyText) appends
the name of the root key to each sample file name.
The sample rate of the samples is used in the file
name.
The bit depth of the samples is used in the file name.
The system date (in the format yymmdd) is used in
the file name.
The system time (in the format hhmm) is used in the
file name.
Example Name Field and Status Messages
The Example Name display informs you about the sample
path and name resulting from your settings.
Below, a status message informs you how many samples
are saved and if duplicate names are created. For example,
if two zones in the Program Tree have the same name, and
you use the variable “$(Zone)”, this results in duplicate file
names. However, file names must be unique. Therefore,
the duplicate file names are automatically numbered.
Samples loaded from HSB files or protected VST Sound
files cannot be exported. The status message informs you
if such protected files exist.
Importing and Exporting Samples
60
Page 61

Files that are in use by HALion or another application can-
!
not be overwritten. In this case, choose a different location
for the samples.
Ö Some systems have problems with file names longer
than 32 characters. Therefore, it is best to use file names
that do not exceed this number.
Replacing Samples
The Replace Samples function allows you to exchange the
sample that is used to play back one or multiple zones.
The zone-specific settings like Pitch, Filter, or Amplifier
are not modified by this.
Setting the File Format
You can export the samples as Wave or AIFF files and
specify a sample rate and bit depth for them, if needed.
Do not change the sample rate of looped samples,
because this can cause audible artifacts.
Including Zone Settings
You can include zone settings when saving the samples.
When you import these samples back into HALion, they
automatically get these settings.
The following settings can be written into the sample file:
Option Description
Key Range Saves the Key Low and Key High settings of each
Velocity Range Saves the Velocity Low and Velocity High settings of
Root Key Saves the Root Key setting of each zone with the
Loop Setting Saves the loop settings of each zone with the
Sample Tune Saves the Tune setting of each zone with the samples.
Sample Gain Saves the Gain setting of each zone with the samples.
zone with the samples.
each zone with the samples.
samples.
samples.
Setting Up General Export Options
In the Export Options section, you can make general settings for the export. The following settings are available:
Option Description
Trim Samples Trims the samples to their actual length, specified with
Use Exported
Samples
Avoid Duplicate
Audio Files
the Sample Start and Sample End parameters of the
zone.
Updates the sample references of the zones to use the
exported samples.
Prevents samples that are used by several zones from
being exported as duplicate audio files.
Replacing a Single Sample
1. In the Program Tree or Mapping editor, select the zone
for which you want to replace the sample.
2. On the context menu for the zone, open the submenu
“Import/Export”, and select “Replace Sample”.
A file dialog opens.
3. Locate and select the new sample and click OK.
Replacing Multiple Samples
1. In the Program Tree or Mapping editor, select the
zones for which you want to replace the samples.
2. On the context menu for one of the zones, open the
Import/Export submenu, and select “Replace Samples”.
3. At the bottom of the file dialog, select the method for
replacing samples that you want to use.
The following methods are available:
Option Description
Replace Identical
Names
Replace by Root Key The samples are replaced by new samples that
The samples are only replaced by new samples if
their names are identical.
Typically, this is the case if you processed the
samples and saved them under the same name in
a different location on your hard disk.
have a matching root key, regardless of the file
name.
Ö If a sample has several zones and these zones have different loop settings, HALion creates duplicates of the file.
Importing and Exporting Samples
61
Page 62

Option Description
Replace by Search
Pattern
This method can be used if only parts of the sample name have changed, for example, due to processing or saving.
Enter the part of the name that has changed in the
text field. Samples are replaced if the remaining
parts of the sample name are identical.
For example, if the name “Sample_Mix_1_C3.wav”
has changed to “Sample_Mix_2_C3.aiff”, enter
“*Mix_2*.aiff” in the text field.
4. Locate the new samples.
The info text in the lower right section shows you how many samples are
replaced in how many zones. If no samples are found, you have to select
another method for finding matching samples.
5. Click OK.
Auditioning Samples before Replacing Them
To listen to the samples before replacing the old ones, activate the Prelisten Sample option and use your MIDI keyboard.
Detecting the Root Key
To listen to the samples with the correct pitch, you have to
select how to detect the root key of the new sample. The
following options are available:
Option Description
Root Key from
Sample File
Root Key Text from
Sample Name
Root Key Number
from Sample Name
Keep Zone
Root Key
The root key is read from the file header of the sample file.
The root key is extracted from the sample file name.
This function searches for the root key in text form,
for example “Sample_Name_C#3”.
The root key is extracted from the sample file name.
This function searches for the root key as a MIDI
note number, for example “Sample_Name_61”.
Instead of using the root key of the new sample, the
root key of the zone is used.
This option is only available when replacing a single
sample.
The “Change Sample Folder” Option
The “Change Sample Folder” option on the Import/Export
submenu of the Program Tree context menu allows you to
relocate samples. This is useful if you processed the sam
ples and saved them in a new location without changing
their names.
-
Importing Third-Party Sampler Programs
HALion allows you to import a wide range of sampler formats from third-party manufacturers. When importing
those formats, HALion translates as many parameters as
possible.
Ö HALion only reads files from standard file systems and
not from proprietary formats like Akai CDs.
Ö Programs that are saved in a protected format cannot
be imported.
Using the Import Editor
The Import editor is divided into the Import Tree on the left
and the results list on the right. The Import Tree shows
one or multiple folder locations and allows you to select
one or more folders. Folders that contain importable pro
grams have a green folder icon, other folders have a yellow folder icon. The result list shows all importable layers
that are located in the selected folders and allows you to
import them via drag and drop.
To import a program, proceed as follows:
1. On the Import editor toolbar, click the “Select Folder”
button.
2. Navigate to the folder that you want to import and click
OK.
The selected folder structure is scanned and the Import Tree shows the
content of this folder and its subfolders.
3. In the Import Tree, select the subfolder that contains
the layers that you want to import.
4. Drag the subfolder or selected layers to the Program
Tree, the Program Table, or the Slot Rack.
You can import folders from the Import Tree that are marked green with
three lines, or drag selected layers from the results list.
5. If the program does not contain the samples, you are
asked to specify the folder in which the samples can be
found.
6. Specify the folder in which you want to save the imported samples.
The HALion program is created.
-
Importing and Exporting Samples
62
Page 63

Adding a Folder
You can add additional folders to the Import Tree using
the Add Folder button.
Specifying a Destination Folder
The folder specified in the “Destination Folder” field is
used to save samples from bank or container files, such as
GigaSampler files (“.gig”). You can type in the path manu
ally or click the button to the right to navigate to a specific
directory.
Ö If you do not specify a destination folder for sampler
formats that use container files, you are asked to do so on
the first import operation. This folder is then used for all
following operations.
When programs are imported, HALion creates a folder for
each program. The name of the folder corresponds to the
name of the imported program. Inside this folder, HALion
creates a subfolder in which the corresponding samples
are saved, if necessary.
Hide Empty Folders
This option allows you to hide all folders that do not contain any importable programs.
Add to MediaBay
This option allows you to automatically create VST presets
for each imported program in the user presets folder of
HALion, thereby making them available in the MediaBay.
When this option is deactivated, no preset is saved and
the program is only available in the current HALion in
stance. If you want to use the program in other projects,
you have to save it first.
-
Importing Sliced Loops
HALion features a Slice Player that can play back sliced
audio loops. You can import sliced loops in the common
REX1 and 2 formats or drag and drop sliced events directly from Cubase.
Importing REX Loops
The import process for REX files includes several steps.
First, the slice information is used to create a sample zone
per slice. These sample zones are then mapped to the
keyboard. The range starts with C3 and uses as many
zones as slices are defined in the loop. The slice informa
tion is also used to create a MIDI phrase that is loaded
into a Slice Player module.
To import REX files, you have the following options:
• Drag a REX file from the Windows Explorer or Mac OS
Finder to the Program Tree and drop it on a program or
layer.
• Open the context menu for a program or layer, open the
Import/Export submenu, select “Import Samples…”, and
select the file via a file dialog.
Ö When working with REX1 files, HALion can directly
play audio from these files. For REX2 files HALion first extracts a WAV file and saves it in the same folder as the
REX file.
Importing Sliced Audio Events from Cubase
You can directly import sliced audio events from Cubase
by drag and drop. When dropping a sliced audio event in
the Program Tree, HALion recognizes that the event con
tains positional information for the different slices. In the
Import Samples dialog, the button “Create Sliced Loop”
becomes available. If you click this button, HALion creates
a sample zone for each slice and adds a Slice Player con
taining the required MIDI information. Any further mapping
options are ignored.
Ö You can also drag selected audio events (from multiple tracks) from a Cubase project into the Program Tree to
create a sliced loop.
-
-
-
Importing and Exporting Samples
63
Page 64

Playing back Sliced Loops
After the import, you can play back the loop in its original
form or in a transposed version. By default, the original
loop is played using C2 (#48), but you can specify another key using the Key Follow and Center Key parameters. Pressing a key below C3 plays transposed versions
of the original loop. The keyboard range above C3 provides the slice sample zones, which are triggered by the
slice player, but can also be triggered manually while the
loop is playing.
Make sure that the very last event ends with the loop end
and not before. Otherwise the generated loop will be too
short and will not run in a perfect cycle.
If the REX file or Cubase audio event contains more than
128 slices, HALion automatically creates additional layers
including MegaTrig modules preconfigured to use key
switches. That way, you can create up to 1024 zones dis
tributed over up to 32 layers.
The Slice Player Controls
Most of the Slice Player controls are the same as for the
FlexPhraser MIDI module. These are described in detail in
the section
that differ for the Slice Player are described in the following sections.
Slice Player Presets
At the top right of the Program Tree, you can load and
save presets for the Slice Player. These presets are saved
in a global folder and can be accessed from any project
you are working in.
Restart Mode
Depending on the selected Restart mode and your playing, you can restart playback from the beginning of the
loop.
You can select one of the following options:
Option Description
Off The loop runs continuously and does not restart upon
First Note The loop restarts when a note is triggered and no other
“The FlexPhraser” on page 141. The controls
note changes.
notes are already held.
Option Description
Each Note The loop restarts each time a note is triggered.
Sync to Host Select this to align the loop with the beats and mea-
sures of your host application. The loop aligns to the
beats and measures each time you start the transport.
Start
This parameter allows you to shift the start of the loop in
steps of 1/4 notes. The length of the loop is shortened
accordingly.
Length
This parameter allows you to shorten the length of the
loop in steps of 1/4 notes.
Ö The control range of the parameters Start and Length
varies with the original length of the loop.
-
Quantize
This parameter allows you to set up a quantization grid, in
fractions of beats. You can also specify dotted and triplet
values. This way, you can force the timing of the slices to
play back only at the selected note value.
Amount
This parameter defines how much of the quantization grid
is applied. A value of 100
% means the slices play back
only at the Quantize note value you specified. Smaller values move the notes only partially towards the next Quantize note value. With a value of 0 % no quantization is
applied at all.
Key Follow
Here you can adjust the pitch modulation by note number.
Set this parameter to positive values to raise the pitch with
notes above the center key. Use negative values to lower
the pitch with notes above the center key. At +100
pitch follows the played note exactly.
Ö The Key Follow parameter is limited to the keys that
trigger the entire loop. It does not affect the keys that play
the single slices.
Center Key
This parameter determines the MIDI note that is used as
the central position for the Key Follow function.
%, the
Importing and Exporting Samples
64
Page 65

Random
You can shuffle the playing order of the slices randomly,
by activating the Random button. To play the slices with
their original order, deactivate the Random button.
The overall timing does not vary through this. Only the
playing order of the slices is affected.
• Use the Depth parameter to adjust how much the playing order of the slices is shuffled. Lower this value to keep
the playing order of slices on the main beats. Raise this
value to vary the playing order of slices on the offbeats as
well.
• Click the Trigger button to trigger a new shuffle. Note
that this changes the pattern number.
• Use the Pattern option to recall a certain random pattern, by entering its pattern number in the value field.
Exporting the Loop Sequence
You can export the loop sequence as a MIDI part for your
host sequencer.
Proceed as follows:
1. Click the MIDI connector icon (to the right of the Random options) and drag it into the Project window of your
host sequencer application.
This creates a MIDI part at the drop position, on an existing or a new MIDI
track.
2. Assign the MIDI track to the corresponding slot in
HALion.
Using Variations
By activating Random and by adjusting the Tempo,
Tempo Scale, Swing, Gate Scale, Quantize, Amount,
Start, and Length parameters, you can save your settings
as up to eight variations. For further information, see
“Working with FlexPhraser Variations” on page 143.
The Loop, Sync, Hold, Trigger Mode, Restart Mode, Key
Follow, and Center Key parameters are not part of the
variations.
Importing and Exporting Samples
65
Page 66

9
Editing Programs and Layers in the
Sound
Editor
Page 67

Introduction
The Sound editor for programs and layers lets you access
parameters that are set globally for the whole program or
individual layers. For example, you can transpose the pitch,
adjust level and pan, and limit the playback to a certain
area on the keyboard.
Programs and layers share the same set of parameters
because they are nearly identical.
The Main Section
The main section contains basic settings for programs
and layers.
Octave
Transposes the pitch in octave steps.
Coarse
Transposes the pitch in semitone steps.
Low Vel
Defines the lowest velocity on which the program or layer
is triggered.
High Vel
Defines the highest velocity on which the program or layer
is triggered.
Sus, FCtrl, FSw, PB, MW, and AT
The Filter options allow you to filter incoming MIDI controllers.
Level
Adjusts the level of the layer. This parameter works as an
offset to the zone settings.
Pan
Defines the position of the layer in the stereo panorama.
This parameter works as an offset to the zone settings.
The Trigger Section
The Trigger section allows you to control the triggering
and releasing behavior.
Fine
Detunes the pitch in cents (1/100 of a semitone).
Level Velocity Curve
Defines how incoming MIDI velocity values are re-mapped
before they are sent to the program or layer. By default,
the curve is set to linear, meaning that incoming and out
going values are identical. The characteristic of each
curve is displayed by a small icon.
Low Key
Defines the lowest key on which the program or layer is
triggered.
High Key
Defines the highest key on which the program or layer is
triggered.
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
Ind MegaTrig
If you want the key switch assignments across different
layers to work individually, activate the individual MegaTrig
management of these layers. This can be necessary when
two layers with different key switches are used together in
one program. For more information about the MegaTrig
module, see
“MegaTrig” on page 148.
Transpose
Transposes the key switches that you set up for the
MegaTrig module.
Start Key
Defines the key that is used as the lowest key switch.
67
Page 68

Key Switch Mode
Defines how long a key switch is active:
• If set to Permanent, the key switch stays active until another key switch is used.
• If set to Temporary, the key switch is only active for as
long as the corresponding key is pressed.
Default Switch
Specifies the default key switch that is active when you
load a program, i. e. before you used the first key switch.
The default key switch is also used in Temporary mode
when no key switch is pressed.
Ö If you set Default Switch to a note value that is not assigned as a key switch, the lowest key switch is automatically used as the default key switch.
Filter Ctrls in Release
Filters out MIDI controllers in the release phase. Modulation destinations that are using controllers keep their value
after the note-off message. The following settings are
available:
Option Description
Off MIDI controllers are processed in the release phase.
On MIDI controllers are filtered out.
Inherit The zones of this layer follow the behavior that was speci-
fied for the parent layer.
Sostenuto
Enables sostenuto for the program or layer. Notes that are
held while pressing the sostenuto pedal sustain. Successive notes do not sustain.
Ind Velocity Mode
Sample-based instruments often use crossfade techniques to optimize the switching between samples with
different velocities. Crossfades are set up in the Mapping
editor, see
“Fading and Crossfading Zones” on page 100.
Activate this option to apply the Velocity Mode settings to
the selected layer and its children.
Velocity Mode
The switching or crossfading between zones can be controlled via velocity or MIDI controller. The following modes
are available:
Option Description
Note-on The velocity is used to trigger the zones.
Controller A MIDI controller is used to replace the velocity, i. e.
Continuous A MIDI controller is used to replace the velocity. De-
the controller value is used to select the zones. The
note-on message triggers the zones selected by the
controller. Only the zones that belong to the corre
sponding velocity are played back.
pending on the “Velocity Fade” setting, the controller
continuously fades between the zones or switches
zones directly. Therefore, all zones belonging to a key
are played back.
-
Repedaling
On an acoustic piano, you can repedal the sustain after
releasing the sustain pedal for as long as the strings vi
brate. The effect is that the strings play on. You can
achieve a similar effect with the Repedaling option. If you
release and press the pedal within the release of the am
plitude envelope, the envelope jumps to the decay segment, resuming at the current level of the release.
Sustain
Enables sustain for the program or layer. When you use
the sustain pedal, notes keep playing until you release the
pedal.
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
Controller
Here, you select the controller that is used when the velocity Mode option is set to Controller or Continuous.
• For the most realistic playback of instruments that use
crossfade techniques, activate “Velocity Fade” and set
“Velocity Mode” to Continuous.
• To save voices during playback of instruments that use
crossfade techniques, deactivate “Velocity Fade” and set
“Velocity Mode” to Note-on.
• Generally, setting “Velocity Mode” to Controller and activating “Velocity Fade” is a good compromise between
performance optimization and realistic playback.
68
Page 69

Velocity Fade
Activate this option to use the velocity crossfades that are
specified in the Mapping editor. When this option is deactivated or if no crossfades have been set up, zones switch
directly between the different velocities.
The Voice Management Section
The Voice Management section allows you to control the
maximum number of notes that you can play and to set
conditions for note stealing and triggering.
Voice Manager
The Voice Manager option controls which Voice Management settings are applied to the selected layer. The following settings are available:
Option Description
Off The layer automatically uses the Voice Management set-
On You can make separate Voice Management settings for
Program The settings of the program are used, regardless of any
tings of the layer that is one step up in the hierarchy. If
there is no layer with active Voice Management settings,
the settings of the program are used.
the selected layer.
Voice Management settings made for layers higher up in
the hierarchy.
Voice Mode
The Voice Mode parameter determines which notes are
stolen during playback and whether new notes are triggered when the Polyphony setting is exceeded. The following settings are available:
Option Description
Low Note Priority Low notes have playback priority over higher
High Note Priority High notes have playback priority over lower
First Note Priority Older notes have playback priority over newer
Last Note Priority New notes have playback priority over the first
Steal Lowest
Amplitude
Steal Released Notes New notes have priority over notes that enter the
notes.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes by
playing a lower note than the ones that are held,
the highest note is stolen and the new note is
triggered.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes by
playing a higher note than the ones that are held,
no note is stolen and no new note is triggered.
notes.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes by
playing a higher note than the ones that are held,
the lowest note is stolen and the new note is
triggered.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes by
playing a lower note than the ones that are held, no
note is stolen and no new note is triggered.
notes.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes
while older notes are still being held, no notes are
stolen. New notes are only triggered if a free voice
is available.
played notes.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes, the
first played notes are stolen in chronological order
(First in/First Out) and the new notes are triggered.
New notes have playback priority over notes with a
low amplitude.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes, the
note with the lowest amplitude is stolen and the
newest note is triggered.
release phase.
- If you exceed the maximum number of notes, the
oldest note that is in its release phase is stolen and
the new note is triggered.
- If no note is playing in release and you exceed the
maximum number of notes, the first played notes
are stolen in chronological order and the new
notes are triggered.
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
69
Page 70

Trigger Mode
The Trigger Mode parameter defines the trigger behavior
for new notes.
The following settings are available:
Option Description
Normal Triggers a new note when the previous note gets stolen.
Resume Does not always trigger a completely new note:
Legato Does not always trigger a completely new note:
The sample and the envelope of the new note are trig
gered from the start.
To minimize discontinuities, use the Fade Out parameter
of the zone (see
- If the new note stays within the same zone, the envelope
is retriggered, but resumes at the level of the stolen note.
The pitch of the zone is set to the new note.
- If the new note plays in a different zone, the sample and
the envelope of the new note are triggered from the start.
- If the new note stays within the same zone, the envelopes keep running. The pitch of the zone is set to the
new note.
- If the new note plays in a different zone, the sample and
the envelope of the new note are triggered from the start.
“Voice Fade Out” on page 43).
-
Ö When Resume or Legato is selected, you might hear
an unnatural attack, depending on the sample. To avoid
this, activate the “Use Start Range” option for the sample
zone (see
“Use Start Range” on page 77).
Voice Groups
By assigning zones to a voice group, you can set their polyphony individually. In addition, you can manage the polyphony across zones that are not part of the same layer.
Furthermore, zones can steal notes from each other, regardless of whether they are in the same layer.
The voice group parameters are shown below the Voice
Management settings.
The maximum number of notes that you can play in a voice
group is limited by the Polyphony setting of the corre
sponding program or layer.
Assigning Zones to Voice Groups
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Program Tree, select the zones that you want to
add to a voice group.
2. Open the Sound editor for the zones.
3. In the Voice Control section, select the Trigger tab.
-
4. On the Voice Group pop-up menu, select a voice
group.
Ö Usually, the voice group numbers relate to the voice
groups of the program. If the zone is part of a layer with
active voice groups, the numbers relate to the voice
groups of the layer instead.
Editing Voice Groups
The Voice Management parameters of voice groups are
edited using the columns in the table below the Voice
Management section.
Exclusive Groups
When voice groups belong to the same exclusive group,
they cannot be played back simultaneously. The last trig
gered voice group has priority over the previously playing
voice groups. Any previously playing voice groups of the
same exclusive group are cut off.
A typical example for assigning voice groups to an exclusive group is a drum set where the closed hi-hat cuts off
the open hi-hat.
• To assign a voice group to an exclusive group, click the
“Excl” field of the voice group, and select a number from
the pop-up menu.
The Poly Tab
The Poly tab contains the polyphony settings for programs
and layers.
Mono
The Mono parameter activates monophonic playback. For
solo instruments, this usually results in a more naturally
sounding performance.
Ö Mono can also be used for programs that use dedicated note-off layers. When the played note is released,
the note-off layer is triggered.
Retrigger
The Retrigger option is only available in Mono mode.
When Retrigger is activated, a note that was stolen by an
other note is retriggered if you still hold the stolen note
when releasing the new one. This way, you can play trills
by holding one note and quickly and repeatedly pressing
and releasing another note, for example.
-
-
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
70
Page 71

Polyphony
When you play a note, one or multiple zones can be triggered. Each triggered zone equals a voice. The number of
voices you trigger with each note is displayed in the Voices
field of the program. Use this parameter to set an upper
limit for the number of notes that can be played simultane
ously in polyphonic mode.
If a program has a lower Polyphony value than its layers,
the maximum number of notes you can play is limited by
the Polyphony value of the program.
Key Poly
With Key Poly (Key Polyphony), you can specify an upper
limit for the number of notes that can be played for a key.
The last played notes have priority. For this parameter to
have an effect, the polyphonic mode needs to be activated.
Ö Key Polyphony is limited by the Polyphony setting. If
the Polyphony setting is lower, this value is used instead.
Low Amp
By default, the “oldest” note is removed first when notes
are stolen due to a Key Poly limitation. Activate Low Amp if
you want the note with the lowest amplitude to be re
-
moved instead.
Min Low Notes
Defines the number of low notes that cannot be stolen, regardless of the Voice Mode setting.
Sustain Mode
While holding the sustain pedal, HALion plays back notes
that you play repeatedly up to the Key Polyphony value.
When you lift the sustain pedal, the notes of the keys that
are no longer held enter the release phase. Depending on
-
the selected Sustain Mode, the notes of the keys that are
still held either keep playing, or also enter the release
phase.
The following settings are available:
Option Description
Hold Loudest The loudest note keeps playing.
Hold Last The last note you played keeps playing.
Hold First The first note you played keeps playing.
Hold All All notes keep playing.
Release All All notes enter the release phase.
Play Release
By default, the release phase of stolen notes is not played
back and the notes fade out in the time specified by the
Fade Out parameter of the zone. Activate this option to
fade out the notes with their normal release phase instead.
The Variation Groups Section
The Sus/Rel Tab
The Sus/Rel tab contains the sustain and release settings
for programs and layers.
Ind Sustain
Activate “Ind Sustain” to use individual sustain settings for
the selected programs or layers.
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
To avoid the so-called machine gun effect that occurs
when the same sample is triggered repeatedly, you can
create programs that use several samples for the same
key and velocity range. These samples can then be trig
gered alternately as variations. To define which samples
are triggered as variations, you can assign them to one the
variation groups. In the Variation Group section you can
also specify the alternation mode for each variation group.
• To use the Variation Group feature, activate the Enable
button and select one of the available modes for each
group.
71
-
Page 72

The following settings are available
Option Description
Off All variations are triggered simultaneously.
Round Robin All variations are triggered alternately in a fixed
Random All variations are triggered randomly. Individual
Random Exclusive All variations are triggered randomly. No variation
order.
variations can be triggered repeatedly.
is directly repeated.
Ö If no variation groups are activated, all zones play simultaneously. To avoid this, activate the variation groups
for the program or layer containing the zones and assign
the zones to the different variation groups.
Assigning Zones to Variation Groups
Proceed as follows:
1. In the Program Tree, select the zones that you want to
add to the voice group.
2. Open the Sound editor for the zones.
3. In the Voice Control section, select the Trigger tab.
4. On the Variation Group pop-up menu, select a voice
group.
Ö Usually, the variation group numbers relate to the vari-
ation groups of the program. If the zone is part of a layer
with active variation groups, the numbers relate to the variation groups of the layer instead.
The Note Expression Section
Cubase’s Note Expression technology is essential for creating realistic instrument performances. Note Expression
allows you to create automated modulations for each
note. In general, HALion supports Note Expression for vol
ume, pan, and tuning. With any of HALion’s programs you
can automate these parameters in Cubase for each note.
But HALion can do more: In programs that give you ac
cess to the modulation matrix, you can assign up to eight
so-called Note Expression controllers to any available
modulation destination. These work in addition to the pre
assigned pitch, pan, and level modulations. When the
Note Expression controller is assigned, you can specify a
name for it to make it available in Cubase.
The eight Note Expression controllers of a program are
shared by all zones. This means that the Note Expression
controller data affects all zones simultaneously. Depend
ing on how the Note Expression controllers are set up in
the modulation matrix, each zone might react differently.
Ö When you use HALion with older versions of Cubase
or other host applications that do not support Note Ex
pression, you still have access to the Note Expression
section and you can see Note Expression controllers in
the modulation matrix. However, they will not have any in
fluence on the program.
-
-
-
-
-
-
The Quick Control Assignments Section
The Quick Controls Assignments section allows you to
manage and edit the assigned quick controls. It is de
scribed in detail in the section “Managing Quick Controls”
on page 45.
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
-
The Note Expression section shows the eight Note Expression controllers on the left (NE1 to NE8) and the assigned modulation destinations on the right. This gives
you a quick overview of how Note Expression controllers
are routed in the modulation matrix and what their influ
ence on the sound will be. One Note Expression controller
can be assigned to several destinations.
Naming Note Expression Controllers
By default, a Note Expression controller is given the name
of the modulation destinations it is assigned to. However,
you can also rename them. After this, any further assign
ments will not change the name.
72
-
-
Page 73

• To rename a Note Expression controller, click in the
Name field of the selected controller and enter the new
name.
Bypassing the Note Expression Controller
Each Note Expression controller has a Bypass button that
allows you to deactivate the effect of the controller.
Ö The Bypass button is linked to the Bypass button of
the corresponding modulation destination in the modulation matrix.
Changing the Modulation Depth
The Depth slider adjusts the intensity of the Note Expression modulation. This allows you to change the modulation
without having to go to the modulation matrix first.
Ö The slider is linked to the Depth slider of the corresponding modulation destination in the modulation matrix.
Editing Programs and Layers in the Sound Editor
73
Page 74

10
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
Page 75

Introduction
All zones are affected
by the editing.
Editing Selected Zones or All Zones
The Sound editor for synth and sample zones contains the
zone parameters in HALion. It allows you to modify the
settings for a single zone, for multiple selected zones or
for all zones at the same time.
Ö If not expressly stated, the functions described in this
chapter apply to both synth and sample zones.
Ö All functions and parameters described here also apply to the Zone Editor.
Global Zone Settings
The global section at the top of the Sound editor allows
you to set up basic zone parameters.
Focused Zone
On the Focused Zone pop-up menu, you can select a
zone for editing when several zones are selected in the
Program Tree.
Low Key/High Key
These parameters determine the lowest key and the highest key on which the zone is triggered.
Low Vel/High Vel
These parameters determine the lowest velocity and the
highest velocity on which the zone is triggered.
When working in the Sound editor, you can apply your editing either to the selected zones (SEL) or to all zones
(ALL), depending on the setting of the corresponding button on the toolbar.
Absolute and Relative Editing
When editing multiple zones, you can either change values absolutely for all the zones (ABS) or make relative
changes (REL), depending on the setting of the corre
sponding button on the toolbar.
• When you use absolute editing and you change a parameter from 50 % to 60 % for one zone, all other zones
will also be set to 60 %.
• When you use relative editing and you change a parameter from 50 % to 60 % in one zone, another selected zone
that was set to 70 % is set to 80 %.
Ö Relative changes can be made for all parameters that
can be adjusted continuously. Changes of parameters
that select one of multiple modes or switch between two
states are always absolute.
-
Root Key
The root key determines the pitch of the zone. Samples
can contain root key information embedded in the file,
which means that when loaded, they are automatically
mapped to the corresponding keys.
Zone Type
HALion allows you to change a sample zone into a synth
zone and vice versa. If you switch a sample zone to a synth
zone, the sample oscillator is replaced by the synth oscillators. You can select the zone type from this pop-up menu.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
HALion 3 compatibility
The button to the left of the REL/ABS button lights up
when you load an FXP file from HALion 3 to indicate that
HALion 4 is in compatibility mode. This way, FXP files
sound like they did in HALion 3. If you deactivate the com
patibility button, some modulations will sound different.
75
-
Page 76

The Voice Control Section
The Voice Control section of the Sound editor has two
tabs: Trigger and Unison/Glide.
The Trigger Tab
On the Trigger tab, you can specify the triggering of a
zone.
Voice Group
You can set the polyphony of a zone individually, by assigning it to one of 128 voice groups. The settings of
voice groups can be edited in the Voice Management sec
tion of the program or layer. For more information on voice
groups, see
Variation Group
To avoid the so-called machine gun effect that occurs
when the same sample is triggered repeatedly, you can
create programs that use several samples for the same
key and velocity range. These samples can then be trig
gered alternately as variations. To define which samples
are triggered as variations, you can assign them to one of
16 variation groups. Use the Variation Group pop-up
menu to specify the alternation mode for the different vari
ation groups.
Priority
Each zone you trigger corresponds to a voice. When the
numbers of played voices (zones) exceed the Maximum
Voices setting of the plug-in instance, zones are cut off
and replaced by other voices. This is called “voice steal
ing”. Use this parameter to specify a priority for this behavior. Zones with higher priority can steal zones with lower
priority, but not vice versa. If there are no zones with lower
priority, zones of the same priority are stolen. Zones with
the priority Hold steal only from lower priorities, but not
from themselves.
Ö To specify how fast the zones are stolen, use the
“Voice Fade Out” parameter in the Options editor.
“Voice Groups” on page 70.
-
-
Fade Out
Whenever a voice is stolen because a polyphony limit is
reached, it is faded out. You can specify this fade out time
for each zone, which allows you to adapt it to different signal types. For example, you might want to cut a stolen
crash cymbal zone less abruptly than a stolen hi-hat zone.
Key On Delay
With this parameter, you can delay the playback of the
zone by a specified time or a note value.
• To synchronize the delay time to the host tempo, activate the Sync button and select a note value from the
pop-up menu. To change the selected note value to a trip
let, activate the “T” button.
With Sync deactivated, the delay is specified in milliseconds. With Sync
activated, the delay is specified in fractions of beats.
-
Release Mode and Amount
The parameters Release Mode and Amount determine
how loud the release samples are played back. Release
samples play back the sound of an instrument when the
note ends. For example, this can be the noise of the
damper touching down on the piano string, or the reverb
tail of an instrument that was recorded in a concert hall. By
setting the release mode, the level of the release samples
can be controlled from different sources, for example. The
Amount parameter adjusts how much the selected option
affects the level of the note-off samples.
To set up the playback of release samples, proceed as fol-
lows:
1. In the Program Tree, place the note-on and note-off
samples into separate layers.
2. Add a MegaTrig Module to the note-off layer and set
the playing condition to “Note-off”.
3. Select all note-off samples.
4. In the Sound editor, open the Voice Control section,
and make settings for Release Mode and Amount.
The following settings are available:
Option Description
Off Deactivates the Release Mode. The level of the
note-off sample is controlled only by the amplifier
section of the zone.
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
76
Page 77

Option Description
Note-on Env The level of the note-off sample is controlled by
Note-off Env The level of the note-off sample is controlled by
Note-on Vel The level of the note-off sample is controlled by
Note-off Vel The level of the note-off sample is controlled by
Current Amplitude The level of the note-off sample is controlled by
Random The level of the release sample is controlled by a
the Amplitude Envelope of the associated note-on
sample: The note-off sample is played back with
the level that the amplitude envelope has at the
moment when the note-off sample is triggered.
In order to find the associated note-on sample, the
mappings of the note-on and note-off samples
must overlap. HALion takes the last running noteon sample as the associated one.
the amplitude envelope of the note-off sample:
The note-off sample is played back with the level
that its amplitude envelope has at the moment
when the note-off sample is triggered.
the incoming MIDI note-on velocity.
the incoming MIDI note-off velocity.
the current amplitude of the associated note-on
sample.
random value. Use the Amount control to set the
depth of the random value.
The Unison/Glide Tab
The Unison/Glide tab has the following parameters:
Unison
Unison allows you to trigger multiple voices simultaneously with each note you play. When you activate the Unison option, the following parameters become available:
Option Description
Voices This determines the number of voices that are triggered
Detune Use this parameter to detune the pitch of each unison
Pan Use this parameter to spread the unison voices across
Delay With this parameter you can introduce a small random
simultaneously (max. 8).
voice in cents. This produces a fatter sound.
the stereo panorama. The higher the value, the broader
the stereo image.
delay for each unison voice. With a value of 0 %, all uni
son voices are triggered at the same time. Values from
1
% to 100 % add a random delay to each unison voice.
The higher the value, the more random the delay. This is
especially useful to avoid comb filter effects with two or
more slightly detuned samples, which can occur if you
play them back at exactly the same time.
Glide
You can use the Glide parameter to bend the pitch between notes that follow each other. You achieve the best
results in Mono mode.
When you activate the Glide option, the following parameters become available:
Option Description
Time This specifies the time needed to bend the pitch from
Sync Activate this option to synchronize the delay time to the
Mode Here, you can specify whether the glide time is con-
Curve You can select one of three curve types to define the
Fingered Activate this parameter to glide the pitch only between
one note to the other.
host tempo. Select a note value from the pop-up menu.
To change the selected note value to a triplet, activate
the “T” button.
stant and independent from the note interval (Constant
Time) or if the time changes with the note interval (Con
stant Speed). When Constant Speed is selected,
larger intervals result in longer glide times.
glide behavior: With the Linear curve, the pitch glides
at continuous speed from the start to the end pitch.
With the Exponential curve, the pitch starts gliding at
higher speed and decelerates towards the end pitch.
This behavior is similar to the natural pitch glide pro
duced by a singer. With the Quantized curve, the pitch
glides in semitones from the start to the end pitch.
notes that are played legato.
Ö If you use Cutoff, Amplitude and Pan Key Follow, the
corresponding parameters also change with the Glide
effect.
Glide Groups
You can assign zones to Glide Groups. This way, the glide
effect can be set independently for the zones. This allows
you to set up zones with overlapping Key Range and dif
ferent settings of Glide Time, for example.
Use Start Range
If a new note plays in a different zone with a different sam-
-
ple assigned, the new sample is used to glide to the new
pitch. Depending on the sample, this can produce an un
natural attack. To avoid this, activate “Use Start Range”.
When this is activated, the sample does not start from the
beginning, but from the position you set with the Sample
Start Range parameter.
-
-
-
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
77
Page 78

The Pitch Section
!
On the Pitch section for synth and sample zones, you can
make settings for tuning and pitch modulation. The following parameters are available:
Pitchbend
Here, you can set the range of the pitch modulation that is
applied when you move the pitchbend wheel.
Octave
Here, you can adjust the pitch in octave steps.
Coarse
Here, you can adjust the pitch in semitone steps.
Fine
This parameter allows you to fine-tune the pitch in cents
(hundredths of a semitone).
Env Amnt (Envelope Amount)
This parameter determines how much the pitch is affected
by the pitch envelope.
Center Key
This specifies the MIDI note that is used as the central position for the Key Follow function.
The Oscillator Section
The Oscillator section for synth zones offers six sound
sources: three main oscillators, the sub oscillator, the ring
modulation and the noise generator. To create interesting
electronic spectra, you can mix any of these sound
sources. The resulting signal is sent to the Filter and Am
plifier sections for further sound shaping.
The three main oscillators (OSC 1, OSC 2 and OSC 3)
offer different wave shapes and algorithms.
• You activate an oscillator by clicking its On/Off button.
Make sure to deactivate any oscillator functions that
are not needed to save processing power.
-
Random
This parameter allows you to randomly offset the pitch
with each played note. Higher values cause stronger variations. At a setting of 100 %, the random offsets can vary
from -6 to +6 semitones.
Key Follow
Here you can adjust the pitch modulation by MIDI note
number. Set this parameter to positive values in order to
raise the pitch the higher you play. Use negative values to
lower the pitch the higher you play. At a setting of
%, the pitch follows the played note exactly.
+100
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
78
Page 79

OSC 1/2/3 Type
The Oscillator Type defines the basic sound character of
the oscillator. The pop-up menu lists the waveforms (Sine,
Triangle, Saw or Square), followed by the algorithm
(PWM, Sync, CM or XOR). The combination of waveform
and algorithm controls the sound of the oscillator.
• To select an oscillator type, click the icon that indicates
the wave shape for OSC1, OSC2, or OSC3 and select
the wave shape and algorithm you want to use from the
pop-up menu.
The following algorithms are available:
Algorithm Description
PWM
(Pulse Width
Modulation)
Sync This algorithm provides different hard-sync oscillators,
CM
(Cross
Modulation)
PWM is only supported by the square waveform. The
Waveform parameter sets the ratio between the high
and low value of the square wave. A setting of 50
produces a pure square wave. With settings below or
% the oscillator produces rectangular waves.
above 50
where each is a combination of a master and slave os
cillator. The wave shape of the slave oscillator (Sine,
Triangle, Saw or Square) is reset with each full wave
cycle of the master oscillator. This means that a single
oscillator can produce a rich sync-sound without using
other oscillators as slave or master. The Waveform pa
rameter adjusts the pitch of the slave oscillator, producing the typical sync sound.
This algorithm provides a combination of two oscillators
where a master oscillator is modulating the pitch of a
slave oscillator (Sine, Triangle, Saw or Square) at the
rate of the audio sample. The Waveform parameter ad
justs the pitch ratio between slave and master oscillator, resulting in a sound close to frequency modulation.
%
-
-
-
Algorithm Description
XOR
(Exclusive or)
This algorithm compares two square waveforms with
an XOR operation. Depending on the outcome of the
XOR operation, the waveform shape of a third oscillator
(Sine, Triangle, Saw or Square) is reset. The Waveform
parameter adjusts the pitch ratio of the square oscilla
tors resulting in a sound close to ring modulation of the
third oscillator.
-
Ö Except for PWM, all algorithms support the Sine, Triangle, Saw and Square wave shapes. PWM supports
Square wave only.
Ö The waveform parameters for OSC1, OSC2 and
OSC3 can be assigned as modulation destinations in the
modulation matrix.
OSC 1/2/3 Waveform
The waveform parameter allows you to modify the sound
of the oscillator algorithm. Its effect depends on the selected oscillator type.
OSC 1/2/3 Octave (Oct)
Here, you can adjust the pitch in octave steps.
OSC 1/2/3 Coarse (Crs)
Here, you can adjust the pitch in semitone steps.
OSC 1/2/3 Fine
This parameter allows you to fine-tune the pitch in steps of
cents (hundredths of a semitone).
OSC 1/2/3 Level
This adjusts the output level of the oscillator.
Ö The waveform, pitch and level of oscillator 1, 2, and 3
can be modulated separately in the modulation matrix.
Sub Oscillator (SUB)
The pitch of the sub oscillator is always one octave below
the overall pitch of the synth zone. If you modulate the pitch
of the synth zone, the pitch of the sub oscillator follows.
• To activate and deactivate the sub oscillator, click its
On/Off button.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
79
Page 80

The following parameters are available:
Parameter Description
Sub Oscillator
Type
Sub Oscillator
Level
Here, you can select the wave shape of the sub oscillator. You can choose between Sine, Triangle, Saw,
Square, Pulse Wide and Pulse Narrow.
This adjusts the output level of the sub oscillator.
Ring Modulation (RING)
Ring modulation produces sums and differences between
the frequencies of two signals.
• To activate ring modulation, click the On/Off button.
The following parameters are available:
Parameter Description
Ring Modulation
Source 1/2
Ring Modulation
Level
This allows you to select the sources to be ring modulated. You can select OSC1 or Sub as Source 1
and OSC2 or OSC3 as Source 2.
This adjusts the output level of the ring modulation.
Noise
The Noise parameter is used for non-pitched sounds. In
addition to standard white and pink noise, there are also
band-pass filtered versions of white and pink noise.
• To activate the noise generator, click its On/Off button.
The following parameters are available:
Parameter Description
Noise Type Here, you can select the sound color of the noise. You
Noise Level This adjusts the output level of the noise generator.
Ö Sub level, ring modulation level and noise level can be
modulated separately in the modulation matrix (see
Modulation Matrix Section” on page 92).
can choose between White, Pink, White BPF (BPF =
band-pass filtered), and Pink BPF.
“The
The Sample Oscillator Section
The sample oscillator controls various playback parameters as well as loop parameters.
The Main Tab
Playback Mode
The following playback modes are available:
Option Description
Normal The sample is played back from the beginning to
Reverse The sample is played backwards, ignoring any
One Shot The sample is played back from the beginning to
Reverse One Shot The sample is played back from the end to the be-
Ö In One Shot and Reverse One Shot mode, the zones
ignore any MIDI Note Off messages. All envelopes and
LFOs play until their sustain is reached and then remain
on this level for as long as the sample plays back. Any re
lease segments of the envelopes and LFOs are not
played. However, if you activate One Shot mode in the Envelope section, the release nodes of the envelopes are included in the playback.
Quality
When samples are not played with their original pitch or
tempo, HALion calculates the transposed versions in real
time using algorithms that require different CPU perfor
mance depending on the Quality setting.
Changing the quality mode is particularly noticeable in the
high frequencies. The higher the setting, the better the
suppression of artifacts. For samples with little high-fre
quency content, you can safely use the “Standard” option.
For programs that use different samples for every key (no
resampling is necessary) you should always use the
“Standard” option to save computing power.
the end. If any loops are defined they are played
according to their loop settings.
loop settings.
the end, ignoring any loop settings.
ginning, ignoring any loop settings.
-
-
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
80
Page 81

Preload
HALion provides two different ways of working with sample data. A sample can either be loaded completely into
RAM or it can be streamed from the hard disk. However,
when samples are streamed, HALion needs to preload a
portion of these samples to be able to play a voice without
having to search for the sample data first. The size of this
preload buffer can be set in the Options editor. The Pre
load setting enables you to adapt this buffer size for individual sample zones by setting a multiplier from 1 to 16.
Increasing the buffer size can be useful if a sample can be
transposed in a wide range and HALion needs to read out
the sample data faster, for example.
If you set Preload to its maximum, HALion preloads the
complete sample. This option is useful for smaller samples.
Sample Start Range
The Sample Start Range parameter allows you to determine the range for sample start offset modulation. When
Sample Start is selected as a modulation destination in
the modulation matrix, the Sample Start Range parameter
controls the range, that is the sample portion that is af
fected by the start offset modulation. If this parameter is
set to zero, no sample start modulation is performed.
For example, if note-on velocity is used to modulate the
sample start parameter, a high key velocity starts playback
later in the sample, and the range of this modulation is de
termined by the Range Start parameter.
Fixed Pitch
When a sample zone is triggered by a MIDI note other
than the one defined by the Root Key setting, the sample
is normally pitched accordingly. When Fixed Pitch is acti
vated, the relation between played note and root key is
disregarded and all keys play the sample just like it was
recorded.
Ö You can still apply the usual pitch modulations in the
Pitch section and set the sample to follow the keyboard
according to the Key Follow Root Key setting.
The Filter Section
The Filter section for synth and sample zones allows you
to adjust the tone color of the sound.
Filter Type
By selecting the filter type, you specify the basic sound
character of the filter. Note that filters without distortion
use less processing power.
The following filter types are available:
Filter type Description
Off The filter section is switched off.
Classic This filter type offers 24 filter shapes with resonance.
Tube Drive This filter type offers a lot of character by adding warm,
Hard Clip This filter type adds bright, transistor-like distortion.
Bit Red
-
(Bit Reduction)
Rate Red This filter type adds digital distortion by means of alias-
Rate Red KF As above, but with Key Follow: The rate reduction fol-
-
Waldorf This filter type offers 14 filter shapes, including two
HALion 3 This filter type offers the 5 legacy filter shapes from
tube-like distortion. You can set the amount of tube
drive with the Distortion parameter.
You can set the amount of hard clipping with the Dis
tortion parameter.
This filter type adds digital distortion by means of quantization noise. You can adjust the bit reduction with the
Distortion parameter.
ing. You can adjust the rate reduction with the Distortion parameter.
lows the keyboard, so the higher you play, the higher
the sample rate.
comb filters.
HALion 3.
-
The Loop Tab
The options on the Loop tab are identical with the loop
options on the Loop tab of the Sample editor, see
ing Loops” on page 108.
“Creat-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
81
Page 82

Filter Mode
The buttons on the left of the Filter section determine the
overall filter structure. The filter types provide the following
options:
Filter mode Description
Single Filter This mode uses one filter with one selectable filter shape.
Dual Filter
rial
Se
Dual Filter
Parallel
Morph 2 This mode morphs between filter shape A and B. You can
Morph 4 This mode morphs sequentially from filter shape A to D.
Morph XY This mode morphs freely between the filter shapes A, B,
This mode uses two separate filters connected in series.
You can select the filter shapes for each filter indepen
dently. The parameters Cutoff and Resonance control
both filters simultaneously. However, you can offset the
cutoff and resonance of the second filter with the param
eters CF Offset and Res Offset.
This mode uses two separate filters connected in parallel.
You can select the filter shapes for each filter indepen
dently. The parameters Cutoff and Resonance control
both filters simultaneously. However, you can offset the
cutoff and resonance of the second filter with the param
eters CF Offset and Res Offset.
select the filter shapes for filter shape A and B indepen
dently. Adjust the morphing with the Morph Y parameter.
You can select the filter shapes for filter shape A, B, C,
and D independently. Adjust the morphing with the
Morph Y parameter.
C, and D. You can select the filter shapes for filter shape
A, B, C, and D independently. Adjust the morphing with
the Morph X and Morph Y parameters.
-
-
-
-
-
Ö For compatibility reasons, the filter types HALion 3
and Waldorf are included. These filters always use Single
filter mode.
Filter Shape
Each filter type offers 24 different filter shapes. By selecting the filter shape you determine which frequencies are
affected. Depending on the chosen filter mode, you can
either select one, two, or four shapes.
Filter shape Description
LP24 Low-pass filter with 24 dB/oct. Frequencies above the
LP18 Low-pass filter with 18 dB/oct. Frequencies above the
LP12 Low-pass filter with 12 dB/oct. Frequencies above the
LP6 Low-pass filter with 6 dB/oct. Frequencies above the
BP12 Band-pass filter with 12 dB/oct. Frequencies below
cutoff are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
and above the cutoff are attenuated.
Filter shape Description
BP24 Band-pass filter with 24 dB/oct. Frequencies below
HP6+LP18 High-pass filter with 6 dB/oct plus low-pass filter with
HP6+LP12 High-pass filter with 6 dB/oct plus low-pass filter with
HP12+LP6 High-pass filter with 12 dB/oct plus low-pass filter with
HP18+LP6 High-pass filter with 18 dB/oct plus low-pass filter with
HP24 High-pass filter with 24 dB/oct. Frequencies below the
HP18 High-pass filter with 18 dB/oct. Frequencies below the
HP12 High-pass filter with 12 dB/oct. Frequencies below the
HP6 High-pass filter with 6 dB/oct. Frequencies below the
BR12 Band-reject filter with 12 dB/oct. Frequencies around
BR24 Band-reject filter with 24 dB/oct. Frequencies around
BR12+LP6 Band-reject filter with 12 dB/oct plus low-pass filter
BR12+LP12 Band-reject filter with 12 dB/oct plus low-pass filter
BP12+BR12 Band-pass filter with 12 dB/oct plus band-reject filter
HP6+BR12 High-pass filter with 6 dB/oct plus band-reject filter
HP12+BR12 High-pass filter with 12 dB/oct plus band-reject filter
AP All-pass filter with 18 dB/oct. Frequencies around the
AP+LP6 All-pass filter with 18 dB/oct plus low-pass filter with
HP6+AP High-pass filter with 6 dB/oct plus all-pass filter with
and above the cutoff are attenuated.
dB/oct (asymmetric band-pass filter). Frequencies
18
below and above the cutoff are attenuated. Attenuation
is more pronounced for the frequencies above the cutoff.
dB/oct (asymmetric band-pass filter). Frequencies
12
below and above the cutoff are attenuated. Attenuation
is more pronounced for the frequencies above the cutoff.
6
dB/oct (asymmetric band-pass filter). Frequencies below and above the cutoff are attenuated. Attenuation is
more pronounced for the frequencies below the cutoff.
6
dB/oct (asymmetric band-pass filter). Frequencies below and above the cutoff are attenuated. Attenuation is
more pronounced for the frequencies below the cutoff.
cutoff are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
the cutoff are attenuated.
the cutoff are attenuated.
with 6
dB/oct. Frequencies around and above the cut-
off are attenuated.
dB/oct. Frequencies around and above the cut-
with 12
off are attenuated.
dB/oct. Frequencies below, above and around
with 12
the cutoff are attenuated.
dB/oct. Frequencies below and around the cut-
with 12
off are attenuated.
with 12
dB/oct. Frequencies below and around the cut-
off are attenuated.
cutoff are attenuated.
dB/oct. Frequencies around and above the cutoff are
6
attenuated.
dB/oct. Frequencies around the cutoff are attenuated.
18
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
82
Page 83

Cutoff
Here, you can adjust the cutoff frequency of the filter. The
effect depends on the selected filter type.
X/Y Control
The X/Y control allows you to adjust two parameters simultaneously. This is especially useful with the morphing
filters, where the X/Y control adjusts the mix between the
filter shapes. For the other filter modes, the X/Y control
adjusts cutoff and resonance. Depending on the selected
filter type, the X/Y control adjusts different parameters:
Filter Description
Single, Dual
Serial & Dual
Parallel
Morph 2 and 4 The X/Y control adjusts the morphing between the filter
Morph XY The X/Y control adjusts the morphing between the filter
The X/Y control adjusts the cutoff frequency on the
horizontal and resonance on the vertical axis.
shapes on the vertical (Morph Y) axis. The horizontal
axis adjusts the cutoff frequency.
shapes AD and BC on the horizontal (Morph X) and AB
and DC on the vertical axis (Morph Y).
Resonance
This parameter emphasizes the frequencies around the
cutoff. For an electronic sound, increase the resonance.
At higher resonance settings, the filter self-oscillates,
which results in a ringing tone.
Distortion
This parameter adds distortion to the signal. The effect
depends largely on the selected filter type. At higher set
tings, it creates a very intense distortion effect.
Ö This parameter is only available for the Tube Drive,
Hard Clip, Bit Red, Rate Red and Rate Red KF filter types.
CF Offset
For the dual filters, this parameter allows you to offset the
cutoff frequency of the second filter (filter shape B).
Res Offset
For the dual filters, this parameter allows you to offset the
resonance of the second filter (filter shape B).
Velocity
This parameter adjusts the cutoff modulation from velocity.
Set this parameter to positive values to increase the cutoff
with higher velocities. Use negative values to decrease the
cutoff with higher velocities.
Norm
The Norm option allows you to normalize the velocity values that are used to modulate the filter. This means that
the velocity range for the zone is remapped to a full veloc
ity range.
For example, if a zone ranges from 40 to 80 on the mapping velocity scale, an incoming velocity of 40 results in a
velocity value of 0 being sent to the cutoff, an incoming
velocity of 80 results in 127. This way, you can adapt ve
locity-layered zones in such a way that each zone starts
with a damped filter setting and opens completely towards the zone above.
Fatness
This parameter (only available for the algorithms Waldorf
and HALion 3) adds a warm, tube-like filter distortion to
the signal.
Env Amnt (Envelope Amount)
Use this parameter to adjust the cutoff modulation from
the filter envelope. Setting negative values inverts the direction of the modulation from the filter envelope.
-
Key Follow
Here, you can adjust the cutoff modulation using the note
number. Set this parameter to positive values to raise the
cutoff with notes above the center key. Use negative val
ues to lower the cutoff with notes below the center key. At
+100
% the cutoff follows the played pitch exactly.
Center Key
This parameter determines the MIDI note that is used as
the central position for the Key Follow function.
Bypass
The Bypass buttons in the top right of the section allow
you to listen to the zone without modulation of the filter envelope and without any filtering.
-
-
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
83
Page 84

The Amplifier Section
The Amplifier section has two tabs: Main and AUX.
The Main Tab
The Main tab gives you access to the Level and Pan settings of the zone.
Level
Here, you can adjust the loudness of the zone.
Headroom
Use this parameter to specify the headroom for polyphonic playback. By default, HALion uses a headroom of
dB. For monophonic programs, such as drum loops,
12
set the headroom to 0 dB. If you work with low polyphony
values, a headroom of 6 dB is sufficient.
Key Follow
Use this parameter to control the volume depending on
the note pitch. Positive values mean that the volume is
higher the higher the notes you play. With negative values,
the volume decreases the higher the notes you play.
Center Key
This parameter determines the MIDI note that is used as
the central position for the Key Follow function.
Pan
Here, you can set the position of a sound in the stereo
panorama. At a setting of -100
hard left and at +100
%, it is panned hard right.
Mode
With this option you can specify how the loudness
changes across the stereo panorama. The following
modes are available:
• 0dB: This option works like a balance control.
Setting the pan control towards the left fades out the right channel and
vice versa. At the center position, the loudness is not cut.
%, the sound is panned
• -3dB: This option uses the cosine/sine pan law
The loudness is cut by -3dB at the center position, but the energy is preserved when moving the source signal across the stereo panorama. The
-3dB option sounds more natural. The transition from hard left to hard
right sounds much smoother than with the 0dB or the -6dB setting.
• -6dB: This option uses the linear pan law.
The loudness is cut by -6dB at the center position, and the energy is not
preserved when moving the source signal across the stereo panorama.
The -6dB option sounds more synthetic. The transition from hard left to
hard right sounds more abrupt than with the -3dB setting.
• When set to Off, no panning is applied.
Random
This parameter allows you to offset the pan position randomly with each played note. Higher values cause stronger variations. At a setting of 100 %, the random offsets
can vary from fully left to fully right.
Alternate
This parameter allows you to alternate the pan position
each time you play a note. If you want to start panning on
the left, use negative values. Use positive values to begin
on the right. At a setting of +100
%, the first note plays
hard right, the second note hard left, and so on.
Reset
The initial pan position is set once when HALion is loaded.
Then, HALion counts each note you play to determine the
next pan position. To reset this counter, click the Reset
button next to the Alternate control.
Key Follow
Here you can adjust the pan modulation via the MIDI note
number. Set this parameter to positive values to offset the
pan position towards the right for notes above and to
wards the left for notes below the center key. Use negative values to offset the pan position towards the left for
notes above and towards the right for notes below the
center key. At the maximum setting of +200
%, the pan
position moves from hard left to hard right within two octaves: Fully left is reached one octave below and fully right
is reached one octave above the center key.
Center Key
This parameter determines the MIDI note that is used as
the central position for the Key Follow function.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
84
Page 85

The AUX Tab
The AUX tab allows you to send the zone to the four
global AUX busses and to directly route the zone to one of
the plug-in output busses.
AUX 1-4
In HALion, you can send the zone signal to the four global
AUX busses. You can control the signal level that is sent
to the busses with the knobs AUX 1-4.
Output
HALion allows you to route a zone directly to one of the
output busses. In this case, the zone does not pass
through the layer, program and slot busses.
The Envelope Section
The Envelope section for synth and sample zones gives
you access to the four envelopes of the zone: Amp, Filter,
Pitch, and User. Each of these is a multisegment envelope
with up to 128 nodes. The Amp, Filter and Pitch envelopes
are pre-assigned to the amplitude, the filter cutoff fre
quency and the pitch of the zone. You can adjust the preassigned modulations in the corresponding sections of the
zone. The purpose of the User envelope is freely definable.
• Click the Amp button to display the parameters of the
amplifier envelope.
The amplifier envelope shapes the volume over time.
-
• Click the Pitch button to display the parameters of the
pitch envelope.
The pitch envelope modulates the pitch over time. The pitch envelope is
bipolar, which means it allows for negative and positive values to bend
the pitch.
• Click the User button to display the parameters of the
freely assignable user envelope.
It is bipolar, which means it allows for negative and positive values, for instance, to modulate the pan from left to right.
Zooming and Navigating in the Graphical
Envelope Editor
The vertical axis of the graphical envelope editor displays
the level. The horizontal axis displays the time.
You can zoom in and out in the following ways:
• To zoom in on the horizontal axis, use the “+” button to
the right of the scrollbar below the graphical editor.
• To zoom out, click the “-” button.
• In the timeline, click and drag up or down to zoom in or
out at the current position.
• To zoom to a certain region, hold [Alt]/[Option] and drag
the mouse over the region.
You can navigate to a certain position in the following way:
• Drag the scrollbar to the left or right to scroll the envelope editor.
• Click in an empty space next to the scrollbar to jump to
the corresponding position in the envelope editor.
• Click the triangles to the left and right of the scrollbar to
scroll through the envelope step by step.
• Click the Filter button to display the parameters of the
filter envelope.
The filter envelope controls the cutoff frequency to shape the harmonic
content over time.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
Envelope Zoom Snapshots
Envelope zoom snapshots save the current state of the
graphical envelope editor. For example, by saving two en
velope zoom snapshots, one for the beginning and one for
the end of the envelope, you can conveniently switch between editing the attack and release of the envelope.
85
-
Page 86

Saving and Loading Envelope Zoom Snapshots
To the right of the scrollbar, you can find three numbered
buttons that allow you to save and load envelope zoom
snapshots for the current envelope editor. An envelope
zoom snapshot also includes the zoom factor and scroll
position of the graphical envelope editor. These are re
-
stored when loading the snapshot.
• To save the current state of the graphical envelope editor as snapshot, [Shift]-click one of the numbered buttons
to the right of the scrollbar.
• To load a previously saved envelope zoom snapshot,
click the corresponding button. The button color changes
to green indicating the snapshot is active. Zooming or
scrolling with the graphical envelope editor deactivates
the envelope zoom snapshot.
Adjusting the Time Parameter
The Time parameter specifies the period of time between
two nodes. Depending on the Sync mode, the Time parameter is displayed in milliseconds and seconds, or fractions of beats.
To set the Time parameter, select the nodes you want to
edit, and enter a value in the Time field.
You can also adjust the Time parameter in the graphical
envelope editor, by dragging the nodes left or right, to de
crease or to increase the time span.
• For a higher resolution, hold [Shift] while moving the
nodes.
• Hold [Ctrl]/[Command] while dragging to limit the
movement to the time axis (horizontal positioning only).
-
Editing the Envelope
Each multisegment envelope has up to 128 nodes with
the Time, Level and Curve parameters. The nodes and
their parameters specify the overall shape of the envelope.
You can edit one or multiple nodes in the graphical enve
lope editor or by typing in values.
Selecting Nodes
• You select a node by clicking on it in the graphical editor. Selected nodes turn light blue. The focused node is
indicated by an orange frame. The focused node displays
its parameters in the value fields to the left of the graphical
envelope editor.
• When multiple nodes are selected, you can use the
Node pop-up menu above the value fields to set the focus
to a different node without losing the current selection.
• [Shift]-click on a node to add it to the selection. Selected nodes are edited together.
• You can select multiple nodes by drawing a rectangle
around the nodes with the mouse.
• With a single node selected, use the left or right arrow
key to select the next or previous node. In a multiselection,
the focused node changes and the previous or next node
within the multiselection is focused.
Adjusting the Level Parameter
The Level parameter specifies the amplitude of the envelope at the position set by the Time parameter. The Amp
and Filter envelopes are unipolar. Therefore, the value
range for the level is 0 % to +100 % (positive values only).
The Pitch and User envelopes are bipolar, the value range
for the level is from -100
% to +100 % (negative and pos-
itive values) for these envelopes.
Ö You can change the polarity of the envelopes in the
modulation matrix, for instance, to map the range of the
Amplifier Envelope (unipolar) to Pan (bipolar). However,
the envelopes always display their values with their default
polarity.
To set the Level parameter, select the nodes you want to
edit and enter a value in the Level field.
You can also adjust the Level parameter in the graphical
envelope editor by dragging the selected nodes up or
down, to decrease or increase the levels.
• For a higher resolution, hold [Shift] while moving the
nodes.
• Hold down [Alt]/[Option] while dragging to limit the
movement to the level axis (vertical positioning only).
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
86
Page 87

Adjusting the Curve Parameter
The Curve parameter allows you to adjust the curvature
between two nodes from linear to logarithmic or exponential behavior.
To set the Curve parameter, select the nodes you want to
edit and enter a value in the Curve field. Positive curve values change the curvature towards logarithmic and negative values towards exponential behavior.
You can also adjust the Curve parameter in the graphical
envelope editor by dragging the curvature of an envelope
segment.
• [Ctrl]/[Command]-click a curvature to reset it to linear.
Adding and Removing Nodes
The envelopes Amp, Filter, Pitch, and User can have up to
128 nodes. All nodes added after the sustain node always
affect the release stage of the envelope.
• To add a node, double-click at the position where you
want to add the node.
• To remove a node, double-click it.
• To delete several selected notes, press [Delete] or
[Backspace].
Ö You cannot remove the first, the last or the sustain
node.
Adding Nodes Using the Fill Function
The Fill function allows you to add multiple envelope
nodes after the selected nodes:
1. On the pop-up menu to the right of the Fill button, select the number of nodes you want to add.
2. In the graphical envelope editor, select the node after
which you want to add nodes. If several nodes are se
lected, the new nodes are inserted after all selected
nodes.
3. If the Fixed function is deactivated, the added nodes
are placed with the interval specified by the Time parame
ter of the selected node. If multiple nodes are selected,
the interval is specified by the focused node.
By activating Sync, you can specify the interval with the Sync note value.
For example, if 1/4 is selected, new nodes are added at exact quarter
note intervals.
4. If the Fixed function is activated, the added nodes fill
the space between the last selected node and the following one.
5. Click the “Fill” button.
The nodes are added.
Fixed
When Fixed is activated, only the selected nodes are
moved on the time axis. With Fixed deactivated, nodes
that follow the currently edited nodes are also moved on
the time axis.
Snap
You can select a second envelope to be displayed in the
background of the edited envelope. Nodes you position
with Snap activated snap to the nodes of the envelope
that is shown in the background.
• You select the envelope to be displayed in the background from the pop-up menu to the right of the Snap
button.
Using Sync
You can synchronize the envelopes to the tempo of your
host application. This allows you to set envelope times
that relate to musical time intervals (for example 1 bar),
regardless of tempo changes made later on.
1. Click Sync to activate sync mode for the envelope.
Sync is active when the button is highlighted. A grid spaced in fractions
of beats appears in the graphical envelope editor.
2. On the pop-up menu located to the right of the Sync
button, select a note value.
This sets the resolution of the grid. For example, if you specify a 1/4 note
value, the nodes snap to 1/4 note steps. If the “T” button is activated, the
note values correspond to triplet values.
You can also manually enter note values and triplets in the
value field.
• The Time field of a node displays times in fractions of
beats. The fraction is always reduced to the smallest pos
sible value. “2/16” is displayed as “1/8”, for example.
• Envelope nodes that do not exactly match a note value
display the closest note value.
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
87
Page 88

• Nodes that exactly match a note value are indicated by a
red dot inside the handle of the node. This can be useful,
for example, when you switch the grid between triplets
and normal note values: The triplet nodes still indicate that
they match a note value, even if the grid shows normal
note values.
Selecting an Envelope Mode
You can select one of four envelope modes to specify
how the envelope is played back each time you hit a key.
These modes are selected from the Mode pop-up menu.
The following options are available:
• Sustain: The envelope starts playback from the first
node to its sustain. The sustain level is held as long as you
play the note. When you release the note, the envelope
continues with the stages behind the sustain. This mode is
ideal for looped samples.
• Loop: The envelope starts playback from the first node
to the loop nodes. The loop is repeated for as long as the
key is held. The envelope plays the stages behind the sustain when you release the note. This mode is ideal for adding motion to the sustain.
• One Shot: The envelope is played from the first to the
last node, even if you release the key. The envelope has no
sustain. This mode is ideal for drum samples.
• Sample Loop: This mode allows you to preserve the
natural attack of the sample. The decay of the envelope
does not start until the sample has reached the sample
loop start. Set the second node to the maximum level.
Then, use any of the following nodes to shape the decay
during the loop phase of the sample. This way, the enve
lope only affects the level during the loop phase of the
sample. The attack of the envelope is still executed.
Ö The Sample Loop mode is only available for sample
zones.
Setting Up the Loop
You can set up the envelope to repeat its playback between the nodes you select. Proceed as follows:
1. Set the envelope mode to Loop.
2. Adjust the loop with the graphical envelope editor.
• The loop is indicated by the green region in the graphi-
cal envelope editor. You can specify the loop start and
end by dragging the borders of the region.
Ö The loop region can only be set up in the decay of the
envelope.
Level Velocity Curve
You can select the curve type to specify how the incoming
velocity translates to the level of the envelope. The characteristic of each curve is displayed by a small icon.
Level Velocity (Vel>Lev)
Use this parameter to specify how the velocity affects the
level of the envelope. The level depends on this parameter
and how hard you hit a key. Positive values increase and
negative values decrease the level of the envelope the
harder you hit a key.
Norm
The Norm option allows you to normalize the velocity val-
ues that are used to control the envelope. This option is
also available in the Filter section, see
“Norm” on page 83.
Time Velocity (Vel>Time)
Use this parameter to adjust the influence of velocity on
the times of the envelope. Positive values decrease the
times for higher velocity values. Negative values increase
the times for higher velocity values.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
88
Page 89

Segments
On the Segments pop-up menu, you can select which
stages of the envelope are affected by the Time Velocity
parameter.
Option Description
A The velocity affects the attack time only.
A+D The velocity affects all times until the sustain.
D The velocity affects all times until the sustain but without
A+R The velocity affects the attack and the release times.
All The velocity affects all times.
the attack.
Key Follow and KeyF Rel
With Key Follow and KeyF Rel (Key Follow Release) you
can scale the envelope times across the keyboard. Key
Follow scales all times before the sustain node. KeyF Rel
scales all times after the sustain node (which equals the
release of the envelope). You can set a center key that is
used as the central position for the Key Follow and KeyF
Rel functions. The envelope times depend on the position
where you play the keyboard and on the corresponding
Key Follow setting. Positive values decrease the times for
notes above and increase the times for notes below the
center key; the envelope becomes faster the higher you
play. Negative values increase the times for notes above
and decrease the times for notes below the center key;
the envelope becomes slower the higher you play.
Center Key
This parameter determines the MIDI note that is used as
the central position for the Key Follow and KeyF Rel
functions.
The LFO Section
The synth and sample zones offer two polyphonic LFOs.
Polyphonic means the LFOs are calculated per voice al
lowing for independent modulations with each triggered
note. You can use this to create a richer sound, for example, with an independent pitch modulation per note. The
LFOs can be assigned freely in the modulation matrix and
they have an additional envelope that allows you to shape
the modulation intensity over time.
You can also configure monophonic LFOs using a MIDI
Module, see
“Mono LFO” on page 147.
• To access the LFOs, click the corresponding button at
the top of the LFO section.
LFO Waveform and Shape
Waveform selects the basic type of waveform. Shape
changes the characteristic of the waveform.
Option Description
Sine This produces smooth modulation, suitable for vibrato
Triangle This is similar to Sine. Shape continuously changes the
Saw This produces a ramp cycle. Shape continuously
Pulse This produces stepped modulation, where the modula-
Ramp This is similar to the Saw waveform. Shape increasingly
Log Shape continuously changes the logarithmic curvature
or tremolo. Shape adds additional harmonics to the
waveform.
triangle waveform to a trapezoid.
changes the waveform from ramp down to triangle to
ramp up.
tion switches abruptly between two values. Shape continuously changes the ratio between the high and low
state of the waveform. With Shape set to 50
square wave is produced.
puts silence before the sawtooth ramp up begins.
from negative to positive.
-
%, a
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
89
Page 90

Option Description
S & H 1 This produces randomly stepped modulation, where
S & H 2 This is similar to S & H 1. The steps alternate between
each step is different. Shape puts ramps between the
steps and changes the S&H into a smooth random sig
nal when fully turned right.
random high and low values. Shape puts ramps be
tween the steps and changes the S & H into a smooth
random signal when fully turned right.
-
Delay
Delay determines the delay time between the moment you
play a note and the moment the LFO comes into effect.
-
Fade In
Fade In determines how long the LFO takes to fade in after the note was triggered and the delay time has elapsed.
Sync Mode
You can sync the LFO to the tempo of the host application. The behavior of the Frequency parameter changes
with the selected option:
Option Description
Off Select this to adjust the speed of the modulation in
Tempo +
Retrig
Tempo + Beat Select this to adjust the speed of the modulation in
Hertz.
Select this to adjust the speed of the modulation in
fractions of beats. You can also set dotted and triplet
note values. The restart behavior of the LFO depends
on the Retrigger Mode.
fractions of beats. You can also set dotted and triplet
note values. The LFO restarts with the transport of the
host and lines up to the beats of the song. The Retrig
ger setting is not taken into account.
-
Retrigger Mode
This defines whether the LFO is restarted when a note is
triggered. The waveform restarts at the position you specify with the Phase parameter.
The polyphonic LFOs can switch between Retrigger On
and Off: When it is off, the LFO runs freely, when set to
On, the LFO starts with each triggered note.
Frequency
This controls the frequency of the modulation, that is the
speed of the LFO. When Sync is activated, the frequency
is set in fractions of beats.
Phase
This sets the initial phase of the waveform when the LFO
is retriggered.
Rnd (Random)
When this is activated, each note starts with a randomized
start phase. The Phase control is automatically disabled.
Hold
Hold determines the amount of time the LFO is running
before the fade out begins.
Use the envelope modes “One Shot” or “Hold + Fade
Out” to activate the Hold time. With all other envelope
modes, the Hold time is omitted and acts as Sustain.
Fade Out
Fade Out determines how long the LFO takes to fade out
after the hold time has elapsed or a note has been released.
Use the envelope modes “One Shot + Sustain” or “Sustain” to deactivate the fade out. This prevents changes of
the modulation when the note has been released.
Inv (Invert Envelope)
When the Inv option is activated, the behavior of the LFO
envelope is inverted. The LFO modulation starts at its
maximum level and decreases to zero in the time specified
by the Fade In. After the Hold time has elapsed, or when
the key is released, the modulation increases to its maxi
-
mum level in the time specified by the fade out.
Envelope Mode
Here, you can specify how the LFO envelope reacts to
your playing on the keyboard. The One Shot modes do not
react to note-off events. In addition, you can select
whether the Hold and Fade Out segments act as sustain.
Option Description
One Shot Select this mode to play the envelope from start to end
One Shot +
Sustain
in the time specified by Delay, Fade In, Hold, and Fade
Out.
This mode is similar to One Shot. The Delay and Fade
In parameters are always applied when you play a note.
The Hold and Fade Out parameters are not taken into
account. Instead, they act as sustain.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
90
Page 91

Option Description
Hold +
Fade Out
Sustain +
Fade Out
Sustain When you play a note, the Delay and Fade In parame-
When you play a note, the Delay and Fade In parameters are applied. The envelope fades out after the time
specified by the Hold parameter, or when a key is re
leased. Releasing a key during the fade in starts the
fade out from the current level.
When you play a note, the Delay and Fade In parameters are applied. The Hold parameter acts as sustain.
The fade out is applied when releasing the key. Releas
ing a key during the fade in starts the fade out from the
current level.
ters are applied. Both the Hold and Fade Out parameters act as sustain. Releasing a key during the Fade In
sustains the current level. This prevents a change in
modulation when a key is released.
-
-
Graphical Envelope Editing
You can adjust the times of the envelope in the graphical
editor by dragging nodes left or right.
• The first node adjusts the Delay time.
• The second node adjusts the Fade In time.
• The third node adjusts the Hold time.
• The fourth node adjusts the Fade Out time.
The Step Modulator Section
Synth and sample zones feature a polyphonic step modulator for creating rhythmic control sequences. The step
modulator can be freely assigned in the modulation matrix.
The sequence can have up to 32 steps.
At the top right of the Step Modulator section, you can
load and save presets for the step modulator.
• To adjust all steps at once, [Shift]-drag a step.
• To reset a step to a level of 0 %, [Ctrl]/[Command]-click
the step.
• To reset all steps, [Shift]-[Ctrl]/[Command]-click in the
graphical editor.
• To draw a ramp with steps, [Alt]/[Option]-click and draw
a line.
• To draw symmetric ramps, [Shift]-[Alt]/[Option]-click
and draw a line.
• You can also enter a value directly in the value field for
the step.
• To increment or decrement the selected step, use the
up and down arrow keys.
By default, the increment or decrement is in steps of 1 %. Hold [Shift] to
increment or decrement the selected step in steps of 0.1
%.
Steps
Here you set the number of steps the sequence plays.
Sync Mode
You can synchronize the steps to the tempo of the host
application by setting a note value. Alternatively, you can
specify a frequency at which the sequence repeats.
Whether you can set a note value or a frequency depends
on the option you select here:
Option Description
Off Select this to adjust the speed at which the sequence
Tempo +
Retrig
Tempo + Beat As above, but the sequence restarts with the transport
repeats (in Hertz). Whether the sequence restarts
when you play a note depends on the Retrigger mode.
Select this to adjust the length of the steps in fractions
of beats. The speed of the modulation depends on the
number of steps, the note value and the tempo you set
in your host application. Activate the T option to use
triplet note values. Whether the sequence restarts
when you play a note depends on the selected Retrigger mode.
of the host and lines up to the beats of the project. The
Retrigger setting is not taken into account.
Editing Steps
To adjust the steps using the mouse, proceed as follows:
• To set the level of a step, click in the graphical editor.
• To change the value of a single step, drag it up/down.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
Frequency
When Sync mode is set to Off, this controls the speed at
which the sequence is repeated.
91
Page 92

Note
When the Sync mode is set to one of the Tempo settings,
this adjusts the length of the steps in fractions of beats.
You can also select dotted and triplet values.
Triplets
Activate the “T” option to use triplet note values.
Retrigger Mode
Here, you can determine whether the sequence restarts
when you play a note. The Retrigger Mode parameter is
only available when Sync mode is set to Off or “Tempo +
Retrig”. The following parameters are available:
Option Description
Off The sequence is not restarted. Instead, it resumes play-
First Note The sequence restarts when a note is triggered and no
Each Note The sequence restarts each time a note is triggered.
back at the position at which you released the key.
other notes are held.
Slope
Depending on the setting you select here, the step modulator jumps from step to step or creates ramps between
the steps. The following settings are available:
Option Description
None This setting produces hard steps.
Rising Ramps are created only for rising edges.
Falling Ramps are created only for falling edges.
All Ramps are created for all edges.
Amount
When Slope is set to Rising, Falling or All, the Amount
parameter
determines the time of the ramp between two
steps. The higher the setting, the smoother the transitions
between steps.
Step
Use this to select a certain step.
Level
This shows the level of the selected step.
Snap
When Snap is activated, the level of each step can only be
adjusted in quantized steps of 1/12th.
Producing Modulations in Steps of Semitones
Proceed as follows:
1. Activate the Snap option.
2. In the modulation matrix, assign the Step Modulator to
Pitch.
3. Set the Modulation Depth to +12.
Now, the levels of the steps represent semitone intervals.
4. Go back to the step modulator and adjust each step
to the interval that you want to use.
The Modulation Matrix Section
The concept of controlling one parameter by another is
called modulation. The Modulation Matrix section of synth
and sample zones gives you access to additional modulations of the zone.
Assigning modulations means to interconnect modulation
sources, such as LFOs and envelopes, with modulation
destinations like pitch, cutoff, amplitude, etc. The modula
tion matrix offers you up to 32 freely assignable modulations, each with a source, a modifier and a destination with
adjustable depth. All modulation sources and destinations
can be assigned several times. The polarity of each source
can be switched between unipolar and bipolar. An addi
tional modifier and user-definable curves and ranges give
you further control over the modulation.
-
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
92
Page 93

The modulation matrix is divided into two sections. On the
left, the modulation rows are displayed. Here, you can assign modulation sources to destinations and adjust the
modulation depth. The section on the right contains settings for the curve and range editor, where you can make
further settings for the selected modulation source.
• To remove a modulation row, select “Remove Modulation Row” from the context menu.
An empty modulation row is appended to the list to keep a constant
number of 32 rows.
Ö You can copy modulation rows across different programs or even between different instances of HALion.
Using the Modulation Rows
The modulation rows allow you to interconnect modulation
sources with modulation destinations and to adjust the
modulation depth.
• The parameters for setting up a modulation can be accessed via 32 rows. Each row is identified by a number.
• You can select modulation sources on the Source 1
pop-up menu at the top left of each row.
• The Source 2 pop-up menu below the Source 1 popup menu for each row allows you to select a second mod
ulation source that controls the intensity of the first source
or a modifier that alters the modulation signal of the first
source.
• To switch the polarity of a source between unipolar and
bipolar, click the button to the right of the corresponding
source.
• To select the modulation destination, use the pop-up
menu to the right.
• Use the horizontal fader below the destination to adjust
the modulation depth. Usually, the modulation depth is adjusted in percent. If you select pitch as modulation destination, the modulation depth is adjusted in semitones.
• Click the Bypass button in front of the depth control to
switch off the modulation temporarily.
Managing Modulation Rows
To copy a modulation row, proceed as follows:
1. On the context menu for the source row, select “Copy
Modulation Row”.´
To move a modulation row, select “Cut Modulation Row” for the source
row.
2. On the context menu for the target row, select “Paste
Modulation Row”.
• To insert an empty row, select “Insert Modulation Row”
from the context menu.
Unipolar vs. Bipolar Sources
The polarity of a modulation source specifies the value
range it produces.
• Unipolar sources modulate between 0 and +1.
• Bipolar sources modulate between -1 and +1.
By default, some sources are unipolar and others are bipolar. However, you can change the polarity of a modulation source at any time.
• To change the polarity of a source, click the button to
the right of the corresponding source.
Using the Curve and Range Editor
You can set up a curve and range for each modulation
source.
• The curve and range editor displays the settings of the
selected source. To adjust the settings of a different
source, click the button to the left of the source you want
to edit.
• The curve editor allows you to change the characteristic
of a modulation. The displayed curve is superimposed on
the modulation source.
This way, you can change the modulation from linear to exponential or
logarithmic, for example.
• By setting the minimum and maximum values, the modulation stays within the specified range only. In addition,
you can specify an offset and a range for the modulation.
For example, with an offset and range of +50 %, only the second half of
the displayed curve is superimposed on the modulation.
The curve editor offers different presets that you can select from the pop-up menu above the curve. To set up
your own curve, select the Custom preset.
• Double-click in the editor to insert a new node.
Double-click on a node to delete it.
• Drag the nodes to new positions to adjust the basic
shape of the curve.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
93
Page 94

• Drag the lines between the nodes up or down to
change the curvature.
Setting Up a Modulation
Proceed as follows:
1. Select the zone that you want to adjust.
2. Open the Modulation Matrix section.
3. In one of the modulation rows, select a modulation
source and destination (for example LFO1 as source and
Pitch as destination).
4. Use the horizontal fader below the destination to adjust the modulation depth.
5. Play a few notes to hear the modulation.
6. You can select a modifier or change the polarity of the
source.
For example, from the “Source 2” pop-up menu, select Pitch Bend as the
modifier and set its polarity to unipolar.
7. Play a few notes to hear the modulation and use the
pitchbend wheel.
8. Finally, use the curve and range editor to limit the modulation range or to adjust the characteristic of the modulation.
Modulation Sources
The modulation sources are available from the Source and
Modifier pop-up menus. HALion offers you the following
modulation sources:
Option Description
LFO P1 The first LFO of the zone, which produces cyclic mod-
LFO P2 The second LFO of the zone, which produces cyclic
Amp Envelope The amplifier envelope of the zone (unipolar). The
Filter Envelope The filter envelope of the zone (unipolar). The shape of
Pitch Envelope The pitch envelope of the zone (bipolar). The shape of
User Envelope The user envelope of the zone (bipolar). The shape of
Step
Modulator
Glide The glide signal of the source (unipolar).
ulation signals.
modulation signals.
shape of the envelope equals the modulation signal.
the envelope equals the modulation signal.
the envelope equals the modulation signal.
the envelope equals the modulation signal.
The step modulator of the zone (bipolar). This produces
cyclic, rhythmically stepped modulation signals.
Option Description
Key Follow This produces an exponential modulation signal derived
Note-on Vel Note-on velocity (how fast you hit a key) can be used
Note-on Vel
Squared
Note-on Vel
Normalized
Note-off Vel Note-off velocity (how fast you released a key) can be
Pitchbend The position of the pitchbend wheel can be used as a
Modulation
Wheel
Aftertouch Aftertouch (how hard you keep a key pressed after you
MIDI Controller Any of the 127 available MIDI controllers can be used
Quick Control The quick controls of the program or layer the zone be-
Note
Expression
Noise Produces a random modulation signal. Noise is bipolar.
Output The audio output of the zone can be used as a modula-
Bus 1-16 Modulations that have been sent to one of the sixteen
from the MIDI note number. Exponential means this
source works with destinations such as Pitch or Cutoff.
Key follow is bipolar.
as a modulation signal. Note-on Vel is unipolar.
The squared version of Note-on Vel. Squared means
you have to press the key harder to produce higher
modulation values.
The note-on velocity is normalized via the velocity range
of the corresponding zone. At the lowest velocity of the
zone the modulation is 0, at the highest velocity it is 1.
used as a modulation signal. Note-off Vel is unipolar.
While most of the MIDI keyboards cannot send note-off
velocity messages, most sequencer software is able to
produce such messages.
modulation signal. Pitchbend is bipolar.
The position of the modulation wheel can be used as a
modulation signal. Modulation Wheel is unipolar.
hit it) can be used as a modulation signal. Aftertouch is
unipolar. Some MIDI keyboards cannot send aftertouch
messages. However, most sequencer software is able
to produce such messages.
as a modulation signal. You can select the MIDI con
troller from the corresponding submenu.
longs to can be used as a modulation signal. You can
select the quick control from the corresponding sub
menu.
The eight note expression parameters of the program
can be used as modulation signals for the zone. You
can select the note expression parameter from the cor
responding submenu.
tion signal. Output is unipolar.
busses can be used as sources again. This way, you
can combine several modulations to produce more
complex signals. Select the corresponding modulation
bus to assign it as source.
-
-
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
94
Page 95

Modulation Destinations
Depending on the selected type of zone, the available
modulation destinations vary. HALion offers you the following modulation destinations:
Option Description
Pitch Modulates the pitch of the zone. For example, assign
Cutoff Modulates the filter cutoff of the zone. For example, as-
Resonance Modulates the filter resonance of the zone. Resonance
Morph X Modulates the x-axis of the filter in Morph XY mode. Use
Morph Y Modulates the y-axis of the filter in Morph 2, Morph 4,
Cutoff Offset Modulates the cutoff offset of the second filter in serial
Resonance
Offset
Pan Modulates the position of the zone in the panorama.
Level This modulation adds to the level setting of the zone. It
Volume 1 This modulates the gain of the zone. The volume modu-
Volume 2 As Volume 1. Volume 1 is multiplied with volume 2. This
LFO1
Frequency
LFO1 Shape Modulates the waveform of LFO1. For example, assign
LFO2
Frequency
LFO2 Shape Same as LFO1 Shape, but for LFO2.
Step Mod
Frequency
one of the LFOs to create a vibrato effect. When Pitch
is selected, the modulation depth adjusts in semitones
(-60 to +60).
sign the step modulator to create rhythmic patterns in
the spectral timbre.
changes the character of the filter. For example, assign
velocity to resonance to accent the filter the harder you
hit a key.
this to morph between the filter shapes AD and BC.
or Morph XY mode. For example, use this to morph be
tween the filter shapes AB and DC.
or parallel mode. For example, assign the modulation
wheel to lower or raise the cutoff of the second filter
while you play.
Modulates the resonance offset of the second filter in
serial or parallel mode. For example, assign the modula
tion wheel to lower or raise the resonance of the second filter while you play.
is ideal for effects such as tremolo.
lation multiplies with the level of the zone. It is ideal for
crossfades between zones.
way, you can build more complex modulations. For ex
ample, use Volume 1 for crossfading between zones
and Volume 2 for fading them in or out.
Modulates the speed of LFO1. For example, assign Aftertouch to control the speed of a vibrato effect while
you play.
Key Follow to vary the waveform with the playing posi
tion on the keyboard.
Same as LFO1 Freq, but for LFO2.
Modulates the speed of the step modulator. For example, assign an LFO to increase or decrease the speed
cyclically.
Option Description
Step Mod
Slope
Amp Env
Attack Time
Amp Env
Decay Time
Amp Env
Sustain Level
Amp Env
Release Time
Filter Env
-
Attack Time
Filter Env
Decay Time
-
Filter Env
Sustain Level
Filter Env
Release Time
Pitch Env
Attack Time
Pitch Env
Decay Time
Pitch Env
Sustain Level
Pitch Env
Release Time
User Env
Attack Time
Modulates the shape of the edges of the step modulator (the Slope parameter has to be active). For example,
assign the modulation wheel to blend from hard to
smooth edges.
Modulates the time of the amplitude envelope attack
(the first segment of the envelope). The attack time
cannot be modulated continuously. The time is updated
only when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the amplitude envelope decay
(all segments after the attack and before the sustain).
The decay time cannot be modulated continuously. The
time is updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the level of the amplitude envelope sustain.
The sustain level cannot be modulated continuously.
The level is updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the amplitude envelope release
(all segments after the sustain). The release time can
not be modulated continuously. The time is updated
only when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the filter envelope attack (the first
segment of the envelope). The attack time cannot be
modulated continuously. The time is updated only when
the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the filter envelope decay (all segments after the attack and before the sustain). The decay time cannot be modulated continuously. The time is
updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the level of the filter envelope sustain. The
sustain level cannot be modulated continuously. The
level is updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the filter envelope release (all
segments after the sustain). The release time cannot be
modulated continuously. The time is updated only when
the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the pitch envelope attack (the
first segment of the envelope). The attack time cannot
be modulated continuously. The time is updated only
when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the pitch envelope decay (all
segments after the attack and before the sustain). The
decay time cannot be modulated continuously. The
time is updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the level of the pitch envelope sustain. The
sustain level cannot be modulated continuously. The
level is updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the pitch envelope release (all
segments after the sustain). The release time cannot be
modulated continuously. The time is updated only when
the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the user envelope attack (the first
segment of the envelope). The attack time cannot be
modulated continuously. The time is updated only when
the segment starts.
-
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
95
Page 96

Option Description
User Env
Decay Time
User Env
Sustain Level
User Env
Release Time
Bus 1-16 You can send any modulation to one of the sixteen bus-
Modulates the time of the user envelope decay (all segments after the attack and before the sustain). The decay time cannot be modulated continuously. The time is
updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the level of the user envelope sustain. The
sustain level cannot be modulated continuously. The
level is updated only when the segment starts.
Modulates the time of the user envelope release (all
segments after the sustain). The release time cannot be
modulated continuously. The time is updated only when
the segment starts.
ses, for example, to produce more complex modulation
signals. Select the bus you want to send the signals to
as a destination. To use the modulation that was sent to
a bus, assign the corresponding bus as a modulation
source.
The following destination is only available for sample
zones:
Option Description
Sample Start Modulates the start position of the sample play-
back. For example, assign note-on velocity to play
back more of the attack of a sample the harder you
hit a key. The sample start cannot be modulated
continuously. The parameter is updated only when
you hit a key.
Sample & Hold
The Sample & Hold modifier takes a sample of the modulation source whenever it receives a trigger signal. It holds
the sampled value until it receives a new trigger. This way,
you can quantize a continuous modulation signal. The
Sample & Hold modifier offers the following options:
Option Description
Trigger on
Note On
Trigger on
LFO1
Trigger on
LFO2
Trigger on
Modulation
Wheel
Trigger on
Sustain
Sample until
Release
Select this to trigger the Sample & Hold modifier manually. Each time you hit a key, the modifier takes a sample.
Select this for periodic triggering of the Sample & Hold
modifier. It takes a sample each time the waveform of
LFO1 crosses the zero line upwards.
Select this for periodic triggering of the Sample & Hold
modifier. It takes a sample each time the waveform of
LFO2 crosses the zero line upwards.
Select this to trigger the Sample & Hold modifier manually. It takes a sample each time the modulation wheel
passes the center position.
Select this to trigger the Sample & Hold modifier manually. Each time you press the sustain pedal, the Sample & Hold modifier takes a sample.
Select this to trigger the Sample & Hold modifier
through releasing a key. It constantly takes samples
and holds the last sample when receiving a note-off.
The following destinations are only available for synth
zones:
Option Description
Osc1/2/3 Pitch Modulates the pitch of the corresponding oscillator.
Osc1/2/3 Level Modulates the volume of the corresponding oscilla-
Osc1/2/3
Waveform
Sub Osc Level Modulates the volume of the sub oscillator. For exam-
Ring Mod Level Modulates the volume of the ring modulation effect.
Noise Gen Level Modulates the volume of the noise generator. For ex-
For example, assign one of the LFOs to detune the
oscillator cyclically.
tor. For example, assign the modulation wheel to fade
the oscillator in and out while you play.
Modulates the shape and character of the corresponding oscillator. For example, assign one of the
envelopes to change the character of the oscillator
over time.
ple, assign the modulation wheel to fade in the oscillator while you play.
For example, assign the modulation wheel to fade in
the ring modulation while you play.
ample, assign the modulation wheel to fade in the
noise generator while you play.
Editing Zones in the Sound Editor
Using Global MIDI Controllers
HALion features eight global MIDI controllers (“Contr. A –
Contr. H”), which can be used as placeholders in the
modulation matrix. With these controllers, you can remap
specific MIDI controllers to the placeholder controllers, for
example, from the CC Mapper. This allows you to use the
global controller in several places and set up the assign
ment only once.
96
-
Page 97

11
Mapping Zones
Page 98

Introduction
In HALion, you can edit the sample mapping manually in
the Mapping editor. The Mapping functions are based on
information like key range, root key, and velocity range.
The Mapping Editor
The Mapping editor allows you to view and edit the distribution of zones inside a program. All zones are mapped to
the key range on the horizontal axis and the velocity range
on the vertical axis. In the upper area, you have access to
mapping ranges and sample parameters for the selected
zone.
Zones are displayed as boxes. Selected zones are shown
with a red border, and the focused zone with an orange
border. Overlaying zones are semi transparent, so that
overlapping areas can easily be recognized.
When playing notes on a MIDI keyboard, the Mapping editor shows you which note you play on the Mapping editor
keyboard. Furthermore, you can see the current velocity in
the velocity scale on the left.
The Toolbar
The toolbar at the top of the window shows the name of
the focused zone and a number of editing options for the
mapping.
The Zone Range Section
Below the toolbar, the zone range section is located. Here
you can set the values for Low and High Key, Low and
High Velocity, Root Key, Tune, and Gain of a zone. The
Tune and Gain parameters are only available for sample
zones.
The Mapping Editor Keyboard
The Mapping editor keyboard allows you to see with
which keys a zone can be triggered. It can also be used to
trigger notes. Depending on the vertical position at which
you click the key, it produces a lower or higher velocity.
The context menu for a key contains submenus that show
information on pitch and velocity as well as the zones that
are mapped to a key.
Ö Keys with no zones assigned to them are grayed out.
Testing the Sample Mapping
• [Ctrl]/[Command]-click a key on the Mapping editor
keyboard and keep the mouse button pressed. HALion
plays this key and all following keys at the same velocity,
for as long as you press the mouse button.
• Hold down [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Alt]/[Option] and click a
key to play each zone ten times, at increasing velocities
from 1 to 127.
The Velocity Scale
The velocity scale on the left provides an orientation when
adjusting the velocity range of a zone. In the background
of the scale, a meter indicates the incoming velocity value.
After each note, the meter automatically falls back to zero
and leaves a marker on the last velocity value.
Setting the Focus in a Multi-Selection
When multiple zones are selected, you can click on a zone
to set the focus. Alternatively, you can use the Focused
Zone pop-up menu on the toolbar to select a different
zone.
98
Mapping Zones
Page 99

Zooming and Scrolling
The Mapping editor can zoom and scroll in two dimensions: keyboard and velocity.
• To zoom in or out, click the “+” or “-” button on the
scrollbars.
Once you have zoomed in, you can use the scrollbar to move to a specific velocity or keyboard area.
• To zoom in or out, press [H] or [G] on the computer keyboard.
• To zoom in on a specific zone, double-click it. To zoom
out, double-click again.
• To zoom in on an area where two or more zones are
overlapping, double-click the area. To zoom out, doubleclick again.
• To zoom to the selection, activate the S button next to
the scrollbar.
• To zoom out completely or return to the last zoom state,
click the A button next to the scrollbar.
Automatic Scrolling to a Tree Selection
When “Scroll Position follows Tree Selection” is activated
on the toolbar and you select a zone in the Program Tree,
the Mapping editor automatically scrolls the view to keep
the selection in the center. This works on both the key
-
board and the velocity axes.
Zoom Snapshots
Zoom Snapshots save the current zoom state in the Mapping editor. For example, by saving a snapshot for the
lower and a snapshot for the upper range of the keyboard,
you can switch between editing the two areas.
The snapshot handling is the same as for envelopes, see
“Envelope Zoom Snapshots” on page 85.
Selecting Zones
• Click a zone to select it.
• [Ctrl]/[Command]-click to select several zones.
• Hold down [Ctrl]/[Command] and draw a selection rect-
angle covering the zones that you want to select.
• Press [Ctrl]/[Command]-[A] to select all zones.
• Click on the velocity scale to select all zones that be-
long to a certain velocity.
Moving Zones
Selected zones can be moved in the Mapping editor.
• Click in the middle of one of the zones and drag to move
all the zones together.
To limit the movement to the vertical or horizontal direction, start dragging the zone in one direction and press [Ctrl]/[Command] or [Alt]/[Option], respectively.
When you move sample zones horizontally, they are transposed. To make moved samples play back at the right
pitch again you have to adapt the Root Key setting or acti
vate the “Move Root Key with Zones” button on the toolbar first.
Move Lock
By clicking the Move Lock button on the toolbar, you can
prevent accidental moving or resizing of zones.
Setting Key and Velocity Range
Graphically
To set the key and velocity ranges, move your mouse to one
of the borders of a zone, so that the mouse pointer changes
to a double arrow, and drag. If you drag the left border, you
set the lowest key for the key range, for example.
When you select multiple zones and drag the border of
adjoining zones that are part of the selection, you can adjust the low and high values of the corresponding zones
simultaneously.
Numerically
You can also set the key and velocity range values using
the value fields at the top of the window.
When multiple zones are selected, only the values of the
focused zone are displayed in the edit fields. However,
changing the values affects all selected zones. Like in the
Sound editor for a zone, you can choose between abso
lute and relative editing, see “Absolute and Relative Edit-
ing” on page 75.
-
-
99
Mapping Zones
Page 100

Muting and Soloing Zones
You can mute and solo zones in the Mapping editor using
the context menu.
Showing and Hiding Zones
You can show and hide zones using the Visibility context
menu options.
Auto Visibility
The Auto Visibility option on the Visibility submenu allows
you to control the visibility of zones inside the Mapping
editor. When it is activated, only the selected zone and the
other zones that are part of the same layer are shown.
Fading and Crossfading Zones
Zones in HALion can partially or totally overlap. Fades can
be created in the horizontal (key) and the vertical (velocity)
direction. This allows you to successively add certain
sound components over the key or the velocity range.
To create fades or crossfades, proceed as follows:
1. Select the zones that you want to fade or crossfade.
2. Open the context menu, select the Crossfades sub-
menu, and choose “Enable Crossfades on Keyboard
Axis”, or “Enable Crossfade on Velocity Axis”, or both.
HALion displays the fade handles.
3. Drag the handles to adjust the fade ranges.
Faded regions are shown in green.
Curve Shape
By default, the fade curve is exponential, but you can
change the curvature by dragging the curve up and down.
The maximum curve setting represents an equal power
curve. This is useful for velocity crossfades.
Auto Crossfades
The Crossfade option on the toolbar can be set to Auto
(the icon turns blue). In this mode, the crossfade range is
automatically adjusted when you move overlapping zones.
Symmetric Crossfades
You can create symmetric crossfades for zones that have
an identical key range and an adjacent velocity range.
Proceed as follows:
1. Select the two zones, open the context menu and on
the Crossfades submenu, select “Enable Crossfade on
Velocity Axis”.
The crossfade handles are displayed.
2. On the toolbar of the Mapping editor, set the Crossfade option to Symmetric.
The icon turns yellow.
3. Drag the handles to set up the crossfade.
Setting the Root Key
The root key determines the original pitch of a zone. In
other words, it defines the key on which the zone is played
without being transposed. Samples can contain root key
information embedded in the sample file. When they are
loaded, they are automatically mapped to the correspond
ing keys.
The sample collections included with HALion contain both
multi-sampled instrument programs and single-shot sample programs. The former contains samples of a specific
instrument (usually containing only one sample zone per
key on the keyboard). The latter contain different sample
zones that are mapped across the keyboard, without any
relationship between key and pitch. For multi-sampled in
strument programs, there is no need to change the root
key settings, but for single-shot sample programs, you
might want to move sample zones.
If you have moved sample zones in the Mapping editor,
you can make them play back at the original pitch by setting the root key.
You have the following possibilities:
• Directly enter the value in the Root Key value field.
• Hold [Alt]/[Option] and click the corresponding key on
the Mapping editor keyboard.
When you move a sample zone, you can make the root key
move with the zone by holding [Ctrl]/[Command]-[Alt]/
[Option] while dragging or by activating “Move Root Key
with Zones” on the toolbar.
Triggering Zones
You can trigger zones in the Mapping editor. To activate
trigger mode, click the Trigger Zones button on the toolbar.
-
-
100
Mapping Zones
 Loading...
Loading...