Sony HDV TECHNOLOGY BOOK Operating manual

Contents
worryfreedigital™ video .................................................................... 2
Toward worryfreedigital™ High Definition video............................... 2
Arrival of the HDV™ Standard .......................................................... 2
HDV Advantages............................................................................... 4
HDV Specifications ........................................................................... 6
HDV Compression............................................................................. 7
HDV Recording ................................................................................. 9
HDV Playback ................................................................................... 10
Questions and Answers .................................................................... 12
Appendix 1: Advantages of HDTV .................................................... 16
Appendix 2: HDTV as a Global Movement....................................... 21
Appendix 3: Glossary........................................................................ 24
Confidential
The information contained in this handbook is current as of August 1,2004.
It may not be reproduced for use in catalogs, Web pages, pamphlets, etc.
1

worryfreedigital™ video
Moments worth recording on video take place at any time, which is precisely why Sony®
Handycam® camcorders feature worryfreedigital video. It's never been easier to immortalize
your memories in stunning sight, sound and motion. Intuitive controls, compact design,
unparalleled resolution and amazing innovations seamlessly work together, allowing you to
simply capture life as it happens.
worryfreedigital video makes moviemaking fun again. It's technology Like No Other for
camcorders Like No Other™.
Toward worryfreedigital™ High Definition video
Now Sony is poised to extend the worryfreedigital concept to High Definition moviemaking.
Imagine all the benefits of Sony Handycam® camcorders together with all the amazing
resolution of High Definition. Such a combination is made possible by a new videocassette
recording standard, called HDV™.
Arrival of the HDV Standard
High Definition Television (HDTV) means viewing that's far more real and compelling than
any previous broadcast system. HDTV means greater detail that you can enjoy on a bigger
television screen. HDTV means more beautiful, more vivid color. And HDTV means the
superlative accuracy of digital pictures accompanied by digital surround sound. It's no wonder
that countries all over the world are adopting HDTV standards.
As HDTV becomes accepted in country after country, it is also becoming available through more
and more delivery pipelines:
■ Over-the-air (terrestrial) HDTV broadcasting is bringing the benefits of High Definition to
■ HDTV satellite broadcasting is helping to speed the acceptance of High
HDV TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
■ HDTV cable service can provide a rich range of programming.
■ HDTV personal video recorders (PVRs) let you capture HD programming on a hard disk
■ HD Blu-ray Disc® (BD) recorders enable you to build your own, personal library of High
hundreds of millions of potential viewers.
Definition.
drive for playback at a later time.
Definition content.
2

The conversion to High Definition touches the entire A/V environment.
As the home entertainment system increasingly makes the move to High Definition, the next stage
will be HD personal content creation, with the consumer HD camcorder. That's the idea behind the
HDV™ standard.
On September 30, 2003, the HDV standard was finalized and agreed upon by four companies:
Canon Inc., Sharp Corporation, Sony Corporation, and the Victor Company of Japan, Limited.
The agreement has tremendous implications for consumers the world over.
Thanks to HDV, you can capture weddings, birthdays and family vacations with the exceptional
clarity and impact of High Definition. Thanks to HDV, your memories are more vivid, more
detailed and more like life itself. Thanks to HDV, your home videos are better suited to playback on
big-screen television. And thanks to HDV, home video achieves an entirely new level of quality.
HDV camcorders represent the conversion of personal content to High Definition.
3

HDV Advantages
The HDV™ standard enables consumers to record superb, High Definition imagery onto DV
tape. In this way, HDV camcorders leverage the broad availability of DV recording media—and
the considerable development costs already devoted to DV recording mechanisms. This makes
HDV a practical, affordable alternative for real-world home video.
1. Personal memories in High Definition
At last, the spectacular picture quality of High Definition is no longer limited to Hollywood and
the broadcasting professionals. Thanks to HDV, you can capture the memories of your life with
the gorgeous resolution, lifelike color and vivid contrast of digital High Definition at 1080i and
720p.
2. Digital picture quality
While analog video recording exposes the picture to noise and distortion, digital video recording
maintains low noise, high accuracy and incredibly rich, vivid color. In addition, component digital
recording with separate channels for Y (luminance), B-Y (blue color difference) and R-Y (red
color difference) makes for a wider range of recorded colors.
3. 16:9 widescreen recording
HDV captures images in the same 16:9 widescreen format that is used for High Definition
television. Because this widescreen image is a better match for the human field of vision, it
results in a more lifelike, more immersive experience—closer to the feeling of "being there."
4. Digital sound quality
The HDV format sound tracks use MPEG-1 Audio Layer II digital encoding. In this way, home
videos approach the sound quality Compact Disc, at far lower bitrates.
5. Affordable DV tapes
HDV uses exactly the same cassette tapes that are already popular for DV recording. Even the
recording time is the same. In addition, the tape transport and head drum are identical to those
used in current DV recording systems.
HDV TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
6. MPEG-2 compression
HDV uses the same MPEG-2 compression that is already used for digital broadcasts and DVDs.
The MPEG-2 system is so widely used because it employs "interframe" compression in addition
to the "intraframe" compression employed in DV recording.
4
Using both compression technologies enables HDV to achieve a superb High Definition picture
at the same bitrates as Standard Definition DV. While MPEG decoding appears in a wide range
of consumer products, including all DVD players, MPEG encoding had been too complex for
consumer products until recently. Advances in large-scale integrated circuits (LSIs) and signal
processing technology have now made High Definition MPEG encoding available for consumer
products like HDV camcorders.
7. Powerful error correction
Compared to DV, HDV uses higher compression ratios. This makes HDV more susceptible
to visual impairment when recorded data is missing during playback. For this reason, the
HDV format incorporates greater error correction redundancy and more robust error correction
methods. While the DV correction method operates only within recorded tracks, the HDV method
operates among multiple tracks.The result is a dramatic improvement in error
correction. Even when data is lost, the HDV picture can continue to look sensational.
8. Both 720p and 1080i recording
For added flexibility, the HDV standard embraces two types of High Definition recording.The
1080-line interlace scan (1080i) recording takes advantage of 1440 horizontal pixels per line
(1440 x 1080). The 720-line progressive scan (720p) recording incorporates 1280 horizontal
pixels per scanning line (1280 x 720).
5
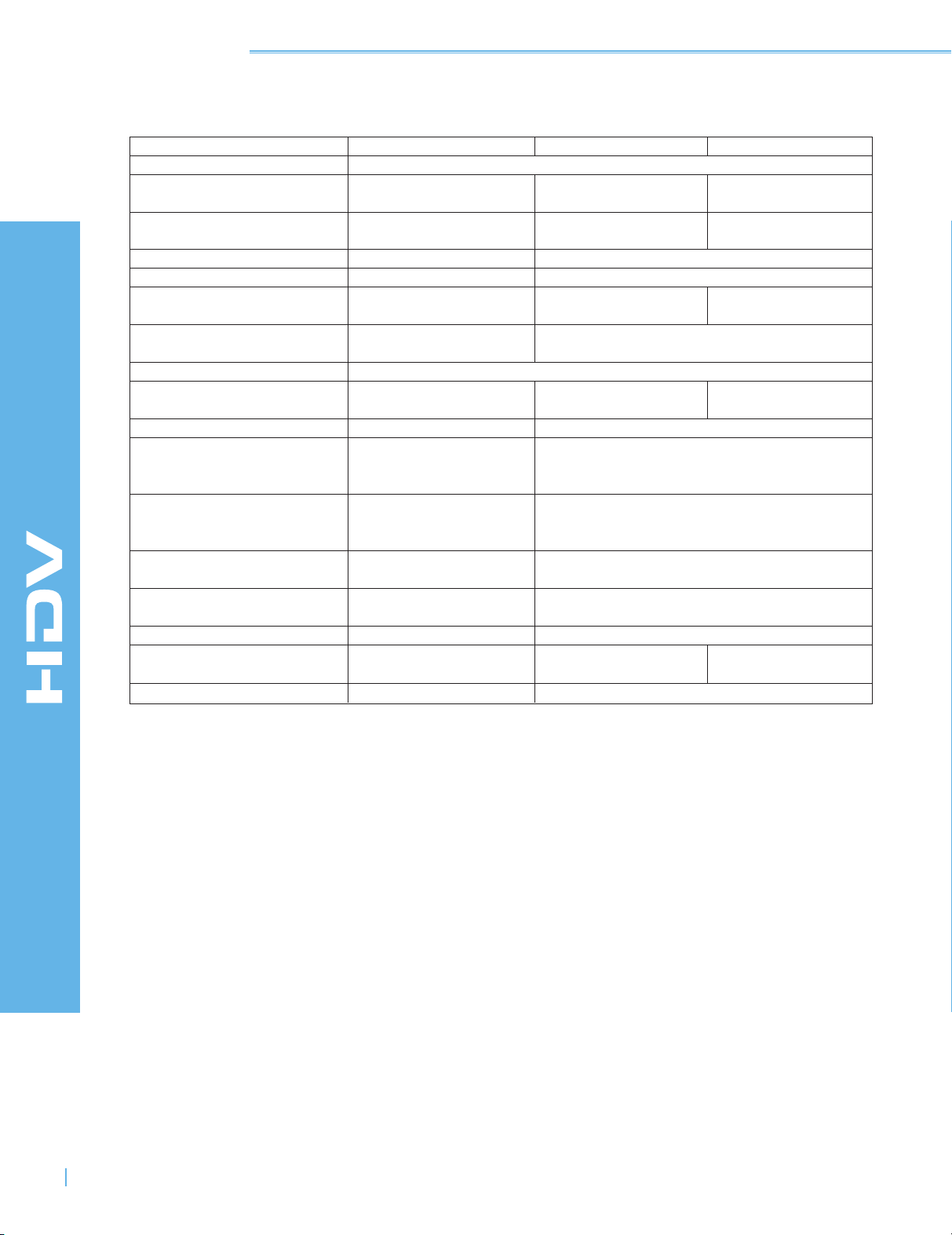
HDV™ Specifications
DV HDV (720p) HDV (1080i)
Media
Video Signal 576/50i (PAL) 720/25p, 720/50p, 1080/50i, 1080/60i
480/60i (NTSC) 720/30p, 720/60p
Number of Pixels 720 x 576 (PAL) 1280 x 720 1440 x 1080
720 x 480 (NTSC)
Aspect Ratio 4:3 (16:9) 16:9
Video Compression DV MPEG-2 Main Profile at High-14 Level
Luminance Sampling 13.5 MHz 74.25 MHz 55.6875 MHz
Frequency
Video sampling Format 4:2:0 (PAL) 4:2:0
4:1:1 (NTSC)
Video quantization 8 bit
Video bitrate after 25 Mbps 19 Mbps 25 Mbps
compression
Audio compression n/a MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
Audio sampling frequency 48 kHz/44.1 kHz (2- 48 kHz
ch. mode)
32 kHz (4-ch. mode)
Audio quantization 16 bit (2-ch. mode) 16 bit
12 bit non-linear (4ch. mode)
Audio bitrate after 1.5 Mbps 384 Mbps
compression
Audio Mode
Data format n/a MPEG-2 system
Stream type n/a Transport Stream Packetized
Stream Interface IEEE 1394 (DV) IEEE 1394 (MPEG-2-TS)
Stereo (2-ch.) Stereo (2-ch.)
Stereo x2 (4-ch.)
DV tape
elementary stream
Aspect Ratio: Ratio of picture width to picture height.
Sampling Frequency: The number of digital samples per second.
Sampling Format: In digital video systems, the frequency ratios of the Y/B-Y/R-Y channels.
HDV TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
Quantization: The number of bits used to express a digital sample. 16-bit quantization
yields 216 or 65,536 possible levels.
Bitrate: The number of bits per second. 1 Mbps equals 1 million bits per second.
Data format: The standard used for audio and video data.
Stream type: The system for combining audio and video data in the MPEG-2 system.
Stream interface: The data transmission standard.
6
HDV Compression
To appreciate the MPEG-2 compression system used for HDV™ technology, it helps to first
consider the simpler, "intraframe" compression system used for DV. The system works because
one pixel of blue sky is almost exactly the same as the next. By encoding only the differences
between pixels—in fact, only the differences you can see—DV compression can cut the data
rate by 80%. That's a 5:1 compression ratio, which reduces an initial bitrate of roughly 124 Mbps
to a recorded bitrate of 25 Mbps after compression.
Intraframe compression works because each pixel of blue sky is
.
almost exactly the same as the one next to it.The system needs to
record only the differences.
Because it records a High Definition signal, HDV must handle far higher initial bitrates. For
example, the 1080/60i HDV signal (1440 x 1080) has 4.5 times as much data as the 480/60i DV
signal used in NTSC countries (720 x 480 pixels).
For this reason, HDV must use a more powerful compression engine: MPEG-2. MPEG-2 starts
with intraframe compression, similar to the DV compression system. But MPEG-2 goes on to
add "interframe" compression. This system works because, in the typical sequence of pictures,
one frame of video is almost exactly the same as the next. By encoding only the differences
between frames, MPEG-2 can achieve another major round of bitrate reduction!
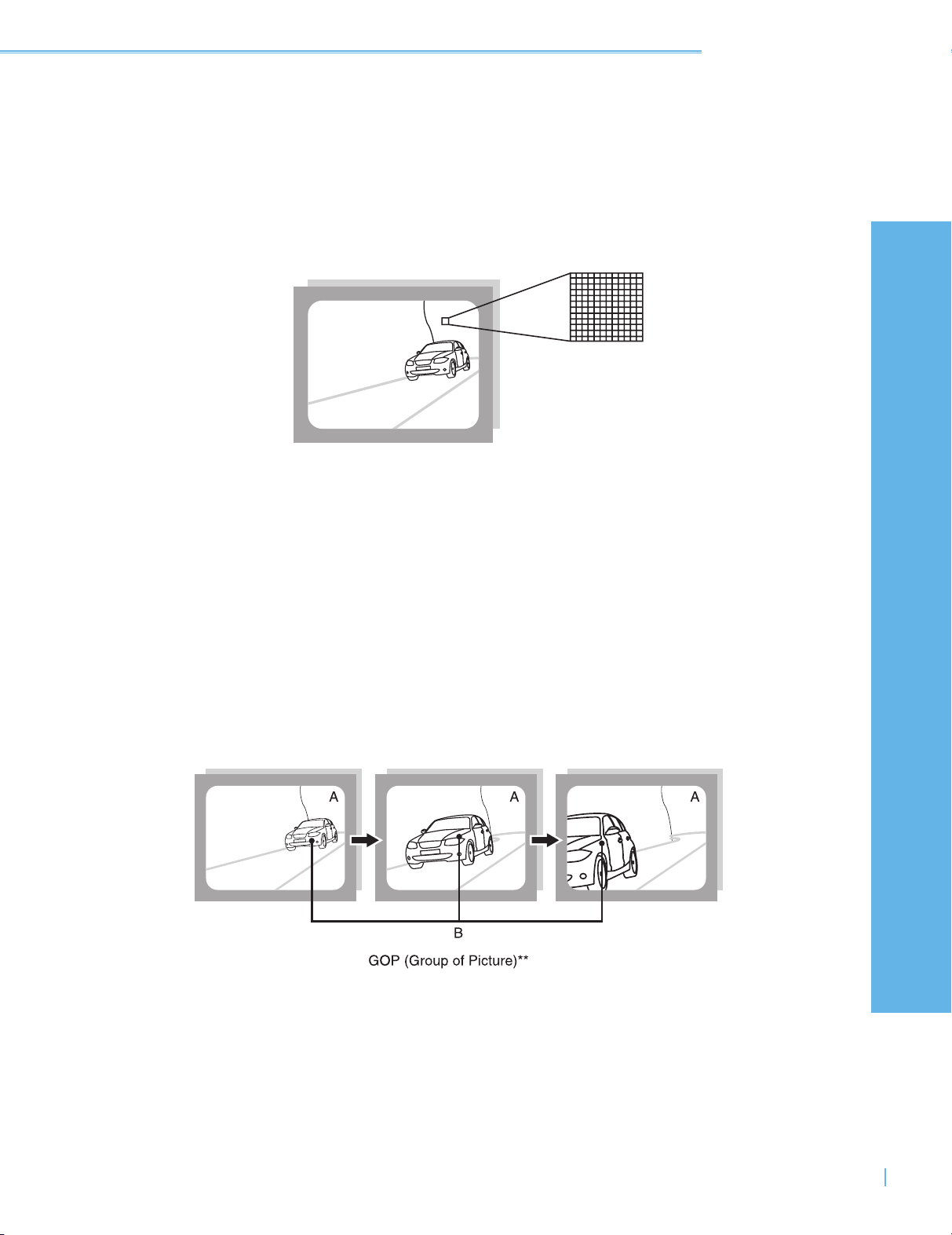
The interframe compression of MPEG-2 works because of the
similarities between most video frames. In this example, the
background "A" stays same while only the car "B" moves. The
system can reduce data by encoding only the differences
between frames rather than the frames themselves.
7
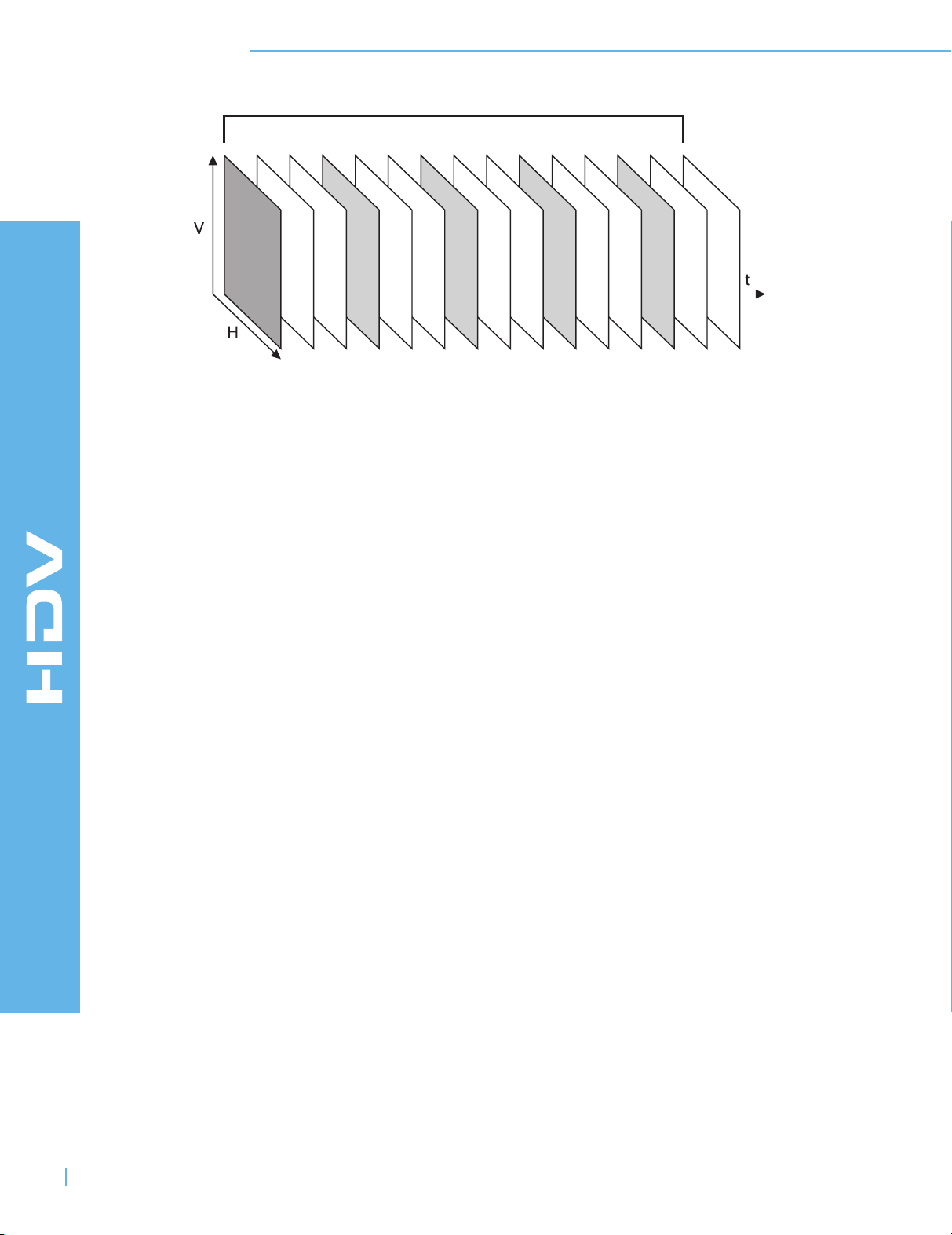
By combining the power of both intraframe and interframe compression, the MPEG-2 system of
HDV is far more efficient than DV compression. In this way, even though HDV encodes a signal
with up to 4.5 times the data of DV, it can achieve comparable quality at the same bitrates as DV.
HDV TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK
MPEG-2 organizes frames into a Group of Pictures or GOP. Each
GOP begins with a fully-described frame (at left). Other frames in
the GOP are described in terms of difference only.
8
 Loading...
Loading...