Page 1

1
AT Command Manual
for
Brodersen Products with Siemens MC55
Modem Engine
V. 04.00 / April 2006 / Doc 40232
Brodersen Controls A/S ● Industrivej 3 ● DK-4000 Roskilde ● Tel: +45 46 74 00 00 ● Fax: +45 46 75 73 36
E-mail: bc@brodersencontrols.com ● Internet: www.brodersencontrols.com
Page 2

Document Name:
Version:
Date:
DocId:
Status
General Notes
Product is deemed accepted by recipient and is provided without interface to recipient’s products. The documentation and/or product are provided for testing, evaluation, integration and information purposes. The documentation and/or product are provided on an “as is” basis only and may contain deficiencies or inadequacies. The
documentation and/or product are provided without warranty of any kind, express or implied. To the maximum
extent permitted by applicable law, Siemens further disclaims all warranties, including without limitation any implied warranties of merchantability, completeness, fitness for a particular purpose and non-infringement of thirdparty rights. The entire risk arising out of the use or performance of the product and documentation remains with
recipient. This product is not intended for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where a malfunction
of the product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Applications incorporating the described
product must be designed to be in accordance with the technical specifications provided in these guidelines. Failure to comply with any of the required procedures can result in malfunctions or serious discrepancies in results.
Furthermore, all safety instructions regarding the use of mobile technical systems, including GSM products,
which also apply to cellular phones must be followed. Siemens or its suppliers shall, regardless of any legal theory upon which the claim is based, not be liable for any consequential, incidental, direct, indirect, punitive or other
damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business interruption,
loss of business information or data, or other pecuniary loss) arising out the use of or inability to use the documentation and/or product, even if Siemens has been advised of the possibility of such damages. The foregoing
limitations of liability shall not apply in case of mandatory liability, e.g. under the German Product Liability Act, in
case of intent, gross negligence, injury of life, body or health, or breach of a condition which goes to the root of
the contract. However, claims for damages arising from a breach of a condition, which goes to the root of the
contract, shall be limited to the foreseeable damage, which is intrinsic to the contract, unless caused by intent or
gross negligence or based on liability for injury of life, body or health. The above provision does not imply a
change on the burden of proof to the detriment of the recipient. Subject to change without notice at any time. The
interpretation of this general note shall be governed and construed according to German law without reference
to any other substantive law.
MC55 AT Command Set
04.00
March 17, 2006
MC55_ATC_V04.00
Confidential / Released
Copyright
Transmittal, reproduction, dissemination and/or editing of this document as well as utilization of its contents and
communication thereof to others without express authorization are prohibited. Offenders will be held liable for
payment of damages. All rights created by patent grant or registration of a utility model or design patent are reserved.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2006
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 2 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 3

Contents
1. Introduction............................................................................................................................................ 13
1.1 Scope of the document ................................................................................................................. 13
1.2 Related documents ....................................................................................................................... 14
1.3 Document conventions.................................................................................................................. 15
1.3.1 Quick reference table..................................................................................................... 15
1.3.2 Superscript notation for parameters and values ............................................................ 16
1.4 AT Command Syntax .................................................................................................................... 17
1.4.1 Using Parameters .......................................................................................................... 17
1.4.2 Combining AT commands on the same command line ................................................. 18
1.5 Supported character sets .............................................................................................................. 19
1.5.1 GSM alphabet tables and UCS2 character values ........................................................ 21
1.5.2 UCS2 and GSM data coding and conversion for SMS text mode ................................. 23
1.5.2.1 Implementing output of SIM data to Terminal (direction TA to TE) ................................ 23
1.5.2.2 Implementing input of Terminal data to SIM (direction TE to TA)................................... 24
1.6 Serial Interface Flow Control ......................................................................................................... 25
1.6.1 Software Flow Control (XON/OFF Handshake)............................................................. 25
1.6.2 Hardware Flow Control (RTS/CTS Handshake) ............................................................ 25
1.7 Unsolicited Result Code Presentation........................................................................................... 26
1.7.1 Communication between Customer Application and MC55 .......................................... 26
1.8 Common PCN Handset Specification (CPHS) .............................................................................. 27
1.9 Errors and Messages .................................................................................................................... 28
2. Configuration Commands..................................................................................................................... 29
2.1 AT&F Set all current parameters to manufacturer defaults ......................................................... 29
2.2 AT&V Display current configuration ............................................................................................30
2.2.1 AT&V responses............................................................................................................ 31
2.3 AT&W Stores current configuration to user defined profile ......................................................... 32
2.4 ATQ Set result code presentation mode ..................................................................................... 33
2.5 ATV Set result code format mode ...............................................................................................34
2.5.1 Verbose and numeric result codes ................................................................................ 34
2.6 ATX Set CONNECT result code format and call monitoring ....................................................... 35
2.7 ATZ Set all current parameters to user defined profile................................................................ 36
2.8 AT+CFUN Set phone functionality .............................................................................................. 37
2.8.1 Wake up the ME from SLEEP mode ............................................................................. 40
2.9 AT^SMSO Switch off mobile station............................................................................................ 42
2.10 AT+GCAP Request complete TA capabilities list........................................................................ 43
2.11 AT+CMEE Mobile Equipment Error Message Format ................................................................ 44
2.11.1 CME/CMS Error Code Overview ................................................................................... 45
2.12 AT+CSCS Select TE character set ............................................................................................. 49
2.13 AT^SCFG Extended Configuration Settings ............................................................................... 50
2.14 AT^SM20 Set M20 compatibility mode ....................................................................................... 59
3. Status Control Commands ................................................................................................................... 60
3.1 AT+CMER Mobile Equipment Event Reporting .......................................................................... 60
3.2 AT+CIND Indicator control .......................................................................................................... 62
3.3 AT^SIND Extended Indicator Control.......................................................................................... 65
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 3 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 4

3.4 AT+CEER Extended Error Report............................................................................................... 71
3.4.1 Cause Location ID for the extended error report ........................................................... 72
3.4.2 GSM release cause for L3 Radio Resource (RR).......................................................... 73
3.4.3 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Radio Resource (RR).................................................. 73
3.4.4 GSM release cause for Mobility Management (MM) or Session Management (SM)..... 74
3.4.5 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Mobility Management (MM) ........................................ 75
3.4.6 GSM release cause for L3 Call Control (CC)................................................................. 75
3.4.7 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Call Control (CC)......................................................... 77
3.4.8 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Advice of Charge (AOC) ............................................. 77
3.4.9 GSM Release cause for Supplementary Service Call ................................................... 77
3.4.10 SIEMENS release cause for Call-related Supplementary Services (CRSS) ................. 79
3.4.11 SIEMENS release cause for Session Management (SM) ............................................. 80
3.4.12 GSM cause for L3 Protocol module or other local cause ............................................. 80
3.4.13 SIEMENS release cause for GPRS API ........................................................................ 80
3.4.14 SIEMENS release cause for PPP/IP-Stack ................................................................... 80
3.5 ATS18 Extended call release report............................................................................................81
3.6 AT+CPAS Mobile equipment activity status................................................................................ 83
3.7 AT+WS46 Select wireless network ............................................................................................. 84
4. Serial Interface Control Commands..................................................................................................... 85
4.1 AT\Q Flow control........................................................................................................................ 85
4.2 AT&C Set Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Line mode ....................................................................... 86
4.3 AT&D Set circuit Data Terminal Ready (DTR) function mode..................................................... 87
4.4 AT&S Set circuit Data Set Ready (DSR) function mode ............................................................. 88
4.5 ATE Enable command echo........................................................................................................ 89
4.6 AT+ILRR Set TE-TA local rate reporting..................................................................................... 90
4.7 AT+IPR Set fixed local rate ......................................................................................................... 92
4.7.1 Autobauding................................................................................................................... 93
4.8 AT+CMUX Enter multiplex mode ................................................................................................ 95
4.8.1 Restrictions on Multiplex mode...................................................................................... 96
4.8.2 Second serial interface ASC1........................................................................................ 98
5. Security Commands .............................................................................................................................. 99
5.1 AT+CPIN PIN Authentication ...................................................................................................... 99
5.1.1 What to do if PIN or password authentication fails? .................................................... 101
5.2 AT+CPIN2 PIN2 Authentication ................................................................................................ 103
5.3 AT^SPIC Display PIN counter...................................................................................................105
5.4 AT+CLCK Facility lock .............................................................................................................. 109
5.5 AT^SLCK Facility lock ............................................................................................................... 114
5.6 AT+CPWD Change Password .................................................................................................. 115
5.7 AT^SPWD Change Password................................................................................................... 119
6. Identification Commands.................................................................................................................... 120
6.1 ATI Display product identification information ........................................................................... 120
6.2 AT+CGMI Request manufacturer identification......................................................................... 121
6.3 AT+GMI Request manufacturer identification ........................................................................... 121
6.4 AT+CGMM Request model identification .................................................................................. 122
6.5 AT+GMM Request model identification..................................................................................... 122
6.6 AT+CGMR Request revision identification of software status................................................... 123
6.7 AT+GMR Request revision identification of software status ..................................................... 123
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 4 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 5

6.8 AT+CGSN Request International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) ......................................... 124
6.9 AT+GSN Request International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) ........................................... 124
6.10 AT+CIMI Request International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)............................................ 125
7. Call related Commands....................................................................................................................... 126
7.1 Call Status Information ................................................................................................................ 126
7.2 ATA Answer a call ..................................................................................................................... 127
7.3 ATD Mobile originated call to specified number........................................................................ 128
7.4 ATD><mem><n> Mobile originated call using specific memory and index number ................. 130
7.5 ATD><n> Mobile originated call from active memory using index number ............................... 132
7.6 ATD><str> Mobile originated call from active memory using corresponding field .................... 133
7.7 ATDI Mobile originated call to ISDN number............................................................................. 134
7.8 ATDL Redial last number used ................................................................................................. 135
7.9 ATH Disconnect existing connection......................................................................................... 136
7.10 AT+CHUP Hang up call ............................................................................................................ 137
7.11 ATS0 Set number of rings before automatically answering a call ............................................. 138
7.12 ATS6 Set pause before blind dialing ......................................................................................... 139
7.13 ATS7 Set number of seconds to wait for connection completion .............................................. 140
7.14 ATS8 Set number of seconds to wait for comma dialing modifier............................................. 141
7.15 ATS10 Set disconnect delay after indicating the absence of data carrier ................................. 142
7.16 ATO Switch from command mode to data mode / PPP online mode........................................ 143
7.17 +++ Switch from data mode to command mode ....................................................................... 144
7.18 AT+CBST Select bearer service type ....................................................................................... 145
7.19 AT+CRLP Select radio link protocol parameters for originated non-transparent data calls...... 146
7.20 AT+CLCC List current calls of ME ............................................................................................ 147
7.21 AT^SLCC Siemens defined command to list current calls of ME.............................................. 149
7.22 AT+CR Service reporting control ..............................................................................................155
7.23 AT+CRC Set Cellular Result Codes for incoming call indication .............................................. 156
7.24 AT+CSNS Single Numbering Scheme...................................................................................... 157
7.25 AT^SCNI List Call Number Information ..................................................................................... 158
7.26 AT^SLCD Display Last Call Duration ........................................................................................ 159
7.27 AT^STCD Display Total Call Duration....................................................................................... 160
7.28 ATP Select pulse dialing ........................................................................................................... 161
7.29 ATT Select tone dialing ............................................................................................................. 161
8. Network Service Commands .............................................................................................................. 162
8.1 AT+COPN Read operator names ............................................................................................. 162
8.2 AT+COPS Operator Selection .................................................................................................. 163
8.3 AT^SOPS Extended Operator Selection................................................................................... 166
8.4 AT+CREG Network registration ................................................................................................ 168
8.5 AT+CSQ Signal quality ............................................................................................................. 171
8.6 AT^SMONC Cell Monitoring......................................................................................................172
8.7 AT^SMOND Cell Monitoring......................................................................................................174
8.8 AT^MONI Monitor idle mode and dedicated mode ................................................................... 177
8.8.1 AT^MONI responses.................................................................................................... 178
8.8.2 Service states .............................................................................................................. 179
8.9 AT^MONP Monitor neighbour cells ........................................................................................... 180
8.9.1 AT^MONP responses .................................................................................................. 181
8.10 AT^SMONG GPRS Monitor ...................................................................................................... 182
8.10.1 AT^SMONG Cell Info Table......................................................................................... 183
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 5 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 6

8.11 AT^SALS Alternate Line Service...............................................................................................184
8.12 AT^SHOM Display Homezone .................................................................................................. 186
8.13 AT^SPLM Read the PLMN list .................................................................................................. 187
8.14 AT+CPOL Preferred Operator List ............................................................................................ 188
8.15 AT^SPLR Read entry from the preferred operators list............................................................. 189
8.16 AT^SPLW Write an entry to the preferred operators list ........................................................... 190
9. Supplementary Service Commands .................................................................................................. 191
9.1 AT+CACM Accumulated call meter (ACM) reset or query ........................................................ 191
9.2 AT^SACM Advice of charge and query of ACM and ACMmax ................................................. 192
9.3 AT+CAMM Accumulated call meter maximum (ACMmax) set or query.................................... 194
9.4 AT+CAOC Advice of Charge information.................................................................................. 195
9.5 AT+CCUG Closed User Group ................................................................................................. 196
9.6 AT+CCFC Call forwarding number and conditions control ....................................................... 198
9.7 AT+CCWA Call Waiting ............................................................................................................ 202
9.8 AT+CHLD Call Hold and Multiparty........................................................................................... 206
9.9 AT+CLIP Calling Line Identification Presentation ..................................................................... 208
9.10 AT+CLIR Calling line identification restriction ........................................................................... 210
9.11 AT+COLP Connected Line Identification Presentation ............................................................. 211
9.12 AT+CPUC Price per unit and currency table............................................................................. 213
9.13 AT+CSSN Supplementary service notifications ........................................................................ 215
9.14 AT+CUSD Supplementary service notifications........................................................................ 217
10. Internet Service Commands ............................................................................................................... 219
10.1 AT^SICS Internet Connection Setup Profile.............................................................................. 222
10.1.1 Example: Default values of a CSD connection profile ................................................. 224
10.1.2 Example: GPRS connection profile ............................................................................. 225
10.2 AT^SICI Internet Connection Information.................................................................................. 226
10.2.1 Checking Connection Profile Status ............................................................................ 227
10.3 AT^SISS Internet Service Setup Profile .................................................................................... 228
10.4 AT^SISI Internet Service Information ........................................................................................ 237
10.5 AT^SISO Internet Service Open ............................................................................................... 239
10.5.1 Example: Accepting / Rejecting Socket Connection Request from Remote Client ..... 242
10.6 AT^SISC Internet Service Close ...............................................................................................244
10.7 AT^SISR Internet Service Read Data ....................................................................................... 245
10.7.1 Example: Socket Host Reads Small Amounts of UDP Data Packets (URC Mode)..... 246
10.8 AT^SISW Internet Service Write Data....................................................................................... 248
10.8.1 Usage of parameter <eodFlag> ................................................................................... 250
10.9 AT^SISE Internet Service Error Report..................................................................................... 251
10.10 Internet Service URC "^SIS" ....................................................................................................... 252
10.10.1 Information Elements Related to the Service Application............................................ 253
10.10.2 Information Elements Related to FTP Service............................................................. 254
10.10.3 Information Elements Related to HTTP Service .......................................................... 255
10.10.4 Information Elements Related to POP3 Service .......................................................... 255
10.10.5 Information Elements Related to SMTP Service ......................................................... 255
10.11 Examples of how to Configure and Use Internet Service Profiles............................................... 256
10.11.1 Selecting URC Mode or Polling Mode ......................................................................... 256
10.11.2 Configuring Socket Listener......................................................................................... 256
10.11.3 Configuring Socket Client for Calling a Socket Listener on Another Host ................... 257
10.11.4 Socket Client Sends Data via TCP Connection (Polling Mode)................................... 257
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 6 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 7

10.11.5 Socket client sends data via TCP connection with URCs............................................ 258
10.11.6 Configuring and Using FTP Download (URC Mode) ................................................... 258
10.11.7 Configuring and Using FTP Upload (URC Mode) ........................................................ 259
10.11.8 Configuring SMPT Service Profile ............................................................................... 259
10.11.9 Sending Email (URC Mode) ........................................................................................ 260
10.11.10 Sending Email (Polling Mode) ..................................................................................... 261
10.11.11 Configuring POP3 Service Profile................................................................................ 262
10.11.12 Retrieving Email (URC Mode) ..................................................................................... 262
10.11.13 Retrieving Email (Polling Mode) .................................................................................. 263
10.11.14 HTTP POST (Polling Mode) ........................................................................................ 264
10.11.15 HTTP GET (Polling Mode) ........................................................................................... 265
11. GPRS Commands ................................................................................................................................ 266
11.1 AT+CGACT PDP context activate or deactivate ....................................................................... 266
11.2 AT+CGANS Manual response to a network request for PDP context activation ...................... 268
11.3 AT+CGATT GPRS attach or detach ......................................................................................... 270
11.4 AT+CGAUTO Automatic response to a network request for PDP context activation ............... 271
11.5 AT+CGEREP GPRS event reporting ........................................................................................ 273
11.6 AT+CGDATA Enter data state .................................................................................................. 275
11.6.1 Automatic deactivation of PDP context during dial-up PPP......................................... 276
11.7 AT+CGDCONT Define PDP Context ........................................................................................ 277
11.8 AT+CGPADDR Show PDP address ......................................................................................... 279
11.9 AT+CGQMIN Quality of Service Profile (Minimum acceptable) ................................................ 280
11.10 AT+CGQREQ Quality of Service Profile (Requested) .............................................................. 284
11.11 AT+CGREG GPRS Network Registration Status...................................................................... 288
11.12 AT+CGSMS Select service for MO SMS messages ................................................................. 290
11.13 AT^SGAUTH Set type of authentication for PPP connection.................................................... 291
11.14 AT^SGCONF Configuration of GPRS related Parameters ...................................................... 292
11.15 ATA Manual response to a network request for PDP context activation................................... 293
11.16 ATD*99# Request GPRS service.............................................................................................. 294
11.17 ATD*98# Request GPRS IP service ......................................................................................... 295
11.18 ATH Manual rejection of a network request for PDP context activation.................................... 296
11.19 ATS0 Automatic response to a network request for PDP context activation............................. 297
11.20 Using GPRS AT commands (Examples)..................................................................................... 298
11.21 Using the GPRS dial command ATD .......................................................................................... 300
12. FAX Commands ................................................................................................................................... 301
12.1 FAX parameters .......................................................................................................................... 301
12.1.1 Summary of Fax Class 2 URCs defined by EIA PN-2388 ........................................... 303
12.2 AT+FBADLIN Bad Line Threshold ............................................................................................ 304
12.3 AT+FBADMUL Error Threshold Multiplier ................................................................................. 305
12.4 AT+FBOR Query data Bit Order ............................................................................................... 306
12.5 AT+FCIG Query or set the Local Polling ID .............................................................................. 307
12.6 AT+FCLASS Fax: Select, read or test service class................................................................. 308
12.7 AT+FCQ Copy Quality Checking .............................................................................................. 309
12.8 AT+FCR Capability to Receive .................................................................................................310
12.9 AT+FDCC Query or set capabilities .......................................................................................... 311
12.10 AT+FDFFC Data Compression Format Conversion ................................................................. 312
12.11 AT+FDIS Query or set session parameters .............................................................................. 313
12.12 AT+FDR Begin or continue phase C Data Reception ............................................................... 314
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 7 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 8

12.13 AT+FDT Data Transmission...................................................................................................... 315
12.14 AT+FET End a page or document ............................................................................................ 316
12.15 AT+FK Kill operation, orderly FAX abort ................................................................................... 317
12.16 AT+FLID Query or set the Local Id setting capabilities ............................................................. 318
12.17 AT+FMDL Identify Product Model ............................................................................................ 319
12.18 AT+FMFR Request Manufacturer Identification........................................................................ 320
12.19 AT+FOPT Set bit Order independently ..................................................................................... 321
12.20 AT+FPHCTO DTE Phase C Response Timeout....................................................................... 322
12.21 AT+FREV Identify Product Revision ......................................................................................... 323
12.22 AT+FRH Receive Data Using HDLC Framing .......................................................................... 324
12.23 AT+FRM Receive Data ............................................................................................................. 325
12.24 AT+FRS Receive Silence.......................................................................................................... 326
12.25 AT+FTH Transmit Data Using HDLC Framing.......................................................................... 327
12.26 AT+FTM Transmit Data............................................................................................................. 328
12.27 AT+FTS Stop Transmission and Wait....................................................................................... 329
12.28 AT+FVRFC Vertical Resolution Format Conversion ................................................................. 330
13. Short Message Service (SMS) Commands........................................................................................ 331
13.1 SMS parameters ......................................................................................................................... 331
13.2 AT+CMGC Send an SMS command......................................................................................... 335
13.3 AT+CMGD Delete short message............................................................................................. 336
13.4 AT+CMGF Select SMS message format .................................................................................. 337
13.5 AT+CMGL List SMS messages from preferred store................................................................ 338
13.6 AT+CMGR Read SMS messages............................................................................................. 340
13.7 AT+CMGS Send Short Message .............................................................................................. 342
13.8 AT+CMGW Write Short Messages to Memory ......................................................................... 344
13.9 AT+CMSS Send short messages from storage ........................................................................ 346
13.10 AT+CNMA New Message Acknowledgement to ME/TE, only phase 2+ .................................. 347
13.11 AT+CNMI New short Message Indication ................................................................................. 348
13.12 AT+CPMS Preferred SMS message storage............................................................................ 351
13.13 AT+CSCA SMS Service Center Address .................................................................................. 353
13.14 AT+CSCB Select Cell Broadcast Message Indication .............................................................. 354
13.15 AT+CSDH Show SMS text mode parameters........................................................................... 355
13.16 AT+CSMP Set SMS text Mode Parameters.............................................................................. 356
13.17 AT+CSMS Select Message Service.......................................................................................... 358
13.18 AT^SLMS List SMS Memory Storage ....................................................................................... 360
13.19 AT^SMGL List Short Messages from preferred store without setting status to REC READ ..... 361
13.20 AT^SMGO Set or query SMS overflow presentation mode or query SMS overflow ................. 362
13.21 AT^SMGR Read short message without setting status to REC READ..................................... 364
13.22 AT^SSCONF SMS Command Configuration ........................................................................... 365
13.23 AT^SSDA Set SMS Display Availability .................................................................................... 366
13.24 AT^SSMSS Set Short Message Storage Sequence ................................................................. 367
14. SIM related Commands ....................................................................................................................... 368
14.1 AT+CRSM Restricted SIM Access ............................................................................................ 368
14.2 AT^SXSM Extended SIM Access.............................................................................................. 370
14.3 AT^SCKS Query SIM and Chip Card Holder Status ................................................................. 372
14.4 AT^SCID Display SIM card identification number ..................................................................... 374
14.5 AT+CXXCID Display card ID..................................................................................................... 375
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 8 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 9

15. SIM Application Toolkit (SAT) Commands ........................................................................................ 376
15.1 AT^SSTA SAT Interface Activation ........................................................................................... 376
15.2 ^SSTN SAT Notification ............................................................................................................ 378
15.3 AT^SSTGI SAT Get Information ............................................................................................... 379
15.4 AT^SSTR SAT Response .........................................................................................................380
16. Phonebook Commands....................................................................................................................... 381
16.1 Sort Order for Phonebooks ......................................................................................................... 381
16.2 AT+CPBR Read from Phonebook............................................................................................. 382
16.3 AT+CPBS Select phonebook memory storage ......................................................................... 385
16.4 AT+CPBW Write into Phonebook ............................................................................................. 387
16.5 AT^SPBC Find first matching entry in sorted phonebook ......................................................... 390
16.6 AT^SPBD Purge phonebook memory storage.......................................................................... 391
16.7 AT^SPBG Display phonebook entries in alphabetical order ..................................................... 392
16.8 AT^SPBS Step through the selected phonebook alphabetically............................................... 395
16.9 AT+CNUM Read own numbers................................................................................................. 399
16.10 AT^SDLD Delete the 'last number redial' memory .................................................................... 400
17. Audio Commands ................................................................................................................................ 401
17.1 Audio programming model .......................................................................................................... 401
17.2 ATL Set monitor speaker loudness ........................................................................................... 402
17.3 ATM Set monitor speaker mode................................................................................................ 402
17.4 AT+CLVL Loudspeaker volume level........................................................................................ 403
17.5 AT+CMUT Mute control ............................................................................................................ 404
17.6 AT+VTD Tone duration ............................................................................................................. 405
17.7 AT+VTS DTMF and tone generation......................................................................................... 406
17.8 AT^SAIC Audio Interface Configuration .................................................................................... 407
17.9 AT^SNFA Set or query of microphone attenuation .................................................................. 409
17.10 AT^SNFD Set audio parameters to manufacturer default values ............................................. 411
17.11 AT^SNFI Set microphone path parameters .............................................................................. 412
17.12 AT^SNFM Set microphone audio path and power supply......................................................... 413
17.13 AT^SNFO Set audio output (= loudspeaker path) parameter ................................................... 415
17.14 AT^SNFPT Set progress tones .................................................................................................417
17.15 AT^SNFS Select audio hardware set........................................................................................ 418
17.16 AT^SNFTTY Signal TTY/CTM audio mode capability............................................................... 421
17.17 AT^SNFV Set loudspeaker volume........................................................................................... 422
17.18 AT^SNFW Write audio setting in non-volatile store .................................................................. 423
17.19 AT^SRTC Ring tone configuration ............................................................................................ 424
18. Hardware related Commands ...................................................................................................
18.1 AT+CCLK Real Time Clock....................................................................................................... 426
18.2 AT+CALA Set alarm time ......................................................................................................... 427
18.3 AT^SBC Battery Charge Control............................................................................................... 430
18.3.1 Responses returned by read command....................................................................... 432
18.4 AT^SBV Battery/Supply Voltage ............................................................................................... 433
18.5 AT^SCTM Set critical operating temperature presentation mode or query temperature........... 434
18.6 AT^SSYNC Configure SYNC Pin.............................................................................................. 437
18.6.1 ME status indicated by status LED patterns ................................................................ 438
19. Miscellaneous Commands.................................................................................................................. 439
19.1 A/ Repeat previous command line ............................................................................................ 439
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 9 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
.......... 426
Page 10

19.2 ATS3 Set command line termination character......................................................................... 440
19.3 ATS4 Set response formatting character .................................................................................. 441
19.4 ATS5 Write command line editing character ............................................................................. 442
20. Appendix .............................................................................................................................................. 443
20.1 Restricted access to SIM data after SIM PIN authentication....................................................... 443
20.2 Star-Hash (*#) Network Commands............................................................................................ 444
20.3 Available AT Commands and Dependency on SIM PIN ............................................................. 447
20.4 Availability of AT Commands Depending on Operating Mode of ME.......................................... 454
20.5 AT Command Settings storable with AT&W................................................................................ 461
20.6 Factory Default Settings Restorable with AT&F.......................................................................... 464
20.7 Summary of Unsolicited Result Codes (URC)............................................................................. 467
20.8 Alphabetical List of AT Commands ............................................................................................. 470
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 10 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 11

List of Tables
Table 1.1: Symbols used to mark the type of parameters ...........................................................................16
Table 1.2: Symbols used to indicate the correlations with other commands ............................................... 16
Table 1.3: Symbols used to mark different types of default values of parameters ..................................... 16
Table 1.4: Types of AT commands and responses .................................................................................... 17
Table 1.5: Examples for character definitions depending on alphabet ........................................................ 20
Table 2.1: Current configuration on ASC0 / MUX channel 1 (example) ...................................................... 31
Table 2.2: Current configuration on ASC1 and MUX channels 2 and 3 (example) .................................... 31
Table 2.3: Wake-up events in NON-CYCLIC and CYCLIC SLEEP modes ................................................. 40
Table 2.4: General "CME ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.07) .......................................................................... 45
Table 2.5: General "CME ERROR" Codes (SIEMENS) ............................................................................ 46
Table 2.6: GPRS related "CME ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.07) ................................................................. 46
Table 2.7: SMS related "CMS ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.05) ................................................................... 46
Table 4.1: Availability of AT Commands on Virtual Channels .................................................................... 96
Table 4.2: Summary of AT commands with Different Behavior in Multiplex Mode ..................................... 97
Table 10.1: Applicability of AT^SICS <conParmTag> values ................................................................... 222
Table 10.2: Applicability of AT^SISS <srvParmTag> values ................................................................... 228
Table 12.1: Summary of Fax Class 2 URCs defined by EIA PN-2388 ........................................................ 303
Table 18.1: Modes of the LED and indicated ME functions......................................................................... 438
Table 20.1: Star-Hash (*#) Command Overview ........................................................................................ 444
Table 20.2: Abbreviations of Codes and Parameters used in Table 20.1 .................................................. 445
Table 20.3: Star-Hash Command Response Parameters .......................................................................... 446
Table 20.4: Star-Hash Commands for Supplementary Services ................................................................ 446
Table 20.5: Available AT Commands and Dependency on SIM PIN........................................................... 447
Table 20.6: Availability of AT Commands Depending on Operating Mode of ME ....................................... 454
Table 20.7: Settings Stored to User Profile on ASC0 / MUX Channel 1...................................................... 461
Table 20.8: Settings Stored to User Profile on ASC1 / MUX Channels 2 and 3.......................................... 462
Table 20.9: Factory Default Settings Restorable with AT&F ....................................................................... 464
Table 20.10: Summary of Unsolicited Result Codes (URC) .......................................................................... 467
Table 20.11: Alphabetical List of AT Commands........................................................................................... 470
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 11 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 12

List of Figures
Figure 1.1: Main character table of GSM 03.38 alphabet ............................................................................. 21
Figure 1.2: Extension character table of GSM 03.38 alphabet ..................................................................... 22
Figure 17.1: Audio programming model for MC55 Module ........................................................................... 401
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 12 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 13

1. Introduction
1.1 Scope of the document
This document presents the AT Command Set for the Siemens Cellular Engine
MC55 Release 04.00.
Before using the Cellular Engine or upgrading to a new firmware version please read the latest product information provided in the Release Notes [1].
More information is available at the Siemens Website: http://www.siemens.com/wm
.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 13 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 14

1.2 Related documents
[1] MC55 Release Notes, Version 04.00
[2] MC55 Hardware Interface Description, Version 04.00
[3] GPRS Startup User's Guide
[4] Remote-SAT User's Guide
[5] Multiplexer User's Guide
[6] Multiplex Driver Developer's Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
[7] Multiplex Driver Installation Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
[8] Application Note 02: Audio Interface Design
[9] Application Note 16: Updating MC55 Firmware
[10] Application Note 24: Application Developer's Guide
[11] Application Note 22: Using TTY / CTM equipment with MC55
[12] ISO/IEC10646: "Universal Multiple-Octet Coded Character Set (UCS)"; UCS2, 16 bit coding
[13] ITU-T Recommendation V.24: List of definitions for interchange circuits between data terminal equipment
(DTE) and data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE)
[14] ITU-T Recommendation V.250: Serial asynchronous automatic dialling and control
[15] 3GPP TS 100 918/EN 300 918 (GSM 02.04): General on supplementary services
[16] 3GPP TS 100 907 (GSM 02.30): Man-Machine Interface (MMI) of the Mobile Station (MS)
[17] 3GPP TS 23.038 (GSM 03.38): Alphabets and language specific information
[18] 3GPP TS 27.005 (GSM 07.05): Use of Data Terminal Equipment - Data Circuit terminating Equipment (DTE
- DCE) interface for Short Message Service (SMS) and Cell Broadcast Service (CBS)
[19] 3GPP TS 27.007 (GSM 07.07): AT command set for User Equipment (UE)
[20] 3GPP TS 27.060 (GSM 07.60): Mobile Station (MS) supporting Packet Switched Services
[21] 3GPP TS 51.011 (GSM 11.11): Specification of the Subscriber Identity Module - Mobile Equipment (SIM -
ME) interface
[22] 3GPP TS 11.14 (GSM 11.14): Specification of the SIM Application Toolkit for the Subscriber Identity Module
- Mobile Equipment (SIM - ME) interface
[23] 3GPP TS 22.101 (GSM 22.101): Service principles
[24] Common PCN Handset Specification (CPHS) v4.2
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 14 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 15

1.3 Document conventions
Throughout the document, the GSM engines are referred to as ME (Mobile Equipment), MS (Mobile Station), TA
(Terminal Adapter), DCE (Data Communication Equipment) or facsimile DCE (FAX modem, FAX board).
To control your GSM engine you can simply send AT Commands via its serial interface. The controlling device
at the other end of the serial line is referred to as TE (Terminal Equipment), DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) or
plainly 'the application' (probably running on an embedded system).
All abbreviations and acronyms used throughout this document are based on the GSM specifications. For definitions please refer to TR 100 350 V7.0.0 (1999-08), (GSM 01.04, version 7.0.0 release 1998).
1.3.1 Quick reference table
Each AT command description includes a table similar to the example shown below. The table is intended as a
quick reference to indicate the following functions:
PIN: Is the AT command PIN protected?
% Yes
! No
§ Usage is dependent on conditions specified for the command, or not all command types are PIN
protected (for example write command PIN protected, read command not).
Note: The table provided in Section 20.3, Available AT Commands and Dependency on SIM
PIN uses the same symbols.
ASC0: Is the AT command supported on the first physical serial interface ASC0?
% Yes
! No
ASC1: Is the AT command supported on the second physical serial interface ASC1?
% Yes
! No
MUXn: Is the AT command usable on the Multiplexer channels MUX1, MUX2, MUX3?
% Yes
! No
§ AT command is usable, but under the restrictions specified in the section related to the command.
Note: The columns MUX1, MUX2 and MUX3 are relevant only when the GSM engine operates in Mul-
tiplexer mode, that is, when the first physical serial interface is partitioned into 3 virtual channels
% Yes
! No
Charge: Is the AT command supported in CHARGE ONLY mode?
% Yes
! No
§ AT command is usable, but under the restrictions specified in the section related to the command.
Last: If commands are concatenated, this AT command must be the last one.
% Yes
! No
Note: See also Section 1.4, AT Command Syntax for details on concatenated AT commands.
Example:
PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
! % % § § § % ! !
by using the Multiplexer protocol. Usage is the same on ASC0 and MUX1.
Is the AT command supported in ALARM mode?
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 15 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 16

1.3.2 Superscript notation for parameters and values
Table 1.1: Symbols used to mark the type of parameters
Parameter type Meaning
<param>
<param>
Table 1.2: Symbols used to indicate the correlations with other commands
Parameter option Meaning
<param>
<param>
<param>
<param>
Table 1.3: Symbols used to mark different types of default values of parameters
Value option Meaning
[x] Default value: if the parameter is omitted, the value 'x' will be assumed
(&F)
x
(P)
x
(D)
x
(num)
(str)
(&W)
(&V)
(ˆSNFW)
(+CSCS)
Parameter value must be numeric type
Parameter value must be string type
Parameter value will be stored with AT&W
Parameter value will be displayed with AT&V
Parameter value will be stored with AT^SNFW
Parameter value has to be (is) coded according to current setting of <chset> (see
AT+CSCS for details)
Factory default value, will be restored to 'x' with AT&F
Powerup default value of a parameter which is not stored at power down
Delivery default value of a parameter which cannot be restored automatically
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 16 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 17

1.4 AT Command Syntax
The "AT" or "at" prefix must be set at the beginning of each command line. To terminate a command line enter
<CR>. Commands are usually followed by a response that includes "<CR><LF><response><CR><LF>". Through-
out this document, only the responses are presented,
Table 1.4: Types of AT commands and responses
AT command type Syntax Function
Test command AT+CXXX=? The mobile equipment returns the list of parameters and value
ranges set with the corresponding Write command or by internal
processes.
Read command AT+CXXX? This command returns the currently set value of the parameter or
parameters.
Write command AT+CXXX=<...> This command sets user-definable parameter values.
Exec(ution) command AT+CXXX The execution command reads non-variable parameters deter-
mined by internal processes in the GSM engine.
<CR><LF> are omitted intentionally.
1.4.1 Using Parameters
• Optional parameters are enclosed in square brackets. If optional parameters are omitted, the current settings
are used until you change them.
• Optional parameters or subparameters can be omitted unless they are followed by other parameters. If you
want to omit a parameter in the middle of a string it must be replaced by a comma. See also example 1.
• A parameter value enclosed in square brackets represents the value that will be used if an optional parameter
is omitted. See also example 2.
• When the parameter is a character string, e.g. <text> or <number>, the string must be enclosed in quotation
marks, e.g. "Charlie Brown" or "+49030xxxx". Symbols in quotation marks will be recognized as strings.
• All spaces will be ignored when using strings without quotaton marks.
• It is possible to omit the leading zeros of strings which represent numbers.
• If an optional parameter of a V.250 command is omitted, its value is assumed to be 0.
Example 1: Omitting parameters in the middle of a string
AT+CCUG?
+CCUG: 1,10,1
OK
AT+CCUG=,9
OK
AT+CCUG?
+CCUG: 1,9,1
OK
Example 2: Using default parameter values for optional parameters
AT+CFUN=5
OK
AT+CFUN?
+CFUN: 5
OK
AT+CFUN=
OK
+CFUN: 1
OK
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 17 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Query current setting
Set only the middle parameter
Query new setting
Activate CYCLIC SLEEP mode, don't reset ME
Query ME mode
Set ME back to normal (default parameters: 1,0)
Page 18

1.4.2 Combining AT commands on the same command line
You may enter several AT commands on the same line. This eliminates the need to type the "AT" or "at" prefix
before each command. Instead, it is only needed once at the beginning of the command line. Use a semicolon
as command delimiter.
The table below lists the AT commands you cannot enter together with other commands on the same line. Otherwise, the responses may not be in the expected order.
AT command type Comment
V.250 commands with FAX commands (Prefix AT+F)
GSM 7.07 commands with Siemens commands, Prefix AT^S)
GSM 7.05 commands (SMS) To be used standalone
Commands starting with AT& To be used standalone
AT+IPR To be used standalone
Note: When concatenating AT commands please keep in mind that the sequence of processing may be different
from the sequential order of command input. Therefore, if the consecutive order of the issued commands and
the associated responses is your concern, avoid concatenating commands on the same line.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 18 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 19

1.5 Supported character sets
The ME supports two character sets: GSM 03.38 (7 bit, also referred to as GSM alphabet or SMS alphabet) and
UCS2 (16 bit, refer to ISO/IEC 10646). See AT+CSCS for information about selecting the character set. Character
tables can be found below.
Explanation of terms
• International Reference Alphabet (IRA)
IRA means that one byte is displayed as two characters in hexadecimal format. For example, the byte 0x36
(decimal 54) is displayed as "36" (two characters). IRA is used here for input 8-bit or 16-bit data via terminal
devices using text mode. This means only characters 'A'..F','a'..'f' and '0'..'9' are valid.
• Escape sequences
The escape sequence used within a text coded in the GSM default alphabet (0x1B) must be correctly interpreted by the TE, both for character input and output. To the module, an escape sequence appears like any
other byte received or sent.
• Terminal Adapter (TA)
TA is used equivalent to Mobile Equipment (ME) which stands for the GSM module described here. It uses
GSM default alphabet as its character set.
• Terminal Equipment (TE)
TE is the device connected to the TA via serial interface. In most cases TE is an ANSI/ASCII terminal that
does not fully support the GSM default alphabet, for example MS Hyperterminal.
• TE Character Set
The character set currently used by Terminal Equipment is selected with AT+CSCS.
• Data Coding Scheme (dcs)
DCS is part of a short message and is saved on the SIM. When writing a short message to the SIM in text
mode, the dcs stored with AT+CSMP is used and determines the coded character set.
The behavior when encountering characters, that are not valid characters of the supported alphabets, is undefined.
Due to the constraints described below it is recommended to prefer the USC2 alphabet in any external application.
If the GSM alphabet is selected all characters sent over the serial line (between TE and TA) are in the range from
0 to 127 (7 Bit range). CAUTION: ASCII alphabet (TE) is not GSM alphabet (TA/ME) !
Several problems resulting from the use of GSM alphabet with ASCII terminal equipment:
• "@" character with GSM alphabet value 0 is not printable by an ASCII terminal program (e.g. Microsoft©
Hyperterminal®).
• "@" character with GSM alphabet value 0 will terminate any C string! This is because the 0 is defined as C
string end tag. Therefore, the GSM Null character may cause problems on application level when using a 'C'function as "strlen()". This can be avoided if it is represented by an escape sequence as shown in the table
below.
By the way, this may be the reason why even network providers often replace "@"with "@=*" in their SIM
application.
• Other characters of the GSM alphabet are misinterpreted by an ASCII terminal program. For example, GSM
"ö" (as in "Börse") is assumed to be "|" in ASCII, thus resulting in "B|rse". This is because both alphabets mean
different characters with values hex. 7C or 00 and so on.
• In addition, decimal 17 and 19 which are used as XON/XOFF control characters when software flow control
is activated, are interpreted as normal characters in the GSM alphabet.
When you write characters differently coded in ASCII and GSM (e.g. Ä, Ö, Ü), you need to enter escape
sequences. Such a character is translated into the corresponding GSM character value and, when output later,
the GSM character value can be presented. Any ASCII terminal then will show wrong responses.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 19 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 20
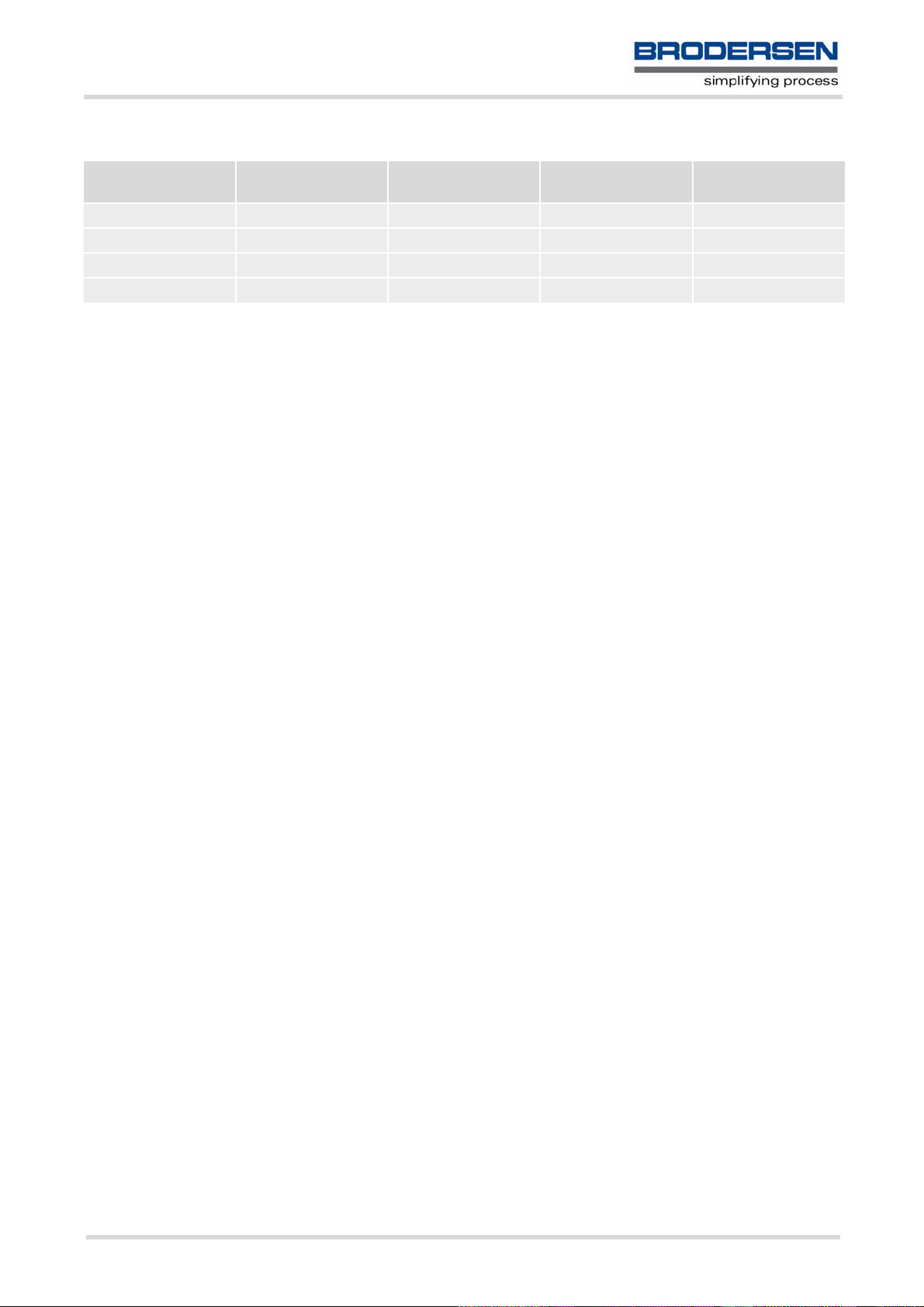
Table 1.5: Examples for character definitions depending on alphabet
GSM 03.38
character
Ö 5C \ \5C 5C 35 43
" 22 " \22 5C 32 32
ò 08 BSP \08 5C 30 38
@ 00 NULL \00 5C 30 30
CAUTION: Often, the editors of terminal programs do not recognize escape sequences. In this case, an escape
sequence will be handled as normal characters. The most common workaround to this problem is to write a script
which includes a decimal code instead of an escape sequence. This way you can write, for example, short messages which may contain differently coded characters.
GSM character
hex. value
Corresponding
ASCII character
ASCII
Esc sequence
Hex Esc
sequence
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 20 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 21
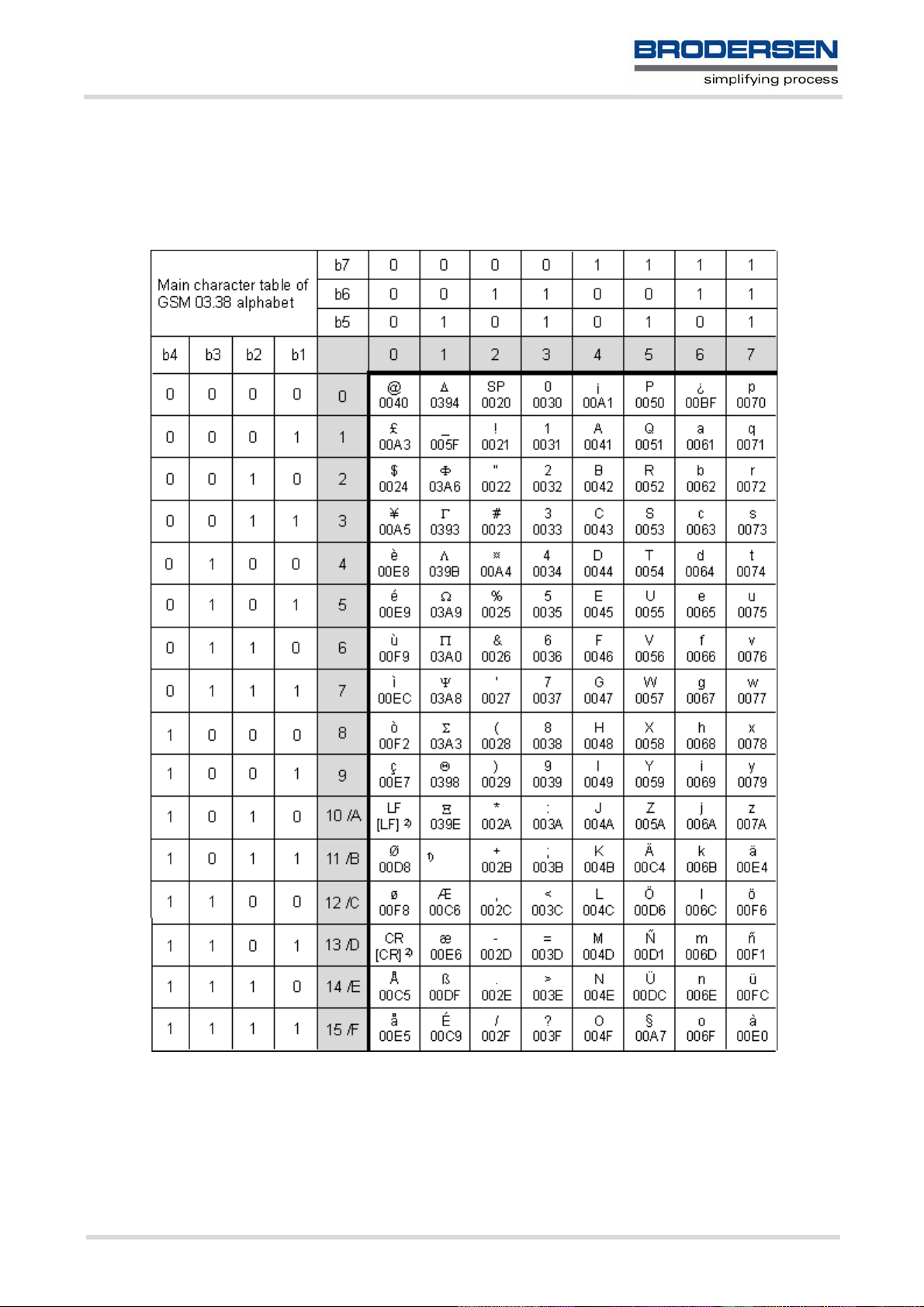
1.5.1 GSM alphabet tables and UCS2 character values
This section provides tables for the GSM 03.38 alphabet supported by the ME. Below any GSM character find
the corresponding two byte character value of the UCS2 alphabet.
(For related mapping definition see: http://www.unicode.org/Public/MAPPINGS/ETSI/GSM0338.TXT)
Figure 1.1: Main character table of GSM 03.38 alphabet
1) This code is an escape to the following extension of the 7 bit default alphabet table.
2) This code is not a printable character and therefore not defined for the UCS2 alphabet. It shall be treated as the accompanying control character.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 21 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 22
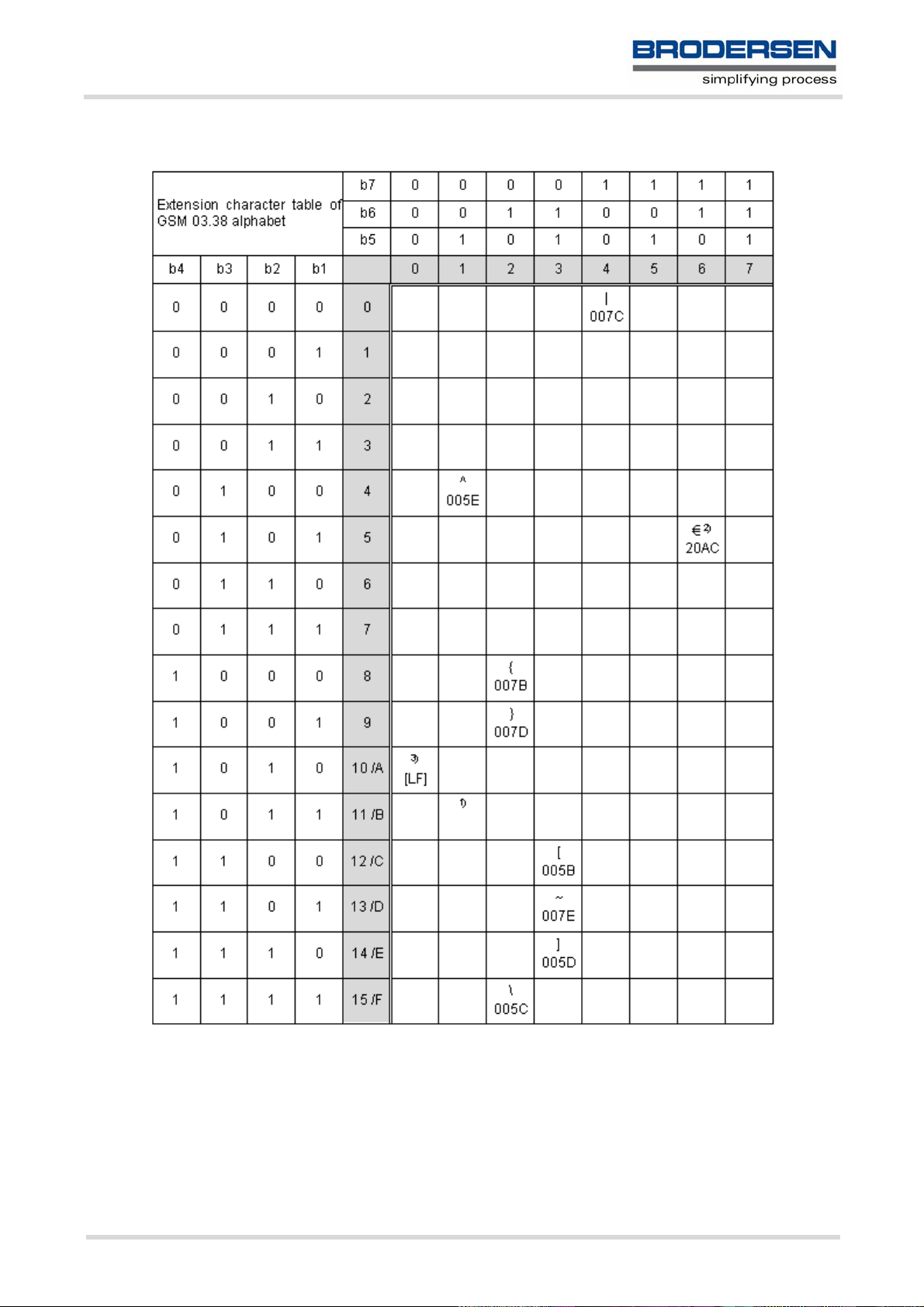
Figure 1.2: Extension character table of GSM 03.38 alphabet
1) This code value is reserved for the extension to another extension table. On receipt of this code, a receiving entity shall
display a space until another extension table is defined.
2) This code represents the EURO currency symbol. The code value is the one used for the character 'e'. Therefore a receiving entity which is incapable of displaying the EURO currency symbol will display the character 'e' instead.
3) This code is defined as a Page Break character and may be used for example in compressed CBS messages. Any mobile
which does not understand the 7 bit default alphabet table extension mechanism will treat this character as Line Feed.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 22 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 23

In the event that an MS receives a code where a symbol is not represented in Figure 1.2, Extension character
table of GSM 03.38 alphabet the MS shall display the character shown in the main default 7 bit alphabet table
(see Figure 1.1, Main character table of GSM 03.38 alphabet).
1.5.2 UCS2 and GSM data coding and conversion for SMS text mode
This section provides basic information on how to handle input and output character conversion for SMS text
mode and Remote-SAT if internal (TA) and external (TE) character representation differ, i.e. if the Data Coding
Scheme and the TE character use different coding.
1.5.2.1 Implementing output of SIM data to Terminal (direction TA to
TE)
Used character set DCS = 7 bit
GSM
GSM Case 1
GSM (1:1)
UCS2 Case 4
GSM to IRA (1:4)
Note: The ratio of SIM bytes to output bytes is given in parentheses.
Case 1
Every GSM character is sent to the TE as it is (8-bit value with highest bit set to zero).
Example: 47'H, 53'H, 4D'H → 47'H, 53'H, 4D'H, displayed as "GSM"
Case 2
Every data byte is sent to the TE as 2 IRA characters each representing a halfbyte.
Example: B8'H (184 decimal) → 42'H, 38'H, displayed as "B8"
Case 3
Every 16-bit UCS2 value is sent to the TE as 4 IRA characters.
Example: C4xA7'H (50343 decimal) → 43'H, 34'H, 41'H, 37'H, displayed as "C4A7"
Problem: An odd number of bytes leads to an error because there are always two bytes needed for each USC2
character
Case 4
Every GSM character is sent to the TE as 4 IRA characters to show UCS2 in text mode.
Example: 41'H ("A") → 30'H, 30'H, 34'H, 31'H, displayed as "0041"
DCS = 8 bit
Data
Case 2
8 bit to IRA (1:2)
Case 5
8 bit to IRA (1:4)
DCS = 16 bit
UCS2
Case 3
UCS2 to IRA (2:4)
Case 6
UCS2 to IRA (2:4)
Case 5
Every data byte is sent to the TE as IRA representation of UCS2 (similar to case 4).
Example: B2'H → 30'H, 30'H, 42'H, 32'H, displayed as "00B2"
Case 6
Every 16-bit value is sent to the TE as IRA representation of it. It is assumed that number of bytes is even.
Example: C3x46'H → 43'H, 33'H, 34'H, 36'H, displayed as "C346"
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 23 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 24
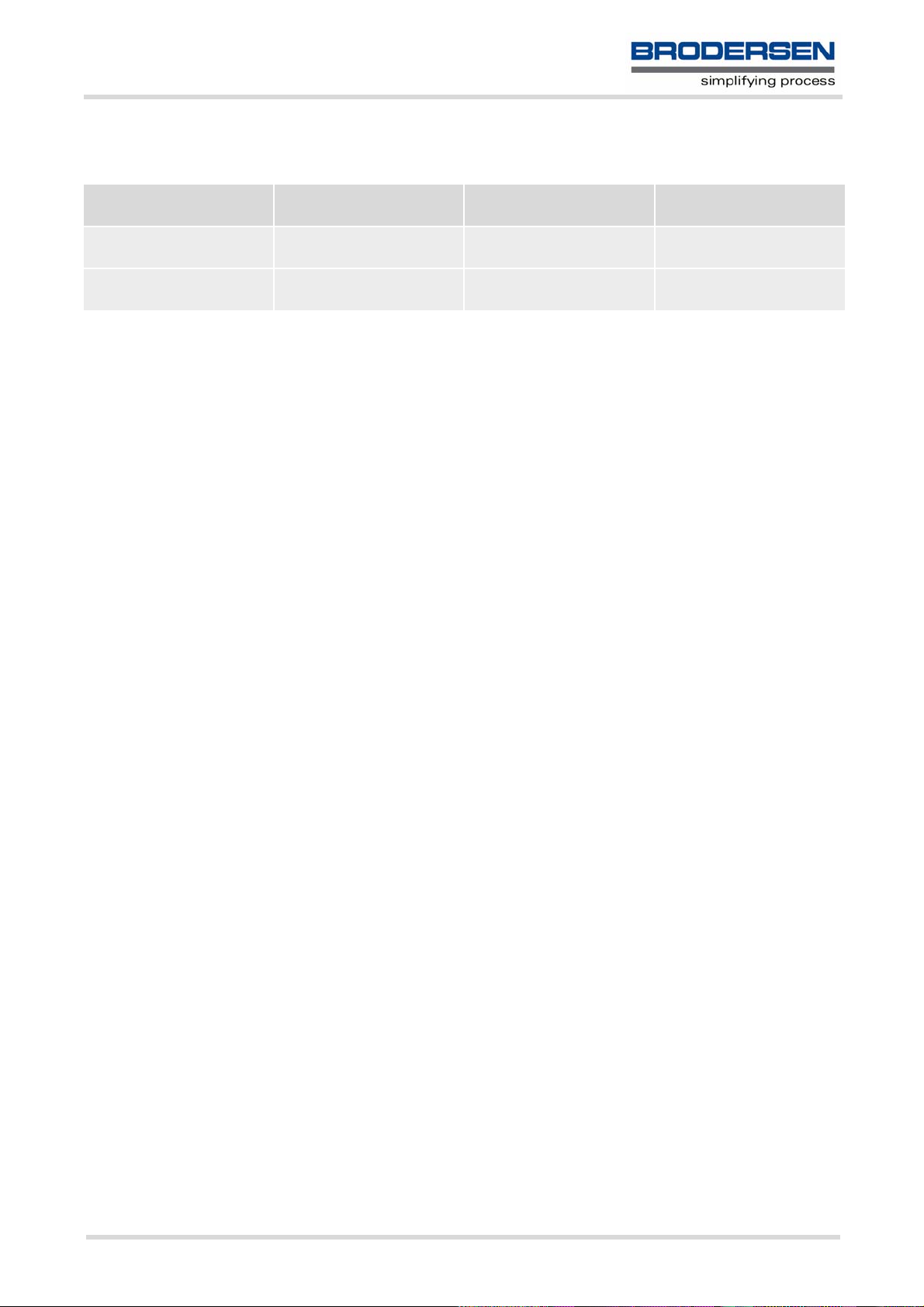
1.5.2.2 Implementing input of Terminal data to SIM (direction TE to TA)
Used character set DCS = 7 bit
GSM
GSM Case 1
GSM (1:1)
UCS2 Case 4
UCS2 to GSM (4:1)
Note: The ratio between the number of input characters and bytes stored on the SIM is given in parentheses.
Case 1
Every character is sent from TE to TA as GSM character (or ASCII with standard terminal emulation, e.g. Hyperterminal).
Character value must be in range from 0 to 127 because of 7-bit GSM alphabet.
To reach maximum SMS text length of 160 characters in 140 bytes space characters will be compressed on SIM.
This must be set using the parameter <dcs> of AT+CSMP (add 64).
Example: "ABCDEFGH" typed is sent and stored uncompressed as → 4142434445464748'H (stored compressed as 41E19058341E91'H)
Case 2
Every data byte is sent as 2 IRA characters.
Maximum text length is 280 IRA characters which will be converted into 140 bytes SMS binary user data
Example: "C8" typed is sent as 43'H, 38'H → stored as C8'H
Case 3
Every 16-bit value is sent as 4 IRA characters.
Maximum text length is 280 IRA characters which will be convertedinto 70 UCS2 characters (16-bit each)
Number of IRA characters must be a multiple of four because always 4 half bytes are needed for a 16-bit value
Example: "D2C8" typed is sent as 44'H, 32'H, 43'H, 38'H → stored as D2C8'H
DCS = 8 bit
Data
Case 2
IRA to 8 bit (2:1)
Case 5
UCS2 to 8 bit (4:1)
DCS = 16 bit
UCS2
Case 3
IRA to 16 bit (4:2)
Case 6
UCS2 to 16 bit (4:2)
Case 4
Every GSM character is sent as 4 IRA characters representing one UCS2 character.
Example: To store text "ABC" using UCS2 character set you have to type "004100420043".
This is sent as 30'H,30'H,34'H,31'H, 30'H,30'H,34'H,32'H, 30'H,30'H,34'H,33'H → detected as IRA representation of 3 UCS2 characters, converted to GSM character set and stored as 41'H, 42'H, 43'H.
Maximum input is 640 IRA characters repesenting 160 UCS2 characters when compression is active. These are
converted to 160 GSM 7-bit characters.
Without compression only 140 GSM characters can be stored which are put in as 560 IRA characters.
Values of UCS2 characters must be smaller than 80'H (128 decimal) to be valid GSM characters.
Number of IRA characters must be a multiple of four. Problems:
• "41" → Error, there are four IRA characters (two bytes) needed
• "0000" → Error, not an UCS2 character
• "4142" → Error, value of UCS2 character > 7F'H
• "008B" → Error, value of UCS2 character > 7F'H
This affects the maximum input length of a string)
Case 5
Every UCS2 character is sent as 4 IRA characters and is converted into two 8-bit values. This means that the
first two characters have to be '00'.
Example: UCS2 character 009F'H typed as "009F" is sent as 30'H,30'H,39'H,46'H → converted into 8-bit value
9F'H.
Maximum number of UCS2 characters is 140 which are represented by 560 IRA characters. Number of IRA characters must be a multiple of four.
Case 6
Every UCS2 character is sent as 4 IRA characters each and is converted into a 16-bit value again.
Example: UCS2 character 9F3A'H typed as "9F3A" is sent as 39'H,46'H,33'H,41'H → converted into 9F3A'H.
Maximum number of UCS2 characters is 70 which are represented by 280 IRA characters. Number of IRA characters must be a multiple of four.
Invalid UCS2 values must be prevented.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 24 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 25

1.6 Serial Interface Flow Control
Flow control is essential to prevent loss of data or avoid errors when, in a data or fax call, the sending device is
transferring data faster than the receiving side is ready to accept. When the receiving buffer reaches its capacity,
the receiving device should be capable to cause the sending device to pause until it catches up.
There are basically two approaches to regulate data flow: Software flow control and hardware flow control. The
High Watermark of the input/output buffer should be set to approximately 60% of the total buffer size. The Low
Watermark is recommended to be about 30%. The data flow should be stopped when the capacity rises close to
the High Watermark and resumed when it drops below the Low Watermark. The time required to cause stop and
go results in a hysteresis between the High and Low Watermarks.
During Multiplex mode (AT+CMUX) it is recommended to use hardware flow control.
1.6.1 Software Flow Control (XON/OFF Handshake)
Software flow control sends different characters to stop (XOFF, decimal 19) and resume (XON, decimal 17) data
flow. The only advantage of software flow control is that three wires would be sufficient on the serial interface.
1.6.2 Hardware Flow Control (RTS/CTS Handshake)
Hardware flow control sets or resets the RTS/CTS wires. This approach is faster and more reliable, and therefore, the better choice. When the High Watermark is reached, CTS is set inactive until the transfer from the buffer
has completed. When the Low Watermark is passed, CTS goes active again.
To achieve smooth data flow, ensure that the RTS/CTS lines are present on your application platform. The application should include options to enable RTS/CTS handshake with the GSM engine. This needs to be done with
the AT command AT\Q3 - it is not sufficient to set RTS/CTS handshake in the used Terminal program only.
The default setting of the GSM engine is AT\Q0 (no flow control) which must be altered to AT\Q3 (RTS/CTS
hardware handshake on). The setting is stored volatile and must be restored each time after the GSM engine
was switched off.
AT\Q has no read command. To verify the current setting of AT\Q, simply check the settings of the active profile
with AT&V.
Often, fax programs run an intialization procedure when started up. The intialization commonly includes enabling
RTS/CTS hardware handshake, eliminating the need to set AT\Q3 once again. However, before setting up a
CSD call, you are advised to check that RTS/CTS handshake is set.
RTS/CTS hardware handshake must also be set if you want to take advantage of the CYCLIC SLEEP modes.
For further details refer to AT+CFUN.
Note: After deactivating the RTS line, the ME may still send up to 264 bytes (worst case). This can be easily
handled if the buffer of the host application is sufficiently sized, and if a hysteresis is implemented regarding its
Rx buffer. For host applications that are required to handle a large amount of data at high speed, a total buffer
capacity of 512 bytes is recommended.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 25 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 26

1.7 Unsolicited Result Code Presentation
URC stands for Unsolicited Result Code and is a report message issued by the ME without being requested by
the TE, i.e. a URC is issued automatically when a certain event occurs. Hence, a URC is not issued as part of
the response related to an executed AT command.
Typical events leading to URCs are incoming calls ("RING"), waiting calls, received short messages, changes in
temperature, network registration etc.
A list of all URCs can be found in Section 20.7, Summary of Unsolicited Result Codes (URC).
To announce a pending URC transmission the ME will do the following:
• The ME activates its RING line (logic "1") for 1 second, i.e. the RING line changes to the physical "Low" level.
This allows the TE to stay in power saving mode until an ME related event requests service.
If several URCs occur coincidently or in quick succession each URC triggers the RING line independently,
although the line will not be deactivated between each URC. As a result, the RING line may stay low for more
than 1 second.
If an incoming call is answered within less than 1 second (with ATA or if autoanswering is set to ATS0=1) than
the RING line will be deactivated earlier.
The "^SHUTDOWN" URC will not activate the RING line.
• If the AT command interface is busy a "BREAK" will be sent immediately but the URC will not be issued until
the line is free. This may happen if the URC is pending in the following cases:
- During the processing of an AT command (i.e. the time after the TE echoes back the first character "A" of
an AT command just sent by itself until the ME responds with "OK" or "ERROR").
- During a data call.
Please note that AT command settings may be necessary to enable in-band signaling, e.g. refer to AT+CMER
or AT+CNMI.
It is strongly recommended to use the multiplex mode to map logical communication channels onto the serial line
of the MC55, for details refer to [5] and AT command AT+CMUX. Doing so it is possible to use one channel to still
process URCs while having a data call active on another.
For most of these messages, the ME needs to be configured whether or not to send a URC. Depending on the
AT command, the URC presentation mode can be saved to the user defined profile (see AT&W), or needs to be
activated every time you reboot the ME. Several URCs are not user definable, such as "^SYSSTART",
"^SYSSTART <text>", "^SHUTDOWN" and the Fax Class 2 URCs listed in Section 12.1, FAX parameters.
If autobauding is enabled (as factory default mode or set with AT+IPR=0), URCs generated after restart will be
output with 57600 bps until the ME has detected the current bit rate. The URCs "^SYSSTART", "^SYSSTART
<text>", however, are not presented at all. For details please refer to Section 4.7.1, Autobauding. To avoid problems we recommend to configure a fixed bit rate rather than using autobauding.
1.7.1 Communication between Customer Application and MC55
Leaving hardware flow control unconsidered the Customer Application (TE) is coupled with the MC55 (ME) via
a receive and a transmit line.
Since both lines are driven by independent devices collisions may (and will) happen, i.e. while the TE issues an
AT command the MC55 starts sending an URC. This will probably lead to the TE's misinterpretation of the URC
being part of the AT command's response.
To avoid this conflict the following measures must be taken:
• If an AT command is finished (with "OK" or "ERROR") the TE shall always wait at least 100 milliseconds
before sending the next one.
This gives the MC55 the opportunity to transmit pending URCs and get necessary service.
Note that some AT commands may require more delay after "OK" or "ERROR" response, refer to the following
command specifications for details.
• The TE shall communicate with the MC55 using activated echo (ATE1), i.e. the MC55 echoes characters
received from the TE.
Hence, when the TE receives the echo of the first character "A" of the AT command just sent by itself it has
control both over the receive and the transmit paths.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 26 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 27
1.8 Common PCN Handset Specification (CPHS)
The ME provides features to implement a device following the prerequisites of the Common PCN Handset Specification (CPHS) Phase 2.
CPHS Feature Description/Remarks AT command
Alternate Line Service Using two phone numbers with one SIM card. AT^SALS
Voice Message Waiting
Indication
Operator (Service provider) name from SIM
Network and Service Provider Lock
Call Forwarding Get and set diverted call status. Access specific Elementary
Customer Service Profile
(CSP)
Information numbers Hierarchically structured service numbers phonebook on
Indicate the receipt of a short message coded as Voice Message Waiting Indicator as defined by the CPHS Phase 2
standard.
Read specific Elementary Files (6F14h, 6F18h) from SIM. AT+CRSM
Lock/Unlock an ME to specific HPLMN and service provider. AT+CLCK,
File (6F13h) from SIM.
Setting services and their menu entries depending on cus-
tomer profiles.
SIM according to CPHS 4.2 (mandatory).
AT^SIND,
AT+CMER, indicators
"vmwait1" and
"vmwait2"
(AT+CPIN)
AT+CCFC, AT+CRSM
AT+CRSM
AT+CRSM
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 27 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 28

1.9 Errors and Messages
The command result codes "+CME ERROR: <err>" and "+CMS ERROR: <err>" indicate errors related to mobile
equipment or network functionality.
The format of <err> can be either numeric or verbose and is selectable via AT+CMEE.
A result error code terminates the execution of the command and prevents the execution of all remaining commands that may follow on the same command line. If so, neither "ERROR" nor "OK" result codes are returned
for these commands. A 30 seconds timeout will deliver "ERROR" when the input of a command is not complete.
Using the wrong command syntax may result in errors: For example, using the execute command syntax
although the command has no execute format, causes "ERROR" to be returned. Likewise, using the write command syntax although the command has no write format causes "+CME ERROR: <err>" to be returned.
See also:
• Section 2.11.1, CME/CMS Error Code Overview
• Section 2.5.1, Verbose and numeric result codes
• Section 3.4, AT+CEER
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 28 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 29

2. Configuration Commands
The AT Commands described in this chapter allow the external application to determine the MC55's behaviour
under various conditions.
2.1 AT&F Set all current parameters to manufacturer defaults
AT&F sets all current parameters to the manufacturer defined profile. All defined GPRS contexts which are not
activated or not online will be undefined (see AT+CGDCONT).
Syntax
Exec Command
AT&F[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
[0] Set all TA parameters to manufacturer defaults
(num)
Notes
• List of parameters reset to manufacturer default can be found in Section 20.6, Factory Default Set-
tings Restorable with AT&F.
• In addition to the default profile, you can store an individual one with AT&W. To alternate between the two profiles enter either ATZ (loads user profile) or AT&F (restores factory profile).
• Every ongoing or incoming call will be terminated.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 29 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 30

2.2 AT&V Display current configuration
AT&V returns the current parameter setting. The configuration varies depending on whether or not PIN authen-
tication has been done and whether or not Multiplex mode is enabled (see AT+CMUX).
Syntax
Exec Command
AT&V[<value>]
Response(s)
ACTIVE PROFILE:
... (see Section 2.2.1, AT&V responses)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % § % § § ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)
[0] Profile number
Notes
• The parameters of AT^SMGO can only be displayed after the SMS data from the SIM have been read successfully for the first time. Reading starts after successful SIM authentication has been performed, and may take
up to 30 seconds depending on the SIM used. While the read process is in progress, an attempt to read the
parameter will result in empty values.
• The parameter of AT+CSDH will only be displayed in SMS PDU mode, see AT+CMGF.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 30 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 31

2.2.1 AT&V responses
The following tables show four different kinds of responses depending on whether or not the PIN is entered and
whether or not the Multiplex mode is enabled (see AT+CMUX).
Table 2.1: Current configuration on ASC0 / MUX channel 1 (example)
PIN authentication done No PIN authentication
ACTIVE PROFILE:
E1 Q0 V1 X4 &C1 &D2 &S0 \Q0
S0:000 S3:013 S4:010 S5:008 S6:000 S7:060 S8:000
S10:002 S18:000
+CBST: 7,0,1
+CRLP: 61,61,78,6
+CR: 0
+FCLASS: 0
+CRC: 0
+CMGF: 1
+CSDH: 0
+CNMI: 0,0,0,0,1
+ILRR: 0
+IPR: 57600
+CMEE: 2
^SMGO: 0,0
+CSMS: 0,1,1,1
^SACM: 0,"000000","000000"
^SLCC: 0
^SCKS: 0,1
+CREG: 0,1
+CLIP: 0,2
+CAOC: 0
+COPS: 0,0,"operator"
+CGSMS: 3
OK
ACTIVE PROFILE:
E1 Q0 V1 X4 &C1 &D2 &S0 \Q0
S0:000 S3:013 S4:010 S5:008 S6:000 S7:060 S8:000
S10:002 S18:000
+CBST: 7,0,1
+CRLP: 61,61,78,6
+CR: 0
+FCLASS: 0
+ILRR: 0
+IPR: 57600
+CMEE: 2
^SCKS: 0,1
OK
Table 2.2: Current configuration on ASC1 and MUX channels 2 and 3 (example)
PIN authentication done No PIN authentication
ACTIVE PROFILE:
E1 Q0 V1 X4 &C1 &D0 &S0 \Q0
S0:000 S3:013 S4:010 S5:008
+CR: 0
+CRC: 0
+CMGF: 1
+CSDH: 0
+CNMI: 0,0,0,0,1
+ILRR: 0
+IPR: 57600
+CMEE: 2
^SMGO: 0,0
+CSMS: 0,1,1,1
^SACM: 0,"000000","000000"
^SLCC: 0
^SCKS: 0,1
+CREG: 0,1
+CLIP: 0,2
+CAOC: 0
+COPS: 0,0,"operator"
+CGSMS: 3
OK
ACTIVE PROFILE:
E1 Q0 V1 X4 &C1 &D0 &S0 \Q0
S0:000 S3:013 S4:010 S5:008
+CR: 0
+ILRR: 0
+IPR: 57600
+CMEE: 2
^SCKS: 0,1
+CGSMS: 3
OK
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 31 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 32

2.3 AT&W Stores current configuration to user defined profile
AT&W stores the currently set parameters to a user defined profile in the non-volatile memory.
Syntax
Exec Command
AT&W[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR/+CME ERROR <err>
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)
[0] Number of profile
Notes
• The user defined profile will be restored automatically after power-up. Use ATZ to restore user profile and
AT&F to restore factory settings. Until the first use of AT&W, ATZ works as AT&F.
• AT&W stores all global settings and the current local settings of the interface, on which the command is executed.
• A list of parameters stored to the user profile can be found in Section 20.5, AT Command Settings stor-
able with AT&W.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 32 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 33

2.4 ATQ Set result code presentation mode
This parameter setting determines whether or not the TA transmits any result code to the TE. Information text
transmitted in response is not affected by this setting.
Syntax
Exec Command
ATQ[<n>]
Response(s)
If <n>=0:
OK
If <n>=1:
(none)
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
(num)(&W)(&V)
<n>
(&F)
[0]
1 Result codes are suppressed and not transmitted
DCE transmits result code
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 33 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 34

2.5 ATV Set result code format mode
This command determines the contents of header and trailer transmitted with AT command result codes and
information responses. Possible responses are described in Section 2.5.1, Verbose and numeric result codes.
Syntax
Exec Command
ATV[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)(&W)(&V)
[0] Information response: <text><CR><LF>
Short result code format: <numeric code><CR>
(&F)
1
Information response: <CR><LF><text><CR><LF>
Long result code format: <CR><LF><verbose code><CR>
2.5.1 Verbose and numeric result codes
Verbose format Numeric format Meaning
OK 0 Command executed, no errors
CONNECT 1 Link established
RING 2 Ring detected
NO CARRIER 3 Link not established or disconnected
ERROR 4 Invalid command or command line too long
NO DIALTONE 6 No dial tone, dialling impossible, wrong mode
BUSY 7 Remote station busy
CONNECT 2400/RLP 47 Link with 2400 bps and Radio Link Protocol
CONNECT 4800/RLP 48 Link with 4800 bps and Radio Link Protocol
CONNECT 9600/RLP 49 Link with 9600 bps and Radio Link Protocol
CONNECT 14400/RLP 50 Link with 14400 bps and Radio Link Protocol
ALERTING Alerting at called phone
DIALING Mobile phone is dialing
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 34 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 35

2.6 ATX Set CONNECT result code format and call monitoring
ATX determines whether or not the TA detects the presence of dial tone and busy signal and whether or not TA
transmits particular result codes.
Syntax
Exec Command
ATX[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)(&W)(&V)
[0] CONNECT result code only returned, dial tone and busy detection are both dis-
abled.
1 CONNECT <text> result code only returned, dial tone and busy detection are
both disabled.
2 CONNECT <text> result code returned, dial tone detection is enabled, busy
detection is disabled.
3 CONNECT <text> result code returned, dial tone detection is disabled, busy
detection is enabled.
(&F)
4
CONNECT <text> result code returned, dial tone and busy detection are both
enabled.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 35 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 36

2.7 ATZ Set all current parameters to user defined profile
ATZ sets all current parameters to the user profile stored with AT&W. If a connection is in progress, it will be ter-
minated.
All defined GPRS contexts which are not activated or not online will be undefined (see AT+CGDCONT).
The user defined profile is stored to the non-volatile memory.
Syntax
Exec Command
ATZ[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)
[0] Reset to user profile
Notes
• First the profile will be set to factory default (see AT&F). If there is a valid user profile (stored with AT&W), this
profile will be loaded afterwards.
• Any additional commands on the same command line may be ignored. A delay of 300 ms is required before
next command is sent, otherwise "OK" response may be corrupted.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 36 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 37

2.8 AT+CFUN Set phone functionality
The AT+CFUN command serves to control the functionality level of the ME. It can be used to reset the ME, to
choose one of the SLEEP modes or to return to full functionality.
Intended for power saving, SLEEP mode reduces the functionality of the ME to a minimum and thus minimizes
the current consumption. SLEEP mode falls in two categories:
• NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode <fun>=0
• and CYCLIC SLEEP modes, selectable as <fun>= 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9.
NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode permanently blocks the serial interface. The CYCLIC SLEEP mode, however, is a
dynamic process which alternatingly enables and disables the serial interface. The major benefit of all CYCLIC
SLEEP modes is that the serial interface remains accessible and that, in intermittent wake-up periods, characters
can be sent or received without terminating the selected mode. The best choice is using <fun>= 7, 8 or 9, since
in these modes MC55 automatically resumes power saving, after you have sent or received a short message or
made a call. <fun>=5 or 6 do not offer this feature to the same extent and are only supported for compatibility
with earlier releases. In all CYCLIC SLEEP modes, you can enter <fun>=1 to permanently wake up MC55 and
take it back to full functionality. Please refer to Section 2.8.1, Wake up the ME from SLEEP mode for a summary
of all SLEEP modes and the different ways of waking up the module.
For CYCLIC SLEEP mode (<fun>= 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9) both the ME and the application must be configured to use
hardware flow control. This is necessary since the CTS signal is set/reset every time when the ME listens to a
paging message from the base station. This is the way how the module indicates to the application when the
UART is active. For detailed information on the timing of the CTS signal refer to [2]. The default setting of hardware flow control is AT\Q0 which must be altered to AT\Q3. For use after restart you are advised to add it to the
user profile saved with AT&W.
If both interfaces ASC0 and ASC1 are connected, hardware flow control must be set in either application.
The AT+CFUN test command returns the values of the supported parameters.
The AT+CFUN read command returns the current functionality value.
The AT+CFUN write command can be used to reset the ME, to choose one of the SLEEP modes or to return to
full functionality.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CFUN=?
Response(s)
+CFUN: (list of supported <fun>s) , (list of supported <rst>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+CFUN?
Response(s)
+CFUN: <fun>
OK
Write Command
AT+CFUN=[<fun>[, <rst>]]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 ! % % § § § ! ! !
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 37 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 38

Unsolicited Result Codes
URC 1
^SYSSTART
Indicates that the ME has been started and is ready to operate. If autobauding is active (AT+IPR=0) the URC
is not generated.
URC 2
^SYSSTART CHARGE ONLY MODE
Indicates that the ME has entered the CHARGE ONLY mode. This occurs if the charger is connected while
the ME is in POWER DOWN mode. If autobauding is active (AT+IPR=0) the URC is not generated. In
CHARGE ONLY mode the ME is neither registered to the GSM network nor are the serial interfaces fully
accessible. Only the AT commands listed in Section 20.4, Availability of AT Commands Depending
on Operating Mode of ME can be used. For further details on charging refer to the Hardware Interface
Description [2].
Parameter Description
<fun>
(num)
0 NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode:
In this mode, the AT interface is not accessible. Consequently, after setting
<fun>=0, do not send further characters. Otherwise these characters remain
in the input buffer and may delay the output of an unsolicited result code.
The first wake-up event stops power saving and takes the ME back to full functionality level <fun>=1.
(&F)(P)
[1]
Full functionality.
If the ME is in one of the CYCLIC SLEEP modes you can issue AT+CFUN=1
to stop power saving and return to full functionality.
Keep in mind that, unlike the reset command described below, this action does
not restart the ME but only changes the level of functionality. See parameter
<rst> for details on the reset.
5 CYCLIC SLEEP mode:
In this mode, the serial interface is shortly enabled while CTS is active. If characters are recognized on the serial interface, the ME stays active for 2 seconds
after the last character was sent or received.
6 CYCLIC SLEEP mode:
In this mode, the serial interface is shortly enabled while CTS is active. If characters are recognized on the serial interface, the ME stays active for 10 minutes after the last character was sent or received.
To ensure that power saving takes effect immediately, the ME stays active for
only 2 seconds after <fun>=6 was entered.
7 CYCLIC SLEEP mode:
In this mode, the serial interface is shortly enabled while CTS is active. If characters are recognized on the serial interface, the ME stays active for 2 seconds
after the last character was sent or received. ME exits SLEEP mode only, if
AT+CFUN=1 is entered.
8 CYCLIC SLEEP mode:
In this mode, the serial interface is shortly enabled while CTS is active. If characters are recognized on the serial interface, the ME stays active for 10 minutes after the last character was sent or received. ME exits SLEEP mode only,
if AT+CFUN=1 is entered.
To ensure that power saving takes effect immediately, the ME stays active for
only 2 seconds after <fun>=8 was entered.
9 CYCLIC SLEEP mode:
In this mode, the serial interface is shortly enabled while CTS is active. If characters are recognized on the serial interface, the ME stays active after the last
character was sent or received for at least the time, which can be configured
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 38 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 39

by AT^SCFG="PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout",<psm9to> (temporary wakeup).
In contrast to SLEEP modes 5,6,7 and 8 assertion of RTS can also be used to
temporarily wake up the ME. In this case too, activity time is at least the time
set with AT^SCFG="PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout",<psm9to>. RTS can be
activated either from ASC0 or ASC1.
ME exits SLEEP mode only, if AT+CFUN=1 is entered.
<rst>
(num)
The parameter can only be used if the serial interface is enabled.
Due to the command syntax, you need to enter parameter <fun>, followed by <rst>, where <fun> is only a
placeholder and has no effect. See examples below.
[0] Placeholder for <fun> as stated above.
1 ME resets and restarts to full functionality. After reset and restart, PIN 1
authentication is necessary (AT+CPIN). If autobauding is enabled, it is recommended to wait 3 to 5 seconds before entering the first AT command. For
details on autobauding refer to Section 4.7.1, Autobauding.
Notes
• If both serial interfaces ASC0 and ASC1 are connected, any functionality level set with AT+CFUN takes effect
on both of them. In Multiplex mode, the CFUN profile is shared by all multiplexer channels.
• If the ME is in Multiplexer mode, it is not recommended to activate SLEEP mode with AT+CFUN=<fun>. The
best approach to properly control SLEEP mode in this case is to issue the PSC messages described in [5],
Section "Power saving control".
• When a circuit-switched call is in progress, <fun>=7 or 8 or 9 can be activated without terminating the call.
However, setting <fun>=0, 5 or 6 during a circuit-switched call immediately disconnects this call.
• Please keep in mind that power saving works properly only when PIN authentication has been done. If you
attempt to activate power saving while the SIM card is not inserted or the PIN is not correctly entered, the
selected <fun> level will be set, though power saving does not take effect. For the same reason, power saving cannot be used if MC55 operates in Alarm mode. Furthermore, in order to accept incoming calls, SMS or
network related URCs in SLEEP mode the ME must be registered when it enters the SLEEP mode.
• To check whether power saving is on, you can query the status with the read command AT+CFUN? only if
the module is in full functionality mode or in CYCLIC SLEEP mode. If available, you can also take advantage
of the status LED controlled by the SYNC pin (see AT^SSYNC and [2]). The LED remains "off" while the module is in any of the SLEEP modes. However, the module can wake up temporarily from power saving without
leaving its CYCLIC SLEEP mode (without changing +CFUN "<fun>"), e.g. for a network scan after a loss of
radio coverage, or after receipt of serial data during CYCLIC SLEEP mode. During this "temporary wakeup
state" the LED will operate as if the ME was in full functionality mode.
• Recommendation: In NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode, you can set an RTC alarm to wake up the ME and return
to full functionality. This is a useful approach because, in this mode, the AT interface is not accessible.
Examples
EXAMPLE 1
To check the level of functionality use the read command:
AT+CFUN?
+CFUN: 1
Remember that the AT interface is not accessible in NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode. Consequently, the read
command is only useful when the ME is set to full functionality or, when <fun> is set to 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9.
AT+CFUN?
+CFUN: 5
EXAMPLE 2
To set the ME to NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode enter
AT+CFUN=0
OK
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 39 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Default mode after ME was restarted
CYCLIC SLEEP mode
Page 40

When, for example, an SMS is being received and indicated by an unsolicited result code (URC), the ME
wakes up to full operation.
+CMTI: "SM",5
Note that the URC used in this example will appear only, if
AT+CNMI=1,1 was configured before.
After this, you may want to verify the operating status:
AT+CFUN?
+CFUN: 1
EXAMPLE 3
Indicates that ME has entered full functionality mode.
To stop CYCLIC SLEEP mode and return to full functionality:
AT+CFUN?
+CFUN: 5
OK
AT+CFUN=1
OK
Remember that this approach is not applicable to the NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode (since the serial interface
is disabled). The NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode ends with the first wake-up event.
EXAMPLE 4
To reset and restart the ME:
AT+CFUN=1,1
or alternatively, AT+CFUN=0,1 or 5,1 or 6,1 or 7,1 or 8,1 or 9,1
OK
^SYSSTART
The ^SYSSTART URC confirms that the ME has been rebooted. Note
that ^SYSSTART appears only if AT+IPR ≠ 0. If the ME is in autobaud
mode, it is recommended to wait 3 to 5 seconds before entering the first
AT command. Remember to enter the SIM PIN after restart.
2.8.1 Wake up the ME from SLEEP mode
A wake-up event is any event that causes the ME to draw more current. Depending on the selected mode, the
wake-up event either switches the SLEEP mode off and takes the ME back to full functionality AT+CFUN=1, or
activates the ME temporarily without terminating the selected SLEEP mode.
Definitions of the state transitions described in Table 2.3:
• Quit: ME exits SLEEP mode.
• Temporary: ME becomes active temporarily for the duration of the event and the mode-specific follow-up time
after the last character was sent or received on the serial interface.
• No effect: Event is not relevant in the selected SLEEP mode. The ME does not wake up.
Table 2.3: Wake-up events in NON-CYCLIC and CYCLIC SLEEP modes
Event Selected mode:
<fun>=0
Ignition line No effect No effect No effect
/RTS0 or /RTS1 activation Quit No effect (RTS is only
Unsolicited Result Code
Quit Quit Temporary
(URC)
Incoming voice or data
Quit Quit Temporary
call
Selected mode:
<fun>=5 or 6
used for flow control)
Selected mode:
<fun>=7 or 8 or 9
Mode 7 and 8: No effect
(RTS is only used for flow
control)
Mode 9: Temporary
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 40 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 41

Event Selected mode:
<fun>=0
Any AT command (incl.
outgoing SMS, voice or
data call)
Incoming SMS (AT+CNMI
is set to 0,0 (this is the
default setting)
Incoming SMS (AT+CNMI
is set to 1,1)
GPRS data transfer Not possible (UART dis-
RTC alarm line Quit Quit Temporary
AT+CFUN=1 Not possible (UART dis-
Not possible (UART disabled)
No effect No effect No effect
Quit Quit Temporary
abled)
abled)
Selected mode:
<fun>=5 or 6
Temporary Temporary
Temporary Temporary
Quit Quit
Selected mode:
<fun>=7 or 8 or 9
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 41 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 42

2.9 AT^SMSO Switch off mobile station
AT^SMSO initiates the power-off procedure. Low level of the module's VDD pin and the URC "^SHUTDOWN" notify
that the procedure has completed and the module has entered the POWER DOWN mode. Therefore, be sure
not to disconnect the operating voltage until VDD is low or until the URC "^SHUTDOWN" is displayed. Otherwise,
you run the risk of losing data. For further details on how to turn off the module see the [2].
Syntax
Test Command
AT^SMSO=?
Response(s)
OK
Exec Command
AT^SMSO
Response(s)
^SMSO: MS OFF
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
SIEMENS ! % % % % % % % %
Unsolicited Result Code
^SHUTDOWN
Indicates that the power-off procedure is finished and the module will be switched off in less than 1 second.
Notes
• Do not send any other AT command after AT^SMSO.
• If AT^SMSO is entered on one of the Multiplexer channels the ME closes the Multiplexer channels, terminates
the Multiplexer and deactivates all other functions. Then, the URC "^SHUTDOWN" will be issued on the phys-
ical serial interface (ASC0). The URC will be transmitted at the bit rate last activated on ASC0 for use with
the Multiplex driver.
• If both interfaces ASC0 and ASC1 are connected the URC appears on both of them.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 42 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 43

2.10 AT+GCAP Request complete TA capabilities list
AT+GCAP returns a list of additional capabilities.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+GCAP=?
Response(s)
OK
Exec Command
AT+GCAP
Response(s)
+GCAP: <name>
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<name>
(str)
e.g.: +CGSM,+FCLASS
Note
• +CGSM: The response text shows which GSM commands of the ETSI standard are supported.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 43 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 44

2.11 AT+CMEE Mobile Equipment Error Message Format
AT+CMEE controls the format of the error result codes that indicates errors related to MC55 functionality. Format
can be selected between plain "ERROR" output, error numbers or verbose "+CME ERROR: <err>" and "+CMS
ERROR: <err>" messages.
Possible error result codes are listed in Table 2.4, General "CME ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.07)Table 2.5, Gen-
eral "CME ERROR" Codes (SIEMENS)Table 2.6, GPRS related "CME ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.07) and Table
2.7, SMS related "CMS ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.05).
In multiplex mode (refer AT+CMUX) the setting applies only to the logical channel where selected. The setting on
the other channels may differ.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CMEE=?
Response(s)
+CMEE: (list of supported<errMode>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+CMEE?
Response(s)
+CMEE: <errMode>
OK
Write Command
AT+CMEE=<errMode>
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<errMode>
(&F)(D)
0
1 Enable error result code with numeric values.
2 Enable error result code with verbose (string) values.
(num)(&W)(&V)
Disable result code, i.e. only "ERROR" will be displayed.
Example
To obtain enhanced error messages it is recommended to choose <errMode>=2.
AT+CMEE=2
OK
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 44 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 45

2.11.1 CME/CMS Error Code Overview
Table 2.4: General "CME ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.07)
<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
0 phone failure
1 no connection to phone
2 phone-adapter link reserved
3 Operation not allowed
4 Operation not supported
5 PH-SIM PIN required
6 PH-FSIM PIN required
7 PH-FSIM PUK required
10 SIM not inserted
11 SIM PIN required
12 SIM PUK required
13 SIM failure
14 SIM busy
15 SIM wrong
16 Incorrect password
17 SIM PIN2 required
18 SIM PUK2 required
20 Memory full
21 invalid index
22 not found
23 Memory failure
24 text string too long
25 invalid characters in text string
26 dial string too long
27 invalid characters in dial string
30 no network service
31 Network timeout
32 Network not allowed emergency calls only
40 Network personalization PIN required
41 Network personalization PUK required
42 Network subset personalization PIN required
43 Network subset personalization PUK required
44 service provider personalization PIN required
45 service provider personalization PUK required
46 Corporate pe sonalization PIN required
47 Corporate personalization PUK required
48 Master Phone Code required
100 unknown
132 service option not supported
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 45 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 46

<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
133 requested service option not subscribed
134 service option temporarily out of order
256 Operation temporary not allowed
257 call barred
258 phone busy
259 user abort
260 invalid dial string
261 ss not executed
262 SIM blocked
263 Invalid Block
Table 2.5: General "CME ERROR" Codes (SIEMENS)
<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
615 network failure
616 network is down
639 service type not yet available
640 operation of service temporary not allowed
764 missing input value
765 invalid input value
767 operation failed
Table 2.6: GPRS related "CME ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.07)
<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
103 Illegal MS
106 Illegal ME
107 GPRS services not allowed
111 PLMN not allowed
112 Location area not allowed
113 Roaming not allowed in this location area
148 unspecified GPRS error
149 PDP authentication failure
150 invalid mobile class
Table 2.7: SMS related "CMS ERROR" Codes (GSM 07.05)
<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
1 Unassigned (unallocated) number
8 Operator determined barring
10 Call barred
21 Short message transfer rejected
27 Destination out of service
28 Unidentified subscriber
29 Facility rejected
30 Unknown subscriber
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 46 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 47

<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
38 Network out of order
41 Temporary failure
42 Congestion
47 Resources unavailable, unspecified
50 Requested facility not subscribed
69 Requested facility not implemented
81 Invalid short message transfer reference value
95 Invalid message, unspecified
96 Invalid mandatory information
97 Message type non-existent or not implemented
98 Message not compatible with short message protocol state
99 Information element non-existent or not implemented
111 Protocol error, unspecified
127 Interworking, unspecified
128 Telematic interworking not supported
129 Short message Type 0 not supported
130 Cannot replace short message
143 Unspecified TP-PID error
144 Data coding scheme (alphabet) not supported
145 Message class not supported
159 Unspecified TP-DCS error
160 Command cannot be actioned
161 Command unsupported
175 Unspecified TP-Command error
176 TPDU not supported
192 SC busy
193 No SC subscription
194 SC system failure
195 Invalid SME address
196 Destination SME barred
197 SM Rejected-Duplicate SM
198 TP-VPF not supported
199 TP-VP not supported
208 D0 SIM SMS storage full
209 No SMS storage capability in SIM
210 Error in MS
211 Memory Capacity Exceeded
212 SIM Application Toolkit Busy
213 SIM data download error
255 Unspecified error cause
300 ME failure
301 SMS service of ME reserved
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 47 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 48

<err> Code Text (if AT+CMEE=2)
302 Operation not allowed
303 Operation not supported
304 Invalid PDU mode parameter
305 Invalid text mode parameter
310 SIM not inserted
311 SIM PIN required
312 PH-SIM PIN required
313 SIM failure
314 SIM busy
315 SIM wrong
316 SIM PUK required
317 SIM PIN2 required
318 SIM PUK2 required
320 Memory failure
321 Invalid memory index
322 Memory full
330 SMSC address unknown
331 no network service
332 Network timeout
340 NO +CNMA ACK EXPECTED
500 Unknown error
512 User abort
513 unable to store
514 invalid status
515 invalid character in address string
516 invalid length
517 invalid character in pdu
518 invalid parameter
519 invalid length or character
520 invalid character in text
521 timer expired
522 Operation temporary not allowed
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 48 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 49

2.12 AT+CSCS Select TE character set
The AT+CSCS write command informs the TA which character set <chset> is used by the TE. This enables the
TA to convert character strings correctly between TE and ME character sets. See also Section 1.5, Supported
character sets.
Note that when the TA-TE interface is set to 8-bit operation and the used TE alphabet is 7-bit, the highest bit will
be set to zero.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CSCS=?
Response(s)
+CSCS: (list of supported<chset>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+CSCS?
Response(s)
+CSCS: <chset>
OK
Write Command
AT+CSCS=[<chset>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07, GSM 11.11 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<chset>
"GSM"
"UCS2" 16-bit universal multiple-octet coded character set (ISO/IEC10646 [32]); UCS2
(str)
(&F)(P)
GSM default alphabet (GSM 03.38 subclause 6.2.1);
Note: This setting may cause software flow control problems since the codes
used to stop and resume data flow (XOFF = decimal 19, XON = decimal 17)
are interpreted as normal characters.
character strings are converted to hexadecimal numbers from 0000 to FFFF;
e.g. "004100620063" equals three 16-bit characters with decimal values 65, 98
and 99.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 49 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 50

2.13 AT^SCFG Extended Configuration Settings
AT^SCFG can be used to query and configure various settings of the MC55.
The AT^SCFG read command returns a list of all supported parameters and their current values.
The AT^SCFG write command queries a configuration parameter (if no value is entered) or sets its value(s).
Input of parameter names is always coded in GSM character set, parameter values are expected to be given as
specified via AT+CSCS.
The following error messages may be returned by the AT^SCFG write commands:
• "+CME ERROR: operation temporary not allowed"
Change of parameter value(s) temporarily not allowed.
• "+CME ERROR: invalid index"
Invalid parameter name or value(s).
• "+CME ERROR: invalid characters in text string"
Character set conversion of parameter value(s) failed.
• "+CME ERROR: memory failure"
Could not allocate necessary memory or storing a parameter failed.
• "+CME ERROR: operation not allowed"
Change of parameter value(s) not allowed
• "+CME ERROR: unknown"
Other error
Syntax
Test Command
AT^SCFG=?
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Audio/AMR", (list of supported <amr>s)
^SCFG: "Call/SpeechVersion1", (list of supported <csv1>s)
^SCFG: "GPRS/ATS0/withAttach", (list of supported <gs0aa>s)
^SCFG: "GPRS/RingOnIncomingData", (list of supported <groid>s)
^SCFG: "PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout", (list of supported <psm9to>s)
^SCFG: "Radio/Band/HandOver", (list of supported <HandOverStatus>s)
^SCFG: "Tcp/IRT", (list of supported <tcpIrt>)
^SCFG: "Tcp/MR", (list of supported <tcpMr>)
^SCFG: "Tcp/OT", (list of supported <tcpOt>)
^SCFG: "Tcp/WithURCs", (list of supported <tcpWithUrc>)
^SCFG: "URC/CallStatus/CIEV", (list of supported <succ>s)
^SCFG: "URC/CallStatus/SLCC", (list of supported <sucs>s)
^SCFG: "URC/Datamode/Ringline", (list of supported <udri>s)
^SCFG: "URC/Ringline", (list of supported <uri>s)
^SCFG: "URC/Ringline/ActiveTime", (list of supported <urat>s)
OK
Read Command
AT^SCFG?
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Audio/AMR", <amr>1[, <amr>2[, <amr>3...[<amr>10]]]
^SCFG: "Call/SpeechVersion1", <csv1>
^SCFG: "GPRS/ATS0/withAttach", <gs0aa>
^SCFG: "GPRS/RingOnIncomingData", <groid>
^SCFG: "PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout", <psm9to>
^SCFG: "Radio/Band/HandOver", <HandOverStatus>
^SCFG: "Tcp/IRT", <tcpIrt>
^SCFG: "Tcp/MR", <tcpMr>
^SCFG: "Tcp/OT", <tcpOt>
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 50 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 51

Read Command (Continued)
AT^SCFG?
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Tcp/WithURCs", <tcpWithUrc>
^SCFG: "URC/CallStatus/CIEV", <succ>
^SCFG: "URC/CallStatus/SLCC", <sucs>
^SCFG: "URC/Datamode/Ringline", <udri>
^SCFG: "URC/Ringline", <uri>
^SCFG: "URC/Ringline/ActiveTime", <urat>
OK
Write Command
Adaptive Multi Rate (AMR):
AT^SCFG="Audio/AMR"[, <amr>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Audio/AMR", <amr>1[, <amr>2[, <amr>3...[<amr>10]]]
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Query/Configure SpeechVersion1
AT^SCFG="Call/SpeechVersion1"[, <csv1>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Call/SpeechVersion1", <csv1>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
GPRS ATS0 with automatic attach
AT^SCFG="GPRS/ATS0/withAttach"[, <gs0aa>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "GPRS/ATS0/withAttach", <gs0aa>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Ring on incoming GPRS IP data packets
AT^SCFG="GPRS/RingOnIncomingData"[, <groid>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "GPRS/RingOnIncomingData", <groid>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Query/Set timeout value for power saving mode 9
AT^SCFG="PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout"[, <psm9to>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout", <psm9to>
OK
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 51 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 52

Write Command (Continued)
Query/Set timeout value for power saving mode 9
AT^SCFG="PowerSaver/Mode9/Timeout"[, <psm9to>]
Response(s)
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Control Special Call Handover Setting
AT^SCFG="Radio/Band/HandOver"[, <HandOverStatus>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Radio/Band/HandOver", <HandOverStatus>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Configuration of TCP parameter 'InitialRetransmissionTimeout':
AT^SCFG="Tcp/IRT"[, <tcpIrt>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Tcp/IRT", <tcpIrt>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Configuration of TCP parameter 'MaxRetransmissions':
AT^SCFG="Tcp/MR"[, <tcpMr>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Tcp/MR", <tcpMr>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Configuration of TCP parameter 'OverallTimeout':
AT^SCFG="Tcp/OT"[, <tcpOt>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Tcp/OT", <tcpOt>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Configuration of Internet Service URCs:
AT^SCFG="Tcp/WithURCs"[, <tcpWithUrc>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "Tcp/WithURCs", <tcpWithUrc>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 52 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 53

Write Command
Configuration of URC "+CIEV: call" Call Status Indication
AT^SCFG="URC/CallStatus/CIEV"[, <succ>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "URC/CallStatus/CIEV", <succ>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Configuration of URC "^SLCC" Call Status Indication
AT^SCFG="URC/CallStatus/SLCC"[, <sucs>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "URC/CallStatus/SLCC", <sucs>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
URC indication in datamode via Ring line:
AT^SCFG="URC/Datamode/Ringline"[, <udri>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "URC/Datamode/Ringline", <udri>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
URC indication via Ring line:
AT^SCFG="URC/Ringline"[, <uri>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "URC/Ringline", <uri>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Write Command
Duration of active RING line for URC indications:
AT^SCFG="URC/Ringline/ActiveTime"[, <urat>]
Response(s)
^SCFG: "URC/Ringline/ActiveTime", <urat>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
! % % % % % ! ! !
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 53 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 54

Parameter Description
<amr>
(str)(+CSCS)
Adaptive Multi Rate
This parameter can be used to control the usage of the feature "Adaptive Multi Rate" (AMR). It is possible to
enable or disable this feature for all network operators, or to enable it for selected operators (max. 10). If the
feature is enabled for all operators, any request to enable it for a specific operator will result in a "+CME ERROR:
operation temporary not allowed".
Changes of this parameter become active with the next call.
Parameter is global for all interfaces, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
"enabled"
(P)
AMR is used for every operator.
"disabled" AMR is not used for any operator.
00000...999999 Enable AMR for the specified operator (in BCD or IRA format; see AT+COPS).
<csv1>
(str)(+CSCS)
Call Speech Version1
This parameter can be used to query or configure the speech version 1 indication in the bearer capabilities in
case of voice calls (see GSM 04.08). Speech version 2 (EFR) is always enabled; speech version 3 ( AMR) is
not affected by this command.
If you try to change this parameter as long as a circuit switched call is active, the command returns the new value
and "OK", but the changes will not take effect before next call setup.
Parameter is global for the ME, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
(P)
"0"
FR and HR codecs are enabled for speech calls - full rate codec is preferred.
"1" FR and HR codecs are enabled for speech calls - half rate codec is preferred.
"2" Half rate codec is disabled for speech calls.
<gs0aa>
(str)(+CSCS)
GPRS ATS0 with Attach
This parameter can be used to control the behaviour of ATS0.
Parameter is global for all interfaces, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
(P)
"on"
When the ATS0=<n> (<n>>0) command is received, the MT will attempt to per-
form a GPRS attach.
"off" When the ATS0=<n> (<n>>0) command is received, the MT will not attempt to
perform a GPRS attach.
<groid>
(str)(+CSCS)
Ring on incoming GPRS IP data packets
This parameter can be used to control the behaviour of the RING line for incoming IP packets in GPRS online
mode.
Parameter is local for the interface, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
"on" If the ME is in power saving mode 7 or 8 or 9 (see AT+CFUN) and hardware
flow control is in use (AT\Q3) and the RTS line is inactive and there are incom-
ing IP packets for a GPRS context which is online, then the RING line will be
activated once, for a time which is configured by the parameter "URC/Ringline/
ActiveTime" (<urat>). The RING line to be used can be configured with the
parameter "URC/Ringline" (<uri>).
(P)
"off"
RING line is not activated for incoming IP packets.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 54 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 55

<psm9to>
(str)(+CSCS)
Power saving mode 9 timeout
This parameter can be used to query or configure the wake up time for power saving mode 9 (see AT+CFUN with
parameter <fun>=9).
Parameter is global for the ME, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
(P)
5...20
...36000 The granularity of the timeout value is 100ms (i.e. a value of 10 equal 1 sec-
ond). The minimum timeout value that can be applied is 5, but accuracy is only
guaranteed for timeout values greater than 20.
<HandOverStatus>
(str)(+CSCS)
Call Handover Status
This parameter offers a workaround to prevent problems during call handover into the 1900 MHz (or 1800 MHz)
band, caused by non-conforming configurations of the 1900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) GSM network.
(P)
"0"
Disable workaround.
"1" Enable workaround. This value should be selected when handover into a 1900
MHz (or 1800 MHz) GSM network fails. If required for permanent use the value
needs to be set each time the ME is restarted.
<tcpIrt>
(str)(+CSCS)
Initial Retransmission Timeout (IRT)
(&F)(D)
1...3
...60 This parameter determines the time (in seconds) the TCP/IP stack will wait
before starting the first retransmission of packets during the initial connection
establishment phase.
The TCP protocol ensures the retransmission of packets several times at
increasing intervals until some upper limit is reached.
This mechanism prevents packet loss and serious congestion problems. In
addition, the parameters <tcpMr> and <tcpOt> can be set to further optimize
this mechanism for special conditions depending on the mobile network.
Parameter is global for the ME and non-volatile. Use of default value is recom-
mended. If changed the new value takes effect the next time you start an Inter-
net service with AT^SISO.
<tcpMr>
(str)(+CSCS)
Maximum Number of Retransmissions (MR)
(&F)(D)
1...10
...30 This parameter determines the maximum number of times to retransmit TCP
packets.
The value set with <tcpMr> will be assumed as default for the <srv-
ParmTag> "tcpMR" when a new service profile is created with AT^SISS. In
each service profile, you can set another "tcpMR" value which has precedence
over the global value set with AT^SCFG. Existing service profiles are not
affected when you change the global value via AT^SCFG.
Parameter is global for the ME and non-volatile. Use of default value is recom-
mended.
<tcpOt>
(str)(+CSCS)
Overall TCP Timer for outstanding connections (tcpOT)
1...6000
(&F)(D)
This parameter specifies the number of seconds to wait before closing a con-
nection if TCP/IP packets are not acknowledged.
Setting the maximum value is practically equivalent to deactivating the tcpOT
mechanism because the maximum time would never be reached by the TCP/
IP stack.
The value set with <tcpOt> will be assumed as default for the <srv-
ParmTag> "tcpOT" when a new service profile is created with AT^SISS. How-
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 55 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 56

ever, in each service profile, you can set another "tcpOT" value which has
precedence over the global value set with AT^SCFG. Existing service profiles
are not affected when you change the global value via AT^SCFG.
Parameter is non-volatile. Use of default value is recommended.
<tcpWithUrc>
(str)(+CSCS)
URC mode or polling mode for Internet service commands
This parameter enables or disables the presentation of the following URCs related to Internet service com-
mands: "^SISR" URC, "^SISW" URC and "^SIS" URC for parameter <urcCause>=0 (Internet service events).
"^SIS" URCs with <urcCause>=1 or 2 used to indicate incoming Socket connections are always enabled.
Parameter is global for the ME and non-volatile.
(&F)(D)
"on"
Enable URCs related to Internet service commands.
Throughout the Chapter "Internet Service AT Commands" the mode is also
referred to as URC mode.
"off" Disable URCs related to Internet service commands.
This requires the host application to employ polling techniques when using the
Internet service AT commands: The host application is responsible to retrieve
all status information needed to control an Internet session. The method is
referred to as polling mode.
<succ>
(str)(+CSCS)
CIEV Call Status Indication
This parameter can be used to control the behaviour of URC "+CIEV: call". See also AT+CIND, AT+CMER and
Section 7.1, Call Status Information.
Parameter is global for all interfaces and will not be reset by AT&F.
"restricted"
(P)
URC "+CIEV: call" will be issued only when a Call Status transition ends in
state "active" or "unknown" (see Section 7.1, Call Status Information) for a call
in the list of active calls.
"verbose" URC "+CIEV: call" will be issued when any state transition (including transi-
tions beginning or ending in state "unknown") occurs in the list of active calls,
or when a traffic channel is established.
<sucs>
(str)(+CSCS)
SLCC Call Status Indication
This parameter can be used to control the behaviour of URC "^SLCC". See also AT^SLCC and Section 7.1, Call
Status Information.
Parameter is global for all interfaces and will not be reset by AT&F.
"restricted" URC "^SLCC" will be issued only when a Call Status transition ends in state
"active" or "unknown" (see Section 7.1, Call Status Information) for a call in the
list of active calls
"verbose"
(P)
URC "^SLCC" will be issued when any state transition (including transitions
beginning or ending in state "unknown") occurs in the list of active calls, or
when a traffic channel is established.
<uri>
(str)(+CSCS)
URC RING line
This parameter can be used to control the behaviour of the RING line to indicate URCs (both for idle interfaces
and, if configured by the parameter "URC/Datamode/Ringline", if link is reserved) and, if configured, the indicator
for incoming IP packets (see parameter "GPRS/RingOnIncomingData" (<groid>).
Parameter is local for the interface, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
"off" URC is not indicated by RING.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 56 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 57

(P)
"local"
URC will be indicated by an activated RING line of the interface on which the
URC appears
"asc0" URC is indicated by an activated RING0 line.
<udri>
(str)(+CSCS)
URC Datamode RING line
This parameter specifies whether RING or BREAK is used for the signaling of URCs when the TA-TE link is
reserved (e.g. during circuit-switched data calls, fax connections, in GPRS data mode or during the execution
of an AT command).
Parameter is global for all interfaces, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
(P)
"off"
URC will be indicated by BREAK
"on" URC is indicated by an active RING line for a time which is configured by the
parameter "URC/Ringline/ActiveTime" (<urat>). The RING line which will be
used, can be configured by the parameter "URC/Ringline" (<uri>).
<urat>
(str)(+CSCS)
URC RING line Active Time
This parameter can be used to control how long the RING line is activated to indicate URCs (both for idle inter-
faces and, if configured by the parameter "URC/Datamode/Ringline" (<udri>), if link is reserved) and, if configured by the parameter "GPRS/RingOnIncomingData", to indicate incoming GPRS IP data packets
(<groid>).
Parameter is global for all interfaces, volatile and will not be reset by AT&F.
"0" RING line will be activated for a time between 4.6 and 9.2 ms.
"1" RING line will be activated for about 100ms.
(P)
"2"
RING line will be activated for about 1s.
Note
• Parameters "GPRS/ATS0/withAttach" (<gs0aa>) and "GPRS/RingOnIncomingData" (<groid>) are avail-
able only for modules supporting GPRS.
Examples
EXAMPLE 1
Usage of "Audio/AMR":
AT+CSCS="UCS2"
OK
AT^SCFG?
...
^SCFG:"Audio/AMR","0065006E00610062006C00650064"
...
OK
AT+CSCS="GSM"
OK
AT^SCFG?
...
^SCFG:"Audio/AMR","enabled"
...
OK
AT^SCFG="Audio/AMR","disabled"
^SCFG:"Audio/AMR","disabled"
OK
AT^SCFG="Audio/AMR","23405"
Switch to UCS2 character set.
Query all parameters.
AMR will be used for any operator.
AMR is disabled for any operator.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 57 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 58

^SCFG:"Audio/AMR","23405"
OK
AT^SCFG="Audio/AMR","23203"
^SCFG:"Audio/AMR","23405","23203"
OK
AT^SCFG="Audio/AMR"
^SCFG:"Audio/AMR","23405","23203"
OK
EXAMPLE 2
Usage of "URC/Ringline" and "URC/Datamode/Ringline":
AT+CSCS="GSM"
OK
AT^SCFG?
...
^SCFG:"URC/Datamode/Ringline","off"
^SCFG:"URC/Ringline","local"
...
OK
AT^SCFG="URC/Datamode/Ringline","on"
^SCFG:"URC/Datamode/Ringline","on"
OK
AT^SCFG="URC/Ringline","asc0"
^SCFG:"URC/Ringline","asc0"
OK
AT^SCFG="URC/Datamode/Ringline","off"
^SCFG:"URC/Datamode/Ringline","off"
OK
AT^SCFG="URC/Ringline"
^SCFG:"URC/Ringline","off"
OK
AMR is disabled for any operator, but enabled for
operator "23405".
AMR is disabled for any operator, but enabled for
operators "23405" and "23203".
Query parameter "Audio/AMR"
Switch to GSM character set.
Query all parameters.
While the TA-TE link is reserved URCs will be indicated by BREAK.
URCs on this interface will be indicated by Ring line
associated to the interface (e.g. RING0 for ASC0).
While the TA-TE link is reserved URCs will be indicated by an activated "local" Ring line.
URCs on this interface will be indicated by an activated RING0 no matter whether or not the TA-TE link
is reserved.
URCs on this interface will be indicated by an activated RING0 if the TA-TE link is not reserved and by
BREAK if the TA-TE link is reserved.
Disable any Ring line indication for URCs on this
interface.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 58 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 59

2.14 AT^SM20 Set M20 compatibility mode
M20 is an earlier, widely used SIEMENS GSM engine. The AT^SM20 command selects different modes of
responses returned upon execution of the commands ATD and sms commands like e.g. AT+CMGW. Please note
that the AT^SM20 command has no effect on any other features and is not intended to adjust other differences
between M20 and MC55.
Syntax
Test Command
AT^SM20=?
Response(s)
OK
Read Command
AT^SM20?
Response(s)
^SM20:<CallMode>, <CmgwMode>
OK
Write Command
AT^SM20=<CallMode>[, <CmgwMode>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
SIEMENS ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<CallMode>
Call setup response mode
Applies only to voice calls.
0 Set compatibility to Siemens mobile phones.
(&F)
1
<CmgwMode>
Response mode for sending and writing short messages
Applies to the sms commands like e.g. AT+CMGS and AT+CMGW command.
0 Set compatibility to Siemens mobile phones.
(&F)
1
(num)
ME will return "OK" immediately after attempting a call with the ATD command.
In case of failure, additional call release indications, such as "NO DIAL TONE,
"NO CARRIER", "BUSY" will follow.
Default call setup mode, compatible to M20.
ME will return "OK" in case of a successful connection, otherwise one of the
call release indications "NO DIAL TONE, "NO CARRIER", "BUSY" are indicated.
(num)
ME will return +CMS ERROR: <err> when writing or sending of short messages fails.
Default mode for sending and writing short messages, compatible to M20.
ME will return "OK", no matter whether or not sms command was successfully
executed.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 59 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 60

3. Status Control Commands
The AT Commands described in this chapter allow the external application to obtain various status information
from the MC55.
3.1 AT+CMER Mobile Equipment Event Reporting
This command controls details of the "+CIEV" URC presentation related to AT^SIND and AT+CIND. If registered
via these commands the URCs are sent whenever a value of the related indicator changes.
In addition, AT+CMER controls "^SLCC" URCs related to AT^SLCC. For details refer to Call Status Infor-
mation, AT^SLCC and AT^SCFG, parameter <sucs>.
The read command returns the URC presentation mode <mode> and among others, the indicator event reporting
status <ind>.
The write command enables and disables the presentation of "+CIEV: <indDescr>, <indValue>
Value>
]" URCs. <indDescr> refers to the name of a "+CIEV" indicator and <indValue> is the new value of
2
this indicator. After AT+CMER has been switched on, URCs for all registered indicators will be issued. See examples provided in Section 3.2, AT+CIND and Section 3.3, AT^SIND.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CMER=?
Response(s)
+CMER: (list of supported<mode>s), (list of supported <keyp>s), (list of supported <disp>s), (list of
supported <ind>s), (list of supported <bfr>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+CMER?
Response(s)
+CMER: <mode>, <keyp>, <disp>, <ind>, <bfr>
OK
Write Command
AT+CMER=[<mode>[, <keyp>[, <disp>[, <ind>[, <bfr>]]]]]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
[, <ind-
1
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 % % % % % % ! ! !
Unsolicited Result Code
+CIEV: <indDescr>, <indValue>1[, <indValue>2]
A value of an indicator has changed.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 60 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 61

Parameter Description
<mode>
(&F)
0
(num)
Discard "+CIEV" and "^SLCC" URCs.
1 Discard "+CIEV" and "^SLCC" URCs when TA-TE link is reserved, e.g. in
online data mode. Otherwise they are forwarded directly to the TE.
2 Buffer "+CIEV" and "^SLCC" URCsin the TA while TA-TE link is reserved, e.g.
in online data mode, and flush them to the TE afterwards. Otherwise they are
forwarded directly to the TE.
3Forward "+CIEV" and "^SLCC" URCs directly to the TE. If MC55 is in online
data mode, URCs are signaled via sending BREAK (100ms) and stored in a
buffer. Once it is back in command mode e.g. after +++ was entered, all URCs
stored in the buffer will be output.
<keyp>
(&F)
0
<disp>
(&F)
0
<ind>
(&F)
0
(num)
Keypad event reporting is not supported by MC55.
(num)
Display event reporting is not supported by MC55.
(num)
Disable indicator event reporting.
2 Enable indicator event reporting.
(&F)
(num)
TA buffer of URCs defined within this command is cleared when <mode> 1..3
<bfr>
0
is entered.
<indDescr>
(str)
Name of indicator; for a list of all supported indicators please refer to AT+CIND and AT^SIND.
<indValue>
(num)
Value of indicator; for a list of all values for the supported indicators please refer to AT+CIND and AT^SIND.
Note
• If the ME operates on different instances (MUX channels 1, 2, 3 or ASC0/ASC1) avoid different settings for
routing and indicating SMS. For example, if messages shall be routed directly to one instance of the TE (set
with AT+CNMI, AT^SSDA), it is not possible to activate the presentation of URCs with AT+CMER or AT+CNMI
on another instance. Any attempt to activate settings that conflict with existing settings on another interface,
will result in CME ERROR, or accordingly CMS ERROR.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 61 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 62

3.2 AT+CIND Indicator control
The AT+CIND command controls the presentation of Indicator Event Reports related to various functions such
as battery charge level, signal quality, service availability, sound generation, indication of unread short messages, full SMS storage, call in progress or roaming activities.
Use of AT+CIND has become outdated. Rather we recommend the more powerful AT^SIND command which is
easier to use and provides additional indicators. All indicators provided by AT+CIND can be handled with
AT^SIND as well.
AT+CIND supports two ways to get the values related to indicators:
• One approach is to query the current status of each indicator by using the read command AT+CIND?. It
returns the status no matter whether the indicator has been registered with the write command
AT+CIND=[<mode>[,<mode>[,...]]].
• The other way is an event-driven notification based on the "+CIEV" URCs. In this case, the ME will automatically send a message to the application, whenever the value of an indicator changes. The application should
be designed to react adequately when receiving a URC.
The presentation of these URCs depends on two settings:
- The indicators must be registered with the write command AT+CIND=[<mode>[,<mode>[,...]]]. When the
ME is switched on all of them are in registered mode. Any indicator can be excluded if deregistered with
<mode>=0. To register or deregister an indicator the AT+CIND write command requires to type the value
<mode>=1 or 0 exactly at the position where the indicator is located in the list. This is not necessary with
AT^SIND which allows to specify indicators by name. See examples below.
- The presentation of the registered indicators must be enabled with AT+CMER.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CIND=?
Response(s)
+CIND: (<indDescr>, list of supported <indValue>s)[, (<indDescr>, list of supported <indValue>s)[,
...]]
OK
Read Command
AT+CIND?
Response(s)
+CIND: <indValue>[, <indValue>[, ...]]
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Write Command
AT+CIND=<mode>[, <mode>[, ...]]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<indValue>
Integer type value, which shall be in range of corresponding <indDescr>
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 62 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
(num)
Page 63

<indDescr>
(str)
String values and their <indValue> ranges.
More indications are available via AT^SIND. Therefore use of AT^SIND for control of all indications is recommended.
The following indications are accessible via AT+CIND:
"battchg" Battery charge level 0..4 or 5 if no measuring is performed, e.g because no bat-
tery is connected. Also refer to AT^SBC.
"signal" Signal quality (0..7) or (99) if not measurable
The indicated value is the bit error rate of the signal received. Bit errors are estimated values. See also AT+CSQ.
"service" Service availability (0-1)
0: Not registered to any network
1: Registered to home network or, if "roam"=1 then registered to another network
"sounder" Sounder activity (0-1)
Reports every event that causes the ME to generate a tone.
Value 1 means for example:
Incoming call - ME is ringing. Note that the URC "+CIEV: sounder" will be output only if ringing tones are activated with AT^SRTC.
Waiting call - ME generates waiting call tone (if call waiting is enabled).
Outgoing call - ME generates Call Progress tone.
Outgoing call - ME generates BUSY tone.
The value changes to 0 when the tone stops.
"message" Unread short message at memory location <mem1> (0-1); refer to AT+CPMS
"call" Call in progress (0-1). Indicator value is "1" if at least one call is in state "active"
or "held".
Depending on the parameter <succ> selected with AT^SCFG the indicator
"call" will be issued
• when a state transition ends in state "active" or state "unknown", if
<succ>="restricted",
• when any state transition (including transitions beginning or ending in state
"unknown") occurs in the list of active calls or when a traffic channel is
established, if <succ>="verbose".
Also refer to Section 7.1, Call Status Information.
"roam" Roaming indicator (0-1)
0: Registered to home network or not registered
1: Registered to other network
"smsfull" A short message memory storage in the MT has become full (1) or memory
locations are available (0), i.e. range is (0-1)
"rssi" Received signal (field) strength (0..5) or (99) if not measurable
0: signal strength <= -112 dbm
1-4: signal strength in 15 dbm steps
5: signal strength >= -51 dbm
Received signal (field) strength can also be obtained with AT+CSQ. However,
the signal strength is scaled to value range 0..31 by this command.
<mode>
(num)
0 Indicator is deregistered. The indicator will not be presented as "+CIEV" URC,
but can be queried with AT+CIND?.
(&F)(P)
[1]
Indicator is registered, indicator event report allowed.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 63 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 64

Notes
• Due to its restrictive value range, indicator "call" does not clearly reflect specific call states (such as alerting,
active, held etc.), but rather serves to trigger the application to retrieve the new call status from the list of current calls with the AT commands AT^SLCC, AT+CLCC or AT^SCNI.
• If AT^SCFG setting <succ>="verbose", indicator "call" will be issued also when a traffic channel is established, or when a call enters states "terminating" or "dropped" (see Call Status Information).
In these cases, the relevant information about the cause of the display is available only from AT command
AT^SLCC.
Examples
EXAMPLE 1
^SYSSTART
AT+CPIN=9999
OK
AT+CIND?
+CIND: 5,99,1,0,0,0,0,0
OK
AT+CMER=2,0,0,2
OK
+CIEV: battchg,5
+CIEV: signal,99
+CIEV: service,1
+CIEV: sounder,0
+CIEV: message,0
+CIEV: call,0
+CIEV: roam,0
+CIEV: smsfull,0
+CIEV: rssi,5
ATD0123456;
OK
+CIEV: sounder,1
+CIEV: call,1
+CIEV: sounder,0
+CIEV: call,0
NO CARRIER
AT+CIND=,,,0,,0
OK
ATD0123456;
OK
NO CARRIER
EXAMPLE 2
Deactivation of indicator "sounder" via AT+CIND
AT+CIND?
+CIND: 5,99,1,0,1,0,0,0,4
OK
AT+CIND=,,,0
OK
EXAMPLE 3
Deactivation of indicator "sounder" via AT^SIND
AT^SIND="sounder",0
^SIND: sounder,0,0
OK
The battery is either full or no battery is connected to the ME. The bit
error rate of the signal quality is not available (since there is no call in
progress). The ME is registered to its home network.
Now activate the Indicator Event Report with AT+CMER.
Full receive signal strength.
Make a call.
A set of "+CIEV" URCs is received.
Called party hangs up.
Deregister the indicators "sounder" and "call".
Dial the same call.
This time, no URCs are displayed.
Called party hangs up.
Query the current status of indicators.
To deactivate indicator "sounder" (= fourth item in list of indicators).
To deactivate indicator "sounder".
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 64 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 65

3.3 AT^SIND Extended Indicator Control
Designed for extended event indicator control AT^SIND
• offers greater flexibility than the standard command AT+CIND,
• offers several extra indicators,
• can show the current status of all indicators supported by AT+CIND and AT^SIND,
• can be used to register or deregister the indicators of both commands,
• displays all indicator event reports via "+CIEV" URCs.
Presentation mode of the generated URCs is controlled via AT+CMER.
The AT^SIND read command provides a list of all indicators supported by AT+CIND and AT^SIND. Each indicator is represented with its registration mode and current value.
The AT^SIND write command can be used to select a single indicator in order to modify its registration and to
view the current value.
Syntax
Test Command
AT^SIND=?
Response(s)
^SIND: (<indDescr>, list of supported <indValue>s)[, (<indDescr>, list of supported <indValue>s)[,
...]], (list of supported <mode>s)
OK
Read Command
AT^SIND?
Response(s)
^SIND: <indDescr>, <mode>, <indValue>
[^SIND: <indDescr>, <mode>, <indValue>]
...
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Write Command
AT^SIND=<indDescr>, <mode>
Response(s)
^SIND: <indDescr>, <mode>, <indValue>
In case of: <indDescr>="eons" and <mode>=2
^SIND: <indDescr>, <mode>, <indValue>, <eonsOperator>, <servProvider>
In case of: <indDescr>="nitz" and <mode>=2
^SIND: <indDescr>, <mode>, <nitzUT>, <nitzTZ>, <nitzDST>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
SIEMENS ! % % % % % ! ! !
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 65 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 66

Unsolicited Result Codes
URC 1
Format of the standard indicator:
+CIEV: <indDescr>, <indValue>
Value related to an indicator has changed.
URC 2
Format of the Voice Message indicator, if the number of waiting messages is delivered by the network:
+CIEV: <indDescr>, <indValue>, <vmCounter>
If the number of waiting messages is not delivered the standard indicator applies.
URC 3
Format of the "eons" indicator:
+CIEV: <indDescr>, <indValue>, <eonsOperator>, <servProvider>
One URC is issued for each new LAI (Location Area Information) broadcast by the network.
URC 4
Format of the "nitz" indicator:
+CIEV: <indDescr>, <nitzUT>, <nitzTZ>, <nitzDST>
Parameter Description
<indDescr>
(str)
String values and their <indValue> ranges.
All indicators supported by AT+CIND are accessible with this command, too. A detailed description of these indicators can be found there.
The following indicators are accessible via AT^SIND only:
"audio" Activity of the built-in audio unit.
0 Audio unit not active.
1 Value 1 means for example:
Outgoing voice call: Indicator appears when dialing starts.
Incoming voice call: Indicator appears prior to the RING result code.
"vmwait1" Voice Message Waiting Indication for line 1
0 The value 0 notifies that no new voice message is available, and is pro-
vided by the service center to clear the voice message indication after
the subscriber has retrieved all voice messages.
1 The value 1 notifies the subscriber that the mailbox contains one or
several messages.
"vmwait1" and "vmwait2" indicate the receipt of a special short message with
a Voice Message Waiting Indicator. The service must be provisioned by the
operator.
The numbers 1 or 2 in "vmwait1" and "vmwait2" are related to the two lines of
the Alternate Line Service (ALS), also defined in CPHS Phase 2 standard. For
further details refer to the AT^SALS command.
The presentation mode of the indicator varies with the operator: If more than
one message are waiting, some operators only indicate the first one, others
deliver the indicator each time a new voice message is put into the mailbox.
After the subscriber has retrieved all voice messages the service center automatically sends another message indication which provides the value 0.
Some operators may also send the number of waiting voice messages along
with the indication. In this case, the number will be displayed by the MC55 as
part of the URC. For example, "+CIEV: vmwait1,1,5" notifies that five new voice
messages are waiting. However, it should be noted that neither the read command AT^SIND? nor the write command AT^SIND=<mode>,2 display the
number of waiting messages.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 66 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 67

The "vmwait" indicators do not apply if a network provider signals new voice
mail(s) via standard SMS. In this case the indicator "message" will be displayed
(see AT+CIND).
"vmwait2" Voice Message Waiting Indication for line 2
0 See description of "vmwait1".
1 See description of "vmwait1".
"ciphcall" Ciphering Status Change Indication
0 Current call or SMS is not ciphered.
1 Current call or SMS is ciphered.
As stated in GSM specifications 02.07 and 02.09 the ciphering indicator feature
allows the MC55 to detect that ciphering is not switched on and to indicate this
to the user.
The ciphering indicator feature may be disabled by the home network operator
setting data in the "administrative data" field (EF
GSM 11.11.
If this feature is not disabled by the SIM, then whenever a connection is in
place, which is, or becomes unenciphered, an indication shall be given to the
user. This enables the user's decision how to proceed.
Read command returns valid ciphering status only if a call is in progress or
active.
If EF
setting disables the ciphering indicator feature read command always
AD
indicates a ciphered link and no URC presentaion will take place.
The following restrictions apply if the same serial channel is used for AT^SIND
"ciphcall" indication and for the action triggering this URC. In general, the recommended solution is to use a dedicated channel for all status signalling via
URCs.
• If an unciphered mobile originated SMS is performed, AT^SIND "ciphcall"
URCs on the same serial channel will be issued after the related "OK" and
indicate the ciphering state at this time. Because the SMS is already sent at
this time, two URCs will be issued on this channel, but both are indicating
that ciphering is enabled.
• If an unciphered mobile originated data call is performed, AT^SIND "ciph-
call" URCs on the same serial channel will be issued after the interface is
not longer blocked by the call (call is released or temporarily stopped) and
indicate the ciphering state at this time.
) in the SIM, as defined in
AD
"eons" Enhanced Operator Name String (EONS) Indication
The Enhanced Operator Name String indicator feature allows the MC55 to output various operator names for different PLMN identities via URC. It also allows
the output of a different operator name based on a subset of the registered network by using a range of Location Area Codes (LACs) or a single LAC.
The presentation of the "eons" indicator is determined by network activity. For
example, the indicator appears every time a location update occurs or a NITZ
information is sent, no matter whether or not the status of the EONS information has changed. This means that the same EONS information may be
reported several times.
The EONS tables are stored in the SIM card and will be read at power-up.
Following are the SIM Elementary Files that are affected by the introduction of
EONS feature in the SIM card:
EF
(SIM Service Table) - describes which features are active.
SST
EF
(Operator PLMN List) - contains the PLMN identification and location ID
OPL
together with the index of the corresponding PNN record
EF
(PLMN Network Name) - contains the full and short form version of the
PNN
network name for the registered PLMN
If the Operator Name Source is CPHS Operator Name String long and short
form, refer to <indValue>, the following two SIM Elementary Files will be
used:
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 67 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 68

EF
(Operator Name String) - contains the name of the PLMN operator
ONString
who issued the SIM.
EF
(Operator Name Short form) - contains a short form of the name of
OPShort
the PLMN operator who issued the SIM.
"nitz" Network Identity and Time Zone indication
This indicator shows the time relevant information elements of an MM Information (MMI) or GMM Information (GMMI) message received from the network
(see GSM 24.008, ch. 9.2.15a and 9.4.19). The network usually sends a NITZ
indicator when the mobile attaches to the network, when it enters a location
area with different time zone or when a daylight change occurs.
A NITZ indicator may consist of the following parameters: Universal Time (UT),
local Time Zone (TZ), Daylight Saving Time (DST). All information elements of
MMI/GMMI are optional and therefore, the presentation of the parameters
<nitzUT>, <nitzTZ>, <nitzDST> varies with the network. For example, the
network may send all three parameters UT, TZ, DST, or only UT and TZ or only
TZ.
UT is indicated in usual date/time format and represents the current world time
(GMT) at the moment when sent.
TZ is given as a positive (east) or negative (west) offset from UT in units of 15
minutes.
DST shows the number of hours added to the local TZ because of daylight saving time (summertime) adjustment. Usually DST is 1 hour but it can be also 2
hours in certain locations.
Example for time and time zone with DST:
+CIEV: nitz,"04/07/23,13:39:20",-28,1
In this example TZ is -28, showing a time offset of -7 hours (west) to Universal
Time/GMT (which never changes for DST). DST is 1 which indicates that one
hour was added to TZ because of Daylight Saving Time. If a network does not
send the DST parameter the TZ value would be -32 (8 hours west) as would
be done in winter:
+CIEV: nitz,"04/11/23,13:39:20",-32
Please be aware that despite the last NITZ value can be looked up again via
"AT^SIND=nitz,2" the returned values may be out of date. Especially the UT
value is obsolete because there is no internal NITZ clock and therefore no continuation of UT.
NITZ values are lost when the module detaches from network. Also when a
manual network selection fails and the module automatically falls back to the
previous network the NITZ values cannot be recalled. Nevertheless an indicated time zone is valid until a new MMI/GMMI will trigger another NITZ indication.
<indValue>
(num)
Integer type value in the range stated above for the corresponding <indDescr>.
Notes specific to the EONS feature:
If the indicator is "eons", the <indValue> is a type associated to the operator name according to GSM 22.101
[23]. This type depends on the source of the operator name.
Priority of types associated to the operator names is defined as follows (the type listed first has the highest priority). If a type cannot be indicated the next one will be used.
0 Not registered.
1 EF-OPL and EF-PNN (alphanumeric format, can contain up to 24 characters.)
2 Operator Name String in long and short format according to Common PCN
Handset Specification (CPHS) [24] (alphanumeric format, can contain up to 16
characters).
3 Name information received by the NITZ service long and short form (alphanu-
meric format, can contain up to 16 characters). The short form will be displayed
only if EF
from CPHS is available.
OPShort
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 68 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 69

4 Any operator name stored internal to the ME (alphanumeric format, can con-
tain up to 16 characters).
5 Broadcast MCC-MNC (numeric format which consists of a 3-digit country code
plus a 2- or 3-digit network code).
If the type is 2, 4 or 5, AT+COPS with the appropriate <mode> displays the same operator name.
<mode>
(num)
0 Indicator is deregistered, i.e. no such indicator event report (URC) will be
issued. <mode>=0 is power-up and factory default of indicators defined by
AT^SIND only.
1 Indicator is registered.
• Indicator event reports are controlled via AT+CMER.
• All indicators can be registered or deregistered via AT^SIND, but different
default settings apply: Power-up and factory default of the indicators supported by AT+CIND is <mode>=1, while, as stated above, indicators defined
by AT^SIND only are set to <mode>=0.
2 Query the registration status and the current value of a single indicator type.
<vmCounter>
If delivered by the network: Number of new voice messages sent as part of the Voice Message Waiting Indicator.
Refer to <indDescr>.
<eonsOperator>
Operator in format which depends on the type associated to the operator name. Refer to <indValue>.
<servProvider>
(str)
Service Provider Name according to the status settings (SIM Service No. 17) in the SIM Service Table (SST) of
the SIM.
<nitzUT>
Universal Time delivered as part of the "nitz" Indicator. Refer to <indDescr>.
<nitzTZ>
Time Zone delivered as part of the "nitz" Indicator. Refer to <indDescr>.
<nitzDST>
Adjustment for Daylight Saving Time as part of the "nitz" Indicator. Refer to <indDescr>.
Example
Activation and use of indicator "audio":
AT^SIND="audio",1
^SIND: audio,1,0
OK
AT+CMER=2,,,2
OK
+CIEV: battchg,5
+CIEV: signal,99
+CIEV: service,1
You register the indicator "audio".
You activate the Indicator Event Report with AT+CMER.
A set of all registered URCs is presented. (Please note that the example
includes the indicators registered due to the power-up default settings
of AT+CIND.)
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 69 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 70

+CIEV: sounder,0
+CIEV: message,1
+CIEV: call,0
+CIEV: roam,0
+CIEV: smsfull,0
+CIEV: rssi,4
+CIEV: audio,0
ATD030123456
OK
+CIEV: audio,1
+CIEV: sounder,1
+CIEV: call,1
+CIEV: signal,0
+CIEV: sounder,0
ATH
OK
+CIEV: call,0
+CIEV: rssi,3
+CIEV: audio,0
+CIEV: signal,99
+CIEV: rssi,4
You make a call.
You hang up.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 70 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 71

3.4 AT+CEER Extended Error Report
AT+CEER returns an extended error report regarding the reason of the last
• call release
• failure to set up a call (both mobile originated or terminated)
• failure to modify a call by using Supplementary Services
• failed attempt to activate, register, query, deactivate or deregister a Supplementary Service
• unsuccessful GPRS attach or unsuccessful PDP context activation
• GPRS detach or PDP context deactivation
The release cause report is presented in numeric format. Default output in case of a none-error-situation is
+CEER: 0,0,0. A description associated with each number can be found in the tables given in the following subclauses and the relevant GSM specifications.
The first parameter <locationID> serves to locate the other two parameters. Depending on the failure or
release cause either <reason> or <ssRelease> are applicable, i.e. if <reason> ≠ 0, then <ssRelease> = 0.
Vice versa, if <reason> = 0, then <ssRelease> may be ≠ 0.
AT+CEER is not available for data calls, please use ATS18=1 instead. In case of loosed net coverage, MC55 will
disconnect the call but no network release cause is available and the default output will still be given out.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CEER=?
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Exec Command
AT+CEER
Response(s)
+CEER: <locationID>, <reason>, <ssRelease>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 % % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<locationID>
Location ID as number code. Location IDs are listed in Section 3.4.1, Cause Location ID for the extended error
report. Each ID is related with another table that contains a list of <reason>s or <ssRelease>s.
<reason>
Reason for last call release as number code. The number codes are listed in several tables, sorted by different
categories in the following subclauses. The tables can be found proceeding from the Location ID given in Section 3.4.1, Cause Location ID for the extended error report.
<ssRelease>
Release cause for last Supplementary Service call (listed in Section 3.4.9, GSM Release cause for Supplemen-
tary Service Call) or last call related use of a Supplementary Service (listed in Section 3.4.10, SIEMENS release
cause for Call-related Supplementary Services (CRSS)).
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 71 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
(num)
(num)
(num)
Page 72

Examples
EXAMPLE 1
ATD"01751223344";
NO CARRIER
AT+CEER
+CEER: 8,21,0
OK
A mobile originated call is rejected by the remote party.
Call setup is terminated with NO CARRIER.
To check the cause, the caller enters AT+CEER.
The Location ID 8 in Section 3.4.1 points to Section 3.4.6, where 21 =
"Call rejected". 0 = "No error" refers to parameter <ssRelease> that is
not applicable.
EXAMPLE 2
The user attempts to activate call barring, but uses a wrong password.
AT+clck=oi,1,"0000",3
+CME ERROR: incorrect password
AT+CEER
+CEER: 35,0,38
OK
The Location ID 35 in Section 3.4.1 points to Section 3.4.9, where 38 =
"NegativePWCheck" may mean that a wrong password was tried for the
first time. 0 = "No error" refers to parameter <reason> that is not applicable.
3.4.1 Cause Location ID for the extended error report
ID Description
0 No error (default)
1 SIEMENS L2 cause
2 GSM cause for L3 Radio Resource Sublayer (GSM 04.08 annex F)
3 SIEMENS cause for L3 Radio Resource Sublayer
4 GSM cause for L3 Mobility Management (GSM 04.08 annex G)
5 SIEMENS cause for L3 Mobility Management
6 GSM cause for L3 Mobility Management via MMR-SAP (GSM 04.08 annex G)
7 SIEMENS cause for L3 Mobility Management via MMR-SAP
8 GSM cause for L3 Call Control (GSM 04.08 10.5.4.11 and annex H)
9 SIEMENS cause for L3 Call Control
11 SIEMENS cause for L3 Advice of Charge Entity
12 GSM cause for L3 SMS CP Entity
13 SIEMENS cause for L3 SMS CP Entity
14 GSM cause for L3 SMS RL Entity
15 SIEMENS cause for L3 SMS RL Entity
16 GSM cause for L3 SMS TL Entity
17 SIEMENS cause for L3 SMS TL Entity
18 SIEMENS cause for DSM Entity
21 GSM cause for L3 Call-related Supplementary Services
22 SIEMENS cause for L3 Call-related Supplementary Services
32 SIEMENS cause for Supplementary Services Entity
33 SIEMENS cause for Supplementary Services Manager
34 Network cause for Supplementary Services (GSM 04.08 10.5.4.11 and annex H)
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 72 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 73

ID Description
35 Supplementary Services network error (GSM 04.80 3.6.6)
48 GSM cause for GPRS Mobility Management (GSM 04.08 annex G.6)
49 SIEMENS cause for GPRS Mobility Management
50 GSM cause for Session Management (GSM 04.08 annex I)
51 SIEMENS cause for Session Management
127 SIEMENS cause for protocol module or other local cause
128 Supplementary Services general problem (GSM 04.80 3.6.7)
129 Supplementary Services invoke problem (GSM 04.80 3.6.7)
130 Supplementary Services result problem (GSM 04.80 3.6.7)
131 Supplementary Services error problem (GSM 04.80 3.6.7)
241 SIEMENS cause for GPRS API
242 SIEMENS cause for Link Management
243 SIEMENS cause for PPP/IP-Stack
3.4.2 GSM release cause for L3 Radio Resource (RR)
Number Description
0 Normal event
1 Abnormal release, unspecified
2 Abnormal release, channel unacceptable
3 Abnormal release, timer expired
4 Abnormal release, no activity on the radio path
5 Pre-emptive release
8 Handover impossible, timing advance out of range
9 Channel mode unacceptable
10 Frequency not implemented
65 Call already cleared
95 Semantically incorrect message
96 Invalid mandatory information
97 Message type non-existent or not implemented
98 Message type not compatible with protocol state
100 Conditional information element error
101 No cell allocation available
111 Protocol error unspecified
3.4.3 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Radio Resource (RR)
Number Description
1 Racchs not answered
2 Racchs rejected
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 73 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 74

Number Description
3 Access class of the SIM is barred by the network provider
4 SABM failure
5 Radio link counter expiry or PerformAbnormalRelease
6 Confirm ABORT of the MM
7 Respond to DEACT REQ
8 Loss of coverage
9 Reestablishment not possible
3.4.4 GSM release cause for Mobility Management (MM) or Session Management (SM)
Number Description
Causes related to MS identification
2 IMSI unknown in HLR
3 Illegal MS
4 IMSI unknown in VLR
5 IMEI not accepted
6 Illegal ME
Cause related to subscription options
11 PLMN not allowed
12 Location Area not allowed
13 Roaming not allowed in this location area
Causes related to PLMN specific network failures and congestion
17 Network failure
22 Congestion
Causes related to nature of request
25 PDP context is deactivated because of a LLC or SNDCP failure
32 Service option not supported
33 Requested service option not subscribed
34 Service option temporarily out of order
36 Regular PDP context deactivation
38 Call cannot be identified
Causes related to invalid messages
95 Semantically incorrect message
96 Invalid mandatory information
97 Message type non-existent or not implemented
98 Message not compatible with protocol state
99 Information element non-existent or not implemented
100 Conditional information element error
101 Messages not compatible with protocol state
111 Protocol error, unspecified
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 74 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 75

Number Description
Causes related to GPRS
7 GPRS services not allowed
8 GPRS services not allowed in combination with non-GPRS services
9 MS identity cannot be identified by the network
10 Implicitly detached
14 GPRS services not allowed in current PLMN
16 MSC temporarily unreachable
3.4.5 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Mobility Management (MM)
Number Description
1 No SIM available
8 No MM connection
9 Authentification failure
11 MM performs detach
17 Registration failed and will be re-attempted in a short term
18 CM connection establishment failed
19 Registration failed and will be re-attempted in a long term
20 RR connection is released
21 MS tries to register
22 SPLMN is not available
23 An MTC is in progress
24 A PLMN scan is in progress
25 The MM is detached, the MS is in MS class C GPRS only
3.4.6 GSM release cause for L3 Call Control (CC)
Number Description
0 No error
Normal class
1 Unassigned (unallocated) number
3 No route to destination
6 Channel unacceptable
8 Operator determined barring
16 Normal call clearing
17 User busy
18 No user responding
19 User alerting, no answer
21 Call rejected
22 Number changed
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 75 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 76

Number Description
25 Pre-emption
26 Non-selected user clearing
27 Destination out of order
28 Invalid number format (incomplete number)
29 Facility rejected
30 Response to STATUS ENQUIRY
31 Normal, unspecified
Resource unavailable class
34 No circuit/channel available
38 Network out of order
41 Temporary failure
42 Switching equipment congestion
43 Access information discarded
44 Requested circuit/channel not available
47 Resource unavailable, unspecified
Service or option not available class
49 Quality of service unavailable
50 Requested facility not subscribed
55 Incoming calls barred within the CUG
57 Bearer capability not authorized
58 Bearer capability not presently available
63 Service or option not available, unspecified
Service or option not implemented
65 Bearer service not implemented
68 ACM equal or greater than ACMmax
69 Requested facility not implemented
70 Only restricted digital information bearer capability is available
79 service or option not implemented, unspecified
Invalid message (e.g. parameter out of range) class
81 Invalid transaction identifier value
87 User not member of CUG
88 Incompatible destination
91 Invalid transit network selection
95 Semantically incorrect message
Protocol error (e.g. unknown message) class
96 Invalid mandatory information
97 Message type non-existant or not implemented
98 Message type not comaptible with protocol state
99 Information element non-existent or not implemented
100 Conditional information element error
101 Message not compatible with protocol
102 Recovery on timer expiry
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 76 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 77

Number Description
111 Protocol error, unspecified
Interworking class
127 Interworking, unspecified
3.4.7 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Call Control (CC)
Number Description
1 Call dropped
2 Service not available
3 Hold procedure not available
4 Temporary no service, previous procedure not yet finished
5 No speech service available
6 Call reestablishment procedure active
7 Mobile received a release (complete) message during a modify procedure (modify reject)
8 Call clearing, because loss of radio connection, if no reestablishment is allowed (call not
active)
10 Number not included in FDN list
Notifications
300 Called party barred incoming call
3.4.8 SIEMENS release cause for L3 Advice of Charge (AOC)
Number Description
1 SIM data not available
2 SIM does not support AOC
3 SIM data access error
4 ACM limit almost reached ACM range overflow
5 ACM range overflow
3.4.9 GSM Release cause for Supplementary Service Call
Number Description
0 No error (default)
1 UnknownSubscriber
9 IllegalSubscriber
10 BearerServiceNotProvisioned
11 TeleserviceNotProvisioned
12 IllegalEquipment
13 CallBarred
15 CUGReject
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 77 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 78

Number Description
16 IllegalSSOperation
17 SSErrorStatus
18 SSNotAvailable
19 SSSubscriptionViolation
20 SSIncompatibility
21 FacilityNotSupported
27 AbsentSubscriber
29 ShortTermDenial
30 LongTermDenial
34 SystemFailure
35 DataMissing
36 UnexpectedDataValue
37 PWRegistrationFailure
38 NegativePWCheck
43 NumberOfPWAttemptsViolation
71 UnknownAlphabet
72 USSDBusy
126 MaxNumsOfMPTYCallsExceeded
127 ResourcesNotAvailable
General Problem Codes
300 Unrecognized Component
301 Mistyped Component
302 Badly Structured Component
Invoke Problem Codes
303 Duplicate Invoke ID
304 Unrecognized Operation
305 Mistyped Parameter
306 Resource Limitation
307 Initiating Release
308 Unrecognized Linked ID
309 Linked Response Unexpected
310 Unexpected Linked Operation
Return Result Problem Codes
311 Unrecognize Invoke ID
312 Return Result Unexpected
313 Mistyped Parameter
Return Error Problem Codes
314 Unrecognized Invoke ID
315 Return Error Unexpected
316 Unrecognized Error
317 Unexpected Error
318 Mistyped Parameter
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 78 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 79

3.4.10 SIEMENS release cause for Call-related Supplementary Services (CRSS)
Number Description
0 ECT procedure failed (timer expired)
1 Call has been cleared without receiving an answer to ECT request
2 Initial conditions not fulfilled (one active, one held call)
3 Received "return error"
4 Call has been cleared without receiving an answer to CCBS request
5 Initial conditions for CCBS not fulfilled (Idle CRSS)
Causes related to nature of request
25 LLC or SNDCP failure
26 Insufficient resources
27 Unknown or missing access point name
28 Unknown PDP address or PDP type
29 User authentification failed
30 Activation rejected by GGSN
31 Activation rejected, unspecified
32 Service option not supported
33 Requested service option not subscribed
34 Service option temporarily out of order
35 NSAPI already used
36 Regular PDP context deactivation
37 QoS not accepted
38 Network failure
39 Reactivation requested
40 Feature not supported
Causes related to invalid messages
81 Invalid transaction identifier value
95 Semantically incorrect message
96 Invalid mandatory information
97 Message type non-existant or not implemented
98 Message type not comaptible with protocol state
99 Information element non-existent or not implemented
100 Conditional information element error
101 Message not compatible with protocol
111 Protocol error, unspecified
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 79 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 80

3.4.11 SIEMENS release cause for Session Management (SM)
Number Description
3 The MS has not got any answer to the ACTIVATE PDP CONTEXT request message sent five
times to the network
4 A MT PDP context which is active or in the activation process is deactivated because another
MT PDP context with the same TI is requested by the network to be activated
5 A MT PDP context which is active or in the activation process is deactivated because another
MT PDP context with the same TI is requested by the network to be activated. The activation
request is rejected by the SM sending the cause 'insufficient resources' to the network
because the SM was not able to perform the necessary comparisons for a static PDP address
collision detection.
6 A MT PDP context which is active or in the activation process is deactivated because another
MT PDP context with the same TI is requested by the network to be activated. As a static PDP
address collision with an MO activating PDP context has been detected by the SM the SM discards the activation request
7 A MT PDP context request has been indicated but could not be processed in time. The acti-
vation request is rejected by the SM sending the cause 'insufficient resources' to the network.
3.4.12 GSM cause for L3 Protocol module or other local cause
Number Description
2 No detailed cause
3.4.13 SIEMENS release cause for GPRS API
Number Description
0 Regular deactivation of the call
1 Action temporarily not allowed
2 Wrong connection type
3 Specified data service profile invalid
4 PDP type or address is unknown
5 FDN Check was not successful; GPRS Attach and PDP Context Activation blocked
255 Undefined
3.4.14 SIEMENS release cause for PPP/IP-Stack
Number Description
0 Regular call deactivation
1 LCP stopped
255 Undefined
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 80 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 81

3.5 ATS18 Extended call release report
ATS18 controls the presentation of extended call release reports for circuit switched fax and data calls. Extended
call release reports related to voice calls are controlled via AT+CEER.
The call release report is presented in numeric format and shows as follows:
+CAUSE:
If enabled the message will be reported every time a fax or data call is released or fails to be established.
Syntax
Read Command
ATS18?
Response(s)
<n>
OK
Write Command
ATS18=<n>
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
<locationID>:<reason>
V.250 ! % ! % ! ! ! ! !
Parameter Description
(num)(&W)(&V)
<n>
An odd number enables the presentation of the extended call release report. Any even number disables this
feature.
(&F)
0
...255
<locationID>
Location ID as number code, see also <locationID> of AT+CEER.
Location IDs are listed in Section 3.4.1, Cause Location ID for the extended error report. Each ID is related to
another table that contains a list of <reason>s.
<reason>
Reason for last call release as number code (see also <reason> of AT+CEER).
<reason> numbers and the associated descriptions are listed in several tables, sorted by different categories
at AT+CEER. The tables can be found proceeding from the Location IDs listed in Section 3.4.1, Cause Location
ID for the extended error report.
(num)
(num)
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 81 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 82

Examples
EXAMPLE 1
ATS18=1
OK
ATD03012345678
+CAUSE: 8:17
BUSY
EXAMPLE 2
ATS18=1
OK
ATD03012345678
CONNECT 9600/RLP
Hello,....
+++
+CAUSE: 8:16
NO CARRIER
Enables the presentation of extended call release reports.
Now, a mobile originated data call fails.
An extended error report is output, followed by the result code BUSY.
The Location ID 8 stated in Section 3.4.1 points to Section 3.4.6, with 17
= "User busy".
Enables the presentation of extended call release reports.
Now, a mobile originated data call is set up.
Call ends after remote party hung up.
Normal call release is reported, followed by the result code NO CARRIER.
The Location ID 8 stated in Section 3.4.1 points to Section 3.4.6, with 16
= "Normal call clearing".
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 82 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 83

3.6 AT+CPAS Mobile equipment activity status
The AT+CPAS execute command indicates the activity status of the ME.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CPAS=?
Response(s)
+CPAS: (list of supported<pas>s)
OK
Exec Command
AT+CPAS
Response(s)
+CPAS: <pas>
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<pas>
(num)
0 Ready
3 Incoming call (ringing)
4 Call in progress or call hold
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 83 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 84

3.7 AT+WS46 Select wireless network
Syntax
Test Command
AT+WS46=?
Response(s)
+WS46: (list of supported<n>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+WS46?
Response(s)
<n>
OK
Write Command
AT+WS46=[<n>]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
(num)
<n>
12 GSM digital cellular
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 84 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 85

4. Serial Interface Control Commands
The AT Commands described in this chapter allow the external application to determine various settings related
to the MC55's serial interface.
4.1 AT\Q Flow control
Syntax
Exec Command
AT\Q[<n>]
Response(s)
OK
If RTS/CTS flow control is not supported by interface and <n> is 2 or 3:
ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
SIEMENS ! % % § § § ! ! !
Parameter Description
(num)(&W)(&V)
<n>
(&F)
[0]
1 XON/XOFF software flow control
2 Only CTS by DCE (TA)
3 RTS/CTS hardware flow control
Disable flow control
Recommended for the following procedures: incoming or outgoing data calls,
fax calls, MUX mode.
Often, the initialization routine of Fax programs includes enabling RTS/CTS
handshake, eliminating the need to issue AT\Q3 once again.
Notes
• When using XON/XOFF flow control (AT\Q1) in online mode, +++ should not be used while the data trans-
mission is paused with XOFF. Before entering the command mode with +++ the paused transmission should
be resumed using the XON character.
• For compatibility reasons, the AT\Q command can be used in Multiplex mode, though the settings will not
take effect. However, be aware that whenever you use the AT\Q write command in Multiplex mode and then
save the current configuration to the user profile with AT&W, the changed AT\Q setting will become active after
restart.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 85 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 86

4.2 AT&C Set Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Line mode
The AT&C command determines how the state of the DCD line (circuit 109) reflects the MC55's internal activity.
Syntax
Exec Command
AT&C[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 , SIEMENS ! % ! % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)(&W)(&V)
[0] DCD line shall always be on.
(&F)
1
DCD line shall be on only when data carrier signal is present.
2 DCD line shall be on when one or more Internet services defined on the related
serial channel are in state "Connecting" or "Up" as described below. For details
on the various service states refer to AT^SISI, parameter <srvState> or
AT^SISO, parameter <srvState>.
• SOCKET, HTTP, SMTP, POP3: DCD shall be on when
<srvState>="Connnecting" or "Up"
• FTP: DCD shall be on when data channel is connected, i.e.
<srvState>="Up"
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 86 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 87

4.3 AT&D Set circuit Data Terminal Ready (DTR) function mode
The AT&D determines how the TA responds when circuit 108/2 (DTR) is changed from ON to OFF during data
mode.
Syntax
Exec Command
AT&D[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % § % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)(&W)(&V)
[0] TA ignores status of DTR.
1 ON->OFF on DTR: Change to command mode while retaining the connected
call.
(&F)
2
ON->OFF on DTR: Disconnect data call, change to command mode. During
state DTR = OFF auto-answer is off.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 87 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 88

4.4 AT&S Set circuit Data Set Ready (DSR) function mode
The AT&S command determines how the TA sets circuit 107 (DSR) depending on the communication state of
the TA interfacing TE.
Syntax
Exec Command
AT&S[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % ! % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(&F)
[0]
(num)(&W)(&V)
DSR line is always ON
1 TA in command mode: DSR is OFF.
TA in data mode: DSR is ON.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 88 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 89

4.5 ATE Enable command echo
The ATE command determines whether or not the TA echoes characters received from TE during command
state.
Syntax
Exec Command
ATE[<value>]
Response(s)
OK
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % % % % % ! ! !
Parameter Description
<value>
(num)(&W)(&V)
[0] Echo mode off
(&F)
1
Echo mode on
Note
• In case of using the command without parameter, <value> is set to 0.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 89 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 90

4.6 AT+ILRR Set TE-TA local rate reporting
The command AT+ILRR controls whether or not the intermediate result code "+ILRR" is transmitted from the TA
to the TE while a connection is being set up. The result code indicates the local rate. It is issued before the final
result code of the connection, e.g. CONNECT, is transmitted to the TE.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+ILRR=?
Response(s)
+ILRR: (list of supported <value>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+ILRR?
Response(s)
+ILRR: <value>
OK
Write Command
AT+ILRR=<value>
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 % % ! % ! ! ! ! !
Intermediate Result Code
+ILRR: <rate>
Indicates local port rate setting upon connection setup.
Parameter Description
<value>
(&F)
0
1 Enables reporting of local port rate
<rate>
Port rate setting upon connection setup (bps)
0 Autobauding (see Section 4.7.1, Autobauding). Not supported on ASC1.
300
600
1200
2400
4800
9600
14400
(num)(&W)(&V)
Disables reporting of local port rate
(num)
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 90 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 91

19200
28800
38400
57600
115200
230400
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 91 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 92

4.7 AT+IPR Set fixed local rate
The command AT+IPR can be used to set or query the TE-TA interface bit rate.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+IPR=?
Response(s)
+IPR: (list of supported auto-detectable <rate>s) , (list of supported fixed-only <rate>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+IPR?
Response(s)
+IPR: <rate>
OK
Write Command
AT+IPR=<rate>
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
V.250 ! % § § § § ! ! !
Command Description
The test command returns the values of the supported automatically detectable bit rates and the values of the
supported fixed bit rates.
The read command returns the current bit rate of the interface.
The write command specifies the bit rate to be used for the interface. When you set a fixed-rate, make sure that
both TE (DTE) and TA (DCE) are configured to the same rate. When you select autobauding, the TA will automatically recognize the bit rate currently used by the TE.
The setting is stored in the non-volatile memory and will be used whenever the engine is powered up again. However, in case of autobaud mode (AT+IPR=0) the detected TA bit rate will not be saved and, therefore, needs to
be resynchronized after restarting the GSM engine (see Section 4.7.1, Autobauding).
Parameter Description
<rate>
bit rate per second (bps)
0 Activates autobauding. Not supported on ASC1. See Section 4.7.1, Autobaud-
300
600
1200
2400
4800
9600
(num)(&V)
ing for further details.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 92 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 93

14400
19200
28800
38400
57600
115200
230400
Notes
• Delivery value for <rate> is autobauding enabled (AT+IPR=0) on ASC0 and 57600bps on ASC1. It will not
be restored with AT&F.
• The current setting of AT+IPR will be preserved when you download firmware (i.e. a firmware update does
not restore the factory setting) or in the event of power failure.
• Generally, AT+IPR should be used as a standalone command. If nethertheless combinations with other com-
mands on the same command line cannot be avoided, there are several constraints to be considered:
- Avoid combinations with the AT commands listed in Section 1.4.2, Combining AT commands on the same
command line.
- Take into account, that a pause of 100ms is required between the response to the last command (e.g. OK)
and the next command.
- When you enter AT+IPR=0, autobauding will be activated after the response to the last command is
received.
- When local echo is active (ATE1) and you enter AT+IPR=x with other commands you may encounter the
following problem: if switching to the new bit rate takes effect while a response is being transmitted, the
last bytes may be sent with the new bit rate and thus, not properly transmitted. The following commands
will be correctly sent at the new bit rate.
• In order to account for greater amounts of data it is recommended to choose a minimum bit rate of 2400 bps.
If the ME shall be operated in Multiplex mode we suggest a minimum bit rate of 4800bps.
• In Multiplex mode, the write command AT+IPR=<rate> will not change the bit rate currently used, but the
new bit rate will be stored and becomes active, when the module is restarted.
• A selected bit rate takes effect after the write commands returns OK.
4.7.1 Autobauding
To take advantage of autobaud mode specific attention must be paid to the following requirements:
• Synchronization between TE and TA
Ensure that TE and TA are correctly synchronized and the bit rate used by the TE is detected by the TA. To
allow the bit rate to be synchronized simply use an "AT" or "at" string. This is necessary
- after you have activated autobauding
- when you start up the GSM engine while autobauding is enabled. It is recommended to wait 3 to 5 seconds
before sending the first AT character. Otherwise undefined characters might be returned.
If you want to use autobauding and autoanswer at the same time, you can easily enable the TE-TA synchronization, when you activate autobauding first and then configure the autoanswer mode (ATS0 ≠ 0).
• Restrictions on autobauding operation
- The serial interface shall be used with 8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit (factory setting), e.g. 2 stop bits
are not supported for autobaud mode.
- The command A/ cannot be used.
- Only the strings "AT" or "at" can be detected (neither "At" nor "aT").
- URCs that may be issued before the ME detects a new bit rate (by receiving the first AT character) will be
sent at the previously detected bit rate or, after ME restart, at 57600 bps.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 93 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 94

- It is not recommended to switch to autobauding from a bit rate that cannot be detected by the autobaud
mechanism (e.g. 300 bps). Responses to AT+IPR=0 and any commands on the same line might be corrupted.
• Autobauding and bit rate after restart
The most recently detected bit rate is stored when the ME is powered down (with AT^SMSO). Therefore, each
time the module is restarted the correct bit rate must be found as described above. Unless the bit rate is determined, the following constraints apply:
- An incoming CSD call or a network initiated GPRS request cannot be accepted. This must be taken into
account when autobauding and autoanswer mode (ATS0 ≠ 0) are enabled at the same time, escpecially
if SIM PIN 1 authentication is done automatically and the setting ATS0 ≠ 0 is stored to the user profile with
AT&W.
- Until the bit rate is found, URCs generated after restart will be output at 57600 bps. This applies only to
user defined URCs, such as "+CREG", "CCWA", "^SCKS" etc. The URCs "^SYSSTART", "^SYSSTART
CHARGE-ONLY MODE" and "^SYSSTART ALARM MODE" will not be indicated when autobauding is
enabled.
Note: To avoid any problems caused by undetermined bit rates in the direction from TA to TE we strongly
recommend to configure a fixed bit rate rather than autobauding.
• Autobauding and multiplex mode
If autobauding is active you cannot switch to multiplex mode (see AT+CMUX).
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 94 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 95

4.8 AT+CMUX Enter multiplex mode
All information provided in this section applies to the ASC0 interface only. The second interface ASC1 has no
support of Multiplex mode.
Multiplex mode according to the ETSI TS 101 669 and GSM 07.10 enables one physical serial asynchronous
interface to be partitioned into three virtual channels. This allows you to take advantage of up to 3 simultaneous
sessions running on the serial interface. For example, you can send or receive data or make a call on the first
channel, while the other two channels are free to control the module with AT commands.
The MC55 module incorporates an internal multiplexer and thus integrates all the functions needed to implement
full-featured multiplex solutions. For the application on top, customers have the flexibility to create their own multiplex programs conforming to the multiplexer protocol. To help system integrators save the time and expense of
designing multiplexer applications, SIEMENS AG offers WinMUX2k, a ready-to-use multiplex driver for Windows
2000 and Windows XP. Another approach is to develop customized solutions based on the sources of the
WinMux2k driver.
Refer to [5] which provides a detailed description of the multiplex architecture and step-by-step instructions of
how to install and configure the multiplex mode. The WinMUX2k driver and its source files can be supplied on
request. Please contact your local distributor to obtain the latest installation software and user's guide.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CMUX=?
Response(s)
+CMUX: (list of supported<mode>s)
OK
Read Command
AT+CMUX?
Response(s)
+CMUX: <mode>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Write Command
AT+CMUX=<mode>
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07, GSM 07.10 ! % ! ! ! ! ! ! %
Parameter Description
<mode>
Multiplexer transparency mechanism
0 Basic option
<subset>
Subparameters defined in GSM07.07 are adjusted for control and logical channels as follows
0 UIH frames used only (control channel)
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 95 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
(num)
(num)
Page 96

Notes
• The write command is used to enter the multiplex mode. The setup of the logical channels is initiated by the
TE, i.e. the TE acts as initiator. This means that the TE shall ensure that logical channels are established
before any further actions on the channels can be started.
• There is a timeout of five seconds, if the multiplexer protocol is enabled and no multiplexer control channel is
established. The GSM engine returns to AT command mode.
• The parameter maximum frame size (N1) of AT+CMUX in GSM 07.10 is fixed to 98 bytes and cannot be
changed. All other parameters are not available.
4.8.1 Restrictions on Multiplex mode
When the serial interface ASC0 is in multiplex mode, data and fax calls can only be set up on logical channel 1.
Due to this restriction, AT commands have a different behavior on channels 2+3 compared to channel 1. Several
commands are not available, others return different responses. This section summarizes the concerned commands. For general rules and restrictions to be considered in Multiplex mode please refer to [5].
Table 4.1: Availability of AT Commands on Virtual Channels
Command Behavior on channel 1 Behavior on channel 2+3
+++ not usable, but see note
2)
not usable, but see note
AT+CBST as described not usable
AT+CRLP as described not usable
AT+CG... (GPRS commands) as described see note
3)
AT+F... (Fax commands) as described not usable
AT&S as described not usable
ATA as described no Data Calls
ATD as described no Data Calls
ATDI as described not usable
ATL as described not usable
ATM as described not usable
ATO as described not usable
1)
ATS6
ATS7
ATS8
ATS10
ATS18
1)
1)
1)
1)
as described not usable
as described not usable
as described not usable
as described not usable
as described not usable
2)
1) Siemens GSM engines support the registers S0 - S29. You can change S0,S3,S4,S5,S6,S7,S8,S10 and S18 using the
related ATSn commands (see starting from
2) The applicability of the
Protocol. Recommendations for implementing an appropriate modem status command (MSC) are provided in [5], Section
"Escape Sequence".
3) PDP contexts can be defined on any channel, but are visible and usable only on the channel on which they are defined
(thus it is not possible to define a context on channel 2 and activate it on channel 3). GPRS connections can be established on two channels at a time.
+++ escape sequence depends on the customer's external application based on the Mulitplexer
ATS0). The other registers are read-only and for internal use only!
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 96 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 97

Table 4.2: Summary of AT commands with Different Behavior in Multiplex Mode
Command Description
AT\Q It is recommended to use hardware flow control (AT\Q3). XON/XOFF flow control
(AT\Q1) is not supported in Multiplex mode.
See note regarding AT\Qn settings stored with AT&W if Multiplex mode is active.
AT&V Different default configurations on channels 1, 2 and 3.
AT&W Different user profiles can be stored on each channel.
AT+IPR Before you start Multiplex mode, it is recommended to set the ME to 57600 bps
(minimum should be 4800 bps). For GPRS we suggest to use 115200 bps or
230400 bps.
In Multiplex mode, the write command AT+IPR=<rate> will not change the bit rate
currently used, but the new bit rate will be stored and becomes active, when the
module is restarted.
AT+IPR=0 Multiplex mode cannot be activated while autobauding is enabled.
AT+CALA On each channel an individual <text> message can be stored. but only one time
setting applies to all channels. This means an alarm <time> set on one of the
channels overwrites the time setting on all remaining channels. Therefore, the total
number of alarm events returned by the read command AT+CALA? will always be
<n>=0, no matter whether individual text messages are stored.
When the alarm is timed out and executed the ME sends the URC only on the
channel where the most recent alarm setting was made. The alarm time will be
reset to "00/01/01,00:00:00" on all channels.
AT+CMEE Presentation mode can be separately configured for each channel.
AT+CNMA If Multiplex mode is activated the +CNMI parameter will be set to zero on all chan-
nels, if one channel fails to acknowledge an incoming message within the required
time.
AT+CNMI Phase 2+ parameters can only be used on one channel. The parameter for <mt>
and <ds> on the other channels have to be set to zero. If either a SM or a Status
Report is not acknowledged, all +CNMI parameter will be set to zero on all channels.
AT+CFUN If the ME is in Multiplexer mode, it is not recommended to activate SLEEP mode
with AT+CFUN=<fun>. The best approach to properly control SLEEP mode in this
case is to issue the PSC messages described in [5], Section "Power saving control
(PSC)".
AT+CPMS Parameter <mem3> will be the same on all instances, but the settings of <mem1>
and <mem2> may vary on each instance.
AT^SSDA If one instance is set to <da>=1 and <mt>=1, then all other instances must be con-
figured for <mt>=0.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 97 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 98

4.8.2 Second serial interface ASC1
The second serial interface ASC1 is intended as an auxiliary interface for applications which need multiple parallel access to the module (e.g. to query status information during a data call), but cannot use the GSM 07.10
multiplexing protocol. Therefore this interface offers limited functionality only.
• No DTR, DSR, DCD, RING signals. These hardware lines do not exist. As a result, AT commands controlling
the behavior of these lines (AT&D, AT&C, AT&S) are not allowed and return ERROR.
• No presentation of ^SYSSTART URCs on ASC1. After restart or reset of the ME, either check that the URC
has been sent on ASC0 or wait approximately 3 seconds before entering the first AT command on ASC1.
• No Autobauding. The hardware is not capable of automatically detecting the baudrate on this interface, so
the AT command which selects autobauding (AT+IPR=0) is not allowed and returns ERROR.
• No CSD calls, so all related AT commands cannot be used and return ERROR.
• No fax calls, so all AT+F commands cannot be used and return ERROR.
• No GSM 07.10 Multiplexer. If issued on the second interface AT+CMUX=0 returns ERROR.
ASC1 is disabled when the multiplexer is enabled on the first serial interface ASC0. Yet, both ASC1 and the multiplexer channel 2 are using the same parameters, and thus, the same user defined profile (if any). As a result,
a user profile stored on multiplexer channel 2 takes effect on ASC1 after closing the multiplexer and starting up
ASC1. Likewise, a user profile stored on ASC1 will be loaded on multiplexer channel 2.
This may be a problem when ASC1 is not connected, but flow control (for example AT\Q1 or AT\Q3) is stored to
the user profile on the multiplexer channel 2. In this case, flow control takes effect on ASC1, when the multiplexer
is switched off. If then for example a large amount of URCs is generated, their transmission might be stopped
due to the flow control. To avoid this problem we recommend that you do not activate flow control on multiplexer
channel 2 when you set up a user profile with AT&W.
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 98 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 99

5. Security Commands
The AT Commands described in this chapter allow the external application to determine various security related
settings.
5.1 AT+CPIN PIN Authentication
AT+CPIN controls network authentication of the MC55.
The read command returns an alphanumeric string indicating whether or not network authentication is required.
The write command allows the MC55 to store the entered password. This may be for example the SIM PIN1 to
register to the GSM network, or the SIM PUK1 to replace a disabled SIM PIN1 with a new one, or the PH-SIM
PIN if the client has taken precautions for preventing damage in the event of loss or theft etc.
If no PIN1 request is pending (for example if PIN1 authentication has been done and the same PIN1 is entered
again) MC55 responds "+CME ERROR: operation not allowed"; no further action is required.
Each time a password is entered with AT+CPIN the module starts reading data from the SIM. The duration of
reading varies with the SIM card. This may cause a delay of several seconds before all commands which need
access to SIM data are effective. See Section 20.1, Restricted access to SIM data after SIM PIN authentication
for further detail.
Syntax
Test Command
AT+CPIN=?
Response(s)
OK
Read Command
AT+CPIN?
Response(s)
+CPIN: <code>
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Write Command
AT+CPIN=<pin>[, <new pin>]
Response(s)
OK
ERROR
+CME ERROR: <err>
Reference(s) PIN ASC0 ASC1 MUX1 MUX2 MUX3 Charge Last
GSM 07.07 ! % % % % % ! ! !
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 99 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
Page 100

Parameter Description
<pin>
(str)
Password (string type), usually SIM PIN1.
If the requested password was a PUK, such as SIM PUK1 or PH-FSIM PUK or another password, then <pin>
must be followed by <new pin>.
<new pin>
(text)
If the requested code was a PUK: specify a new password or restore the former disabled password. See Section
5.1.1, What to do if PIN or password authentication fails? for more information about when you may need to
enter the PUK.
<code>
(text)
SIM PIN authentication
READY PIN has already been entered. No further entry needed.
SIM PIN ME is waiting for SIM PIN1.
SIM PUK ME is waiting for SIM PUK1 if PIN1 was disabled after three failed attempts to
enter PIN1.
SIM PIN2 ME is waiting for PIN2. This is only applicable when an attempt to access a
PIN2 related feature was acknowledged with +CME ERROR: 17 ("SIM PIN2
required"), for example when the client attempts to edit the FD phonebook). In
this case the read command AT+CPIN? also prompts for SIM PIN2. Normally,
the AT+CPIN2 command is intended for SIM PIN2.
SIM PUK2 ME is waiting for PUK2 to unblock a disabled PIN2. As above, this is only nec-
essary when the preceding command was acknowledged with +CME ERROR:
18 ("SIM PUK2 required") and only if the read command AT+CPIN? also
prompts for SIM PUK2. Normally, the AT+CPIN2 command is intended for SIM
PUK2.
Phone security locks set by client or factory
PH-SIM PIN ME is waiting for phone-to-SIM card password if "PS" lock is active and the cli-
ent inserts other SIM card than the one used for the lock. ("PS" lock is also
referred to as phone or antitheft lock).
PH-SIM PUK ME is waiting for Master Phone Code, if the above "PS" lock password was
incorrectly entered three times.
PH-FSIM PIN ME is waiting for phone-to-very-first-SIM card. Necessary when "PF" lock was
set. When powered up the first time, ME locks itself to the first SIM card put into
the card holder. As a result, operation of the mobile is restricted to this one SIM
card (unless the PH-FSIM PUK is used as described below).
PH-FSIM PUK ME is waiting for phone-to-very-first-SIM card unblocking password to be
given. Necessary when "PF" lock is active and other than first SIM card is
inserted.
PH-NET PUK ME is waiting for network personalisation unblocking password
PH-NS PIN ME is waiting for network subset personalisation password
PH-NS PUK ME is waiting for network subset unblocking password
PH-SP PIN ME is waiting for service provider personalisation password
PH-SP PUK ME is waiting for service provider personalisation unblocking password
PH-C PIN ME is waiting for corporate personalisation password
PH-C PUK ME is waiting for corprorate personalisation un-blocking password
MC55_ATC_V04.00 Page 100 of 475 3/17/06
Confidential / Released
 Loading...
Loading...