Page 1

s
Java User’s Guide
Siemens Cellular Engines
Version: 12
DocId: wm_java_usersguide_v12
Products: TC65, AC65, AC75, XT65, XT75
User’s Guide
Page 2

Java User’s Guide
s
Document Name:
Version:
Date:
DocId:
Status
Supported Products:
GENERAL NOTES - EXCLUSION OF LIABILITY
PRODUCT IS DEEMED ACCEPTED BY RECIPIENT AND IS PROVIDED WITHOUT INTERFACE TO RECIPIENT'S PRODUCTS. THE DOCUMENTATION AND/OR PRODUCT ARE PROVIDED FOR TESTING, EVALUATION, INTEGRATION AND INFORMATION PURPOSES. THE DOCUMENTATION AND/OR PRODUCT ARE
PROVIDED ON AN "AS IS" BASIS ONLY AND MAY CONTAIN DEFICIENCIES OR INADEQUACIES. THE DOCUMENTATION AND/OR PRODUCT ARE PROVIDED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, SIEMENS FURTHER DISCLAIMS
ALL WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
COMPLETENESS, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD-PARTY
RIGHTS. THE ENTIRE RISK ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT AND DOCUMENTATION REMAINS WITH RECIPIENT. THIS PRODUCT IS NOT INTENDED FOR USE IN LIFE SUPPORT
APPLIANCES, DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WHERE A MALFUNCTION OF THE PRODUCT CAN REASONABLY BE
EXPECTED TO RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY. APPLICATIONS INCORPORATING THE DESCRIBED PRODUCT MUST BE DESIGNED TO BE IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS PROVIDED IN
THESE GUIDELINES. FAILURE TO COMPLY WITH ANY OF THE REQUIRED PROCEDURES CAN RESULT IN
MALFUNCTIONS OR SERIOUS DISCREPANCIES IN RESULTS. FURTHERMORE, ALL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS REGARDING THE USE OF MOBILE TECHNICAL SYSTEMS, INCLUDING GSM PRODUCTS, WHICH
ALSO APPLY TO CELLULAR PHONES MUST BE FOLLOWED. SIEMENS OR ITS SUPPLIERS SHALL,
REGARDLESS OF ANY LEGAL THEORY UPON WHICH THE CLAIM IS BASED, NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY
CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE OR OTHER DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION OR DATA, OR OTHER PECUNIARY LOSS) ARISING OUT THE USE
OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE DOCUMENTATION AND/OR PRODUCT, EVEN IF SIEMENS HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE FOREGOING LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY SHALL
NOT APPLY IN CASE OF MANDATORY LIABILITY, E.G. UNDER THE GERMAN PRODUCT LIABILITY ACT, IN
CASE OF INTENT, GROSS NEGLIGENCE, INJURY OF LIFE, BODY OR HEALTH, OR BREACH OF A CONDITION WHICH GOES TO THE ROOT OF THE CONTRACT. HOWEVER, CLAIMS FOR DAMAGES ARISING FROM
A BREACH OF A CONDITION, WHICH GOES TO THE ROOT OF THE CONTRACT, SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE
FORESEEABLE DAMAGE, WHICH IS INTRINSIC TO THE CONTRACT, UNLESS CAUSED BY INTENT OR
GROSS NEGLIGENCE OR BASED ON LIABILITY FOR INJURY OF LIFE, BODY OR HEALTH. THE ABOVE PROVISION DOES NOT IMPLY A CHANGE ON THE BURDEN OF PROOF TO THE DETRIMENT OF THE RECIPIENT. SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE AT ANY TIME. THE INTERPRETATION OF THIS GENERAL
NOTE SHALL BE GOVERNED AND CONSTRUED ACCORDING TO GERMAN LAW WITHOUT REFERENCE TO
ANY OTHER SUBSTANTIVE LAW.
Java User’s Guide
12
2008-02-25
wm_java_usersguide_v12
Confidential / Released
TC65, AC65, AC75, XT65, XT75
Copyright
Transmittal, reproduction, dissemination and/or editing of this document as well as utilization of its contents and communication thereof to others without express authorization are prohibited. Offenders will
be held liable for payment of damages. All rights created by patent grant or registration of a utility model
or design patent are reserved.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2008
Trademark notice
Microsoft and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 2 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 3

Java User’s Guide
Content
123
s
Content
1 Preface ....................................................................................................................... 11
2 Overview .................................................................................................................... 12
2.1 Related Documents ......................................................................................... 12
2.2 Terms and Abbreviations ................................................................................. 13
3 Installation ................................................................................................................. 15
3.1 System Requirements...................................................................................... 15
3.2 Installation CD for AC65/AC75 and XT65/XT75 .............................................. 16
3.3 Installation CD for TC65................................................................................... 17
3.3.1 Components........................................................................................ 18
3.3.1.1 Module Exchange Suite ...................................................... 18
3.3.1.2 WTK .................................................................................... 18
3.3.1.3 SDK / JDK........................................................................... 19
3.3.1.4 NetBeans IDE 5.0 ............................................................... 19
3.3.1.5 NetBeans IDE 5.5.1 ............................................................ 19
3.3.1.6 Eclipse 3.1.2 IDE and Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.x................... 20
3.3.1.7 Eclipse 3.2.2 IDE and Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.5 or 1.6.8...... 20
3.3.1.8 GPS Evaluation Software.................................................... 21
3.3.1.9 Integrated Documentation Suite (IDS) ................................ 21
3.4 Set up Java Development Environment with Eclipse IDE (Quick Start-up) ..... 22
3.5 Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation ................................................................ 24
3.5.1 Installing the Standard Development Toolkit ...................................... 24
3.5.2 Installing the SMTK Environment........................................................ 24
3.5.3 Installing NetBeans IDE 5.0 / NetBeans IDE 5.5.1 ............................. 26
3.5.4 Installing Eclipse 3.0, Eclipse 3.1 or Eclipse 3.2................................. 26
3.5.5 Installing Borland JBuilder X, 2005 and 2006 Enterprise/Developer .. 27
3.5.6 Installing Module Exchange Suite (MES)............................................ 27
3.6 SMTK Uninstall ................................................................................................ 27
3.7 Upgrades ......................................................................................................... 27
4 Software Platform ..................................................................................................... 28
4.1 Software Architecture....................................................................................... 28
4.2 Interfaces ......................................................................................................... 29
4.2.1 ASC0 - Serial Device .......................................................................... 29
4.2.2 General Purpose I/O ........................................................................... 29
4.2.3 DAC/ADC............................................................................................ 29
4.2.4 ASC1................................................................................................... 29
4.2.5 Digital Audio Interface (DAI) ............................................................... 29
4.2.6 I2C/SPI................................................................................................ 29
4.2.7 GPS .................................................................................................... 30
4.2.8 JVM Interfaces .................................................................................... 31
4.2.8.1 IP Networking...................................................................... 31
4.2.8.2 Media .................................................................................. 31
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 3 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 4

Java User’s Guide
Content
123
4.2.8.3 Other Interfaces .................................................................. 31
4.3 Data Flow of a Java Application Running on the Module ................................ 32
4.4 Handling Interfaces and Data Service Resources ........................................... 33
4.4.1 Module States ..................................................................................... 33
4.4.1.1 State 1: Default – No Java Running .................................... 33
4.4.1.2 State 2: No Java Running, General Purpose I/O
and I2C/SPI......................................................................... 34
4.4.1.3 State 4: Default – Java Application Active........................... 34
4.4.1.4 State 5: Java Application Active, General Purpose I/O and
I2C/SPI34
4.4.2 Module State Transitions .................................................................... 35
5 Maintenance .............................................................................................................. 36
5.1 IP Service......................................................................................................... 36
5.2 Remote SIM Access ........................................................................................ 37
5.3 Power Saving................................................................................................... 37
5.4 Charging .......................................................................................................... 38
5.5 Airplane Mode.................................................................................................. 38
5.6 Alarm................................................................................................................ 38
5.7 Shutdown ......................................................................................................... 39
5.7.1 Automatic Shutdown ........................................................................... 39
5.7.2 Manual Shutdown ............................................................................... 39
5.7.3 Restart after Switch Off....................................................................... 39
5.7.4 Watchdog............................................................................................ 39
5.8 Special AT Command Set for Java Applications ............................................. 40
5.8.1 Switching from Data Mode to Command Mode .................................. 40
5.8.2 Mode Indication after MIDlet Startup .................................................. 40
5.8.3 Long Responses ................................................................................. 40
5.8.4 Configuration of Serial Interface ......................................................... 40
5.8.5 Java Commands ................................................................................. 41
5.8.6 AutoExec Function.............................................................................. 41
5.9 System Out ...................................................................................................... 41
5.9.1 Serial interfaces .................................................................................. 41
5.9.2 File ...................................................................................................... 42
5.9.3 UDP .................................................................................................... 42
5.10 GPIO ................................................................................................................ 42
5.11 Restrictions ...................................................................................................... 42
5.11.1 Flash File System ............................................................................... 42
5.11.2 Memory ............................................................................................... 42
5.12 Performance .................................................................................................... 43
5.12.1 Java .................................................................................................... 43
5.12.2 Pin I/O ................................................................................................. 44
5.12.3 Data Rates on RS-232 API ................................................................. 44
5.12.3.1 Plain Serial Interface ........................................................... 45
5.12.3.2 Voice Call in Parallel ........................................................... 45
5.12.3.3 Scenarios with GPRS/EGDE Connection ........................... 45
s
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 4 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 5

Java User’s Guide
Content
123
5.12.3.4 Upload................................................................................. 46
5.12.3.5 Download ............................................................................ 47
5.13 System Time .................................................................................................... 49
6 MIDlets ....................................................................................................................... 50
6.1 MIDlet Documentation ..................................................................................... 50
6.2 MIDlet Life Cycle.............................................................................................. 50
6.3 Hello World MIDlet ........................................................................................... 52
7 File Transfer to Module............................................................................................. 53
7.1 Module Exchange Suite ................................................................................... 53
7.1.1 Windows Based .................................................................................. 53
7.1.2 Command Line Based ........................................................................ 53
7.2 Over the Air Provisioning ................................................................................. 53
7.3 Security Issues................................................................................................. 54
7.3.1 Module Exchange Suite ...................................................................... 54
7.3.2 OTAP .................................................................................................. 54
s
8 Over The Air Provisioning (OTAP) .......................................................................... 55
8.1 Introduction to OTAP ....................................................................................... 55
8.2 OTAP Overview ............................................................................................... 55
8.3 OTAP Parameters............................................................................................ 56
8.4 Short Message Format .................................................................................... 57
8.5 Java File Format .............................................................................................. 58
8.6 Procedures....................................................................................................... 59
8.6.1 Install/Update ...................................................................................... 59
8.6.2 Delete.................................................................................................. 60
8.7 Time Out Values and Result Codes................................................................. 61
8.8 Tips and Tricks for OTAP................................................................................. 61
8.9 OTAP Tracer.................................................................................................... 62
8.10 Security ............................................................................................................ 62
8.11 How To............................................................................................................. 62
9 Compile and Run a Program without a Java IDE ................................................... 64
9.1 Build Results .................................................................................................... 64
9.2 Compile............................................................................................................ 65
9.3 Run on the Module with Manual Start.............................................................. 65
9.4 Run on the Module with Autostart.................................................................... 66
9.4.1 Switch on Autostart ............................................................................. 66
9.4.2 Switch off Autostart ............................................................................. 66
10 Compile and Run a Program with a Java IDE......................................................... 67
10.1 Eclipse 3.1.2 (with ME Plugin 1.2.3) ................................................................ 67
10.1.1 Setup a New Project ........................................................................... 67
11 Debug Environment .................................................................................................. 72
11.1 Data Flow of a Java Application in the Debug Environment............................ 72
11.2 Emulator........................................................................................................... 73
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 5 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 6

Java User’s Guide
Content
123
11.3 Java IDE .......................................................................................................... 75
11.3.1 NetBeans IDE 5.0, NetBeans 5.5 or NetBeans 5.5.x.......................... 75
11.3.2 Eclipse 3.0 and Eclipse 3.1................................................................ 81
11.3.3 Borland JBuilder X .............................................................................. 91
11.3.4 Borland JBuilder 2005 and JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer........ 94
11.4 Breakpoints ...................................................................................................... 95
11.5 Switching Java “System.out” to IDE Debug Window ....................................... 96
11.6 Important Information for Java Debugging on Windows Vista ......................... 97
s
11.3.1.1 Switching Emulator to IMP-NG Emulator ............................ 76
11.3.1.2 Templates............................................................................ 77
11.3.1.3 Examples ............................................................................ 78
11.3.1.4 Compile and Run ................................................................ 79
11.3.1.5 Starting Debug Session without Downloading Java Files ... 79
11.3.1.6 Displaying Java "System.out" in NetBeans IDE window..... 80
11.3.2.1 Eclipse 3.0........................................................................... 81
11.3.2.2 Eclipse 3.1........................................................................... 81
11.3.2.3 Eclipse 3.2........................................................................... 81
11.3.2.4 Using Eclipse with ME Plugin up to Version 1.2.3............... 82
11.3.2.5 Using Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.x..................................... 83
11.3.2.6 Using Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.6.x..................................... 85
11.3.2.7 Import Example ................................................................... 86
11.3.2.8 Compile and Debug ............................................................ 87
11.3.2.9 Starting Debug Session without Downloading Java Files ... 89
11.3.3.1 Examples ............................................................................ 92
11.3.3.2 Starting Debug Session without Downloading Java Files ... 93
11.3.4.1 Examples ............................................................................ 95
12 Java Security ............................................................................................................. 98
12.1 Secure Data Transfer....................................................................................... 98
12.1.1 Create a Secure Data Transfer Environment Step by Step.............. 100
12.2 Execution Control........................................................................................... 103
12.2.1 Change to Secured Mode Concept................................................... 104
12.2.2 Concept for the Signing the Java MIDlet .......................................... 105
12.3 Application and Data Protection..................................................................... 106
12.4 Structure and Description of the Java Security Commands .......................... 106
12.4.1 Structure of the Java Security Commands ....................................... 107
12.4.2 Build Java Security Command.......................................................... 108
12.4.3 Send Java Security Command to the Module................................... 109
12.5 Create a Java Security Environment Step by Step........................................ 110
12.5.1 Create Key Store .............................................................................. 110
12.5.2 Export X.509 Root Certificate ........................................................... 110
12.5.3 Create Java Security Commands ..................................................... 110
12.5.4 Sign a MIDlet .................................................................................... 112
12.6 Attention......................................................................................................... 112
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 6 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 7

Java User’s Guide
Content
123
13 Java Tutorial ............................................................................................................ 113
13.1 Using the AT Command API.......................................................................... 113
13.1.1 Class ATCommand........................................................................... 113
13.1.1.1 Instantiation with or without CSD Support......................... 113
13.1.1.2 Sending an AT Command to the Device, the send() Method..
114
13.1.1.3 Data Connections.............................................................. 115
13.1.1.4 Synchronization................................................................. 117
13.1.2 ATCommandResponseListener Interface......................................... 117
13.1.2.1 Non-Blocking ATCommand.send() Method....................... 117
13.1.3 ATCommandListener Interface ......................................................... 118
13.1.3.1 ATEvents........................................................................... 118
13.1.3.2 Implementation.................................................................. 119
13.1.3.3 Registering a Listener with an ATCommand Instance ...... 120
13.2 Programming the MIDlet ................................................................................ 121
13.2.1 Threads............................................................................................. 121
13.2.2 Example ............................................................................................ 121
s
14 Differences to the TC45 .......................................................................................... 123
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 7 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 8

Java User’s Guide
Tabl e s
8
s
Tables
Table 1: GPRS upload data rate with different number of timeslots, CS2 ................... 46
Table 2: GPRS upload data rate with different number of timeslots, CS4 ................... 46
Table 3: EDGE upload data rate with two timeslots, CS5............................................ 46
Table 4: EDGE upload data rate with two timeslots, CS9............................................ 46
Table 5: GPRS Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS2.............. 48
Table 6: GPRS Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS4.............. 48
Table 7: EDGE Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS5.............. 48
Table 8: EDGE Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS9.............. 48
Table 9: A typical sequence of MIDlet execution ......................................................... 51
Table 10: Parameters and keywords ............................................................................. 56
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 8 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 9

Java User’s Guide
Figures
10
s
Figures
Figure 1: Overview ........................................................................................................ 12
Figure 2: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: Dialog box Feature Updates............ 22
Figure 3: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: Dialog box Updates sites to visit...... 22
Figure 4: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: dialog box Search Results............... 23
Figure 5: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: dialog box Restart Eclipse ............... 23
Figure 6: Interface Configuration................................................................................... 31
Figure 7: Data flow of a Java application running on the module.................................. 32
Figure 8: Module State 1............................................................................................... 33
Figure 9: Module State 2............................................................................................... 34
Figure 10: Module State 4............................................................................................... 34
Figure 11: Module State 5............................................................................................... 34
Figure 12: Module State Transition Diagram................................................................... 35
Figure 13: Test case for measuring Java command execution throughput..................... 43
Figure 14: Test case for measuring Java MIDlet performance and handling pin-IO....... 44
Figure 15: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1........................................................ 45
Figure 16: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1 with a voice call in parallel ............. 45
Figure 17: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1 with GPRS data upload ................. 47
Figure 18: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1 with GPRS data download............. 47
Figure 19: OTAP Overview ............................................................................................. 55
Figure 20: OTAP: Install/Update Information Flow (messages in brackets are optional) 59
Figure 21: OTAP: Delete Information Flow (messages in brackets are optional) ........... 60
Figure 22: Create new Eclipse project: Create a J2ME MIDP Midlet Suite..................... 67
Figure 23: Create new Eclipse project: New J2ME Project............................................. 67
Figure 24: Create new Eclipse project: Midlet Suite Properties ...................................... 68
Figure 25: Create new Eclipse project: work area with new created project................... 68
Figure 26: Create new Eclipse project: Create a J2ME Midlet........................................ 69
Figure 27: Create new Eclipse project: Create a New J2ME Midlet................................ 69
Figure 28: Create new Eclipse project: Edit some Java commands............................... 70
Figure 29: Create new Eclipse project: Edit “deployed” path to Jar file........................... 70
Figure 30: Data flow of a Java application in the debug environment............................. 72
Figure 31: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - installed emulators......................................................... 76
Figure 32: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - Switching to IMP-NG emulator....................................... 76
Figure 33: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - Selecting an IMP-NG MIDlet template
(e.g. project “Test”)......................................................................................... 77
Figure 34: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - selecting sample project “Hello World Sample” ............. 78
Figure 35: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - confirmation of sample project “Hello World Sample”.... 78
Figure 36: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - add emulator option “-noload”
(e.g. project “HelloSample”) ........................................................................... 79
Figure 37: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - Displaying Java “System.out” in NetBeans IDE window 80
Figure 38: Eclipse – Display of different integrated emulators........................................ 82
Figure 39: Eclipse – J2ME platform ................................................................................ 83
Figure 40: Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.0 – Display of different integrated emulators...... 84
Figure 41: Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.0 – J2ME platform.............................................. 85
Figure 42: Eclipse – Project import ................................................................................. 86
Figure 43: Eclipse - Example .......................................................................................... 86
Figure 44: Eclipse – Create package .............................................................................. 87
Figure 45: Eclipse - Configuration................................................................................... 88
Figure 46: Eclipse - Configuration................................................................................... 89
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 9 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 10

Java User’s Guide
Figures
10
Figure 47: Eclipse 3.2.x ME1.5.x and 1.6.x select System Java Thread
for showing breakpoint line in Java source .................................................... 90
Figure 48: JBuilder X – JDK settings............................................................................... 91
Figure 49: JBuilder X – Siemens Library......................................................................... 91
Figure 50: JBuilder X – Sample Projects......................................................................... 92
Figure 51: JBuilder X – Starting the debugging session ................................................. 92
Figure 52: JBuilder X – Edit project properties for starting the emulator......................... 93
Figure 53: JBuilder - Runtime Configuration ................................................................... 93
Figure 54: JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer – JDK settings ...................................... 94
Figure 55: JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer – Siemens Library ................................ 94
Figure 56: JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer – Sample Projects ................................ 95
Figure 57: Emulator configuration file “switching Java System.out to serial port”........... 96
Figure 58: Using Windows Vista: Set Eclipse.exe perament to "Run as administrator".. 97
Figure 59: Mode 1 – Customer Root Certificate does not exist....................................... 99
Figure 60: Mode 2 - Server Certificate and Certificate into module are identical............ 99
Figure 61: Mode 2 - Server Certificate and self signed root Certificate
in module form a chain................................................................................. 100
Figure 62: Insert Customer Root Certificate.................................................................. 104
Figure 63: Prepare MIDlet for Secured Mode ............................................................... 105
Figure 64: Build Java Security Command..................................................................... 108
s
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 10 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 11

Java User’s Guide
1 Preface
11
s
1Preface
This document covers the full range of IMP-NG Java products from Siemens, currently including:
1. TC65 Module
2. TC65 Terminal
3. AC75/AC65 Module
4. XT75/XT65 Module
Differences between the products are noted in the particular chapters. Throughout the document, all supported products are referred to as ME (Mobile Equipment). For use in file, directory
or path names, the string “<productname>” represents the actual name of a product, for example TC65. Screenshots are provided as examples and, unless otherwise stated, apply to all
supported products.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 11 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 12
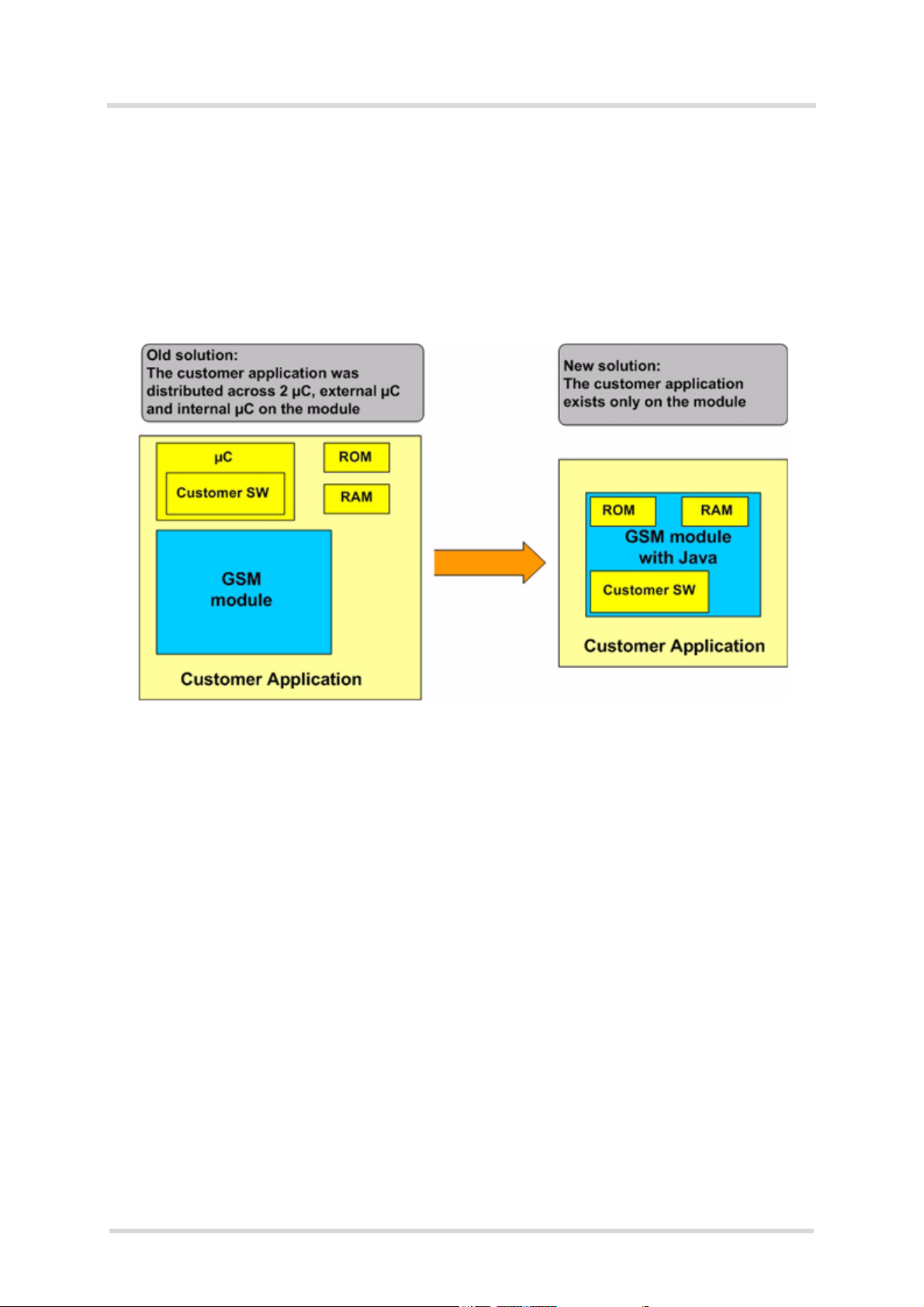
Java User’s Guide
2 Overview
14
s
2Overview
The ME features an ultra-low profile and low-power consumption for data (CSD and GPRS),
voice, SMS and fax. Java technology and several peripheral interfaces on the module allow you
to easily integrate your application.
This document explains how to work with the ME, the installation CD and the tools provided on
the installation CD.
Figure 1: Overview
2.1 Related Documents
List of documents referenced throughout this manual:
[1] AT Command Set of your Siemens Wireless product
[2] Hardware Interface Description of your Siemens Wireless product
[3] Java doc \wtk\doc\html\index.html
[4] IMP-NG, JSR228, Standard
For further documents see Chapter 3.2.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 12 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 13
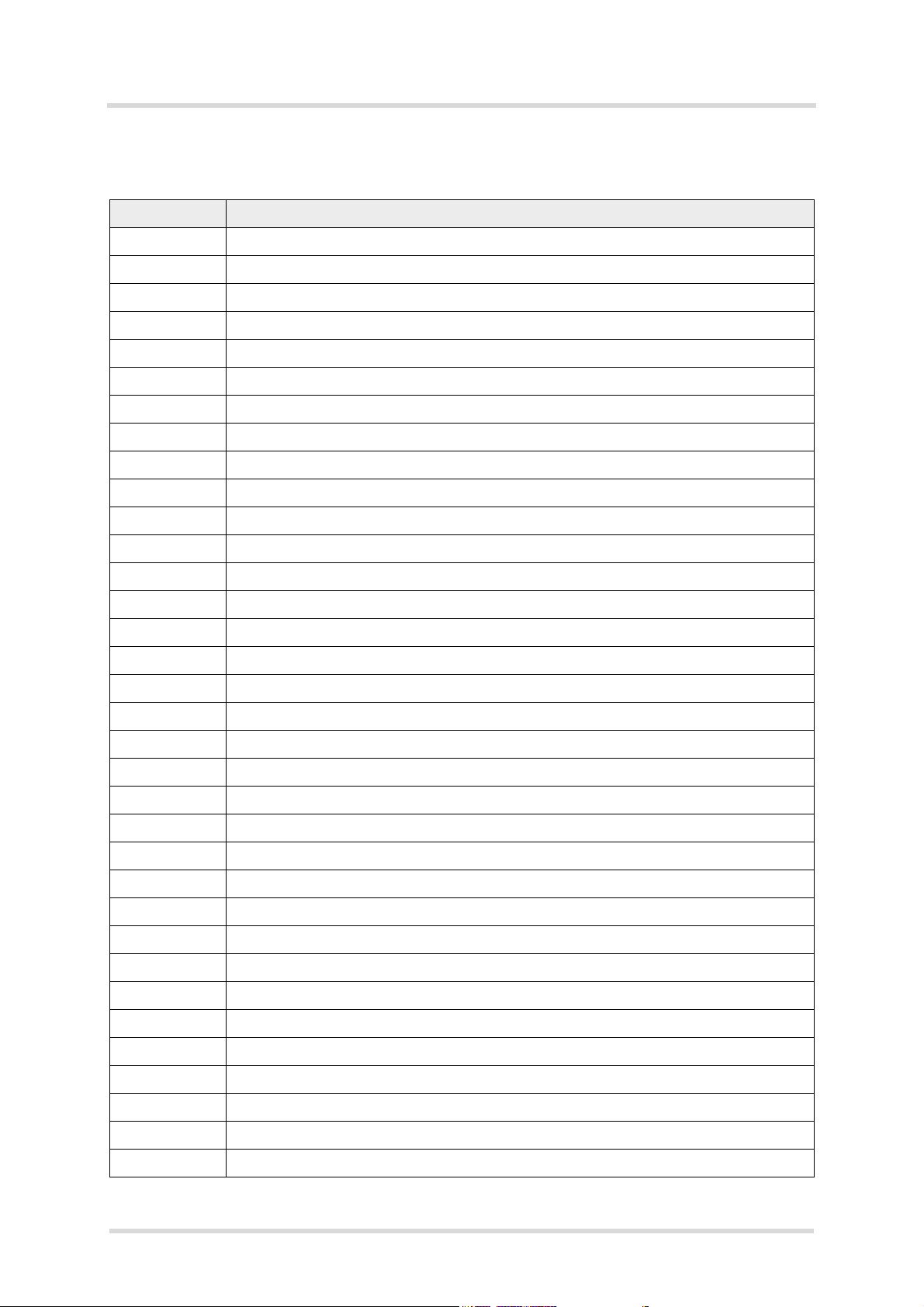
Java User’s Guide
2.2 Terms and Abbreviations
14
2.2 Terms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
API Application Program Interface
ASC Asynchronous Serial Controller
CLDC Connected Limited Device Configuration
CSD Circuit-Switched Data
DAI Digital Audio Interface
DCD Data Carrier Detect
DSR Data Set Ready
GPIO General Purpose I/O
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GPS Global Positioning System
s
HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol
I/O Input/Output
IDE Integrated Development Environment
IDS Integrated Documentation Suite
IP Internet Protocol
Java ME
Java SE
JAD Java Application Description
JAR Java Archive
JDK Java Development Kit
JVM Java Virtual Machine
LED Light Emitting Diode
ME Mobile Equipment
MES Module Exchange Suite
MIDP Mobile Information Device Protocol
OTA Over The Air
OTAP Over The Air Provisioning of Java Applications
™
™
Java Mobile Edition aka. J2ME
Java Standard Edition
PDP Packet Data Protocol
PDU Protocol Data Unit
SDK Standard Development Kit
SMS Short Message Service
SMTK Siemens Mobile Toolkit
TCP Transfer Control Protocol
URC Unsolicited Result Code
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 13 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 14
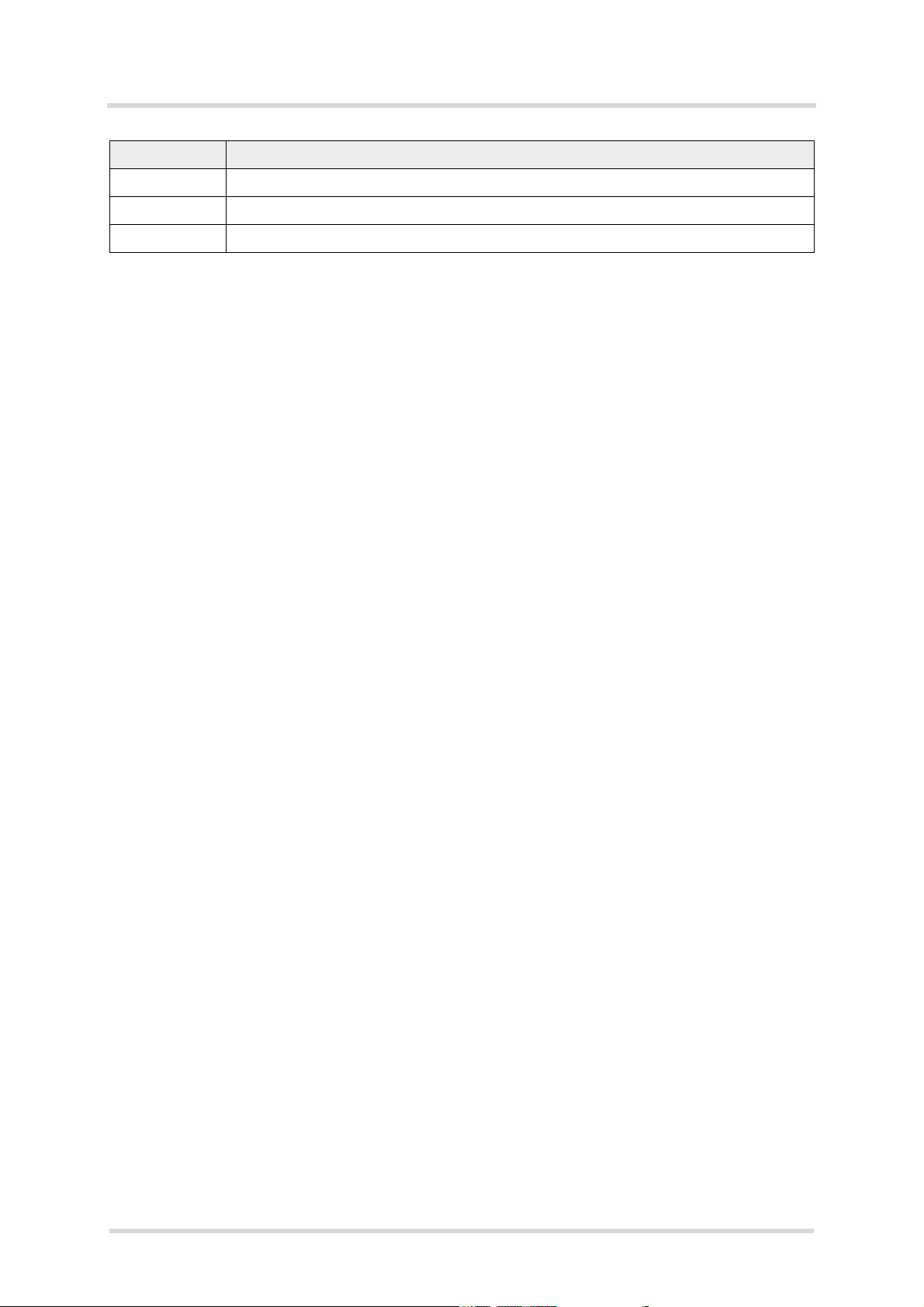
Java User’s Guide
2.2 Terms and Abbreviations
14
Abbreviation Description
URL Universal Resource Locator
VBS Visual Basic Script
WTK Wireless Toolkit
s
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 14 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 15

Java User’s Guide
3 Installation
27
3Installation
3.1 System Requirements
s
The Siemens Mobility Toolkit (SMTK) requires that you have:
1
1. Windows 2000, Windows XP or Windows Vista
installed
2. 110 Mbytes free disk space for SMTK
3. Administration privileges
4. Java 2 SDK, Standard Edition 1.4. To install the JDK version 1.4.2_09 provided, follow the
instructions in Section 3.5.1
Java 2 SDK, Standard Edition 1.5 is required for TC65.
If a Java IDE such as NetBeans IDE 5.0, NetBeans IDE 5.5.1
1
Eclipse 3.1.0, Eclipse 3.1.1, Eclipse 3.1.2, Eclipse 3.2.x
, JBuilder X, 2005 or 2006 Enterprise/
1
, Eclipse 3.0.1, Eclipse 3.0.2,
Developer is installed, it can be integrated into the SMTK environment during the installation of
the SMTK. To install one of the IDEs, follow the installation instructions in Section 3.5.3 and
Section 3.5.4 respectively.
If you wish to access the module via USB ensure that the USB cable is plugged between the
module’s USB interface and the PC. Unless already done, install the appropriate USB modem
driver. To do so, use the "usbmodem.inf" file supplied with your Siemens module.
1.
Supported only for TC65
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 15 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 16

Java User’s Guide
3.2 Installation CD for AC65/AC75 and XT65/XT75
27
s
3.2 Installation CD for AC65/AC75 and XT65/XT75
The Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation CD includes:
• Module Exchange Suite (MES setup is distributed on CD under "MES\Setup.exe")
• WTK (is distributed as zip file on the CD e.g. "WTK\ac75_wtk.zip")
bin
- various tools
doc
-html
- java docs for APIs
lib
- classes.zip
src
- various examples
• Java SDK
J2sdk-1_4_2_09-windows-i586-p.exe
• NetBeans IDE 5.0
netbeans-5_0-windows.exe (NetBeans IDE 5.0)
netbeans_mobility-5_0-win.exe (NetBeans Mobility package 5.0)
• Eclipse 3.1.2
eclipse-SDK-3.1.2-win32.zip (Eclipse 3.1.2)
• EclipseME plugin 1.2.3
eclipseme.feature_1.2.3_site.zip (Eclipse ME Plugin 1.2.3)
• EclipseME plugin 1.5.0
eclipseme.feature_1.5.0_site.zip (Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.0)
• EclipseME plugin WM (only required for Eclipse 3.0.1 and Eclipse 3.0.2)
• GPS Evaluation Software
ucentersetup.exe (GPS Evaluation SW)
• Integrated Documentation Suite (IDS)
IDS.zip
• Documents:
DSB75_HW_Description.pdf
<productname>_AT_Command_Set.pdf
<productname>_HW_Description.pdf
<productname>T_HW_Description.pdf (only if terminal version is available)
<productname>_ReleaseNote.pdf
Java_UserGuide.pdf (this document)
Remote_SAT_Guide.pdf
AN_02_Audio.pdf
AN_07_Battery.pdf
AN_16_FW_Update.pdf
AN_17_OTA_FW_Update.pdf
AN_22_TTY.pdf
AN_24_Dev_Guide.pdf
AN_32_USB.pdf
Some of the content can only be accessed after the installation.
2
3
4
2.
EclipseME plugin 1.2.1 is also supported, but not distributed as part of the CD.
3.
EclipseME plugin 1.5.0 is supported by TC65, XT65/XT75 and AC65/AC75. It is distributed as part of the
installation CD.
4.
GPS Evaluation Software is only distributed as part of the XT75 CD (only for products with GPS)
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 16 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 17

Java User’s Guide
3.3 Installation CD for TC65
27
s
3.3 Installation CD for TC65
The Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation CD includes:
• Module Exchange Suite (MES setup is distributed on CD under "MES\Setup.exe")
• WTK (is distributed as zip file on the CD e.g. "WTK\tc65_wtk.zip")
bin
- various tools
doc
-html
- java docs for APIs
lib
- classes.zip
src
- various examples
• Java SDK
jdk-1_5_0_07-windows-i586-p.exe
• NetBeans IDE 5.5.1
netbeans-5_5_1-windows.exe (NetBeans IDE 5.5.1)
netbeans_mobility-5_5_1-windows.exe (NetBeans Mobility package 5.5.1)
• Eclipse 3.1.2
eclipse-SDK-3.1.2-win32.zip (Eclipse 3.1.2)
• Eclipse 3.2.2
eclipse-SDK-3.2.2-win32.zip (Eclipse 3.2.2)
• EclipseME plugin 1.5.5
eclipseme.feature_1.5.5_site.zip (Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.5)
• EclipseME plugin 1.6.8
eclipseme.feature_1.6.8_site.zip (Eclipse ME Plugin 1.6.8)
• Integrated Documentation Suite (IDS)
IDS.zip
• Documents:
<productname>_Datasheet.pdf
DSB75_HW_Description.pdf
<productname>_AT_Command_Set.pdf
<productname>_HW_Description.pdf
<productname>T_HW_Description.pdf (only if terminal version is available)
<productname>_ReleaseNote.pdf
Java_UserGuide.pdf (this document)
Remote_SAT_Guide.pdf
AN_02_Audio.pdf
AN_07_Battery.pdf
AN_16_FW_Update.pdf
AN_22_TTY.pdf
AN_24_Dev_Guide.pdf
AN_26_Power_Supply.pdf
AN_32_USB.pdf
AN_45_Jamming_Detection_RLS.pdf
Some of the content can only be accessed after the installation.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 17 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 18

Java User’s Guide
3.3 Installation CD for TC65
27
s
3.3.1 Components
3.3.1.1 Module Exchange Suite
The Module Exchange Suite allows the developer to access the Flash file system on the cellular engine from the development environment over a serial interface. File transfers from PC to
module are greatly facilitated by this suite.
The Module Exchange Suite (MES) will be installed under the following directories:
• MES executables (e.g. MESCopy.exe, etc.) in the windows system directory
(e.g. C:\WINDOWS\system32)
The version of the MES executables can be read out by using the Windows Explorer context menu → Properties and selecting the Version tab (e.g. MESCopy.exe Version 1.0.0.12,
etc.)
• MES server files under "\ModuleExchange" directory (e.g. C:\Program Files\Module-
Exchange)
The version of the dll files can be read out by using the Windows Explorer context menu
→ Properties and selecting the Version tab (e.g. MESShellExt.dll Version: 2.0.0.19,
MESServer.exe Version: 2.0.0.38, MESSearchApp.exe Version: 2.0.0.5 )
The MES installation version can be found under Control Panel
selecting the installed MES program and clicking on support information (e.g. version
1.00.0008).
→ Add or Remove Programs
3.3.1.2 WTK
WTK is the directory where all the necessary components for product specific Java application
creation and debugging are stored.
The version of the installed WTK is stored under the root of the WTK directory in a text file.
(e.g. C:\Program Files\Siemens\SMTK\<product name>\WTK\VersionWTK.txt)
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 18 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 19

Java User’s Guide
3.3 Installation CD for TC65
27
s
3.3.1.3 SDK / JDK
This is software provided by SUN to support Java application development.
SMTK emulator uses the following JDK (stored in JavaSoft Registry key) for starting the Debug
Agent:
• Registry path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\JavaSoft\Java Development Kit\1.4
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\JavaSoft\Java Development Kit\1.5
• Registry key:
JavaHome (e.g. "C:\j2sdk1.4.2_09")
JavaHome (e.g. "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.5.0_07")
5
• Registry path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\JavaSoft\Java Runtime Environment\1.4
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\JavaSoft\Java Runtime Environment\1.5
• Registry key:
JavaHome (e.g. "C:\Program Files\Java\j2re1.4.2_09")
JavaHome (e.g. "C:\Program Files\Java\j2re1.5.0_07")
5
5
5
3.3.1.4 NetBeans IDE 5.0
This is a Java IDE provided by SUN to support Java application development.
3.3.1.5 NetBeans IDE 5.5.1
This is a Java IDE provided by SUN to support Java application development. NetBeans IDE
5.5.1 is only supported on TC65 CD.
5.
required for TC65
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 19 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 20

Java User’s Guide
3.3 Installation CD for TC65
27
s
3.3.1.6 Eclipse 3.1.2 IDE and Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.x
This is a Java IDE provided by the Eclipse Foundation to support Java application development. The integration of SMTK into Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.0 is supported by the TC65,
XT65/XT75 and AC65/AC75 CDs. Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.5 is only distributed on TC65 CD. The
installed Eclipse Version and ME Plugin can be read out after starting Eclipse and selecting:
• Eclipse menu Help
e.g. Version: 3.1.2 Build id: M20060118-1600
• Eclipse menu Help
ME Plugin version:
e.g. EclipseME J2ME Development Tools for the Eclipse Version: 1.5.0
→ About Eclipse SDK and looking for the Eclipse version:
→ About Eclipse SDK, press the Feature Details button and look for the
Used JDK from IDE (e.g. selecting Eclipse menu Help
Details and look for "java.version" and "java.vm.version").
→ About Eclipse SDK → Configuration
3.3.1.7 Eclipse 3.2.2 IDE and Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.5 or 1.6.8
This is a Java IDE provided by the Eclipse Foundation to support Java application development. The integration of SMTK into Eclipse 3.2.2 with ME Plugin 1.6.8 is only supported by the
TC65 CD. The installed Eclipse Version and ME Plugin can be read out after starting Eclipse
and selecting:
• Eclipse menu Help
e.g. Version: 3.2.2 Build id: M20070212-1330
• Eclipse menu Help
Plugin version:
e.g. EclipseME J2ME Development Tools for the Eclipse Version: 1.5.5
e.g. EclipseME J2ME Development Tools for the Eclipse Version: 1.6.8
Used JDK from IDE (e.g. selecting Eclipse menu Help
Details and look for "java.version" and "java.vm.version").
→ About Eclipse SDK and looking for the Eclipse version:
→ About Eclipse SDK, press Feature Details button and look for the ME
→ About Eclipse SDK → Configuration
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 20 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 21

Java User’s Guide
3.3 Installation CD for TC65
27
s
3.3.1.8 GPS Evaluation Software
The GPS Evaluation Software (u-center) was developed by u-blox AG, Switzerland. This software demonstrates the capabilities of global positioning system (GPS) part incorporated in the
XT75 module.
The latest version of the GPS Evaluation Software (u-center) can be downloaded for free from
the internet: http://www.u-blox.com/products/u_center.html.
The installed GPS Evaluation Software Version can be read out after starting u-center and
selecting:
u-center menu Help
e.g. Version 4.00 Build
Inside this dialog box you will find contact and support address as well.
Please make the following preparations before using the u-center tool together with XT75
(module with GPS support):
Step 1:
Install u-center
→ GPS_Evaluation_SW\ucentersetup.exe (on XT75 CD)
Step 2:
Switch to transparent GPS mode by using the AT command
AT^SGPSS=1,1
Step 3:
Configure the connected COM port (ASC0 of the XT75 module) by using the
u-center menu Receiver
→ About u-center... and looking for the u-center version:
→ Port and Receiver → Baudrate
Now the XT75 module and the u-center are ready for operation.
3.3.1.9 Integrated Documentation Suite (IDS)
The Integrated Documentation Suite (IDS) is installed together with SMTK and can be
accessed via index.html file under the directory “\IDS” with a browser. Another possibility to
access IDS is by using the IMP-NG Java documentation “Javadoc” inside the IDE and selecting
the hyperlink IDS placed inside the main menu of IMP-NG Javadoc.
Please keep in mind that the internal structure of JBuilder IDE does not support opening the
IDS from inside the JBuilder IDE using hyperlinks.
A further hyperlink to IDS is located in the start menu of <productname> and can be selected
via “Integrated Documentation Suite (IDS)”.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 21 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 22
Java User’s Guide
3.4 Set up Java Development Environment with Eclipse IDE (Quick Start-up)
27
s
3.4 Set up Java Development Environment with Eclipse IDE
(Quick Start-up)
Please complete the following steps to set up your Eclipse Java development environment:
Step 1:
Install JDK 1.4.2_09
→ JDK 1.4\j2sdk-1_4_2_09-windows-i586-p.exe
For TC65 install JDK 1.5.0_07 , if no JDK 1.5 or higher is installed on your machine.
Step 2:
Install Eclipse 3.1.2
→ Unzip from CD ("\Eclipse\eclipse-SDK-3.1.2-win32.zip") to "C:\Program Files\Eclipse"
(Installation of Eclipse 3.2.2 to be employed with TC65 is completed in the same way.)
Step 3:
Installation Eclipse ME plugin 1.2.3:
(Installation of Eclipse ME plugin 1.6.8 to be employed with TC65 is completed in the same
way)
- Start Eclipse IDE
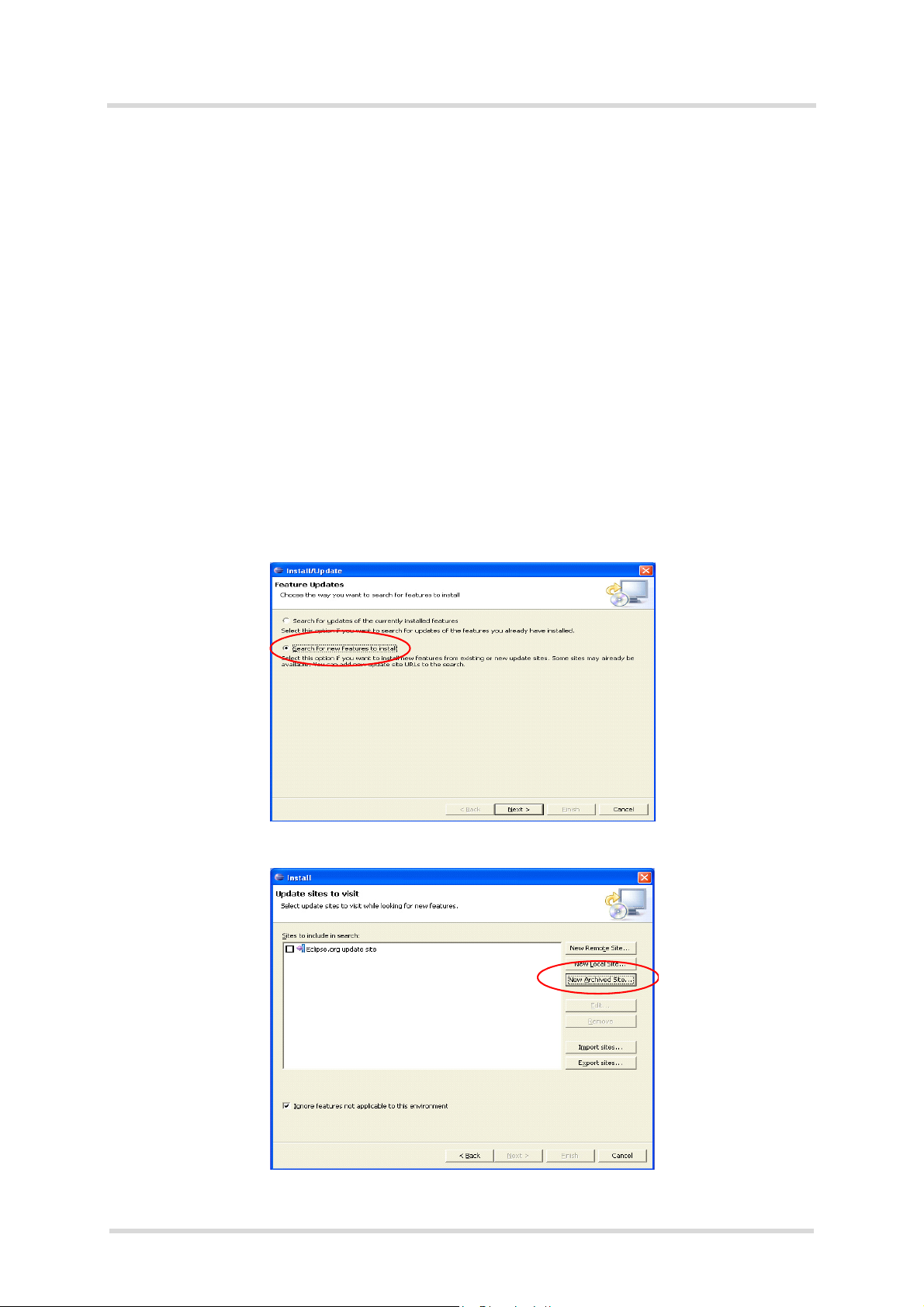
- Select the default workspace suggested by Eclipse
- Start ME plugin installer using Eclipse menu
→ Software Updates → Find and Install.
Help
Figure 2: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: Dialog box Feature Updates
Figure 3: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: Dialog box Updates sites to visit
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 22 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 23
Java User’s Guide
3.4 Set up Java Development Environment with Eclipse IDE (Quick Start-up)
27
- Select the path where Eclipse ME plugin is located on CD (EclipseMEplugin_123\.....")
and select „eclipseme.feature_1.2.3_site.zip"
s
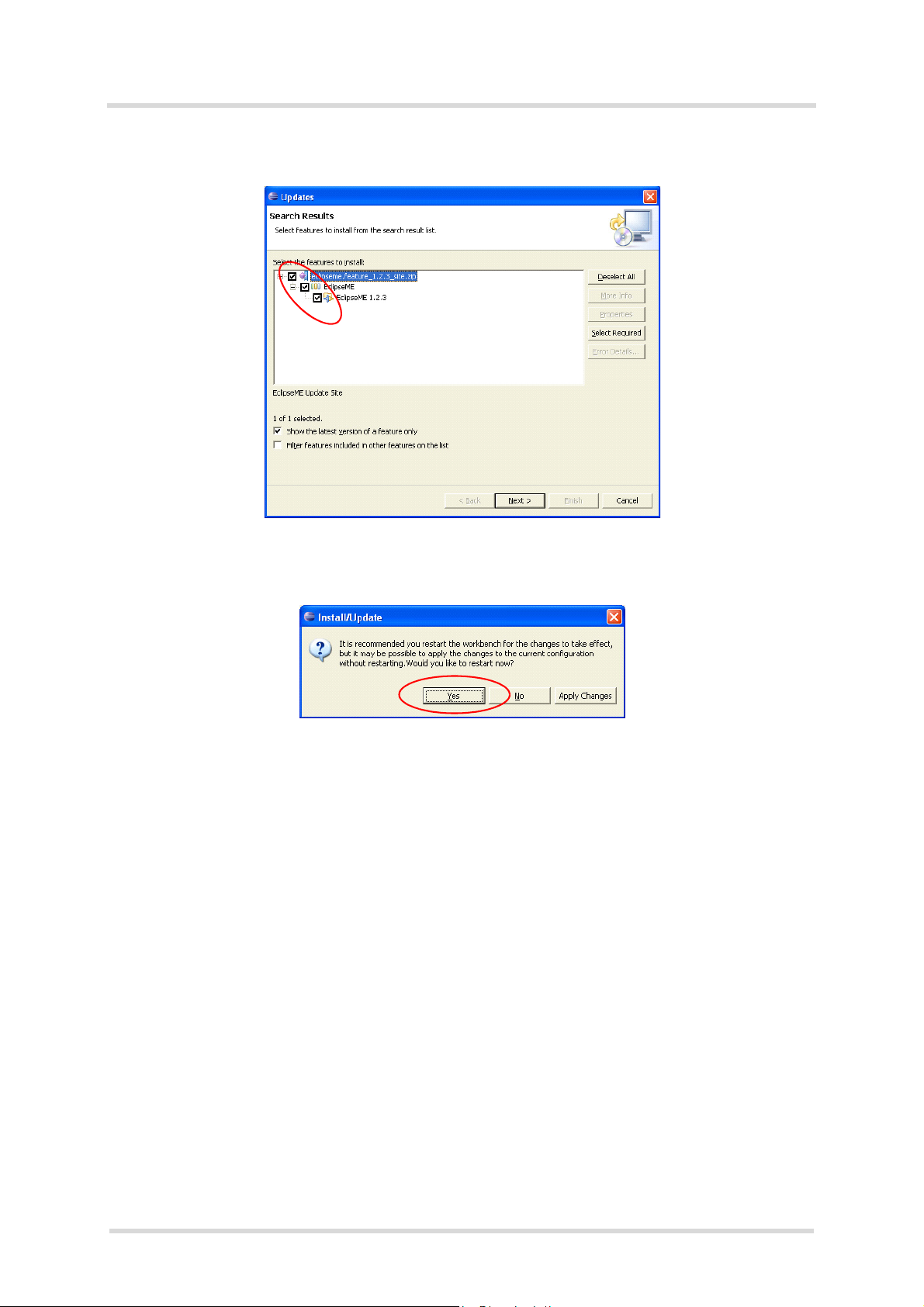
Figure 4: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: dialog box Search Results
- In the dialog box Verification, select Install All.
- In the dialog box Install/Update, select Yes to restart Eclipse.
Figure 5: Installation of Eclipse ME-Plugin 1.2.3: dialog box Restart Eclipse
- Eclipse IDE is restarted. Please close Eclipse IDE before continuing with installation of
SMTK!
Step 4:
Installation of the product’s SMTK:
- Start "setup.exe" from CD root path.
- Choose the destination folder of Eclipse "C:\Program Files\Eclipse" in the dialog box
Select Eclipse Folder.
- Select SMTK (e.g. C:\Program Files\Siemens\SMTK) in dialog box Destination Folder.
- Use the the dialog box Select COM Port to specify the connection type for on-device
debugging and MES transfer (downloading the MIDlet to the module):
a) Standard 19200 Modem: Choose the COM port and set the baud rate (e.g. 115200).
b) USB modem: Select "Siemens AG WM USB Modem". Note that the USB modem has
to be installed previously using Siemens "usbmodem.inf" file.
- After that, MES will be installed without further user action. Please wait until setup is complete.
-Click Finish in the summary dialog to confirm the completed installation.
A detailed description of the SMTK installation is given in the following chapters.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 23 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 24

Java User’s Guide
3.5 Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation
27
s
3.5 Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation
The SMTK comes with an installation CD. The installation program automatically installs the
necessary components and IDE integrations. Software can be uninstalled and updated with the
install program. The next sections cover the installation and removal of the SMTK and the
installation of the SDK and the supported IDEs.
3.5.1 Installing the Standard Development Toolkit
1. The JDK version 1.4.2_09 is provided on the SMTK installation disk in the subdirectory
“JDK 1.4”. To begin the installation, start the “j2sdk-1_4_2_09-windows-i586-p.exe“ and follow the instructions of the JDK setup procedure. If there is no JDK installed on the target
machine the installation of the provided JDK will be offered automatically during the SMTK
installation process. The JDK version 1.5.0_07 is provided and required for TC65.
2. Once the toolkit has been installed, the environment variable “path” can be altered to comfortably use the JDK tools. This is not necessary for using the Siemens SMTK.
3. Open the Control Panel:
- Open System.
- Click on Advanced.
- Click on the Environment Variables button.
- Choose path from the list of system variables.
- Append the path for the bin directory of the newly installed SDK to the list of directories
for the path variable.
3.5.2 Installing the SMTK Environment
Before you start the installation please make sure all applications, especially the IDEs are
closed.
1. Insert the CD, start setup.exe. When the dialog box appears press the Next button.
2. You will be asked to read the license agreement. If you accept the agreement, press Yes
to continue with the installation.
3. A file including special information about the installation and use of the SMTK is shown.
Press Next to continue.
4. You will be asked to enter the path name where Eclipse 3.0.1, 3.0.2, 3.1.0, 3.1.1, 3.1.2 or
5. The installation software checks for the Java SDK. If there is no SDK on the system the
6. At this point, the installation software checks for a Java IDE to be integrated with the SMTK.
6
is installed. Please type in the folder where Eclipse with the ME plugin is installed and
3.2.x
press Next. If you have not installed Eclipse or do not want to integrate the SMTK into
Eclipse, please press Next without typing in a selected folder.
installation procedure now offers to install the provided JDK. If this step is refused, the setup
process will not continue because a properly installed JDK is mandatory for using the SMTK
environment.
A Java IDE is not necessary to use the SMTK. The IDE installation can be done at any time
even if the SMTK is already installed. To integrate the SMTK into the Java IDE run the
SMTK setup program in maintenance mode again. However, you can continue the setup
procedure and install the IDE installation later or cancel the setup program at this stage and
restart it after installing one of the supported Java IDEs. In case you wish to install a Java
6.
Supported only for TC65
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 24 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 25

Java User’s Guide
3.5 Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation
27
IDE please follow the instructions below and in Section 3.5.3. If no installed IDE is found
the SMTK offers to install NetBeans IDE 5.0 and NetBeans Mobility package 5.0 (NetBeans
5.5.1 and NetBeans Mobility package 5.5.1 is distributed with TC65 CD). Alternatively, you
can install the SUN IDE by following the instructions in Section 3.5.3.
7. If the SDK and one or more Java IDEs are found, you will be asked to choose which IDE
you want integrated into the development environment. Once an IDE has been found and
selected, press Next to continue. Ensure that your Java IDE is closed.
8. Select the folder where the SMTK will be installed. A folder will be suggested to you but you
may browse to select a different one.
9. Choose the path that SMTK will appear under in the Start Menu.
10. In the next installation dialog box you will be asked to to create a Dial-up Network connection for on-device debugging. This Dial-up Network connection can be configured either for
the Standard 119200 bps Modem integrated in Windows or the USB modem. As a result, a
Dial-up Network connection will be created named "IP connection for remote debugging"
(the connection will be available after the entire installation of the SMTK environment).
- If a Dial-up Network connection named "IP connection for remote debugging" is already
available for another Siemens IMP-NG product, you can choose to reconfigure the existing connection by pressing Yes or leave it unchanged by pressing No.
- If you have selected Yes or if there was no on-device connection before, check either
"Serial COM port for using the standard modem installation" or "USB COM port for using
the USB modem installation".
- If you have chosen the Standard 119200 bps Modem select the COM port number, click
Next. In the resulting dialog box select the baud rate and click Next again.
- If you have chosen the USB modem the available USB modems will be listed. Choose
the "Siemens AG WM USB Modem" and click Next.
Note: You can reconfigure the COM port for the Dial-Up Network connection any time after
the installation by starting the SMTK setup in maintenance mode and selecting “Repair”
mode.
11. Select the IP address used for IMP-NG on-device debugging and the UPD port number
used for switching the Java “System.out” direction to serial port output.
12. A brief summary of all entries made is shown. Press Next to continue.
13. A status message box informs you that the Module Exchange Suite (MES) will be installed
now. A separate MES setup wizard opens. Please follow the setup wizard’s instructions.
14. All necessary files will be copied from the CD into the target folder.
15. This is the final step. Again, a listing of all installed components appears. Please press Fin-
ish to end the installation.
s
How to use the "Modify" or "Repair" mode:
To open either mode click Control Panel
tion and press “Modify” or “Repair”:
Please keep in mind, that Windows system requires the same location of the installation CD, if
you like to use “Modify” or “Repair” for the SMTK installation. The installer is searching for *.msi
file and an installer message box will pop up, telling the user to locate the installation CD in the
corresponding drive and path. If the installation CD is not located on the displayed drive and
path, please insert the CD or copy the CD contents into the required location (drive and path).
Note for installing the SMTK environment on Windows 2000 systems:
Please delete all modems with device name "Standard 19200 bps Modem" before installing the
SMTK environment on a Windows 2000 system, because this modem device is used during
automatic modem installation and on-device debugging.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 25 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
→ Add or Remove Programs. Select SMTK installa-
Page 26

Java User’s Guide
3.5 Siemens Mobility Toolkit Installation
27
s
3.5.3 Installing NetBeans IDE 5.0 / NetBeans IDE 5.5.1
1. NetBeans IDE 5.0 is provided on the SMTK installation disk in the subdirectory
“NETBEANS_5_0”. To begin installation, start first “netbeans-5_0-windows.exe” and follow
the NetBeans IDE 5.0 setup procedure instructions.
TM
2. Please install next the Mobility package of Sun
NetBeans IDE 5.0. The Mobility package
is required before integration of SMTK!
TM
The Sun
windows.exe" for installation of Sun
dows.exe" for installation of Mobility package of Sun
NetBeans IDE 5.5.1 is distributed with the TC65 CD. Please start "netbeans-5_5_1-
TM
NetBeans 5.5.1 and "netbeans_mobility-5_5_1-win-
TM
NetBeans IDE 5.5.1.
Note: The integration of the SMTK into SunTM NetBeans IDE 5.0 / SunTM NetBeans IDE 5.5.1
is done for all users.
3.5.4 Installing Eclipse 3.0, Eclipse 3.1 or Eclipse 3.2
Eclipse 3.1.2 (CD directory “\Eclipse\”) and Eclipse ME Plugin 1.2.3 (CD directory
“\EclipseME_123\”)
provided on the SMTK CD. The installation of Eclipse is shortly described in Section 3.4.
7
or Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.0 (CD directory “\EclipseMEplugin_150\”) are
8
Eclipse can be freely downloaded from http://www.eclipse.org. In order to use Eclipse with the
ME the EclipseME plug-in is also needed. It can be downloaded from http://eclipseme.org.
Using Eclipse 3.0.1 or Eclipse 3.0.2:
A customized version of this plug-in (CD directory “\EclipseME_WM\”)
9
for Eclipse 3.0.1 and
3.0.2 comes with SMTK. It is required to use this plug-in for Eclipse 3.0.1 and Eclipse 3.0.2,
because EclipseME plugin 1.2.3 requires Eclipse 3.1.0 and later and not installable for the older
Eclipse versions 3.0.1 and 3.0.2.
Using Eclipse 3.1.0, Eclipse 3.1.1 or Eclipse 3.1.2:
Please use EclipseME plug-in 1.2.1 or 1.2.3 for Eclipse version 3.1.0, Eclipse 3.1.1 or Eclipse
3.1.2.
Using Eclipse 3.2. (only supported for TC65):
Please use EclipseME plug-in 1.5.5 or 1.6.x.
It is recommended to use Eclipse 3.2.2 with ME 1.5.5 for working with Java Debugging session.
Note: Only one selection for an Eclipse version at a time for SMTK integration is possible.
7.
Eclipse ME Plugin 1.2.3 is not provided on TC65 CD.
8.
Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.0 is supported on the TC65, XT65/XT75 and AC65/AC75 CDs.
9.
"\EclipseME_WM" CD directory is not included on TC65 CD.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 26 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 27

Java User’s Guide
3.6 SMTK Uninstall
27
s
3.5.5 Installing Borland JBuilder X, 2005 and 2006 Enterprise/
Developer
Borland JBuilder can be purchased from http://www.borland.com/jbuilder. There are also 30
days trial versions available on the website. Installation instructions can be found there.
Note: The installation path name of JBuilder should not include space characters.
3.5.6 Installing Module Exchange Suite (MES)
The Module Exchange Suite (MES) is installed during the SMTK installation. If you would like
to install the Module Exchange Suite separately, repair or remove it, please use the Module
Exchange Suite (MES) setup.exe, which is located on the SMTK installation disk in the subdirectory “MES”.
3.6 SMTK Uninstall
The SMTK install package comes with an uninstall facility. The entire SMTK or parts of the
package can be removed. To start the uninstall facility, open the Control Panel, select Add/
Remove Programs, select the desired SMTK, e.g. TC65 Software Development Kit and follow
the instructions. The standard modem and Dial-Up Network connection (DUN) are uninstalled
automatically, if no SMTK IMP-NG product is installed in parallel. The user will be asked for
uninstall of standard modem and Dial-Up Network (DUN) in the case, that another SMTK IMPNG product is installed.
The Module Exchange Suite (MES) is not uninstalled automatically with the SMTK. If you would
like to uninstall the Module Exchange Suite (MES) as well, please run the MES uninstall facility.
To run the uninstall program, open the Control Panel, select Add/Remove Programs, select
Siemens Module Exchange Suite (MES) and follow the instructions.
Please keep in mind, that standard modem (or USB modem), Dial-Up Network connection and
Module Exchange Suite (MES) are required for a proper work of SMTK on-device debugging.
Note for customers migrating from TC45 to TC65:
If you uninstall the TC45 software after the installation of TC65 you need to run the TC65 SDK
and MES setup in maintenance mode to restore several files required for TC65. To do so, open
the Windows Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs, select “TC65 Software
Development Kit”, press the Change/Remove button and select Repair. In the same manner,
reinstall the Siemens Module Exchange Suite (MES)" As an alternative, to avoid this step,
remove the TC45 package, before installing TC65 SDK and MES.
3.7 Upgrades
The SMTK can be modified, repaired or removed by running the setup program on the Installation CD.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 27 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 28

Java User’s Guide
4 Software Platform
35
s
4 Software Platform
In this chapter, we discuss the software architecture of the SMTK and the interfaces to it.
4.1 Software Architecture
The SMTK enables a customer to develop a Java application on a PC and have it be executable on the Java enabled module. The application is then loaded onto the module. The platform
comprises:
•Java
• Additional Java virtual machine interfaces:
• Memory space for Java programs:
• Additional accessible periphery for Java applications
TM
Micro Edition (Java METM), which forms the base of the architecture.
The Java ME
ically designed for embedded systems and has a small memory footprint. The ME uses:
CLDC 1.1 HI, the connected limited device configuration hot spot implementation.
IMP-NG, the information module profile 2
MIDP 2.0 but without the lcdui package.
AT Command API
File I/O API
The data flow through these interfaces is shown in Figure 7 and Figure 29.
Flash File System: around 1700k (1200k in XT75)
RAM: around 400k
Application code and data share the space in the flash file system and in RAM.
- A maximum of ten digital I/O pins usable, for example, as:
Output: status LEDs
- Input: Emergency Button
- One I2C/SPI Interface.
- One Digital Analog Converter and two Analog Digital Converters.
- Serial interface (RS-232 API): This standard serial interface could be used, for example,
with an external GPS device or a current meter.
For detailed information see Section 4.2.
TM
is provided by SUN Microsystems, http://java.sun.com/javame/. It is specif-
nd
generation, this is for the most part identical to
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 28 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 29

Java User’s Guide
4.2 Interfaces
35
s
4.2 Interfaces
4.2.1 ASC0 - Serial Device
ASC0, an Asynchronous Serial Controller, is a 9-wire serial interface. It is described in [2]. Without a running Java application the module can be controlled by sending AT commands over
ASC0. Furthermore, ASC0 is designed for transferring files from the development PC to the
module. When a Java application is started, ASC0 can be used as an RS-232 port or/and System.out. Refer to [3] for details.
4.2.2 General Purpose I/O
There are ten I/O pins that can be configured for general purpose I/O. One pin can be configured as a pulse counter. All lines can be accessed under Java by AT commands or a Java API.
See [1] and [2] for information about usage and startup behavior.
4.2.3 DAC/ADC
There are two analogue input lines and one analogue output line. They are accessed by AT
commands. See [1] and [2] for details.
The TC65 Terminal does not feature DAC interface.
4.2.4 ASC1
ASC1 is the second serial interface on the module. This is a 4-pin interface (RX, TX, RTS,
CTS). It can be used as a second AT interface when a Java application is not running or by a
running Java application as RS-232 port or/and System.out.
The TC65 Terminal and products with GPS do not feature ASC1.
4.2.5 Digital Audio Interface (DAI)
The ME has a seven-line serial interface with one input data clock line and input/output data
and frame lines to support the DAI. Refer to [1] and [2] for more information.
TC65 Terminal does not feature a DAI interface.
4.2.6 I2C/SPI
There is a 4 line serial interface which can be used as I2C or SPI interface. It is described in
[2]. The AT^SSPI AT command configures and drives this interface. For details see [1].
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 29 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 30

Java User’s Guide
4.2 Interfaces
35
s
4.2.7 GPS
The on-board GPS functionality can be accessed in 4 different ways from a Java application.
• AT commands via ATCommand
• Java API JSR179
• transparent via CommConnection
• transparent via ATCommand
It is discouraged to use the forth possibility since it uses up a valuable ATCommand instance.
Use Java API for non-transparent, use CommConnection for transparent GPS access. Transparent and non-transparent modes can not be used concurrently but it is possible and in some
cases may be necessary to use AT commands concurrently with the Java API e.g. for GPS
power saving modes. For details about AT command related GPS functionality see [1].
The usage of CommConnection for GPS access is very straight forward. Calling Connector.open with port-id “gps0” opens a transparent channel to the GPS module. Then all protocols
supported by the GPS hardware can be used.
The Java location API (JSR179) offers three basic functionalities (for details see [3]):
• location listener, a periodic call-back with current location information
• proximity listener, a call-back when a specified location is close
• landmark store, a storage for landmarks/way-points
The landmark store is persistent. The stores are saved to FFS under a:/lmstores/store_X.xml,
where X is the number of the store (0 is the default store).
There can be 8 stores plus 1 default store each containing up to 100 landmarks in up to 8 categories (“no category” also counts as a category). Using AddressInfo with the landmarks might
decrease the maximum number of possible landmarks in a store, depending on the amount of
AddressInfo data being used. An IOException indicates that a store is full.
There is only one store active at a time. The current store information is kept in RAM and only
written to FFS when the application switches to a different store or terminates. Saving a store
might take up to 45s! During this time period the VM is blocked, no processing can be done in
parallel.
One of the examples that come with the product CD is a tracking application that uses the Java
location API.
GPS is only supported in XT75/XT65.
Products with GPS do not feature ASC1. So System.out is set to “null” device by default (see
Section 5.9).
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 30 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 31

Java User’s Guide
4.2 Interfaces
35
s
4.2.8 JVM Interfaces
Figure 6: Interface Configuration
Java ME, CLDC and MIDP were implemented by SUN. IMP-NG is a stripped down version of
MIDP 2.0 prepared by Siemens and does not include the graphical interface LCDUI. Siemens
developed additional APIs like the File I/O and the AT command API. Documentation for Java
ME and CLDC can be found at http://java.sun.com/javame/. Documentation for the other APIs
is found in [3].
4.2.8.1 IP Networking
IMP-NG provides access to TCP/IP similarly to MIDP 2.0.
Because the used network connection, CSD or GPRS, is fully transparent to the Java interface,
the CSD and GPRS parameters must be defined separately either by the AT command
AT^SJNET [1] or by parameters given to the connector open method, see [3].
4.2.8.2 Media
The playTone method and the tone sequence player are supported. For optimum performance
use notes in the range of 48 to 105. Tones outside this range are affected by audio hardware
filtering (see [2]).
Media package is only supported in TC65. See [3].
4.2.8.3 Other Interfaces
Neither the PushRegistry interfaces and mechanisms nor any URL schemes for the PlatformRequest method are supported. See [3].
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 31 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 32

Java User’s Guide
4.3 Data Flow of a Java Application Running on the Module
35
s
4.3 Data Flow of a Java Application Running on the Module
Figure 7: Data flow of a Java application running on the module.
The diagram shows the data flow of a Java application running on the module. The data flow
of a Java application running in the debug environment can be found in Figure 29.
The compiled Java applications are stored as JAR files in the Flash File System of module.
When the application is started, the JVM interprets the JAR file and calls the interfaces to the
module environment.
The module environment consists of the:
• Flash File System: available memory for Java applications
• TCP/IP: module internal TCP/IP stack
• GPIO: general purpose I/O
• ASC0: Asynchronous serial interface 0
• ASC1: Asynchronous serial interface 1
• I2C: 12Cbus interface
• SPI: Serial Peripheral Interface
• DAC: digital analog converter
• ADC: analog digital converter
• AT parser: accessible AT parser
The Java environment on the module consists of the:
• JVM: Java Virtual Machine
• AT command API: Java API to AT parser
• File API: Java API to Flash File System
• IMP-NG: Java API to TCP/IP and ASC0
• GPIO API: Java API to GPIO pins and pulse counter
• Watchdog API: Java API to HW watchdog
• Bearer Control API: Java API for bearer state information and hang-up.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 32 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 33

Java User’s Guide
4.4 Handling Interfaces and Data Service Resources
35
s
4.4 Handling Interfaces and Data Service Resources
To develop Java applications the developer must know which resources, data services and
hardware access are available.
• There are multiple AT parsers available
• There is hardware access over
- two serial interfaces: ASC1 and ASC0 (both fully accessible).
- general purpose I/O. To configure the hardware access, please refer to [1] and [2].
- I2C/SPI
- All restrictions of combinations are described in Section 4.4.1
• A Java application has:
- instances of the AT command class, one with CSD and the others without, each of which
would, in turn, be attached to one of the AT parsers.
- two instances of access to a serial interface, ASC0 and ASC1, through the CommCon-
nection API. Access to the control lines of these interfaces through CommConnectionControlLines (TC65 only).
- System.out over any serial interface or into the file system
4.4.1 Module States
The module can exist in the following six states in relation to a Java application, the serial interfaces, GPIO and I2C/SPI. See [1] for information about the AT commands referenced. A state
transition diagram is shown in Figure 11.
This section shows how Java applications must share AT parsers, GPIO pins and I2C/SPI
resources. DAC, ADC and DAI are not discussed here.
Color legend for the following figures:
4.4.1.1 State 1: Default – No Java Running
This is the default state. The Java application is inactive and there is an AT interface with CSD
on ASC0 as well as ASC1. The initial state of the pins is according to [4].
Figure 8: Module State 1
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 33 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 34

Java User’s Guide
4.4 Handling Interfaces and Data Service Resources
35
s
4.4.1.2 State 2: No Java Running, General Purpose I/O and I2C/ SPI
The Java application is inactive. There is an AT parser with CSD on ASC0 as well as ASC1.
Up to ten I/O pins are used as general purpose I/O plus a I2C/SPI interface. The pins are configured by AT^SCPIN and AT^SSPI (refer [1]).
Figure 9: Module State 2
4.4.1.3 State 4: Default – Java Application Active
The Java application is active and ASC0 and ASC1 are used as System.out and/or CommConnection. Java instances of AT commands are connected to the available AT parsers. The Java
application is activated with AT^SJRA (refer to [1]) or autostart.
Figure 10: Module State 4
4.4.1.4 State 5: Java Application Active, General Purpose I/O and I2C/SPI
The Java application is active and ASC0 and ASC1 are used as System.out and/or CommConnection. The Java application is activated with AT^SJRA. The I/O pins are configured with
AT^SCPIN, the I2C/SPI interface with AT^SSPI. Refer to [1] for AT command details.
Figure 11: Module State 5
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 34 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 35

Java User’s Guide
4.4 Handling Interfaces and Data Service Resources
35
4.4.2 Module State Transitions
s
Figure 12: Module State Transition Diagram
Note: No AT parser is available over serial interface ASC0 or ASC1 while a Java application is
running on the module.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 35 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 36

Java User’s Guide
5 Maintenance
49
s
5 Maintenance
The basic maintenance features of the ME are described below. Explicit details of these functions and modes can be found in [1] and [2].
5.1 IP Service
Apart from the standard Java IP networking interfaces (UDPDatagramConnection, SocketConnection, ...) the ME also supports a set of Internet Services controlled by AT command. There
are some correlations between the Java and the AT IP Services.
• The connection profile 0 is also used by Java: when Java starts up a networking connection
it tries to set and activate connection profile 0 with the parameters configured by AT^SJNET
or in the connector.open method.
• Java tries to (re-)use an active Internet Service profile: if using connection profile 0 fails,
because e.g. this (or another) connection profile is already used by the Internet Services,
Java networking also uses this, already active, profile.
• Deactivation of the connection profile happens when all applications are finished: Java has
its networking idle time. For the Internet Services an inactivity timeout referred to as parameter <inactTO> is available (configurable by AT^SICS and AT^SCFG).
So that means that Java networking and AT Internet Services can be used in parallel but care
has to be taken about configuring and activation of the connection profile. In the simplest case
use connection profile 0 for the Internet Services and set the parameters to the same values
as the Java networking parameters. This way it makes no difference whether the connection is
activated by the Internet Services or Java.
There are some aspects which have to be kept in mind for all IP Services (Java and AT command):
• When an open TCP connection is cut (e.g. the other side dies/is switched off) it takes
around 10 minutes during which retransmissions are send, until the situation is detected as
an error (in Java an exception is thrown).
• The number of IP services used in parallel should be kept small. An active IP service uses
up resources and may deteriorate the overall performance.
• If a user rapidly closes and opens TCP/IP connections (e.g. SocketConnection, HTTPCon-
nection), a ConnectionNotFoundException reading "No buffer space available" may be
thrown, explaining that all TCP/IP socket resources are exhausted. In the worst case, opening further TCP/IP connections is locked for up to 60 seconds.
• If a service is re-opened on the same port shortly after having closed the ServerSocketCon-
nection, the ServerSocketConnection may not work properly. To ensure that the service
works correctly the host is required to wait at least two minutes before reopening a server.
• For information about the bearer state, use the specific IP service command AT^SICI and,
in addition, the general network commands AT+COPS and/or AT+CREG.
Some Java products feature the BearerControl class. This class provides bearer state information and a method to hang-up.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 36 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 37

Java User’s Guide
5.2 Remote SIM Access
49
s
5.2 Remote SIM Access
While Remote SIM Access (RSA) is normally closely coupled with the GSM 07.10 multiplexer
there are some things to keep in mind when using it with Java.
• Java must not be started when RSA and/or the GSM 07.10 multiplexer is activated.
• When activating the RSA mode (AT^SRSA) via a Java AT Command channel while Java
is running the parameter <muxChan> of the AT^SRSA command is ignored and RSA is
activated on the channel where the command was issued. The Input- and Outputstream
can then be used to transfer RSA protocol data.
5.3 Power Saving
The module supports several power saving modes which can be configured by the AT command AT+CFUN [1]. Power saving affects the Java application in two ways. First, it limits
access to the serial interface (RS-232-API) and the GPIO pins. Second, power saving efficiency is directly influenced by the way a Java application is programmed.
Java hardware access limitations:
• In NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode (cfun=0) the serial interface cannot be accessed. Toggling
RTS does end NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode. In CYCLIC SLEEP mode (CFUN=7 or 9) the
serial interface can be used with hardware flow control (CTS/RTS).
• In all SLEEP modes the GPIO polling frequency is reduced so that only signal changes
which are less than 0.2Hz can be detected properly. Furthermore, the signal must be constant for at least 2.7s to detect any changes. For further details see AT^SCPOL in [1] or
refer to [2].
Java power saving efficiency:
• As long as any Java thread is active, power consumption cannot be reduced, regardless
whether any SLEEP mode has been activated or not. A Java application designed to be
power efficient should not have any unnecessarily active threads (e.g. no busy loops).
Threads waiting in a blocking method (e.g. read) do not hinder power saving.
• When using networking functionality close all connectors and hang-up the bearer manually
(using ATH for circuit switched connections or AT+CGATT=0 in case of GPRS) every time
you intend to reduce power consumption. Disable the network idle timeout (=0).
When going to low power mode there always might be a transition time of around 10s till low
power consumption state is reached.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 37 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 38

Java User’s Guide
5.4 Charging
49
s
5.4 Charging
Please refer to [1] and [2] for general information about charging. Charging can be monitored
by the running Java application. The JVM is active in Charge mode and in Charge-Only mode
if autostart is activated. Only a limited number of AT commands are available when the module
is in Charge-Only mode. A Java application must be able to handle the Charge-Only mode and
reset the module to reinstate the normal mode. See [2] for information about the Charge-Only
mode. The Charge-Only mode is indicated by URC “^SYSSTART CHARGE-ONLY MODE”.
Note: When a Java application is started in Charge-Only mode only AT Command APIs without
CSD are available. The mode-indicating URC is created after issuing the very first AT command on any opened channel. To read the URC it is necessary to register a listener (see [3])
on this AT command API instance before passing the first AT command.
5.5 Airplane Mode
The main characteristic of this mode is that the RF is switched off and therefore only a limited
set of AT commands is available. The mode can be entered or left using the appropriate
AT^SCFG command. This AT command can also be used to configure the airplane mode as
the standard startup mode, see [2]. The JVM is started when autostart is enabled. A Java application must be able to handle this mode. The airplane mode is indicated by URC “SYSSTART
AIRPLANE MODE”. Since the radio is off all classes related to networking connections, e.g.
SocketConnection, UDPDatagramConnection, SocketServerConnection, HTTPConnection,
will throw an exception when accessed.
5.6 Alarm
The ALARM can be set with the AT+CALA command. Please refer to the AT Command Set [1]
and Hardware Interface Description [2] for more information. One can set an alarm, switch off
the module with AT^SMSO, and have the module restart at the time set with AT+CALA. When
the alarm triggers the module restarts in a limited functionality mode, the “airplane mode”. Only
a limited number of AT commands are available in this mode, although the JVM is started when
autostart is enabled. A Java application must be able to handle this mode and reset the module
to reinstate the normal mode. The mode of a module started by an alarm is indicated by the
URC “^SYSSTART AIRPLANE MODE”.
Note: For detailed information which functionality is available in this mode see [1] and [2]. The
mode indicating URC is created after issuing the very first AT command on any opened channel.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 38 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 39

Java User’s Guide
5.7 Shutdown
49
s
5.7 Shutdown
If an unexpected shutdown occurs, data scheduled to be written will get lost due to a buffered
write access to the flash file system. The best and safest approach to powering down the module is to issue the AT^SMSO command. This procedure lets the engine log off from the network
and allows the software to enter a secure state and save all data. Further details can be found
in [2].
5.7.1 Automatic Shutdown
The ME is switched off automatically in different situations:
• under- or overtemperature
• under- or overvoltage
Appropriate warning messages transmitted by the ME to the host application are implemented
as URCs. To activate the URCs for temperature conditions use the AT^SCTM command. Undervoltage and overvoltage URCs are generated automatically when fault conditions occur.
For further detail refer to the commands AT^SCTM and AT^SBC described in the AT Command Set [1]. In addition, a description of the shutdown procedures can be found in [2].
5.7.2 Manual Shutdown
The module can be switched off manually with the AT command, AT^SMSO or when using the
TC65 Terminal by pressing the ignition key for a period of time (see [2]). In these cases the
midlets destroyApp method is called and the application has 5s time to clean up and call the
notifydestroy method. After the 5s the VM is shut down.
5.7.3 Restart after Switch Off
When the module is switched off without setting an alarm time (see the AT Command Set [3]),
e.g. after a power failure, external hardware must restart the module with the Ignition line (IGT).
The Hardware Interface Description [2] explains how to handle a switched off situation.
5.7.4 Watchdog
The Watchdog class allows to access the HW watchdog of the system from application level.
Depending on the setting (at^scfg) the userware watchdog can do nothing, switch-off or reboot
the system.
Watchdog class is only available in TC65.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 39 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 40

Java User’s Guide
5.8 Special AT Command Set for Java Applications
49
s
5.8 Special AT Command Set for Java Applications
For the full AT command set refer to [1]. There are differences in the behaviour AT commands
issued from a Java application in comparison to AT commands issued over a serial interface.
5.8.1 Switching from Data Mode to Command Mode
Cancellation of the data flow with “+++” is not available in Java applications, see [1] for details.
To break the data flow use breakConnection(). For details refer to [3].
5.8.2 Mode Indication after MIDlet Startup
After starting a module without autobauding on, the startup state is indicated over the serial
interface. Similarly, after MIDlet startup the module sends its startup state (^SYSSTART,
^SYSSTART AIRPLANE MODE etc.) to the MIDlet. This is done via a URC to the AT Command API instance which executes the very first AT Command from within Java. To read this
URC it is necessary to register a listener (see [3]) on this AT Command API instance before
passing the first AT Command.
5.8.3 Long Responses
The AT Command API can handle responses of AT commands up to a length of 1024 bytes.
Some AT commands have responses longer than 1024 bytes, for these responses the Java
application will receive an Exception.
Existing workarounds:
• Instead of listing the whole phone book, read the entries one by one
• Instead of listing the entire short message memory, again list message after message
• Similarly, read the provider list piecewise
• Periods of monitoring commands have to be handled by Java, e.g. AT^MONI, AT^SMONG.
These AT commands have to be used without parameters, e.g. for AT^MONI the periods
must be implemented in Java.
5.8.4 Configuration of Serial Interface
While a Java application is running on the module, only the AT Command API is able to handle
AT commands. All AT commands referring to a serial interface are ignored. This includes the
commands:
• AT+IPR (sets a fixed local bit rate)
• AT\Q1, AT\Q2 and AT\Q3 (sets type of flow control)
If Java is running, the firmware will ignore any settings from these commands. Responses to
the read, write or test commands will be invalid or deliver „ERROR“.
Note: When a Java application is running, all settings of the serial interface are done with the
class CommConnection. This is fully independent of any AT commands relating to a serial
interface.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 40 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 41

Java User’s Guide
5.9 System Out
49
s
5.8.5 Java Commands
There is a small set of special Java AT commands:
• AT^SJRA, start a Java application
• AT^SJNET, configuration of Java networking connections
• AT^SJOTAP, start and configuration of over the air provisioning
• AT^SJSEC, security configuration
Refer to the AT command Set [1].
5.8.6 AutoExec Function
Under Java, the AutoExec function’s AT command execution has some restrictions (see [1] for
details on the AutoExec function). If an AT command is executed, neither URC nor command
response are indicated to the Java application. Therefore, it is recommended to use the
AutoExec function under Java only with commands that shut down the module, e.g., with
AT+CFUN=0,1, as a watch dog. Any other AT command execution should be implemented with
Java means and the ATCommand class.
5.9 System Out
Any output printed to the System.out stream by a Java application can be redirected to one of
the serial interfaces, a file, a "NULL" device (i.e. the output will be discarded) or a UDP socket
for using the debugger from an IDE. The configuration can be done at any time using the AT
command AT^SCFG (see [1] for details) and is non-volatile.
5.9.1 Serial interfaces
System.out can be written to any of the serial interfaces ASC0, ASC1 or USB. If System.out is
redirected to one of the interfaces used for the Java CommConnection, the interface will be
shared between System.out and the CommConnection. This will result in mixed output, if data
is written to the CommConnections OutputStream and something is printed via System.out at
the same time.
Using System.out and CommConnection on the same serial interface may be done if a device
connected to the serial port is only transmitting data to the module. It is recommended to
ensure already in the HW design that output from the module cannot be transferred to a connected device.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 41 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 42

Java User’s Guide
5.10 GPIO
49
s
5.9.2 File
The System.out print can be redirected into log files within the module’s flash file system. The
output will be written alternatingly into two files which can be concatenated afterwards to have
a single log file.
Writing the output to a file will slow down the virtual machine. To reduce the impact of logging
the output may be written first to a buffer before it is written to the file (buffered mode). The buffered output is written either if the buffer is filled or after 200 ms. If the buffer is not used (secure
mode) the output is written directly to the file. Because excessive writing to the module’s flash
file system decreases the life time of the flash memory, we recommend using the System.out
to file redirection only during development phases.
5.9.3 UDP
Redirection to a UDP socket is used in conjunction with the debugger. UDP is used by default
when using on-device-debugging (Chapter 10). This can be changed by editing the emulator’s
ini-file.
If the output is redirected to an UDP socket, any changes of the System.out configuration are
ignored while the Virtual Machine is running. The UDP Socket settings will not be stored in the
module.
5.10 GPIO
The GPIO Java API (classes: InPort, OutPort, InPortListener, StartStopPulseCounter, LimitPulseCounter and LimitPulseCounterListener) is a replacement for the GPIO AT commands
(AT^SPIO, AT^SCPIN, ...). Using these classes frees up AT command resources and improves
performance. Both APIs can only be used alternatively. Of course the basic system characteristics of a poll interval of 4.6ms (in SLEEP mode up to 2.7s) for pin state change detection does
also apply here.
GPIO Java API is only supported in TC65.
5.11 Restrictions
5.11.1 Flash File System
The maximum length of a complete path name, including the path and the filename, is limited
by the Flash file system on the module to 124 characters. It is recommended that names of
classes and files be distinguished by more than case sensitivity.
5.11.2 Memory
The CLDC 1.1 HI features a just-in-time compiler. This means that parts of the Java byte code
which are frequently executed are translated into machine code to improve efficiency. This feature uses up RAM space. There is always a trade off between code translation to speed up execution and RAM space available for the application.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 42 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 43

Java User’s Guide
5.12 Performance
49
s
5.12 Performance
The performance study was focused on comparable performance values under various circumstances.
5.12.1 Java
This section gives information about the Java command execution throughput (“jPS”= Java
statements per second). The scope of this measurement is only the statement execution time,
not the execution delay (Java command on AT interface
tion on GPIO).
→ Java instruction execution → reac-
Figure 13: Test case for measuring Java command execution throughput
The following Java instruction was used for calculation of the typical jPS:
value = ( 2 x number of calculation statements ) /
( (1 / frequencyB ) - ( 1 / frequencyA ) );
Measurement and calculation were done using:
• duration of each loop = 600 s
• number of calculation statements = 50 “result=(CONSTANT_VALUE/variable_value);”-
Instructions (executed twice per pin cycle)
• frequencyA as measured with a universal counter
• frequencyB as measured with a universal counter
The reference loop has the same structure as the measurement loop except that the measurement sequence is moved.
State jPS-Value (mean)
ME in IDLE mode / Not connected ~49000
CSD connection ~46000
Since only a small amount of Java code is executed in this test, it is easily optimized by the
CLDC’s HI just-in-time compiler. More complex applications might not reach that execution
speed.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 43 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 44

Java User’s Guide
5.12 Performance
49
s
5.12.2 Pin I/O
The pin I/O test was designed to find out how fast a Java MIDlet can process URCs caused by
Pin I/O and react to these URCs. The URCs are generated by feeding an input pin with an
external frequency. As soon as the Java MIDlet is informed about the URC, it tries to regenerate the feeding frequency by toggling another output pin.
Figure 14: Test case for measuring Java MIDlet performance and handling pin-IO
The results of this test show that the delay from changing the state on the input pin to a state
change on the output pin is at least around 50 ms, but that time strongly depends on the amount
of garbage to collect and number of threads to be served by the virtual machine. Consequently,
pin I/O is not suitable for generating or detecting frequencies.
5.12.3 Data Rates on RS-232 API
For details about the software platform and interfaces refer to Chapter 4, "Software Platform".
This section summarises limitations and preconditions for performance when using the interface CommConnection from package com.siemens.mp.io (refer to [3]).
The data rate on RS232 depends on the size of the buffer used for reading from and writing to
the serial interface. It is recommended that method read (byte[ ] b) be used for reading from
the serial interface. The recommended buffer size is 2kbyte. To achieve error free data transmission the flow control on CommConnection must be switched on: <autorts> and <autocts>,
the same for the connected device.
Different use cases are listed to give an idea of the attainable data rates. All applications for
measurement use only one thread and no additional activities other than those described were
carried out in parallel.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 44 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 45

Java User’s Guide
5.12 Performance
49
s
5.12.3.1 Plain Serial Interface
Scenario: A device is connected to ASC0 (refer to Section 4.2.4). The Java application must
handle data input and output streams. A simple Java application (with only one thread) which
loops incoming data directly to output, reaches data rates up to 180kbit/s. Test conditions:
hardware flow control enabled (<autorts> and <autocts>), 8N1, and baud rate on ASC0 set to
230kbaud (
→ theoretical maximum: 184kbit/s net data rate).
Figure 15: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1
5.12.3.2 Voice Call in Parallel
Same scenario as in Section 5.12.3.1, but with a voice call added. The application reflects
incoming data directly to output and, additionally, handles an incoming voice call. The data
rates are also up to 180kbit/s. Test conditions: same as in Section 5.12.3.1.
Figure 16: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1 with a voice call in parallel
5.12.3.3 Scenarios with GPRS/EGDE Connection
The biggest challenges to the module performance are setting up a GPRS/EDGE connection,
receiving data on javax.microedition.io interfaces and sending or receiving the data on the
RS232 API with the help of a Java application.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 45 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 46

Java User’s Guide
5.12 Performance
s
49
5.12.3.4 Upload
The ME supports up to four uplink time slots for GPRS and up to two for EGDE. The Java application receives data over RS232 API and sends them over GPRS to a server.
Table 1: GPRS upload data rate with different number of timeslots, CS2
Upload data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 2
[kbit/s]
1
timeslot
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
2
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
3
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
4
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
9 12 75% 15 24 63% 20 36 55% 16 48 33%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
Table 2: GPRS upload data rate with different number of timeslots, CS4
Upload data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 4
[kbit/s]
1
timeslot
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
2
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
3
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
4
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
13 20 65% 22 40 55% 20 60 33% 13 80 16%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
Table 3: EDGE upload data rate with two timeslots, CS5
Upload data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 5
[kbit/s]
2 timeslots theor.
Value
1
% from theor.
Value
33 44 73%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
Table 4: EDGE upload data rate with two timeslots, CS9
Upload data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 9
[kbit/s]
2
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
% from theor.
Value
72 118 61%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 46 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 47

Java User’s Guide
5.12 Performance
49
Figure 17: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1 with GPRS data upload
s
5.12.3.5 Download
The data rate for downloading data over GPRS/EDGE depends on the number of assigned
timeslots and the coding schemes given by the net. The ME supports up to four downlink time
slots. For the measurements, the Java application receives data from the server over GPRS
and sends them over RS232 to an external device.
Figure 18: Scenario for testing data rates on ASC1 with GPRS data download
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 47 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 48

Java User’s Guide
5.12 Performance
s
49
The tables below show the download data rates that can be achieved if hardware flow control
is enabled on the CommConnection interface and the port speed is set to 460800.
Table 5: GPRS Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS2
Download data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 2
[kbit/s]
1
timeslot
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
2
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
3
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
4
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
11 12 91% 21 24 87% 29 36 81% 35 48 73%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
Table 6: GPRS Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS4
Download data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 4
[kbit/s]
1
timeslot
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
2
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
3
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
4
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
17 20 85% 31 40 78% 35 60 58% 38 80 48%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
Table 7: EDGE Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS5
Download data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 5
[kbit/s]
1
timeslot
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
4
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
20 22 91% 78 89 87%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
Table 8: EDGE Download data rate with different number of timeslots, CS9
Download data rate with x timeslots
Coding scheme 9
[kbit/s]
1
timeslot
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
Value
4
timeslots
theor.
Value
1
%
from
theor.
value
50 59 85% 184 236 77%
1.
net transmission rates for LLC layer
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 48 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 49

Java User’s Guide
5.13 System Time
49
s
5.13 System Time
When Java starts up, it initializes its time base from the system’s real time clock. If the RTC is
changed by AT command (AT+CCLK) later on, the Java time does not adjust. So, the time you
get with (AT+CCLK) and the time you get with System.currentTimeMilis() may not necessarily
be identical.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 49 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 50

Java User’s Guide
6 MIDlets
52
6 MIDlets
s
The Java ME
ing wireless applications. The MIDP runs on top of the Connected Limited Device Configuration
(CLDC), which in turn, runs on top of the Java ME
MIDlets. MIDlets are controlled by the mobile device implementation that supports the CLDC
and MIDP. Since IMP-NG is a subset of MIDP 2.0, IMP includes MIDlets. The MIDlet code
structure is very similar to applet code. There is no main method and MIDlets always extend
from the MIDlet class. The MIDlet class in the MIDlet package provides methods to manage a
MIDlet’s life cycle.
TM
Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP) provides a targeted Java API for writ-
TM
. MIDP applications are referred to as
6.1 MIDlet Documentation
MIDP and MIDlet documentation can be found at http://wireless.java.sun.com/midp/ and in the
html document directory of the wtk,
…\Siemens\SMTK\<productname>\wtk\doc\index.html
6.2 MIDlet Life Cycle
The MIDlet life cycle defines the protocol between a MIDlet and its environment through a simple well-defined state machine, a concise definition of the MIDlet’s states and APIs to signal
changes between the states. A MIDlet has three valid states:
• Paused – The MIDlet is initialised and is quiescent. It should not be holding or using any
shared resources.
• Active – The MIDlet is functioning normally.
• Destroyed – The MIDlet has released all of its resources and terminated. This state is only
entered once.
State changes are controlled by the MIDlet interface, which supports the following methods:
• pauseApp() – the MIDlet should release any temporary resources and become passive.
• startApp() – the MIDlet starts its execution, needed resources can be acquired here or in
the MIDlet constructor.
Note: Take care that the startApp() method is always properly terminated before calling the
destroyApp() method. For example, avoid that threads launched by startApp() enter a
closed loop, and be sure that all code was entirely executed. This is especially important
for OTAP, which needs to call destroyApp().
• destroyApp() – the MIDlet should save any state and release all resources
Note: To destroy only the Java application without switching off the module, the
destroyApp() method can be called explicitly. To destroy the Java application and switch off
the module at the same time, it is sufficient to send the AT^SMSO command from somewhere in your code, because this procedure implies calling the destroyApp() method. Likewise, resetting the module with AT+CFUN=x,1 also implies calling the destroyApp()
method. Note that AT+CFUN=x,1 will restart the module – to restart Java afterwards either
use the autostart mode configured with AT^SCFG or restart Java with AT^SJRA.
From this you can see that the commands AT^SMSO and AT+CFUN=x,1 should never be
sent within the destroyApp() method. It is good practice to always call the notifyDestroyed()
method at the end of your destroyApp method. And use the destroyApp method as single
exit point of your midlet.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 50 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 51

Java User’s Guide
6.2 MIDlet Life Cycle
52
s
• notifyDestroyed() – the MIDlet notifies the application management software that it has
cleaned up and is done.
Note: the only way to terminate a MIDlet is to call notifyDestroyed(), but destroyApp() is not
automatically called by notifyDestroyed(). You must not terminate your midlet (i.e. having
no threads left) and not calling notifyDestroyed() before.
• notifyPaused() – the MIDlet notifies the application management software that it has
paused
• resumeRequest() – the MIDlet asks application management software to be started again.
Table 9: A typical sequence of MIDlet execution
Application Management Software MIDlet
The application management software creates a new instance of a
MIDlet.
The application management software has decided that it is an
appropriate time for the MIDlet to run, so it calls the MIDlet.startApp
method for it to enter the Active state.
The application management software no longer needs the application be active, so it signals it to stop performing its service by calling
the MIDlet.pauseApp method.
The application management software has determined that the
MIDlet is no longer needed, or perhaps needs to make room for a
higher priority application in memory, so it signals the
is a candidate to be destroyed by calling the MIDlet.destroyApp
method.
MIDlet that it
The default (no argument) constructor for the MIDlet is called; it
is in the Paused state.
The MIDlet acquires any
resources it needs and begins to
perform its service.
The MIDlet stops performing its
service and might choose to
release some resources it currently holds.
If it has been designed to do so,
the
MIDlet saves state or user
preferences and performs clean
up.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 51 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 52

Java User’s Guide
6.3 Hello World MIDlet
52
6.3 Hello World MIDlet
Here is a sample HelloWorld program.
/**
* HelloWorld.java
*/
package example.helloworld;
import javax.microedition.midlet.*;
import java.io.*;
public class HelloWorld extends MIDlet {
/**
* HelloWorld - default constructor
*/
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld: Constructor");
}
s
/**
* startApp()
*/
public void startApp() throws MIDletStateChangeException {
System.out.println("HelloWorld: startApp");
System.out.println("\nHello World!\n");
destroyApp();
}
/**
* pauseApp()
*/
public void pauseApp() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld: pauseApp()");
}
/**
* destroyApp()
*/
public void destroyApp(boolean cond) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld: destroyApp(" + cond + ")");
notifyDestroyed();
}
}
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 52 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 53

Java User’s Guide
7 File Transfer to Module
54
s
7 File Transfer to Module
7.1 Module Exchange Suite
The Module Exchange Suite allows you to view the Flash file system on the module as a directory from Windows Explorer. Make sure that the module is turned on and that one of the module’s serial interfaces (ASC0, ASC1 or USB) is connected to the COM port that the Module
Exchange Suite is configured to. The configured COM port can be checked or changed under
Properties of the Module directory. Please note that the Module Exchange Suite can be used
only if the module is in normal mode and the baud rate is configured to a fixed value of 460800,
230400, 115200, 57600, 38400 or 19200. While running the module with the Module
Exchange Suite, subdirectories and files can be added to the flash file system of module. Keep
in mind that a maximum of 200 flash objects (files and subdirectories) per directory in the flash
file system of the module is recommended.
7.1.1 Windows Based
The directory is called “Module” and can be found at the top level of workspace “MyComputer”.
To transfer a file to the module, simply copy the file from the source directory to the target directory in the “Module
→ Module Disk (A:)”.
7.1.2 Command Line Based
A suite of command line tools is available for accessing the module’s Flash file system. They
are installed in the Windows System directory so that the tools are available from any directory.
The module’s file system is accessed with mod:. The tools included in this suite are MESdel,
MEScopy, MESxcopy, MESdir, MESmkdir, MESrmdir, MESport, MESclose and MESformat.
Entering one of these commands without arguments will describe the command’s usage. The
tools mimic the standard directory and file commands. A path inside the module’s file system
is identified by using “mod:” followed by the module disk which is always “A:” (e.g. “MESdir
mod:a:” lists the contents of the module’s root directory).
7.2 Over the Air Provisioning
See Chapter 8 for OTA provisioning.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 53 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 54

Java User’s Guide
7.3 Security Issues
54
s
7.3 Security Issues
The developer should be aware of the following security issues. Security aspects in general are
discussed in Chapter 12.
7.3.1 Module Exchange Suite
The serial interface should be mechanically protected.
The copy protection rules for Java applications prevent opening, reading, copying, moving or
renaming of JAR files. It is not recommended that the name of a Java application (for example
<name>.jar) be used for a directory, since the copy protection will refuse access to open, copy
or rename such directories.
7.3.2 OTAP
• A password should be used to update with OTA (SMS Authentication)
• Parameters should be set to fixed values (AT^SJOTAP) whenever possible so that they
cannot be changed over the air.
• The HTTP server should be secure. (e.g. Access control via basic authentication).
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 54 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 55

Java User’s Guide
8 Over The Air Provisioning (OTAP)
63
s
8 Over The Air Provisioning (OTAP)
8.1 Introduction to OTAP
OTA (Over The Air) Provisioning of Java Applications is a common practice in the Java world.
OTAP describes mechanisms to install, update and delete Java applications over the air. The
ME implements the Over The Air Application Provisioning as specified in the IMP-NG standard
(JSR228).
The OTAP mechanism described in this document does not require any physical user interaction with the device; it can be fully controlled over the air interface. Therefore it is suitable for
Java devices that are designed not to require any manual interaction such as vending
machines or electricity meters.
8.2 OTAP Overview
To use OTAP, the developer needs, apart from the device fitted with the Java enabled module,
an http server, which is accessible over a TCP/IP connection either over GPRS or CSD, and
an SMS sender, which can send Class1, PID $7d short messages. This is the PID reserved for
a module’s data download.
Figure 19: OTAP Overview
The Java Application Server (http Server) contains the .jar and the .jad file to be loaded on the
device. Access to these files can be protected by http basic authentication.
The OTAP Controller (SMS Sender) controls the OTAP operations. It sends SMs, with or without additional parameters, to the devices that are to be operated. These devices then try to contact the http server and download new application data from it. The OTAP Controller will not
get any response about the result of the operation. Optionally the server might get a result
response over http.
There are two types of OTAP operations:
• Install/Update: A new JAR and JAD file are downloaded and installed.
• Delete: A complete application (.jar, .jad, all application data and its directory) is deleted.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 55 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 56

Java User’s Guide
8.3 OTAP Parameters
63
s
8.3 OTAP Parameters
There is a set of parameters that control the OTAP procedures. These parameters can either
be set by AT command (AT^SJOTAP, refer to [1] during the production of the device, or by SM
(see Section 8.4) during operation of the device in the field. None of the parameters, which are
set by AT command, can be overwritten by SM.
• JAD File URL: the location of the JAD file is used to install or update procedures. The JAD
file needs to be located on the net (e.g. http://someserver.net/somefile.jad or http://
192.168.1.2/somefile.jad ).
• Application Directory: this is the directory where a new application (JAD and JAR file) is
installed. The delete operation deletes this directory completely. When entering the application directory with AT^SJOTAP or a short message ensure that the path name is not terminated with a slash. For example, type "a:" or "a:/otap" rather than "a:/" or "a:/otap/". See
examples provided in Chapter 6.
• http User: a username used for authentication with the http server.
• http Password: a password used for authentication with the http server.
• Bearer:
• APN or Number: depending on the selected network bearer this is either an access point
name for GPRS or a telephone number for CSD.
• Net User: a username used for authentication with the network.
• Net Password: a password used for authentication with the network.
• DNS: a Domain Name Server’s IP address used to query hostnames.
• NotifyURL: the URL to which results are posted. This parameter is only used when the
MIDlet-Install-Notify attribute or MIDlet-Delete-Notify attribute is not present in descriptor.
the network bearer used to open the HTTP/TCP/IP connection, either GPRS or CSD.
There are parameters that can only be set by AT command:
• SM Password: it is used to authenticate incoming OTAP SMs. Setting this password gives
an extra level of security.
Note: If a password set by AT command, all SMs must include this password
• Ignore SM PID (TC65 only): when setting this the PID in received SMs is ignored.
• Hide HTTP authentication parameters (TC65 only): this allows to hide the http authentica-
tion parameters in the at^sjotap read command and the otap tracer.
Table 10: Parameters and keywords
Parameters Max. Length AT Keyword SM Install/update delete
JAD File URL 100 JADURL mandatory unused
Application Directory 50 APPDIR mandatory mandatory
HTTP User 32 HTTPUSER optional unused
HTTP Password 32 HTTPPWD optional unused
Bearer -- BEARER mandatory optional/P
APN or Number 65 APNORNUM mandatory for CSD optional/P
Net User 32 NETUSER optional optional/P
Net Password 32 NETPWD optional optional/P
DNS -- DNS optional optional/P
Notify URL 100 NOTIFYURL optional optional/P
SM Password 32 PWD optional optional
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 56 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 57

Java User’s Guide
8.4 Short Message Format
63
Table 10: Parameters and keywords
Parameters Max. Length AT Keyword SM Install/update delete
Ignore SM PID -- -- -- --
s
Hide HTTP authentication parameters
The length of the string parameters in the AT command is limited (see Table 10), the length in
the SM is only limited by the maximum SM length.
The minimum set of required parameters depends on the intended operation (see Table 10).
“optional/P” indicates that this parameter is only necessary when a POST result is desired.
-- -- -- --
8.4 Short Message Format
An OTAP control SM must use a Submit PDU with Class1, PID $7d and 8 bit encoding. As a
fallback for unusual network infrastructures the SM can also be of Class0 and/or PID $00. The
content of the SM consists of a set of keywords and parameter values all encoded in ASCII
format. These parameters can be distributed over several SMs. There is one single keyword to
start the OTAP procedure. For parameters that are repeated in several SMs only the last value
sent is valid. For example, an SM could look like this:
Install operation:
First SM:
OTAP_IMPNG
PWD:secret
JADURL:http://www.greatcompany.com/coolapps/mega.jad
APPDIR:a:/work/appdir
HTTPUSER:user
HTTPPWD:anothersecret
Second SM:
OTAP_IMPNG
PWD:secret
BEARER:gprs
APNORNUM:access.to-thenet.net
NETUSER:nobody
NETPWD:nothing
DNS:192.168.1.2
START:install
Delete operation:
OTAP_IMPNG
PWD:secret
APPDIR:a:/work/appdir
START:delete
The first line is required: it is used to identify an OTAP SM. All other lines are optional and their
order is insignificant, each line is terminated with an LF: '\n' including the last one. The keywords, in capital letters, are case sensitive. A colon separates the keywords from their values.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 57 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 58

Java User’s Guide
8.5 Java File Format
63
s
The values of APPDIR, BEARER and START are used internally and must be lower case. The
password (PWD) is case sensitive. The case sensitivity of the other parameter values depends
on the server application or the network. It is likely that not all parameters can be sent in one
SM. They can be distributed over several SMs. Every SM needs to contain the identifying first
line (OTAP_IMPNG) and the PWD parameter if a mandatory password has been enabled.
OTAP is started when the keyword START, possibly with a parameter, is contained in the SM
and the parameter set is valid for the requested operation. It always ends with a reboot, either
when the operation is completed, an error occurred, or the safety timer expired. This also
means that all parameters previously set by SM are gone.
Apart from the first and the last line in this example, these are the parameters described in the
previous section. Possible parameters for the START keyword are: “install”, “delete” or nothing.
In the last case, an install operation is done by default.
The network does not guarantee the order of SMs. So when using multiple SMs to start an
OTAP operation their order on the receiving side might be different from the order in which they
were sent. This could lead to trouble because the OTAP operation might start before all parameters are received. If you discover such problems, try waiting a few seconds between each SM.
8.5 Java File Format
In general, all Java files have to comply with the IMP-NG and ME specifications. There are certain components of the JAD file that the developer must pay attention to when using OTAP:
• MIDlet-Jar-URL: make sure that this parameter points to a location on the network where
your latest JAR files will be located, e.g. http://192.168.1.3/datafiles/mytest.jar, not in the
filesystem like file://a:/java/mytest/mytest.jar. Otherwise this JAD file is useless for OTAP.
• MIDlet-Install-Notify: this is an optional entry specifying a URL to which the result of an
update/install operation is posted. That is the only way to get any feedback about the outcome of an install/update operation. The format of the posted URL complies with the IMPNG OTA Provisioning specification. In contrast to the jar and jad file this URL must not be
protected by basic authentication.
• MIDlet-Delete-Notify: this is an optional entry specifying a URL to which the result of a
delete operation is posted. That is the only way to get any feedback about the outcome of
a delete operation. The format of the posted URL complies with the IMP-NG OTA Provisioning specification. In contrast to the jar and jad file this URL must not be protected by basic
authentication.
• MIDlet-Name, MIDlet-Version, MIDlet-Vendor: are mandatory entries in the JAD and Man-
ifest file. Both files must contain equal values, otherwise result 905 (see Section 8.7) is
returned.
• MIDlet-Jar-Size must contain the correct size of the jar file, otherwise result 904 (see Sec-
tion 8.7) is returned.
Example:
MIDlet-Name: MyTest
MIDlet-Version: 1.0.1
MIDlet-Vendor: TLR Inc.
MIDlet-Jar-URL: http://192.168.1.3/datafiles/MyTest.jar
MIDlet-Description: My very important test
MIDlet-1: MyTest, , example.mytest.MyTest
MIDlet-Jar-Size: 1442
MicroEdition-Profile: IMP-NG
MicroEdition-Configuration: CLDC-1.1
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 58 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 59

Java User’s Guide
8.6 Procedures
63
A suitable Manifest file for the JAD file above might look like:
Manifest-Version: 1.0
MIDlet-Name: MyTest
MIDlet-Version: 1.0.1
MIDlet-Vendor: TLR Inc.
MIDlet-1: MyTest, , example.mytest.MyTest
MicroEdition-Profile: IMP-NG
MicroEdition-Configuration: CLDC-1.1
8.6 Procedures
8.6.1 Install/Update
s
Figure 20: OTAP: Install/Update Information Flow (messages in brackets are optional)
When an SM with keyword START:install is received and there is a valid parameter set for the
operation, the module always reboots either when the operation completed, an error occurred
or the safety timer expired. If there is any error during an update operation the old application
is kept untouched, with one exception. If there is not enough space in the file system to keep
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 59 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 60

Java User’s Guide
8.6 Procedures
63
the old and the new application at the same time, the old application is deleted before the download of the new one, therefore it is lost when an error occurs.If install/update was successful,
autostart is set to the new application.
s
8.6.2 Delete
Figure 21: OTAP: Delete Information Flow (messages in brackets are optional)
When an SM with keyword START: delete is received and there is a valid parameter set for this
operation, the module reboots either when the operation completed, an error occurred or the
safety timer expired. If there is any error the application is kept untouched. Autostart is not
changed.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 60 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 61

Java User’s Guide
8.7 Time Out Values and Result Codes
63
s
8.7 Time Out Values and Result Codes
Timeouts:
• Closedown Timeout: 10 seconds
• Safety Timeout: 10 minutes
Result Codes: Supported status codes in body of the http POST request:
• 900 Success
• 901 Insufficient memory in filesystem
• 902 - not supported-
• 903 - not supported-
• 904 JAR size mismatch, given size in JAD file does not match real size of jar file
• 905 Attribute mismatch, one of the mandatory attributes MIDlet-name, MIDlet-version,
MIDlet-Vendor in the JAD file does not match those given in the JAR manifest
• 906 Invalid descriptor, something is wrong with the format of the .jad file
• 907 invalid JAR, the JAR file was not available under MIDlet-Jar-URL, files could not be
extracted from JAR archive, or something else is wrong with the format of the file.
• 908 incompatible configuration or profile
• 909 application authentication failure, signature did not match certificate
• 910 application authorization failure, tried to replace signed with unsigned version
• 911 -not supported-
• 912 Delete Notification
All HTTP packets (GET, POST) sent by the module contain the IMEI number in the User-Agent
field, e.g.
User-Agent: <productname>/000012345678903 Profile/IMP-NG Configuration/CLDC-1.1
This eases device identification at the HTTP server.
8.8 Tips and Tricks for OTAP
• For security reasons it is recommended that an SMS password be used. Otherwise the
ìdeleteî operation can remove entire directories without any authentication.
• For extra security, set up a private CSD/PPP Server and set its phone number as a fixed
parameter. This way, applications can only be downloaded from one specific server.
• As a side effect, OTAP can be used to simply reboot the module. Simply start an OTAP pro-
cedure with a parameter set which will not really do anything, such as a delete operation on
a nonexistent directory.
• If you do not want to start OTAP by SMS let your Java application do it by issuing the
AT^SJOTAP command. This triggers an install/update operation as described in Section
8.6.1 but without the SMS part.
Note: If a malfunctioning Java application is loaded the SM method will still be needed for
another update.
• The OTAP procedure cannot be tested in the debug environment
• Be aware that the module needs to be logged into the network to do OTAP. That means
that either the Java application must enter the PIN, the PIN needs to be disabled or Autopin
(see [1]) needs be used.
• The OTAP procedure might fail due to call collision, e.g. an incoming call when OTAP tries
to start a CSD connection.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 61 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 62

Java User’s Guide
8.9 OTAP Tracer
63
s
8.9 OTAP Tracer
For easy debugging of the OTAP scenario, the OTAP procedure can be traced over the serial
interface. The trace output shows details of the OTAP procedure and the used parameters. To
enable the OTAP trace output use the AT command AT^SCFG, e.g.
AT^SCFG=Trace/Syslog/OTAP,1
The serial interface on which you issue this command is then exclusively used for the OTAP
tracer. All other functionality which is normally present (AT commands or CommConnection
and System.out in Java) is not available when the tracer is on.
This feature is intended to be used during development phase and not in deployed devices.
8.10 Security
Java Security as described in Chapter 12 also has consequences for OTAP. If the module is in
secured mode the MIDlet signature is also relevant to the OTAP procedure. This means:
• If the application is an unsigned version of an installed signed version of the same applica-
tion then status code 910 is returned.
• If the applications signature does not match the module’s certificate then status code 909
is returned.
8.11 How To
This chapter is a step-by-step guide for using OTAP.
1. Do you need OTAP? Is there any chance that it might be necessary to update the Java
application, install a new one or delete it? It could be that device is in the field and you cannot or do not want to update it over the serial line. If the answer is “yes” then read through
the following steps, if the answer is “no” then consider simply setting the OTAP SMS password to protect your system. Then you are finished with OTAP.
2. Take a look at the parameters (Section 8.3), which control OTAP. You need to decide which
of them you want to allow to be changed over the air (by SMS) and which you do not. This
is mainly a question of security and what can fit into a short message. Then set the
“unchangeable” parameters with the AT command (AT^SJOTAP).
3. Prepare the http server. The server must be accessible from your device over TCP/IP. That
means there is a route from your device over the air interface to the http server and back.
When in doubt, write a small Java application using the httpConnection Interface to test it.
4. Prepare the JAR and JAD files which are to be loaded over the air. Make sure that these
files conform to the requirements listed in Section 8.5 and that they represent a valid application which can be started by AT^SJRA.
5. Put the files (JAR and JAD) on the http Server. The files can either be publicly available or
protected through basic authentication. When in doubt try to download the files from the
server by using a common Web browser on a PC, which can reach your http server over
TCP/IP.
6. Prepare the SM sender. The sender must be able to send SMs, which conform to Section
8.4, to your device. When in doubt try to send “normal” SMs to your device which can than
be read out from the AT command interface.
7. Test with a local device. Send a suitable short message to your device, which completes
the necessary parameter, sets and starts the operation. The operation is finished when the
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 62 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 63

Java User’s Guide
8.11 How To
63
device reboots. You can now check the content of the file system and if the correct jar and
jad files were loaded into the correct location.
8. Analyze errors. If the above test failed, looking at your device’s behavior and your http serv-
ers access log can give you a hint as to what went wrong:
- Ιf the device did not terminate the running Java application and did not reboot, not even
after the safety timeout, either your SM was not understood (probably in the wrong format) or it did not properly authenticate (probably used the wrong password) or your
parameter set is incomplete for the requested operation.
- If the device terminated the running Java application, but did not access your http server,
and rebooted after the safety timeout, there were most likely some problems when opening the network connection. Check your network parameters.
- If the device downloaded the jad and possibly even the jar file but then rebooted without
saving them in the file system, most likely one of the errors outlined in Section 8.5
occurred. These are also the only errors which will return a response. They are posted to
the http server if the jad file contains the required URL.
9. Start update of remote devices. If you were able to successfully update your local device,
which is hopefully a mirror of all your remote devices, you can start the update of all other
devices.
s
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 63 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 64

Java User’s Guide
9 Compile and Run a Program without a Java IDE
66
s
9 Compile and Run a Program without a Java IDE
This chapter explains how to compile and run a Java application without a Java IDE.
9.1 Build Results
A JAR file must be created by compiling an SMTK project. A JAR file will contain the class files
and auxiliary resources associated with an application. A JAD file contains information (file
name, size, version, etc.) on the actual content of the associated JAR file. It must be written by
the user. The JAR file has the “.jar” extension and the JAD file has the “.jad” extension. A JAD
file is always required no matter whether the module is provisioned with the Module Exchange
Suite, as described in Section 7.1, or with OTA provisioning. OTA provisioning is described in
Chapter 7.
In addition to class and resource files, a JAR file contains a manifest file, which describes the
contents of the JAR. The manifest has the name manifest.mf and is automatically stored in the
JAR file itself. An IMP manifest file for:
package example.mytest;
public class MyTest extends MIDlet
includes at least:
Manifest-Version: 1.0
MIDlet-Name: MyTest
MIDlet-Version: 1.0.1
MIDlet-Vendor: Siemens
MIDlet-1: MyTest, example.mytest.MyTest
MicroEdition-Profile: IMP-NG
MicroEdition-Configuration: CLDC-1.1
A JAD file must be written by the developer and must include at least:
MIDlet-Name: MyTest
MIDlet-Version: 1.0.1
MIDlet-Vendor: Siemens
MIDlet-1: MyTest, example.mytest.MyTest
MIDlet-Jar-URL: http://192.168.1.3/datafiles/MyTest.jar
MIDlet-Jar-Size: 1408
MicroEdition-Profile: IMP-NG
MicroEdition-Configuration: CLDC-1.1
A detailed description of these attributes can be found in [4].
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 64 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 65

Java User’s Guide
9.2 Compile
66
s
9.2 Compile
• Launch a Command Prompt. This can be done from the Programs menu or by typing „cmd“
at the Run... prompt in the Start menu.
• Change to the directory where the code to be compiled is kept.
Compile the program with the SDK. Examples of build batch files can be found in each sample program found in the examples directory, \Siemens\SMTK\<productname>
\wtk\src\example.
• If the compile was successful the program can be run from the command line. Examples of
run batch files can be found in the examples directories listed above as well.
The batch files for compiling and running the samples refer to master batch files in the …\Sie-
mens\SMTK\<productname>\wtk\bin directory and use the system environment variables
IMPNG_JDK_DIR and IMPNG_DIR. IMPNG_JDK_DIR points to the root directory of the
installed JDK and IMPNG_DIR points to the root directory of the Siemens-SMTK-<productname>-IMPNG installation. The installation process sets these environment variables. A modification is usually not necessary. They may be modified as requested (e.g. when switching to
a different JDK) via the advanced system properties.
9.3 Run on the Module with Manual Start
• Compile the application at the prompt as discussed in Section 9.2 or in an IDE.
• Transfer the .jar and .jad file from the development platform to the desired directory on the
module using the Module Exchange Suite or OTA provisioning. Chapter 7 explains how to
download your application to the module.
• Start a terminal program and connect to ASC0.
• The command AT^SJRA is used to start the application and is sent to the module via your
terminal program. Either the application can be started by .jar or by .jad file.
Example:
In your terminal program enter: AT^SJRA=a:/java/jam/example/helloworld/helloworld.jar
If you prefer to start with .jad file: AT^SJRA=a:/java/jam/example/helloworld/helloworld.jad
The Flash file system on the module is referenced by “a:”.
Depending on which file you specify the java application manager tries to find the corresponding file in the same directory. This search is not done by name, but by comparing the contained
attributes. The first file which contains the same values for MIDlet-Name, MIDlet-Version and
MIDlet-Vendor is used.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 65 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 66

Java User’s Guide
9.4 Run on the Module with Autostart
66
s
9.4 Run on the Module with Autostart
• Compile the application at the prompt as discussed in Section 9.2 or in an SMTK integrated
IDE.
• Transfer the .jar and .jad file from the development platform to the desired directory on the
module using the Module Exchange Suite or OTA provisioning. See Chapter 7.
9.4.1 Switch on Autostart
• There is an AT command, AT^SCFG, for configuring the autostart functionality. Please refer
to [1].
• Restart the module.
9.4.2 Switch off Autostart
There are three methods for switching off the autostart feature:
• the AT^SCFG command, or
• the graphical “autoexec_off.exe“ tool (included in the Installation CD software under wtk/
bin), or
• the command line “cmd_autoexec_off.exe“ tool (included in the Installation CD software
under wtk/bin).
To disable the automatic start of a user application in a module these steps must be carried out:
Using the graphical “autoexec_off.exe” tool:
1. Connect the module to the PC
2. Make sure, that the module is switched off
3. Start the “Autoexec_Off” program
4. Select the COM-Port
5. Press the “AutoExec Off” button
Using the command line tool “cmd_autoexec_off.exe”:
1. Connect the module to the PC
2. Make sure, that the module is switched off
3. Start the command line tool “cmd_autoexec_off” with option <com-port> (com1 up to
com99 for com port selection)
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 66 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 67

Java User’s Guide
10 Compile and Run a Program with a Java IDE
71
s
10 Compile and Run a Program with a Java IDE
10.1 Eclipse 3.1.2 (with ME Plugin 1.2.3)
The following description assumes that Eclipse 3.1.2 is installed from SMTK CD as described
in Section 3.3.1.6
10.1.1 Setup a New Project
Step 1:
Create new Java Project:
- Select Eclipse menu File → New → Other…
- Select J2ME Midlet Suite:
Figure 22: Create new Eclipse project: Create a J2ME MIDP Midlet Suite
- Type in the used name (e.g. Project01) and path for the new project:
Figure 23: Create new Eclipse project: New J2ME Project
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 67 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 68

Java User’s Guide
10.1 Eclipse 3.1.2 (with ME Plugin 1.2.3)
71
- Select e.g. TC65 Release 2 emulator:
s
Figure 24: Create new Eclipse project: Midlet Suite Properties
- A new Java Project has been created:
Figure 25: Create new Eclipse project: work area with new created project
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 68 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 69

Java User’s Guide
10.1 Eclipse 3.1.2 (with ME Plugin 1.2.3)
71
- Select “Project01” and press <Ctrl+N> and select “J2ME Midlet”:
s
Figure 26: Create new Eclipse project: Create a J2ME Midlet
- Fill in Midlet parameters (package directory, name of Java source file) and press <Fin-
ish>:
Figure 27: Create new Eclipse project: Create a New J2ME Midlet
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 69 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 70

Java User’s Guide
10.1 Eclipse 3.1.2 (with ME Plugin 1.2.3)
71
Step 2:
Modify Java source file “printme.java” template:
s
Figure 28: Create new Eclipse project: Edit some Java commands
This application prints the given line via ASC1 (default setting). Please keep in mind to add
“notifyDestroyed();” in destroyApp() method. Please refer to Chapter 6 “MIDlets” for more
details about Midlet life cycles.
Step 3:
Configure Jad file:
- Double click on “Project01.jad” to open the editor and add “deployed\” path in Midlet Jar
URL edit line.
Figure 29: Create new Eclipse project: Edit “deployed” path to Jar file
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 70 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 71

Java User’s Guide
10.1 Eclipse 3.1.2 (with ME Plugin 1.2.3)
71
Step 4:
Create Jad and Jar file:
- Select “Project01”
- Open context menu of “Project01” and select Create Package from item J2ME
- Jad and Jar file are be created under the “deployed” directory (default setting of Eclipse)
Step 5:
Download Jad and Jar file into the Flash File System of the module and start the Java application:
Manual download and start of Java application:
- Copy Jad and Jar files manually using MES (e.g MES Windows Explorer) into the module
- Start the Java application by using at command “AT^SJRA=a:/Project01.jar” (e.g. using
ASC1)
- The Java “System.out” is printed via ASC1 (default setting) and is displayed on terminal
programs (e.g. “Print this line.”).
Automatic download and start of Java application using IDE:
- Open the context menu of “printme.java” and select Emulated J2ME Midlet from item Run
As.
- The SMTK emulator downloads Jar and Jad file into the Flash File of the module (trans-
mission via MES port that was selected during installation) and automatically starts the
Java application.
- The Java “System.out” is printed via ASC1 (default setting) and is displayed on terminal
programs (e.g. “Print this line.”).
s
Further information about importing an existing Java project into Eclipse based on the “Hello
World” example is described in Section 11.3.2.7.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 71 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 72

Java User’s Guide
11 Debug Environment
97
s
11 Debug Environment
11.1 Data Flow of a Java Application in the Debug Environment
Figure 30: Data flow of a Java application in the debug environment
In the debug environment the module is connected to a PC via a serial interface. This can be
a USB or an RS232 line. The application can then be edited, built, debugged or run within an
IDE on the PC. When running or debugging the MIDlet under IDE control it is executed on the
module (on-device execution) not on the PC. This can be either debugging mode, where the
midlet execution can still be controlled from the IDE (on-device debugging) or normal mode,
where the midlet is copied to the module and started normally. This ensures that all interfaces
behave the same whether debugging mode is used or not.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 72 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 73

Java User’s Guide
11.2 Emulator
97
s
11.2 Emulator
The ME emulator is part of the SMTK and is used as the controlling entity for on-device debugging. Some values can be configured in the file wtk/bin/WM_Debug_config.ini (see below note
for TC65). The emulator is running fine without changes in WM_Debug_config.ini file, because
the settings for the serial interface (COM port and baudrate) are configured during installation
of SMTK.
Note: For TC65 the file "WM_Debug_config.ini" is stored under the "Application Data" folder of
the currently logged in user. Depending on the Windows operation system it can be found
under the following directory:
Windows 2000:
e.g. "c:\Documents and Settings\<your login>\Application Data\
Siemens\SMTK\TC65_R3\WM_Debug_Config.ini"
Windows XP:
e.g. "c:\Documents and Settings\<your login>\Application Data\
Siemens\SMTK\TC65_R3\WM_Debug_Config.ini"
Windows Vista:
e.g. "c:\Users\<your login>\AppData\Roaming\
Siemens\SMTK\TC65_R3\WM_Debug_Config.ini"
In case the Application Data folder is not visible, it is possible to set the option to show hidden
folders (choose Explorer menu Tool -> Folder option.. -> and select "show hidden folder").
Debugging information between the Debugger (IDE) and the JVM is transferred over an IP connection. In order to establish this IP connection between the PC and the module the emulator
needs a special Dial-Up-Network (DUN):
• ISP name: "IP connection for remote debugging“
• Modem: either "Standard 19200 bps Modem“ or "<productname> 14400 bps Modem“ or
USB modem
• Phone number: *88#
• Disable the Redial if line dropped option.
• Enable Connect automatically
This Dial-Up Network (DUN) connection is installed automatically together with a standard
modem or selecting USB modem during installation of SMTK. The emulator uses always the
COM port or USB modem settings configured for this Dial-Up Network connection.
You can use any of the three serial interfaces (ASC0, ASC1, USB) to connect with module, but
you will lose the functionality which is normally present on the interface. Because of this loss
and because of its speed it is recommended that the USB interface be used.
Please keep in mind, that if you like to use a USB modem connection, you have to install and
configure that modem connection before starting SMTK installation manually and select Siemens USB modem during SMTK installation. The Dial-up Network will be installed and configured with USB modem during SMTK installation. There are some points to notice in case of
using the USB interface in a debugging session. If you are starting a debugging session very
quickly once again after end of a previous debugging session, the emulator is not able to select
the USB interface and is selecting a standard modem connection. Please wait some seconds
to avoid this operation system dependent problem, because the Windows operation system
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 73 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 74

Java User’s Guide
11.2 Emulator
97
needs some seconds to enable the USB port once again after the "IP connection for remote
debugging" is closed.
If necessary, the IP addresses used for the debug connection can also be changed. This is
done in the file "WM_Debug_config.ini". For details, see also the AT^SCFG command and its
“Userware/DebugInterface” parameters described in [1]. Please keep in mind, that the IP
address range 10.x.x.x is not supported for the configuration of debugging!
During installation of SMTK some new programs are installed for handling the debugging session in conjunction with the IDE. The installation routine of the SMTK doesn't change any configuration of an existing firewall on your PC.
In the case, that a firewall is installed on your PC and the local configured and used IP connection (Dial-Up Network connection for debugging) is blocked or disturbed by this firewall, please
configure the firewall or the Dial-Up Network connection manually to accept the new installed
programs and the port or to use another port or contact your local PC administrator for help.
s
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 74 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 75

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3 Java IDE
The SMTK is integrated into your Java IDE during installation. Please note that the IDE integration is intended to create MIDlets suitable for the Java enabled module and for debugging
using the emulator. JAR files used in the module must be configured according to the batch file
examples given. If the SMTK install succeeded, you can easily switch between the Siemens
environment and Standard-JDK environment, the special libraries/APIs and emulators are
available, and AT commands can be sent to the module. Regular function of the IDE for nonSiemens projects is unchanged.
Using the debugger please keep in mind that the MIDlet-URL, included in the Jad file, has to
indicate and store the location where the emulator will find the corresponding Jar file. Generally
the location will only be the file name for the Jar file.
If you are using Eclipse IDE the location of the Jar file is “deployed\<filename>.jar”. Please
check this path name inside the Jad file before starting a debugging session with Eclipse IDE
and change it manually, if the “deployed” subdirectory is missing. Please keep in mind, that the
subdirectory “deployed” is used as a default setting in the Eclipse IDE and can be changed by
the user within the Eclipse menu.
While using "on-device debugging" the ME is restarted after the end of each debugging session. This is independent of the used IDE (Eclipse 3.0.1, Eclipse 3.0.2, Eclipse 3.1.0, Eclipse
3.1.1, Eclipse 3.1.2, Eclipse 3.2.x
2005, JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer).
Please note that the USB port has to be disconnected manually before the module is restarted,
in case of using a connected terminal program on USB port for directing the Java “System.out”.
It is recommended to use ASC0 or ASC1 for directing Java “System.out” to avoid closing manually the COM port.
Please keep in mind, that it is not possible to use obfuscated files for a debugging session.
When writing and debugging a midlet be aware of the midlet life cycle (see Section 6.2 “MIDlet
Life Cycle”).
10
, NetBeans IDE 5.0, NetBeans 5.5.x10, JBuilder X, JBuilder
11.3.1 NetBeans IDE 5.0, NetBeans 5.5 or NetBeans 5.5.x
Integration for NetBeans IDE 5.5 and 5.5.x is only supported for TC65. The described steps for
using Netbeans IDE 5.0 are identical for NetBeans IDE 5.5 and Netbeans 5.5.x.
This section indicates the changes to your IDE you will see after integrating the SMTK and
describes how to exploit these features to build and debug your applications.
All installed emulators can be found using the NetBeans IDE 5.0 menu
→ Java Platform Manager. See Figure 31.
Tools
10.
only supported for TC65
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 75 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 76

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
Figure 31: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - installed emulators
11.3.1.1 Switching Emulator to IMP-NG Emulator
You can switch to the SMTK emulator project dependent using the context menu for project
properties (e.g. "Hello Sample" <properties>) and select the emulator platform and the device
e.g. “Siemens IMP-NG TC65 R2 Wireless Toolkit” and “IMP_NG_TC65_R2” for TC65
Release 2. See Figure 32.
Figure 32: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - Switching to IMP-NG emulator
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 76 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 77

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.1.2 Templates
Templates for a Siemens MIDlet can be found in the file explorer and under NetBeans IDE 5.0
menu File
cation.
The New File wizard opens. Select category “IMP-NG” and File Type “IMP-NG MIDlet” and
press the Next button for working with this skeleton.
→ New File... The MIDlet template provides the skeleton of an IMP-NG MIDlet appli-
Figure 33: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - Selecting an IMP-NG MIDlet template (e.g. project “Test”)
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 77 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 78

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.1.3 Examples
There are three IMP-NG MIDlet sample projects (“HelloSample”, “NetDemo” and
“RS232Sample”) included. Each sample project can be selected directly in NetBeans IDE 5.0.
You can open the sample project (e.g. “HelloSample”) using the NetBeans IDE 5.0 menu File
→ New Project... The New Project wizard opens. Select Category Samples → Mobile → IMP-
NG and select (e.g. “Hello World Example”). Press the Next button.
Figure 34: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - selecting sample project “Hello World Sample”
Figure 35: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - confirmation of sample project “Hello World Sample”
Press the Finish button to end the selection of the sample project.
Note: Keep in mind, that if you are selecting the "HelloWorld-Sample" you have to choose the
used emulator after loading the "HelloWorld-Sample".
Please select project properties in the "HelloWorld" project’s context menu and choose the
emulator (e.g. "TC65_R3") for the Java debugging session. Otherwise NetBeans 5.x indicates
a reference problem, because it does not know, which kind of emulator has to be used!
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 78 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 79

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.1.4 Compile and Run
Ensure that the proper emulator will be used and compile the project as normal. Any output will
be shown in the output window in the IDE together with some debugging information of the IDE.
The html help files of the SMTK can be accessed directly by pressing Alt+F1.
11.3.1.5 Starting Debug Session without Downloading Java Files
It is possible to start a debugging session without download of the Java files (*.jad and *.jar)
again. The emulator has to be started with an additional parameter “-noload” and downloading
of the Java files is suppressed.
If you like to suppress downloading of *.jar and *.jad file, please use the project context menu
Properties, select category “Running” and type in “-noload” as extra parameter for the emulator
as shown in the following figure:
Figure 36: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - add emulator option “-noload” (e.g. project “HelloSample”)
Keep in mind that you have to remove this emulator option before starting debugging session
with download of Java files. The Java files are not updated in the Flash Files System of the
module while option “-noload” is set!
Note: This feature is not working in current NetBeans IDE 5.0
(included on the SMTK CD).
11.
Supported for TC65 only.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 79 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
or NetBeans IDE 5.5.111 version
Page 80

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.1.6 Displaying Java "System.out" in NetBeans IDE window
Please prepare redirection of Java “System.out” during a debugging session as described in
Section 11.5 Switching Java “System.out” to IDE debug window.
The Debugging Console tab of the NetBeans IDE window is selected by default after starting
the debugging session.
To display the Java “System.out”s after starting the debugging session select the “build.xml
(debug)” tab as shown in the below figure:
Figure 37: NetBeans IDE 5.0 - Displaying Java “System.out” in NetBeans IDE window
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 80 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 81

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2 Eclipse 3.0 and Eclipse 3.1
We recommend that Eclipse 3.0.1 or higher is to be used.
11.3.2.1 Eclipse 3.0
Please use the customized Eclipse ME Plugin version that is distributed with the SMTK CD
under the directory “EclipseMEplugin_WM” only for Eclipse 3.0.1 and 3.0.2 and install Eclipse
ME as described in Section 3.4. However, instead of selecting "eclipseme.feature_1.
2.3_site.zip" choose “\EclipseMEpluging_WM\plugin.zip”
New Archived Site… button.
12
from SMTK CD after clicking the
11.3.2.2 Eclipse 3.1
If Eclipse is not installed, please follow the steps as described in Section 3.4.
Please use and install EclipseME plugin 1.2.1, 1.2.3 or 1.5.x for Eclipse 3.1.0, 3.1.1 or 3.1.2.
11.3.2.3 Eclipse 3.2
If Eclipse is not installed, please follow the steps as described in Section 3.4.
Please use and install EclipseME plugin 1.5.5 or 1.6.8.
It is recommended to use Eclipse 3.2.2 with ME 1.5.5 for working with Java Debugging session.
12.
Eclipse WM Plugin is not included anymore on TC65 CD
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 81 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 82

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.4 Using Eclipse with ME Plugin up to Version 1.2.3
11.3.2.4.1 Additional Configuration of Integrated Emulator
The following configuration is displayed after SMTK integration into Eclipse by using the
Eclipse menu Windows
→ Preferences → J2ME → Platform Components:
Figure 38: Eclipse – Display of different integrated emulators
To use the debugger it is necessary to increase the debug server delay timeout of Eclipse IDE.
Please set the timeout under Windows
25000. If you develop an extremely large application you may have to increase this timeout.
→ Preferences → J2ME → Debug Server Delay to
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 82 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 83

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.4.2 Switching Emulators
You can easily switch between different installed emulators by using the preferences of a
project and choosing e.g. Siemens IMP-NG TC65 R2 Module, see figure below.
Figure 39: Eclipse – J2ME platform
11.3.2.5 Using Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.x
Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.x is supported by the TC65, XT65/XT75 and AC65/AC75 CDs. This
Eclipse ME Plugin is using a completely new device management concept to integrate different
emulators. The integration and disintegration of the TC65 resp. XT65/XT75 or AC65/AC75
emulator is only automatically possible by using the TC65 resp. XT65/XT75 or AC65/AC75
SMTK CD!
Please note that selecting the TC65 resp. XT65/XT75 or AC65/AC75 emulator by using the
Eclipse menu Window
ing to the respective emulator directory will not integrate the emulator.
Note: Manual emulator integration (by using Eclipse menu) is supported by Eclipse with using
ME Plugin 1.5.5 and later. Automatic emulator integration using SMTK CD is possible for all
Eclipse ME Plugin 1.5.x.
→ Preferences → J2ME → Device Management → Import and brows-
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 83 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 84

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.5.1 Additional Configuration of Integrated Emulator
The following configuration is displayed after SMTK integration into Eclipse by using the
Eclipse menu Windows
→
Preferences → J2ME → Device Management:
Figure 40: Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.0 – Display of different integrated emulators
To use the debugger it is necessary to increase the debug server delay timeout of Eclipse IDE.
Please set the timeout under Windows
25000. If you develop an extremely large application you may have to increase this timeout.
→ Preferences → J2ME → Debug Server Delay to
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 84 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 85

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.5.2 Switching Emulators
You can easily switch between different installed emulators by using the properties of a project
and choosing a Device Group, e.g. "Siemens IMP-NG XT75 Wireless Toolkit". You can select
a device also by using the Manage Devices… button, see figure below.
Figure 41: Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.5.0 – J2ME platform
11.3.2.6 Using Eclipse with ME Plugin 1.6.x
Automatic integration into Eclipse ME Plugin 1.6.x is supported by using the TC65 CD. All configurations, settings and using the Eclipse IDE are done in a very similar way as for Eclipse ME
Plugin 1.5.x and are described in the Section 11.3.2.5.1 and Section 11.3.2.5.2.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 85 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 86

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.7 Import Example
You can import an existing Eclipse project using the following steps:
- Open menu: File
- Choose the root directory of the Eclipse project (e.g. “Hello World” example of the SMTK
CD). See figure below.
→ Import → Existing Project into Workspace
Figure 42: Eclipse – Project import
The following figure shows the “Hello World” example in the IDE.
Figure 43: Eclipse - Example
The html help files of the SMTK can be accessed directly by pressing Shift+F2 while the cursor
points to a Java expression in a Java source file.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 86 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 87

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.8 Compile and Debug
To build the jar and jad files you have rebuild the project with the Create Package function.
Open the context menu of the project and go to J2ME
→ Create Package.
Figure 44: Eclipse – Create package
Now you are ready to debug your project. Run → Debug…
An emulator launcher with pre-settings is provided for starting the debugging session.
Please ensure that you have selected the right project and executable midlet.
Note: Before starting Java debugging session with the HelloWorld-Sample it is recommended
to check the setting of used emulator (e.g. TC65_R3 emulator in project properties see Section
11.3.2.5.2), to clean the project with configuration "automatically build" (using Eclipse menu
→
Project
loWorld" project select J2ME
Reason: Eclipse is storing internally old settings for an old used "HelloWorld-Sample", if you
have used Eclipse with "HelloWorld-Sample" for another IMP-NG product before!
Clean…) and to compile it completely (using project’s context menu of the "Hel-
→
Create Package).
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 87 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 88

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
Figure 45: Eclipse - Configuration
Restriction:
The integration of the SMTK using the SMTK installer depends selecting the offered default
workspace “\workspace” of Eclipse (e.g. Eclipse 3.0.1 and 3.0.2 “..\eclipse\workspace\..” or
Eclipse 3.1.0, 3.1.1 and 3.1.2 “..\Documents and Settings\<user name>\workspace\..”).
If you like to use the SMTK integration inside other workspaces, please integrate SMTK manually in these workspaces using Eclipse menu Window
Components (as shown in Figure 36). Please keep in mind that all manually integrated SMTKs
have to be removed manually as well in case of removing SMTK.
Note for using Eclipse 3.2.2 ME 1.6.8:
Start debugging using "TC65 Rel.3 emulator" please select in "Midlet" the "HelloWorld" Midlet
sample from the list of Midlets. The project name will be selected automatically.
Remarks using Eclipse under Windows Vista (only supported for TC65):
The Eclipse workspace directory differs from the location used under Windows 2000 and Windows XP. Using Windows Vista the following loaction is used for automatic integration of TC65
into Eclipse:
"<drive name>:\Users\<your login>\AppData\workspace"
(e.g. "c:\Users\<your login>\AppData\workspace")
→ Preferences → J2ME → Platform
Please select this workspace before starting Java debugging with Eclipse!
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 88 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 89

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.2.9 Starting Debug Session without Downloading Java Files
It is possible to start a debugging session without download of the Java files (*.jad and *.jar)
again. The emulator has to be started with an additional parameter “-noload” and downloading
of the Java files is suppressed. Please add the parameter in the following emulator configuration line as described in the figure:
Figure 46: Eclipse - Configuration
Please keep in mind that you have to remove this emulator option before starting debugging
session with download of Java files. The Java files are not updated in the Flash files system of
the module while option “-noload” is set!
Note for Eclipse 3.2.2 ME 1.6.8:
The option "-noload" does not take previously set breakpoints into account. In other words, if
you have set breakpoints in your Java source file and would like to start the debugging session
with the "-noload" parameter, no previous set breakpoint is reached.
Please use Eclipse 3.2.2 ME 1.5.5 for starting debugging session with "-noload" parameter.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 89 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 90

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
Note for using Eclipse 3.2.x ME 1.5.x and 1.6.x:
During debugging it is sometimes possible, that if a breakpoint is reached, the Java program
stops, but no breakpoint is indicated in the Java source line (Java source windows). In this case
please select the Java Thread in the "Debug" window and select "System Thread" where the
hit breakpoint is shown. The corresponding source line is highlighted inside the Java source
windows (e.g. "HelloWorld.java") as well for the hit breakpoint. See the following figure.
s
Figure 47: Eclipse 3.2.x ME1.5.x and 1.6.x select System Java Thread for showing breakpoint line in Java source
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 90 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 91

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.3 Borland JBuilder X
If you want to use JBuilder X and it is not installed, first install JBuilder X and follow the installation wizard instructions. Run the SMTK installation program in maintenance mode. The
SMTK will find the installed JBuilder X IDE. Select JBuilder X to integrate the SMTK into
JBuilder X.
After integration of SMTK into JBuilder X you can examine the integration by opening the menu
→ Configure JDKs… (see Figure below).
Tools
Figure 48: JBuilder X – JDK settings
The libraries included with the SMTK can be examined by opening the menu
Tools
→ Configure Libraries… (see Figure below).
Figure 49: JBuilder X – Siemens Library
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 91 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 92

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.3.1 Examples
There are sample projects provided with the SMTK. These projects can be found in the JBuilderSamples directory of the SMTK installation directory. This directory is accessed by opening
a project using the menu File
→ Open Project… (see Figure below).
Figure 50: JBuilder X – Sample Projects
Open the Project (e.g. “HelloWorld.jpx”), rebuild the sources and start the debugger using the
micro edition (context menu “HelloWorld.jad”
→ Micro Debug using “HelloWorld” ).
Figure 51: JBuilder X – Starting the debugging session
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 92 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 93

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.3.2 Starting Debug Session without Downloading Java Files
It is possible to start a debugging session without download of the Java files (*.jad and *.jar)
again. The emulator has to be started with an additional parameter “-noload” and downloading
of the Java files is suppressed. Please add the parameter in the following emulator running
configuration line as described in the figures above.
Select the project properties (e.g. “HelloWorld.jpx”) and edit the emulator configuration.
Figure 52: JBuilder X – Edit project properties for starting the emulator
Set the additional emulator parameter “-noload” and press OK.
Figure 53: JBuilder - Runtime Configuration
Keep in mind, that you have to remove this emulator option before starting debugging session
with download of Java files. The Java files are not updated in the Flash files system of the module while option “-noload” is set!
The same procedure is used for all different JBuilder IDE versions.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 93 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 94

Java User’s Guide
11.3 Java IDE
97
s
11.3.4 Borland JBuilder 2005 and JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Devel-
oper
If JBuilder 2005 or JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer is not installed, run the JBuilder 2005
or JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer install program and follow the installation wizard instructions. Use the SMTK installation routine in maintenance mode. The SMTK will find the installed
JBuilder 2005 or JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer IDE. Select JBuilder 2005 or JBuilder
2006 Enterprise/Developer to integrate the SMTK into JBuilder 2005 or JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer.
After the integration of the SMTK into JBuilder 2005 or JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer you
can examine the integration by opening the menu Tools
below).
→ Configure → JDKs… (see Figure
Figure 54: JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer – JDK settings
The libraries included with the SMTK can be examined by opening the menu Tools → Config-
→ Libraries… (see Figure below).
ure
Figure 55: JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer – Siemens Library
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 94 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 95

Java User’s Guide
11.4 Breakpoints
97
s
11.3.4.1 Examples
There are sample projects provided with the SMTK. These projects can be found in the JBuilderSamples directory of the SMTK installation directory. This directory is accessed by opening
a project using the menu File
→ Open Project… (see Figure below).
Figure 56: JBuilder 2006 Enterprise/Developer – Sample Projects
Starting the debugging session is done in the same way as for JBuilder X (see chapter for
JBuilder X above).
11.4 Breakpoints
Breakpoints can be set as usual within the IDE. The debugger cannot step through methods or
functions whose source code is not available.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 95 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 96

Java User’s Guide
11.5 Switching Java “System.out” to IDE Debug Window
97
s
11.5 Switching Java “System.out” to IDE Debug Window
The Java “System.out” can be redirected during a debugging session using a UDP socket connection as described in Section 5.9 “System Out” and Section 5.9.3 “UDP”. Switching between
Java “System.out” using serial port and Java “System.out” using UDP socket is done by a setting inside of the emulator configuration file “WM_Debug_config.ini” (e.g. TC65 Release 2:
located under “TC65_R2\WTK\bin”, TC65 Release 3: located Windows OS dependent under
"Application Data" folder as described in Section 11.2). Switching Java “System.out” to serial
port is used as default setting.
Figure 57: Emulator configuration file “switching Java System.out to serial port”
The following line of the “WM_Debug_config.ini” file is used for switching the Java “System.out”
direction:
#UDPport=12345
To switch the Java “System.out” direction to the UDP socket and display it on a IDE window
please remove “#”. The configuration line looks as follows:
UDPport=12345
To switch the Java “System.out” direction to serial port output please add “#” (default setting).
The configuration line looks as follows:
#UDPport=12345
Remarks:
Please keep in mind that the handling of Java “System.out” is done asynchronous. It is possible, that not all Java “System.out” data are written into the IDE window. To avoid this problem
please set a breakpoint in front of the Java function call “notifyDestroyed()” inside your Java
source.
Java “System.out” using IDE window is only supported during debugging session.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 96 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 97

Java User’s Guide
11.6 Important Information for Java Debugging on Windows Vista
97
s
11.6 Important Information for Java Debugging on Windows Vista
This section applies only to TC65.
Java Debugging on Windows Vista requires that administrator privileges be set. To do so, follow these steps:
1. Log on your system using an administrator account.
2. Start each IDE with option "Run as administrator" for starting Java debugging:
- Temporarily: Right-click the IDE icon (on your desktop) and select "Run as administrator"
or
- Permanently: Open the Windows Explorer and change the option for the IDE executable.
For example, right-click the "Eclipse.exe", select Properties and tab Compatibility, then
select "Run this program as an administrator" in section "Privilege Level" (see figure
below).
Figure 58: Using Windows Vista: Set Eclipse.exe perament to "Run as administrator"
3. Eclipse workspace directory is located at <drive name>:\Users\<login>\AppData\workspace
(e.g. "c:\Users\MyLoginName\AppData\workspace")
Please select this workspace before starting Java debugging with Eclipse!
The automatic integration of TC65 is only done in this workspace.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 97 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 98

Java User’s Guide
12 Java Security
112
s
12 Java Security
The Java Security Model follows the specification of MIDP 2.0 and is IMP-NG conforming. It
integrates only a simple protection domain concept since protection domains are not needed
for module use cases.
Java Security is divided into two main areas:
• Secure MIDlet data links (HTTPS, Secure Connection) (see Section 12.1)
• Execution of signed/unsigned MIDlets (see Section 12.2)
The interface of Java Security offers the following functionality.
• Insert/delete X.509 certificate (default is no certificate, see Section 12.2.1)
• Switch between trusted and untrusted mode for the execution of MIDlet
(default is trusted after inserting the certificate, see Section 12.2.1)
• Enable/disable untrusted domain in trusted mode (default is disabled)
• Switch MES (default is ON see Section 12.3)
• Switch https certificate verification (default is OFF, see Section 12.1)
Restrictions:
• The module does not supply users independent date/time base. Therefore no examination
of the validity of the expiration date/time of the certificate takes place.
12.1 Secure Data Transfer
This feature makes it possible for MIDlets to use safe data links to external communications
partners. The specification IMP-NG defines two java classes with this characteristic - HTTPSConnection and SecureConnection
.
The Siemens implementation follows the recommendations in IMP-NG:
HTTPSConnection
• HTTP over TLS as documented in RFC 2818
RFC 2246
SecureConnection
• TLS Protocol Version 1.0 as specified in RFC 2246
.
and TLS Protocol Version 1.0 as specified in
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 98 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 99

Java User’s Guide
12.1 Secure Data Transfer
112
Two modes exist for safe data links.
Mode 1:
• No examination of the server certificate takes place when setting up the connection. The
authenticity of the server certificate is not verified. See Figure 59.
s
Figure 59: Mode 1 – Customer Root Certificate does not exist
Mode 2 (see Section 12.2.1, 1. Step):
• Customer Root Certificate is inside of the module.
• Command: Switch on Certificate Verification for HTTPS Connections was sent.
• The server certificate is examined when setting up a connection. Two configurations are
valid. The server certificate is identical to the certificate in the module (both certificates are
self signed root certificates) or the server certificate forms a chain with the certificate of the
module. Thus the authenticity of the server certificate can be examined with the help of the
certificate of the module. See Figure 60 and Figure 61.
Figure 60: Mode 2 - Server Certificate and Certificate into module are identical
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 99 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
Page 100

Java User’s Guide
12.1 Secure Data Transfer
112
s
Figure 61: Mode 2 - Server Certificate and self signed root Certificate in module form a chain
12.1.1 Create a Secure Data Transfer Environment Step by Step
The following steps describe the configuration:
• The certificate exists within the module (see Section 12.2.1, Step 1).
• Certificate verification is activated for a data connection (HTTPS or SecureConnection).
The steps described below use the cygwin + openssl environment (for installation see http://
www.cygwin.com/. The openssl documentation can be found here http://www.openssl.org/
docs/apps/openssl.html)
A CA Root certificate is generated. This certificate can be placed on the HTTPS-Server.
Another possibility is to use the private key of the certificate in order to sign thereby a server
certificate. Both certificates form then a chain, which can be examined by the ME. A step-bystep description for the latter scenario can be found below.
wm_java_usersguide_v12 Page 100 of 123 2008-02-25
Confidential / Released
 Loading...
Loading...