Page 1

Local Service Organization Service Manual
BE INSPIRED
SIEMENS COMMUNICATIONS LIMITED
Our innovation shapes the future
Page 2

Table of Content
CHAPTER 1
Cellular Communication
Coverage Concept 2
GSM Network Architecture 3
Subscriber Identity Module 4
SIM Application Toolkit 5
Extended GSM 900 - EGSM 5
WAP 6
CHAPTER 2
Level 2 Service Guide
Introduction 7
General Information 7
Different between A50 and 1168 7
A50 Series Technical Information 8
Accessories 10
A50/1168 Mechanical Diagram 12
Mechanical Concept 13
A50/1168 Spare Parts Level 1 & Level 2 14
Disassemble the A50/1168 15
Assemble the A50/1168 19
Mobile Software Programming 22
Customer Specific Initialization 25
International Mobile Equipment Identity 25
Phone Unblocking 26
Internet Solution 27
CHAPTER 3
Siemens Service Equipment
Introduction 28
Other equipment 30
Software Installation 31
Configuring the test software 32
Running the test sequence 33
ANNEX A – Test SIM Information 37
ANNEX B – Service Equipment List 38
1
Page 3
Ch
r
apte
Cellular Communication
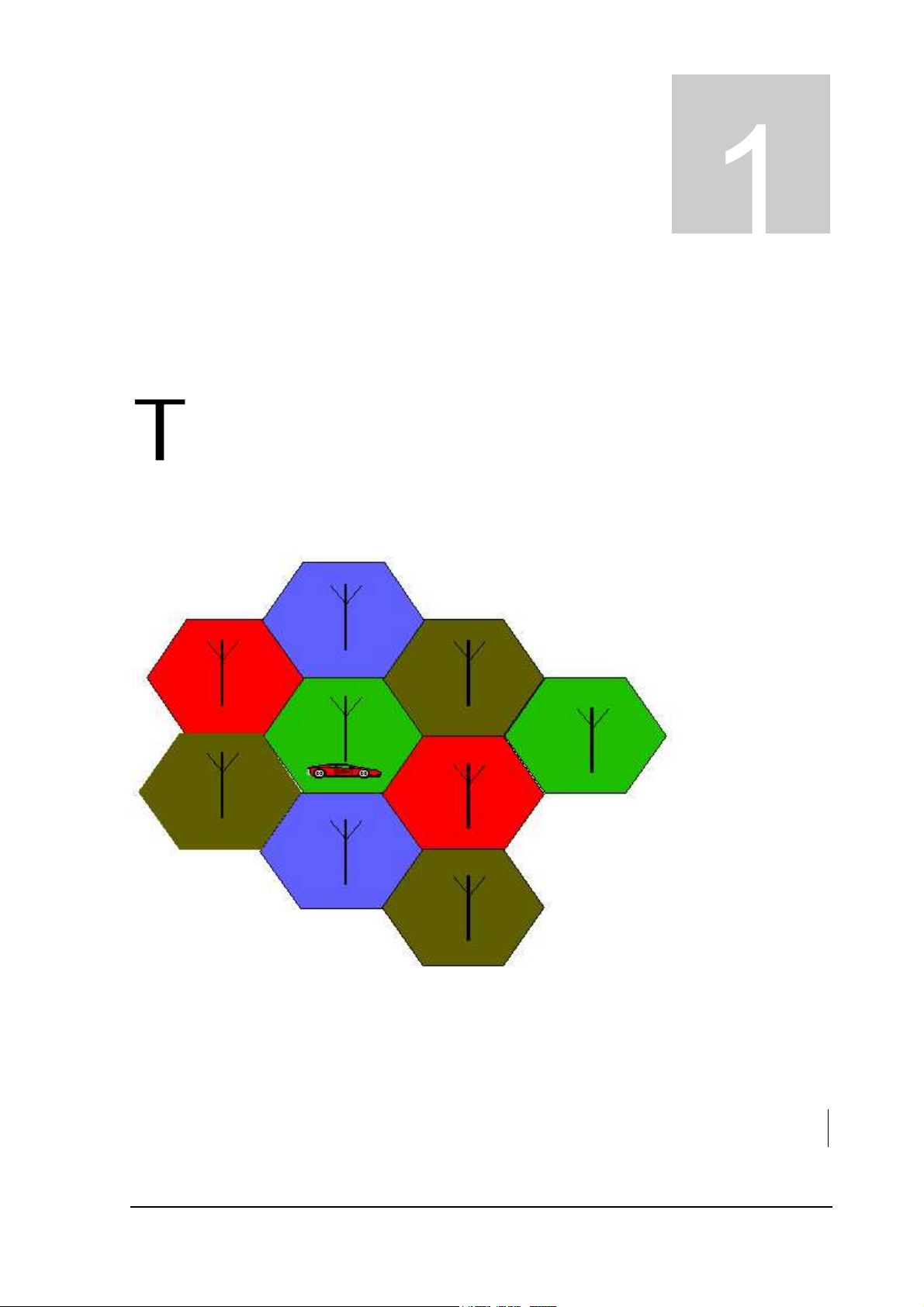
Coverage Concept.
he cellular systems is made up of numerous transmitting and receiving sites, whose
individual coverage areas partially overlap. The concept of frequency re-use, same
frequency is used by several sites, allows a high traffic density in a wide area. Due to the
limited transmission range of the terminals, cellular systems are based on a large
number of base stations on the infrastructure side, scattered over the area to cover, with each
covering a fairly small geographical zone called cell. Cells are often represented by hexagons
(see figure 1.1.).
FIGURE 1.1 CELLULAR COVERAGE REPRESENTATION.
2
Page 4
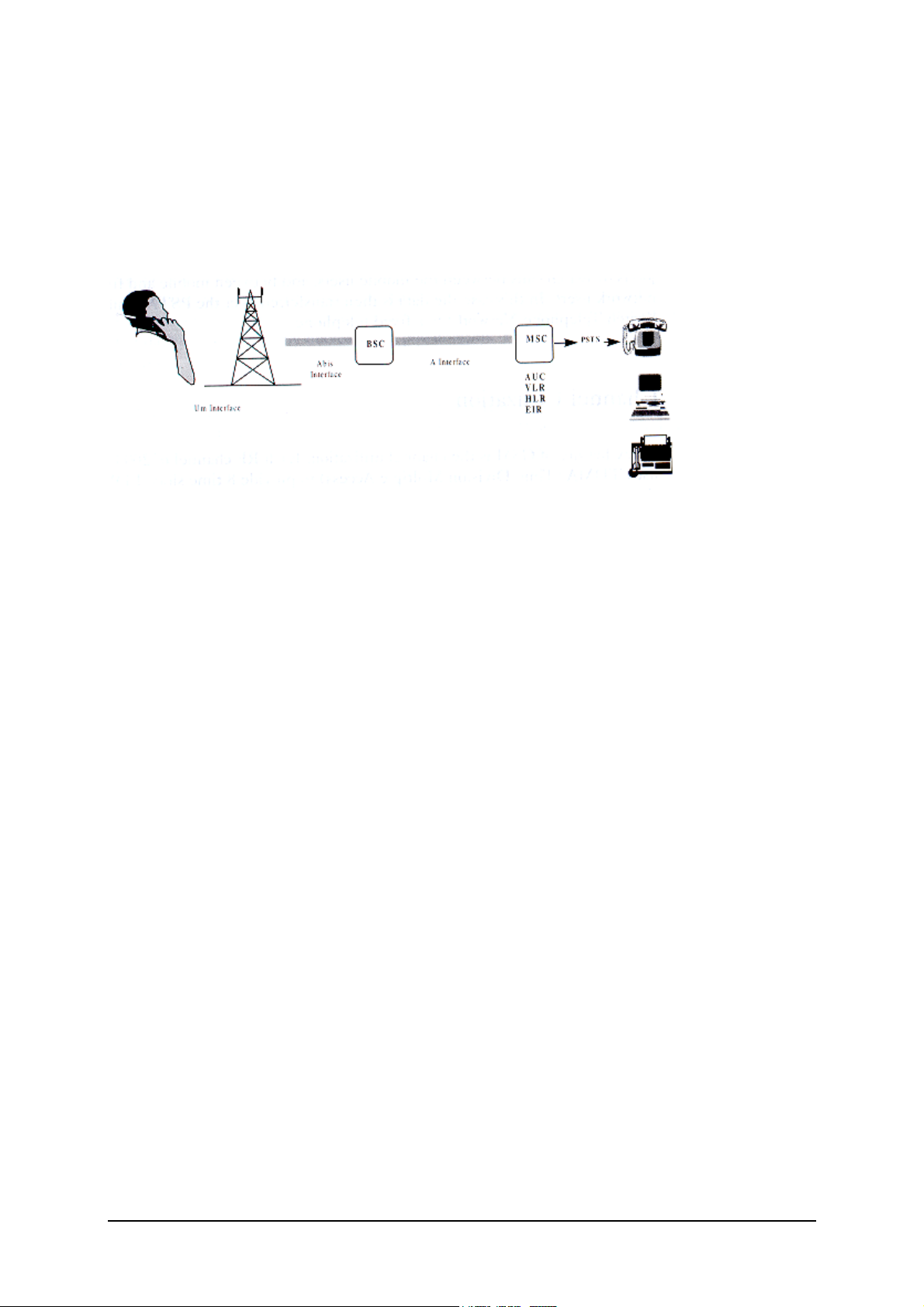
GSM Network Architecture.
GSM network can be broadly divided into three broad parts, namely:
1. Mobile Station(MS) carried by the subscriber,
2. Base Station Sub-system(BSS) which controls the radio link with the mobile station.
3. Mobile Switching Center(MSC) which performs the switching of calls between the mobile
users, and between mobile and fixed network users.
FIGURE 1.2 GSM ARCHITECTURE
Each mobile station is given a unique identity. As soon as the mobile phone is turned on, it
registers with the network and is authenticated; as such the network could always find the mobile
phone.
Larger amount of data is being exchanged to and from the following functional blocks in the MSC:
Visitor Location Register, VLR
Stores information about mobile subscribers that enter it coverage area, which is associated with
the geographical area where the mobile is currently roaming. When there is an incoming call for
the mobile, the HLR is interrogated about the present address of the VLR.
Home Location Register, HLR
A database that contains all data concerning the subscription of the mobile subscriber, i.e. their
access capabilities, subscribed services, and supplementary services. It also contains information
about the VLR that is handling the mobile station currently. When the mobile changes location,
the HLR is updated accordingly. It also provides the MSC with information about the MSC area
where the mobile is actually located to allow incoming calls to be routed immediately to the called
party.
Authentication Center, AUC
Stored information that is necessary to protect communication through the air interface against
any intrusions. The legitimacy of the subscriber is established through authentication and
ciphering, which protects the user information against unwanted disclosure.
Equipment Identity Register, EIR
An option the network operator can use to enforce security. With this feature the network can
identify defective or stolen mobile that may not be used in the network.
3
Page 5

Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
SIM is a smart card, which has a computer, and memory chip that is permanently installed in the
mobile equipment. It comes in either the size of a credit card or smaller version known as the
plug-in SIM.
The subscriber information, which includes a unique number called the International Mobile
Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is stored in the SIM card. SIM card identifies the subscriber to the
network.
To protect the SIM card from improper use, a security feature, a four digits personal identification
number (PIN), is built in. The PIN is stored in the SIM card and can be changed by the
subscriber. PIN2 is required for additional functions available with a special SIM card (Consult the
operator for more information about the PIN 2).
A code (PUK) is provided for unlocking the SIM card if the SIM card is blocked
.
4
Page 6

SIM Application Toolkit
This is a new GSM feature that has been integrated into the GSM standards in Release 96, with
further enhancements added as part of the Release 97 feature set. This feature came about
because of a desire by Network Operators to offer differentiated services, without the need for the
Mobile Manufacturers having to build different variant for different customers. The unique service
offered by the Operator is placed as an application on the SIM and that could work on any mobile
that supports the Toolkit feature.
There is a distinct set of commands between the mobile and the SIM specifically for the Toolkit
that allows the SIM Toolkit and the mobile to communicate independently of the GSM
communication between the SIM and the mobile. Henceforth, the SIM Application Toolkit and
GSM functionality on the SIM are separated logically. The Toolkit can interact directly with the
mobile itself and adding itself to the mobile menu.
Currently, Toolkit application on the SIM and its “other half” communicate by using the Short
Message Service(SMS). “Proactive SIM” is a mechanism whereby the SIM can initiate actions to
be taken by the mobile. These actions include:
· Display text from the SIM on the Mobile display
· Send short message
· Set up a voice call to a number held by the SIM
· Set up a data call to a number and bearer capabilities held by the SIM
· Send a Supplementary Service (SS) control or Unstructured Supplementary Services Data
(USSD) string
· Play a tone in the mobile’s ear piece or ringer
· Initiate a dialogue with the user
· Provide local information from the mobile to the SIM.
· Data download to the SIM from network
· Call control by the SIM.
SIM Applications Toolkit (SAT) allows the flexibility to update the SIM, to change the services and
download new services over the air. In the SAT specification, the short message service is a key
mechanism for personalizing the SIM in each user’s GSM phone. It is designed as a client-server
application. A50 series supports SAT Class 3 specification.
When active, the name of the service may appear in the menu, and there will be sub-menu if
more than one application is active. Figure 1.4 is the SAT icon.
FIGURE 1.4 SAT ICON
Extended GSM 900, E-GSM
This is a new standard that allows Network Operators to increase their capacity through an
extended frequency. The frequency range of E-GSM is as follows:
· Mobile Transmit: 880,2 - 914,8 MHz
· Mobile Receive: 925,2 - 959,8 MHz
A50/1168 series is a GSM Phase 2 / Phase 2+ Dualband E-GSM / GSM 1800 mobile phone.
5
Page 7

Wireless Application Protocol, WAP.
Wireless Application Protocol takes a client-server approach that uses the in-built micro-browser
to make a request, in wireless markup language (WML), for information or service. The request is
passed to a WAP Gateway, which then retrieves the information from a Internet server, in HTML
format, and translate it into WML. The requested information is then sent to from the WAP
Gateway to WAP client (mobile) using the available and most appropriate mobile network bearer
services.
Wireless Protocol Stack.
Wireless Application Environment (WAE)
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP)
Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP)
Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS)
Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP)
Bearers e.g. Data, SMS, USSD
TABLE 1..1 WAP PROTOCOL STACK
1. Wireless Application Environment
Defines the user interface on the phone. WAE contains the WML,WML script and the
wireless telephony application (WTA).
2. Wireless Session Protocol
Link the WAE to two session services – one connection oriented operating above the WTP
and a connectionless service operating above WDP.
3. Wireless Transaction Protocol
Runs on top of the datagram service and part of the standard suite of TCP/IP protocols, to
provide a simplified protocol suitable for low bandwidth mobile station.
4. Wireless Transport Layer Security
WTLS incorporates security features that are based upon the established Transport layer
Security (TLS) protocol standard, that include data integrity checks, privacy on the WAP
Gateway to client leg and authentication.
5. Wireless Datagram Protocol
Allows WAP to be bearer independent by adapting the transport layer of the under-laying
bearer. WDP presents a consistent data format to the higher layer on the WAP stack.
WAP Internet access via the A50 is possible with the inclusion of Wireless Application Protocol
(WAP) browser 1.2.1.
Note: The Asian variant phone (1168) does not support WAP.
6
Page 8

Ch
r
apte
Level 2 Service Guide
Introduction
The chapter is intended to help you carry out repair up to Level 2 on the A50 mobile phone.
General Information
A50/1168 is a dual band (GSM 900 and GSM 1800) Siemens GSM Smart handset.
Due to different requirements of the markets, the A50 has different variants, which broadly
classified under International version and Asian version. Marketing name for international version
is A50, whereas Asian version is 1168.
The A50 and 1168 share the same phone accessories.
Difference between A50 and 1168
The differences between the A50 and 1168 are the phone hardware code and the phone
software.
1168 is a Asian variant of A50 phone for the China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore and Malaysia
markets featuring support for English, Simplified Chinese and Traditional Chinese language.
The repair for international version A50 and the Asian variants 1168 are identical unless
otherwise noted, therefore the description herein is confined to A50 only.
All repairs have to be carried out in an environment set up
according to ESD regulations defined in international standards.
1
7
Page 9

A50/1168 Technical Information
System GSM Phase 2, Dual Band
EGSM 900, Class 4(2 Watt)
GSM 1800, Class 1(1 Watt)
Operating Voltage 3.6V
Size (LxWxH)
Volume 85 cm
109 x 46 x 23 mm (L x W x H)
3
including battery (approx)
Weight 97g including battery (approx)
Battery 650mAH Li-ion Battery (A50 Standard)
Standby time
Talk time
1
up to 250 hours (standard battery)
1
up to 300 minutes (standard battery)
Charging Time < 2 hours for 100%
SIM support Plug in card 1.8 V or 3V, SIM Application Tool Kit Class 3
Antenna Integrated
Speech codec Triple rate voice coder Enhance Full Rate/Full Rate/Half Rate
Display
5 lines, 64x101 pixels
Keypad 12 numeric keys (10 numeric, #, *)
2 function keys (Send, End-ON/OFF)
2 multifunctional softkey and 1 phone book key
Key Sound Click/DTMF/None
Key Lock Activation and Deactivation by #-key or
Automatic
Dialing Last 10 outgoing calls (Redial)
Last 10 incoming with date/time stamp
Last 10 missed calls with date/time stamp
Ringer On/Beep/Off
16+4 individual melodies and 5 ringer volume settings
Speaker Volume Adjustable in 4 levels during call via softkey
Silent Alert Built-in vibrator
Phone Book Storage depends on the SIM card capacity (up to 255)
1
Actual time dependent on the network.
8
Page 10

Internal phonebook of 50 entries.
SMS Support MT, MO, CB
Predictive Text Input, Tegic T9.
Supplementary Call Forwarding, Call Hold, Call Wait,
Services Multiparty Conference, CLIP, CLIR, AoCC
AoCI, FDN, LND USSD and SAT
Ciphering A5/1 and A5/2 supported
PIN control PIN 1 & 2 Code Control
Phone code 4 to 8 digit code
Network function Automatic and manual network selection
Chipset Infineon EGOLD+
WAP Browser Version 1.2
Other Features
· Calling Faces & Calling Symbols
· Predefined EMS sounds & pictures
· Concatenated SMS
· Various animations (menu, welcome)
· Silent Alert
· Various user profiles
· Text modules
· Intelligent Typing (T9) + Libraries
· Chinese menu and input (xx88)
· Alarm / Date
· Date & Time Stamp
· 50 additional phone book entries in the phone
· Mobile Internet Access
· Grouping SMS
9
Page 11

Accessories:
L36104-F3090-X903 Handsfree Loudspeaker S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36145-K1310-X187 Battery NiMh 550mAh
L36145-K1310-X196 Battery NIMH CHN
L36145-K1310-X215 Battery LI-ION
L36145-K1310-X216 Battery LI-ION CHN
L36146-A3043-D Phone Adapter Cable S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36146-A3061-D Y-Adapter
L36158-A58-C35 Mounting for Car Cradle S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36254-Z6-C95 Handsfree Microphone aktiv S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36280-Z4-C354 Plug-In Power Sup TAI
L36280-Z4-C355 Power Supply CHN
L36880-N4501-A101 Desk Top Charger S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A102 Car-Cradle Standard S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A103 Car-Cradle with Antenna Cab S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A115 Soft Data Link 5.0 S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A134 Car Data Adapter S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A135 Push to Talk Key S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A137 Multi Media Card 32 MB S45, ME45, C45, M45
L36880-N4501-A143 Desk Top Charger China S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36880-N4501-A144 Car-Cradle Standard China S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36880-N4501-A145 Data Cable China S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36880-N4501-A148
L36880-N4701-A100 Battery NiMH 550mAh
L36880-N4701-A101 Belt Clip
L36880-N4701-A112 Battery LI-Ion 600mAh
L36880-S4501-A300 E-Box Carkit Voice S45/ME45/C45/M45 german
L36880-S4501-A301 E-Box Carkit Voice S45/ME45/C45/M45 english
L36880-S4501-A302 E-Box Carkit Voice S45/ME45/C45/M45 french
L36880-S4501-A600 Phone Adapter Cable Voice S45/ME45/C45/M45
L36880-S4501-A700 Phone Adapter Cable GPS S45/ME45/C45/M45
For the updated list, please refer to the list in e-Commerce from time to time
URL address: https://communication-market.siemens.de/so/welcome.lookup.asp
Data Cable S45/ME45/C45/M45/S25/C35/C35i/
M35/S35i/SL42/SL45
.
10
Page 12

11
Page 13

A50 Mechanical Diagram
FIGURE 2.1 A50 MECHANICAL DIAGRAM.
12
Page 14

Mechanical Concept
Please take note that the number(s) used here IS NOT the part
number, DO NOT used it in your spare parts purchase order.
Always refer to the SERVICE PART PRICE LIST
for your spare part order.
Note: All numbers refer to mechanical drawing in Figure 2.1.
The mechanical concept of the A50/1168 is similar in various points from other Siemens mobile
telephones.
The first thing you will experience is how the housing is locked. In A50/1168 no screws are used
to keep the housing closed. Also inside the telephone no screws are used anymore. To open the
housing, which is kept closed by catches only, a special opening tool has been defined. Once the
phone is open the catches will be damage and a new housing need to be used. For details on
disassembly tool please refer to Photo 2.5 in the Disassembly Section of this chapter.
Inside, the A50/1168 consists of just one board (1010), which carries control part and RF section
of the mobile.
The display module (1170) and the keypad module (1010) are connected to the board by the
flexible cable which is inserted into a plug-in connector. In case the display or keypad is defective
electrically or mechanically it can be exchanged very easily.
A50/1168 does have an external connector of a new type. Since S6 a so-called “Molex”connector was used, which also offered the possibility to connect an external antenna to it. The
new “Lumberg”-connector, which is used in A50/1168, does not feature such a connection,
because the connector for external antenna is located at the back side of the upper end of the
mobile, close to the internal antenna. As a consequence of this there is no need anymore for a
RF cable mounted to the board or for a RF plug on it to connect this cable. This improves RFproperties of the mobile and lowers production costs.
To be able to do measurements on and software update of the telephone, an adapter cable
between Molex and Lumberg connector will be available. See photos in Additional Tools of
Chapter 3.
A50/1168 antenna is an integral part of the lower case shell (1030).
The A50/1168 is a dual-band mobile operating on GSM900 and
GSM1800, the antenna is an integral part of the lower housing.
The keypad, the microphone and the loudspeaker are mounted into the upper case shell (1020).
Make sure that the microphone and the earphone contact springs are not dirty or damaged
during repair process.
13
Page 15

Mobile Phone A50/1168 Spare Parts Level 1 and Level 2 / 2.5
Reference: E-Commerce
Swap Unit
L36880-S5110-X100 A50 Mobile Phone Swap
Spare Parts Level 1
L36158-A54-A452 Upper mounting frame A50
(Complete with ear piece, keypad and microphone)
L36158-A54-A448 Lower mounting frame A50
L36158-A54-C240 Vibra Clip
L36197-F5008-F290 Display Module Philips
L36197-F5008-F291 Display Module Epson
L36197-F5008-F292 Display Module Hyundai
L36453-Z5-C115 Vibra-Alert Unit
Spare Parts Level 2
L36880-Q5110-A10 RF Control Board A50
Spare Parts Level 2,5
L36158-A54-C211 Cardreader
L36158-A54-C215 Battery Connector
L36195-Z26-C629 ZIF Connector C35/C35i/S35i/M35i/C45
L36334-Z93-C261 Antenna Contact/Koax/BUC/STVS C25/S25/C45
L36334-Z93-C262 I/O Connector/STV
C25/S25/C35/C35i/S35i/M35i/SL45/A35/S45/
ME45/A40/SL42/C45
L36840-L2055-D670 Display LED Amber S35i/S45/ME45/C45
L36840-L2056-D670 Keyboard LED Amber S35i/S45/ME45/C45
Repair
L36880-Q5110-A10 RF Control Board A50
Documentation and Software
L36008-H5110-A1--7619 User Guide UG1 A50 english
L36008-H5110-A2--19 User Guide UG2 A50 german
L36008-H5110-A3--7219 User Guide UG3 A50 italian
For the updated list, please refer to the list in e-Commerce from time to time.
URL address: https://communication-market.siemens.de/so/welcome.lookup.asp
14
Page 16

Disassemble of the A50/1168
STEP 1:
Remove the battery cover by pushing in the direction as shown in PHOTO 2.0
PHOTO 2.0 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 1
STEP 2:
Remove the battery by releasing the catch and lifting the battery simultaneously as in Photo 2.1
PHOTO 2.1 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 1
15
Page 17

STEP 3:
Remove the front housing by pushing upwards to release the catch on both sides of the phone as
illustrated in PHOTO 2.2, 2.3 & 2.4
PHOTO 2.2 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 3 PHOTO 2.3 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 3
PHOTO 2.4 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 3
STEP 4:
Separate the Upper and Lower internal housing using the opening tool as shown in PHOTO 2.5 &
2.6
PHOTO 2.5 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 4 PHOTO 2.6 DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 4
16
Page 18

PHOTO 2.7DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 4 PHOTO 2.8DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 4
STEP 5:
Separate the Lower Internal housing, Upper Internal housing and the Control Board Assembly as
shown in PHOTO 2.9
PHOTO 2.9DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 5
STEP 6:
Separate the LCD and the Control Board Assembly by lifting the catches on the side, repeat the same
process on the reverse side as shown in PHOTO 2.10 & 2.11
PHOTO 2.10DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 6 PHOTO 2.11DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 6
17
Page 19

STEP 7:
Carefully lift up the display connector locking part to 45° and pull the display module away from
the connector to remove it as illustrated in PHOTO 2.12 & 2.13
PHOTO 2.12DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 6 PHOTO 2.13DISASSEMBLE A50– STEP 6
18
Page 20

Assemble the A50/1168
STEP 1:
Fit back the LCD and lock down the catch onto the PCB, place the control board on the Back
Internal Housing and place the keypad on the Front Internal Housing as illustrated in PHOTO
2.14.
PHOTO 2.14 Assembly A50– STEP 1
STEP 2:
Place the Front and Back Internal housing and lock down all the catches by the side of the as
illustrated in PHOTO 2.15
PHOTO 2.15 Assembly A50– STEP 2
19
Page 21

STEP 3:
Place the Assemble the External Front housing by pressing it down to the Internal housing as
shown in PHOTO 2.16 & 2.17
PHOTO 2.16 Assembly A50– STEP 3 PHOTO 2.17 Assembly A50– STEP 3
STEP 4:
Insert the SIM card fully into the phone as shown in the PHOTO 2.18 & 2.19
PHOTO 2.16 Assembly A50– STEP 3 PHOTO 2.17 Assembly A50– STEP 3
20
Page 22

STEP 5:
Slot in the battery at a 45° angle, so that the groove on the edge of the battery fits well into the
guiding groove on the back housing of the phone as illustrated in PHOTO 2.18 & 2.19
PHOTO 2.18 Assembly A50– STEP 5 PHOTO 2.19 Assembly A50– STEP 5
STEP 6:
Slide the External Back Housing onto the phone and lock it down in place. PHOTO 2.20
PHOTO 2.20 Assembly A50– STEP 6
All contact pins must not be dirty, damaged or
bent! ALL CATCHES MUST ENGAGE
COMPLETELY!
If any part is not O.K please replace it with a
new part.
21
Page 23

Mobile Software Programming
Due to this separation of common mobile software and customer specific initialization, it is
possible to fulfill the demands of the market requiring customization and flexibility.
As a consequence the software programming process in the LSO is divided into two different
steps as followed:
1. Software update to actual version and appropriate language group
2. Programming of CUSTOMER SPECIFIC INITIALIZATION
RS232 Port
FIGURE 2.24 C45 SERIES SOFTWARE PROGRAMMING SETUP
Mobile Software Updating
The software of the mobile, A50/1168, is loaded from a PC directly. Hardware interconnection
between the mobile and the PC is shown in Figure 2.24
Because of the new type of external connector used in X35 (Lumberg type) an additional adaptor
cable between mobile and boot adaptor is required if the “black boot adaptor” is used. Table 2.1
listed all the hardware requirements
If you use the battery dummy, make sure that the power supply voltage is correctly adjusted.
Description Part No.
Bootadapter 2000 incl. AC-Adapter, serial
L36880-N9241-A200
cable and mobile connection cable
IBM Compatible PC – Pentium -
TABLE 2.1 EQUIPMENT LIST FOR SOFTWARE PROGRAMMING.
22
Page 24

Languague Groups
There are over 20 languages for the A50/1168 series in total. These languages are divided into
groups as follows
Language groups K45 Languages Tegic Languages
LG 1 International
LG 2 Nordic English, German,
LG 3 Eastern Europe English, German, Czech,
LG 4 Mediterranean English, Turkish, Greek,
LG 5 Iberia English, German,
LG 6 South East Europe
LG 7 South East Asia English, German,
English, German,
French, Turkish, Dutch,
Italian, Arab
Danish, Norwegian
Swedish, Finnish
Polish, Slovak, Russian,
Hungarian
Hebrew, Russian,
Bulgarian, Arab
French, Spanish,
Portuguese, Catalan,
Braz.Port
English, German,
French, Italian, Slovene,
Croatian
French, Thai, Bahasa
Malaysia, Bahasa
Indonesian
English, German,
French, Turkish, Dutch,
Italian
English, German,
Danish, Norwegian,
Swedish, Finnish
English, German, Czech,
Polish
English, Turkish, Greek
English, German,
French, Spanish,
Portuguese
English, German,
French, Italian
English, German, French
LG 8 Asia English, Simpl. Chinese,
German (if enough
place)
LG 9 Taiwan English, Trad. Chinese,
German (if enough
place)
English, Simpl. Chinese,
German
English, Trad. Chinese,
German
This information is subject to change!
Contact your Service Manager for the order number of the right
version of mobile software for your market.
This executable file needs a definition or init file, named SWUP.INI
language preferences and the hardware communication port set up.
The content of this file consists of the following text:
, to define the message
23
Page 25

Language=English
COM=x
Where x is the number that corresponds to the serial port that is used, either 1, 2 or 3.
Plug in the Boot
Adaptor to the PC
and Mobile
Power up the
PC in DOS
environment
Software
upgrading in
progress
Connect the AC
adaptor to the
Boot Adaptor
Execute the
“Mobile S/W”
Error ?
Power up Boot
Adaptor &
Check LED
Error ?
No
Test Mobile
Ok ?
Check AC
Adaptor
Check
H/W setup =
Correct settings.
Take note of
error and repeat
process again
Feedback Error
to ICM CD ASC
END
Faulty AC
Adaptor
Faulty Boot
Adaptor
24
FLOWCHART 2.1 SOFTWARE PROGRAMMING. PROCESS
Page 26

Customer Specific Initialization
Refer to the Customization Guide
LSO has to make sure that after repair the
customer gets the mobile with correct variant
specific initialization.
For more information about the configuration
tool, refer to Service Information dated 30th April 1999, or
contact your Service Manager.
International Mobile Equipment Identity, IMEI
The mobile equipment is uniquely identified by the International Mobile Equipment Identity, IMEI,
which consists of 15 digits. Type approval granted to a type of mobile is allocated 6 digits. The
final assembly code is used to identify the final assembly plant and is assigned with 2 digits. 6
digits have been allocated for the equipment serial number for manufacturer and the last digit is
spare.
The part number for the A50 is S30880-S5110-Axxx where the last 4 letters specify the housing
and software variant.
A50 series IMEI label is accessible by removing the battery.
Re-use of IMEI label is possible by using a hair-dryer to remove the IMEI label.
On this IMEI label, Siemens has also includes the date code for production or service, which
conforms to the industrial standard DIN EN 60062. The date code comprises of 2 characters: first
character denotes the Year and the second character denotes the Month. Fr example, the IMEI
above show date code M3.
Year Date Code Month Date Code
1999 L December D
2000 M January 1
2001 N February 2
TABLE 2.3 DIN EN 60062 DATE CODE
25
Page 27

Phone Unblocking
When the phone is disable due to wrong entry of PHONECODE, it can be re-activated by
entering the right unblocking code. This unblocking code is derived from the IMEI number of the
mobile.
The unblocked code, also known as Master Phone Code, has to be entered in the following
format:
*#0003*--------#
The Master Phone Code can be obtained by:
1. Fax to Siemens Hotline in Germany
Siemens AG
ICP CD SH
World Service Center, Bocholt, Germany
+49-2871-91-3007
2. Fax to Siemens Hotline in Singapore
Siemens Pte Ltd
ICM MP CCQ ASC/ASP
Ms Ellis Siew
Tel: +65- 6845 4817
Fax:: +65-6842 6641
26
Page 28

3. Internet Solution
A password protected homepage where LSO can enter IMEI number of a disable phone. The
generated Master Code will then be presented for unblocking purpose. This service is offered to
all LSOs.
PHOTO 2.19 INTERNET PAGE
PHOTO 2.20 INTERNET PAGE: MASTER PHONE CODE
Contact your Service Manager for more information regarding setting
up of the INTERNET SOLUTION & its installation procedure,
27
Page 29

Ch
r
apte
Siemens Service Equipment
USER MANUAL
Introduction
Every LSO repairing Siemens handset must ensure that the quality standards are observed.
Siemens has developed an automatic testing system that will perform all necessary
measurements. This testing system is known as
Siemens Mobile Service Equipment
Using this system vastly simplifies the repair of the phones and will make sure that:
1. All possible faults are detected
2. Set which pass the test will be good enough to return to customer.
Starting from the P35 Series, Siemens will introduce a simpler and faster testing platform for
testing a repaired Siemens mobile phone. The testing platform are either base on R&S CMD
53/55, CMU200; CTS55 GSM test set.
There is also test software available for testing with the Wavetek 4201S, 4400 and the 4107 GSM
test set.
THE LSO WILL HAVE TO PURCHASE THE SYSTEM, CHOOSING BETWEEN
THE COMPLETE PACKAGE OR SUB-SET OF IT.
A FULLY AUTOMATIC TEST PROCEDURE IS ONLY
POSSIBLE IF THE COMPLETE SYSTEM IS
INSTALLED.
Make sure that your CTS firmware is Version 3.01 or higher. For CMD
it must be Version 4.03 and higher. Please check with the Service
Info SB_0500 for the CTS/CMD Hardware Options.
28
Page 30

R&S CMD55 Test Station
R&S CTS55 Test Station
29
Page 31

Wavetek 4201S / 4400 Test Station
Other equipment
One PC Windows NT 4 with a serial port to connect to the GSM test set through the PC serial
cable provided for the GSM test set.
One Test SIM card and a fully charged battery for used with the mobile phone model.
Additional RF connector will be needed for setup using Wavetek 4107 test set and Wavetek
Antenna Coupler.
For LSO Test Station setup base on the Wavetek 4107 test set, you need a TNC(male) to
SMA(female) connector. For the Wavetek Antenna Coupler, you need a TNC(female) to
SMA(female) connector. The part number for the connectors will be announced soon.
For Wavetek GSM test set For Wavetek Antenna Coupler
30
Page 32

Software Installation
Before executing the test software, it is important to ensure that the software configuration
matches that of the hardware set up. Each GSM Tester will have a specific test software. The
test software are name CMD_GO, CTS_GO; CMU_GO and for Wavetek test set, CAT4200/4400
respectively.
First, copy the installation software for the specific GSM tester to a temporary directory on the
harddisk of the Window PC and then Run the Setup from the first sub directory – Disk1 for
CMD_GO test software.
After the installation for the test software, RUN the Test software and check the configuration
setting for the Serial port.
31
Page 33

Configuring the test software
For each model of the P35 series mobile phone, Siemens will distribute the testing configuration
file for the specific test station. For testing the phone, just go to the File menu and select Load
Configuration.
32
Page 34

Running the test sequence
Make sure that your CTS firmware is Version 3.01 or higher. For
CMD 55 it must be Version 4.03 and higher. Please check with the
Service Info SB_0500 for the CTS/CMD Hardware Options.
Insert a Test SIM card and a fully charged battery into the Siemens mobile phone and place it
onto the phone holder on the Antenna Coupler. Switch the RF switch to INT ANT position and
select the Start button to run the test sequence in the configuration file.
Follow the instruction on the screen and switch on the phone. The mobile phone will start
Network Search and doing Location Update to the GSM test set through the off-air signal from
Antenna Coupler.
33
Page 35

Next, the GSM test set will initial a call to the mobile phone through the Antenna Coupler. Press
the Call key when the mobile phone ring, and the GSM test set will start Tx Power measurements
on the GSM and GSM1800 channel specified by the configuration setting.
Next, the GSM test set will end the call to the mobile phone and the screen will prompt for Dialing
from the mobile phone. At this test step, please move the mobile phone to the Antenna Cradle
and switch the RF switch to EXT ANT position. Once the mobile phone log to the GSM test set,
dial 1234 and the Send key.
34
Page 36

The GSM test set will make Tx Power measurements, Rx BER measurement, Echo Loop test on
the GSM and GSM1800 channel specified by the configuration setting. There will be a Echo Loop
Back test for checking the speech quality. Speak into the mobile phone when prompted and listen
the voice after appr. 1 second and check the speech quality. If not O.K, it may be microphone or
the earphone defective.
The last test is Disconnect Call from the mobile phone. Press the End Call key and the test
sequence will end.
35
Page 37

A measurement report screen will show up and a hardcopy can be printed if a printer is
connected to the PC. To close the measurement report screen, click the third button from the
left.
Once the mobile phone pass all the test steps, please make a check for all the key and the
display. After this we can confirm on the proper functioning of the mobile phone after repair and
return the phone back to the customer.
36
Page 38

ANNEX A
Test SIM card Information
For testing purposes, in combination with the Rohde & Schwarz GSM tester, CMD or CTS, it is
mandatory to use the enclosed test SIM card.
If you do not use this test SIM card, you will encounter difficulties in getting correct measurement
for the Bit Error Rate.
When the SIM card simulation is set to ‘1’ in the INI file, then this
test SIM card is not needed at all
There are two different PIN numbers stored in the SIM card. The PINs and
their respective Master-PIN are:
PIN 1 12 34
Master-PIN 1 76 54 32 10
PIN 2 56 78
Master-PIN 2 98 76 54 32
TABLE A.7 D25 TO D25 CONNECTION
37
Page 39

ANNEX B
Service Equipment List
All purchases of jigs, tools and test equipment must be order directly from Siemens Germany. Attach the
standard form with your purchase order and send it to ICM MP SL and ICM MP CCQ ASC/ASP.
For detail information, contact your Service Manager,
or download the valid from the internet “technical support”
1
Disclaimer: This content is subjected to change without notice.
Copyright ã 2002 Siemens Pte Ltd
ICM MP CCQ ASC/ASP,
164, Kallang Way, #04-22, Kolam Ayer Industrial Estate, Singapore 349248
Author: Lee Kian Meng.
Phone +65-68454806 • Fax +65-68426641
First Print: Sep, 02
Revised Print: N.A.
Date Print: 18 Sep 2002
The reproduction and transmission of this document to unauthorized parties is not permitted without
written authority. Offender will be liable for any damages that may arise directly or indirectly through the
misuse of the document.
38
 Loading...
Loading...