Page 1
Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
A35, A36
Level 2.5
Repair Documentation
V 1.0
V1.1 Page 1 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 2

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
Table of Contents:
1 INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................................... 3
2 BOTTOM CONNECTOR (LUMBERG) ..................................................................................................... 4
3 DISPLAY CONNECTOR ............................................................................................................................. 8
4 KEYBOARD LEDS ..................................................................................................................................... 12
5 DISPLAY LEDS ........................................................................................................................................... 15
6 CHARGING DIODE V201.......................................................................................................................... 18
7 BUFFER CAPACITOR C162 ..................................................................................................................... 23
8 DIPLEXER Z503 .......................................................................................................................................... 27
V1.1 Page 2 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 3

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
1 Introduction
A35/A36 product family, also referred to as A3x, consists of 2 different dualband handsets
(GSM-900 and GSM-1800), which can easily be distinguished from the second block of the
partnumber printed on the IMEI label. There is also an Asian variant of A35 named 1118. All
information below also applies to the Asian variant unless otherwise noted.
Partnumber on IMEI label:
1) A35/1118: S30880-S4350-Xxxx
2) A36: S30880-S4300-Xxxx
This manual is intended to help you carry out repairs on level 2.5, meaning limited
component repairs. Failure highlights are documented and should be repaired in the local
workshops.
It must be noted that all repairs have to be carried out in an environment set up according to
the ESD (Electrostatic Discharge Sensitive Devices) regulations defined in international
standards.
If you have any questions regarding the repair procedures or spare parts do not hesitate to
contact our technical support team in Kamp-Lintfort, Germany:
Tel.: +49 2842 95 4666
Fax: +49 2842 95 4302
e-mail: dominik.schnoor@klf.siemens.
V1.1 Page 3 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 4

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
2 Bottom Connector (Lumberg)
2.1 Affected Units
2.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
2.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
2.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
2.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3LUC
2.2 Fault Description
2.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Charging problems.
Problems with external loudspeaker or microphone
when using a car kit.
Problems with accessories connected at the bottom
connector.
Problems with SW booting.
2.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
This problem cannot be detected with a GSM-Tester.
2.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 4 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 5

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
2.4 Repair Documentation
2.4.1 Description of procedure:
2.4.1.1 Diagnosis
Visually check the bottom connector. Watch for dry joints!
2.4.1.2 Repair by component change
Use hot air blower remove defective bottom connector.
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!
Resolder new bottom connector afterwards.
2.4.1.3 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
2.4.1.4 Test
Retest handset after repair.
2.4.2 List of needed material
2.4.2.1 Components
Bottom Connector A35/A36/1188
Part-Number: L36334-Z93-C262
2.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Hot Air Blower
Soldering Iron
2.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
V1.1 Page 5 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 6
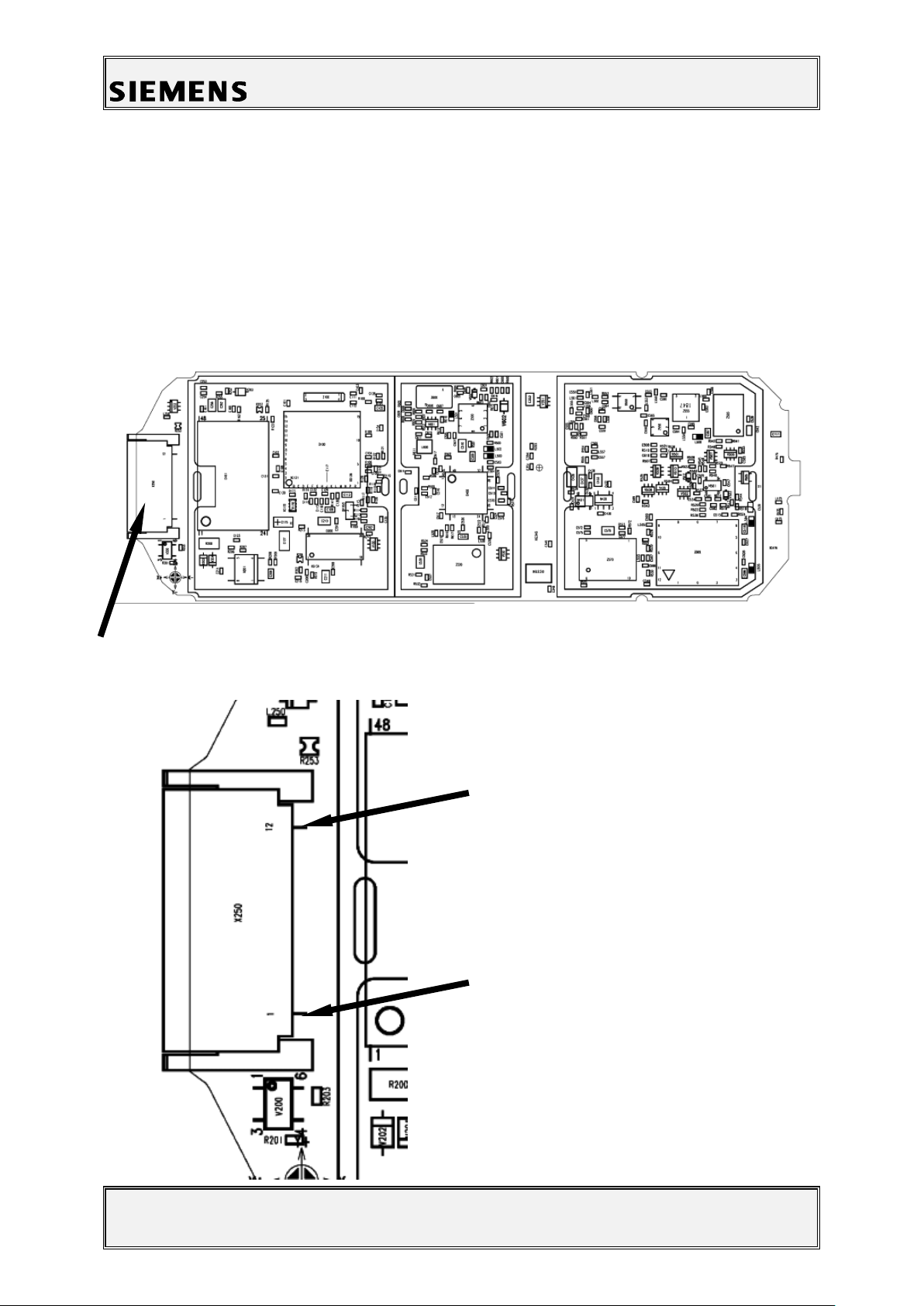
Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3x Board Bottom Connector Side
Figure 2: X35 Bottom Connector Placement (Top View)
Pin 12
Pin 1
Devices
2.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
2.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 6 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 7
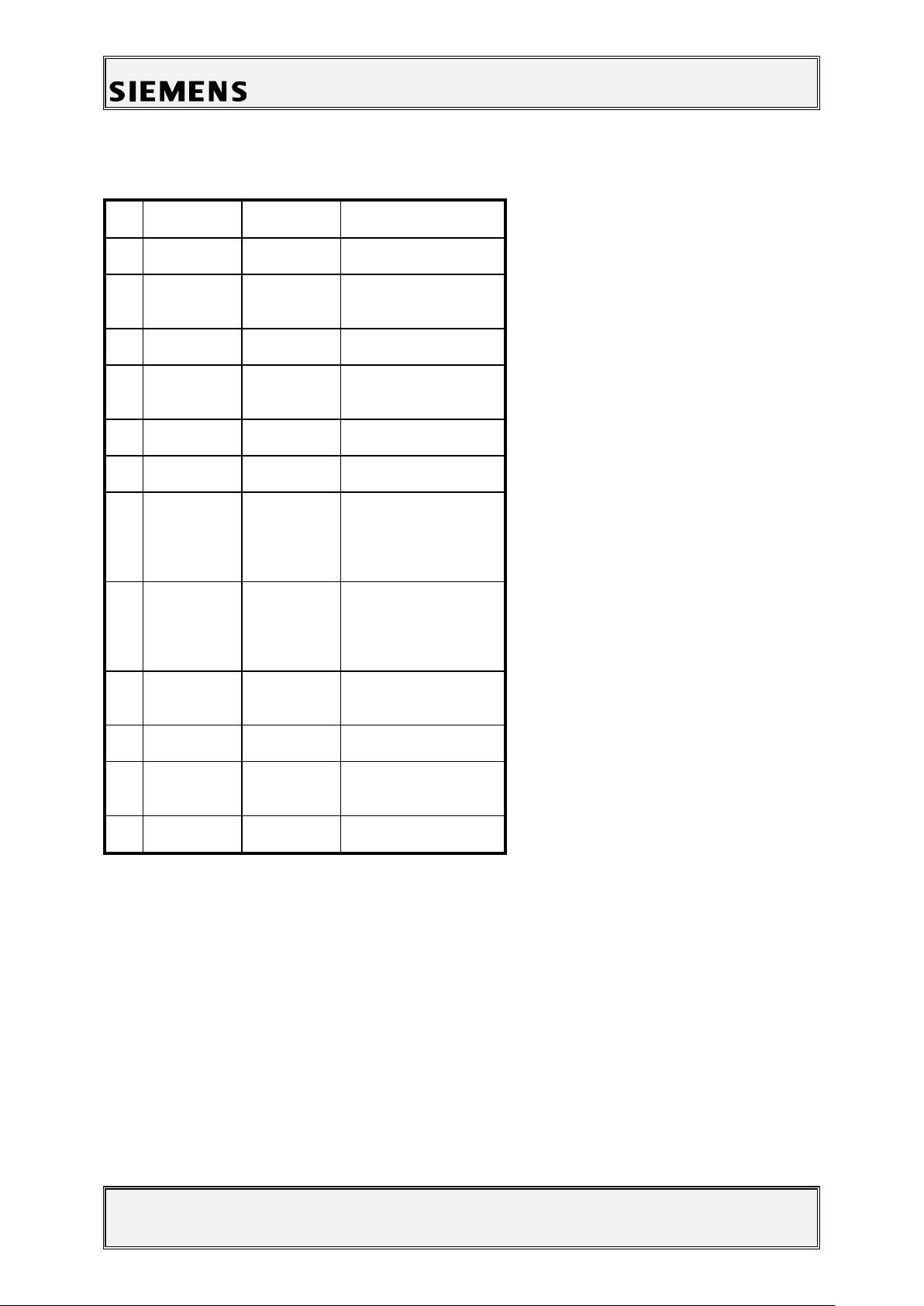
Information and Communication Mobile
Pin
Name
IN/OUT
Notes
1
GND
2
SB
I/O
Charger coding and
charger control.
3
POWER
I
Charging Current
4
FBatt+
O
Power supply for the
accessories.
5
TX O Serial interface
6
RX I Serial interface
7
ZUB_CLK
I/O
Clock line for
accessory bus
Use as DTC In data
operation
8
ZUB_DATA
I/O
Data line for
accessory bus.
Use as CTS in data
operation
9
GND_MIC
For external
microphone
10
HF_MIC
I
External microphone
11
AUDO
O
Trigger for external
loudspeaker
12
GNDA
For external
loudspeaker
Table 1: X35 Bottom Connector Pin Description
Devices
V1.1 Page 7 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 8

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
3 Display Connector
3.1 Affected Units
3.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
3.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
3.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
3.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3DIC
3.2 Fault Description
3.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Display problems, like missing lines or columns on the
LCD or display contrast problems.
3.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
Display test fails.
3.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 8 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 9

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
3.4 Repair Documentation
3.4.1 Description of procedure:
3.4.1.1 Diagnosis
Visually check the status of the display connector. Watch for oxidation
and dry solder joints.
Mechanically check the opening / closing mechanism.
3.4.1.2 Repair by component change
Use hot air to remove defective connector
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!!
Resolder new connector afterwards
3.4.1.3 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
3.4.1.4 Test
Retest handset after repair.
V1.1 Page 9 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 10

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
3.4.2 List of needed material
3.4.2.1 Components Display connector A3x:
Part-Number: L36195-Z26-C624
3.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Soldering Iron
Hot Air Blower
3.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
3.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
V1.1 Page 10 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 11

Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3x board display connector side
Figure 2: A3x display connector placement (Top View)
Devices
3.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 11 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 12

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
4 Keyboard LEDs
4.1 Affected Units
4.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
4.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
4.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
4.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3LED
4.2 Fault Description
4.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Keyboard Illumination not working.
4.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
This fault cannot be detected with a GSM-Tester
4.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 12 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 13

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
4.4 Repair Documentation
4.4.1 Description of procedure:
4.4.1.1 Diagnosis
Use the diode test function of a multimeter to check the status of the
diode.
The typical voltage drop on the diode is 1.7V when testing the diode
function with the multimeter.
4.4.1.2 Repair by component change
Use soldering iron to remove defective diode
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!
Resolder new diode afterwards.
4.4.1.3 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
4.4.1.4 Test
Retest handset after repair.
4.4.2 List of needed material
4.4.2.1 Components
LED keyboard A3x
Part-Number: L36820-L2031-D670
4.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Hot Air Blower
Soldering Iron
V1.1 Page 13 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 14

Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3x board keyboard LED Side
Figure 2: A3x keyboard LED placement (top view)
Devices
4.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
4.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
4.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 14 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 15

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
5 Display LEDs
5.1 Affected Units
5.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
5.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
5.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
5.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3LED
5.2 Fault Description
5.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Display Illumination not working.
5.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
This fault cannot be detected with a GSM-Tester
5.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 15 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 16

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
5.4 Repair Documentation
5.4.1 Description of procedure:
5.4.1.1 Diagnosis
Use the diode test function of a multimeter to check the status of the
diode.
The typical voltage drop on the diode is 1.7V when testing the diode
function with the multimeter.
5.4.1.2 Repair by component change
Use soldering iron to remove defective diode
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!
Resolder new diode afterwards.
5.4.1.3 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
5.4.1.4 Test
Retest handset after repair.
5.4.2 List of needed material
5.4.2.1 Components
Display LED A3x
Part-Number: L36840-L2051-D670
5.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Hot Air Blower
Soldering Iron
V1.1 Page 16 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 17

Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3x board display LED Side
Figure 2: A3x board display LED placement
Devices
5.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
5.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
5.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 17 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 18

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
6 Charging Diode V201
6.1 Affected Units
6.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
6.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
6.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
6.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3CHD
6.2 Fault Description
6.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Charging symbol in the display even if no charger is
connected.
Very low standby time and deeply discharged batteries.
6.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
This fault cannot be detected with a GSM-Tester.
6.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 18 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 19

Information and Communication Mobile
Charging
Voltage
input
V201
Devices
6.4 Repair Documentation
6.4.1 Description of procedure:
6.4.1.1 General Information
The purpose of the diode V201 is to prevent the feedback of the
battery voltage to the charging circuitry. That would make the
microprocessor detect a charging voltage which is not present in reality
causing
a) The charging symbol to appear on the display and/or
b) The battery to be drained constantly, even when the phone is
switched off.
The above circuit diagram extract shows the power supply IC including the charging circuitry.
The charging voltage coming from the bottom connector is called POWER and it is
connected to the charging circuitry and to the microporocessor as a signal called
EXT_POWER_UC. This signal is the charging voltage divided down by the two resistors
R204-1 and R204-2 and it is led to one of the microprocessor port pins. It indicates the
presence of the charger to the microprocessor triggering the display of the charging symbol.
V1.1 Page 19 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 20

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
If the diode V201 is defective it opens from pin 1 to pin 2, meaning it does not block the
battery voltage from going to the charging transistor V200 anymore. This FET has a
(unwanted) diode from pin 1,2,5,6 to pin 4 which opens and connects the battery voltage
with the POWER signal and therefore also with the EXT_POWER_UC signal. In this case
the charging symbol appears on the display. Sometimes, if the battery voltage is very low,
the charging symbol may not appear, but the constant current flow will discharge the battery
anyway, even when the phone is switched off.
This will of course significantly reduce the standby time and may even lead to a
deeply discharged battery!
6.4.1.2 Diagnosis
Check the status (reverse blocking) of the diode V201 with a
multimeter.
6.4.1.3 Repair by component change
Use soldering iron to remove defective diode.
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!!
Resolder new diode afterwards
6.4.1.4 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
V1.1 Page 20 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 21

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
6.4.1.5 Test
Retest handset after repair
6.4.2 List of needed material
6.4.2.1 Components Diode V201
Part-Number: L36840-D5028-D670
6.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Soldering Iron
Hot Air Blower
6.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
6.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
V1.1 Page 21 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 22

Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3x board V201 side
Figure 2: A3x V201 placement (Top View)
Devices
6.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 22 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 23

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
7 Buffer Capacitor C162
7.1 Affected Units
7.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
7.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
7.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
7.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3BUC
7.2 Fault Description
7.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Phone does not switch on.
7.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
This fault cannot be detected with a GSM-Tester.
7.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 23 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 24

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
7.4 Repair Documentation
7.4.1 Description of procedure:
7.4.1.1 General Information
The purpose of the 100µF capacitor C162 is to buffer the battery
voltage. This is especially necessary during the Tx burst, when a high
current is taken from the battery.
If the cap is defective it is most likely burned and may cause a short
from the battery to ground.
7.4.1.2 Diagnosis
Check the status of the capacitor with a multimeter.
7.4.1.3 Repair by component change
Use soldering iron to remove defective capacitor.
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!!
Watch the polarity of the capacitor!
Resolder new capacitor afterwards
7.4.1.4 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
7.4.1.5 Test
Retest handset after repair
7.4.2 List of needed material
7.4.2.1 Components Capacitor C162
Part-Number: L36384-F4107-M3
7.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Soldering Iron
Hot Air Blower
V1.1 Page 24 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 25

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
7.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
7.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
V1.1 Page 25 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 26

Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3x board C162 side
Figure 2: A3x C162 placement (Top View)
Devices
7.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 26 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 27

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
8 Diplexer Z503
8.1 Affected Units
8.1.1 Type: A35/A36/1188
8.1.2 Affected IMEIs / Date Codes: All / All
8.1.3 Affected SW-Versions: All
8.1.4 Fault Code for LSO reporting: 3DIP
8.2 Fault Description
8.2.1 Fault Symptoms for customers:
Handset cannot register with the GSM-900/1800
network.
8.2.2 Fault Symptom on GSM-Tester:
Handset Rx/Tx-Sensitivity is too low.
8.3 Priority:
........ Mandatory
........ Repair
........ Optional
........ Not Yet Defined
V1.1 Page 27 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 28

Information and Communication Mobile
Z503
Devices
8.4 Repair Documentation
8.4.1 Description of procedure:
8.4.1.1 General Information
The purpose of the diplexer is the following:
A) Switching the Rx RF signal coming from the antenna to either the
GSM-900 or GSM-1800 receiver chain.
B) Switching of the Tx RF signal from either the GSM-900 or GSM-
1800 Tx output to the antenna.
V1.1 Page 28 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 29

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
The above circuit diagram extract shows the diplexer IC including the external circuitry. The
diplexer switching direction is controlled by the four control inputs VC1 (pin 2), VC2 (4), VC3
(8), VC4 (10).
The input VC2 is used to switch the Rx_GSM-900 direction. If the diplexer is defective then
the diplexer cannot switch to this direction anymore. As a result of this the phone loses about
25-30 dB when receiving GSM-900 signals.
Important: There are two different types of diplexer used for A35/A36/1188. Only the
silver type produced by Murata, labeled with a small M is affected by the
problem described above.
There is also another type produced by TDK. This type has a golden housing
and a small hole in the upper right corner. This type is not affected. The
different types have a different external circuitry and are not interchangeable!
8.4.1.2 Diagnosis
Check the status of the diplexer Z503 with a multimeter. Measure the
resistance of pin 4 against ground. It must be around 20k Ohms. If the
diplexer is defective the measured value will be significantly lower, e.g.
2k Ohms. This value however may differ.
8.4.1.3 Repair by component change
Use hot air to remove defective diplexer.
Avoid excessive heat!
Watch surrounding components!!
Resolder new diplexer afterwards.
8.4.1.4 Repair by SW-Booting
Not possible!
8.4.1.5 Test
Retest handset after repair
8.4.2 List of needed material
V1.1 Page 29 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 30

Information and Communication Mobile
Devices
8.4.2.1 Components
Diplexer Z503 (same as C/M/S35 !! )
Part-Number: L36145-K280-Y137
8.4.2.2 Jigs and Tools
Soldering Iron
Hot Air Blower
8.4.2.3 Special Tools
None
8.4.2.4 Working materials
Desolder Wick / Braid
Solder
V1.1 Page 30 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
Page 31

Information and Communication Mobile
Figure 1: A3X Z503 side
Figure 2: A3X Z503 placement (Top View)
Z503
Devices
8.4.3 Drawings
V1.1 Page 31 of 31 ICM D CC ST
D. Schnoor
07/01
 Loading...
Loading...