Page 1

Drive Technology \ Drive Automation \ System Integration \ Services
Manual
Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B
EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Edition 05/2009 16798813 / EN
Page 2

SEW-EURODRIVE—Driving the world
Page 3

1 General Information ............................................................................................... 7
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
1.1 How to use the manual .......... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... ... ... .... ... .... 7
1.2 Structure of the safety notes .......................................................................... 7
1.3 Rights to claim under limited warranty........................................................... 8
1.4 Exclusion of liability........................................................................................ 8
1.5 Copyright notice............................................................................................. 8
2 Safety Notes ......................... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ........................... 9
2.1 Other applicable documentation .................................................................... 9
2.2 General safety notes for bus systems............................................................ 9
2.3 Safety functions ............... ... ... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ... ........... 9
2.4 Hoist applications....................................................................... ... ... ... .... ... .... 9
2.5 Product names and trademarks.......................................................... .... ....... 9
2.6 Waste disposal............................................................................................. 10
3 Introduction .......................................................................................................... 11
3.1 Content of the manual......................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... .. 11
3.2 Characteristics ............................................................................................. 11
3.2.1 Process data exchange .................................................................... 11
3.2.2 Parameter access ............................................................................. 11
3.2.3 Monitoring functions .......................................................................... 12
4 Assembly and Installation Instructions ............................................................. 13
4.1 Installation options of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway................................... 13
4.2 Voltage supply ............................................................................................. 14
4.2.1 Voltage supply in the MOVIAXIS
4.2.2 Voltage supply in the UOH21B gateway housing ............................. 16
4.3 Connecting inverters and engineering-PC................................................... 17
4.3.1 Functional description of the terminals, DIP switches
and LED of the UFR41B option ........................................................ 17
4.3.2 Connecting CAN 1 system bus (X33 connector)/ CAN 2
(X32 connector) ................................................................................ 18
4.3.3 Connecting SBUSplus system bus (terminal X36) ............................ 22
4.3.4 Ethernet interface terminal (terminal X37) ........................................ 22
4.4 Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway .............................................. 23
4.5 DIP switch S1 default IP address................................................................. 24
4.6 SD memory card type OMG4.B ................................................................... 24
4.7 Connecting the UFR41B fieldbus gateway to an Ethernet network ............. 25
4.8 Pin assignment X30-1, X30-2 and X37........................................................ 25
4.9 Shielding and routing bus cables................................................................. 26
4.10 The integrated Ethernet switch .................................................................... 27
4.11 Setting the DIP switches ..................... ... .... ... ... ... ....................................... .. 28
4.12 Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway .............................................. 29
4.12.1 Status LED in EtherNet/IP and Modbus/TCP operation ................... 29
4.12.2 Status LED in PROFINET operation ................................................ 30
4.12.3 Link / Activity LEDs .......................................................................... 31
4.13 TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks......................................................... 32
4.14 Setting the IP address parameters............................................................... 34
4.15 Procedure for repla cin g the un it....................................................... ... ......... 36
®
master module ........................... 14
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP , Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
3
Page 4

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5 Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter................................. 37
5.1 Description of the gateway functions ........................................................... 37
5.1.1 Introduction ....................................................................................... 37
5.1.2 Autosetup .......................................................................................... 37
5.1.3 Customized configuration ................................................................. 39
5.1.4 Configuring fieldbus gateway and slave units ................................... 40
5.1.5 Data backup ...................................................................................... 42
5.2 Startup procedure ........................................................................................ 45
5.2.1 Checking hardware installation and communication settings ........... 45
5.2.2 Establishing an engineering connection ........................................... 45
5.2.3 Configuring the fieldbus gateways .................................................... 47
5.2.4 Last settings in the slave units .......................................................... 48
5.2.5 Monitoring and controlling process data ........................................... 50
5.2.6 Saving inverter data in the fieldbus gateway
and using MOVITOOLS
5.2.7 Error processing and status messages ............................................. 55
6 Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP).......................................................... .. 58
6.1 Validity of the EDS file for UFR41B.............................................................. 58
6.2 Configuring the master (EtherNet/IP scanner)............................................. 59
6.3 Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000 . ...................................... .... ... .. 62
6.3.1 UFR41B fieldbus gateway with 16 PD data exchange ..................... 62
6.3.2 Access to UFR41B fieldbus gateway parameters ............................. 64
6.3.3 Access to unit parameters of lower-level units .................................. 67
®
MotionStudio ............................................ 53
7 Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP) .................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... .. 70
7.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 70
7.2 Process data exchange ............................................................................... 70
7.3 CIP object directory...................................................................................... 71
7.4 Return codes of the parameterization via explicit messages....................... 84
8 Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP) ....... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .. 88
8.1 Unit description file for Modbus/TCP............................................................ 88
8.2 Configuring the master (Modbus scanner)................................................... 88
8.3 Project planning examples in PL7 PRO....................................................... 91
8.3.1 UFR41B fieldbus gateway with 16 PD data exchange ..................... 91
8.4 Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP............................................ 92
8.4.1 Writing and reading process data ..................................................... 93
8.4.2 Parameter access ............................................................................. 95
9 Modbus Protocol (Modbus/TCP)......................................................................... 97
9.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 97
9.1.1 Mapping and addressing .................................................................. 97
9.1.2 Services (function codes) .................................................................. 98
9.1.3 Access .............................................................................................. 98
9.2 Protocol structure......................................................................................... 99
9.2.1 Header .............................................................................................. 99
9.2.2 Service FC3 - Read Holding Registers ........................................... 100
9.2.3 Service FC16 - Write Multiple Registers ......................................... 101
9.2.4 Service FC23 - Read/Write Multiple Registers ............................... 102
9.2.5 Service FC43 - Read Device Identification ..................................... 103
4
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 5

9.3 Connection management........................................................................... 104
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9.3.1 Sending process output data (requesting controlling connection) .. 104
9.3.2 Disconnecting connections ............................................................. 105
9.3.3 Timeout monitoring ......................................................................... 105
9.4 Parameter access via Modbus/TCP. ....................................... ... ... ... ... ....... 106
9.4.1 Procedure with FC16 and FC3 ....................................................... 106
9.4.2 Procedure with FC23 ...................................................................... 106
9.4.3 Protocol structure ............................................................................ 107
9.4.4 MOVILINK
9.5 Error codes (exception codes) ................................................................... 109
10 Configuring PROFINET IO....................................................... .......................... 110
10.1 Configuring PROFINET IO co nt ro ller.................................................. .... ... 110
10.1.1 Installing the GSD file .................................................................... 110
10.1.2 Assigning a PROFINET device name ............................................ 111
10.2 Configuring PROFINET connection for UFR41B fieldbus gateway ........... 113
10.2.1 Creating a new project ................................................................... 113
10.2.2 Configuring a station ...................................................................... 115
10.3 PROFINET configuratio n with top ology detection...................................... 117
10.3.1 Introduction .................................................................................... 117
10.3.2 Configuring the PROFINET topology ............................................. 118
10.3.3 Changing the port properties ......................................................... 120
10.3.4 Topology diagnostics ..................................................................... 122
10.3.5 Port statistics .................................................................................. 123
10.4 PROFINET diagnostic alarm s.................................................... ................ 125
10.4.1 Activating diagnostic alarms ........................................................... 125
10.4.2 Determining the cause of an error .................................................. 126
®
parameter channel ...................................................... 108
11 Operating Characteristics (PROFINET IO)....................................................... 127
11.1 Process data exchange with the UFR41B fieldbus gateway...................... 127
11.2 Parameterization via PROFIdrive dataset 47............................................. 129
11.2.1 PROFINET data records ................................................................ 129
11.2.2 Structure of the \PROFINET parameter channel ........................... 132
11.2.3 Parameterization procedure via data set 47 .................................. 133
11.2.4 Processing sequence for controller ................................................ 134
11.2.5 Addressing connected inverters ..................................................... 135
11.2.6 MOVILINK
11.2.7 PROFIdrive parameter orders ........................................................ 141
11.2.8 Example program for SIMATIC S7 ................................................. 146
12 Operating MOVITOOLS
12.1 About MOVITOOLS
12.1.1 Tasks ............................................................................................. 148
12.1.2 Establishing communication with units ........................................... 148
12.1.3 Executing functions with the units .................................................. 148
12.2 First steps .................................................................................................. 149
12.2.1 Starting the software and creating a project ................................... 149
12.2.2 Establishing communication and scanning the network ................. 149
12.3 Communication mode................................................................................ 150
12.3.1 Overview ........................................................................................ 150
12.3.2 Selecting communication mode (online or offline) ......................... 151
®
parameter requests .................................................... 136
®
MotionStudio............... ...................................... .... ... 148
®
MotionStudio ................................. ... .... ................... 148
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP , Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
5
Page 6

Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
12.4 Communication via USB (direct)................................................................ 152
12.4.1 Connect the unit with the PC using USB connection cables .......... 152
12.4.2 Installing the drivers ....................................................................... 153
12.4.3 Configuring USB communication ................................................... 153
12.4.4 USB communication parameters ................................................... 155
12.5 Communication via Ethernet...................................................................... 156
12.5.1 Connecting the unit with the PC via Ethernet ................................. 156
12.5.2 Address Editor ............................................................................... 156
12.5.3 Configuring the communication channel via Ethernet .................... 160
12.5.4 Setting communication parameters for SMLP ................................ 161
12.6 Executing function s with the units.......... .... ... ... ... ... .................................... 163
12.6.1 Parameterizing units in the parameter tree .................................... 163
12.6.2 Reading/changing unit parameters ................................................ 163
12.6.3 Starting up the units (online) .......................................................... 164
12.7 Special configura tion an d dia g no stic s tool s ..................... ... .... ................... 164
13 Error Diagnostics............................................................................................... 165
13.1 Error messages of the fieldbus gateway.................................................... 165
13.1.1 General errors of the fieldbus gateway .......................................... 166
13.1.2 Error during process data processing ............................................ 167
13.1.3 Error during unit replacement ......................................................... 168
13.2 Diagnostic procedure for operation on EtherNet/IP and Modbus/TCP ...... 169
13.3 Diagnostic procedure for operation on PROFINET IO............................... 170
13.3.1 Diagnostic problem: The UFR41B fieldbus gateway
does not operate on PROFINET IO ................................................ 171
14 Technical Data.................................................................................................... 172
14.1 General technical data............................................................................... 172
14.2 UFR41B fieldbus gateway.......................................................................... 173
14.3 Dimension drawings................................................................................... 174
14.3.1 Dimension drawing fieldbus gateway UFR41B / UOH21B ............. 174
14.3.2 Dimension drawing MOVIAXIS
15 Appendix............................................................................................................. 176
15.1 Parameter access to lower-level units via EtherNet/IP.............................. 176
15.2 Parameter access to lower-level units via Modbus/TCP or PROFINET .... 177
15.3 Parameter access to lower-level units via engineering interface............... 178
16 Index.................................................................................................................... 179
®
master module MXM / UFR41B . 175
6
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 7
General Information
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
How to use the manual
1
1 General Information
Manual
1.1 How to use the manual
The manual is part of the product and contains important information on operation and
service. The manual is written for all employees who assemble, install, startup, and
service the product.
The manual must be accessible and legible. Make sure that persons responsible for the
system and its operation, as well as persons who work independently on the unit, have
read through the manual carefully and understood it. If you are unclear about any of the
information in this documentation, or if you require further information, contact SEWEURODRIVE.
1.2 Structure of the safety notes
The safety notes in this manual are structured as follows:
Pictogram SIGNAL WORD
Type and source of danger.
Possible consequence(s) if the safety notes are disregarded.
• Measure(s) to prevent the danger.
Pictogram Signal word Meaning Consequences if
disregarded
Example:
General danger
Specific danger,
e.g. electric shock
DANGER Imminent danger Severe or fatal injuries
WARNING Possible dangerous situation Severe or fatal injuries
CAUTION Possible dangerous situation Minor injuries
NOTICE Possible damage to property Damage to the drive system or its environ-
ment
TIP Useful information or tip.
Simplifies the handling of the
drive system.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
7
Page 8

1
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
General Information
Rights to claim under limited warranty
1.3 Rights to claim under limited warranty
A requirement of fault-free operation and fulfillment of any rights to claim under limited
warranty is that you adhere to the information in the manual. Therefore, read the manual
before you start operating the device.
1.4 Exclusion of liability
You must comply with the information in the manual and the documentation of the units
connected to the fieldbus gateway to ensure safe operation and to achieve the specified
product characteristics and performance features. SEW-EURODRIVE assumes no
liability for injury to persons or damage to equipment or property resulting from nonobservance of the operating instructions. In such cases, any liability for defects is
excluded.
1.5 Copyright notice
© 2008 - SEW-EURODRIVE. All rights reserved.
Copyright law prohibits the unauthorized duplication, modification, distribution, and use
of this document, in whole or in part.
8
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 9

Other applicable documentation
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2 Safety Notes
2.1 Other applicable documentation
• Installation and startup may be carried out only by trained personnel observing the
relevant accident prevention regulations and the following documents:
– "MOVIDRIVE
– "MOVITRAC
– "MOVIAXIS
• Read through these documents carefully before you commence installation and
startup of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway.
• As a prerequisite to fault-free operation and fulfillment of warranty claims, you must
adhere to the information in the documentation.
2.2 General safety notes for bus systems
This communication system lets you adjust inverters and servo inverters to a variety of
different applications. As with all bus systems, there is a danger of invisible, external (as
far as the inverter is concerned) modifications to the parameters which give rise to
changes in the unit behavior. This may result in unexpected (not uncontrolled) system
behavior.
®
MDX60B/61B" operating instructions
®
B" operating instructions
®
" operating instructions
Safety Notes
2
2.3 Safety functions
The inverters and servo drives are not allowed to perform any safety functions unless
they are subordinate to other safety systems. Use higher-level safety systems to ensure
protection of equipment and personnel.
For safety applications, ensure that the information in the following publications is
observed: "Safe Disconnection for MOVIDRIVE
2.4 Hoist applications
MOVIDRIVE® MDX60B/61B, MOVITRAC® B and MOVIAXIS® must not be used as a
safety device in hoist applications.
Use monitoring systems or mechanical protection devices as safety equipment to avoid
possible damage to property or injury to people.
2.5 Product names and trademarks
The brands and product names contained within this manual are trademarks or
registered trademarks of the titleholders.
®
B / MOVITRAC® B / MOVIAXIS®".
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
9
Page 10

2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
2.6 Waste disposal
Safety Notes
Waste disposal
Observe the applicable national regulations.
Dispose of the following materials separately in accordance with the country-specific
regulations in force, as:
• Electronics scrap
• Plastic
• Sheet metal
• Copper
10
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 11

3 Introduction
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.1 Content of the manual
This user manual describes how to:
• Connect the UFR41B fieldbus gateway to MOVIDRIVE
and to the MOVIAXIS
• Startup MOVIDRIVE
• Startup the fieldbus gateway UFR41B on the fieldbus system EtherNet/IP,
Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO.
• Configure the EtherNet/IP master with EDS files.
• Configure the Modbus/TCP master.
• Configure the PROFINET IO master using GSD files.
3.2 Characteristics
Introduction
Content of the manual
®
®
servo inverter.
®
B, MOVITRAC® B and MOVIAXIS® for gateway operation.
B, MOVITRAC® B inverters
3
The powerful, universal fieldbus interfaces of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway enable you
to use the option to connect to higher-level automation systems via EtherNet/IP,
Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO.
3.2.1 Process data exchange
The UFR41B fieldbus gateway allows for digital access to most parameters and
functions via EthernetNet/IP, Modbus/TCP, and PROFINET IO interfaces. Control is
performed via fast, cyclic process data. Via this process data channel, you can enter
setpoints and trigger various control functions, such as enable, normal stop, rapid stop,
etc. At the same time you can also use this channel to read back actual values, such as
actual speed, current, unit status, error number or reference signals.
3.2.2 Parameter access
In EtherNet/IP operation, the parameters of the inverter are set solely via explicit
messages.
In Modbus/TCP operation, the controller can access the parameters via the 8 byte
MOVILINK
In PROFINET operation, two parameter access options are available:
• The PROFIDRIVE data record 47 offers access to all unit information also in
PROFINET operation
• The parameter mechanism offers universal access to any unit information
®
parameter channel.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
11
Page 12

3
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
3.2.3 Monitoring functions
Introduction
Characteristics
Using a fieldbus system requires additional monitoring functions, for example, time
monitoring of the fieldbus (fieldbus timeout) or rapid stop concepts. You can determine,
for instance, which fault responses should be triggered in the event of a bus error. The
parameters for the fault response can be set in the servo inverter / inverter. A rapid stop
is useful for many applications. This is why the fieldbus gateway will stop the lower-level
drives in the event of a fieldbus timeout. As the range of functions for the control terminals is also guaranteed in fieldbus mode, you can continue to implement rapid stop
concepts using the servo inverters/inverters connected to the fieldbus gateway.
12
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 13
Assembly and Installation Instructions
EURODRIVE
X26
1
23456
7
X24
H1
H2
MOVIAXIS
MOVIAXIS®MXM UFR41B/ UOH21B
UFR41B
2
2
0
1
X35
X36
X30-1
X30-2
X37
XM
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
X32X33
S1
342
1
L14
L13
T1
L5
L4
L3
L2
L1
ON
1
2
3
X38
L12
L11
UFR41B
2
2
0
1
X35
X36
X30-1
X30-2
X37
XM
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
X32X33
S1
342
1
L14
L13
T1
L5
L4
L3
L2
L1
ON
1
2
3
X38
L12
L11
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Installation options of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
4 Assembly and Installation Instructions
4
This chapter contains information on the assembly and installation of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway in a MOVIAXIS
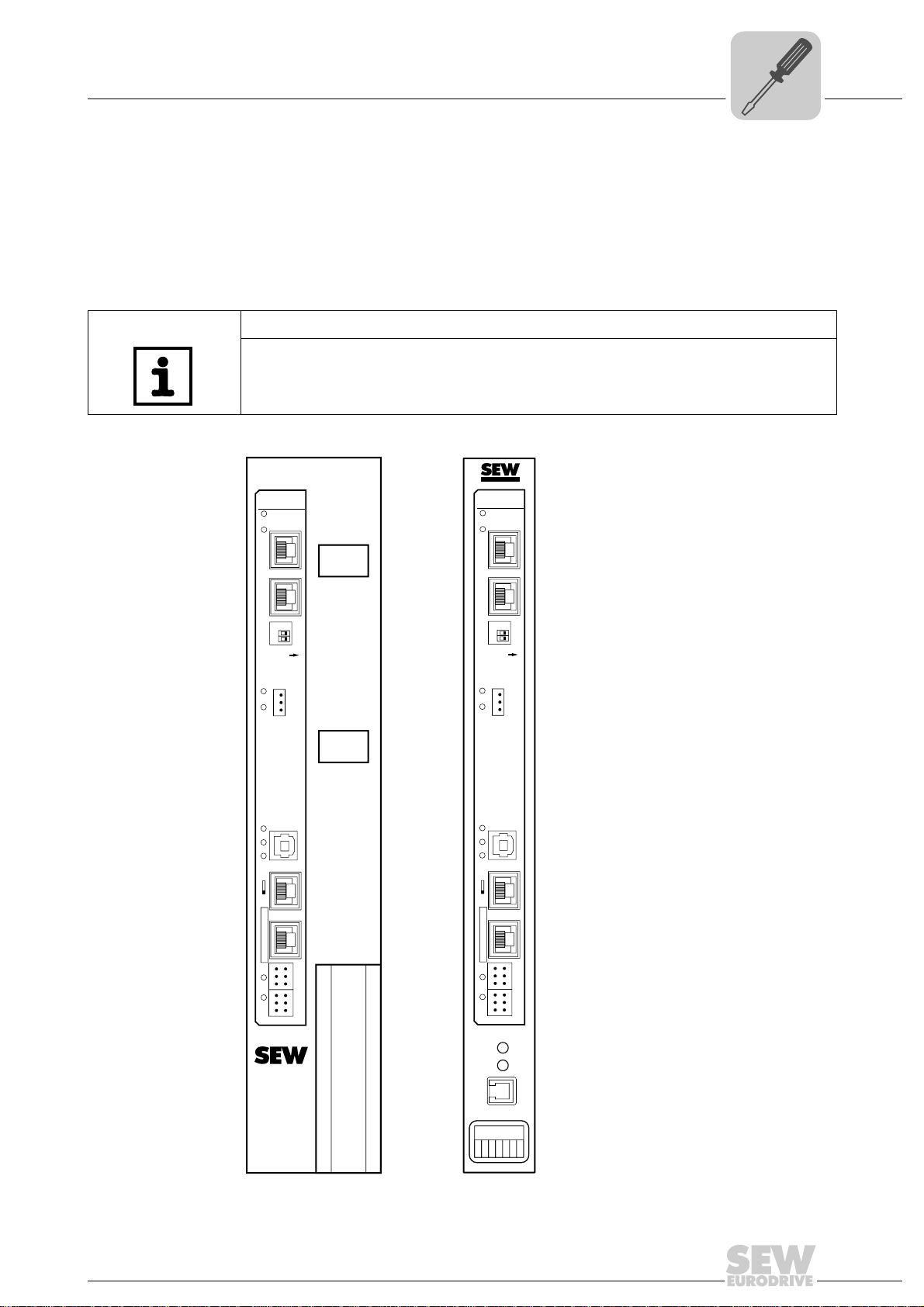
4.1 Installation options of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
Observe the following installation instructions:
TIP
Only SEW-EURODRIVE is allowed to install/remove the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
into/from a MOVIAXIS
®
master module MXM or in an UOH21B gateway housing.
®
master module MXM and an UOH21B gateway housing.
65055AXX
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
13
Page 14
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
4.2 Voltage supply
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Voltage supply
Voltage supply, system bus and fieldbus interfaces as well as the engineering interface
are located at different potential levels (see chapter 13.1).
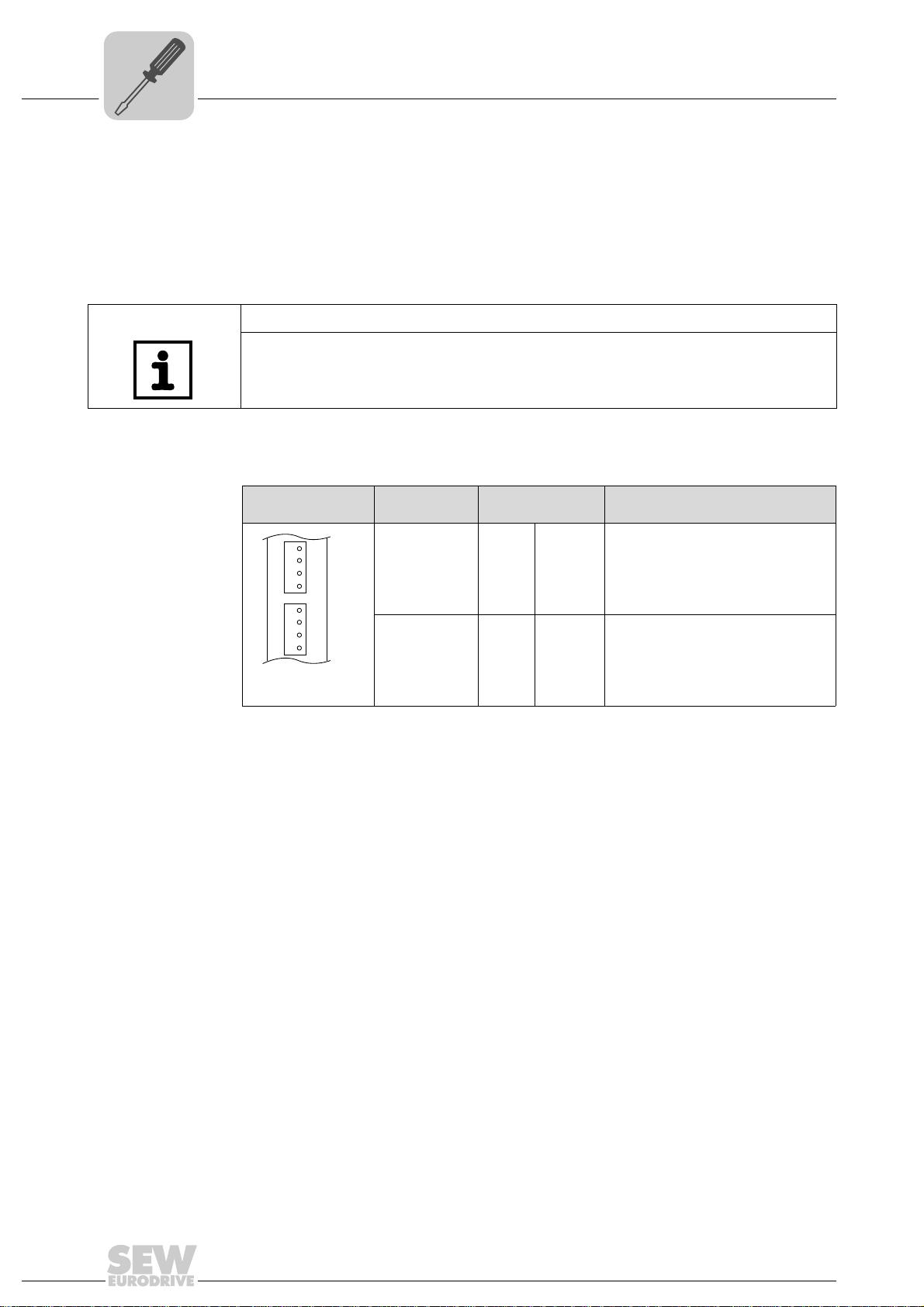
4.2.1 Voltage supply in the MOVIAXIS
®
master module
TIP
The MOVIAXIS® master module MXM provides additional connections, which are
described in the following section.
Functional description of the terminals, X5a/X5b (MOVIAXIS
MOVIAXIS® master
module MXM
1
X5b
2
3
4
1
X5a
2
3
4
59233AXX
• The X5a and X5b connectors are connected in parallel. In this way, the voltage
supply of the MOVIAXIS
from below to X5a. With connection to X5a, further modules can be connected via
X5b (e.g. supply module, axis module). The voltage supply for the brake (X5a/b:3, 4)
is fed through the MOVIAXIS
• The UFR41B fieldbus gateway can be supplied from the MOVIAXIS
power supply (MXS) or from an external voltage source. To do so, connect X5
between the individual units.
• If the UFR41B fieldbus gateway is connected with DC 24 V from the MOVIAXIS
switched-mode power supply, the functioning of the option is maintained after disconnection from the power supply. This is the case if the DC link voltage is maintained or an external DC 24 V supply is present from the MOVIAXIS
power supply.
Designation Terminal Function
X5b connector X5b:1
X5a connector X5a:1
®
X5b:2
X5b:3
X5b:4
X5a:2
X5a:3
X5a:4
master module can be provided from the right to X5b or
®
master module.
®
master module)
DC 24 V
DGND
DC 24 V
BGND
DC 24 V
DGND
DC 24 V
BGND
Voltage supply for control electronics
E
Reference potential for control
electronics
B
Voltage supply for brake
Reference potential for brake
connection
Voltage supply for control electronics
E
Reference potential for control
electronics
B
Voltage supply for brake
Reference potential for brake
connection
®
switched-mode
®
switched-mode
®
14
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 15
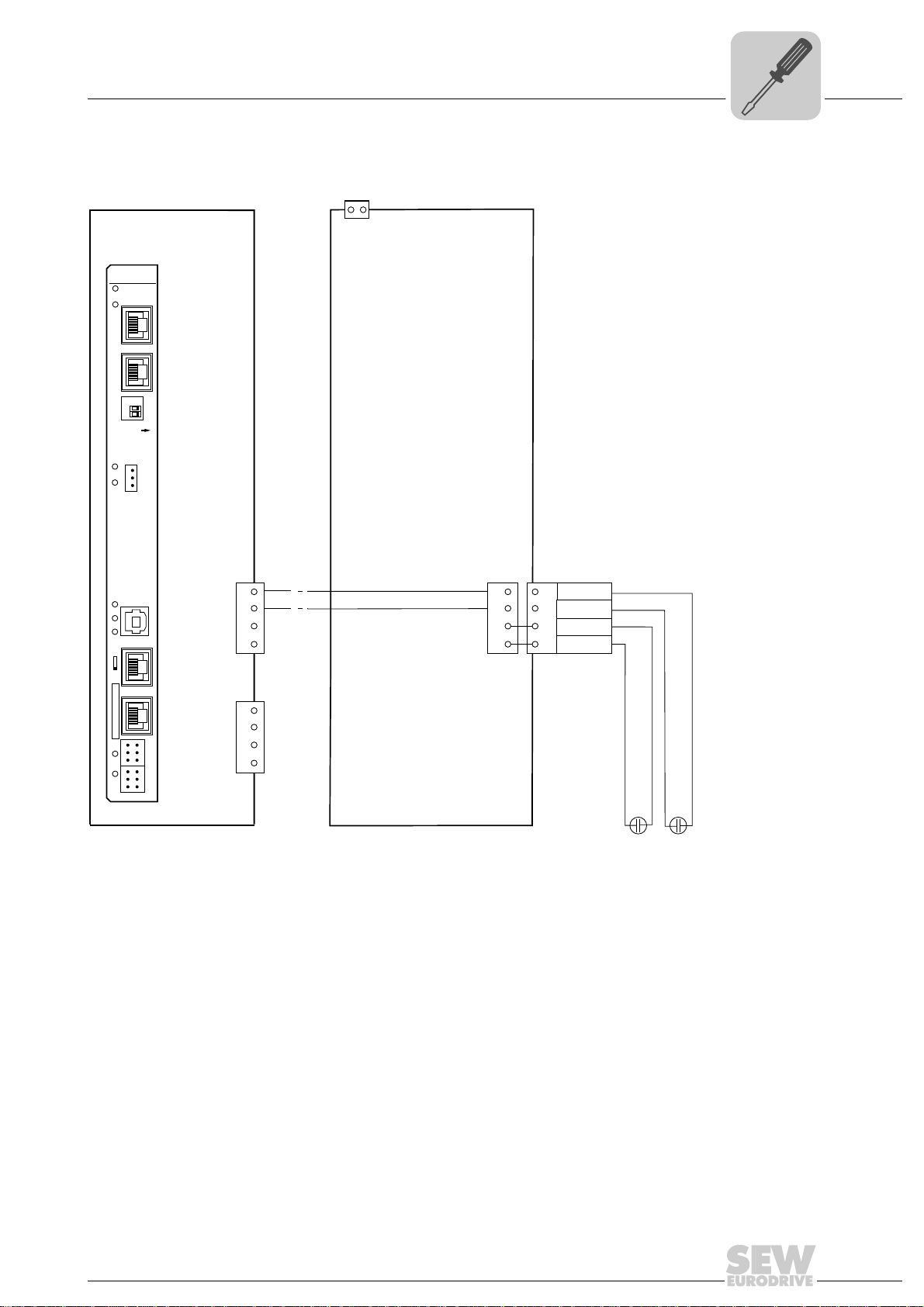
Wiring diagram
MOVIAXIS®
master module MXM
2
X5b
1
DC 24V
E
DGND
3
DC 24V
B
4 BGND
DC 24 V for
brake supply
DC 24 V supply
for control electronics
+-+-
X16
-
+
DC 24 V external
X5a
2
1
3
4
X5a
2
1
3
4
X5b
2
1
3
4
MOVIAXIS®
switched-mode
power supply MXS
UFR41B
2
2
0
1
X35
X36
X30-1
X30-2
X37
XM
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
X32X33
S1
342
1
L14
L13
T1
L5
L4
L3
L2
L1
ON
1
2
3
X38
L12
L11
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Voltage supply
4
65056AEN
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
15
Page 16
4
X24
H1
H2
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Voltage supply
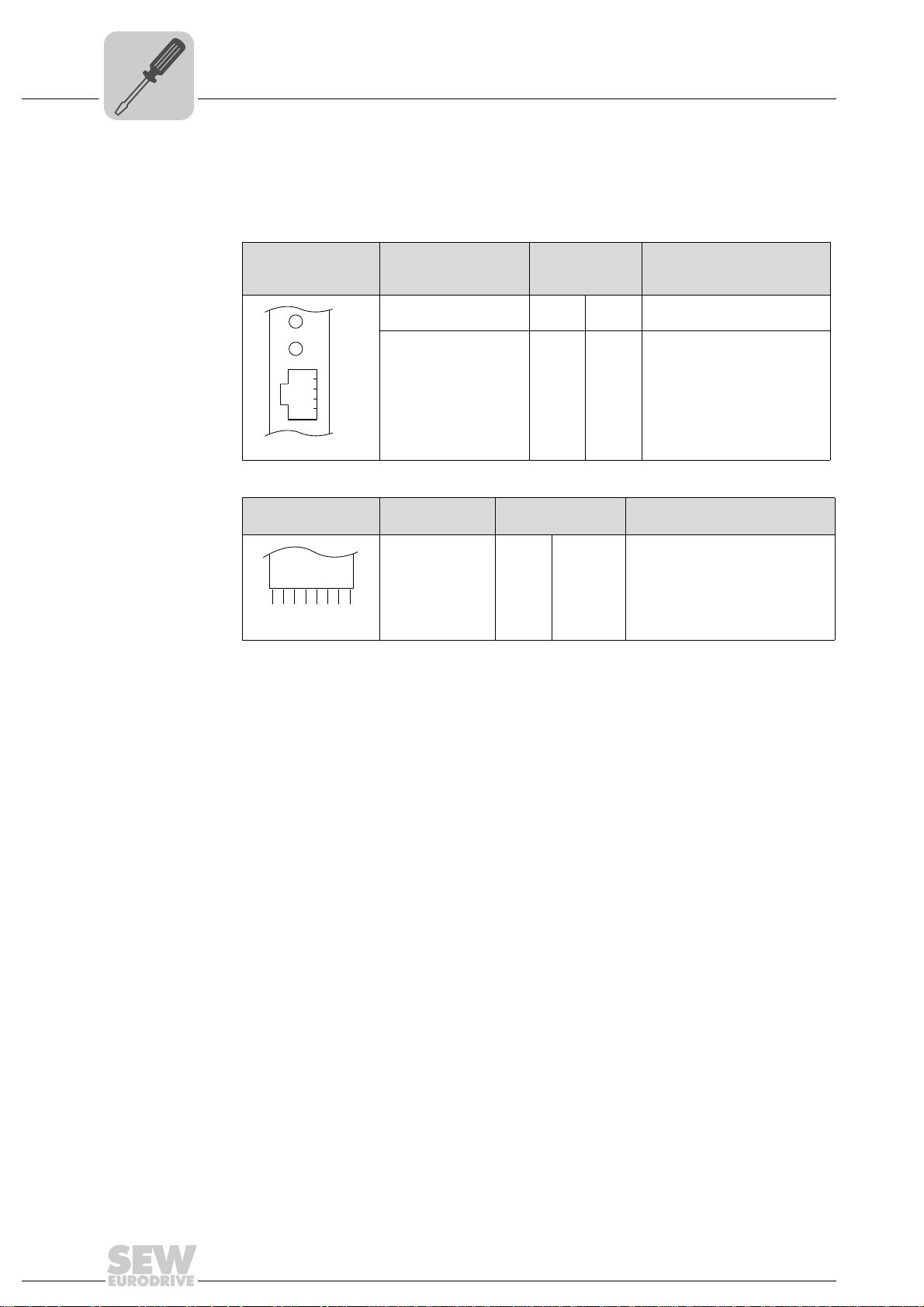
4.2.2 Voltage supply in the UOH21B gateway housing
Description of the terminals and LED functions
Front view
MOVITRAC
compact controller
Side view
Compact controller
X26
2345671
®
B /
58905AXX
58906AXX
X26:1
X24:2
X24:3
X24:4
X26:5
X26:6
X26:7
LED
Terminal
H2
X24:4
X24:3
X24:2
X24:1
CAN1H
CAN1L
DGND
Reserved
Reserved
DGND
DC 24 V
Function
Reserved
Reserved
No function.
Engineering cannot be
performed using X24.
System bus CAN 1 high
System bus CAN 1 low
Reference potential control/CAN1
-
Reference potential for UFx41B
Voltage supply for controller
Designation
LED H1
X24 connector:
RJ10 socket
Designation Terminal Function
X26 connector:
CAN 1 and
voltage supply
(plug-in terminal)
Connection of CAN 1 system bus / voltage supply (X26 connector)
The connections for CAN 1 (X26:1/2/3 and connector X33) are connected in parallel.
The UFR41B fieldbus gateway is supplied with voltage in the UOH21B gateway housing
via X26:6/7.
16
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 17
Assembly and Installation Instructions
UFF41B
X35
X36
X37
Version
1
2
3
1
342
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
X32X33
S1
L1 L2 L3L5
XM
L4
T1
UFR41B
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
4.3 Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
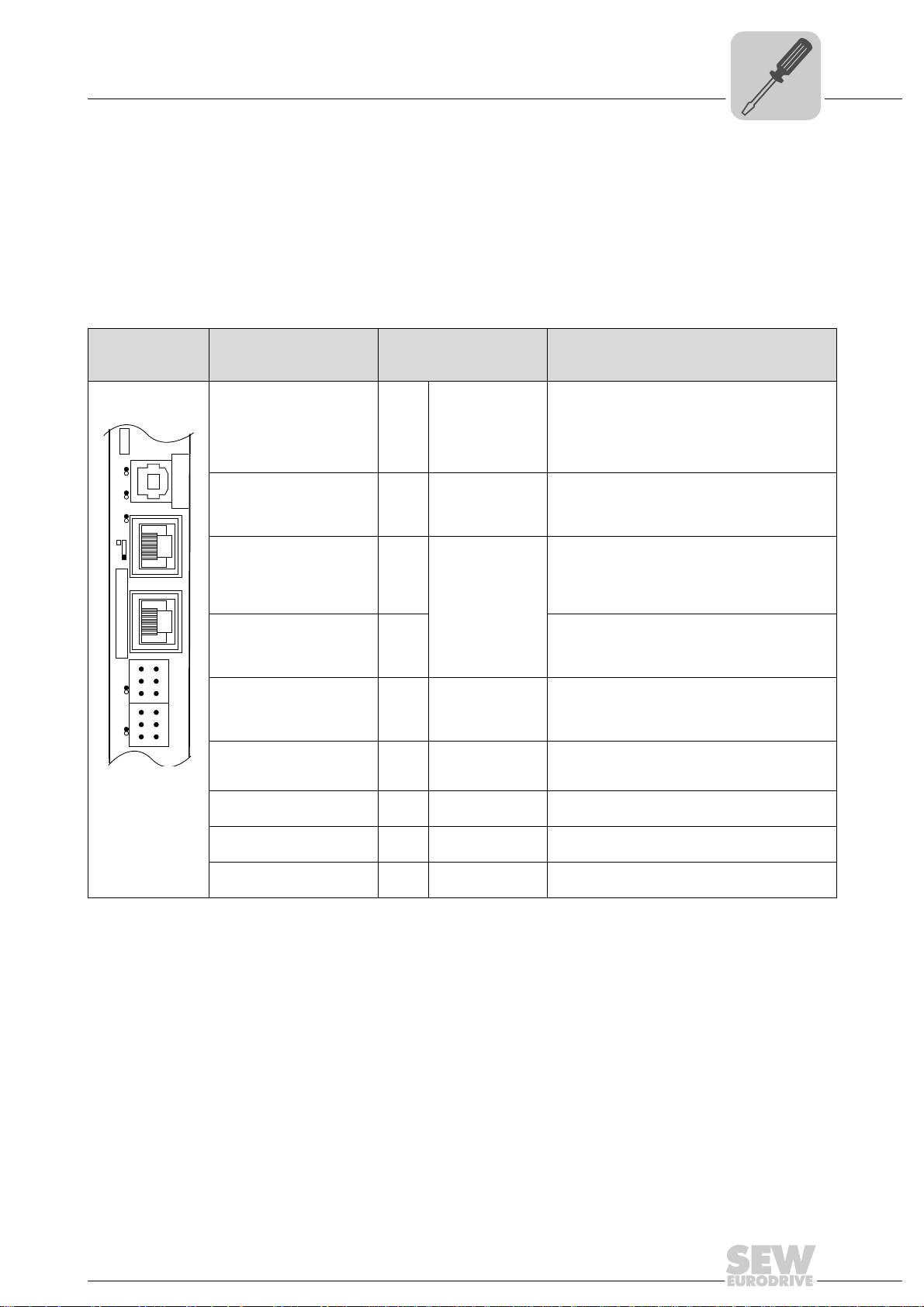
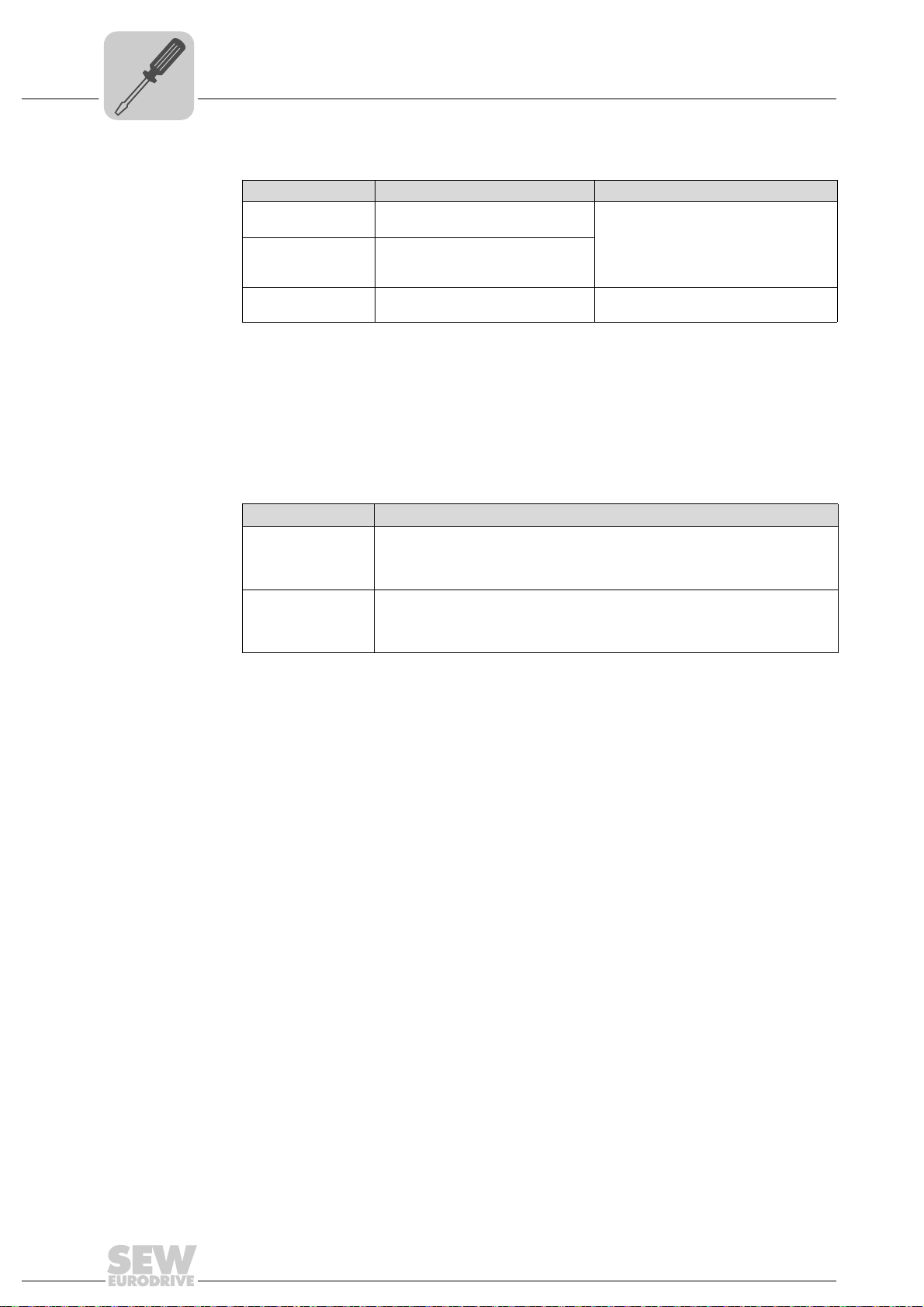
4.3.1 Functional description of the terminals, DIP switch es and LED of the UFR41B option
Connectors, LEDs and DIP switches in the upper area of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
allow for connection to EtherNet/IP (see chapter "Connecting the UFR41B fieldbus system to an EtherNet/IP network"), Modbus/TCP (see chapter "Connecting the UFR41B
fieldbus to a Modbus/TCP network") and PROFINET IO fieldbus systems (see chapter
"Connecting the UFR41B fieldbus gateway to a PROFINET IO network")
4
Front view
UFR41B fieldbus
gateway
64418AXX
LED
Designation
DIP switch
Terminal
LED LED 1
LED 2
LED 3
LED 4
LED 5
X35 connector:
USB connection
X35:1
X35:2
X35:3
X35:4
X36 connector:
X36
Connection of an EtherCAT based
system bus (RJ45 socket)
X37 connector:
X37 Ethernet for engineering
Ethernet connection
(RJ45 socket)
X32 connector:
System bus CAN 2
(electrically isolated)
X32:1
X32:2
X32:3
(plug-in terminals)
X33 connector:
System bus CAN 1
(plug-in terminals)
X33:1
X33:2
X33:3
DIP switch S1
Memory card M1
Button T1
CAN 1 status
CAN 2 status
Program status
Gateway status
Gateway error
USB+5 V
USBUSB+
DGND
Standard Ethernet
assignment
BZG_CAN 2
CAN 2H
CAN 2L
DGND
CAN 1H
CAN 1L
To p
Bottom
Function
Status of CAN 1 system bus
Status of CAN 2 system bus
Status of gateway program
Status of gateway firmware
Status of gateway error (see section "Error messages of the fieldbus gateway")
DC 5 V voltage supply
USB- signal
USB+ signal
Reference potential
plus
System bus SBUS
(in preparation)
Reference potential for system bus CAN 2
System bus CAN 2 high
System bus CAN 2 low
Reference potential for system bus CAN 1
System bus CAN 1 high
System bus CAN 1 low
Default IP address (192.168.10.4)
IP parameter from SD memory card
Memory for firmware, gateway application,
gateway configuration, and inverter parameters
For Bootloader update
(see section "SD memory card OMG4.B")
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
17
Page 18
4
UFF41B
DGND
MDX60B/61B
X12
SC11
2
1
3
SC12
UFR41B
X31X32X33
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
2
3
1
ON OFF
S12
X45
X46
1
23456HL
FSC11B
MOVITRAC® B
S1
OFF
ON
7
S2
X44
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
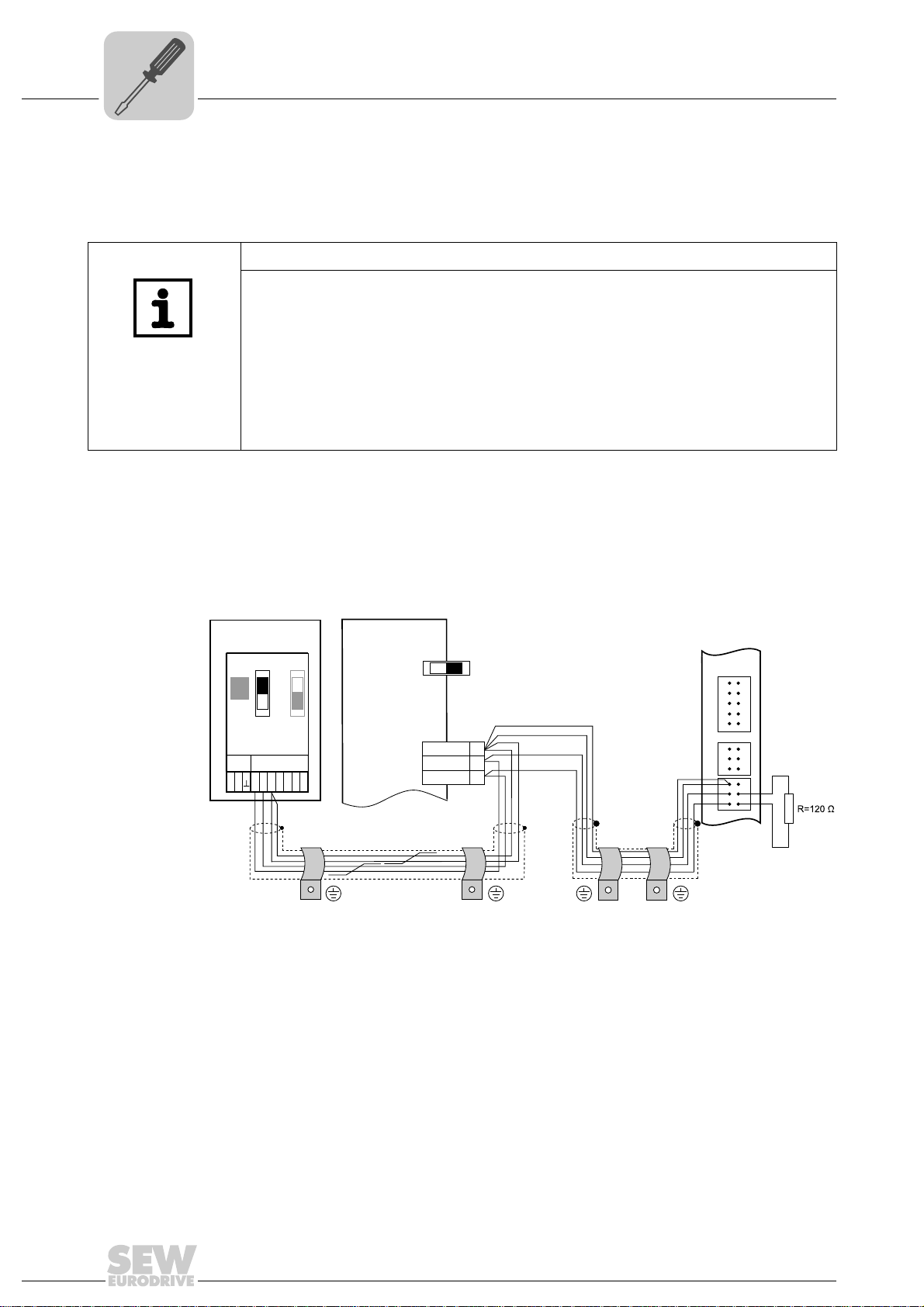
4.3.2 Connecting CAN 1 system bus (X33 connector)/ CAN 2 (X32 connector)
Do not connect more than 16 units to the CAN 1 or CAN 2 system bus in gateway
operation.
TIPS
• The CAN 1 system bus is not electrically isolated. Therefore, it is recommended to
use the CAN 1(X33 or X26 with UFR41B/UOH21B) interface to connect inverters
via the system bus in the control cabinet. Set the P881 SBus address parameter in
increasing order to values 1 - 16 if the slave unit is connected to CAN 1 or the fieldbus gateway.
• The CAN 2 system bus is electrically isolated. Therefore, preferably use interface
CAN 2 (X32) for connecting field units or units in other control cabinets. Set the
P881 SBus address parameter in increasing order to values 17 - 34 if the unit is
connected to CAN 2 or the fieldbus gateway.
The CAN system bus supports transmission systems compliant with ISO 11898. For
detailed information on the CAN system bus, refer to the "MOVIDRIVE
®
Communication
and Fieldbus Device Profile" manual. You can order this manual from SEWEURODRIVE.
®
Wiring diagram for MOVIDRIVE
B, MOVITRAC® B on CAN 1 system bus
64714AXX
Cable specification • Use a 2 x 2-core twisted and shielded copper cable (data transmission cable with
braided copper shield). Clamping without conductor end sleeves is possible in accordance with IEC 60999. The cable must meet the following specifications:
2
– Cable cross-section 0.2 to 1.0 mm
(AWG 24 - AWG 18)
– Cable resistance 120 Ω at 1 MHz
Cable length • The permitted total cable length depends on the baud rate setting of the system bus:
– Capacitance per unit length = 40 pF/m at 1 kHz
Suitable cables include CAN bus or DeviceNet cables.
– 125 kBd → 500 m
– 250 kBd → 250 m
– 500 kBaud → 100 m
– 1000 kBd → 40 m
18
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 19
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
4
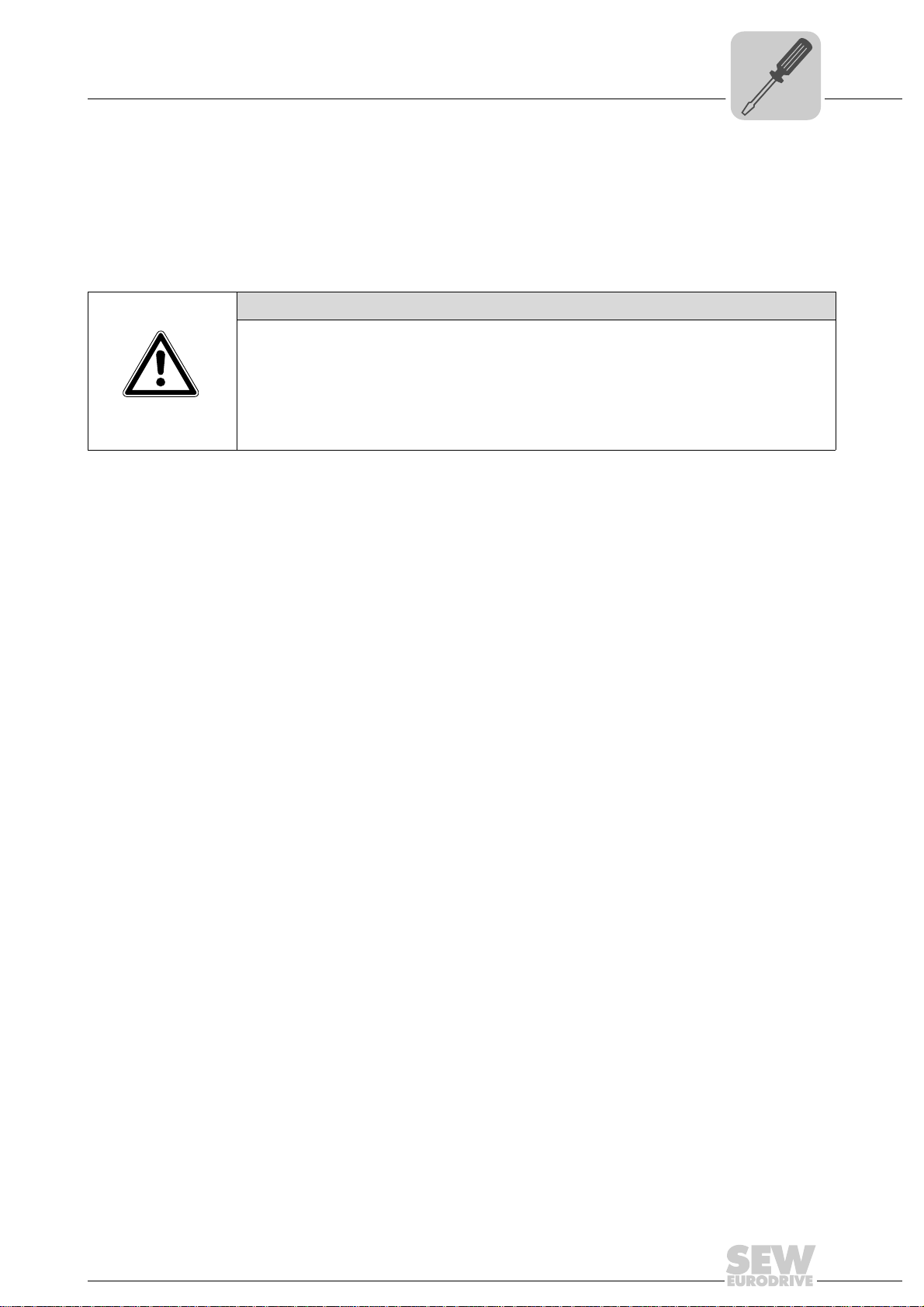
Terminating
resistor
• Switch on the system bus terminating resistor at the start and end of the CAN system
bus connection (MOVIDRIVE
S1 = ON). For all other devices, switch off the terminating resistor (MOVIDRIVE
DIP switch S12 = OFF; MOVITRAC
way is, for example, located at the end of the CAN 2 system bus, you have to connect
a terminating resistor of 120 Ω between pins X32:2 and X32:3 (for CAN 1: terminating
resistor between pins X33:2 and X33:23).
®
B, DIP switch S12 = ON; MOVITRAC® B, DIP switch
®
B, DIP switch S1 = OFF). If the fieldbus gate-
®
B,
CAUTION
•There must not be any potential displacement between the units connected via the
CAN 2 system bus.
•There must not be any potential displacement between the units connected via the
CAN 1 system bus.
• Take suitable measures to avoid potential displacement, such as connecting the
unit ground connectors using a separate cable.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
19
Page 20
4
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
[1]
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
Wiring diagram for MOVIAXIS® on CAN 1 system bus
[1] Terminating resistor
Overview of system connection cables
Type Part number Description
CAN system cable 0819 692 3
CAN1 connection cable,
750 mm, RJ45-RJ45
CAN1 connection cable,
3000 mm, RJ45-RJ45
CAN2 adapter cable 1810 1607
CAN2 connection cable 1810 1585
CAN2 connection cable 1810 1593
Terminating resistor CAN 2 1810 1615 Terminating resistor for CAN 2 connections between axis modules
20
System cable UFR41B gateway CAN 1 post connector (or CAN 2) to MOVIAXIS
supply/regenerative power module CAN 1 system bus RJ45, length: 750 mm
0819 7261
0819 8993
CAN1 connection cable between MOVIAXIS
system, length: 750 mm
CAN1 connection cable between MOVIAXIS
system, length: 3000 mm
CAN2 post connector between master module and CAN2 SUB-D9 MOVIAXIS
length: 500 mm
CAN2 SUB-D9 MOVIAXIS
modules
CAN2 SUB-D9 MOVIAXIS
®
and CAN2 SUB-D9 MOVIAXIS®, to connect 3 axis
®
and CAN2 SUB-D9 MOVIAXIS®, to connect 4 axis
®
axis system and MOVIAXIS® axis
®
axis system and MOVIAXIS® axis
modules
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
64784AXX
®
®
,
Page 21
Assembly and Installation Instructions
X46
ON
OFF
S
2
S
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0
1
0
1
0
1
X12
MOVIAXIS
®
MOVITRAC
®
MOVIDRIVE
®
123
MOVITRAC
®
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
Wiring diagram for MOVIAXIS®, MOVIDRIVE® B and MOVITRAC® B on CAN 1 system bus
4
Overview of system connection cables
Type Part number Description
CAN1 connection cable,
750 mm, RJ45 litz wire
CAN1 connection cable,
3000 mm, RJ45 litz wire
0819 7288
0819 7563
CAN connection cable MOVIAXIS
length: 750 mm
CAN connection cable MOVIAXIS
length: 3000 mm
®
axis system to MOVIDRIVE® and MOVITRAC®,
®
axis system to MOVIDRIVE® and MOVITRAC®,
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
64783AXX
21
Page 22
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Connecting inverters and engineering-PC
4.3.3 Connecting SBUS
plus
system bus (terminal X36)
Terminal X36 is intended for connecting a system bus based on EtherCAT (SBUS
4.3.4 Ethernet interface terminal (terminal X37)
You can connect an engineering PC to the Ethernet interface (terminal X37).
UFF41B
UFR41B
X35
342
1
Version
X36
S1
X37
1
1
XM L4
2
2
X32X33
3
3
1
1
2
2
3
3
L1 L2 L3L5
plus
).
65057AXX
The Ethernet interface (X37) supports auto crossing auto negotiation for baud rate and
duplex mode. The IP parameters are defined depending on DIP switch S1 (see section
"DIP switches S1 default IP address").
In addition to the engineering access via terminal X37, there is another engineering
access via PROFIBUS (see section "Operation of MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio").
22
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 23
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
4.4 Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
4
LED L1 (CAN 1
status)
LED L2 (CAN 2
status)
The LED L1 indicates the status of the CAN 1 system bus.
Status of the L1
LED
Orange The CAN 1 system bus is being
Green The CAN 1 system bus is initialized.
Flashing green
(0.5 Hz)
Flashing green
(1 Hz)
Red The CAN 1 system bus is off (BUS-
Flashing red
(1 Hz)
Diagnostics Remedy
initialized.
The CAN 1 system bus is currently in
SCOM suspend mode.
The CAN 1 system bus is currently in
SCOM On mode.
OFF).
Warning on the CAN 1 system bus. 1. Check and correct the cabling of the
-
1. Check and correct the cabling of the
CAN 1 system bus.
2. Check and correct the baud rate set
for the CAN 1 system bus.
3. Check and correct the terminating
resistors of the CAN 1 system bus.
CAN 1 system bus.
2. Check and correct the baud rate set
for the CAN 1 system bus.
The LED L2 indicates the status of the CAN 2 system bus.
Status of the L2
LED
Orange The CAN 2 system bus is being
Green The CAN 2 system bus is initialized. -
Flashing green
(0.5 Hz)
Flashing green
(1 Hz)
Red The CAN 2 system bus is off (BUS-
Flashing red
(1 Hz)
Diagnostics Remedy
initialized.
The CAN 2 system bus is currently in
SCOM suspend mode.
The CAN 2 system bus is currently in
SCOM On mode.
OFF).
Warning on the CAN 2 system bus. 1. Check and correct the cabling of the
-
-
-
1. Check and correct the cabling of the
CAN 2 system bus.
2. Check and correct the baud rate set
for the CAN 2 system bus.
3. Check and correct the terminating
resistors of the CAN 2 system bus.
CAN 2 system bus.
2. Check and correct the baud rate set
for the CAN 2 system bus.
LED L3 (program
status)
LED L3 indicates the status of the gateway program.
Status of L3 Diagnostics Remedy
Green Gateway program is running. -
Off No gateway program is loaded. Load a gateway program into the controller.
Flashing orange
(1 Hz)
Program has stopped. Bootloader update required (see section
"SD memory card type OMG4.B")
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
23
Page 24
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
DIP switch S1 default IP address
LED 4 (PLC
status)
LED L4 indicates the firmware status of the fieldbus gateway.
Status of the L4 LED Diagnostics Remedy
Flashing green
(1 Hz)
Red • No SD card plugged in.
Flashing orange
(1 Hz)
The firmware of the fieldbus gateway
is running properly.
-
• File system of the SD card
corrupt.
Program has stopped. Bootloader update required (see section
"SD memory card type OMG4.B")
LED L5 (user) LED L5 is lit up red if the gateway program has detected an error and if this error can
®
only be eliminated after diagnostics with MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio.
4.5 DIP switch S1 default IP address
With DIP switch S1, you can set a default IP address for the Ethernet connection (X37).
The set IP address is applied in the next boot process.
S1 switch setting Meaning
Top IP p a r am e t e r :
Bottom The IP parameters defined on the memory card of the UFR41B gateway are used.
• IP address: 192.168.10.4
• Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
• Standard gateway: 1.0.0.0
The IP parameters for engineering interface X37 are entered in the file '...\System\NetConfig.cfg' in section 'Ethernet 2'. You can adjust the file using a text editor
(e.g. Notepad).
4.6 SD memory card type OMG4.B
The SD memory card type OMG4.B is required for operating the UFR41B fieldbus gate-
Bootloader
update
way and contains the firmware, the gateway program, and the gateway configuration.
With a MOVIAXIS
terization in case an axis needs to be replaced.
The SD memory card type OMG4.B is included in the scope of delivery of the UFR41B
fieldbus gateway.
Only use type OMG4.B memory cards in a UFR41B fieldbus gateway.
When the LEDs L3 and L4 flash orange at a 1 Hz frequency after power-on, a bootloader
update is required. Proceed as follows:
• Do not switch off the power supply during the entire process.
• Press the reset button T1 on the front of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway for 3 seconds.
When the bootloader update starts, only LED 4 is flashing.
• The bootloader update has been successful when L4 flashes green.
®
axis module, it is also used for data backup and automatic parame-
24
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 25
Assembly and Installation Instructions
UFR41B
2
2
0
1
X30-1
X30-2
L14
L13
ON
1
2
3
X38
L12
L11
[3]
[2]
[1]
2
3
6
1
[6]
AB
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Connecting the UFR41B fieldbus gateway to an Ethernet network
4.7 Connecting the UFR41B fieldbus gateway to an Ethernet network
4
Front view
UFR41B fieldbus
gateway
65052AXX
Designation
LED
X30-1: Ethernet connection
LED Link (green)
LED Activity (yellow)
X30-2: Ethernet connection
LED Link (green)
LED Activity (yellow)
DIP switch 2
X38: CAN for safetyrelevant communication
LED
DIP switch
Function
Terminal
In EtherNet/IP and Modbus/TCP operation:
L14
L13
MODULE STATUS
NETWORK STATUS
In PROFINET operation:
L14
L13
L12
L11
0
= ON Resets the address parameters to their default values and
RUN
BUS FAULT
Reserved
Reserved
deactivates DHCP
• IP address: 192.168.10.4
• Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
• Gateway: 192.168.10.4
1
= ON
2
1
= OFF
2
X38:1
X38:2
X38:3
EtherNet/IP and Modbus/TCP protocol is active
PROFINET protocol is active
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
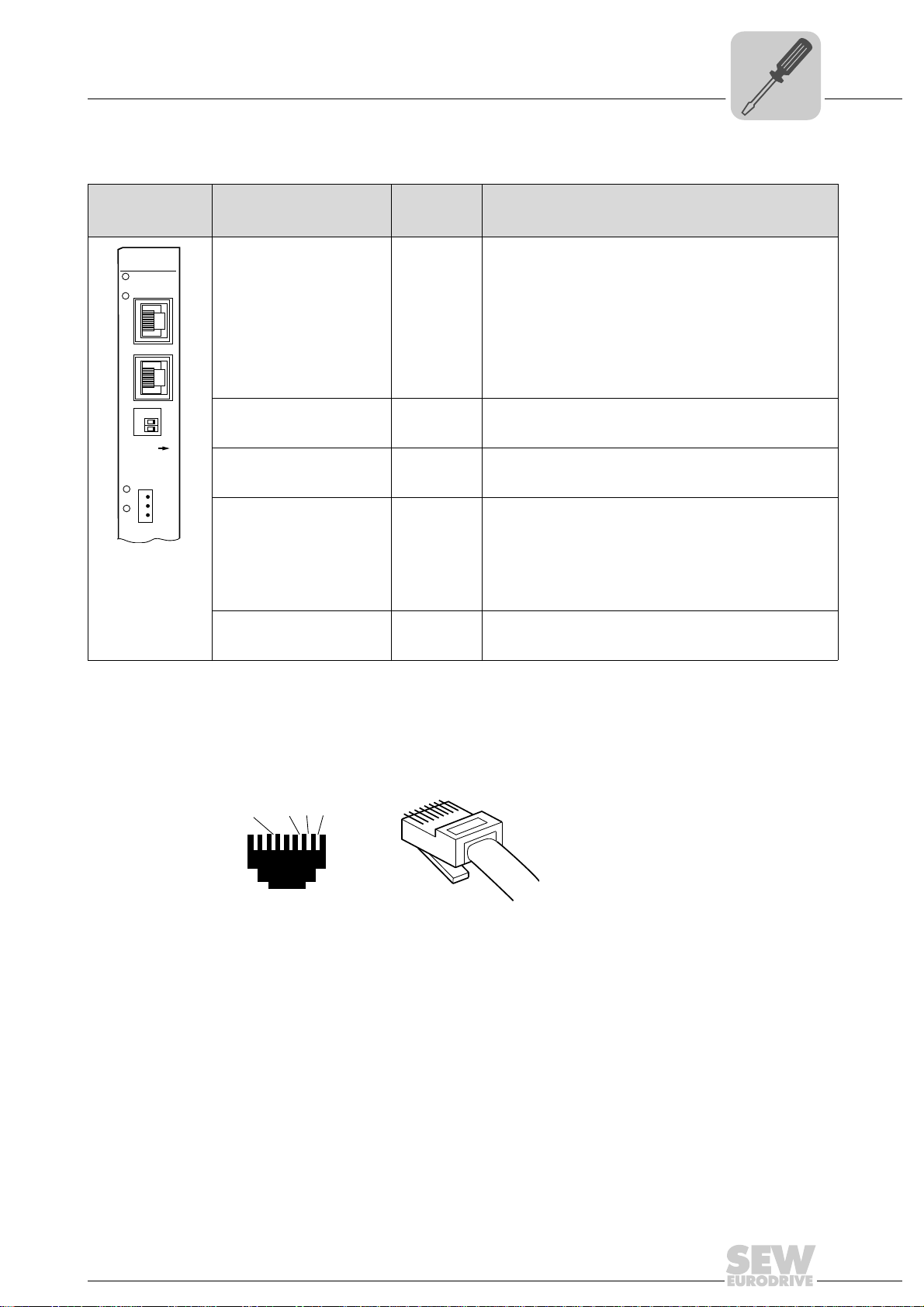
4.8 Pin assignment X30-1, X30-2 and X37
Use prefabricated, shielded RJ45 plug connectors compliant with IEC 11801 edition 2.0,
category 5.
54174AXX
A View from front B View from back
[1] Pin 1 TX+ Transmit Plus [2] Pin 2 TX- Transmit Minus
[3] Pin 3 RX+ Receive Plus [6] Pin 6 RX- Receive Minus
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
25
Page 26

4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Connecting UFR41B fieldbus gateway to Ethernet
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Shielding and routing bus cables
To connect UFR41B to the Ethernet, connect the Ethernet interface (X30-1, X30-2 or
X37) to the other network stations using a category 5, class D shielded twisted-pair
cable in accordance with IEC 11801 edition 2.0. The integrated switch provides support
for implementing a line topology using X30-1 and X30-2, and offers auto crossing
functions.
TIPS
• According to IEC 802.3, the maximum cable length for 10/100 MBaud Ethernet
(10BaseT / 100BaseT), e.g. between two network stations, is 100 m.
• We recommend that you do not directly connect non-SEW end devices to the
UFR41B option in order to minimize the load on the end devices in EtherNet/IP networks caused by undesired multicast data traffic. Connect non-SEW devices via a
network component that supports the IGMP snooping functionality (e.g. managed
switch).
Managed switches with IGMP snooping functionality is not required for PROFINET
IO and Modbus TCP networks.
4.9 Shielding and routing bus cables
Only use shielded cables and connection elements that meet the requirements of
category 5, class D according to IEC 11801 edition 2.0.
Correct shielding of the bus cable attenuates electrical interference that can occur in
industrial environments. The following measures ensure the best possible shielding:
• Manually tighten the mounting screws on the connectors, modules, and equipotential
bonding conductors.
• Use only connectors with a metal housing or a metallized housing.
• Connect the shielding in the connector over a wide surface area.
• Apply the shielding of the bus cable on both ends.
• Route signal and bus cables in separate cable ducts. Do not route them parallel to
power cables (motor leads).
• Use metallic, grounded cable racks in industrial environments.
• Route the signal cable and the corresponding equipotential bonding close to each
other using the shortest possible route.
• Avoid using plug connectors to extend bus cables.
• Route the bus cables closely along existing grounding surfaces.
CAUTION
In case of fluctuations in the ground potential, a compensating current may flow via the
bilaterally connected shield that is also connected to the protective earth (PE). Make
sure you supply adequate equipotential bonding according in accordance with relevant
VDE regulations in such a case.
26
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 27
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The integrated Ethernet switch
4.10 The integrated Ethernet switch
You can use the integrated Ethernet switch to implement line topologies using X30-1
and X30-2 known from the fieldbus technology. Other bus topologies, such as star or
tree, are also possible. Ring topologies are not supported.
TIP
The number of Industrial Ethernet switches connected in line impacts on the telegram
runtime. If a telegram passes through the units, the telegram runtime is delayed by the
store & forward function of the Ethernet switch:
• for a telegram length of 64 bytes by approximately 10 µs (at 100 Mbit/s)
• for a telegram length of 1500 bytes by approximately 130 µs (at 100 Mbit/s)
This means that the more units a telegram has to pass through, the higher the telegram
runtime is.
Auto crossing The two ports leading out of the Ethernet switch have auto crossing functionality. This
means that they can use both patch and cross-over cables to connect to the next Ethernet station.
4
Auto negotiation The baud rate and the duplex mode is negotiated by both Ethernet nodes when
establishing the connection. For this purpose, both Ethernet ports of the EtherNet/IP
connection support an auto negotiation functionality and work with a baud rate of either
100 Mbit or 10 Mbit in full duplex or half-duplex mode.
Notes on multicast handling
• The integrated Ethernet switch does not provide a filter function for Ethernet multicast telegrams. Multicast telegrams that are usually sent in Ethernet/IP networks
from the adapters to the scanners (PLC) are passed on to all switch ports.
• IGMP snooping (managed switch) is not supported.
• SEW-EURODRIVE therefore recommends to connect the UFR41B option in EtherNet/IP networks only with network components that support IGMP snooping (e.g.
managed switch) or that have safety mechanisms integrated against excess multicast load (e.g. units from SEW-EURODRIVE). Units that do not have this integrated
function can fail due to high network loads. This restriction does not apply to
PROFINET IO or MODBUS TCP networks.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
27
Page 28
4
UFR41B
2
2
0
1
ON
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Setting the DIP switches
4.11 Setting the DIP switches
TIP
De-energize the UFR41B fieldbus gateway before you change a DIP switch setting.
The DIP switch settings are adopted during initialization only.
65053AXX
20 (Def IP) if the switch "2
are set when the DC 24 V backup voltage is switched on:
• IP address: 192.168.10.4
• Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
• Default gateway: 192.168.10.4
• P785 DHCP / Startup configuration: Saved IP parameters (DHCP is deactivated)
1
2
(protocol) DIP switch "2
1
•2
= "1" (= right = ON): The EtherNet/IP and Modbus TCP/IP fieldbus protocol is
active.
1
•2
= "0" (= left = OFF): The PROFINET fieldbus protocol is active.
0
" is set to "1" (= right = ON), the following default IP address parameters
1
" is used to set the protocol that is used for communication.
28
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 29
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
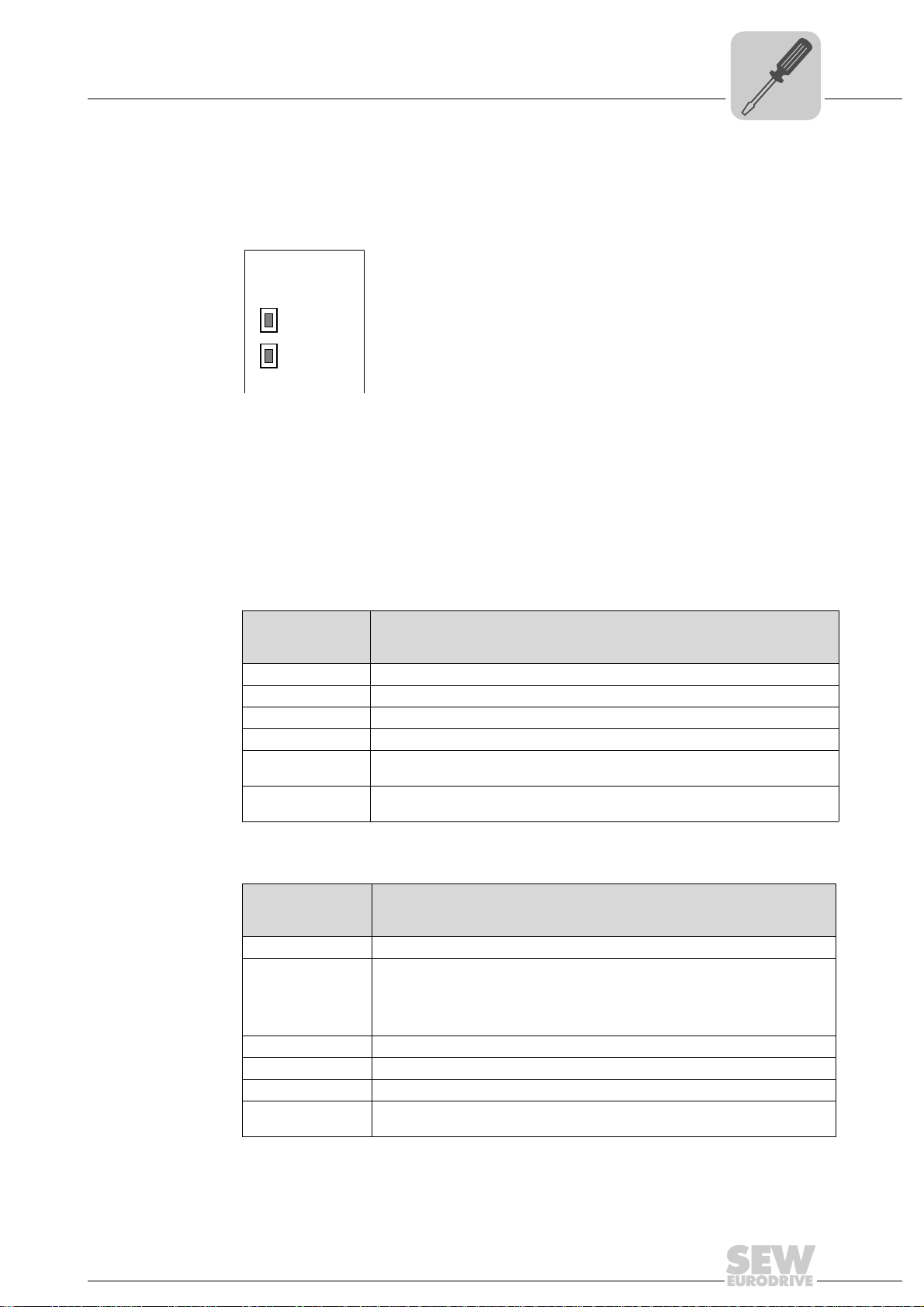
4.12 Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
The LEDs of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway indicate the current status of the UFR41B
option and the fieldbus system. The LEDs have a different meaning depending on the
set protocol.
UFR41B
L14
L13
4.12.1 Status LED in EtherNet/IP and Modbus/TCP operation
4
65054AXX
LED L13
(NETWORK
STATUS)
LED L14
(MODULE
STATUS)
Chapter 9 provides a summary of the status of the fieldbus interface corresponding to
the LED status.
The LED L13 (NETWORK STATUS) indicates the state of the fieldbus system.
States of the
NETWORK STA TUS
LED
Off The UFR41B option does not yet have any IP parameters.
Flashing green/red The UFR41B option card performs an LED test.
Flashing green There is no controlling IO connection.
Green There is a controlling EtherNet/IP or Modbus/TCP connection.
Red Conflict detected in the assigned IP addresses. Another station in the network uses
Flashing red The previously established controlling IO connection is in timeout status. The status
Meaning
the same IP address.
is reset by restarting communication.
LED L14 (MODULE STATUS) indicates that the bus electronics are operating correctly.
States of the
MODULE STATUS
LED
Off The UFR41B option card is either not supplied with voltage or it is faulty.
Flashing green • If the NETWORK STATUS LED is off at the same time, the TCP/IP stack of the
Flashing green/red The UFR41B option card performs an LED test.
Green The UFR41B option card is in normal operating state.
Red The UFR41B option card is in fault state.
Flashing red Conflict detected in the assigned IP addresses. Another station in the network uses
Meaning
UFR41B option card will be started. If this status continues and DHCP is
activated, the UFR41B option card waits for data from the DHCP server.
• If the NETWORK STATUS LED is flashing green at the same time, the
application of the UFR41B option card is started.
the same IP address.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
29
Page 30
4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
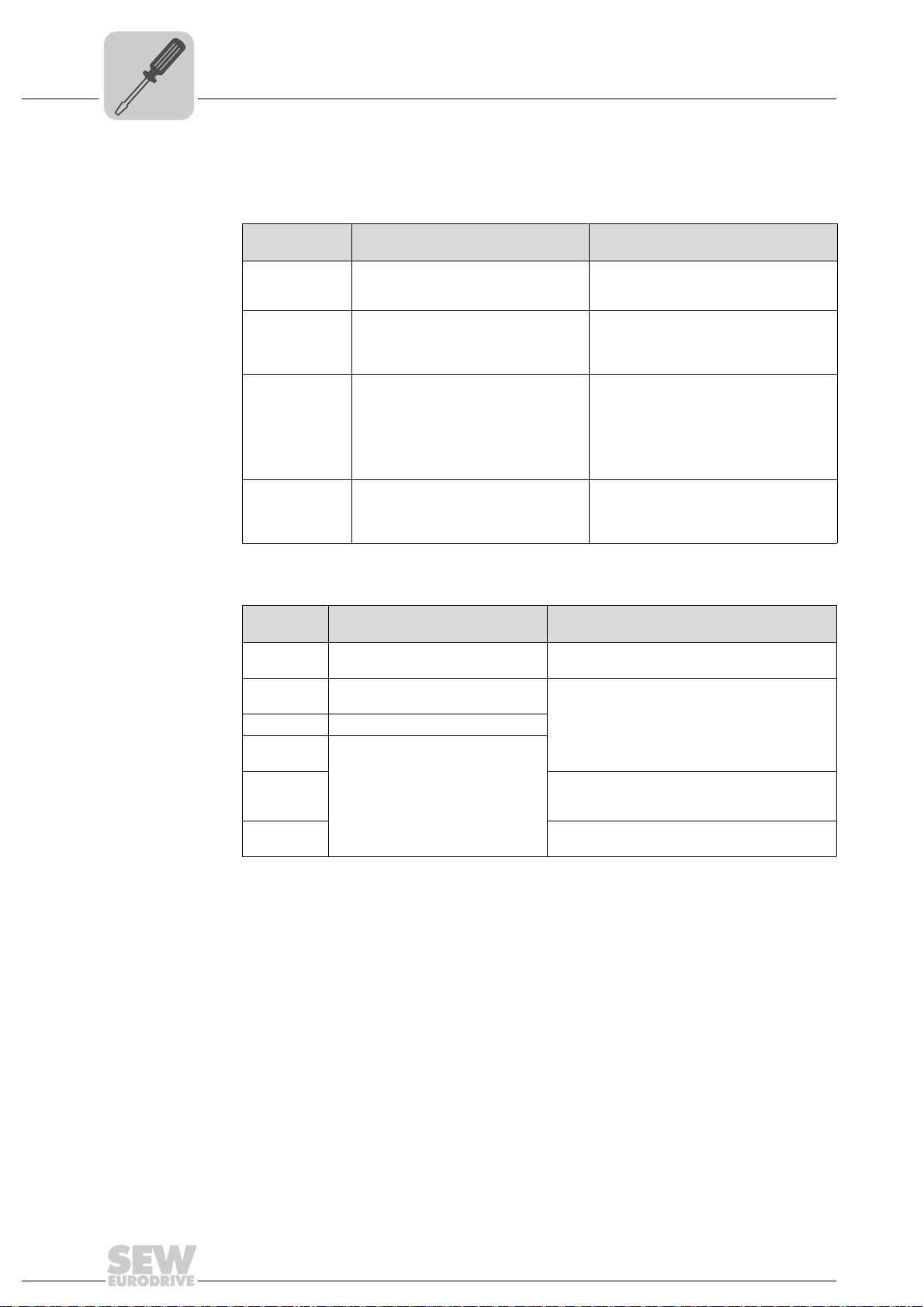
4.12.2 Status LED in PROFINET operation
L13 LED (BUS
FAULT)
The LED L13 (BUS FAULT) indicates the status of the PROFINET.
Status of the
L13 LED
Off • PROFINET IO device is currently
Flashing green
Flashing
green/red
Red • Connection to the PROFINET IO
Yellow
Flashing yellow
Cause of error Remedy
exchanging data with the PROFINET
IO controller (data exchange).
• The flashing function in the
PROFINET IO controller configuration is activated to visually localize
the stations.
controller has failed.
• PROFINET IO device does not
detect a link
• Bus interruption
• PROFINET IO controller is not in
operation
• The STEP 7 hardware configuration
contains a module that is not
permitted.
-
-
• Check the PROFINET connection of
the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
• Check the PROFINET IO controller
• Check the cabling of your PROFINET
network
• Switch the STEP 7 hardware
configuration to ONLINE and analyze
the status of the components of the
slots in the PROFINET IO device.
LED L14 (RUN) LED L14 (RUN) indicates that the bus electronics are operating correctly.
Status of the
L14 LED
Green • UFR41B hardware OK.
Off • UFR41B is not ready for
Red • Error in the UFR41B hardware
Flashing
green
Flashing
yellow
Yellow • Switch the unit on again. Consult SEW service
Cause of error Remedy
• Functions properly
operation.
• Hardware of the UFR41B does
not boot up.
-
• Switch the unit on again. Consult SEW service
if the error occurs again.
• Switch the unit on again. Set default IP
address parameter using DIP switch "S1".
Consult SEW service if the error occurs again.
if the error occurs again.
30
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 31

4.12.3 Link / Activity LEDs
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The two LEDs Link (green) and Activity (yellow), integrated in the RJ45 plug
connectors (X30-1, X30-2), indicate the status of the Ethernet connection.
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Status LED of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway
4
LED "Link"
LED "Activity"
LED/status Meaning
Link/green There is an Ethernet connection.
Link/off There is no Ethernet connection.
Link/flashes Function for localizing in the SEW address editor (see chapter "Operating MOVITOOLS
Activity/
yellow
X30-1
X30-2
63365AXX
MotionStudio")
Data is currently being exchanged via Ethernet.
®
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
31
Page 32

4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks
4.13 TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks
Introduction The settings for the address of the IP protocol are made using the following parameters:
• MAC address
• IP address
• Subnetwork mask
• Standard gateway
The addressing mechanisms and subdivision of the IP networks into sub-networks are
explained in this chapter to help you set the parameters correctly.
MAC address The MAC address (Media Access Controller) is the basis for all address settings. The
MAC address is a worldwide unique 6-byte value (48 bits) assigned to the Ethernet
device. SEW Ethernet devices have the MAC address 00-0F-69-xx-xx-xx. The MAC
address is difficult to handle for larger networks. This is why freely assignable IP
addresses are used.
IP address The IP address is a 32 bit value that uniquely identifies a station in the network. An IP
address is represented by four decimal numbers separated by decimal points.
Example: 192.168.10.4
Each decimal number stands for one byte (= 8 bits) of the address and can also be
represented using binary code (see following table).
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
11000000 . 10101000 . 00001010 . 00000100
The IP address comprises a network address and a station address (see following
table).
Network address Station address
192.168.10 4
The part of the IP address that denotes the network and the part that identifies the
station is determined by the network class and the subnetwork mask.
Station addresses cannot consist of only zeros or ones (binary) because they represent
the network itself or a broadcast address.
Network classes The first byte of the IP address determines the network class and as such represents
the division into network addresses and station addresses.
Value range
Byte 1
0 ... 127 A 10.1.22.3 10 = Network address
128 ... 191 B 172.16.52.4 172.16 = Network address
192 ... 223 C 192.168.10.4 192.168.10 = Network address
Network class
Complete network address
(Example)
Meaning
1.22.3 = Station address
52.4 = Station address
4 = Station address
This rough division is not sufficient for a number of networks. They also use an explicit,
adjustable subnetwork mask.
32
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 33

Assembly and Installation Instructions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
TCP / IP addressing and subnetworks
4
Subnetwork
mask
A subnetwork mask is used to divide the network classes into even finer sections. Like
the IP address, the subnetwork mask is represented by four decimal numbers separated
by decimal points.
Example: 255.255.255.128
Each decimal number stands for one byte (= 8 bits) of the subnetwork mask and can
also be represented using binary code (see following table).
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
11111111 . 11111111 . 11111111 . 100 00000
If you compare the IP addresses with the subnetwork masks, you see that in the binary
representation of the subnetwork mask all ones determine the network address and all
the zeros determine the station address (see following table).
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4
IP address
Subnetwork mask
decimal 192 . 168. . 10 . 129
binary 11000000 . 10101000 . 00001010 . 10000001
decimal 255 . 255 . 255 . 128
binary 11111111 . 11111111 . 11111111 . 10000000
The class C network with the address 192.168.10. is further subdivided into
255.255.255.128 using the subnetwork mask. Two networks are created with the
address 192.168.10.0 and 192.168.10.128.
The following station addresses are permitted in the two networks:
• 192.168.10.1 ... 192.168.10.126
• 192.168.10.129 ... 192.168.10.254
The network stations use a logical AND operation for the IP address and the subnetwork
mask to determine whether there is a communication partner in the same network or in
a different network. If the communication partner is in a different network, the standard
gateway is addressed for passing on the data.
Standard gateway The standard gateway is also addressed via a 32-bit address. The 32-bit address is
represented by four decimal numbers separated by decimal points.
Example: 192.168.10.1
The standard gateway establishes a connection to other networks. In this way, a
network station that wants to address another station can use a logical AND operation
with the IP address and the subnetwork mask to determine whether the desired station
is located in the same network. If this is not the case, the station addresses the standard
gateway (router), which must be part of the actual network. The standard gateway then
takes on the job of transmitting the data packages.
If for the standard gateway, the same address is set as for the IP address, the standard
gateway is deactivated. The address of the standard gateway and the IP address must
be in the same subnetwork.
DHCP (Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol)
Instead of setting the three parameters IP address, subnetwork mask and standard
gateway manually, they can be assigned in an automated manner by a DHCP server in
the Ethernet network.
This means the IP address is assigned from a table, which contains the allocation of
MAC address to IP address.
Parameter P785 indicates whether the UFR41B option expects the IP parameters to be
assigned manually or via DHCP.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
33
Page 34

4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Setting the IP address parameters
4.14 Setting the IP address parameters
Initial startup If the EtherNet/IP and MODBUS TCP protocol is set using DIP switch, the default
protocol for the UFR41B option will be "DHCP" (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
This means the option card expects its IP address parameters from a DHCP server.
TIP
Rockwell Automation provides a DHCP server free-of-charge on their homepage. The
tool is known as "BOOTP Utility" and can be downloaded from the following website:
Once the DHCP server has been configured and the settings have been made for the
subnetwork screen and the standard gateway, the UFR41B must be inserted in the
assignment list of the DHCP server. The MAC ID of the UFR41B option is allocated a
valid IP address.
TIP
The configured IP address parameters are adopted permanently by the parameter set
when DHCP is deactivated after the IP address has been assigned.
Changing the IP address parameters after successful initial startup
TIP
If the PROFINET IO setting is avtive via DIP switch, then the IP address will be
assigned using the engineering system of the IO controller (see chapter "PROFINET
IO configuration").
If the UFR41B was started using a valid IP address, you can also access the IP address
parameters via the Ethernet interface.
There are various ways to change the IP address parameters via Ethernet:
®
• Using the MOVITOOLS
• Using the EtherNet/IP TCP/IP interface object ( see section "EtherNet/IP CIP object
directory")
• Using the SEW Address Editor
You can also change the IP address parameters via the other interface of UFR41B.
If the IP address parameters are assigned to the UFR41B option via DHCP server, then
you can only change the parameters by adjusting the settings of the DHCP server.
The options listed above for changing the IP address parameters only come into effect
once the supply voltages (DC 24 V) have been switched off and back on again.
MotionStudio software
TIP
If PROFINET IO is used, the IP address must be changed in the engineering system
of the IO controller because the IO controller overwrites the IP address of the fieldbus
gateway after a restart (power off and on).
34
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 35

Assembly and Installation Instructions
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Setting the IP address parameters
4
Deactivating /
activating DHCP
Resetting the IP
address
parameters
The type of IP address allocation is determined by the setting of the attribute Configuration Control of the EtherNet/IP TCP / IP interface object. The value is displayed or
modified in the parameter P785 DHCP / Startup Configuration.
• Setting "Saved IP parameters"
The saved IP address parameters are used.
• Setting "DHCP"
The IP address parameters are requested by a DHCP server.
If you use the DHCP server from Rockwell Automation, you can activate or
deactivate the DHCP via a button. In this case, an EtherNet/IP telegram is sent to the
TCP/IP interface object of the station that is being addressed.
If you do not know the IP address parameters and there is no other interface for reading
the IP address, you can reset the IP address parameters to the default values using DIP
switch "2
This action resets the UFR41B option to the following default values:
• IP address: 192.168.10.4
• Subnetwork mask: 255.255.255.0
• Default gateway: 192.168.10.4
• DHCP / Startup Configuration: Saved IP parameters (DHCP is deactivated)
0
".
SEW Address
Editor
Proceed as follows to reset the IP address parameters to the default values:
• Switch off the 24 V DC supply voltage and the mains voltage.
• Set the DIP switch "2
• Switch the DC 24 V supply voltage and the line voltage back on.
You can also use the SEW Address Editor to access the IP settings of UFR41B without
the Ethernet settings of the PC and UFR41B having to match.
The IP settings of all SEW units can be made and displayed in the local subnetwork
using Address Editor in MOVITOOLS
• In this way, you can determine the PC settings required to provide for an access with
the required diagnostics and engineering tools via Ethernet while the installation is in
progress.
• When starting up a unit, the IP settings for the UFR41B can be assigned without
changing the network connections or PC settings.
0
" on the UFR41B option to "1".
®
MotionStudio (see chapter 10).
TIP
• DHCP remains deactivated when you reset the DIP switch "20" (Def IP) to "0". You
can re-activate DHCP via the EtherNet/IP TCP/IP interface object (see section
'EtherNet/IP CIP object directory'), via the parameter, or via the DHCP server from
Rockwell Automation.
• DHCP is activated again when the values are reset to the factory setting.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
35
Page 36

4
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Assembly and Installation Instructions
Procedure for replacing the unit
4.15 Procedure for replacing the unit
• Use the OMG4.B memory card of the old unit when replacing the fieldbus gateway.
Simply insert the memory card in the new unit. All configuration data are stored on
the memory card, including the PROFINET device name.
• If DIP switch "2
0
" (Def IP) of the new UFR41B must also be set to "1" (= ON). Other IP parameter
"2
settings are not required.
• If DHCP is active, the assignment list of the DHCP server must be updated when the
UFR41B option is replaced. The MAC address of the UFR41B option is printed on its
front panel for this purpose.
• If DHCP is not active, the IP parameters saved on the memory card of UFR41B will
be used.
If the memory card of UFR41B is not plugged into the new unit when replacing the
old one, you will have to perform a complete startup of the new UFR41B (if DHCP is
not active including the IP parameters). Instead, you can load a data backup created
with the MOVITOOLS
0
" (Def IP) is set to "1" (= ON) at the UFR41B option, then DIP switch
®
MotionStudio software to the new unit.
36
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 37

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Description of the gateway functions
5 Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
5.1 Description of the gateway functions
5.1.1 Introduction
With the UFF41B and UFR41B fieldbus gateways, SEW-EURODRIVE offers innovative
solutions for integrating SEW inverter technology in fieldbus systems.
For this purpose, process data of the higher-level control in the fieldbus gateway are
processed and sent via CAN (SBus) to the devices connected to the fieldbus gateway.
Type UFx41B fieldbus gateways can transmit up to 64 process data (PD) from the fieldbus to up to 16 lower-level slave units. The data length per slave unit is limited to 16
process data.
Two different unit configurations are supported:
• Auto setup configuration
For automatic configuration of the fieldbus gateway and connected devices.
• Customized configuration
For individual configuration of the process data length and the CAN connection of the
individual slave units.
Special features of the UFx41B fieldbus gateways are data backup and data restoration
(see chapter "Data Backup", section "Restore mechanism") after replacement of a slave
unit. For this purpose, all parameters of the connected slave units are saved on the SD
card of the fieldbus gateway and a possible unit replacement is monitored. When a unit
is replaced, the fieldbus gateway automatically loads the unit parameters to the replaced
unit.
The fieldbus gateway is configured in MOVITOOLS
way Configurator" tool.
®
MotionStudio using the "UFx Gate-
5
5.1.2 Autosetup
The "Autosetup" function is activated in the "UFx Gateway Configurator" tool. Autosetup
results in automatic configuration of the fieldbus gateway and the slave units connected
to it, which optimally cover a wide range of applications.
The "autosetup" function performs the following configurations automatically:
• Stopping process data communication in direction of the SBus
®
axis
®
• Scanning the CAN 1 system bus to detect the connected units (MOVIAXIS
MOVIDRIVE
• Assigning the process data length: 6 process data with MOVIAXIS
data with MOVIDRIVE
• Configuring the necessary process data objects (PDO) of the MOVIAXIS
modules
• Saving the configuration in the UFx41B fieldbus gateway (no data backup)
®
B and MOVITRAC® B; up to max. 16 units)
®
B and MOVITRAC® B
®
and 3 process
,
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
37
Page 38

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Description of the gateway functions
• Starting process data communication
12082AEN
During unit scan, the first 16 units found in the slave unit configuration saved in the fieldbus gateway will apply.
If the value of 64 PD is exceeded due to the process data lengths set for the individual
slave units, the gateway application will automatically reduce the process data length of
the slave units. In this case, 3 PD are set for MOVIDRIVE
units. The remaining free PD length will be divided by the number of MOVIAXIS
units. This is the resulting process data length for the individual MOVIAXIS
procedure applies no matter whether the autosetup function is enabled or not.
®
B and MOVITRAC® B slave
®
slave
®
units. The
TIP
"Autosetup" assumes that all slave units are connected to the CAN 1 system bus.
Scanning is performed using the CAN 1 system bus only.
The start words in the process image are set in such a way that the data of the slaves
follows one another without overlapping.
The auto setup configuration is saved in the UFx41B fieldbus gateway and is checked
by scanning the slave units each time power supply is switched on.
To ensure successful communication and configuration of MOVIAXIS
MOVIAXIS
®
parameter setting level must be set to "Planning Engineer".
®
units, the
38
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 39

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.1.3 Customized configuration
The "customized configuration" function allows for configuring the process data length
individually and for using the CAN 2 terminal on the fieldbus gateway. The CAN cycle
time can be reduced by dividing the slave units among the two CAN interfaces of the
fieldbus gateway. The data transmission performance can be increased in this way.
Customized configuration means that users can configure the process data length for
each slave unit, the start word in the process image in direction of the fieldbus, and the
SBus (CAN 1 or CAN 2). Status word and data length are the same both for the process
input and process output data of the slave unit.
Description of the gateway functions
5
12103AEN
The fieldbus gateway uses these data to automatically determine the cycle time for the
CAN interfaces as well as the number, data length, and CAN-IDs of process data objects
(PDO) on the SBus. The duration of the cycle time is always the same for both CAN
interfaces.
Pressing the [Apply configuration] button saves the configuration data in the fieldbus
gateway. These are the number of slave units, their process data length, their
connection to the CAN1 or CAN2 system bus, and their timeout interval. Additionally,
the settings required for establishing the communication with the fieldbus gateway are
made automatically in the MOVIAXIS
"autosetup of process data" function ("autosetup process data" selection field "off"), the
user has to set the parameters for the process data in the slave units accordingly.
Changes made to the process data configuration in the fieldbus gateway will take effect
in the fieldbus gateway by pressing the [Apply configuration] button.
®
slave units. For MOVIAXIS® units with disabled
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
39
Page 40

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.1.4 Configuring fieldbus gateway and slave units
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Description of the gateway functions
Setting the MOVIAXIS
If the "autosetup" or "customized configuration" functions are performed using the UFx
Gateway Configurator, then the slave unit parameters (MOVIAXIS
and MOVITRAC
®
servo inverter
Process data communication is automatically configured in the axis module for each
MOVIAXIS
function, or, in the case of "customized configuration" of this slave unit, if the the process
data objects required for communication between fieldbus gateway and MOVIAXIS
axis module are configured. The unit-internal further processing of process data
depends on the application and is not affected by the configuration by the fieldbus
gateway.
®
B) described in the following sections have to be made.
®
slave unit if the fieldbus gateway was configured using the "autosetup"
®
, MOVIDRIVE® B
®
TIP
• It is important that no other axis-to-axis communication between the individual
slave units was configured via the same CAN bus in order to ensure process data
exchange and engineering between fieldbus gateway and slave units.
• If the application requires axis-to-axis communication, use the CAN2 bus of the axis
module for MOVIAXIS
40
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
®
, and the free CAN bus for MOVIDRIVE® B.
12083AEN
Page 41

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Description of the gateway functions
Setting the MOVIDRIVE® B and MOVITRAC® B inverters
5
With MOVIDRIVE
cally set the parameters. In this case, the following settings have to be made via the
UFx41B fieldbus gateway for operating the MOVIDRIVE
®
B and MOVITRAC® B, the "autosetup" function does not automati-
®
B or MOVITRAC® B inverters
(see following figure).
11845AXX
®
Before controlling the MOVIDRIVE
B or MOVITRAC® B inverter via the fieldbus gate-
way, you have to set control signal source (P101) and setpoint sou rce (P100) to SBus1.
The SBus setting1 means the inverter parameters are set for control and setpoint entry
via fieldbus gateway. The inverter then responds to the process output data transmitted
from the master programmable controller.
It is necessary to set the SBus1 timeout interval (P883) to a value other than 0 ms for
the inverter to stop in the event of faulty SBus communication. We recommend a value
in the range between 50 and 200 ms. Activation of the control signal source and setpoint
source SBus is signaled to the higher-level controller using the "SBus mode active" bit
in the status word.
Activation of the control signal source and setpoint source SBus is signaled to the
machine controller using the "Fieldbus mode active" bit in the status word. For safety
®
reasons, you must also enable the MOVIDRIVE
B inverter at the terminals for control
via the fieldbus gateway. Consequently, you must wire and program the terminals in
such a way that the inverter is enabled via the input terminals. The simplest way of
enabling the inverter using terminals is, for example, to connect the DIØØ input terminal
®
(function /CONTROLLER INHIBIT) for MOVIDRIVE
®
MOVITRAC
B to a +24 V signal and to program the remaining terminals to NO
B, and DI01 = CW/stop for
FUNCTION.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
41
Page 42

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.1.5 Data backup
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Description of the gateway functions
TIPS
• If the slave unit is connected to the CAN 1 system bus of the fieldbus gateway, set
the P881 SBus address parameter in increasing order to values 1 - 16 . Set the
basic address of the CAN 1 system bus of the axis block to values > 0 in particular
when using MOVIAXIS
• If the slave unit is connected to the CAN 2 system bus of the fieldbus gateway, set
the P881 SBus address parameter in increasing order to values 17 - 34 .
• The SBus address 0 is used by the UFx41B fieldbus gateway and cannot be
assigned.
•Set P883 SBus timeout to a value between 50 and 200 ms.
•For MOVIDRIVE
®
axis blocks.
®
B, set P889 / P899 Parameter channel 2 to ON
Fieldbus gateways of the type UFx41B allow for saving all parameters of the connected
slave units to the SD memory card of the fieldbus gateway. Besides, the fieldbus gateway monitors a possible unit replacement and in this case loads the unit parameters
automatically to the replaced unit. The parameter sets of the slave units and the configuration data of the UFx41B fieldbus gateway are centrally saved on the SD memory card
of the fieldbus gateway and will be used when replacing a unit.
42
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
12090AEN
Page 43

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Description of the gateway functions
This means the fieldbus gateway serves as data memory for the data sets of the slave
units and of the startup data of the fieldbus gateway.
Once you have taken up operation of the drive system, the data sets are copied to the
data memory (SD card) when pressing the [Data backup] button. This function lets you
save the parameter sets of each slave unit, their UUID (Universally Unique Identifier)
and the configuration data of the fieldbus gateway itself. If the parameters of individual
slave units should change after the data backup, then the change will also have to be
updated in the data backup. This can be easily done by pressing the [Save data] button
of the relevant slave unit.
When restarting the system, the system checks whether an axis has been replaced. If
yes, the data set saved at startup will automatically be loaded into the replaced axis.
This mechanism only works for units with a UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) (so far
only for MOVIAXIS
Automatic unit update is only performed for fieldbus gateway slave units, which means
for units the user has manually entered in the device list of the fieldbus gateway either
using the user interface or during the system bus auto scan. Units that are connected to
the SBus but are not listed in the device list of the fieldbus gateway, will neither be
included in the data backup nor in the unit replacement function.
®
).
5
Saving data to SD
memory card
The prerequisite for automatic update after a unit replacement is that the system has
been taken into operation and that its data sets are available on the data memory (SD
memory card for UFx) of the fieldbus gateway. These data sets are created by activating
the "Data backup" function using the UFx Gateway Configurator. Make sure that the unit
replacement function of the fieldbus gateway is active. To do so, set the "Unit replacement function" to "ON" on the "Gateway parameters" tab of the UFx Gateway
Configurator.
Data backup means the data sets of the connected units are saved as well as their
UUIDs. The configuration of the fieldbus gateway is also saved.
If you want the unit replacement function to be active for all units included in the device
list, you have to enable the relevant parameters before activating data backup.
The user has to restart the SBus process data once data backup is completed. Bit 9
("configured") in the gateway status indicates that the data memory contains valid data.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
43
Page 44

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Description of the gateway functions
Restore
mechanism
Automatic unit
update after a
slave timeout
If the unit replacement function of the fieldbus gateway is active and bit 9 ("configured")
is set, all slave units will be checked for unit replacement during startup. If a replaced
unit is detected and if the axis replacement function for this slave unit is also active, the
unit will be updated with the data set saved in the data memory.
If the unit replacement function for the fieldbus gateway is disabled, the units will not be
checked for replacements and, consequently, the slave units will not be updated.
If an error occurs during automatic update of a slave unit, no process data communication will be established with this unit. This applies for errors occurring during the update
as well as for errors while reading the UUID.
TIPS
When replacing a unit, make sure that the previous SBus address is set on the
replaced units.
This is ensured when replacing a MOVIAXIS
is not changed and the fieldbus gateway is connected to the CAN 1 system bus of the
MOVIAXIS
With MOVIDRIVE
parameters. This also applies to MOVIAXIS
of the axis module.
A possible cause for a slave timeout is a unit replacement while the system is running.
The UUID of the unit is read and compared with the saved UUID as soon as the slave
timeout has elapsed.
If a unit replacement is detected and the unit replacement function is activated for the
fieldbus gateway and the relevant slave, and bit 9 is set in the fieldbus gateway status,
then the replaced slave unit will be updated with the data set in the data memory.
The fieldbus gateway continues to send the timeout status word in the process image of
the relevant slave to the fieldbus master both while the UUID is being transmitted and
during a possible update of the slave unit. The process data on the SBus are not
stopped. The fieldbus gateway sends "0" signals in all process data words to the
relevant slave unit.
If errors occur while checking the UUID or downloading the data set, "0" are continued
to be sent to the slave unit via SBus. The fieldbus gateway enters the error bit and an
error code in the process image of this slave.
If timeout monitoring is disabled for a slave, no slave timeout will be signaled. This is the
reason why no unit replacement verification is carried out during gateway operation. The
unit replacement function during startup of the fieldbus gateway is not affected by this
setting.
®
axis block.
®
B and MOVITRAC® B, the addresses have to be set using
®
unit if the address on the supply module
®
when the gateway is connected to CAN 2
44
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 45

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure
5.2 Startup procedure
5.2.1 Checking hardware installation and communication settings
• Check the CAN connection between fieldbus gateway and slave units according to
the documentation.
• Check the terminating resistors (120 ohms) on the UFx41B fieldbus gateway and the
last slave unit (see also chapter "Connecting the CAN 1 / CAN 2 system bus").
• Set the SBus address and baud rate (see chapter "Configuring the fieldbus gateway
and slave units").
All slave units connected to the fieldbus gateway must have different SBus
addresses but the same SBus baud rate.
You can make these settings using the keypads DBG60B, FBG11B (only for
MOVITRAC
– Set the P881 SBus address parameter in increasing order to values 1 - 16 if the
slave unit is connected to the CAN 1 system bus of the fieldbus gateway.
– SBus address 0 is used by the UFx41B gateway and must therefore not be used.
–Set P883 SBus timeout to values between 50 to 200 ms.
®
B) or using MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio (see chapter 11.7.2).
5
5.2.2 Establishing an engineering connection
Do the following for configuring units online using MOVITOOLS
1. Start MOVITOOLS
following path:
Start\Programs\SEW\MOVITOOLS MotionStudio
2. Create a project with name and storage location.
3. Set up communication for communicating with your units.
4. Scan the network (unit scan). To do so, click the [Start network scan] button [1] in the
toolbar.
®
MotionStudio from the WINDOWS® start menu using the
®
MotionStudio:
64334AXX
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
45
Page 46

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Startup procedure
5. Make sure that all slave units connected to the fieldbus gateway are displayed after
the unit scan. If no slave units are detected, check the installation (CAN bus terminating resistors). Also check whether all slave units have different SBus addresses
with values higher than zero (see following figure).
12105AEN
6. Select the UFx41B gateway you want to configure and open the context menu with
a right mouse click. You will see a number of unit-specific tools to execute various
functions with the units.
7. Open the "UFx Gateway Configurator" tool (see following figure)
46
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
12104AEN
Page 47

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure
5.2.3 Configuring the fieldbus gateways
Autosetup If you want to carry out the configuration using the "autosetup" function, press the
[Autosetup] button in the UFx Gateway Configurator. All drives will be stopped.
The slave units connected to the CAN 1 system bus will be scanned and configured
automatically in the case of MOVIAXIS
symbol during execution of the "Autosetup" function.
The autosetup function assigns the following process data length:
• 6 process data for MOVIAXIS
• 3 process data for MOVIDRIVE
With MOVIAXIS
modules are configured automatically.
With MOVIDRIVE
baud rate have to be configured for the slave units as described in chapter "Configuring
the fieldbus gateway and slave units".
The number of slave units and their settings are saved in the fieldbus gateway and are
checked by scanning the slave units each time power supply is enabled.
Observe that the "autosetup" function requires that all slave units are connected to the
CAN 1 system bus. Scanning is performed using the CAN 1 system bus only.
If the "Autosetup" function was executed successfully and if fieldbus communication has
already been established, then the process data are started and the UFx Gateway
Configurator indicates proper operation.
®
, all necessary process data objects (PDO) of the MOVIAXIS® axis
®
B and MOVITRAC® B, the SBus address, SBus timeout, and SBus
®
®
. The UFx Gateway Configurator displays a
, and
®
B and MOVITRAC® B
5
Customized
configuration
If you want to carry out the configuration using the "customized" function, press the
[Customized configuration] button in the UFx Gateway Configurator. The UFx Gateway
Configurator opens the "Process data configuration" tab. Press the [Process data - Stop]
button. All drives will be stopped.
The "customized configuration" functions lets you configure the process data length
individually and is necessary if slave units are connected to the CAN 2 system bus of
the fieldbus gateway.
The CAN cycle time can be reduced by dividing the slave units among the two CAN
interfaces of the fieldbus gateway. The data transmission performance can be increased
in this way.
12103AEN
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
47
Page 48

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Startup procedure
Set the following for each slave unit:
• Process data length
• SBus timeout interval
• CAN interface (CAN 1 or CAN 2 system bus) to which the slave unit is connected
The entry in the "Start word process image" is determined automatically.
The start word in the process image in direction of the fieldbus as well as the process
data length are the same for the process input and output data of the slave unit.
Pressing the [Apply configuration] button will perform the settings automatically in the
MOVIAXIS
"autosetup process data" parameter is set to "OFF", the settings in the relevant
"MOVIAXIS" unit will not be made automatically so they have to be made by the user
afterwards.
Pressing the [Process data - Start] button will start communication between fieldbus
gateway and slave unit. The following symbol appears when communication has been
established successfully.
®
units where the "autosetup process data" parameter is set to "ON". If the
5.2.4 Last settings in the slave units
Now execute the "Startup wizard" tool for every unit as you have access to all
parameters of the slave units via the engineering interface of the fieldbus gateway.
Doing so will adjust the inverter to the connected motor and, if required, the control loops
will be adjusted to the load conditions of the application.
If available, you can load a matching parameter file to the inverter / servo inverter. It is
important that the SBus address and in particular the SBus baud rate are not changed.
TIP
In particular with MOVIAXIS®, you have to check the communication settings of the
IN-PDOs and OUT-PDOs. If the communication settings were changed by loading the
parameter set, you can correct these settings by reloading the customized configuration or by executing the "autosetup" function again.
•MOVIAXIS
Process data communication is automatically configured in the axis module for each
MOVIAXIS
unit is set to "ON". Only the process data objects required for communication
between fieldbus gateway and MOVIAXIS
®
®
slave unit if the gateway parameter "autosetup process data" for this
®
axis module are configured.
12107AXX
48
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 49

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure
The unit-internal further processing of process data depends on the application and
is not affected by the configuration by the fieldbus gateway.
After having configured the fieldbus gateway, you can set the parameters for the
individual MOVIAXIS
"Parameter tree" to link the necessary IN and OUT PDOs used by the fieldbus gateway with the relevant control and status words.
®
•MOVIDRIVE
Since the fieldbus gateway does not perform an automatic configuration for these
inverters, you have to check the settings again as described in chapter "Configuring
the fieldbus gateway and slave units".
Make sure that the following parameters are not changed when setting the inverter
parameters to match your application:
– P100 control signal source
– P101 setpoint source
– P880 / P890 SBus protocol
– P881 / P891 SBus address
– P884 / P894 SBus baud rate
– P883 / P892 SBus timout interval
– P889/899 parameter channel 2 = ON (only with MOVIDRIVE
B and MOVITRAC® B
®
axis modules. To do so, use the "PDO Editor" tool or
®
B)
5
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
49
Page 50

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.2.5 Monitoring and controlling process data
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Startup procedure
Process data
diagnostics
In the UFx Gateway Configurator, open the "Process data monitor" tab (see following
figure).
Check the data between fieldbus gateway and master controller. To apply different
number formats to the individual numerical fields, make a right mouse click.
50
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
12084AEN
Page 51

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure
5
Checking
process data in
slave units
Do the following to check whether communication between fieldbus gateway and slave
unit works properly:
•MOVIAXIS
You can use the PDO Editor to check process data. The input process data objects
(IN-PDO) and output process data objects (OUT-PDO) are displayed (see following
figure).
®
®
•MOVIDRIVE
In MOVITOOLS
"Parameter tree" tool in parameter group 09 "Bus diagnostics" (see following figure).
The two tools "UFx Gateway Configurator" and "Parameter tree" can be open at the
same time (see following figure).
B and MOVITRAC® B
®
MotionStudio, you can check the process data using the
12085AEN
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
12086AEN
51
Page 52

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Startup procedure
Manual
specification
(forcing) of
process output
data
The process data monitor also lets you manually specify process output data without
master controller (referred to as forcing).
52
12084AEN
Activate force mode and enter the values in the now active fields. Clicking the "Send
process data" button will send the entered values to the slave units via SBus instead of
the valued received via fieldbus. Process input data cannot be specified manually.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 53

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure
5.2.6 Saving inverter data in the fieldbus gateway and using MOVITOOLS® MotionStudio
After having successfully configured the fieldbus gateway and after complete and
verified parameterization of the slave units, the inverter parameters of the slave units
can be saved on the SD card of the fieldbus gateway and on your PC using the project
management of MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio.
5
Saving data on
the SD memory
card of the
fieldbus gateway
Saving data using
the project
management in
MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio
®
To save the data of the slave units on the SD memory card of the fieldbus gateway, click
on the [Data backup] tab in the UFx Gateway Configurator and click the [Data backup]
button. For this purpose, all drives must be at standstill and process data communication
must be stopped.
Clicking the [Data backup] button of the displayed slave units will copy the parameter
set of this unit to the SD card of the fieldbus gateway.
Setting the "Automatic update" function to "OFF" disables the restore function for this
unit after unit replacement (see also chapter 5.1.5).
Proceed as follows to configure existing units in the network:
1. Switch to the network view with the "Network view" tab.
2. Perform a unit scan.
This will display all units that are physically connected and accessible online.
3. Select the unit you want to configure.
4. Drag the scanned unit from the network view into project view (drag and drop) or
select the [Project unit] command from the context menu.
This opens the "Project unit" window.
5. Use the name (signature) of the unit that is accessible online.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
12116AEN
53
Page 54

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Startup procedure
TIP
Proceed as follows if you do NOT want to transfer the name (signature) from the unit
that is available online:
• Enter a new signature.
• Activate the "Accept signature in online unit" control field.
Doing so ensures that the unit can be clearly identified in the future.
6. Click [Finish].
The parameters are then transferred from the unit, which can be accessed online, to
the working memory.
7. Confirm with [OK].
The mini symbol on the unit node will then disappear in the network view.
8. Save your project.
The parameter is then transferred from the working memory to the parameter file
where it is permanently saved.
12117AEN
54
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 55

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
5.2.7 Error processing and status messages
The fieldbus gateway distinguishes between status and error messages of the fieldbus
gateway and individual slave units. For every slave, a status word is stored in an individual parameter. The following table gives an overview of the assignment of individual
bits of the slave status word.
Status word slave
Bit Assignment
2 Slave timeout
3 Configuration error in project planning
4 Configuration error in process data
5 Update error
9 Data backup
10 Update in progress
11 Replaced axis detected
15 Error while saving data
17 Error while reading UUID during data backup
30 Unit update after timeout
Startup procedure
5
The status of the fieldbus gateway is stored in a parameter in bit code. The following
table gives an overview of the assignment of individual bits of the fieldbus gateway
status word. The fieldbus gateway status results from ORing the bits in the individual
slave states if the bit assignment in the slave and fieldbus gateway states corresponds.
Fieldbus gateway status word
Bit Assignment
0 Malfunction
1 Fieldbus timeout
2 Slave timeout
3 Configuration error in project planning
4 Configuration error in process data
5 Update error
6 Process data started
7 Process data stopped
8 Configured
9 Data backup
10 Update in progress
11 Replaced axis detected
12 Bus scan
13 Autosetup slaves
14 SBus initialization
15 Error during data backup
30 Unit update after timeout
This allows for detailed error diagnostics. For example, if the fieldbus gateway indicates
a configuration error during configuration (bit 3), the slave where this error has occurred
can be determined from the status of the slaves. Bits, which indiate an error, are reset
with an error reset (bits 0 - 5, bit 11, bit 15, bit 30).
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
55
Page 56

5
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Startup procedure
Communication
error between
fieldbus gateway
and slave unit
If the fieldbus gateway detects a timeout during communcation with a slave unit, then
the fieldbus gateway automatically shows fault number F111 in the first word of the
process image of the relevant slave unit.
A timeout is detected by monitoring the process data communication between fieldbus
gateway and slave. A communication error is automatically reset as soon as the
malfunction is eliminated.
The following parameters must be set in these units to enable the fieldbus gateway to
signal error states of connected units to the master controller:
•MOVIDRIVE
P873 = Status word 1 or status word 3
•MOVIAXIS
®
B, MOVITRAC® B
®
(see following figure)
12108AEN
Status word settings:
– Selection field "Layout": Progr. layout/fault code
– Selection field "Bit 5: Malfunction"
This status word is linked with the corresponding output process data object (see
following figure).
12109AEN
56
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 57

Configuring the UFx41B Fieldbus Gateway and Inverter
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Startup procedure
TIP
The fieldbus gateway does not verify correct parameter setting of the status word. A
deviating parameter setting will cause the controller to not correctly detect either
communication timeouts with the slave units or other errors.
Fieldbus timeout The fieldbus gateway detects a failed communication with the master controller (fieldbus
master). In this case, the fieldbus gateway sends "0" signals to all slave units in their
process image and in this way stops all drives using the set rapid stop ramp. Fieldbus
communication will automatically be resumed after a fieldbus timeout.
Used CAN IDs
The following CAN IDs are used for communication between fieldbus gateway and slave
units.
5
Number of Calculation of CAN IDs of
process data per drive CAN telegrams process inputs PI process outputs PO
3 process data for
MOVIDRIVE
MOVITRAC
1 to 4 process data for
MOVIAXIS
5 to 8 process data for
MOVIAXIS
9 to 12 process data for
MOVIAXIS
13 to 16 process data for
MOVIAXIS
®
®
®
®
®
®
B and
B
1 to 3 CAN
telegrams
1 CAN telegram 8 x SBus address + 3 8 x SBus address + 0
2 CAN telegrams 1. CAN telegram:
3 CAN telegrams 1. CAN telegram:
4 CAN telegrams 1. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 3 8 x SBus address + 4
8 x SBus address + 3
2. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 4
8 x SBus address + 3
2. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 4
3. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 5
8 x SBus address + 3
2. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 4
3. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 5
1. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 0
2. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 1
1. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 0
2. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 1
3. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 2
1. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 0
2. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 1
3. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 2
4. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 7
TIPS
A sychronization telegram is also transmitted to ensure data consistency:
SyncID for CAN 1 and CAN 2 = 1
This calculation directive ensures the consistency of IDs calculated for MOVIAXIS
using the "Single-axis positioning" technology editor.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
4. CAN telegram:
8 x SBus address + 6
®
57
Page 58

6
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
Validity of the EDS file for UFR41B
6 Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
This chapter provides you with information on the configuration of the EtherNet/IP
master and startup of the fieldbus gateway for fieldbus operation. Prerequisite is the
correct connection and setting of the IP address parameters of UFR41B as described in
the "Assembly and Installation Instructions" chapter.
6.1 Validity of the EDS file for UFR41B
TIP
Do not edit or amend the entries in the EDS file. SEW assumes no liability for inverter
malfunctions caused by a modified EDS file!
SEW-EURODRIVE provides the following EDS file for projecting the scanner
(EtherNet/IP master):
• SEW_GATEWAY_UFR41B.eds
TIP
Current versions of the EDS files for the UFR41B option are available on the SEW
homepage under the heading "Software".
58
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 59

Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the master (EtherNet/IP scanner)
6.2 Configuring the master (EtherNet/IP scanner)
The following example refers to the configuration of the AllenBradley CompactLogix
1769-L32E controller with RSLogix 5000 programming software. The EtherNet/IP interface is already integrated in the CPU component.
TIP
If a CPU without an EtherNet/IP interface is used, an Ethernet communication interface
must first be added to the IO configuration.
6
Process data
exchange
In the following project planning example, the UFR41B option is added to a project. To
do so, go to the view "Controller Organizer" in the RSLogix 5000 program as shown in
the screenshot below (use the tree structure on the left side of the screen).
• In the "I/O Configuration" folder, select the entry "1769-L32E Ethernet Port
LocalENB" as the Ethernet communication interface. Make a right mouse click to
open the context menu and choose "New Module". The selection window "Select
Module Type" appears.
• To add the UFR41B option to the project, select the entry "ETHERNET MODULE"
from the category "Communications". Confirm your selection by clicking [OK].
• The "New Module" window opens.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
11709AXX
59
Page 60

6
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
Configuring the master (EtherNet/IP scanner)
First enter the name under which the data is stored in the controller tags for the newly
created module, and then enter the IP address.
12127AXX
• For the data format, open the dropdown menu "Comm-Format"and choose the
entry "Data - INT". Process data for UFR41B always contains 16 bits (INT).
• In the "Connection Parameters" group box, enter the value "172" in the "Input
Assembly Instance" input field. The input data of the PLC must be linked to the output
instance of UFR41B .
• To establish a controlling connection, in the "Connection Parameters" group box,
enter the value "162" in the "Output Assembly Instance" input field. The input data of
the PLC must be linked to the output instance of UFR41B .
• In the selection fields "Input Size" and "Output Size," set a maximum value of "64"
(16 bit) as the data length.
• In the "Configuration Size" selection field, enter the value "0." The "Configuration
Assembly Instance" is not used in this case.
• Click [OK] to complete the process.
• To ensure compatibility with existing DeviceNet configurations, you can also choose
the data type "SINT" in the "Comm Format" selection field. In this case, you must
ensure that an even number of bytes (2 - 128) is configured and that data consistency
is maintained during operation when the IO data is accessed.
60
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 61

Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the master (EtherNet/IP scanner)
Other settings The "Connection" tab page is used to set the data rate and, if required, the error
response of the controller.
6
11712AXX
• The UFR41B option supports a minimum data rate (input field "Requested Packet
Interval (RPI)") of 4 ms. Longer cycle times can be implemented without any
problems.
• Click [OK]. You have now configured process data exchange with a UFR41B.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
61
Page 62

6
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
6.3 Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
6.3.1 UFR41B fieldbus gateway with 16 PD data exchange
1. Set the IP address of the DFE33B option see chapter "Setting the IP address
parameters").
2. Add the UFR41B fieldbus gateway to the EtherNet/IP configuration as described in
chapter 5.2.
3. You can now start integration into the RSLogix project.
To do so, create a controller tag with a user-defined data type to create a simple, data
consistent interface to the process data of UFR41B (see following figure).
The description for the process input and output data of the controller tag can match
the definition of the process data (PD) in the inverters.
62
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
11962AXX
Page 63

Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
4. To copy the data of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway into the new data structure, a CPS
command is inserted at the beginning of the "MainRoutine". This command reads the
data from the controller tag beginning from the offset (see figure below).
12129AXX
To copy the data from the new data structure to the UFR41B fieldbus gateway, insert
a CPS command at the end of the "MainRoutine" (see following figure). The data of
the individual drives are written to the fieldbus gateway in the data structure and with
the corresponding offset.
6
12130AXX
5. Now save the project and transfer it to the PLC. The PLC is set to RUN mode.
You can now read the actual values from the gateway configurator and write setpoint
values.
The process data should correspond with the values displayed in the Gateway
Configurator of MOVITOOLS
®
MotionStudio (see following figure).
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
63
Page 64

6
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
6.3.2 Access to UFR41B fieldbus gateway parameters
Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
In order to get an easy-to-use read access to parameters of the UFR41B fieldbus
gateway via explicit messages and the register object, follow these steps:
1. Create a user-defined data structure "SEW_Parameter_Channel" (see following
figure)
2. Define the following controller tags (see figure below).
3. Create a rung for the "ReadParameter" execution (following figure).
• For contact, select the tag "ReadParameterStart"
• For the Message Control, select the tag "ReadParameter"
11764AXX
11765AXX
11766AXX
64
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 65

Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
4. Click on in the MSG instruction to open the "Message Configuration" window
(see following figure).
11767AXX
Select "CIP Generic" as "message type". Fill the other fields in the following order:
A Source Element = ReadParameterRequest.Index
B Source Length = 12
C Destination = ReadParameterResponse.Index
D Class = 7
E Instance = 1
F Attribute = 4
G Service Code = e
The service type is set automatically.
hex
hex
hex
6
5. Specify the target device on the "Communication" tab. Click the [Browse] button and
select the required unit from the IO configuration (under Ethernet) in the Message
Path Browser (see following figure).
12131AXX
Do not select the "Connected" checkbox because both the controller and the
UFR41B option permit only a limit number of connections.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
65
Page 66

6
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
6. After downloading the changes to the PLC, the index of the parameter to be rea d can
be entered at ReadParameterRequest.Index. By alte ring ReadParameterStart to "1"
the read request is executed once (see following figure).
11966BXX
On response to the read request, ReadParameterResponse.Index should indicate
the read index and ReadParameterResponse.Data should contain the read data. In
this example, the timeout interval of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway (index 8606) set
by the scanner has been read (012Chex Ⳏ 0.3 s).
®
You can check the value in the MOVITOOLS
figure below). The tooltip of a parameter displays for example ind ex, subindex, factor,
etc. of the parameter.
MotionStudio parameter tree (see
12061AXX
66
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 67

Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
6.3.3 Access to unit parameters of lower-level units
6
Access to the device parameters of, for example, a MOVITRAC
CAN 1 system bus of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway is the same as access to the device
parameters of the UFR41B fieldbus gateway itself (see chapter 5.4.2)
The only difference is that Read/WriteParameterRequest.SubChannel1 must be set
to 3 and Read/WriteParameterRequest.SubAddress1 must be set to the SBus
address of MOVITRAC
®
B connected to UFR41B (see figure below).
®
B connected to the
In this example, MOVITRAC
option with SBus address 7 read the value 150 rpm from P160 Fixed setpoint n 11 (index
8489).
For a schematic representation of the parameter access to lower-level units, refer to the
chapter "Appendix".
®
B connected to a CAN 1 system bus of the UFR41B
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
11775BXX
67
Page 68

6
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
Only a few additions are necessary for activating write access to a parameter.
• Create the controller tags (see following figure).
11771AXX
• Create a rung for executing the "WriteParameter" command (see following figure).
11772AXX
For contact, select the tag "WriteParameterStart"
For message control, select the tag "WriteParameter"
• Click on in the MSG instruction to open the "Message Configuration" window
(see following figure).
11773AXX
Fill the other fields in the following sequence:
• Source Element = WriteParameterRequest.Index
• Source Length = 12
• Destination = WriteParameterResponse.Index
• Class = 7
• Instance = 2
• Attribute = 4
• Service Code = 10
hex
hex
hex
68
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 69

Configuration and Startup (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning examples in RSLogix 5000
• After downloading the changes to the PLC, index and value to be written into the
parameter can be entered at WriteParameterRequest.Index and WriteParameter-
Request.Data. By altering WriteParameterStart to "1", the write request is executed
once (see following figure).
6
11967BXX
On response to the write request, WriteParameterResponse.Index should give the
written index and WriteParameterResponse.Data should contain the written data. In
this example, 21hex (33 dec) was written to index 11001 (H1).
®
You can check the value in MOVITOOLS
MotionStudio.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
69
Page 70

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
Introduction
7 Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
7.1 Introduction
The EtherNet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP) is an open communication standard
based on the classic EtherNet protocols TCP/IP and UDP/IP.
EtherNet/IP has been defined by the Open DeviceNet Vendor Association (ODVA) and
ControlNet International (CI).
EtherNet/IP extends EtherNet technology to include the CIP application protocol
(Common Industrial Protocol). CIP is known in the field of automation engineering
because it is also used for DeviceNet and ControlNet as an application protocol.
7.2 Process data exchange
Up to 64 process data words can be exchanged with an EtherNet/IP master (scanner)
depending on the use of the UFR41B unit. The EtherNet/IP master (scanner) sets the
process data length when opening the connection.
In addition to a controlling "Exclusive Owner Connection", up to two "Listen Only
Connections" are available. This means the actual values of the drive can also be read
out by stand-by controllers or visualization devices.
If one controlling connection is already active via Modbus/TCP, an "Exclusive Owner
Connection" cannot be activated via EtherNet/IP without a power-on reset.
Timeout
response
The timeout status is triggered by the UFR41B option. The timeout interval must be set
by the EtherNet/IP master (scanner) when the connection is established. The EtherNet/IP specification refers to a "Requested Packet Interval (RPI)" instead of a timeout
interval.
®
The timeout interval displayed in the MOVITOOLS
results from the Requested Packet Interval (RPI) multiplied with the "Timeout Multiplier".
This timeout interval is retained in the device when an "Exclusive Owner Connection" is
removed, and the device switches to timeout status after the timeout interval has
elapsed. The timeout status is displayed on the front of the UFR41B option by the flashing red L13 LED.
A you can only activate the timeout delay via the bus, you must not change the value via
MOVITOOLS
The timeout state causes the response programmed in the gateway program to be
executed.
The timeout state can be reset via EtherNet/IP as follows:
• Via reset service of the identity object (class 0x01, instance 0x01, undetermined
attribute)
• By re-establishing the connection
• Via the reset bit in the control word
®
MotionStudio.
MotionStudio parameter tree
70
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 71

7.3 CIP object directory
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
In the Common Industrial Protocol, all unit data can be accessed via objects. The
objects listed in the following table are integrated in the UFR41B option.
Class [hex] Name
01 Identity object
02 Message Router Object
04 Assembly Object
06 Connection Manager Object
07 Register Object
0F Parameter Object
64 Vardata Object
F5 TCP/IP Interface Object
F6 Ethernet Link Object
The meaning of the objects and a description of how to access them is given in the
following section.
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
7
Identity object • The identity object contains general information on the EtherNet/IP device.
• Class code: 01
hex
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 0001 Revision 1
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0001 Maximum instance
Access Name Data
type
Default value
[hex]
Description
Instance 1
Attri-
Access Name Data type Default value [hex] Description
bute
1 Get Vendor ID UINT 013B SEW-EURODRIVE GmbH & Co
2GetDevice
3 Get Product
4Get
5 Get Status WORD See table in "Coding the attribute 5
6 Get Serial num-
7 Get Product
Type
Code
Revision STRUCT of
Major Revision
Minor Revision
ber
Name
UINT 0065 Manufacturer-specific type
UINT 0006 Product no. 6: UFR41B
USINT
USINT
UDINT Unique serial number
SHORT_
STRING
SEW GATEWAY
UFR41B
KG
Revision of the identity object,
depends on firmware version
status"
Product name
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
71
Page 72

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
• Coding attribute 5 "status":
Bit Name Description
0 Owned Controlling connection is active
1- Reserved
2 Configured Configuration complete
3- Reserved
4 - 7 Extended Device Status See table "Coding the extended device status"
8 Minor Recoverable Fault Minor fault that can be remedied
9 Minor Unrecoverable Fault Minor fault that cannot be remedied
10 Major Recoverable Fault Major fault that cannot be remedied
11 Major Unrecoverable Fault Major fault that cannot be remedied
12 - 15 - Reserved
• Coding of the "extended device status " (bits 4 - 7):
Value [binary] Description
0000 Unknown
0010 At least one faulty IO connection
0011 No IO connection established
0110 At least one IO connection active
Supported
services
Service Code [hex] Service Name Class Instance
01 Get_Attributes_All X X
05 Reset - X
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X
72
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 73

Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
CIP object directory
7
Message router
object
Class
Instance 1
Supported
services
• The message router object provides information on the implemented objects.
• Class code: 02
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 0001 Revision 1
Attribute
1 Get Object_List STRUCT of Object list comprising:
2 Get Number
Service code [hex] Service Name Class Instance
01 Get_Attributes_All X -
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X
Access Name Data type Default value
Access Name Data type Default value
hex
[hex]
[hex]
Number UINT 0009
Classes ARRAY of
UINT
UINT 0009 Maximum number of connections
Available
01 00 02 00
04 00 06 00
07 00 0F 00
64 00 F5 00
F6 00
Description
Description
• Number of objects
• List of objects
Assembly object • The assembly object is used to access the UFR41B process data. IO connections
can be created for the instances of the assembly object to exchange cyclic process
data.
• Class code: 04
hex
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 0002 Revision 2
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0082 Maximum instance
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
Description
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
73
Page 74

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
Instance 162 SEW PO data
range
Instance 121 "Heartbeat"
Instance 172 SEW PI data range
This instance is used to access the UFR41B process output data. MOVIDRIVE® can be
controlled by only one scanner. Therefore, only one connection can be established with
this instance.
Attribute
3GetData Array of
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
- OUTPUT assembly
BYTE
Description
This instance is accessed when the scanner wants to establish an input only connection.
No process output data is sent with this type of connection. It is used only to read
process input data.
Attribute
3GetData Array of
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
- OUTPUT assembly
BYTE
Description
Data size = 0
This instance is used to access the UFR41B process output data. Several multicast
connections or a point-to-point connection can be established to this instance.
Attribute
3GetData Array of
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
- INPUT assembly
BYTE
Description
Supported
services
TIP
The names "INPUT assembly" and "OUTPUT assembly" refer to the processes as
seen from the network’s point of view. "INPUT assembly" produces data on the
network, an "OUTPUT assembly" consumes data from the network.
Service code [hex] Service Name Class Instance 161 Instance 121 Instance 171
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X - X
74
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 75

Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
CIP object directory
Register object • The register object is used to access an SEW parameter index.
• Class code: 07
Class
hex
7
Attribute
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0009 Maximum instance
The MOVILINK
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
®
parameter services are mapped in the nine instances of the register
Description
object. The "Get_Attribute_Single" and "Set_Attribute_Single" services are used for
access.
As the register object is designed so that INPUT objects can only be read and OUTPUT
objects can be read and written, the options listed in the following table are available for
addressing the parameter channel.
Instance INPUT/OUTPUT Resulting MOVILINK® service with
Get_Attribute_Single Set_Attribute_Single
1 INPUT READ parameter Invalid
2 OUTPUT READ WRITE parameter
3 OUTPUT READ WRITE VOLATILE parameter
4 INPUT READ MINIMUM Invalid
5 INPUT READ MAXIMUM Invalid
6 INPUT READ DEFAULT Invalid
7 INPUT READ SCALING Invalid
8 INPUT READ ATTRIBUTE Invalid
9 INPUT READ EEPROM Invalid
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
75
Page 76

7
READ EEPROM
Get_Attribute_Single READ
READ MINIMUM
READ MAXIMUM
READ DEFAULT
READ SCALING
READ ATTRIBUTE
WRITE
WRITE VOLATILE
Get_Attribute_Single
Get_Attribute_Single
Set_Attribute_Single
Set_Attribute_Single
Get_Attribute_Single
Get_Attribute_Single
Get_Attribute_Single
Get_Attribute_Single
Get_Attribute_Single
Input
(Instance 1)
Input
(Instance 4)
Input
(Instance 5)
Input
(Instance 6)
Input
(Instance 7)
Input
(Instance 8)
Get_Attribute_Single
Input
(Instance 9)
Output
(Instance 2)
Output
(Instance 3)
EtherNet/IP SEW fieldbus profile
DPRAM
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
76
Figure 1: Description of the parameter channel
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
54185BEN
Page 77

Instance 1 - 9
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
7
Attribute
1 Get Bad Flag BOOL 00 0 = good / 1 = bad
2 Get Direction BOOL 00
3 Get Size UINT 0060 Data length in bits (96 bits = 12 bytes)
4 Get/Set Data ARRAY of BITS Data in format of the SEW parameter
Access Name Data type Default
value [hex]
01
Description
Input register
Output register
channel
TIPS
Explanation of the attributes:
• Attribute 1 indicates whether an error occurred during the previous access to the
data field.
• Attribute 2 indicates the direction of the instance.
• Attribute 3 indicates the data length in bits
• Attribute 4 represents the parameter data. When accessing attribute 4, the SEW
parameter channel must be attached to the service telegram. The SEW parameter
channel consists of the elements listed in the following table.
Name Data type Description
Index UINT SEW unit index
Data UDINT Data (32 bit)
Subindex BYTE SEW unit subindex
Reserved BYTE Reserved (must be '0')
Subaddress 1 BYTE 0
Subchannel 1 BYTE 0 3 Lower-level bus system, e.g. SBus 1
Subaddress 2 BYTE Reserved (must be '0')
Subchannel 2 BYTE Reserved (must be '0')
Parameter of the
UFR41B itself
e.g. SBus address of units connected to
1 ...
the SBus of UFR41B
The subchannels and subaddresses apply depending on the lower-level bus system
from MOVI-PLC
®
advanced DHR41B to the drives.
For a schematic representation of the parameter access to lower-level units, refer to the
chapter "Appendix".
Subchannel 1
0 UFR41B itself 0
1 Reserved 0
2 EtherCAT X36 (in preparation)
3 SBus1 (X33 and X26) 1 - 16
4 SBus2 (X32) 17 - 32
Interface Value range subaddress 1
Supported
services
Service code [hex] Service Name Instance
0x0E Get_Attribute_Single X
0x10 Set_Attribute_Single X
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
77
Page 78

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
Parameter object • In exceptional cases, you can also use the parameter object to access an SEW
parameter channel.
• Class code: 0F
hex
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 0001 Revision 1
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0005 Maximum instance
8GetParameter
9 Get Configura-
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
UINT 0009 Bit 0: Supports parameter instances
Class
Descriptor
UINT 0000 Configuration assembly is not
tion Assembly Interface
Description
Bit 3: Parameters are saved permanently
supported.
The instances of the parameter object should only be used to access SEW parameters
when the EtherNet/IP scanner does not support the option to attach user-defined data
to the services "Get_Attribute_Single" and "Set_Attribute_Single."
When you use the parameter object, it takes a number of steps to address a parameter
index.
• First, the address of the required parameter is set in instances 1 to 4.
• Next, instance 5 is used to access the parameter that is addressed in instances 1 to
4.
Access to an SEW parameter index via the parameter object is complicated and prone
to errors. Consequently, this process should only be used when the EtherNet/IP scanner
does not support configuration using the mechanisms of the register object.
Instance 1 - SEW
parameter index
Attribute
1SetParameter
2 Get Link Path
3 Get Link Path Packed
4 Get Descriptor WORD 0000 Read/write parameter
5 Get Data type EPATH 00C7 UINT
6 Get Data Size USINT 02 Data length in bytes
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
UINT 207A Index of the parameter
Val ue
USINT 00 No link is specified
Size
00 Not used
EPAT H
Description
78
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 79

Instance 2 - SEW
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
subindex
Instance 3 - SEW
subparameter 1
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
Attribute
1SetParameter
2 Get Link Path
3 Get Link Path Packed
4 Get Descriptor WORD 0000 Read/write parameter
5 Get Data type EPATH 00C7 UINT
6 Get Data Size USINT 02 Data length in bytes
Attribute
1SetParameter
2 Get Link Path
3 Get Link Path Packed
4 Get Descriptor WORD 0000 Read/write parameter
5 Get Data type EPATH 00C7 UINT
6 Get Data Size USINT 02 Data length in bytes
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
UINT 0000 Low byte contains the subindex
Val ue
USINT 00 No link is specified
Size
00 Not used
EPAT H
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
UINT 0000 Low byte contains subaddress 1
Val ue
USINT 00 No link is specified
Size
00 Not used
EPAT H
Description
Description
High byte contains subchannel 1
7
Instance 4 - SEW
subparameter 2
Attribute
1SetParameter
2 Get Link Path
3 Get Link Path Packed
4 Get Descriptor WORD 0000 Read/write parameter
5 Get Data type EPATH 00C7 UINT
6 Get Data Size USINT 02 Data length in bytes
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
UINT 0000 Low byte contains subaddress 2
Val ue
USINT 00 No link is specified
Size
00 Not used
EPAT H
Description
High byte contains subchannel 2
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
79
Page 80

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Instance 5 - SEW
read/write
Supported
services
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
Attribute
1SetParameter
2 Get Link Path
3 Get Link Path Packed
4 Get Descriptor WORD 0000 Read/write parameter
5 Get Data type EPATH 00C8 UDINT
6 Get Data Size USINT 04 Data length in bytes
Service code [hex] Service Name Class Instance
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X
10 Set_Attribute_Single - X
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
UDINT The set service executes write
Val ue
USINT 00 No link is specified
Size
00 Not used
EPAT H
Description
access to the parameters
addressed in instances 1 to 4.
The get service executes read
access to the parameters
addressed in instances 1 to 4.
80
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 81

Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
CIP object directory
Vardata object • This manufacturer-specific object is required to use the engineering option of some
of the software tools provided by SEW-EURODRIVE.
• Class code: 64
Class None of the class attributes are supported.
Instance 1
hex
7
Supported
services
Attribute
1 Get Data ARRAY OF
2 Get Size UINT 00F2 Maximum data length in bytes
Service code [hex] Service Name Instance attribute 1 Instance attribute 2
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X
32 Vardata (custom) X -
Access Name Data type Default value
[hex]
--
SINT
Description
The standardized service "Get_Attribute_Single" (Service Code 0x0E) returns a data
stream with the maximum data length (attribute 2) when instance attribute 1 is accessed.
The data content is filled with zeros. If a data stream is added to the request telegram
(Service Type Custom), this data is returned in a mirrored form (Vardata test mode).
The Vardata service (service code 0x32) is a manufacturer-specific service. With this
service, the telegram structure for the request and response is the same. The telegram
contains routing information, the data length of the Vardata user data telegram and the
actual Vardata layer 7 telegram. The data length of the Vardata layer 7 telegram is
variable.
The following table shows the complete telegram structure.
Name Data type
Subaddress 1 BYTE
Subchannel 1 BYTE
Subaddress 2 BYTE
Subchannel 2 BYTE
Data Len Low BYTE
Data Len High BYTE
Reserved BYTE
Reserved BYTE
FC BYTE
Vardata Array of BYTE
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
81
Page 82

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
CIP object directory
TCP/IP interface
object
Class
Instance 1
• The TCP/IP interface object enables the IP parameters to be configured via
EtherNet/IP.
• Class code: F5
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 0001 Revision 1
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0001 Maximum instance
3 Get Number of
Attribute
1 Get Status DWORD 00000001 Valid configuration
2 Get Configuration
3 Set Configuration
4 Get Physical Link
5 Set Interface Con-
6 Get Host Name STRING Not used
Access Name Data type Default
Access Name Data type Default
hex
Description
value [hex]
Instances
Capability
Control
Object
Path Size UINT 0002
Path Padded
figuration
IP Address UDINT Current IP address
Network Mask UDINT Current subnetwork mask
Gateway
Address
Name Server UDINT 00000000 DNS is not supported
Name Server 2 UDINT 00000000 DNS is not supported
Domain Name STRING sew.de
UINT 0001 DHR41B has one TCP/IP interface
Description
value [hex]
DWORD 00000014 The interface configuration attribute
(5) is writable. The DHCP can be
used for configuration.
DWORD 00000002 0 = The unit uses the stored IP
parameters at startup.
2 = The unit waits for its IP
configuration via DHCP at startup.
STRUCT of Reference to the EtherNet link object
(class code 0xF6) as sublayer.
20 F6 24 01
EPAT H
STRUCT of
UDINT Current standard gateway
Supported
services
Service code [hex] Service Name Class Instance
01 Get_Attributes_All X _
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X
10 Set_Attribute_Single - X
82
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 83

Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
CIP object directory
7
EtherNet link
object
Class
Instance 1
Ethernet
connection X30:1
• Information on the Ethernet communication interface is stored in the Ethernet link
object.
• Class code: F6
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 0002 Revision 2
2 Get Max Instance UINT 0002 Maximum instance
3 Get Number of
Attribute
1 Get Interface
2 Get Interface Flags DWORD • Bit 0 displays the active link
3 Get Physical
Access Name Data type Default
Access Name Data type Default
hex
Instances
Speed
Address
Description
value [hex]
UINT 0002 DHR41B has two Ethernet interfaces
value [hex]
UDINT 00000064 Default value = 100 → Transmission
ARRAY of
6 USINTs
00 0F 69
xx xx xx
Description
speed in MBit/s
• Bit 1 displays full duplex mode
• Bit 2 ... bit 4 signal negotiation
status
• Bit 5 shows whether the manual
setting has to be reset
• Bit 6 indicates a local hardware
fault
MAC ID
SEW MAC OUI: 00 0F 69
Instance 2
Ethernet
connection X30:2
Supported
services
Attribute
1 Get Interface
2 Get Interface Flags DWORD • Bit 0 displays the active link
3 Get Physical
Service code [hex] Service Name Class Instance
01 Get_Attributes_All X _
0E Get_Attribute_Single X X
Access Name Data type Default
value [hex]
Speed
Address
UDINT 00000064 Default value = 100 → transmission
ARRAY of
6 USINTs
00 0F 69 xx
xx xx xx
Description
speed in MBit/s
• Bit 1 displays full duplex mode
• Bits 2 - bit 4 indicate the
negotiation status
• Bit 5 shows whether the manual
setting has to be reset
• Bit 6 indicates a local hardware
fault
MAC ID
SEW MAC OUI: 00 0F 69
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
83
Page 84

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
Return codes of the parameterization via explicit messages
7.4 Return codes of the parameterization via explicit messages
If a parameter request via explicit messages fails, a fault code can be used to determine
the cause. An error can be generated either by the UFR41B option, by the EtherNet/IP
system, or by a timeout.
The general error code (ERR) and the additional code (EXERR) can be read out from
the status registers of the message tags (see figure below).
Return codes of
EtherNet/IP
SEW-specific
return codes
11937AXX
EtherNet/IP-specific return codes are returned in the error telegram if the data format is
not maintained during the transfer or if a service is performed that has not been implemented. The coding of these return codes is described in the EtherNet/IP specification
(see section "General error codes"). The General Error Code of a manufacturer-specific
return code is 1F
The return codes that the UFR41B option or lower-level units send in the event of
incorrect parameterization are described in section "MOVILINK
hex
.
®
-specific return codes".
In conjunction with EtherNet/IP, the return codes are returned in the following format.
The following table shows the data format for a parameter response telegram.
Byte offset
0 1 2 3
Function General error code Additional code
Example 1F
hex
Vendor-specific
In the example above, MOVILINK
Length (words)
01
hex
only low word (word 1)
®
error class 08 (General Error) is shown in the high
byte of the additional code. The MOVILINK
®
Additional Code
Word 1 (lowbyte)
10
hex
MOVILINK® Additional Error Code
Additional Code
Word 1 (highbyte)
08
hex
MOVILINK®
Error Class
additional error code 10 (invalid index) is
shown in the low byte of the additional code. This information shows that the system
tried to access a unit index that does not exist.
84
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 85

Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Return codes of the parameterization via explicit messages
7
Timeout of
explicit
messages
General error
codes
The timeout is triggered by the UFR41B option. The timeout interval must be set by the
master after the connection has been established. The EtherNet/IP specification refers
to an "Expected packet rate" rather than a timeout time in this case. The expected
packet rate is calculated from the timeout delay as follows:
t
Timeout_ExplicitMessages
= 4 × t
Expected_Packet_Rate_ExplicitMessages
It can be set using connection object class 5, instance 1, attribute 9. The range of values
runs from 0 ms to 655535 ms in 5 ms steps.
If there is a timeout for the explicit messages, this connection type is automatically
disconnected for the explicit messages. This is the default setting for EtherNet/IP. The
connection for these explicit messages must be re-established to communicate with
these messages again. The timeout is not forwarded to the gateway program.
General error
code (hex)
00 Success Successful
01 Connection failure A connection-specific service has failed.
02 Resource unavailable The source required for performing the service is unavailable.
03 Reserved
04 Path segment error The processing node cannot interpret the "Path segment
05 Path destination unknown The "Path" refers to an object class, object instance or a
06 - 07 Reserved
08 Service not supported The service is not supported for the selected class/instance.
09 Invalid attribute value Invalid attribute data have been sent.
0A - 0B
0C Object state conflict The selected object cannot perform the service in its current
0D Reserved
0E Attribute not settable It is not possible to access the selected object for writing.
10 Device state conflict The current status of the device makes it impossible to
11 - 12 Reserved
13 Not enough data The length of the transferred data is too short for the service
14 Attribute not supported The selected attribute is not supported.
15 Too much data The length of the transferred data is too long for the service to
16 Object does not exist The selected object is not implemented in the device.
17-1D Reserved
1E Embedded Service Error Internal processing error
1F Vendor specific error Manufacturer-specific error (see "Fieldbus Unit Profile"
20 Invalid parameter Invalid parameter. This error message is used when a
21 - FF Reserved
Error name Description
identifier" or the segment syntax.
structural element that is not supported by the processing
node.
status.
perform the required service.
to be performed.
be performed.
manual).
parameter does not satisfy the requirements of the
specification and/or the requirements of the application.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
85
Page 86

7
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
Return codes of the parameterization via explicit messages
MOVILINK®specific return
codes
The following table shows the MOVILINK®-specific return codes (MOVILINK® "Error
Class" and "Additional Code") in the event of an incorrect parameterization.
MOVILINK
Error Class Additional Code Description
0x05
®
0x00 Unknown error
0x01 Illegal Service
0x02 No Response
0x03 Different Address
0x04 Different Type
0x05 Different Index
0x06 Different Service
0x07 Different Channel
0x08 Different Block
0x09 No Scope Data
0x0A Illegal Length
0x0B Illegal Address
0x0C Illegal Pointer
0x0D Not enough memory
0x0E System Error
0x0F Communication does not exist
0x10 Communication not initialized
0x11 Mouse conflict
0x12 Illegal Bus
0x13 FCS Error
0x14 PB Init
0x15 SBUS - Illegal Fragment Count
0x16 SBUS - Illegal Fragment Type
0x17 Access denied
Not used
86
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 87

Ethernet Industrial Protocol (EtherNet/IP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Return codes of the parameterization via explicit messages
7
MOVILINK
Error Class Additional Code Description
0x08
®
0x00 No Error
0x10 Illegal Index
0x11 Not yet implemented
0x12 Read only
0x13 Parameter Blocking
0x14 Setup runs
0x15 Value too large
0x16 Value too small
0x17 Required Hardware does not exist
0x18 Internal Error
0x19 Access only via RS485 (via X13)
0x1A Access only via RS485 (via XT)
0x1B Parameter protected
0x1C "Controller inhibit" required
0x1D Value invalid
0x1E Setup started
0x1F Buffer overflow
0x20 "No Enable" required
0x21 End of File
0x22 Communication Order
0x23 "IPOS Stop" required
0x24 Autosetup
0x25 Encoder Nameplate Error
0x29 PLC State Error
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
87
Page 88

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Unit description file for Modbus/TCP
8 Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
This section provides information about the configuration of the Modbus/TCP master
and startup of the inverter for fieldbus operation. Prerequisite is the correct connection
and setting of the IP address parameters of UFR41B in accordance with chapter
"Assembly and Installation Instructions".
8.1 Unit description file for Modbus/TCP
TIP
There are no specific unit description files for Modbus/TCP.
8.2 Configuring the master (Modbus scanner)
The first example refers to the configuration and programming of a Schneider Electric
control system TSX Premium P57203 using the programming software PL7 PRO. An
ETY4103 is used as the Ethernet component. The information and illustrations are
based on the English version of the PL7 PRO software.
Hardware
configuration
(control
structure)
TIP
• Enter values in PL7 PRO using the keypad.
• As the Ethernet, use bus master components from Schneider Electric that support
IO scanning. The Modbus/TCP interface module for SEW drives cannot be
addressed via "Peer COP". However, Ethernet bus masters that only support "Peer
COP" can access the drives from the PLC program using read and write
commands.
• Start PL7 PRO and enter the control type.
• Enter the hardware configuration for the control system in the application browser
under STATION / Configuration / Hardware Configuration .
88
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
10815AXX
Page 89

Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuring the master (Modbus scanner)
8
Settings for the
Ethernet
component
• To open the configuration window, double-click on the Ethernet component.
• If you have a non-extendable rack, enter a "1" in the "Network" input field in the
"XWAY address" section.
• Enter the number of the slot that the Ethernet component is plugged into (here: 2) in
the input field "Station" in the "XWAY address" section. 2). In this case, the XWAY
address is 1.2.
• In the section "IP address configuration" select the radio button "Configured". Enter
the IP address and the network parameters in the input fields "IP address", "Subnetwork mask" and "Gateway address". If the control system is to receive the address
parameters via a DHCP server, select the radio button "Client/Server configuration"
in the section "IP address configuration".
• In the "Ethernet configuration" section, select the radio button "Ethernet II".
• In the "Module utilities" section, select the checkbox "IO Scanning".
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
10816AXX
89
Page 90

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Configuring the master (Modbus scanner)
Addressing the
drive using IO
scanning
• Choose the "IO Scanning" tab page. In this tab page you specify which of the stations
connected to the Modbus are to exchange cyclical data.
• In the section "Master %MW zones" enter the control memory areas that are to be
used to exchange cyclical data with the Modbus stations. You will use the memory
addresses later in your PLC program.
• Enter the following in the "Scanned peripherals" group:
– In the "IP address" input field, enter the IP address of the SEW drive.
– In the "Unit ID" input field, enter the value "0".
– In the "Repetitive rate" dropdown menu, enter the cycle time that is used to
address the stations.
– Enter the value "4" in the input fields "RD ref.slave" and "WR ref. slave" as the
cyclical process data are available from offset 4.
– In the input fields "RD count" and "WR count" enter the number of words to be
exchanged. The values must be the same in both fields. For the UFR41B option,
you can enter between 1 and 64 words.
90
10817AXX
• Click on the "Confirm" button to confirm the rack configuration and the global
configuration.
• Once you have transferred your settings and started the program, the color of LED
L13 (NETWORK/STATUS) of UFR41B changes to green (see section "Status LEDs
of the UFR41B option").
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 91

Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Project planning examples in PL7 PRO
8.3 Project planning examples in PL7 PRO
8.3.1 UFR41B fieldbus gateway with 16 PD data exchange
1. Set the IP address of the DFE33B option see chapter "Setting the IP address
parameters").
2. Integrate the UFR41B fieldbus gateway into the configuration for the I/O scanning
according to section "Configuring the master (Modbus scanner)".
3. Now, the integration into the PLC project can be performed.
4. Create a new section in PL7 PRO in the application browser under [Station] /
[Program] / [Mast Task] / [Sections] .
5. In this example, the setpoints for the drive start from MW150 (see following figure).
8
6. Now save the project and transfer it to the PLC. The PLC is set to RUN mode.
You can now read the actual values from the UFR41B fieldbus gateway and write
setpoint values.
The process data should correspond with the values displayed in the gateway
program of MOVITOOLS
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
®
MotionStudio (see following figure).
10818AXX
91
Page 92

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP
8.4 Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP
As there are many different master systems and software solutions available for
Modbus/TCP for standard PCs, there is no "reference controller" the examples are
based on. This is why this section gives detailed examples for the telegram structure.
You can compare the telegram structure in your own applications with the telegram
structure in these examples for troubleshooting. There are simple tools for recording
telegrams via the Ethernet network, e.g. Wireshark (see following figure), Packetizer
etc. These freeware tools are available on the Internet.
Observe that tracing all Ethernet telegrams in a network is only possible with a tab, hub
or a switch with a port mirror function. The telegrams sent from and to the PC that is also
used for recording, can always be written of course.
The figure above provides an example of how setpoints are sent to the Modbus/TCP
slave with IP address 10.3.71.119. The 3 process data words are located from offset 4
(reference number) and are addressed via unit ID 255.
All the other examples merely describe the Modbus/TCP part of the telegram. The
TCP/IP part of the telegram, as well as establishing and dropping a TCP/IP connection
are not explained in detail.
92
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
12047AXX
Page 93

Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP
8.4.1 Writing and reading process data
The process data exchange can be performed either via FC3 (read) and FC16 (write),
or FC23 (read and write):
For writing 3 process data words (setpoints) to a Modbus/TCP slave via FC16, the
TCP/IP telegram to port 502 is structured as illustrated above.
Byte Value Meaning Interpretation Help
0
0x00 Transaction identifier
1
2
0x00 Protocol identifier
3
40x00
50x0d
6 0xFF Unit identifier Must be 0 or 255
7 ox10 Function code Service = FC16 (Write Register)
80x00
90x04
10 0x00
11 0x03
12 0x06 Write Byte Count Number of PD × 2 = 6
13 0x00
14 0x11
15 0x22
16 0x33
17 0x44
18 0x55
Length field
Write reference number
Write Word Count
Data
Number of bytes after byte 5:
3 (number PD) × 2 + 7 = 13
Offset where PD start:
Must always be 4
Number of PD (here 3):
Must be PD 1 - 64
Process output data word 1
Process output data word 2
Process output data word 3
8
For a detailed description,
refer to Modbus/TCP specification and section "Modbus
protocol (Modbus/TCP)"
Data mapping and definition,
see IEC program
Only bytes 0-11 are returned in the response telegram of port 502 of the Modbus/TCP
slave, where all values remain unchanged with the exception of byte 5. Byte 5 (low byte
length field) is corrected to value 6.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
93
Page 94

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP
During process data exchange via FC23, the telegram that is used to write and read 3
process data words (PD) each is structured as follows.
Byte Value Meaning Interpretation Help
0
0x00 Transaction identifier
1
2
0x00 Protocol identifier
3
40x00
50x11
6 0xFF Unit identifier Must be 0 or 255
7 0x10 Function code
80x00
90x04
10 0x00
11 0x03
12 0x00
13 0x04
14 0x00
15 0x03
16 0x06 Write Byte Count Number of PD × 2 = 6
17 0x00
18 0x11
19 0x22
20 0x33
21 0x44
22 0x55
Length field
Read reference number
Read Word Count
Write reference number
Write Word Count
Data
Number of bytes after byte 5:
3 (number PD) × 2 + 11 = 17
Service = FC23 (Read + Write
Register)
Offset where PD start:
Must always be 4
Number of PD (here 3):
Must be PD 1 - 64
Offset where PD start:
Must always be 4
Number of PD (here 3):
see read word count
Process output data word 1
Process output data word 2
Process output data word 3
For a detailed description,
refer to Modbus/TCP
specification and section
'Modbus protocol
(Modbus/TCP)'
Data mapping and
definition, see IEC
program
The following data bytes are returned in the response telegram of the Modbus/TCP
slave:
Byte Value Meaning Interpretation Help
0
0x00 Transaction identifier
1
2
0x00 Protocol identifier
3
40x00
50x09
6 0xFF Unit identifier Must be 0 or 255
7 0x17 Function code
8 0x06 Write Byte Count Number of PD × 2 = 6
90x00
10 0xAA
11 0xBB
12 0xCC
13 0xDD
14 0xEE
Length field
Data
Number of bytes after byte 5:
3 (number PD) × 2 + 3 = 9
Service = FC23 (Read + Write
Register)
Process input data word 1
Process input data word 2
Process input data word 3
For a detailed description,
refer to Modbus/TCP
specification and section
"Modbus protocol
(Modbus/TCP)"
Data mapping and
definition, see IEC program
94
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 95

8.4.2 Parameter access
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP
8
FC23 is suitable for the parameter access via the MOVILINK
is possible to realize the request to the MOVILINK
®
service and the collection of the
®
parameter channel as it
response in one Modbus/TCP service.
To read a parameter, the TCP/IP telegram is structured as follows.
Byte Value Meaning Interpretation Help
0
0x00 Transaction identifier
1
2
0x00 Protocol identifier
3
40x00
50x13
6 0x00 Unit identifier
7 0x17 Function code
80x02
90x00
10 0x00
11 0x04
12 0x02
13 0x00
14 0x00
15 0x04
16 0x08 Write Byte Count 8 bytes MOVILINK
17 0x31
18 0x00 Parameter subindex
19 0x20 Parameter index:
20 0x6C
21 0x00 Parameter value Irrelevant for
22 0x00
23 0x00
24 0x00
1) The unit identifier 0 and 0xFF is used to access the parameters of DHR41B directly. For other values, the
request is passed on to a lower-level unit. The assignment of the unit identifier to the downstream units
on the system buses is determined via the routing table of the DHR41B control configuration. This allows
parameter access for inverters that are connected via a DHR41B unit without any restrictions. See the
"Appendix" for a schematic representation of parameter access to lower-level units.
Length field
Read reference number
Read Word Count
Write reference number
Write Word Count
Data:
MOVILINK
channel
®
parameter
Number of bytes after byte 5:
Must be 19 for MOVILINK
1)
Service = FC23 (Read + Write
Register)
Offset where the MOVILINK
parameter channel starts:
Must always be 512
Must always be 4 for the
MOVILINK
Offset where the MOVILINK
parameter channel starts:
Must always be 512
Must always be 4 for the
MOVILINK
Management byte: 0x31 = read
0x206c = 8300 = Firmware part
number
read service
®
parameter channel.
®
parameter channel.
®
®
®
®
For a detailed description,
refer to Modbus/TCP
specification and section
"Modbus protocol (Modbus/TCP)"
Data mapping and definition, see IEC program and
SEW unit profile
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
95
Page 96

8
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Configuration and Startup (Modbus/TCP)
Examples for data exchange via Modbus/TCP
The response telegram receives the response to the MOVILINK® read service.
Byte Value Meaning Interpretation Help
0
0x00 Transaction identifier
1
2
0x00 Protocol identifier
3
40x00
50x11
6 0x00 Unit identifier
7 0x17 Function code
8 0x02 Read reference number 8 bytes MOVILINK
17 0x31
18 0x00 Parameter subindex
19 0x20 Parameter index:
20 0x6C
21 0x00 The parameter value
22 0x00
23 0x00
24 0x00
1) The unit identifier 0 and 0xFF is used to access the parameters of DHR41B directly. For other values, the
request is passed on to a lower-level unit. The assignment of the unit identifier to the downstream units on
the system buses is determined via the routing table of the DHR41B control configuration. This allows
parameter access for inverters that are connected via a DHR41B unit without any restrictions. See the
"Appendix" for a schematic representation of parameter access to lower-level units.
Length field
Data:
MOVILINK
channel
®
parameter
Number of bytes after byte 5:
Must be 11 for MOVILINK
1)
Service = FC23 (Read + Write
Register)
Management byte: 0x31 = read
0x206c = 8300 = Firmware part
number
0xA82e5b0d corresponds to the
firmware part number
28216102.53
®
®
For a detailed description,
refer to Modbus/TCP
specification and section
"Modbus protocol
(Modbus/TCP)"
For data mapping and
definition, see unit setting
and SEW unit profile
96
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 97

Modbus Protocol (Modbus/TCP)
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
9 Modbus Protocol (Modbus/TCP)
9.1 Introduction
Modbus/TCP is an open protocol based on TCP/IP. It was one of the first protocol types
to become standard in industrial Ethernet interfaces for process data transfer.
Modbus frames are exchanged via the TCP/IP port 502. Every master IP address is
accepted. Modbus exclusively uses the coding "BIG ENDIAN" (Motorola data format or
high byte first).
Access via "Peer COP" is not possible. Make sure that the bus master supports "IO
scanning".
9.1.1 Mapping and addressing
The logic Modbus address range is 64 k words and is addressed via the reference
number (offset). Four different tables can be in the address range:
• Binary inputs (RO)
• Binary outputs (RW)
• Input register (RO)
• Output register (RW)
The tables can be separate or overlapping.
Introduction
9
The UFR41B option provides the following data areas:
• For process data transfer, there is a table that allows for write access (for setpoint
values) as well as read access (for actual values).
This table starts at offset 4 and ends at offset 0FF
transferred process data words.
• The process data output words from the controller are also saved in another table. It
allows for one or several additional clients (e.g. visualization) to read the current
setpoint values.
This table starts at offset 104
• A third table is provided for parameter access.
This table starts at offset 200
MOVILINK
• The remaining address scope from offset 400
not be addressed.
The data word at offset 219
reading) the timeout monitoring time.
®
parameter channel (see "Fieldbus Unit Profile" manual).
and ends at offset 1FF
hex
, ends at offset 2FF
hex
hex
(8606
) is a special case, it allows for writing (and
dec
. It contains the 1 64 cyclically
hex
.
hex
and contains 4 words of the
hex
to FFFF
hex
is reserved and must
hex
TIP
For Schneider Electric control systems:
The address range often starts with 40001
value "0".
, which corresponds to an offset with the
hex
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
97
Page 98

9
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Modbus Protocol (Modbus/TCP)
Introduction
9.1.2 Services (function codes)
9.1.3 Access
For process data exchange, parameter data exchange and unit identification, the
DHR41B option provides 4 FC.. services (Function Codes).
• FC 3 Read Holding Registers
• FC16 Write Multiple Registers
• FC23 Read/Write Multiple Registers
• FC43 Read Device Identification
The FC3 and FC16 services allow reading or writing of one or more registers. FC23
allows a register block to be read and written simultaneously. FC43 can be used for a
unit identification by reading out the identity parameters.
The implemented registers and possible services (function codes) for data exchange
are summarized in the following table.
Meaning when
Offset (hex) Read Write Access Comment
0-3 - - - Reserved
4 - FF Process input
100 - 103 - - - Reserved
104 - 1FF Process output
200 - 2FF Result acyclical
300 - FFFF - - - Reserved
Special
case: 219E
(8606
dec
data (actual
values)
data (setpoint
values)
parameter
channel
Fieldbus timeout
interval, read
)
value
Process output data
(setpoint values)
- FC3 For reading the setpoint values by
Request acyclical
parameter channel
Fieldbus timeout
interval, write value
FC3,
FC16,
FC23
FC3,
FC16,
FC23
FC3, FC16 Parameter P819: 16-bit value,
0 - 64 words
a client other than the controlling
one
4 words
timeout interval in ms
98
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
Page 99

9.2 Protocol structure
MBAP Header
Transa ction-ID Protocol-ID Length (1+1+N) UI-D
Function Code-Data
FC N Data
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
The Modbus protocol consists of a header and function code data. The header is the
same for all request and response telegrams and error messages (exceptions). A varying number of data is added to it depending on the function code (see following figure).
9.2.1 Header
The protocol bytes of the header are described in the following table:
Byte Designation Meaning
0
1
2
3
4 Length field (upper byte) 0
5 Length field (lower byte) Number of function codes data bytes + 1 (unit identifier)
6 Unit identifier (slave address) This is the slave address. In order to access the UFR41B process
7 Function code Requested service
8 ... Data Data depending on requested service
Modbus Protocol (Modbus/TCP)
Protocol structure
Transaction identifier Often 0, is simply copied by the server (slave)
Protocol identifier 0
data, it must be set to "0" (0x00) or 255 (0xFF).
The following address assignments apply to the parameter
channel access (Offset 200 - 203
• 0 or 254 for parameters of the UFR41B
• 1 - 253 for parameters of a lower-level unit connected to
UFR41B. The assignment of unit identifier to the units on the
system buses is determined via the routing table on the
UFR41B memory card (see section "Appendix").
hex
):
9
64064AXX
• The slave simply copies the transaction identifier (byte 0 and 1). It can help the
master to identify related actions.
• The protocol identifier (byte 2 and 3) must always be "0".
• The length bytes (byte 4 and 5) specify the number of bytes occurring in the length
field. As the maximum telegram length is 255 bytes, the "upper byte" must be "0".
• The unit identifier (byte 6) can be used for distinguishing between several connected
stations (e.g. bridges or gateways). It works as a subaddress that is only used for the
parameter access for SEW devices. The process data are always mapped to the unit
that is addressed via the unit identifier 0 or FF
hex
.
• The 7 bytes of the header are followed by the function code and the data.
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
99
Page 100

9
MBAP Header Function Code-Data(FC03)
FC
(0x03)
Read Address Read WordCount
T- ID (0x00) Prot-ID (0x00) Length (1+5)
UI-D
00
I
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: info@clrwtr.com
Modbus Protocol (Modbus/TCP)
Protocol structure
9.2.2 Service FC3 - Read Holding Registers
With the service FC3 Read holding registers, you can read a variable number of
registers (see following figure).
Example Request:
Byte Designation Meaning/permitted values
0 - 6 MBAP header See chapter "Header".
7 Function code Requested service: 3 (Read Holding Register)
8 Reference number (high) Offset
9 Reference number (low) Offset
10 Word count (high) Number of words (register)
11 Word count (low) Number of words (register)
64065AXX
Response:
Byte Designation Meaning/permitted values
0 - 6 MBAP header See chapter "Header".
7 Function code Service: 3 (Read Holding Register)
8 Byte count Number of following bytes
9.... Data 2 - ... Data bytes depending on the length
Exception:
Byte Designation Meaning/permitted values
0 - 6 MBAP header See chapter "Header".
7 Function code 83
8 Exception Code Error code
hex
100
Manual – Fieldbus Gateway UFR41B EtherNet/IP, Modbus/TCP and PROFINET IO
 Loading...
Loading...