Page 1

®
TM
NetBotz
Rack Monitor 250
User Guide
NBRK0250
NBACS125
NBACS1356
990-9890D
Publication Date: October 2018
Page 2

APC by Schneider Electric Legal Disclaimer
The information presented in this manual is not warranted by APC by Schneider Electric to be authoritative,
error free, or complete. This publication is not meant to be a substitute for a detailed operational and site
specific development plan. Therefore, APC by Schneider Electric assumes no liability for damages, violations of
codes, improper installation, system failures, or any other problems that could arise based on the use of this
Publication.
The information contained in this Publication is provided as is and has been prepared solely for the purpose of
evaluating data center design and construction. This Publication has been compiled in good faith by APC by
Schneider Electric. However, no representation is made or warranty given, either express or implied, as to the
completeness or accuracy of the information this Publication contains.
IN NO EVENT SHALL APC BY SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC, OR ANY PARENT, AFFILIATE OR SUBSIDIARY
COMPANY OF APC BY SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC OR THEIR RESPECTIVE OFFICERS, DIRECTORS, OR
EMPLOYEES BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE, SPECIAL, OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS,
CONTRACT, REVENUE, DATA, INFORMATION, OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) RESULTING FROM,
ARISING OUT, OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OF, OR INABILITY TO USE THIS PUBLICATION OR
THE CONTENT, EVEN IF APC BY SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC HAS BEEN EXPRESSLY ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. APC BY SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC RESERVES THE RIGHT TO MAKE
CHANGES OR UPDATES WITH RESPECT TO OR IN THE CONTENT OF THE PUBLICATION OR THE
FORMAT THEREOF AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE.
Copyright, intellectual, and all other proprietary rights in the content (including but not limited to software, audio,
video, text, and photographs) rests with APC by Schneider Electric or its licensors. All rights in the content not
expressly granted herein are reserved. No rights of any kind are licensed or assigned or shall otherwise pass to
persons accessing this information.
This Publication shall not be for resale in whole or in part.
Page 3
Table of Contents
Introduction ............................................................................................................1
Types of User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Watchdog Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Network interface watchdog mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Resetting the network timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Automatic logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Security lockout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Recover from a lost password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Command Line Interface........................................................................................5
How to Access the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Local access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Remote access through Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Remote access through SSH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
About the Main Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
How to use the CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Command help syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Command response codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Argument quoting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Escape sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Prompts for user input during command execution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Delimiter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Options and arguments inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Rack Monitor 250 System Command Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
? or help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
about . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
alarmcount . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
bye, exit, or quit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
cd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
cipher . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
clrrst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
date . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
dir . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
dns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
eventlog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ftp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
lang . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
lastrst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
ledblink . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
logzip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
netstat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
ntp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
portSpeed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide i
Page 4

prompt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
pwd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
quit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
radius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
resetToDef . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
smtp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
snmp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
snmpv3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
snmptrap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
tcpip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
tcpip6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
userdflt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
whoami . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
xferINI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
xferStatus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Rack Monitor 250 Device Command Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
modbus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
nbabout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
nbbeacon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
nboutlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
nbrack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
nbrelay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
nbsensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
spabout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
spsensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
zw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
zwsyslog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Web Interface ......................................................................................................56
Access the Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Web Interface Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Quick status links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Current session preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Quick links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Limited Status Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Display Menu Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Home Tab............................................................................................................59
NetBotz Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Rack Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Reset Alarms Link. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Status Tab ...........................................................................................................61
View and Manage Wireless Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
View and Manage Wired Sensors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Filter wired sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Mass-configure sensor settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Configure individual sensor settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
View and Manage Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
View Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guideii
Page 5

View the Network Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Current IPv4 settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Current IPv6 settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Domain name system status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Port speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Control Tab.......................................................................................................... 69
Manage User Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Reset/Reboot the Network Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
View and Manage Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Lock/Unlock Rack Access Handles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Configuration Tab................................................................................................ 71
Configure Settings for an Appliance or Sensor Pod. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Filter modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configure appliance settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configure Sensor Pod 150 settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Configure Settings for Wired Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Filter wired sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Mass-configure sensor settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configure individual sensor settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configure Wireless Sensors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
The Wireless Sensor Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Add sensors to the Wireless Sensor Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Modify wireless sensor settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configure Output Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Configure Rack Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Register a new proximity card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Registered users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Unregistered users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
User Authentication Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Rack access handles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Schedule automatic unlocking events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Configure Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Session management settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Ping response . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Local users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Default settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Remote users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Configure the RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Configure a RADIUS server on UNIX® with shadow passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Supported RADIUS servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Firewall. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Enable/disable the firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Set the active policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
View active rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Create/edit a policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Import a firewall policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Test a firewall policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide iii
Page 6

Configure Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
TCP/IP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Port speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
DNS server settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
Network configuration for web access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
SSL certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
SNMPv1 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
SNMPv3 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Enable Modbus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
FTP server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Event actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Configure event actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
E-mail notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
SNMP trap receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
SNMP traps test screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
General Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Set the date and time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
Use a configuration file (.ini) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Configure quick links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Syslog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Tests Tab...........................................................................................................109
LED Blink test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
Logs Tab............................................................................................................110
Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Color code the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Filter the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Delete the event log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Reverse lookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Event log size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
Data Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
Graph the data log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
Data log collection interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
Configure data log rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
Data log size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Use FTP or SCP to Retrieve Log Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Use FTP to retrieve event.txt or data.txt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
FTP delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Use SCP to retrieve event.txt or data.txt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Firewall Log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
About the Rack Monitor 250 .............................................................................. 116
Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
Device IP Configuration Wizard......................................................................... 117
System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
How to Export Configuration Settings................................................................ 118
Contents of the .ini file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guideiv
Page 7

Detailed Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Use FTP to retrieve the .ini file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Customize the .ini file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Export the .ini file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
The Upload Event and Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Errors generated by overridden values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Related Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
CLI Script File (.csf) Settings............................................................................. 121
Firmware Upgrades........................................................................................... 122
Firmware Module Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Firmware File Transfer Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Use the Firmware Upgrade Utility on Windows systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Use the Utility for Manual Upgrades, Primarily on Linux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Use FTP to Upgrade the Rack Monitor 250 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Use SCP to Upgrade the Rack Monitor 250 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Use XMODEM to Upgrade the Rack Monitor 250 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Use the Firmware Upgrade Utility for Multiple Upgrades on Windows . . . . . . . 125
Verify Upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Verify the Success of the Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Last Transfer Result codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Verify the Version Numbers of Installed Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Wireless Firmware Upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Troubleshooting................................................................................................. 128
Rack Monitor 250 Access Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
SNMP Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Source Code Copyright Notice.......................................................................... 130
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide v
Page 8

Page 9

Introduction
The APC by Schneider Electric NetBotz® Rack Monitor 250 is a rack-mountable central hardware
appliance for an environmental monitoring and control system. Once installed, you monitor and control
your system using a network or serial connection.
The Rack Monitor 250 includes ports for connecting the following devices:
• Temperature and humidity sensors (with or without digital displays)
• Fluid detection sensors
• Third-party dry contact sensors
• Door switch sensors
• Rack door handles
• Smoke sensors
• Vibration sensors
You can expand your system in the following ways:
• Connect the Rack Monitor 250 to your building management system.
• Connect up to six NetBotz Rack Sensor Pod 150s and additional sensors.
• Add up to 47 sensors to the wireless sensor network.
See the NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 Installation and Quick Configuration manual on www.apc.com for
more information.
The Rack Monitor 250 uses the following standards:
• Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
• HTTP over Secure Sockets Layer (HTTPS)
• File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
• Telnet
• Secure SHell (SSH)
• Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
• Secure Copy (SCP)
• Modbus TCP and serial Modbus
• TCP/IP v4 and v6
• USB A-USB mini B serial connection
• SMTP-based secure email
• RADIUS (Remote Access Dial In User Service)
• Network Time Protocol (NTP)
6
NOTE: The Rack Monitor 250 cannot be connected to or networked with any other NetBotz appliances,
such as the Rack Monitor 570. It uses unique software that is not compatible with other NetBotz
appliances.
NOTE: The Rack Monitor 250 is not a PoE compatible device. Do not connect a Rack Monitor 250 to a
PoE (Power over Ethernet) switch.
1 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 10

Types of User Accounts
The Rack Monitor 250 has various levels of access (Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-Only
User, and Network-Only User), which have user name and password requirements. Both user names
and passwords are case-sensitive and have a 64 byte maximum, supporting up to 64 ASCII characters
(fewer for multi-byte languages).
The Rack Monitor 250 is initially configured with three default user accounts: a Super User account, a
Device account, and a Read only account. It is recommended that non-default user name and
passwords be set for all users. You can create additional accounts for any type of user except the Super
User.
• An Administrator or the Super User can use all of the menus in the web interface and all of the
commands in the CLI. The Super User and administrators can create, edit, and enable or disable
other types of user accounts. Administrator user types can be deleted, but the Super User cannot
be deleted.
The default user name and password for the Super User are both apc.The Super User cannot
be renamed or deleted, but it can be disabled. It is recommended that the Super User account is
disabled once any additional Administrator accounts are created. Make sure there is at least one
Administrator account enabled before the Super User account is disabled.
• A Device User has read and write access to device-related screens. Administrative functions like
Session Management under the Security menu and Firewall under Logs are grayed out.
The default user name for this account is device, and the default password is apc.
• A Read-Only User has access to the same menus as a Device User, but without the capability to
change configurations, control devices, delete data, or use file transfer options. Links to
configuration options are visible but disabled. The event and data logs display no button to clear
the log.
The default user name for this account is readonly, and the default password is apc.
• A Network-Only User can only log on using the web interface and CLI (Telnet or SSH). A user
with network-only access has read/write permission to the network related menus only.
See “Local users” on page 82 for more information.
Watchdog Features
To detect internal problems and recover from unanticipated inputs, the Rack Monitor 250 uses internal,
system-wide watchdog mechanisms. When it restarts to recover from an internal problem, a Network
Interface Restarted event is recorded in the event log.
Network interface watchdog mechanism
The Rack Monitor 250 implements internal watchdog mechanisms to protect itself from becoming
inaccessible over the network. For example, if the Rack Monitor 250 does not receive any network traffic
for 9.5 minutes (either direct traffic, such as SNMP, or broadcast traffic, such as an Address Resolution
Protocol [ARP] request), it assumes that there is a problem and restarts its network interface.
Resetting the network timer
To ensure that the Rack Monitor 250 does not restart if the network is quiet for 9.5 minutes, the Rack
Monitor 250 attempts to contact the Default Gateway every 4.5 minutes. If the gateway is present, it
responds to the Rack Monitor 250, and that response restarts the 9.5-minute timer. If your application
does not require or have a gateway, specify the IP address of a computer that is running on the network
and is on the same subnet. The network traffic of that computer will reset the 9.5-minute timer frequently
enough to prevent the Rack Monitor 250 from restarting.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide2
Page 11

Getting Started
You must configure the following TCP/IP settings before the Rack Monitor 250 can operate on a
network:
• IP address of the Rack Monitor 250
• Subnet mask
• IP address of the default gateway
NOTE: If a default gateway is unavailable, use the IP address of a computer that is located on the same
subnet as the Rack Monitor 250 and that is usually running. The Rack Monitor 250 uses the default
gateway to test the network when traffic is very light.
NOTE: Do not use the IPv4 loop back address (127.0.0.1), or the IPv6 loop back address (::1) as the
default gateway address for the Rack Monitor 250. Doing so disables the appliance and requires you to
reset TCP/IP settings to their defaults using a local serial login.
For more information on configuring the TCP/IP settings, see the NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 Installation
Manual in printed form, or available as a PDF on www.apc.com.
Access
You can log on to the Rack Monitor 250 using the following methods:
• Local access to the Command Line Interface (CLI) from a computer with a direct serial
connection.
NOTE: If you are unable to access the appliance using the console port, you may need to install a
serial-to-USB virtual COM port driver. The USB vendor is FTDI; the driver type is VCP. Driver
downloads are available on the FTDI Chip website.
For more information, see the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) article FA158350. Go to
www.apc.com. Navigate to Support > Resources and Tools > FAQS. Then enter the article
number in the search bar.
• Telnet or Secure SHell (SSH) access to the CLI from a remote computer.
• Web access: either directly or through StruxureWare Data Center Expert
®
.
Automatic logout
By default, users are automatically logged out of the Rack Monitor 250 Web Interface and CLI after
3 minutes of inactivity.
You can adjust he default logout time through the web interface
1. Navigate to Configuration > Security I’ Local Users > Management.
2. Click the user name hyperlink for the account you want to change.
3. Under Session Timeout, modify the number of minutes.
Automatic Logout Duration (min)
Default 3
Minimum 1
Maximum 60 (1 Hr)
Security lockout
If a valid user name is used with an invalid password consecutively, for the number of times specified in
Configuration > Security > Local Users > Default Settings, the account will be locked until a Super
User re-enables the account.
NOTE: A Super User cannot be locked out.
3 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 12

Recover from a lost password
1. Connect the USB A–USB mini B configuration cable to the console port on the Rack Monitor 250
and to a USB port of the computer.
NOTE: You may need to install a serial-to-USB virtual COM port driver. The USB vendor is FTDI;
the driver type is VCP. Driver downloads are available on the FTDI Chip website. For more
information, see FAQ article FA158350 on www.apc.com.
2. Open a terminal program such as HyperTerminal or PuTTY, configure the port as follows, and
press
ENTER.
Default baud rate : 9600 bps
Data Bits : 8
Parity : None
Stop Bits : 1
Flow Control : None
3. Press
ENTER on the computer, repeatedly, until the User Name prompt is displayed. If the User
Name prompt is not displayed, verify the following:
– The USB port is not in use by another application.
– The terminal settings are correct.
– The correct cable is being used.
–
SCROLL LOCK is not turned on.
4. Press and release the Reset button near the power LED once. The Status LED will turn off for
5–7 seconds, then flash rapidly orange and green. Press the Reset button a second time while
the Status LED flashes to temporarily reset the user name and password to their default values
(apc/apc).
5. Press
ENTER as many times as necessary to display the User Name prompt, then use the default
user name and password (apc and apc) to log on.
NOTE: If you take longer than 30 seconds to log on, you must repeat steps 4 and 5.
6. At the CLI, use the following commands to change the password setting for the Super User
account, for which the user name is always apc, and the password is now temporarily apc:
user -n apc -pw yourNewSuperUserPassword
Example: to change the Super User's password to p@ssword type:
user -n apc -pw p@ssword
NOTE: Because the Super User can also reset the password for any account, you can reset
other user's passwords as well.
Example: to change the password for user bmadmin to p@ssword type:
user -n bmadmin -pw p@ssword
NOTE: Changing user name information is not supported in the CLI. To change a user name, you
must delete and re-create the user account. The Super User will also have access now to log in
and adjust the password for any other user.
7. Type quit, exit, or bye to log off. Reconnect any USB cable you have disconnected, and
restart any service you have disabled.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide4
Page 13

Command Line Interface
The Command Line Interface (CLI) is used primarily to view system status and issue commands to the
system. Like DOS commands in Windows or the terminal session commands in Linux, the CLI handles
word-like commands. These commands have parameters and options that can be specified at the CLI
prompt(apc> ).
How to Access the CLI
You can access the CLI locally using a USB A–USB mini B serial connection, or remotely using a
secured Telnet or Secure Shell (SSH) connection. Telnet provides the basic authentication of a user
name and password. SSH encrypts all transmitted data, including user name and password. Telnet is
enabled by default. The interface, user accounts, and user access rights are the same whether you
access the CLI through SSH or Telnet.
You must always provide an authentic user name and password to access the CLI. User names and
passwords are case-sensitive.
User name prompt: “User Name : " (User<space>Name<space>:<space>).
Password prompt: “Password : " (Password<space><space>:<space>).
Local access
1. Connect the USB A–USB mini B configuration cable to the console port on the Rack Monitor 250
and to a USB port of the computer.
NOTE: You may need to install a serial-to-USB virtual COM port driver. The USB vendor is FTDI;
the driver type is VCP. Driver downloads are available on the FTDI Chip website,
www.fdichip.com. For more information, see FAQ article FA158350 on www.apc.com.
2. Run a terminal program (HyperTerminal, etc.). Configure the port as follows, and press
(repeatedly if necessary).
Default baud rate : 9600 bps
Data Bits : 8
Parity : None
Stop Bits : 1
Flow Control : None
4. At the prompts, enter user name and password.
5. At the end of the session, log off. Remember to reconnect any USB cable you may have
disconnected.
ENTER
5 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 14
Remote access through Telnet
User Name: apc
Password : ***
Schneider Electric Network Management Card AOS vx.x.x
(c)Copyright 2018 All Rights Reserved NETBOTZ 250 App vx.x.x
-------------------------------------------------------------------------Name : apcxxxxxx Date : 05/30/2018
Contact : Don Adams Time : 5:58:30
Location : Building 3 User : Administrator
Up Time : 0 Days 21 Hours 21 Minutes Stat : P+ N4+ N6+ A+
1. Access a computer on the same network as the Rack Monitor 250.
Open a terminal program that provides telnet support or type “telnet” and the IP address of
the Rack Monitor 250 at a DOS or command prompt and press
Example:
telnet 139.225.6.133
NOTE: The Rack Monitor 250 uses Telnet port 23 by default. If the Rack Monitor 250 has been
configured to use a non-default port number (between 5000 and 32768), you must include a
colon or a space (depending on your Telnet client) between the IP address and the port number.
2. Enter user name and password. The default user name and password for the Super User are
both apc.
ENTER.
Remote access through SSH
Data transmitted over SSH is encrypted using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) encryption. To use SSH, you
must install a properly configured SSH client on your computer.
About the Main Screen
• Two fields identify the operating system (Network Management Card AOS) and Application
Module (NetBotz 250 App) firmware versions.
Network Management Card AOS vx.x.x
NetBotz 250 APP vx.x.x
• Three fields identify the system Name, Contact, and Location values for the device.
Name : apcxxxxxx
Contact : Don Adams
Location : Building 3
• The Up Time is the duration since the last power cycle/reset of the Rack Monitor 250 network
interface
Up Time :
.
0 Days 21 Hours 21 Minutes
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide6
Page 15
• The two fields Date and Time identify when the screen was most recently refreshed.
Date :
Time : 5:58:30
• The User field reports your log-in account type.
User : Administrator
• The Stat field reports the Rack Monitor 250 IPv4 & IPv6 status, and other system variables. See
the Alarm Status Field
Stat : P+ N4+ N6+ A+
P+ The operating system (AOS) is functioning properly.
IPv4
only
N4+ N6+ N4+ N6+ IPv4 AND IPv6 Network Status. The network is functioning
N4? N6? N4? N6? A BOOTP request cycle is in progress.
N4– N6- N4– N6- The Rack Monitor 250 failed to connect to the network.
N4! N6! N4! N6! Another device is using the IP address of the Rack
* The N4 and N6 values can be different from one another: you could, for example, have N4N6+.
05/30/2018
table.
IPv6
only
IPv4 and
IPv6* Description
properly.
Monitor 250.
A+ The application is functioning properly.
A– The application has a bad checksum.
A? The application is initializing.
A! The application is not compatible with the AOS.
NOTE: If the AOS status is not P+, contact the APC by Schneider Electric Customer Care Center
at www.apc.com/support even if you can still access the Rack Monitor 250.
7 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 16
How to use the CLI
At the command line interface, you can use commands to view and configure settings for the appliance.
To use a command, type the command, option (if applicable), and any applicable arguments.
Commands and arguments are not case sensitive. Options are case sensitive.
While using the CLI, you can also do the following:
• Type ? and press
• To obtain information about the purpose and syntax of a specified command, type the command,
a space, and ? or the word help. For example, to view RADIUS configuration options, type:
radius ?
or
radius help
NOTE: See “Command help syntax” on page 8 for more detailed information.
• Press the
the
• Type at least one letter of a command and press the
commands that match the text you typed in the command line.
• Type exit, quit, or bye to close the connection to the command line interface.
UP arrow key to view the command that was entered most recently in the session. Use
UP and DOWN arrow keys to scroll through a list of up to ten previous commands.
Command help syntax
When you use ? or help to obtain information about a specific command, the following syntax defines
how that command can be used:
ENTER to view a list of available commands, based on your account type.
TAB key to scroll through a list of valid
Item Description
- Options are preceded by a hyphen.
If a command accepts multiple options or an option accepts
[...]
<...> Angle brackets indicate user-entered text.
Example of a command that supports multiple options:
ftp [-p <port number>] [-S <enable | disable>]
In this example, the ftp command accepts the option -p, which defines the port number, and the option
-S, which enables or disables the FTP feature.
To change the FTP port number to 5010, and enable FTP:
1. Type the ftp command, the port option, and the argument 5010:
2. After the first command succeeds, type the ftp command, the enable/disable option, and the
Example of a command that accepts mutually exclusive arguments for an option:
mutually exclusive arguments, the values may be enclosed in
brackets.
A vertical line between items indicates that the items are mutually
|
exclusive. You must use only one of the items.
ftp -p 5010
enable selection:
ftp -S enable
alarmcount -p [all | warning | critical]
In this example, the option -p accepts only three arguments: all, warning, or critical. For example, to view
the number of active critical alarms, type: alarmcount -p critical
The command will fail if you type an argument that is not specified.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide8
Page 17
Command response codes
All CLI commands issue:
<three digit response code>:<space> (followed by a readable text (response message))
This can be followed by <cr><lf> and the output of the command (if applicable).
Example:
E000: Success (followed by the output of the command, if applicable)
These response codes allow automated processes to detect error conditions without having to match
error message text.
Successful command operations have a response code less than 100. Any response code of 100 or
greater indicates a failure of some type.
E[0-9][0-9][0-9]: Error message
Response Codes
Code Message Notes
E000 Success N/A
E001 Successfully Issued N/A
E002 Success, Reboot Required N/A
E100 Command Failed N/A
E101 Command Not Found N/A
E102 Parameter Error Reported when there is any problem with the
arguments supplied to the command: too few,
too many, wrong type, etc.
E103 Command Line Error N/A
E104 User Level Denial N/A
E105 Command Prefill Not actually used in code, but it is set aside.
E106 Data Not Available Or the provided data cannot be read.
E107 Serial Lost Communications Serial communications with Rack Monitor 250
has been lost
E200 The provided arguments were
invalid. To view 'command'
help, type 'command ?'.
E201 The provided value does not
match expectations for length
or range.
E202 The current user does not have
'write' privileges.
E203 The target item is not
configurable.
E204 The requested operation cannot
be completed with the device(s)
specified.
E205 System error: The requested
operation could not be
completed.
E206
System error: Buffer
allocation failed.
The command was recognized, but subsequent
arguments were not.
Numeric values cannot be written to the device
if they are outside of a specific range, and
strings cannot be written if they are too long or
too short.
A read-only user was prevented from
configuring the device.
User failed to input a target or target was out of
range.
The current hardware available does not allow
the user input to be acted upon.
An system error occurred while acting on user
input.
A system error occurred before the user's input
could be interpreted.
9 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 18

Argument quoting
Argument values may optionally be enclosed in double quote characters (ASCII 0x22). String values
beginning or ending with spaces, or containing commas or semicolons, must be enclosed in quotes for
both input and output. Quote and backslash ("\", decimal code 92) characters appearing inside strings
should NOT be encoded using traditional escape sequences (see Escape Sequences below).
All binary characters (ASCII decimal ranges 0..31, 127..159) that appear inside strings are treated as
unreadable characters and rejected. When a quote or backslash character is supplied as a part of an
input string, the input string must be enclosed in double quotes.
Escape sequences
Escape sequences, traditionally a backslash followed by a lower case letter or by a combination of digits,
are ignored and should not be used to encode binary data or other special characters and character
combinations.
The result of each escape sequence is parsed as if it were both a backslash and the traditionally
escaped character.
Example:
<command> <arg1> [<agr2> <arg3a | arg3b> [<arg4a | arg4b | arg4c>]]
– arg1 must be used, but arg2 - 4 are optional.
– If arg2 is used, then arg3a or arg3b must also be used.
– arg4 is optional, but arg1 - 3 must precede arg4.
With most commands, if the last argument is omitted, the command provides information, otherwise the
last argument is used to change/set new information.
Example:
apc>ftp -p (displays the port number when omitting the arg2)
E000: Success
FTP Port: 5001
apc>ftp -p 21 (sets the port number to arg2)
E000: Success
Prompts for user input during command execution
Certain commands require additional user input (ex. transfer .ini prompting for baud rate). There is a
fixed timeout of 1 minute for such prompts. If you do not enter any text within the timeout period, then the
command prints E100: Command Failed. and the command prompt is redisplayed.
Delimiter
The Rack Monitor 250 CLI uses <space> (ASCII 0x20) as the delimiter between commands and
arguments. Extra white space between commands and arguments is ignored.
Command responses have all fields delimited with commas for efficient parsing.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide10
Page 19

Options and arguments inputs
Entering a command with no options or arguments returns the current value of all options available from
that command.
Entering the command and an option with no arguments returns the current value of that option only.
Any command followed by a question mark "?" returns help explaining the command.
<space> ::= (" " | multiple" ")
<valid letter_number> ::= (a-z | A-Z | 0-9)
<string> ::= (1 - 64 consecutive printable valid ASCII characters [ranging from hex 0x20 to
0x7E inclusive] )
NOTE: If the string includes a blank, the entire string MUST be surrounded by quotes(" ").
<option> ::= "-"(<valid letter_number> | <valid letter_number><valid
letter_number>)
<argument> ::=
<helpArg> | <alarmcountArg> | <bootArg> | <cdArg> | <consoleArg> | <dateArg>
| <deleteArg> | <ftpArg> | <pingArg> | <portspeedArg> | <promptArg> |
<radiusArg> | <resettodefArg> | <systemArg> | <tcpipArg> | <userArg> |
<webArg> | <string>
<optionArg> ::= <option><argument>
11 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 20

Rack Monitor 250 System Command Descriptions
Courier font is used to show the user input or text output of the Rack Monitor 250. Text enclosed in ‘< >’
is a user-defined variable.
? or help
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: View a list of all the CLI commands available to your account type. To view help text for a
specific command, type the command followed by a question mark.
Parameters: [<command>]
Example 1:
apc> ?
System Commands:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
For command help: command ?
? about alarmcount boot bye cd
cipher clrrst console date delete dir
dns email eventlog exit firewall format
ftp help lang lastrst ledblink logzip
netstat ntp ping portspeed prompt pwd
quit radius reboot resetToDef session smtp
snmp snmptrap snmpv3 system tcpip tctpip6
user userdflt web whoami xferINI xferStatus
Device Commands:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
modbus nbabout nbbeacon nboutlet nbrack nbrelay
nbsensor spabout spsensor zw zwsyslog
Example 2:
apc>help boot
Usage: boot -- Configuration Options
boot [-b <dhcpBootp | dhcp | bootp | manual>] (IPv4 Boot Mode)
[-c <enable | disable>] (Require DHCPv4 Cookie)
[-v <vendor class>]
[-i <client id>]
[-u <user class>]
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide12
Page 21
about
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Displays system information (Model Number, Serial Number,
Manufacture Dates, etc.)
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>about
E000: Success
Hardware Factory
---------------
Model Number: AP9XXX
Serial Number: ST0913012345
Hardware Revision: HW05
Manufacture Date: 6/23/2018
MAC Address: 00 05 A2 18 00 01
Management Uptime: 0 Days 1 Hour 42 Minutes
Error Message: E000
alarmcount
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only
Description: Displays alarms present in the system.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-p all View the number of active alarms reported by the Rack Monitor 250.
Information about the alarms is provided in the event log.
warning View the number of active warning alarms.
critical View the number of active critical alarms.
Example:
To view all active warning alarms, type:
apc>alarmcount
E000: Success
AlarmCount: 0
Error Message: E000, E102
13 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 22
boot
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: View or set the network startup configuration of the device, such as setting boot mode
(DHCP vs BOOTP vs MANUAL).
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-b
<boot
mode>
-c enable | disable
-v <vendor class> Vendor Class is APC
-i <client id> The MAC address of the NMC, Which uniquely
-u <user class> The name of the application firmware module.
Example:
apc>boot
E000: Success
Boot Mode: manual
DHCP Cookie: enable
Vendor Class: <device class>
Client ID: XX XX XX XX XX XX
dhcp | bootp | manual Define how the TCP/IP settings will be
configured when the Rack Monitor 250 turns
on, resets, or restarts. See “TCP/IP Settings”
on page 89 for information about each boot
mode setting.
dhcp boot mode only. Enable or disable the
(Require DHCP Cookie)
requirement that the DHCP server provide the
APC cookie.
identifies it on the network.
User Class: <user class>
Error Message: E000, E102
bye, exit, or quit
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Exit from the CLI session.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>exit
Bye
Error Message: None
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide14
Page 23

cd
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Set the working directory of the file system. The working directory is set back to the root
directory ‘/’ when you log out of the CLI.
Parameters: <directory name>
Example:
apc>cd logs
E000: Success
apc>cd /
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
cipher
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Enable or disable cryptographic algorithms for Web UI sessions. You cannot enable or
disable these algorithms directly from the Web UI. You must reboot your appliance after enabling or
disabling algorithms for changes to take effect.
There are three categories of algorithms: Authentication algorithms, Block Cipher algorithms, and MAC
algorithms. Available and Blocked Cipher Suites are also listed.
NOTE: Disabling the only algorithm will block all SSL/TLS sessions.
NOTE: The status of an algorithm is toggled when the cipher command is executed. It is recommended
that you check the status of an algorithm before enabling or disabling it.
Parameters:
Option Description
-3des Triple-DES
-rc4 RC4
-aes AES
-dh DH
-rsake RSA Key Exchange
-rsaau RSA Authentication
-md5 MD5
-sha1 SHA
-sha2 SHA256
Example 1: Disable the triple-DES block cipher.
apc>cipher -3des
E002: Success
Reboot required for change to take effect.
15 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 24

Example 2: Retrieve a list of each available cryptographic algorithm and its status.
apc>cipher
E000: Success
Key Exchange Algorithms
-----------------------
DH enabled
RSA Key Exchange enabled
Authentication Algorithms
-------------------------
(Warning: disabling the only algorithm in category
will block all SSL/TLS sessions)
RSA Authentication enabled
Block Cipher Algorithms
-----------------------
triple-DES enabled
RC4 enabled
AES enabled
MAC Algorithms
--------------
MD5 enabled
SHA enabled
SHA256 enabled
Available Cipher Suites
-----------------------
1 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
2 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
3 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
4 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
5 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
6 SSL_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
7 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
8 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
9 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
10 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
11 SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
12 SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_MD5
13 SSL_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_RC4_40_MD5
Blocked Cipher Suites
---------------------
None
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide16
Page 25
clrrst
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Clear reset reason.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>clrrst
E000: Success
Error Message: E000
console
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Define whether users can access the CLI using Telnet, which is enabled by default, or
Secure SHell (SSH), which provides protection by transmitting user names, passwords, and data in
encrypted form. You can change the Telnet or SSH port setting for additional security. Alternately,
disable network access to the CLI.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-s enable | disable
(ssh)
-t enable | disable
(telnet)
-pt <telnet port n> Define the Telnet port used to communicate with the
-ps <SSH port n> Define the SSH port used to communicate with the Rack
-b 2400 | 9600 | 19200 |
38400
Example 1:
To enable SSH access to the CLI, type:
apc>console -s enable
Example 2:
To change the Telnet port to 5000, type:
apc>console -pt 5000
Telnet: enabled
SSH: disabled
Telnet Port: 5000
SSH Port: 22
Baud Rate: 9600
Enable or disable access to the CLI through SSH.
Enabling SSH enables SCP.
Disable or enable access to the CLI through Telnet.
Rack Monitor 250 (23 by default).
Monitor 250 (22 by default).
Configure the speed of the serial port connection (9600
bps by default).
Error Message: E000, E102.
17 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 26
date
Access: Super User, Administrator
Definition: Get and set the date and time of the system.
To configure an NTP server to define the date and time for the Rack Monitor 250, see “Set the date and
time” on page 105.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-d <“datestring”> View or set the current date. The format must match the
current -f setting.
-t <00:00:00> View or set the current time, in hours, minutes, and seconds.
Use the 24-hour clock format.
-f mm/dd/yy | dd.mm.yyyy
| mmm-dd-yy |
dd-mmm-yy |
yyyy-mm-dd
-z <time zone offset> View or set the difference with GMT to specify your time
Example 1:
View or set the numerical format in which to display all dates
in this user interface. Each letter m (for month), d (for day),
and y (for year) represents one digit. Single-digit days and
months are displayed with a leading zero.
zone. This lets you synchronize with other people in different
time zones.
To display the date using the format yyyy-mm-dd, type:
date -f yyyy-mm-dd
Example 2:
To define the date as July 1, 2018, type:
date -d “2018-07-01”
Example 3:
To define the time as 5:21:03 p.m., type:
date -t 17:21:03
Error Message: E000, E100, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide18
Page 27

delete
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Delete a file in the file system.
Parameters:
Argument Description
<file name> Type the name of the file to delete.
Example:
apc>delete /event.txt
E000: Success
Error Messages: E000, E102
dir
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Displays the content of the working directory.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>dir
E000: Success
--wx-wx-wx 1 apc apc 3145728 Jun 23 2018 aos.bin
--wx-wx-wx 1 apc apc 3145728 Jun 23 2013 app.bin
-rw-rw-rw- 1 apc apc 45000 Jul 1 2018 config.ini
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 ssl/
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 ssh/
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 logs/
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 sec/
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 dbg/
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 fwl/
drwxrwxrwx 1 apc apc 0 Mar 18 2018 rms/
Error Messages: E000
19 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 28
dns
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Definition: View or configure the manual Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
Parameters:
Parameter Argument Description
-OM enable | disable Override the manual DNS.
-p <primary DNS server> Set the primary DNS server.
-s <secondary DNS server> Set the secondary DNS server.
-d <domain name> Set the domain name.
-n <domain name IPv6> Set the domain name IPv6.
-h <host name> Set the host name.
-y enable | disable System-hostname sync
Example 1:
apc>dns -h
E000: Success
Host Name: HostName
Example 2:
apc>dns -h myHostName
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide20
Page 29

Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: Use the following commands to configure the parameters for email.
Parameters:
Parameters Argument
-g[n] enable | disable (Generation)
-t[n] <To Address>
-o[n] long | short (Format)
-l[n] <Language Code>
-r [n] Local | recipient | custom (Route)
Custom Route Option
-f[n] <From Address>
-s{n} <SMTP Server>
-p[n] <Port>
-a[n] enable | disable (Authentication)
-u[n] <User Name>
-w[n] <Password>
-e[n] none | ifsupported | always | implicit
(Encryption)
-c[n] enable | disable (Required
Certificate)
-i[n] <Certificate File Name>
n = Email Recipient Number 1, 2, 3, or 4
Example:
apc>email -o1 short
Error Message: E000, E102
21 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 30
eventlog
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: View the date and time you retrieved the event log, the status of the Rack Monitor 250, and
the status of sensors connected to the Rack Monitor 250. View the most recent device events and the
date and time they occurred. Use the following keys to navigate the event log:
Key Description
ESC
ENTER
SPACEBAR
B
D
Example:
Close the event log and return to the CLI.
Update the log display. Use this command to view events that were recorded after you
last retrieved and displayed the log.
View the next page of the event log.
View the preceding page of the event log. This command is not available at the main
page of the event log.
Delete the event log. Follow the prompts to confirm or deny the deletion. Deleted
events cannot be retrieved.
apc>eventlog
---- Event Log -----------------------------------------------------
Date: 04/23/2018 Time: 13:22:26
------------------------------------
T/H sensors: Normal Outputs: Normal
Input Sensors: Normal
Date Time Event
---------------------------------------------------------------
04/23/2018 13:17:22 apc CLI user ‘apc’ logged in from
10.218.197.121
<ESC>- Exit, <ENTER>- Refresh, <SPACE>- Next, <D>- Delete
Error Message: E000, E100
exit
See “bye, exit, or quit” on page 14.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide22
Page 31

firewall
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Establishes a barrier between a trusted, secure internal network and another network.
Parameters:
Parameters Argument Description
-S enable | disable Enable or disable the Firewall.
-f <file name to activate> Name of the firewall to activate.
-t <file name to test>
<duration time in minutes>
-fe no argument Shows active file errors.
-te no argument Shows test file errors.
-c no argument Cancel a firewall test.
-r no argument Shows active firewall rules.
-l no argument Shows firewall activity log.
Error Message: E000, E102
Name of firewall to test and
duration time in minutes.
format
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Format the flash file system. This deletes all configuration data (including network
settings), event and data logs, certificates and keys.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>format
Format FLASH file system
Warning: This will delete all configuration data,
event and data logs, certs and keys.
Enter 'YES' to continue or <ENTER> to cancel:
apc>
Error Message: None
23 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 32

ftp
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Get/set the FTP server configuration of the Network Interface, to allow/restrict FTP access.
NOTE: The system will reboot if any configuration is changed.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-p <port number> Define the TCP/IP port that the FTP server uses to
communicate with the Rack Monitor 250 (21 by default).
The FTP server uses both the specified port and the port
one number lower than the specified port.
Valid port numbers are 21 and 5000–32768.
-S enable | disable Configure access to the FTP server.
Example:
To change the TCP/IP port to 5001, type:
apc>ftp -p 5001
E000: Success
apc>ftp
E000: Success
Service: Enabled
Ftp Port: 5001
apc>ftp -p 21
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
help
See “? or help” on page 12.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide24
Page 33

lang
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Language in use.
Parameters: None
Example: .
apc>lang
E000: Success
Languages
enUs - English
Error Message: E000
lastrst
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Last reset reason.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>lastrst
09 Coldstart Reset
E000: Success
Error Message: E000
ledblink
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Sets the blink rate to the LED on the Rack Monitor 250.
Parameters: <duration time in minutes>
Example:
apc> ledblink 1
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
25 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 34

logzip
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Places large logs into a zip file before sending.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-m <email recipient> Email recipient number (1–4).
Example:
apc>logzip -m 1
Generating files
Compressing files into /dbg/debug_ZA1023006009.tar
Emailing log files to email recipient - 1
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
netstat
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Displays active network addresses.
Parameters: None
Example: .
apc>netstat
Current IP Information:
Family mHome Type IPAddress Status
IPv6 4 auto FE80::2C0:B7FF:FE51:F304/64 configured
IPv6 0 manual ::1/128 configured
IPv4 0 manual 127.0.0.1/32 configured
Error Message: None
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide26
Page 35

ntp
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: Synchronizes the time of the Network Interface to the time of the specified NTP server.
The time is defined as Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), formerly Greenwich Mean Time. The
timezone must be set correctly using the date command. See “date” on page 18.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-OM enable | disable Override the manual settings.
-p <primary NTP server> Specify the primary server.
-s <secondary NTP server> Specify the secondary server.
Example 1:
To enable the override of manual setting, type:
apc>ntp -OM enable
Example 2:
To specify the primary NTP server, type:
apc>ntp -p 150.250.6.10
Error Message: E000, E102
ping
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Network-Only User
Description. Send a network ICMP message (‘ping’) to any external network device.
Parameters:
Argument Description
<IP address or DNS name> Type an IP address with the format
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, or the DNS name
configured by the DNS server.
Example:
apc>ping 192.168.1.50
E000: Success
Reply from 192.168.1.50: time(ms)= <10
Reply from 192.168.1.50: time(ms)= <10
Reply from 192.168.1.50: time(ms)= <10
Reply from 192.168.1.50: time(ms)= <10
Error Message: E000, E100, E102
27 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 36

portSpeed
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: Get/set the network port speed.
NOTE: The system will reboot if any configuration is changed.
Parameters:
Option Arguments Description
-s auto | 10H |
10F | 100H |
100 F
H = Half Duplex
F = Full Duplex
Example:
apc>portspeed
E000: Success
Port Speed: Auto_negotiation
Current Port Speed: 100 Full_Duplex
apc>portspeed -s 10h
E000: Success
apc>portspeed
E000: Success
Port Speed: 100 Half_Duplex
Define the communication speed of the Ethernet port. The auto
command lets the Ethernet devices negotiate to transmit at the
highest possible speed. See “Port speed” on page 92 for more
information about the port speed settings.
10 = 10 Meg Bits
100 = 100 Meg Bits
Current Port Speed: 100 Half_Duplex
apc>portspeed -s auto
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide28
Page 37

prompt
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Network-Only User
Description: Change the format of the prompt, either short or long
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-s long The prompt includes the account type of the currently logged-in user.
short The default setting. The prompt is four characters long: APC>
Example:
apc>prompt –s long
E000: Success
Administrator@apc>prompt –s short
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
pwd
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Used to output the path of the current working directory.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>pwd
/
Error Message: None
quit
See “bye, exit, or quit” on page 14.
radius
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: View the existing RADIUS settings, enable or disable RADIUS authentication, and
configure basic authentication parameters for up to two RADIUS servers.
Additional authentication parameters for RADIUS servers are available in the web interface of the Rack
Monitor 250.
For a summary of RADIUS server configuration and a list of supported RADIUS servers, see
“Configure the RADIUS server” on page 85.
For detailed information about configuring your RADIUS server, see the Security Handbook, available at
www.apc.com.
29 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 38

Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-a local |
radiusLocal |
radius
Configure RADIUS authentication:
local—RADIUS is disabled. Local authentication is enabled.
radiusLocal—RADIUS, then Local Authentication. RADIUS and
local authentication are enabled. Authentication is requested from the
RADIUS server first. If the RADIUS server fails to respond, local
authentication is used.
radius—RADIUS is enabled. Local authentication is disabled.
-p1
-p2
<server port> The server port of the primary or secondary RADIUS server.
NOTE: RADIUS servers use port 1812 by default to authenticate
users. The Rack Monitor 250 supports ports 1812, 5000 to 32768.
-o1
<server IP> The IP address of the primary or secondary RADIUS server.
-o2
-s1
-s2
-t1
-t2
<server
secret>
<server
timeout>
The shared secret between the primary or secondary RADIUS server
and the Rack Monitor 250.
The time in seconds that the Rack Monitor 250 waits for a response
from the primary or secondary RADIUS server.
Example 1:
To view existing RADIUS settings for the Rack Monitor 250, type radius and press
apc>radius
E000: Success
Access: Local Only
Primary Server: 0.0.0.0
Primary Server Port: 1812
Primary Server Secret: <Password Hidden>
Primary Server Timeout: 5
Secondary Server: 0.0.0.0
Secondary Server Port: 1812
Secondary Server Secret: <Password Hidden>
Secondary Server Timeout: 5
ENTER:
Example 2:
To enable RADIUS and local authentication, type:
apc>radius -a radiusLocal
Example 3:
To configure a 10-second timeout for a secondary RADIUS server, type:
apc>radius -t2 10
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide30
Page 39

reboot
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: Restart the Rack Monitor 250 interface only. Forces the network device to reboot. You
must confirm this operation by entering a “YES” after the command has been entered.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>reboot
E000: Success
Reboot Management Interface
Enter 'Y' to continue or <ENTER> to cancel : <user enters ‘YES’>
Rebooting...
Error Message: E000, E100
resetToDef
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Reset all parameters to their default.
Parameters:
Option Arguments Description
-p all | keepip all = all configuration data, including the IP address.
keepip = all configuration data, except the IP address.
Reset all configuration changes, including event actions, device
settings, and, optionally, TCP/IP configuration settings.
Example:
To reset all of the configuration changes except the TCP/IP settings for the Rack Monitor 250, type:
apc>resetToDef -p keepip
Enter 'YES' to continue or <ENTER> to cancel : : <user enters ‘YES’>
all User Names, Passwords.
Please wait...
Please reboot system for changes to take effect!
Error Message: E000, E100
31 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 40

session
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Records who is logged in (user), the interface, the Address, time and ID.
Parameters:
Option Arguments Description
-d <session ID> Delete session
-m enable |
disable
-a enable |
disable
Example:
apc>session
User Interface Address Logged In Time ID
------------------------------------------------------------------------
apc Serial 00:00:05 1
Multi-User Enable
Remote Authentication Override
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide32
Page 41

smtp
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Internet standard for electronic mail.
Parameters:
Option Argument
-f <From Address>
-s <SMTP Server>
-p <Port>
NOTE: Port options are 25, 465, 587, and 5000–32768
-a enable | disable (Authentication)
-u <User Name>
-w <Password>
-e none | ifavail | always | implicit (Encryption)
-c enable | disable (Require Certificate)
-i <Certificate File Name>
Example:
apc>smtp
E000: Success
From: address@example.com
Server: mail.example.com
Port: 25
Auth: disabled
User: User
Password: <not set>
Encryption: none
Req. Cert: disabled
Cert File: <n/a>
Error Message: E000, E102
33 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 42
snmp
Access: Super User, Administrator,Network-Only User
Description: View the existing SNMPv1 settings, enable or disable SNMP, and configure basic SNMP
parameters.
Parameters:
Option Arguments Description
-c <Community> Identify the group of Rack Monitor 250
-a read | write | writeplus | disable Set the access level
-n <IP or Domain Name> The host’s name or address
-S enable | disable Enable or disable the respective
version of SNMP
Example:
To change the name of SNMP access control community 3, enter:
apc>snmp -c3 myCommunity
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
snmpv3
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: View the existing SNMPv3 settings, enable or disable SNMP, and configure basic SNMP
parameters.
Parameters:
Option Arguments Description
-S enable | disable Enable or disable the respective version of SNMP
-u[n] <User Name> User Name
-a[n] <Auth phrase> Authphrase of User profile
-c[n] <Crypth phrase> Crypthphrase of User profile
-ap[n] sha | md5 | none Authentication Protocol
-pp[n] aes | des | none Privacy Protocol
-ac[n] enable | disable Access
-au[n] <User Profile Name> Access User Profile
-n[n] <IP or Domain Name> The host’s name or address
Example:
To change the authentication protocol of SNMP access control 2 to SHA-1, type:
apc>snmpv3 -ap2 sha
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide34
Page 43

snmptrap
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: View the existing SNMP trap receiver settings, enable or disable SNMP trap receivers, and
configure basic SNMP trap receiver parameters.
Parameters:
Option Arguments
-c{n} <Community>
-r[n] <Receiver NMS IP>
-l[n] <language code>
-t[n] snmpV1 | snmpV3 (Trap Type)
-g[n] enable | disable (Trap Generation)
-a[n] enable | disable (Auth Trap)
-u[n] profile1 | profile2 | profile3 | profile4 (User Name)
n = Trap receiver # = 1,2,3,4,5 or 6
Example:
To change the trap type of SNMP trap receiver 1 to SNMPv3, type:
apc>snmptrap -t1 snmpV3
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
35 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 44

system
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: View and set the system identification, contact, and location. View up time, date and time,
the logged-on user, and the high-level system status P, N, A. See “About the Main Screen” on page 6 for
more information about system status.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-n <system-name> Define the device name, the name of the person responsible for
-c <system-contact>
-l <system-location>
-m <system-message> When defined, a custom message will appear on the log on
-s enable | disable Enable or disable System-host name sync. This feature
the device, and the physical location of the device.
NOTE: These values are also used by StruxureWare Data
Center Expert and the Rack Monitor 250’s SNMP agent.
screen for all users.
synchronizes the host name with the system name so both fields
automatically contain the same value.
NOTE: When enabling this feature, the system name identifier
can no longer contain a space character (since it will be
synchronized to the host name field).
Example 1:
To set the device location as Test Lab, type:
system -l “Test Lab”
Example 2:
To set the system name as Rack 5, type:
system -n “Rack 5”
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide36
Page 45

tcpip
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: View and manually configure these network settings for the Rack Monitor 250.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-i <IP address> Type the IP address of the Rack Monitor 250 using the format
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
-s <subnet mask> Type the subnet mask for the Rack Monitor 250.
-g <gateway> Type the IP address of the default gateway. Do not use the
loopback address (127.0.0.1) as the default gateway.
-d <domain name> Type the DNS name configured by the DNS server.
-h <host name> Type the host name that the Rack Monitor 250 will use.
-S enable | disable Enable or disable IPv4.
Example 1:
To view the network settings of the Rack Monitor 250, type tcpip and press
apc>tcpip
E000: Success
Active IPv4 Settings
--------------------
Active IPv4 Address: 10.150.60.232
Active IPv4 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Active IPv4 Gateway: 10.150.60.1
Manually Configured IPv4 Settings
---------------------------------
IPv4: enabled
Manual Settings: disabled
IPv4 Address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask: 0.0.0.0
Gateway: 0.0.0.0
MAC Address: 00 C0 B2 32 D7 7A
Domain Name: example.com
Host Name: apc52D270
ENTER:
Example 2: To manually configure an IP address of 150.250.6.10 for the Rack Monitor 250, type:
tcpip -i 150.250.6.10
Error Message: E000, E102
37 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 46

tcpip6
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: Enable IPv6 and view and manually configure these network settings for the Rack Monitor
250.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-S enable | disable Enable or disable IPv6.
-man enable | disable Enable manual addressing for the IPv6 address of the Rack
Monitor 250.
-auto enable | disable Enable the Rack Monitor 250 to automatically configure the
IPv6 address.
-i <IPv6 address> Set the IPv6 address of the Rack Monitor 250.
-g <IPv6 gateway> Set the IPv6 address of the default gateway.
loopback address (::1) as the default gateway.
-d6 router | statefull
| statelss | never
Set the DHCPv6 mode, with parameters of router controlled,
statefull (for address and other information, they maintain their
status), stateless (for information other than address, the status
is not maintained), never.
Do not use the
Example 1:
To view the network settings of the Rack Monitor 250, type:
tcpip6 and press
apc>tcpip6
E000: Success
IPv6: enabled
Manual Settings: disabled
IPv6 Address: ::/64
MAC Address: 00 C0 B7 92 F2 71
Gateway: ::
IPv6 Manual Address: disabled
IPv6 Autoconfiguration: enabled
DHCPv6 Mode: router controlled
ENTER:
Example 2: To manually configure an IPv6 address of 2001:0:0:0:0:FFD3:0:57ab for the Rack
Monitor 250, type:
tcpip6 -i 2001:0:0:0:0:FFD3:0:57ab
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide38
Page 47

user
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Configure the user name, password, and inactivity timeout for configured users. You
cannot edit a user name; you must delete it and then create a new user. For information on the
permissions granted to each account type, see “Types of User Accounts” on page 2.
Parameters:
Option Argument Description
-n <user> Specify these options for a user.
-pw <user password>
-pe <user permission>
-d <user description>
-e enable | disable Enable overall access.
-st <session timeout> Specify how long a session lasts waits before logging off a
user when the keyboard is idle.
-sr enable | disable Bypass RADIUS by using the serial console (CLI)
connection, also known as Serial Remote Authentication
Override
-el enable | disable Indicate the Event Log color coding.
-lf tab | csv Indicate the format for exporting a log file.
-ts us | metric Indicate the temperature scale, fahrenheit or celsius.
-df mm/dd/yyyy |
dd.mm.yyyy | mmm-ddyy | dd-mmm-yy |
yyyy-mm-dd
-lg <language code (e.g.
enUs)>
-del <user name> Delete a user.
-l no argument Display the current user list.
Specify a date format.
Specify a user language.
Example:
To change the log off time for the user “jdoe” to 10 minutes, enter:
user -n jdoe -st 10
Error Message: E000, E102
39 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 48

userdflt
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Complimentary function to “user” establishing default user preferences. There are two
main features for the default user settings:
• Determine default values when the Super User or Administrator-level account creates a new user.
These values can be changed before the settings are applied to the system.
• For remote users (user accounts not stored in the system that are remotely authenticated, such
as RADIUS), these values are used when a value is not provided by the authenticating server. For
example, if a RADIUS server does not provide the user with a temperature preference, the value
defined in this section will be used.
Parameters:
Options Argument Description
-e enable | disable By default, user will be enabled or disabled upon
creation.
-pe <Administrator | Device |
Read-Only | Network-Only>
-d <user description> Provide a user description.
-st <session timeout in minutes> Provide a default session timeout.
-bl <bad login attempts> Number of incorrect login attempts a user has
-el enable | disable Enable or disable event log color coding.
-lf tab | csv Specify the log export format, tab or CSV.
-ts <us | metrics> Specify the user's temperature scale. This setting is
-df mm/dd/yyyy | dd.mm.yyyy |
mmm-dd-yy | dd-mmm-yy | yyyymm-dd>
-lg <language code
(enUs, etc)>
-sp enable | disable Strong password
-pp <interval in days> Required password change interval
Specify the user's permission level and account
type.
before the system disables their account. Upon
reaching this limit, a message is displayed
informing the user the account has been locked.
The Super User or an Administrator-level account
is needed to re-enable the account to allow the
user to log back in.
NOTE: A Super User account cannot be locked
out, but can be manually disabled if necessary.
also used by the system when a user preference is
not available (for example, email notifications).
Specify the preferred date format.
User language
Error Message: E000, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide40
Page 49

web
Access: Super User, Administrator, Network-Only User
Description: Enable access to the web interface using HTTP or HTTPS.
For additional security, you can change the port setting for HTTP and HTTPS to any unused port from
5000 to 32768. Users must then use a colon (:) in the address field of the browser to specify the port
number. For example, for a port number of 5000 and an IP address of 152.214.12.114, type:
http://152.214.12.114:5000
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-h enable | disable Enable or disable access to the user interface for HTTP.
-s enable | disable Enable or disable access to the user interface for HTTPS.
When HTTPS is enabled, data is encrypted during
transmission and authenticated by digital certificate.
-mp SSL3.0 | TLS1.0 | TLS1.1
| TLS1.2
-ph <http port #> Specify the TCP/IP port used by HTTP to communicate
-ps <https port #> Specify the TCP/IP port used by HTTPS to communicate
Specify the minimum HTTPS protocol to use.
with the Rack Monitor 250 (80 by default). The other
available range is 5000–32768.
with the Rack Monitor 250 (443 by default). The other
available range is 5000–32768.
Example 1:
To prevent all access to the web interface, type:
web -s disable
Example 2:
To define the TCP/IP port used by HTTP, type:
apc>web
E000: Success
Service: http
Http Port: 5000
Https Port: 443
apc>web -ph 80
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
41 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 50

whoami
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device Only, Read Only, Network-Only User
Description: Provides login information on the current user.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>whoami
E000: Success
Error Message: None
xferINI
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Use XMODEM to upload an INI file while you are accessing the CLI through a serial
connection. After the upload completes:
• If there are any system or network changes, the CLI restarts and you must log on again.
• If you selected a baud rate for the file transfer that is not the same as the default baud rate for the
Rack Monitor 250, you must reset the baud rate to the default to reestablish communication with
the Rack Monitor 250.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>xferINI
Enter 'YES' to continue or <ENTER> to cancel : <user enters ‘YES’>
------- File Transfer Baud Rate------------------------------
1- 2400
2- 9600
3- 19200
4- 38400
> <user enters baudrate selection>
Transferring at current baud rate (9600), press <ENTER>...
<user presses <ENTER>>
Start XMODEM-CRC Transfer Now!
CC
<user starts sending INI>
150 bytes have successfully been transmitted.
apc>
Error Message: None
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide42
Page 51

xferStatus
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: View the result of the last file transfer. See “Verify Upgrades” on page 126 for descriptions
of the transfer result codes.
Parameters: None
Example:
apc>xferStatus
E000: Success
Result of last file transfer: Failure unknown
Error Message: E000
43 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 52

Rack Monitor 250 Device Command Descriptions
modbus
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: View or configure modbus options.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-a enable | disable Enable or disable Modbus.
-br 9600 | 19200 Specify the baud rate.
-pr even | odd | none Select even or odd or no parity. The number of stop bits is
automatically selected: for no parity, 2 stop bits, and for
even/odd parity,1 stop bit in Modbus master.
-s <1 - F7> Specify the Modbus slave address in hexidecimal.
-rDef no argument Restore default settings.
-tE enable | disable Enable or disable Modbus TCP.
-tP <1 - 65535> Specify the Modbus TCP port number.
Example 1:
To enable modbus, type:
modbus -a enable
Example 2:
To disable modbus, type:
apc>modbus -a disable
E000: Success
apc>modbus
E000: Success
Slave Address = 0x1
Status = DISABLED
Baud Rate = 9600
Parity = EVEN (8, E, 1)
TCP Status = DISABLED
TCP Port Number = 502
Error Message: E000, E101, E102
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide44
Page 53
nbabout
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View or configure information about the Rack Monitor 250.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <name> View or set a name for the appliance (up to 20
characters).
-l <location> View or set the location of the appliance (up to 20
characters).
-a no argument View the cumulative alarm status.
-mn no argument View the model number.
-sn no argument View serial number.
-fw no argument View the firmware version of the sensor access controller.
-hw no argument View hardware version.
Example:
apc> nbabout -n New_Name
Old Name: NetBotz
New Name: New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
nbbeacon
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View or configure information for the NetBotz beacon attachment.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <name> View or set a name for the beacon (up to 20 characters).
-l <location> View or set the location of the beacon (up to 20
characters).
-s Off | On Turn the beacon off or on.
Example:
apc>nbbeacon -n New_Name
Old Name : Beacon NB
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
45 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 54

nboutlet
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View information about the switched outlet.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <Name> View or set a name for the outlet (up to 20 characters).
-l <Location> View or set the location of the outlet (up to 20 characters).
-s Off | On View or set the current switched outlet state.
-ns Off | On View or set the normal switched outlet state.
Example:
apc>nboutlet -n New_Name
Old Name : Outlet
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide46
Page 55

nbrack
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View or configure rack access information.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-c HID26b | HID37b |
HID37Fac | Corp1000 |
Mifare4B | Mifare7B |
MifareD | MifareP |
iCLASS8B
-r no argument View the number of registered rack access card users.
-rr <1–200> View the RFID number associated with a registered user’s
-rn <1–200> <user name> Identify a registered user (1–200) and assign him or her a
-rc <1–200> <Contact
information>
-rs <1–200>
<Disabled | Enabled |
Delete>
-u no argument View the number of unregistered users that have held a
-ur <1–10> View the RFID number associated with for an
-us <1–10>
<Register | Delete>
-cs disabled | enabled View the card reader status, or enable/disable the card
-ds <1–2> View the state of the door sensors.
-ls <1–2> <locked |
unlocked>
-fw no argument View the firmware version of the rack access controller.
Enter the type of rack-access cards used with the
appliance.
rack access card.
user name.
Identify a registered user (1–200) and enter his or her
contact information.
Identify a registered user (1–200). Disable or enable rack
acces for that user, or delete the user account.
rack access card up to a lock configured for rack access.
unregistered user’s rack access card.
Identify an unregistered user (1–10).
Register or delete that user.
readers.
View or set the state of the rack locks.
Example:
apc>nbrack -c HID-37
Old Card : HID-26
New Card : HID-37
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
47 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 56

nbrelay
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View or configure information about the output relay.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <Name> View or set a name for the relay (up to 20 characters).
-l <Location> View or set the location of the relay (up to 20 characters).
-s Closed | Open View or set the current relay output state.
-ns Closed | Open View or set the normal relay output state.
Example:
apc>nbrelay -n New_Name
Old Name : Relay
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
nbsensor
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View and configure settings for sensors connected to universal sensor ports 1–6. Select
the sensor by the port it is connected to, then view or configure settings for that sensor. Enter whole
numbers without units to configure sensor settings.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <1–6> <Name> View or set a name for the sensor (up to 20
characters).
-l <1–6> <Location> View or set the location of the sensor (up to 20
characters).
-tp <1–6> View the sensor type.
-a <1–6> View active alarms.
-ds <1–6> <Info | Warn |
Crit>
Temperature sensor thresholds.
-t <1–6> View the current temperature.
-tmx <1–6>
<Max temperature alarm
threshold>
-th <1–6> <High temperature
alarm threshold>
View or set the severity of alarms generated by a
discrete sensor (informational, warning, or critical).
View or set the maximum allowable temperature. If the
temperature rises above this value, a critical alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the high temperature
alarm. If the temperature rises above this value, a
warning alarm is generated.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide48
Page 57

Option Argument Definition
-tl <1–6>
<Low temperature alarm
threshold>
-tmn <1–6>
<Minimum temperature
alarm threshold>
-thy <1–6>
<Temperature hysteresis
alarm threshold>
View or set the threshold for the low temperature
alarm. If the temperature goes below this value, a
warning alarm is generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum allowable
temperature. If the temperature goes below this value,
a critical alarm is generated.
View or set hysteresis for temperature alarms.
This hysteresis value determines the point at which
temperature alarms are cleared (the clearing point).
The clearing point for a high/maximum alarm is the
alarm threshold minus the hysteresis value. The
clearing point for a low/minimum alarm is the threshold
plus the hysteresis value.
For example, if you have a low temperature threshold
of 26 degrees and a hysteresis value of 5, the clearing
point for a low temperature alarm would be 31 degrees
(26 plus 5).
Long term rate of change thresholds: View or set alarms to indicate a change in temperature over
several hours. All rate of change threshold violations result in critical alarms.
-tlim <1–6>
<Temperature increase,
magnitude>
-tlit <1–6>
<Temperature increase,
time>
-tldm <1–6>
<Temperature decrease,
magnitude>
-tldt <1–6>
<Temperature decrease,
time>
View or set the maximum number of degrees the
temperature can increase within a specified time before
an alarm is generated.
View or specify a number of hours. If the temperature
increases too much within the time period you specify,
an alarm is generated.
View or set the maximum number of degrees the
temperature can decrease before an alarm is
generated.
View or set the number of hours. If the temperature
decreases too much within the time period you specify,
an alarm is generated.
Short term rate of change thresholds: View or set alarms to indicate a change in temperature or
humidity over several minutes. All rate of change threshold violations result in critical alarms.
-tsim <1–6>
<Temperature increase,
magnitude>
-tsit <1–6>
<Temperature increase,
time>
-tsdm <1–6>
<Temperature decrease,
magnitude>
-tsdt <1–6>
<Temperature decrease,
time>
View or set the maximum number of degrees the
temperature can increase within a specified time before
an alarm is generated.
View or specify a number of minutes. If the temperature
increases too much within the time period you specify,
an alarm is generated.
View or set the maximum number of degrees the
temperature can decrease before an alarm is
generated.
Specify a number of minutes. If the temperature
decreases too much within the time period you specify,
an alarm is generated.
49 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 58

Option Argument Definition
Humidity sensor thresholds.
-h <1–6> View the humidity level.
-hmx <1–6>
<Max humidity alarm
threshold>
-hh <1–6>
<High humidity alarm
threshold>
-hl <1–6>
<Low humidity alarm
threshold>
-hmn <1–6>
<Min humidity alarm
threshold>
-hhy <1–6>
<Humidity hysteresis
alarm threshold>
View or set the maximum allowable humidity. If the
humidity rises above this value, a critical alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the high humidity alarm. If
the humidity rises above this value, a warning alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the low humidity alarm. If
the humidity goes below this value, a warning alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum allowable
humidity. If the humidity goes below this value, a critical
alarm is generated.
This hysteresis value determines the point at which
humidity alarms are cleared (the clearing point). The
clearing point for a high/maximum alarm is the alarm
threshold minus the hysteresis value. The clearing
point for a low/minimum alarm is the threshold plus the
hysteresis value.
For example, if you have a high humidity threshold of
26% and a hysteresis value of 5, the clearing point for a
high humidity alarm would be 21% (26 minus 5).
Example:
apc>nbsensor -n 1 New_Name
Old Name : Sensor NB:1
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide50
Page 59

spabout
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View or configure sensor pod settings. Identify the senor pod by its reference number
(1–12). You can view the reference number on the LED display of your sensor pod.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <1–12> <name> Enter a name for the sensor pod (up to 20 characters).
-l <1–12> <location> Enter the location of the sensor pod (up to 20 characters).
-a <1–12> View the alarm status of all sensor pod sensors.
-mn <1–12> View the model number.
-sn <1–12> View the serial number.
-fw <1–12> View the firmware version.
-hw <1–12> View the hardware version.
-r <1–12> View the reference number.
Example:
apc>spabout -n 1 New_Name
Old Name : NBPod150
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
spsensor
Access: Super User, Administrator, Device User, Read-only User
Description: View and configure settings for wired sensors connected to a Sensor Pod 150. Identify the
senor pod by its reference number (1–12). (You can view the reference number on the LED display of
your sensor pod.) Then identify the sensor by the port to which it is connected (1-6).
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-n <1–12> <1-6> <Name> View or set a name for the sensor (up to 20
characters).
-l <1–12> <1-6> <Location> View or set the location of the sensor (up to
20 characters).
-tp <1–12> <1-6> View the sensor type.
-a <1–12> <1-6> View active alarms.
-ds <1–12> <1-6>
<Info | Warn | Crit>
View or set the severity of alarms generated
by a discrete sensor (informational, warning,
or critical).
51 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 60

Option Argument Definition
Temperature sensor thresholds.
-t <1–12> <1-6> View the current temperature.
-tmx <1–12> <1-6>
<Max temperature alarm
threshold>
-th <1–12> <1-6> <High temperature
alarm threshold>
View or set the maximum allowable
temperature. If the temperature rises above
this value, a critical alarm is generated.
View or set the threshold for the high
temperature alarm. If the temperature rises
above this value, a warning alarm is
generated.
-tl <1–12> <1-6>
<Low temperature alarm
threshold>
-tmn <1–12> <1-6>
<Minimum temperature alarm
threshold>
View or set the threshold for the low
temperature alarm. If the temperature goes
below this value, a warning alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum
allowable temperature. If the temperature
goes below this value, a critical alarm is
generated.
-thy <1–12> <1-6>
<Temperature hysteresis alarm
threshold>
View or set hysteresis for temperature
alarms.
This hysteresis value determines the point at
which temperature alarms are cleared (the
clearing point). The clearing point for a high/
maximum alarm is the alarm threshold minus
the hysteresis value. The clearing point for a
low/minimum alarm is the threshold plus the
hysteresis value.
For example, if you have a low temperature
threshold of 26 degrees and a hysteresis
value of 5, the clearing point for a low
temperature alarm would be 31 degrees (26
plus 5).
Long term rate of change thresholds: View or set alarms to indicate a change in temperature over
several hours. All rate of change threshold violations result in critical alarms.
-tlim <1–12> <1-6>
<Temperature increase,
magnitude>
-tlit <1–12> <1-6>
<Temperature increase, time>
View or set the maximum number of degrees
the temperature can increase within a
specified time before an alarm is generated.
View or specify a number of hours. If the
temperature increases too much within the
time period you specify, an alarm is
generated.
-tldm <1–12> <1-6>
<Temperature decrease,
magnitude>
-tldt <1–12> <1-6>
<Temperature decrease, time>
View or set the maximum number of degrees
the temperature can decrease before an
alarm is generated.
View or set the number of hours. If the
temperature decreases too much within the
time period you specify, an alarm is
generated.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide52
Page 61

Option Argument Definition
Short term rate of change thresholds: View or set alarms to indicate a change in temperature or
humidity over several minutes. All rate of change threshold violations result in critical alarms.
-tsim <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Temperature increase,
magnitude>
-tsit <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Temperature increase, time>
View or set the maximum number of degrees
the temperature can increase within a
specified time before an alarm is generated.
View or specify a number of minutes. If the
temperature increases too much within the
time period you specify, an alarm is
generated.
-tsdm <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Temperature decrease,
magnitude>
-tsdt <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Temperature decrease, time>
View or set the maximum number of degrees
the temperature can decrease before an
alarm is generated.
Specify a number of minutes. If the
temperature decreases too much within the
time period you specify, an alarm is
generated.
Humidity sensor thresholds.
-h <1–12> <1-6> <Display number> View the humidity level.
-hmx <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Max humidity alarm threshold>
-hh <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<High humidity alarm threshold>
View or set the maximum allowable humidity.
If the humidity rises above this value, a critical
alarm is generated.
View or set the threshold for the high humidity
alarm. If the humidity rises above this value, a
warning alarm is generated.
-hl <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Low humidity alarm threshold>
-hmn <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Min humidity alarm threshold>
View or set the threshold for the low humidity
alarm. If the humidity goes below this value, a
warning alarm is generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum
allowable humidity. If the humidity goes below
this value, a critical alarm is generated.
-hhy <1–12> <1-6> <Display number>
<Humidity hysteresis alarm
threshold>
This hysteresis value determines the point at
which humidity alarms are cleared (the
clearing point). The clearing point for a high/
maximum alarm is the alarm threshold minus
the hysteresis value. The clearing point for a
low/minimum alarm is the threshold plus the
hysteresis value.
For example, if you have a high humidity
threshold of 26% and a hysteresis value of 5,
the clearing point for a high humidity alarm
would be 21% (26 minus 5).
Example:
apc>spsensor -n 2 New_Name
Old Name : Sensor SP 06:2
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
53 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 62

zw
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: View information for all Zigbee wireless sensors, or select a wireless sensor (1–48) to view
and edit its settings.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-c no argument View the number of commissioned sensors.
-ch <1–48> View the wireless channel of the sensor.
-n <1–48> <name> View or configure sensor name (up to 20 characters).
-l <1–48> <location> View or configure sensor location (up to 20 characters).
-sn <1–48> View the serial number.
-mn <1–48> View the model number.
-tp <1–48> View sensor type
-a <1–48> View sensor active alarm severity.
-xa <1–48> View the extended address.
-fw <1–48> View the firmware version.
-s <1–48> View the signal strength.
-sl <1–48> <low signal
strength threshold>
-smn <1–48> <minimum signal
strength threshold>
-b <1–48> View the battery voltage.
-bl <1–48> <low battery
threshold>
-bmn <1–48> <min battery
alarm>
Temperature settings
-t <1–48> View the temperature.
-tmx <1–48> <max temperature
alarm>
-th <1–48><high temperature
alarm>
-tl <1–48> <low temperature
alarm>
-tmn <1–48> <min temperature
alarm>
View or set the threshold for low signal strength. If the
signal strength goes below this value, an alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum allowable
signal strength. If the signal strength goes below this
value, an alarm is generated.
View or set the low battery threshold. If the battery
voltage drops below this threshold, an alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum allowable
battery voltage. If the battery voltage goes below this
value, an alarm is generated.
View or set the threshold for the maximum allowable
temperature. If the temperature rises above this value, an
alarm is generated.
View or set the high temperature threshold. If the
temperature rises above this threshold, an alarm is
generated.
View or set the low temperature threshold. If the
temperature drops below this threshold, an alarm is
generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum allowable
temperature. If the temperature drops below this value,
an alarm is generated.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide54
Page 63

Option Argument Definition
Humidity settings
-h <1–48> View the humidity.
-hmx <1–48> <max humidity
alarm>
-hh <1–48> <high humidity
alarm>
-hl <1–48> <low humidity
alarm>
-hmn <1–48> <min humidity
alarm>
Example:
apc>zw -n 1 New_Name
Old Name : Wireless Sensor
New Name : New_Name
E000: Success
View or set the threshold for the maximum allowable
humidity. If the humidity rises above this value, an alarm
is generated.
View or set the high humidity threshold. If the humidity
rises above this threshold, an alarm is generated.
View or set the low humidity threshold. If the humidity
drops below this threshold, an alarm is generated.
View or set the threshold for the minimum allowable
temperature. If the humidity drops below this value, an
alarm is generated.
Error Message: E000, E200, E201, E202, E203, E204
zwsyslog
Access: Super User, Administrator
Description: Enable or disable forwarding of Zigbee wireless Sensor Data Packets (SDP) to a
configured syslog server. This command is typically used for troubleshooting with APC by Schneider
Electric support.
NOTE: You must configure a syslog server on the Rack Monitor 250 to use the zwsyslog command. See
“Servers” on page 107 for instructions to configure a syslog server.
Parameters:
Option Argument Definition
-d enable | disable Enable: Enable forwarding of SDP over Syslog.
Disable: Disable forwarding of SDP over Syslog.
Example:
apc>zwsyslog -d enable
E000: Success
Error Message: E000, E102
55 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 64

Web Interface
The web user interface provides options to view the status and manage the Rack Monitor 250.
Modern web browsers are compatible with the Rack Monitor 250 web interface. Use the most recent
version of your browser to mitigate the risk of software security vulnerabilities.
Access the Web Interface
To access the Rack Monitor 250 in a web browser, you must disable any proxy server services. Access
to the Rack Monitor 250 through a proxy server is not available at this time. If a proxy server is required,
it must be configured so the IP address of the Rack Monitor 250 is not proxied.
Type the IP address of the Rack Monitor 250 in the web browser’s address field:
• For an IP address of 139.225.6.133, when the Rack Monitor 250 uses the default port (80), enter:
http://139.225.6.133 if HTTP is your access mode.
https://139.225.6.133 if HTTPS is your access mode.
• For a System IP address of 139.225.6.133, when the Rack Monitor 250 uses a non-default port
(5000, in this example), enter:
http://139.225.6.133:5000 if HTTP is your access mode.
https://139.225.6.133:5000 if HTTPS is your access mode.
• If your DNS system has been configured with entries for the Rack Monitor 250
(Web1 in this example), enter:
http://Web1 if HTTP is your access mode.
https://Web1 if HTTPS is your access mode.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide56
Page 65

Web Interface Features
When you log on to the Rack Monitor 250 web interface, a quick status area in the top right displays
information about the system. Click the headings in the menu bar to display popup menus listing related
options.
Quick status links
The Quick Status area in the upper right corner of every screen displays the number and severity of
active alarms. Click any Quick Status icon to return to the home screen.
Blue “informational” icon
Green “device operating normally” icon
Yellow “Attention required” warning icon
Red “Alarm detected” critical icon
Current session preferences
Click the user name link to access your user preferences. Go to Configuration > Security > Local
Users > Management for more user settings.
Help
Click Help in the upper right corner to view context-sensitive information.
Quick links
There are three user configurable links on the lower left of each page. By default, the links access the
following web pages:
• Link 1: Website homepage
• Link 2: Demonstrations of web-enabled products
• Link 3: Information on Schneider Electric Remote Monitoring Services
Limited Status Access
The Limited Status Access option provides a read-only, public web page with basic device status without
requiring you to log on. This feature is disabled by default. Go to Configuration > Network > Web >
Access to enable it. Check the Use as default page box to display this device status page instead of
the log on screen when you access the device with only its IP address or host name. To log on to the
device from the device status page, use the Log On link on the menu bar.
Otherwise, when only the Limited Status Access option is enabled, click the Limited Status hyperlink on
the log on screen in the lower left corner to access the basic device status screen.
57 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 66
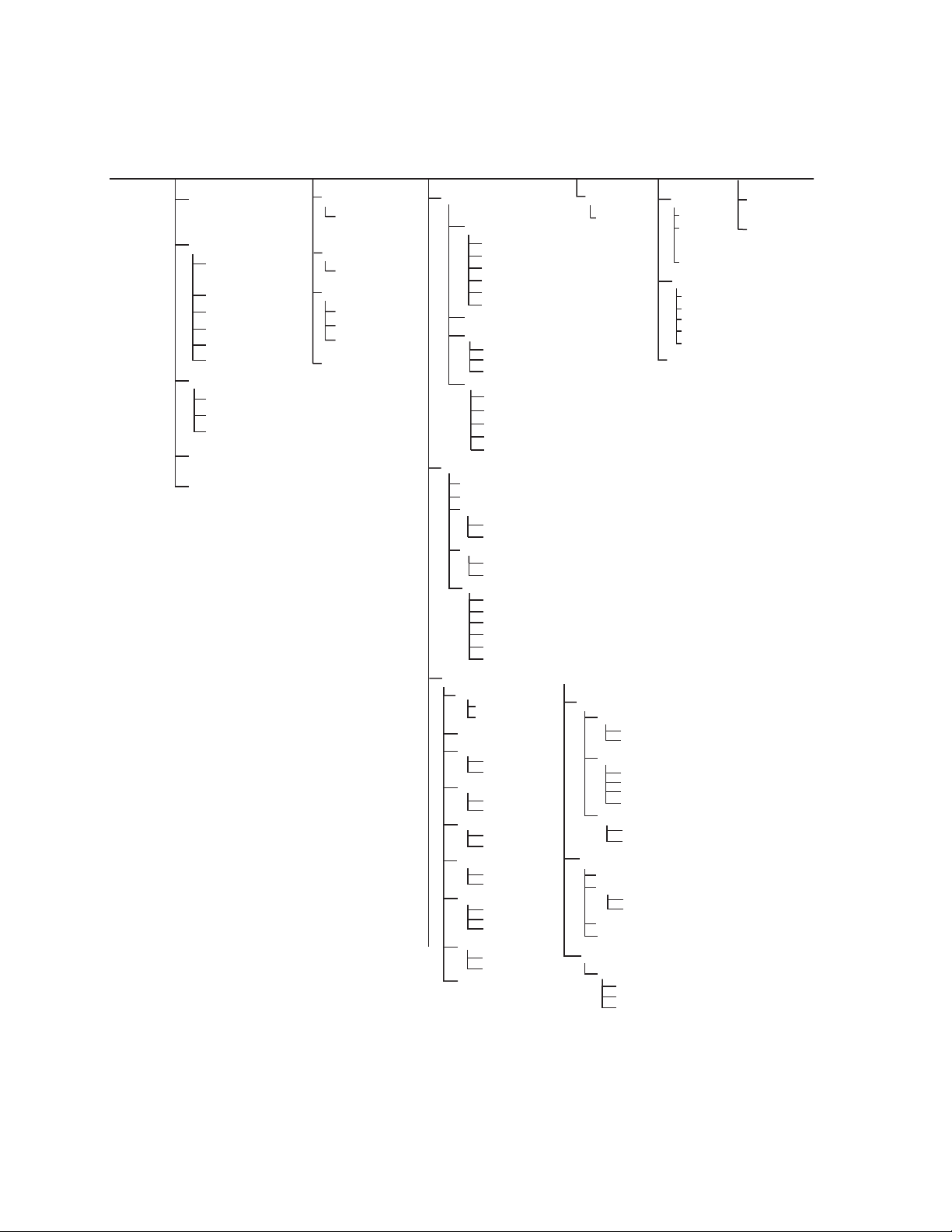
Display Menu Tree
Wireless
Sensor Network
Events
Firewall
Network
Support
Data
Network
Reverse
Lookup
Graphing
Rotation
Log
Size
Log
Size
LED Blink
Tests Logs AboutStatus Control
Interval
Home
Network
Reset/Reboot
Management
Default Settings
Authentication
RADIUS
Active Policy
Active Rules
Create/Edit Policy
Load Policy
Test
Security
Session Management
Ping Response
Local Users
Remote Users
Firewall
IPv4 Settings
IPv6 Settings
SSH Host Key
Access Control
Access Control
Test
Access
Access
Access
Access
Serial
TCP
Network
Port Speed
FTP Server
TCP/IP
DNS
Web
Console
SNMPv1
SNMPv3
Modbus
By Event
By Group
Server
Recipients
Trap Receivers
Test
Test
Event Actions
SNMP Traps
E-mail
Mode
Daylight Savings
Servers
Settings
Test
General
Logs
Date/Time
Quick Links
Syslog
Wired Sensor
Outputs
Alarm Status
Network
Fluid Detector
Door Sensor
Temperature
& Humidity
Dry Contact Inputs
Beacon
Relay Output
Switched Outlet
Lock Control
Outputs
Beacon
Relay Output
Switched Outlet
Temp/Humidity
Dry Contact Inputs
Beacon
Relay Output
Unregistered Users
Device
NetBotz
Wired Sensors
Outputs
Rack Access
Smoke
Vibration
Fluid Detector
Door Sensor
Wireless Sensor Network
Switched Outlet
Registered Users
Identication
Lock Properties
Schedule
mpg0472d
Security
Session
Management
RADIUS
Notication
Conguration
Smoke
Vibration
Conguration
Conguration
SSL Certicate
User Proles
SSL Certicates
User Cong File
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide58
Page 67

Home Tab
Home is the default page when you log on. To change the login page to a different page, go to that page,
then click the green pushpin at the top right side of the browser window.
The Home tab displays the alarm status of system devices: Critical (device requires immediate
attention), Warning (attention required), or Normal (no alarms).
A maximum of ten alarms is displayed for each device. Recent Device Events displays the last five
device events. View the Alarm Status page to see all alarms for all connected devices, or the Event Log
to see all device events.
59 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 68

NetBotz Alarms
View alarms for modules. (This area appears only if a module is in an alarm state.)
For the following sensor types, view the number of connected sensors and their status. Click More to
view all connected sensors of this type. Click the name of each sensor to view its settings.
• Wireless sensors
• Temperature & humidity sensors
• Dry contact input sensors
• Vibration sensors
• Smoke sensors
• Fluid detector
• Door sensors
For the following sensor types, click the name of the sensor to view its settings.
• Beacon
• Output relay
• Switched outlet
Rack Access
View the status of Door 1 and Door 2. Click the link to control the lock:
• Status: Secure or not secure
• Lock: Locked or unlocked
• Handle: Open or closed
• Door: Open or closed
Click Lock Control to control the lock.
Reset Alarms Link
If communication is lost with a device, or if a temperature sensor's rate-of-change is exceeded, a Reset
Alarms link will appear. Click the link to clear the alarm if, for example, you intentionally disconnected a
sensor or to acknowledge a rate of change.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide60
Page 69

Status Tab
On these pages, you can view detailed information about wireless sensors, wired sensors, outputs,
alarms, and current network settings. You can also configure settings for sensors and outputs.
View and Manage Wireless Sensors
Path: Status > Wireless Sensor Network
View all connected wireless temperature and temperature/humidity sensors.
Setting Description
Status Critical (device requires immediate attention), Warning (attention
required), and Normal. By default, all information is sorted by Status. To
sort by another column heading, click its name.
Name Name of the monitored device (up to 20 characters). Click a sensor name
to configure the device.
Extended Address The extended address (MAC) of each sensor in the wireless network.
Location The location of each sensor in the wireless network (up to 20 characters).
Typ e The sensor type of each sensor in the wireless network.
Tem p e rature The temperature reading on each sensor in the wireless network.
Humidity The humidity reading on each sensor in the wireless network.
Signal The Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). The strength of the
wireless signal between each sensor and the Router or Coordinator to
which it sends data. A reading above 30% is ideal.
Battery The battery voltage for each sensor in the wireless network.
You can also select a sensor by its Name to edit settings for that sensor:
Setting Description
Name Enter a name (up to 20 characters).
Extended Address The extended address (MAC) of the wireless sensor.
Location Enter the location of the sensor (up to 20 characters).
Alarm Generation Enable or disable. When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system
continues to monitor the state of the sensor, but does not generate an
alarm. Alarms are not recorded in the event log when Alarm Generation is
disabled.
Temperature/
Humidity
Thresholds
Battery/Signal
Thresholds
• Maximum: The maximum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
rises above this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• High: If the temperature or humidity rises above this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Low: If the temperature or humidity falls below this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Minimum: The minimum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
falls below this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• Low: If the battery voltage or signal strength drops below its low
threshold for the sensor, an alarm occurs.
• Minimum: If the battery voltage or signal strength drops below its
minimum threshold for the sensor, an alarm occurs.
61 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 70

View and Manage Wired Sensors
Path: Status > Wired Sensor > Sensor Type
On these pages, you can view information for all sensors, create a filter to show only specific sensors,
use the mass configuration feature to configure all sensors on a page, or configure individual sensor
settings.
All wired sensors display the following information:
Setting Description
Status Critical (device requires immediate attention), Warning (attention
required), and Normal. By default, all information is sorted by Status.
Name Select a sensor name to configure the sensor settings.
Location The location of each sensor.
Module Name Name of the module to which the sensor is connected: the Rack Monitor
250 or the Sensor Pod 150. Click a module name to view the module's
factory information and all devices connected to the module, or to
configure the module's name and location.
Each wired sensor type displays additional information. Click the sensor name to configure its settings.
Setting Description
Temperature and Humidity
Temperature Temperature of the air surrounding the sensor. To change the
temperature units for this user session only, click the thermometer icon.
To change the temperature units for the current and future sessions for
one user, select Configuration > Security> Local Users >
Management. Select the user, then Temperature Scale.
To change the temperature units for the current and future sessions for all
users, select Configuration > Security> Local Users > Default
Settings, then select Temperature Scale.
Humidity Relative humidity of the air surrounding the sensor.
Dry Contact Inputs
State Open/Low or Closed/High
Smoke
State No Smoke, or Smoke Detected
Vibration
State No Vibration, or Vibration Detected
Fluid Detector
State No Fluid, or Fluid Detected
Door Sensor
State Open or closed
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide62
Page 71

Filter wired sensors
Show only sensors that meet the criteria of your filter. Sensors that do not match all selected criteria will
not be shown. Select Create Filter, then enter one or more filter settings.
Setting Description
Status Select one or more alarm statuses.
Critical: Critical alarm
Warning: Warning alarm
Information: Informational alarm
Normal: No alarm
State Select the current state of the sensor.
Name Enter the name of the sensor (up to 20 characters). Then select filter
parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Location Enter a sensor location. Then select filter parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Module Name Filter by the appliance or sensor pod that sensors are attached to. Enter
the Module Name of an appliance or sensor pod, and select filter
parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Tem p e rature Enter a temperature value. From the drop down list, select whether to
view sensors that detect a temperature Less Than, Equal To, or Greater
Than that value.
Humidity Enter a humidity value. From the drop down list, select whether to view
sensors that detect a humidity Less Than, Equal To, or Greater Than
that value.
You can select Clear Filter to remove the filter, or you can create a new filter to override the previous
one.
63 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 72

Mass-configure sensor settings
Change the settings for all sensors of a certain type at once.
Select Mass Configuration, then select the settings you want to configure. Then click Next to configure
those settings. Available settings depend on the type of device.
Setting Description
General • Name: The name of the sensor
• Location: The location of the sensor
Enter up to 20 characters in each field. You can use these wild cards:
• %m: the parent module ID
• %p: the sensor port number
• %l: the parent module location
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensor, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not recorded
in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Severity Select the severity of alarms generated for these sensors. Alarm severities
for temperature and humidity senors are not editable.
Normal State Select the normal state of the sensor. An alarm is generated when the
sensor changes to an abnormal state.
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensors, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not
recorded in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Temperature/Humidity
Thresholds
Rate Of Temperature
Change
• Maximum: The maximum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
rises above this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• High: If the temperature or humidity rises above this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Low: If the temperature or humidity falls below this value, a warning alarm
is generated.
• Minimum: The minimum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
falls below this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• Hysteresis: This value specifies how far above or below a threshold the
temperature or humidity must return to clear a threshold violation.
For Maximum and High threshold violations, the clearing point is the
threshold minus the hysteresis. For Minimum and Low threshold
violations, the clearing point is the threshold plus the hysteresis.
Configure the acceptable short-term and long-term changes in
temperature. When the rate of change is exceeded, the appliance
generates a critical alarm.
• S.T. Increase: Short-term temperature increase
• L.T. Increase: Long-term temperature increase
• S.T. Decrease: Short-term temperature decrease
• L.T. Decrease: Long-term temperature decrease
• Reset Rate Alarms: Clear all existing rate of change alarms.
Click Apply to save your changes or Cancel to discard them.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide64
Page 73

Configure individual sensor settings
Path: Configuration > Device > Wired Sensor > Sensor Type
Select a sensor’s name to configure its settings. Available settings vary by sensor type.
Setting Description
General • Name: The name of the sensor
• Location: The location of the sensor
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensor, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not recorded
in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Severity Select the severity of alarms generated for these sensors. Alarm severities
for temperature and humidity senors are not editable.
Normal State Select the normal state of the sensor. An alarm is generated when the
sensor changes to an abnormal state.
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensors, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not
recorded in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Temperature/Humidity
Thresholds
Rate Of Temperature
Change
Select Threshold Settings to set the following threshold values for
temperature and humidity:
• Maximum: The maximum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
rises above this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• High: If the temperature or humidity rises above this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Low: If the temperature or humidity falls below this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Minimum: The minimum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
falls below this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• Hysteresis: This value specifies how far above or below a threshold the
temperature or humidity must return to clear a threshold violation.
For Maximum and High threshold violations, the clearing point is the
threshold minus the hysteresis. For Minimum and Low threshold
violations, the clearing point is the threshold plus the hysteresis.
Select Rate of Change Settings to configure the acceptable short-term
and long-term changes in temperature. When the rate of change is
exceeded, the appliance generates a critical alarm.
• S.T. Increase: Short-term temperature increase
•
L.T. Increase: Long-term temperature increase
• S.T. Decrease: Short-term temperature decrease
• L.T. Decrease: Long-term temperature decrease
• Reset Rate Alarms: Clear all existing rate of change alarms.
Click Apply to save your changes or Cancel to discard them.
65 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 74
View and Manage Outputs
Path: Status > Outputs
Select an output (Beacon, Output Relay, and Switched Outlet). Devices connected to these outputs are
controlled by the output settings.
The following information is shown for all outputs:
Setting Description
Module Name Name of Module to which the output is connected.
Module Location Location of Module to which the output is connected, the Rack Monitor
250 or the Sensor Pod 150. ‘Unknown’ if no location is configured.
Alarm Status Critical (device requires immediate attention), Warning (attention
required), and Normal. By default, all information is sorted by Status. To
sort by another column heading, click its name.
You can configure the following settings for each output:
Setting Description
Name Enter a name for the output (up to 20 characters).
Location Enter the location of the sensor (up to 20 characters).
Normal State Set the normal state of the output (excluding the beacon): On/Off or
Open/Closed
Control Change the state of the output to On/Off or Open/Closed.
Alarm Mapping The beacon, output relay and switched outlet can be activated by alarm
states of sensors on the NetBotz module only.
1. Select one or more alarm states that will change the state of the
output.
2. By default, each sensor connected to the NetBotz module is mapped
to activate the output when the sensor is in an abnormal state. Click
the name of the alarm state to view the sensors connected to the
module.
3. Select sensors to include in the alarm. Any selected sensor, in its
abnormal state, activates the output.
NOTE: The Output pages under the Status, Control, and Configuration menus are the same, and
contain all the tasks for each menu option.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide66
Page 75

View Alarms
Path: Status > Alarm Status
The Alarm Status page displays the alarm status of system devices: Critical (device requires immediate
attention), Warning (attention required), or Normal (no alarms present).
Setting Description
Module Alarms View alarms for modules. (This area appears only if aRack Monitor 250 or
Sensor Pod 150 module is in an alarm state.)
Wireless Sensors View the number of connected sensors and their status. Click the name of
a sensor in the alarm state to view its settings.
Temperature &
Humidity Sensors
Dry Contact Input
Sensors
Vibration Sensors View the number of connected sensors and their status. Click the name of
Smoke Sensors View the number of connected sensors and their status. Click the name of
Fluid Detector View the number of connected sensors and their status. Click the name of
Beacon View the status of the beacon. Click the name of the beacon to view its
Relay Output View the status of the relay output. Click the name of the relay output to
Switched Outlet View the status of the switched outlet. Click the name of the switched
Rack Access View the status of Door 1 and Door 2:
Reset Alarms link If communication with a device is lost, or a temperature sensor's rate-of-
View the number of connected sensors and their status. Click the name of
a sensor in the alarm state to view its settings.
View the number of connected sensors and their status. Click the name of
a sensor in the alarm state to view its settings.
a sensor in the alarm state to view its settings.
a sensor in the alarm state to view its settings.
a sensor in the alarm state to view its settings.
settings.
view its settings.
outlet to view its settings.
• Status: Secure or not secure
• Lock: Locked or unlocked
• Handle: Open or closed\
• Door: Open or closed
change is exceeded, the Reset Alarms link appears. Click the link to clear
the alarm if, for example, you intentionally disconnected a sensor, or you
want to acknowledge a rate of change alarm.
67 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 76

View the Network Status
Path: Status > Network
Network Status provides an overview of critical network status information, including current IPv4 and
IPv6 settings, DNS status, and port speed.
You can configure network settings on the Configuration > Network pages.
Current IPv4 settings
Setting Description
System IP The IP address of the unit.
Subnet Mask The IP address of the sub-network.
Default Gateway The IP address of the router used to connect to the network.
MAC Address The MAC address of the unit.
Mode How the IPv4 settings are assigned: Manual, DHCP, or BOOTP.
DHCP Server The IP address of the DHCP server. This is only displayed if Mode is
DHCP.
Lease Acquired The date/time that the IP address was accepted from the DHCP server.
Lease Expires The date/time that the IP address accepted from the DHCP server
expires and will need to be renewed.
Current IPv6 settings
Setting Description
Typ e How the IPv6 settings are assigned.
IP Address The IP address of the unit.
Prefix Length The range of addresses for the sub-network.
Domain name system status
Setting Description
Active Primary DNS
Server
Active Secondary
DNS Server
Active Host Name The host name of the active DNS server.
Active Domain
Name (IPv4/IPv6)
Active Domain
Name (IPv6)
The IP address of the primary DNS server.
The IP address of the secondary DNS server.
The IPv4/IPv6 domain name that is currently in use.
The IPv6 domain name that is currently in use.
Port speed
Current Speed: The current speed assigned to the Ethernet port.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide68
Page 77

Control Tab
You can use these pages to manage user sessions, reset the network interface, view and manage
outputs, and manually control rack access handles.
Manage User Sessions
Path: Control > Security > Session Management
Lists all of the currently logged in users, the interface from which they are logged in, their IP address,
and the amount of time they have been logged in. To terminate a specific user session, with the
appropriate authority, select the user name and click Terminate.
Reset/Reboot the Network Interface
Path: Control > Network > Reset/Reboot
Action Description
Reboot
Management
Interface
Reset All • If you do not select “Exclude TCP/IP,” all configured values and settings are
Reset Only Select one or more of the following options:
Restarts the device’s network interface without turning off and restarting the
device itself.
reset to their default values, including the setting that determines how this
device must obtain its TCP/IP configuration values. The default is DHCP.
• If you select “Exclude TCP/IP,” all configured values and settings, except the
setting that determines how this device must obtain its TCP/IP configuration
values, are reset to their default values.
• TCP/IP: Resets only the setting that determines how this device must obtain its
TCP/IP configuration values. The default is DHCP.
• Event Configuration: Resets events to their default configuration. Any
specially configured event or group will also revert to the default value.
• Lost Communication Alarms: Clears lost communication alarms if, for
example, you intentionally disconnected a sensor.
• Temperature Rate of Change Alarms: Clears temperature rate of change
alarms to acknowledge a rate of change.
• Module Configuration: Resets the to its default configuration.
• User Configurations: Resets all users to their default configuration.
69 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 78

View and Manage Outputs
Path: Control > Outputs
Select an output (Beacon, Output Relay, and Switched Outlet). Devices connected to these outputs are
controlled by the output settings.
The following information is shown for all outputs:
Setting Description
Module Name Name of Module to which the output is connected.
Module Location Location of Module to which the output is connected, the Rack Monitor
250 or the Sensor Pod 150. ‘Unknown’ if no location is configured.
Alarm Status Critical (device requires immediate attention), Warning (attention
required), and Normal. By default, all information is sorted by Status. To
sort by another column heading, click its name.
You can configure the following settings for each output:
Setting Description
Name Enter a name for the output (up to 20 characters).
Location Enter the location of the sensor (up to 20 characters).
Normal State Set the normal state of the output (excluding the beacon): On/Off or
Open/Closed
Control Change the state of the output to On/Off or Open/Closed.
Alarm Mapping The beacon, output relay and switched outlet can be activated by alarm
states of sensors on the NetBotz module only.
1. Select one or more alarm states that will change the state of the
output.
2. By default, each sensor connected to the NetBotz module is mapped
to activate the output when the sensor is in an abnormal state. Click
the name of the alarm state to view the sensors connected to the
module.
3. Select sensors to include in the alarm. Any selected sensor, in its
abnormal state, activates the output.
NOTE: The Output pages under the Status, Control, and Configuration menus are the same, and
contain all the tasks for each menu option.
Lock/Unlock Rack Access Handles
Path: Control > Lock Control
Lock and unlock the rack access handle connected to the Door Handle 1 and Door Handle 2 ports.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide70
Page 79

Configuration Tab
You can use these pages to view and configure settings for modules (the appliance and attached sensor
pods), wired sensors, wireless sensors, and outputs. You can also configure rack access, security
settings, firewall policies, network settings, notifications, general system settings, and Syslog settings.
Configure Settings for an Appliance or Sensor Pod
Path: Configuration > Device > NetBotz
On this page, you can create a filter to show only specific modules (the host appliance and attached
Sensor Pod 150 units). You can also select a Module Name to view factory information and configure
settings for a specific module and any connected devices.
Filter modules
Show only modules that meet the criteria of your filter. Modules that do not match all selected criteria will
not be shown. Select Create Filter, then enter one or more filter setting.
Setting Description
Status Select one or more alarm statuses:
Lost Comm: Lost communication
Critical: Critical alarm
Warning: Warning alarm
Information: Informational alarm
Normal: No alarm
FW Upgrade: The module firmware is being upgraded
Module Name Enter a Module Name. Then select filter parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Location Enter a module location. Then select filter parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Module ID Enter the Module ID of an appliance or sensor pod.
NOTE: The module number for each Sensor Pod 150 is also displayed on
its Identifier LED.
You can select Clear Filter to remove the filter, or you can create a new filter.
Configure appliance settings
Enter the Name and Location of the Rack Monitor 250. Select an attached device to configure settings
for that device. (See “Configure Settings for Wired Sensors” on page 72, “Configure Wireless Sensors”
on page 75, or “Configure Output Settings” on page 77)
Configure Sensor Pod 150 settings
Enter the Name and Location of the sensor pod. Select Blink Identifier LED to make the Identifier LED
on the selected Sensor Pod 150 module blink for the number of minutes you specify. Select an attached
device to configure settings for that device (see “Configure Settings for Wired Sensors” on page 72).
71 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 80

Configure Settings for Wired Sensors
Path: Configuration > Device > Wired Sensor > Sensor Type
On these pages, you can do the following:
• Create a filter to show only specific wired sensors.
• Use the Mass Configuration feature to configure settings for all sensors of a certain type.
• Select sensors by Name to configure settings for individual sensors.
• Select a Module Name to view information for the appliance or sensor pod a sensor is
connected to.
Filter wired sensors
Show only sensors that meet the criteria of your filter. Sensors that do not match all selected criteria will
not be shown. Select Create Filter, then enter one or more filter settings.
Setting Description
Status Select one or more alarm statuses.
Critical: Critical alarm
Warning: Warning alarm
Information: Informational alarm
Normal: No alarm
State Select the current state of the sensor.
Name Enter the name of the sensor (up to 20 characters). Then select filter
parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Location Enter a sensor location. Then select filter parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Module Name Filter by the appliance or sensor pod that sensors are attached to. Enter
the Module Name of an appliance or sensor pod, and select filter
parameters:
• Case Sensitive: Select to make the filter case sensitive.
• Whole Word: Include only complete word matches. If this is not
selected, the filter will include partial word matches.
Tem p e rature Enter a temperature value. From the drop down list, select whether to
view sensors that detect a temperature Less Than, Equal To, or Greater
Than that value.
Humidity Enter a humidity value. From the drop down list, select whether to view
sensors that detect a humidity Less Than, Equal To, or Greater Than
that value.
You can select Clear Filter to remove the filter, or you can create a new filter to override the previous
one.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide72
Page 81

Mass-configure sensor settings
Change the settings for all sensors of a certain type at once.
Select Mass Configuration, then select the settings you want to configure. Then click Next to configure
those settings. Available settings depend on the type of device.
Setting Description
General • Name: The name of the sensor
• Location: The location of the sensor
Enter up to 20 characters in each field. You can use these wildcards:
• %m: any parent module IDs
• %p: any sensor port number
• %l: the parent module location
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensor, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not recorded
in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Severity Select the severity of alarms generated for these sensors. Alarm severities
for temperature and humidity senors are not editable.
Normal State Select the normal state of the sensor. An alarm is generated when the
sensor changes to an abnormal state.
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensors, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not
recorded in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Temperature/Humidity
Thresholds
Rate Of Temperature
Change
• Maximum: The maximum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
rises above this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• High: If the temperature or humidity rises above this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Low: If the temperature or humidity falls below this value, a warning alarm
is generated.
• Minimum: The minimum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
falls below this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• Hysteresis: This value specifies how far above or below a threshold the
temperature or humidity must return to clear a threshold violation.
For Maximum and High threshold violations, the clearing point is the
threshold minus the hysteresis. For Minimum and Low threshold
violations, the clearing point is the threshold plus the hyster
Configure the acceptable short-term and long-term changes in
temperature. When the rate of change is exceeded, the appliance
generates a critical alarm.
• S.T. Increase: Short-term temperature increase
• L.T. Increase: Long-term temperature increase
• S.T. Decrease: Short-term temperature decrease
• L.T. Decrease: Long-term temperature decrease
• Reset Rate Alarms: Clear all existing rate of change alarms.
esis.
Click Apply to save your changes or Cancel to discard them.
73 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 82

Configure individual sensor settings
Path: Configuration > Device > Wired Sensor > Sensor Type
Select a sensor’s name to configure its settings. Available settings vary by sensor type.
Setting Description
General • Name: The name of the sensor
• Location: The location of the sensor
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensor, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not recorded
in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Severity Select the severity of alarms generated for these sensors. Alarm severities
for temperature and humidity senors are not editable.
Normal State Select the normal state of the sensor. An alarm is generated when the
sensor changes to an abnormal state.
Alarm Generation When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system continues to monitor the
state of the sensors, but does not generate alarms. Alarms are not
recorded in the event log when Alarm Generation is disabled.
Temperature/Humidity
Thresholds
Rate Of Temperature
Change
Select Threshold Settings to set the following threshold values for
temperature and humidity:
• Maximum: The maximum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
rises above this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• High: If the temperature or humidity rises above this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Low: If the temperature or humidity falls below this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Minimum: The minimum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
falls below this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• Hysteresis: This value specifies how far above or below a threshold the
temperature or humidity must return to clear a threshold violation.
For Maximum and High threshold violations, the clearing point is the
threshold minus the hysteresis. For Minimum and Low threshold
violations, the clearing point is the threshold plus the hysteresis.
Select Rate of Change Settings to configure the acceptable short-term
and long-term changes in temperature. When the rate of change is
exceeded, the appliance generates a critical alarm.
• S.T. Increase: Short-term temperature increase
• L.T. Increase: Long-term temperature increase
• S.T. Decrease: Short-term temperature decrease
• L.T. Decrease: Long-term temperature decrease
• Reset Rate Alarms: Clear all existing rate of change alarms.
Click Apply to save your changes or Cancel to discard them.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide74
Page 83

Configure Wireless Sensors
Path: Configuration > Device > Wireless Sensor Network
The Wireless Sensor Network
The Zigbee wireless sensor network is made of a host appliance, a coordinator, routers, and end
devices.
• The host appliance (your Rack Monitor or Room Monitor) collects data from the wireless sensor
network and generates alerts based on sensor readings.
• The coordinator is connected directly to the host appliance via USB. It reports data from the
sensors on the network and provides available firmware updates to the wireless network. Each
wireless sensor network must have only one coordinator, which is connected to a USB Type A
port on the NetBotz appliance. The coordinator comes installed on the NetBotz Rack Monitor 250.
• Routers extend the range of the wireless sensor network. Routers pass information between
themselves and the coordinator, and between the coordinator and end devices. Routers are
optional. In a data center environment where obstructions are common, routers are
recommended if sensors are more than 50 feet from the coordinator. Each router is powered by
an AC-USB adapter, not directly connected to the NetBotz appliance.
• End devices monitor attached and internal sensors and send data back to the host appliance
through the network. End devices are powered by batteries.
The following devices can be configured on your wireless network:
Wireless device Range Network role
USB Coordinator & Router (NBWC100U) up to 30.5 m (100 ft),
line of sight
Wireless Temperature Sensor (NBWS100T) up to 30.5 m (100 ft),
line of sight
Wireless Temperature/Humidity Sensor
(NBWS100H)
NOTE: In a data center environment where obstructions are common, a range of 15 m (50 ft) is typical
for any wireless device.
The order in which you configure your wireless sensor network and apply power to your wireless devices
is important:
1. Select the coordinator and routers: Choose the USB Coordinator & Router that will become
the coordinator. Note the extended address of the coordinator. Choose one or more USB
Coordinator & Routers to become routers.
2. Mount the sensors. Choose the locations for the routers and end devices. Do not power the
routers or end devices at this time.
3. Power the coordinator first: Connect one USB Coordinator & Router to a USB Type A port on
the host appliance, or turn on the appliance.
4. Apply power to the routers: Power each router using an AC-USB adapter. Do not connect them
directly to the appliance.
5. Power the end devices: To preserve battery life, do not power the end devices until after the
coordinator and the routers are powered.
up to 30.5 m (100 ft),
line of sight
coordinator or router
end device
end device
Complete the configuration of the wireless network on the Web UI of your appliance (see “Add sensors
to the Wireless Sensor Network” on page 76).
75 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 84

Add sensors to the Wireless Sensor Network
1. Position and turn on your wireless sensor(s).
2. Enable Auto Join until all the wireless sensors in the network have been discovered, or click
Add New Sensor to add sensors manually. Modify the sensor settings (see “Modify wireless
sensor settings” on this page), then click Apply.
NOTE: You must enter the extended address (MAC) for each sensor you manually add to the
network.
Modify wireless sensor settings
Select a sensor to modify its settings:
Setting Description
Name Enter a name (up to 20 characters).
Extended Address The extended address (MAC) of the wireless sensor.
Location Enter the location of the sensor (up to 20 characters).
Alarm Generation Enable or disable. When Alarm Generation is disabled, the system
continues to monitor the state of the sensor, but does not generate an
alarm. Alarms are not recorded in the event log when Alarm Generation is
disabled.
Temperature/
Humidity
Thresholds
Battery/Signal
Thresholds
• Maximum: The maximum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
rises above this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• High: If the temperature or humidity rises above this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Low: If the temperature or humidity falls below this value, a warning
alarm is generated.
• Minimum: The minimum allowable value. If the temperature or humidity
falls below this value, a critical alarm is generated.
• Low: If the battery voltage or signal strength drops below its low
threshold for the sensor, an alarm occurs.
• Minimum: If the battery voltage or signal strength drops below its
minimum threshold for the sensor, an alarm occurs.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide76
Page 85

Configure Output Settings
Path: Configuration > Device > Outputs
Select an output (Beacon, Output Relay, and Switched Outlet). Devices connected to these outputs are
controlled by the output settings.
The following information is shown for all outputs:
Setting Description
Module Name Name of Module to which the output is connected.
Module Location Location of Module to which the output is connected, the Rack Monitor
250 or the Sensor Pod 150. ‘Unknown’ if no location is configured.
Alarm Status Critical (device requires immediate attention), Warning (attention
required), and Normal.
You can configure the following settings for each output:
Setting Description
Name Enter a name for the output (up to 20 characters).
Location Enter the location of the sensor (up to 20 characters).
Normal State Set the normal state of the output (excluding the beacon): On/Off or
Open/Closed
Control Change the state of the output to On/Off or Open/Closed.
Alarm Mapping The beacon, output relay and switched outlet can be activated by alarm
states of sensors on the NetBotz module only.
1. Select one or more alarm states that will change the state of the
output.
2. By default, each sensor connected to the NetBotz module is mapped
to activate the output when the sensor is in an abnormal state. Click
the name of the alarm state to view the sensors connected to the
module.
3. Select sensors to include in the alarm. Any selected sensor, in its
abnormal state, activates the output.
NOTE: The Output pages under the Status, Control, and Configuration menus are the same, and
contain all the tasks for each menu option.
77 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 86

Configure Rack Access
Register a new proximity card
1. Navigate to Configuration > Device > Rack Access > Lock Properties.
2. Select Enable to enable the card reader. Specify the card type for the installed handle(s), the
auto-relock time (10 - 60 seconds), and the time to wait before the door open alarm is activated
for Door 1, Door 2, or both (1 - 120 minutes). Click Apply.
3. Hold the card in front of the proximity reader on the handle until you hear a beep.
4. Go to Configuration > Device > User Access > Unregistered Users.
5. Click the card ID number to specify the user name, door access (Door 1, Door 2, or both), the
access schedule (24 x 7 by default), and enable account access. Click Apply.
To view, modify, or delete registered users, go to Configuration > Device > User Access > Registered
Users.
Registered users
Path: Configuration > Device > Rack Access > Registered Users
Select a registered user's name to view the card ID number and to edit name, contact information, and
access permissions.
Setting Description
Name The name of the user (up to 20 characters)
Contact The contact information for the user (up to 20 characters).
Door Access The doors the access card is configured to unlock: Door 1 only, Door 2
only, or both doors.
Time Scheduled Either Granted (the user's access schedule is configured) or Not
Configured (the user's access schedule is not configured). Until the
schedule is configured, this card cannot unlock enclosure doors.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide78
Page 87

Unregistered users
Path: Configuration > Device > Rack Access > Unregistered Users
View the ID number of any unconfigured access card that has been held in front of the lock, and the date
and time it was held in front of the lock.
To register a user, select the number of the card that will be assigned to the user, and specify the
following:
Setting Description
Name Enter a name for the user (up to 20 characters).
Contact Enter the contact information for the user (up to 20 characters).
Card ID The identification number of the card assigned to the user. This option is
not configurable.
Account Access Check the box to activate the card. To temporarily disable the access
permission for the card without deleting the user, uncheck the box.
Door Access Configure the card to open Door 1 only, the Door 2 only, or both doors.
Granted Access
Schedule
Apply Click to save your changes.
Cancel Click to discard your changes.
Delete User Click to erase the configured information and remove the card from the
Check the box for each day the card is permitted to unlock the doors, and
configure the hours during each enabled day the user can access the
rack. Valid values are 00:00 to 23:59.
list of registered users. If the deleted card is held in front of the lock, the
card number appears in the list of unregistered users.
User Authentication Methods
Path: Configuration > Device > Rack Access > RADIUS
Specify how users will be authenticated when they access the rack:
Setting Description
Lock user
authentication
RADIUS server
settings
• Local NetBotz appliance only: RADIUS is disabled. Rack access is
controlled by the local authentication configured in the Registered Users
option.
• RADIUS, then Local NetBotz appliance: RADIUS is enabled, and local
rack access authentication is enabled. Authentication is requested from
the RADIUS server first; local rack access authentication is used only if
the RADIUS server fails to respond.
• RADIUS only: RADIUS is enabled. Local rack access authentication is
disabled. If the RADIUS server fails to authenticate the user, access is
denied.
NOTE: The message “No RADIUS servers have been configured”
indicates you must add a properly configured RADIUS server so that
RADIUS authentication can operate.
RADIUS New password/Confirm password: The complex password for
RADIUS (1 - 64 characters) is enabled by default. The default RADIUS
password is the serial number of the NetBotz appliance, displayed in the
About > Network option.
79 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 88

Rack access handles
Path: Configuration > Device > Rack Access > Lock Properties
Both rack access handles must be the same model, either two 125 kHZ handles or two 13.56 MHz
handles. Use Door 1 and Door 2 ports for door switches used with handles; otherwise, use the universal
sensor ports for door switches used without handles.
The proximity card type must be the same for both handles.
Setting Description
Card Reader Enable or disable the card reader on the door lock. When disabled, you must
use a key to access the enclosure.
Card Format The rack access feature supports multiple access card formats. Choose the
format of the card you are configuring.
Cards compatible with the 125 kHz Handle Kit (NBHN125 or NBACS1356):
• H10301 - Standard 26 bit: An access card with a 26-bit card ID number and
a facility code.
• H10302 - 37 bit w/o facility code: An access card with a 37-bit card ID
number and no facility code.
• H10304 - 37 bit w/ facility code: An access card with a 37-bit card ID
number and a facility code.
• CORP1000 - Corporate 1000: An access card with a 35-bit card ID number
and a unique company ID code.
Cards compatible with the 13.56 MHz Handle Kit (NBHN1356 or
NBACS1356):
• MIFAREC4 - Mifare Classic 4 byte card.
• MIFAREC7 - Mifare Classic 7 byte.
• MIFAREDF - Mifare DESfire.
• MIFAREPL - Mifare Plus.
• iCLASS - iCLASS 8byte
Auto-Relock Enter the number of seconds that elapse before the door re-locks, if the door
is not opened within this period of time.
Door Open Alarm Check the box to enable the alarm for Door 1, Door 2, or both, and enter the
number of minutes the door can remain open before an alarm occurs.
Schedule automatic unlocking events
Path: Configuration > Device > Rack Access > Schedule
Schedule a date and time to automatically unlock the doors.
Setting Description
One-time Schedule Enable or disable the scheduled unlock.
Date Specify the date the doors will unlock.
Time Specify the time the doors will unlock, in hours and minutes. Valid values are
00:00 to 23:59.
Unlock Doors Unlock Door 1, Door 2, or both doors.
Remain Unlocked Choose the units (minutes or hours) and enter the number of minutes or
hours the doors will remain unlocked before causing an alarm.
Disable relock for
the duration
Check the box to prevent the door from locking if it is closed during the
scheduled unlock.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide80
Page 89

Configure Security
Session management settings
Path: Configuration > Security > Session Management
Allow concurrent logins: Check to allow multiple simultaneous logged in users. Otherwise, only one
user can be logged into the system at a time.
NOTE: Each interface (FTP, HTTP, Console Telnet, Console USB Serial, etc...) counts as a logged in
user.
NOTE: Precedence functionality of pre 6.x systems no longer applies. An attempted USB serial console
login does NOT supersede an http login.
Remote Authentication Override: Check to allow user authentication by remote servers (RADIUS, for
example) to supersede local user authentication.
See “Manage User Sessions” on page 69 for more information.
Ping response
Configuration > Security > Ping Response
Control whether or not the Rack Monitor 250 responds to a network ping. If enabled, and the Rack
Monitor 250 does not respond to an IPv4 ping, see “Rack Monitor 250 Access Problems” on page 128.
81 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 90

Local users
Path: Configuration > Security > Local Users > Management
Create and manage user profiles on the Rack Monitor 250. The initial view is a list of the current user
profiles, separated by type. Click any user name to edit that user account, or click Add User to create a
new user account.
Setting Description
Access Check the box to enable access to log into the Rack Monitor 250. Clear
the box to disable access.
User Name The name of the selected user. Set the case-sensitive user name (the 64
byte maximum supports up to 64 ASCII characters, less for multi-byte
languages).
You cannot modify a user name after you create the user account. To
change the user name after the account has been created, you must
delete the user and recreate it with the proper value.
NOTE: The user name for the Super User cannot be changed.
Current Password To make changes to the Super User account, enter the existing
password.
New Password and
Confirm Password
User Type (General User only): User account type used to determine various access
User Description Field used for additional notes to describe this particular user.
Session Timeout Amount of time (in minutes) the user has before they are logged out due
Serial Remote
Authentication
Override
Set the case-sensitive password (64 byte maximum supports up to 64
ASCII characters; Less for multi-byte languages). Passwords with no
characters (blank passwords) are not allowed.
permissions to the system:
• Administrator: The Administrator user has full access just as the Super
User does, but this user type can be deleted.
• Device: The Device user has read-write access to the device-related
menus only. The Administrator can enable or disable the Device user
account.
• Read-Only: The Read-Only User account has read-only access through
the web interface to view status, but not to control a device or change
any configured value. The Administrator can enable or disable the
Read-Only user account.
• Network-Only: The Network-Only user has read-write access to the
network-related menus only. The Administrator can enable or disable
the Network-Only user account.
to inactivity (3 minutes by default).
Determines whether or not this account can login serially even when the
NMC authentication is set to RADIUS.
Your changes will take effect after you log off. For more information about User Account types, see
“Types of User Accounts” on page 2“.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide82
Page 91

Default settings
Path: Configuration > Security > Local Users > Default Settings
There are two main features for the default user settings:
1. Determine the default values when the Super User or Administrator account creates a new user.
These values can be changed before the settings are applied to the system.
2. For remote users (user accounts not stored in the system that are remotely authenticated, such
as RADIUS), these are the values not provided by the authenticating server. For example, if a
RADIUS server does not provide the user with a temperature preference, the value defined in
this section will be used.
Setting Description
Access Select Enable to allow access to the appliance.
User Type Select the user type from the drop-down list. See “Types of User
Accounts” on page 2 for detailed information.
User Description Type the user description in the box.
Session Timeout The number of minutes a user can be inactive before he or she is
automatically logged out.
Bad Login
Attempts
Event Log Color
Coding
Export Log Format Configure the event log format when exported (downloaded). Tab
Temperature Scale Specify the temperature scale preference. The default temperature scale
Date Format Select the user interface date format from the drop-down box.
Strong Passwords Select Enable to require new passwords to have these features:
Password Policy Enter the duration (in days) after which the user will be required to change
The number of incorrect login attempts before the system disables the
account. When users reach this limit, a message is displayed informing
them that the account has been locked. The Super User or an
Administrator can re-enable the account to allow the user to log back in.
NOTE: A Super User account cannot be automatically disabled, but it can
be manually disabled.
Configure whether text in the event log is color-coded based on event
severity.
(default) allows fields to be tab-delimited; CSV is comma-separated.
is Metric, Celsius (°C); the US Customary scale, Fahrenheit (°F), is also
available. This value can be changed at a later time.
• at least one lowercase character
• at least one uppercase character
• at least one number
• at least and one symbol
their password. A value of 0 days disables this feature.
83 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 92

Remote users
Authentication.
Path: Configuration > Security > Remote Users > Authentication
Select how to administer remote access to the Rack Monitor 250. For information about local
authentication (not using the centralized authentication of a RADIUS server), see the Security
Handbook, available at www.apc.com.
APC by Schneider Electric supports the authentication and authorization functions of RADIUS (Remote
Access Dial-In User Service).
• When a user accesses a Rack Monitor 250 that has RADIUS enabled, an authentication request
is sent to the RADIUS server to determine the user’s permission level.
• RADIUS user names used with the Rack Monitor 250 are case-sensitive, and have a 64 byte
maximum that supports up to 64 ASCII characters, less for multi-byte languages. Passwords with
no characters (blank passwords) are not allowed.
Select one of the following:
Setting Description
Local Authentication
Only
RADIUS, then Local
Authentication
RADIUS Only RADIUS is enabled. Only the RADIUS server will be contacted. Local
NOTE: The message "No RADIUS servers have been configured" indicates that you must add a properly
configured RADIUS server so that RADIUS authentication can operate.
If RADIUS Only is selected, and the RADIUS server is unavailable, improperly identified, or improperly
configured, the only way to recover is through a serial USB connection to the CLI, and change the
Access setting to Local Authentication Only or RADIUS, then Local Authentication to regain
access.
NOTE: The Serial Remote Authentication Override option must be enabled for any local user
attempting to log in using the CLI when RADIUS only is selected.
RADIUS is disabled. Local authentication is enabled.
RADIUS and local authentication are enabled. Authentication is
requested from the RADIUS server first. If the RADIUS server fails to
respond, local authentication is used.
authentication is disabled. If the RADIUS server fails to authenticate the
user, access is denied.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide84
Page 93
RADIUS.
Configuration > Security > Remote Users > RADIUS
You can set up the device to use a RADIUS server to authenticate remote users. Specify up to two
properly configured RADIUS servers. To add a server, click Add Server. To modify an existing server,
click the server's name.
Setting Description
RADIUS Server The name or IP address of the RADIUS server.
Port The port the RADIUS server listens on, 1812 by default.
NOTE: You can change the port setting to any unused port 5000-32768.
Secret The secret shared by the RADIUS server and the device.
Reply Timeout The time the device waits for a response from the RADIUS server (1-30
seconds).
Tes t Setting s Enter the user name and password of any account on the device to test your
settings before you apply them.
Skip Test and
Apply
Applies the settings without verifying they are configured correctly.
Configure the RADIUS server
You must configure your RADIUS server to work with the Rack Monitor 250. For examples of the
RADIUS users file with Vendor Specific Attributes (VSAs), and an example of an entry in the dictionary
file on the RADIUS server, see the Security Handbook.
1. Add the IP address of the Rack Monitor 250 to the RADIUS server client list (file).
2. Users must be configured with Service-Type attributes unless Vendor Specific Attributes (VSAs)
are defined. If no Service-Type attributes are configured, users will have read-only access. See
your RADIUS server documentation for information about the RADIUS users file.
3. VSAs can be used instead of Service-Type attributes provided by the RADIUS server. Using
VSAs needs a dictionary entry and RADIUS users file. In the dictionary file, define the names for
ATTRIBUTE and VALUE, but not the numeric values. If numeric values are changed, RADIUS
authentication and authorization fails. VSAs take precedence over standard RADIUS attributes.
Configure a RADIUS server on UNIX® with shadow passwords
If UNIX shadow password files are used (/etc/passwd) with the RADIUS dictionary files, the following two
methods can be used to authenticate users:
• If all UNIX users have administrative privileges, add the following to the RADIUS “user” file. To
allow only Device Users, change the Service-Type to Device.
DEFAULTAuth-Type = System
APC-Service-Type = Admin
• Add user names and attributes to the RADIUS “user” file, and verify password against /etc/
passwd. The following example is for users bconners and thawk:
bconnersAuth-Type = System
APC-Service-Type = Admin
thawkAuth-Type = System
APC-Service-Type = Device
85 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 94

Supported RADIUS servers
FreeRADIUS v1.x and v2.x, and Microsoft Server 2008 and 2012 Network Policy Server (NPS) are
supported. Other commonly available RADIUS applications may work, but may not have been fully
tested.
Firewall
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall
The Rack Monitor 250 provides a configurable network firewall. The firewall can allow or deny network
traffic to and from the appliance based on user-configured rules, which are ordered by priority. In the
web interface, you can use the firewall policy editor to create or edit a custom firewall policy.
Though the Rack Monitor 250 can store multiple firewall policies, only one policy can be active at once.
When a firewall is enabled and a custom policy file is applied, the policy is checked for syntax errors. If
an error is found, the policy will not be loaded.
A sample firewall policy (.fwl) is provided in the file system for reference. It is available for download via
FTP or SCP, from the /firewall directory of the file system.
Use the Test Policy option to test and verify a custom firewall policy. It is recommended that a firewall
policy be tested before it is applied to a production environment.
Enable/disable the firewall
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall > Configuration
Enable or disable the overall firewall functionality.
Set the active policy
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall > Active Policy
Select an active policy from the available firewall policies.
View active rules
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall > Active Rules
View the individual rules that are currently enforced based on the active policy.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide86
Page 95

Create/edit a policy
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall > Create/Edit Policy
Create a new policy, edit an existing policy, or delete an existing policy.
To create a new policy, click Add Policy, and type in the file name for the new firewall file. The filename
should have a .fwl file extension. If the filename does not have this file extension, .fwl will be appended to
the name automatically.
It is recommended that you add one of the following as the lowest priority rule in your firewall policy:
• To use the firewall as a white list, add
250 Dest any / Source any / protocol any / discard
• To use the firewall as a black list, add
250 Dest any / Source any / protocol any / allow
It is recommended that you do not edit active policies. Instead, disable the firewall, edit the policy, test it,
and then re-enable the policy.
To edit a policy,
1. Select the policy you want to edit from the Policy Name drop-down list, and click Edit Policy.
2. Click Add Rule or select the Priority of an existing rule to go to the Edit Rule page. From this
page, you can change the rule settings or delete the selected rule.
Setting Description
Priority If 2 rules conflict, the rule with the higher priority will determine what
happens. The highest priority is 1; the lowest is 250.
Type host: In the IP/any field, you will enter a single IP address.
subnet: In the IP/any field, you will enter a subnet address.
range: In the IP/any field, you will enter a range of IP addresses.
IP/any Specify the IP address or range of addresses this rule applies to, or
select one of the following:
• any: The rule applies regardless of the IP address.
• anyipv4:The rule applies for any IPv4 address.
• anyipv6:The rule applies for any IPv6 address.
Port Specify a port the rule will apply to.
• None: The rule will apply to any port.
• Common Configured ports: Select a standard port.
• Other: Specify a non-standard port number.
Protocol Specify which protocol the rule applies to.
• any: any protocol
• tcp: used for reliable information transfer between applications
• udp: alternative to TCP used for faster, lower bandwidth information
transfer. Though it has fewer delays, UDP is less reliable than TCP.
• icmp: used to report errors for troubleshooting
• icmpv6: used to report errors for troubleshooting on applications
using IPv6
Action allow: Allow the packet that matches this rule.
discard: Discard the packet that matches this rule.
Log If this rule applied to a packet, regardless of whether the pac
blocked or allowed, this will add an entry to the Firewall Log (see
“Firewall Log” on page 115).
ket is
87 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 96

Import a firewall policy
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall > Load Policy
Load a policy file (.fwl suffix) from a source external to this device.
Test a firewall policy
Path: Configuration > Security > Firewall > Test Policy
Temporarily enforce the rules of a chosen policy.
NOTE: The firewall is disabled by default..
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide88
Page 97

Configure Network Settings
TCP/IP Settings
IPv4 settings.
Path: Configuration > Network > TCP/IP > IPv4 Settings
The default TCP/IP configuration setting, DHCP, assumes a properly configured DHCP server is
available to provide TCP/IP settings to the Rack Monitor 250.
Otherwise, you can configure the default setting for BOOTP. A user configuration (.ini) file can function
as a BOOTP or DHCP boot file. For more information, see the TCP/IP configuration section of the
Network Management Card User’s Guide, available from www.apc.com.
View and configure current IPv4 settings, and enable or disable IPv4. You can also opt to manually
override the automatic settings for System IP, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway.
Setting Description
Manual Configure the IPv4 settings (IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway) manually.
Click Apply.
BOOTP A BOOTP server provides the TCP/IP settings. At 32-second intervals, the Rack Monitor
250 requests a network assignment from any BOOTP server:
• If it receives a valid response, the network services start.
• If it finds a BOOTP server, and receives a valid response, the device requests network
assignment from any BOOTP server, and network services are initiated.
• If a request to that server fails or times out, the Rack Monitor 250 stops requesting
network settings until it is restarted.
• By default, if no valid response is received with the new settings, and previously
configured network settings exist, five attempts to connect will be made (the original
and four retries), then the prior settings will be used.
DHCP At 32-second intervals, the device requests network assignment from any DHCP server:
• Optionally, the device requires the vendor specific cookie from the DHCP server in
order to accept the lease and start the network services.
• If it finds a DHCP server, but the request to that server fails or times out, it stops
requesting network settings until it is restarted.
Vendor Cookie: Check to require vendor specific cookie to accept DHCP address
(disabled by default).
NOTE: The default values for these three settings generally do not need to be changed:
• Vendor Class: APC
• Client ID: The MAC address of the device. If you change this value, the new value
must be unique on the LAN.
• User Class: The name of the application firmware module, NB250.
89 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 98

Advanced DHCP Configuration. You can use a RFC2131/RFC2132-compliant DHCP server to
configure the TCP/IP settings for the Rack Monitor 250.
1. The Rack Monitor 250 sends out a DHCP request that uses the following to identify itself:
– A Vendor Class Identifier, APC by default.
– A Client Identifier, the MAC address of the Rack Monitor 250 by default.
– A User Class Identifier, NB250 by default, the identification of the application firmware installed
on the Rack Monitor 250.
2. A properly configured DHCP server responds with a DHCP offer that includes all the settings the
Rack Monitor 250 needs for network communication. The DHCP offer also includes the Vendor
Specific Information option (DHCP option 43). The Rack Monitor 250 can be configured to ignore
DHCP offers that do not encapsulate the APC cookie in DHCP option 43 using the following
hexadecimal format. This cookie is not required by default.
Option 43 = 01 04 31 41 50 43
where:
– the first byte (01) is the code
– the second byte (04) is the length
– the remaining bytes (31 41 50 43) are the APC cookie.
For additional information on supported DHCP (DHCPv4) options sent and received by the Rack Monitor
250, see the FAQ article FA156110 on www.apc.com.
For more detail about how a DHCP server can configure the network settings for a Rack Monitor 250,
see “DHCP Configuration” in the Network Management Card 2 User’s Guide, available from
www.apc.com.
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide90
Page 99

IPv6 Settings.
Path: Configuration > Network > TCP/IP > IPv6 Settings
Current IPv6 Settings
Setting Description
Typ e Indicates the IP address is assigned Manually or Automatically.
IP Address The IPv6 address of the device.
Prefix Length Indicates the number of bits used to identify the network.
IPv6 Configuration
Setting Description
Enable Check to enable or disable IPv6 communications.
Manual Configuration Check the box to enable manual configuration, and then enter the
system IPv6 address and default gateway if you are not using
automated addressing.
Auto Configuration Check the box to enable obtaining addressing prefixes from the router, if
available, to automatically configure IPv6 addresses.
DHCPv6 Mode
Router Controlled Select to control DHCPv6 by the M (Managed Address Configuration)
and O (Other Stateful Configuration) flags received in IPv6 Router
Advertisements.
When a router advertisement is received, the Rack Monitor 250 checks
whether the M and O flags are set. The Rack Monitor 250 interprets the
state of the M and O ‘bits’ for the following cases:
• Neither is set: Indicates the local network has no DHCPv6
infrastructure. The Rack Monitor 250 uses Router Advertisements
and/or manual configuration to get non-link-local addresses and other
settings.
• M, or M and O are set: Full DHCPv6 address configuration occurs.
DHCPv6 is used to obtain addresses AND other configuration
settings. This is known as DHCPv6 stateful. Once the M flag is
received, the DHCPv6 address configuration stays in effect until the
interface has been closed, even if subsequent Router Advertisement
packets are received where the M flag is not set. If an O flag is
received first, and an M flag is received subsequently, the Rack
Monitor 250 performs full address configuration when it receives the M
flag.
• Only O is set: The Rack Monitor 250 sends a DHCPv6 Info-Request
packet. DHCPv6 is used to configure ‘other’ settings, such as location
of DNS servers, but NOT to provide addresses. This is known as
DHCPv6 stateless.
Address and Other
Information
Non-Address
Information Only
With this radio box selected, DHCPv6 is used to obtain addresses AND
other configuration settings. This is known as DHCPv6 stateful.
With this radio box selected, DHCPv6 is used to configure "othe
r"
settings (such as location of DNS servers), but NOT to provide
addresses. This is known as DHCPv6 stateless.
Never With this radio box selected, DHCPv6 is NOT used for any configuration
settings.
91 NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide
Page 100

Port speed
Path: Configuration > Network > Port Speed
The Port Speed setting defines the communication speed of the TCP/IP port.
Setting Description
Auto-Negotiation Ethernet devices negotiate to transmit at the highest possible speed. If
the supported speeds of two devices do not match, the slower speed is
used.
10 Half-Duplex 10 Mbps communication in one direction at a time.
10 Full-Duplex 10 Mbps communication in both directions on the same channel
simultaneously.
100 Half-Duplex 100 Mbps communication in both directions on the same channel
simultaneously.
100 Full-Duplex 100 Mbps communication in one direction at a time.
DNS server settings
Configuration.
Path: Configuration > Network > DNS > Configuration
The Rack Monitor 250 supports the use of Domain Name System (DNS) servers. If a DNS name is
configured, you can access the Rack Monitor 250 by its assigned DNS name instead of IP address. For
the Rack Monitor 250 to send email, the primary DNS server must be defined.
Setting Description
Override Manual DNS
Settings
System Name
Synchronization
Host Name Configure a host name.
Domain Name (IPv4/
IPv6)
Domain Name (IPv6)
When selected, configuration data from other sources, typically DHCP,
take precedence over the manual configurations.
Check the box to override manual DNS settings, and specify the IP
address of the Primary DNS Server and, optionally, the Secondary
DNS Server. The primary server is always tried first.
Select Enable to synchronize the system name with the host name so
both fields automatically contain the same value. Click the System
Name link to view the system name on the Configuration > General >
Identification page.
Configure the domain name, added automatically whenever you enter
only a host name in a field that accepts domain names (except e-mail
addresses).
NetBotz Rack Monitor 250 User Guide92
 Loading...
Loading...