
Programming Manual
Logix 5000 Controllers ASCII Strings
1756 ControlLogix, 1756 GuardLogix, 1769 CompactLogix,
1769 Compact GuardLogix, 1789 SoftLogix, 5069
CompactLogix, 5069 Compact GuardLogix, Studio 5000
Logix Emulate
Original Instructions
Logix 5000 Controllers ASCII Strings
personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
Attentions help you identify a hazard, avoid a hazard, and recognize the consequence.
IMPORTANT
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that dangerous voltage may be present.
temperatures.
for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Important User Information
Read this document and the documents listed in the additional resources section about installation, configuration, and
operation of this equipment before you install, configure, operate, or maintain this product. Users are required to familiarize
themselves with installation and wiring instructions in addition to requirements of all applicable codes, laws, and standards.
Activities including installation, adjustments, putting into service, use, assembly, disassembly, and maintenance are required to
be carried out by suitably trained personnel in accordance with applicable code of practice.
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may be
impaired.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use
or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or liability for
actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or software
described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc., is
prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment, which may lead to
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
Labels may also be on or inside the equipment to provide specific precautions.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that surfaces may reach dangerous
ARC FLASH HAZARD:
will cause severe injury or death. Wear proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Follow ALL Regulatory requirements for safe work practices and
Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a motor control center, to alert people to potential Arc Flash. Arc Flash
2 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020
Summary of Changes
Change
Topic
Updated branding.
Throughout
This manual includes new and updated information. Use these reference
tables to locate changed information.
Grammatical and editorial style changes are not included in this summary.
Global changes
This table identifies changes that apply to all information about a subject in
the manual and the reason for the change. For example, the addition of new
supported hardware, a software design change, or additional reference
material would result in changes to all of the topics that deal with that subject.
This table identifies changes that apply to all information about a subject in
the manual and the reason for the change. For example, the addition of new
supported hardware, a software design change, or additional reference
material would result in changes to all of the topics that deal with that subject.
Updated Legal notices.
New or enhanced features
None in this release.
Legal Notices on page 8
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 3


Summary of Changes
Communicating with an
ASCII device
Processing ASCII characters
ASCII character codes
Index
Table of Contents
Preface
Studio 5000 environment .......................................................................... 7
Additional resources ................................................................................... 7
Legal Notices ............................................................................................... 8
Chapter 1
Introduction ................................................................................................ 9
Connect the ASCII device ........................................................................... 9
Configure the Serial Port ..........................................................................10
Configure the User Protocol ...................................................................... 12
Create string data types ............................................................................. 13
Read characters from the device ............................................................... 14
Send characters to the device .................................................................... 15
Enter ASCII characters .............................................................................. 16
Chapter 2
Introduction ............................................................................................... 19
Extract a part of a Bar Code ...................................................................... 19
Look up a Bar Code ..................................................................................... 19
Create the PRODUCT_INFO Data Type ............................................ 20
Search for the characters ..................................................................... 21
Identify the Lane Number ................................................................... 21
Reject bad characters .......................................................................... 22
Enter the Product IDs and Lane Numbers ........................................ 22
Check the Bar Code characters ................................................................. 22
Convert a value ...........................................................................................23
Decode an ASCII message ........................................................................ 24
Build a string ............................................................................................. 25
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 5
Appendix A
ASCII character codes .............................................................................. 27


Resource
Description
at http://ab.rockwellautomation.com
and other certification details.
Studio 5000 environment
Additional resources
Preface
This manual shows how to manipulate ASCII strings in Logix 5000
controllers. This manual is one of a set of related manuals that show common
procedures for programming and operating Logix 5000 controllers.
For a complete list of common procedures manuals, refer to the
Logix 5000
Controllers Common Procedures Programming Manual, publication 1756-
PM001.
The term Logix 5000 controller refers to any controller based on the Logix
5000 operating system.
The Studio 5000 Automation Engineering & Design Environment® combines
engineering and design elements into a common environment. The first
element is the Studio 5000 Logix Designer® application. The Logix Designer
application is the rebranding of RSLogix 5000® software and will continue to
be the product to program Logix 5000™ controllers for discrete, process,
batch, motion, safety, and drive-based solutions.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 7
The Studio 5000® environment is the foundation for the future of
Rockwell Automation® engineering design tools and capabilities. The Studio
5000 environment is the one place for design engineers to develop all
elements of their control system.
These documents contain additional information concerning related
Rockwell Automation products.
Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding
Guidelines, publication 1770-4.1
Product Certifications webpage, available
Provides general guidelines for installing a Rockwell
Automation industrial system.
Provides declarations of conformity, certificates,
View or download publications
at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature
. To order paper copies of
technical documentation, contact the local Rockwell Automation distributor
or sales representative.

Preface
Legal Notices
Rockwell Automation publishes legal notices, such as privacy policies, license
agreements, trademark disclosures, and other terms and conditions on
the Legal Notices
page of the Rockwell Automation website.
End User License Agreement (EULA)
You can view the Rockwell Automation End-User License Agreement ("EULA")
by opening the License.rtf file located in your product's install folder on your
hard drive.
Open Source Licenses
The software included in this product contains copyrighted software that is
licensed under one or more open source licenses. Copies of those licenses are
included with the software. Corresponding Source code for open source
packages included in this product are located at their respective web site(s).
Alternately, obtain complete Corresponding Source code by contacting
Rockwell Automation via the Contact form on the Rockwell Automation
website:
us/contact/contact.page
Please include "Open Source" as part of the request text.
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/global/about-
A full list of all open source software used in this product and their
corresponding licenses can be found in the OPENSOURCE folder. The default
installed location of these licenses is
Files\Rockwell\Help\FactoryTalk Services Platform\Release
Notes\OPENSOURCE\index.htm
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common
.
8 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020
Introduction
Connect the ASCII device
Chapter 1
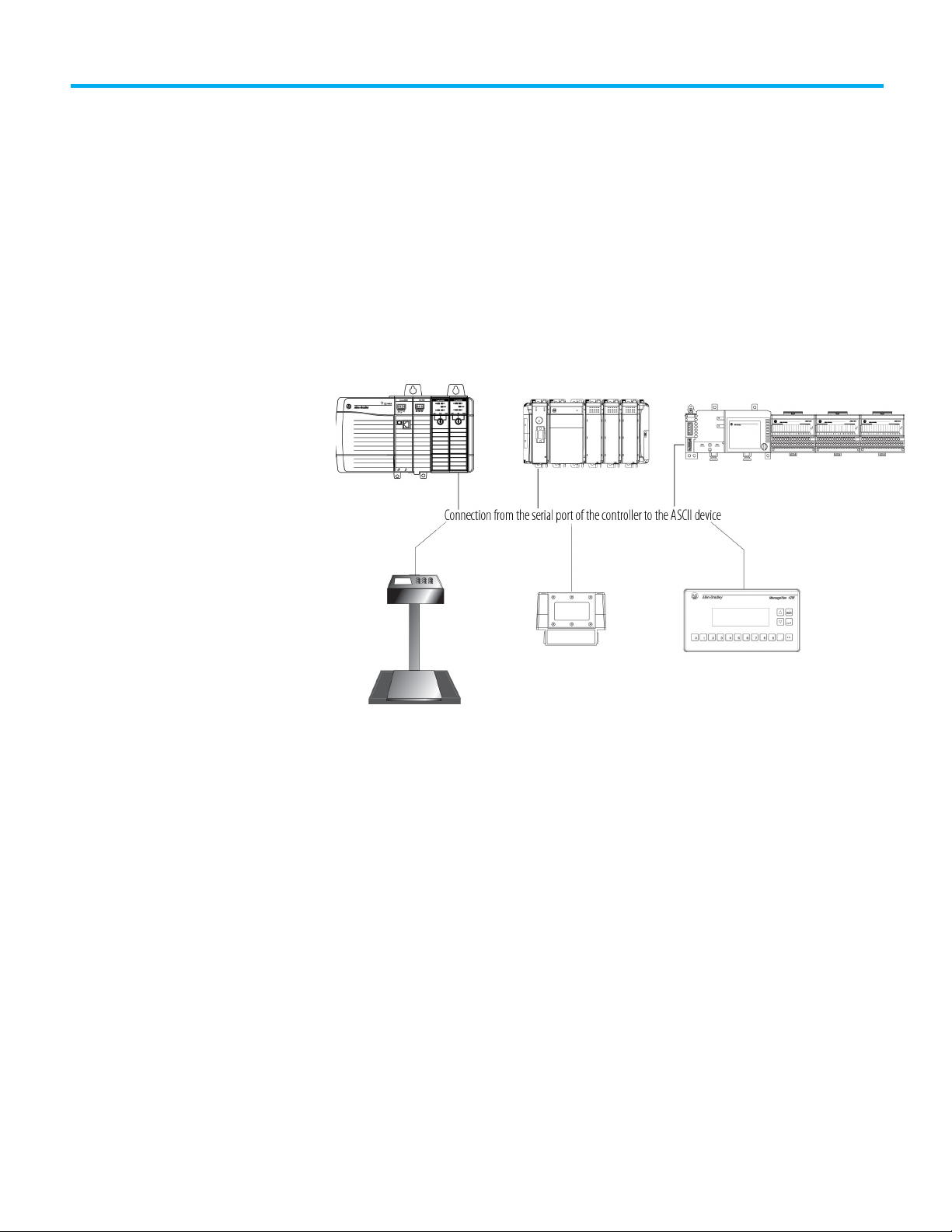
Communicating with an ASCII device
You can exchange ASCII data with a device through the serial port of the
controller. For example, you can use the serial port to:
• Read ASCII characters from a weigh scale module or bar code reader.
• Send and receive messages from an ASCII triggered device, such as a
MessageView terminal.
Firmware revision 3.1 and later of the 1756-EWEB EtherNet/IP Web Server
module supports the controller serial port and a socket interface that lets
Logix 5000 controllers exchange ASCII data using TCP or UDP socket
services.
To connect to the ASCII device, use these steps.
1. On the serial port of the ASCII device, determine which pins send
signals and which pins receive signals.
2. Connect sending pins to corresponding receiving pins and attach
jumpers.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 9

Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
If the communications
Then wire the connectors
Do not handshake
Configure the Serial Port
Handshake
3. Attach the cable shield to the connectors.
4. Connect the cable to the controller and the ASCII device.
To configure the serial port, use these steps.
1. On the Online toolbar, click the Controller Properties button.
2. On the Controller Properties dialog box, click the Serial Port tab.
10 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020

If
And
And this is the
Choose
Then
modem
link are full-duplex
box.
half-duplex
box (default).
Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
3. On the Mode menu, choose User and type the configuration settings
for the serial port.
• choose the baud rate, data bits, parity, and stop bits.
• in the Control Line menu, choose the Control Line option:
You are not using a
You are using a modem Modems in a point-to-point
---------------------------------------------------------------> No Handshaking
Master modem is full-duplex
while slave modem is halfduplex
All modems in the system are
-----------------------------> Full Duplex
master controller. Full Duplex
slave controller Half Duplex Select the Continuous Carrier check
-----------------------------> Half Duplex Clear the Continuous Carrier check
• in the RTS Send Delay box, type the delay (in 20 ms units) between
the time the RTS signal turns on (high) and the time that data is
sent. For example, a value of 4 produces an 80 ms delay.
• in the RTS Off Delay box, type the delay (in 20 ms units) between
the time the last character is sent and the time that the RTS signal
turns off (low).
4. Click Apply.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 11

Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
If the device sends
Then
Tips
each character.
To append
Then
Tips
Two characters
In the
and 2 boxes, type
character.
Configure the User Protocol
To configure the user protocol, use these steps.
1. In the Controller Properties dialog box, click the User Protocol tab.
• Enter a buffer size greater than or equal to the greatest number of
characters in a transmission. Twice the number of characters is a
good guideline.
• For ABL or ARL instructions, enter termination characters to mark
the end of the data. For ASCII codes, see ASCII Character Codes
on page 27.
One termination character • In the Termination Character 1 box, type
the hexadecimal ASCII code for the first
character.
• In the Termination Character 2 box, type
$FF.
Two termination characters In the Termination Character 1 and 2
boxes, type the hexadecimal ASCII code for
• For AWA instruction, enter append characters. For ASCII codes,
see ASCII Character Codes on page 27
One character • In the Append Character 1 box, type the
hexadecimal ASCII code for the first
character.
•
In the Append Character 2 box, type $FF.
Append Character 1
the hexadecimal ASCII code for each
• If the ASCII device is configured for XON/XOFF flow control, select
the XON/XOFF check box.
• If the ASCII device is a CRT or pre-configured for half duplex
transmission, select the Echo Mode check box.
• Choose the Delete Mode using the following considerations:
For printable characters, such as 1 or A, type
the character.
.
For printable characters, such as 1 or A, type
the character.
12 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020

If the ASCII device is
Select
Tips
BACKSPACE ( $08 $20 $08).
You can use the default STRING data type. It
or You can create a string data type to store the number
IMPORTANT
Use caution when you create a string data type. If you decide later to change the size
If you
Then
• The LEN does not change.
Make a string data type larger
The data and LEN resets to zero.
Create string data types
Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
CRT CRT • The DEL character ($7F) and the character that precedes the DEL
character are not sent to the destination.
•
If echo mode is selected and an ASCII instruction reads the DEL
character, the echo returns three characters: BACKSPACE SPACE
Printer Printer • The DEL character ($7F) and the character that precedes the DEL
character are not sent to the destination.
• If echo mode is selected and an ASCII instruction reads the DEL
character, the echo returns two characters: / ($2F) followed by the
character that was deleted.
None of the above Ignore The DEL character ($7F) is treated as any other character.
2. Click OK.
Store ASCII characters in tags that use a string data type.
stores up to 82 characters.
of characters that you define.
of the string data type, you may lose data in any tags that currently use that data
type.
Make a string data type smaller • The data truncates.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 13

Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
EXAMPLE
continuously counts the characters in the buffer.
Read characters
To create string data types
1. In the Controller Organizer, right-click Strings and choose New String
Type.
2. In the Name box, type the name for the data type.
3. In the Maximum Characters box, enter the maximum number of
characters that the string data type stores.
4. Select OK.
from the device
As a general rule, before you read the buffer, use an ACB or ABL instruction to
verify that the buffer contains the required characters.
• An ARD or ARL instruction continues to read the buffer until the
instruction reads the required characters.
• While an ARD or ARL instruction reads the buffer, no other ASCII
Serial Port instructions, except the ACL, can execute.
• Verifying that the buffer contains the required characters prevents the
ARD or ARL from holding up the execution of other ASCII Serial Port
instructions while the input device sends its data.
For additional information on ASCII Serial Port instructions, see Logix 5000
Controllers General Instruction Set Reference
Manual http://literature.rockwellautomation.com/idc/groups/literature/documents/rm
/1756-rm003_-en-p.pdf.
In the following example, the device sends a fixed number of characters, such
as a bar code reader:
A bar code reader sends bar codes to the serial port (channel 0) of the controller. Each bar code
contains 24 characters. To determine when the controller receives a bar code, the ACB instruction
14 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020
When the buffer contains at least 24 characters, the controller received a bar code. The ARD
instruction moves the bar code to the bag_bar_code tag.

EXAMPLE
• When the ABL finds a carriage return, its sets the FD bit.
EXAMPLE
message.
Send characters
Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
In the following example, the device sends a variable number of characters,
such as a message or display terminal.
Continuously test the buffer for a message.
• Because each message ends in a carriage return ($0D), the carriage return is configured as
the termination character in the Controller Properties dialog box, User Protocol tab.
When the ABL instruction finds the carriage return (MV_line.FD is set), the controller removes the
characters from the buffer, up to and including the carriage return, and places them in the
MV_msg tag.
to the device
When you send characters to the device, you must determine either to send
the same number of characters each time or to append terminations
characters to the data.
In the following example, you always send the same number of characters and
want to automatically append one or two characters to the end of the data.
When the temperature exceeds the high limit (temp_high is on), the AWA instruction sends
five characters from the string[1] tag to a MessageView terminal.
• The $14 counts as one character. The hex code for the Ctrl-T character.
• The instruction also sends (appends) the characters defined in the user protocol. In this
example, the AWA instruction sends a carriage return ($0D), which marks the end of the
And then to always send the same number of characters:
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 15

Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
EXAMPLE
character. The hex code for the Ctrl-T character.)
EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE
• In MV_msg, the $16 counts as one character. The hex code for the Ctrl-V character.
IMPORTANT
Enter ASCII characters
In the following example, you send a different number of characters each time
and want to automatically append one or two characters to the end of the
data:
When the temperature reaches the low limit (temp_low is on), the AWT instruction sends
nine characters from the string[2] tag to a MessageView terminal. (The $14 counts as one
When alarm is on, the AWA instruction sends the characters in alarm_msg and appends a
termination character.
• Because the number of characters in alarm_msg varies, the rung first moves the length
of alarm_msg (alarm_msg.LEN) to the length of the AWA instruction (alarm_write.LEN).
•
In alarm_msg, the $14 counts as one character. The hex code for the Ctrl-T character.
Send a different number of characters each time:
When MV_update is on, the AWT instruction sends the characters in MV_msg.
• Because the number of characters in MV_msg varies, the rung first moves the length of
MV_msg (MV_msg.LEN) to the length of the AWT instruction (MV_write.LEN).
To enter the ASCII characters, use these steps.
This String Browser window shows the characters up to the value of the LEN member
of the string tag. The string tag may contain additional data, which the String Browser
window does not show.
16 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020

tag can hold.
Chapter 1 Communicating with an ASCII device
1. In the AWA instruction, double-click the value area of Source.
Dollar sign ($24)
Single quote ($27)
Line feed ($0A)
New line ($0D$0A)
Form feed ($0C)
2. In the text box, type the characters for the string.
3. Click OK.
Carriage return ($0D)
Tab ($09)
The number of characters that you see in
the window. The same as the LEN member
of the string tag.
The maximum number of characters that
the string
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 17


EXAMPLE
In the baggage handling conveyor of an airport, each bag gets a bar code. Characters
destination airport to the bag_flt_and_dest tag.
Introduction
Extract a part of a Bar Code
Look up a Bar Code
Chapter 2
Processing ASCII characters
You can process ASCII characters to do many things, including:
• Interpret a bar code and take action based on the bar code.
• Use a weight from a weigh scale when the weight is sent as ASCII
characters.
• Decode a message from an ASCII triggered device, such as an operator
terminal.
• Build a string for an ASCII triggered device using variables from your
application.
For example, a bar code may contain information about a bag on a conveyor
at an airport. To check the flight number and destination of the bag, you
extract characters 10 - 18.
Airline Origin Flight # Destination Date
Bar code N W A
Character number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
H O P
5 0 5 8
5 0 5 8
9 characters
A M S
A M S
0 2 2 2 0 1
10 - 18 of the bar code are the flight number and destination airport of the bag. After the
bar code is read (bag_read.EM is on) the MID instruction copies the flight number and
For example, in a sorting operation, an array of a user-defined data type
creates a table that shows the lane number for each type of product. To
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 19

Chapter 2 Processing ASCII characters
the Help menu, click Vendor Sample Projects.
Data Type: PRODUCT_INFO
Name
PRODUCT_INFO
Description
identify the item
Members
Name
Data Type
Style
Description
Create the PRODUCT_INFO
determine which lane to route a product, the controller searches the table for
the product ID (characters of the bar code that identify the product).
To look up a bar code, follow these procedures:
Data Type
• Create the PRODUCT_INFO Data Type on page 20
.
• Search for the Characters on page 20.
• Identify the Lane Number on page 21.
• Reject Bad Characters on page 22.
• Enter the Product IDs and Lane Numbers on page 22.
Tip: To copy the above components from a sample project, open the Samples
To create a Product_Info user-defined date type in the Controller Organizer,
right-click User-Defined and click New Data Type. Configure the userdefined data type as follows.
Identifies the destination for an item based on an ASCII string of characters that
Product_ID STRING
Lane DINT Decimal Destination for the item, based on its ID
ASCII characters that identify the item
folder. On
20 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020

Search for the characters
Identify the Lane Number
Chapter 2 Processing ASCII characters
You can search for characters by creating the following ladder logic routine.
The SIZE instruction performs the following:
• Counts the number of elements in the sort_table array (type
PRODUCT_INFO). This array contains the product ID for each item
and the corresponding lane number for the item.
• Counts the number of elements in Dimension 0 of the array. In this
case, the only dimension.
• Sets the Length of the subsequent FSC instruction equal to the size of
the sort_table array.
The FSC instruction searches each Product_ID member in the sort_table array
until the instruction finds a match to the product_id tag.
• The sort_table_search tag controls the FSC instruction.
• Although the previous instruction sets the Length of this instruction,
you enter an initial value to verify the project.
• The product_id tag contains the bar code characters that you want to
find.
Add the following rung to the routine to identify the LANE member.
When the FSC instruction finds the product ID within the sort_table array,
the instruction sets the FD bit. The POS member indicates the element
number within the sort_table array of the match. The corresponding LANE
member indicates the lane number of the match.
Based on the POS value, the MOV instruction moves the corresponding lane
number into the lane tag. The controller uses the value of this tag to route the
item.
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 21

Chapter 2 Processing ASCII characters
To see if the string is:
Enter this instruction:
Not equal to specific characters
NEQ
Reject bad characters
Check the Bar
After the MOV instruction sets the value of the lane tag, the RES instruction
resets the FSC instruction so it can search for the next product ID.
If the FSC instruction does not find the product ID within the sort_table
array, the instruction sets the DN bit. The MOV instruction moves 999 into the
lane tag to notify the controller to reject or reroute the item.
After the MOV instruction sets the value of the lane tag, the RES instruction
resets the FSC instruction so it can search for the next product ID.
Enter the Product IDs and Lane Numbers
Code characters
In the sort_table array, enter the ASCII characters to identify each item and
the corresponding lane number for the item.
Use a compare instruction (EQU, GEQ, GRT, LEQ, LES, NEQ) to check for
characters.
• The hexadecimal values of the characters determine if one string is less
than or greater than another string.
• When the two strings are sorted, as in a telephone directory, the order
of the strings determines which one is greater.
22 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020
Use one of the following compare instruction.
Equal to specific characters EQU

To see if the string is:
Enter this instruction:
Equal to or greater than specific characters
GEQ
Less than specific characters
LES
Equal to or less than specific characters
LEQ
EXAMPL
EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE
When MV_read.EM is on, the STOD instruction converts the first set of numeric characters in
Convert a value
Greater than specific characters GRT
Chapter 2 Processing ASCII characters
When bag_flt_and_dest is equal to gate[1], xfer[1] turns on. This routes the bag to the required gate.
E
You can convert the ASCII representation of a value to an DINT or REAL value
that you can use in your application.
• The STOD and STOR instructions skip any initial control or non-
numeric characters (except the minus sign in front of a number).
• If the string contains multiple groups of numbers that are separated by
delimiters (for example, / ), the STOD and STOR instructions convert
only the first group of numbers.
The following rung converts ASCII characters to a floating-point value:
After reading the weight from the scale (weight_read.EM is on), the STOR instruction converts
the numeric characters in weight_ascii to a REAL value and stores the result in weight.
The following rung converts ASCII characters to an integer value:
MV_msg to an integer value. The instruction skips the initial control character ($06) and stops at
the delimiter ( \ ).
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 23

Chapter 2 Processing ASCII characters
Rung A: Find and Convert a
Decode an ASCII message
Floating-Point Value
You can extract and convert a value from an ASCII message that contains
multiple values. A message may look like the following example:
24 Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020
The FIND instruction locates characters within a string.
• The Source contains the string tag to search.
• The Result contains the location where the FIND instruction locates
the search value you specify.
The MID instruction identifies a group of characters within a string and
places them in their own string tag.
• The source is the same string tag as for the FIND instruction.
• The quantity values tells the MID instruction how many characters to
pull from the source.
• The start value is the same as the Result value from the FIND
instruction. This tells the MID instruction where to start pulling
characters from the Source.
• The Destination contains the characters you located.

EXAMPLE
IMPORTANT
and stores the final string in msg.
IMPORTANT
Build a string
Chapter 2 Processing ASCII characters
The following example builds a string that contains two variables. For
example, an operator terminal may require a string that looks like the
following:
• For more variables, use additional INSERT or CONCAT instructions.
• If you must send a floating-point value, use a RTOS instruction in
place of the DTOS instruction.
• The final string excludes the termination character. When you send
the string, use an AWA instruction to automatically append the
termination character.
To trigger a message in a MessageView terminal, the controller sends the terminal
a message in this format: [Ctrl-T] message # \ address [CR]
When send_msg is on, the rung does the following:
• The first DTOS instruction converts the message number to ASCII characters.
• The INSERT instruction inserts the message number (in ASCII) after the control
character [Ctrl-T]. (The hex code for Ctrl-T is $14.)
• The second DTOS instruction converts the node number of the terminal to ASCII
characters.
• The CONCAT instruction puts the node number (in ASCII) after the backslash [ \ ]
To send the message, an AWA instruction sends the msg tag and appends the
carriage return [CR].
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 25


Character
Dec
Hex Character
Dec
Hex Character
Dec
Hex Character
Dec
Hex
[ctrl-B] STX
2
$2 “
34
$22 B
66
$42 b
98
$62
[ctrl-L] FF
12
$0C ,
44
$2C L
76
$4C l
108
$6C
[ctrl-O] SI
15
$0F /
47
$2F O
79
$4F o
111
$6F
[ctrl-T] DC4
20
$14 4
52
$34 T
84
$54 t
116
$74
[ctrl-Y] EM
25
$19 9
57
$39 Y
89
$59 y
121
$79
ASCII character codes
ASCII character codes
Appendix A
[ctrl-@] NUL 0 $0
[ctrl-A] SOH 1 $1
[ctrl-C] ETX 3 $3
[ctrl-D] EOT 4 $4
[ctrl-E] ENQ 5 $5
[ctrl-F] ACK 6 $6
[ctrl-G] BEL 7 $7
[ctrl-H] BS 8 $8
[ctrl-I] HT 9 $9
[ctrl-J] LF 10 $l ($0A)
[ctrl-K] VT 11 $0B
[ctrl-M] CR 13 $r ($0D)
[ctrl-N] SO 14 $0E
[ctrl-P] DLE 16 $10
[ctrl-Q] DC1 17 $11
[ctrl-R] DC2 18 $12
[ctrl-S] DC3 19 $13
SPACE 32 $20
! 33 $21
# 35 $23
$ 36 $24
% 37 $25
& 38 $26
‘ 39 $27
( 40 $28
) 41 $29
* 42 $2A
+ 43 $2B
- 45 $2D
. 46 $2E
0 48 $30
1 49 $31
2 50 $32
3 51 $33
@ 64 $40
A 65 $41
C 67 $43
D 68 $44
E 69 $45
F 70 $46
G 71 $47
H 72 $48
I 73 $49
J 74 $4A
K 75 $4B
M 77 $4D
N 78 $4E
P 80 $50
Q 81 $51
R 82 $52
S 83 $53
‘ 96 $60
a 97 $61
c 99 $63
d 100 $64
e 101 $65
f 102 $66
g 103 $67
h 104 $68
i 105 $69
j 106 $6A
k 107 $6B
m 109 $6D
n 110 $6E
p 112 $70
q 113 $71
r 114 $72
s 115 $73
[ctrl-U] NAK 21 $15
[ctrl-V] SYN 22 $16
[ctrl-W] ETB 23 $17
[ctrl-X] CAN 24 $18
[ctrl-Z] SUB 26 $1A
ctrl-[ ESC 27 $1B
[ctrl-\] FS 28 $1C
ctrl-] GS 29 $1D
[ctrl-^] RS 30 $1E
[ctrl-_] US 31 $1F
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 27
5 53 $35
6 54 $36
7 55 $37
8 56 $38
: 58 $3A
; 59 $3B
< 60 $3C
= 61 $3D
> 62 $3E
? 63 $3F
U 85 $55
V 86 $56
W 87 $57
X 88 $58
Z 90 $5A
[ 91 $5B
\ 92 $5C
] 93 $5D
^ 94 $5E
_ 95 $5F
u 117 $75
v 118 $76
w 119 $77
x 120 $78
z 122 $7A
{ 123 $7B
| 124 $7C
} 125 $7D
~ 126 $7E
DEL 127 $7F


Index
S
Index
A
ASCII
configure serial port 10
configure user protocol 12
enter characters 16
manipulate characters 19
organize data 13
read characters 14
write characters 15
C
configure
serial port for ASCII 10
user protocol for ASCII 12
create
string data type 13
send
ASCII characters 15
serial
configure port for ASCII 10
string
data type 13
enter characters 16
manipulate 19
organize data 13
read characters 14
write characters 15
string data type
create 13
T
tag
string 13
U
user protocol
configure for ASCII 12
D
data
ASCII 13
enter ASCII characters 16
E
enter
ASCII characters 16
M
manipulate string 19
O
organize
strings 13
R
read
ASCII characters 14
W
write
ASCII characters 15
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020 29

Technical Support Center
Find help with how-to videos, FAQs, chat, user forums, and product notification
rok.auto/support
Knowledgebase
Access Knowledgebase articles.
rok.auto/knowledgebase
Local Technical Support Phone Numbers
Literature Library
Product Compatibility and Download Center
Rockwell Automation support
Use these resources to access support information.
updates.
Locate the telephone number for your country. rok.auto/phonesupport
Find installation instructions, manuals, brochures, and technical data publications. rok.auto/literature
(PCDC)
Get help determining how products interact, check features and capabilities, and
find associated firmware.
rok.auto/pcdc
Documentation feedback
Your comments help us serve your documentation needs better. If you have any suggestions on how to improve our content, complete the form
at rok.auto/docfeedback
.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
At the end of life, this equipment should be collected separately from any unsorted municipal waste.
Rockwell Automation maintains current product environmental information on its website at rok.auto/pec.
Allen-Bradley, expanding human possibility, Logix, Rockwell Automation, and Rockwell Software are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
EtherNet/IP is a trademark of ODVA, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
Rockwell Otomayson Ticaret A.Ş. Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752, İçerenkÖy, İstanbul, Tel: +90 (216) 5698400 EEE YÖnetmeliğine Uygundur
Rockwell Automation Publication 1756-PM013G-EN-P - September 2020
Supersedes Publication 1756-PM013F-EN-P - February 2018 Copyright © 2020 Rockwell A utomation Technologies, Inc. All Rights Rese rved. Printed in the U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...