Philips 74HCT299U, 74HCT299N, 74HCT299DB, 74HCT299D, 74HC299N Datasheet
...
DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
December 1990
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74HC/HCT299
8-bit universal shift register; 3-state
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines

December 1990 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit universal shift register; 3-state 74HC/HCT299
FEATURES
• Multiplexed inputs/outputs provide improved bit density
• Four operating modes:
– shift left
– shift right
– hold (store)
– load data
• Operates with output enable or at high-impedance
OFF-state (Z)
• 3-state outputs drive bus lines directly
• Can be cascaded for n-bits word length
• Output capability: bus driver (parallel I/Os),
standard (serial outputs)
• ICC category: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT299 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices
and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL
(LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC
standard no. 7A.
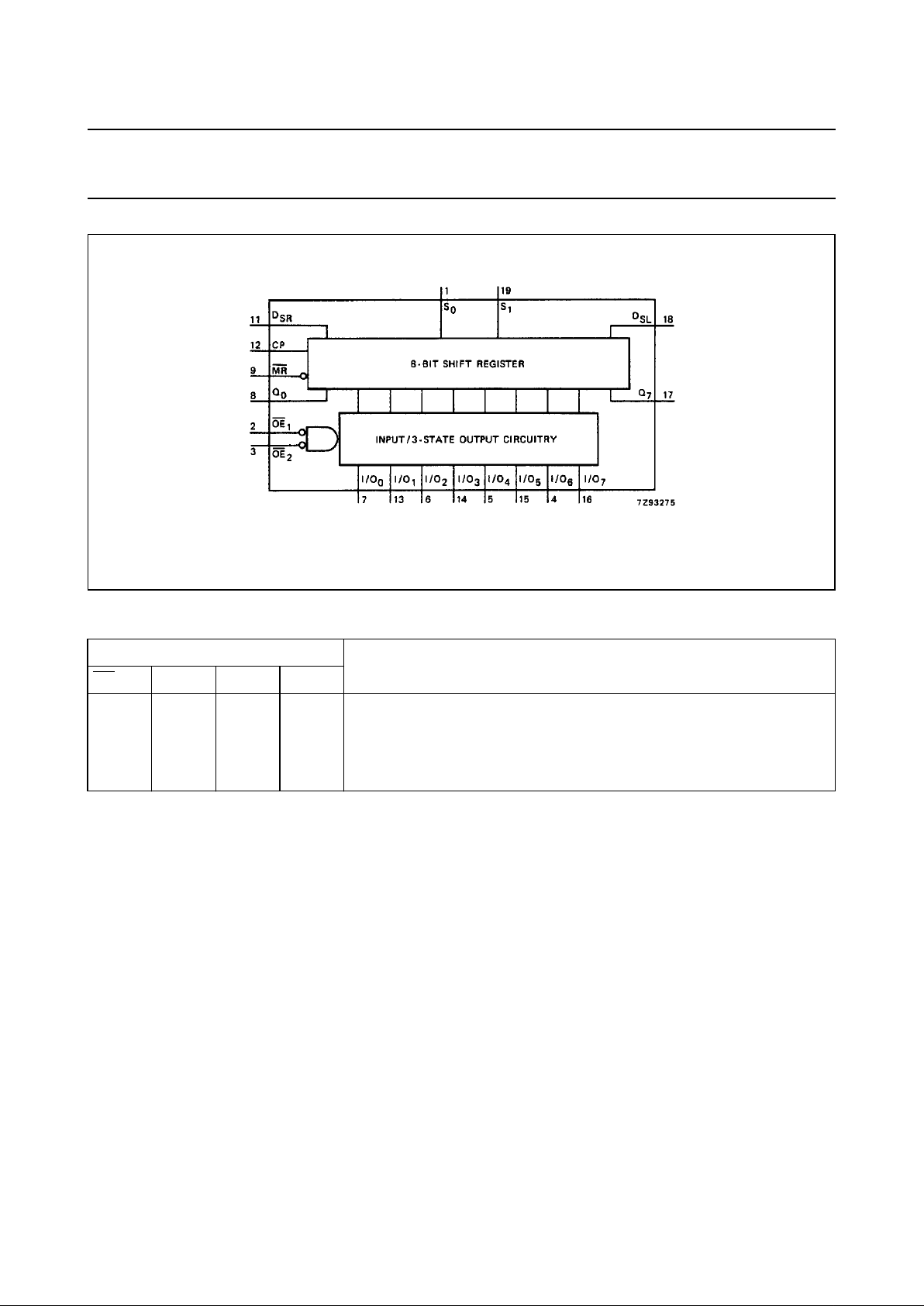
The 74HC/HCT299 contain eight edge-triggered D-type
flip-flops and the interstage logic necessary to perform
synchronous shift-right, shift-left, parallel load and hold
operations. The type of operation is determined by the
mode select inputs (S
0
and S1), as shown in the mode
select table.
All flip-flop outputs have 3-state buffers to separate these
outputs (I/O0 to I/O7) such, that they can serve as data
inputs in the parallel load mode. The serial outputs (Q0 and
Q7) are used for expansion in serial shifting of longer
words.
A LOW signal on the asynchronous master reset input
(MR) overrides the Sn and clock (CP) inputs and resets the
flip-flops. All other state changes are initiated by the rising
edge of the clock pulse. Inputs can change when the clock
is either state, provided that the recommended set-up and
hold times, relative to the rising edge of CP, are observed.
A HIGH signal on the 3-state output enable inputs (OE1 or
OE2) disables the 3-state buffers and the I/On outputs are
set to the high-impedance OFF-state. In this condition, the
shift, hold, load and reset operations can still occur. The
3-state buffers are also disabled by HIGH signals on both
S0 and S1, when in preparation for a parallel load
operation.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
amb
=25°C; tr=tf= 6 ns
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
t
PHL/ tPLH
propagation delay CL= 15 pF; VCC=5 V
CP to Q
0
, Q
7
20 19 ns
CP to I/O
n
20 19 ns
t
PHL
MR to Q0, Q7 or I/O
n
20 23 ns
f
max
maximum clock frequency 50 46 MHz
C
I
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
C
I/O
input/output capacitance 10 10 pF
C
PD
power dissipation capacitance per package notes 1 and 2 120 125 pF
Notes
1. CPD is used to determine the dynamic power
dissipation (PD in µW):
PD=CPD× V
CC
2
× fi+ ∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) where:
fi= input frequency in MHz
fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) = sum of outputs
CL= output load capacitance in pF
VCC= supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is V
I
= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
ORDERING INFORMATION
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package
Information”
.

December 1990 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit universal shift register; 3-state 74HC/HCT299
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1, 19 S
0
, S
1
mode select inputs
2, 3
OE1, OE
2
3-state output enable inputs (active LOW)
7, 13, 6, 14, 5, 15, 4, 16 I/O
0
to I/O
7
parallel data inputs or 3-state parallel outputs (bus driver)
8, 17 Q
0
, Q
7
serial outputs (standard output)
9
MR asynchronous master reset input (active LOW)
10 GND ground (0 V)
11 D
SR
serial data shift-right input
12 CP clock input (LOW-to-HIGH, edge-triggered)
18 D
SL
serial data shift-left input
20 V
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol. Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
December 1990 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit universal shift register; 3-state 74HC/HCT299
MODE SELECT TABLE
Notes
1. H = HIGH voltage level
L = LOW voltage level
X = don’t care
↑ = LOW-to-HIGH CP transition
INPUTS
RESPONSE
MR S
1
S
0
CP
L X X X asynchronous reset; Q
0−Q7
= LOW
H
H
H
H
H
L
H
L
H
H
L
L
↑
↑
↑
X
parallel load; I/O
n
→ Q
n
shift right; DSR→ Q0, Q0 → Q1 etc.
shift left; DSL→ Q7, Q7→ Q6 etc.
hold
Fig.4 Functional diagram.
 Loading...
Loading...