
Hybrid IP-PBX
Feature Guide
KX-TDA15/KX-TDA30
Model KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200
Thank you for purchasing the Panasonic KX-TDA15/KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200, Hybrid IP-PBX.
Please read this manual carefully before using this product and save this manual for future use.
KX-TDA15/KX-TD A30/KX-TDA100/KX-TD A200: V ersion 1.1

Introduction
About this Feature Guide
This Feature Guide is designed to serve as an overall feature reference for the Panasonic
Hybrid IP-PBX.
It explains what this PBX can do, and how to obtain the most out of its many features and
facilities.
This manual contains the following sections:
Section 1, Call Handling Features
Provides details about the call handling features.
Section 2, System Configuration and Administration Features
Provides details about the system configuration and administration features.
Section 3, Programming
Provides system programming instructions.
Section 4, Appendix
Provides tables listing capacity of system resources, and tones and ring tones. It also provides
the list of abbreviations.
Index
Provide feature titles, important words to help you access the required information easily.
Terms used in this Feature Guide
Installation Manual References
The required installation instruction titles described in the Installation Manual are noted f or your
reference.
Feature Guide References
The related feature titles described in this Feature Guide are noted for your reference.
User Manual References
The operation required to implement the feature described in the User Manual is noted for your
reference.
Abbreviations
There are many abbreviations used in this manual (e.g., "PT" which stands for proprietary
telephone). Please refer to the list in this manual ( 4.3 List of Abbreviations) for the meaning
of each abbreviation.
About the other manuals
Along with this Feature Guide, the following manuals are available to help you install, and use
this PBX:
2 Feature Guide

Installation Manual
h
Changed from:
The KX-TDA30E, the KX-TDA30NE, the KX-TDA30GR, and the
KX-TDA30CE are designed to interwork with the:
Provides instruct ion s for installing the hardware and mai nte nan ce of the PBX .
User Manual
Provides operating instructions for end users using PTs, SLTs, PSs, or DSS Consoles.
The KX-TDA15E/KX-TDA30E, the KX-TDA15NE/KX-TDA30NE, the KX-TDA15GR/KXTDA30GR, and the KX-TDA30CE are designed to interwork with the:
Analogue Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) of a European country
Pan-European Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) using ISDN basic rate access
The KX-TDA100E/KX-TDA200E, the KX-TDA100NE/KX-TDA200NE, the KX-TDA100GR/
KX-TDA200GR, and the KX-TDA100CE/KX-TDA200CE are designed to interwork with the:
Analogue Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) of a European country
Pan-European Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) using ISDN basic rate access
Pan-European Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) using ISDN primary rate access
ONP 2048 kbit/s digital structured leased lines (D2048S)
We, Panasonic Communications Co., Ltd./Panasonic Communications Company (U.K.) Ltd.,
declare that this equipment is in compliance with the essential requirements and other relevant
provisions of Directive 1999/5/EC.
If you would like to receive a copy of the original Declaration of Conformity of our products whic
relates to the R&TTE, please visit our web address:
http://doc.panasonic.de
Trademarks
• Microsoft and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
• Intel and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its
subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
• All other trademarks identified herein are the property of their respective owners.
• Screen shots reprinted with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
Notes
• There are some optional service cards, PTs, and features which are not available in
some areas. Additionally, there are some optional service cards and features for the
KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 which are not available for the KX-TDA15/KX-TDA30, or
vice versa. Please consult your certified Panasonic dealer for more information.
• Displays are described in English as samples.
• While all system programming can be performed through PC programming ( 2.3.1
PC Programming), PT programming can only cover a subset ( 2.3.2 PT
Programming). In Section 1 Call Handling Features and Section 2 System
Configuration and Administration Features, programming references such as "
Date & Time [000]" indicate that system programming can be done by PT
programming.
Feature Guide 3

For further details, please refer to the on-line help of the Maintenance Console (
3.2.1 Installing and Starting the Maintenance Console).
Feature Highlights
Networking Features
This PBX supports the following networking features:
TIE Line Service
A TIE line is a privately leased communication line between two or more PBXs, which
provides cost effective communications between company members at different locations.
( 1.28.1 TIE Line Service)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
VPN is a service provided by the telephone company . It uses an existing line as if it were
a private line. ( 1.28.2 Virtual Private Network (VPN))
QSIG Network
QSIG is a protocol which is based on ISDN (Q.931) and offers enhanced PBX features in
a private network. ( 1.28.3 QSIG Network)
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Network
The PBX can connect to another PBX via a private IP network. In this case, voice signals
are converted into IP packets and sent through this network. ( 1.28.4 Voice over Internet
Protocol (VoIP) Network)
Built-in Small Call Centre Features
An incoming call distribution group ( 1.2.2 Incoming Call Distribution Group Features) can
be used as a small call centre with the following features:
Queuing Feature
When a preprogrammed number of extensions in an incoming call distribution group are
busy, additional incoming calls can wait in a queue. While calls are waiting in the queue,
the calls are handled by the Queuing Time Table, which can be assigned for each time
mode (day/lunch/break/night). ( 1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature)
Log-in/Log-out
Incoming call distribution group members can join (Log-in) or leave (Log-out) the groups
manually. While logged-in, a member extension can have a preprogrammed time period
automatically for refusing calls after completing the last call (Wrap-up). ( 1.2.2.6 Login/Log-out)
VIP Call
It is possible to assign a priority to incoming call distribution groups. If an extension
belongs to multiple groups and the extension becomes idle, queuing calls in the groups
will be distributed to the extension in priority order. ( 1.2.2.4 VIP Call)
Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) Features
Connecting a personal computer (PC) to this PBX (via a DPT, or via a Server PC on a LAN)
enables extension users to make use of advanced features by using the stored data in the PC
or in the Server PC. ( 1.29.1 Computer Telephony Integration (CTI))
Voice Mail Features
This PBX supports Voice Processing Systems (VPS) with DTMF Integration as well as DPT
(Digital) Integration. ( 1.23 Voice Mail Features)
4 Feature Guide

Parallelled Telephone Features
By connecting telephones in parallel, you can increase the number of telephones connected
to the PBX without adding additional extension cards. ( 1.10.9 Parallelled Telephone)
Parallel Mode
An SL T can be connected to an APT or DPT which is connected to a Super Hybrid port of
the PBX. The SLT shares the same extension number with the APT or DPT.
EXtra Device Port (XDP) Mode
An SL T can be connected to a DPT which is connected to a Super Hybrid port of the PBX.
Unlike parallel mode, XDP mode allows each telephone to act as an independent
extension with its own extension number.
Digital XDP
A DPT can be connected to another DPT which is connected to a DPT port or a Super
Hybrid port of the PBX. Similar to XDP mode, each DPT acts as an independent extension
with its own extension number.
Portable Station (PS) Features
PSs (e.g., KX-TD7590, KX-TD7690) can be connected to this PBX. It is possible to use the
PBX features using the PS like a PT. A PS can also be used in parallel with a wired telephone
(Wireless XDP Parallel Mode). In this case, the wired telephone is the main telephone and
the PS is the sub telephone. ( 1.24 Portable Station (PS) Features)
PC Phone/PC Console Features
This PBX supports PC Phone and PC Console. These Panasonic CTI applications provide
advanced features.
Feature Guide 5

Table of Contents
1 Call Handling Feat ures ............................. ... ................. .. ..............15
1.1 Incoming Call Features.................................. ......................... .. ...........................16
1.1.1 Incoming Trunk Cal l Feature s.. .. ............................................................................. 16
1.1.1.1 Incoming Trunk Call Features—SUMMARY.........................................................................................16
1.1.1.2 Direct In Line (DIL)...............................................................................................................................19
1.1.1.3 Direct Inward Dialling (DID)/Direct Dialling In (DDI).............................................................................21
1.1.1.4 Multiple Subscriber Number (MSN) Ringing Service...........................................................................24
1.1.1.5 Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution.........................................................................................27
1.1.1.6 Intercept Routing..................................................................................................................................29
1.1.1.7 Intercept Routing—No Destination.......................................................................................................32
1.1.2 Interna l C a ll Featur e s....... ... ................................................................................... 33
1.1.2.1 Internal Call Features—SUMMARY.....................................................................................................33
1.1.2.2 Internal Call Block................................................................................................................................34
1.1.3 Incoming Call In d ic a tion Features........ ... ............................................................... 36
1.1.3.1 Incoming Call Indication Features—SUMMARY..................................................................................36
1.1.3.2 Ring Tone Pattern Selection.................................................................................................................37
1.1.3.3 Call Waiting................................ ...... ............................................. ..... ...... ............................................38
1.2 Receiving Group Features................................................................................... 40
1.2.1 Idle Extensio n Hun ting ........................................................................................... 40
1.2.2 Incoming Call Distribution Group Features.............................................................42
1.2.2.1 Incoming Call Distribution Group Features—SUMMARY ....................................................................42
1.2.2.2 Group Call Distribution.........................................................................................................................46
1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature ..................................................................................................................................49
1.2.2.4 VIP Call................................................................................................................................................51
1.2.2.5 Overflow Feature..................................................................................................................................52
1.2.2.6 Log-in/Log-out......................................................................................................................................54
1.2.2.7 Supervisory Feature.................................... ...... ..... ............................................. ...... ...........................56
1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Feat ures............................ ....... 58
1.3.1 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND)................................. .. .. .................. 58
1.3.1.1 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND)—SUMMARY...............................................................58
1.3.1.2 Call Forwa rdi ng (FWD).... ...... ..... ...... ............................................. ..... ...... ............................................61
1.3.1.3 Do Not Disturb (DND)..........................................................................................................................65
1.4 Answering Features............................................................................................. 66
1.4.1 Answering Features................................................................................................ 66
1.4.1.1 Answering Features—SUMMARY........................................................................................................66
1.4.1.2 Line Preference—Incoming..................................................................................................................67
1.4.1.3 Call Pickup........................................................ ..... ...... ...... ..... .............................................................68
1.4.1.4 Hands-free Answerback.......................................................................................................................69
1.5 Making Call Features ...........................................................................................70
1.5.1 Predialling............................................................................................................... 70
1.5.2 Automatic Extension Release................................................................................. 71
1.5.3 Intercom Call.......................................................................................................... 72
1.5.4 Tru n k C a ll Features .......... ... ................................................................................... 73
1.5.4.1 Trunk Call Features—SUMMARY........................................................................................................73
1.5.4.2 Emergency Call....................................................................................................................................74
1.5.4.3 Account Code Entry.............................................................................................................................75
1.5.4.4 Dial Type Selection................................................. ...... ...... ..... ...... .......................................................76
1.5.4.5 Reverse Circuit.....................................................................................................................................77
1.5.4.6 Pause Insertion ....................................................................................................................................78
1.5.4.7 Host PBX Access Code (Access Code to the Telephone Company from a Host PBX)....... ................79
1.5.4.8 Special Carrier Access Code...............................................................................................................81
1.5.5 Seizing a Line Features.......................................................................................... 82
1.5.5.1 Seizing a Line Features—SUMMARY..................................................................................................82
6 Feature Guide

1.5.5.2 Line Preference—Outgoing .................................................................................................................83
1.5.5.3 Trunk Access .......................................................................................................................................84
1.6 Memory Dialling Features....................................................................................86
1.6.1 Memory Dialling Features.......................................................................................86
1.6.1.1 Memory Dialling Features—SUMMARY.............................................................................................. 86
1.6.1.2 One-touch Dialling...............................................................................................................................88
1.6.1.3 KX-T7710 One-touch Dialling (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)............................................................ 89
1.6.1.4 Last Number Redial.............................................................................................................................90
1.6.1.5 Speed Dialling—Personal/System....................................................................................................... 91
1.6.1.6 Quick Dialling....................................................................................................................................... 92
1.6.1.7 Hot Line................................................................................................................................................ 93
1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features...........................................................................94
1.7.1 Automatic Callback Busy (C a m p - o n ) ............... .. ........................................ .. ... ........94
1.7.2 Executive Busy Override................. ........................................................................95
1.7.3 Call Monitor.............................................................................................................96
1.7.4 Second Call Notification to Busy Extension................................. ........................ ...97
1.7.4.1 Second Call Notification to Busy Extension—SUMMARY...................................................................97
1.7.4.2 Call Waiting Tone ................................................................................................................................. 99
1.7.4.3 Off-hook Call Announcement (OHCA)...............................................................................................100
1.7.4.4 Whisper OHCA..................................................................................................................................101
1.8 Toll Restriction (TRS)/Call Barring (Barring) Features....................................102
1.8.1 Toll Restriction (TRS)/Call Barring (Barring).........................................................102
1.8.2 Budget Management.............................................................................................107
1.8.3 Extension Lo ck..... .. ........................... .. .. ............. ... .. .......................... ... .. ............. ..108
1.8.4 Dial Tone Transfer........................................................... ......................................109
1.8.5 Walking COS...... ...................................................................................................110
1.8.6 Verified Code Entry......................................... ......................... .. ...........................111
1.9 Automatic Ro u te S el e c ti o n (ARS) Feature s ......... ........................... .. .. .............113
1.9.1 Automatic Route Sele c tion (ARS).........................................................................113
1.10 Conversation F e at ures ... ... .................................................................................118
1.10.1 Hands-free Operation ...........................................................................................118
1.10.2 Off-hook Monitor...................................................................................................119
1.10.3 Mute......................................................................................................................120
1.10.4 Headset Operation ................................................................................................121
1.10.5 Data Line Security.................................................................................................122
1.10.6 Flash/Recall/Terminate .........................................................................................123
1.10.7 Externa l Featur e Ac c e ss (E FA)........... .. .. .............. .. .. ........................... .. .. .............124
1.10.8 Trunk Call Limitation..............................................................................................125
1.10.9 Parallelled Telephon e............... .. ...........................................................................126
1.10.10 Calling Party Control (CPC) Signal Detection.......................................................129
1.11 Transferring Features.........................................................................................130
1.11.1 Call Transfer..........................................................................................................130
1.12 Hold in g Fe a tures.................................................................................................132
1.12.1 Call Hold ...............................................................................................................132
1.12.2 Call Park................................................................................................................134
1.12.3 Call Splitting..........................................................................................................135
1.12.4 Music on Hold ................. ......................................................................................136
1.13 Conference Features............................. ............................. .. ..............................137
1.13.1 Conference Features ............................................................................................137
1.13.1.1 Conference Features—SUMMARY....................................................................................................137
1.13.1.2 Conference........................................................................................................................................138
1.13.1.3 Privacy Release................................................................................................................................. 140
1.14 Paging Features.... ............................................. ........................ ........................ .141
Feature Guide 7

1.14.1 Paging .................................................................................................................. 141
1.15 Broadcasting Features (KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only) ................ 143
1.15.1 Broadcasting (KX-TD A30/KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)........................ .. .......... 143
1.16 Optional Device Features.............................................. .................................... 146
1.16.1 Doorphone Call .................................................................................................... 146
1.16.2 Door Open.. ... .. ..................................................................................................... 148
1.16.3 Tru n k A nswer From Any Station (TAFAS)............................................................. 149
1.16.4 Background Music (BGM).................................................................................... 150
1.16.5 Outgoing Message (OGM)................................................................................... 151
1.16.6 Direct Inward System Access (DISA)................................................................... 153
1.17 Caller ID Features.................... ..................................................... ... .. ............. .. .. 160
1.17.1 Caller ID ............................................................................................................... 160
1.17.2 Incoming Call L og......... .. ...................................................................................... 165
1.18 Message Features.............................................................................................. 167
1.18.1 Message Waiting.................................................................................................. 167
1.18.2 Absent Message................................................................................................... 170
1.19 Proprietary Telephone (PT) Features ............................................................... 171
1.19.1 Fixed Buttons ....................................................................................................... 171
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons.................................................................................................... 174
1.19.3 LED Indication...................................................................................................... 177
1.19.4 Display Information............................................................................................... 180
1.20 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) Service Features....................... 182
1.20.1 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)......................................................... 182
1.20.1.1 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)—SUMMARY............................................. ...... ...... ........182
1.20.1.2 Calling/Connected Line Identification Presentation (CLIP/COLP) .....................................................186
1.20.1.3 Advice of Charge (AOC) ....................................................................................................................188
1.20.1.4 Call Forwarding (CF)—by ISDN (P-MP)............................................. ...... ...... ..... ...... .........................189
1.20.1.5 Call Forwarding (CF)—by ISDN (P-P)...................................................... ..........................................191
1.20.1.6 Call Hold (HOLD)—by ISDN..............................................................................................................193
1.20.1.7 Call Transfer (CT)—by ISDN..............................................................................................................194
1.20.1.8 Three-party Conference (3PTY)—by ISDN........................................................................................195
1.20.1.9 Malicious Call Identification (MCID)...................................................................................................196
1.20.1.10 Completion of Calls to Busy Subscriber (CCBS)...............................................................................197
1.20.1.11 ISDN Extension................................ ............................................. ..... ...... ...... ....................................198
1.20.1.12 ISDN Service Access by Keypad Protocol.........................................................................................200
1.21 E1 Line Service Features (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)........ .. ..................... 201
1.21.1 E1 Line Service (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only).......... .. ............................. ......... 201
1.22 T1 Line Service Features (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only) ...............................203
1.22.1 T1 Line Service (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)....................... .. .........................203
1.23 Voice Mail Features ............................................................................................ 205
1.23.1 Voice Mail (VM ) G r ou p ......................................................................................... 205
1.23.2 Voice Mail DTMF In tegration ... .. ... ........................................................................ 208
1.23.3 Voice Mail DPT (Digital) Integratio n......... ............................................................. 215
1.24 Portable Station (PS) Features.......................................................................... 220
1.24.1 Portable Station (PS) Connection.........................................................................220
1.24.2 PS Ring Group..................................................................................................... 222
1.24.3 PS Directory......................................................................................................... 225
1.24.4 PS Feature Buttons.............................................................................................. 226
1.24.5 Wireless XDP Parallel Mode ................................................................................227
1.25 Administrative Information Output Features................................................... 230
1.25.1 Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR).................................. .. .....................230
1.25.2 Charge Meter ....................................................................................................... 236
8 Feature Guide

1.26 Extension Controlling Features............... ..........................................................239
1.26.1 Extension Personal Identification Number (PIN)...................................................239
1.26.2 Extension Feature Cle a r ........ .. .. ........................... .. .. ............. ... .. ..........................241
1.26.3 Walking E xt e n s io n......... ........................................................................................242
1.26.4 Timed Reminder ...................................................................................................243
1.26.5 Remote Extension Control by User.......................................................................244
1.27 Audible Tone Features........................................................................................245
1.27.1 Dial Tone...............................................................................................................245
1.27.2 Confirmation Tone.................................................................................................246
1.28 Networking Features................................................................................. .. ........247
1.28.1 TIE Line Service....................................................................................................247
1.28.2 Virtual Private Network (VPN)...............................................................................266
1.28.3 QSIG Network................. ......................................................................................268
1.28.3.1 QSIG Network—SUMMAR Y.................................................... ............................................. ............. 268
1.28.3.2 Calling/Connected Line Identification Presentation (CLIP/COLP) and Calling/Connected Name
Identification Presentation (CNIP/CONP)—by QSIG......................................................................... 270
1.28.3.3 Call Forwarding (CF)—by QSIG ........................................................................................................272
1.28.3.4 Call Transfer (CT)—by QSIG............................................................................................................. 274
1.28.3.5 Completion of Calls to Busy Subscriber (CCBS)—by QSIG..............................................................276
1.28.4 Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) Network.........................................................277
1.29 Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) Features................................ .. ............278
1.29.1 Computer Telephony Integration (CTI)..................................................................278
2 System Configuration a nd Adm ini s tra ti on Fe a ture s............... 281
2.1 System Configuration—Hardware.....................................................................282
2.1.1 Extension Port Con figuration ................................................................................282
2.2 System Configuration—Software......................................................................283
2.2.1 Class of Service (COS ). ..................................................... .. .. .............. .. .. .............283
2.2.2 Group....................................................................................................................284
2.2.3 Tenant Service......................................................................................................287
2.2.4 Time Service.........................................................................................................290
2.2.5 Operator Features.................................................................................................294
2.2.6 Manager Features................................ .................................................................295
2.3 System Data Control...........................................................................................297
2.3.1 PC Programming...................................................................................................297
2.3.2 PT Programming............. .. ........................... .. .. ............. ... .. ............. .. ... ............. .. ..300
2.3.3 Quick Setup...... ..................................................... .. .. ............. ... .. ............. .. .. .........302
2.3.4 Automatic Setup....................................................................................................303
2.3.5 Flexible Numbering /F ixed Nu mb e ring. .. ................................................................305
2.3.6 Floating Extension ................................................................................................310
2.3.7 Software Upgrading ...... .. .. .............. .. .. ............. .. ... .......................... .. ... ............. .. ..311
2.4 Fault Recovery/Diagnostics...............................................................................312
2.4.1 Power Failure Transfer (KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)......................312
2.4.2 Po w er Failure Restart............................................................................................314
2.4.3 Local Alarm Information......... .. .............................................................................315
3 Programming Instructions......................................................... 317
3.1 Introduction.........................................................................................................318
3.1.1 Introduction ...........................................................................................................318
3.2 PC Programmin g...................... ...........................................................................319
3.2.1 Ins talling and Starting the Maintenance Console.................... ....................... .......319
3.3 PT Programmin g .................... .. .. ..................................................................... ....3 24
Feature Guide 9

3.3.1 Programming Ins tructions ....... ........................................ .. .. .............. .. .. ............... 324
3.3.2 Basic Programming.............................................................................................. 329
Date & Time [000]..............................................................................................................................329
System Speed Dialling Number [001]................................................................................................329
System Speed Dialling Name [002] ...................................................................................................329
Extension Number [003].......................................................... ...... ..... ................................................329
Extension Name [004]............................................ ............................................. ...... ..... ....................330
Extension Personal Identification Number (PIN) [005].......................................................................330
Operator Assignment [006]................................................................................................................330
Console Paired Telephone [007]........................................................................................................330
Absent Message [008].......................................................................................................................330
Charge Margin [010]..........................................................................................................................331
Charge Tax [011]................................................................................................................................331
Charge Rate per Unit [012]................................................................................................................331
3.3.3 System Programming........................................................................................... 332
Flexible Numbering [100]...................................................................................................................332
Time Service Switching Mode [101]...................................................................................................332
Time Service Starting Time [102] ......................................................................................................332
Idle Line Access (Local Access) [103]...............................................................................................333
System Password for Administrator—for PT Programming [110].......................................................333
System Password for User—for PT Programming [111]....................................................................333
Manager Password [112]...................................................................................................................333
Verified Code [120].............................................................................................................................333
Verified Code Name [121]..................................................................................................................333
Verified Code Personal Identification Number (PIN) [122].................................................................333
V e rified Code COS Number [123 ]......................................................................................................334
Decimal Point Position for Currency [130]..........................................................................................334
Currency [131]....................................................................................................................................334
Main Processing (MPR) Software Version Reference [190]...............................................................334
3.3.4 Time Programmin g............................................................................................... 335
Hold Recall Time [200]........................................... ............................................. ...... .........................335
Transfer Recall Time [201].......................... ...... ..... ...... ...... ..... ............................................. .. ............335
Intercept Time [203]...........................................................................................................................335
Hot Line Waiting Time [204]...............................................................................................................335
Automatic Redial Repeat Times [205]................................................................................................335
Automatic Redial Interval [206]..........................................................................................................335
Door Open Duration Time [207].........................................................................................................335
Call Duration Count Starting Time for LCOT [208].............................................................................336
DISA Delayed Answer Time [209]......................................................................................................336
DISA Trunk-to-Trunk Call Prolong Time [210]....................................................................................336
DISA Intercept Time [211]..................................................................................................................336
3.3.5 TRS/Barring/ARS Programming........................................................................... 337
TRS/Barring Override by System Speed Dialling [300]......................................................................337
TRS/Barring Denied Code [301] ........................................................................................................337
TRS/Barring Exception Code [302]....................................................................................................337
Special Carrier Access Code [303]....................................................................................................337
Emergency Number [304]..................................................................................................................337
ARS Mode [320]............................................................................................. ..... ...... .........................337
ARS Leading Number [321]...............................................................................................................338
ARS Routing Plan Table Number [322]..............................................................................................338
ARS Exception Number [325]....................................................... ..... ...... ...... ....................................338
ARS Routing Plan Time Table [330].............................................. ..... ...... ...... ..... ...............................338
ARS Routing Plan Table (1–16) [331–346]........................................................................................339
ARS Carrier Name [350]....................................................................................................................339
ARS Trunk Group for Carrier Access [351]........................................................................................339
ARS Removed Number of Digits for Carrier Access [352].................................................................339
ARS Carrier Access Code [353] ................................................... ..... ...... ...... ..... ...............................339
3.3.6 Tru n k P ro gram m in g .... .. ........................................................................................ 340
LCOT/BRI Trunk Connection [400].....................................................................................................340
10 Feature Guide

LCOT/BRI Trunk Name [401]............................................................................................................. 340
LCOT/BRI Trunk Group Number [402]............................................................................................... 340
LCOT/BRI Trunk Number Reference [409]........................................................................................341
LCOT Dialling Mode [410]..................................................................................................................341
LCOT Pulse Rate [411]......................................................................................................................341
LCOT DTMF Minimum Duration [412]...............................................................................................341
LCOT CPC Signal Detection Time—Outgoing [413]......................................................................... 341
LCOT CPC Signal Detection Time—Incoming [414]......................................................................... 341
LCOT Reverse Circuit [415]..................................................... ...... ...... ..... ...... ..... ..............................341
LCOT Pause Time [416].................................................................................................................... 342
LCOT Flash/Recall Time [417]...........................................................................................................342
LCOT Disconnect Time [418].............................................................................................................342
BRI Network Type [420]..................................................................................................................... 342
BRI DIL/DDI/MSN Selection [421]..................................................................................................... 342
BRI Subscriber Number [422]............................................................................................................ 342
BRI Layer 1 Active Mode [424]..........................................................................................................342
BRI Layer 2 Active Mode [425]..........................................................................................................343
BRI Configuration [426]......................................................................................................................343
BRI TEI Mode [427]...........................................................................................................................343
DIL 1:1 Destination [450]................................................................................................................... 343
DID Number [451].............................................................................................................................. 343
DID Name [452].................................................................................................................................344
DID Destination [453]......................................................................................................................... 344
Trunk Group Intercept Destination [470]............................................................................................ 344
Host PBX Access Code [471]............................................................................................................344
Extension-to-Trunk Call Duration [472]..............................................................................................344
Trunk-to-Trunk Call Duration [473]..................................................................................................... 344
DISA Silence Detection [475].............................................................................................................345
DISA Continuous Signal Detection [476]...........................................................................................345
DISA Cyclic Signal Detection [477].......................................... ............................................. ...... ....... 345
Caller ID Signal Type [490] (KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)............................................345
Pay Tone Signal Type [491] (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only).............................................................. 345
3.3.7 COS Programming................................................................................................346
Trunk Group Number [500]................................................................................................................ 346
TRS/Barring Level [501].....................................................................................................................346
Trunk Call Duration Limitation [502]................................................................................................... 346
Call Transfer to Trunk [503]................................................................................................................ 346
Call Forwarding to Trunk [504]...........................................................................................................346
Executive Busy Override [505]...........................................................................................................347
Executive Busy Override Deny [506] ................................................................................................. 347
DND Override [507]................................ ............................................. ..... ...... ...................................347
Account Code Mode [508].................................................................................................................347
TRS/Barring Level for System Speed Dialling [509] ..........................................................................347
TRS/Barring Level for Extension Lock [510]......................................................................................347
Manager Assignment [511]................................................................................................................347
Permission for Door Open Access [512]............................................................................................ 348
Time Service Manual Switching [514]................................................................................................ 348
Wireless XDP Parallel Mode for Paired Telephone [515]...................................................................348
Programming Mode Limitation [516]..................................................................................................348
3.3.8 Extension Pro gra mm ing........... ..................................................... .. .. ....................349
EXtra Device Port (XDP) Mode [600].................................................................................................349
Terminal Device Assignment [601].....................................................................................................349
Class of Service [602]............................. ..... ...... ...... ............................................ ...... ...... ... ............... 349
User Group [603]...............................................................................................................................349
Extension Intercept Destination [604]................................................................................................349
Call Forwarding—No Answer Time [605]........................................................................................... 349
CLIP/COLP Number [606]........................... ...... ...... ..... ............................................. ...... ..... ............. 350
Incoming Call Distribution Group Member [620]................................................................................ 350
Incoming Call Distribution Group Delayed Ringing [621]...................................................................350
Feature Guide 11

Incoming Call Distribution Group Floating Extension Number [622]..................................................350
Incoming Call Distribution Group Name [623]....................................................................................350
Incoming Call Distribution Group Distribution Method [624] ..............................................................350
Destination for Overflow Time Expiration [625]..................................................................................351
Overflow Time [626]...........................................................................................................................351
Destination When All Busy [627]........................................................................................................351
Queuing Call Capacity [628] ..............................................................................................................351
Queuing Hurry-up Level [629]............................................................................................................351
Queuing Time Table [630]..................................................................................................................352
Sequences in Queuing Time Table [631] ...........................................................................................352
Maximum Number of Agents [632].....................................................................................................352
User Groups of a Paging Group [640]................................................................................................352
External Pagers of a Paging Group [641]...........................................................................................352
User Groups of a Pickup Group [650]................................................................................................353
VM Group Floating Extension Number [660].....................................................................................353
Idle Extension Hunting Type [680]......................................................................................................353
Idle Extension Hunting Group Member [681] .....................................................................................353
PS Registration [690]......................................................... ..... ...........................................................354
PS Termination [691]......................................... ..... ...... ...... ............................................ ....................354
Personal Identification Number (PIN) for PS Registration [692].........................................................354
CS Status Reference [699] ................................................................................................................354
3.3.9 Resource/In t e rface Pro gra m m i n g......... ..................................................... ... .. ...... 355
External Pager Floating Extension Number [700]..............................................................................355
Music Source Selection for BGM (with the KX-TDA15/KX-TDA30)/BGM2 (with the KX-TDA100/KX-
TDA200) [710]....................................................................................................................................355
Music on Hold [711]...........................................................................................................................355
Music for Transfer [712]......................................................................................................................355
Doorphone Call Destination [720]......................................................................................................356
Doorphone Number Reference [729]....................................................... ...... ..... ...............................356
Outgoing Message (OGM) Floating Extension Number [730]............................................................356
Outgoing Message (OGM) Name [731].............................................................................................357
DISA Security Mode [732]..................................................................................................................357
3.3.10 SMDR & Maintenance Programming...................................................................358
RS-232C Paramete r—New Line Code [800]............................................ ...... ....................................358
RS-232C Parameter—Baud Rate [800].............................................................................................358
RS-232C Parameter—Word Length [800]..........................................................................................358
RS-232C Parameter—Parity Bit [800]................................................................................................358
RS-232C Paramete r—Stop Bit Length [800]..... ..... ...... ...... ............................................ ...... ...... ........358
External Modem Control [801]...........................................................................................................358
SMDR Page Length [802]..................................................................................................................358
SMDR Skip Perforation [803].............................................................................................................359
SMDR Outgoing Call Printing [804] ...................................................................................................359
SMDR Incoming Call Printing [805] ...................................................................................................359
Remote Programming [810]...............................................................................................................359
Modem Floating Extension Number [811]..........................................................................................359
ISDN Remote Floating Extension Number [812 ].......... ............................................. ..... ....................359
3.3.11 Card Programmin g ..... .. .. ...................................................................................... 360
Slot Card Type Reference [900].........................................................................................................360
Slot Card Deletion [901].....................................................................................................................360
Slot Card Reset [902].........................................................................................................................360
OPB3 Option Card Type Reference [910] (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)........................................360
OPB3 Option Card Deletion [911] (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)....................................................360
4 Appendix......................................................................................361
4.1 Capacity of System Resources......................................................................... 362
4.1.1 Capacity of System Resources ............................................................................ 362
4.2 Tones/Ring Tones....................................... .. ............................. .........................365
4.2.1 Tones/Ring Tones.............................. ........................... .. ...................................... 365
12 Feature Guide

4.3 List of A bbr eviations ............... ........................... .. ........................................ .. .. ..367
4.3.1 List of Abbreviations..............................................................................................367
4.4 Revision History..................................................................................................369
4.4.1 KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 Version 1.1....................................................................369
4.4.2 KX-TDA30 Version 1.1 .... .. ....................................................................................3 71
Index .................................................................................................. 373
Feature Guide 13

14 Feature Guide

Section 1
Call Handling Features
Feature Guide 15

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.1 Incoming Trunk Call Features
1.1.1.1 Incoming Trunk Call Features—SU MMA RY
Description
Incoming calls via a trunk (public line) are distributed to their destination using a suitable
distribution feature.
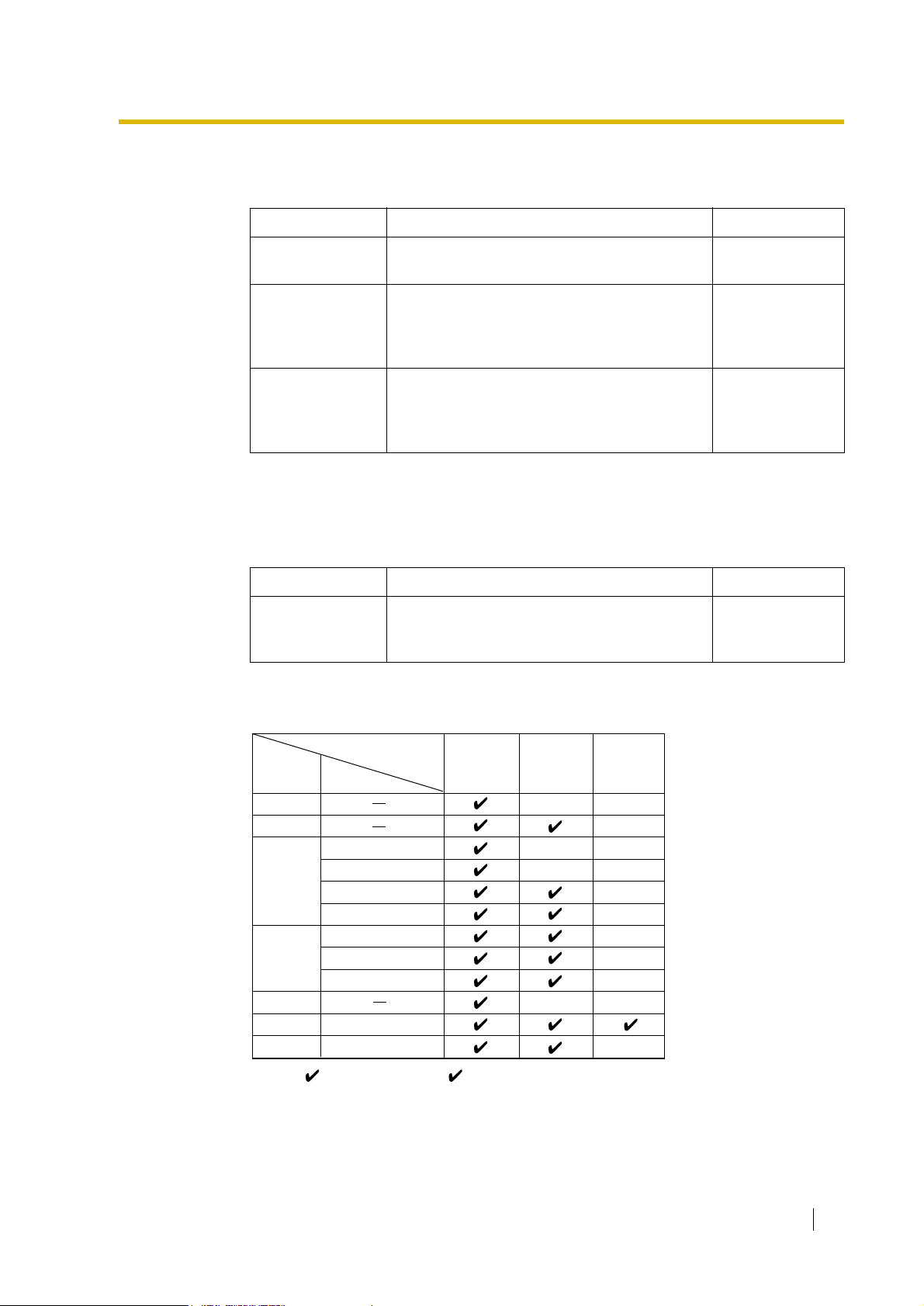
1. Available Networking Type for Each Optional Trunk Card Type
Each trunk port of an optional trunk card can be assigned its networking type: Public,
Private, or VPN (Virtual Private Network).
Trunk
Card
Type
Networking
Type
Channel Type
Public
(DIL/DID/
DDI/MSN)
LCOT
DID
LCOT
GCOT
T1
DID
TIE (E & M)
OPX (EXTN.)
DR2
E1
E & M-C
E & M-P
E&M
CO
BRI/PRI
Extension
QSIG-Master
QSIG-Slave
IP-GW
Note: : Enable (default), : Enable
*1
*2
*
1.28.1 TIE Line Service
:
1.28.2 Virtual Private Network (VPN)
:
Private
(TIE)*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Virtual Private
1
Network
(VPN)*
2
16 Feature Guide
2. Distribution Feature
One of the following features can be assigned to each trunk port:
Feature Description Details in
1.1 Incoming Call Features
Direct In Line
(DIL)
Direct Inward
Dialling (DID)
Directs a call to a preprogrammed single
destination (e.g., Operator).
Directs a call with a DID number from a DID
line to a preprogrammed destination.
DID is also known as Direct Dialling In (DDI).
• 1.1.1.2 Direct In
Line (DIL)
• 1.1.1.3 Direct
Inward Dialling
(DID)/Direct
Dialling In (DDI)
Multiple
Subscriber
Number (MSN)
Ringing Service
Directs a call with an MSN from an ISDN line to
a preprogrammed destination.
• 1.1.1.4 Multiple
Subscriber
Number (MSN)
Ringing Service
3. Destination Change with the Caller’s Identification Number
The Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution feature works in conjunction with the DIL/
DID/DDI/MSN features.
Feature Description Details in
Calling Line
Identification
(CLI) Distribution
Directs a call to a CLI destination if the caller’s
identification number has been assigned to the
Caller ID Table.
• 1.1.1.5 Calling
Line Identification
(CLI) Distribution
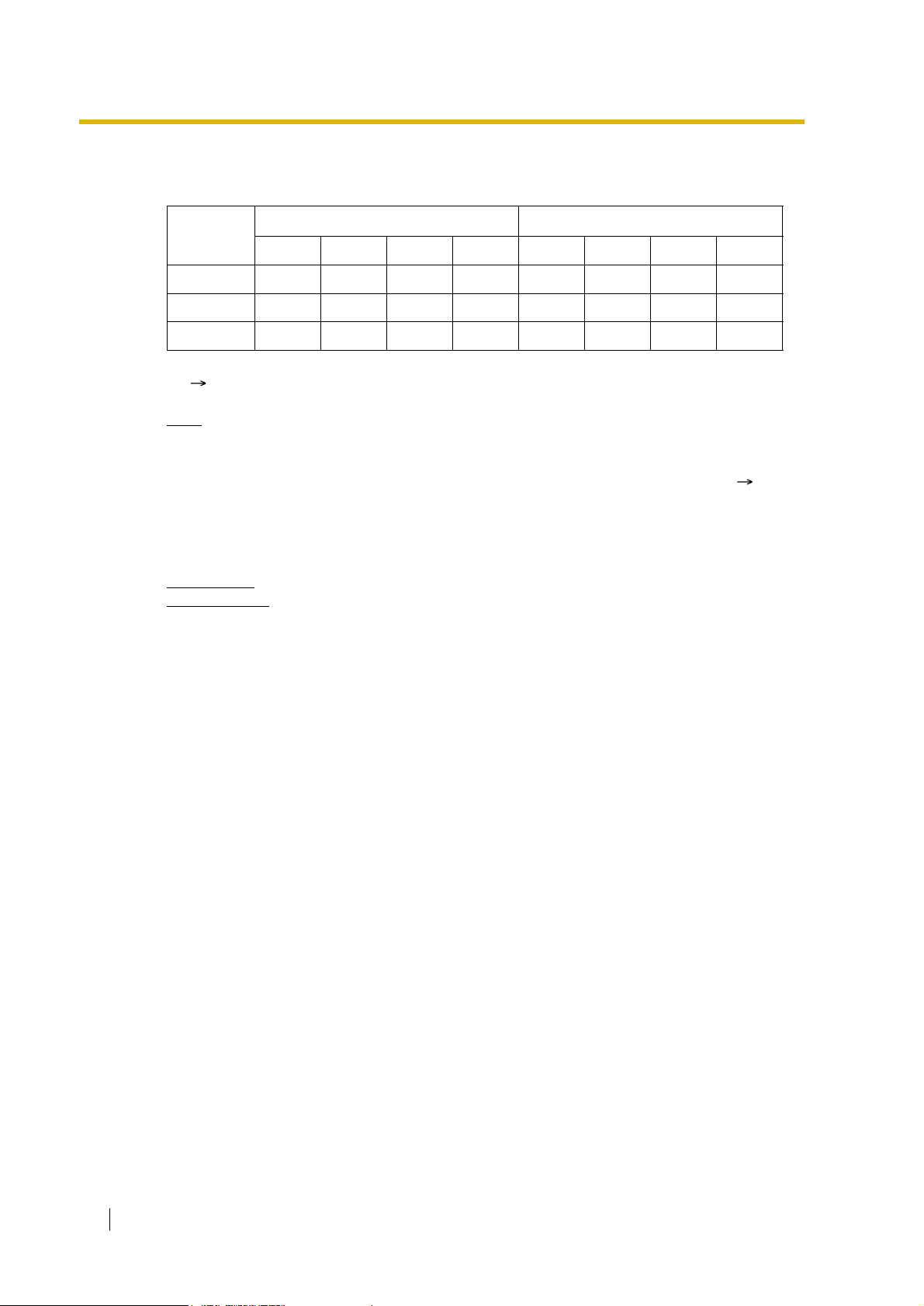
4. Available Distribution Feature for Each Optional Trunk Card Type
Trunk
Feature
Card
Type
LCOT
Channel Type
*
DID
*
*
T1
LCOT
GCOT
DID
TIE (E & M)
*
DR2
E1
E & M-C
E & M-P
E&M
BRI
PRI
Note: : Enable (default), : Enable
*
CO
CO
*
*
*
DID/DDIDIL
*
*
*
*
*
MSN
Feature Guide 17

1.1 Incoming Call Features
5. Available D estination
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/ISDN Extension/T1-OPX)
PS
Incoming Call Distribution Group
PS Ring Group
VM Group (DTMF/DPT)
External Pager (TAFAS)
DISA
Analogue/ISDN Remote Maintenance
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no.
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no.
Destination Availability
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code)
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX Code)
6. Intercept Routing
After distribution, the following features may be required.
Feature Description Details in
Intercept
Routing
No Answer
(IRNA)
If a called party does not answer a call within
a preprogrammed time period (Intercept
time), it is redirected to the preprogrammed
destination.
Busy/DND If a called party is busy or in DND mode, the
call is redirected to the preprogrammed
destination.
No
Destination
If a destination is not assigned, the call is
redirected to the operator.
• 1.1.1.6
Intercept
Routing
• 1.1.1.7
Intercept
Routing—No
Destination
18 Feature Guide

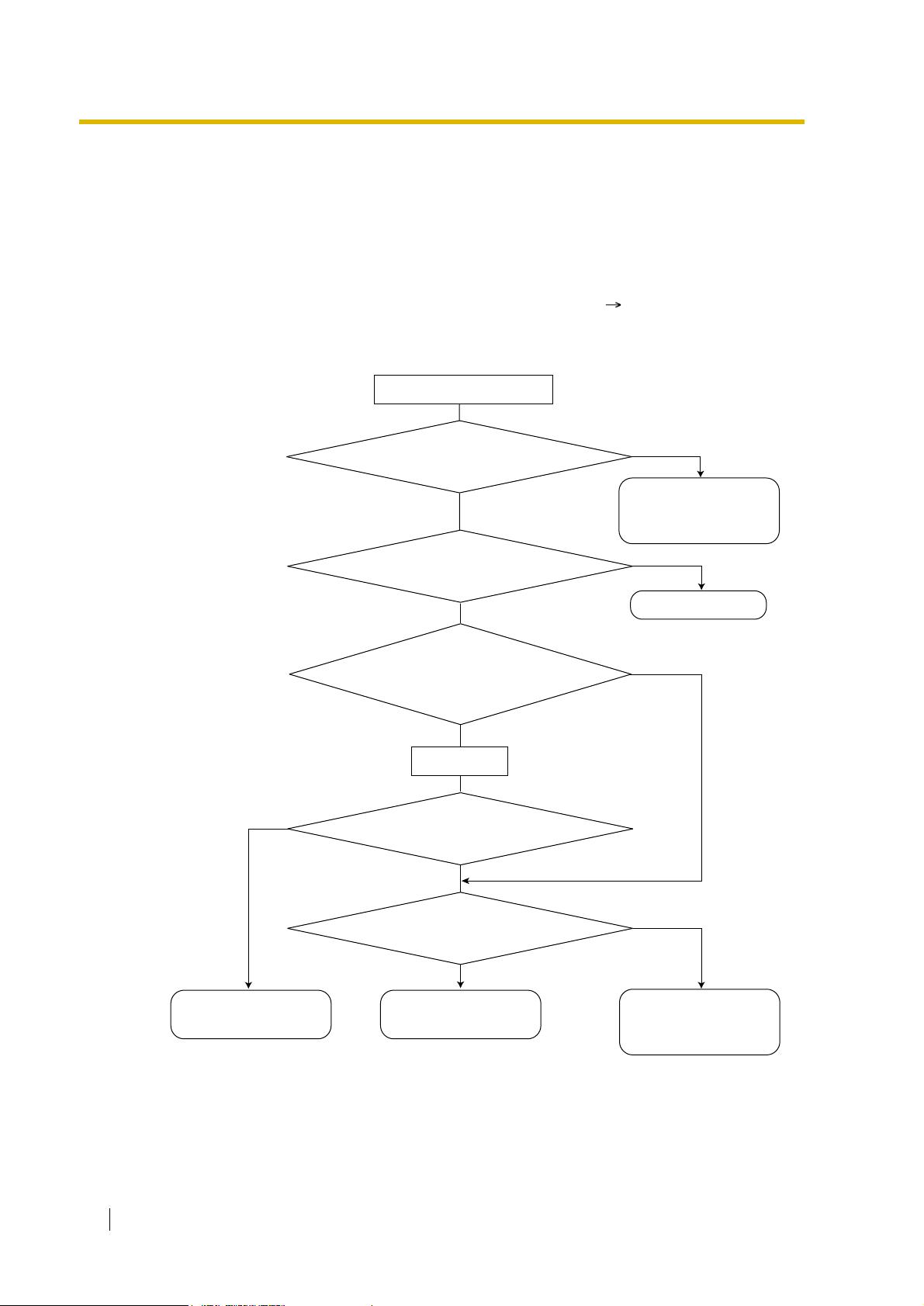
1.1.1.2 Direct In Line (DIL)
Description
Provides automatic direction of an incoming trunk call to a preprogrammed destination. Each
trunk has a destination for each time mode (day/lunch/break/night).
[Method Flowchart]
1.1 Incoming Call Features
A trunk call is received.
Does the call have its CLI*
information and is CLI mode enabled
for the trunk and the time mode?
Yes
CLI works.
Yes
The call is routed to the
CLI destination.
*: Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution:
If the CLI routing is enabled and the caller's identification number is assigned in the Caller ID
Table, the call will not be routed to the DIL destination, but routed to the CLI destination.
Is the CLI destination
assigned?
No
Is the DIL destination of
the time mode assigned?
Yes
The call is routed to the
DIL destination.
The call is routed to the
operator (Intercept Routing
—No Destination).
No
No
Feature Guide 19
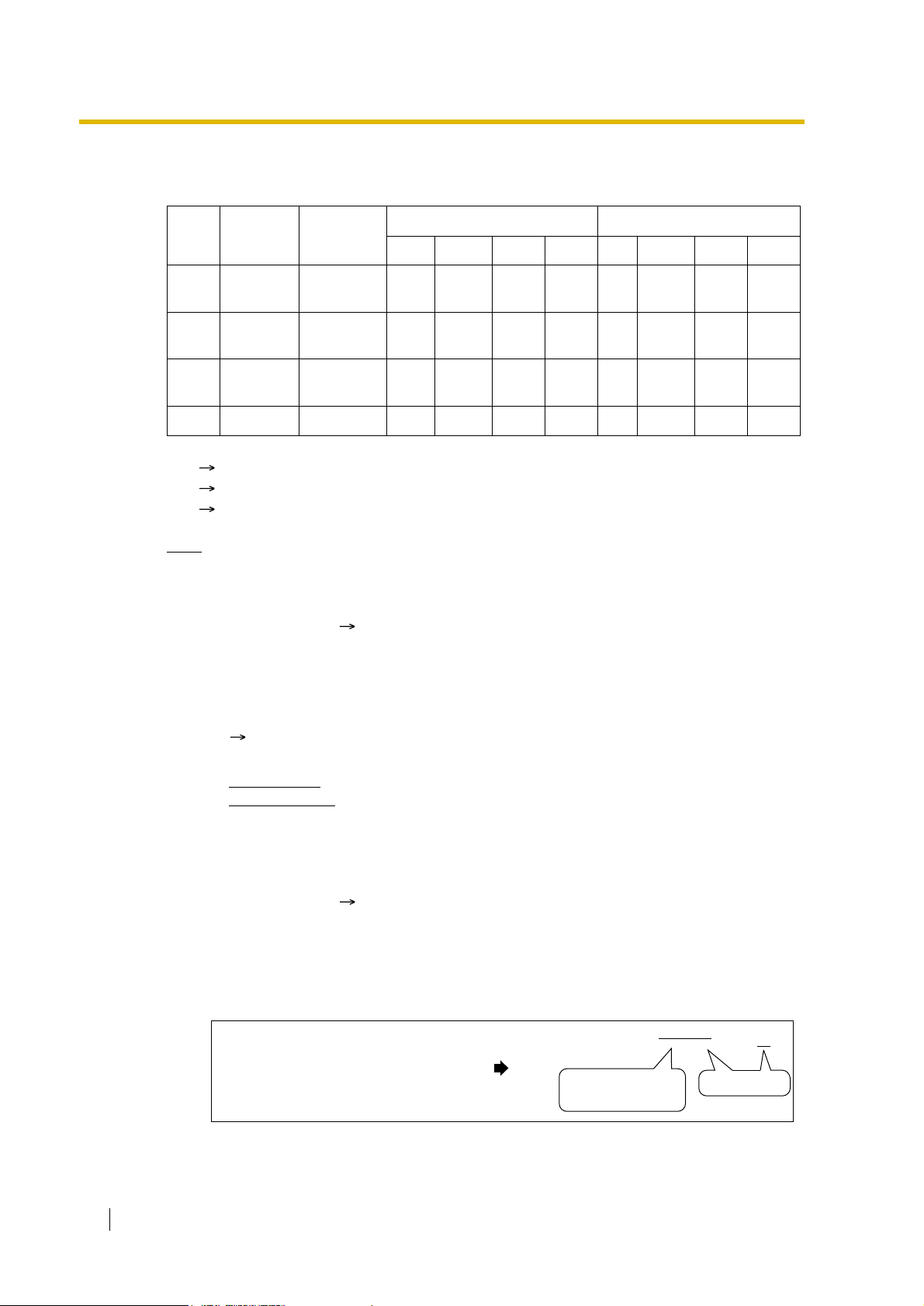
1.1 Incoming Call Features
[Programming Example of DIL Table]
The table can be programmed for each trunk.
Trunk No.
Day Lunch Break Night Day Lunch Break Night
01 Enable Disable Enable Disable 101 100 101 100
02 Enable Disable Disable Disable 102 100 102 100
: ::::::::
*
DIL 1:1 Destination [450]
:
Note
T enant number and VPS trunk group number can also be assigned in the DIL table. T enant
number is used to determine the time mode (day/lunch/break/night) for the corresponding
trunk. VPS trunk group number is used in Voice Mail DPT (Digital) Integration ( 1.23.3
Voice Mail DPT (Digital) Integration).
Explanation:
If a trunk call is received from trunk 01;
In Day mode
In Lunch mode
: CLI is enabled. Route to CLI destination.
: CLI is disabled. Route to DIL destination, extension 100.
Feature Guide References
CLI
Destination
*
1.1.1.5 Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution
2.2.4 Time Service
20 Feature Guide

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.1.3 Direct Inward Dialling (DID)/Direct Dialling In (DDI)
Description
Provides automatic direction of an incoming call with a DID/DDI number to a preprogrammed
destination. Each DID/DDI number has a destination for each time mode (day/lunch/break/
night).
[Method Flowchart]
A trunk call is received.
Yes
Is the DID/DDI number found in
the DID/DDI table?
Yes
Does the call have its CLI*
information and is CLI mode
enabled for the time mode?
Yes
CLI works.
Is the CLI destination assigned?
No
Is the DID/DDI destination
for the time mode assigned?
Yes
No
The call is routed to the
operator (Intercept
Routing—No Destination).
No
No
The call is routed to the
CLI destination.
*: Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution:
If the CLI routing is enabled and the caller's identification number is assigned in the Caller ID
Table, the call will not be routed to the DID/DDI destination, but routed to the CLI destination.
The call is routed to the
DID/DDI destination.
The call is routed to the
operator (Intercept
Routing—No Destination).
Feature Guide 21
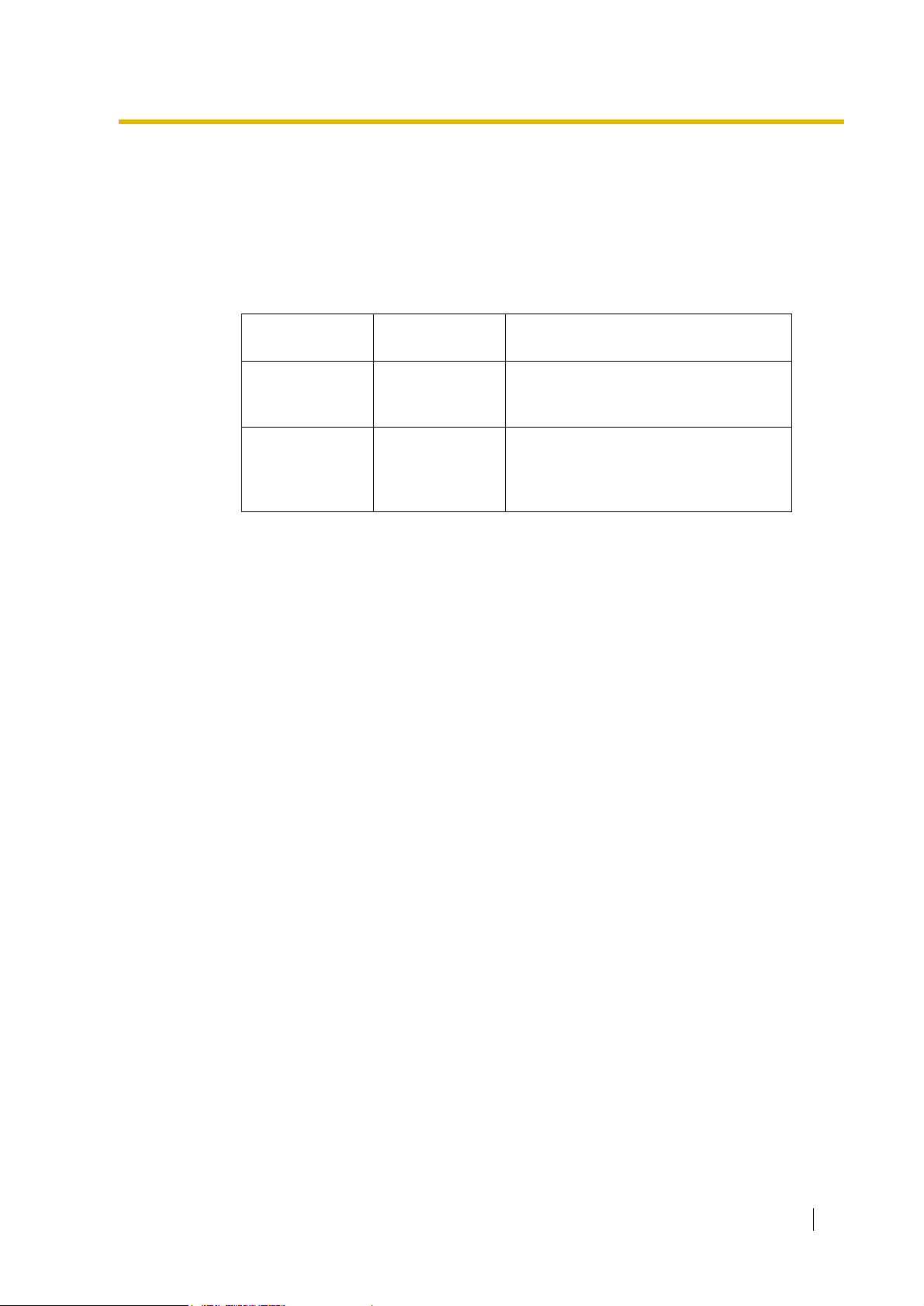
1.1 Incoming Call Features
1
[Programming Example of DID/DDI Table]
DDI can be programmed as DID.
Locat
ion
DID/DDI
*1
No.
DID/DDI
*2
Name
0001 123-4567 John White
0002 123-2468 Tom Smith
0003 123-456 A company
CLI
DID/DDI Destination
Day Lunch Break Night Day Lunch Break Night
EnableDisableEnableDisabl
EnableDisableDisableDisabl
EnableDisableDisableDisabl
105 100 105 100
e
102 100 102 100
e
101 101 101 100
e
*3
:: :::::::::
*1
*2
*3
DID Number [451]
:
DID Name [452]
:
DID Destination [453]
:
Note
Tenant number and VPS trunk group number can also be assigned in the DID/DDI table.
Tenant number is used to determine the time mode (day/lunch/break/night) for the
corresponding DID/DDI number. VPS trunk group number is used in Voice Mail DPT
(Digital) Integration ( 1.23.3 Voice Mail DPT (Digital) Integration).
Explanation:
If the DID/DDI number is "123-4567":
1. Checks the number in the table.
Matches the number in location 0001.
2. Checks the time mode.
In Day mode:
In Lunch mode:
CLI is enabled. Route to CLI destination.
CLI is disabled. Route to DID/DDI destination, extension 100.
Conditions
• To use this feature, the DID/DDI service must be assigned for a trunk port as the
• DID/DDI Number Modification
22 Feature Guide
distribution method ( BRI DIL/DDI/MSN Selection [421] *For BRI only).
It is possible to modify a received DID/DDI number, which may be convenient when
programming the DID/DDI table. Modification method (removed number of digits/added
number) can be programmed on a trunk port basis.
[Modification Example]
Removed number of digits: 6
Modified DID/DDI number: 876543 21 = 102
Added number: 10
Received DID/DDI number: 87654321
1) Remove the
first 6 digits.
2) Add "10".
1.1 Incoming Call Features
• The Inter-digit Time
When the Inter-digit time expires, the PBX stops receiving DID/DDI number and starts to
check the DID/DDI table. (Refer to the [Programming Example of DID/DDI Table] above).
Even if the Inter-digit time does not expire, the PBX stops receiving the DID/DDI number
when the received number is found in the DID/DDI table. The PBX then routes the call to
the corresponding destination. If the received number matches several DID/DDI numbers
in the table, the DID/DDI number of the lowest numbered location has priority.
[Example] If a call is received in Lunch mode;
Received
Number
123-4567 Extn. 100 The PBX finds the match in location 0001
123-456 Extn. 101 The Inter-digit time expired after
Feature Guide References
1.1.1.5 Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution
2.2.4 Time Service
Destination Explanation
in the table after receiving "7". So the call
is routed to extension 100.
receiving "6". The PBX finds the match in
location 0003 in the table. So the call is
routed to extension 101.
Feature Guide 23
1.1 Incoming Call Features
).
).
1.1.1.4 Multiple Subscriber Number (MSN) Ringing Serv ice
Description
Provides automatic direction of an incoming ISDN-BRI (Basic Rate Interface) line call with an
MSN to a preprogrammed destination. One ISDN-BRI port can support a maximum of 10
MSNs. Each MSN has a destination for each time mode (day/lunch/break/night).
Point-to-multipoint must be selected for the ISDN configuration ( BRI Configuration [426]).
[Method Flowchart]
A trunk call is received.
Yes
Are any MSNs assigned
in the MSN table?
Yes
Is the MSN found in the
MSN table?
Yes
Does the call have its CLI*
information and is CLI mode
enabled for the time mode?
Yes
CLI works.
Is the CLI destination
assigned?
No
No
The call is routed to the
operator (Intercept
Routing—No Destination
No
The call is ignored.
No
The call is routed to the
CLI destination.
*: Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution:
If the CLI routing is enabled and the caller's identification number is assigned in the Caller ID
Table, the call will not be routed to the MSN destination, but routed to the CLI destination.
24 Feature Guide
Is the MSN destination for
the time mode assigned?
Yes
The call is routed to the
MSN destination.
No
The call is routed to the
operator (Intercept
Routing—No Destination

1.1 Incoming Call Features
[Programming Example of MSN Table for ISDN BRI Port 1]
A table can be programmed for each ISDN-BRI port. Each BRI port has 10 MSN locations.
Locat
ion
01
02
10: : ::::::::
Note
Explanation:
If the MSN "123-4567" is received from BRI port 1:
MSN
123-
4567A Company
123-
2468C Company
:: : ::::::::
Tenant number and VPS trunk group number can also be assigned in the MSN table.
Tenant number is used to determine the time mode (day/lunch/break/night) for the
corresponding MSN. VPS trunk group number is used in Voice Mail DPT (Digital)
Integration ( 1.23.3 Voice Mail DPT (Digital) Integration).
1. Checks the number in the table.
Matches the number in location 01.
2. Checks the time mode.
In Day mode:
In Lunch mode:
MSN
Name
CLI is enabled. Route to CLI destination.
Day Lunch Break Night Day Lunch Break Night
Enable
Enable
CLI is disabled. Route to MSN destination, extension 100.
CLI MSN Destination
Disabl
DisableDisableDisabl
Enable
e
Disabl
e
e
101 100 101 100
102 100 102 100
Conditions
• To use this feature, the MSN service must be assigned for a trunk port as the distribution
method ( BRI DIL/DDI/MSN Selection [421]).
• M SN Modification
It is possible to modify a received MSN to make it shorter, which may be convenient when
programming the MSN table. Modification method (removed number of digits/added
number) can be programmed on a trunk port basis.
[Modification Example]
Removed number of digits: 6
Added number: 10
Received MSN: 87654321
• When using point-to-multipoint configuration with a BRI, do not connect another ISDN
terminal device in parallel with the PBX. As only two channels can be used at one time
with the BRI, the other ISDN termina l device may monopolise both chann els.
Feature Guide References
1.1.1.5 Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution
Modified MSN: 876543 21 = 1021
1) Remove the first
6 digits.
2) Add "10".
Feature Guide 25

1.1 Incoming Call Features
2.2.4 Time Service
26 Feature Guide

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.1.5 Calling Line Identification (CLI) Distribution
Description
Directs an incoming trunk call to a destination when the caller’s identification number (e.g.,
Caller ID) matches the number in the System Speed Dialling T able which is used as the Caller
ID Table. Each Caller ID number (telephone number for each System Speed Dialling number)
can have its own destination.
CLI Feature Description Details in
Caller ID (KX-TDA30/KXTDA100/KX-TDA200 only)
Calling Line Identification
Presentation (CLIP)
Automatic Number
Identification (ANI) (KXTDA100/KX-TDA200 only)
CLI always works in conjunction with the following call distribution methods:
Caller’s number is sent from an analogue
trunk.
Caller’s number is sent from an ISDN line. • 1.20.1.2
Caller’s number is sent from an E1 or T1
line.
• 1.17.1 Caller
ID
Calling/
Connected
Line
Identification
Presentation
(CLIP/COLP)
• 1.21.1 E1
Line Service
(KX-TDA100/
KX-TDA200
only)
• 1.22.1 T1
Line Service
(KX-TDA100/
KX-TDA200
only)
a) DIL
b) DID/DDI
c) MSN Ringing Service
Each trunk (for DIL) and the DID/DDI/MSN number can enable or disable the CLI feature for
each time mode (day/lunch/break/night) ( 2.2.4 Time Service).
When the call has its Caller ID and the CLI is enabled for the time mode, the call will be handled
by the CLI method.
[Programming Example of System Speed Dialling Table for CLI]
Location
(System Speed
Dialling No.)
000 901234567890 ABC Company 200
001 : : :
::::
Telephone No.
System Speed
*1
Dialling Name
CLI Destination
*2
Feature Guide 27

1.1 Incoming Call Features
*1
*2
System Speed Dialling Number [001]
:
System Speed Dialling Name [002]
:
Explanation:
If the caller’s number is "0123-456-7890" (The Trunk Access number is disregarded.):
1. Checks the number in the table.
Matches the number in location 000.
2. The call is routed to the CLI destination, extension 200.
Conditions
• Automatic Caller ID Number Modification
The Caller ID number is used after modification by the Automatic Caller ID Number
Modification. ( 1.17.1 Caller ID)
Feature Guide References
1.1.1.2 Direct In Line (DIL)
1.1.1.3 Direct Inward Dialling (DID)/Direct Dialling In (DDI)
1.1.1.4 Multiple Subscriber Number (MSN) Ringing Service
1.6.1.5 Speed Dialling—Personal/System
28 Feature Guide
1.1.1.6 Intercept Routing
Description
Provides automatic redirection of incoming trunk calls. There are two types of Intercept Routing
as follows:
Feature Description
1.1 Incoming Call Features
Intercept Routing—No
Answer (IRNA)
Intercept Routing—
Busy/DND
The available intercept destination is as follows:
Type 1: The destination assigned on the extension port which the original destination joins.
( Extension Intercept Destination [604])
Type 2: The destination assigned on the trunk group which receives the call.
( Trunk Group Intercept Destination [470])
Original Destination The Available Intercept Destination
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/ISDN
Extension/T1-OPX)
PS Type 1
Incoming Call Distribution Group Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call
If a called party does not answer a call within a preprogrammed
time period (Intercept time) ( Intercept Time [203]), it is
redirected to the preprogrammed destination.
If a called party is busy or in DND mode, the call is redirected to
the preprogrammed destination.
Type 1
Distribution Group works ( 1.2.2.5 Overflow
Feature). The overflow destination is assigned on
the incoming call distribution group which the
original destination joins ( Destination for
Overflow Time Expiration [625]).
PS Ring Group Type 2
VM Group (DTMF/DPT) Type 2
External Pager (TAFAS) Type 2
DISA Type 2*
Analogue/ISDN Remote
Maintenance
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no. Not available
Trunk Group Access no. +
Trunk Group no. + Phone no.
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no
PBX Code)
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX
Code)
Not available
Not available
Not available
Not available
Feature Guide 29
1.1 Incoming Call Features
*: This is applied only when a trunk call arrives on a DISA line but the line is busy at that time.
Once the call reaches the destination extension by using the DISA feature, the Intercept
Routing feature of the extension works.
Each of them can have different intercept destinations for each time mode (day/lunch/break/
night) ( 2.2.4 Time Service).
[Available Intercept Destination]
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/ISDN Extension/T1-OPX)
PS
Incoming Call Distribution Group
PS Ring Group
VM Group (DTMF/DPT)
External Pager (TAFAS)
DISA
Intercept Destination Availability
Analogue/ISDN Remote Maintenance
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no.
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no.
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code)
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX Code)
Conditions
• Intercept Routing—Busy/DND on/off
Each Intercept Routing—Busy and Intercept Routing—DND can be enabled or disabled
through system programming.
If disabled, one of the following is activated depending on the trunk card type which a call
arrives through:
a) LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) Card: The incoming trunk call will ring at the original
b) Other Trunk Cards: A busy tone will be sent to the caller.
• If the intercept destination cannot receive the call:
a) Intercept Routing—No Answer: Intercept timer will restart at the original
b) Intercept Rout ing—Busy/DND: Th e call wi ll be s ent bac k t o the orig inal dest inat ion
• Idle Extension Hunting
If an extension is a member of an idle extension hunting group, calls to that extension will
not be redirected by Intercept Routing—Busy/DND. If the extension is busy or in DND
mode, calls to that extension will be redirected to the next extension in the idle extension
hunting group.
destination while the caller hears a ringback tone.
destination, until the call is answered.
when the call arrives through the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card. When the call
arrives through other trunk cards the caller will hear a busy tone.
30 Feature Guide

Feature Guide References
1.3.1 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND)
1.1 Incoming Call Features
Feature Guide 31

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.1.7 Intercept Routing—No Destination
Description
Provides automatic redirection of an incoming trunk call which does not have a destination
assigned. The intercept destination is an operator (tenant/PBX) ( Operator Assignment [006]
*For PBX operator only).
Conditions
• Intercept Routing—No Destination on/off
The Intercept Routing—No Destination feature can be enabled or disabled through system
programming.
If disabled, reorder tone will be sent to the caller. However, the Intercept Routing—No
Destination feature always works for calls through the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card
even when disabled.
• If an operator (tenant/PBX) is not assigned:
The lowest jack numbered extension will be the intercept destination.
• Intercept Routing—No Destination also applies to:
Calls from doorphones.
Feature Guide References
2.2.5 Operator Features
32 Feature Guide

1.1.2 Internal Call Features
1.1.2.1 Internal Call Feat ures—SUMMARY
Description
The following incoming calls reach their destination:
Feature Description Details in
Intercom Call A call from one extension to another. • 1.5.3
1.1 Incoming Call Features
Intercom Call
Doorphone Call When a call from a doorphone reaches its destination,
the recipient can talk to the visitor.
[Available Destination]
The destinations of doorphone calls can be assigned for each time mode (day/lunch/break/
night) ( 2.2.4 Time Service) on a doorphone port basis ( Doorphone Call Destination
[720]).
Calling from
Destination
Extension Doorphone
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/ISDN Extension/T1-OPX)
PS
Incoming Call Distribution Group
PS Ring Group
VM Group (DTMF/DPT)
External Pager (TAFAS)
DISA
• 1.16.1
Doorphone
Call
Analogue/ISDN Remote Maintenance
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no.
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no.
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code)
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX Code)
Available
:
Feature Guide 33

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.2.2 Internal Call Block
Description
Internal calls can be restricted on a COS basis. Each COS of the caller can enable or disable
this feature for each COS of the called party.
[Programming Example]
Caller
COS 1
COS 2
COS 3
:::::
Block
:
Explanation:
a) COS 1 can make calls to all extensions.
b) COS 2 can make calls to COS 1 only. (COS 2 cannot make calls to COS 2.)
c) COS 3 can make calls to COS 3 only.
Extn. 100 Extn. 101
COS 1 COS 2 COS 3 ...
COS 1
Called Party
Conditions
• Restricted extension numbers cannot be the parameter of the feature settings (e.g.,
• All extensions can make an Operator Call ( 2.2.5 Operator Features) regardless of the
34 Feature Guide
COS 2
Extn. 102 Extn. 103
Walking Extension).
Internal Call Block.
COS 3
Extn. 104 Extn. 105
Extn. 106

1.1 Incoming Call Features
• This feature can also restrict calling a doorphone from an extension on a COS of the
extension and a COS of the doorphone port basis. Each doorphone port can be assigned
a COS. ( 1.16.1 Doorphone Call)
Feature Guide 35

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.3 Incoming Call Indication Features
1.1.3.1 Incoming Call Indic at ion Features—SUMMARY
Description
Incoming calls are indicated by various methods as follows:
Type Feature Description Details in
Ring Tone Ring Tone
Pattern
Selection
Voice-calling Alternate
Receiving—
Ring/Voice
LED
(LED: Light
Emitting
Diode)
Display
(Caller’s
Information)
External Pager Trunk Answer
Tone/Voice
during a
Conversation
LED Indication The light shows line conditions with a variety
Display
Information
from Any
Station
(TAFAS)
Call Waiting A busy extension hears a tone, or voice from
A telephone rings when receiving a call. The
ring tone patterns can be changed for each
incoming call type.
A PT user can select to receive intercom
calls by ring tone or by voice, through
personal programming.
of light patterns.
The display shows the caller’s information. • 1.19.4
The external pager sends a ring tone when
receiving a call .
the handset/built-in speaker indicating that
another incoming call is waiting.
• 1.1.3.2
Ring Tone
Pattern
Selection
• 1.5.3
Intercom
Call
• 1.19.3
LED
Indication
Display
Information
• 1.16.3
Trunk
Answer
From Any
Station
(TAFAS)
• 1.1.3.3
Call Waiting
36 Feature Guide

1.1.3.2 Ring Tone Pattern Selection
S
D
T
S
Description
A ring tone pattern can be selected for each incoming call type on a Ring Tone Pattern Table
basis, which can be assigned for each extension.
[Ring Tone Patterns]
1 280 ms
ingle
ouble
riple
-Double
1.1 Incoming Call Features
[Programming Example of Ring Tone Pattern Table]
There are a specified number of programmable tables each of which allows the assignment of
ring tone patterns for the following incoming call types:
For trunk calls (including trunk call hold recalls) and doorphone calls, select ring tone patterns
on a trunk group or a doorphone port basis.
Table
No.
1 Double Single Single
2 Single Double Double
:: :::::::::
Each extension can select one of the tables.
Conditions
•"PT Ring off Setting" can be enabled or disabled through system programming. If
disabled, PT users cannot set the ring off.
Intercom
Call/Hold
Recall
Trunk Call/Hold
Recall
Doorphone Call
TRG1 TRG2 ... Port 1 Port 2 ...
Timed
Reminder
Call
Back
LCS
Feature Guide 37

1.1 Incoming Call Features
1.1.3.3 Call Waiting
Description
Used to inform a busy extension that another incoming call is waiting. The busy extension user
can answer the second call by disconnecting the current call or placing it on hold.
The following notification method can be assigned for each extension depending on the call
waiting and the telephone type:
a) Call Waiting Tone: Tone from the handset or built-in speaker
b) OHCA: Voice from the built-in speaker
c) Whisper OHCA: Voice from the handset
d) Off: No notification.
Intercom Call Call Waiting tone/OHCA/
Trunk Call* Call Waiting tone/Off
*: Including a doorphone call, call via an incoming call distribution group, and a transferred
trunk call from another extension.
This feature is also known as Busy Station Signalling (BSS).
Conditions
• Call Waiting call for an extension in a VM group (DPT/DTMF) is not available.
• Data Line Security
Setting Data Line Security cancels the Call Waiting setting. ( 1.10.5 Data Line Security)
• Call Waiting Tone
A PT user can hear different Call Waiting tones for trunk call and intercom call if "Tone 2"
has been selected through personal programming (Call Waiting Tone Type Selection). If
"Tone 1" has been selected, the same Call Waiting tone will be heard for both trunk call
and intercom call.
All Call Waiting tone patterns have a default ( 4.2.1 Tones/Ring Tones).
• Caller Information
With the Call Waiting tone, the caller’s information flashes on the display for five seconds
at 15-second intervals.
• Call Waiting from the Telephone Company
Besides the Call Waiting service within the PBX, the Call Waiting tone offered by an
analogue line from your telephone company informs the extension user of another
incoming trunk call that is waiting. He can answer the second call by disconnecting the
current call or placing it on hold. For details, consult your telephone company.
Call Waiting Caller ID (Visual Caller ID) (KX-TDA30/KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only):
With the Call Waiting tone offered by an analogue line from the telephone company, the
Caller ID number can be received and flash on the display twice for five seconds at 15second intervals.
Call Type
Notification Method
DPT Other Telephone
Call Waiting tone/Off
Whisper OHCA/Off
38 Feature Guide

Feature Guide References
1.7.4 Second Call Notification to Busy Extension
User Manual References
User Manual
1.4.4 Answering Call Waiting
1.7.3 Receiving Call Waiting (Call Waiting/Off-hook Call Announcement [OHCA]/Whisper
OHCA)
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
1.1 Incoming Call Features
Feature Guide 39

1.2 Receiving Group Features
1.2 Receiving Group Features
1.2.1 Idle Extension Hunting
Description
If a called extension is busy or in DND mode, Idle Extension Hunting redirects the incoming call
to an idle member of the same idle extension hunting group, which can be programmed
through system programming ( Idle Extension Hunting Group Member [681]). Idle
extensions are automatically searched according to a preprogrammed hunting type ( Idle
Extension Hunting Type [680]).
This feature is also known as Station Hunting.
Type Description
Circular Hunting An idle extension is searched for in the order specified in the idle
extension hunting group in a circular way.
Incoming call
Terminated Hunting An idle extension is searched for in the order specified in the idle
Conditions
• Idle Extension Hunting applies to:
Intercom, trunk, and doorphone calls to a single destination.
• An extension user can belong to only one idle extension hunting group.
Extn.
Assigned order
Busy
Extn.
Extn. Extn.
extension hunting group until reaching the last assigned extension.
Incoming call
Extn.
Assigned order
Busy
Extn.
Extn. Extn.
40 Feature Guide

1.2 Receiving Group Features
• If all the searched extensions are busy:
The PBX redirects the call to an overflow destination which can be assigned for each idle
extension hunting group and each time mode (day/lunch/break/night) ( 2.2.4 Time
Service).
[Available Destination]
Destination Availability
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/ISDN Extension/T1-OPX)
PS
Incoming Call Distribution Group
PS Ring Group
VM Group (DTMF/DPT)
External Pager (TAFAS)
DISA
Analogue/ISDN Remote Maintenance
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no.
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no.
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code)
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX Code)
• FWD/DND Mode
While searching for an idle extension within an idle extension hunting group, any extension
which has set FWD—All Calls or DND feature will be skipped, and the call will go to the
next extension in the group.
Feature Guide References
1.3.1 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND)
Feature Guide 41

1.2 Receiving Group Features
1.2.2 Incoming Call Distribution Group Features
1.2.2.1 Incoming Call Dist ribution Gr oup Features—SUMMARY
Description
An incoming call distribution group is a group of extensions programmed through system
programming ( Incoming Call Distribution Group Member [620]). An incoming call
distribution group receives calls directed to the group. Each incoming call distribution group
has a floating extension number.
Incoming calls directed to an incoming call distribution group are distributed to the member
extensions in the group using a distribution method. When a preprogrammed number of
extensions in the group are busy, the incoming calls can wait in a queue.
Each incoming call distribution group and member extensions can be programmed as desired
to handle incoming calls. Calls to the group can be monitored by an extension assigned as a
supervisor (supervisor extension).
Programming Item Example for Incoming Call Distribution Group 1 with
Diagram
A through F in the table are described in the following diagram.
ABCDEF
Group
No.
1
2
3
:
Floating
Extn. No
290
291
Group
*1
Name
.
Sales
Engineering
*2
Distribution
Method
Ring
UCD
Max. No. of
Busy
*3
Extensions
3
Max.
Queuing
Call
*4
Capacity
5
11
Hurry-up
*5
Level
3
8
*6
Overflow
*7
Time
60
90
Overflow Destination
...
...
Day
100
200
Night
...
...
100
...
...
200
*8
Tenant
*9
No.
1
5
*1
*2
*3
*4
*5
*6
*7
*8
*9
Incoming Call Distribution Group Floating Extension Number [622]
:
Incoming Call Distribution Group Name [623]
:
Incoming Call Distribution Group Distribution Method [624]
:
Maximum Number of Agents [632]
:
Queuing Call Capacity [628]
:
Queuing Hurry-up Level [629]
:
Overflow Time [626]
:
Destination for Overflow Time Expiration [625]/Destination When All Busy [627]
:
Tenant number is required to determine the time mode (day/lunch/break/night) (
:
2.2.4 Time Service ) and the music source (for Music on Hold) for each group.
42 Feature Guide

r
D
Queuing Feature
Five calls are
waiting in a queue.
B
Group Call Distribution
Calls are distributed by the
assigned method.
(Only three extensions
[agents] can answer the
call for Busy on Busy.)
Supervisor Extension
Extn.
100
Monitors or controls the
incoming call distribution
group status.
1.2 Receiving Group Features
Calls arriving at incoming call
distribution group 1.
Overflow Feature
9
F
a) Sends a busy tone (Busy on Busy), o
8
b) Redirects to the overflow destination.
7
6
5
E
4
Manual Queue Redirection
10
*
The longest waiting call in a queue
3
2
1
C
11
*
Extn.
101
Extn.
102
A
Incoming Call
Extn.
103
can be redirected to the overflow
destination by pressing the Hurry-up
button. The button shows the Hurryup status.
Extn.
104
Extn.
105
Extn.
105
Log-outLog-in
12
*
Distribution Group 1
(Floating extension no.: 290,
Name: Sales)
*10
*11
*12
1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature
:
1.2.2.7 Supervisory Feature
:
1.2.2.6 Log-in/Log-out
:
1. Group Call Distribution [ 1.2.2.2 Group Call Distribution]
Incoming calls are distributed using one of the following methods:
Distribution Method Description
Uniform Call
Distribution (UCD)
Calls go to a different extension uniformly each time a call
is received.
Priority Hunting An idle extension is searched in the specified order.
Ring All extensions in the incoming call distribution group ring
simultaneously.
2. Queuing Feature [ 1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature]
If a preprogrammed numbers of extensions in an incoming call distribution group are busy ,
a preprogrammed number of additional calls can wait in a queue.
While calls are waiting in the queue, an outgoing message (OGM) or Music on Hold can
be sent to the waiting callers.
3. VIP Call [ 1.2.2.4 VIP Call]
It is possible to assign a priority to incoming call distribution groups so that an incoming
Feature Guide 43

1.2 Receiving Group Features
call can be received from the groups in priority order.
4. Overflow Feature [ 1.2.2.5 Overflow Feature]
A call is redirected to a preprogrammed destination when it cannot be answered or queued
(Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group). It is also
possible to send a busy tone (Busy on Busy) or disconnect the line.
5. Incoming Call Distribution Group Controlling Feature
Feature Description Details in
Conditions
• One extension can belong to multiple incoming call distribution groups.
• ICD Group button
An Incoming Call Distribution (ICD) Group button can be assigned on a flexible button for
each incoming call distribution group. It receives the incoming calls to the group.
One extension can have more than one ICD Group button of the same or different
incoming call distribution groups (Multiple ICD Group). If all ICD Group buttons in the
same incoming call distribution group are occupied, the next incoming call will be held in
a queue or will overflow. If the ICD Group button is not assigned, incoming calls will arrive
at the INTERCOM or CO button.
Even though an extension can have an ICD Group button for an incoming call distribution
group that the extension has not been programmed to be included through system
programming ( Incoming Call Distribution Group Member [620]), the ICD Group button
will not receive calls to that group.
• Group FWD
The FWD feature can be assigned on an incoming call distribution group basis.
• COS for Incoming Call Distribution Groups
Each incoming call distribution group is assigned a COS number. Group FWD to an
outside party can be enabled or disabled for each COS. The COS for incoming call
distribution groups is also used for the Internal Call Block feature; when an extension user
calls an incoming call distribution group, the PBX checks the COS of the calling extension
against the COS of the incoming call distribution group ( 1.1.2.2 Internal Call Block).
Log-in/Log-out Member extensions can join the group to
handle calls (Log-in) or leave the group
for a break (Log-out).
They can leave the group temporarily
when they are away from their desks, to
prevent calls being sent to their
extensions.
Supervisory
Feature
Incoming
Call Queue
Monitor
Log-in/Logout Monitor
and Remote
Control
The supervi sor extension can monit or
various information about the incoming
calls for each incoming call distribution
group on his display.
Monitor: The supervisor extension can
monitor the log-in/log-out status of the
group members.
Remote Control: The supervisor
extension can change the status of the
members.
• 1.2.2.6 Login/Log-out
• 1.2.2.7
Supervisory
Feature
44 Feature Guide

Feature Guide References
1.3.1.2 Call Forwarding (FWD)
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
1.2 Receiving Group Features
Feature Guide 45

1.2 Receiving Group Features
1.2.2.2 Group Call Distribution
Description
The Incoming calls directed to an incoming call distribution group are distributed to the member
extensions using the distribution method until a preprogrammed number of extensions (agents)
( Maximum Number of Agents [632]) are available to accept a call. When incoming calls
exceed the number, the calls enter a queue ( 1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature).
1. Distribution Method
There are three distribution methods which can be assigned to each incoming call
distribution group ( Incoming Call Distribution Group Distribution Method [624]).
Distribution
Method
Uniform Call
Distribution
(UCD)
Calls go to a different extension uniformly each time a call is
received. Extensions are hunted in a circular way in the
preprogrammed order for the group, starting at the extension after
Description
the extension which received the last call.
Extn.
A
Received
the last call.
Extn.
B
Extn.
C
Starts searching from
extn. B. (Skips extn. A.)
Extn.
D
Priority Hunting An idle extension is searched for using the preprogrammed order
for the group.
1st Priority 2nd Priority 3rd ....
Extn.
A
Extn.
B
Always starts searching from
the first assigned extension.
Extn.
C
Extn.
D
46 Feature Guide
Ring All extensions in the group ring simultaneously.
Delayed Ringing:
Delayed ringing or no ringing can be programmed for each
extension in the group ( Incoming Call Distribution Group
Delayed Ringing [621]). The call can be answered by pressing the
flashing button even if no ring or a delayed time is set.
Extn.
A
Extn.
B
Rings immediately simultaneously.
Extn.
C
Extn.
D
Delayed Ringing:
Rings after a
specified time delay.

1.2 Receiving Group Features
2. Call Waiting for Incoming Call Distribution Group (Group Call Waiting)
When there are no available extensions in an incoming call distribution group, the group
members can receive the Call Waiting tone. To use this feature:
• Select the Group Call Waiting mode through system programming. This determines
the distribution method for waiting calls.
• Member extensions must assign the Call Waiting mode individually , or they will not be
notified. ( 1.1.3.3 Call Waiting)
[How the Group Call Wa iting Feature Activates]
Programming Conditions
Group Call
Waiting Mode
Distribution
All
Distribution Method
UCD
Priority Hunting
Ring
UCD/Priority Hunting/
Ring
Group Call
Group Call Waiting
Distribution Method
UCD
Priority Hunting
Not available*
Ring
Result
Capable
Telephone
PT/PS with idle
ICD Group button
Any telephone
*: Incoming calls enter the queue immediately . Member extensions do not receive the
Call Waiting tone.
[Example]
•
Group Call Waiting mode: All
Group call distribution method
•
for idle extensions: UCD
All extensions hear the Call
Waiting tone (Ring).
[ICD Group Button for Group Call Waiting]
The way that the Group Call Waiting feature works depends on the Group Call Waiting
Distribution method as follows:
a) Ring: The Group Call Waiting feature activates for all busy member extensions
(even when the extensions do not have ICD Group buttons) simultaneously for
only one incoming call — additional calls will wait in a queue.
b) UCD/Priority Hunting: The Group Call Waiting feature activates on an idle ICD
Group button located on busy member extensions in a certain order. (This order
depends on the type: UCD or Priority Hunting.) Calls will arrive at idle buttons
until all ICD Group buttons are occupied — additional calls will wait in a queue.
Note
In the method b), if an extension has one or more ICD Group buttons for an
incoming call distribution group and all the ICD Group buttons on the extension
are occupied, the Group Call Waiting feature for the group will not work at the
extension.
Feature Guide 47

1.2 Receiving Group Features
3. No Reply Redirection (UCD or Priority Hunting Method)
If a call received at a member extension is not answered within a preprogrammed time
period (No Answer time), the call will be redirected to the next member extension. If there
is no idle group member, the call queues at target extension until a group member
becomes available.
Conditions
• FWD/DND Extension
System programming for each incoming call distribution group is required to skip or ring
the extension which has FWD or DND feature set. If it rings, the FWD/DND settings are
ignored. ( 1.3.1 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND))
• Group Call Waiting feature cannot be used with the VIP Call feature ( 1.2.2.4 VIP Call)
and/or Wrap-up feature ( 1.2.2.6 Log-in/Log-out). Because to use the VIP Call feature
and/or Wrap-up feature, Call Waiting mode on each extension should be off.
Incoming Call
Distribution
Group 1
(Floating
extension
no.: 200)
Incoming Call
Distribution
3
Group 2
(Floating
2
extension
no.: 300)
1
ICD Group 200 (Call Waiting)
ICD Group 200 (Call Waiting)
ICD Group 300 (Answering the Call)
48 Feature Guide

1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature
Description
When a preprogrammed number of extensions ( Maximum Number of Agents [632]) in an
incoming call distribution group are busy, additional incoming calls can wait in a queue. The
number of calls which can be in the waiting queue is programmable ( Queuing Call Capacity
[628]).
While calls are waiting in the queue, the calls are handled by the Queuing Time Table (
Queuing Time T able [630]), which can be assigned for each time mode (day/lunch/break/night)
( 2.2.4 Time Service). Each Queuing Time T able has a specified number of sequences. The
following procedures are provided to make up a Queuing Time Table:
[Procedure Table]
Command Description Condition
1.2 Receiving Group Features
OGM a An outgoing message (OGM) a
(01–64 [with the KX-TDA100/KXTDA200] or 01–32 [with the KXTDA15/KX-TDA30]) is sent to the
caller.
b × 5 s Puts the caller in the waiting
queue for b (01–16) × 5 seconds.
Sequence c Redirects to sequence c (01–16). None
Overflow Redirects to overflow destination. None
Disconnect Disconnects the line. None
None
Redirects to the next sequence. If assigned on sequence 01, the
(No command)
[Programming Example of Queuing Time Table]
Queuing
Sequence
Time
Table
Sequence 01Sequence 02Sequence 03Sequence
No.
After the outgoing message (OGM),
Music on Hold will be sent and redirects
to the next sequence.
If an outgoing message (OGM) has not
been sent to the caller, the caller hears
a ringback tone.
If an outgoing message (OGM) has
been sent to the caller, the caller hears
Music on Hold.
Queuing Time Table will not be
activated.
*1
Sequence
*2
16
04
...
01 OGM 01 6 × 5 s OGM 03 Overflow
02
03
:::::::
*1
*2
Sequences in Queuing Time Table [631]
:
The call will be disconnected if the destination is not determined after sequence 16.
:
Feature Guide 49

1.2 Receiving Group Features
Explanation for Queuing Time Table 01:
The call
queues.
Conditions
• If the call is transferred to the incoming call distribution group a nd is handled by the
Queuing Time Table:
Transfer Recall will not occur even if the Transfer Recall time expires.
• Manual Queue Redirection
It is possible to redirect the longest waiting call in a queue to the overflow destination by
pressing the Hurry-up button. (When the call is already ringing on any extension, the call
is not redirected.)
This feature is also known as Hurry-up Transfer.
• Hurry-up Button
A flexible button can be customised as the Hurry-up button. The number of calls queuing
before Manual Queue Redirection may be performed is programmable ( Queuing Hurryup Level [629]). The button shows the current status as follows:
Sequence 01
OGM 01 is sent.
Thank you for
calling Panasonic.
The department you
are calling is busy.
Please hold the line.
We will answer your
call shortly.
The call is connected to the member
extension as soon as the extension
becomes available.
Queuing Time Table 01
Sequence 02
Music on Hold
is sent for 30
seconds.
Sequence 03
OGM 03 is sent.
We are sorry to
keep you holding.
The department
is still busy. We
are transferring
you to the
operator.
Sequence 04
Redirects to
the overflow
destination.
Overflow
destination
answers.
Light Pattern Calls in the Waiting Queue
Off No queued call
Red on At or under the assigned number for Hurry-up
Rapid red flashing Over the assigned number for Hurry-up
Feature Guide References
1.2.2.5 Overflow Feature
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
1.8.3 Forwarding a Waiting Call (Manual Queue Redirection)
50 Feature Guide

1.2.2.4 VIP Call
I
D
G
(
Description
It is possible to assign a priority to incoming call distribution groups. If an extension belongs to
multiple groups and the extension becomes idle, queuing calls in the groups will be distributed
to the extension in priority order.
Each incoming call distribution group can enable or disable the VIP Call mode. When multiple
groups enable the VIP Call mode, the incoming call distribution group with the lowest
numbered group has the highest priority. When multiple groups disable the VIP Call mode,
queuing calls are distributed to extensions uniformly.
[Example]
In the call centre, incoming call distr i bution groups 1 and 3 enable the VIP Call mode, while
incoming call distribution groups 2 and 4 disable the VIP Call mode.
1.2 Receiving Group Features
Calls have been distributed by DIL/DID/DDI/CLI.
(The number in the circle is the queuing order.)
ncoming Call
istribution
roup 1
for VIP)
6
1
1st
Priority
Incoming Call
Distribution
Group 2
(for general
customers)
Extn.
101
5
3
Extn.
102
Incoming Call
Distribution
Group 3
(for special
customers)
3rd
Priority
Extn.
103
Incoming Call
Distribution
4
Group 4
(for general
2
customers)
2nd
Priority
Distribution order:
From: Group 1 Group 3 Groups 2 and 4
8
7
3rd
Priority
1 6 2 4 3 7
5 8
Feature Guide 51

1.2 Receiving Group Features
1.2.2.5 Overflow Feature
Description
When waiting calls exceed the waiting queue capacity ( Queuing Call Capacity [628]), they
may be redirected to a preprogrammed destination or a busy tone may be sent to the callers
by the following features:
1) Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group
2) Busy on Busy
1. Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group
The Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group works in one of
following conditions:
a) There is no space in the waiting queue.
b) The Queuing Time Table is not assigned and there are no extensions logged-in.
c) An Overflow command is assigned to the Queuing Time Table.
d) The Overflow time ( Overflow Time [626]) expires.
e) Manual Queue Redirection is performed.
[Available Destination]
The overflow destinations can be assigned for each incoming call distribution group and
each time mode (day/lunch/break/night) ( 2.2.4 Time Service). The two different
destinations can be assigned, one for the a) and b) ( Destination When All Busy [627]),
and one for c), d), and e) ( Destination for Overflow Time Expiration [625]).
Destination Availability
Wired Extension (PT/SLT/ISDN Extension/T1-OPX)
PS
Incoming Call Distribution Group
PS Ring Group
VM Group (DTMF/DPT)
External Pager (TAFAS)
DISA
Analogue/ISDN Remote Maintenance
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no.
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no.
52 Feature Guide
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code)
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX Code)

1.2 Receiving Group Features
2. Busy on Busy
The Busy on Busy feature works when the destination for the Intercept Routing—Overflow
in an Incoming Call Distribution Group feature is not assigned in one of the following
conditions:
a) There is no space in the Waiting queue.
b) The Queuing Time Table is not assigned and there are no extensions logged-in.
[Example of a)]
When the answering agent number ( Maximum Number of Agents [632]) is "2", and the
queuing call number ( Queuing Call Capacity [628]) is "0":
There are five assistants in the shop. If two of them are engaged on the phone, the next
caller will hear a busy tone to prevent the caller from thinking that there is no one in the
shop or that the shop is closed.
Conditions
[Intercept Routing—Overflow in an Incoming Call Distribution Group]
• If the Overflow time expires, and the overflow destination is unavailable:
a) If the trunk call arrives through the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card: (1) The line is
disconnected when the call was once in a queue and an outgoing message (OGM)
was sent to the call, or when the call reached an incoming call distribution group by
using the DISA feature ( 1.16.6 Direct Inward System Access (DISA)). (2) Except
for the above, redirection is ignored and the Overflow timer activates again.
b) If the call arrives through the other cards: Redirection is ignored and the Overflow
timer activates again.
[Busy on Busy]
• If a trunk call arrives through the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card, a busy tone will not be
sent to the caller.
Feature Guide References
1.2.2.3 Queuing Feature
Feature Guide 53

1.2 Receiving Group Features
1.2.2.6 Log-in/Log-out
Description
Incoming call distribution group members can join (Log-in) or leave (Log-out) the groups
manually.
They can leave the group temporarily when they are away from their desks, to prevent calls
being sent to their extensions. They can return to the group when they are ready to answer
calls.
Wrap-up:
While logged-in, a member extension can have a preprogrammed time period automatically for
refusing calls after completing the last call (Wrap-up time). While Wrap-up timer is active, calls
to all incoming call distribution groups to which the extension belongs will skip the extension so
that he can make some report or etc.
Wrap-up mode can also be activated manually (Not Ready) by pressing the Wrap-up button.
[Log-in/Log-out and Wrap-up Status Example]
<When the incoming call distribution group is in Priority Hunting distribution method>
Incoming call
Extn.
101
Ready ReadyReady
Extn.
102
Extn.
102
Log-out
Conditions
• It is programmable whether the last remaining logged-in extension can log out.
• Log-in/Log-out Button
Ready
Waiting for a call
The Wrap-up
time expires.
Wrap-up
Making a report
Press the
Wrap-up button.
Not Ready
Making a report/
temporary break
Press the
Wrap-up button.
Extn.
103
Log-in
Extn.
104
Not Ready
Extn.
105
Wrap-up
Extn.
106
Answering a call
After
completing
the call
A flexible button can be customised as the Log-in/Log-out button with the following
parameters:
Light Pattern
Parameter Usage
Red on Off
54 Feature Guide
No parameter Used with an ICD Group button, or with a
floating extension number of an incoming
call distribution group, or with (All).
——

1.2 Receiving Group Features
Parameter Usage
Floating extension
number of a
specified incoming
call distribution
group
(All)
• If an ICD Group button is assigned, it also shows the log-in/log-out status of the
corresponding group. The light pattern is the same as the Log-in/Log-out button which
includes the group number.
• Wrap-up Button
A flexible button can be customised as the Wrap-up button. It shows the current status as
follows:
Light pattern Status
Slow red flashing Wrap-up
Red on Not Ready
Used to log-in or log-out from the
specified incoming call distribution group.
Used to log-in or log-out from all incoming
call distribution groups to which you
belong.
Light Pattern
Red on Off
Log-out
Status
After Logout
Operation
Log-in
Status
After Login
Operation
Off Ready (Wrap-up mode cancel)
• When a PS in Wireless XDP Parallel Mode completes a call, neither the PS nor its wired
telephone can have Wrap-up time. ( 1.24.5 Wireless XDP Parallel Mode)
• Automatic Log-out
A member extension may be logged-out automatically, if the Unanswered time expires a
preprogrammed number of times consecutively. The number of consecutive unanswered
calls can be assigned for each incoming call distribution group. If the extension is a
member of more than one incoming call distribution group, the unanswered number is
counted across all corresponding incoming call distribution groups. It is possible to return
to the log-in mode manually.
Automatic Log-out feature does not work for the extension in an incoming call distribution
group in Ring distribution method ( 1.2.2.2 Group Call Distribution).
• Log-in/Log-out Monitor
The supervisor extension can monitor and control the log-in/log-out status of the incoming
call distribution group members. ( 1.2.2.7 Supervisory Feature)
• Log-in/Log-out Information on SMDR
Log-in/Log-out information can be printed out on SMDR. ( 1.25.1 Station Message
Detail Recording (SMDR))
Feature Guide References
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
1.8.1 Leaving an Incoming Call Distribution Group (Log-in/Log-out, Wrap-up)
Feature Guide 55

1.2 Receiving Group Features
<Incoming Call Queue Monitor Display>
<
l
s
1.2.2.7 Supervisory Feature
Description
An extension preprogrammed as a supervisor (supervisor extension) can monitor and control
each member’s status within the incoming call distribution group using a 6-line display PT.
Feature Description
Incoming Call Queue
Monitor
Log-in/Log-out
Monitor and Remote
Control
[Example]
31 Jan. 08:13AM FRI
250:Sales Section
Waiting Calls Now :00006
Max. Waiting Time :05'10
EXIT LOG SPRVS
Log-in/Log-out Monitor/Remote Control Mode with DSS Button light>
The supervisor extension can monitor the status of an incoming
call distribution group with the display.
Monitor: The supervisor extension can monitor the log-in/log-out
status of the incoming call distribution group members through the
corresponding DSS button light.
Remote Control: The supervisor extension can change the status
of the members by pressing the corresponding DSS button.
--- Date and time
--- Floating extension number/name of incoming call distribution group
--- The number of queuing calls
--- The longest queuing time
Since 29 JAN. 09:10AM
Total Calls :00996
Overflow Calls :00131
Lost Calls :00039
Average Waiting :02'12
EXIT CLEAR
--- Monitoring starting date and time
--- Total number of incoming calls
--- Total number of overflowed calls
--- The number of lost calls
--- Average queuing time
31 Jan. 08:13AM FRI
250:Sales Section
Waiting Calls Now :00006
Max. Waiting Time :05'10
EXIT
With
Log-in/Log-out Monitor
DSS buttons of the incoming call
distribution group members show
Log-in/Log-out Remote Contro
Pressing the button change
the status as follows:
their status.
Light pattern
Green on
Slow Green Flashing
Red on
Off
Status
Log-in (Ready)
Log-in (Not Ready)
Log-out
Extension in another
incoming call distribution
group
Status
Log-out
Log-in (Ready)
Light pattern
Red on
Green on
56 Feature Guide

Conditions
• Available Extension as a Supervisor Extension
a) One supervisor extension can be assigned for each incoming call distribution group,
b) One extension can be the supervisor extension of more than one incoming call
• Available Paired DSS Console
The KX-T7640, KX-T7440, and KX-T7441 are available for this feature.
• A ccu mulation Value Clear
Accumulation value (total incoming calls/total overflowed calls/lost calls/average queuing
time) can be cleared manually. The date and time of clearing is saved and it is shown on
the display (monitoring starting date and time). When the value exceeds 99999, before
clearing, "****" will be shown.
• If a call to an incoming call distribution group is overflowed:
If the display is in idle status, it will change to monitor mode for the corresponding incoming
call distribution group automatically.
If the display is monitoring another incoming call distribution group, it will not change.
• Other Features while in Monitor Mode
The supervisor extension can use other features (making calls, pressing the MESSAGE
button, etc.) even while in monitor mode. When each operation is finished, his telephone
returns to the queue monitor display.
1.2 Receiving Group Features
but it need not belong to the group.
distribution group.
User Manual References
User Manual
1.8.2 Monitoring and Controlling the Call Status of an Incoming Call Distribution Group
(Incoming Call Distribution Group Monitor)
Feature Guide 57

1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb
(DND) Features
1.3.1 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND)
1.3.1.1 Ca ll Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND)—
SUMMARY
Description
When an extension user cannot answer calls (e.g., busy, not at the desk), it is possible to
forward or refuse the calls using the following features:
1) Call Forwarding (FWD)
2) Do Not Disturb (DND)
1. FWD
Extensions and incoming call distribution groups can forward their incoming calls to preset
destinations. ( 1.3.1.2 Call Forwarding (FWD))
2. DND
An extension user can send the tone to let the caller know he is not available. ( 1.3.1.3
Do Not Disturb (DND))
Conditions
• FWD and DND features apply to:
Intercom calls (including doorphone calls), and trunk calls (including a call from an
extension that placed a trunk call on a consultation hold.)
• FWD/DND Button
Both the FWD and DND features for the extension can be customised on a flexible button.
Only one of the features will work at a time.
Multiple types of FWD/DND buttons can be customised on an extension.
• Group FWD Button
The FWD feature for the incoming call distribution group can be customised on a flexible
button. Multiple types of Group FWD buttons can be customised on an extension.
[FWD/DND Button and Group FWD Button Types]
FWD/DND for
Extension
Type Description
FWD/DND—Internal Works for incoming intercom calls
FWD/DND—External Works for incoming trunk calls
58 Feature Guide
FWD/DND—Both Works for all incoming calls

1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
Type Description
FWD for
Incoming Call
Distribution
Group
Group FWD—Internal Works for incoming intercom calls
Group FWD—External Works for incoming trunk calls
Group FWD—Both Works for all incoming calls
[Button Status—FWD/DND Button]
The FWD/DND button shows the current status as follows:
Light Pattern Status (default)
Red on FWD on
Slow red flashing DND on
Off FWD/DND off
The functions assigned to the "on" and "flashing" patterns can be changed through system
programming.
[Button Status—Group FWD Button]
The Group FWD button shows the current status as follows:
Light Pattern Status (default)
Red on FWD on
Off FWD off
[Mode Change]
When either the FWD or DND feature is assigned, pressing the FWD/DND button changes
the on/off setting alternately. When both the features are assigned simultaneously,
pressing the button changes the settings as follows:
FWD DND Off
Note
Pressing the FWD/DND button (fixed button) in idle status will produce one of the
following results, selected through system programming:
When in FWD/DND Setting Mode:
Pressing the button will enter personal programming mode for the FWD/DND setting.
When in FWD/DND Cycle Switch Mode:
Pressing the button will cycle the settings as shown above in [Mode Change].
A FWD/DND button customised on a flexible button is always in FWD/DND Cycle
Switch mode, and the mode cannot be changed.
• When intercom calls are set to be handled differently from trunk calls (forwarding type,
forward destination, DND on/off), we recommend establishing buttons for both FWD/
DND—Internal and FWD/DND—External, and/or Group FWD—Internal and Group
FWD—External, because:
a) the light patterns of the FWD/DND—Both button (including FWD/DND button [fixed
button]) and the Group FWD—Both button will indicate the setting for either trunk calls
Feature Guide 59

1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
or intercom calls, but not both.
Note
The FWD and DND icons on a PS display reflect the settings for trunk calls only.
b) pressing the FWD/DND—Both button (including FWD/DND button [fixed button]) or
the Group FWD—Both button will not change the FWD or DND mode for intercom
calls and trunk calls separately.
Feature Guide References
1.19.1 Fixed Buttons
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
60 Feature Guide

1.3.1.2 Call Forwarding (FWD)
Description
Extensions and incoming call distribution groups can forward their calls to preset destinations.
The circumstances under which the calls are forwarded are as follows:
Type Circumstance
All Calls Any time
Follow Me:
When an extension user fails to set this feature before leaving the
desk, this feature can be set from the destination extension.
Busy When the extension user’s line is busy.
No Answer When the extension user does not answer within a preprogrammed
time ( Call Forwarding—No Answer Time [605]).
Busy/No Answer When the extension user’s line is busy or the user does not answer
within a preprogrammed time ( Call Forwarding—No Answer
Time [605]).
1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
Depending on the type of incoming intercom or trunk calls, it is possible to set different
destination for each.
Intercom Calls
Intercom Calls
to Extension
to Extension
Trunk Calls to
Extension
Intercom Calls to
Incoming Call
Distribution Group
Trunk Calls to
Incoming Call
Distribution Group
Extension
Available Forwarding Type:
Incoming Call Distribution Group
All Calls
Busy
No Answer
Busy/No Answer
Forwards to
Another Extension
Forwards to
Outside Party
Forwards to
Another Extension
Forwards to
Outside Party
Available Forwarding Type: All Calls
Feature Guide 61

1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
[Available Destination]
Destination Availability
Condition for Original
Extension/Incoming Call
Distribution Group
Wired Exte nsion (PT/SLT/ISDN Extension/T1OPX)
PS
Incoming Call Distribution Group
PS Ring Group –
VM Group (DTMF/DPT) –
External Pager (TAFAS) –
DISA Only available for incoming
Analogue/ISDN Remote Maintenance –
Idle Line Access no. + Phone no. Only available when FWD to
Trunk Group Access no. + Trunk Group no. +
Phone no.
Other PBX Extension (TIE with no PBX Code) –
Only available when FWD to
extension is allowed through
COS programming.*
trunk calls. Incoming
intercom and doorphone
calls cannot be forwarded to
a DISA floating extension
number.
trunk is allowed through
COS programming.
Other PBX Extension (TIE with PBX Code) Only available when FWD to
*: If an extension user cannot call certain extensions on a COS basis ( 1.1.2.2 Internal Call
Block), the FWD feature to the extension does NOT work.
Conditions
[General]
• FWD for Trunk Calls/Intercom Calls
The FWD feature can be set for trunk calls, for intercom calls, or for both of them by the
extension user.
• FWD from Incoming Call Distribution Group (Group FWD)
COS programming determines the incoming call distribution groups that can use this
feature.
• FWD to Trunk
COS programming determines the extensions or incoming call distribution groups that can
forward calls externally ( Call Forwarding to Trunk [504]).
The original extension’s TRS/Barring and ARS still apply to the forwarded call.
trunk is allowed through
COS programming.
62 Feature Guide

1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
• Trunk Call Duration
If a call between an extension user and an outside party, or between two outside parties
is established, the call duration can be restricted by a system timer ( Extension-to-T runk
Call Duration [472] and Trunk-to-T runk Call Duration [473]). If the timer expires, the line will
be disconnected. ( 1.10.8 Trunk Call Limitation)
• Multiple FWD
Calls can be forwarded up to four times. The following forwarding features are counted as
Multiple FWD:
– FWD—Busy or Busy/No Answer (in case a destination extension is busy), or All
Calls
– Idle Extension Hunting—Overflow
– Intercept Routing—Busy/DND (in case a destination extension is busy or in DND
mode)
– Incoming Call Distribution Group—Overflow
Incoming
call
Original
destination
123 54
A B C D EF
In the above illustration, forwarding stops at the extension E. However , f orwarding can go
farther in the following cases:
– If a destination extension rings, and then the call is redirected to the forward
destination by the FWD—No Answer or Busy/No Answer feature.
– If a destination extension rings, and then the call is redirected to the intercept
destination by the Intercept Routing—No Answer feature.
– If a call waits in a queue of an incoming call distribution group, and then the call
is redirected to the overflow destination by the Queuing Time Table. ( 1.2.2.3
Queuing Feature)
In the above cases, the forwarding counters reset to zero, and calls can be forwarded up
to four times again from the applicable extension that occurred in the case above.
Incoming
call
Original
destination
123 21
A B C D EF
FWD—No Answer
• Boss & Secretary feature
It is possible to call the original extension from the destination extension regardless of the
forward setting.
Incoming
call
FWD—All Calls
Boss
(Original)
Call or
transfer a call
Secretary
(FWD destination)
Feature Guide 63

1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
• Message Waiting
While calls are forwarded, Message Waiting information is not forwarded. The Message
button light turns on at the originally called extension. ( 1.18.1 Message Waiting)
• Idle Extension Hunting
Idle Extension Hunting applies to calls forwarded to a busy extension in an idle extension
hunting group.
[All Calls and Busy]
• If the forward destination is not available to answer a call, this feature is cancelled and the
original destination will ring for the following type of call:
– Doorphone call
– Trunk calls via the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) cards
[No Answer and Busy/No Answer]
• No Answer Time
The number of rings before the call is forwarded is programmable for each extension (
Call Forwarding—No Answer Time [605]).
[Follow Me]
• This feature is only available when the original extension has disabled the "Deny Remote
Operation by Other Extension" setting on a COS basis.
Feature Guide References
1.1.1.6 Intercept Routing
1.2.1 Idle Extension Hunting
1.2.2.5 Overflow Feature
User Manual References
User Manual
1.5.1 Forwarding Calls
64 Feature Guide

1.3.1.3 Do Not Disturb (DND)
Description
An extension user can make use of the DND feature. If this feature is set, calls will not arrive
at the extension, but arrive at other extension by using the Idle Extension Hunting feature (
1.2.1 Idle Extension Hunting) or the Intercept Routing—Busy/DND feature ( 1.1.1.6 Intercept
Routing). When a destination cannot be found, the calling extension will hear the DND tone,
while the calling outside party will hear a busy tone.
Conditions
• DND for Trunk Calls/Intercom Calls
The DND feature can be set for trunk calls, for intercom calls, or for both of them by the
extension user.
• DSS button in DND Mode
The DSS button light will turn red if the assigned extension has set DND.
• DND Override
An extension in DND mode can be called by other extension users who are allowed to
override DND in their COS ( DND Override [507]).
• Paging DND
It is programmable whether the PBX pages extensions in DND mode through system
programming. ( 1.14.1 Paging)
• I ntercept Routing—Busy/DND
If a call arrives at the extension in DND mode, the call can be redirected to the
preprogrammed destination by the Intercept Routing—Busy/DND feature.
• Idle Extension Hunting
While searching for an idle extension within an idle extension hunting group, any extension
which has DND set will be skipped. The call will go to the next extension in the group, not
the Intercept Routing—Busy/DND destination.
• If (1) the trunk call via the LCOT or T1 (LCOT/GCOT) card arrives at the extension in DND
mode and (2) the Intercept Routing—Busy/DND destination is not available and (3) there
is no available extension in the idle extension hunting group, then the original extension in
DND mode will ring.
• Calls from a doorphone arrive at the extension even when the extension is in DND mode.
1.3 Call Forwarding (FWD)/Do Not Disturb (DND) Features
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.4 When the Dialled Line is Busy or There is No Answer
1.7.2 Refusing Incoming Calls (Do Not Disturb [DND])
Feature Guide 65

1.4 Answering Features
1.4 Answering Features
1.4.1 Answering Features
1.4.1.1 Answering Features—SUMMARY
Description
An extension user can answer incoming calls by the following methods:
Destination Feature Description Details in
At the own
extension
(PT only)
At another
extension
Line
Preference—
Incoming
Direct Onetouch
Answering
Hands-free
Answerback
Call Pickup—
Directed/Group
A user can select the line seized when going
off-hook.
A user can answer an incoming call simply
by pressing the flashing button.
A user can receive a call automatically and
establish a hands-free conversation.
A user can pick up a specified extension’s
call or a call in a specified call pickup group.
• 1.4.1.2
Line
Preference
—Incoming
–
• 1.4.1.4
Hands-free
Answerback
• 1.4.1.3 Call
Pickup
66 Feature Guide

1.4.1.2 Line Prefer en ce —In co m in g
Description
A PT user can select the method used to answer incoming calls from the following three line
preferences:
Each of these line preferences can be assigned on each extension through personal
programming (Preferred Line Assignment—Incoming).
Type Description
No Line Selects a line by pressing the desired Line Access button to answer
an incoming call after you go off-hook.
Prime Line Answers a call arriving at a Flexible CO or ICD Group button (on
which the "Prime Line" is assigned) simply by going off-hook. This
works even when multiple calls are received simultaneously.
1.4 Answering Features
Ringing Line
(default)
Answers the longest ringing call at one’s telephone simply by going
off-hook when multiple calls arrive.
Conditions
[Prime Line]
• The priority of the incoming call is as follows:
1) The call arriving at a button on which the "Prime Line" is assigned.
2) The call arriving at the INTERCOM button.
User Manual References
User Manual
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
Feature Guide 67

1.4 Answering Features
1.4.1.3 Call Pickup
Description
An extension user can answer a call ringing at any other extension.
The following types are available:
Type Picking up Call Type
Directed A specified extension’s call.
Group A call within a specified call pickup group.
Call Pickup Deny:
Preventing other extensions from picking up calls ringing at your extension is also possible.
Conditions
• Call Pickup applies to:
Intercom, trunk, and doorphone calls
• Internal Call Block
An extension which cannot call certain extensions on a COS basis ( 1.1.2.2 Internal Call
Block) also cannot pick up any calls ringing at those extensions.
[Directed Call Pickup]
• A user can also pick up a specified extension’s call (except an ISDN extension’s call and
broadcasting call) by pressing the corresponding DSS button. COS programming
determines the extensions that can use this feature.
The light pattern of a DSS button for an incoming call to an extension or incoming call
distribution group can be programmed through system programming. Call Pickup is
available only when the DSS button is red flashing.
[Group Call Pic kup]
• A specified number of call pickup groups can be created ( User Groups of a Pickup
Group [650]), each of which consists of user groups. One user group can belong to several
call pickup groups. ( 2.2.2 Group)
[Example]
Call Pickup Group 1
User Group 1
Extn. 100 Extn. 101
Call Pickup Group 2 Call Pickup Group 3
User Group 2
Extn. 102 Extn. 103
User Group 3
Extn. 104 Extn. 105
User Group 4
Extn. 106 Extn. 107
User Manual References
User Manual
1.3.3 Answering a Call Ringing at Another Telephone (Call Pickup)
68 Feature Guide

1.4.1.4 Hands-free Answerback
Description
A PT user with a speakerphone can talk to a caller without lifting the handset. If the user
receives a call in Hands-free Answerback mode, a hands-free conversation is established in
the following method:
Type Answering Method
Intercom Call Established immediately after a beep tone at the called extension
and the caller hears a confirmation tone.
Trunk Call* Established after a specified number of rings, a called extension
hears a beep tone.
*: Including a call from an extension that placed a trunk call on a consultation hold.
Conditions
• Hands-free Answerback applies to:
Intercom calls and trunk calls, including calls directed to an incoming call distribution group
in UCD or Priority Hunting distribution method. ( 1.2.2.2 Group Call Distribution)
• Hands-free Answerback for Trunk Calls
System programming is required to use this feature.
• Secret Monitor
The beep tone which the called party hears before answering can be eliminated through
system programming.
• A lte rnat e Rece iving /Ca lling Mode (Rin g/Voice) Override
Hands-free Answerback overrides the Alternate Receiving mode preset on the telephone
and the Alternate Calling mode from the caller.
• Hands-free Answerback with Headset
The Hands-free Answerback feature can also be used with a headset.
1.4 Answering Features
Feature Guide References
1.5.3 Intercom Call
User Manual References
User Manual
1.3.2 Answering Hands-free (Hands-free Answerback)
Feature Guide 69

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.1 Predialling
Description
A display PT user can check and correct the number to be dialled on-hook. The call will be
initiated after going off-hook.
Conditions
• Storing the Predialled Number in the Personal Speed Dialling
The predialled number can be stored in the Personal Speed Dialling by pressing the AUTO
DIAL/STORE button. ( 1.6.1.5 Speed Dialling—Personal/System) In this case, the
extension will enter into the personal programming mode automatically so that a name can
be assigned for the stored number.
User Manual References
User Manual
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
70 Feature Guide

1.5.2 Automatic Extension Release
Description
After going off-hook, if an extension user fails to dial any digits within a preprogrammed time
period, the user will hear reorder tone. This operation applies to intercom calls only.
This feature is also known as Automatic Station Release.
Conditions
• A PT/PS user hears reorder tone for a preprogrammed time period, and then the PT/PS
goes back to the idle status automatically. Ho wever , an SLT user will just hear reorder tone
until he goes on-hook.
• This feature works in one of the following cases:
When making an intercom call
a) The first digit has not been dialled within a preprogrammed time period.
b) After a digit is dialled, if subsequent digits are not dialled within a preprogrammed time
period.
1.5 Making Call Features
Feature Guide 71

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.3 Intercom Call
Description
An extension user can call another extension user.
Conditions
• Extension Number/Name Assignment
Extension numbers ( Extension Number [003]) and names ( Extension Name [004])
are assigned to all extensions. The assigned number and name are shown on display PTs
during intercom calls.
• DSS Button
It is possible to access another extension with one-touch by pressing the corresponding
Direct Station Selection (DSS) button. A flexible button can be customised as a DSS
button.
• Call Directory—Extension Dialling
Display PT users can make a call by selecting stored names on the display.
• Alternate Receiving —Ring/Voice
A PT user can select to receive intercom calls by ring tone or by voice, through personal
programming (Alternate Receiving—Ring/V oice). If a user selects voice-calling, the calling
party talks to the user immediately after a confirmation tone. Denying voice-calling can
also be selected.
• Alternate Calling—Ring/Voice
A caller can change the called party’s preset call receiving method (ring tone or voice). By
doing so, ring-calling is switched to voice-calling, or vice versa, at the called party. The
called party may deny voice-calling.
• Tone after Dialling
After dialling an extension number, a user will hear one of the following:
Type Description
Ringback Tone Indicates the called party is being called.
Confirmation Tone Indicates the called party has set voice-calling.
Busy Tone Indicates the called party is busy.
DND Tone Indicates the called party has set DND.
Feature Guide References
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.1 Basic Calling
1.2.6 Alternating the Calling Method (Alternate Calling—Ring/Voice)
1.11.2 Using the Directories
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
72 Feature Guide

1.5.4 Trunk Call Features
1.5.4.1 Trunk Call Features—SUMMARY
Description
An extension user can use the following features when making a trunk call:
Feature Description Details in
1.5 Making Call Features
Emergency Call A user can dial the preprogrammed emergency
numbers regardless of the restrictions imposed
on the extension.
Account Code
Entry
Pulse to Tone
Conversion
Pause Insertion A user can insert a preprogrammed Pause time
A user can enter an account code to identify
outgoing calls for accounting and billing
purposes.
A user can temporarily convert the Pulse mode
to DTMF mode to access special services.
into a dialling number by pressing the PAUSE
button, or it is automatically inserted between
the user-dialled code (e.g., Host PBX Access
code or Special Carrier Access code) and the
following digits.
• 1.5.4.2 Emergency
Call
• 1.5.4.3 Account Co de
Entry
• 1.5.4.4 Dial Type
Selection
• 1.5.4.6 Pause
Insertion
• 1.5.4.7 Host PBX
Access Code (Access
Code to the Telephone
Company from a Host
PBX)
• 1.5.4.8 Special
Carrier Access Code
Feature Guide 73

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.4.2 Emergency Call
Description
An extension user can dial the preprogrammed emergency numbers ( Emergency Number
[304]) after seizing a trunk regardless of the restrictions imposed on the extension.
Conditions
• A specified number of emergency numbers can be stored (some may have default v alues).
• Emergency numbers may be called even when:
– in Account Code—Forced mode ( 1.5.4.3 Account Code Entry)
– in any TRS/Barring levels ( 1.8.1 Toll Restriction (TRS)/Call Barring (Barring))
– after the preprogrammed call charge limit is reached ( 1.8.2 Budget
Management)
– in Extension Lock ( 1.8.3 Extension Lock)
• CLIP Number Notification (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200 only)
When dialling an emergency number, the preassigned CLIP number for the extension will
be sent as a location identification number. ( 1.20.1.2 Calling/Connected Line
Identification Presentati on (CLI P/COL P) )
The CLIP number assigned to the extension will be sent regardless of the settings such
as CLIR or CLIP number assigned to an ISDN port to be used. This feature is only
available when using a PRI (PRI23) line, with E911 compatible services.
74 Feature Guide

1.5.4.3 Account Code Entry
Description
An account code is used to identify outgoing trunk calls for accounting and billing purposes.
The account code is appended to the SMDR call record. Therefore, for example, the firm uses
an account code for each client so that the firm can determine what calls were made for the
client, and can submit a bill to the client according to the client’s account code on the SMDR
call record.
There are two methods of entering account codes as follows:
One of the methods is selected for each extension on a COS basis ( Account Code Mode
[508]).
Mode Description
Option A user can enter an account code if needed at any time desired.
1.5 Making Call Features
Forced
Conditions
• An account code can be stored into Memory Dialling (e.g., One-touch Dialling).
• Account Button
A flexible button can be customised as the Account button. The Account button is used in
place of the feature number for entering an account code. This button is useful because it
can be used at any time, while the feature number entry is allowed only when hearing a
dial tone before seizing a trunk.
• Account code entry after receiving a disconnection signal from a trunk must be done while
hearing reorder tone. Otherwise the SMDR call record is output and entry becomes
impossible afterwards.
• If the account code is entered more than once, the code entered last is printed out in the
SMDR.
• Even in Forced mode, emergency numbers can be dialled out without an account code.
( 1.5.4.2 Emergency Call)
• PT users can also enter an account code for incoming trunk calls during a conversation.
• Verified Code Entry
To identify who made a trunk call for accounting and billing purpose, a verified code is
used. This code can be used at any extension. ( 1.8.6 Verified Code Entry)
A user must always enter an account code before seizing a trunk so as
not to forget enteri ng the code.
Feature Guide References
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
1.25.1 Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR)
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.1 Basic Calling
Feature Guide 75

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.4.4 Dial Type Selection
Description
The dialling mode (rotary or tone) can be selected for each analogue trunk through system
programming ( LCOT Dialling Mode [410]) regardless of originating extension (under
contract with the telephone company).
There are the following modes:
Mode Description
DTMF (Dual Tone
Multi-Frequency)
Pulse Dial (Rotary) The dialling signal from an extension is converted to rotary dialling.
Conditions
• Pulse to Tone Conversion
It is possible f or an extension u se r t o t emp orarily convert the Pulse mo de t o D TMF m ode
so that the user can access special services such as computer-accessed long distance
calling or voice mail services. To convert to the DTMF mode, wait for a preprogrammed
time period (Default: 5 seconds) after the trunk is connected, or press . This feature
works only on trunks set to Pulse mode. DTMF mode cannot be changed to Pulse mode.
• It is possible to select a pulse rate for the trunk port which has been set to Pulse mode (
LCOT Pulse Rate [411]). There are two pulse rates: Low (10 pps) and High (20 pps).
• It is possible to assign the minimum duration of the DTMF signal sent to the trunk port
which has been set to DTMF mode ( LCOT DTMF Minimum Duration [412]).
The dialling signal from an extension is converted to tone dialling.
DTMF signals are transmitted to the trunk.
Rotary pulses are transmitted to the trunk.
76 Feature Guide

1.5.4.5 Reverse Circuit
Description
The circuit in the PBX can detect the reverse signal from the telephone company when an
extension user is trying to make a trunk call. This detects the start (a called party goes offhook) and end (the called party goes on-hook) of an outgoing trunk call. When an trunk call is
received, the circuit can also detect the reverse signal after an outside caller goes on-hook.
The duration of call can be verified on SMDR using this feature ( 1.25.1 Station Message
Detail Recording (SMDR)).
It is possible to select whether the PBX detects the reverse signal for outgoing trunk calls only,
or for both outgoing and incoming trunk calls, or for no trunk call (disable the detection) through
system programming ( LCOT Reverse Circuit [415]).
1.5 Making Call Features
Feature Guide 77

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.4.6 Pause Insertion
Description
A preprogrammed Pause time ( LCOT Pause Time [416]) will be inserted manually or
automatically.
Manual Insertion: Pressing the PAUSE button.
Automatic Pa use In sertion: A pause will be automatically inserted between the user-dialled
codes below and the following digits.
a) Host PBX Access code ( 1.5.4.7 Host PBX Access Code (Access Code to the
Telephone Company from a Host PBX))
b) Special Carrier Access code ( 1.5.4.8 Special Carrier Access Code)
c) Second Dial Tone Waiting code
Conditions
• The Pause time is programmable for each trunk.
• Pause can be stored in Memory Dialling.
• Pressing the P AUSE button while dialling a number inserts a pause for a preprogrammed
time period.
• When a preprogrammed Second Dial Tone Waiting code is dialled after seizing a trunk,
pauses are inserted a preprogrammed number of times after the code.
78 Feature Guide

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.4.7 Host PBX Access Code (Access Code to the Telephone
Company from a Host PBX)
Description
This PBX can be installed behind an existing host PBX. This is performed by connecting
extension ports of the host PBX to trunk ports of this PBX. A Host PBX Access code assigned
through system programming ( Host PBX Access Code [471]) is required to access the
telephone company from the host PBX. The T runk Access number of the host PBX should be
stored as a Host PBX Access code on a trunk group of this PBX basis.
A preprogrammed Pause time ( LCOT Pause Time [416]) will be automatically inserted
between the user-dialled Host PBX Access code and the following digits. ( 1.5.4.6 Pause
Insertion)
[Example]
Telephone Company
Host PBX
Access Code: 0
Host PBX
Idle Line
Access No.: 9
TRG1
PBX
Dials "9-0-01-23-4567".
Idle Line
Access No.
Telephone No.
Host PBX
Access Code
Outside Party
(01-23-4567)
Extn. 101 Extn. 102
Dials "0-01-23-4567".
Host PBX
Access Code
Dials "9-101".
Idle Line
Access No.
Extn. No.
of the Host PBX
Telephone
No.
Note: "0" should be assigned as a Host PBX Access code for trunk group (TRG) 1 of this PBX.
Feature Guide 79

1.5 Making Call Features
Conditions
• TRS/Barring
TRS/Barring checks only the dialled telephone number excluding the Host PBX Access
code when accessing the telephone company through the host PBX. ( 1.8.1 Toll
Restriction (TRS)/Call Barring (Barring))
• SMDR
The dialled number including the Host PBX Access code can be recorded on the SMDR
when accessing the telephone company through the host PBX.
• To record on the SMDR only long distance calls (not local calls) originated via the specific
trunk group, assign the long distance call code as a Host PBX Access code to the trunk
group.
Feature Guide References
1.25.1 Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR)
80 Feature Guide

1.5.4.8 Special Carrier Access Code
Description
If the PBX has access to multiple telephone companies, a Special Carrier Access code
assigned through system programming ( Special Carrier Access Code [303]) is required
every time when a trunk call is made.
A preprogrammed Pause time ( LCOT Pause Time [416]) will be automatically inserted
between the user-dialled Special Carrier Access code and the following digits. ( 1.5.4.6
Pause Insertion)
Conditions
• TRS/Barring
TRS/Barring checks only the dialled telephone number excluding the Special Carrier
Access code. ( 1.8.1 Toll Restriction (TRS)/Call Barring (Barring))
• If this PBX is installed behind an existing host PBX:
A Special Carrier Access code and a Host PBX Access code should be assigned
separately: these codes cannot be assigned together as one code. ( 1.5.4.7 Host PBX
Access Code (Access Code to the Telephone Company from a Host PBX))
1.5 Making Call Features
Feature Guide 81

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.5 Seizing a Line Features
1.5.5.1 Seizing a Line Features —SU MMA RY
Description
An extension user can select the line seized for making calls by the following methods:
Feature Description Details in
Line Preference—
Outgoing
Trunk Access A user can select the Trunk Access method
A user can select the line seized when going
off-hook.
every time he makes a trunk call.
• 1.5.5.2 Line
Preference—
Outgoing
• 1.5.5.3 Trunk
Access
82 Feature Guide

1.5.5.2 Line Prefer en ce —O utgoing
Description
A PT user can select the outgoing line he prefers to originate calls on, from the following line
preferences, through personal programming (Preferred Line Assignment—Outgoing):
Feature Description
Intercom When an extension user goes off-hook, an extension line is selected
automatically.
Idle Line When an extension user goes off-hook, an idle trunk is selected
automatically from the assigned trunk groups.
No Line When an extension user goes off-hook, no line is selected. He must
select the desired line to make a call.
Prime Line When an extension user goes off-hook, the preset line is selected
automatically. A prime line can be selected from the Line Access
buttons: S-CO, G-CO, L-CO, ICD Group.
1.5 Making Call Features
Conditions
• Line Preference Override
A user can override the preset Line Preference temporarily by pressing the desired Line
Access button or Memory Dialling button (e.g., One-touch Dialling) before going off-hook.
• To select Idle Line Preference, the trunk groups available to the extension should be
progra mmed on a COS b asis ( Trunk Group Numb er [500 ]). A lso trun k grou ps a vai lab le
for Idle Line Access should be assigned ( Idle Line Access (Local Access) [103]).
User Manual References
User Manual
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
Feature Guide 83

1.5 Making Call Features
1.5.5.3 Trunk Access
Description
There are the following features to access a trunk.
Feature Description Accessing method
Idle Line
Access (Local
Access)
Trunk Group
Access
S-CO Line
Access
Conditions
• COS programming determines the trunk groups available for making calls ( T runk Group
Number [500]).
• Trunk numbers can be referred on a trunk port basis ( LCOT/BRI Trunk Number
Reference [409]).
• Button Assignment
A flexible button can be customised as a G-CO, L-CO, or S-CO button as follows:
Selects an idle trunk
automatically from the assigned
trunk groups.
Selects an idle trunk from the
corresponding trunk group.
Selects the desired trunk directly. Dial the S-CO Line Access number and
Type Assignable parameter
Loop-CO (L-CO)
Dial the Idle Line Access number. Or
press a L-CO button.
Dial the Trunk Group Access number
and a trunk group number. Or press a
G-CO button.
the trunk number. Or press the S-CO
button.
No parameter (All assigned trunk groups
through system programming are applied.)
• Direct Trunk Access
• Group Hunting Order for Idle Line Access
84 Feature Guide
Group-CO (G-CO) A trunk group is assigned.
Single-CO (S-CO) A specified trunk is assigned.
It is possible to assign trunks in the following ways:
– The same trunk to the S-CO button and to a G-CO button
– The same trunk group to more than one G-CO button
– More than one L-CO button
Dialling the T runk Access number selects a CO button according to the priority: S-CO
G-CO L-CO
By pressing an idle CO button, it automatically switches on the hands-free operation mode
and allows a user to use On-hook Dialling. The user need not press the SP-PHONE
button, MONITOR button, or lift the handset.
An idle trunk is selected from the trunk groups assigned for Idle Line Access. If multiple
trunk groups are available, the trunk group hunting sequence can be determined through
system programming.

• Trunk Hunting Order for Idle Line Access and Trunk Group Access
The trunk hunting sequence in a trunk group; from lowest numbered trunk, from highest
numbered trunk or rotation, can be determined through system programming.
• A company name or customer name can be assigned on a trunk port basis ( LCOT/BRI
Trunk Name [401]) so that the operator or extension user can view the destination which
the caller is trying to reach before answering.
• It is possible to identify the trunk port that has a trunk connected to it ( LCOT/BRI Trunk
Connection [400]). This prevents extension users from originating a call to a trunk which
is not connected.
Feature Guide References
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.1 Basic Calling
1.5 Making Call Features
Feature Guide 85

1.6 Memory Dialling Features
1.6 Memory Dialling Features
1.6.1 Memory Dialling Features
1.6.1.1 Memory Dialling Features—SUMMARY
Description
An extension user can store frequently dialled numbers in the PBX extension data and/or the
PBX system data. A stored number is dialled automatically with a simple operation.
1. Features
Feature Storing Method Details in
One-touch Dialling • Personal Programming
• System Programming
(PC Programming only)
KX-T7710 One-touch
Dialling (KX-TDA100/
KX-TDA200 only)
Last Number Redial
(Outgoing Call Log)
Speed
Dialling
Quick Dialling System Programming
Hot Line • Personal Programming
Personal • Personal Programming
System System Programming
System Programming
(PC Programming only)
The last dialled telephone number(s) is
automatically stored.
• Personal Operation with the Feature
Number
• System Programming
(PC Programming only)
(PC Programming only)
• Personal Operation with the Feature
Number
• System Programming
(PC Programming only)
• 1.6.1.2 Onetouch Dialling
• 1.6.1.3 KXT7710 One-touch
Dialling (KXTDA100/KXTDA200 only)
• 1.6.1.4 Last
Number Redial
• 1.6.1.5 Speed
Dialling—
Personal/System
• 1.6.1.6 Quick
Dialling
• 1.6.1.7 Hot Line
86 Feature Guide
Incoming Call Log Incoming call information is automatically
stored.
• 1.17.2 Incoming
Call Log

2. Valid Input
.
1.6 Memory Dialling Features
Input
Display while
Entering
Description
0–9/ /# 0–9/ /# Stores the digits, and #.
PAUSE (Pause) P Stores a pause by pressing the PAUSE button.
( 1.5.4.6 Pause Insertion)
FLASH/RECALL
(Hooking)*
F Stores a flash/recall signal (EFA mode) by
pressing the FLASH/RECALL button at the
beginning of the number. ( 1.10.7 External
Feature Access (EFA))
INTERCOM
(Secret)*
[/] Conceals all or part of the number by pressing the
INTERCOM button at the beginning and at the
end of the number to be concealed. It is
programmable whether the concealed part will
appear on the SMDR.
TRANSFER
(Transfer)*
T S tores a transfer command by pressing the
TRANSFER button at the beginning of the
number (u se d o n ly for a One-to uc h D i al li ng ). (
1.11.1 Call Transfer)
[Example] Storing "T + 305"= Transferring a call
to extension 305.
*: Available only when in the system/personal programming mode
[Example]
When storing the number "9-123-456-7890" and concealing the telephone number "123456-7890",
Notes
Conditions
• Trunk Access by Memory Dialling
A specific Trunk Access number can be stored with the telephone number in Memory
Dialling. However, if Memory Dialling is done after selecting a trunk, the stored Trunk
Access number is ignored and the telephone number is sent using the selected trunk.
Enter
INTERCOM9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 INTERCOM
• It is possible to store a Memory Dialling feature number in the beginning of the
Memory Dialli ng numbers.
• It is possible to store several feature numbers in one Memory Dialling location.
Feature Guide 87

1.6 Memory Dialling Features
1.6.1.2 One-touc h Dialling
Description
A PT user can access a person or feature by one-touch. This is activated by storing the number
(e.g., extension number, telephone number, or f eature number) in a One-touch Dialling button.
Conditions
• One-touch Dialling Button
A flexible button can be customised as a One-touch Dialling button.
• Full One-touch Dialling
There is no need to go off-hook before pressing the One-touch Dialling button.
Feature Guide References
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.2 Easy Dialling
88 Feature Guide

1.6 Memory Dialling Features
1.6.1.3 KX-T7710 One-touch Dialling (KX-TDA100/KX-TDA200
only)
Description
The Message button and One-touch buttons on all KX-T7710 telephones connected to the
PBX can be customised at once through system programming. The same extension number,
telephone number, or feature number will be assigned to the same buttons on each KX-T7710,
useful for hotel room extensions or similar applications.
[Programming Example]
Button Desired Number
MESSAGE
One-touch Dial 01 100 (Front Desk)
One-touch Dial 02
One-touch Dial 03 102 (Restaurant)
::
The MESSAGE button is programmed by default to call back a caller who left a message
waiting indication, however, the MESSAGE button can be programmed to perform other
features. The eight One-touch buttons have no default setting.
702 (Message Waiting [To Call Back])
7601 (Wake-up Call)
Conditions
• The KX-T7710 has two modes, NORMAL mode and PBX mode, selected by a switch on
the telephone. This feature is available only when the KX-T7710 is in the PBX mode.
• This feature is available while hearing a dial tone.
• Please refer to the Quick Reference Guide of the KX-T7710 for additional information.
Feature Guide References
1.19.2 Flexible Buttons
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.2 Easy Dialling
Feature Guide 89

1.6 Memory Dialling Features
1.6.1.4 Last Number Redial
Description
Every extension automatically saves the last external telephone number dialled to allow the
same number to be dialled again.
Automatic Redial:
If Last Number Redial is performed in hands-free mode and the called party is busy, redialling
will be automatically retried a preprogrammed number of times ( Automatic Redial Repeat
Times [205]) at preprogrammed intervals ( Automatic Redial Interval [206]). The Redial Call
No-answer Ring Duration time is programmable.
This feature is available only on certain PT models which have the SP-PHONE button.
Outgoing Call Log:
The last five dialled numbers are automatically stored at each extension. A display PT user can
redial easily any of the stored numbers.
Conditions
• The memorised telephone number is replaced by a new one.
• If any dialling operation is done or an incoming call is answered during Automatic Redial,
Automatic Redial is cancelled.
• Automatic Redial is not available for some countries/areas when using an analogue trunk.
• Interrupt Redial
When the called party or the seized trunk is busy , it is possible to press the REDIAL button
continuously until the called party or the trunk becomes idle. There is no need to go offhook, before pressing the REDIAL button.
• Outgoing Call Log Display by REDIAL Button
Pressing the REDIAL button on a display DPT while on-hook can display the Outgoing Call
Log. System programming is required for this operation.
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.3 Redial
1.11.1 Using the Call Log
90 Feature Guide

1.6.1.5 Speed Dialling—Personal/System
Description
An extension user can make calls using abbreviated dialling for frequently dialled numbers
which are stored in the PBX extension data, or the PBX system data ( System Speed Dialling
Number [001]).
Personal Speed Dialling is also known as Station Speed Dialling.
Conditions
[General]
• Any number (e.g., telephone number, feature number) can be stored in a speed dialling
number. A name can be assigned to each Personal Speed Dialling number through
personal programming, and System Speed Dialling number ( System Speed Dialling
Name [002]).
• Call Directory—Speed Dialling
Display PT users can make a call by selecting stored names on the display.
1.6 Memory Dialling Features
[Personal Speed Dialling]
• Personal Speed Dialling Display Lock
An extension user can lock the Personal Speed Dialling number display to prevent other
users from viewing the number. In this case, the Incoming and Outgoing Call Log
information displays are also locked. An extension personal identification number (PIN) is
required to use this feature. ( 1.26.1 Extension Personal Identification Number (PIN))
[System Speed Dialling]
• TRS/Barring Override by System Speed Dialling
It is possible to override the TRS/Barring using the System Speed Dialling ( TRS/
Barring Level for System Speed Dialling [509]). ( 1.8.1 Toll Restriction (TRS)/Call
Barring (Barring))
• System Speed Dialling Display by AUTO DIAL/STORE Button
Pressing the AUTO DIAL/STORE button on a display DPT while on-hook can display the
System Speed Dialling Directory.
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.2 Easy Dialling
1.11.1 Using the Call Log
1.11.2 Using the Directories
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
3.3 Customising Your System (System Programming)
Feature Guide 91

1.6 Memory Dialling Features
1.6.1.6 Quick Dialling
Description
An extension user can access a person or feature easily. This is enabled by storing the number
(e.g., extension number, telephone number or feature number) for Quick Dialling.
Conditions
• Quick Dialling is convenient in the following cases:
– Room service calls in a hotel
– Calling another branch via the public network. The extension user needs to dial
only the extension number of another branch.
• Quick Dialling numbers follow the flexible numbering plan.
( 2.3.5 Flexible Numbering/Fixed Numbering)
• The storing example is as follows:
Location No. Quick Dialling No. Desired Number
Quick Dialling 01 110 9110 (Trunk Call)
Quick Dialling 02 5 3016 (Room Service)
Quick Dialling 03 2011 90123456789 (Another Branch)
:: :
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.2 Easy Dialling
92 Feature Guide

1.6.1.7 Hot Line
Description
An extension user can make an outgoing call by only going off-hook, if the user has previously
stored the telephone number or the extension number.
If the Hot Line feature is set and the user goes off-hook, a dial tone is generated for a specified
Waiting time assigned through system programming ( Hot Line Waiting Time [204]) and then
dialling starts. During the Waiting time the user can dial another party , o verriding the Hot Line
feature.
This feature is also known as Pickup Dialling.
Conditions
• Capable Telephone
PT, SLT, T1-OPX, and PS
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.2 Easy Dialling
1.6 Memory Dialling Features
Feature Guide 93

1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
1.7.1 Automatic Callback Busy (Camp-on)
Description
If the line is busy when a call is made, callback ringing will inform the caller when the line
becomes free using this feature. After the extension answers the callback ringing, the dialled
number is automatically redialled.
Conditions
• If the callback ringing is not answered within 10 seconds, the callback is cancelled.
• If the extension hears a busy tone before dialling the telephone number, only the trunk or
trunk group is reserved. After answering the callback ringing, the extension should dial the
telephone number.
• An extension can set only one Automatic Callback Busy. The last setting is effective.
• Multiple extension users can set this feature to one trunk simultaneously.
However, a maximum of four extension users can set this feature to one extension.
• The priority of the callback is the setting order.
• This feature cannot be used for calls to a VPS or an ISDN extension.
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.4 When the Dialled Line is Busy or There is No Answer
94 Feature Guide

1.7.2 Executive Busy Override
Description
Allows an extension user to interrupt an existing call to establish a three-party conference call.
Executive Busy Override Deny:
It is possible for extension users to prevent their calls from being intercepted by another
extension user.
Conditions
• COS programming determines extension users who can use the Executive Busy Override
( Executive Busy Override [505]) and set the Executive Busy Override Deny mode (
Executive Busy Override Deny [506]).
• This feature does not work when the busy extension is in one of the following conditions:
a) Executive Busy Override Deny or Data Line Security ( 1.10.5 Data Line Security)
has been set.
b) While being monitored by another extension ( 1.7.3 Call Monitor).
c) While receiving OHCA ( 1.7.4.3 Off-hook Call Announcement (OHCA)) or Whisper
OHCA ( 1.7.4.4 Whisper OHCA).
d) During a Conference call ( 1.13.1 Conference Features).
e) During a doorphone call ( 1.16.1 Doorphone Call).
f) While Live Call Screening (LCS) or T wo-way Record is activated ( 1.23.3 V oice Mail
DPT (Digital) Integration).
g) During Consultation Hold.
1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
(Consultation Hold: Allows an extension user to place a call on hold temporarily to
perform Call Transfer, Conference, or Call Splitting.)
• This feature is not available for a trunk-to-trunk call via DISA.
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.4 When the Dialled Line is Busy or There is No Answer
1.7.7 Preventing Other People from Joining Your Conversation (Executive Busy Override
Deny)
Feature Guide 95

1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
1.7.3 Call Monitor
Description
Allows an extension user to listen to the busy extension user’s existing conversation. The user
can hear the conversation, but the user’s voice is not heard. If desired, interrupting the call to
establish a three-party conference call is available.
Conditions
• COS programming determines extension users who can use this feature.
• This feature is available only when the busy extension is in a conversation with another
extension or outside party.
• This feature does not work when the busy extension is in one of the following conditions:
a) Executive Busy Override Deny ( 1.7.2 Executive Busy Override) or Data Line
Security ( 1.10.5 Data Line Security) has been set.
b) While receiving OHCA ( 1.7.4.3 Off-hook Call Announcement (OHCA)) or Whisper
OHCA ( 1.7.4.4 Whisper O HCA).
c) During a Conference call ( 1.13.1 Conference Features).
d) During a doorphone call ( 1.16.1 Doorphone Call).
e) While Live Call Screening (LCS) or T wo-way Record is activated ( 1.23.3 V oice Mail
DPT (Digital) Integration).
f) During Consultation Hold.
(Consultation Hold: Allows an extension user to place a call on hold temporarily to
perform Call Transfer, Conference, or Call Splitting.)
• This feature stops when the busy extension user presses the following buttons during a
conversation ( 1.19.1 Fixed Buttons and 1.19.2 Flexible Buttons):
– FLASH/RECALL button
– HOLD button
– TRANSFER button
– CONF (Conference) button
– DSS button
– EFA button
– Two-way Record button
– Two-way Transfer button
– One-touch Two-way Transfer button
– Voice Mail (VM) Transfer button
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.4 When the Dialled Line is Busy or There is No Answer
96 Feature Guide

1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
1.7.4 Second Call Notification to Busy Extension
1.7.4.1 Secon d Call Notification to Busy Extension — SUMMARY
Description
When attempting to call a busy extension (ringing or having a conversation), an extension user
can send call waiting indication to the busy extension (Call Waiting). The notification receiving
method depends on the called extension’s personal setting and the telephone type:
Receiving Method
Call Waiting Tone Sends the Call Waiting tone to the busy
Off-hook Call
Announcement
(OHCA)
Whisper OHCA Give a message to the busy extension through
Conditions
• Each extension user can choose to receive Call Waiting tone, OHCA, Whisper OHCA, or
none of these.
• OHCA and Whisper OHCA are enabled or disabled by the COS of the calling extension.
• OHCA and Whisper OHCA do not work for some telephone types. In such cases, the Call
Waiting tone will be sent to the called extension.
Notification
Calling
Extension’s
OHCA COS
Mode
Description Details in
• 1.7.4.2 Call
extension.
Talk with the busy extension using the built-in
speaker and microphone of the called extension
while the existing call is made using the handset.
the handset.
Called Extension’s Call Waiting Mode
OFF ON
Cancel Call Waiting Tone OHCA Whisper OHCA
Waiting Tone
• 1.7.4.3 Offhook Call
Announcement
(OHCA)
• 1.7.4.4
Whisper OHCA
Disable C al l Waiting
disabled
Enable Call Waiting
disabled
• The notification receiving methods (Call Waiting tone, OHCA, and Whisper OHCA) are
available when the called extension is having a conversation with other party. If not, the
calling extension will be kept waiting until the called extension becomes available to
receive the notification. Even while waiting, the calling extension will hear a ringback tone.
• If none of these notification receiving methods, Call Waiting tone, OHCA, or Whisper
OHCA is set at the called party, the caller will hear reorder tone.
Call Waiting tone Call Waiting
tone
Call Waiting tone OHCA
(or Call Waiting
tone)
Call Waiting tone
Whisper OHCA
(or Call Waiting
tone)
Feature Guide 97

1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
Feature Guide References
1.1.3.3 Call Waiting
User Manual References
User Manual
1.2.4 When the Dialled Line is Busy or There is No Answer
98 Feature Guide

1.7.4.2 Call Waiting Tone
Description
When an extension user attempts to call a busy extension (ringing or having a conversation),
the Call Waiting tone can be sent to the called extension to let him know another call is waiting.
Conditions
• This feature only works if the called extension has activated Call Waiting. If it is activated,
the calling extension will hear a ringback tone.
• Call Waiting tone can be selected (Tone 1 or Tone 2) through personal programming (Call
Waiting Tone Type Selection).
User Manual References
User Manual
3.1.2 Settings on the Programming Mode
1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
Feature Guide 99

1.7 Busy Line/Busy Party Features
1.7.4.3 Off-hook Call Announcement (OHCA)
Description
An extension user can talk with a busy extension through the built-in speaker and microphone
of the called party’s PT. If the existing call is using a handset, a second conversation is made
using the speakerphone and microphone so that the called extension can talk to both parties.
Conditions
• COS programming determines which extensions can use this feature.
• This feature is available when the called extension
– KX-T7625, KX-T7630, KX-T7633, KX-T7636
–KX-T7536
–KX-T7436
– KX-T7235 (except KX-T7235G/FR/SL/NE)
• If the KX-T7235G/FR/SL/NE are connected to the PBX, the OHCA feature for the
KX-T7235 should be disabled through system programming.
• The OHCA feature cannot be used in the following cases:
uses one of the following telephones:
(a) COS or called extension's telephone type is not available for this feature.
(b) The called extension (DPT) is connected to a PC (PC Console or PC Phone)
via the USB Module.
(c) The called extension (DPT) is in the Digital XDP connection.
The Call Waiting tone is sent to the called extension. ( 1.7.4.2 Call Waiting Tone)
• While an extension is receiving OHCA, if the extension user places the current trunk call
on hold or transfers the current intercom call or trunk call, OHCA will become disabled and
the calling extension will start to hear a ringback tone.
• While an extension is receiving OHCA, if the extension user places the current intercom
call on hold, the called extension can talk to the calling extension through the handset.
100 Feature Guide
 Loading...
Loading...