
OPEL
KADETT
Oct
Havnes
1984
to
L-
Oct
-
1991
rvice
and
petroi
r
-
Includes
Fault
Finding
and
MOT
Test
Check
Sections

a
For
the
car
driver...
n.---.-.
MANUAL
For
~~~~
&ng
~srsnrigjns.....'~ùy~k~
~Im~~popular~,
-and~Mkeawtmfrom
-~mm=-
-@ww~m-w
db~rmdrqmuywr~.
For
the
W
my
the
biker
motorbike-rider..
Wng
his
cycli
I
--
.
I
L'.
,,
-.,&r?


Contents
LIVING
Introduction
-
Acknowledgements
Safety First!
.-
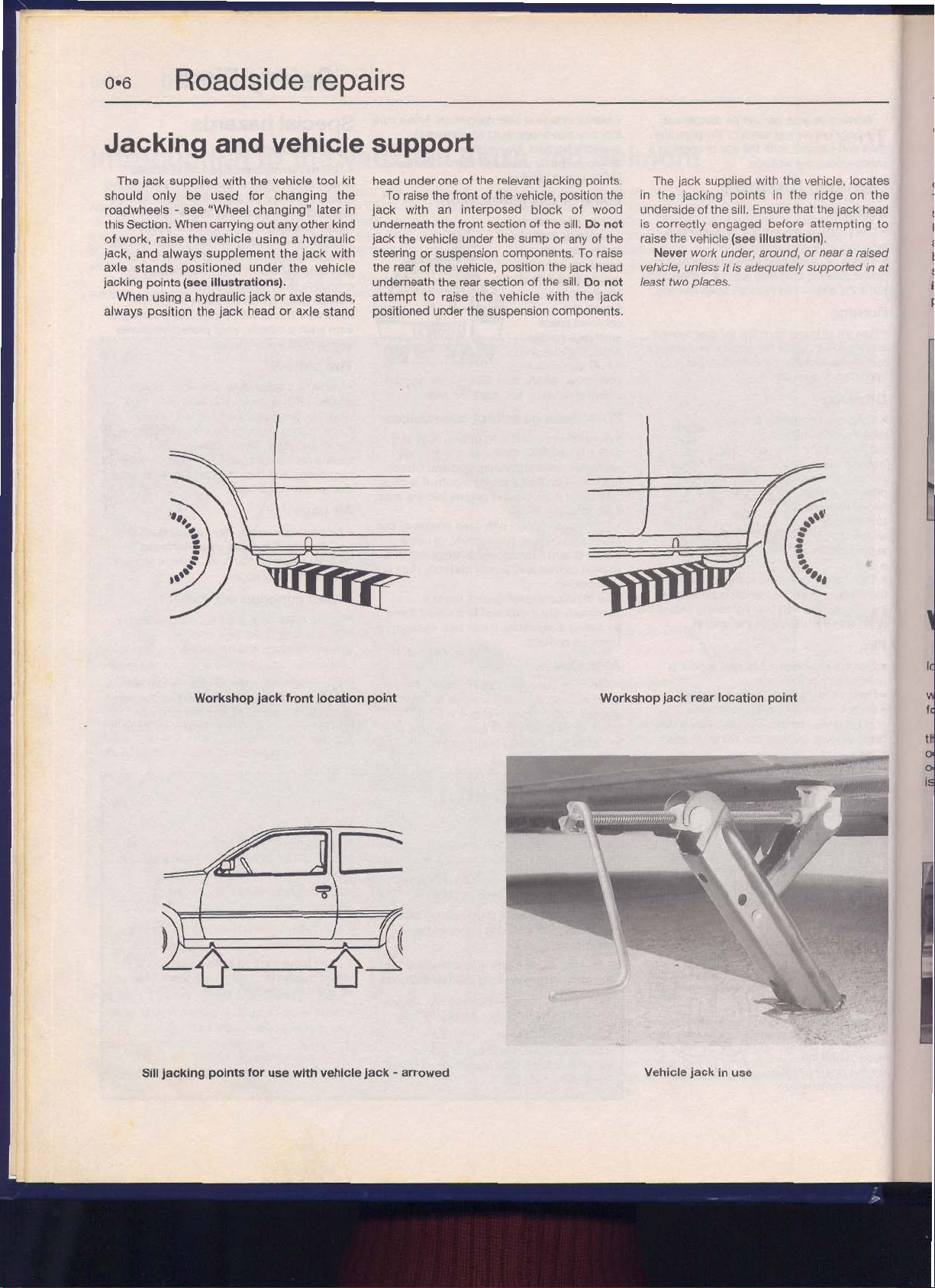
Roadside
Jaching
--
Tow!ng
-.
Wheel changing
Identify ing
-
Booster
-
WITH
to
the
--
-
Repairs
aiid vehicle
-
-
leaks
-.
hattery
(jump}
YOUR
Vauxhall
suppori
Astra
-- --
.-
.-
--
startinç
MAINTENANCE
Weekly
Introduction
-
Underbonnet
--
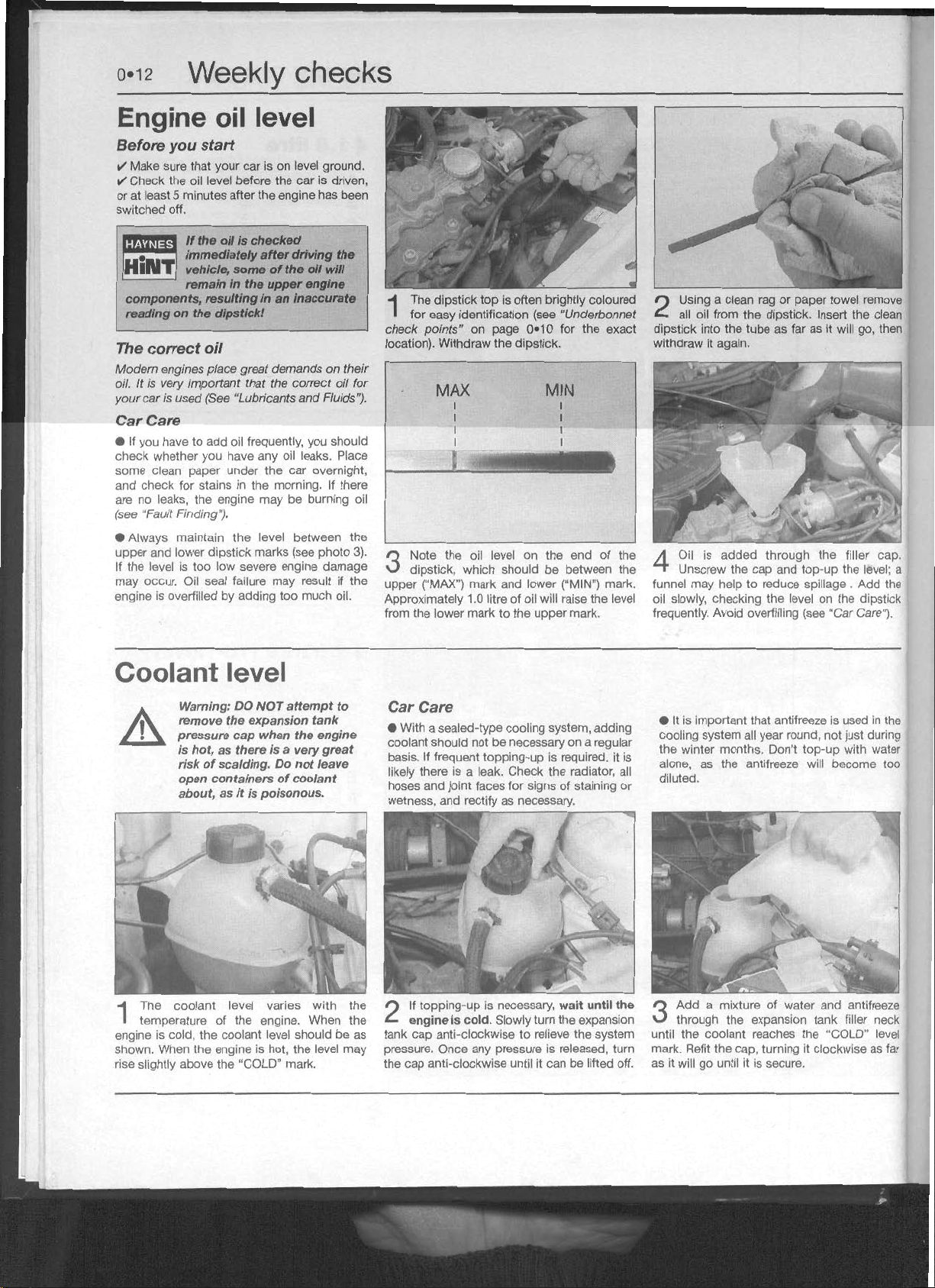
Engine oil levei
-. -.
Coolant
Screen
Brake
Power
Èkricalsystern
-.
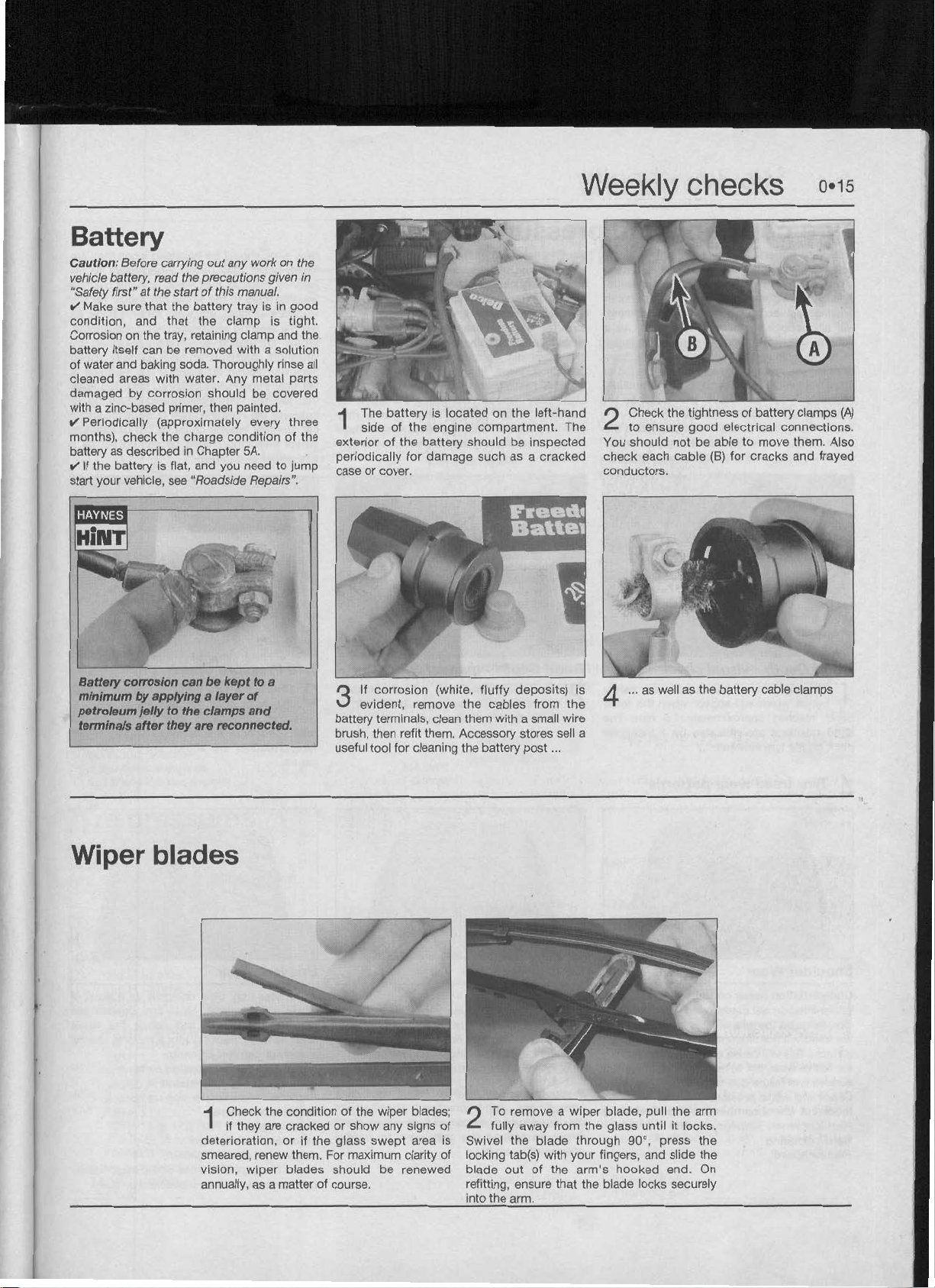
Battew
-.
Wiper blade
-
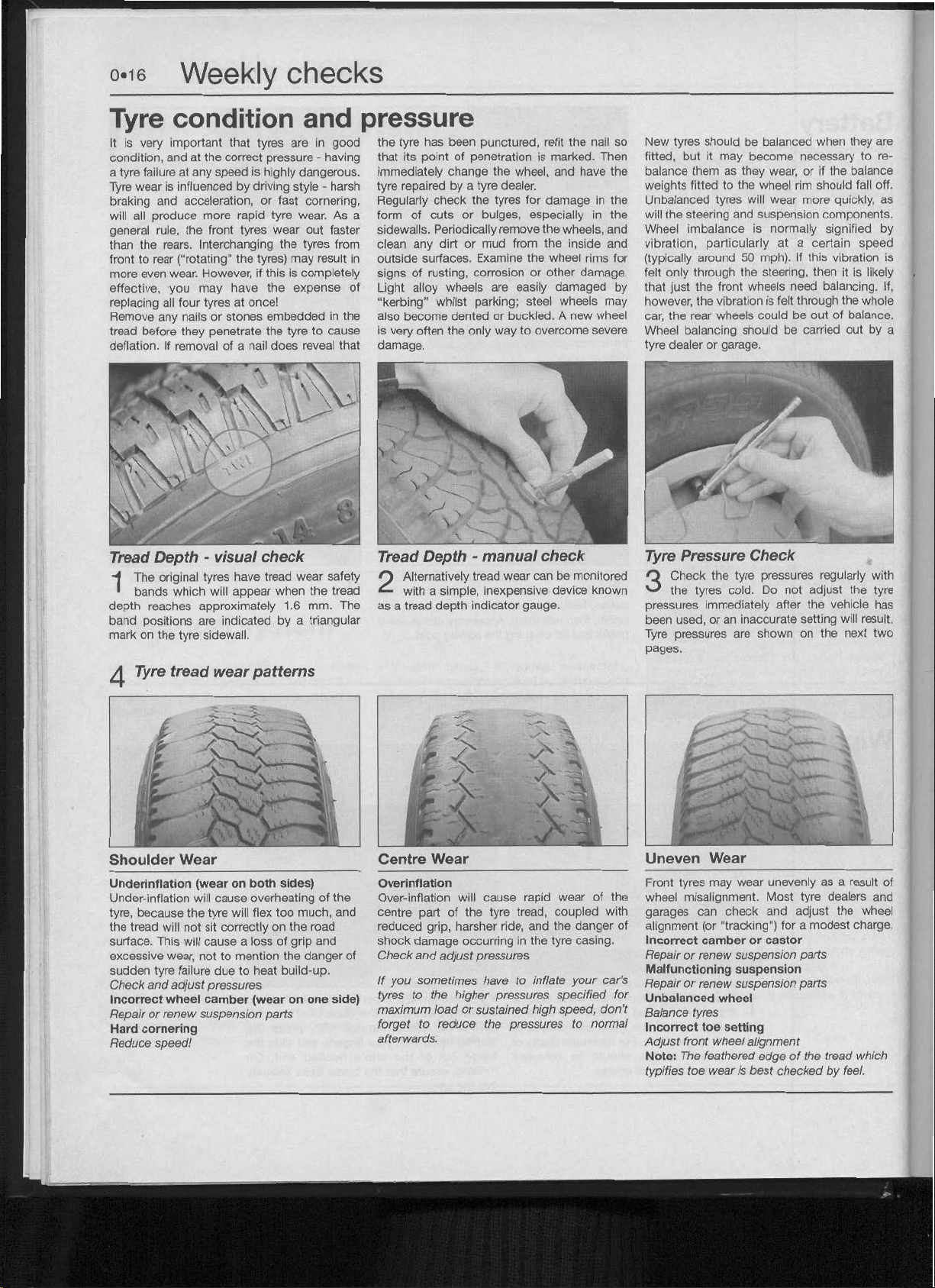
Tyre
Lubricants and
.-
Capacities
Tyre
-
checks
-
check
-
check
levei
check
.
v~asher
flurd level
-.
steering fl~id levei
-
cneck
-
condition
pressures
fluid leve1
check
check
-
and
fluids
--
. -.
.-
check
przçsure
points
-.
--
check
.-
check
-. .-
-. -.
check
-.
VAUXHALL
-.
-.
.- -.
-.
.-
--
ASTRA
-.
-.
.
Page
.
Page
Page
-.
.-
Page
Page
--
-.
Page
Page
--
--
.
--
--
.-
--
Page
Page
Page
--
Page
-
Page
Page
Page
-.
-
--
--
.
--
--
..
.
-
Page
.-
Paye O*t4
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
-
-
Page
-
.
--
-.
0*4
0*4
-
0-5
-
0*6
0*7
0*7
--
0-8
--
0.9
O*tO
O*~O
0*12
-
0.12
0.13
-
0.73
-
0414
0.15
0.15
0-16
--
0.17
-
0-17
..
0*17
.
Routine
Maintenarice schedule
-
Introductioii
hlaintenance
--
Servicing Specifcations
--
Maintenance
--
procedures
--
and
Servicing
--
-.
--
-.
-
-
-.
--
-
-
-
.
--
Page
-.
Page
Page
Page
1.1
.
1.7
--
i.8
1.19

REPAIRS & OVERHAUL
Contents
Engine
OHV
~~c-~ngine
DOHC
Cooling. heating
Fuel and exhaust system -carblGtor rnodels
Fuel
Starting and charging systems
-.
Contact breaker ignition
Electronic (breakerless) ignition systems
and
Associated
Engine
(1
6-valve)
and
exhaust systems -fuel injected rnodels Page
-.
Engine
-.
and
..........
..
-.
... -.-.-.....
ventilation systems
-
.
.-.
- -
system
-
-
Systems
...-.........
-
-
-.
-
....
..
.-.
-
-
-. . -....... -.......
-.
.....
Page
.....
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
-
Page
Transmission
Clutch
Manual transmission Page
Autornatic transmission
.
.
Driveshafts
Brakes
Brakrng
Suspension
system
...
......
and
Suspension
and
steering
-.
-
.
.- .
---
.........
-..
Page
Page
Page
Page
Body Equipment
Bodywork and fittings
Body
electrical
system
.....
....
. . --.
.
Page
Page
-
-
-. ....
.
---
2A.1
-
28.1
2C.1
3*1
4A*1
-.
48.1
5A.l
-
56.1
..
5C.1
7A.1
7B*l
8*1
9*1
10*1
lt*l
12.1
.
Wiring Diagrams
. .
-. .--.
REFERENCE
Dimensions and
Conversion Factors
.....
Buying
-
Vehicle identification
-.
spare
-
......
General Repair
Tools
and
ET
Test
Checks carried out
Checks carried out with the vehicle on the around
Checks carried out with the vehicle raised
Checks carried out
Fault Diagnosis
-
.-
..
Glossary
Index
....
....
weights
parts
-
....
...
---
numbers
~tocedures
----
......
-
..
........
Working Facilities
Checks
from
the
........
on
of
Technical Terms Page
driver's seat
-.
.
your vehicie's exhaust emission
-.-.-...
-
-
- - -.-
....
.-.
--
.........
system
.-...--.
..
Page
12i15
Page
Pase
Page
Page
-
-
- ------
......
.
........
Page
Page
Page
Page
Paqe
Page
Page
--
Page
REF*1
REF*2
REF.3
REF.3
REF.4
.
REF.5
REF*7
REF.7
REF.8
REF.9
REF*IO
REF.11
REF.18
Page
REF.23
.......
-
-..---











Chapter 1
Routine maintenance and servicing
Air cleaner filter element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Automatic transmission fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Battery check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Brake pad, caliper and disc check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Carburettor fuel inlet filter cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Clutch adjustment check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Driveshaft CV joint and gaiter check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Electrical system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Engine oil and filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Fluid level checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Fuel filter renewal - fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Fuel pump filter cleaning - carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Handbrake adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Headlamp aim check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Hinge and lock lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Hose and fluid leak check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Idle speed and mixture adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Ignition system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Manual transmission oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Rear brake shoe, wheel cylinder and drum check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Rear wheel bearing adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Roadwheel bolt tightness check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Tyre checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Vauxhall Astra/Belmont maintenance schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Wiper blade check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
The maintenance intervals in this manual are provided with the
assumption that you, not the dealer, will be carrying out the work.
These are the minimum maintenance intervals recommended by the
manufacturer for vehicles driven daily. If you wish to keep your vehicle
in peak condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these
procedures more often. We encourage frequent maintenance, because
it enhances the efficiency, performance and resale value of your
vehicle. If the vehicle is driven in dusty areas, used to tow a trailer, or
driven frequently at slow speeds (idling in traffic) or on short journeys,
more frequent maintenance intervals are recommended.
When the vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a factoryauthorised dealer service department, in order to preserve the factory
warranty.
1•1
Easy, suitable for
novice with little
experience
Fairly easy, suitable
for beginner with
some experience
Fairly difficult, suitable
for competent DIY
mechanic
Difficult, suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanic
Very difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Contents
1
1 Vauxhall Astra/Belmont maintenance schedule
1•2 Maintenance schedule
Every 9000 miles (15 000 km) or
6 months, whichever comes first
mm Renew the engine oil and filter - early (pre-1987) models
(Section 6)
Every 9000 miles (15 000 km) or
12 months, whichever comes first
mm Renew the engine oil and filter - later (1987-on) models
(Section 6)
mm Renew the spark plugs (Section 7)
mm Check and adjust the valve clearances - 1.2 litre models
(Chapter 2A)
mm Check all underbonnet and underbody components, pipes and
hoses for leaks (Section 8)
mm Check the condition of the auxiliary drivebelt, and renew if
necessary (Section 9)
mm Check the ignition system components and renew the contact
breaker points (Section 10)
mm Check idle speed and mixture adjustments (Section 11)
mm Clean the fuel pump filter (carburettor models) (Section 12)
mm Check the throttle cable adjustment (Chapter 4A or 4B)
mm Check the automatic transmission fluid level (Section 13)
mm Check the operation of the horn, all lights, and the wipers and
washers (Section 14)
mm Check the condition of the wiper blades (Section 15)
mm Check the tightness of the roadwheel bolts (Section 16)
mm Check the condition of the front, and rear (where fitted) brake
pads (renew if necessary), and the calipers and discs
(Section 17)
mm Check the rear wheel bearings adjustment (Section 18)
mm Check the handbrake adjustment (Section 19)
mm Check the driveshaft CV joints and gaiters for condition
(Section 20)
mm Lubricate locks and hinges (Section 21)
mm Check the exhaust system for condition and security
(Section 22)
mm Road test the vehicle (Section 23)
Every 2 years
(regardless of mileage)
In addition to all the relevant items listed previously, carry out the
following:
mm Renew the coolant (Section 32)
Every 36 000 miles (60 000 km) or
4 years, whichever comes first
In addition to all the relevant items listed previously, carry out the
following:
mm Renew the automatic transmission fluid (Section 33)
mm Renew the camshaft toothed belt -
1.3, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre 8-valve engines (Chapter 2B),
2.0 litre 16-valve engines (Chapter 2C)
Every 54 000 miles (90 000 km) or
3 years, whichever comes first
In addition to all the relevant items listed previously, carry out the
following:
mm Renew the braking system seals and hose (Chapter 9)
Every 18 000 miles (30 000 km) or
12 months, whichever comes first
In addition to all the items listed previously, carry out the following:
mm Renew the air cleaner filter element (Section 24)
mm Renew the fuel filter (fuel injection models) (Section 25)
mm Clean the carburettor fuel inlet filter (Section 26)
mm Check the manual transmission oil level (Section 27)
mm Check the clutch adjustment (Section 28)
mm Check the condition of the rear brake shoes (renew if
necessary), wheel cylinders and drums (Section 29)
mm Renew the brake fluid (Section 30)
mm Check the headlamp alignment (Section 31)
Every 250 miles (400 km) or weekly
mm See Weekly checks

Maintenance - component location 1•3
1
1 Wiper motor
2 Heater blower motor
3 Heater blower motor resistor
4 Windscreen washer tube
5 Screen washer reservoir
6 Suspension turrets
7 Coolant expansion tank
8 Ignition coil
9 Battery
10 Coolant hose
11 Radiator cooling fan
12 Distributor cover
13 Engine oil filler
14 Bonnet catch
15 Radiator
16 VIN plate
17 Engine breather
18 Air cleaner hot air pick-up
19 Thermostat housing
20 Fuel hoses
21 Fuel pump
22 Alternator
23 Accelerator cable
24 Carburettor
25 Choke cable
26 Servo non-return valve
27 Steering rack bellows
28 Air cleaner breather hose
29 Brake fluid reservoir
30 Brake servo
Underbonnet view of an early 1.6 litre model (air cleaner removed for clarity)

1•4 Maintenance - component location
1 Screen washer reservoir
2 Headlamp washer filler cap
3 Headlamp washer relay and fuse
4 Suspension turrets
5 Coolant expansion tank filler
6 Control relay (fuel injection system)
7 Ignition coil
8 Horn
9 Battery
10 Coolant hose
11 Radiator fan
12 Distributor
13 Engine oil filler
14 Bonnet catch
15 Radiator
16 VIN plate
17 Engine breather
18 Thermostat housing
19 Air cleaner
20 Airflow meter
21 Breather hose
22 Throttle valve housing
23 Fuel rail
24 Fuel pressure regulator
25 Servo non return valve
26 Steering rack bellows
27 Accelerator cable
28 Brake fluid reservoir
29 Brake servo
Underbonnet view of an early 1.8 litre model
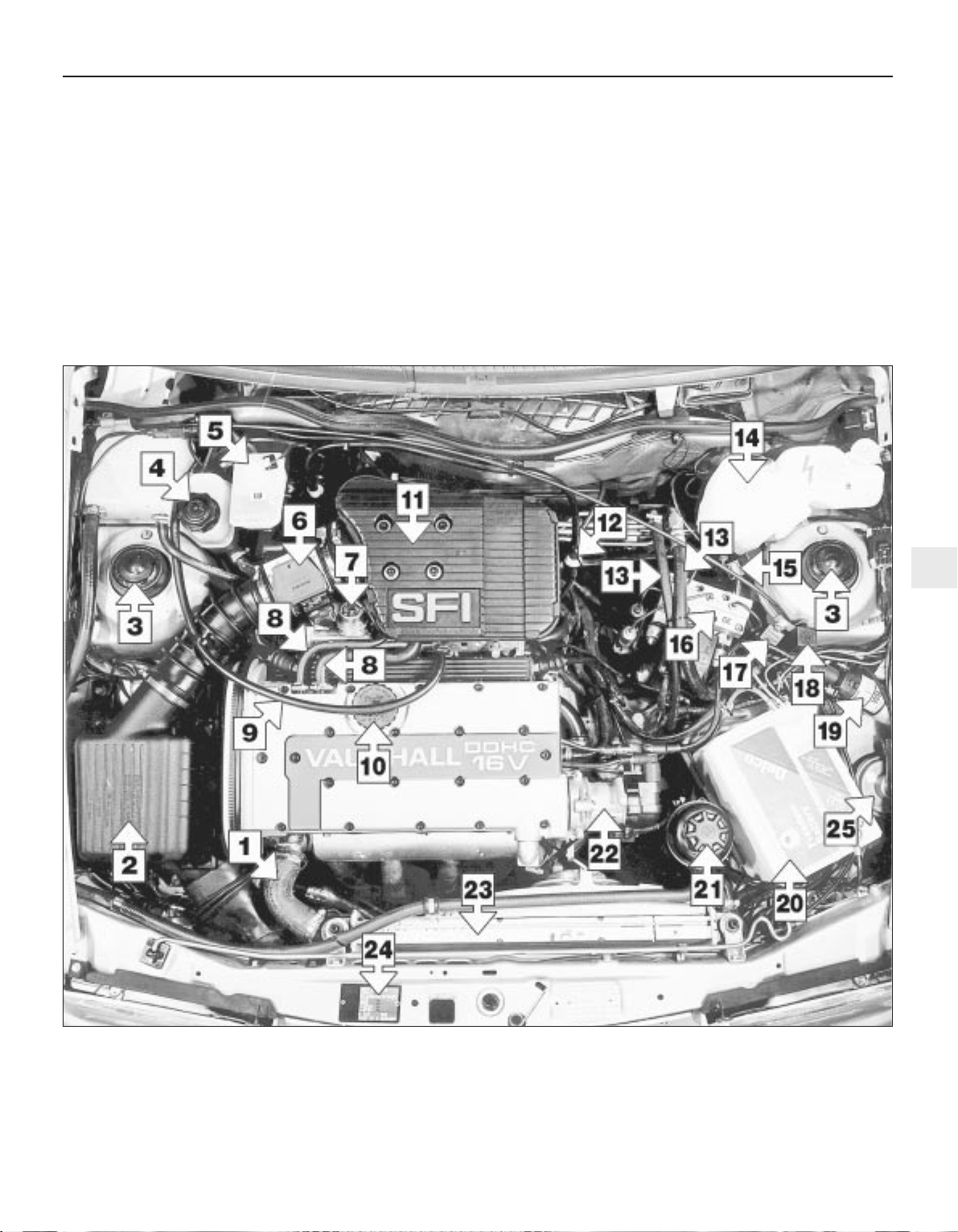
Maintenance - component location 1•5
1
1 Radiator top hose
2 Air cleaner
3 Suspension turrets
4 Coolant filler cap
5 Brake fluid reservoir
6 Air mass meter
7 Fuel pressure regulator
8 Breather hoses
9 Throttle cable
10 Engine oil filler cap
11 Pre-volume chamber
12 Brake servo non-return valve
13 Power steering hoses
14 Windscreen washer reservoir
15 Headlamp washer relay
16 ABS hydraulic unit
17 ABS surge arrester relay
18 Fuel injection control relay
19 Ignition coil
20 Battery
21 Power steering fluid reservoir
22 Distributor
23 Radiator
24 Vehicle identification plate
25 Horn
Underbonnet view of a 2.0 litre 16-valve model
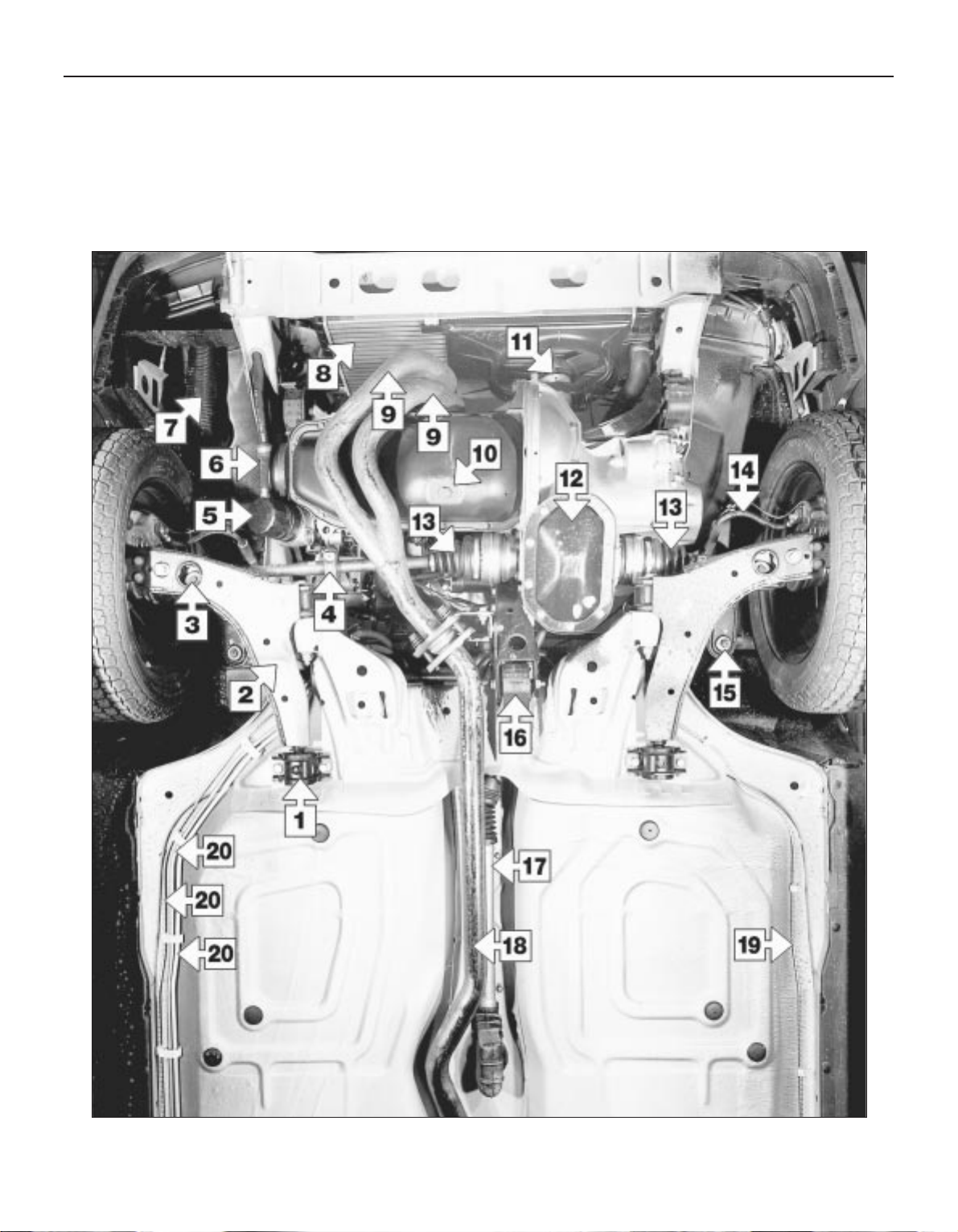
1•6 Maintenance - component location
1 Control arm rear bush
2 Control arm
3 Anti-roll bar link
4 Driveshaft damper weight
5 Engine oil filter
6 Oil cooler hose
7 Air induction trunking
8 Radiator
9 Exhaust downpipes
10 Sump drain plug
11 Radiator fan
12 Gearbox sump
13 Driveshaft bellows
14 Brake hose
15 Steering balljoint attachment
16 Engine/transmission rear mounting
17 Gearchange tube
18 Exhaust pipe
19 Brake pipe
20 Brake and fuel pipes
Front underbody view of a 1.8 litre model - other models similar
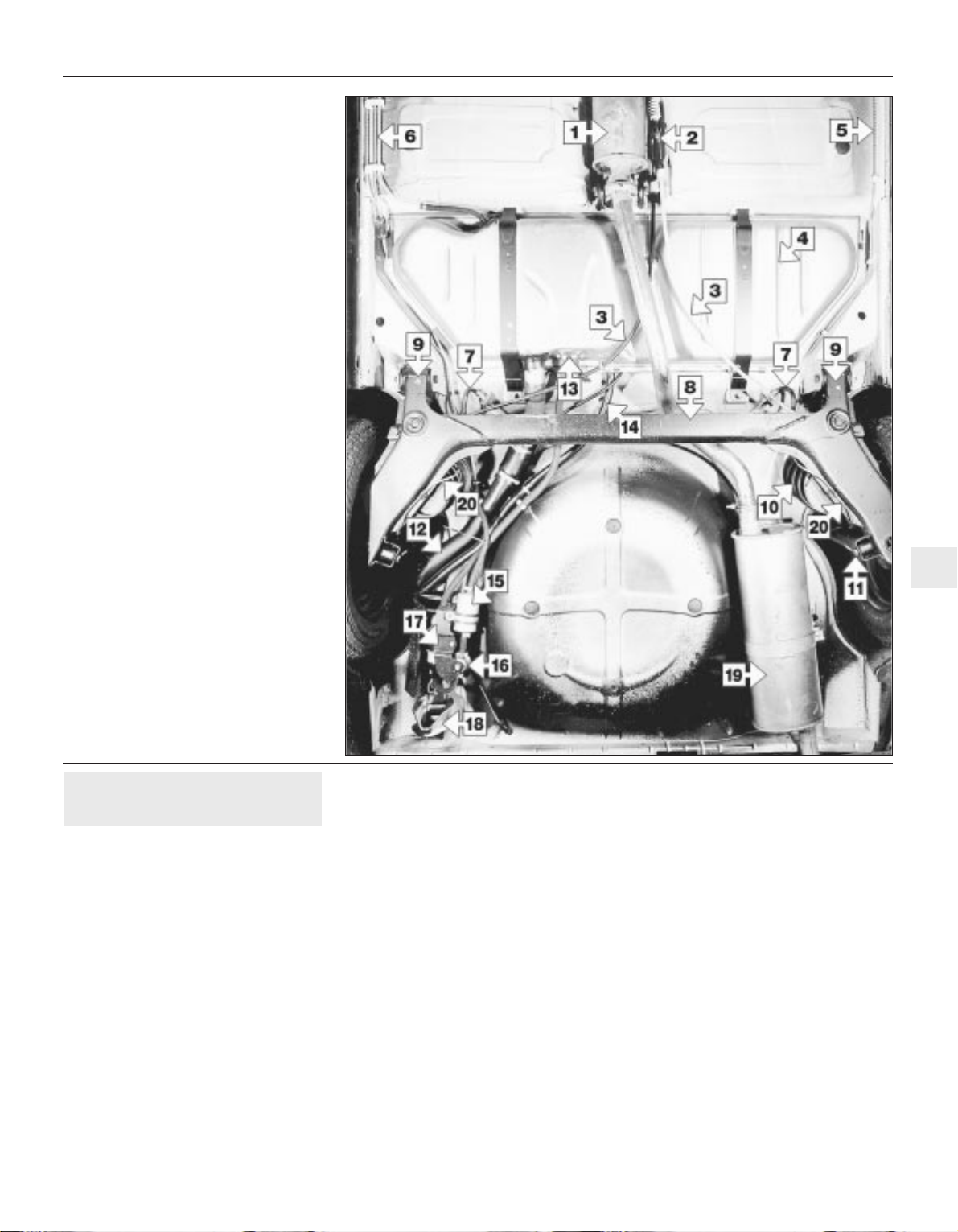
Maintenance - introduction 1•7
1
1 Centre silencer
2 Handbrake adjuster
3 Handbrake cables
4 Fuel tank
5 Brake pipe
6 Brake and fuel pipes
7 Brake hoses
8 Axle beam
9 Axle mountings
10 Spring
11 Shock absorber mounting
12 Fuel filler pipe
13 Fuel gauge sender/fuel tank outlet
14 Fuel tank breather
15 Fuel filter*
16 Fuel pressure regulator*
17 Fuel pump*
18 Towing eye
19 Rear silencer
20 Rear brake pipes
*Fuel injection models only
Rear underbody view of a 1.8 litre model -
other models similar
General information
This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain his/her vehicle for safety,
economy, long life and peak performance.
The Chapter contains a master
maintenance schedule, followed by sections
dealing specifically with each task on the
schedule. Visual checks, adjustments,
component renewal and other helpful items
are included. Refer to the accompanying
illustrations of the engine compartment and
the underside of the vehicle for the locations
of the various components.
Servicing of your vehicle in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following sections will provide a planned
maintenance programme, which should result
in a long and reliable service life. This is a
comprehensive plan, so maintaining some
items but not others at the specified service
intervals, will not produce the same results.
As you service your vehicle, you will
discover that many of the procedures can and should - be grouped together, because of
the particular procedure being performed, or
because of the close proximity of two
otherwise-unrelated components to one
another. For example, if the vehicle is raised
for any reason, the exhaust can be inspected
at the same time as the suspension and
steering components.
The first step in this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
sections relevant to the work to be carried
out, then make a list and gather together all
the parts and tools required. If a problem is
encountered, seek advice from a parts
specialist, or a dealer service department.
Intensive maintenance
If, from the time the vehicle is new, the
routine maintenance schedule is followed
closely, and frequent checks are made of fluid
levels and high-wear items, as suggested
throughout this manual, the engine will be
kept in relatively good running condition, and
the need for additional work will be minimised.
It is possible that there will be times when
the engine is running poorly due to the lack of
regular maintenance. This is even more likely
if a used vehicle, which has not received
regular and frequent maintenance checks, is
purchased. In such cases, additional work
may need to be carried out, outside of the
regular maintenance intervals.
If engine wear is suspected, a compression
test (Chapter 2) will provide valuable
information regarding the overall performance
of the main internal components. Such a test
can be used as a basis to decide on the
extent of the work to be carried out. If for
example a compression test indicates serious
internal engine wear, conventional
maintenance as described in this Chapter will
not greatly improve the performance of the
engine, and may prove a waste of time and
money, unless extensive overhaul work
(Chapter 2) is carried out first.
2 Introduction

1 Frequent oil and filter changes are the most
important preventative maintenance
procedures which can be undertaken by the
DIY owner. As engine oil ages, it becomes
diluted and contaminated, which leads to
premature engine wear.
2 Before starting this procedure, gather
together all the necessary tools and materials.
Also make sure that you have plenty of clean
rags and newspapers handy, to mop up any
spills. Ideally, the engine oil should be warm,
as it will drain more easily, and more built-up
sludge will be removed with it. Take care not
to touch the exhaust or any other hot parts of
the engine when working under the vehicle.
To avoid any possibility of scalding, and to
protect yourself from possible skin irritants
and other harmful contaminants in used
engine oils, it is advisable to wear gloves
when carrying out this work. Access to the
underside of the vehicle will be greatly
improved if it can be raised on a lift, driven
onto ramps, or jacked up and supported on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”). Whichever method is chosen,
make sure that the vehicle remains level, or if
it is at an angle, that the drain plug is at the
lowest point. The drain plug is located at the
rear of the sump.
3 Remove the oil filler cap from the camshaft
cover (twist it through a quarter-turn anticlockwise and withdraw it).
4 Using a spanner, or preferably a socket and
bar, slacken the drain plug about half a turn
(see illustration). Position the draining
container under the drain plug, then remove
the plug completely. If possible, try to keep the
plug pressed into the sump while unscrewing it
by hand the last couple of turns. As the plug
releases from the threads, move it away
sharply, so that the stream of oil from the sump
runs into the container, not up your sleeve!
5 Allow some time for the oil to drain, noting
that it may be necessary to reposition the
container as the oil flow slows to a trickle.
6 After all the oil has drained, wipe the drain
plug and the sealing washer with a clean rag.
Examine the condition of the sealing washer,
and renew it if it shows signs of scoring or
other damage which may prevent an oil-tight
seal. Clean the area around the drain plug
opening, and refit the plug complete with the
washer. Tighten the plug securely, preferably to
the specified torque, using a torque wrench.
7 The oil filter is located at the right-hand end
of the engine.
8 Move the container into position under the
oil filter.
9 Use an oil filter removal tool to slacken the
filter initially, then unscrew it by hand the rest
of the way (see illustration). Empty the oil
from the old filter into the container.
10 Use a clean rag to remove all oil, dirt and
sludge from the filter sealing area on the
engine. Check the old filter to make sure that
the rubber sealing ring has not stuck to the
engine. If it has, carefully remove it.
11 Apply a light coating of clean engine oil to
the sealing ring on the new filter, then screw
the filter into position on the engine. Tighten the
filter firmly by hand only - do not use any tools.
12 Remove the old oil and all tools from
under the vehicle then, if applicable, lower the
vehicle to the ground.
13 Fill the engine through the filler hole in the
camshaft cover, using the correct grade and
type of oil (refer to Section 3 for details of
topping-up). Pour in half the specified quantity
of oil first, then wait a few minutes for the oil
to drain into the sump. Continue to add oil, a
small quantity at a time, until the level is up to
the lower mark on the dipstick. Adding a
further 1.0 litre (approx.) will bring the level up
to the upper mark on the dipstick.
14 Start the engine and run it for a few
minutes, while checking for leaks around the oil
filter seal and the sump drain plug. Note that
there may be a delay of a few seconds before
the low oil pressure warning light goes out when
6 Engine oil and filter renewal
1•8 Maintenance procedures
6.4 Removing the sump drain plug 6.9 Using an oil filter removal tool to
unscrew the oil filter
Every 250 miles or weekly
The following series of operations are those
most often required to improve the
performance of a generally poor-running
engine:
Primary operations
a) Clean, inspect and test the battery
(Section 4).
b) Check all the engine-related fluids
(Section 3).
c) Check the condition and tension of the
auxiliary drivebelt (Section 9).
d) Renew the spark plugs (Section 7).
e) Inspect the ignition system components
(Section 10).
f)| Inspect the ignition HT leads (Section 10).
g) Check the condition of the air filter, and
renew if necessary (Section 24).
h) Check the condition of all hoses, and
check for fluid leaks (Section 8).
If the above operations do not prove fully
effective, carry out the following secondary
operations:
Secondary operations
All items listed under “Primary operations”,
plus the following:
a) Check the charging system (Chapter 5A).
b) Check the fuel system (Chapter 4A or 4B).
c) Renew the air filter (Section 24).
d) Renew the distributor cap and rotor arm
(Section 10).
e) Renew the ignition HT leads (Section 10).
See “Weekly checks” See “Weekly checks” See “Weekly checks”
5 Tyre checks4 Battery check3 Fluid level checks
Every 9000 miles

the engine is first started, as the oil circulates
through the new oil filter and the engine oil
galleries before the pressure builds up.
15 Stop the engine, and wait a few minutes
for the oil to settle in the sump once more.
With the new oil circulated and the filter now
completely full, recheck the level on the
dipstick, and add more oil as necessary.
16 Dispose of the used engine oil safely, with
reference to “General repair procedures”.
1 The correct functioning of the spark plugs is
vital for the correct running and efficiency of
the engine. It is essential that the plugs fitted
are appropriate for the engine, the suitable
type being specified at the end of this
Chapter. If the correct type of plug is used
and the engine is in good condition, the spark
plugs should not need attention between
scheduled renewal intervals, except for
adjustment of their gaps. Spark plug cleaning
is rarely necessary, and should not be
attempted unless specialised equipment is
available, as damage can easily be caused to
the firing ends.
2 To remove the plugs, first open the bonnet.
On 1.2 litre models remove the air cleaner as
described in Chapter 4A. On 2.0 litre 16-valve
engines undo the retaining screws and remove
the spark plug lead cover from the engine.
3 Mark the HT leads 1 to 4, to correspond to
the cylinder the lead serves (No 1 cylinder is
nearest the timing belt end of the engine). Pull
the HT leads from the plugs by gripping the
end connectors, not the leads, otherwise the
lead connections may be fractured.
4 It is advisable to remove any dirt from the
spark plug recesses using a clean brush,
vacuum cleaner or compressed air, before
removing the plugs, to prevent the dirt
dropping into the cylinders.
5 Unscrew the plugs using a spark plug
spanner, a suitable box spanner, or a deep
socket and extension bar (see illustration).
Keep the socket in alignment with the spark
plugs, otherwise if it is forcibly moved to either
side, the porcelain top of the spark plug may
be broken off. As each plug is removed,
examine it as follows.
6 Examination of the spark plugs will give a
good indication of the condition of the engine.
If the insulator nose of the spark plug is clean
and white, with no deposits, this is indicative
of a weak mixture or too hot a plug (a hot plug
transfers heat away from the electrode slowly,
while a cold plug transfers heat away quickly).
7 If the tip and insulator nose are covered
with hard black-looking deposits, then this is
indicative that the idle mixture is too rich.
Should the plug be black and oily, then it is
likely that the engine is fairly worn, as well as
the mixture being too rich.
8 If the insulator nose is covered with lighttan to greyish-brown deposits, then the
mixture is correct and it is likely that the
engine is in good condition.
9 The spark plug gap is of considerable
importance as, if it is too large or too small,
the size of the spark and its efficiency will be
seriously impaired. For the best results, the
spark plug gap should be set in accordance
with the Specifications at the end of this
Chapter.
10 To set the spark plug gap, measure the
gap between the electrodes with a feeler
blade, and then bend open, or close, the outer
plug electrode until the correct gap is
achieved (see illustrations). The centre
electrode should never be bent, as this may
crack the insulation and cause plug failure, if
nothing worse.
11 Special spark plug electrode gap
adjusting tools are available from most motor
accessory shops (see illustration).
12 Before fitting the new spark plugs, check
that the threaded connector sleeves on the
top of the plug are tight, and that the plug
exterior surfaces and threads are clean.
13 Screw in the spark plugs by hand where
possible, then tighten them to the specified
torque. Take extra care to enter the plug
threads correctly, as the cylinder head is of
light alloy construction.
14 Reconnect the HT leads in their correct
order. On 1.2 litre models refit the air cleaner
(Chapter 4A) and on 2.0 litre 16-valve models,
refit the spark plug lead cover.
7 Spark plug renewal
Every 9000 miles 1•9
1
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling bank,
call this
number free.
7.10a Measuring a spark plug electrode
gap using a feeler blade
7.5 Removing a spark plug - 1.6 litre
engine shown
7.10b Measuring a spark plug electrode
gap using a wire gauge
7.11 Adjusting a spark plug electrode gap
using a special tool
It is very often difficult to insert spark
plugs into their holes without crossthreading them. To avoid this, fit a short
length of 5/16-inch internal diameter
hose over the end of the spark plug. The
flexible hose acts as a universal joint to
help align the plug with the plug hole.
Should the plug begin to cross-thread,
the hose will slip on the spark plug,
preventing thread damage to the
aluminium cylinder head.
 Loading...
Loading...