Page 1

CC Technical Documentation
RM-11 Series Transceivers
System Module
Issue 1 02/2004 Confidential ©2004 Nokia Corporation
Page 2

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Document atio n
Contents Page
Introduction.................................................................................................................... 4
BB Hardware Characteristics ......................................................................................4
Technical Summary .....................................................................................................5
Functional Description .................................................................................................5
Modes of Operation................................................................................................... 5
RM-11 BB Functional Blocks .....................................................................................7
UEM and UPP........................................................................................................... 8
Battery....................................................................................................................... 9
Charger Detection ................................................................................................... 11
Charger Interface Protection ................................................................................... 12
LED Driver Circuit.................................................................................................. 12
LCD Display ........................................................................................................... 13
RF Interface Block .................................................................................................. 14
Combo Memory Module......................................................................................... 14
Combo Memory Interface....................................................................................... 14
SRAM Memory Description................................................................................... 14
Flash Memory Description...................................................................................... 15
Flash Architecture................................................................................................... 15
Keyboard (UI Module)............................................................................................ 15
Keyboard ESD Protection....................................................................................... 15
Internal Audio ......................................................................................................... 16
External Audio Connector....................................................................................... 17
External Microphone Connection ........................................................................... 18
External Earphone Connection................................................................................ 18
IrDa Interface .......................................................................................................... 19
Vibra........................................................................................................................ 19
FM Radio................................................................................................................. 19
Camera .................................................................................................................... 20
Flashlight................................................................................................................. 20
System Connector (Tomahawk).............................................................................. 21
PWB Strategy ............................................................................................................22
PWB Construction................................................................................................... 22
PWB Immunity ....................................................................................................... 22
Keyboard................................................................................................................. 23
Audio Lines............................................................................................................. 23
Microphone Lines ................................................................................................... 23
EAR Lines............................................................................................................... 23
Charger Lines.......................................................................................................... 23
HEADINT............................................................................................................... 23
Battery Supply Filtering.......................................................................................... 23
System Connector ................................................................................................... 24
Mechanical Shielding.............................................................................................. 24
EMC Strategy ............................................................................................................24
Test Interfaces ............................................................................................................25
Production / After Sales Interface........................................................................... 25
Flash Interface......................................................................................................... 25
FBUS Interface........................................................................................................ 25
Page 2 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 3

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
BB_RF Interface Connections ...................................................................................26
RF Functional Description .........................................................................................28
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layout ........................................................................ 28
Receiver................................................................................................................... 28
Frequency Synthesizers........................................................................................... 29
Transmitter.............................................................................................................. 29
Antenna ................................................................................................................... 32
Software Compensations ...........................................................................................32
RF Frequency Plan.................................................................................................. 33
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 3
Page 4
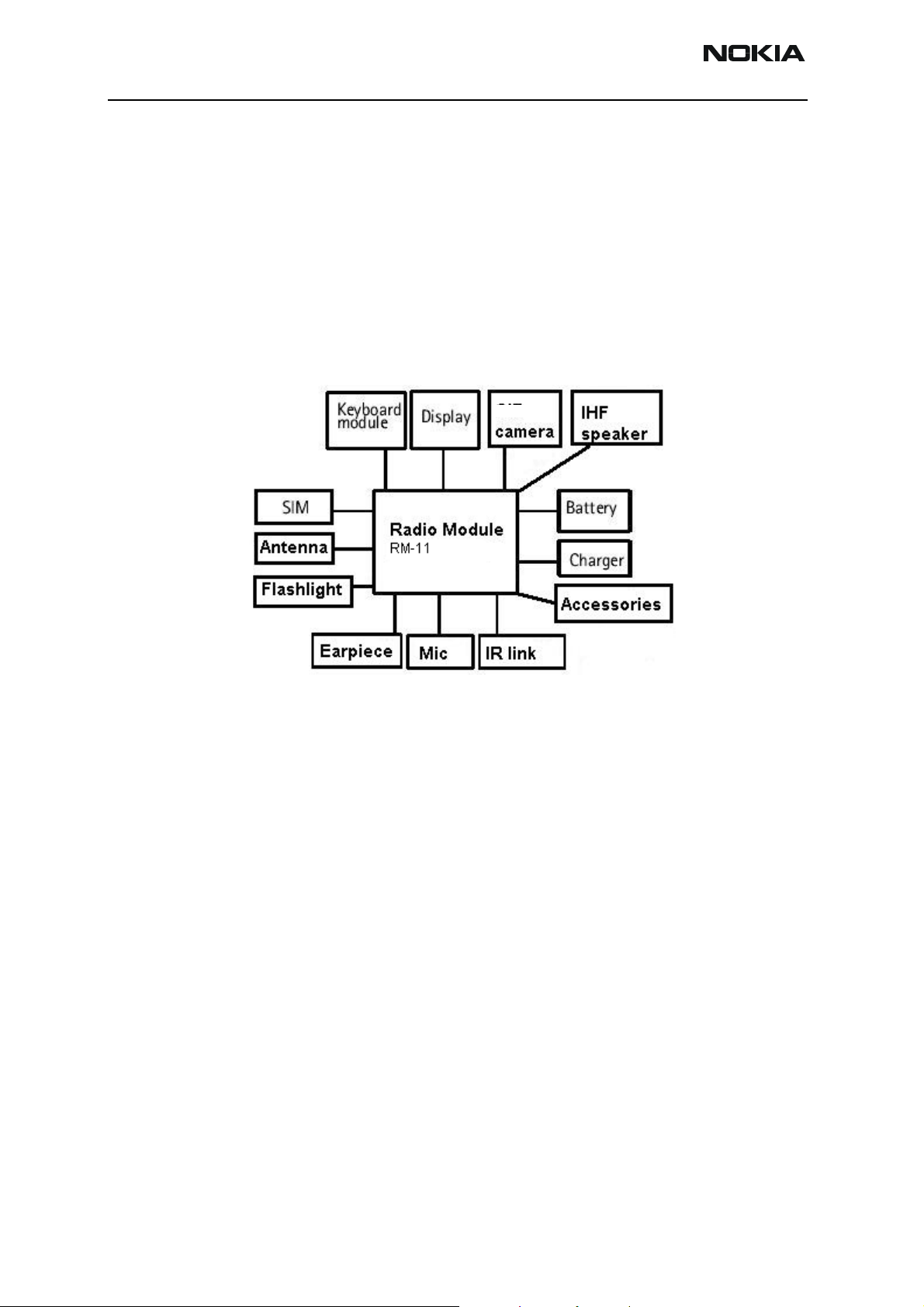
RM-11
System Module CC Technical Document atio n
Introduction
This chapter describes the system module for the RM-11 transceiver.
The baseband module includes the baseband engine chipset, the UI components, and the
acoustic components. The RM-11 is a hand-portable, dual-band CDMA 800/1900 with
AMPS. It has been designed using a DCT4 generation baseband (UEM/UPP) and RF
module. RM-11 includes a template cutter and user-customizable template front and
back covers. Other features include an integrated VGA camera, an IR, and a built-in
flashlight.
The phone requires the BLD-3 battery with a nominal capacity of 780 mAh.
VGA
Figure 1: Interconnection diagram
BB Hardware Characteristics
Following are characteristics for the BB hardware:
• Hi-resolution (128x128 pixel) illuminated color display
• Active LCD pixel area: width 27.6mm X height 27.6mm
• ESD-proof keymat, with five individual keys for multiple key pressing
• Support for internal semi-fixed battery (Janette type BLD-3)
• Audio amplifier and SALT speaker for MIDI support
• Ringing volume 100dB @ 5cm (MIDI tones through SALT speaker)
• Stereo FM receiver as an accessory
• IrDa port/interface
• Internal vibra
• Supports voice dial activation via headset button
• Six white LEDs for the keymat on the UI board, and two for the LCD backlight in
the LCD module
• Six-layer PWB, SMD with components on both sides of the PWB
Page 4 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 5

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
Technical Summary
The baseband module is implemented using two main ASICs — the Universal Energy
Management (UEM) and the Universal Phone Processor (UPP). The baseband module also
contains an audio amplifier for MIDI support and a 128-Mbit Flash/ 8-Mbit SRAM
combo IC. EMC shielding is implemented using a metallized plastic frame. On the other
side, the engine is shielded with PWB ground openings. Heat generated by the circuitry is
conducted out via the PWB ground planes. The RM-11 transceiver module is implemented on a 6-layer, FR-4 material PWB.
Functional Description
Modes of Operation
The RM-11 baseband engine has five different operating modes:
• No supply
• Acting dead
•Active
•Sleep
• Charging
No Supply Mode
In NO_SUPPLY mode, the phone has no supply voltage. This mode is due to the disconnection of the main battery or a low battery voltage level. The phone exits from
NO_SUPPLY mode when a sufficient battery voltage level is detected. The battery voltage
can rise either by connecting a new battery with VBAT > VMSTR+, or by connecting a
charger and charging the battery voltage to above VMSTR+.
Acting Dead Mode
If the phone is powered off when the charger is connected, the phone is powered on and
enters a state called Acting Dead. In this mode, no RF circuitry is powered up. To the user,
the phone acts as if it is switched off. The phone issues a battery-charging alert and/or
shows a battery charging indication on the display to acknowledge to the user that the
battery is charging.
Active Mode
In active mode, the phone is in normal operation, scanning for channels, listening to a
base station, transmitting, and processing information. There are several sub-states in
the active mode depending on if the phone is in burst reception, burst transmission, etc.
SW controls the RF regulators by writing the correct values into the UEM control
registers. VR1A/B and VR2 can be enabled or disabled. VR4 - VR7 can be enabled,
disabled, or forced into low quiescent current mode. VR3 is always enabled in active
mode.
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 5
Page 6

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Document atio n
Sleep Mode
The phone enters Sleep mode when both the MCU and the DSP are in stand-by mode.
Both processors control sleep. When the SLEEPX low signal is detected, the UEM enters
Sleep mode. In this mode, the VCORE, VIO and VFLASH1 regulators are put into low
quiescent current mode. All RF regulators — with the exception of VR2 and VR3 — are
disabled in sleep mode. When the SLEEPX is set high and is detected by the UEM, the
phone enters Active mode and all functions are activated. Sleep mode is exited either by
the expiration of a sleep clock counter in the UEM, or by some external interrupt generated by a charger connection, key press, headset connection, etc. While in Sleep mode,
the main oscillator is shut down and the baseband section uses the 32 kHz sleep clock
oscillator as its reference.
Charging Mode
Charging can be performed in parallel with any other operating mode. The Battery Size
Indicator (BSI) resistor inside the battery pack indicates the battery type/size. The resistor
value corresponds to a specific battery capacity and technology. Under UPP software
control, the UEM's AD converters measure the battery voltage, temperature, size, and
current. The charging control circuitry (CHACON) inside the UEM controls the charging
current delivered from the charger to the battery. The battery voltage rise is limited by
turning the UEM switch off when the battery voltage has reached VBATLim
(programmable charging cut-off limits are 3.6V, 5.0V, 5.25V). Measuring the voltage
drop across a 0.22 Ohm resistor monitors the charging current.
Page 6 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 7
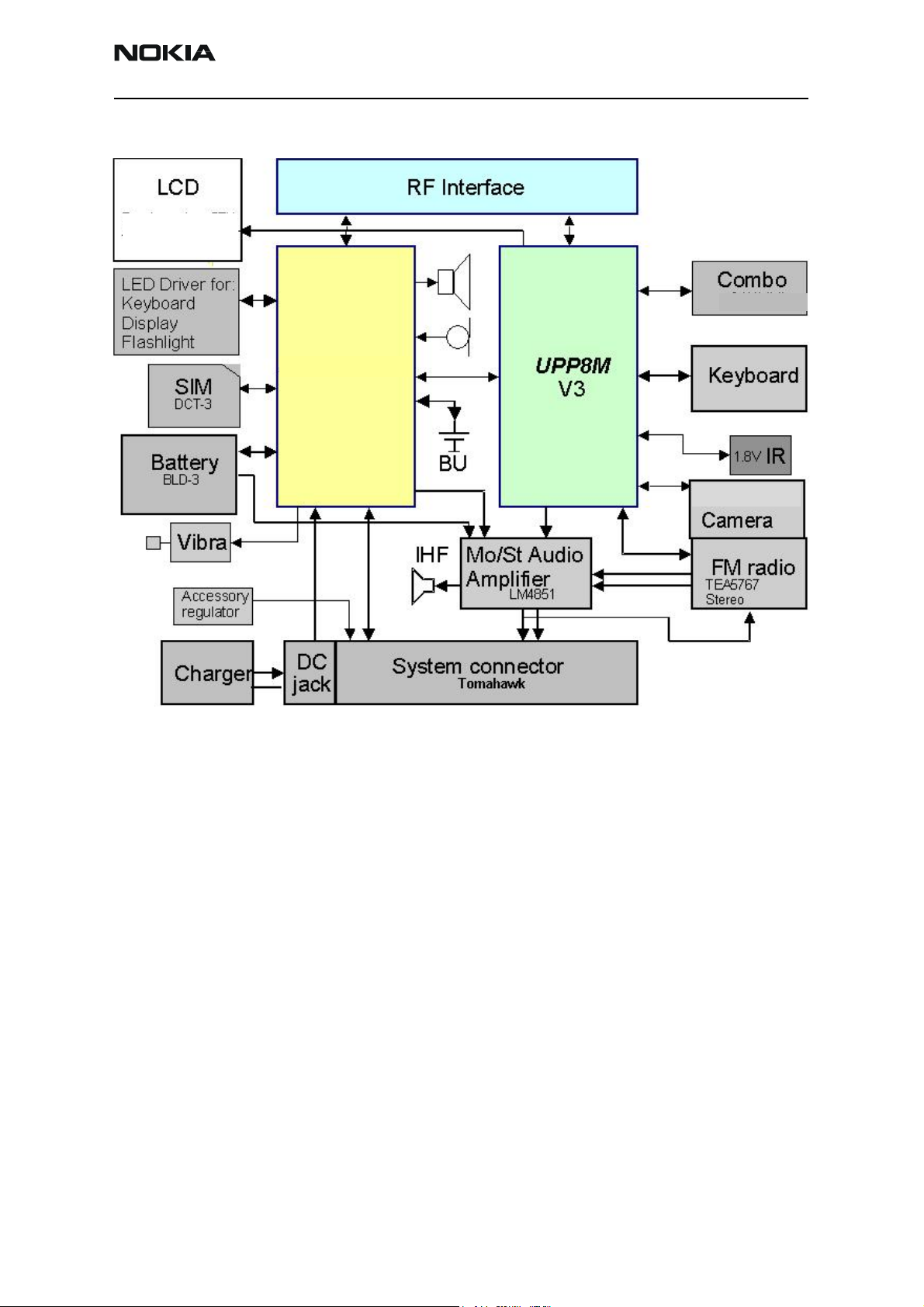
RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
RM-11 BB Functional Blocks
Passive color STN
4096 colors
128/8 Mbit
UEMK
VGA
Figure 2: Baseband block assembly
RM-11 BB functional blocks are listed below:
• UEM and UPP
• Battery
•LED driver
•LCD display
• RF IF block
• Memory module
• Keyboard (UI module)
• External audio connector
•IrDa interface
•Vibra
•FM radio
• System connector (Tomahawk)
• PWB strategy
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 7
Page 8

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
•EMC strategy
• Test interface
UEM and UPP
The UEM contains a series of voltage regulators to supply both the baseband module and
the RF module. Both the RF and baseband modules are supplied with regulated voltages
of 2.78 V and 1.8 V. The UEM contains six linear LDO (low drop-out) regulators for the
baseband and seven regulators for RF circuitry. The RF regulator VR1 uses two LDOs and
a charge pump. The VR1 regulator is used by the RF module. The core of the UPP is supplied with a programmable voltage of 1.0 V, 1.3 V, 1.5 V, or 1.8 V. Note that with the
UEMK, VCORE supply voltage is set to 1.5 V.
The UPP operates from a 19.2 MHz clock generated in the RF ASIC. The DSP and MCU
both contain phase locked loop (PLL) clock multipliers, which can multiply the system
frequency by factors from 0.25 to 31. The actual execution speed is limited by the
memory configuration and process size (Max. DSP speed for C035 is ~ 200MHz).
The UEM contains a real-time clock, sliced down from the 32768 Hz crystal oscillator.
The UPP uses the 32768 Hz clock as the sleep clock.
The communication between the UEM and the UPP is done via the bi-directional serial
busses, CBUS and DBUS. The CBUS is controlled by the MCU and operates at a speed of
1.08 MHz. The DBUS is controlled by the DSP and operates at a speed of 9.6 MHz. Both
processors are located in the UPP.
The interface between baseband and RF is implemented in the UEM and UPP ASIC. The
UEM provides A/D and D/A conversion of the in-phase and quadrature receive and transmit signal paths. It also provides A/D and D/A conversions of received and transmitted
audio signals to and from the user interface. The UEM supplies the analog signals to the
RF section according to the UPP DSP digital control. The RF ASIC is controlled via the UPP
RFBUS serial interface. There are also separate signals for PDM-coded audio. Digital
speech processing is handled by the DSP inside the UPP ASIC. The UEM is a dual voltage
circuit with the digital parts running from the baseband supply (1.8 V) and the analog
parts running from the analog supply of 2.78 V. The input battery voltage (VBAT) is also
used directly by some UEM blocks.
The baseband supports both internal and external microphone inputs as well as speaker
outputs. Input and output signal source selection and gain control are done by the UEM
according to control messages from the UPP. Keypad tones, DTMF, and other audio tones
are generated and encoded by the UPP and transmitted to the UEM for decoding. The
RM-11 has two external serial control interfaces: FBUS and MBUS provided by the UEM.
These busses can be accessed only through production test patterns. RM-11 also uses the
UPP8MV3 and UEMK.
Page 8 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 9
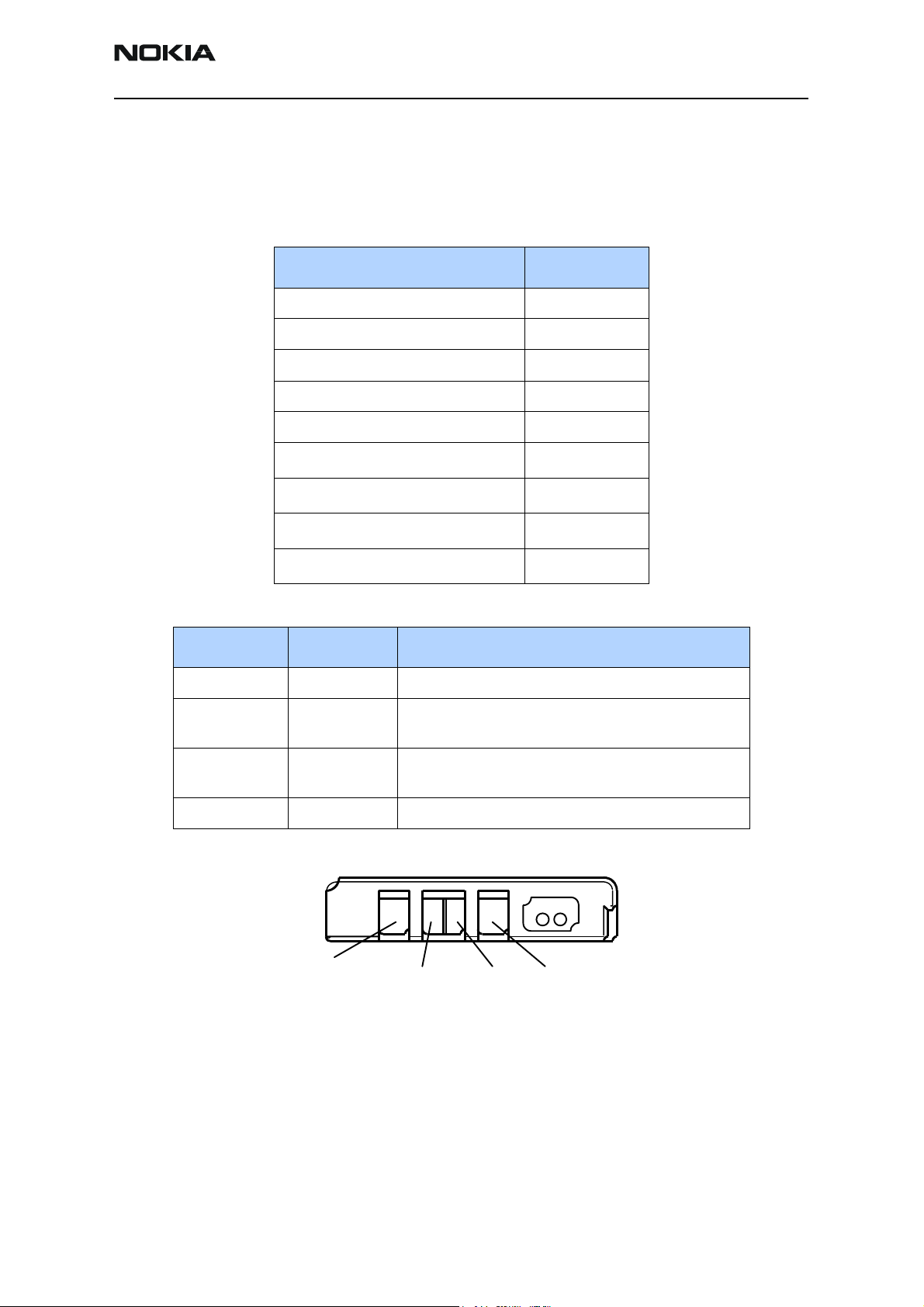
RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
Battery
BLD-3 Li-ion (inbox battery) is used as the main power source. The BLD-3 has a capacity
of 780 mAh.
Table 1: BLD-3 characteristics
Description Value
Nominal discharge cut-off voltage 3.1V
Nominal battery voltage 3.7V
Nominal charging voltage 4.2V
Maximum charger output current 850mA
Minimum charger output current 200mA
Cell pack impedance -20 ... 0
Cell pack impedance 0 ... +20
Cell pack impedance +20 ...+60
Cell pack impedance +60 ...+80
Table 2: Pin numbering of battery pack
o
o
C
C
o
C
o
C
180mΩ max
150mΩ max
130mΩ max
250mΩ max
Signal name Pin number Function
VBAT 1 Positive battery terminal
BSI 2 Battery capacity measurement (fixed resistor inside the
battery pack)
BTEMP 3 Battery temperature measurement (measured by ntc
resistor inside pack)
GND 4 Negative/common battery terminal
2(BSI) 3(BTEMP) 4(GND)
Figure 3: Battery pack contacts
Charge
GND
The BSI fixed resistor value indicates the type and default capacity of a battery. The
NTC-resistor measures the battery temperature.
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 9
Page 10
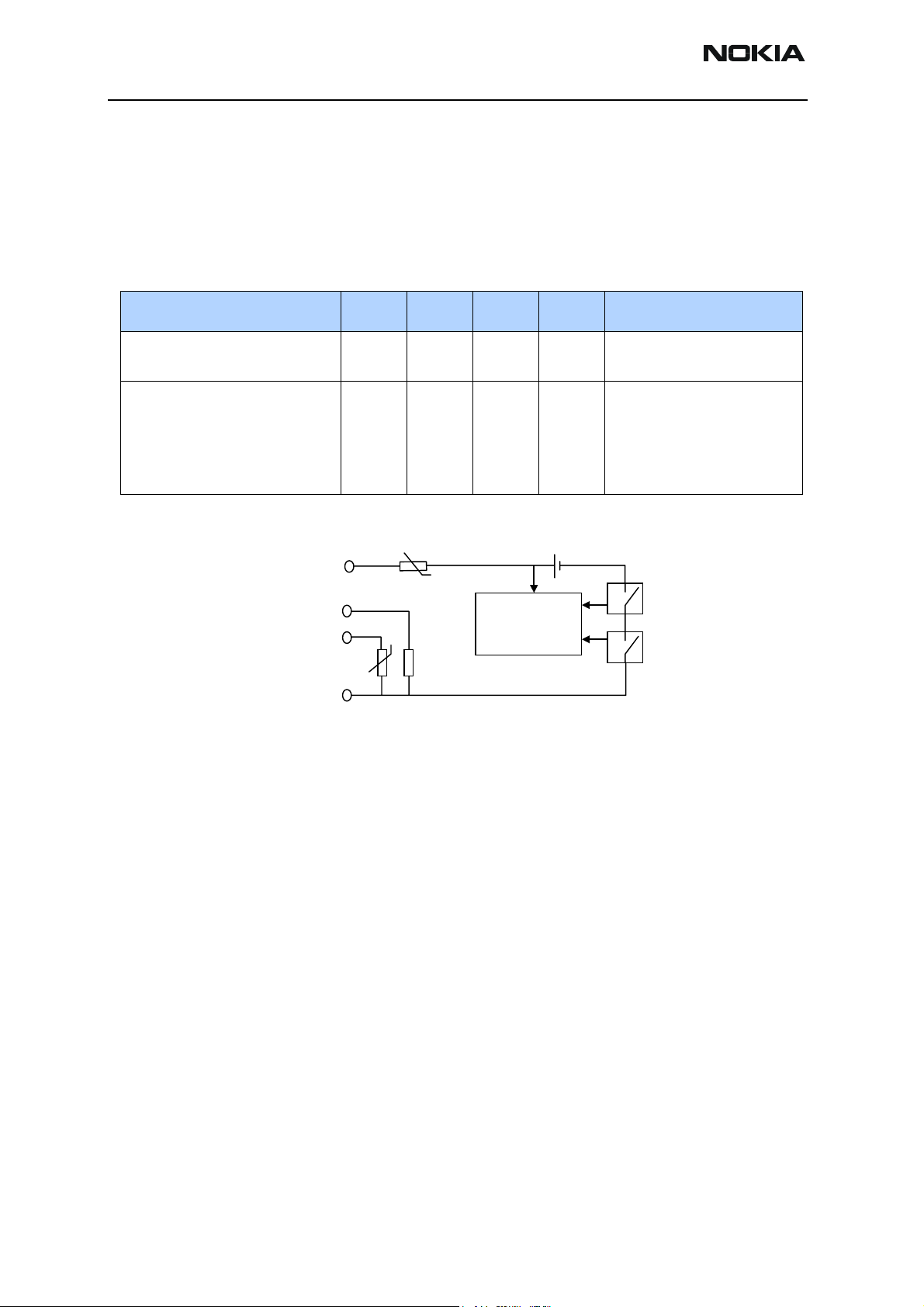
RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
Temperature and capacity information is needed for charge control. These resistors are
connected to the BSI and BTEMP pins of the battery connector. The phone has 100 kW
pull-up resistors for these lines so that they can be read by A/D inputs in the phone. For
safety reasons, the phone software will shut the phone off if it senses a temperature of
38oC or higher on the BTEMP line.
Table 3: BSI resistor values
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
Battery size indicator resistor BSI 75 kΩ Battery size indicator (BLD-3)
Tolerance “1%
NTC thermistor BTEMP 47
VBATT
BSI
BTEMP
EMC
Figure 4: Interconnection diagram
Supply Voltage Regulation
The UEM ASIC controls supply voltage regulation. There are six separate regulators used
by the baseband block. For a more detailed description about the regulator parameters,
see the UEM ASIC Specification document.
4000
kΩ
K
Overcharge /
Overdischarge
protection
Battery temperature indicator (NTC pulldown) 47kΩ“5%
o
@ 25
C
Beta value (B).
Tolerance “5%, 25
Li-Ion
o
C / 85 oC
Charging
The RM-11 baseband supports the NMP charger interface specified in the Janette
Charger Interface document. SW control is specified in the EM SW Specification, ISA EM
Core SW Project document. The UEM ASIC controls charging, and external components
are used to provide EMC, reverse polarity, and transient protection of the charger input
to the baseband module. The charger connection is through the system connector interface. Both 2- and 3-wire type chargers are supported. The operation of the charging
circuit has been specified to limit the power dissipation across the charge switch and to
ensure safe operation in all modes.
Page 10 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 11
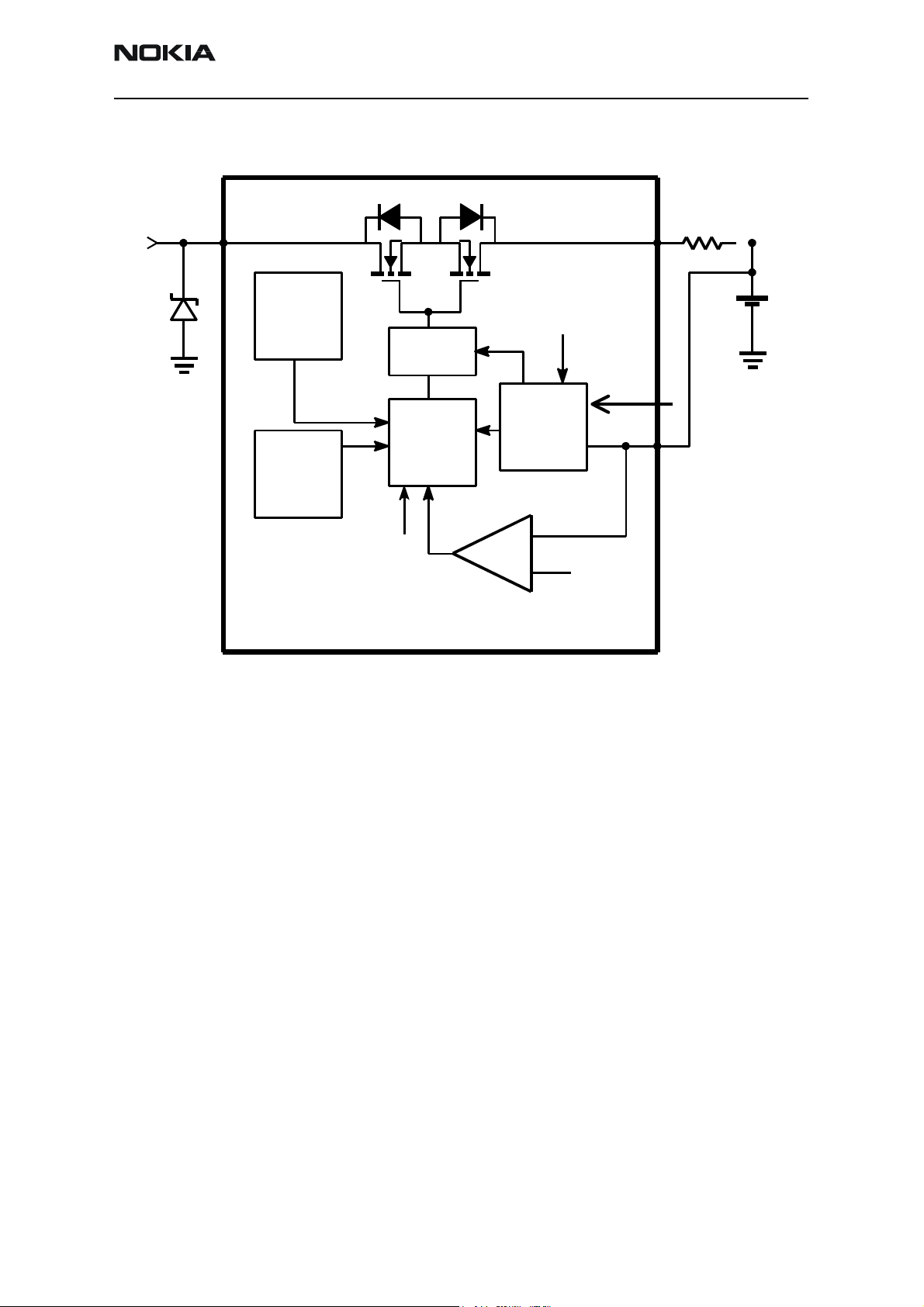
RM-11
V
CC Technical Documentation System Module
UEM
CHAR
VCHARin
Over
Temp.
Detection
WatchDog
Switch
Driver
Current
Ctrl
Logic
Figure 5: UEM charging circuitry
Sensing/
Limit
+
Comp
-
VCHARout
Vmstr
VBATT
VBATTlim
VBATT
Charger Detection
Connecting a charger creates voltage on the VCHAR input to the UEM. When the VCHAR
input voltage level rises above the VCHDET+ threshold, the UEM starts the charging
process. The VCHARDET signal is generated to indicate the presence of the charger for
the SW.
Energy Management (EM) SW controls the charger identification and acceptance. The
charger recognition is initiated when the EM SW receives a "charger connected" interrupt. The algorithm basically consists of the following three steps:
1. Check that the charger output (voltage and current) is within safety limits.
2. Identify the charger.
3. Check that the charger is within the charger window.
If the charger is identified and accepted, the appropriate charging algorithm is initiated.
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 11
Page 12

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
Charger Interface Protection
In order to ensure safe operation with all chargers and in misuse situations, the charger
interface is protected using a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) and a 1.5A fuse. The TVS
device used in RM-11 is rated for 16 V@175 W.
Figure 6: Charger interface diagram
Table 4 includes the values for the TVS.
Table 4: Charger interface TVS characteristics
Characteristic Value
Breakdown voltage (VBR) 17.8Vmin (at IT 1.0mA)
Reverse standoff voltage (VR) 6V
Max reverse leakage current at VR (IR) 5uA
Max peak impulse current (Ipp) 7A (at Ta=25*C, current waveform: 10/1000us)
Max clamping voltage at Ipp (Vc) 26V
LED Driver Circuit
In RM-11, white LEDs are used for LCD and keypad lighting. Two LEDs are used for LCD
lighting and six are used for the keyboard. A step-up DC-DC converter (TK11851) is used
as the white LED driver.
The display LEDs are driven in serial mode to achieve stable backlight quality. This means
that constant current flows through LCD LEDs. Serial resistance RLCD is used to define
the proper current. The feedback signal (FB) is used to control the current. The driver
increases or decreases the output voltage for LEDs to keep the current stable.
Keyboard LEDs are driven in 2-serial/3 parallel modes. Serial resistance R is used to limit
the current through LEDs. The feedback signal is not used to control the current. The
driver is controlled by the UEM via the DLIGHT output. This signal is connected to driver
EN-pin (on/off). It is possible to control the LED brightness by PWM to achieve smooth
on/off operation.
Page 12 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 13

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
VBAT
Cin
DLIGHT
Cosc
Figure 7: Shared LED driver circuit for LCD and keyboard backlight
LCD Backlight
The LCD backlight consists of two white LEDs, which are integrated with the
LCD module.
Keyboard Illumination
The keyboard light consists of six white LEDs on the UI board. They are placed under the
keyboard for proper illumination of the keypad.
V in
En
Cx
Coil
Is
Ext
LED Driver
Schottky
Vovp
FB
Gnd
Cout
Rlcd
LCD Illumination
R
Keyboard Illu mi na ti on
LCD Display
The LCD is a CSTN 130 x 130, full-dot matrix display with 12bit (4096 colors) color resolution and a single pixel border area around the content area, which makes the total
active area 128 x 128 pixels.
Table 5: LCD general specifications
LCD parameter Value
Glass size, width x height x thickness 33.98 mm x 37.95 mm x 1.71 mm
Glass thickness 0.50 mm
Viewing area (width x height) 30.29 mm x 30.29 mm
Active pixel area (width x height) 27.29 mm x 27.29 mm
Number of pixels 130 x 130 pixels
Technology CSTN (color super twisted nematic)
Operating temperature range
Main viewing direction 6 o’clock
Illumination mode transflective
-25
o
C to +70 oC
Color tone
Background: Neutral/Black
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 13
Page 14

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
C
Driver
Top View
Active area
128x128
C C
C 0 C 128
R 0
R 128
Figure 8: Color LCD module
RF Interface Block
The interface between the baseband and the RF module can be divided into two
categories: the digital interface and the analog interface. The digital interface is between
the UPP and the RF chip. The serial digital interface is used to control the operation of
the different blocks in the RF chip. The analog interface is between the UEM and the RF.
The entire BB-RF interface is discussed in the RF-BB Interface Specification RH-27
document.
Combo Memory Module
The RM-11 baseband memory module consists of a combo Flash/SRAM chip. It has
128 Mbit burst-type flash memory and 8Mbit of SRAM. In addition, the UPP has 8Mbits
of internal RAM. The UPP RAM is part of the UPP and is not discussed here.
Combo Memory Interface
The memory interface consists of a multiplexed address/data bus MEMADDA [23:0], the
MEMCONT[9:0] memory control bus, and the GENIO[23], which is used for memory
control. The purpose of the memory interface is to reduce the amount of
interconnections by multiplexing the address and data signals on the same bus. Because
the required Flash address space is more than 16bits, the MEMADDA[15:0] are multiplexed address/data lines and MEMADDA[22:16] are only address lines, which in total
allow for 8M addresses (MEMADDA[21:0]). The multiplexed data/address lines require
the memory to store the address during the first cycle in the read/write access. Data
access to the flash is performed as a 16-bit access (MEMADDA[15:0]) in order to improve
the data rate on the bus. The memory interface supports asynchronous read burst mode,
synchronous read, and simultaneous read-while-write/erase — all controlled by the UPP.
SRAM Memory Description
The combo memory chip used in RM-11 has 8 Mbit of SRAM, 16-bits wide running at
1.8 V. It uses a multiplexed address and data bus to minimize the pin count of the device.
Control signals are used to allow byte access to the device.
Page 14 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 15

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
Flash Memory Description
The 128 Mbit density flash with 16-bit data access operates in both asynchronous
random access and synchronous burst access (with crossing partition boundaries) and
has various data protection features. Upon power up or reset, the device defaults to
asynchronous read configuration. Synchronous burst read is indicated to the device by
writing to the flash configuration register and can be terminated by deactivating the
device.
The device supports reads and in-system erase and program operations at Vcc=1.8 V
(Voltage range 1.7-1.9 V). Flashing at production is supported at Vpp=12 V (for limited
exposure length only).
Flash Architecture
The datasheet of RM-11 combo memory contains detailed information about Flash
architecture.
Keyboard (UI Module)
The RM-11 consists of a separate UI board and includes contacts for the keypad domes
and LEDs for keypad lighting. The UI board is connected to the main PWB through a
16-pole, board-to-board connector with springs. A 5x4 matrix keyboard is also used. Key
pressing is detected by a scanning procedure. Keypad signals are connected via the UPP
keyboard interface.
When no key is pressed, row inputs are high due to UPP internal pull-up resistors. The
columns are written zero. When a key is pressed, one row is pulled down and an interrupt
is generated to the MCU. After receiving the interrupt, the MCU starts the scanning
procedure. All columns are first written high and then one column at a time is written
down. All columns, except the column that is written down, are set as inputs. Rows are
read while a column at the time is written down. If a row is down, it indicates that key,
which is at the cross point of the selected column and row that was pressed. After
detecting the pressed key, all registers inside the UPP are reset and columns are written
back to zero.
Keyboard ESD Protection
The SMD chips LEDs on the UI board have 2kV ESD protection. In case the A-cover is
removed, there is a potential risk of damaging the LEDs with electrostatic discharge.
Ground openings are made around LEDs to catch ESD sparks. For additional protection,
the dome sheet is made of conductive metallized tape and grounded to the display
shield.
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 15
Page 16

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
Internal Audio
Internal Microphone
The internal microphone capsule is mounted to in the UI frame. The microphone is
omni-directional and is connected to the UEM microphone input (MIC1P/N). The microphone input is asymmetric and the UEM (MICB1) provides bias voltage. The microphone
input on the UEM is ESD protected. Spring contacts are used to connect the microphone
to the main PWB.
Charge
UEM
MIC1N
Internal Speaker
The internal earpiece is a dynamic earpiece with an impedance of 32 ohms. The earpiece
is low impedance because the sound pressure is to be generated using current and not
voltage as the supply voltage is restricted to 2.7 V. The earpiece is driven directly by the
UEM and the earpiece driver (EARP and EARN outputs) is a fully differential bridge
amplifier with 6 dB gain. In RM-11, an 8 mm leak tolerant PICO earpiece is used.
UEM
MIC1P
EARP
EARN
EMC
Microphone
Figure 9: Internal microphone connection
Common mode
choke
Figure 10: Speaker connection
IHF Speaker and Stereo Audio Amplifier
The Integrated Hands Free (IHF) speaker (16 mm MALT) is used to generate speech audio,
ringing and warning tones. The audio amplifier is controlled by the UPP. The speaker
capsule is mounted in the C-cover. Spring contacts are used to connect the IHF speaker
contacts to the main PWB.
Page 16 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 17

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
Phone
audio
By pass
UPP8M
GenIO(14)
GenIO(15)
GenIO(16)
Enable
Clock
Data
Figure 11: Digital interface of audio amplifier
VB AT
=
LM4855
Output
Mode
Select
SPI
Ri n
Li n
Bias
Amplifier
Amplifier
Amplifier
Digital
Volu me
Control
LM4855
EN
CLK
DATA
Amplifier
Amplifier
Amplifier
GN D
ou t +
ou t -
Rout +
Rout -
Lout +
Lout -
Stereo
IH F Speaker
Headset
The LM4855 features a 32-step, digital volume control and eight distinct output modes.
The digital volume control and output modes are accessed through a 3-wire interface
controlled by the UPP. Digital volume control is needed when the FM radio is activated;
there is no amplifier block in the FM radio module. Output modes are needed when
routing audio to different locations (i.e., headset, IHF).
External Audio Connector
The RM-11 is designed to support a fully differential external audio accessory connection
by using a Tomahawk system connector. The Tomahawk connector has a serial data bus
called Accessory Control Interface (ACI) for accessory insertion and removal detection,
identification, and authentication. The ACI line is used for accessory control purposes
and includes the following:
• 4-wire fully differential stereo audio (used also FM-radio antenna connection)
• 2-wire differential mic input
EN CL K DAT A
Figure 12: Block diagram of audio amplifier
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 17
Page 18

RM-11
Ct
A
System Module CC Technical Documentation
External Microphone Connection
The external microphone input is fully differential and lines are connected to the UEM
microphone input (MIC2P/N). The UEM (MICB2) provides bias voltage. The microphone
input lines are ESD protected.
Creating a short circuit between the headset microphone signals generates the hook
signal. When the accessory is not connected, the UEM resistor pulls up the HookInt
signal. When the accessory is inserted and the microphone path is biased the HookInt
signal decreases to 1.8 V due to the microphone bias current flowing through the
resistor. When the button is pressed, the microphone signals are connected together and
the HookInt input receives half of micbias DC value 1.1 V. This change in DC level causes
the HookInt comparator output to change states, in this case from 0 to 1. The button can
be used for answering incoming calls but not to initiate outgoing calls.
HookInt
MICB2
UEM
MIC2P
MIC2N
Figure 13: External microphone connection
External Earphone Connection
Headset implementation uses separate microphone and earpiece signals. The accessory is
detected by the HeadInt signal when the plug is inserted.
FM Radio
VAFR
VAFL
MIC3P
UEM
MIC3N
XEAR
udio Amplifier
Rin
Lin
PhoneIN (HS)
PhoneIN (IHF)
Rout+
RoutLout+
Lout-
SPKRout+
SPKRout-
XMICP
EMC/ESD
XMICN
EMC/ESD
IHF Speaker
Figure 14: External earphone and IHF connections
Page 18 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 19

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
IrDa Interface
When using transceiver with 1.8V I/O, the IrDa interface is designed into the UPP. The IR
link supports speeds from 9600 bit/s to 1.152 MBit/s up to a distance of 80 cm.
Transmission over the IR is half-duplex.
The length of the transmitted IR pulse depends on the speed of the transmission. When
230.4 kbit/s or less is used as a transmission speed, pulse length is a maximum of
1.63ms. If the transmission speed is set to 1.152Mbit/s, the pulse length is 154ns.
The IR transceiver can be set into SIR or MIR modes. In SIR mode the transceiver is
capable of transmission speeds up to 115.2kbit/s. In MIR mode faster transmission speeds
are used. The maximum speed is 1.152Mbit/s. The IR transceiver can be set into shutdown mode by setting the SD pin to logic '1' to save current.
Vibra
A vibra-alerting device is used to generate a vibration signal for an incoming call. Vibra
is located in the bottom end of the phone and a connection is done with spring contacts.
The vibra interface is the same as in other DCT4 projects. The vibra is controlled by a
PWM signal from the UEM. The frequency can be set to 64, 129, 258, or 520 Hz and the
duty cycle can vary between 3% - 97%. To ensure compatibility with different UEM
versions, the RM-11 uses 40.5% duty cycle of the vibra PWM signal.
FM Radio
FM radio circuitry is implemented by using a highly integrated radio IC (TEA5767).
TEA5767 is a single-chip, electronically tuned, FM stereo radio with fully integrated IF
selectivity and demodulation. The IF frequency is 225 kHz. The radio is completely
adjustment-free and only requires a minimum of small, low-cost, external components.
It has signal-dependent mono/stereo blend [Stereo Noise Cancelling (SNC)]. The radio
can tune the European, US, and Japan FM bands.
Channel tuning and other controls are controlled through a serial bus interface by the
MCUSW. The reference clock (32kHz) is generated by the UPP CTSI block (routed from the
sleep clock).
GenIO(3)
UPP8M
GenIO(12)
GenIO(11)
GenIO(8)
FMCtrlDa
FMCtrlClk
FMWrEn
FMClk
VIO
XTAL2
TEA5767
SDA
SCL
W/R
Figure 15: FM radio digital interface connections
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 19
Page 20

RM-11
A
System Module CC Technical Documentation
Camera
The VGA camera module is connected to the baseband (UPP) through an HW accelerator
IC. And external 1.8 V regulator is used as a power supply (VDIG) for the camera module
and HW accelerator, together with VFLASH2.
UPP
LCDUI(1)
LCDUI(0)
GenIO(27)
GenIO(28)
GenIO(26)
GenIO(3)
VDIG VFLASH2
LCDCamTxDa
LCDCamClk
CamRxDa
CamCSX
CamSDX
CamClk
Figure 16: Camera connections to baseband
HW
ccelerator
VDIG
CCISCL
CCIDA
CCPCLKN
CCPCLKP
CCPDATAN
CCPDATAP
VFLASH2
Camera
The VGA camera has a resolution of 640 x 480 with a pixel size of 5.6um x 5.6um. Both
the camera and the HW accelerator support sleep functionality in order to minimize the
current consumption.
Flashlight
The flashlight feature on C-Rio is driven by the white LED driver and is controlled by
the UEM. The circuit for the flashlight is driven by TK11851TL. In this situation, the driver
is used as a boost DC/DC. Vout is set using three precision resistors in R300, R316, and
R317. Vout = Vfb * (1+ (R316+R317)/ R300). The TK11851L is an active-high enable
device, whose enable signal is tied to Klight/Dlight signals from the UEM. When Klight
goes high it turns on the TK11851TL driver and the V301 transistor, which allows a path
to GND.
Page 20 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 21

RM-11
N
CC Technical Documentation System Module
System Connector (Tomahawk)
The 14-pin Tomahawk bottom connector consists of charging plug socket and Tomahawk
System Connector. The Tomahawk system connector includes signals for the following:
Table 6: Tomahawk system connector signals
Function Notes
Charging Pads for 2-wire charging in cradles
Audio 4-wire fully differential stereo audio output
2-wire differential microphone input
FM radio antenna connection
Power supply for accessories 2.78V/70mA output to accessories
ACI (Accessory Control Interface) Accessory detection/removal and controlling
FBUS Standard FBUS
DKU-5 (similar to USB) (optional) Power in 5V in from DKU-5 cable
ACI
Vout
Charge
Charge GND
Shielding GND
Figure 17: Tomahawk bottom connector (charger plug socket and Tomahawk system connector)
Fbus TX
Fbus RX
XMIC N
XMIC P
DATA GN D
HSEAR_L_P
HSEAR_L_N
Accessory Control Interface (ACI)
The ACI is a point-to-point, bi-directional serial bus. It has three main features:
• The insertion and removal detection of an accessory device
• Acting as a data bus, intended mainly for control purposes
• The identification and authentication of accessory type which is connected
The accessories are detected by the HeadInt signal when the plug is inserted. Normally
when an accessory is not present, the pull-up resistor 100k pulls up the HeadInt signal to
VFLASH1. If the accessory is inserted, the external resistor (located to accessory) works
as a voltage divider and decreases the voltage level below the threshold of Vhead. The
comparator output is then changed to a high state, which causes an interrupt.
If the accessory is removed, the voltage level of HeadInt increases again to VFLASH1. This
voltage level is higher than the threshold of the comparator and so its output is changed
to low, which leads to an interrupt. These HeadInt interrupts are initiated by the accessory detection or removal sequence.
HSEAR_R_N
HSEAR_R_P
Shielding GND
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 21
Page 22

RM-11
3985
System Module CC Technical Documentation
External Accessory Regulator
An external LDO Regulator is needed for accessory power supply purposes. All ACI accessories require this power supply. A regulator input is connected to the battery voltage
VBAT and output is connected to the Vout pin in the Tomahawk connector. The regulator
ON/OFF function is controlled via the UPP.
The pull-down resistor on the enable input of the regulator is needed because in the
switch-off mode of the phone, the output level of the Genio(0) is not defined. If the
Genio(0) is floating, the regulator may be enabled when it should not be.
UPP
GenIO(0)
PWB Strategy
PWB Construction
The PWB consists of a 6-layer board made up of FR4. Via types are through hole, laser,
buried, and blind vias. The PWB build up is shown in Figure 19:
110
Maximum thick ne ss with solder resist 1270um
Electromechanical Thickness with surface finish 1100um ±
VBAT
Voltage
En
regulator
LP
Figure 18: Accessory power supply diagram
Solder resist 20 µm ± 10 µm
Finished cop per 30 µm ± 10 µm
Dielectric Ar amid 100 µm ± 20 µm
Finished copper 17 µm +2/-5 µm
Dielectric 150 µm ± 25 µm
Finished copper 17 µm +2/-5 µm
Dielectric 150 µm ± 25 µm
Finished copper 17 µm +2/-5 µm
Dielectric 150 µm ± 25 µm
Finished copper 17 µm +2/-5 µm
Dielectric Ar amid 100 µm ± 20 µm
Finished cop per 30 µm ±10 µm
Solder resist 20 µm ± 10 µm
Tomahawk btm conn
VOUT
Figure 19: RM-11 PWB build up
PWB Immunity
The PWB has been designed to shield all lines susceptible for radiation. Sensitive PWB
tracks have been drawn with respect to shielding by having ground plane over tracks,
and ground close to the tracks at the same layer.
Page 22 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 23

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
All edges are grounded from both sides of the PWB and a solder mask is opened from
these areas. The purpose is for any ESD pulse to face a ground area when entering the
phone (i.e., between mechanics covers). All holes in the PWB are grounded and plated
through holes.
Keyboard
The keyboard PWB layout consists of a grounded outer ring and either a trefoil pattern
grid (matrix) or an inner pad. This construction makes the keys immune to ESD, as the
key dome has a low ohmic contact with the PWB ground.
Audio Lines
In order to obtain good signal-to-noise ratio and good EMC/ESD immunity, the audio
lines have been carefully routed with respect to obtaining low impedance in the signal
path and obtaining proper shielding.
Microphone Lines
Microphone signals are input lines and therefore very sensitive to radiated fields.
Immunity for radiated fields is done to obtain a low-impedance path and with respect to
a common noise point of view in the signal path. This applies for both internal and
external microphone lines.
EAR Lines
EAR lines are output signals, also routed on layer 2 and 7, to obtain immunity for
conducted emission from the UEM. Internal EAR lines are EMC/ESD protected by radiated
fields from the earpiece by the low-impedance signal path in the PWB.
The same PWB outline has been implemented for the SALT speaker. Low ohm coil
inductors are used in series with the speaker for immunity against incoming fields from
the speaker.
Charger Lines
The ground from the charger is connected directly to a common PWB ground for a low
impedance path to the battery. The positive charger line is ESD, EMC, and short-circuit
protected by appropriate circuits.
HEADINT
The HEADINT line is EMC/ESD protected by routing on shielded layer 2 and by placement
of resistor R154 close to the bottom connector.
Battery Supply Filtering
Battery supply lines to the UEM IC are filtered with LC filters. These filters provide
immunity against conducted RF noise.
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 23
Page 24

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
System Connector
The immunity strategy concerning the bottom connector lines is to shield all lines to this
part in order to prevent radiation in the phone itself when an external accessory is
connected, and to prevent radiated fields from disturbing the lines as well. Appropriate
discrete filters close to the bottom connector are implemented for EMC and ESD
protection.
Mechanical Shielding
The RM-11 has a metal shield over the RF and BB parts to provide immunity for internal
radiation and immunity for external fields.
EMC Strategy
The phone must comply with the given CE requirements concerning EMC and ESD. The
goal is to pass internal SPR requirements. Therefore attention has been paid to obtaining
immunity in the PWB layout itself, and the implementation of filters in the circuit
design.
The baseband EMC strategy is divided into electrical and mechanical items. All electrical
guidelines, clocks, and high-speed signals should be routed in inner layers and away from
the PWB edges. Clock signals distributed to other circuits should have series resistors
incorporated to reduce rise times and reflections. Slew rate-controlled buffers should be
used on custom components wherever possible to reduce the EMC produced by the
circuit. Separate power supplies for digital, analog, and RF-blocks should be used as
much as possible. Baseband and RF supply power rails should be isolated from each other
by means of inductors in the power supply rail to prevent high-frequency components
produced on the baseband power supply rail to spread out over the RF power supply
plane. This might be required to avoid interference from digital circuits to affect the
performance of the RF section.
All external connectors and connections must be filtered using RC or LC networks to
prevent the high-frequency components from entering connection cables that then will
act as antennas. The amount of this type of EMC component is in straight relation to the
amount of external connections. The type of network and amount of components to be
used is determined by the AC and DC impedance characteristic of that particular signal.
Low-impedance signals require LC networks while medium-impedance level signals
(input signals at moderate bandwidth) can use RC networks.
The EMC protection should also prevent external or internal signals to cause interference
to the baseband and, in particular, to audio signals. Internal interference is generated by
the transmitter burst frequency and the switchmode charging. The transmitter burst
frequency interference is likely to cause noise to both microphone and earphone signals.
The transmitter RF interference is likely to cause more problems in the microphone
circuitry than in the earphone circuitry because the earpiece is a low-impedance
dynamic type.
As mechanical guidelines, the baseband and RF sections should be isolated from each
other using EMC shielding, which suppresses radiated interference. The transmitter burst
frequency can also generate mechanical vibrations that can be picked up by the
Page 24 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 25

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
microphone if it is not properly isolated from the chassis using rubber or some other soft
material. Connection wires to the internal microphone and earphone should be as short
as possible to reduce the interference caused by internal signals.
ESD protection has to be implemented on each external connection that is accessible
during normal operation of the phone.
Test Interfaces
Using the Tomahawk connector’s FBUS connections, the phone HW can be tested by PC
software (i.e., Phoenix test software). In addition, RM-11 also supports a Flash programming interface via the service battery, JTAG, and Ostrich test interfaces. JTAG test interface may be removed from the final product for security reasons.
Production / After Sales Interface
Test pads are placed on the engine PWB for service and production purposes. The same
test pattern is used by the After Market Sales (AMS) group for product testing and software upgrades. The following figure shows the top view of the test pads. The FBUS_TX
and RX lines are used to transfer data in or out of the phone. VPP is the Flash programming voltage and the MBUS/CLK line is used as a Flash clock line during flashing.
Flash Interface
Flash programming in production is done through the test pads in Figure 20 on the PWB.
FBUS Interface
The FBUS is an asynchronous data bus that has separate TX and RX signals. The default
bit rate of the bus is 115.2 kbit/s. The FBUS is mainly used for controlling and programming the phone in production. This is the primary interface used in the RM-11.
FBUS_RX FBUS_TX
VPP
MBUS/CLK
Figure 20: Production/test/after market interface
GND
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 25
Page 26

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
BB_RF Interface Connections
The BB and RF parts are connected together without a physical connector.
Rip
Signal
Name
#
DAMPS,
GSM1900
RFICCNTRL(2:0) RF IC Control Bus from UPP to RF IC (TACO)
RFBUSCLK UPP RFIC In Dig
0
RFBUSDA UPP/RFIC RFIC
1
RFBUSEN1X UPP RFIC In Dig
2
PUSL(2:0) Power Up Reset from UEM to RF IC (TACO)
PURX UEM RFIC Out Dig
0
GENIO(28:0) General I/O Bus connected to RF, see also separate collective GENI O(28:0)
TXP1 RFIC UPP Out Dig
5
Connected
from--- to
UPP
BB
I/O
Signal Properties
A/D--Levels---Freq./
Timing resolution
0/1.8V
I/O Dig
(0: <0.4V
9.72 MHz RF Control serial bus bit clock
Bi-directional RF Control serial bus data,
1: >1.4 V)
RFIC Chip Sel X
0/1.8V 10us Power Up Reset for RF IC
SLCLK & SLEEPX not used in RF
table. Control lines from UPP GENIOs to RF
0/1.8V
10 us Low Band Tx enabled
Description / Notes
TXP2 RFIC UPP Out Dig
6
11
BANDSEL
RFIC
UPP Out Dig
0/1.8V
0/1.8V
High Band Tx enabled
Rx Band select. Option for module LNA.
Not used in Stella.
Figure 21: BB_RF interface connections (1)
Page 26 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 27

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
Rip
Signal
Name
#
DAMPS,
GSM1900
RFCLK (not BUS -> no rip #) System Clock From RF To BB, original source VCTCXO, buffered (and
RFCLK
Connected
from--- to
VCTCXO >
RFIC
BB
I/O
Signal Properties
A/D--Levels---Freq./
Timing resolution
frequency shifted, WAM only) in RF IC (TACO)
UPP In Ana 800mVpp
typ (FET
probed)
Bias DC
blocked at
UPP input
Description / Notes
19.2 MHz
19.44 MHz System Clk from RF to BB,
RFClk
GND
RF UPP In Ana 0 System Clock slicer Ref GND, not
separated from pwb GND layer
SLOWAD(6:0) Slow Speed ADC Lines from RF block
5 PDMID
6 PATEMP
RF Power
detection
module
RF Power
detection
module
UEM In
UEM In
Ana
0/2.7V dig 0/VR2 Power detection module identification to
slow ADC (ch 5, previous VCTCXO Temp)
signal to UEM.
Ana
0.1-2.7V - Tx PA Temperature signal to UEM, NTC in
Power Detection Module
RFCONV(9:0) RF- BB differential Analog Signals: Tx I&Q, Rx I&Q and reference voltage
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
RXIP
RXIN
RXQP
RXQN
TXIP
TXIN
TXQP
TXQN
VREFRFO1
RFIC UEM In
UEM RFIC Out
UEM RFIC Out
Ana
Ana
Vref
1.4Vpp
max. diff.
Differential positive/negati ve in -p has e R x
Signal
0.5Vpp typ
bias
1.30V
2.2Vpp
max. diff.
Diff. Positive/negative quadrature phase Rx
Signal
Differential positive/negati ve in -p has e T x
Signal
0.6VppTyp
Bias
1.30V
Differential positive/negative quadrature
phase Tx Signal
1.35 V RF IC Reference voltage from UEM
Figure 22: BB_RF interface connections (2)
Rip
#
Signal
Name
DAMPS,
GSM1900
Connected
from--- to
BB
I/O
Signal Properties
A/D--Levels---Freq./
Timing resolution
Description / Notes
RFAUXCONV(2:0) RF_BB Analog Control Signals to/from UEM
TXPWRDET
1
AFC
2
TXP Det. UEM In Ana
UEM VCTCXO Out Ana
0.1-2.4 V 50 us Tx PWR Detector Signal to UEM
0.1-2.4 V Automatic Frequency Control for VCTCXO
Figure 23: BB_RF interface connections (3)
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 27
Page 28

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
VRF Globals instead of Bus Regulated RF Supply Voltages from UEM to RF. Current values are of the
VR1 A UEM RFIC
VR1 B UEM RFIC
VR2 UEM RFDiscr./
VR3 UEM VCTCXO
VR4 UEM RFIC
VR5 UEM RFIC
VR6 UEM RFIC
VR7 UEM RFIC,
IPA1 UEM RF PA
IPA2 UEM RFPA
VFLASH1 UEM RFIC
VBATT, Global
VBATTRF Batt
Conn
RFIC
UHF VCO
RFPA
regulator specifications, not the measured values of RF
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Vreg
Out Iout
Out Iout
Out Iout
Out Vbatt
4.75 V
+- 3 %
4.75 V
+- 3 %
2.78 V
+- 3 %
2.78 V
+- 3 %
--”-- 50 mA max. UEM linear regulat or. Power Supply for LNA
--”-- 50 mA max. UEM linear regulat or. P ower Supply for RF
--”-- 50 mA max. UEM linear regulat or. P ower supply for RF
--”-- 45mA UEM linear regulator. Power supply for RF
0-5 mA Settable Bias current for RF PA L-Band
0-5 mA Settable Bias current for RF PA H-band
2.78V ~2mA UEM linear regulator common for BB.
3…5V 0…1A
10 mA max. UEM, charge pump + linear regulator
output. Supply for UHF synth phase det ….
10 mA max. UEM, charge pump + linear regulator
output.
100 mA max. UE M linear regul ator. Supply voltage for Tx
IQ filter and IQ to Tx IF mixer.
20 mA max. UEM linear regulator. Supply for VCTCXO +
RFCLK Buffer in RF IC.
/ RFIC Rx chain.
low band PA driver section.
high band PA driver section.
Synths
RFIC digital parts and RF to BB digi IF.
Raw Vbatt for RF PA
2A peak
Figure 24: BB_RF interface connections (4)
RF Functional Description
Most of the RF functions are centered around the RF ASIC. Receiver IF stages, low-band
LNA, PLLs, RXVHF oscillator, TX VHF VCO active part and loop filter, high-band and lowband TX up-converters, TX IF stages, IQ modulator and demodulator and reference oscillator buffering are all integrated on single chip.
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layout
Receiver
The receiver design and system partition is from the Snoopy AD project. The receiver
shows a superheterodyne structure with zero 2nd IF. Low-band and high-band receivers
have separate front ends from the diplexer to the first IF. Most of the receiver functions
are integrated in the RF ASIC. The only functions out of the chip are the high-band LNA,
duplexers, and SAW filters. Receiver characteristics are very similar on both bands.
An active first downconverter sets naturally high-gain requirements for preceding
stages. Losses in very selective front-end filters are minimized down to the limits set by
filter technologies used and component sizes. The LNA gain is set up to 16 dB, which is
close to the maximum available stable gain from a single-stage amplifier. LNAs are not
exactly noise matched in order to keep pass band gain ripple to a minimum. Filters have
relatively tight stop band requirements, which are not all set by the system requirements
Page 28 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 29

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
but the interference free operation in the field. In this receiver structure, linearity lies
heavily on the mixer design. The second order distortion requirements of the mixer are
set by the 'half IF' suppression. A fully balanced mixer topology is required. Additionally,
the receiver third order IIP tends to depend on active mixer IIP3 linearity due to high
LNA gain.
IF stages include a narrow-band SAW filter on the first IF and an integrated lowpass
filtering is on zero IF. The SAW filter guarantees 14 dBc attenuation at alternating
channels, which gives acceptable receiver IMD performance with only moderate VHF
local phase noise performance. The local signal's partition to receiver selectivity and IMD
depends mainly on the spectral purity of the first local. Zero 2nd IF stages include most
of the receiver’s signal gain, AGC control range, and channel filtering.
Receiver requirements and characteristics are presented in detail in the RX specification.
Frequency Synthesizers
The RM-11 synthesizer consists of three synthesizers: one UHF synthesizer and two VHF
synthesizers. The UHF synthesizer is based on an integrated PLL and external UHF VCO,
loop filter, and VCTCXO. Its main goal is to achieve the channel selection, thus for dualband operations associated with dual mode. Due to the RX and TX architecture, this UHF
synthesizer is used for down conversion of the received signal and for final
up-conversion in the transmitter. A common 2 GHz UHFVCO module is used for operation
on both low and high bands. The frequency divider by two is integrated in the RF ASIC.
The two VHF synthesizers consist of the RX VHF synthesizer and the TX VHF
synthesizer.The RX VHF synthesizer includes integrated PLL and VCO and loop filter and
resonator. The output of the RX-VHF PLL is used as a LO signal for the second mixer in
the receiver. The TX VHF Synthesizer and loop filter are integrated into the RF ASIC. See
the depicted block diagrams and synthesizer characteristics from the Synthesizer specification document.
Transmitter
The transmitter RF architecture is up-conversion type (desired RF spectrum is low side
injection) with (RF-) modulation and gain control at IF. The IF frequency is 180.54 MHz.
The cellular band is 824.01-848.97 MHz and the PCS band is 1850.01-1909.95 MHz.
Common IF
The RF modulator is integrated with a Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) and an IF output buffer inside the RFIC chip. I- and Q-signals, which are output signals from the
BB-side SW IQ-modulator, have some filtering inside the RF ASIC before RF modulation
is performed. The required LO-signal from TXVCO is buffered with phase shifting in the
RF ASIC. After modulation (p/4 DQPSK or FM), the modulated IF signal is amplified
in PGA.
Cellular Band
At operation in cellular band, the IF signal is buffered at the IF output stage that is
enabled by TXP1 TX control. The maximum linear (balanced) IF signal level to 50 W load
is about -8 dBm.
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 29
Page 30

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
For proper AMPS-mode receiver (duplex) sensitivity, the IF signal is filtered in a
strip-filter before up-conversion. The upconverter mixer is actually a mixer with a LO and
output driver that is able to deliver about +6dBm linear output power. The mixer is inside
the RF IC. Note that in this point, the term “linear” means -33dB ACP. The required LO
power is about -6dBm. The LO signal is fed from the RF IC.
Before power amplifier RF signal is filter in band filter. The typical insertion loss is about
-2.7dB, and the maximum is less than -3.0dB. The input and output return losses are
about -10dB.
The power amplifier is a 50W/50W module. It does not have its own enable/disable
control signal, but it can be enabled by bias voltage and reference bias current signals.
The gain window is +27 to +31dB and the linear output power is +30dBm (typical condition) with -28dB ACP. The nominal efficiency is 50%.
PCS Band
When operating in the PCS band, the IF signal is routed outside from RF IC to be filtered
in the TX IF strip filter, and after that back to the RF IC, then to the upconverter mixer.
The LO signal to the mixer is buffered and balanced inside the RF IC. The mixer output is
enabled by the TXP2 TX control signal. The maximum linear (balanced) RF signal level to
50 W load is about +7dBm.
Next, the RF IC-balanced RF signal is single-ended in 1:1 balun and then filtered in the
SAW filter. The typical insertion loss is about -4.0dB, and the maximum is less than
-5.0dB. This filter has a relatively high pass band ripple about 1.0-1.5dB with the largest
insertion being at the high end of the band. The input and return losses are about -10dB.
The power amplifier is a 50W/50W module. It does not have its own enable/disable
control signal, but it can be enabled by bias voltage and reference bias current signals.
The gain window is +31 to +36dB and linear output power is +30dBm (typical condition)
with -28dB ACP. The nominal efficiency is 40%.
Power Control
For power monitoring, there is a power detector module (PDM) build up from a dual
coupler, a biased diode detector, and an NTC resistor. RF signals from both bands are
routed via this PDM. The RF isolation between couplers is sufficient not to lose filtering
performance given by duplex filters.
The diode output and NTC voltages are routed to the BB A/D converters for power
control. The TX AGC SW takes samples from the diode output voltage and compares that
value to the target value, and then adjusts the BB I-and Q-signal amplitude and/or RF IC
PGA settings to keep power control in balance.
NTC voltage is used for diode temperature compensation and for thermal shut down
when the radio board's temperature exceeds +85°C.
A false TX indication is based on the detected power measurement when the carrier is
not on.
Page 30 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 31

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
The coupler’s insertion loss is -0.42dB (max) at the cellular band and -0.48dB (max) at
the PCS band. Typical values for insertion losses are about -0.2dB. The filtering performance of the diplexer is taken into account in system calculations.
Antenna Circuit
The antenna circuit stands for duplex filters and diplexer. The cellular band duplex filter
is a band pass type SAW filter with typical insertion loss at about -2.0dB. The PCS band
duplex filter is a band stop (for receiver band) ceramic filter and its typical insertion loss
is about -1.7dB. Insertion losses of the diplexer are -0.45dB and -0.55dB (at maximum)
for cellular and PCS band—typical values being about -0.30dB and -0.35dB.
RF Performance
The output power tuning target for power level 2 after diplexer (or after switch for
external RF) is +27.3dBm for p/4 DQPSK-type modulation and +24.5dBm for FM-type
modulation. Power levels downwards from PL2 are -4dB below next to the highest power
level, PL10 being -4.7dBm (and PL7 +6.5dBm with FM type of modulation). Modulation
accuracy and ACP are within the limits specified in IS-136/137.
Table 7: 800 MHz analog TX
Power
level
2 24.8 +/- 0.25 0.5/-0.5
3 22.0 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
4 18.5 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
5 14.5 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
6 10.5 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
7 6.5 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
Power
level
2 27.3 +/- 0.25 0.5/-0.5
RF power at
external Antenna
Pad (dBm)
Table 8: 800 MHz digital TX
RF power at
external Antenna
Pad (dBm)
Tuning target
tolerant (dB)
Tuning target
tolerant (dB)
Testing limits
(dB)
Testing limits
(dB)
3 23.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
4 19.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
5 15.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
6 11.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
7 7.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
8 3.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 31
Page 32

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
Table 8: 800 MHz digital TX (Continued)
Power
level
9 -0.7 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
10 -4.7 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
RF power at
external Antenna
Pad (dBm)
Table 9: CDMA 1900 TX
Tuning target
tolerant (dB)
Testing limits
(dB)
RF power at
Power level
external
Antenna Pad
Tuning target
tolerant (dB)
Testing limits (dB)
(dBm)
2 26.3*** +/- 0.25 0.5/-0.5
3 23.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
4 19.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
5 15.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
6 11.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
7 7.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
8 3.3 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
9 -0.7 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
10 -4.7 +/-0.5 +/-2.0
*** 26.3 dBm for channel 1000 and 1998; 27.0 dBm for channel 2.
Antenna
The RM-11 antenna solution is an internal dual resonance PIFA antenna. This antenna
has a common feeding point for both antenna radiators, which results in the need for a
diplexer. In a single band transciever, an SMD-compatible through chip can be used.
Software Compensations
The following software compensations are required:
• Power levels temperature compensation
• Power levels channel compensation
• Power level reduction due to low battery voltage
• TX power up/down ramps
• PA's bias reference currents vs. power, temp and operation mode
• RX IQ DC offsets
Page 32 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
Page 33

RM-11
CC Technical Documentation System Module
• RSSI channel compensation
• RSSI temperature compensation
RF Frequency Plan
The RM-11 frequency plan is shown in Figure 25. A 19.44 MHz VCTCXO is used for the
UHF and VHF PLLs and as a baseband clock signal. All RF locals are generated in PLLs.
TX I
TX VHF LO
CELL 346.2 MHz
PCS 416.2 MHz
TX Q
RX I
RX VHF LO
CELL 256.2 MHz
PCS 256.2 MHz
RX Q
TX IF
CELL 173.6 MHz
PCS 208.1 MHz
°0
1
2
°90
UHF LO
CELL 997.14 - 1022.07 MHz, 30 kHz Step
PCS 2058.10 - 2118.05 MHz, 50 kHz Step
°0
1
2
°90
TX Block
RX Block
RX IF
CELL 128.1 MHz
PCS 128.1 MHz
Figure 25: RM-11 frequency plan
CELL
CELL
824.04 - 848.97 MHz
1850.00 - 1909.95 MHz
PCS
869.04 - 893.97 MHz
1930.00 - 1989.95 MHz
PCS
30 kHz Steps
50 kHz Steps
30 kHz Steps
50 kHz Steps
DC Characteristics
Regulators
The regulator circuit is UEM and the specifications are contained in Table 10:
Regulator
name
VR1 a/b 4.75 +/- 3% 10 4 4
VR2 2.78 +/-3% 100 100 76
VR3 2.78 +/-3% 20 2 2
VR4 2.78 +/-3% 50 23 24
VR5 2.78 +/-3% 50 5 0
VR6 2.78 +/-3% 50 tbd tbd
VR7 2.78 +/-3% 45 40 45
Table 10: Regulator circuit information
Output
voltage (V)
Regulator Max
current (mA)
RF total
1GHz
RF total
2GHz
Issue 1 02/2004 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Page 33
Page 34

RM-11
System Module CC Technical Documentation
Table 10: Regulator circuit information (Continued)
Regulator
name
IPA1, IPA2 2.7 max 1 +/- 10%
VREFRF01 1.35 +/- 0.5% 0.12 0.05 0.05
VFLASH1 2.78 +/- 3% 70 1 1
Output
voltage (V)
Regulator Max
current (mA)
3 +/- 4%
3.5 +/- 4%
5 +/- 3%
RF total
1GHz
1.3 - 5.0 1.3 - 3.7
RF total
2GHz
Page 34 ©2004 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 1 02/2004
 Loading...
Loading...