Page 1

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Software Manual
Models:
ReadyNAS 102
ReadyNAS 104
ReadyNAS 312
ReadyNAS 314
ReadyNAS 316
ReadyNAS 516
ReadyNAS 716X
ReadyNAS 2120
ReadyNAS 3220
ReadyNAS 4220
EDA 500
October 2013
202-11207-05
350 East Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
Page 2

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Support
Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product.
After installing your device, locate the serial number on the label of your product and use it to register your
product at https://my.netgear.com. You must register your product before you can use NETGEAR telephone
support. NETGEAR recommends registering your product through the NETGEAR website. For product updates,
additional documentation, and support, visit http://support.netgear.com.
Phone (US & Canada only): 1-888-NETGEAR.
Phone (Other Countries): Check the list of phone numbers at
http://support.netgear.com/general/contact/default.aspx.
Trademarks
NETGEAR, the NETGEAR logo, and Connect with Innovation are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of
NETGEAR, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. Information is subject to
change without notice. © NETGEAR All rights reserved.
Revision History
Publication Part Number Publish Date Comments
202-11207-05 October 2013 Updated to add RN716X to list of supported ReadyNAS
models.
202-11207-04 September 2013 Updated to reflect changes in 6.1.0 firmware.
202-11207-03 August 2013 Updated to reflect changes in 6.0.8 firmware.
202-11207-02 April 2103 Updated manual to support additional ReadyNAS
models.
202-11207-01 March 2013 First publication
2
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Chapter 2 Volume Configuration
Quick-Start Guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Additional Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Supported Operating Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Supported Browsers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Diskless Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Basic Installation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Discover and Set Up Your ReadyNAS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Local Setup Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Local Admin Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Access the Local Admin Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Register Your System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Basic Volume and RAID Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
RAID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Manage Volumes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Change RAID Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
View the Status of a Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Configure the Checksum Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Create and Encrypt a Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Delete a Volume. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Expand Storage Capacity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Add Protection to a Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Maintain Volumes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Chapter 3 Shared Folders
Basic Shared Folder Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Data Organization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Shared Folder Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
File and Folder Names. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
File-Sharing Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Manage Shared Folders. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Create a Shared Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
View and Change the Properties of a Shared Folder. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Delete a Shared Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Browse a Shared Folder. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Shared Folder Access Rights. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
3
Page 4

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
User and Group Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Set Up Access Rights to Files and Folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Access Shared Folders from a Network-Attached Device . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Use a Web Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Use a Windows Device. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Use a Mac OS X Device. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Use a Linux or Unix Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Use FTP and FTPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Use Rsync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Access Shared Folders Using Cloud Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Use ReadyCLOUD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Use ReadyNAS Remote. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Use ReadyDROP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Chapter 4 LUNs
Basic LUN Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Thin and Thick Provisioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .94
Default LUN Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Manage LUNs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Create a LUN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
View and Change the Properties of a LUN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Expand the Size of a LUN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Delete a LUN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
LUN Groups and Access Rights. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Create a LUN Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Assign a LUN to a LUN Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
Remove a LUN from a LUN Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Delete a LUN Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Manage Access Rights for LUN Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
Access LUN Groups from an iSCSI-Attached Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
Set Up Initiator Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
Initialize and Format LUNs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .122
Chapter 5 Snapshots
Basic Snapshot Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Smart Snapshot Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Rolling Back . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Clones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Manually Take a Snapshot. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
Browse Snapshots Using Recovery Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
Roll Back to a Snapshot. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .133
Roll Back to a Snapshot Using Recovery Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .133
Roll Back to a Snapshot Using the Timeline. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .136
Clone Snapshots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .139
Delete Snapshots. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .142
Delete Snapshots Using Recovery Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .142
4
Page 5

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Delete Snapshots Using the Timeline. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Recover Data from a Snapshot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .148
Recover Data from a Snapshot to a Network-Attached Device . . . . . .148
Recover Data from a Snapshot to an iSCSI-Attached Device . . . . . . .149
Chapter 6 Users and Groups
Basic User and Group Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
Home Folders. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
User and Group Account Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .151
User and Group Management Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Create User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .154
Edit User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .156
Delete User Accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .157
Change User Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .157
Group Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
Create Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .159
Edit Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
Delete Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
Cloud Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .163
Grant Access to Cloud Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .163
Cloud User Access Rights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .163
Chapter 7 System Settings
Customize the Basic System Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .166
Set the Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .166
Select the Language. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .167
Set the Administrator Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
Configure System Alerts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .169
Configure the Host Name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .172
Enable Antivirus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .173
Configure the Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .174
Network Basic Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .174
Configure the Ethernet Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .176
Configure Bonded Adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .181
Configure Global Settings for File-Sharing Protocols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
Basic File-Sharing Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .192
Supported File-Sharing Protocols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .193
Configure File-Sharing Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .194
Configure Media Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .199
ReadyDLNA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .199
iTunes Streaming Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .201
Configure Discovery Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .203
Install and Manage Apps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .204
Install Free Apps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .205
Enable the NETGEAR genie+ Marketplace Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .206
Create a NETGEAR genie+ Marketplace Account. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .207
5
Page 6

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Purchase Apps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .209
Manage Installed Apps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .213
Chapter 8 System Maintenance
System Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .215
System and Disk Health Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .215
System Real-Time and Historical Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .216
System Logs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .219
SNMP Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .221
System Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .223
Update Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .223
Reset the Firmware to Factory Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .226
Recover the Administrator Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .227
Shut Down or Restart the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .228
Manage Power Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .229
Optional Uninterruptible Power Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .232
Uninterruptible Power Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .232
UPS Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .232
Manage UPS Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .232
Chapter 9 Backup and Recovery
Back Up or Restore System Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .239
Basic Data Backup and Recovery Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .240
Backup Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .240
Recovery Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .242
Secure Cloud Backups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .243
Backup Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .243
Backup Job Recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .244
Manage Backup and Recovery Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .244
Create a Backup Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .244
Create a Recovery Job. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .245
Configure a Backup or Recovery Job. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .248
Manually Start a Backup or Recovery Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .257
Delete a Backup or Recovery Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .258
View or Clear a Job Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .258
Configure the Backup Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .260
Time Machine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .262
Back Up Your Mac Using Time Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .262
Increase Your Time Machine Backup Capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .264
ReadyNAS Vault. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .266
Dropbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .268
ReadyNAS Replicate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .269
Enable ReadyNAS Replicate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .270
Chapter 10 Help Videos
Available Videos. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
6
Page 7

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
ReadyCLOUD Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Time Machine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Antivirus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
iTunes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
Remote. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
ReadyDROP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .273
ReadyDLNA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
PLEX Media Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Continuous Data Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Tool-less Drive Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Viewing Videos. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .274
Appendix A Notification of Compliance
7
Page 8

1. Getting Started
This manual describes how to configure and manage your ReadyNAS® storage system.
Your ReadyNAS storage system relies on the following applications:
• ReadyCLOUD. Use this online service to discover your ReadyNAS system on your local
area network and access the local admin page.
• Local admin page. Use this browser-based interface to configure and manage your
ReadyNAS system.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Quick-Start Guide
• Additional Documentation
• Supported Operating Systems
• Supported Browsers
• Diskless Systems
• Basic Installation
• Discover and Set Up Your ReadyNAS
• Local Setup Wizard
• Local Admin Page
• Register Your System
1
8
Page 9

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Quick-Start Guide
This manual provides conceptual information about storage systems, detailed instructions
about using your system, and NETGEAR’s recommendations about configuring, managing,
and backing up your system. NETGEAR recommends that you read this manual to make the
best use of your storage system.
To quickly start using your system, review the following sections in this order:
1. Basic Installation on page 11. You use ReadyCLOUD to discover your storage system
on your network.
2. Create a Shared Folder on page 43. Shared folders are the way you organize the data you
store on your ReadyNAS system.
3. Create a LUN on page 95. LUNs are SAN data sets that allow data transfer and storage
over iSCSI.
4. Basic Snapshot Concepts on page 126. Protect the data that is stored in folders and LUNs
by creating snapshots.
5. Create User Accounts on page 154. You create a user account for each person that you
want to allow to access your ReadyNAS system.
6. Configure Global Settings for File-Sharing Protocols on page 192. File-sharing protocols
enable you to transfer files across a network.
7. Basic Data Backup and Recovery Concepts on page 240. You can back up the data that
you store on your ReadyNAS system and you can use your ReadyNAS system to back up
data that you store on other devices.
Additional Documentation
NETGEAR maintains a community website that supports ReadyNAS products. Visit
www.netgear.com/readynas for reviews, tutorials, comparison charts, software updates,
documentation, an active user forum, and much more.
For information about your system’s hardware, see the hardware manual for your system,
which is available at
support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
Getting Started
9
Page 10

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Supported Operating Systems
The ReadyNAS supports the following operating systems:
• Microsoft Windows 8
• Microsoft Windows 7
• Microsoft Windows Vista
• Apple Mac OS X10.5 Leopard or later
• Linux, Unix, Solaris
• Apple iOS
• Google Android
Supported Browsers
The ReadyNAS local admin page supports the following browsers:
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 9.0+
• Apple Safari 5.0+
• Google Chrome 20+
• Mozilla Firefox 14+
If you have difficulty accessing the local admin page or if you notice unexpected behavior , try
using another browser.
Diskless Systems
If you have a diskless ReadyNAS storage system, you must first install and format at least
one disk before you can discover your system with ReadyCLOUD or visit the local admin
page. For more information, see the hardware manual for your system, which is available at
http://support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
You must use supported disks in your ReadyNAS system. For a list of supported disks, visit
http://www.netgear.com/readynas-hcl.
Getting Started
10
Page 11

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Basic Installation
After you follow these instructions, your ReadyNAS system is ready to use in a production
environment. Setup takes approximately 15 minutes.
To install your storage system:
1. Install all available disks that you want to use in your storage system.
Note: If you are using previously formatted disks that contain data, you
must reformat these disks before continuing. For information about
formatting disks, see the hardware manual for your system.
For a list of supported disks, see the Hardware Compatibility List at
http://www.netgear.com/readynas-hcl.
For information about installing disks, see the hardware manual for your system.
2. Place your system in a location that provides adequate ventilation.
High-capacity disks can produce considerable heat. It is important to ensure that the fan
exhausts are unobstructed.
For a complete list of placement considerations, see the hardware manual for your
system.
3. Connect the power adapter to the power cord.
4. Connect the power adapter to the back of the system and plug the power cord into a wall
outlet or power strip.
5. Use an Ethernet cable to connect an Ethernet port on the storage system to your network.
6. If necessary, press the Power button to turn on the system.
7. Wait for the Power LED to turn solid blue or for the status display screen to display the
system’s IP address.
8. Use ReadyCLOUD to discover and set up your system on the network.
See Discover and Set Up Your ReadyNAS on page 12.
Getting Started
11
Page 12

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Discover and Set Up Your ReadyNAS
ReadyCLOUD is the online service that you use to discover and set up ReadyNAS storage
systems on your network. You can also use ReadyCLOUD to access and manage data on
your ReadyNAS systems. For you to use ReadyCLOUD, your computer and storage system
must have Internet access.
Note: If your computer and storage system do not have Internet access,
install and run the RAIDar utility instead. RAIDar is on the resource
CD that came with your system. It includes versions for Windows,
Mac, and Linux operating systems. It is also available at
http://www.netgear.com/raidar.
When you discover your device using ReadyCLOUD, you can choose between two setup
modes:
• ReadyCLOUD Mode.
ReadyNAS system from anywhere that has an Internet connection. If you select
ReadyCLOUD mode, you must create a free ReadyCLOUD account or sign in using your
existing ReadyCLOUD account.
• Offline Mode.
home or office network. Selecting this setup mode takes you directly to the local admin
page for your ReadyNAS system.
To discover and set up your storage system:
1. V
isit http://readycloud.netgear.com on a computer that uses the same local area
network (LAN) and Internet connection as your storage system.
This setup mode makes your ReadyNAS data available only inside your
This setup mode allows you to securely access and manage your
2. Click the Discover button.
Getting Started
12
Page 13
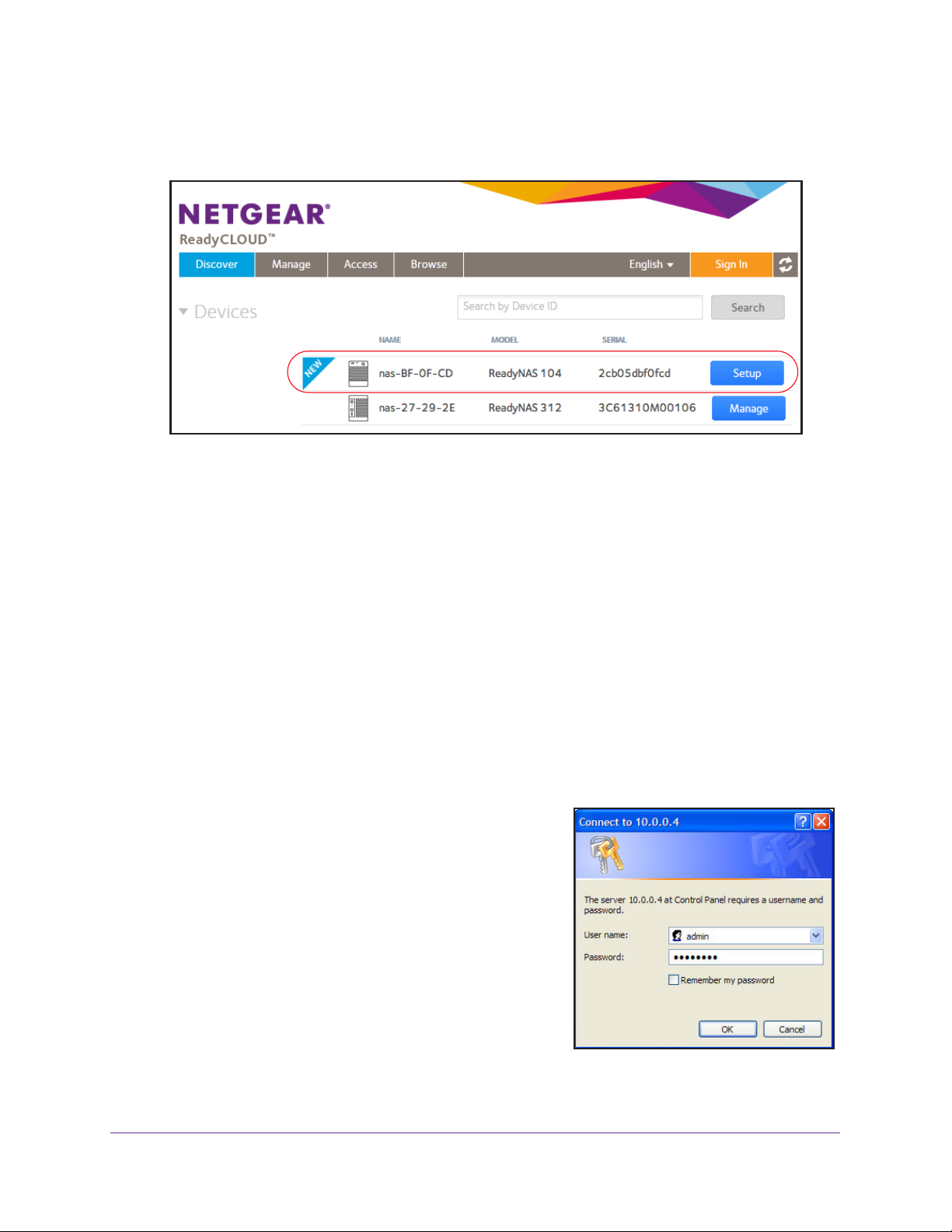
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
ReadyCLOUD automatically detects your ReadyNAS system on the network.
Your new ReadyNAS system is marked with a NEW label.
3. Click the Setup button.
4. Select the mode that you want to use to set up your system:
• Option 1. Select ReadyCLOUD Mode.
a. Sign in to ReadyCLOUD or create a user account.
Tip: If you have a ReadyNAS Remote account, you can sign in to
ReadyCLOUD using your ReadyNAS Remote credentials.
b. Follow the prompts to set up your ReadyNAS system.
For more information about ReadyCLOUD, see Use ReadyCLOUD on page 69.
• Option 2. Select Offline Mode.
An SSL certificate security warning displays. This warning ensures an encrypted
authentication and secure access to the ReadyNAS local admin page for your
storage system.
a. Accept the certificate.
A login prompt displays.
b. Enter admin for the user name, enter
password for the password, and click the
OK button.
Both user name and password are
case-sensitive.
ou can change these credentials when you
Y
configure your system. NETGEAR
recommends that you change your
password as soon as possible.
Getting Started
13
Page 14
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The ReadyNAS local admin page displays in your browser and launches a setup
wizard.
c. Follow the prompts of the setup wizard that launches in your browser.
Local Setup Wizard
The first time you access the local admin page, a setup wizard prompts you to configure the
basic settings of your ReadyNAS storage system.
Note: The local setup wizard is for users who choose to set up their
ReadyNAS system using Offline mode. If you set up your system
using ReadyCLOUD mode and the ReadyCLOUD setup wizard, the
local setup wizard does not display.
Figure 1. Setup wizard (Welcome screen)
You can change the language setting for the setup wizard by clicking Language at the top
right corner of the screen and selecting a language from the drop-down list.
The setup wizard guides you through the initial configuration process to help you quickly
integrate your ReadyNAS storage system into your network. Follow the setup wizard’s
prompts to configure the following settings:
ime and date. For more information, see Set the Clock on page 166.
• T
• Alert contact. For more information, see Configure System Alerts on page 169.
• Host name. For more information, see Configure the Host Name on page 172.
• Administrator password and password recovery. For more information, see Set the
Administrator Password on page 168.
Getting Started
14
Page 15
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
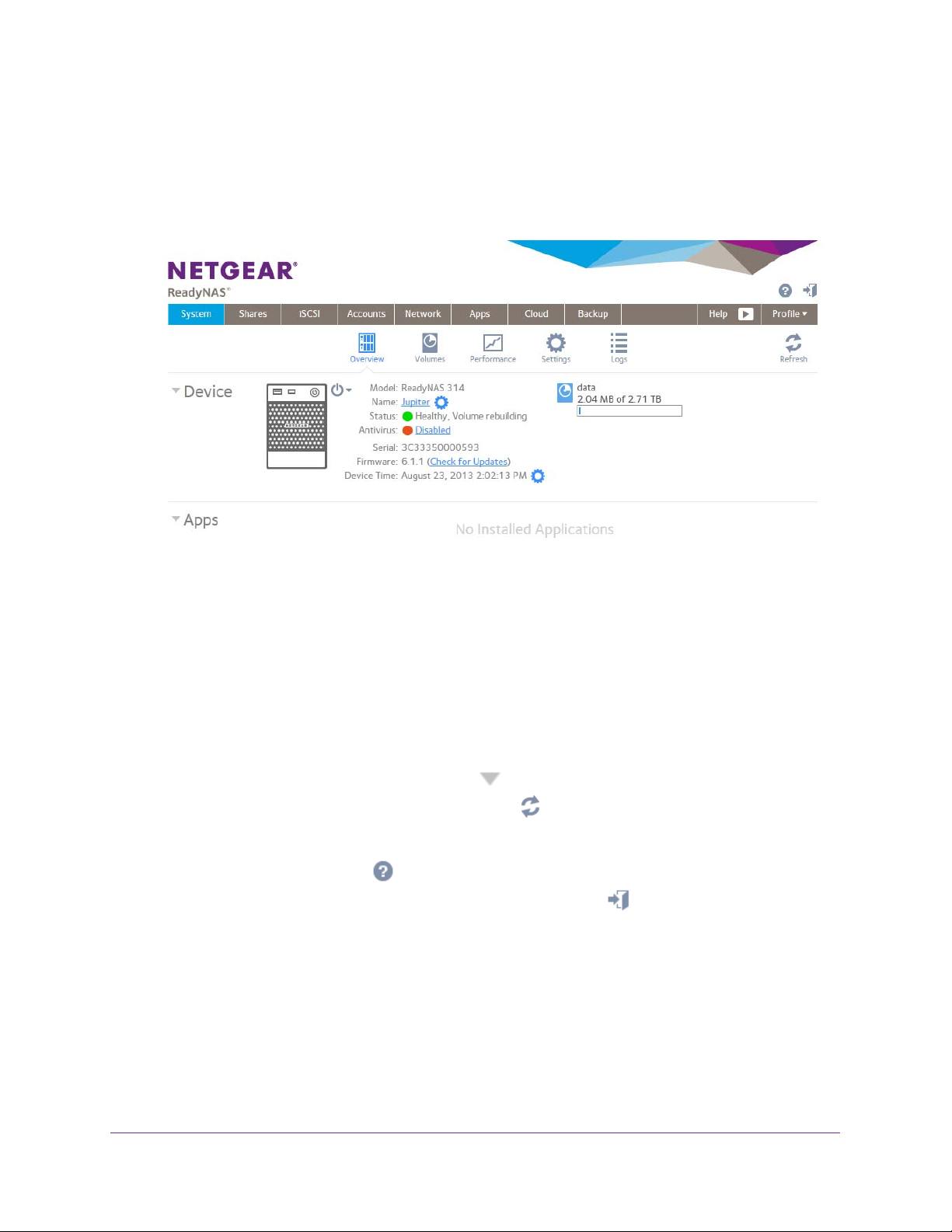
Local Admin Page
The local admin page is a browser-based interface that you use to configure and manage
your ReadyNAS system. When you visit the local admin page, the Overview screen displays,
as shown in the following figure.
Figure 2. Local admin page (Overview screen)
The following list describes the features of the local admin page:
• T
o navigate through the local admin page, use the navigation bar across the top of the
screen and the navigation icons below it.
• Some screens are divided into multiple sections.
the screen by clicking the triangle icons (
• T
o refresh the screen, click the Refresh icon ( ) in the top right corner below the
navigation bar.
• For more information about your product, visit an of
clicking the Support icon (
• T
o log out of the local admin page, click the Logout icon ( ) in the top right corner of
the screen.
Other features of the local admin page are described in other chapters.
In this manual, instructions for navigating through the local admin page begin by specifying
the selection from the navigation bar and then, if necessary
the row of navigation icons and section headings. For example, to configure the global
file-sharing protocols, select System > Settings > Services. System is the selection from
the navigation bar
selection from the section headings on the Settings screen.
. Settings is the selection from the row of navigation icons. Services is the
) in the top right corner of the screen.
You can collapse or expand sections of
) next to each section heading.
ficial NETGEAR support page by
, specifying the selections from
Getting Started
15
Page 16

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Access the Local Admin Page
If your computer is connected to the same LAN as your storage system, follow these
instructions to access the local admin page.
For information about remote access to the local admin page, see the ReadyNAS Remote
User Manual.
To access the local admin page:
1. Open a web browser and visit https://<hostname>.
<hostname> is the name that you assigned to your ReadyNAS system or the default host
name if you did not change it.
Note: You can also enter https://<ReadyNAS IP address>, where
<ReadyNAS IP address> is the IP address of the ReadyNAS.
An SSL certificate security warning displays.
2. Accept the certificate.
A login prompt displays.
3. Enter the login credentials for your system and click the OK button.
If you did not change the credentials, the default credentials are as follows:
• user name. admin
• password. password
Both user name and password are case-sensitive.
The local admin page displays.
You can also access the local admin page from ReadyCLOUD (see Use ReadyCLOUD on
page 69).
Register Your System
You must register your product before you can use NETGEAR telephone support. Register
your ReadyNAS system at the NETGEAR Product Registration web page.
To register your ReadyNAS system:
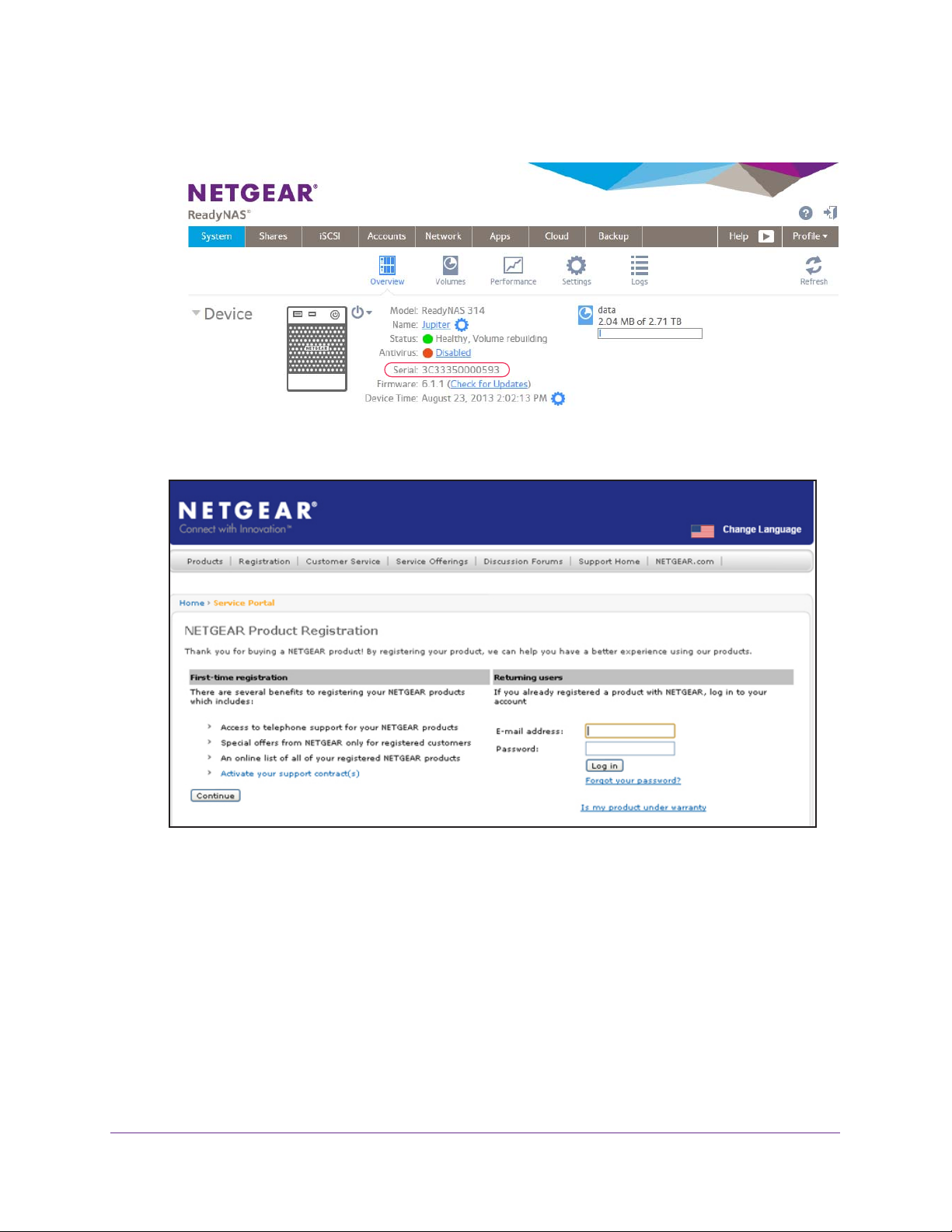
1. Locate the serial number of the system.
Getting Started
16
Page 17
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
You can find the serial number on the Overview screen of local admin page or on the
chassis label of your product.
2. Open a web browser and visit http://www.netgear.com/register.
The Product Registration web page displays.
3. Take one of the following actions:
• If you have never registered a NETGEAR product, click the Continue button.
• If you have registered a NETGEAR product in the past, enter your email address and
password and click the Log in button.
4. Follow the prompts.
The ReadyNAS is registered.
Getting Started
17
Page 18

2. Volume Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure and manage the volumes in your ReadyNAS storage
system. It includes the following sections:
• Basic Volume and RAID Concepts
• Manage Volumes
2
18
Page 19

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Basic Volume and RAID Concepts
To get the most out of your ReadyNAS storage system, it is helpful to understand the basics
of volumes and RAID. Understanding these concepts is the first step to making good
decisions about how to configure, manage, and use your ReadyNAS storage system.
Volumes
In the most general sense, volumes are data storage devices. Your computer treats an
internal hard drive as a volume. It also treats a portable USB thumb drive as a volume.
Volumes can be either physical or logical. Usually, the term physical volume refers to a hard
disk drive. When this term is used in this way, a two-bay storage system can have up to two
physical volumes (hard disk drives). A four-bay storage system can have up to four physical
volumes. A six-bay storage system can have up to six physical volumes.
The term logical volume refers to the way that you divide, or partition, your storage space.
For example:
• Each logical volume can correspond to a hard disk drive.
• A logical volume can be made up of more than one hard disk drive.
In this manual, the term volume refers to a logical volume. The terms hard disk drive and disk
refer to a physical volume.
RAID
Your ReadyNAS storage system allows you to configure your hard disks using one of the
many RAID technologies.
RAID is short for redundant array of independent disks. RAID is a storage technology that
balances data protection, system performance, and storage space by determining how the
storage system distributes data. Many different ways of distributing data have been
standardized into various RAID levels. Each RAID level offers a tradeoff of data protection,
system performance, and storage space. For example, one RAID level might improve data
protection but reduce storage space. Another RAID level might increase storage space but
also reduce system performance.
Your ReadyNAS storage system supports X-RAID2TM mode, a proprietary single-volume
RAID architecture that is easy to administer, and Flex-RAID mode, which allows you to
format your disks in a variety of industry-standard RAID levels.
When you power on your system for the first time or if you reset your system to its factory
default settings, the optimal RAID mode and level are automatically selected for you based
on the number of disks that are installed. You can also configure the RAID settings manually
(see
Change RAID Mode on page 23).
V olume Configuration
19
Page 20

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
X-RAID2
X-RAID2 is an auto-expandable RAID technology that is available only on ReadyNAS
systems. With X-RAID2, you do not need to know intricate details about RAID to administer
your system. X-RAID2 allows you to add storage space without reformatting your drives or
moving your data to another location. Because the expansion happens online, you can
continue to use your ReadyNAS system while the volume capacity increases.
Because X-RAID2 is a single-volume architecture, if you configure your hard disk drives to
use X-RAID2, your storage system has only one volume that is made up of all installed hard
disk drives. X-RAID2’s single-volume architecture has two major advantages:
• Easy system management
• Auto-expansion
With Flex-RAID formatting, if you want to add disks to expand your storage capacity, you
must back up the data to another system, add a disk, reformat the RAID volume, and restore
the data to the new RAID volume. With X-RAID2, none of those administrative tasks are
required. Instead, with X-RAID2, your volume automatically expands to accommodate
additional disks or larger-capacity disks.
With X-RAID2, you can start out with one hard disk, add a second disk for data protection,
and add more disks for additional storage capacity. X-RAID2 accommodates the new disks
automatically. You can replace existing disks with larger-capacity disks and X-RAID2
automatically accommodates the new disks.
X-RAID2 requires a minimum of two hard disks to provide protection against disk failure. If
you have a one-disk ReadyNAS storage system and want protection from disk failure, you
must add a second disk that is at least as large as the first. It can be added while the system
is running.
X-RAID2 uses the capacity of one disk for data storage and reserves the capacity of a
second disk for data protection, which allows the volume to recreate data if a disk fails. In a
two-disk system, the usable storage space is one disk. In a three-disk system, the usable
storage space is two disks. In general, the total capacity of your storage system equals the
capacity of all your disks minus the capacity of one disk.
V olume Configuration
20
Page 21

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
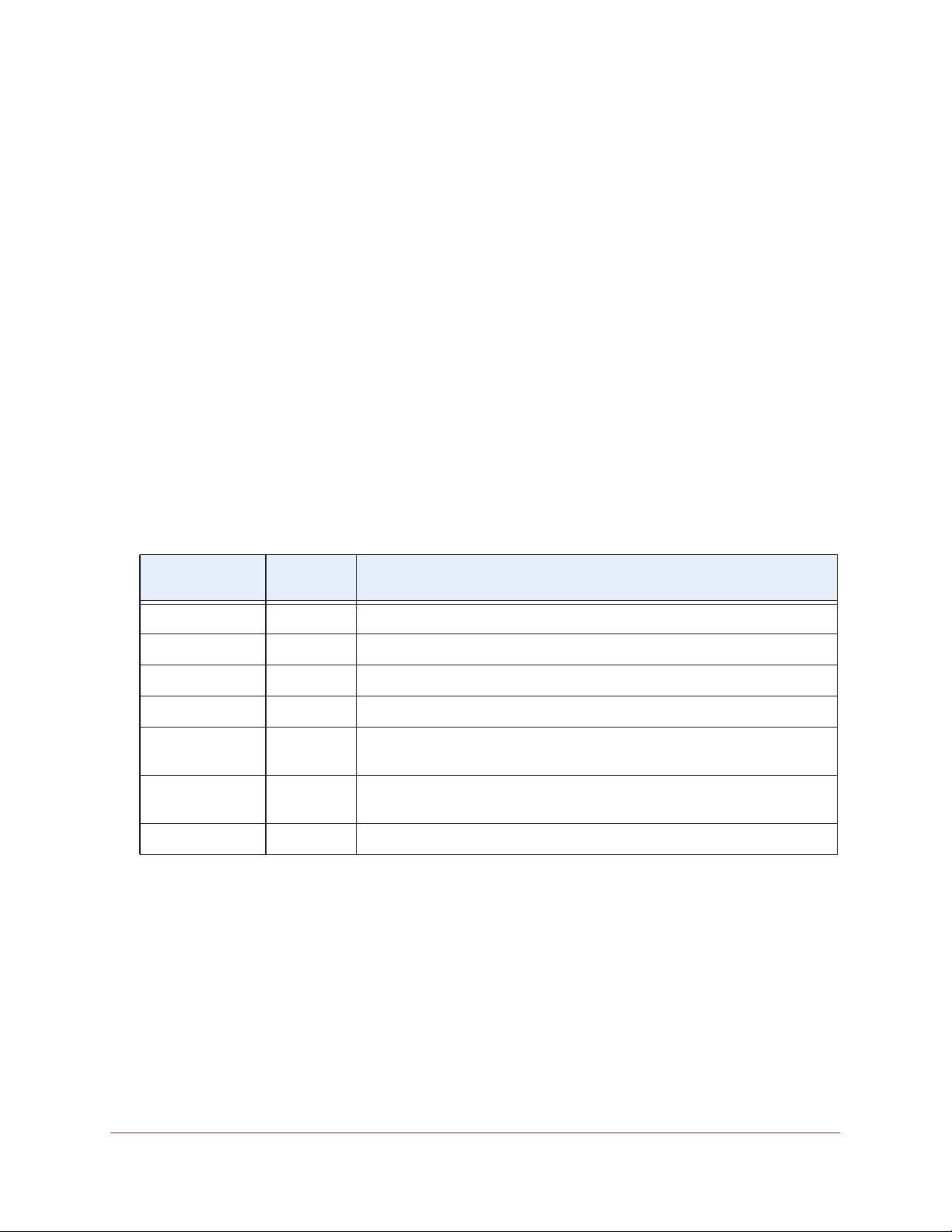
The following figure illustrates how X-RAID2 uses new disks.
c
b
a
Figure 3. X-RAID2 disk usage
a. The first disk that you install is used for initial (unprotected) storage space.
b. The second disk that you install is reserved for data protection (parity information).
c. Installing additional disks increases your storage space.
Note: X-RAID2 reserves the capacity of one disk for data protection. The
actual space reserved for data protection is distributed across all
disks.
Flex-RAID
NETGEAR’s Flex-RAID technology allows you to choose from among several
industry-standard RAID levels:
• JBOD. This most basic RAID level does not protect your data from loss if one of your
drives fails. JBOD is available only on volumes consisting of a single hard disk.
• RAID 0. RAID 0 distributes data across multiple disks, resulting in improved disk
performance compared to systems that do not use RAID formatting.
your storage system equals the capacity of all of your disk drives. RAID 0 is available on
volumes consisting of two or more hard disks.
The total capacity of
• RAID 1. This RAID level provides full redundancy of your data, because it duplicates data
across multiple disks. Exactly the same data is stored on two or more disks at all times.
RAID 1 protects your data from loss if one disk fails.
The total capacity of your storage
system equals the capacity of your smallest disk.
V olume Configuration
21
Page 22
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
• RAID 5. This RAID level also provides data redundancy, but it requires at least three
disks. RAID 5 uses the capacity of one disk to protect you from data loss if one disk fails.
Your data is distributed across multiple disks to improve disk performance. The total
capacity of your storage system equals the capacity of all your disks minus the capacity
of one disk. It is supported on systems with at least four drive bays.
• RAID 6.
This RAID level can recover from the loss of two disks. Your data is distributed
across multiple disks to improve disk performance. The total capacity of your storage
system equals the capacity of all your disks minus the capacity of two disks. It is
supported on systems with at least four drive bays.
• RAID 10 (or 1+0).
This RAID level uses both RAID 1 and RAID 0 technology. First, your
data is duplicated so that exactly the same data is stored on two or more disks. Then, the
data is distributed across additional disks to improve disk performance. It is supported on
systems with at least four drive bays.
The Flex-RAID levels that you can select depend on the number of disks included in the
volume.
The following table describes the Flex-RAID levels that are available for a given
number of disks. It also indicates whether adding a disk for data protection is possible for
each configuration.
Table 1. Flex-RAID levels and data protection
Number of Disks
per Volume
1 RAID 1 Yes. (Additional disk provides redundancy.)
1 JBOD No. (JBOD is available only for volumes consisting of one disk)
2 RAID 1 No. (Volume protection is already redundant.)
2 or more RAID 0 No. (RAID 0 does not offer protection.)
3 or more RAID 5 Yes. (Additional disk provides dual redundancy and converts the volume to
4 or more
(even number)
4 or more RAID 6 No. (Volume is already protected with dual redundancy.)
RAID Level Can I add a disk for data protection?
RAID 6.)
RAID 10 No. (Volume protection is already redundant.)
Manage Volumes
This section discusses volume management on your ReadyNAS system. You can add or
delete volumes from the system. Additionally, you can change the volume’s RAID mode and
level. This section also covers volume status, volume maintenance and volume protection. In
addition to volume topics, this section also covers extending the storage capacity on you
ReadyNAS system.
V olume Configuration
22
Page 23
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Change RAID Mode
You can change the RAID mode that your ReadyNAS storage system uses. By default, your
system’s hard disks are configured into a single X-RAID2 volume.
Change from X-RAID2 to Flex-RAID
Your ReadyNAS system can easily change a volume from X-RAID2 to Flex-RAID mode.
Data on the X-RAID2 volume is preserved when you switch to Flex-RAID. The RAID level of
the resulting Flex-RAID volume is automatically assigned based on the number of disks that
are installed.
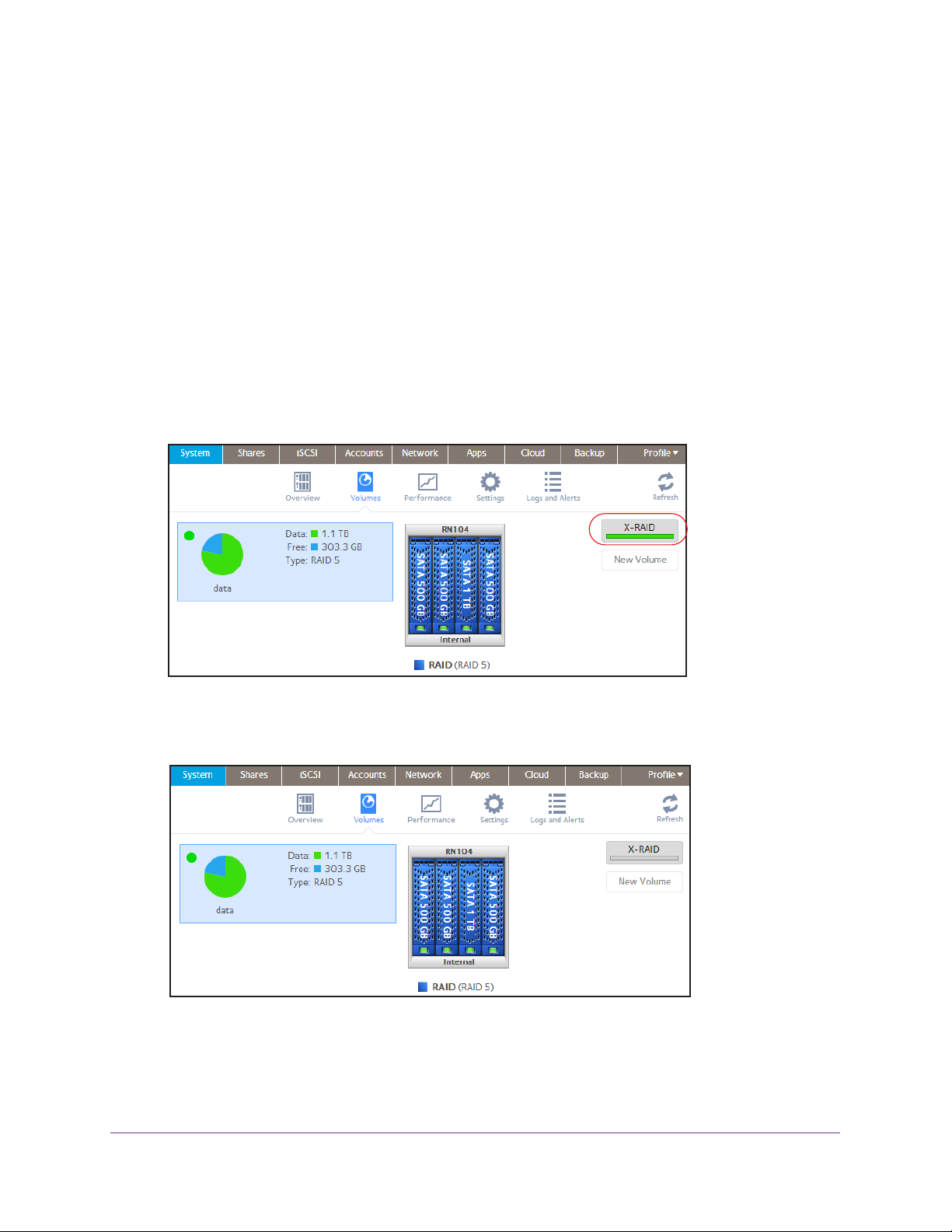
To change from X-RAID2 to Flex-RAID:
1. Select System > V
2. Click the X-RAID button at the right side of the screen.
3. Confirm that you want to switch from X-RAID2 to Flex-RAID.
The volume switches from X-RAID2 mode to Flex-RAID mode and the indicator on the
X-RAID button turns gray
olumes.
.
The RAID level is automatically assigned based on the number of disks that are installed.
V olume Configuration
23
Page 24
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Change from Flex-RAID to X-RAID2
If your system contains only one volume, you can easily switch from Flex-RAID to X-RAID2.
Data on the Flex-RAID volume is preserved when you switch to X-RAID2.
If your system contains multiple volumes, you must first reconfigure your disks into a single
volume.
Note: When you switch to X-RAID2 mode, any extra disks installed in your
system are automatically reformatted and used for storage
expansion.
You cannot change the RAID mode of a RAID 0 or RAID 10 volume.
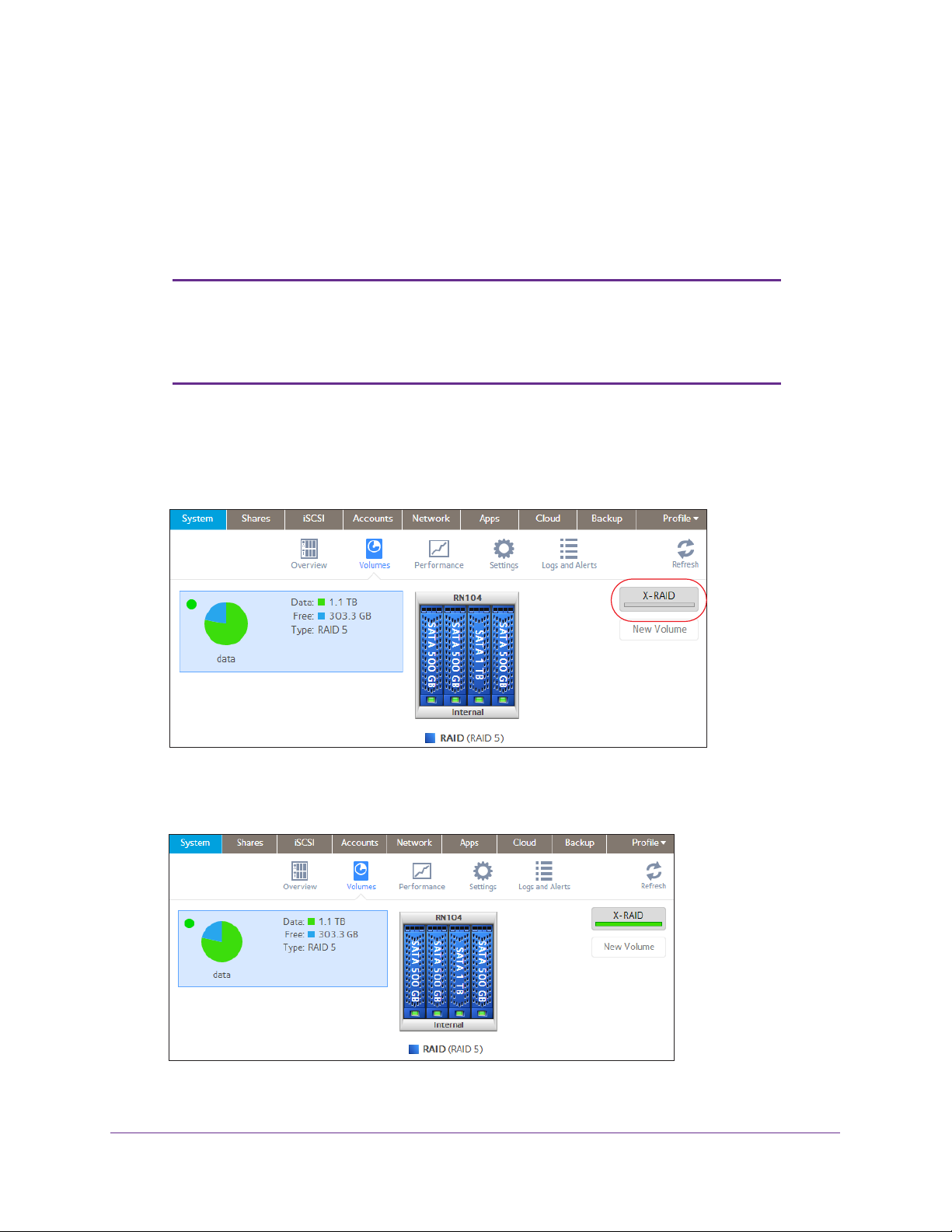
To change from Flex-RAID to X-RAID2 on a single-volume system:
1. Select System > V
olumes.
2. Click the X-RAID button at the right side of the screen.
3. Confirm that you want to switch from X-RAID2 to Flex-RAID.
The volume switches from Flex-RAID mode to X-RAID2 mode and the indicator on the
X-RAID button turns green.
Any available drives are automatically used for storage expansion.
V olume Configuration
24
Page 25
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Change to a Different Flex-RAID Level
In Flex-RAID mode, you assign one of several RAID levels to your volume. Available RAID
levels depend on the number of disks that you want the volume to include. For more
information, see Flex-RAID on page 21. You can reconfigure your volumes to use a different
RAID level.
Note: Changing the RAID level of a volume erases all data. If data is
stored on your system, you must back up the data to another
storage device before changing the RAID level.
You cannot change the RAID level of a RAID 0 volume.
To change to RAID levels:
1. If any data is stored on the volumes that you want to reconfigure, back up your data.
2. Delete the volumes that you want to reconfigure (see Delete a Volume on page 30).
The disks that were part of the volumes become available again for other purposes (the
color of the disks turns black).
3. Create a new volume from the available disks and select the RAID level (see Create and
Encrypt a Volume on page 29).
The volume is formatted according to your specifications. Formatting can take quite a
while, depending on the size of your hard disk drives.
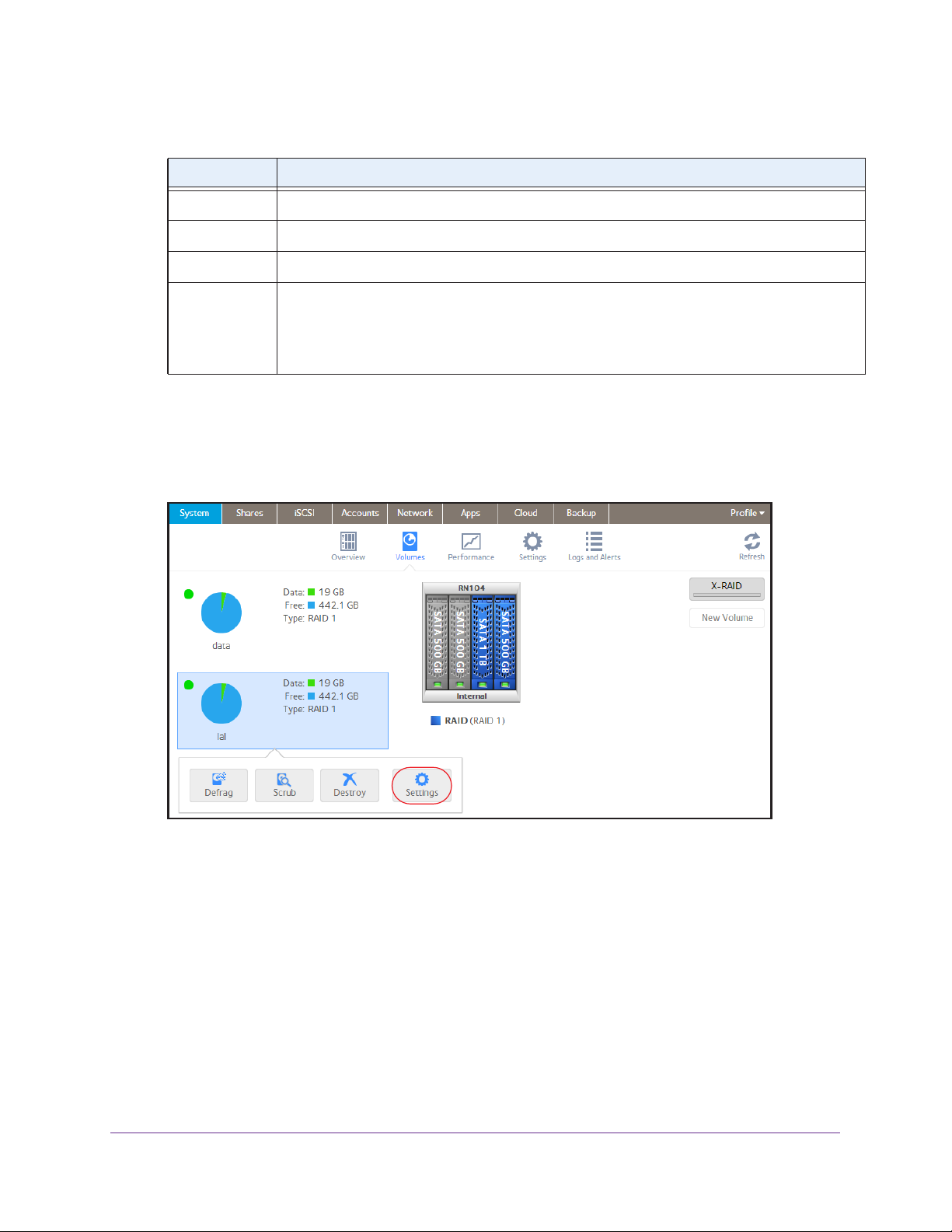
View the Status of a Volume
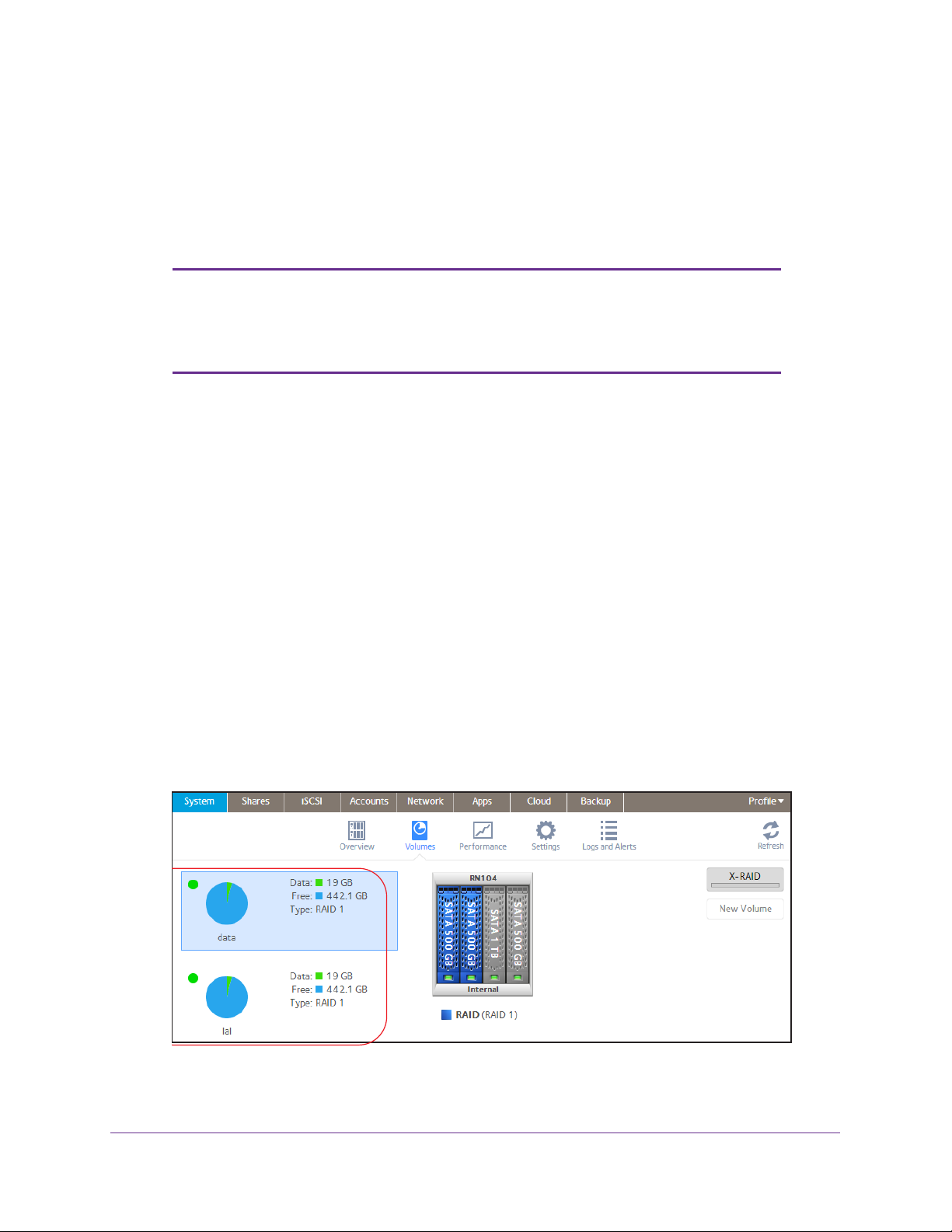
To view a summary of the volume status:
Select System > V
The volumes are listed at the left side of the screen.
olumes.
V olume Configuration
25
Page 26
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The following summary information is displayed next to each volume.
Item Description
Data The storage space that is consumed by data in MB, GB, or TB.
Free The storage space that is available in MB, GB, or TB.
Type The configured RAID level.
Health indicator The color of the indicator to the right of the volume icon indicates the health of the volume:
• Green. The
• Y
ellow. The volume is degraded.
• Red. The
To view the I/O stats and disk status:
volume is healthy.
volume is bad or faulty.
1. Select System > V
olumes.
2. Select the volume from the list on the left.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
V olume Configuration
26
Page 27
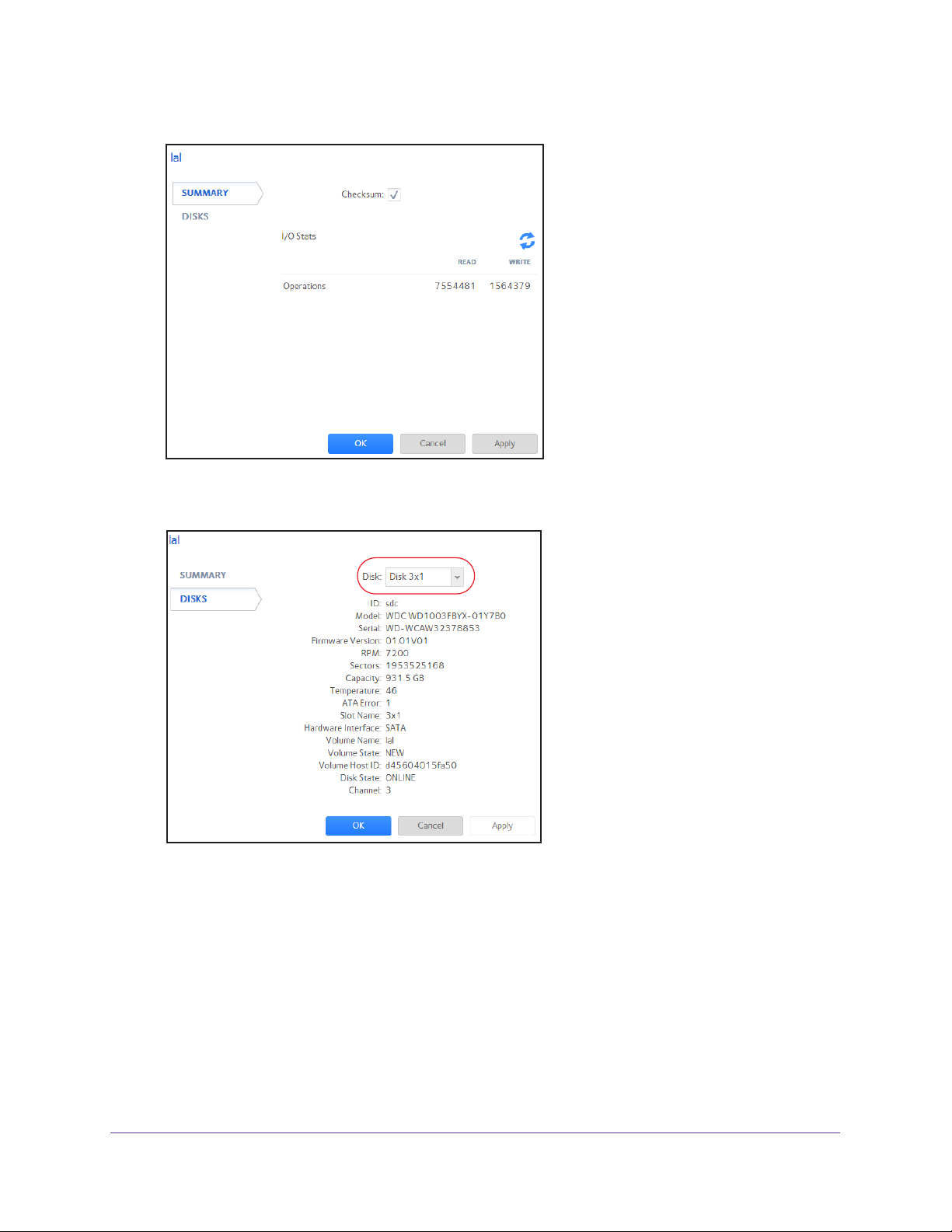
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
A pop-up screen displays the I/O stats in the Summary tab.
4. Click the Disks tab.
5. From the Disk drop-down list, select one of the disks in the volume to view its status.
Note: The disks are listed by their position in the enclosure: <column>x<row>.
For example, Disk 3X1 is the third disk from the left in the top row of the
enclosure.
Configure the Checksum Function
Checksum functions help detect data transmission errors. The ReadyNAS uses a checksum
function to improve accuracy and consistency when writing data to a volume. You can enable
or disable the checksum function on each volume. Enabling the checksum function improves
the integrity of your data but reduces performance speeds.
V olume Configuration
27
Page 28
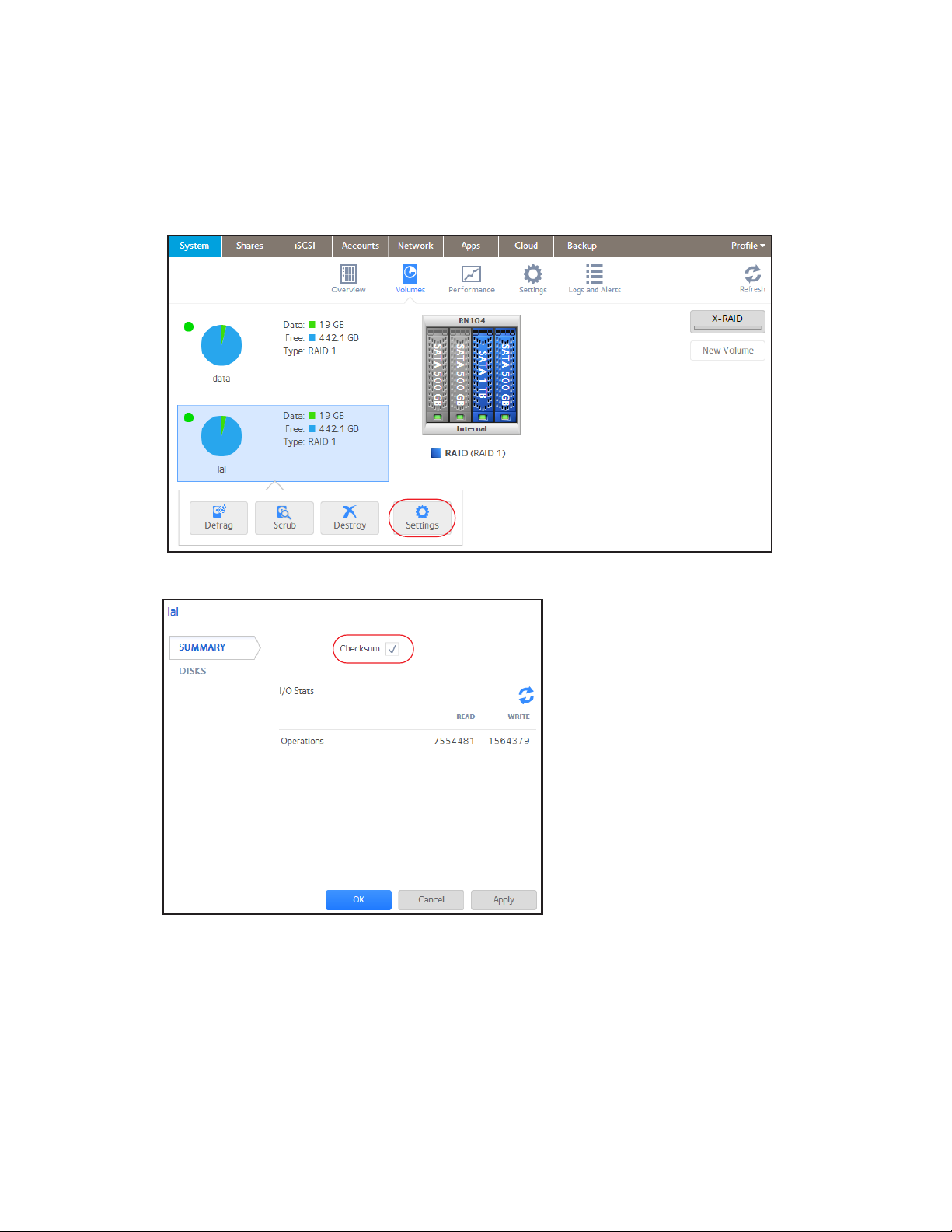
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Enable or disable the checksum function:
1. Select System > Volumes.
2. Select one of the volumes listed on the left side of the screen.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
A pop-up screen displays.
4. In the Summary tab, select or clear the Checksum check box.
5. Click the Apply button.
6. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved.
V olume Configuration
28
Page 29
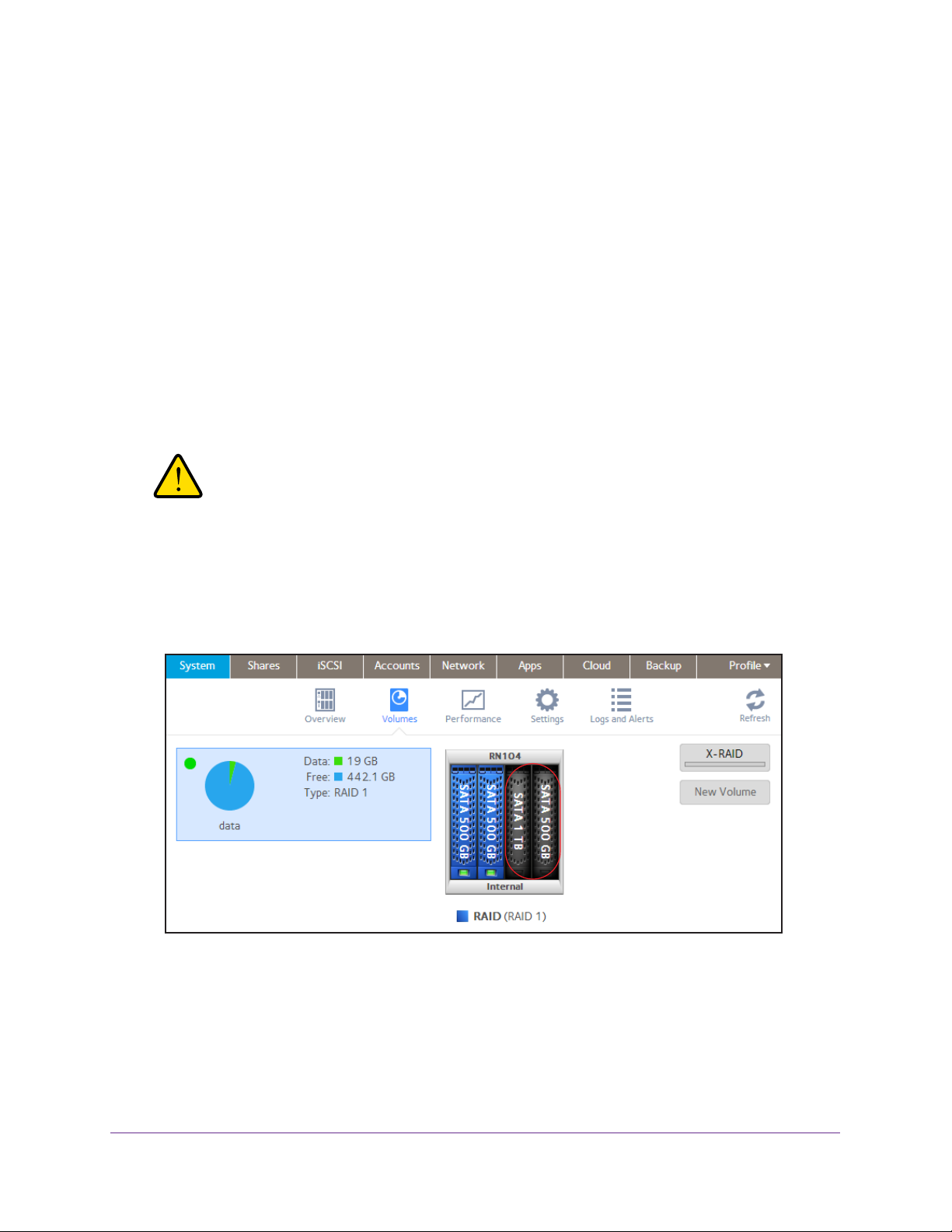
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Create and Encrypt a Volume
During volume creation you can also enable volume encryption. Encryption is optional. When
encryption is enabled, data is encrypted in real time as it is written to the volume. You cannot
encrypt existing volumes. Encryption is possible only when you are creating new volumes.
You need a USB drive to store the encryption key that is generated during volume creation.
ou can also have the encryption key emailed to you for safe keeping. If you lose the USB
Y
drive with the encryption key, you can load the emailed encryption key onto another USB
drive.
You must insert the USB drive with the encryption key into a USB port on the ReadyNAS for
the volume to be unlocked and accessible.
encrypted volume during reboot. You can remove the USB drive after unlocking the volume.
NETGEAR recommends storing the USB drive with the encryption key in a safe and secure
location when not in use.
WARNING:
You must also insert the USB drive to unlock an
If you lose the encryption key, the encrypted drive is
irrecoverable.
To create a volume, select the RAID level and enable encryption:
1. Select System > V
olumes.
2. From the enclosure graphic, select the disks that you want to include in the new volume.
Available disks are colored black.
3. Click the New V
olume button at the right of the screen.
V olume Configuration
29
Page 30
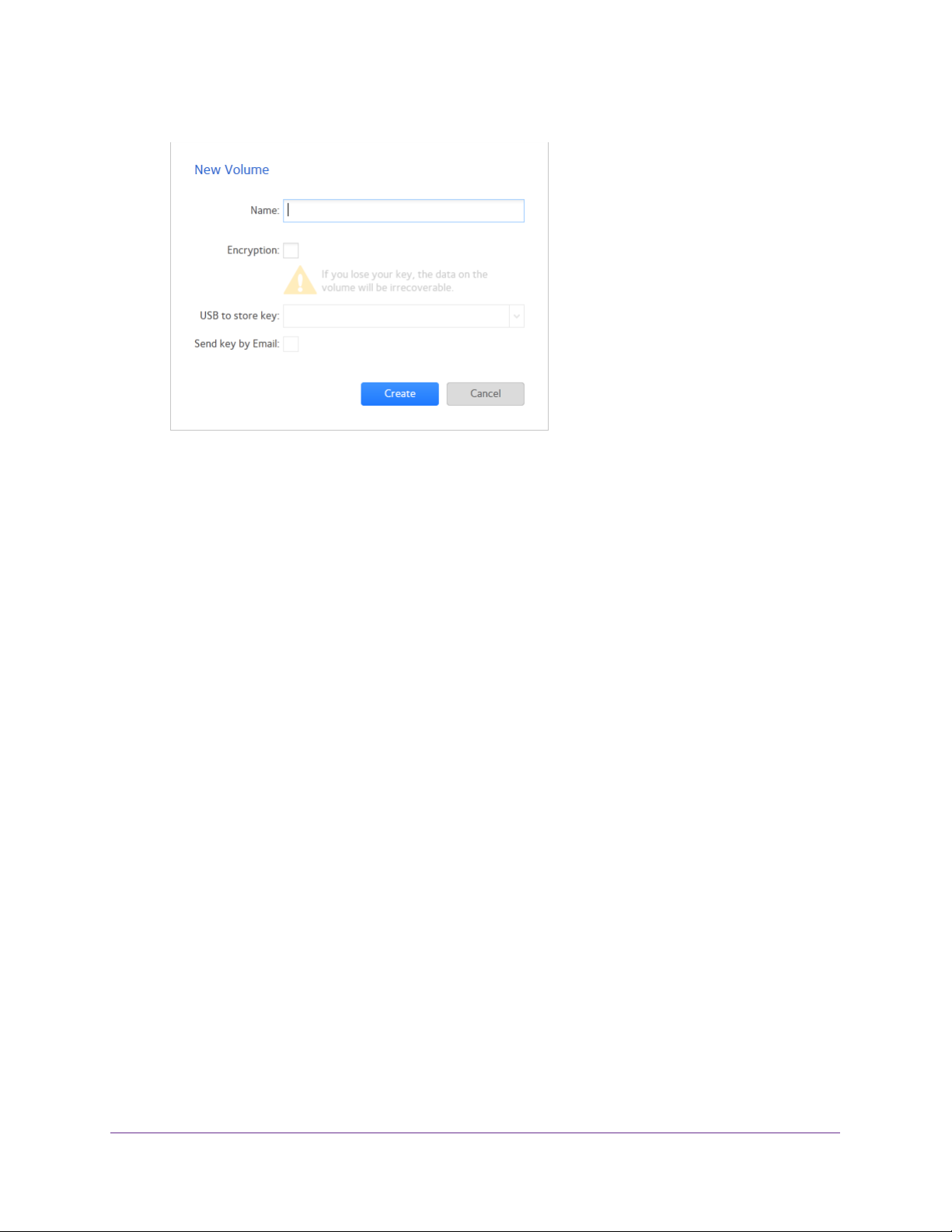
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The New Volume pop-up screen displays.
4. Configure the following settings:
• Name. Enter a name for the volume.
The volume must not have the same name as a
folder in the root folder system. The volume names home, apps, and job_ are
reserved and cannot be used.
• Encryption. Select this check box to enable encryption on the volume.
A key will be
generated. If you lose your key, the data on the volume will be irrecoverable.
• USB to store key. If you enabled encryption, select a USB storage device from the
drop-down list to store the generated key
.
• Send key by Email. If you enabled encryption, select this check box to have the
generated key sent to a email address associated with the admin account.
5. Click the Create button.
The new volume is created and appears in the list of volumes at the left of the screen.
Delete a Volume
Before you delete a volume, make sure that you back up any data (folders and LUNs) that
you want to save to another volume or another storage device.
To delete a volume:
1. Select System > V
2. Select the volume that you want to delete.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Destroy .
olumes.
V olume Configuration
30
Page 31

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Note: The Destroy option is not available when the ReadyNAS has a single
volume only. The Destroy option is available if you have at least two volumes.
A pop-up screen displays.
4. Type DESTROY to confirm your decision.
5. Click the Destroy button.
The volume is deleted. The disks that were part of the volume become available again for
other purposes (the color of the disks turns black).
Expand Storage Capacity
You can expand the storage capacity of an existing volume in two ways:
• Horizontal expansion. Expand the volume by adding more disks to the volume.
• V
ertical expansion. Expand the volume by replacing disks in the volume with
larger-capacity disks.
V olume Configuration
31
Page 32

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
X-RAID2 makes horizontal volume expansion easy. If your X-RAID2 volume includes two or
more disks, the volume expands automatically when you add disks.
You can expand a Flex-RAID volume by adding an additional JBOD disk or two additional
RAID 0 disks.
Vertical expansion is available for X-RAID2 and Flex-RAID volumes.
You can continue to use your ReadyNAS system while the new disks are incorporated in the
background. The process of volume expansion can take several hours. If you set up email
notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the process finishes. For
more information about alert notifications, see
Configure System Alerts on page 169.
Horizontally Expand an X-RAID2 Volume
Horizontal expansion is available for X-RAID2 volumes only.
To horizontally expand an X-RAID2 volume:
Add a disk to an X-RAID2 volume that includes two or more disks.
For more information about how to add a disk to your ReadyNAS system, see the hardware
manual for your system, which is available at
http://support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
The system automatically determines whether the new disk is used for protection or storage.
When you add a second disk, the new disk is used for data protection. When you add a third
or fourth disk, the new disk is used to increase your storage capacity. For more information,
see
X-RAID2 on page 20. New disks are incorporated in the background while you continue
to use your storage system.
Vertically Expand a Volume
Both X-RAID2 and Flex-RAID volumes support vertical expansion.
When you vertically expand a Flex-RAID volume, you must replace all disks in the volume
with larger-capacity disks.
Note: Vertical expansion is not available for RAID 0 volumes.
When you vertically expand an X-RAID2 volume, you must replace disks in the volume
according to the following table.
V olume Configuration
32
Page 33

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Table 2.
RAID Level Disk Replacements Required for Vertical Expansion
RAID 1 Replace 2 or more disks with larger-capacity disks.
RAID 5 Replace 2 or more disks with larger-capacity disks.
RAID 6 Replace 4 or more disks with larger-capacity disks.
X-RAID2 vertical expansion requirements
If you replace fewer disks than required for vertical expansion, the disks are reserved for data
protection. Your available storage capacity does not increase to accommodate the reserved
disks until you replace the required number of disks.
IMPORTANT:
To reduce the risk of data loss, NETGEAR recommends that you
back up your data before vertically expanding a volume.
To vertically expand an X-RAID2 volume:
1. Replace one disk in the volume with a larger-capacity disk.
For more information about how to add a disk to your system, see the hardware manual
for your system, which is available at
http://support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
Note: You must use supported disks in your ReadyNAS system. For a list
of supported disks, visit http://www.netgear.com/readynas-hcl.
ait for the volume to resync your data.
2. W
You can continue to use your ReadyNAS system while the volume is resyncing.
Resyncing can take several hours. The start and completion of the resyncing process is
recorded in the system log (see System Logs on page 219).
If you set up email notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the
process finishes. For more information about alert notifications, see Configure System
Alerts on page 169.
3. Repeat Step 1–Step 2 until you have replaced the required number of disks with
larger-capacity disks.
For more information about X-RAID2 vertical expansion requirements, see Table 2 on
page 33.
To vertically expand a Flex-RAID volume:
1. Replace one disk in the volume with a larger-capacity disk.
V olume Configuration
33
Page 34

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
For more information about how to add a disk to your system, see the hardware manual
for your system, which is available at
http://support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
Note: You must use supported disks in your ReadyNAS system. For a list
of supported disks, visit http://www.netgear.com/readynas-hcl.
2. Wait for the volume to resync your data.
You can continue to use your ReadyNAS system while the volume is resyncing.
Resyncing can take several hours. The start and completion of the resyncing process is
recorded in the system log (see
If you set up email notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the
process finishes. For more information about alert notifications, see
Alerts on page 169.
3. Repeat Step 1-Step 2 until you have replaced each disk in the volume with a larger-capacity
disk.
System Logs on page 219).
Configure System
Add Protection to a Volume
This section discusses protection against disk failure. The types of protection available
depend on the number of hard disks installed in the ReadyNAS system.
Add Protection to an X-RAID2 Volume
X-RAID2 requires a minimum of two hard disks to provide protection against disk failure. If
you have a one-disk ReadyNAS storage system and want protection from disk failure, you
must add a second disk that is at least as large as the first. You can add it while the system is
running. For more information about how to add a disk to your system, see the hardware
manual for your system, which is available at
http://support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
An X-RAID2 volume that includes two or more disks is automatically formatted to protect
against the failure of one disk. If you want to protect your data against the failure of two disks,
you must switch to Flex-RAID and select RAID 6. To use RAID 6, you must install four or
more disks. For more information about how to switch to Flex-RAID, see
X-RAID2 to Flex-RAID on page 23.
Add Protection to a Flex-RAID Volume
In certain cases, you can add a disk to a Flex-RAID volume to increase data protection. The
following table indicates whether adding a disk for data protection is possible for each
Flex-RAID configuration.
Change from
V olume Configuration
34
Page 35

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Table 3.
Number of Disks
per Volume
1 RAID 1 Yes. (Additional disk provides redundancy.)
2 RAID 1 No. (Volume protection is already redundant.)
2 or more RAID 0 No. (RAID 0 does not offer protection.)
3 or more RAID 5 Yes. (Additional disk provides dual redundancy and converts the volume to
4 or more
(even number)
4 or more RAID 6 No. (Volume is already protected with dual redundancy.)
Flex-RAID levels and data protection
RAID
Level
RAID 10 No. (Volume protection is already redundant.)
Can I add a disk to for data protection?
RAID 6.)
Disks added to a Flex-RAID volume can be used only for protection. They cannot be used for
storage (horizontal expansion). If you want to add a disk for increased storage capacity, you
must do one of the following:
• Create a volume using the added disks (see Create and Encrypt a Volume on page 29).
• Change the RAID level (see Change to a Different Flex-RAID Level on page 25).
• Switch to X-RAID2 (see Change from Flex-RAID to X-RAID2 on page 24).
To add a protection to a Flex-RAID volume:
1. Add a disk to your ReadyNAS storage system.
For more information about how to add a disk to your system, see the hardware manual
for your system, which is available at
http://support.netgear.com/product/ReadyNAS-OS6.
2. Select System > V
olumes.
The new disk is displayed in the enclosure graphic and is colored black.
3. Select the new disk from the enclosure graphic.
V olume Configuration
35
Page 36

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
4. Click the Add Parity button next to a volume that allows or requires additional protection.
A pop-up screen appears and asks you to confirm your decision.
5. Click the Y
Your data protection is increased in the background while you continue to use your
storage system.
Y ou can continue to use your ReadyNAS system while the extra disks are incorporated in
the background.
set up email notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the
process finishes. For more information about alert notifications, see Configure System
Alerts on page 169.
es button.
The process of increasing data protection can take several hours. If you
Maintain Volumes
This section covers volume maintenance. Volumes can be srcubbed to check for errors and
defragmented to improve disk performance.
Scrub a Volume
Scrubbing cleans and validates all data on a volume and checks the volume for errors. No
data is deleted. Folders, LUNs, and snapshots on the volume remain intact.
Note: Scrubbing is not an erase function.
To scrub a volume:
1. Select System > V
2. Select the volume that you want to scrub.
olumes.
V olume Configuration
36
Page 37

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Scrub.
The scrubbing process starts.
The start and completion of the volume scrub are recorded in the system log (see System
Logs on page 219).
If you set up email notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the
process finishes. For more information about alert notifications, see Configure System
Alerts on page 169.
Defragment a Volume
Over time, deletion, creation, and modification of files can fragment your data. Defragmenting
a volume improves disk performance and reduces data fragmentation.
To defragment a volume:
1. Select System > V
2. Select the volume that you want to defragment.
olumes.
V olume Configuration
37
Page 38

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Defrag.
The defragmentation process starts.
The start and completion of the volume defragmentation are recorded in the system log
(see System Logs on page 219).
If you set up email notifications for your system, you receive an email message when the
process finishes. For more information about alert notifications, see Configure System
Alerts on page 169.
V olume Configuration
38
Page 39

3. Shared Folders
This chapter describes how to create, manage, and access shared folders on the ReadyNAS. It
includes the following sections:
• Basic Shared Folder Concepts
• Manage Shared Folders
• Shared Folder Access Rights
• Access Shared Folders from a Network-Attached Device
• Access Shared Folders Using Cloud Services
Note: Without a volume, you cannot configure any shared folders. For
information about how to create volumes, see
Volume on page 29.
Create and Encrypt a
3
39
Page 40

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Basic Shared Folder Concepts
The volumes on your ReadyNAS can be divided into shared folders and logical unit numbers
(LUNs), both of which are logical entities on one or more disks. Shared folders and LUNs
enable you to organize data in a volume by type, group, user, department, and so on. A
single volume can contain multiple shared folders and LUNs.
Shared folders are NAS data sets that allow data transfer and storage over a network. You
can create a maximum of 1,024 shared folders on the ReadyNAS.
displays shared folders in the following way:
Figure 4. Shared folder with file-sharing protocols enabled
The local admin page
Figure 5. Shared folder with file-sharing protocols disabled
Shared folders are configured independently of one another, even though multiple shared
folders can reside on the same volume. You can configure properties of a shared folder,
including compression, protection, file-sharing protocols, and access rights. You can also
specify whether and how often a snapshot is created. These properties are explained in this
chapter.
Data Organization
Shared folders are the way that you group your data. You might want to group your data by
type, for example:
• Documents
• Music
• Pictures
• V
ideos
Another option is to group your data by user:
• To
m
• Rick
• Mary
Organizations might choose to group data by department:
• Accounting
Shared Folders
40
Page 41

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
• Sales
• Personnel
You can combine these schemes or come up with your own scheme.
Shared Folder Defaults
If you used ReadyCLOUD or the local setup wizard to configure your ReadyNAS storage
system, the following shared folders are created for you:
• Backup
• Documents
• Music
• Pictures
• readydrop
• Videos
If you want, you can delete or rename these shared folders. You can create other shared
folders to organize your data.
File and Folder Names
A shared folder can contain subfolders to help you organize your data files. If all characters in
the file or folder name are alphanumeric, the maximum length of the name is 255 characters.
If you use other kinds of characters, the maximum length might be reduced. For example, if a
file or folder name uses Kanji or Hanzi characters, the maximum length of the name might be
83 characters.
File-Sharing Protocols
You can access shared folders over a LAN or WAN network. Network access to data stored
on your ReadyNAS system is managed by file-sharing protocols, which handle the transfer of
data. You can access a shared folder on your ReadyNAS from other network-attached
devices (for example, a laptop or a tablet) if you enable the file-sharing protocol that the
network-attached device uses to access the ReadyNAS. You can enable multiple protocols
for an individual shared folder, allowing users to access the shared folder through various
methods.
For information about how to configure and enable file-sharing protocols for shared folders,
see
Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
Shared Folders
41
Page 42

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The following table lists the file-sharing protocols that your ReadyNAS storage system
supports.
Table 4. Supported file-sharing protocols
Protocol Description Recommendation
SMB
(Server Message Block)
NFS
(Network File Service)
AFP
(Apple File Protocol)
FTP
(File Transfer Protocol)
and FTPS
(FTP with SSL
encryption)
Used mainly by Microsoft Windows
computers and sometimes by Mac OS X
computers, this protocol is enabled by
default. It is sometimes referred to as the
CIFS (Common Internet File Service)
file-sharing protocol. SMB uses
Linux and Unix computers use NFS. Mac
OS X users can access NFS shared
folders through console shell access.
Y
our ReadyNAS system supports NFS
v3 over UDP and TCP and NFS v4 over
TCP.
Mac OS X computers use AFP. Your
ReadyNAS system supports
Many public file upload and download
sites use FTP
anonymous or user access for FTP
clients. You can elect to set up port
forwarding to nonstandard ports for
passive FTP, allowing clients to initiate a
connection to the ReadyNAS.
. The ReadyNAS supports
TCP/IP.
AFP 3.3.
If Windows users access your
storage system, enable this protocol.
If Linux or Unix users access your
storage system, enable this protocol.
If only Mac OS X users access your
storage system, enable this protocol.
However, in a mixed Windows and
Mac environment, NETGEAR
recommends using SMB only.
If users access your storage system
using FTP
, enable this protocol.
Rsync Fast file-transfer protocol that uses a
delta-transfer algorithm to send only the
dif
ferences between the source file and
the existing file.
HTTP
(Hypertext Transfer
Protocol)
and
HTTPS
(HTTP with SSL
encryption)
Used on the World Wide Web. If users access your storage system
Shared Folders
42
If users access your storage system
from a device that supports Rsync,
enable this protocol.
from a device with a web browser
including a smartphone or tablet
computer, enable this protocol.
,
Page 43

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Manage Shared Folders
From the local admin page, you can create, modify, delete, and browse shared folders on
your ReadyNAS.
Create a Shared Folder
After you create a volume (see Create and Encrypt a Volume on page 29), you can create
shared folders on that volume.
To create a shared folder:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Click the New Folder button to the right of the volume to which you want to add a shared
folder
.
The New Folder pop-up screen displays:
Shared Folders
43
Page 44

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. Configure the settings as explained in the following table:
Item Description
Name A unique name to identify the shared folder. Do not include spaces in the name.
Description An optional description to help identify the shared folder.
Compression Select the Compression check box to enable data compression. Compression saves
storage space and increases the speed of data transfers, but the compression and
decompression processes require additional resources. By default, the Compression
check box is cleared.
Continuous
Protection
Protocol Select the check box next to each file-sharing protocol that you want to enable on the
Select the Continuous Protection check box to enable data protection through
snapshots and configure how often snapshots are taken. By default, the Continuous
Protection check box is selected. For more information about snapshots, see Chapter 5,
Snapshots.
Interval The interval specifies how often a snapshot is taken. Make a selection from
the drop-down list:
• Hourly. A
• Daily. A
• W
eekly. A snapshot is taken every week on Friday at midnight.
shared folder:
• SMB
• NFS
• AFP
• FTP
• RSYNC
• HTTP
For information about these protocols, see File-Sharing Protocols on page 41.
snapshot is taken every hour on the hour.
snapshot is taken every day at midnight.
4. Click the Create button.
The ReadyNAS confirms the creation of a shared folder with the message “Folder or LUN
successfully created.”
5. Click the OK button.
The new shared folder is added to the Shares screen. Basic information is displayed to
the right of the shared folder
.
Shared Folders
44
Page 45

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
View and Change the Properties of a Shared Folder
To view and change the properties of a shared folder:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the shared folder that you want to configure.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
The folder settings display in a pop-up screen.
4. Change the settings as explained in the following table.
Item Description
Properties
Name A unique name to identify the shared folder. Do not include spaces in the name. All
characters must be alphanumeric.
Shared Folders
45
Page 46

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Item Description
Description An optional description to help identify the shared folder.
Compression Select the Compression check box to enable data compression. Compression saves
storage space and increases the speed of data transfers, but the compression and
decompression processes require additional resources.
Continuous
Protection
Allow Snapshot
Access
ReadyDLNA Select the ReadyDLNA Service check box to enable ReadyDLNA for the folder. For
Select the Continuous Protection check box to enable data protection through
snapshots and configure how often snapshots are taken. By default, the Continuous
Protection check box is selected. For more information about snapshots, see
Snapshots.
Interval The interval specifies how often a snapshot is taken. Make a selection from
the drop-down list:
• Hourly. A snapshot is taken every hour on the hour.
• Daily. A snapshot is taken every day at midnight.
• Weekly. A snapshot is taken every week on Friday at midnight.
Select the Allow Snapshot Access check box to allow snapshot access to anyone who
has permission to access the shared folder. The default snapshot access folder displays
in the Snapshot folder field.
When you allow snapshot access, a subfolder with the name snapshot is created on the
shared folder to allow users access to data from past snapshots. Users can then access
older versions of their files or recover files that were deleted.
more information about ReadyDLNA, see
Media
Type
Specify the type of media that you want to stream from the folder. Make a
selection from the drop-down list:
• All
• Video
• Audio
• Images
ReadyDLNA on page 199.
Chapter 5,
Network Access
For information about how to provide folder access to users and groups, see Set Network Access Rights to
Shared Folders on page 50.
File Access
For information about how to configure access rights for files and folders, see Set Up Access Rights to Files
and Folders on page 60.
5. Click the Apply button.
6. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Shared Folders
46
Page 47

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Delete a Shared Folder
WARNING:
Deleting a shared folder permanently removes the data within that
shared folder, including its snapshots.
To delete a shared folder from a volume:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the shared folder that you want to delete.
3.
From the pop-up menu that displays, select Delete.
4. In the pop-up screen that displays, confirm the deletion by typing DESTROY.
5. Click the Destroy button.
The shared folder is deleted.
Shared Folders
47
Page 48

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Browse a Shared Folder
You can browse the contents of a shared folder or external storage device from the local
admin page.
To browse data on your ReadyNAS:
1. Select Shares > Browse.
A list of shared folders on each volume displays.
2. Select the shared folder or subfolder that you want to browse.
The contents of the folder display.
Shared Folders
48
Page 49

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Tip: Use the forward and back ( ) arrows to browse through folders.
You can view files and folders as a list with details, as small icons, or as
large icons.
To change views, select one of the view icons (
) at
the right side of the screen.
Shared Folder Access Rights
Access rights apply to individual shared folders. For each shared folder, you control the
file-sharing protocols that can be used to access the shared folder and the access rights
granted to each user, group, and host. For example, you might want to grant a user
read/write permission on one shared folder, read-only permission on another shared folder,
and no access rights at all on a third shared folder. By default, all users and groups have
read/write access.
The following table lists access right options
Table 5. Access right options
Access Right Description
Read-only The user with this permission can read files on this shared folder, but cannot edit or
create files on this shared folder
Read/write A user with this permission can read, edit, and create files on this shared folder.
Read-only for everyone
with exceptions
Read/write for everyone
with exceptions
Disabled with exceptions Access to this shared folder is disabled for all users except for one or more users
Access to this shared folder is read-only for all users except for one or more users
who are granted read/write permission.
Access to this shared folder is read/write for all users except for one or more users
who are granted read-only permission.
who are granted either read-only or read/write permission.
.
.
User and Group Authentication
The way that users and groups are authenticated depends on the user and group
management mode that you selected (see User and Group Management Modes on
page 152):
• Local user database. If you use the local database, create group and user accounts
before you set up shared folder access rights. For more information about creating and
managing groups and user accounts, see Chapter 6, Users and Groups.
• Active Directory. If you use an external
Active Directory, the user and group information
is downloaded to the ReadyNAS. User and group access rights are listed when you click
the Access tab in the shared folder settings pop-up screen.
Shared Folders
49
Page 50

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders
To set the network access rights to an individual shared folder, you configure the network
access settings for each file-sharing protocol used to access the shared folder on your
storage system.
To set the network access rights for a shared folder:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the shared folder that you want to configure.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
The shared folder settings display in a pop-up screen.
Shared Folders
50
Page 51

4. Click the Network Access tab.
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
5. Click one of the file-sharing protocol buttons:
• SMB
• NFS
• AFP
• FTP
• RSYNC
• HTTP
The screen adjusts to display the access properties for the selected protocol.
6. Configure the network access settings for the selected protocol.
For more information, see the following sections (not all sections apply to all protocols):
• Configure User and Group Settings on page 52.
• Configure Host Settings on page 54.
• Configure Rsync Credentials on page 56.
• Manage Access to Remote Shared Folders on page 57
• Hide a Shared Folder on page 59.
7. Set the On-Of
o enable the protocol for the selected folder, set the On-Of f slider so that the slider
• T
f slider for the selected protocol:
shows the On position.
Shared Folders
51
Page 52

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The indicator on the protocol button turns green.
Note: When you enable a file-sharing protocol for an individual shared folder,
the protocol is also enabled globally. For more information about global
settings, see Configure Global Settings for File-Sharing Protocols on page 192.
o save the configured access settings but prevent them from taking effect, set the
• T
On-Off slider so that the slider shows the Off position.
The indicator on the protocol button turns gray.
Note: When you disable a file-sharing protocol for an individual shared folder,
the protocol remains enabled globally so that you can still access other folders
that might be using the protocol. For more information about global settings,
see Configure Global Settings for File-Sharing Protocols on page 192.
8. Click the Apply button.
9. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Configure User and Group Settings
For SMB, AFP, FTP, and HTTP , you can configure access rights to an individual shared folder
for users and groups. User and group settings do not apply to NFS and Rsync.
Note: You cannot configure access rights for the ReadyNAS admin ( ) or
for Cloud users (
Access Shared Folders Using Cloud Services on page 68.
To configure user and group network access settings:
1. On the folder settings pop-up screen, click the Network Access tab.
2. Select one of the file-sharing protocol buttons:
• SMB
• AFP
• FTP
• HTTP
). For more information about Cloud users, see
The screen adjusts to display the access properties for the selected protocol.
Shared Folders
52
Page 53

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. Click the Security tab on the left side of the pop-up screen.
4. From the drop-down list, make one of the following selections to specify the information that
you want to view:
• All.
The default group Everyone and all groups that you configured on the local
database or that were downloaded from the Active Directory server are displayed.
This is the default setting.
• Users. Only the individual users that you configured on the local database or that
were downloaded from the
Active Directory server are displayed.
• Groups. Only the groups that you configured on the local database or that were
downloaded from the
Active Directory server are displayed.
For information about using the local database or an Active Directory, see User and
Group Management Modes on page 152.
o search for a particular user or group, use the search field next to the
Tip: T
Search icon (
To update the user and group information, click the Refresh icon (
5. For each individual user (
).
).
) and group ( ) that you want to access the shared folder,
select one of the following check boxes:
• Read Only.
The selected user or group is permitted only to read files on the shared
folder.
• Read/W
rite. The selected user or group is permitted to read, edit, create, and delete
files on the shared folder.
Shared Folders
53
Page 54

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Note: If the ReadyNAS uses the local database, you can select the default
group Everyone to grant all users and groups read-only or read/write access.
6. (Optional for SMB and AFP) Allow anonymous access to the shared folder.
If the ReadyNAS uses the local database and you grant the default group Everyone
access, you can select the Allow anonymous access check box to allow anonymous
access to the shared folder. In this situation, users are not required to provide their
account credentials when accessing the shared folder.
7. Click the Apply button.
8. Click OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Configure Host Settings
For SMB, NFS, FTP, Rsync, and HTTP, you can configure access rights for users on hosts.
Host settings do not apply to AFP. The access rights that you configure for one host apply to
all users on the host. For NFS, you can also configure the access rights that apply to any
host, and, for individual hosts, you can configure whether root access is granted.
To add a host and configure host access settings:
1. On the folder settings pop-up screen, click the Network Access tab.
2. Click one of the file-sharing protocol buttons:
• SMB
• NFS
• FTP
• Rsync
• HTTP
The screen adjusts to display the access properties for the selected protocol.
Shared Folders
54
Page 55

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. Click the Hosts tab on the left side of the pop-up screen.
Note: If the host access list is empty, any host is allowed to access the
shared folder.
If you add at least one host to the list, access to the shared folder is
restricted to hosts on the list only.
4. Click the + button (
).
The Add Host pop-up screen displays.
5. Enter the host IP address in the IP address field.
6. Click the Add button.
The host is added to the host access list.
Note: For SMB, the access rights for each host depend on the access rights
of the user.
Shared Folders
55
Page 56

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
7. (Optional for Rsync) Set the default access rights for users on the listed hosts by selecting
one of the following options from the drop-down list:
• Read Only. The users on the listed hosts are permitted only to read files on the
shared folder.
• Read/Write. The users on the listed hosts are permitted to read, edit, create, and
delete files on the shared folder.
8. (Optional for NFS, FTP, and HTTP) For each host on the host access list, select one of the
following check boxes:
• Read Only. The users on the selected host are permitted only to read files on the
shared folder.
• Read/Write. The users on the selected host are permitted to read, edit, create, and
delete files on the shared folder.
Note: For NFS only, you can set access rights for AnyHost, which is a default
entry in the host access list. You cannot grant root access to AnyHost.
9. (Optional for NFS) For each host for which you want to grant the users root access, select
the Root Access check box.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your changes are saved.
11. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Configure Rsync Credentials
You can require users to enter Rsync credentials when accessing your storage system using
Rsync.
To require credentials for Rsync sessions:
1. On the folder settings pop-up screen, click the Network Access tab.
2. Click the RSYNC file-sharing protocol button.
Shared Folders
56
Page 57

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. Click the Security tab on the left side of the pop-up screen.
4. Select the Enable Password Protection check box.
5. Click the + button ( ) and create at least one Rsync user account and password.
Note: Rsync credentials are completely separate from your ReadyNAS
storage system’s user accounts.
6. Click the Apply button.
7. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Manage Access to Remote Shared Folders
The SMB protocol allows you to access remote shared folders on other network-attached
devices and treat them as if they resided locally on your ReadyNAS system.
To enable access to a remote shared folder:
1. On the folder settings pop-up screen, click the Network Access tab.
2. Click the SMB file-sharing protocol button.
Shared Folders
57
Page 58

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. Click the DFS tab on the left side of the pop-up screen.
4. Select the Enable DFS Root check box.
5. Click the + button ( ) above the list of remote shared folders.
6. In the pop-up screen that displays, enter the following information:
• Name.
The name of the remote shared folder, as you want it to appear on your
ReadyNAS.
• Address.
The IP address of the network-attached device where the remote shared
folder resides.
• Remote share.
The name of the remote shared folder, as it appears on the
network-attached device.
7. Click the Add button.
The new remote shared folder appears on the list.
8. Click the Apply button.
9. Click the OK button.
Shared Folders
58
Page 59

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
10. Make sure that the remote shared folder on the network-attached device is configured for file
sharing.
You can now access the remote shared folder from your ReadyNAS system using the
SMB protocol. For information about how to access your system using the SMB protocol,
see Use a Windows Device on page 64 or Use a Mac OS X Device on page 65.
Hide a Shared Folder
This feature is available for SMB only. Hiding a folder prevents users from discovering the
folder unless they explicitly specify the folder name in the browse path.
To configure advanced settings for SMB:
1. On the folder settings pop-up screen, click the Network Access tab.
2. Click the SMB file-sharing protocol button.
3. Click the Advanced tab on the left side of the pop-up screen.
4. Select the Hide this folder check box.
5. Click the Apply button.
6. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Enable WebDAV
This feature is available only for HTTP (which includes HTTPS, which is required in some
cases). WebDA V is an extension of the HTTP protocol that facilitates document management
and editing. Features of WebDAV include maintenance of document properties such as
author, creation date, and modification date, and it provides overwrite protection. Access is to
a shared folder and the contained files.
Shared Folders
59
Page 60
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
After you enable WebDAV access, you can access the files in the shared folder over the
Internet from a computer or mobile device in a manner similar to accessing the files over a
LAN or through a VPN. The specifics depend on the device and application using WebDAV.
To enable WebDAV on an individual shared folder:
1. On the folder settings pop-up screen, click the Network Access tab.
2. Click the HTTP file-sharing protocol button.
3. Click the WEBDA
V tab on the left side of the pop-up screen.
4. Select the Enable WebDAV check box.
5. Click the Apply button.
6. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Set Up Access Rights to Files and Folders
For each individual shared folder, you can configure the default access rights to files and
folders.
Change Default Access Rights to Files and Folders
By default, owners, groups, and anyone else with access to the shared folder has read/write
access to all files and folders on the shared folder.
To change the default access rights to files and folders on an individual shared folder:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the shared folder that you want to configure.
Shared Folders
60
Page 61

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
The shared folder settings display in a pop-up screen.
4. Click the File Access tab on the pop-up screen.
5. Configure the file and folder access rights as explained in the following table:
Item Setting
Folder Owner You can assign a single user or the administrator as the folder owner. By default,
the folder owner is set to guest.
Folder Group You can assign a single group, a single user, or the administrator as the folder
group. By default, the folder group is set to guest.
Shared Folders
61
Page 62

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Item Setting
Folder Owner Rights Permissions granted to the folder owner. Select one of the check boxes:
• No box selected.
folder.
• Read Only.
• Read/W
default setting.
Folder Group Rights Permissions granted to members of the same group as the owner’s primary
group. Select one of the check boxes:
• No box selected. Members of the group have no access to folders that are
owned by a member of the group.
• Read Only. Members of the group have read-only access to folders that are
owned by a member of the group.
• Read/W
are owned by a member of the group. This is the default setting.
Folder Everyone Rights Permissions granted to users who are not the folder owner and not members of
the folder group. Select one of the check boxes:
• No box selected. No one outside the folder group has access rights to the
folder
• Read Only.
• Read/Write. Anyone outside the folder group has read/write access to the
folder. This is the default setting.
rite. The folder owner has read/write access to the folder . This is the
rite. Members of the group have read/write access to folders that
.
The folder owner does not have access rights to the
The folder owner has read-only access to the folder.
Anyone outside folder group has read-only access to the folder.
To restore the default file and folder access rights on an individual shared folder:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the shared folder that you want to configure
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
The shared folder settings display in a pop-up screen.
Shared Folders
62
Page 63

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
4. Click the File Access tab on the pop-up screen.
5. Click the Reset tab.
6. Click the Reset permissions button.
The default access rights are restored. Owners, groups, and anyone else with access to
the shared folder gains read/write access to all files and folders on the shared folder.
Access Shared Folders from a Network-Attached Device
You can remotely access shared folders and snapshots on your storage system using other
network-attached devices, such as a laptop or tablet. The network-attached device must
support one of the enabled file-sharing protocols. How a shared folder is accessed depends
on the OS of the network-attached device, the file-sharing protocols that you enabled for
shared folder access, and the access rights that you granted (see Shared Folder Access
Rights on page 49).
Note: For snapshots to be accessible to users from their network-attached
devices, you need to select the Allow snapshot access check box
on the shared folder settings pop-up screen. For more information,
see View and Change the Properties of a Shared Folder on
page 45.
Shared Folders
63
Page 64

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Use a Web Browser
You can use a web browser to access files that are stored on your ReadyNAS system.
Note: If you are accessing your files from a network that is outside your
LAN, you must configure port forwarding on your router. For more
information, see your router user manual.
To access a shared folder using a web browser:
1. Ensure that the HTTP file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
2. Launch a web browser.
3. Navigate to the ReadyNAS system and shared folder you want to access using the following
syntax:
http://<hostname>/<shared folder>
• <hostname> is the name that you assigned to your ReadyNAS system or the default
host name if you did not change it.
• <shared folder> is the name of the shared folder that you want to access.
Note: If you cannot access the ReadyNAS using its host name, try entering
http://<ReadyNAS IP address> in the Windows Explore address bar instead.
<ReadyNAS IP address> is the IP address of the ReadyNAS.
• (Optional) For a secure encrypted connection, replace http with https.
You are prompted to log in to your ReadyNAS system.
4. Enter a user ID and password.
You can log in with administrator or user credentials. If you log in as a user, your access
is limited by the settings configured by the ReadyNAS system administrator.
Your shared folders are displayed in a web page.
Use a Windows Device
You can access shared folders on your ReadyNAS system using a network-attached
Windows-based device.
To access a shared folder using a network-attached Windows device:
1. Ensure that the SMB file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
Shared Folders
64
Page 65

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
2. Enter \\<hostname> in the Windows Explorer address bar.
<hostname> is the name that you assigned to your ReadyNAS system or the default host
name if you did not change it.
Note: If you cannot access the ReadyNAS using its host name, try entering
\\<ReadyNAS IP address> in the Windows Explore address bar instead.
<ReadyNAS IP address> is the IP address of the ReadyNAS.
You are prompted to log in to your ReadyNAS system.
3. Enter a user ID and password.
You can log in with administrator or user credentials. If you log in as a user, your access
is limited by the settings configured by the ReadyNAS system administrator
.
Windows Explorer displays the contents of all available shared folders on your
ReadyNAS system.
Use a Mac OS X Device
You can access shared folders on your ReadyNAS system using a network-attached OS X
device.
To access a shared folder using a network-attached OS X device:
1. Ensure that the AFP or SMB file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
2. In Finder
, select Go > Connect to Server.
The Connect to Server dialog box displays.
3. Connect to your ReadyNAS system as follows:
Shared Folders
65
Page 66

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
• If you are using the AFP file-sharing protocol, enter the following command in the
Server Address field:
afp://<hostname>
• If you are using the SMB file-sharing protocol, enter the following command in the
Server Address
smb://<hostname>
In both cases, <hostname> is the name that you assigned to your ReadyNAS system
or the default host name if you did not change it.
Note: If you cannot access the ReadyNAS using its host name, try entering
afp://<ReadyNAS IP address> or smb://<ReadyNAS IP address> instead.
<ReadyNAS IP address> is the IP address of the ReadyNAS.
4. Click the Connect button.
You are prompted to log in to your ReadyNAS system.
field:
5. Enter a user ID and password.
You can log in with administrator or user credentials. If you log in as a user, your access
is limited by the settings configured by the ReadyNAS system administrator
You are prompted to select a volume. Mac OS X calls your ReadyNAS shared folders
volumes
6. Select the volume or volumes (shared folder or folders) you want to access and click the OK
button.
Finder displays the volume contents.
.
.
Use a Linux or Unix Device
Y ou can access shared folders on your ReadyNAS system using a network-attached Linux or
Unix device.
Shared Folders
66
Page 67

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Note: Your ReadyNAS system does not support NIS because it is unable
to correlate NIS information with SMB user accounts. In mixed
environments where you want SMB and NFS integration, manually
specify the user ID and group ID of the user and group accounts to
match your NIS or other Linux or Unix server setting.
To access an SMB shared folder using a network-attached Linux or Unix device:
1. Ensure that the SMB file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
2. Using a terminal program, enter the following command:
mount [-t smb -o username=<user name>,password=<password>]
//<ReadyNAS IP address>/<shared folder name> <mount point>
• <user name> and <password> match the user name and password on the
ReadyNAS.
• <ReadyNAS IP address> is the IP address of the ReadyNAS.
• <shared folder name> is the name of the shared folder that you want to access.
• <mount point> is the name of an empty folder on the Linux or Unix device.
To access an NFS shared folder using a network-attached Linux or Unix device:
1. Ensure that the NFS file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
2. Using a terminal program, enter the following command:
mount [-t nfs] <ReadyNAS IP address>:/<volume name>/<shared folder
name> <mount point>
• <ReadyNAS IP address> is the IP address of the ReadyNAS.
• <volume name> is the name of the volume on which the shared folder resides.
• <shared folder name> is the name of the shared folder that you want to access.
• <mount point> is the name of an empty folder on the Linux or Unix device.
Use FTP and FTPS
You can use FTP and FTPS to access any shared folders that are enabled for the FTP and
FTPS file-sharing protocols.
For better security, use an FTPS client to connect to your ReadyNAS using the FTP
file-sharing protocol. With FTPS, your password and data are encrypted.
If you are using FTPS, you must use explicit mode (also known as FTPES or AUTH TLS) in
your FTP client.
Shared Folders
67
Page 68

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
To access a shared folder using FTP:
1. Ensure that the FTP file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
2. Launch an FTP client or a terminal program.
3. Log in to your ReadyNAS system, as follows:
• If you required user FTP access when you enabled the FTP-file sharing protocol, log
in using user or administrator credentials for your ReadyNAS system. If you log in as
a user, your access is limited by the settings configured by the ReadyNAS system
administrator.
• If you allowed anonymous access when you enabled the FTP-file sharing protocol,
log in as anonymous and use your email address for the password.
Use Rsync
You can use Rsync to access any shared folders that are enabled for the Rsync file-sharing
protocol. Instead of browsing shared folders as you do with some other file-sharing protocols,
with Rsync, you copy files from your ReadyNAS system to another computer that supports
the Rsync file-sharing protocol. If you previously copied these files, Rsync copies only the
differences between the source files and the destination files, making the transfer much
quicker than using other file-sharing protocols. The first time you copy files using the Rsync
file-sharing protocol, you see no performance difference.
To access shared folders using Rsync:
1. Ensure that the Rsync file-sharing protocol is enabled on your ReadyNAS storage
system.
For more information, see Set Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
2. On a network-attached device that supports the Rsync file-sharing protocol, launch a
terminal program or an Rsync client.
3. Enter any required credentials for the shared folder.
For more information about Rsync shared folder access credentials, see Configure Rsync
Credentials on page 56. For more information about Rsync terminal program commands,
visit http://rsync.samba.org. For more information about using an Rsync client application,
see the documentation that accompanies the application.
Access Shared Folders Using Cloud Services
Several cloud-based services are preinstalled on your ReadyNAS system, including
ReadyCLOUD, ReadyNAS Remote, and ReadyDROP. You can use these services to
remotely access your storage system.
Shared Folders
68
Page 69

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Use ReadyCLOUD
ReadyCLOUD is an online service that you use to discover and set up ReadyNAS storage
systems on your network. After you discover your ReadyNAS system using ReadyCLOUD,
you can use ReadyCLOUD to securely access and manage your system from anywhere that
has an Internet connection.
For more information about discovering your device using ReadyCLOUD or creating a
ReadyCLOUD account, see
Using ReadyCLOUD involves these high-level steps:
1. Add your ReadyNAS system to your ReadyCLOUD account.
See Join ReadyCLOUD on page 69.
2. (Optional) Grant access to ReadyCLOUD users.
See Add ReadyCLOUD Users on page 71.
3. Access your data and manage your ReadyNAS system using ReadyCLOUD.
Discover and Set Up Your ReadyNAS on page 12.
See Access Your System Using ReadyCLOUD on page 78.
Join ReadyCLOUD
The ReadyCLOUD service is preinstalled on your ReadyNAS storage system. Before you
can access your system using ReadyCLOUD, you must add your system to your
ReadyCLOUD account.
To add your ReadyNAS system to ReadyCLOUD:
1. On the local admin page, select the Cloud tab.
Shared Folders
69
Page 70

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
2. Set the On-Off slider so the slider shows the On position to enable ReadyCLOUD.
3. On the pop-up screen that displays, enter your ReadyCLOUD account credentials.
4. Click the Join button.
Your system is added to ReadyCLOUD.
The ReadyCLOUD account that you used to add your system to ReadyCLOUD is
automatically granted access to your system as the ReadyCLOUD admin.
You can now use the ReadyCLOUD web portal to access your system from anywhere that
has an Internet connection.
For more information about granting access to ReadyCLOUD users, see Add ReadyCLOUD
Users on page 71.
Shared Folders
70
Page 71

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Note: If you decide to remove your system from ReadyCLOUD, any
ReadyCLOUD users that you added will lose access to the system.
For more information about using the ReadyCLOUD web portal, see Access Your System
Using ReadyCLOUD on page 78.
Add ReadyCLOUD Users
After you add your system to ReadyCLOUD, you can allow other ReadyCLOUD users to
access your system using their ReadyCLOUD accounts.
For more information about joining ReadyCLOUD, see Join ReadyCLOUD on page 69.
Note: When you grant access to a ReadyCLOUD user, that user
automatically gains access to your system from ReadyCLOUD and
ReadyNAS Remote.
To grant access to ReadyCLOUD users:
1. Open a web browser and visit http://readycloud.netgear
.com.
2. From the top menu bar, select Sign In near the top right corner of the screen.
Shared Folders
71
Page 72

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. In the pop-up screen that displays, enter your ReadyCLOUD account credentials and click
the Sign In button.
You are signed in to ReadyCLOUD.
4. From the top menu bar
, select Manage.
The ReadyNAS systems that you added to ReadyCLOUD using this account are
displayed.
5. Next to the system to which you want to grant access, click the Invite User button.
6. In the pop-up screen that displays, enter the user name or email address of the
ReadyCLOUD user that you want to add to your system.
7. Click the Search button.
Shared Folders
72
Page 73

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
8. From the results list, select the ReadyCLOUD user that you want to add and click the Invite
button.
The selected ReadyCLOUD user is added to the Users list. This user can now use his or
her ReadyCLOUD account to access your ReadyNAS system.
Note: When you grant access to a ReadyCLOUD user, that user is also added
to the Cloud Users list on the local admin page for your system.
For more information about using the ReadyCLOUD portal, see Access Your System Using
ReadyCLOUD on page 78.
Delete ReadyCLOUD Users
Y ou must use the ReadyCLOUD web portal to delete a ReadyCLOUD user. When you delete
a ReadyCLOUD user, that user can no longer use his or her ReadyCLOUD account to
access your ReadyNAS system.
Note: When you delete a ReadyCLOUD user, that user automatically
loses access to your system from ReadyCLOUD and ReadyNAS
Remote.
Shared Folders
73
Page 74

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
To delete a ReadyCLOUD user:
1. Open a web browser and visit http://readycloud.netgear.com.
2. From the top menu bar, select Sign In near the top right corner of the screen.
3. In the pop-up screen that displays, enter your ReadyCLOUD account credentials and click
the Sign In button.
You are signed in to ReadyCLOUD.
4. From the top menu bar
, select Manage.
The ReadyNAS systems that you added to ReadyCLOUD using this account display.
5. From the system’
s User list, select the ReadyCLOUD user that you want to delete.
Shared Folders
74
Page 75

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
6. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Delete.
7. Confirm the deletion.
The selected ReadyCLOUD user can no longer use his or her ReadyCLOUD account to
access your ReadyNAS system.
Manage Permissions for ReadyCLOUD Users
By default, when you grant access to ReadyCLOUD users, those users can view and edit
shared folders on your ReadyNAS system.
You use the ReadyCLOUD web portal to configure the access rights to individual shared
folders. For each shared folder, you can specify which ReadyCLOUD users have permission
to view or edit the folder. The following table lists the access right options.
Table 6. Access right options
Access Right Description
Read-only The user with this permission can read files on this shared folder, but cannot edit or
create files on this shared folder
Read/write A user with this permission can read, edit, and create files on this shared folder.
Read-only for everyone
with exceptions
Read/write for everyone
with exceptions
Access to this shared folder is read-only for all users except for one or more users
who are granted read/write permission.
Access to this shared folder is read/write for all users except for one or more users
who are granted read-only permission.
.
Disabled with exceptions Access to this shared folder is disabled for all users except for one or more users
who are granted either read-only or read/write permission.
Shared Folders
75
Page 76

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
To set the ReadyCLOUD access rights for a shared folder:
1. Open a web browser and visit http://readycloud.netgear.com.
2. From the top menu bar, select Sign In near the top right corner of the screen.
3. In the pop-up screen that displays, enter your ReadyCLOUD account credentials and click
the Sign In button.
4. From the top menu bar, select Access.
The ReadyNAS systems that you added to ReadyCLOUD using this account are
displayed.
Note: You can also set ReadyCLOUD permissions from the Browse screen.
5. Select the shared folder that you want to configure.
Shared Folders
76
Page 77

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
6. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Permissions.
The ReadyCLOUD access rights to the shared folder display in a pop-up screen.
7. For each ReadyCLOUD user that you want to access the shared folder, select one of the
following check boxes:
• Read Only.
The selected user or group is permitted only to read files on the shared
folder.
• Read/W
rite. The selected user or group is permitted to read, edit, create, and delete
files on the shared folder.
Shared Folders
77
Page 78

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Note: You can select the default group Everyone and set read-only or
read/write access for all ReadyCLOUD users.
8. Click the Apply button.
9. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved.
Access Your System Using ReadyCLOUD
If you added your system to ReadyCLOUD, you and your ReadyCLOUD users can use the
ReadyCLOUD portal to access your ReadyNAS from anywhere that has an Internet
connection.
For more information about joining ReadyCLOUD, see Join ReadyCLOUD on page 69.
For more information about adding ReadyCLOUD users, see Add ReadyCLOUD Users on
page 71.
To access your data and manage your ReadyNAS using ReadyCLOUD:
1. Open a web browser and visit http://readycloud.netgear
.com.
2. From the top menu bar, select Sign In near the top right corner of the screen.
Shared Folders
78
Page 79

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. In the pop-up screen that displays, enter your ReadyCLOUD account credentials and click
the Sign In button.
You are signed in to ReadyCLOUD. Y ou can now use the ReadyCLOUD web interface to
access your data and manage any systems that you added to your ReadyCLOUD
account.
Use ReadyNAS Remote
ReadyNAS Remote is a web-based service that allows you to drag and drop files between
your ReadyNAS system and your Windows or Mac computer using the SMB file-sharing
protocol. All file permissions and shared folder security settings are retained as if you were
on your LAN. All data is encrypted so that it is transmitted securely.
Shared Folders
79
Page 80

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
ReadyNAS Remote uses preinstalled software on your ReadyNAS system and a small
software program for your Windows or Mac computer.
Using ReadyNAS Remote involves these high-level steps:
1. Enable ReadyNAS Remote on your ReadyNAS storage system.
See Enable ReadyNAS Remote on page 80.
2. Grant access to ReadyNAS Remote users.
See Add ReadyNAS Remote Users on page 81.
3. Install ReadyNAS Remote client software on your computer
.
See Install the ReadyNAS Remote Client on Remote Devices on page 84.
4. Access your shared folders.
See Access Shared Folders Using ReadyNAS Remote on page 85.
For more information about ReadyNAS Remote, see the ReadyNAS Remote User Manual.
Enable ReadyNAS Remote
The ReadyNAS Remote service is preinstalled on your ReadyNAS storage system. Before
you can access shared folders using ReadyNAS Remote, you must enable it on your
ReadyNAS system.
To enable ReadyNAS Remote:
1. On the local admin page, click the Cloud tab.
2.
Set the On-Off slider so the slider shows the On position next to ReadyNAS Remote.
Shared Folders
80
Page 81

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The ReadyNAS Remote service verifies that your Internet connection is working and that
your device is online.
ReadyNAS Remote is enabled.
3. (Optional) Configure advanced settings for the ReadyNAS Remote service:
a. Select Settings next to ReadyNAS Remote.
b. Configure the options in the pop-up screen that displays.
c. Click the Apply button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
Add ReadyNAS Remote Users
After you enable ReadyNAS Remote on your system, you can allow other ReadyNAS
Remote users to access your system using their ReadyNAS Remote accounts.
For more information about enabling ReadyNAS Remote on your system, see Enable
ReadyNAS Remote on page 80.
ReadyNAS Remote users can access your system using enabled file-sharing protocols.
Access to individual shared folders is granted or restricted according to the access rights that
you specify when you configure access to the shared folder.
If you did not enable anonymous access to a shared folder, anyone who tries to access the
system must provide valid ReadyNAS user account credentials.
For more information about managing access to shared folders on your system, see Set
Network Access Rights to Shared Folders on page 50.
Shared Folders
81
Page 82

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Note: ReadyNAS Remote users can access your system using only
ReadyNAS Remote and ReadyDROP. If you also want users to
access your system using ReadyCLOUD, add the users from
ReadyCLOUD instead. See Add ReadyCLOUD Users on page 71.
To grant access to ReadyNAS Remote users:
1. On the local admin page, click the Cloud button.
2. Click the Users button.
A pop-up screen with a list of users displays.
3. Click the Invite Users button.
A pop-up screen displays.
Shared Folders
82
Page 83

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
4. Enter the email address of the ReadyNAS Remote user to whom you want to grant access.
5. Click the Search button.
One of the following screens displays:
• If the email address is linked to a ReadyNAS Remote account, the account’
s user
name displays in the search results list. Select the user name and click the Invite
button. The selected ReadyNAS Remote user can now access your ReadyNAS
system using his or her ReadyNAS Remote account. The user name is added to the
Cloud Users list with a user icon.
• If the email address is not linked to a ReadyNAS Remote account, you are prompted
to send an email inviting the person to create a ReadyNAS Remote account.
The
person’s email address is added to the Cloud Users list with an envelope icon. When
the person creates a ReadyNAS Remote account using that email address, the
envelope icon changes to a user icon.
Remove ReadyNAS Remote Users
When you remove a ReadyNAS Remote user, that user can no longer use his or her
ReadyNAS Remote account to access your ReadyNAS system.
Shared Folders
83
Page 84

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
To remove a ReadyNAS Remote user:
1. On the local admin page, click the Cloud tab.
2. Click the Users button next to ReadyNAs Remote.
Note: The Cloud Users list includes both ReadyNAS Remote and
ReadyCLOUD users. Do not remove ReadyCLOUD users from the
Cloud Users list on the local admin page. If you want to delete a
ReadyCLOUD user, use the ReadyCLOUD portal. See Delete
ReadyCLOUD Users on page 73.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select the user you want to remove.
4. Click the Remove User button.
5. Confirm the removal.
The ReadyNAS Remote user no longer has access to your ReadyNAS system and is
removed from the Cloud Users list.
Install the ReadyNAS Remote Client on Remote Devices
Before you can access shared folders using ReadyNAS Remote, you must install the
ReadyNAS Remote client software on your Windows or Mac computer.
To install the ReadyNAS Remote client on remote devices:
1. Using the device from which you want to remotely access a ReadyNAS system, visit
http://www.netgear.com/ReadyNAS-remote.
2. Download the appropriate client software for your operating system and install it according to
your operating system’
3. Launch the ReadyNAS Remote client.
s instructions.
Shared Folders
84
Page 85

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
4. Log in to your ReadyNAS Remote account or create a free ReadyNAS Remote account.
Tip: If you created a ReadyCLOUD account, you can use your ReadyCLOUD
credentials to log in to ReadyNAS Remote. For more information about
ReadyCLOUD, see Discover and Set Up Your ReadyNAS on page 12.
The ReadyNAS Remote client is installed on your device.
Mac system tray
Windows system tray
The ReadyNAS Remote icon displays in your system tray.
Access Shared Folders Using ReadyNAS Remote
You can use ReadyNAS Remote to drag and drop files between your computer and your
ReadyNAS system, even when your computer is not on the same LAN as your ReadyNAS
system.
To access shared folders using ReadyNAS Remote on a Windows computer:
1. Launch the ReadyNAS Remote client software on your computer
2. Right-click the ReadyNAS Remote icon in the system tray
.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Log In.
The ReadyNAS Remote icon blinks while the device is connecting and displays as blue
when it is connected.
.
4. Click the ReadyNAS Remote icon in the system tray
Shared Folders
85
.
Page 86

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
A list of your ReadyNAS Remote devices displays.
5. Click the system that you want to access.
6. Enter valid ReadyNAS user or admin credentials.
Note: The credentials that you enter to access shared folders on the
system are different from your ReadyNAS Remote credentials.
Accessing shared folders requires you to enter credentials for a user
account on the system.
Your shared folders open in Windows Explorer.
You can now drag and drop files between your computer and your ReadyNAS system as
though you were on the ReadyNAS LAN.
To access shared folders using ReadyNAS Remote on a Mac computer:
1. Launch the ReadyNAS Remote client software on your computer
2. Click the ReadyNAS Remote icon in the system tray
.
.
3. From the drop-down menu that displays, select Shares.
4. From the menu that displays, select the ReadyNAS Remote device that you want to access.
Shared Folders
86
Page 87

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
5. Enter valid ReadyNAS user or admin credentials.
Note: The credentials that you enter to access shared folders on the
system are different from your ReadyNAS Remote credentials.
Accessing shared folders requires you to enter credentials for a user
account on the system.
A list of shared folders on the selected device displays.
6. Select the shared folders you want to access and click the OK button.
Your shared folders open in Finder.
You can now drag and drop files between your Mac and your ReadyNAS system as
though you were on the ReadyNAS LAN.
Use ReadyDROP
ReadyDROP allows you to synchronize files in real time between your ReadyNAS storage
system and ReadyDROP-enabled remote devices. Any files that you put in a ReadyDROP
folder on your ReadyNAS system or on ReadyDROP-enabled remote devices are
synchronized automatically, in the background, as long as the devices have Internet access.
Changes are synchronized to all of your ReadyDROP folders in the background, in real time.
Using ReadyDROP involves these high-level steps:
1. Enable ReadyNAS Remote o
See Enable ReadyNAS Remote on page 80.
2. Enable ReadyDROP on your ReadyNAS storage system.
See Enable ReadyDROP on page 88.
3. Grant access to ReadyNAS Remote users.
n your ReadyNAS storage system.
See Add ReadyNAS Remote Users on page 81.
4. Install ReadyNAS Remote on your remote devices.
See Install the ReadyNAS Remote Client on Remote Devices on page 84.
Shared Folders
87
Page 88

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
5. Manage your ReadyDROP folder using the ReadyDROP portal or from a
ReadyDROP-enabled device.
See Manage Files Using the ReadyDROP Portal on page 89 and Manage ReadyDROP
Files from a ReadyDROP-Enabled Device on page 90.
After you follow these steps, your ReadyNAS system and your remote devices have
ReadyDROP folders that begin to sync immediately in real time as long as the devices have
Internet access. When you add, delete, or edit files in the ReadyDROP folder on your
ReadyNAS system, the changes are made in the ReadyDROP folder on all remote devices.
When you add, delete, or edit files in the ReadyDROP folder on a remote device, the
changes are made in the ReadyDROP folder on your ReadyNAS system and any other
remote devices.
Enable ReadyDROP
ReadyDROP uses ReadyNAS Remote technology. To use ReadyDROP, you must first set
up ReadyNAS Remote (see Use ReadyNAS Remote on page 79.)
To enable ReadyDROP:
1. Click the Cloud tab.
2. Set the On-Of
f slider so the slider shows the On position next to ReadyDROP.
The ReadyDROP service verifies that your Internet connection is working and that your
device is online.
ReadyDROP is enabled.
3. (Optional) If you have more than one volume on your ReadyNAS system, specify the
volume on which you want to create the ReadyDROP folder:
a. Click the Settings button next to ReadyDROP
Shared Folders
88
.
Page 89

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
b. In the pop-up screen that displays, select a volume for the ReadyDROP folder.
A ReadyDROP folder is created on that volume.
Manage Files Using the ReadyDROP Portal
The ReadyDROP portal is a web-based management interface for all of your synchronized
ReadyDROP files.
WARNING:
If you add, create, or rename a file with the same name as an
existing file, your browser cannot warn you of the overwrite risk.
The existing file is immediately overwritten.
To manage files using the ReadyDROP portal:
1. V
isit the ReadyDROP portal at https://readydrop.netgear.com/.
2. Enter your ReadyNAS Remote user name and password and click the Log in button.
Tip: If you created a ReadyCLOUD account, you can use your ReadyCLOUD
credentials to log in to ReadyDROP and ReadyNAS Remote. For more
information about ReadyCLOUD, see Discover and Set Up Your
ReadyNAS on page 12.
Shared Folders
89
Page 90

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
The ReadyDROP portal displays. Your ReadyDROP-enabled devices are listed on the
left.
You can now add, delete, and download files in your system’s ReadyDROP folder.
For more information about using the ReadyDROP portal, see the ReadyNAS Remote
User Manual.
Manage ReadyDROP Files from a ReadyDROP-Enabled Device
You can use your ReadyDROP-enabled device’s native interface to manage ReadyDROP
files.
To manage ReadyDROP files from a Windows device:
1. Launch the ReadyNAS Remote client software on your computer
2. Right-click the ReadyNAS Remote icon in the system tray
.
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Log In.
The ReadyNAS Remote icon blinks while the device is connecting and displays as blue
when it is connected.
4. Right-click the ReadyNAS Remote icon in the system tray
.
5. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Open ReadyDROP.
.
Shared Folders
90
Page 91

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
6. From the drop-down menu that displays, select the device that contains the ReadyDROP
folder that you want to access.
ReadyDROP launches and the ReadyDROP icon displays in the system tray.
7. Click the ReadyDROP icon.
8. From the drop-down menu that displays, select Open ReadyDROP Folder.
The contents of your ReadyDROP folder display in Windows Explorer.
You can now add, delete, or edit files in the ReadyDROP folder using the standard
interface on your Windows device. Changes are synchronized with your ReadyNAS
system and all other ReadyDROP-enabled devices.
To manage ReadyDROP files from a Mac device:
1. Launch the ReadyNAS Remote client software on your computer
2. Click the ReadyNAS Remote icon in the system tray
.
.
3. From the drop-down menu that displays, select ReadyDROP.
4. From the drop-down menu, select the device that contains the ReadyDROP folder that you
want to access.
ReadyDROP launches and a ReadyDROP icon displays in the system tray.
5. Click the ReadyDROP icon in the system tray.
Shared Folders
91
Page 92

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
6. From the drop-down menu that displays, select Open ReadyDROP Folder.
The contents of your ReadyDROP folder display in Finder.
You can now add, delete, or edit files in the ReadyDROP folder using the standard
interface on your Mac device. Changes are synchronized with your ReadyNAS system
and all other ReadyDROP-enabled devices.
Shared Folders
92
Page 93

4. LUNs
This chapter describes how to create, manage, and access LUNs on the ReadyNAS. It includes
the following sections:
• Basic LUN Concepts
• Manage LUNs
• LUN Groups and Access Rights
• Access LUN Groups from an iSCSI-Attached Device
Note: Without a volume, you cannot configure any LUNs. For information
about how to create volumes, see
page 29.
Create and Encrypt a Volume on
4
93
Page 94

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Basic LUN Concepts
The volumes on your ReadyNAS can be divided into shares and logical unit numbers
(LUNs), both of which are logical entities on one or more disks. Shares and LUNs enable you
to organize data in a volume by type, group, user, department, and so on. A single volume
can contain multiple shares and LUNs.
LUNs are SAN (storage area network) data sets that allow data transfer and storage over
iSCSI and Fibre Channel devices.
ReadyNAS system supports up to 256 LUNs. The local admin page displays LUNs in the
following way:
Figure 6. Thin LUN
The ReadyNAS supports iSCSI devices only. Each
Figure 7. Thick LUN
Each LUN is configured independently of other LUNs that reside on the same volume. You
can configure settings such as compression, protection, provisioning, LUN size, and access
rights. You can also specify whether and how often a snapshot is created. These settings are
explained in the following sections.
Thin and Thick Provisioning
You can specify the size of a LUN in two ways:
• Thin.
A thin LUN lets you overallocate its size. That is, you can assign a LUN size that is
larger than the size of the volume. Even though you specify the size of a thin LUN when
you create it, storage space is assigned on demand instead of up front. This method
greatly improves the utilization rate of the LUN because storage space is assigned only
as data is written to the LUN. However, the size of the LUN is reported as the total
storage space that you specify when you create the LUN.
You can expand a volume as needed (if necessary, adding disks in the process) without
expanding the size of the LUN and therefore, without disconnecting users. Make sure
that you watch the volume capacity of the volume on which the overallocated LUN
resides so you do not run out of storage space unexpectedly
.
Note: NETGEAR recommends that you do not use an overallocated LUN for
storage of critical data. Instead, use a thick LUN.
LUNs
94
Page 95

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
• Thick. All storage space that you specify when you create a thick LUN is allocated up
front and the storage space is reserved on the volume. Snapshots, other LUNs, and
shared folders on the volume cannot consume storage space that is reserved. The size of
the LUN is reported as the total storage space that you specify when you create the LUN.
You cannot assign more storage space than the available nonreserved storage space on
the volume.
Default LUN Settings
The following table explains the default settings of a LUN. You can change these settings
when you create or change the LUN.
Table 7. LUN default settings
Item Default State
Compression Disabled
Continuous Protection Enabled
Interval Daily
Provision Thick
Access Denied until you set permissions
Manage LUNs
From the local admin page, you can create, modify, or delete a LUN.
Create a LUN
After you create a volume (see Create and Encrypt a Volume on page 29), you can create
LUNs on that volume. The following procedure describes how to create a LUN from the
Shares screen.
Note: On ReadyNAS 102, 104, and 2120 systems, individual LUNs cannot
To create a LUN:
You can also create a LUN from the iSCSI screen.
exceed 8 TB.
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
LUNs
95
Page 96

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
2. Click the New LUN button to the right of the volume to which you want to add a LUN.
The New LUN pop-up screen displays.
3. Configure the settings as explained in the following table:
Item Description
Name A unique name to identify the LUN. Do not include spaces in the name. All characters must
be alphanumeric.
Description An optional description to help identify the LUN.
Compression Select the Compression check box to enable data compression. Compression saves
storage space and increases the speed of data transfers, but the compression and
decompression processes require additional resources. By default, the Compression check
box is cleared.
LUNs
96
Page 97

Item Description
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Continuous
Protection
Provision Select how storage space is provisioned. Make a selection from the drop-down list:
Size Specify the size of the LUN. The maximum size that you can allocate to the LUN is stated
Select the Continuous Protection check box to enable data protection through snapshots
and configure how often snapshots are taken. By default, the Continuous Protection check
box is selected. For more information about snapshots, see
Interval The interval specifies how often a snapshot is made. Make a selection from the
drop-down list:
• Hourly. A snapshot is taken every hour on the hour.
• Daily. A snapshot is taken every day at midnight. This is the default setting.
• Weekly. A snapshot is taken every week on Friday at midnight.
• Thin. Even though you specify the size of the LUN when you create it, storage space
is assigned on demand instead of up front. The size of the LUN is reported as the total
storage space that you specify when you create the LUN.
• Thick. All storage space that you specify when you create the LUN is also allocated
up
front. The size of the LUN is reported as the total storage space that you specify
when you create the LUN. This is the default method.
Note: Make sure that you watch the volume capacity of the volume on which the
overallocated LUN resides so you do not run out of storage space unexpectedly.
Note: NETGEAR recommends that you do not use an overallocated thin LUN for storage
of critical data. Instead, use a thick LUN.
at the bottom of the screen.
Chapter 5, Snapshots.
Unit Select the unit of measurement from the drop-down list:
• MB.
• GB. This is the default unit of measurement.
• TB.
4. Click the Create button.
The ReadyNAS confirms the creation of a LUN with the message “Folder or LUN
successfully created.”
5. Click the OK button.
The new LUN is added to the Shares screen. Basic information is displayed to the right of
the LUN.
View and Change the Properties of a LUN
To view and change the properties of a LUN:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the LUN that you want to configure.
LUNs
97
Page 98

ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
The LUN settings display in a pop-up screen.
4. Change the settings as explained in the following table.
Item Description
Name A unique name to identify the LUN. Do not include spaces in the name.
Description An optional description to help identify the LUN.
Compression Select the Compression check box to enable data compression. Compression saves
storage space and increases the speed of data transfers, but the compression and
decompression processes require additional resources. By default, the Compression check
box is cleared.
LUNs
98
Page 99

Item Description
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
Continuous
Protection
Provision The provision setting is provided for information only. You cannot change the provision
Size For information about how to expand the size of an existing LUN, see Expand the Size of a
Select the Continuous Protection check box to enable data protection through snapshots
and configure how often snapshots are taken. By default, the Continuous Protection check
box is selected. For more information about snapshots, see
Interval The interval specifies how often a snapshot is made. Make a selection from the
drop-down list:
• Hourly. A snapshot is taken every hour on the hour.
• Daily. A snapshot is taken every day at midnight. This is the default setting.
• Weekly. A snapshot is taken every week on Friday at midnight.
setting of an existing LUN.
LUN on page 99.
Chapter 5, Snapshots.
5. Click the Apply button.
6. Click the OK button.
Your changes are saved and the pop-up screen closes.
For information about how to set access right for a LUN, see LUN Groups and Access Rights
on page 103.
Expand the Size of a LUN
After you create a LUN, you cannot change the provision setting (thin or thick), but you can
expand the size of the LUN.
Expansion is instant, regardless of the data size, but you must first disconnect all users that
are connected to the LUN. Disconnect access to the LUN by removing the LUN from the LUN
group to which the users have access (see
Create a LUN Group on page 103).
Note: On ReadyNAS 102, 104, and 2120 systems, individual LUNs cannot
exceed 8 TB.
To expand the size of a LUN:
1. Select Shares > Shares.
A list of shared folders and LUNs on each volume displays.
2. Select the LUN that you want to expand.
LUNs
99
Page 100
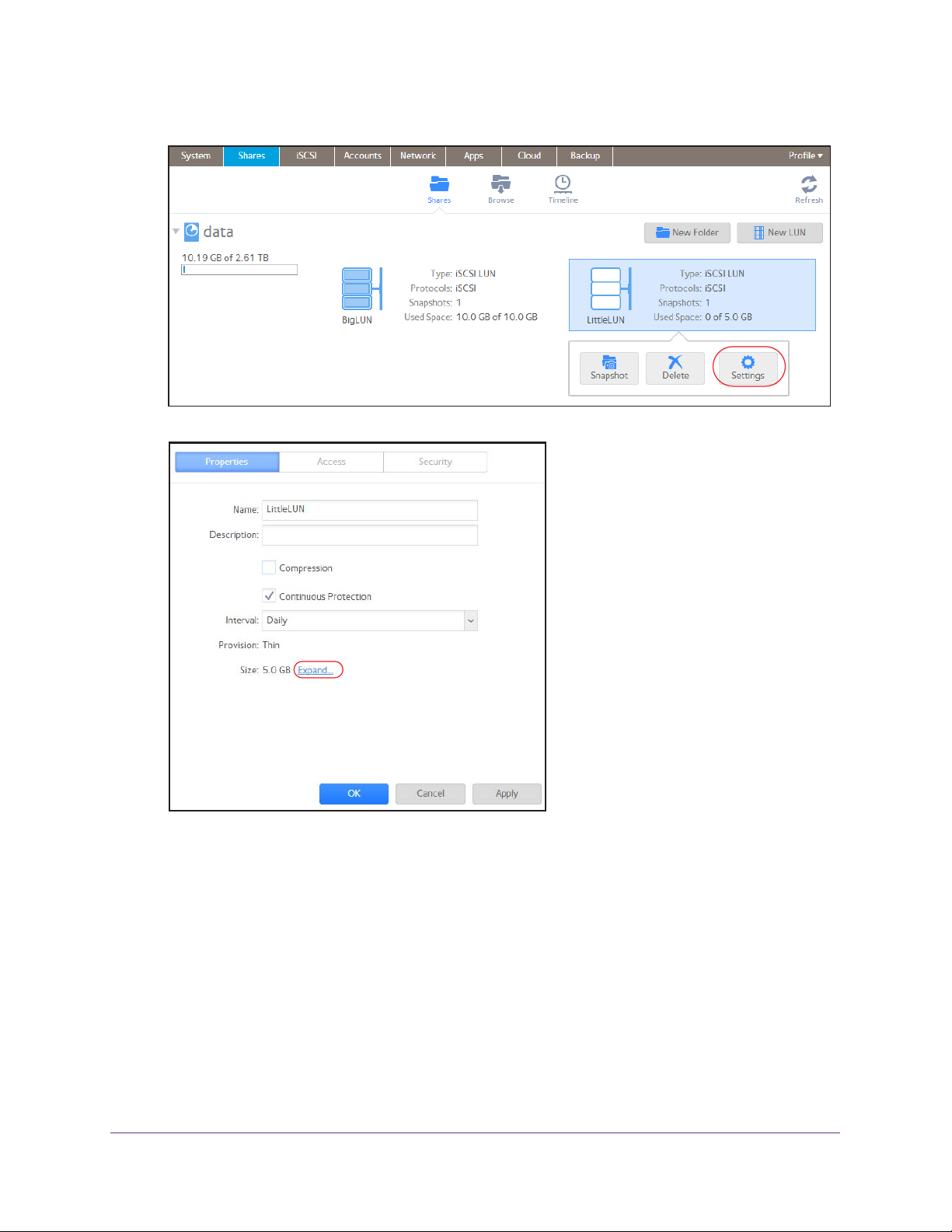
ReadyNAS OS 6.1
3. From the pop-up menu that displays, select Settings.
The LUN settings display in a pop-up screen.
4. Select the Expand link.
LUNs
100
 Loading...
Loading...